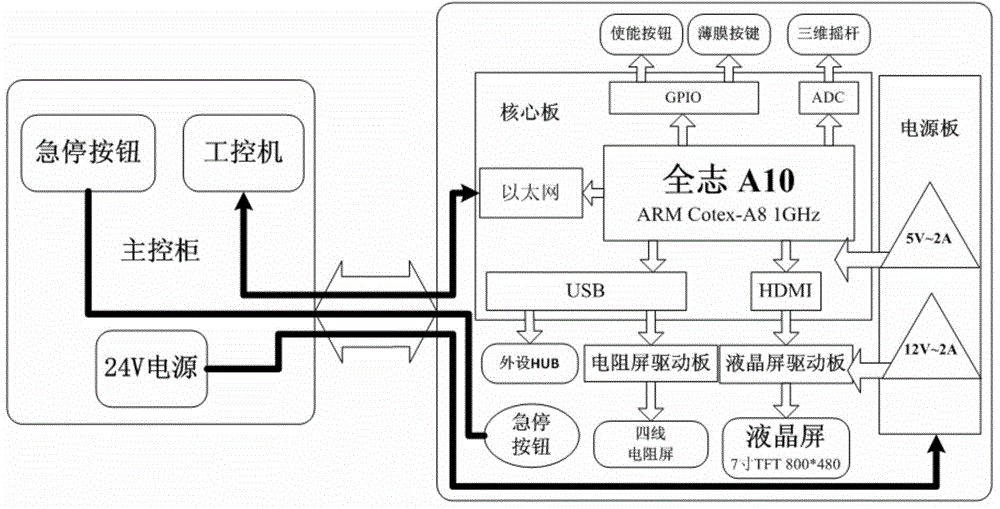
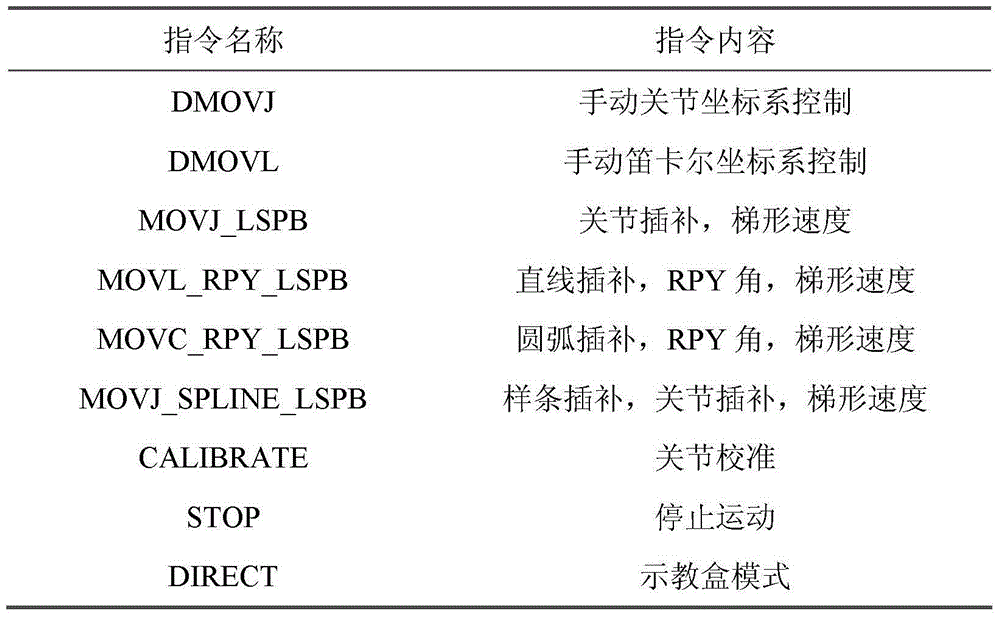
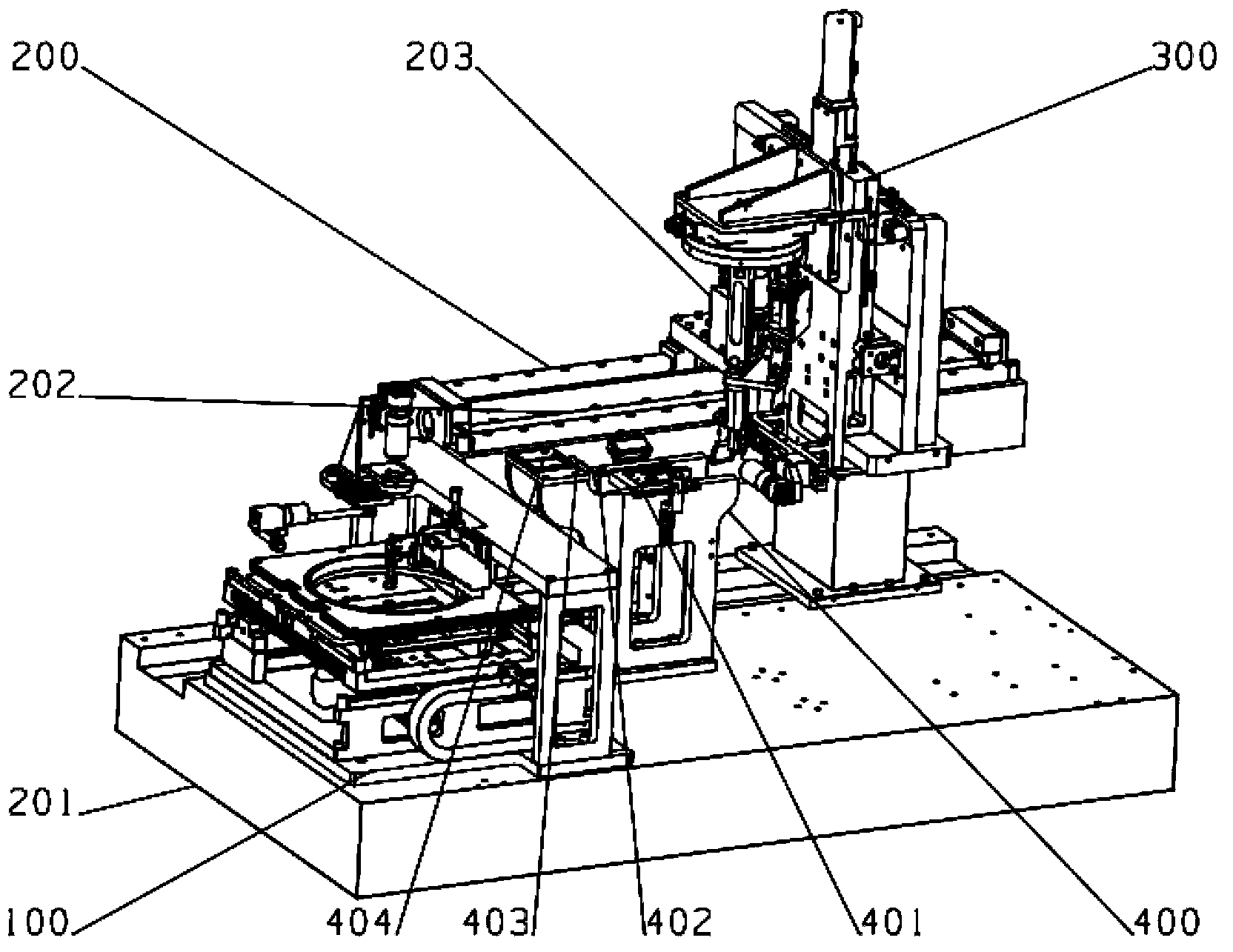
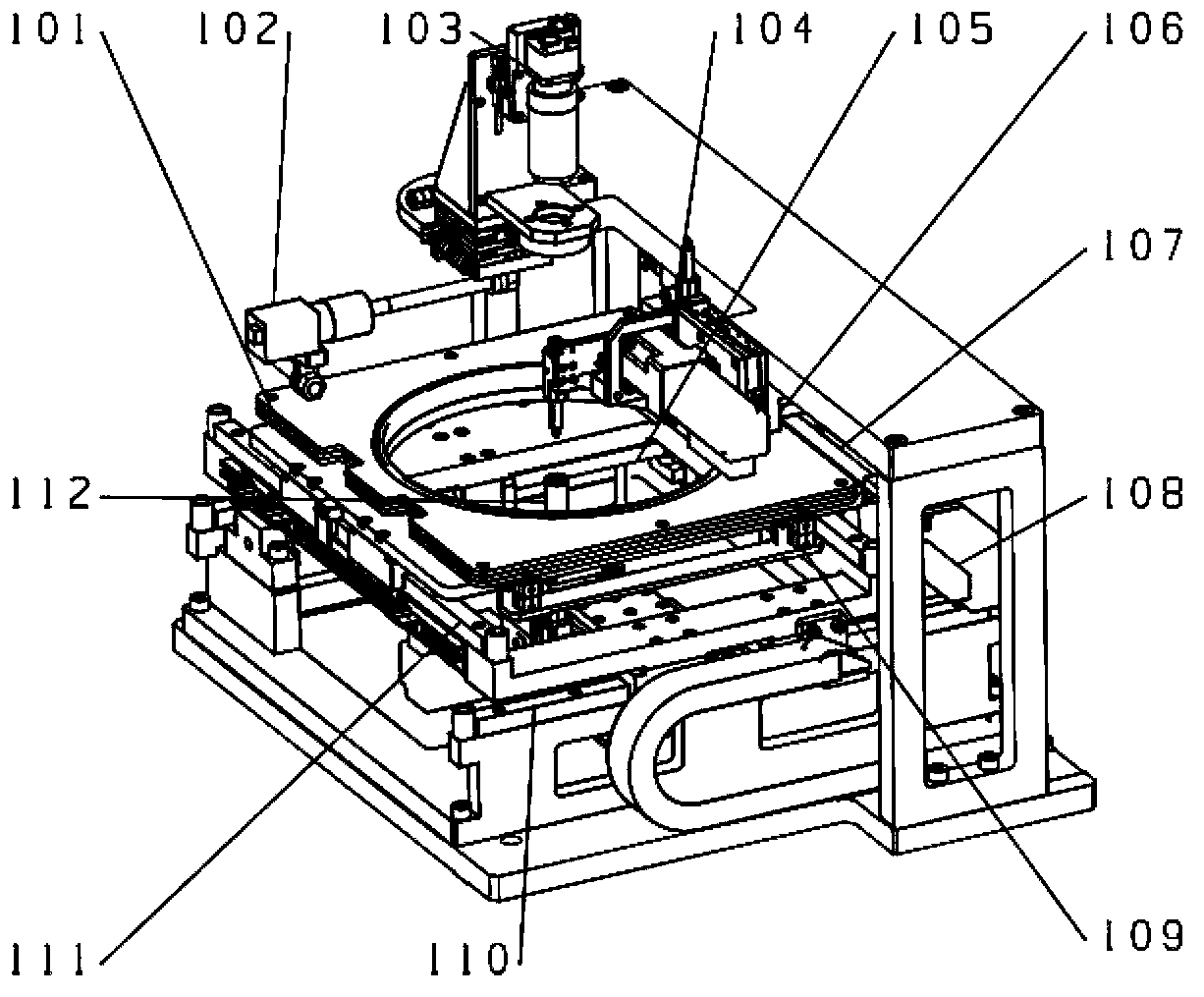
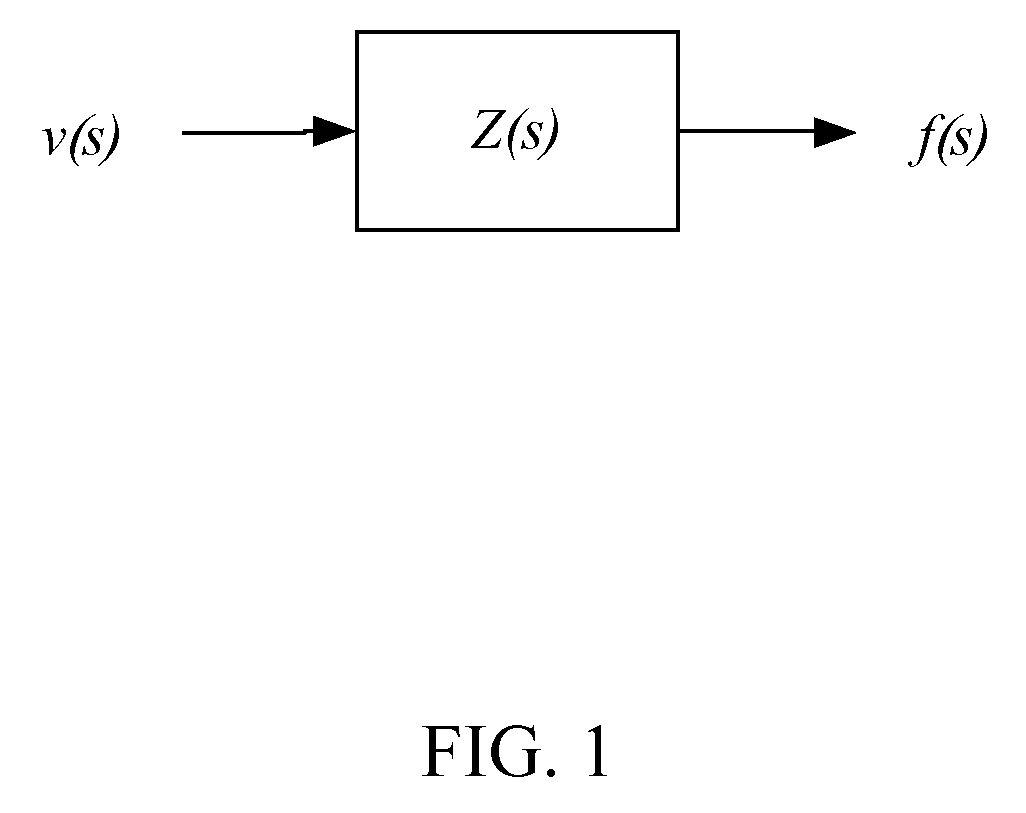
Patents
Literature
2388 results about "Multi degree of freedom" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
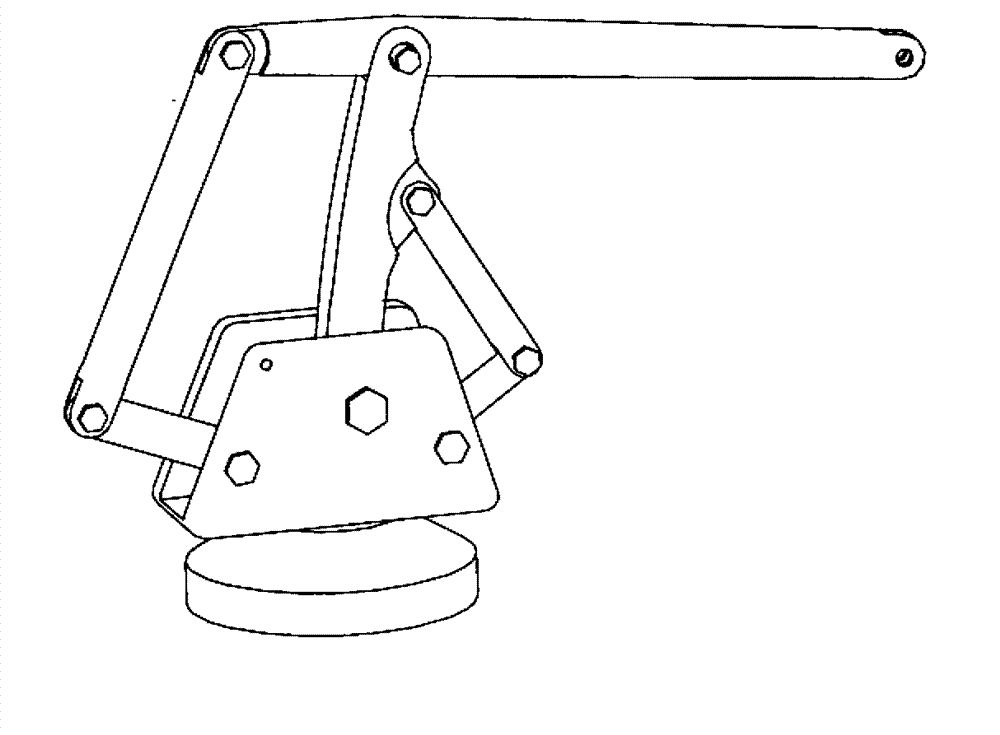
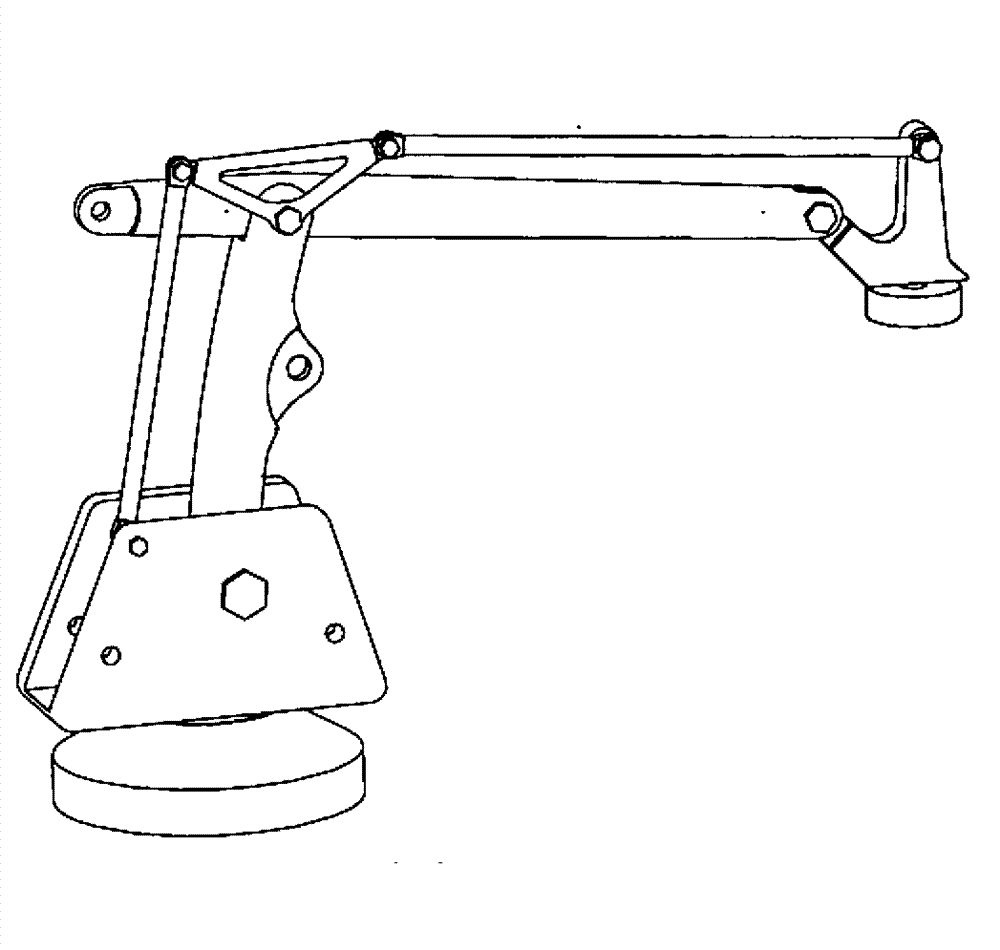
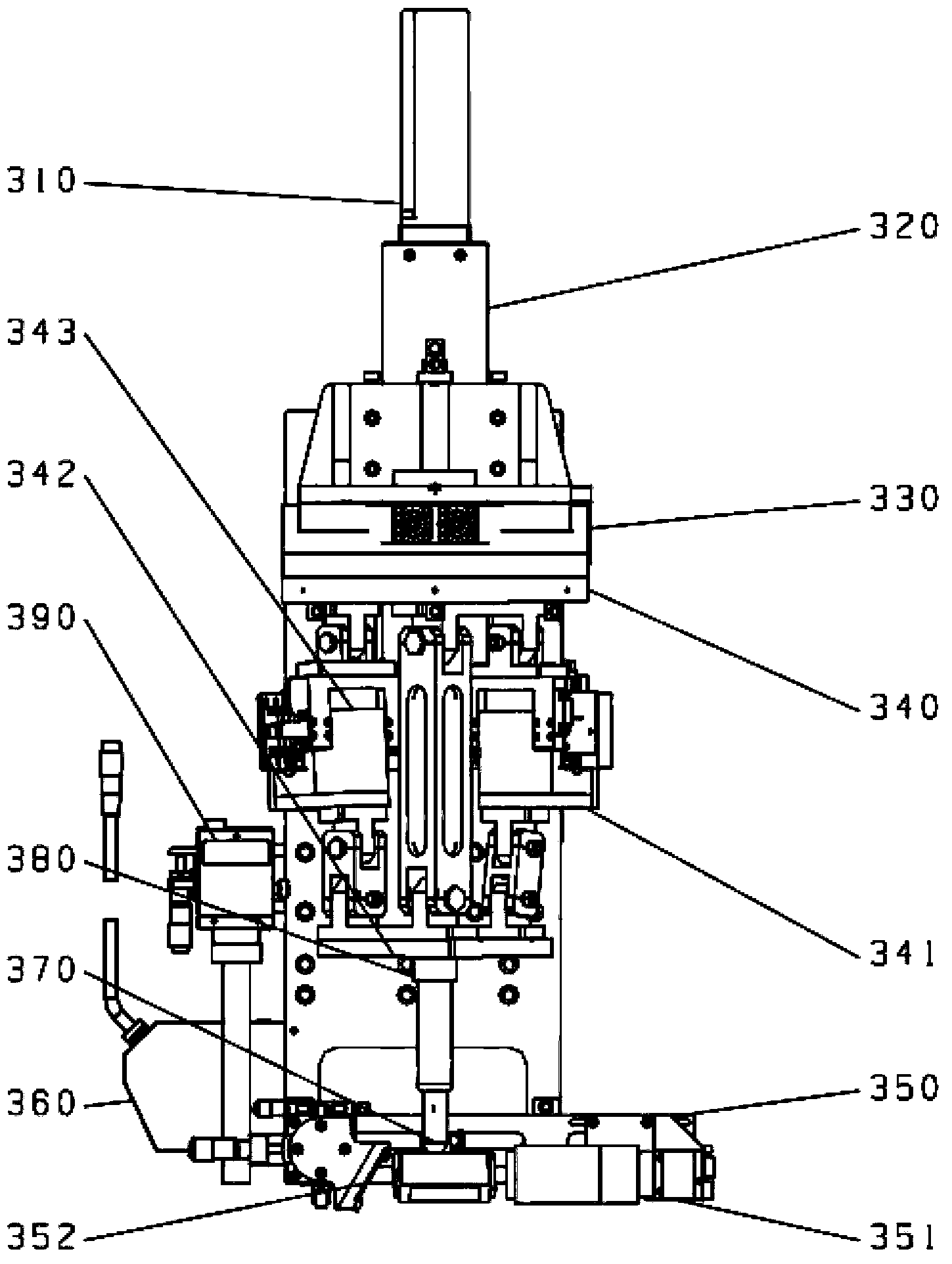
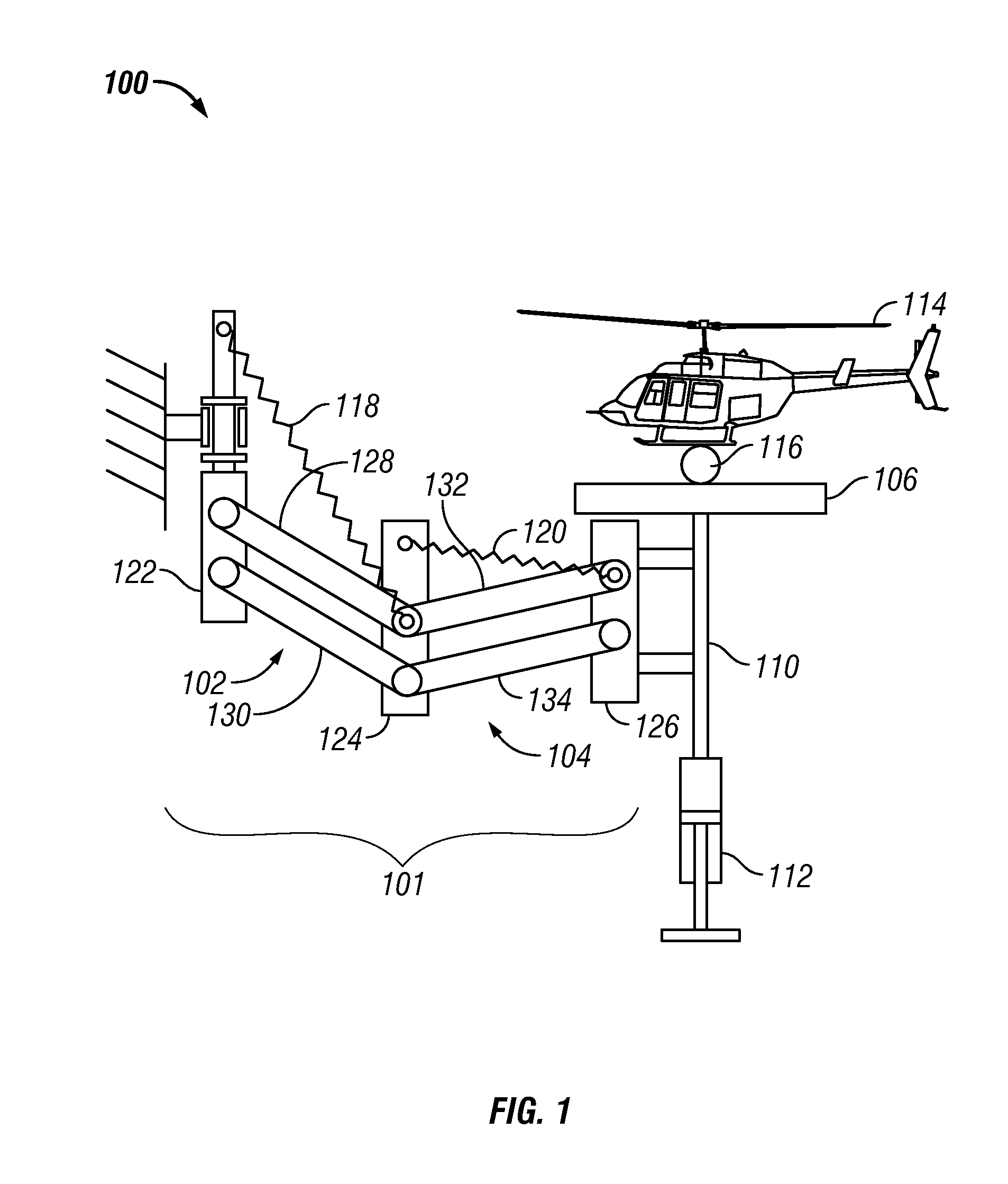
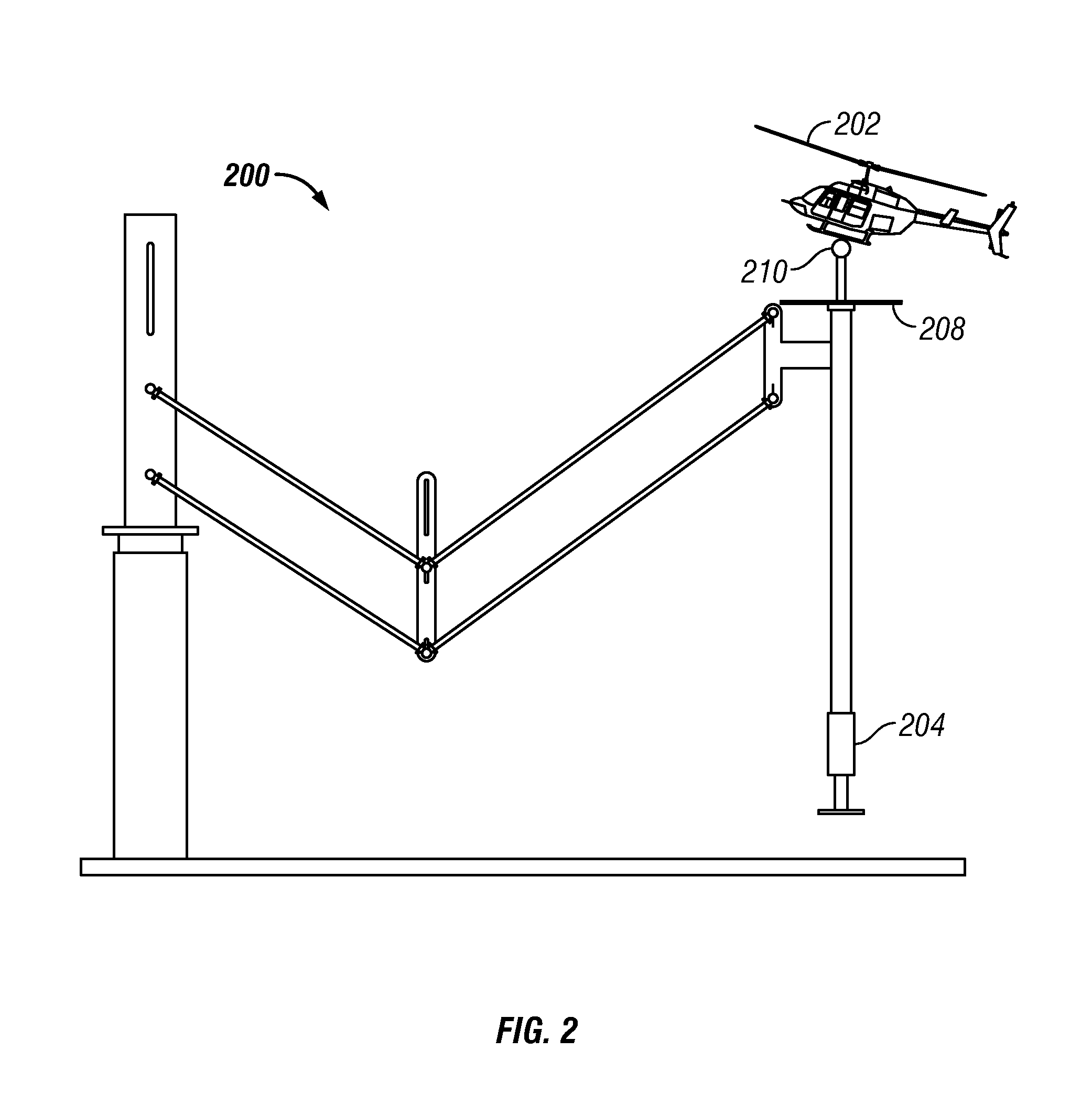
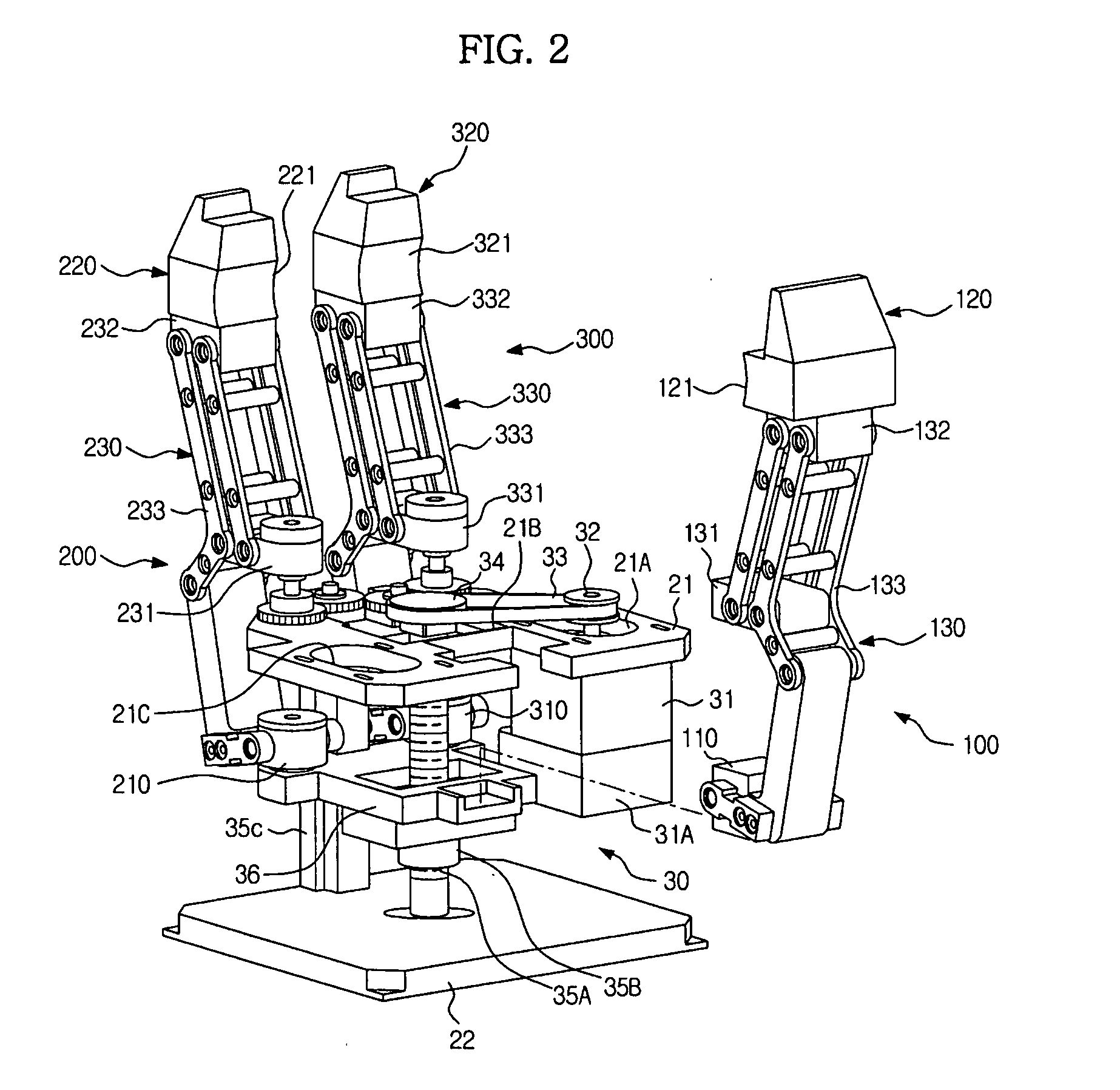
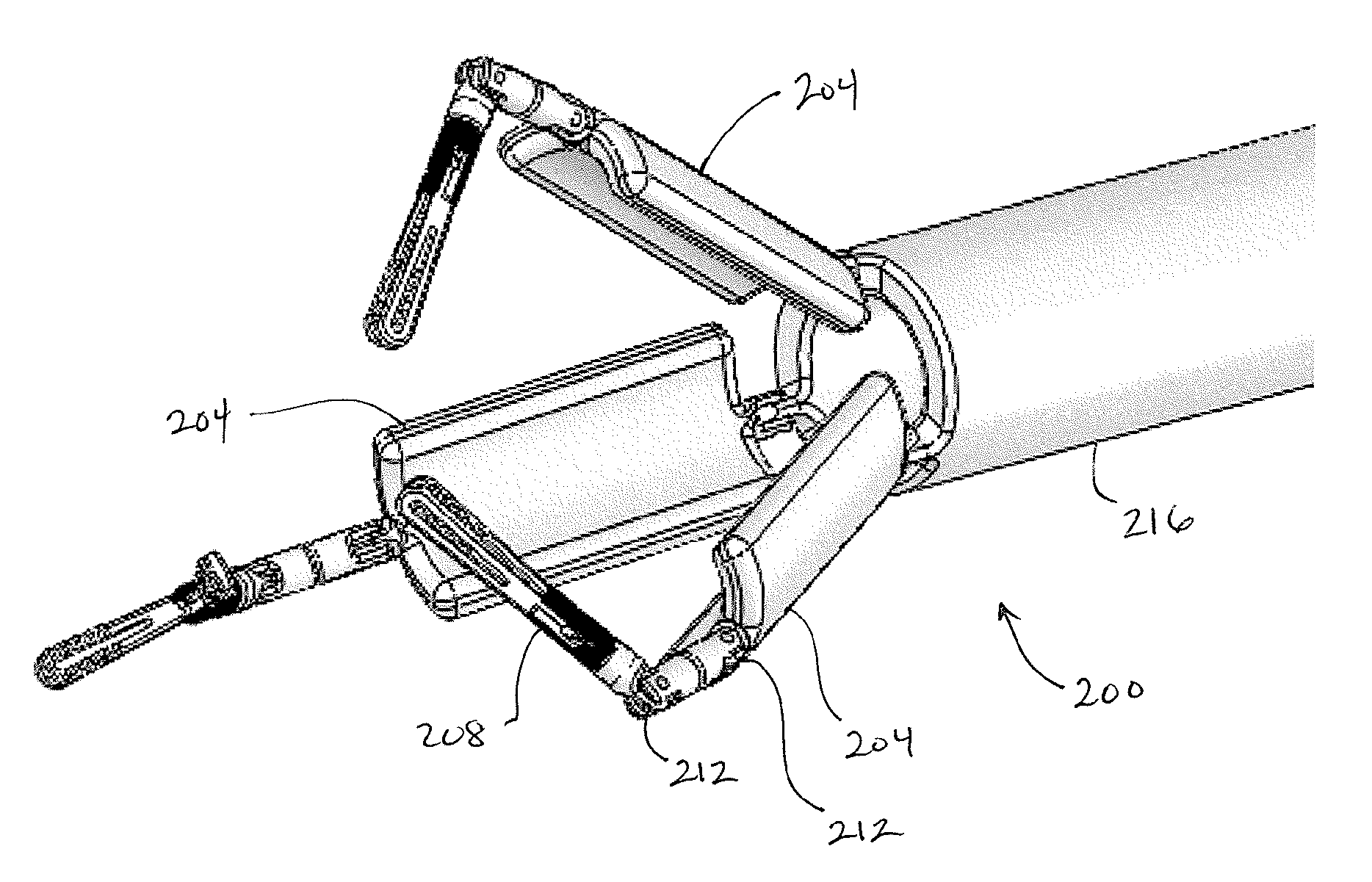
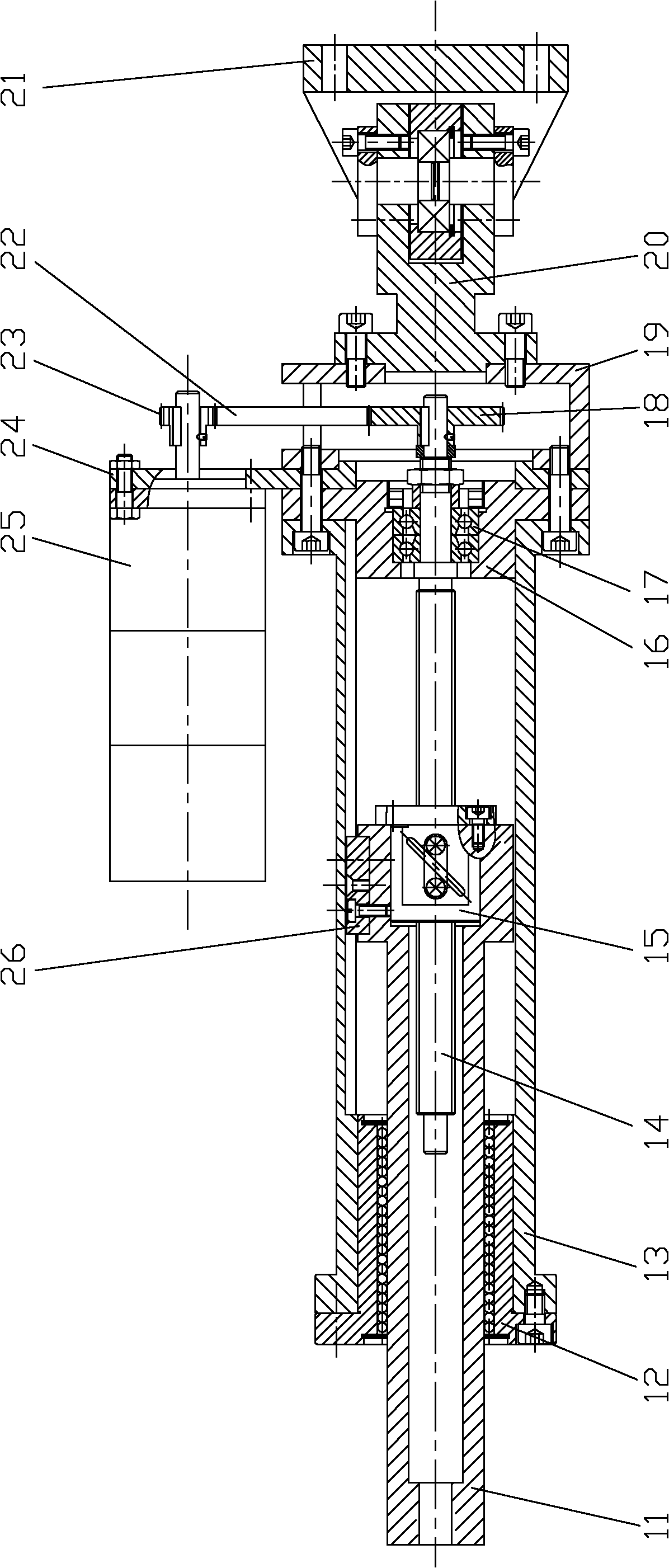
Robotic apparatus
InactiveUS20090012534A1Minimize cost functionProgramme-controlled manipulatorDiagnosticsRobot end effectorEngineering
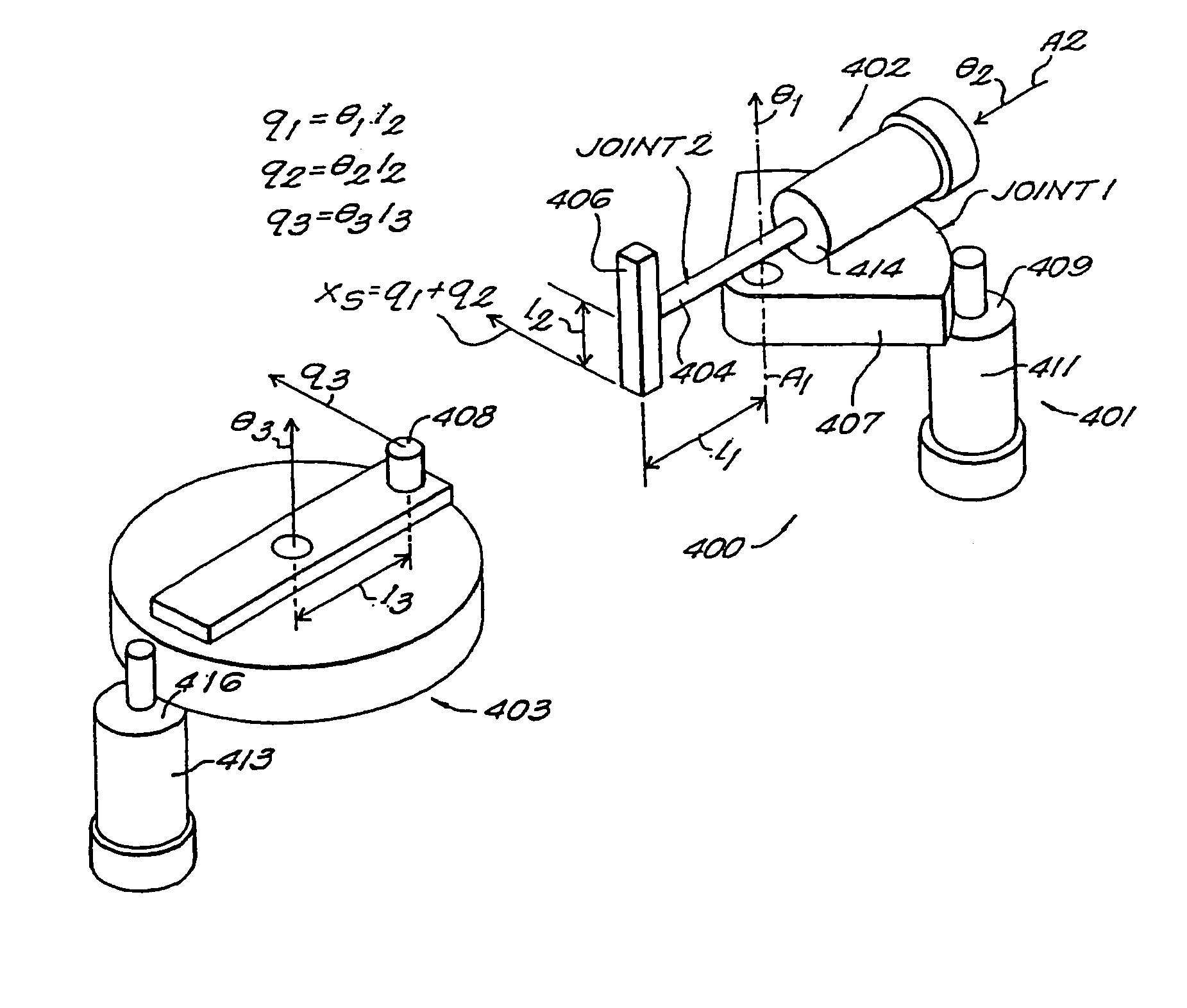
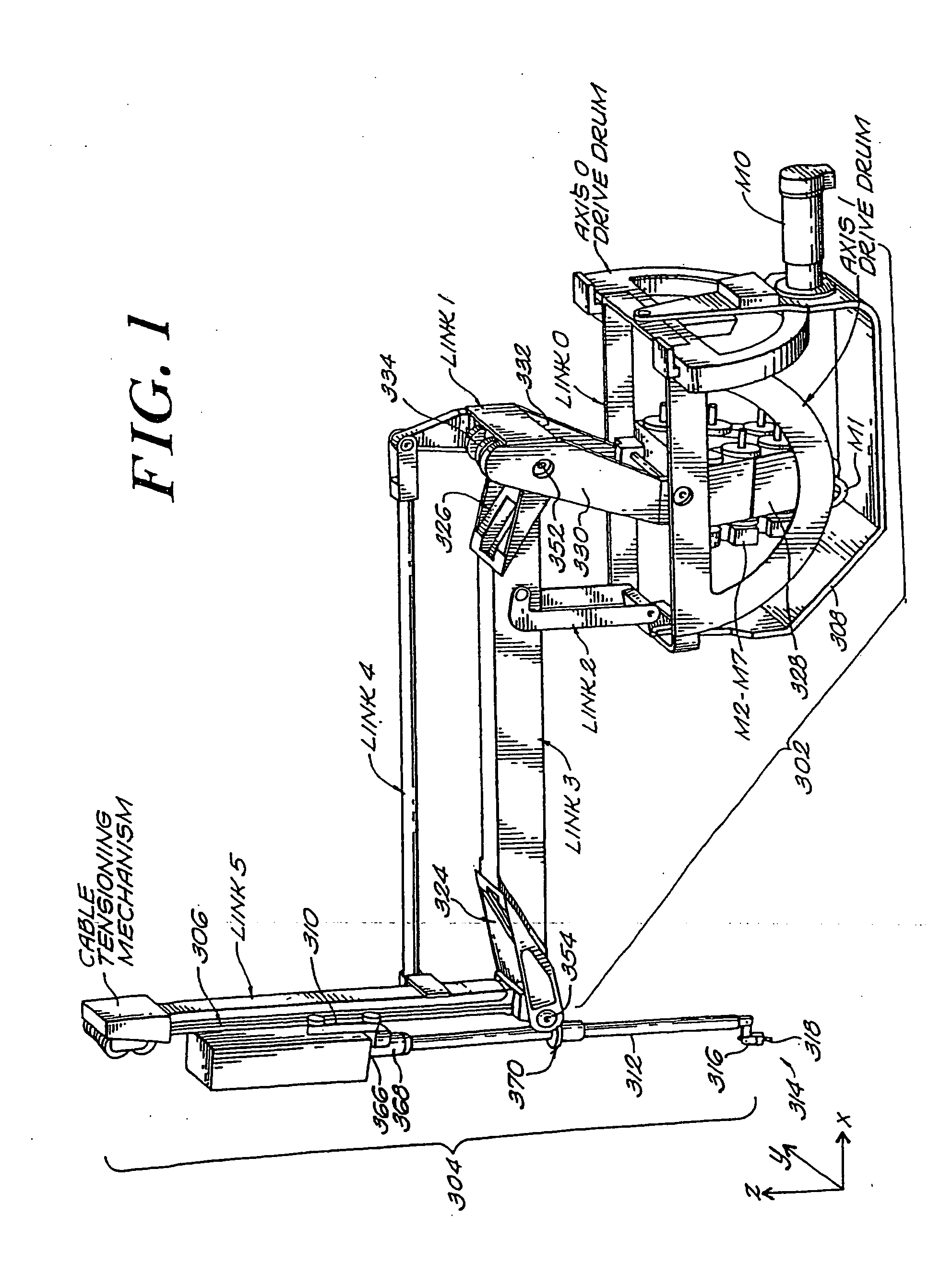
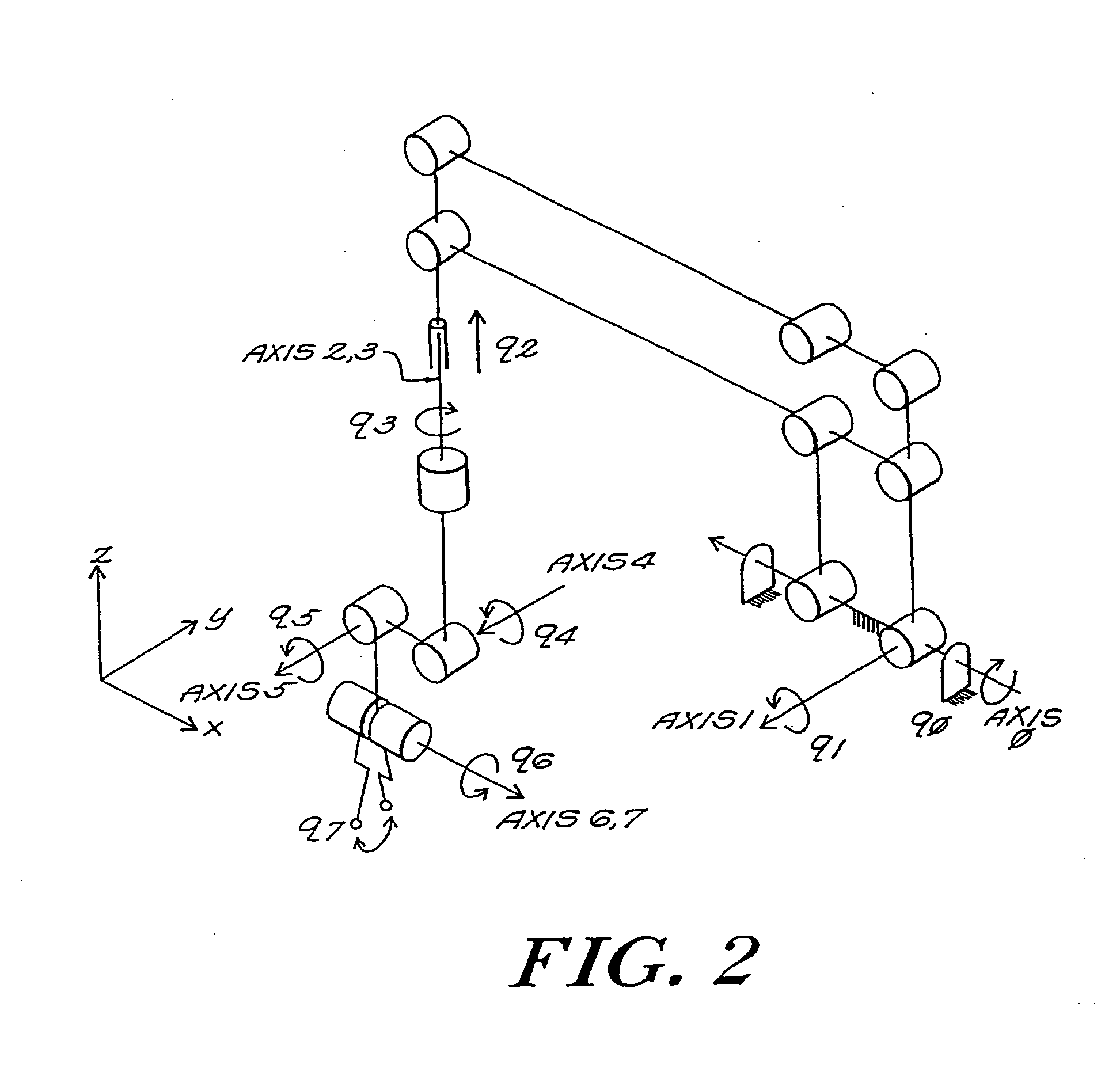
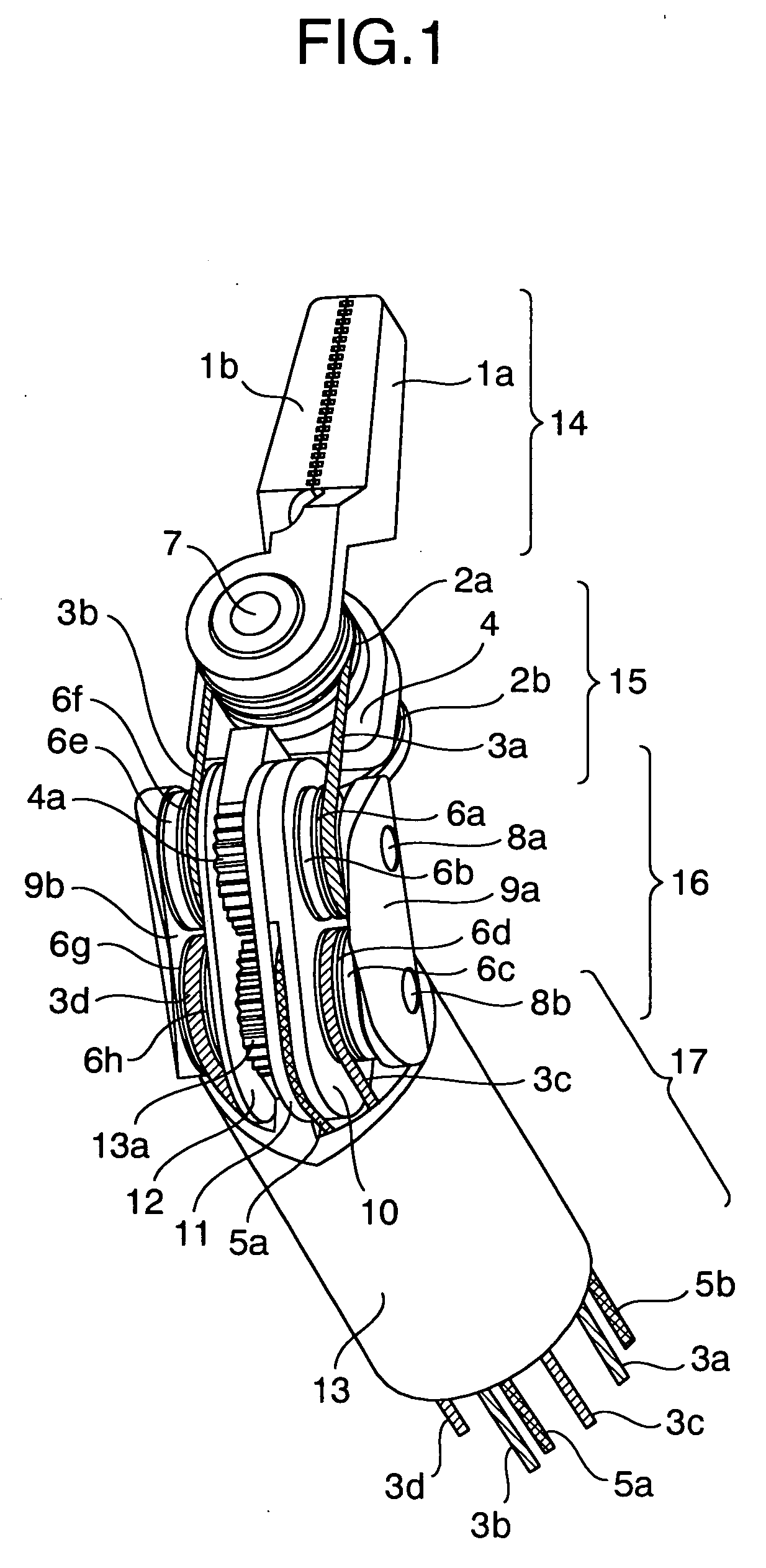
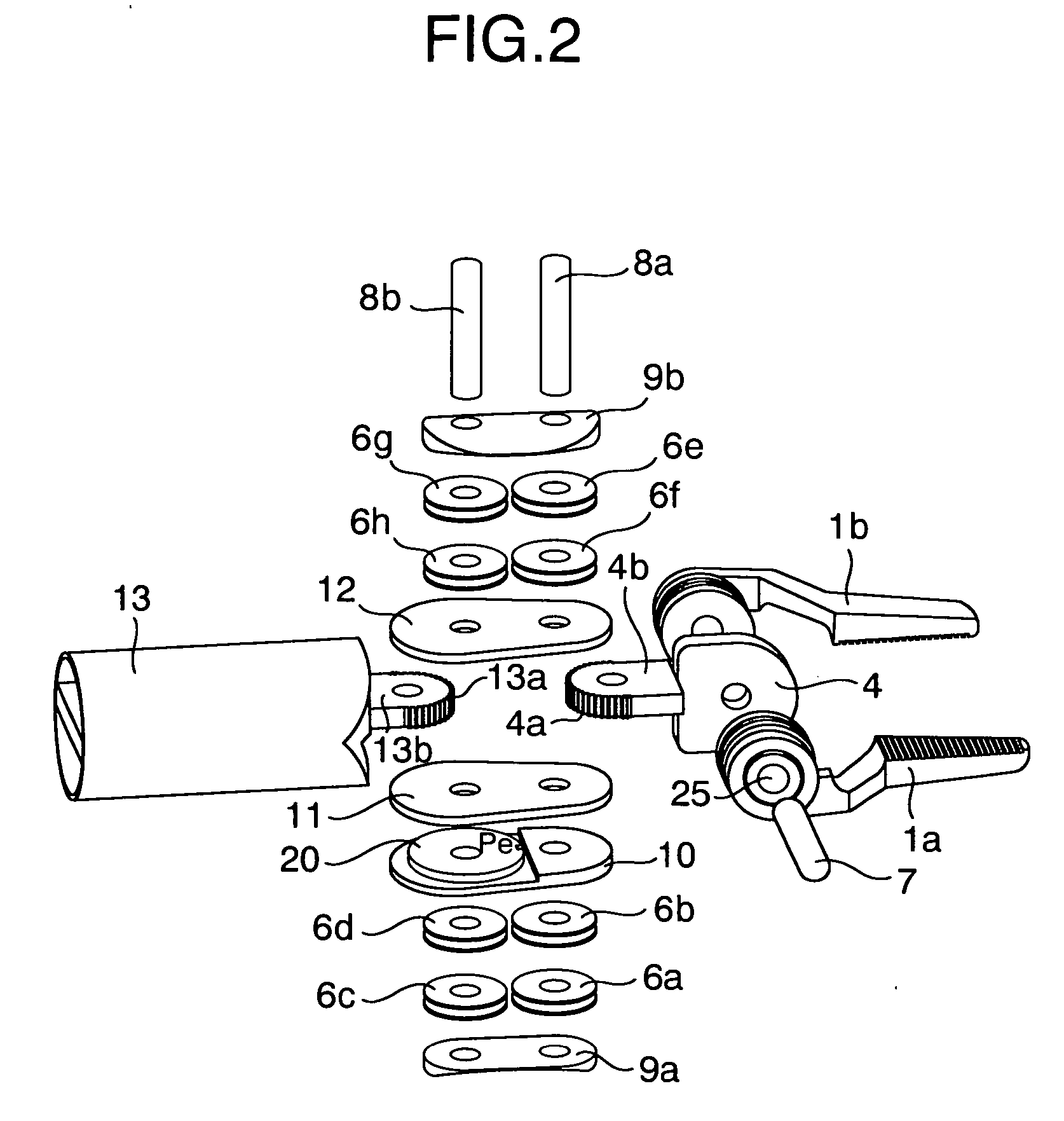
A robotic apparatus has eight actuators (M0-M7) and a linkage (LINK 0-LINK 5) that actuates an end effector. Three serial macro freedoms have large ranges of motion and inertias. Four serial micro freedoms have small ranges of motion and inertias. Translation of the end effector in an y direction is actuated by at least one micro joint and at least one macro joint. The apparatus can be part of a master and slave combination, providing force feedback without any explicit force sensors. The slave is controlled with an Inverse Jacobian controller, and the mater with a Jacobian Transpose controller. A slave having more degrees of freedom (DOFs) than the master can be controlled. A removable effector unit actuates its DOFs with cables. Beating heart surgery can be accomplished by commanding the slave to move with a beating heart and cancelling out any such motion in the motions perceived by the master.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Surgical device
InactiveUS20070208375A1Without requiring lot of skillSimple structureDiagnosticsSurgical manipulatorsForcepsMulti degree of freedom
