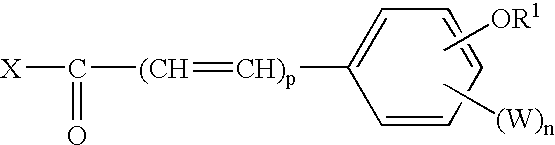Patents
Literature
294 results about "Thermal distortion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
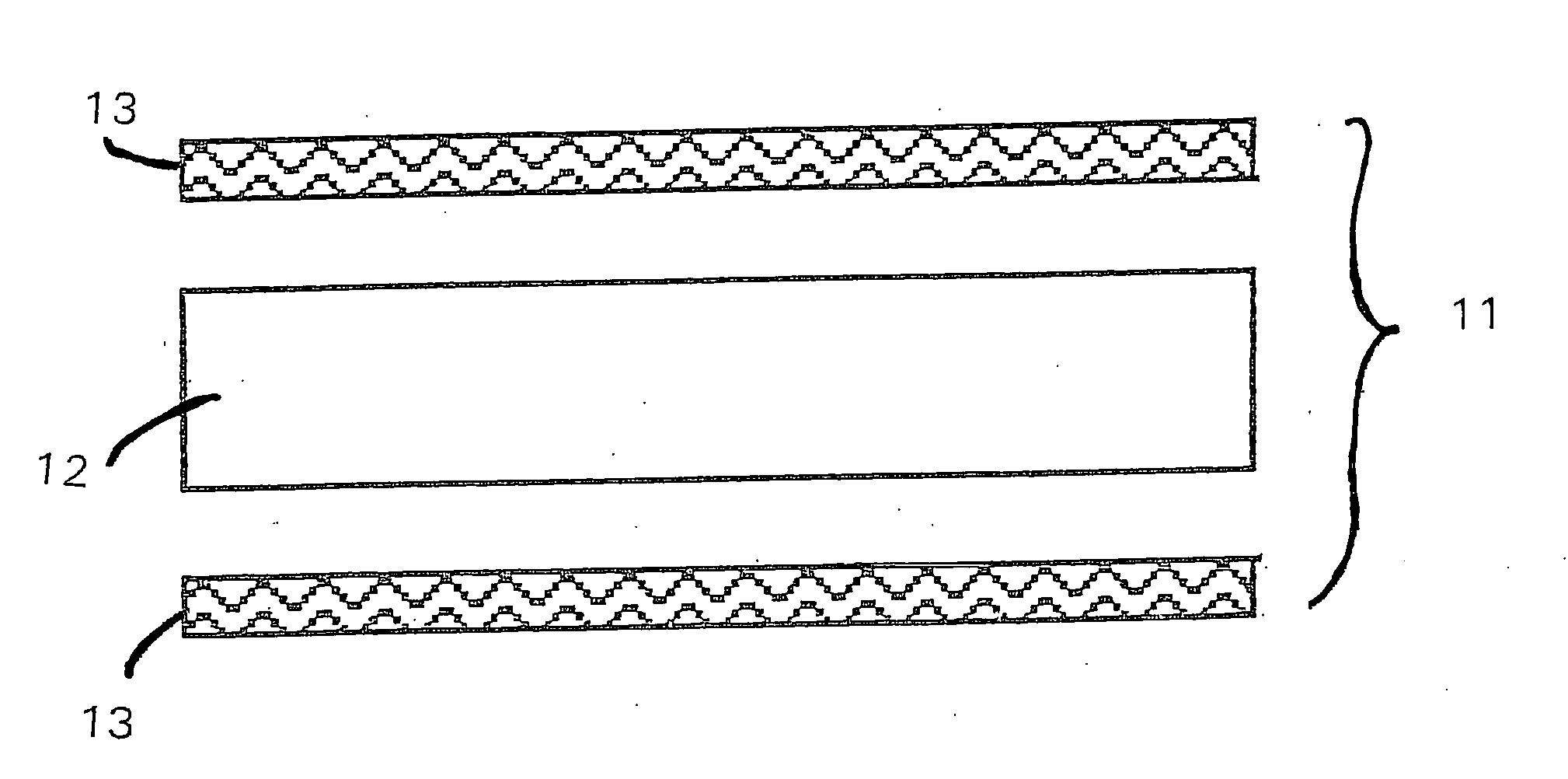
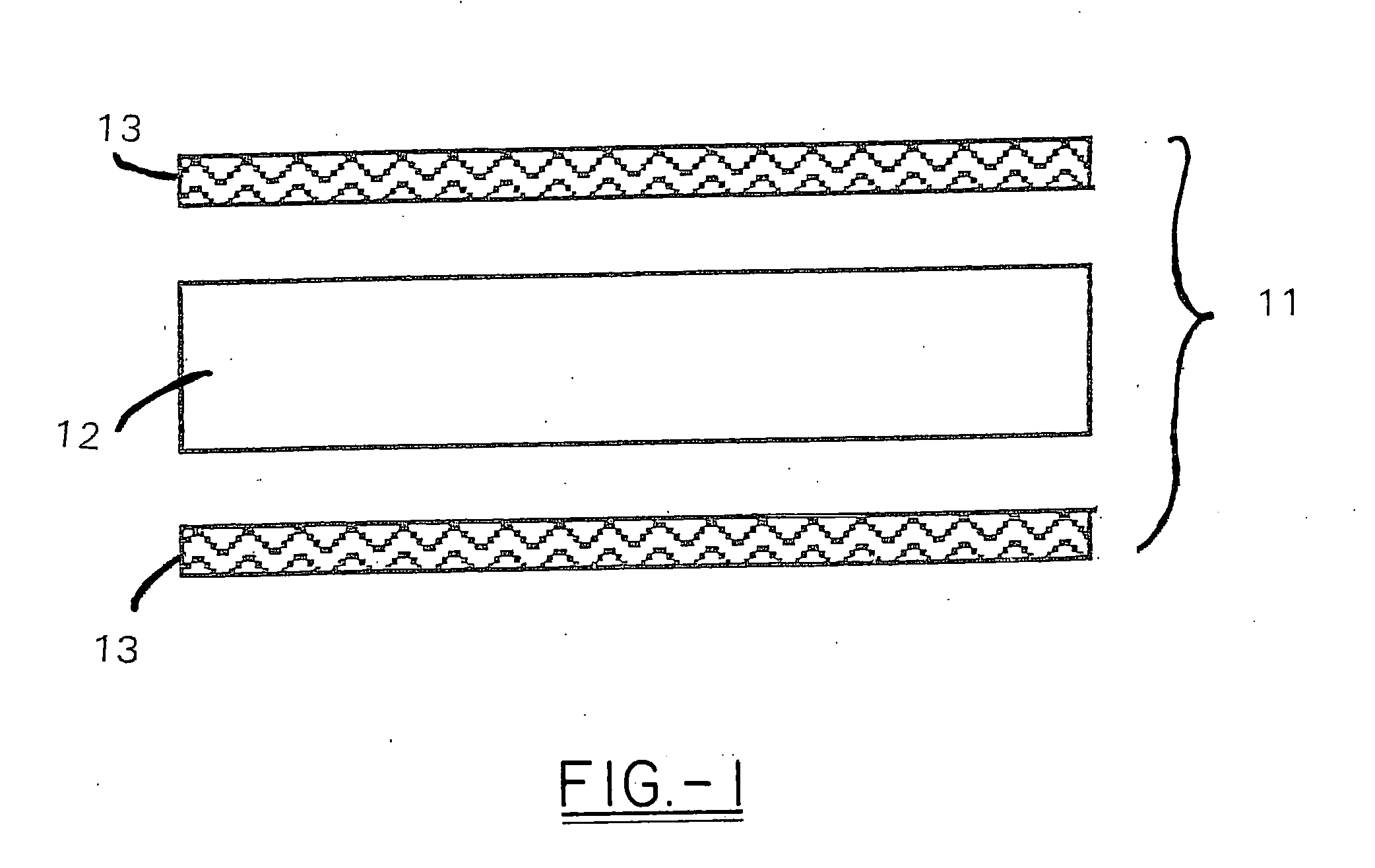
High heat distortion resistant inorganic laminate
InactiveUS20080063875A1High temperature resistanceMaintain good propertiesGlass/slag layered productsNatural mineral layered productsOxyanionPhysical chemistry
A light-weight, heat distortion resistant laminate includes at least one layer of an alkali silicate resin composition derived from an alkali silicate and / or alkali silicate precursor, at least one oxoanionic compound or a reactive acidic glass; and water; and at least one reinforcing core layer comprising an inorganic high-temperature resistant composition. The laminate has a very low quench steepness index value upon rapid quenching as with ambient temperature water.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
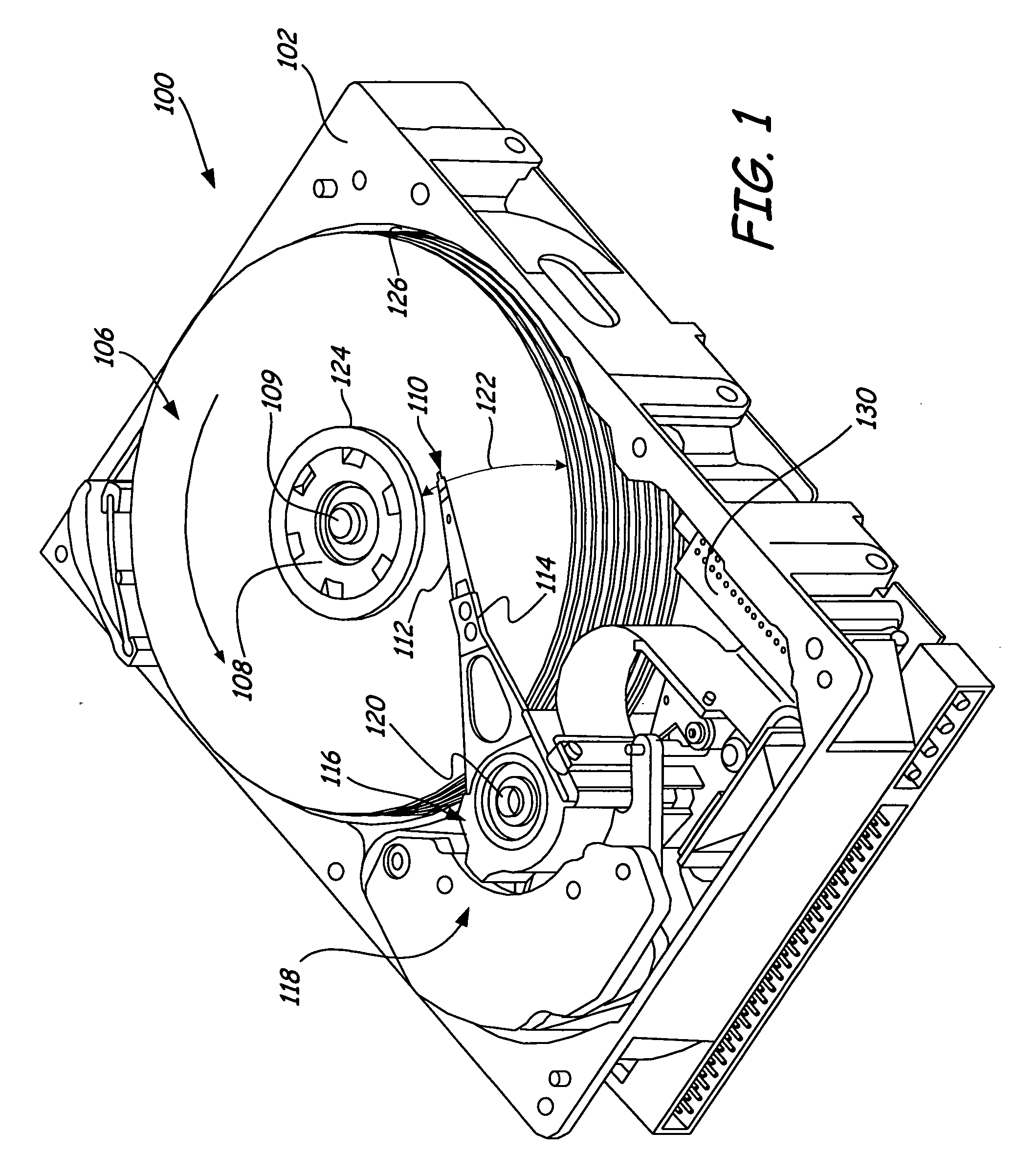
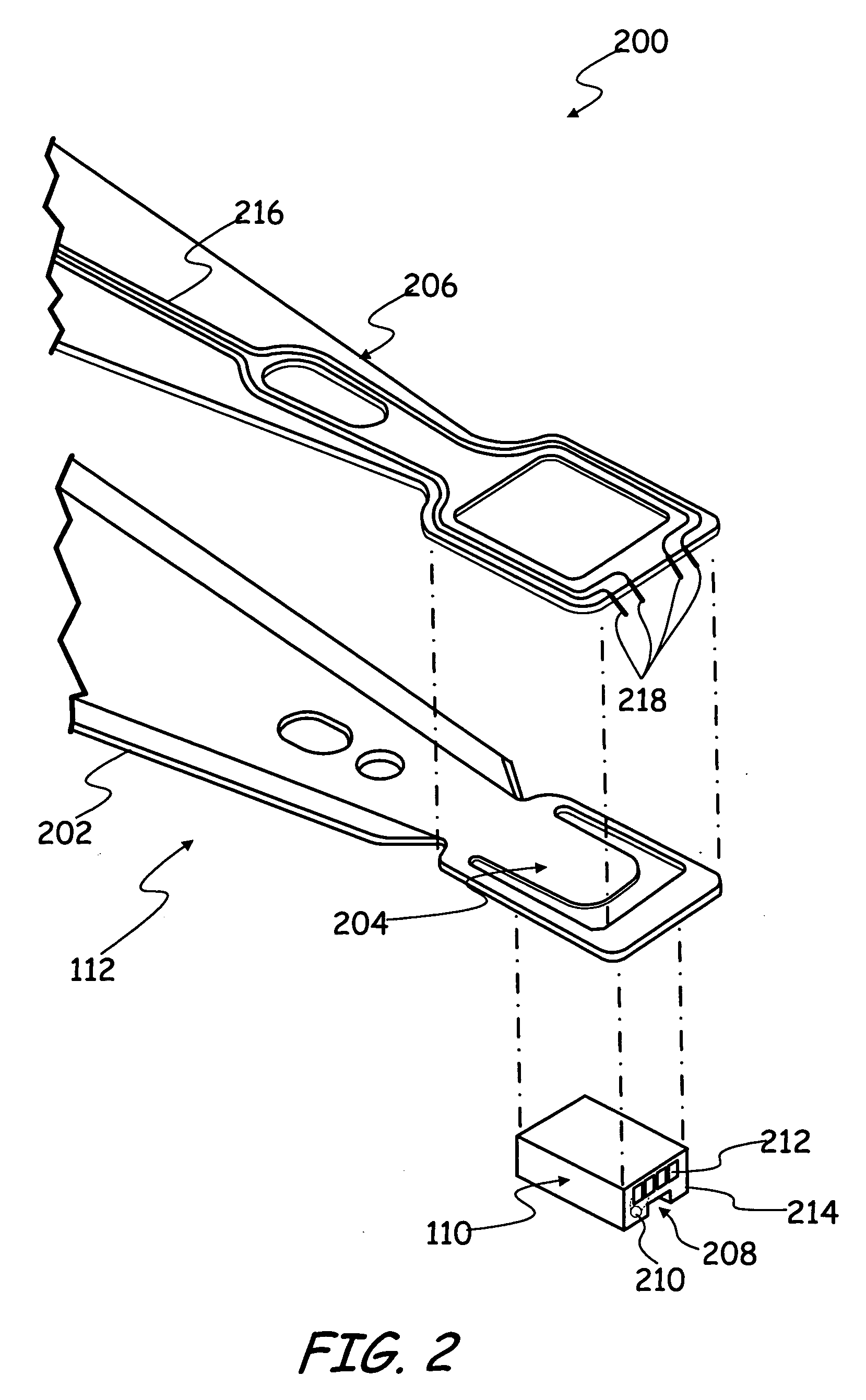
Head gimbal assembly to reduce slider distortion due to thermal stress
InactiveUS20080002299A1Reduce thermal deformationFluid-dynamic spacing of headsRecord information storageThermal expansionThermal distortion
A head gimbal assembly (HGA) is provided. The HGA includes a suspension that has a suspension coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) and a slider that has a slider CTE. A bonding element attaches the slider to the suspension. A compensation layer, having a compensation CTE, is located on the suspension. The compensation layer serves to compensate for a thermal distortion of the slider. A method of forming a HGA is also provided. The method includes providing a suspension having a suspension CTE and forming a slider having a slider CTE. The method further includes attaching the slider to the suspension and depositing a compensation layer, having a compensation CTE, on the suspension. The compensation layer serves to compensate for a thermal distortion of the slider.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Multiple degree of freedom substrate manipulator
InactiveUS20030156270A1Reduce forceIncrease stiffnessMechanical apparatusMotor/generator/converter stoppersHigh bandwidthControl system
A system for manipulating a planar substrate such as a semiconductor wafer is provided. The manipulator is typically used in conjunction with an XY stage to focus and planarize a wafer with respect to a tool. The manipulator employs redundant actuators of different types and a control system that uses low-bandwidth, high efficiency actuators to provide low frequency forces and high-bandwidth, but less efficient, actuators to provide all other forces. The manipulator provides support and manipulation of a substrate while minimizing errors due to thermal distortion.
Owner:ACTIVE PRECISION
Minimizing thermal distortion effects on EUV mirror
InactiveUS20050099611A1Improve thermal conductivityImprove heat transfer performanceMirrorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeat conductingConductive materials
A mirror is provided with throughholes, or channels, formed through its main body and a coolant pipe of a heat-conductive material is inserted in each of the channels for passing a cooling fluid inside. The outer wall of the coolant pipe does not contact the inner wall of the channel, and there is left a gap in between. The gap contains a heat-conducting gas such as helium. The gap is of a width of less than 100 μm such that the gas has a high heat transfer coefficient even if its pressure is not too high. In some applications the gap may be filled with a heat-conductive fluid. It may be preferable, depending upon the circumstances, to form these channels proximally to the surface on which radiation is made incident. Additionally, the surface of the side of the mirror opposite the reflective side may be heated by auxiliary heat sources.