The invention provides a surgical device which can control a position and an attitude of a multi degree of freedom type grip portion (forceps) in a dummy manner on the basis of an operation of an operator in an operating portion. In a surgical device provided with a leading end joint portion having a leading end grip portion, a near-side joint portion having an operation portion, a handle portion supporting the operation portion, and an arm portion storing a wire for linking motions of the leading end joint portion and the near-side joint portion, the leading end joint portion is moved downward and upward by operating the operation portion and the handle portion upward and downward around the near-side joint portion, and the leading end joint portion is moved rightward and leftward by operating the operation portion and the handle portion leftward and rightward, thereby making the leading end joint portion execute a swing motion, and the leading end grip portion is opened and closed by opening and closing finger rests of the operation portion.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
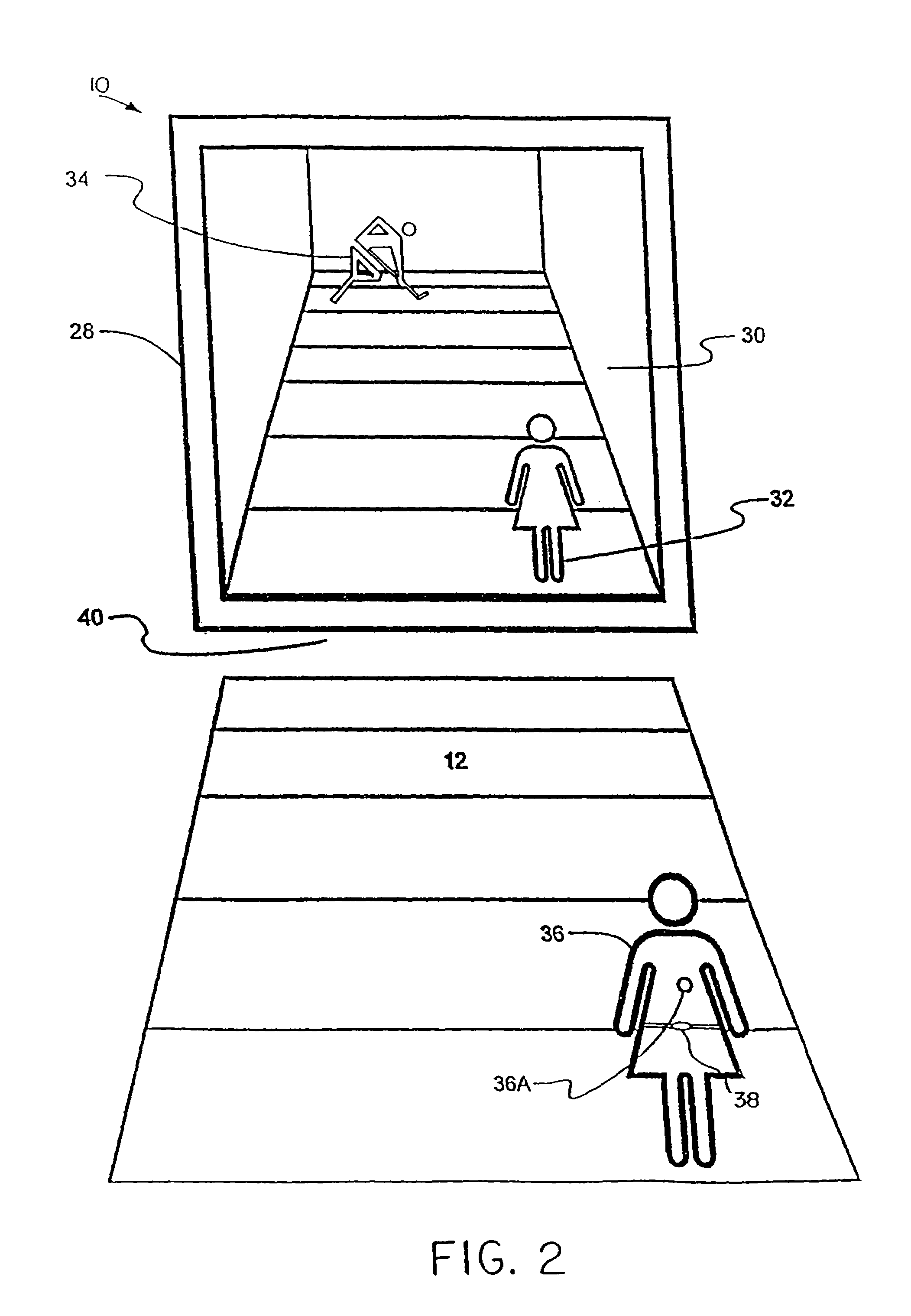
System and method for tracking and assessing movement skills in multidimensional space
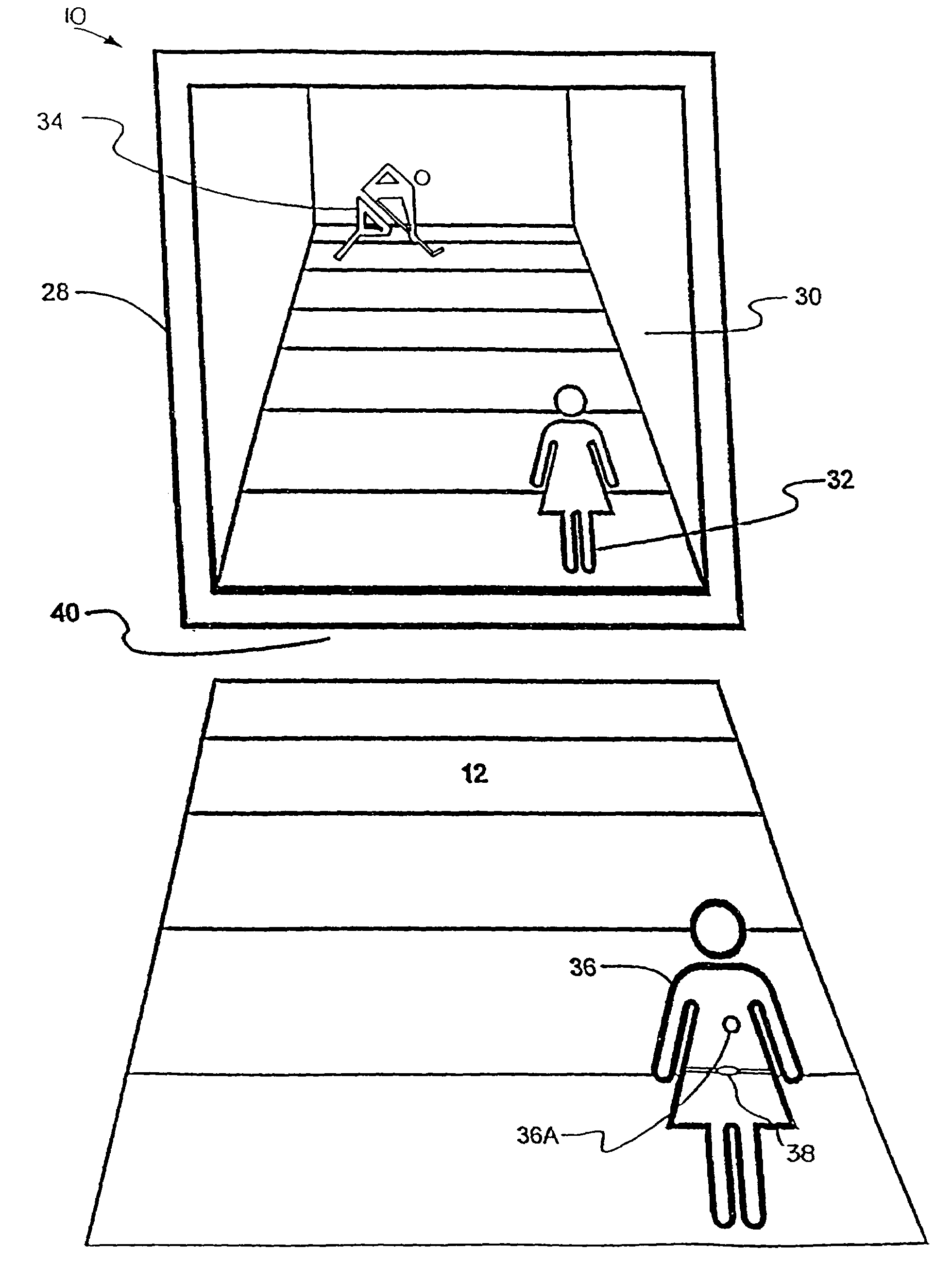
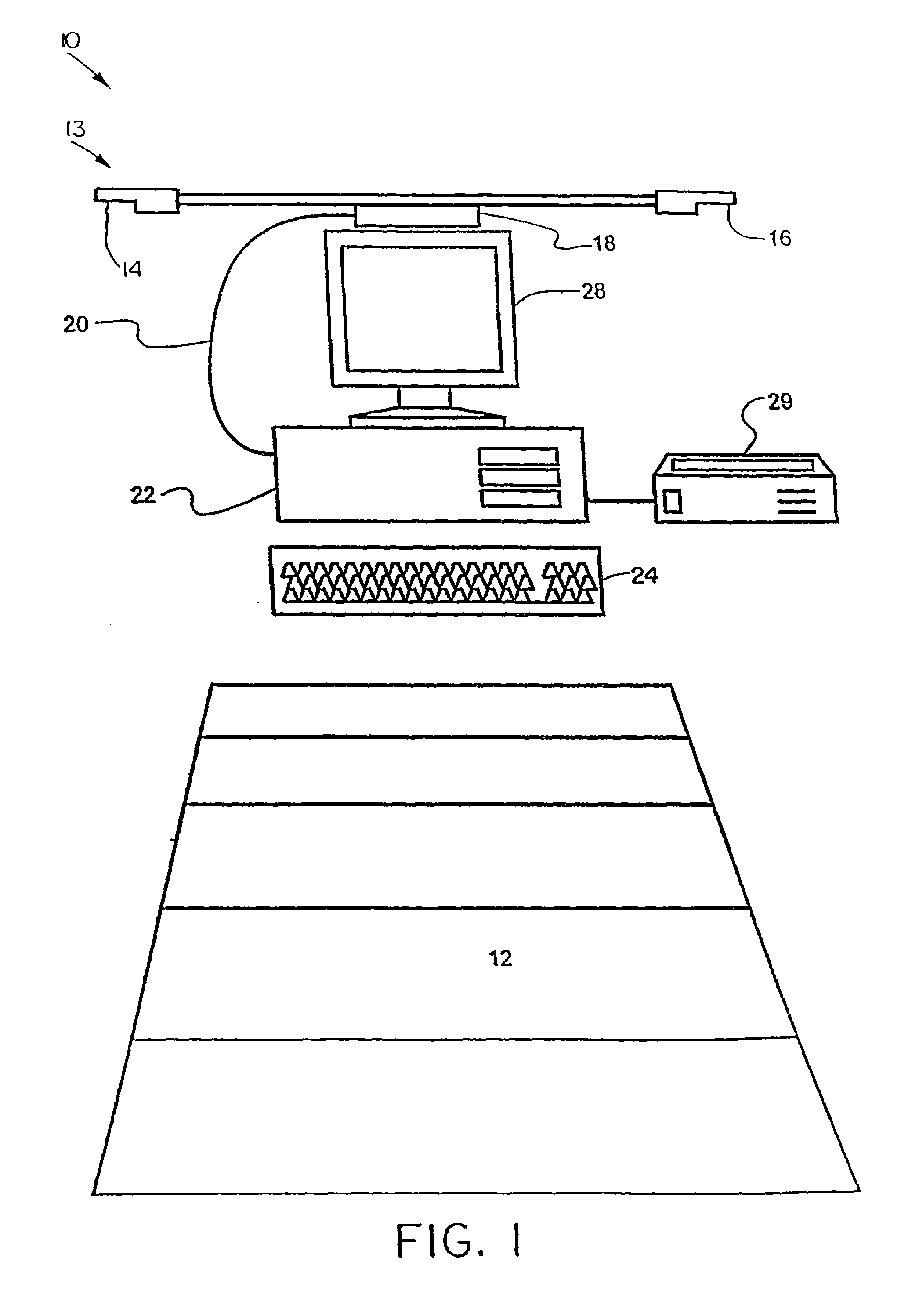
Accurate simulation of sport to quantify and train performance constructs by employing sensing electronics for determining, in essentially real time, the player's three dimensional positional changes in three or more degrees of freedom (three dimensions); and computer controlled sport specific cuing that evokes or prompts sport specific responses from the player that are measured to provide meaningful indicia of performance. The sport specific cuing is characterized as a virtual opponent that is responsive to, and interactive with, the player in real time. The virtual opponent continually delivers and / or responds to stimuli to create realistic movement challenges for the player.
Owner:IMPULSE TECH
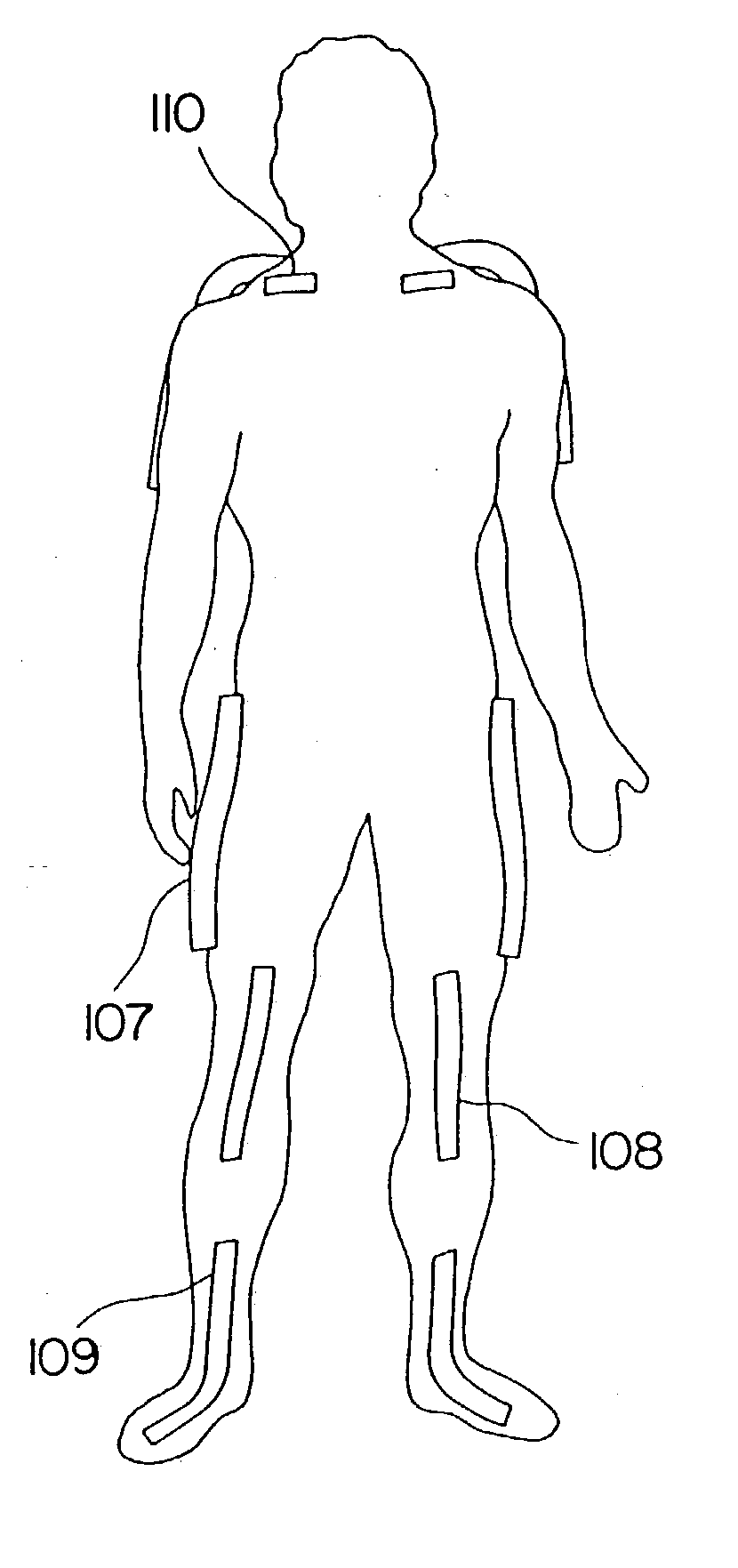
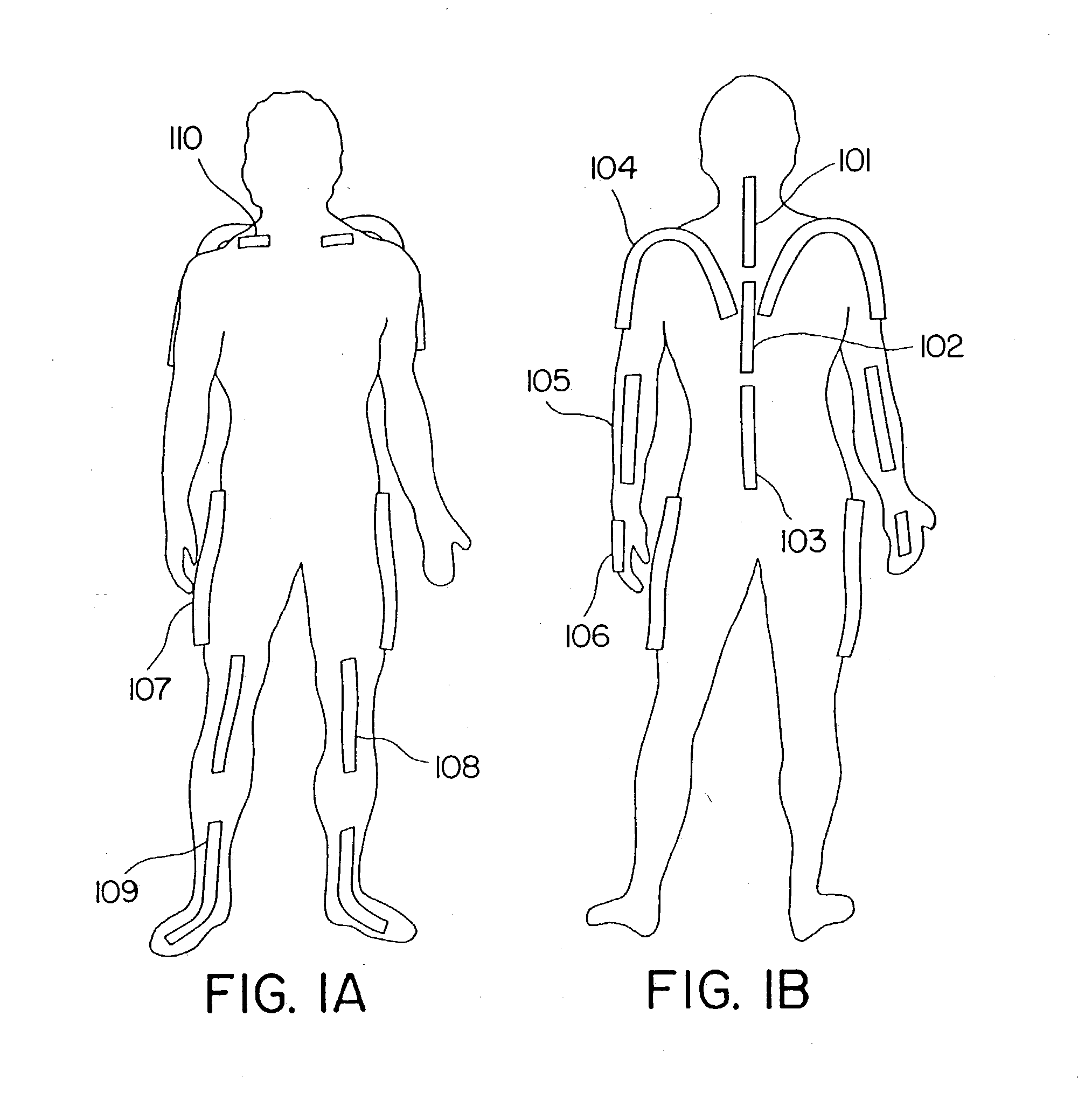
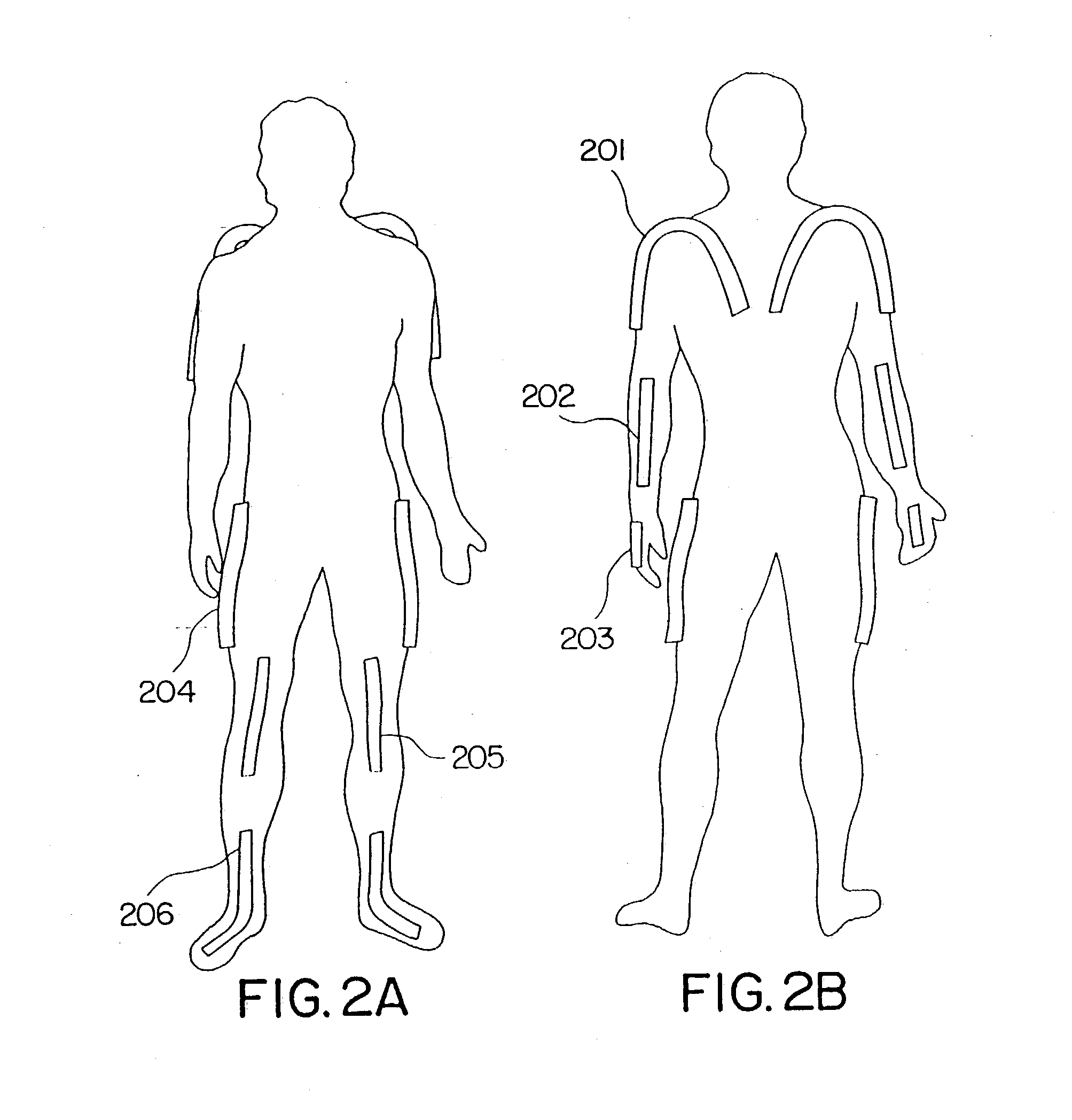
Goniometer-based body-tracking device and method
A sensing system is provided for measuring various joints of a human body for applications for performance animation, biomechanical studies and general motion capture. One sensing device of the system is a linkage-based sensing structure comprising rigid links interconnected by revolute joints, where each joint angle is measured by a resistive bend sensor or other convenient goniometer. Such a linkage-based sensing structure is typically used for measuring joints of the body, such as the shoulders, hips, neck, back and forearm, which have more than a single rotary degree of freedom of movement. In one embodiment of the linkage-based sensing structure, a single long resistive bend sensor measures the angle of more that one revolute joint. The terminal ends of the linkage-based sensing structure are secured to the body such that movement of the joint is measured by the device. A second sensing device of the sensing system comprises a flat, flexible resistive bend sensor guided by a channel on an elastic garment. Such a flat sensing device is typically used to measure various other joints of the body which have primarily one degree of freedom of movement, such as the elbows, knees and ankles. Combining the two sensing devices as described, the sensing system has low sensor bulk at body extremities, yet accurately measures the multi-degree-of-freedom joints nearer the torso. Such a system can operate totally untethered, in real time, and without concern for electromagnetic interference or sensor occlusion.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Interactive video based games using objects sensed by TV cameras
InactiveUS7843429B2Good adhesionIncrease brightnessInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionInteractive videoStereo cameras
A method and apparatus for interactive TV camera based games in which position or orientation of points on a player or of an object held by a player are determined and used to control a video display. Both single camera and stereo camera pair based embodiments are disclosed, preferably using stereo photogrammetry where multi-degree of freedom information is desired. Large video displays, preferably life-size may be used where utmost realism of the game experience is desired.