Owner:NIKON CORP
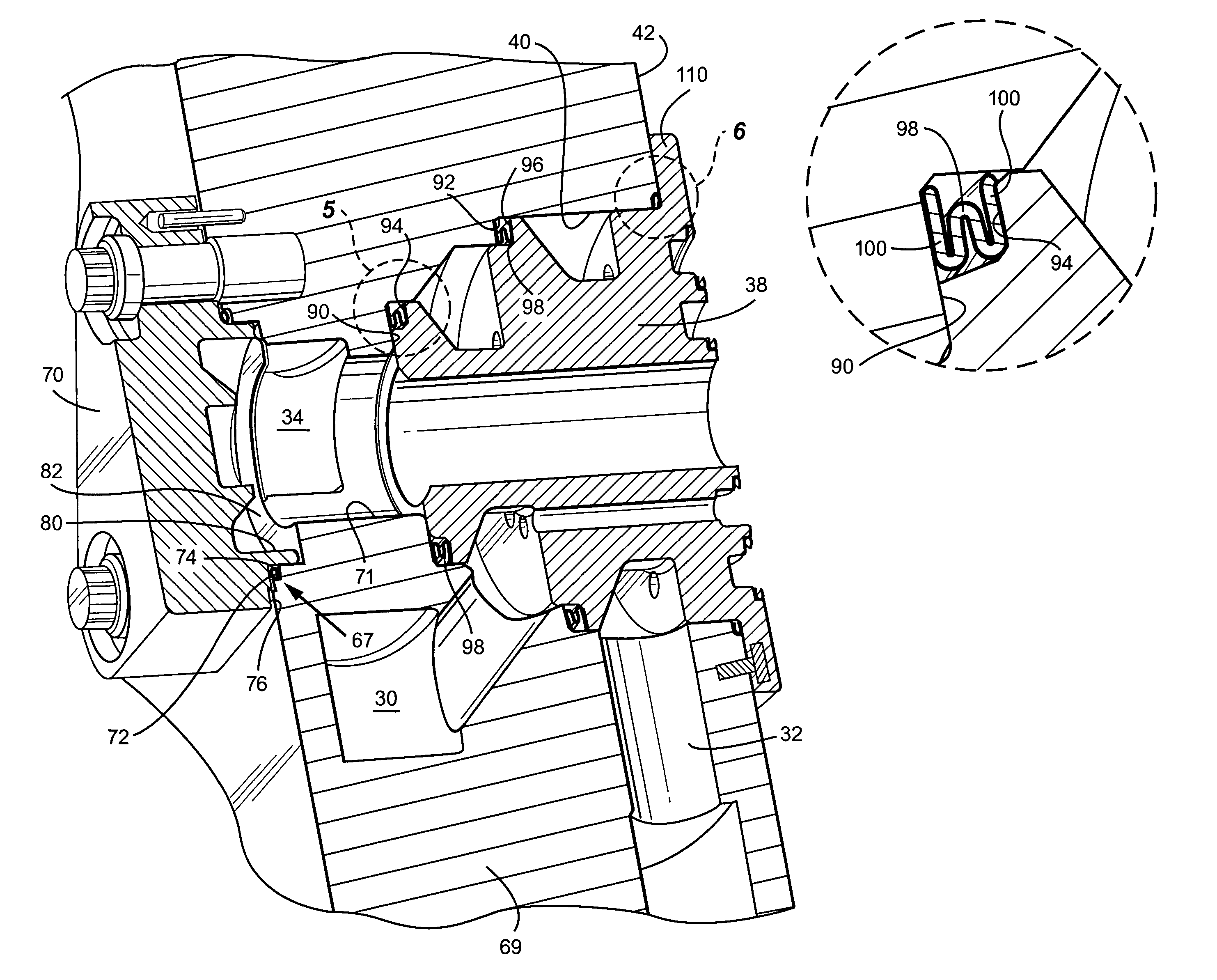
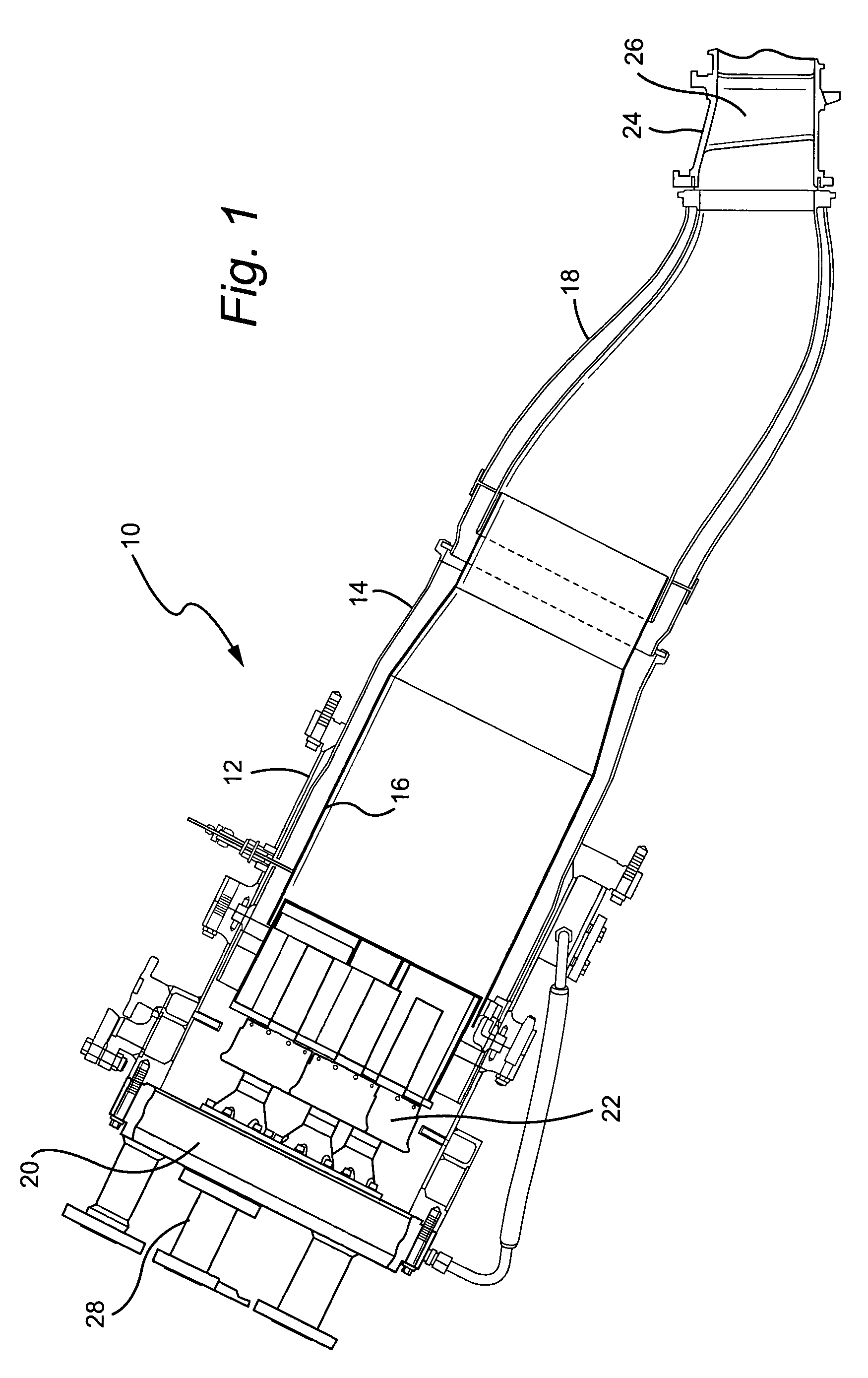
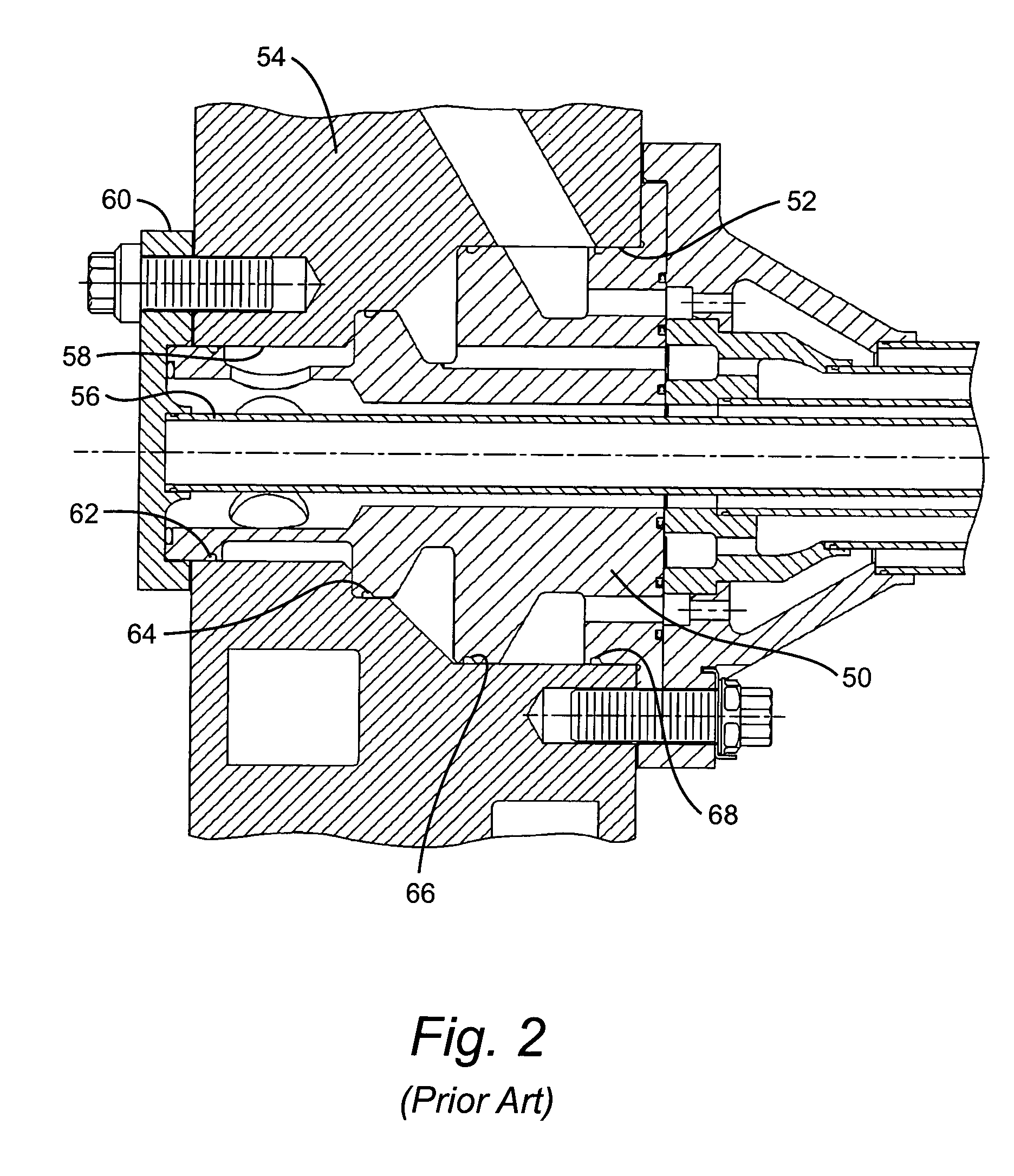
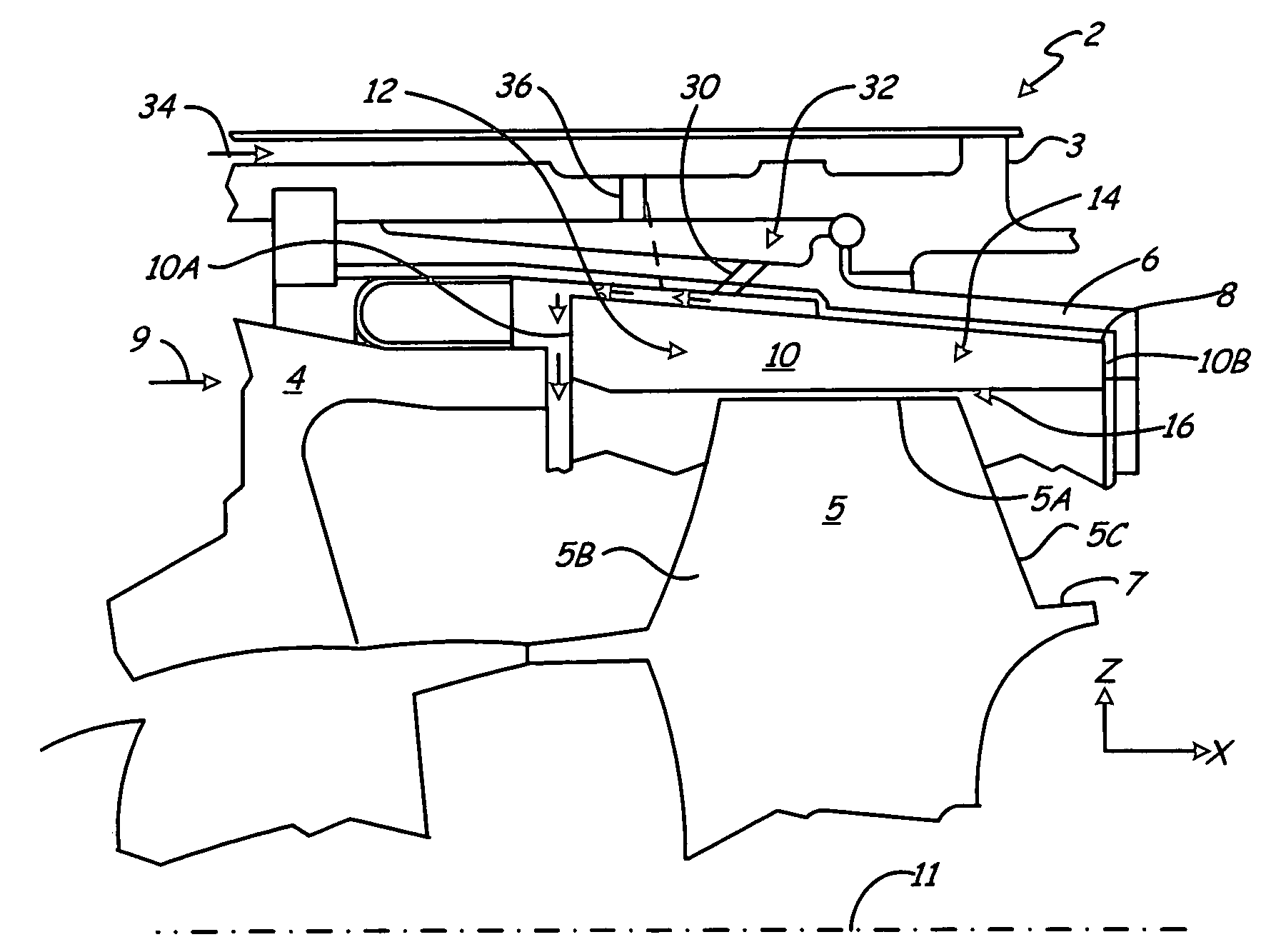
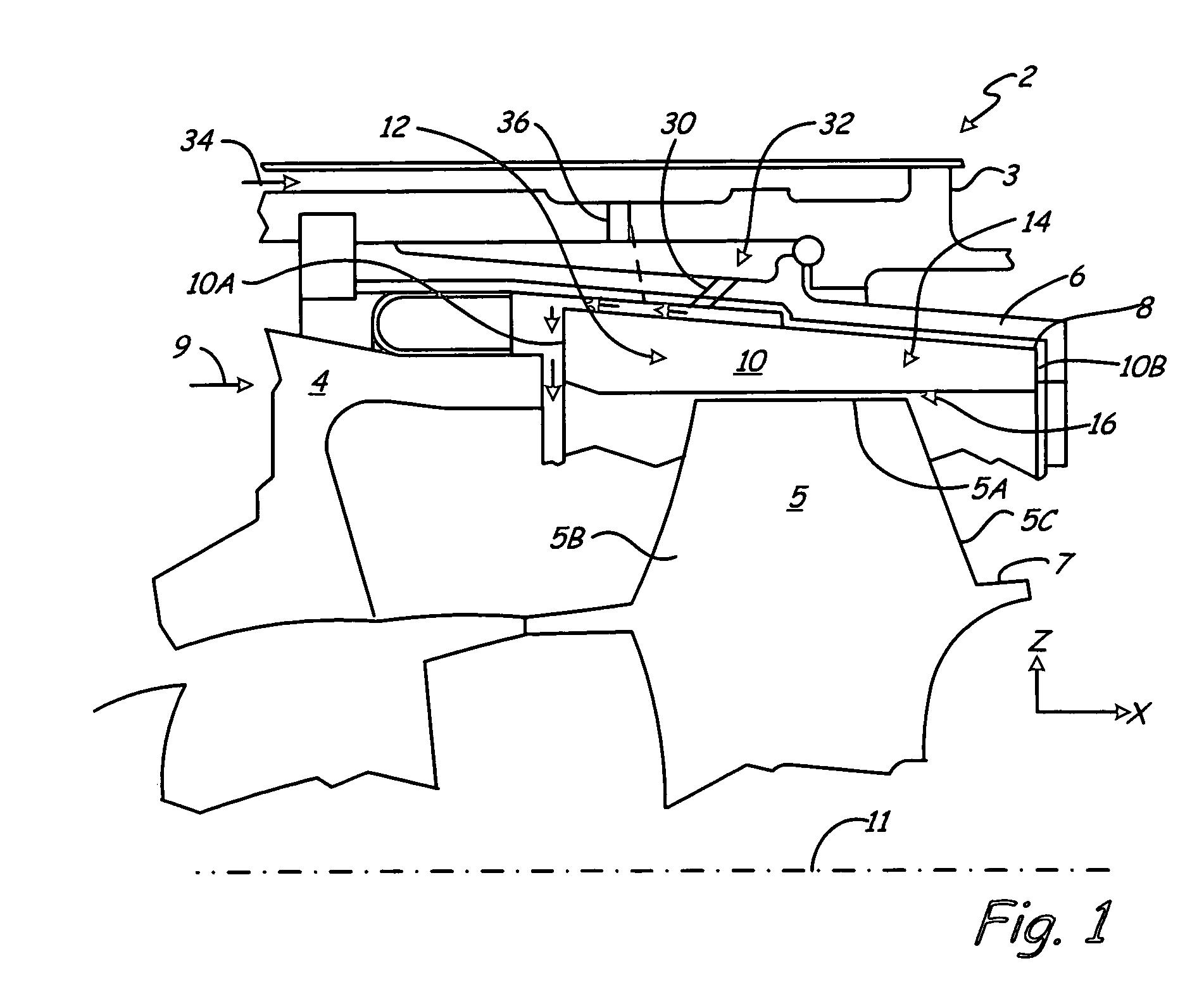
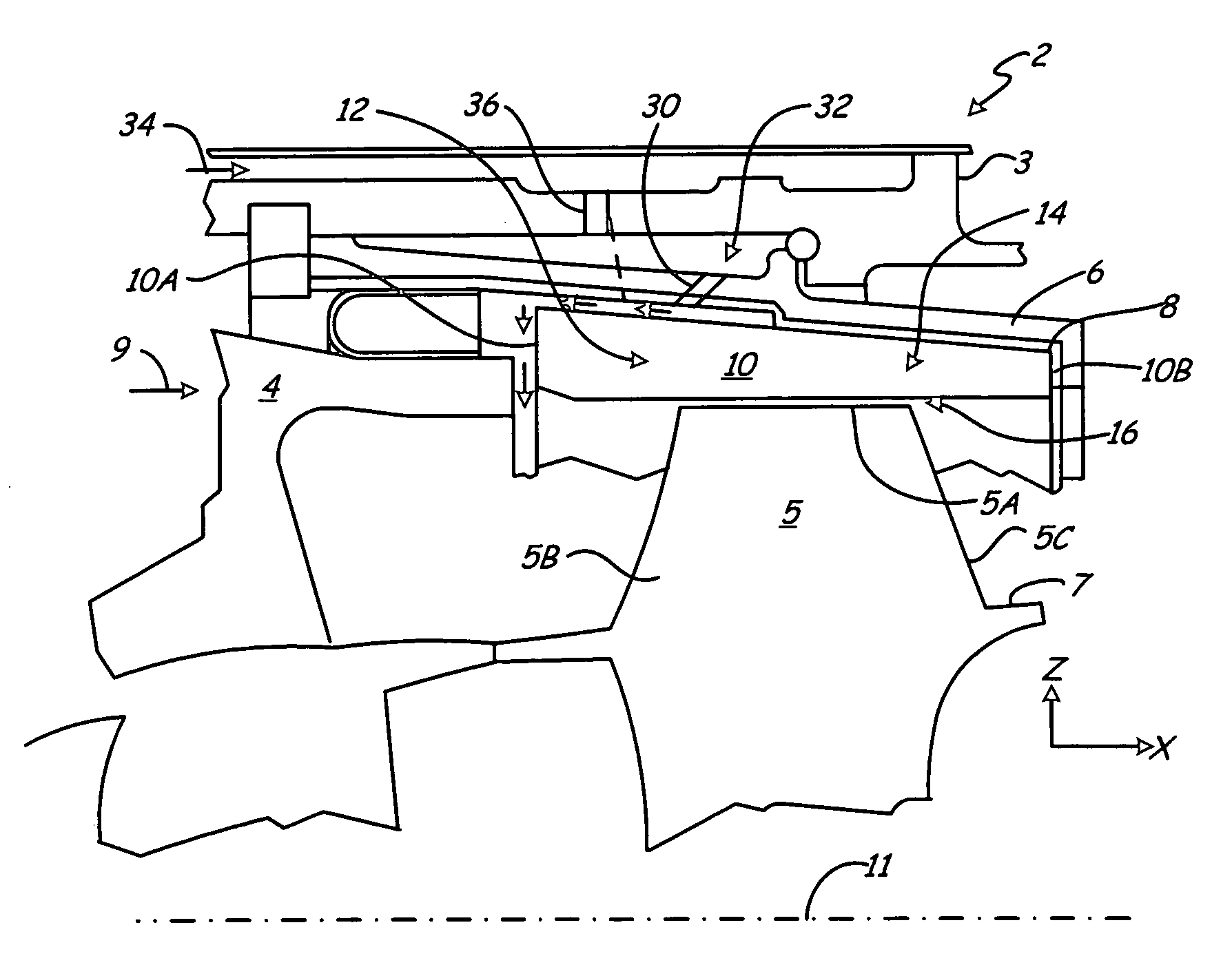
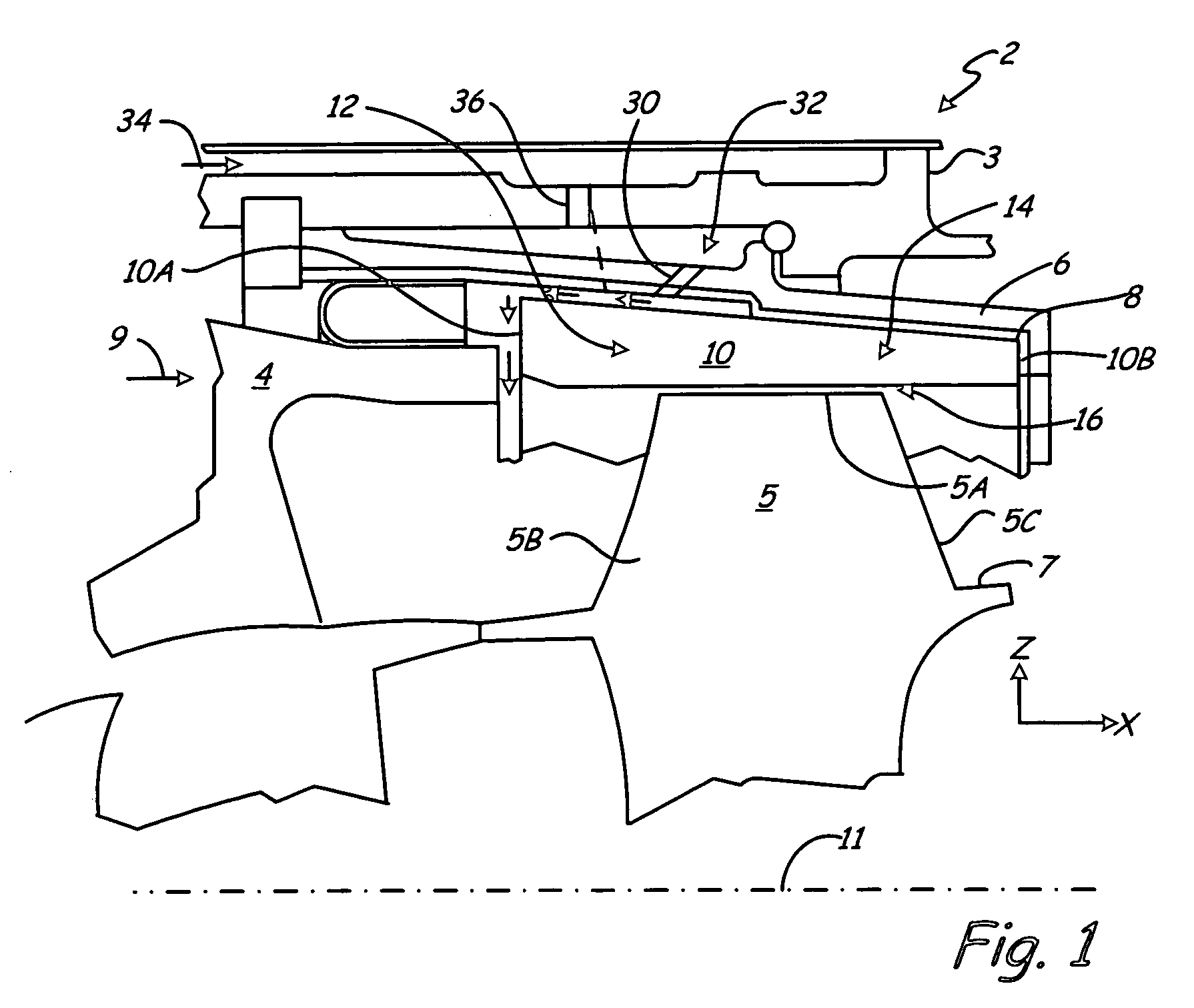
Turbine combustor endcover assembly
ActiveUS7134287B2Easy maintenanceMaintenance freeEngine sealsContinuous combustion chamberCombustorEngineering
The endcover assembly for a combustor includes an endcover having an aperture, an insert disposed in the stepped bore opening through an internal face of the endcover, a fuel cartridge extending through the insert and aperture and a seal cover on the external face of the endcover. Seal cover / endcover annular seals are disposed in registering axial cavities to seal against fluid leakage externally of the endcover assembly. Generally C-shaped and W-shaped seals are disposed in the cavities between the stepped shoulders of the insert and aperture to seal against leakage through the internal face of the endcover. The seals maintain sealing engagement during assembly and thermal distortion during turbine usage.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Multiple degree of freedom substrate manipulator
InactiveUS6756751B2Reduce forceIncrease stiffnessMechanical apparatusMotor/generator/converter stoppersHigh bandwidthControl system