Owner:MOTION GAMES
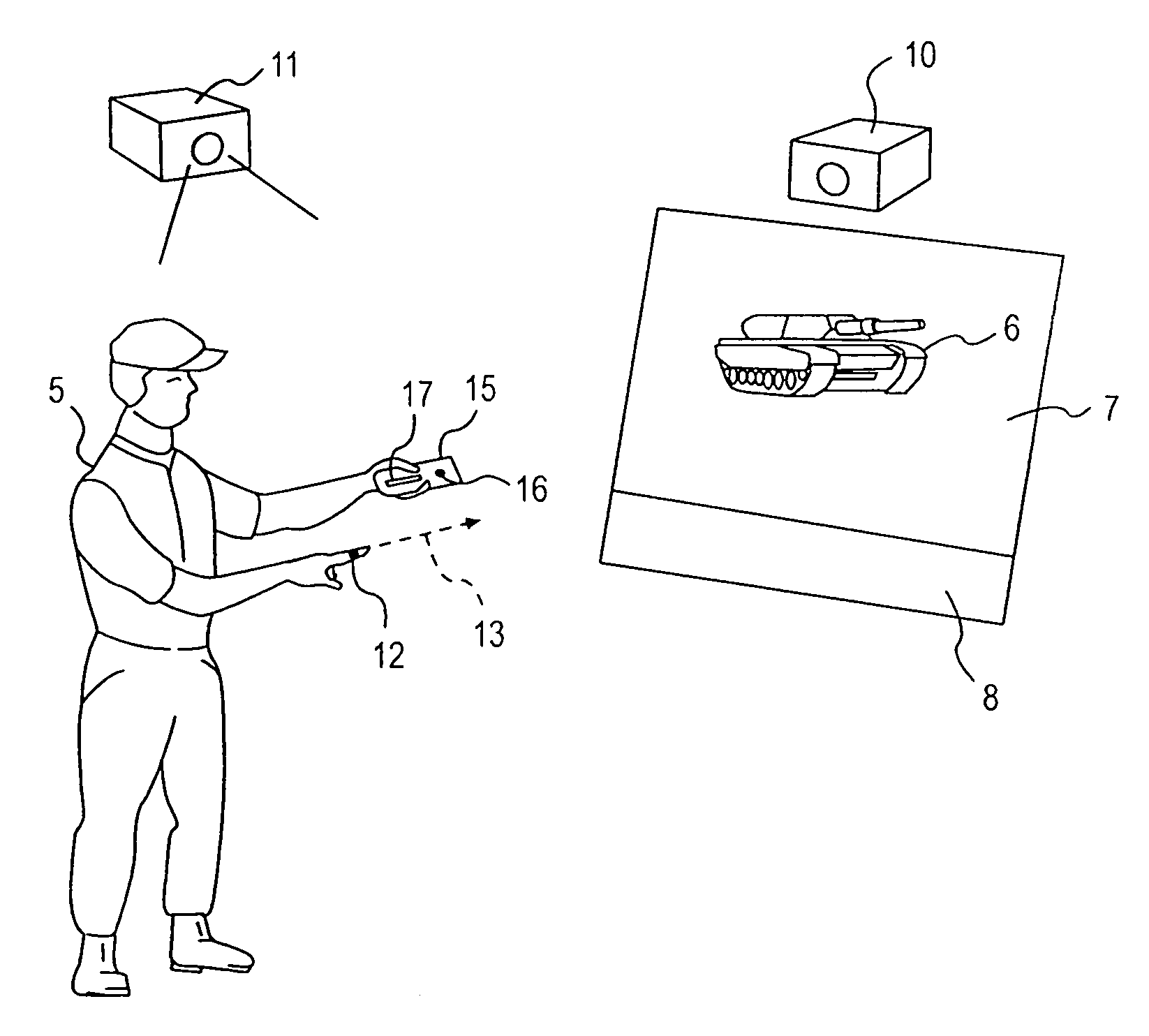
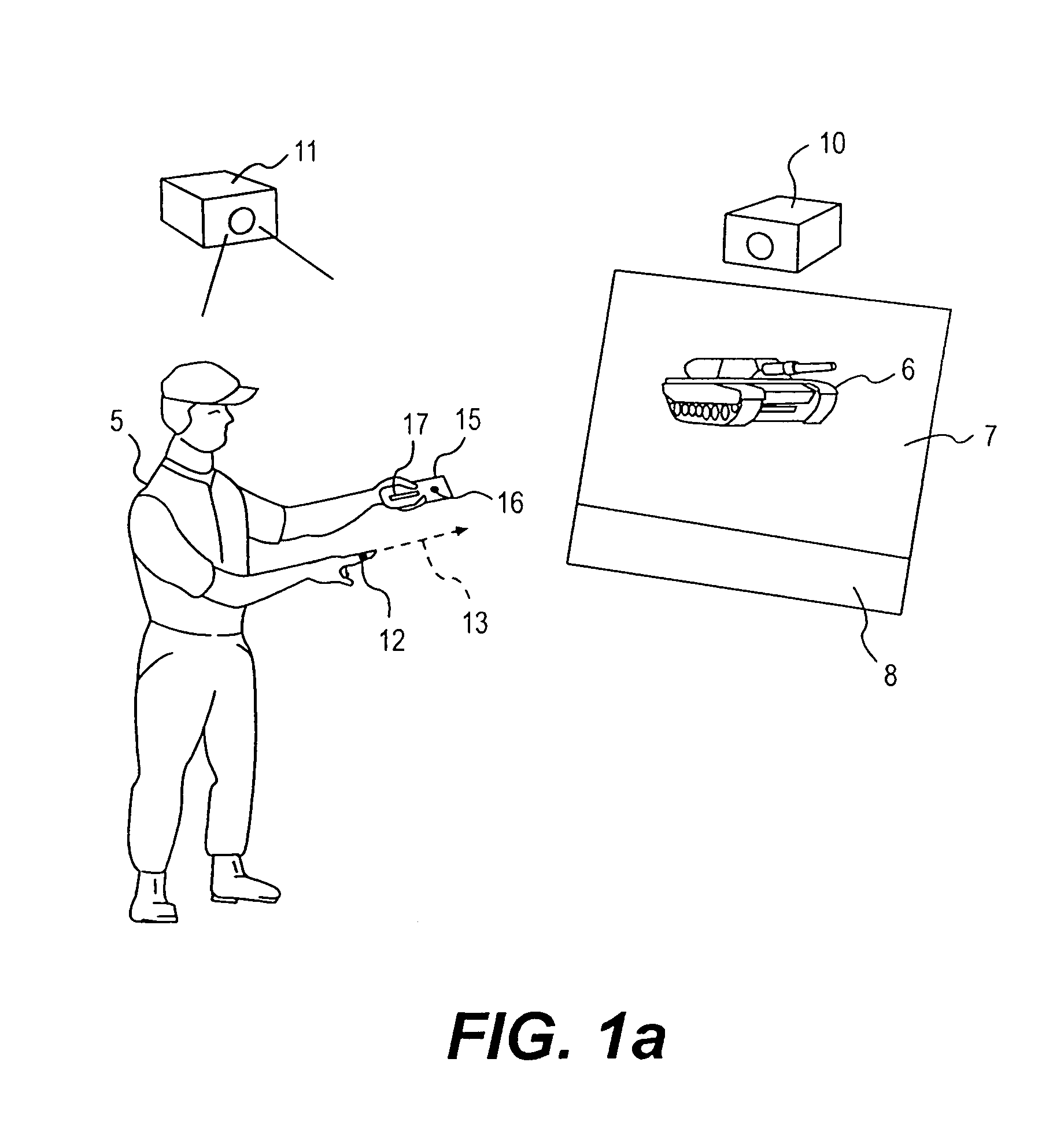
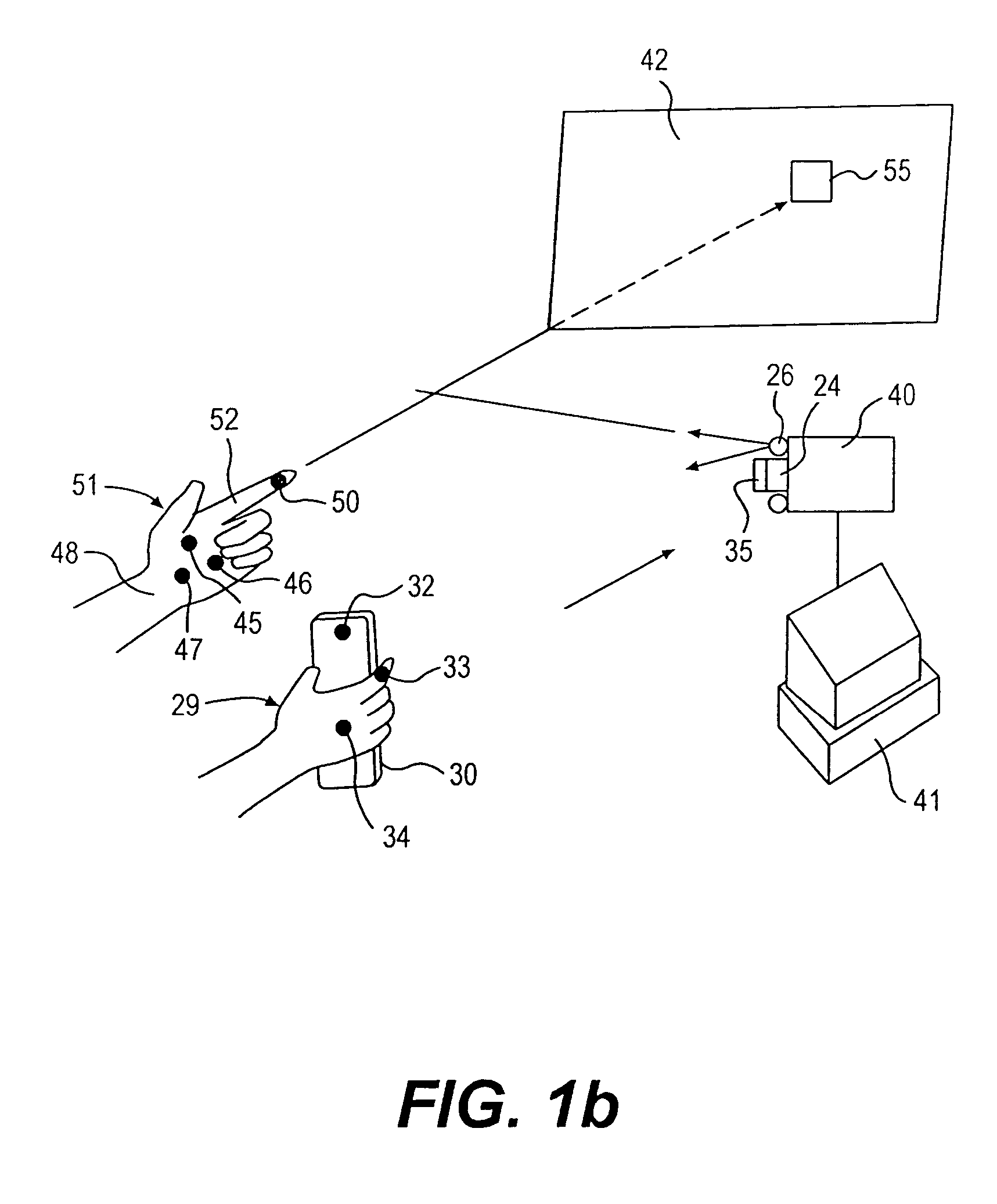
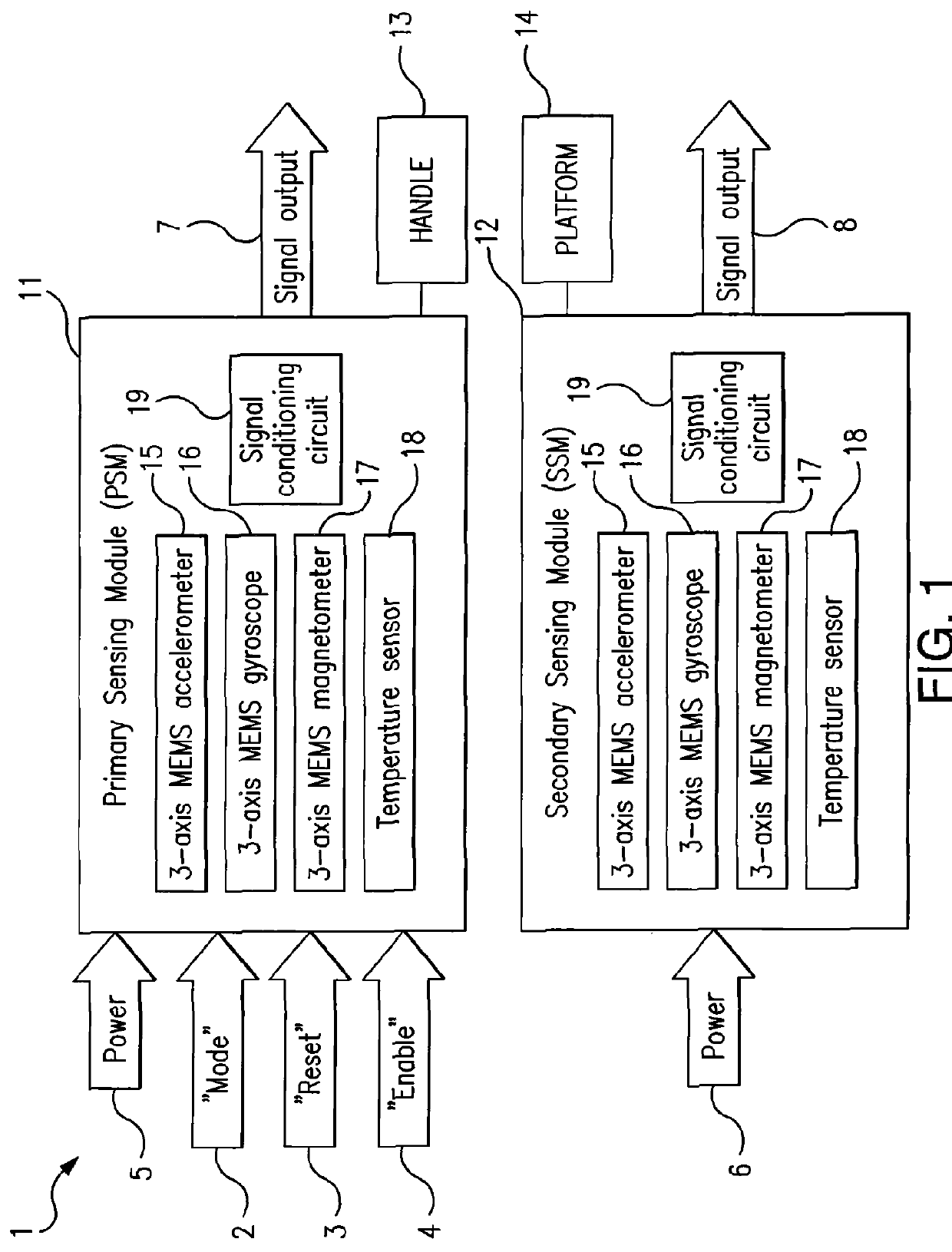
Intuitive multiple degrees of freedom portable control device
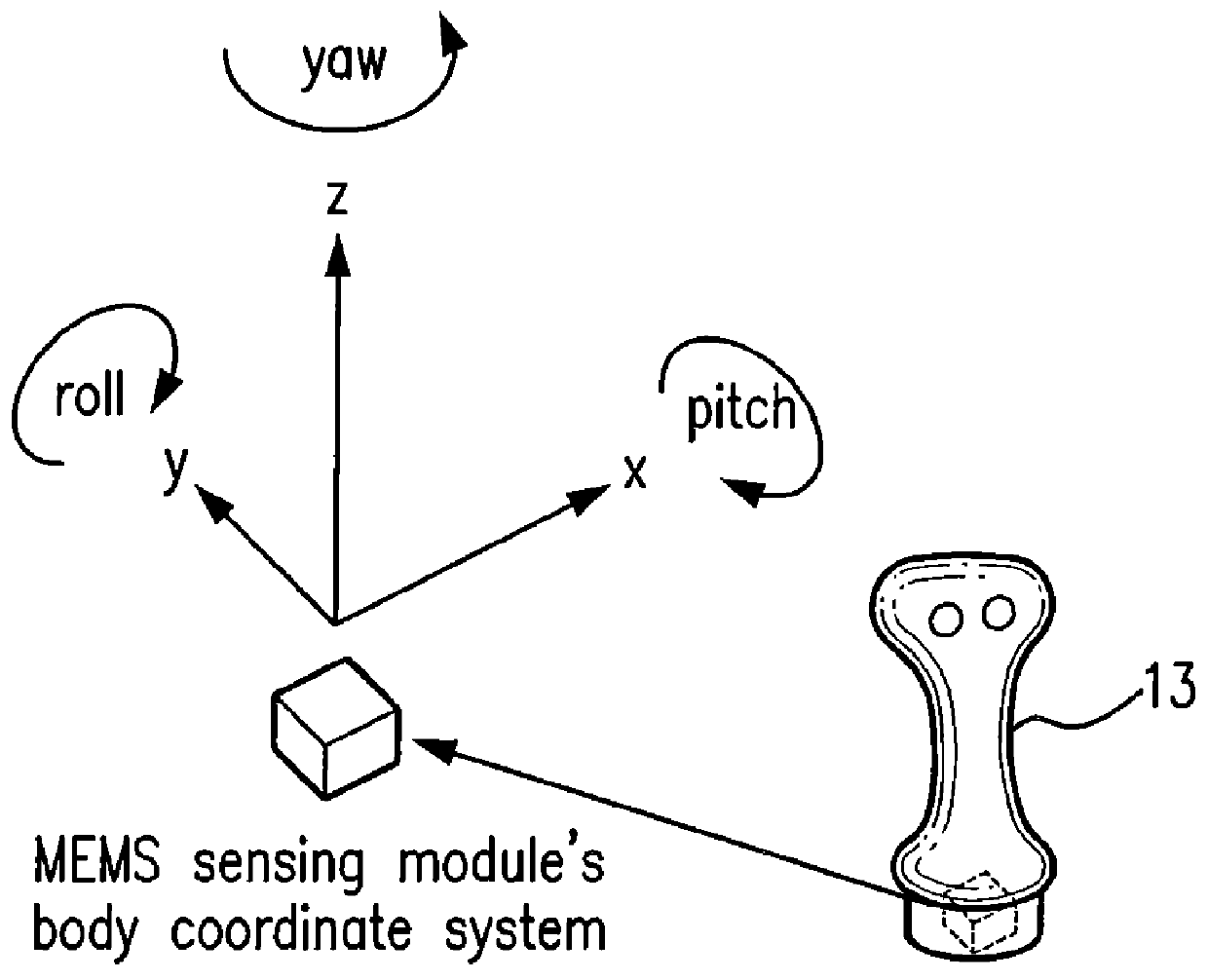
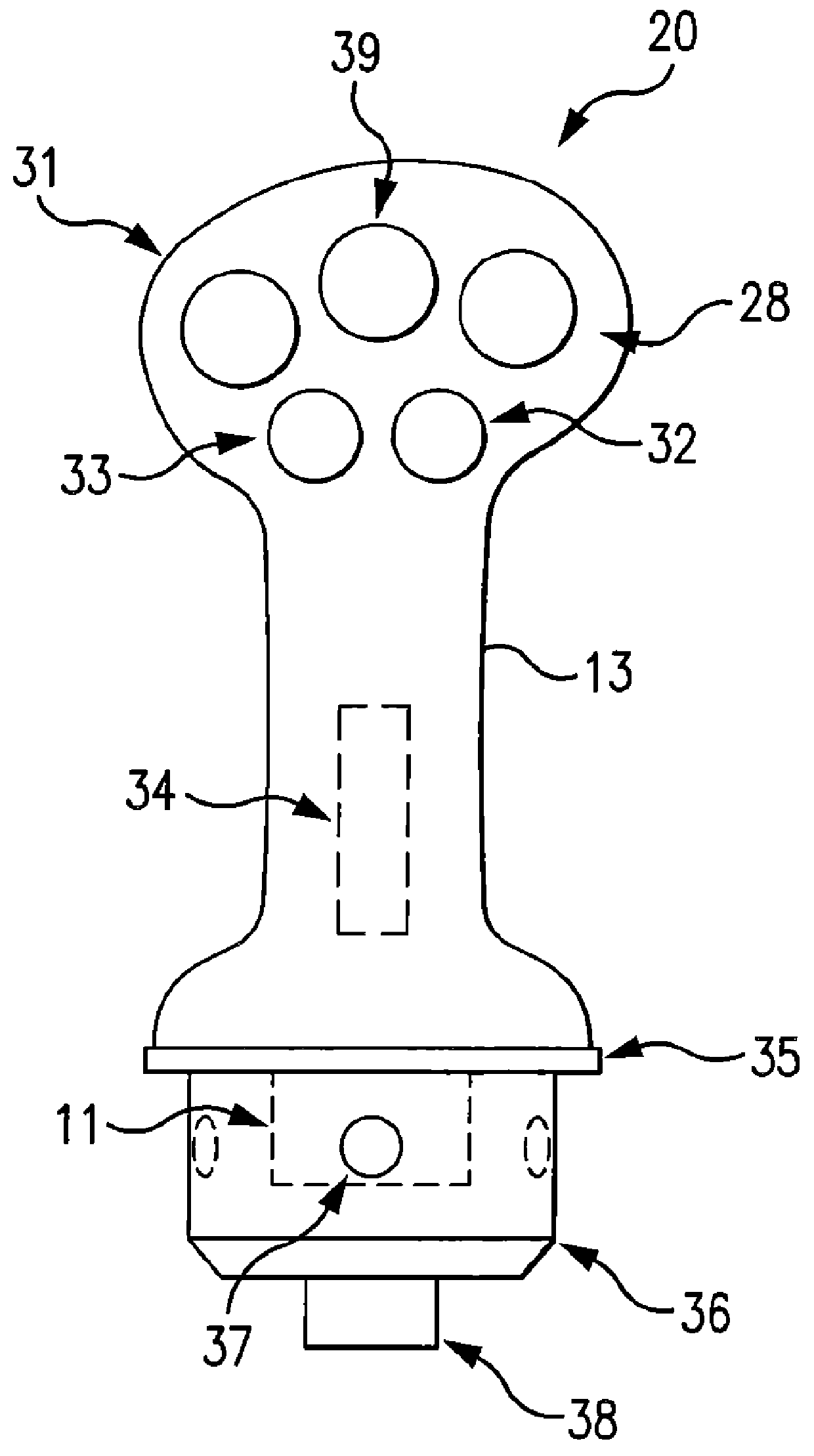
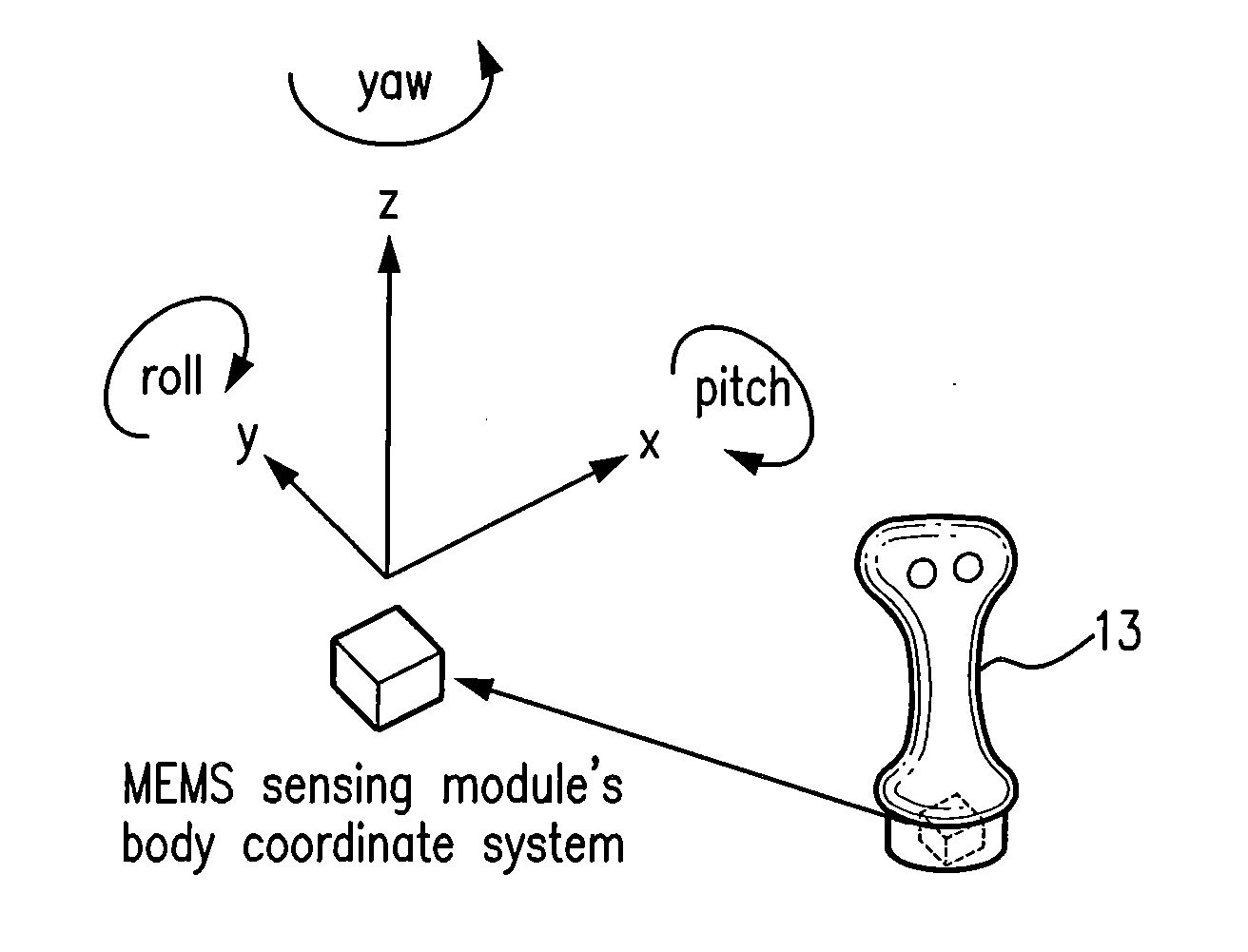
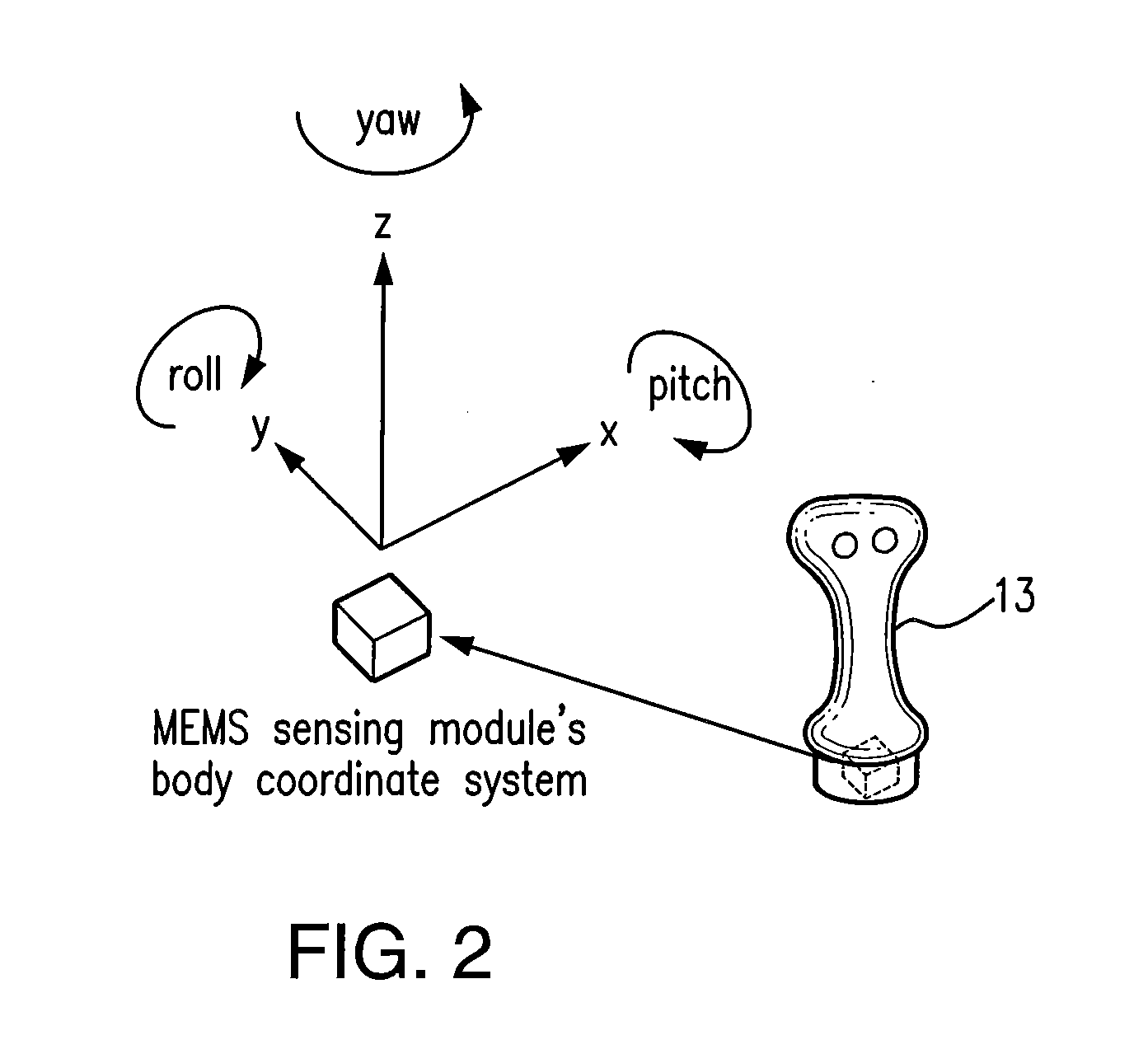
A control device for a vehicle or mechanism includes a portable displacement controller which permits a non-technical user to achieve effective control of the vehicle or mechanism, by moving the portable displacement controller intuitively with little learning effort. A first sensing device, attached to the displacement controller, detects the user's controlling motion. A second sensing device, attached to the object being controlled, detects motion thereof. An interface device receives signals from the sensing devices, processes those signals to determine relative motion of the controlling motion and the object's motion and outputs a control signal in accordance with the processed signals. The sensing devices each detect motion in six degrees of freedom; the sensing devices each include a three-axis accelerometer, a three-axis gyroscope, and a three-axis magnetometer. In specific embodiments, the accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers include micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) devices.
Owner:MEASUREMENT SYST
Six-degree-of-freedom vibration isolation platform based on Stewart parallel mechanism
ActiveCN103587724AImprove reliabilityIsolation of High Frequency DisturbancesNon-rotating vibration suppressionSpacecraft guiding apparatusFlexible MechanismsAttitude control
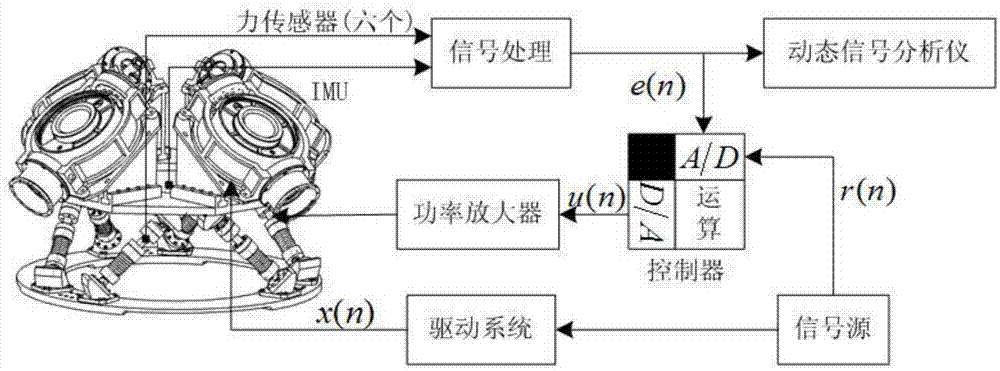
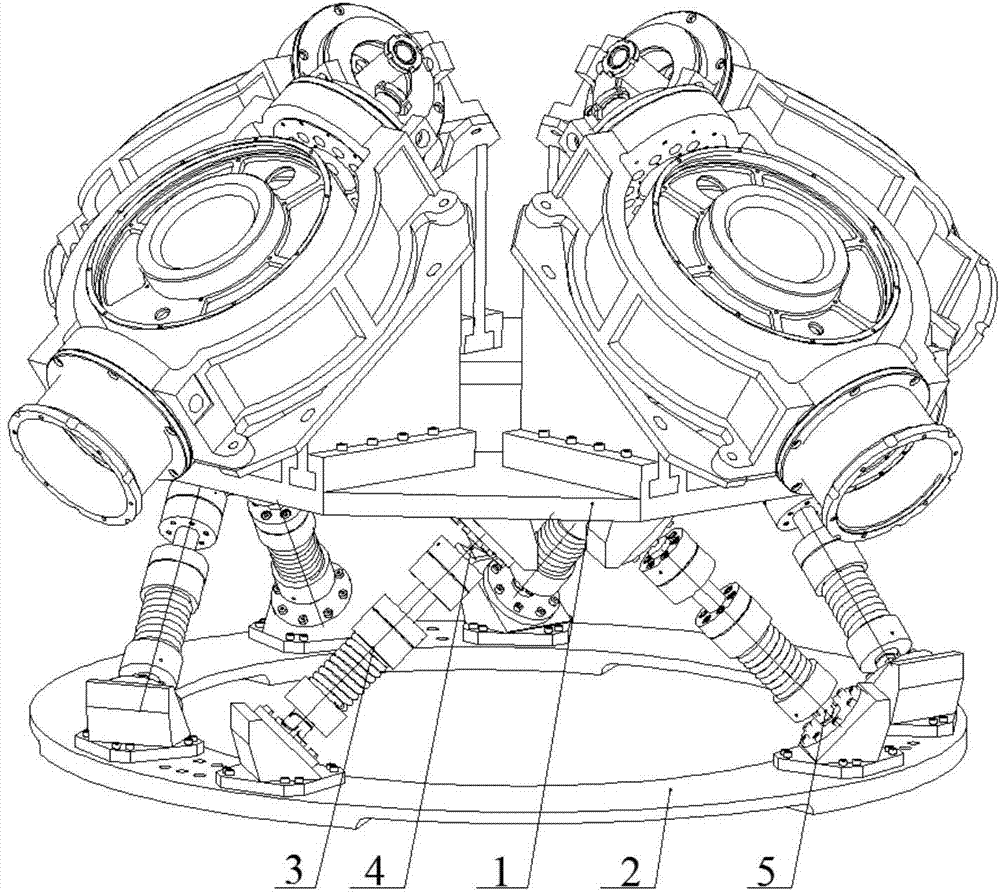
The invention discloses a six-degree-of-freedom vibration isolation platform based on a Stewart parallel mechanism. Through the combination of active vibration isolation technology, passive vibration isolation technology, the optimized design of the spatial six-degree-of-freedom parallel movement mechanism, the design of flexible mechanisms and the like, designed is the six-degree-of-freedom vibration isolation platform which is capable of rigidly transmitting low-frequency attitude control signals and attenuating high-frequency jamming signals and which is resonance free. A control moment gyro group is integrated in the platform; multi-degree-of-freedom disturbance produced by the control moment gyro group is converted into six independent unidirectional linear vibrations. Telescopic bars are exactly the same in structural design and all provided with an active vibration isolation unit and a passive vibration isolation unit, which are used to isolate the six independent linear vibrations respectively.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
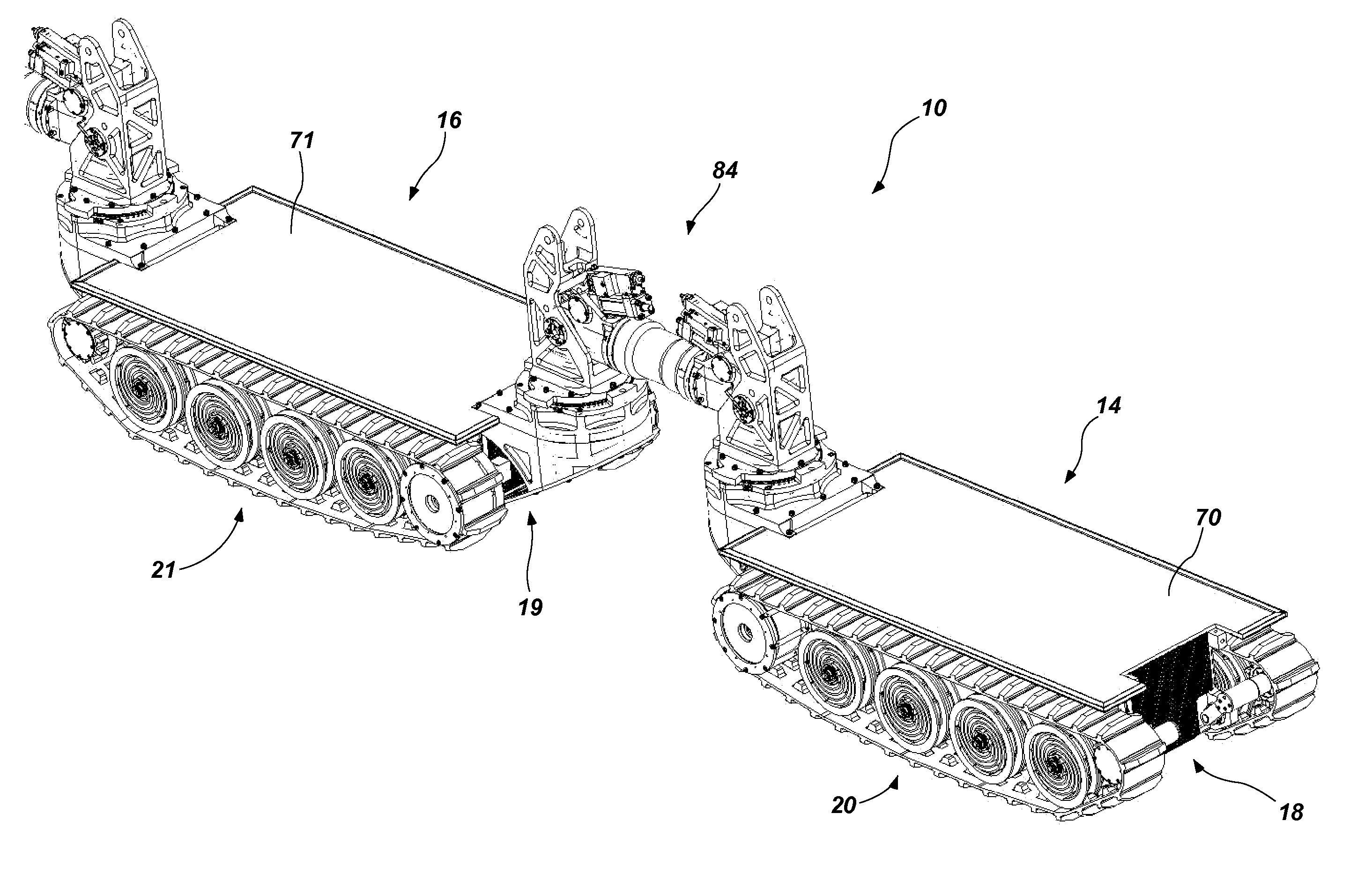
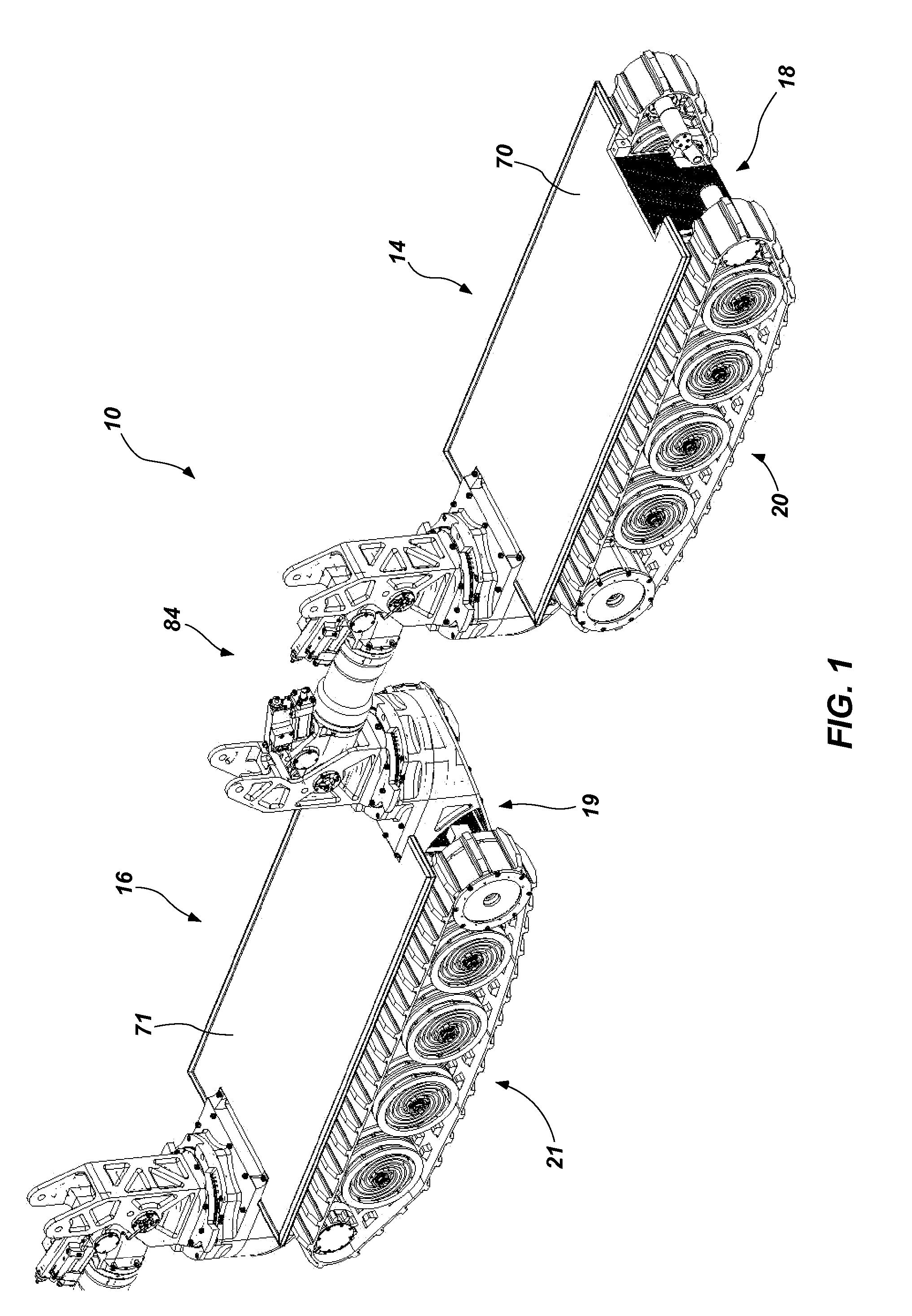
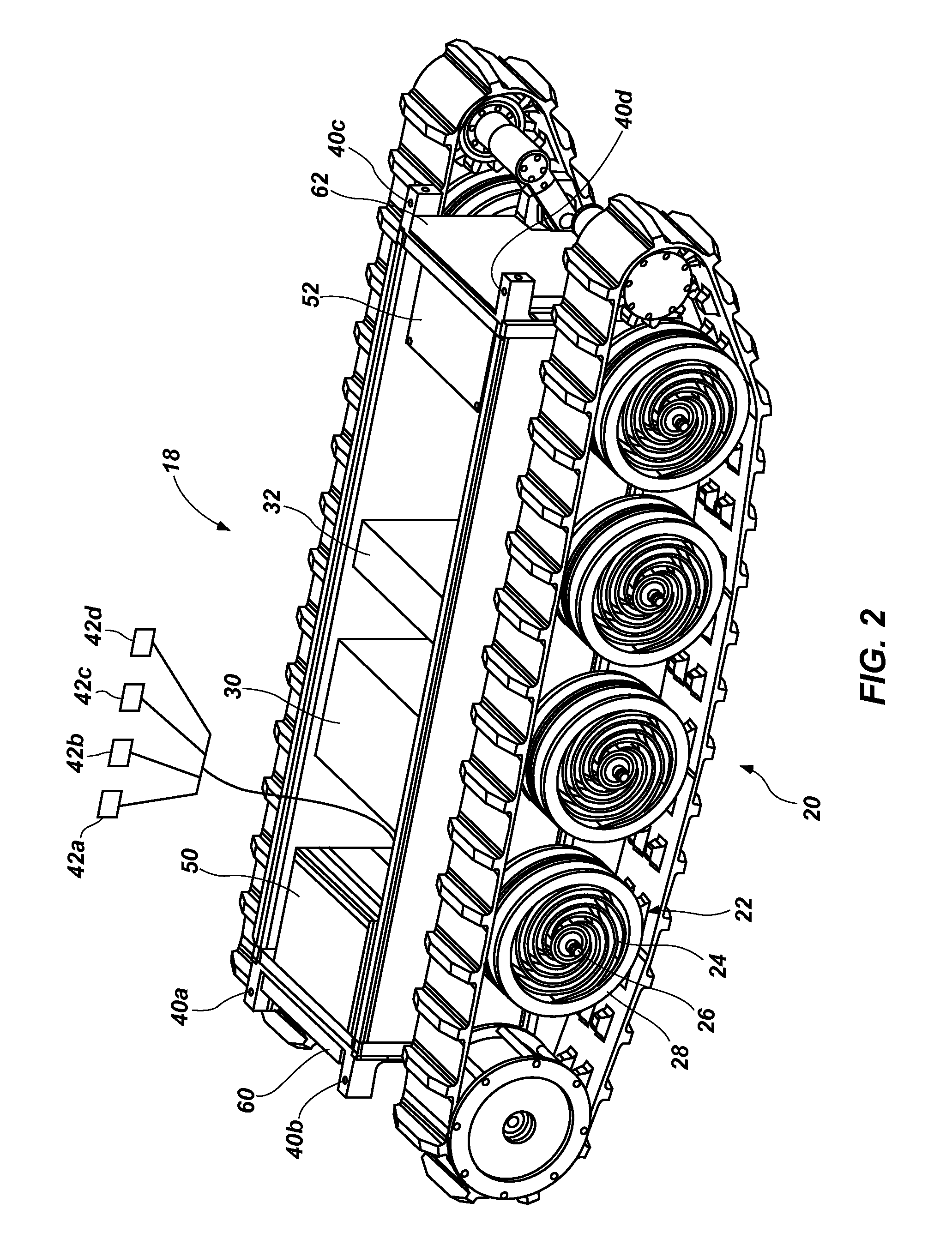
Robotic Mobile Low-Profile Transport Vehicle
ActiveUS20140246257A1Efficiently traverseImprove stabilityVehicle body stabilisationArmoured vehiclesTerrainControl system
A robotic mobile low-profile transport vehicle is disclosed. The vehicle can comprise a first transport module having a frame assembly, a mobility system, and a propulsion system and a second transport module having a frame assembly and a mobility system. A multi-degree of freedom coupling assemblage can join the first and second transport modules together. The vehicle can include a first platform supported about the frame assembly of the first transport module, and a second platform supported about the frame assembly of the second transport module. Each of the platforms can be configured to receive a load for transport. Additionally, the vehicle can include a control system that can operate to facilitate intra-module communication and coordination to provide a coordinated operating mode of the first and second transport modules and the coupling assemblage about a given terrain.
Owner:SARCOS LC
Multiple-freedom degree wearing type rehabilitation training robot for function of hand and control system thereof
InactiveCN101433491AFeel comfortableAdjustable sizeChiropractic devicesManipulatorLittle fingerRobotic arm
The invention discloses a multi-freedom wearable robot for hand function recovery. The robot comprises mechanical arms and mechanical fingers; the mechanical fingers consist of a mechanical thumb, a forefinger, a middle finger, a ring finger and a little finger, wherein the forefinger, the middle finger, the ring finger and the little finger have the same structure as that of the thumb; the mechanical forefinger mainly comprises air muscle, a finger end bracket, a first middle connecting piece, a finger front end bracket and a second middle connecting piece which are connected in turn through a connecting rod; the air muscle drives the second middle connecting piece to move through a rigid string so that the finger of a patient makes lituate and adduction exercises; the inside of each connecting piece is provided with a pressure spring; and inside walls of the two connecting pieces are distributed with rolling beads to reduce friction between the connecting rod and the connecting pieces. The invention also provides a control system and an integrated electricity stimulation system of the robot to assist a patient to rebuild muscle function. The robot provides an assisted exercise mechanism for the fingers, has multiple freedom degrees and dimension adjustable movement mechanism, and can effectively assist the patient to finish repeated training of composite exercise for fingers and complicated finger dividing exercise.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Multi-degree-of-freedom controllable mechanism type stacking robot
InactiveCN103029124AFlexible operationImprove flexibilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsEngineeringMulti degree of freedom
The invention discloses a multi-degree-of-freedom controllable mechanism type stacking robot, which comprises a pedestal, a rotary rack, an arm lifting mechanism, an end effector translation retaining mechanism and a flange, wherein the rotary rack is connected to the pedestal through a rotary pair; the arm lifting mechanism comprises a large arm, a small arm, a first driving rod, a first connecting rod, a second driving rod and a second connecting rod; all the rods are connected through hinges; the end effector translation retaining mechanism comprises a parallelogram mechanism consisting of the large arm, a first auxiliary connecting rod, a triangular auxiliary rack and the rotary rack and a parallelogram mechanism consisting of the small arm, a second auxiliary connecting rod, a triangular auxiliary rack and an end effector translation retainer; all the rods are connected through hinges; the flange is connected to the end effector translation retainer through the rotary pair; and different end effectors can be arranged according to actual requirements. The multi-degree-of-freedom controllable mechanism type stacking robot has the advantages of simple structure, high bearing capacity, large working space, flexibility in operation, capabilities of driving through a servo motor for control, realizing intelligence and digital control and meeting handling and stacking requirements of high speed, heavy load, precision and the like and extremely broad application prospect.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Multiple degree of freedom substrate manipulator
InactiveUS20030156270A1Reduce forceIncrease stiffnessMechanical apparatusMotor/generator/converter stoppersHigh bandwidthControl system
A system for manipulating a planar substrate such as a semiconductor wafer is provided. The manipulator is typically used in conjunction with an XY stage to focus and planarize a wafer with respect to a tool. The manipulator employs redundant actuators of different types and a control system that uses low-bandwidth, high efficiency actuators to provide low frequency forces and high-bandwidth, but less efficient, actuators to provide all other forces. The manipulator provides support and manipulation of a substrate while minimizing errors due to thermal distortion.
Owner:ACTIVE PRECISION
Multiple-degree-of-freedom anti-explosion mechanical arm
InactiveCN101797748AAvoid damageSo as not to damageProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsJoint componentDistributed control system
A multiple-degree-of-freedom anti-explosion mechanical arm relates to an anti-explosion mechanical arm. The anti-explosion mechanical arm comprises a six-degree-of-freedom joint component, a double-camera system, a distributed control system and an expansion system, wherein a front paw can be operated flexibly and diversely through the cooperative control of six joints; the double-camera system is used to provide front vision for rear operating staff so that the mechanical arm can be conveniently controlled to complete special tasks, the double-camera system comprises a main camera fixed on a front arm and a front-end camera fixed on a paw joint; the main camera has broad vision, the focus of the front-end camera is fine; the distributed control system is used to control the synergy movement of the six-degree-of-freedom component and various movements of the six-degree-of-freedom component, the distributed control system comprises a distributed control module, a magnetic absolute position sensing system and the like; and the expansion system is used to add different functions to meet different demands and increase the application range of the mechanical arm.
Owner:武汉若比特机器人有限公司
Intuitive multiple degrees of freedom portable control device
A control device for a vehicle or mechanism includes a portable displacement controller which permits a non-technical user to achieve effective control of the vehicle or mechanism, by moving the portable displacement controller intuitively with little learning effort. A first sensing device, attached to the displacement controller, detects the user's controlling motion. A second sensing device, attached to the object being controlled, detects motion thereof. An interface device receives signals from the sensing devices, processes those signals to determine relative motion of the controlling motion and the object's motion and outputs a control signal in accordance with the processed signals. The sensing devices each detect motion in six degrees of freedom; the sensing devices each include a three-axis accelerometer, a three-axis gyroscope, and a three-axis magnetometer. In specific embodiments, the accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers include micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) devices.
Owner:MEASUREMENT SYST
Robot motion control system
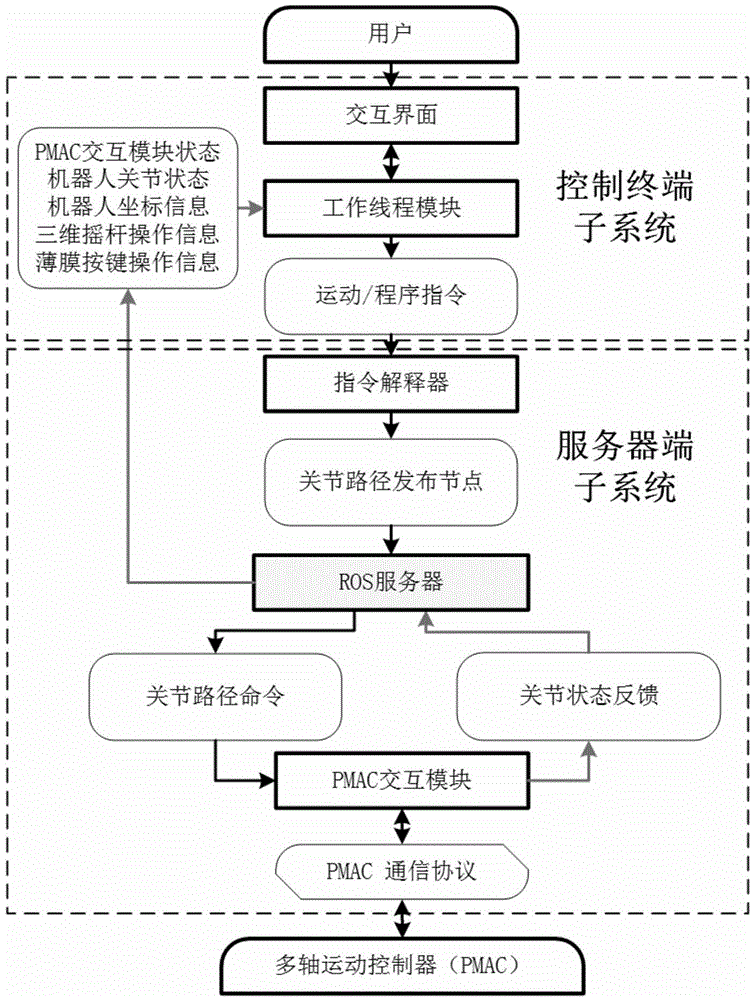
ActiveCN104699122AHigh degree of modularityImprove general performanceControl using feedbackNumerical controlExtensibilityInteraction interface
The invention discloses a robot motion control system, relates to the technical field of robot motion control, and aims to solve the problems of poor universality, poor extensibility and poor system openness existing in the existing robot motion control system. A control terminal subsystem comprises a human-computer interaction interface and a working thread module; a server terminal subsystem comprises an instruction interpreter, a server and an interaction module; a user transmits an operation instruction through the human-computer interaction interface; the operation instruction is converted into an instruction which can be recognized by the instruction interpreter by using the working thread module and is transferred to the instruction interpreter through network; the instruction interpreter is used for converting the received instruction into a joint path command by calling MoveIt ! and releasing on a node of an ROS (Read Only Storage) server; a PMAC (Programmable Multi Axis Controller) interconnection module receives the joint path command from the ROS server and converts into a motion control instruction through a PMAC communication protocol and transfers to PMAC through network. The system has higher modularization degree and extremely strong universality and can be compatible with various multi-degree-of-freedom series robots.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Back bonding platform for superchip
ActiveCN103367208ARigorous processHigh precisionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCircular discMicrometer
The invention discloses a back bonding platform for a superchip. The back bonding platform comprises a substrate, a chip peeling and overturning unit, an X-Y direction movement unit, a multi-degree of freedom bonding head and a mounting platform unit, wherein the chip peeling and overturning unit is used for respectively peeling and overturning a chip on a wafer disk and sending the chip to a to-be-picked position; the multi-degree of freedom bonding head is arranged on a supporting guide rail of the X-Y direction movement unit in a cantilever mode, and has functions of automatically levelling and aligning; the mounting platform unit is used for adsorbing the substrate and matched with the bonding head, so that the chip and the substrate are mutually positioned. In addition, in order to ensure the high-precision movement or matching of units, a plurality of vision positioning systems are configured in the back bonding platform. The back bonding platform can reach micrometer-level alignment accuracy, has the parallel adjusting accuracy of higher than 0.01 degree, and has the advantages of compact structure, convenience for operation and the like, so that the back bonding platform is particularly suitable for back bonding of the superchip.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Multi-degree-of-freedom 3D printer of fiber reinforced composite material and printing method thereof