A system for manipulating a planar substrate such as a semiconductor wafer is provided. The manipulator is typically used in conjunction with an XY stage to focus and planarize a wafer with respect to a tool. The manipulator employs redundant actuators of different types and a control system that uses low-bandwidth, high efficiency actuators to provide low frequency forces and high-bandwidth, but less efficient, actuators to provide all other forces. The manipulator provides support and manipulation of a substrate while minimizing errors due to thermal distortion.
Owner:ACTIVE PRECISION
Liquid crystal display, illuminant module and its manufacturing method
InactiveUS20070076433A1Improve image qualityImprove extraction efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensPoint-like light sourceBond interfaceLiquid-crystal display
When a long illuminant module is constructed, debonding of a bonded interface or bending occurs due to a difference in a magnitude of thermal deformation between a lens material and a metal substrate. In an illuminant module including light emitting elements, a substrate on which the light emitting elements are mounted, a transparent encapsulating resin which encapsulates the light emitting elements, and a lens material having cavities formed therein, in which the respective light emitting elements and transparent encapsulating resin are stored, notches are formed in a surface of the lens material on the side of the substrate, and the notch surfaces of the notches and the surface of the substrate are bonded using a bonding material.
Owner:HITACHI LIGHTING
Spindle thermal distortion compensation method for precision horizontal machining center
InactiveCN102658499AReduce thermal errorsMeasurement/indication equipmentsMaintainance and safety accessoriesElement modelEngineering
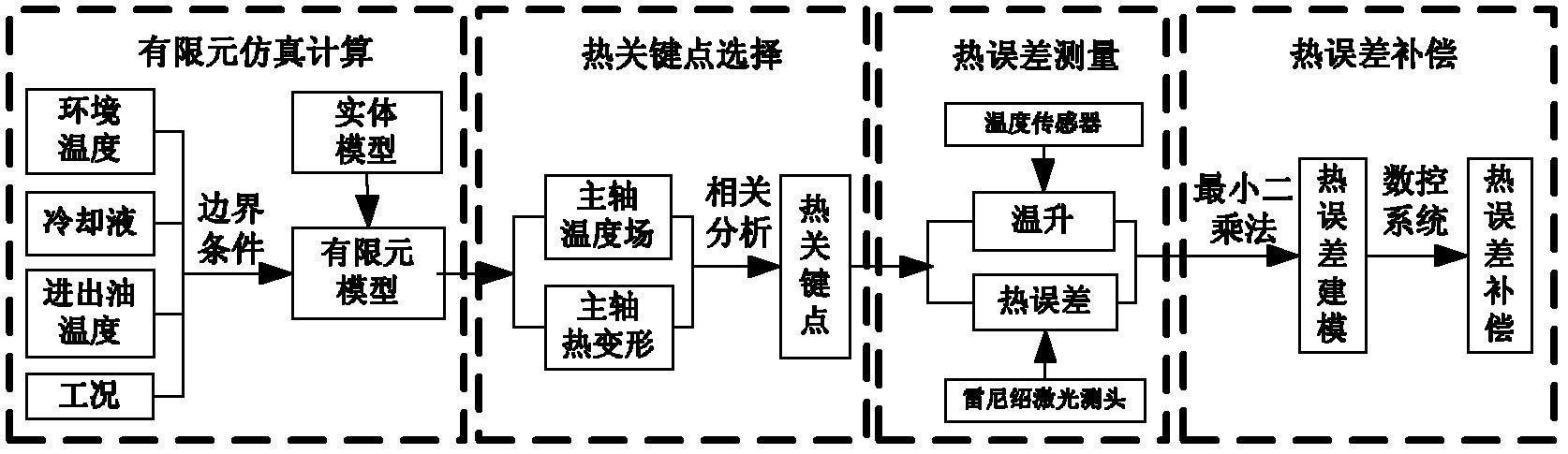
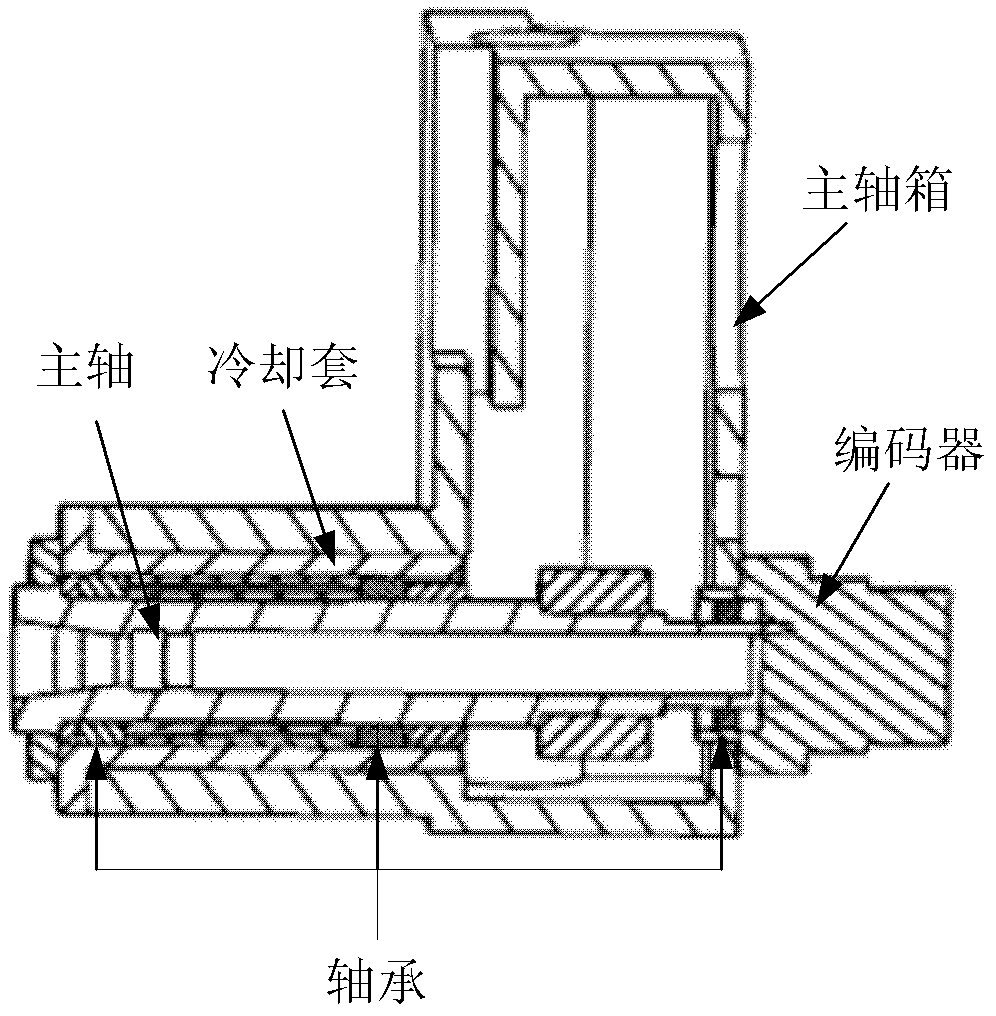
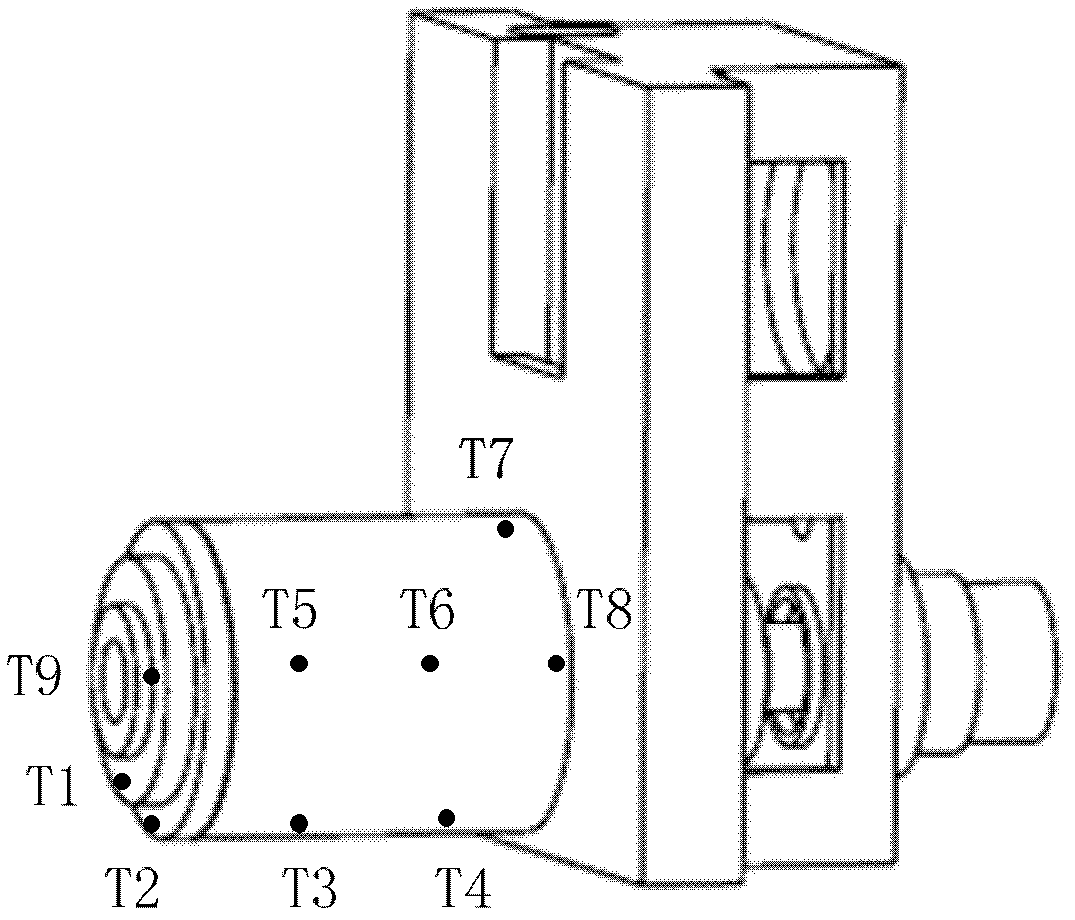
A spindle thermal distortion compensation method for a precision horizontal machining center comprises the steps as follows: a spindle model of a machine tool is simplified structurally; an ANSYS (finite element analysis software)-Workbench is utilized to perform mesh generation on a spindle entity model that is simplified, so as to obtain a spindle finite element model; and boundary conditions are calculated by combining with the practical spindle rotational speed, the environmental temperature, the coolant velocity, the flow rate, the inlet and outlet oil temperature and the like, and configuration is performed. Thermodynamics analysis and statics analysis are carried out in the ANSYS-Workbench to obtain more accurate spindle temperature field distribution and thermal deformation. Based on a finite element emulation result, the spindle temperatures in