The invention discloses a multi-degree-of-freedom 3D printer of a fiber reinforced composite material and a printing method thereof. The 3D printing can be performed with any angle and any movement locus by making use of the flexibility of a manipulator; and a 3D printing head mounted on the multi-degree-of-freedom 3D printer can perform the 3D printing of a high-strength short fiber reinforced composite material, and can perform the splicing and the weaving of continuous resin-based long fiber to produce a structural body of a continuous fiber reinforced resin-based composite material. The multi-degree-of-freedom 3D printer can precisely control the orientation of reinforced fiber in a composite material part in the 3D printing process, and can realize the quick production of the composite material part with specific mechanical, electric and thermal performances and a complex structure. Meanwhile, a mold customized beforehand and a pretreated fiber prepreg tape are not needed in the process; and the multi-degree-of-freedom 3D printer is not only suitable for the production of large parts, but also suitable for the large-batch production of small parts, so that the production cost and the production period are largely reduced, and the wide application of the composite material parts is further promoted.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Multi-degree-of-freedom test stand for unmanned air vehicles
The invention is a multiple degree-of-freedom test stand for unmanned air vehicles, and is particularly useful for small or micro unmanned air vehicles. The stand is gravity balanced using springs such that no weight of any part of the stand becomes a burden to the tested vehicle when it flies while constrained to the stand. A joint and a plurality of members are used to enable multiple degrees of freedom.
Owner:ARROWHEAD CENT
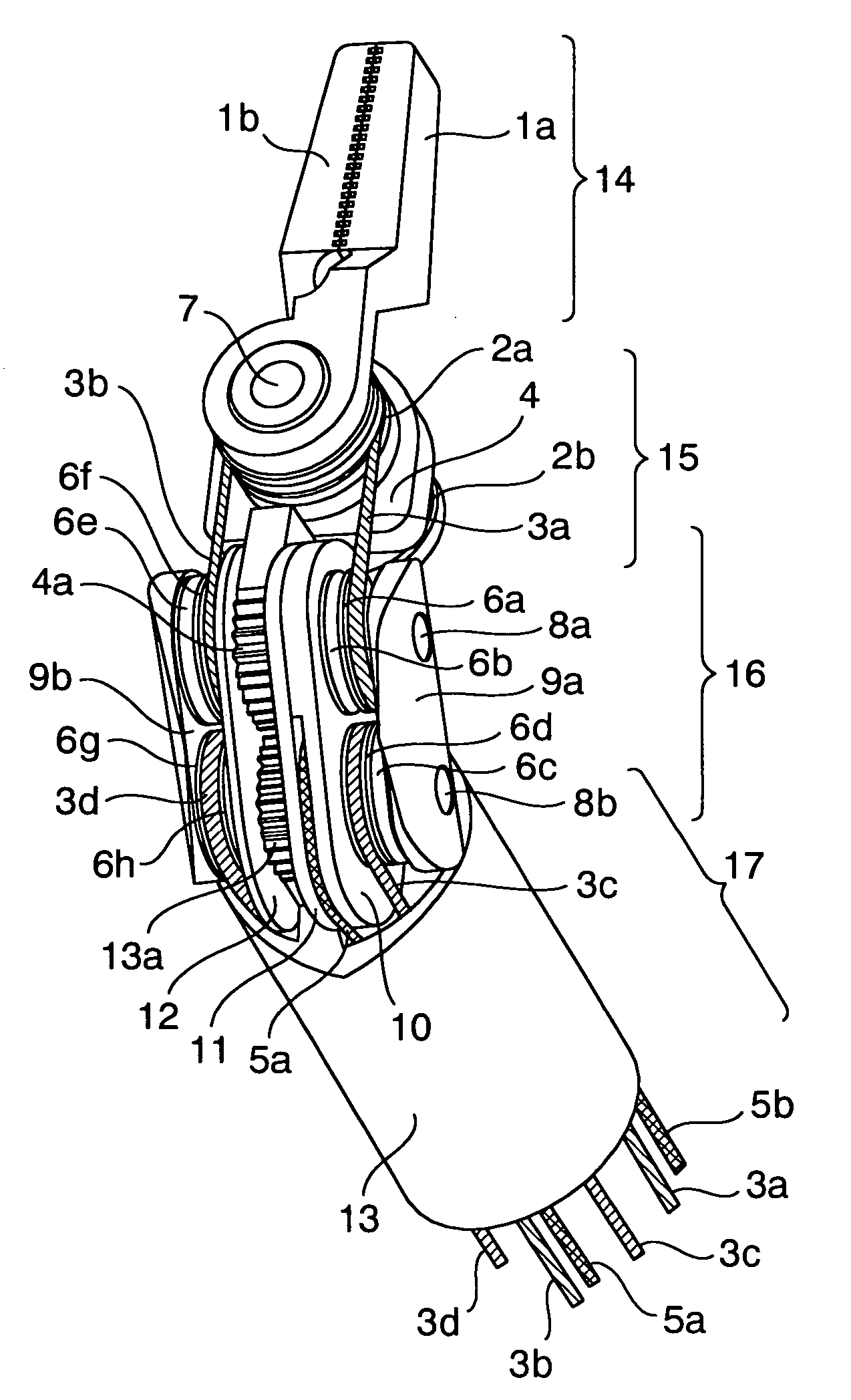
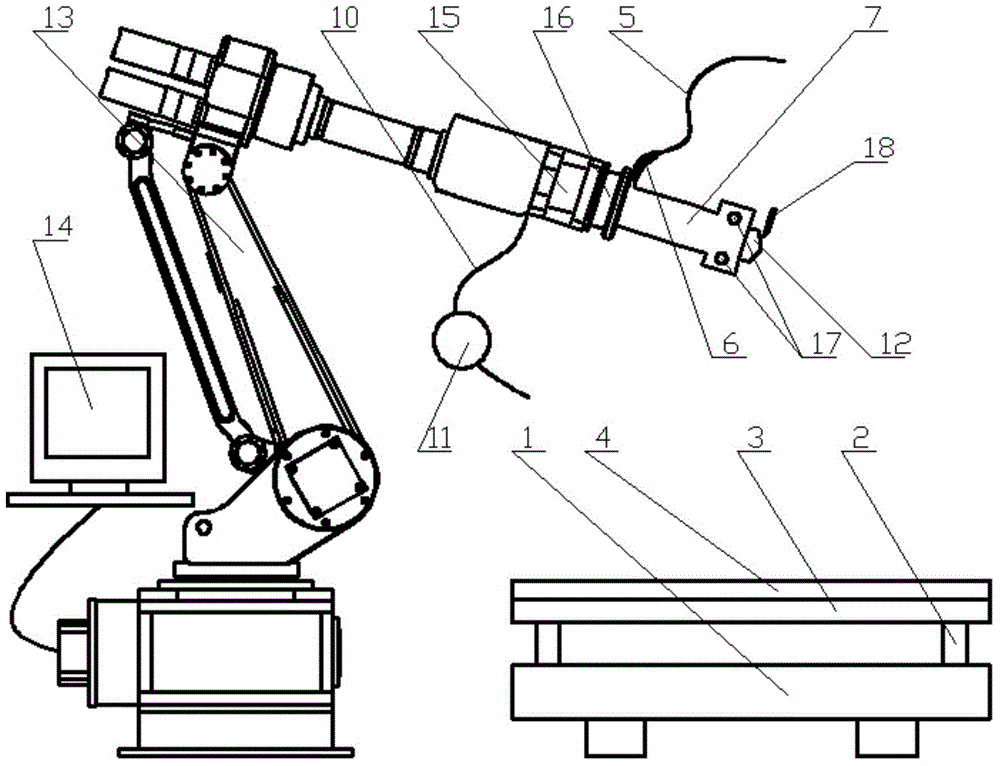
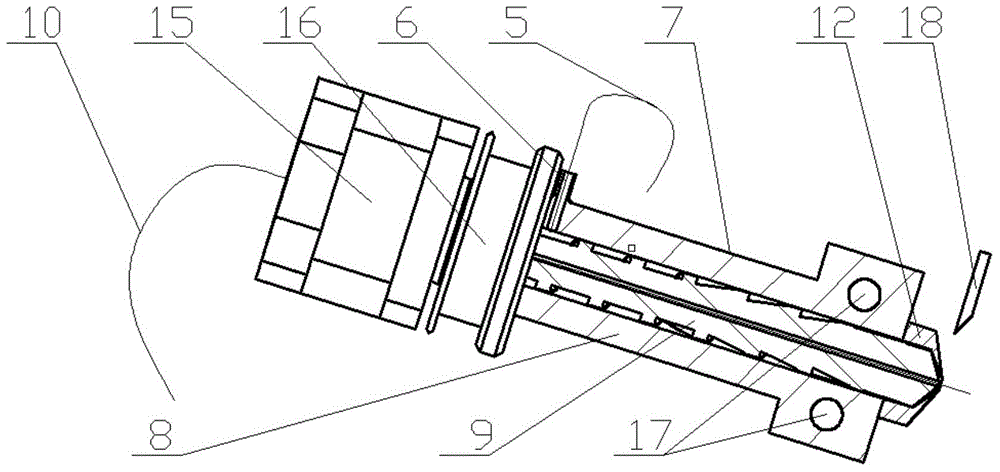
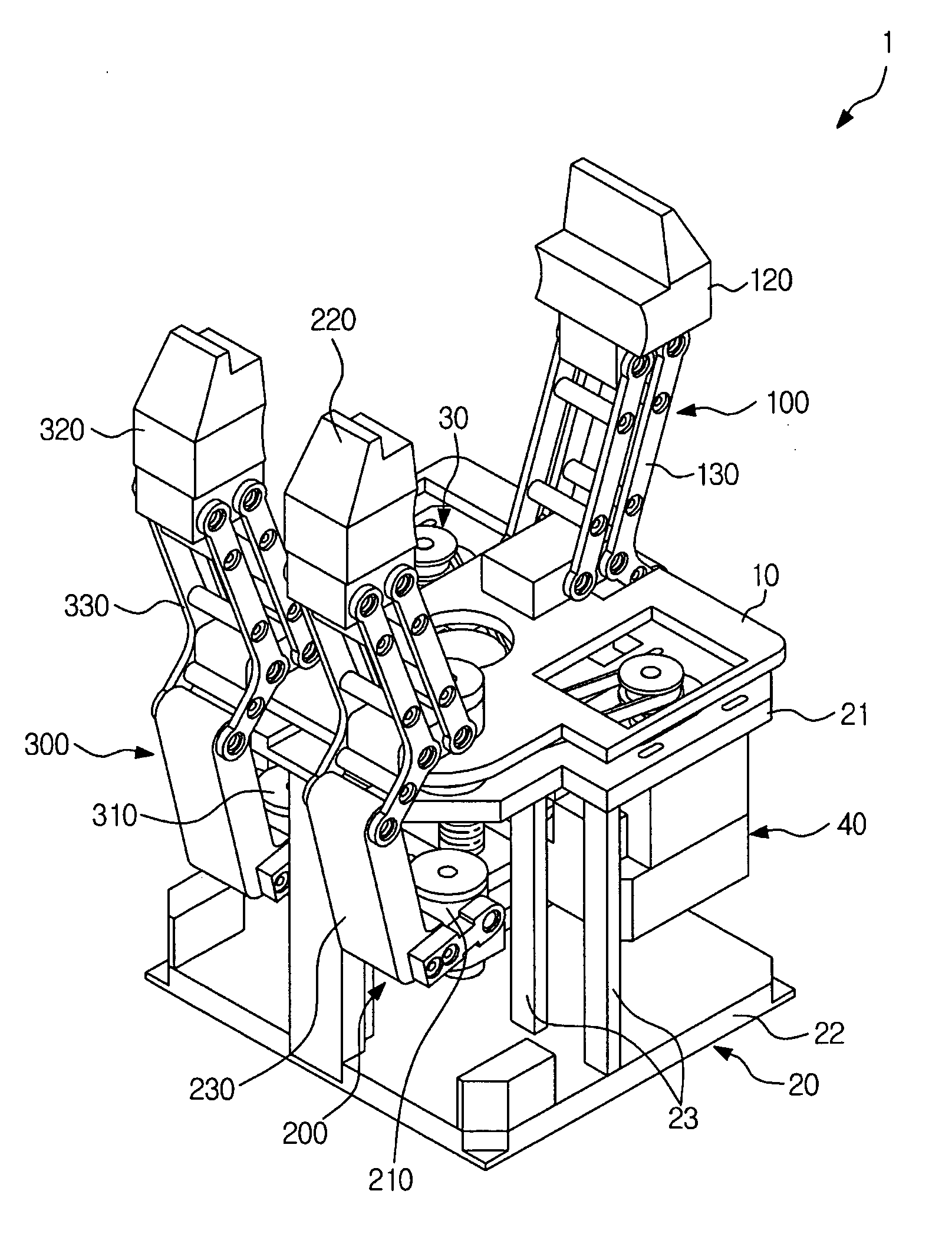
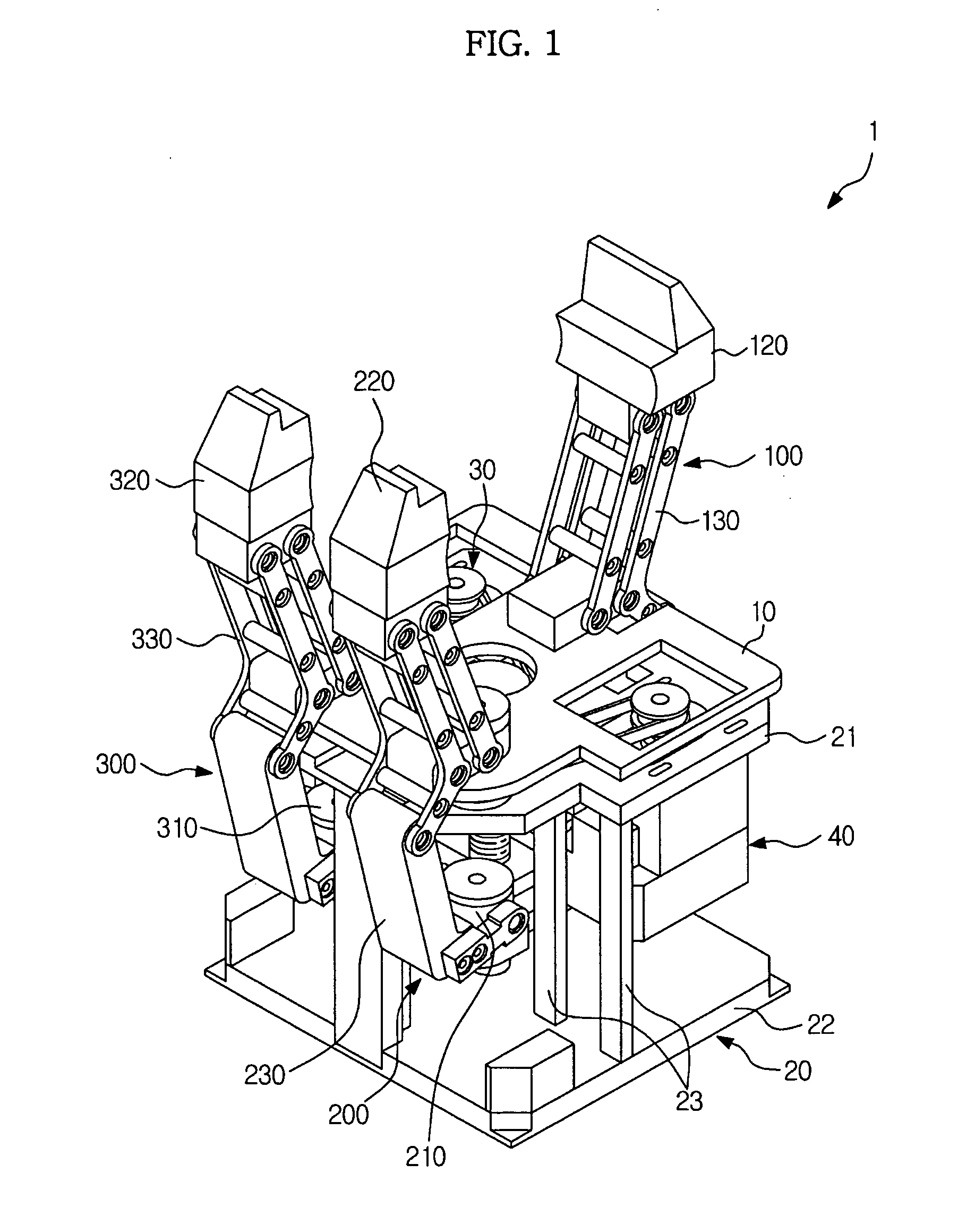
Industrial gripper with multiple degrees of freedom
An industrial gripper includes a base plate, at least three finger units to be moved relative to the base plate, a supporting unit to support the finger units, a first drive unit coupled to the supporting unit to allow simultaneous angular displacement of the finger units toward an object, and a second drive unit coupled to the supporting unit to adjust orientation angles between the finger units. Each of the finger units includes an intermediation member to be moved in a first direction by the first drive unit, a grip member to grip the object by being moved in a second direction different from the first direction as a movement direction of the intermediation member, and a connection member to convert the first direction movement of the intermediation member into the second direction movement of the grip member.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
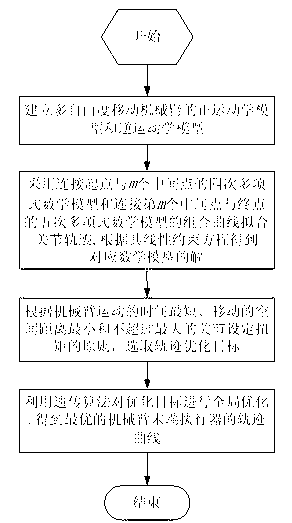
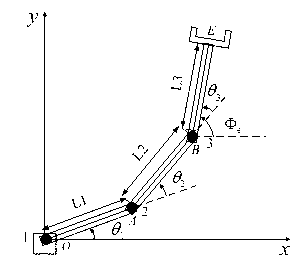
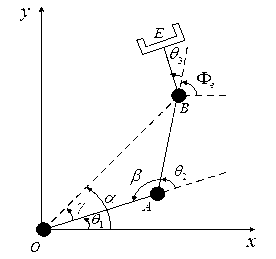
Genetic-algorithm-based trajectory planning optimization method for mobile mechanical arm
The invention relates to a genetic-algorithm-based trajectory planning optimization method for a mobile mechanical arm. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps of first establishing a forward kinematic model and an inverse kinematic model of a multi-degree-of-freedom mobile mechanical arm; then fitting a joint trajectory by adopting a composite curve of a quartic polynomial mathematical model and a quintic polynomial mathematical model, and calculating solutions of the corresponding mathematical models according to a linear constraint equation; next selecting a trajectory optimization target according to the principles of shortest motion time, minimum spatial motion distance and less than or equal to maximum set joint torque of the mobile mechanical arm; and finally globally optimizing the optimization target by utilizing a genetic algorithm to obtain an optimal trajectory curve of an end actuator of the mechanical arm. According to the method, the trajectory planning efficiency and the tracking accuracy of the mechanical arm are improved, and the problems of real-time trajectory planning of the mobile mechanical arm and trajectory planning optimization and control of the mechanical arm in an uncertain environment are also solved; and the trajectory planning optimization method for the mobile mechanical arm is effective.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
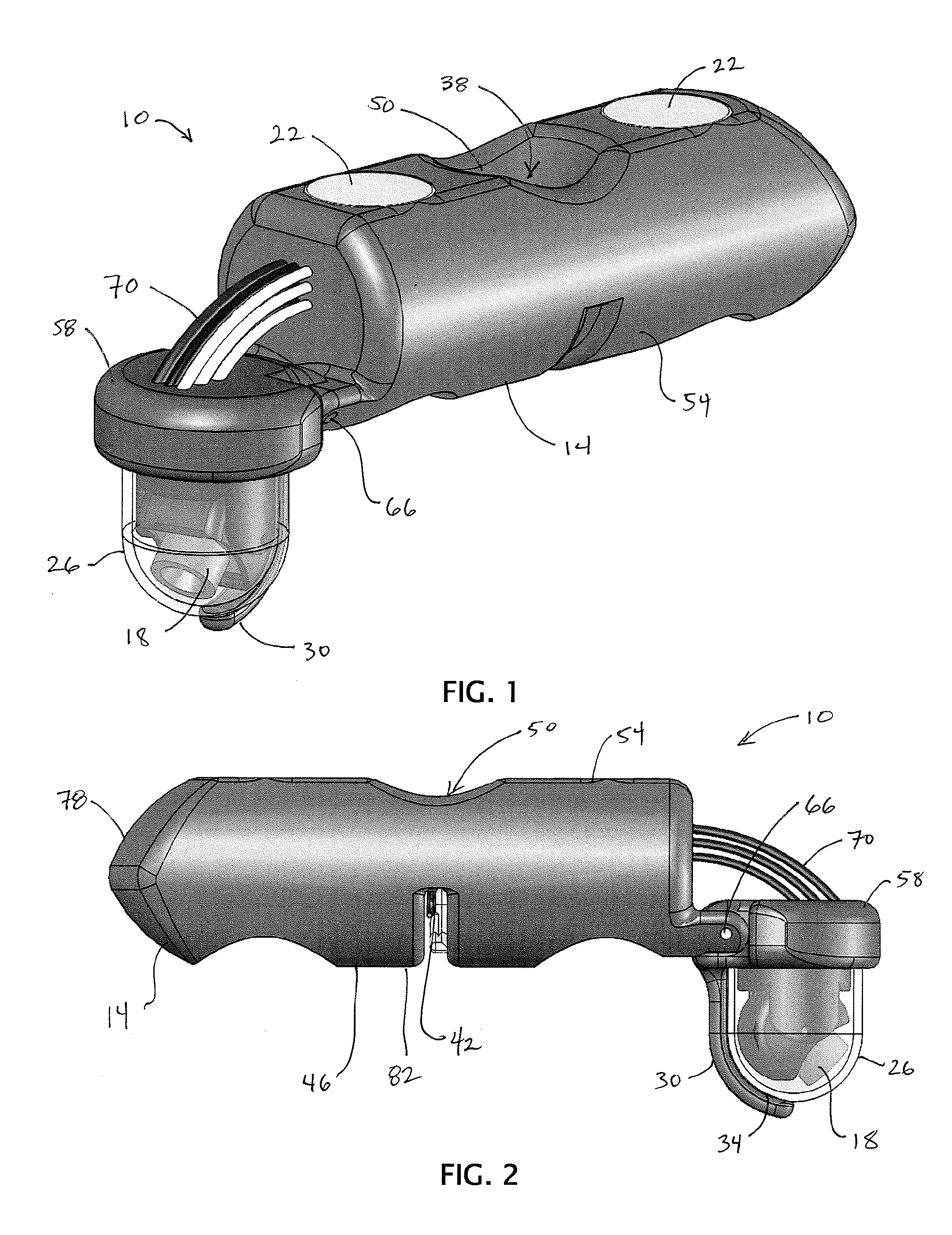
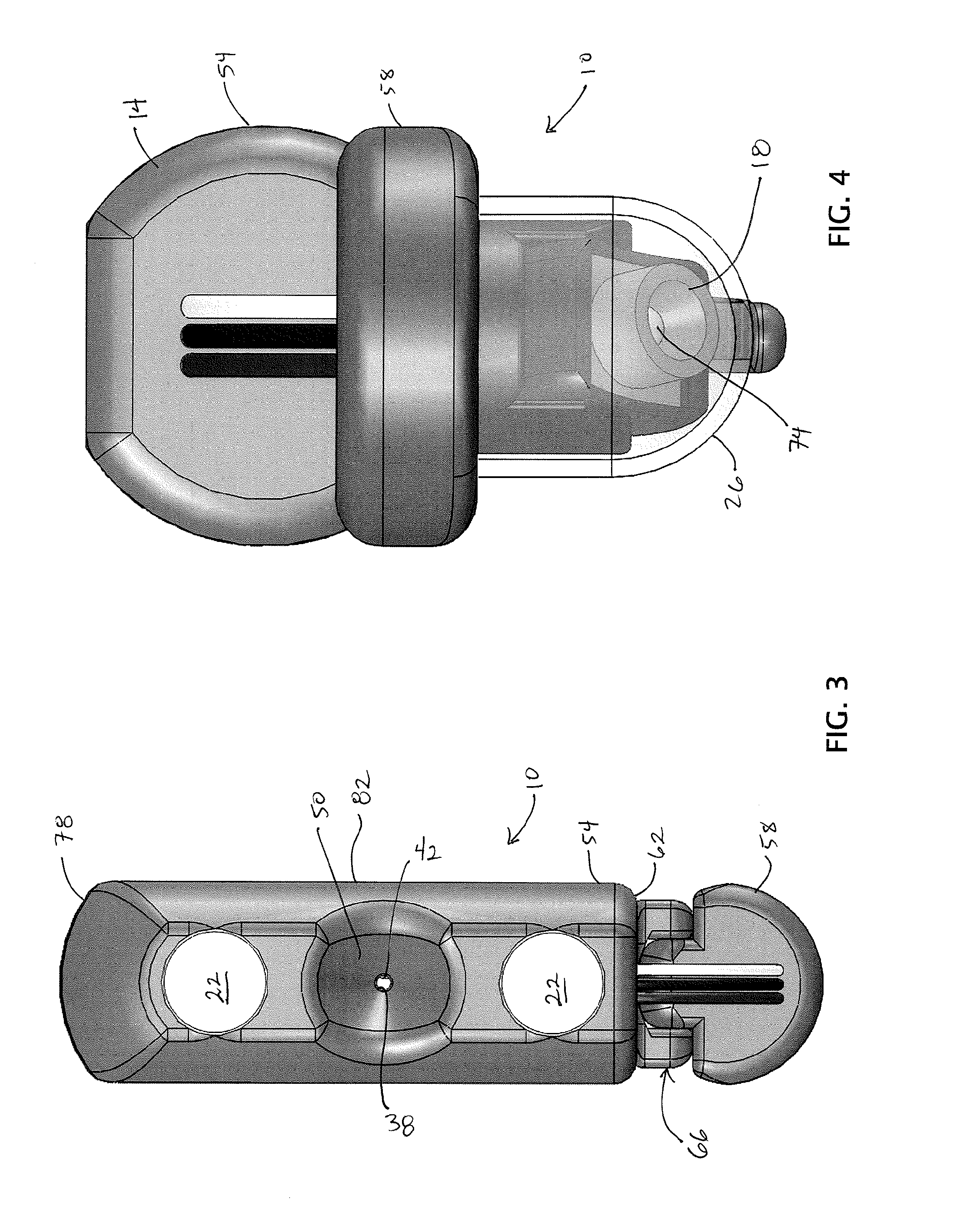
Medical Devices and Methods
The present invention relates generally to medical devices and methods. The present medical devices comprises a platform comprising a magnetically-attractive material, and a camera coupled to the platform and configured to be moved in at least three degrees of freedom relative to the platform, where the camera's movement in each respective degree of freedom is controlled by a separate actuator coupled to the platform. The medical devices further comprise a housing disposed around at least a portion of the camera, the housing being at least partially transparent, and a wiper arm configured to move relative to the housing. Some embodiments of the present multi-degree-of-freedom cameras for a medical procedure, comprises a platform comprising a magnetically-attractive material, an apparatus to moving the platform within a body cavity of a patient when the apparatus is outside the body cavity, the apparatus comprising a magnetic assembly, and a camera coupled to the platform, and configured to be moved in at least three degrees of freedom relative to the platform, where the camera's movement in each respective degree of freedom is controlled by a separate actuator coupled to the platform.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
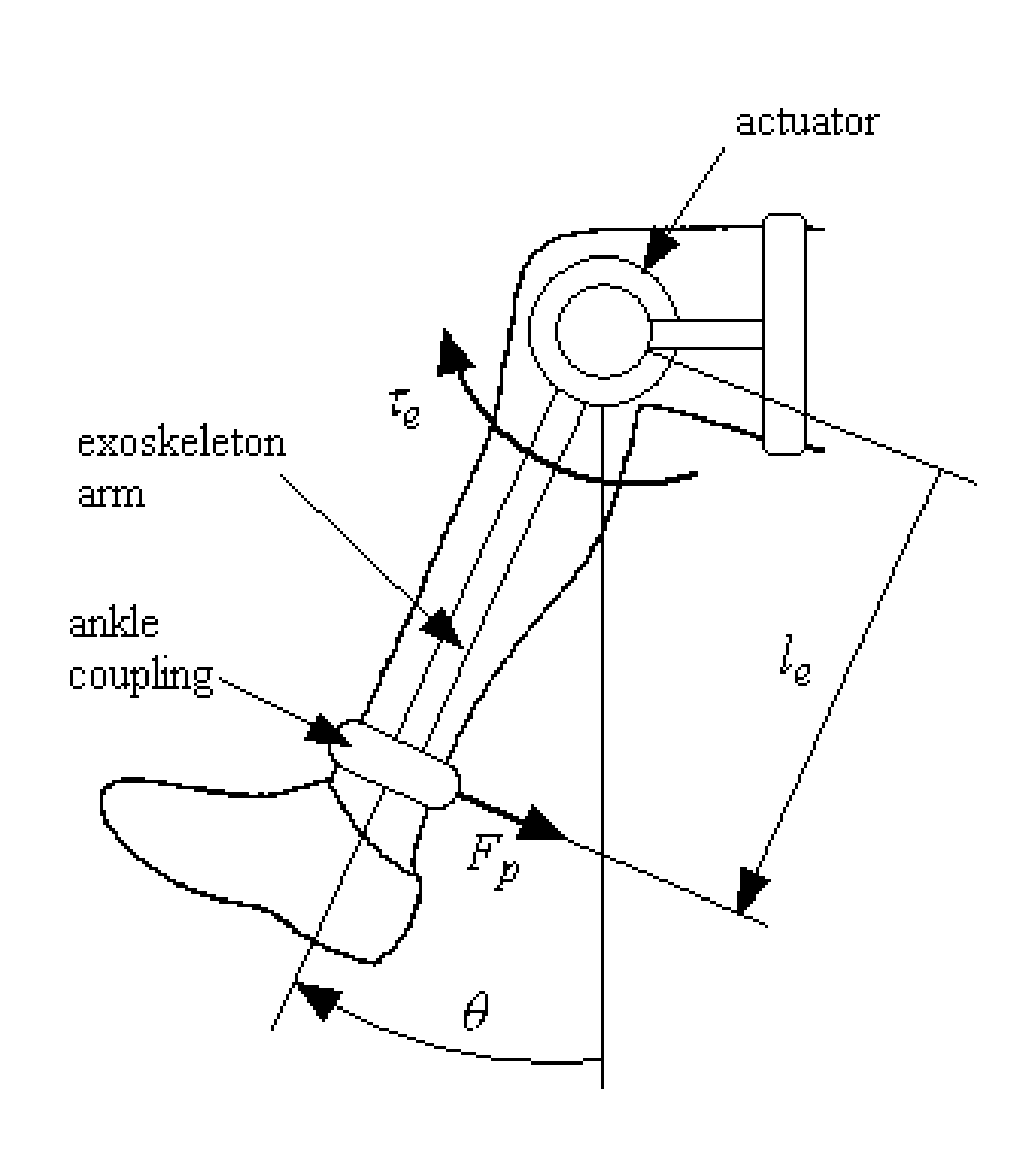
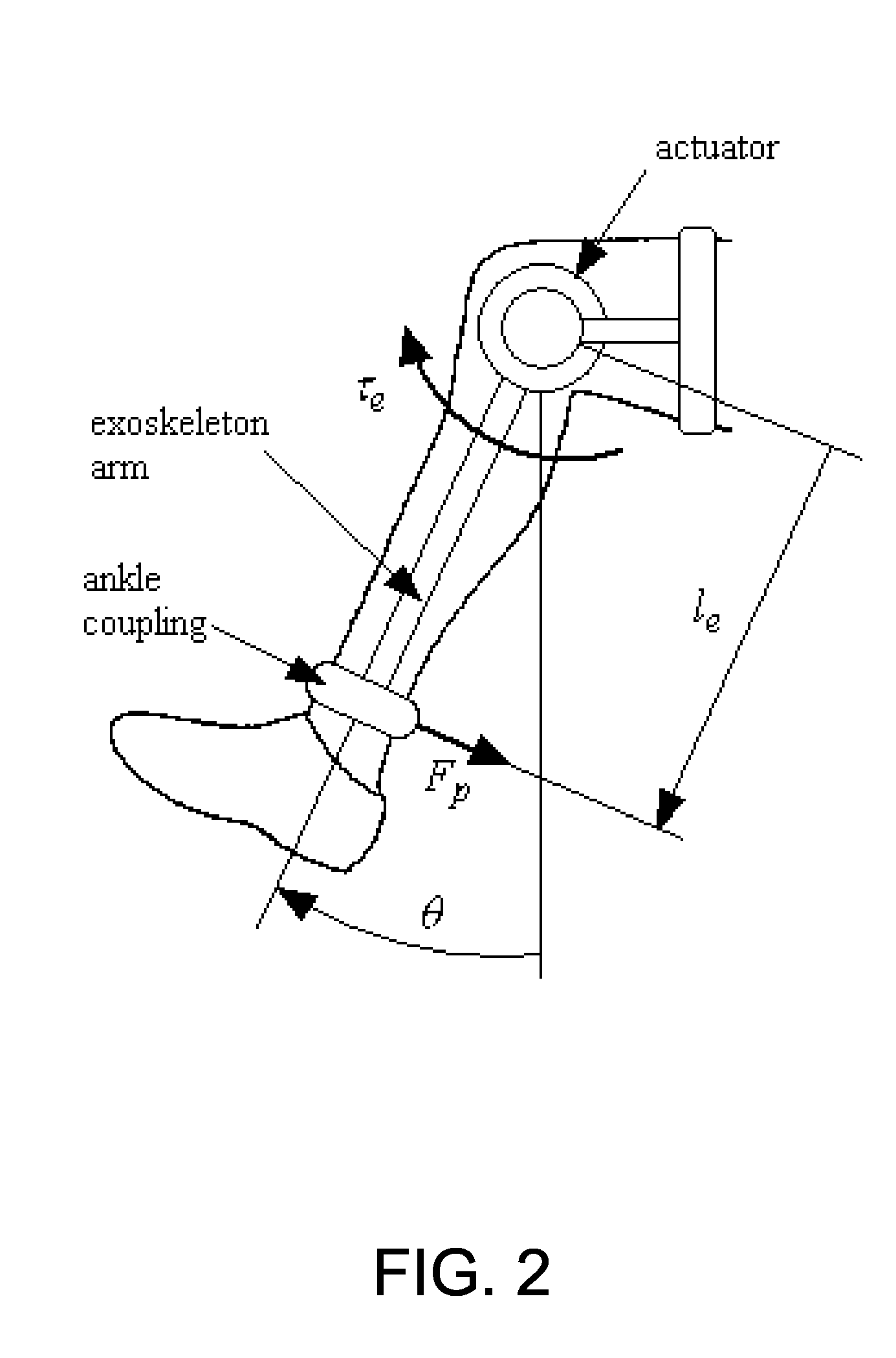
Controller for an assistive exoskeleton based on active impedance
ActiveUS7731670B2Reduce effortElectrotherapyChiropractic devicesMuscle strengthSingle degree of freedom
A system and method are presented to provide assist to a user by means of an exoskeleton with a controller capable of making the exoskeleton display active impedance. The exoskeleton assists the user by reducing the muscle effort required by the user to move his or her extremities. In one embodiment, a single-degree-of-freedom (1-DOF) exoskeleton assists a user with single-joint movement using an active impedance controller. In another embodiment, a multiple-degree-of-freedom (multi-DOF) exoskeleton assists a user with multiple-joint movement using an active impedance controller.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +1
Parallel multi-degree-of-freedom ankle joint rehabilitation trainer
InactiveCN101999970AReduce the burden onImprove rigidityChiropractic devicesThighPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention relates to a parallel multi-degree-of-freedom ankle joint rehabilitation trainer which comprises a thigh support seat, a thigh support seat inner rod, a thigh support seat outer rod, a calf jointing sleeve, a pelma supporting plate, a base plate, a first kinematics limb, a second kinematics limb and a third kinematics limb, wherein the lengths of the first kinematics limb, the second kinematics limb and the third kinematics limb are adjustable, the upper ends of the first kinematics limb, the second kinematics limb and the third kinematics limb are connected with the pelma supporting plate through a spherical hinge, and the lower ends of the first kinematics limb, the second kinematics limb and the third kinematics limb are connected with the base plate through a hook joint.In the invention, a 3-UPS / S-shaped parallel mechanism is adopted, the ankle joint rehabilitation trainer has three rotational degrees of freedom, and the rotational center is an ankle joint, and three types of movements of ankle back stretching and plantar flexion, introversion and extroversion, and internal rotation and external rotation are realized; the ankle joint rehabilitation trainer of the invention has a rigid structure and high carrying capacity, and can relieve the burden of the impaired joint effectively; and the ankle joint rehabilitation trainer invention ensures that the spherical surface movement of the ankle joint can be simulated actually, and has high bio-imitability.
Owner:SHANGHAI DIANJI UNIV
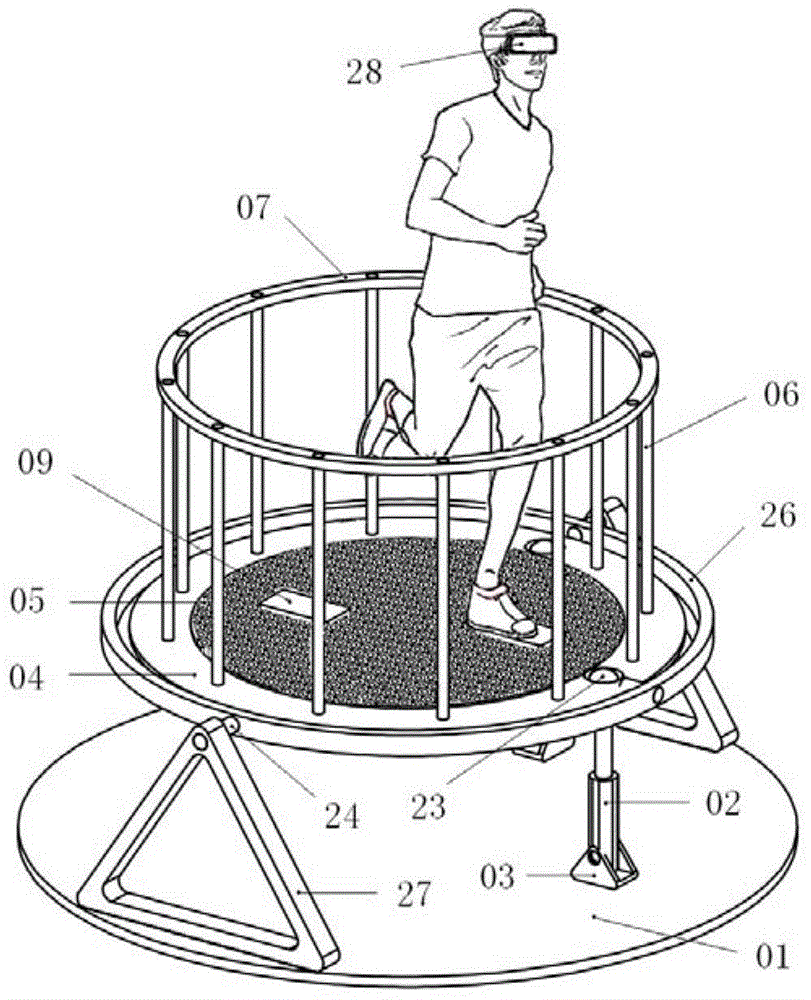
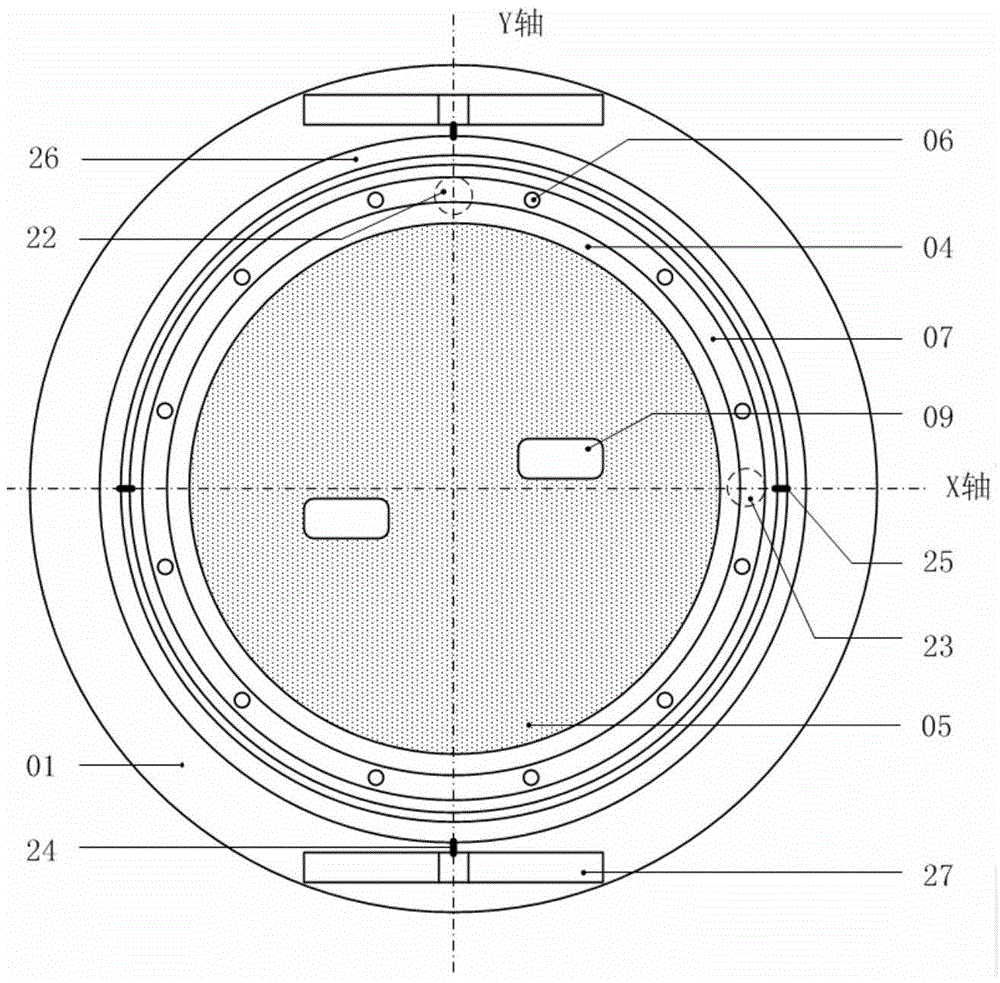
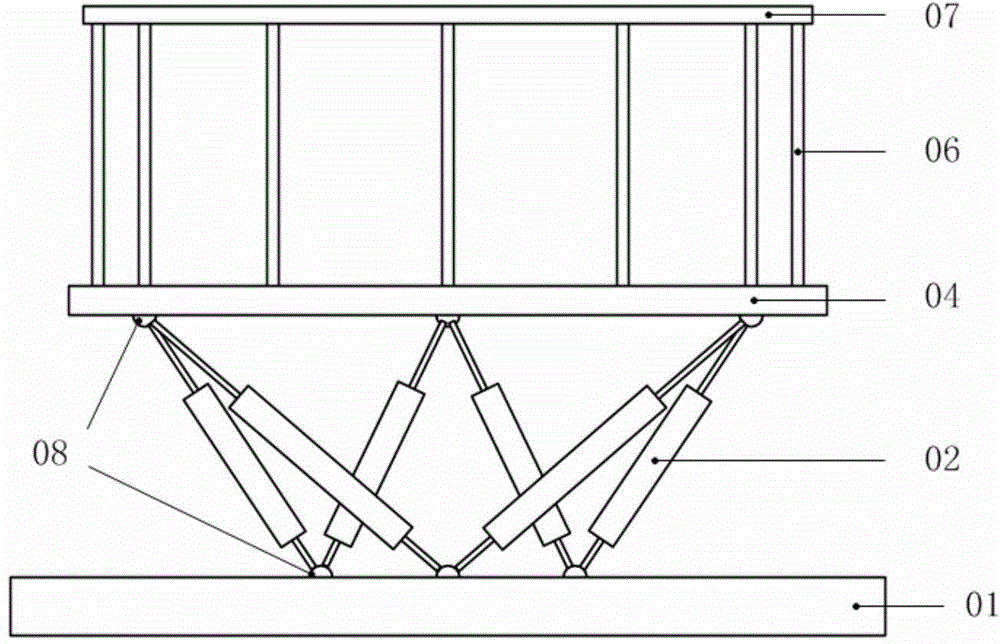
Electromagnetic type multi-degree of freedom virtual roaming platform
ActiveCN104461018AAchieve rotary motionRealize planar driveInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingControl systemEyewear
An electromagnetic type multi-degree of freedom virtual roaming platform comprises a moving platform, a platform tilt actuating mechanism, a platform tilt perception system, two mats, a foot motion perception system, a corresponding flotation structure, a pressure sensor and the like, wherein the moving platform is composed of an array magnetic-driven unit, and the two mats are suspended on the platform and allow a user to directly tread. By means of the virtual reality technology, forward road situations and surrounding panoramic environments are displayed in real time on a helmet displayer or specific glasses of the user, and the user can select and move forward according to the situation. A control system can precisely control the mats so that the mats can bear the feet of the user to equivalently finish walking, running and other motions in the range of the platform, corresponding virtual scenes are changed synchronously according to the specific forwarding situations of the user to achieve the roaming effect. The user can move linearly on site on the platform and can turn left and right, particularly, real ground slope experience can be obtained through proper tilt of the platform.
Owner:河北腾云信息技术有限公司
Multi-degree-of-freedom single-wound-hole robot flexible hand for celiac minimally invasive surgery
ActiveCN102499759ARealize single wound surgeryFlexible operationDiagnosticsSurgical robotsSurgical operationAbdominal cavity
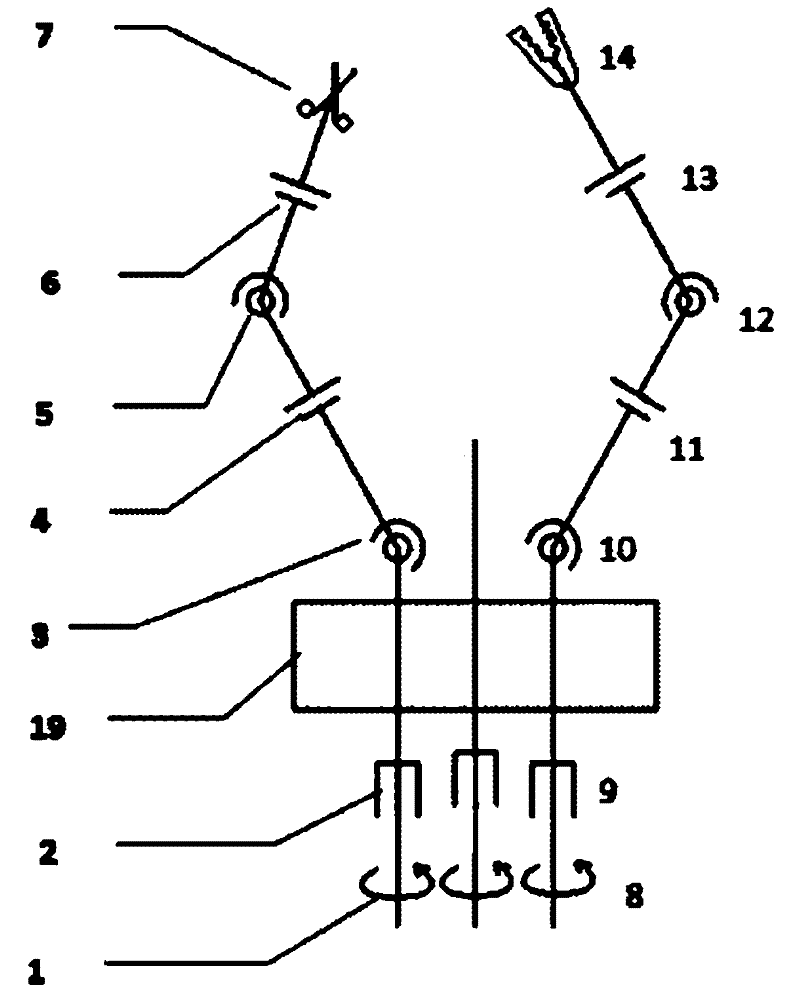
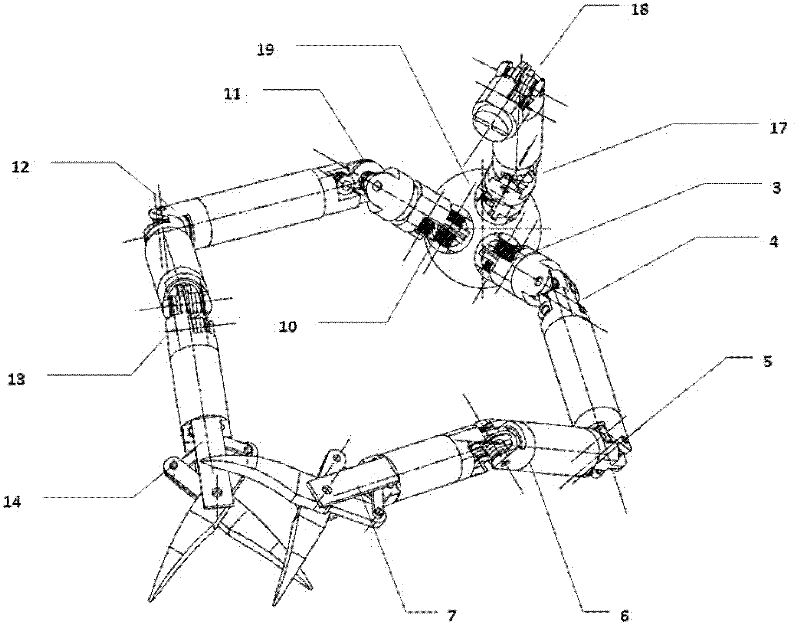
The invention discloses a multi-degree-of-freedom single-wound-hole robot flexible hand for celiac minimally invasive surgery, which comprises two seven-degree-of-freedom mechanical arms and a five-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm. Tail ends of the seven-degree-of-freedom mechanical arms are provided with scalpels, the tail end of the five-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm is provided with a cameral, seven degrees of freedom of each seven-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm include the rotation degree of freedom around a center shaft of the arm, the arm front and back stretching and retracting degree of freedom, the horizontal swinging degree of freedom, the vertical swinging degree of freedom, the horizontal swinging degree of freedom, the vertical swinging degree of freedom and the tool degree of freedom which are successively arranged from the root of the seven-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm, the front and back stretching and retracting degree of freedom and the rotation degree of freedom around a center line of the arm are arranged at the tail end, which contacts with a mouth gag, of the five-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm, three planar swinging degrees of freedom deeply penetrate into the mouth gag and are successively arranged from the root of the five-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm, and transmission of each degree of freedom is controlled via a steel wire. The multi-degree-of-freedom single-wound-hole robot flexible hand is a single-hole operation multi-degree-of-freedom mechanism, and can realize surgical operations including incising, pulling, suturing and the like, so that operability and accuracy of the surgery are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
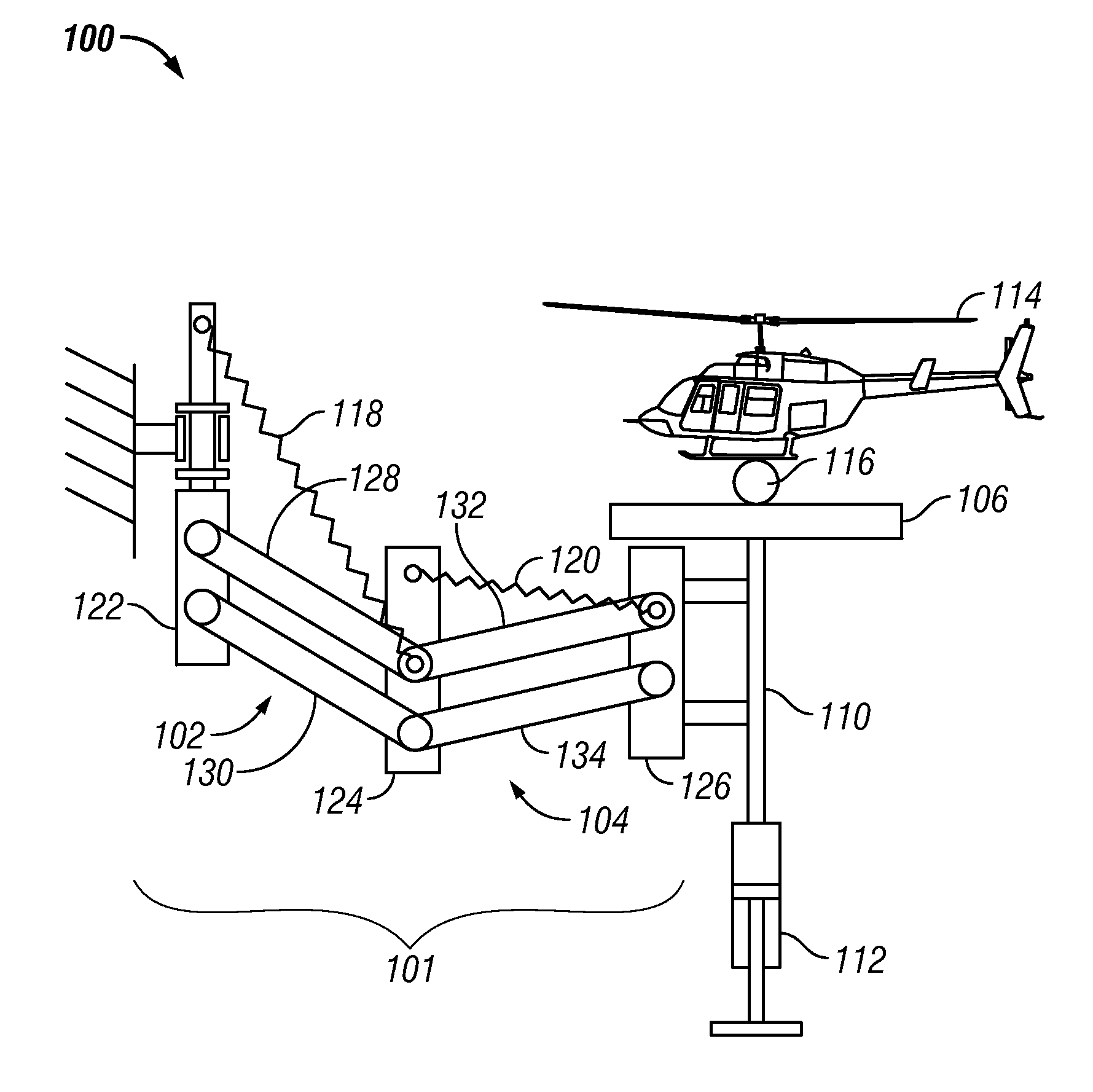
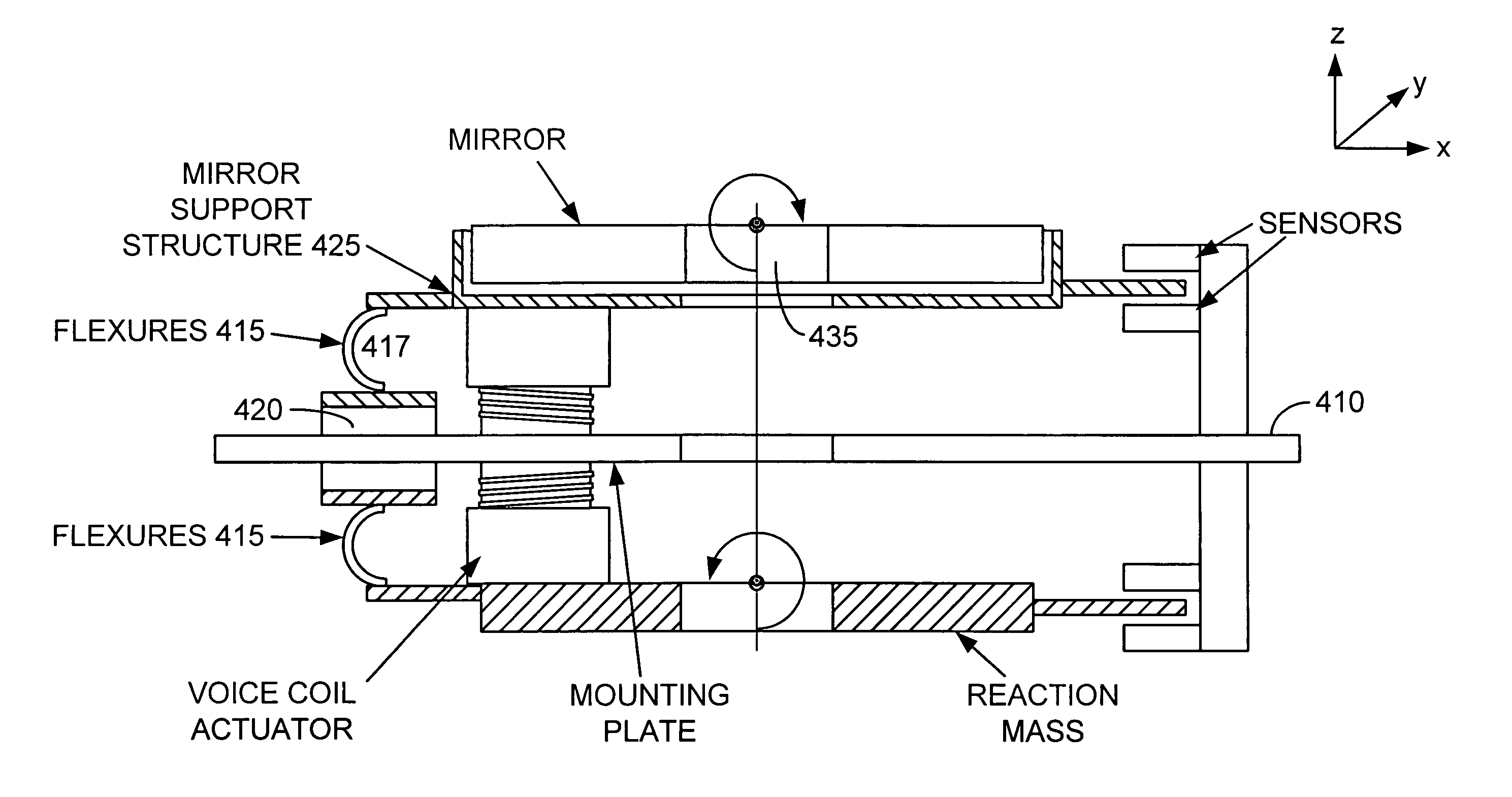
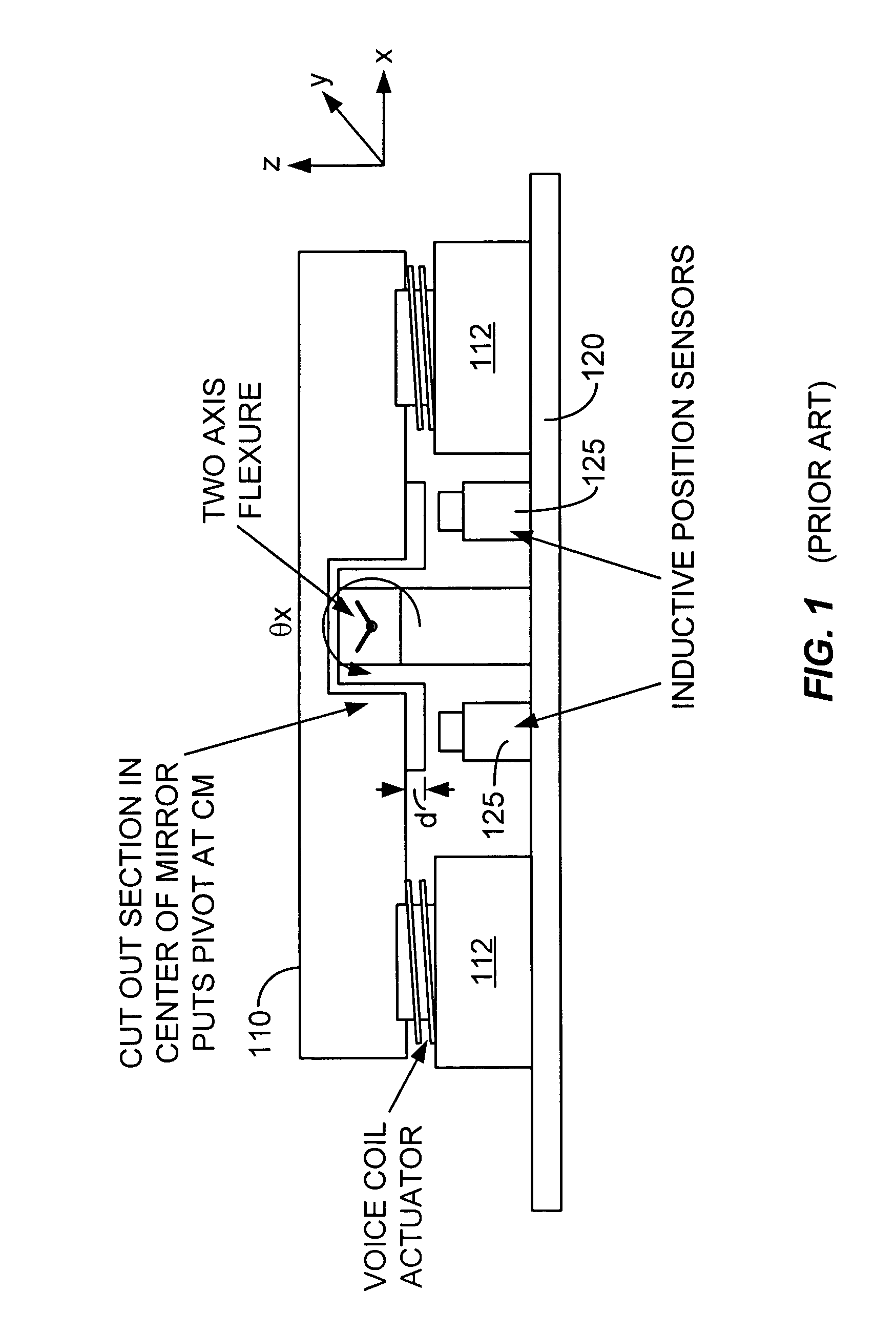
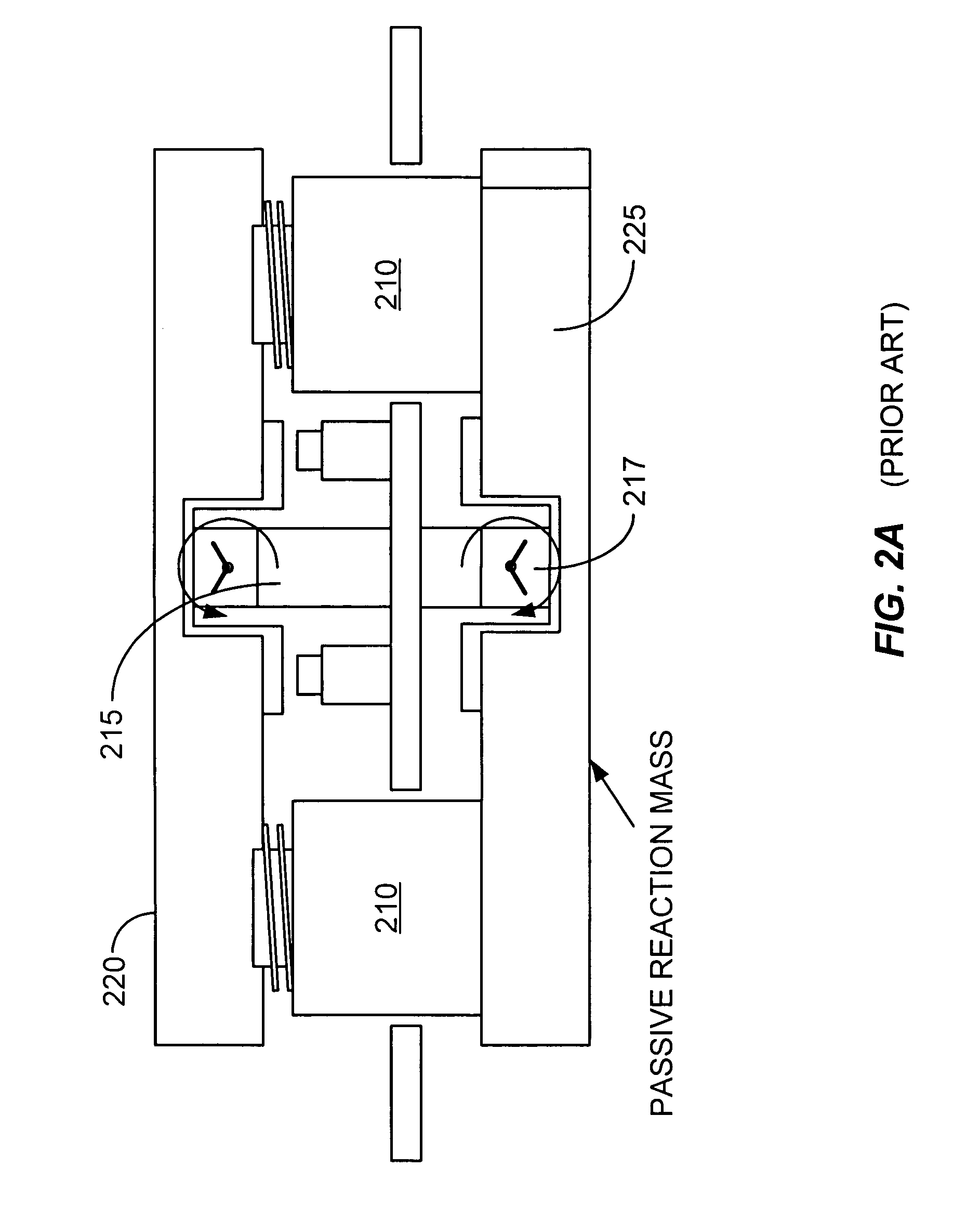
Actively-supported multi-degree of freedom steerable mirror apparatus and method
A steerable mirror assembly, the assembly comprising a mounting plate and a mirror with a mounting surface and a reflective surface. The assembly further comprising at least one flexible connector coupled between the mounting plate and a peripheral portion of the mirror. The flexible connector is adapted to allow the mirror to move within a predetermined range along an axis perpendicular to the surface of the mirror and adapted to allow tilting of the mirror. The assembly also comprising at least one moveable support member coupled between the mounting plate and the mounting surface of the mirror. The moveable support member provides mechanical support to the mirror and is adapted to move the mirror within a predetermined range along an axis perpendicular to the surface of the mirror and adapted to allow tilting of the mirror. The assembly additionally comprising at least one position sensor.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
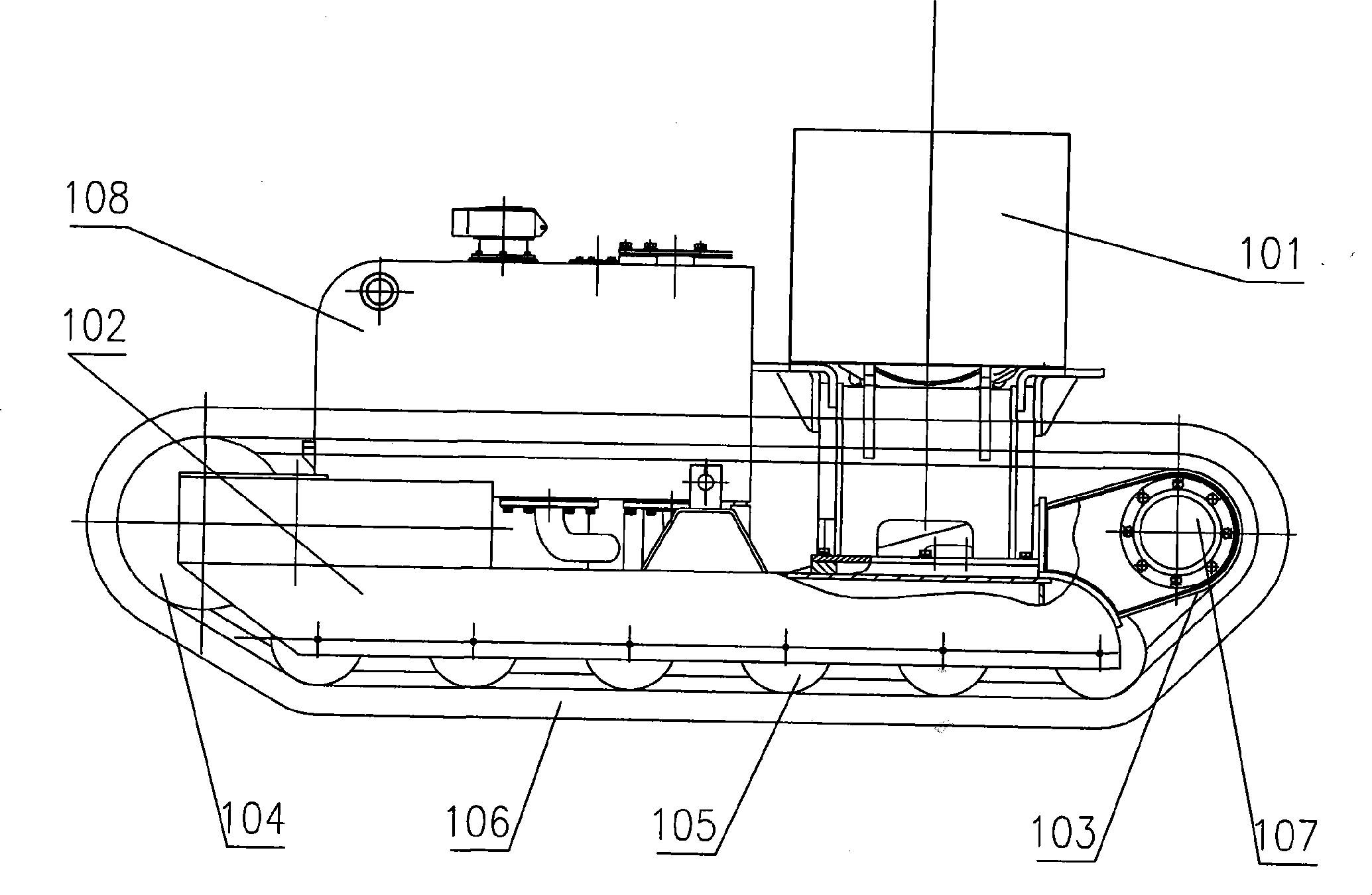
Anti-terrorist explosive-removal robot with multi-degree of freedom and large load manipulator
InactiveCN101362330AWide range of operationsEasy to handleProgramme-controlled manipulatorVehiclesFar distanceX-ray
The invention relates to an anti-terrorist explosive-removal robot with a manipulator with multiple degrees of freedom and heavy load, which belongs to the field of anti-terrorist equipment. The anti-terrorist explosive-removal robot consists of a walking chassis, a manipulator, a control system, an electric generator, a camera system, an external housing and the like. The waling chassis is a track structure, the electric generator is positioned at the tail part of the waling chassis, the manipulator is positioned at the front end of the walking chassis, the control system is arranged at the periphery of the manipulator seat, and the waling chassis, the electric generator and the manipulator seat are packed by the external housing. The camera system is provided with four cameras, wherein, a first camera is arranged in front of the robot for observing the front situation, a second camera is arranged on the manipulator for observing the action of a gripper, a third camera and a fourth camera are arranged above the external housing at the tail part of the robot, the operation condition of the mechanical arm is observed by the third camera, and the peripheral condition of the robot is observed by the fourth camera. In the operation environment of open ground, by the far distance control of an operator, questionable objects with large size can be inspected by the robot with an X-ray machine grasped by the mechanical arm, and questionable objects can be treated. The safety of the explosive-removal personnel can be effectively guaranteed during the treatment of the questionable objects.
Owner:SHANGHAI FIRE RES INST OF THE MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY +1
Multiple degree of freedom substrate manipulator
InactiveUS6756751B2Reduce forceIncrease stiffnessMechanical apparatusMotor/generator/converter stoppersHigh bandwidthControl system
A system for manipulating a planar substrate such as a semiconductor wafer is provided. The manipulator is typically used in conjunction with an XY stage to focus and planarize a wafer with respect to a tool. The manipulator employs redundant actuators of different types and a control system that uses low-bandwidth, high efficiency actuators to provide low frequency forces and high-bandwidth, but less efficient, actuators to provide all other forces. The manipulator provides support and manipulation of a substrate while minimizing errors due to thermal distortion.