different positions and the spindle thermal deformations are analyzed at different rotational speeds by utilizing the Spearman rank correlation analysis, and spindle thermal key points are found out, so that references are provided to spindle thermal error tests and thermal error compensation. Finally, a thermal error compensation model is built up by utilizing a least squares method according to the key point temperature of the spindle and the thermal errors in the practical tests. Based on the thermal error compensation model, the spindle thermal error compensation is carried out by combining with thermal error compensation strategies of a numerical control system of the machine tool.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Adhesive joining for powder metal components
A method of joining multiple powder metal components to form a powder metal component assembly using an adhesive is disclosed. By machining at least one of the powder metal components prior to the adhesive joining, otherwise difficult to machine features can be more easily machined for less cost and at higher production rates. Unlike high temperature joining techniques, the adhesive joins the powder metal components at room temperature. This room temperature adhesive joining eliminates the thermal distortions in pre-joined machined features common to high temperature joining techniques such as brazing or welding that bring these features out of specification during joining.
Owner:SKN SINTER METALS LLC (US) +1
Turbine combustor endcover assembly
ActiveUS20050005610A1Easy maintenanceMaintenance freeEngine sealsContinuous combustion chamberCombustorEngineering
The endcover assembly for a combustor includes an endcover having an aperture, an insert disposed in the stepped bore opening through an internal face of the endcover, a fuel cartridge extending through the insert and aperture and a seal cover on the external face of the endcover. Seal cover / endcover annular seals are disposed in registering axial cavities to seal against fluid leakage externally of the endcover assembly. Generally C-shaped and W-shaped seals are disposed in the cavities between the stepped shoulders of the insert and aperture to seal against leakage through the internal face of the endcover. The seals maintain sealing engagement during assembly and thermal distortion during turbine usage.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
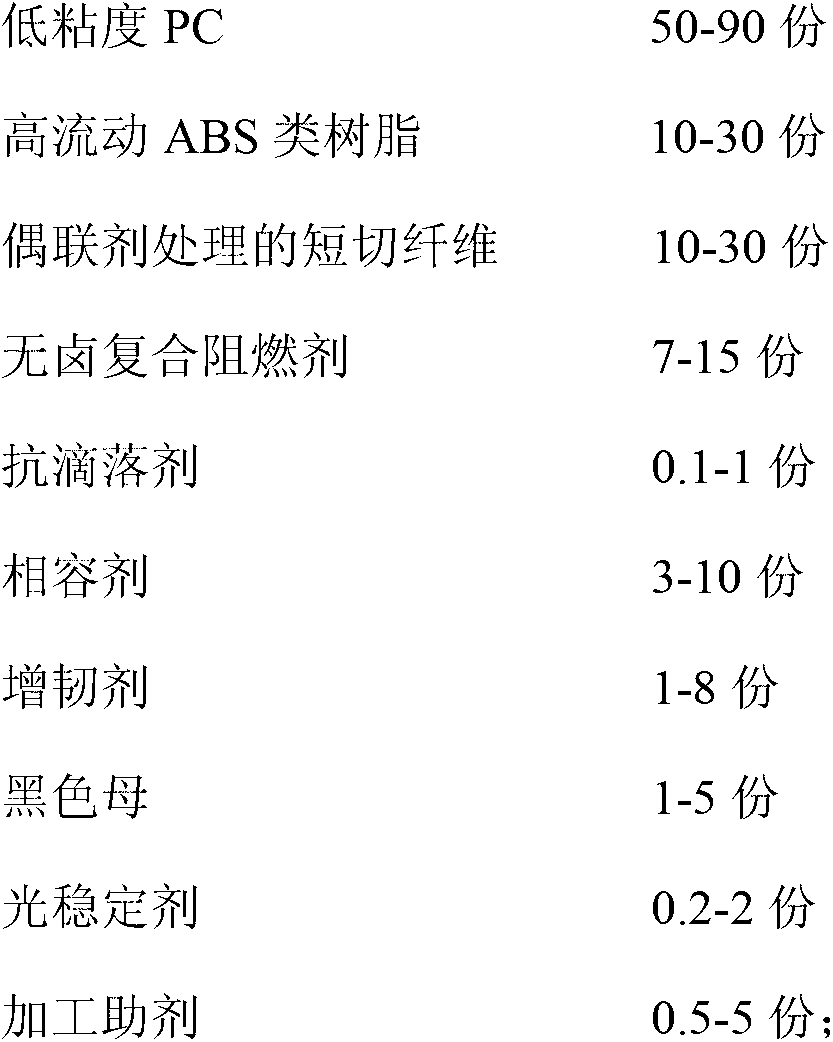
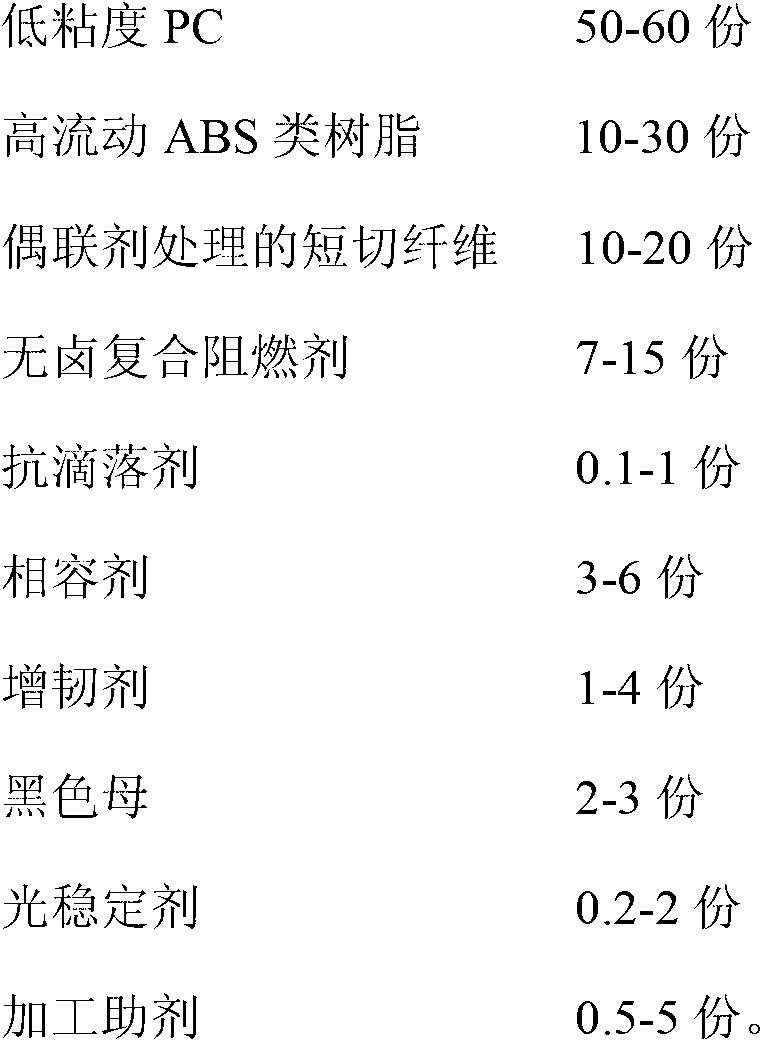
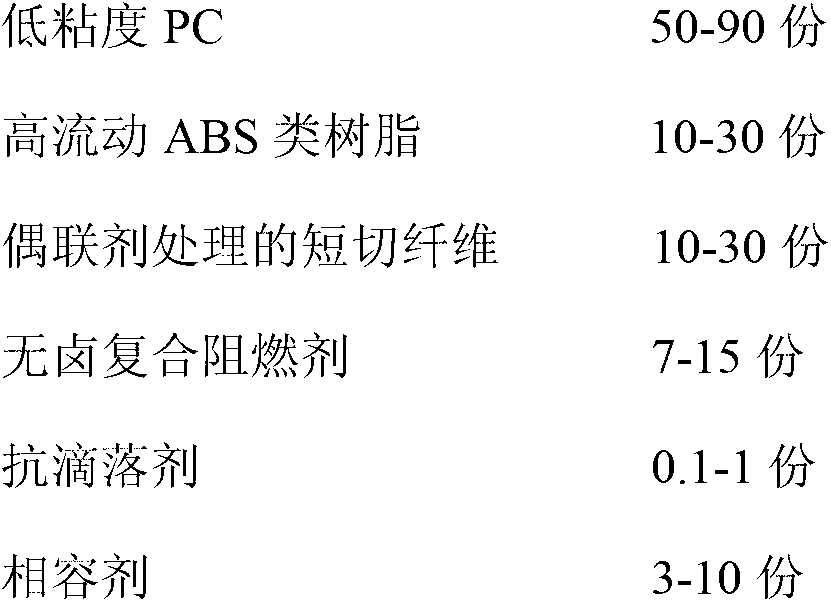
Flame-retardant glass fiber reinforced PC (Polycarbonate)/ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a flame-retardant glass fiber reinforced PC (Polycarbonate) / ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) composite