Owner:ACTIVE PRECISION
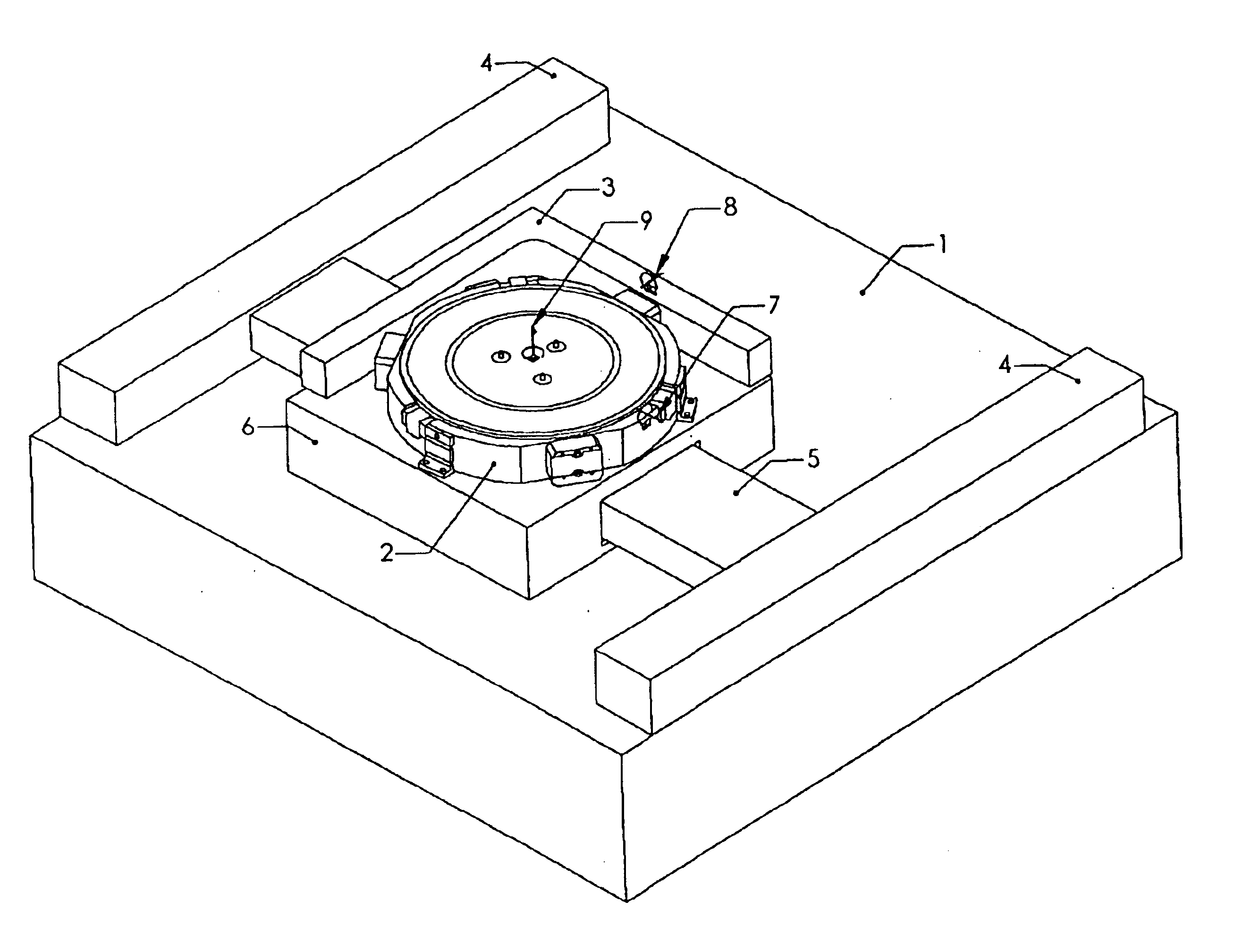
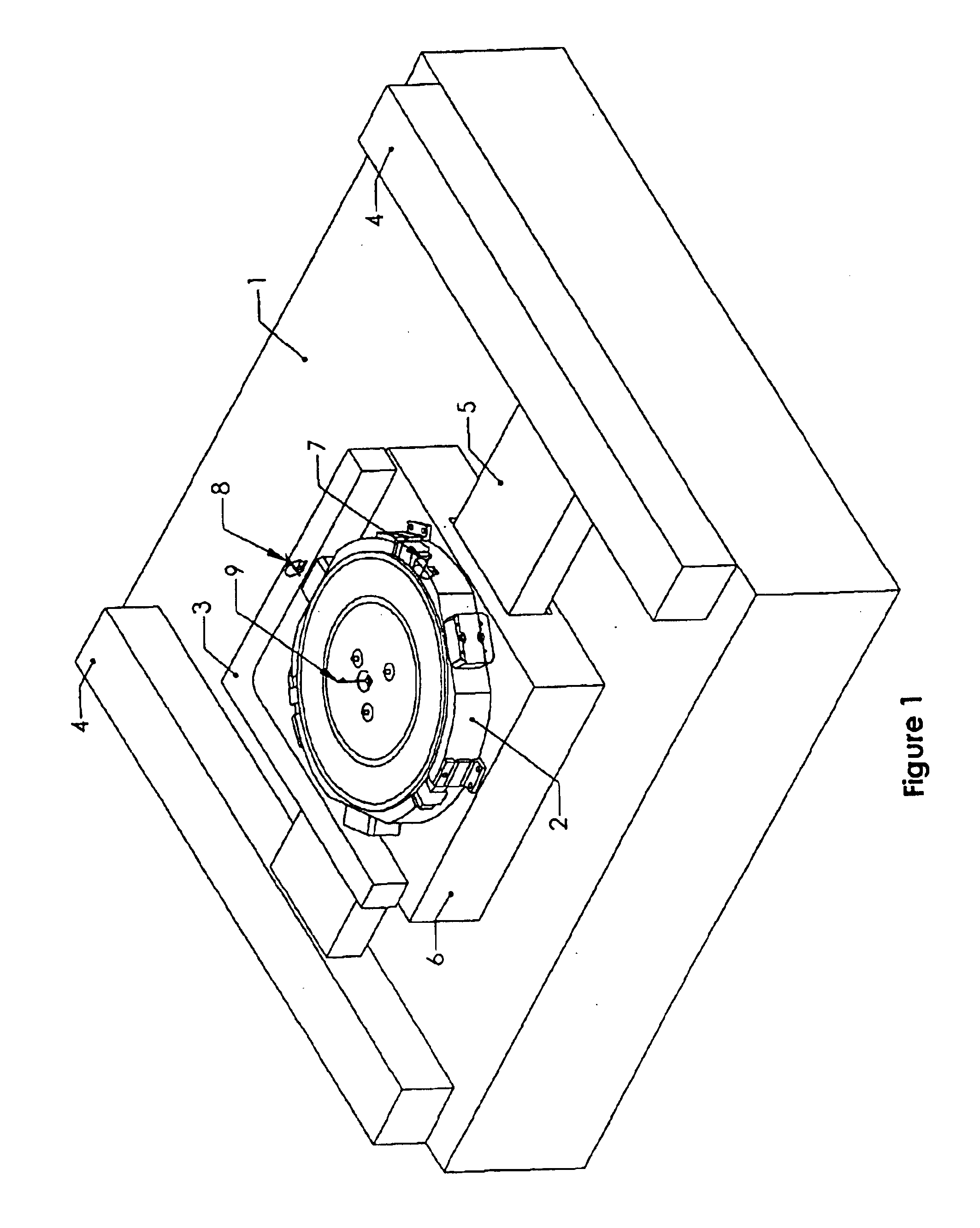
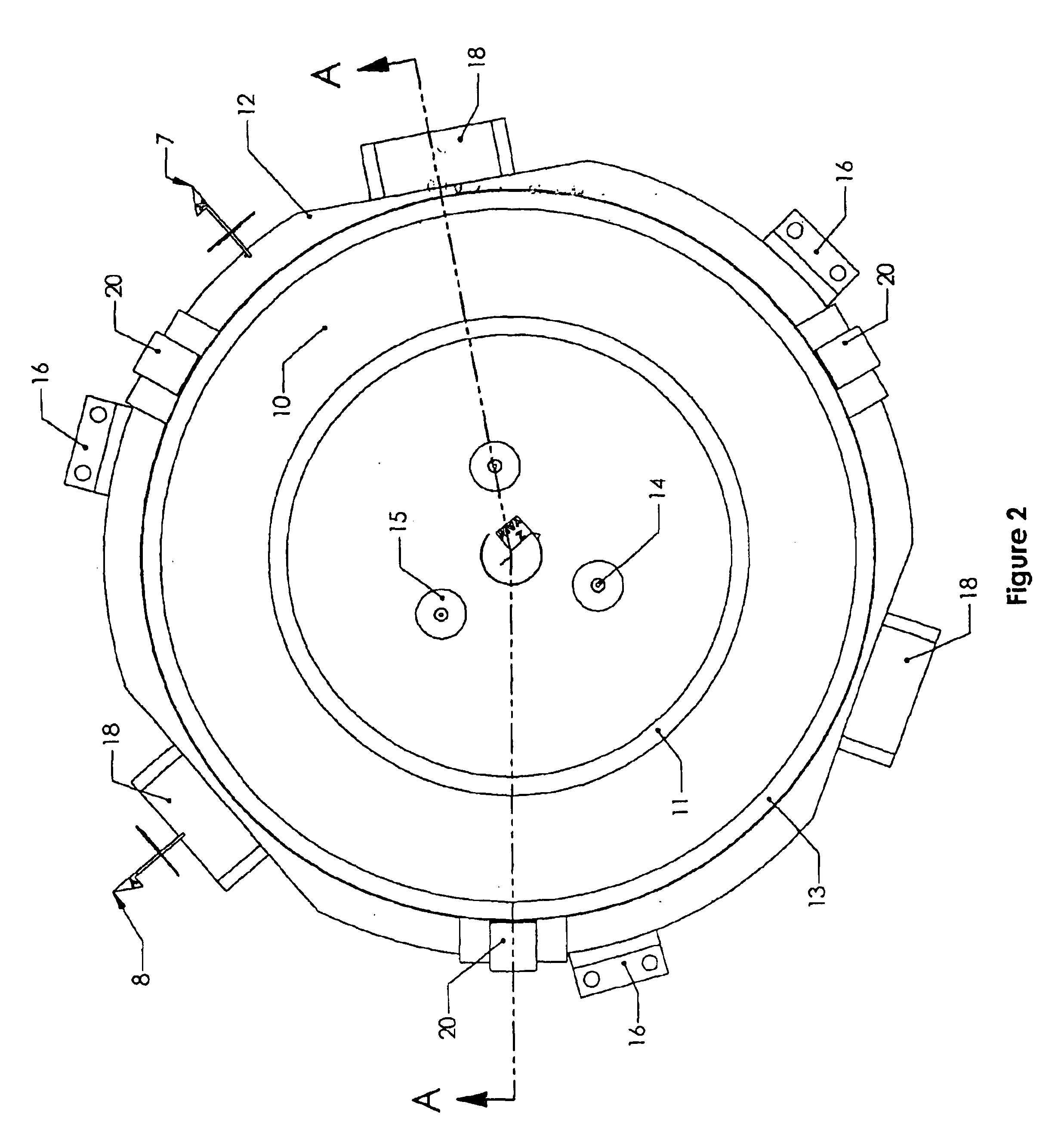
Navigated pin placement for orthopaedic procedures
InactiveUS20050216032A1Reduced resectionReduce high costDiagnosticsJoint implantsMulti degree of freedomPlastic surgery
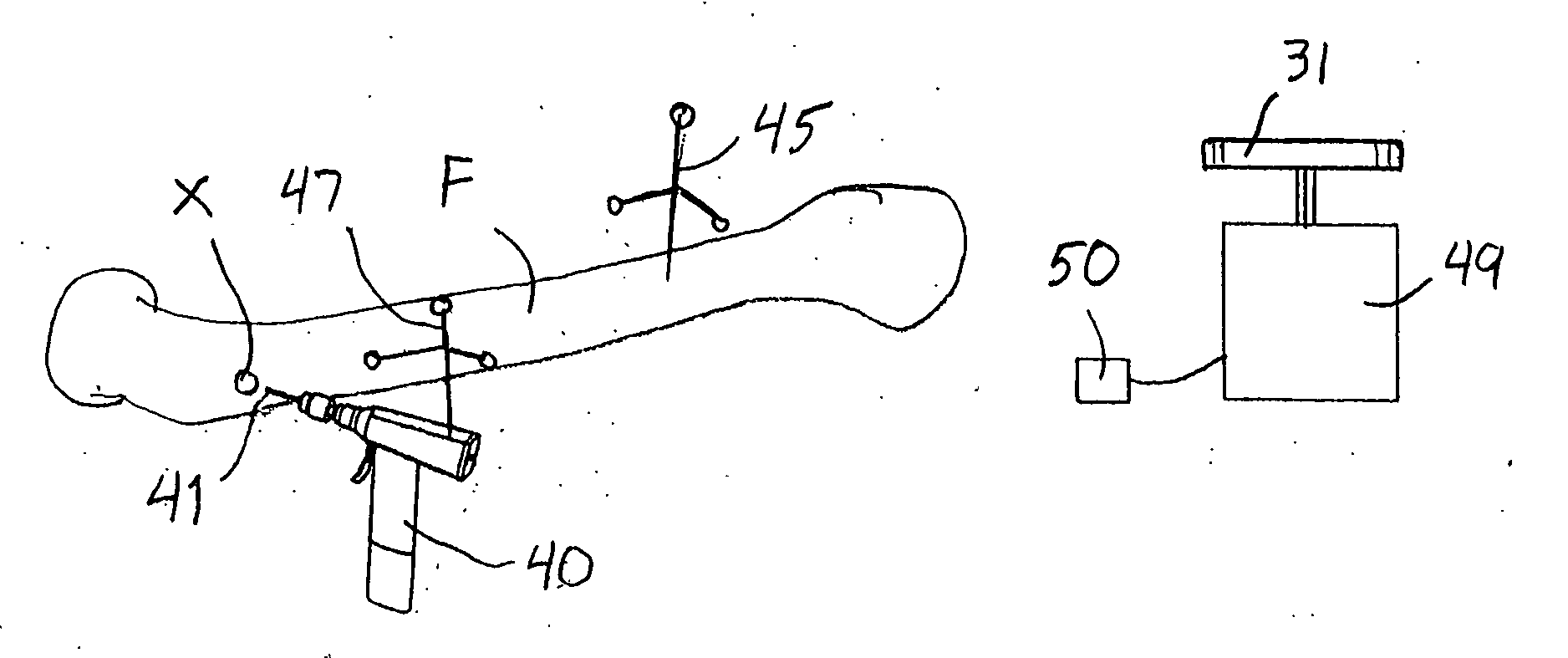
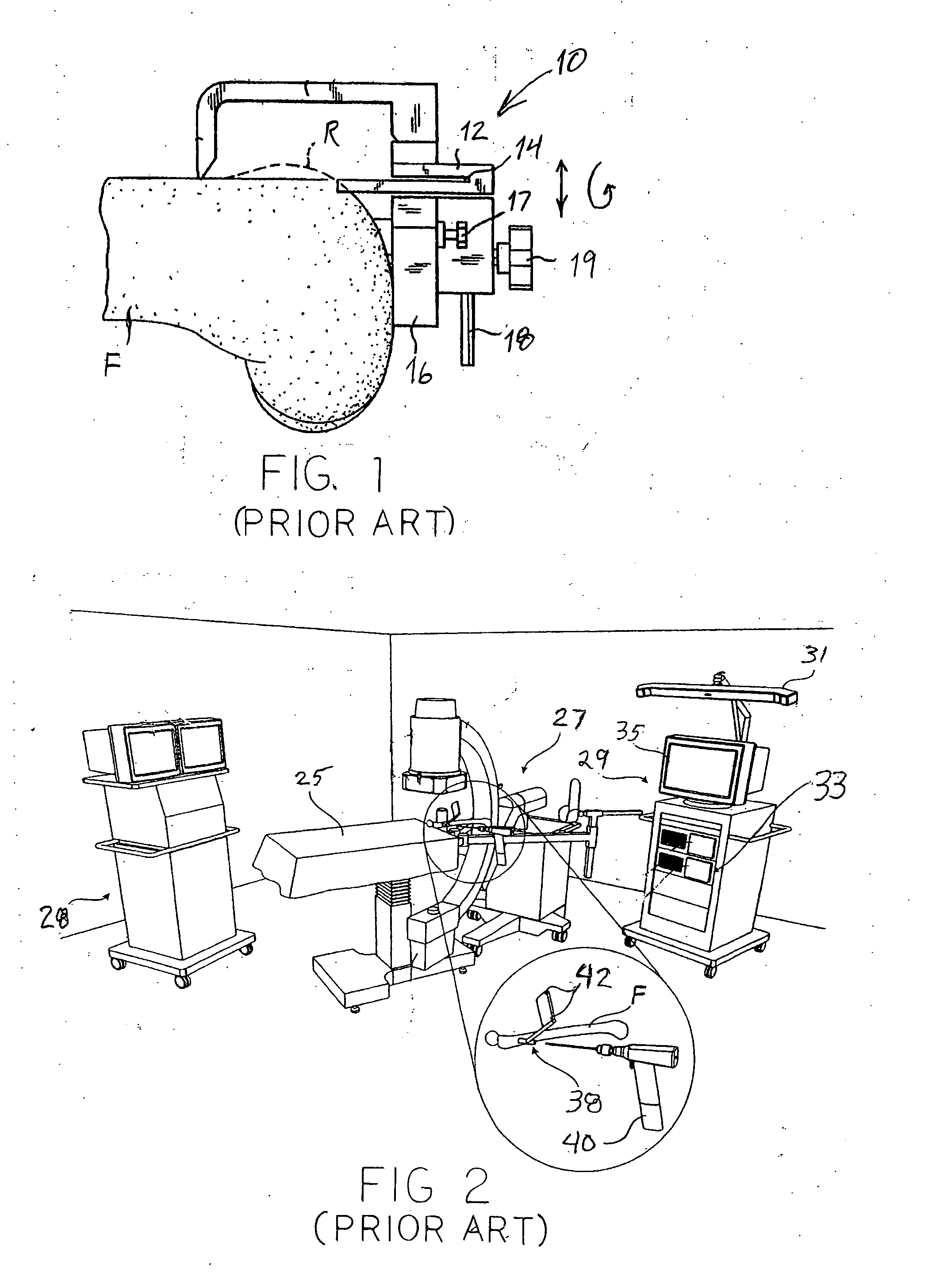
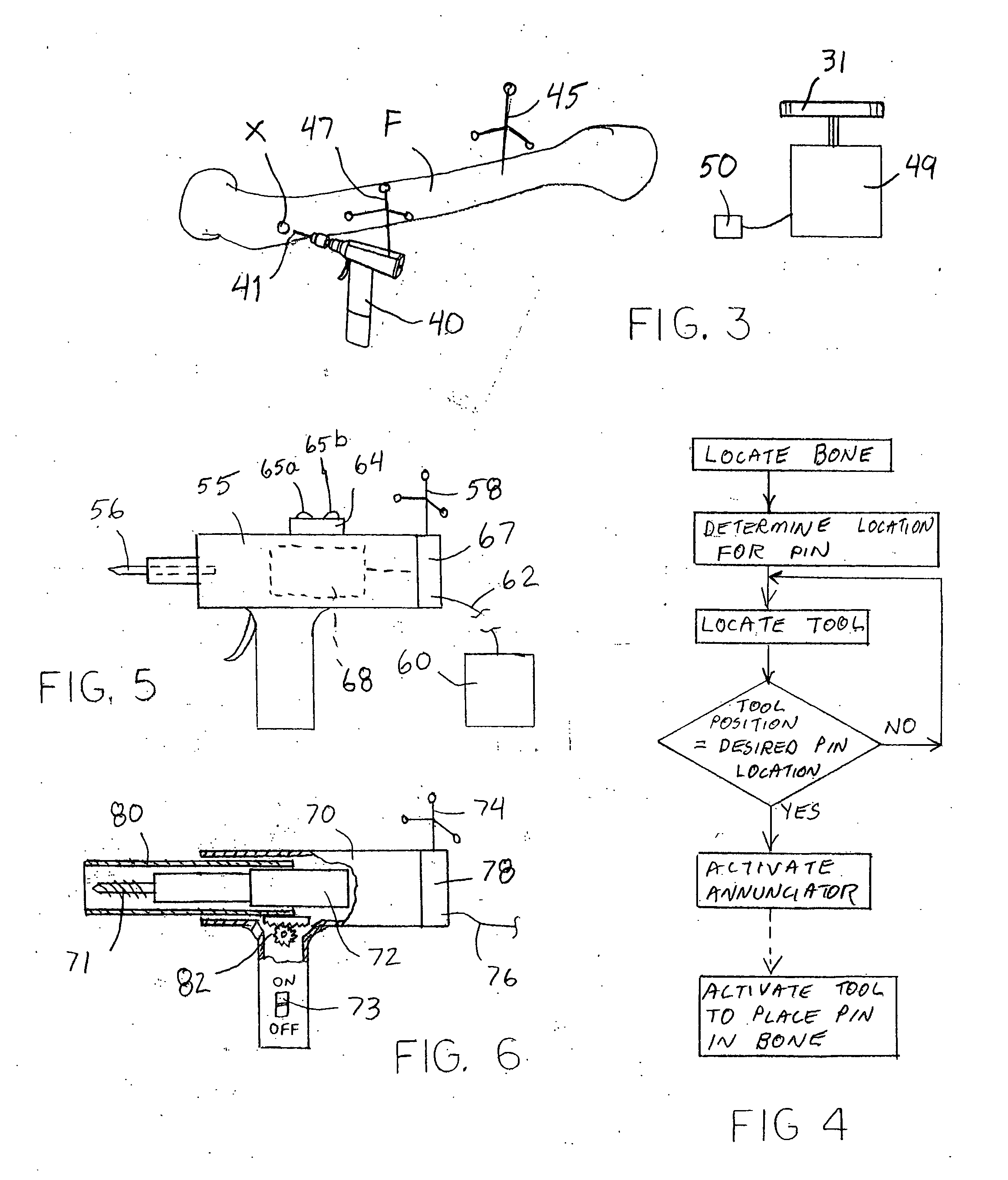
Systems and methods are provided for navigated placement of bone engaging elements, such as support pins used to support a cutting block on a bone for resection. In one embodiment, a tool configured to drive a pin into a bone is outfitted with a position tracking element. The system includes a localizing device that senses a signal from the position tracking element and feeds position information to a processor that makes a real-time comparison of the position of the tool to a location on the bone for placing the pin. When the tool spatial position coincides with the location on the bone, an annunciator is activated providing an audible or visible signal to the surgeon to operate the tool. In another embodiment, when the spatial position coincides, the processor directs an on-board controller of the tool to activate the tool. In another embodiment of the invention, the tool is continuously operating and the on-board processor controls a sheath that initially covers the working end of the tool. In yet another embodiment, a guide apparatus is configured to be mounted to a bone and provides multi-degree of freedom gross and fine adjustments of a pin guide. The pin guide carries a position tracking element so that its real-time spatial position relative to a location on the bone can be evaluated.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Double-foot robot lower limb mechanism with multiple freedom degree
InactiveCN101121424ARealize anthropomorphic gait walkingMany degrees of freedomSelf-moving toy figuresArtificial legsKnee JointGait
The invention provides a lower limb mechanism of a biped robot with multiple degrees of freedom. It includes the waist, thigh, calf and foot, the thigh includes the right thigh and the left thigh, the calf includes the right calf and the left calf, and the foot includes the right foot and the left foot; the waist is composed of two parts, the right hip joint and the left hip joint, connected through the waist Board connection composition; the right hip joint and left hip joint, right thigh and left thigh, right calf and left calf, right foot and left foot are symmetrical structures; the hip joint and thigh are connected in parallel through a Hooke hinge and two connecting rods The thigh and the lower leg are connected through the knee joint connecting rod and the knee joint shaft; the lower leg and the foot are connected in parallel through the Hooke hinge and two ankle joint connecting rods. The invention has the characteristics of many degrees of freedom, and can realize the humanoid gait walking of the biped robot to the greatest extent. The structure is simple, the principle is clear, and the economy is feasible. Large load capacity, compact structure, low cost, low design difficulty, strong feasibility, suitable for biped robot mechanism design requirements.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
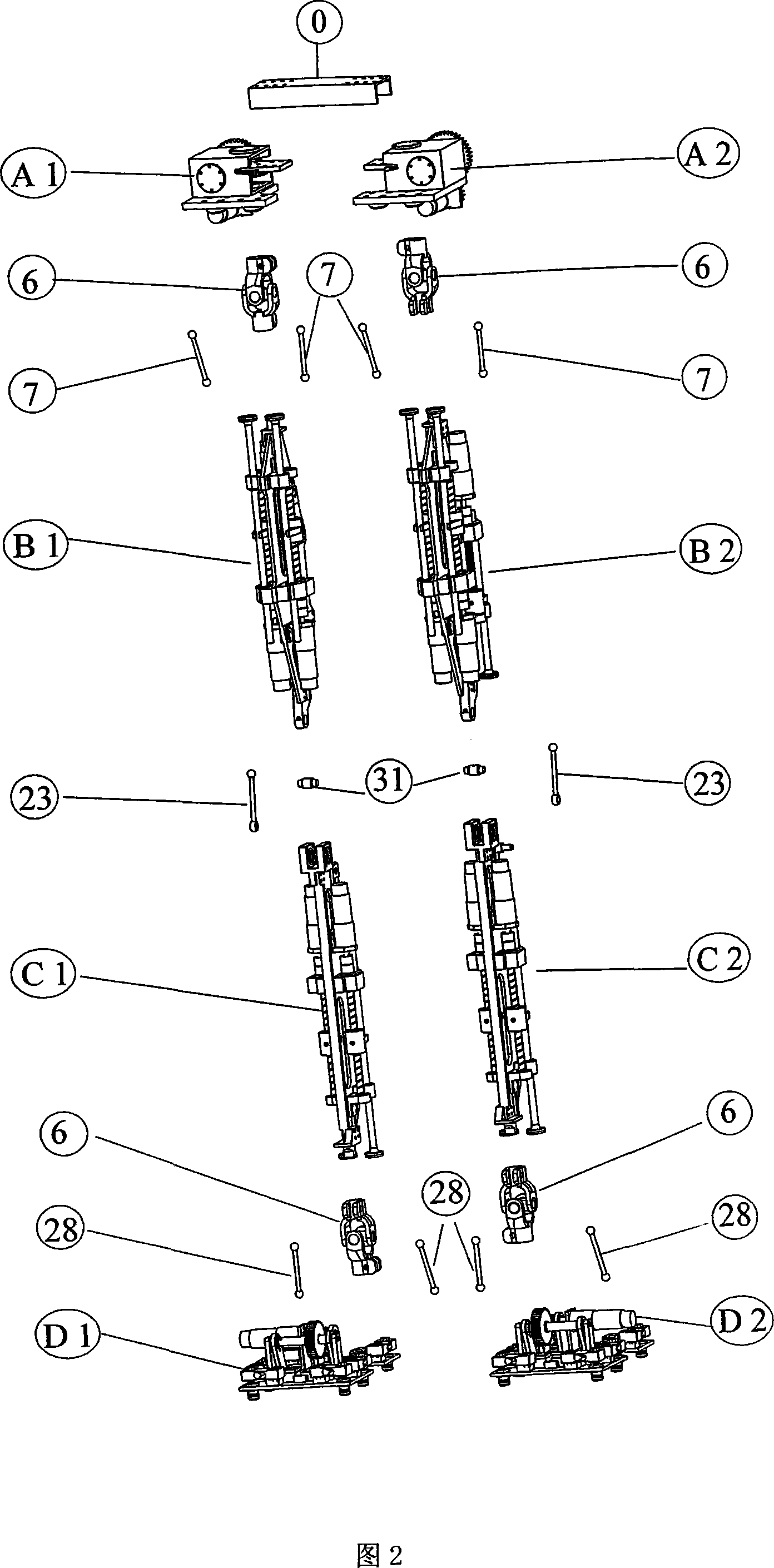
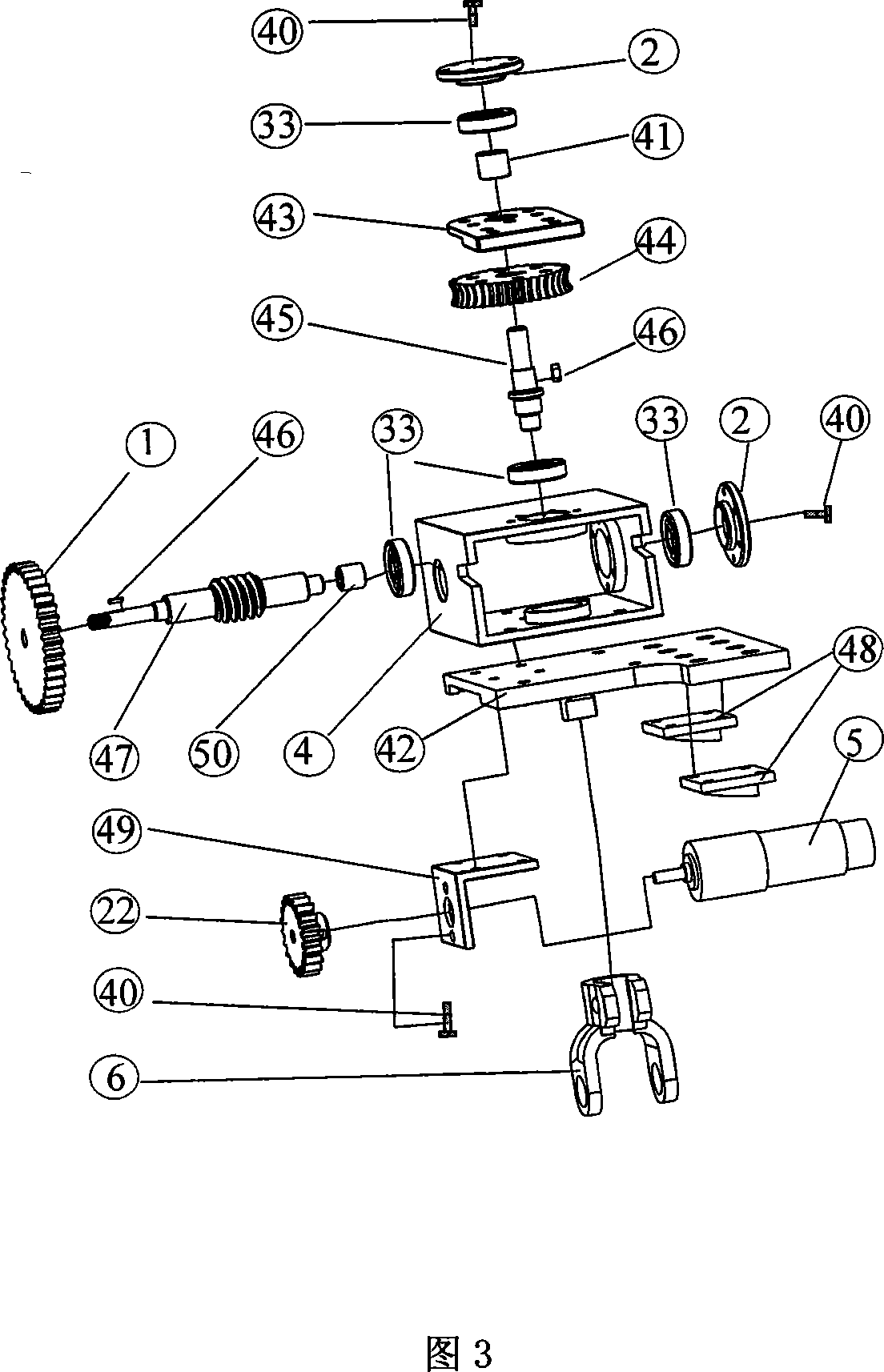
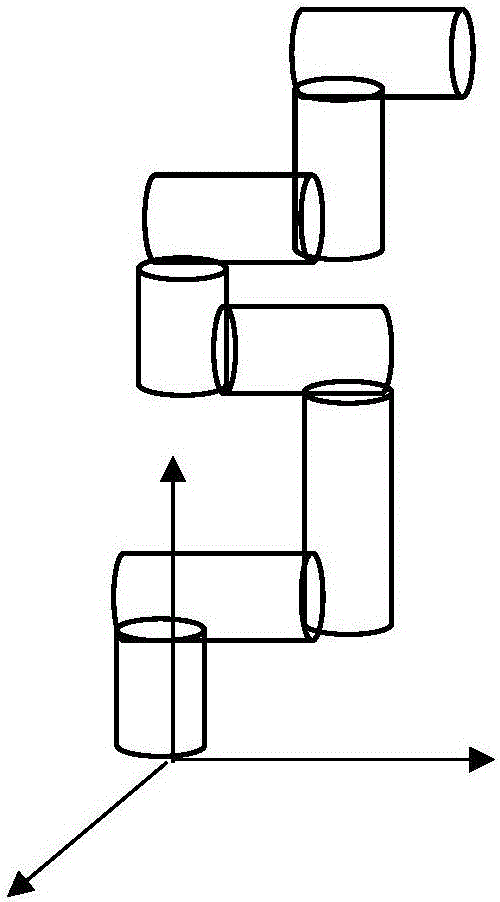
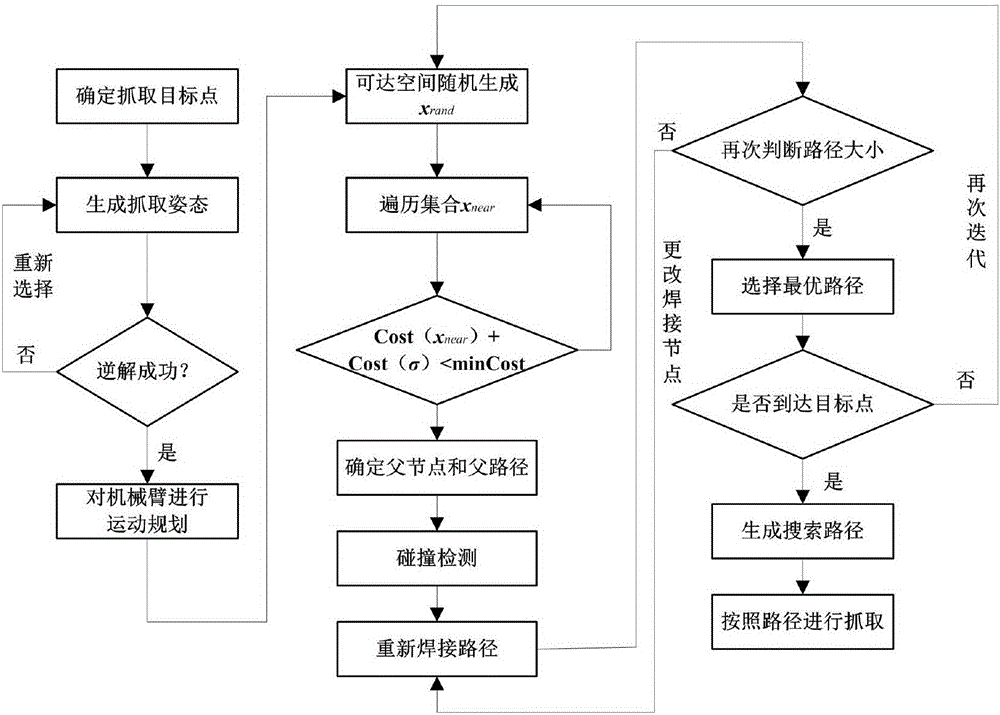
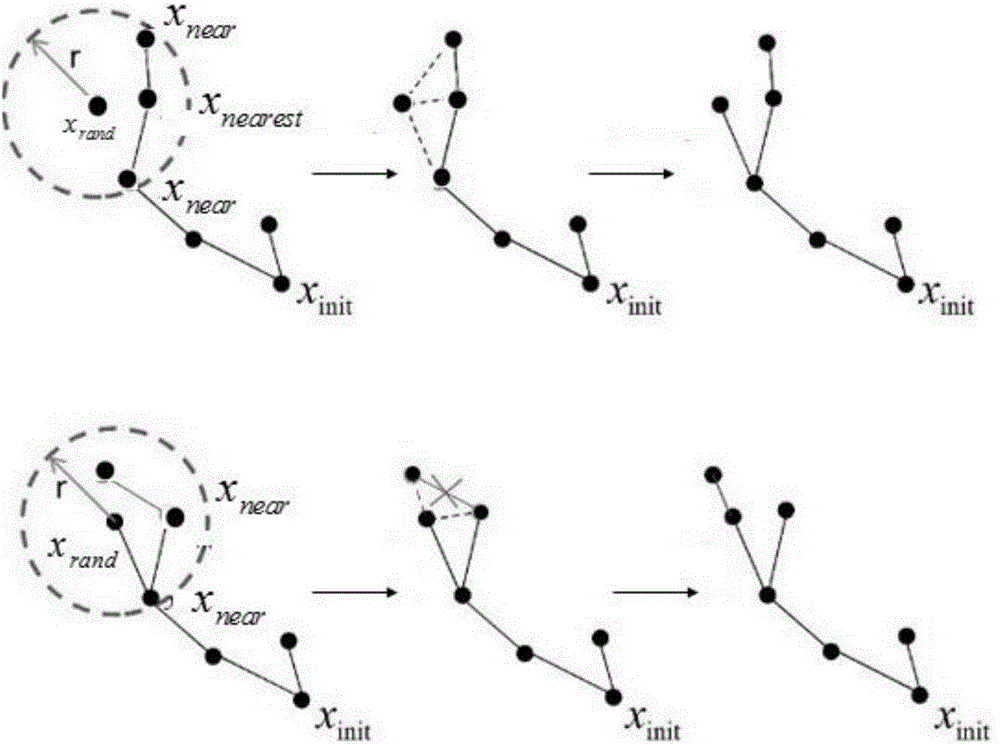
Improved RRT<*> obstacle avoidance motion planning method based on multi-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm
InactiveCN106695802AImprove convergence rateReduce search timeProgramme-controlled manipulatorRegular distributionNODAL
The invention discloses an improved RRT<*> obstacle avoidance motion planning method based on a multi-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm, and belongs to the field of mechanical arm motion planning. A six-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm model with seven connecting rods and six rotary joints is built; parameters in a to-be-searched space are determined; if the distance is shorter than the distance of a path with lowest cost, the distances between a near node in a set to an initial point and the distance between the node to a random point are temporarily determined as the minimum path; a newly generated sigma is subjected to collision detection, and the node and the path are added if the newly generated path does not collide an obstacle interval; the steps are repeated until the optimal path is found; and the generated path is added into a path planning device. Compared with the prior art, the method has the following advantages that the random search characteristic is changed in a mode of adding normal distribution, the algorithm convergence rate can be increased through the heuristic search, the RRT<*> algorithm has the evolutionary optimization path, and a large number of calculations is not needed; and after Gaussian distribution of an inspiration point near a target point is added, the convergence rate is increased, and the search time is shortened.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com