material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of: respectively and fully drying low-viscosity PC, high-flow ABS resin, chopped fibers treated by using silane coupling agent, a halogen-free composite flame retardant, an anti-dripping agent, a black color base and a processing agent; fully mixing other raw materials except for the alkali-free chopped fibers treated by using the silane coupling agent in a high-speed mixer according to a proportion; then feeding the raw material into a double-screw extruder; laterally adding the alkali-free chopped fibers treated by using the silane coupling agent; and mixing, extruding, drawing, cooling, grain-sized dicing, and drying to obtain a finished injection molding raw material. The preparation method of the flame-retardant glass fiber reinforced PC / ABS composite material, disclosed by the invention, keeps certain impact intensity and rational MFR (Melt Flow Rate), thermal distortion temperature, vicat softening point and the like of the material while obtaining high intensity, high rigidity and flame retardant properties by selecting an assistant and proportions of the raw materials reasonably and adding the fibers as well as the flame retardant.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +1
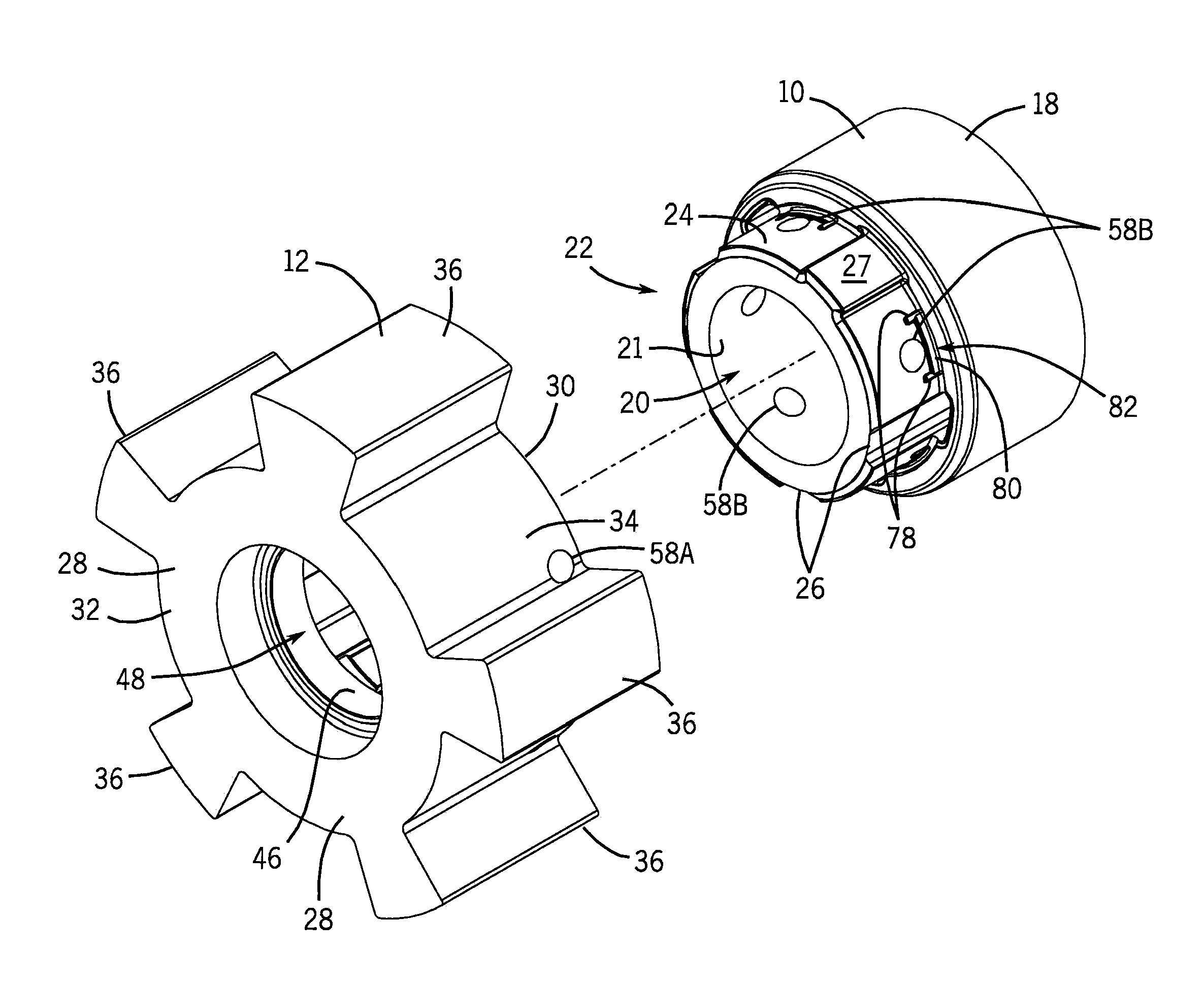
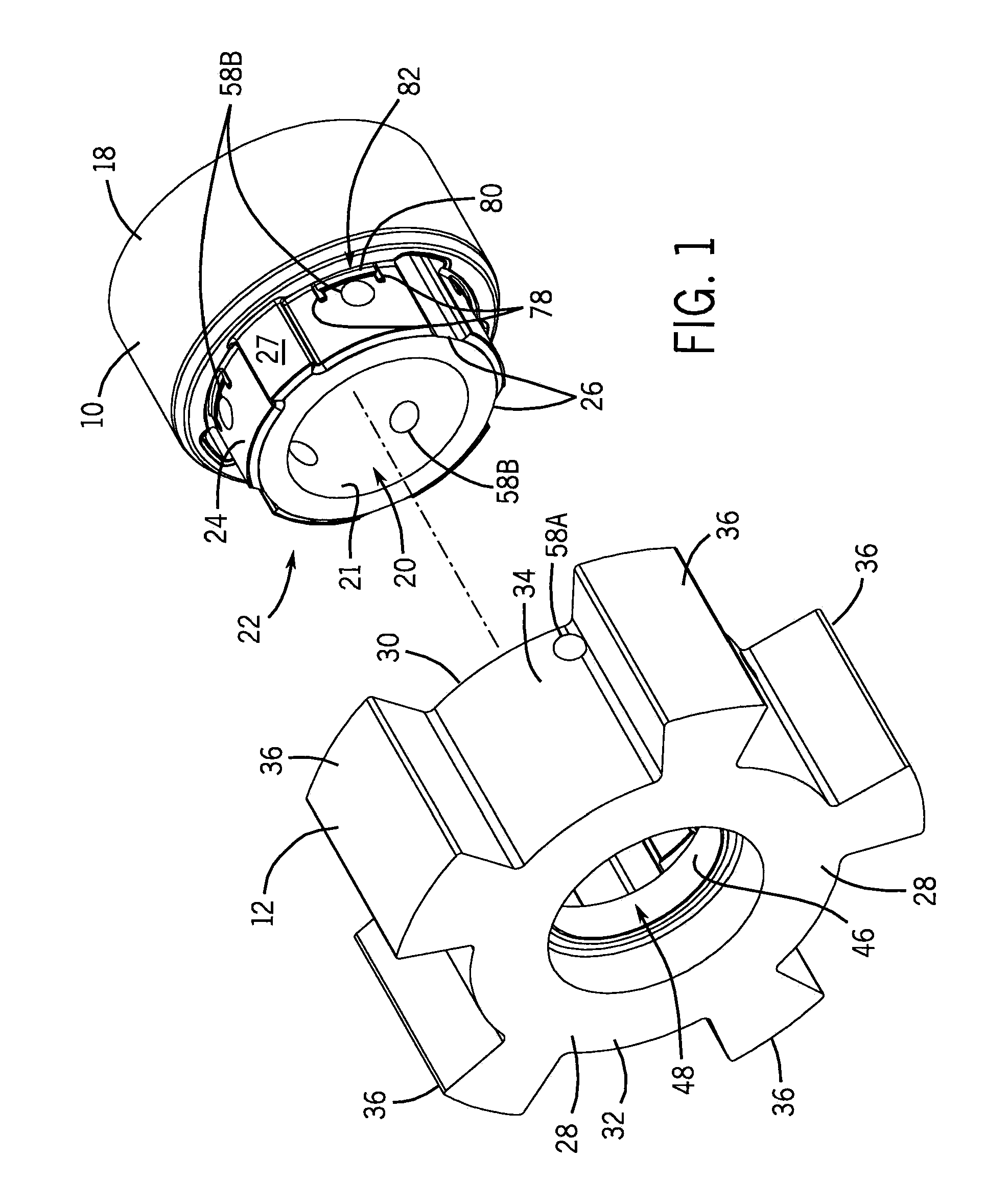
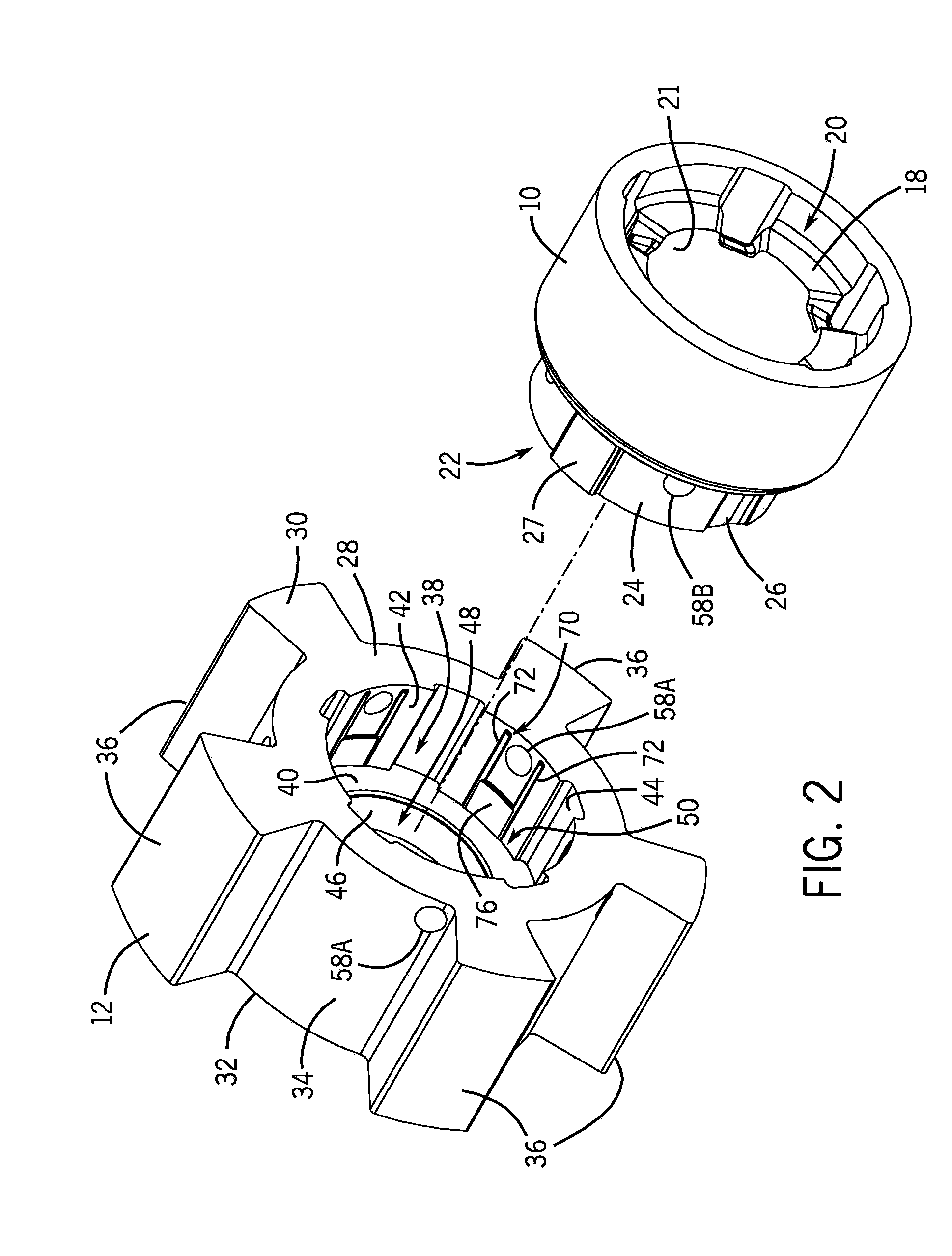
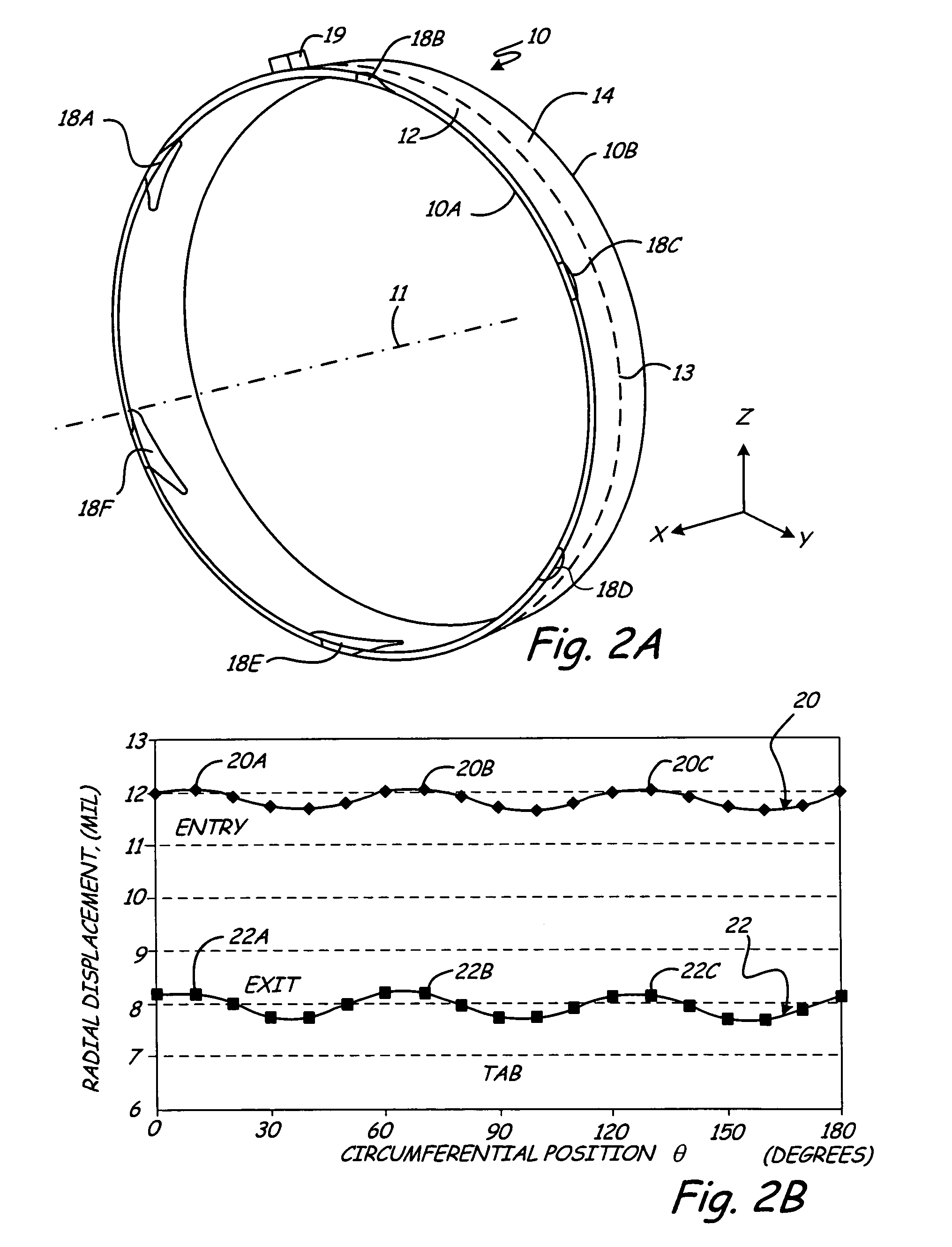
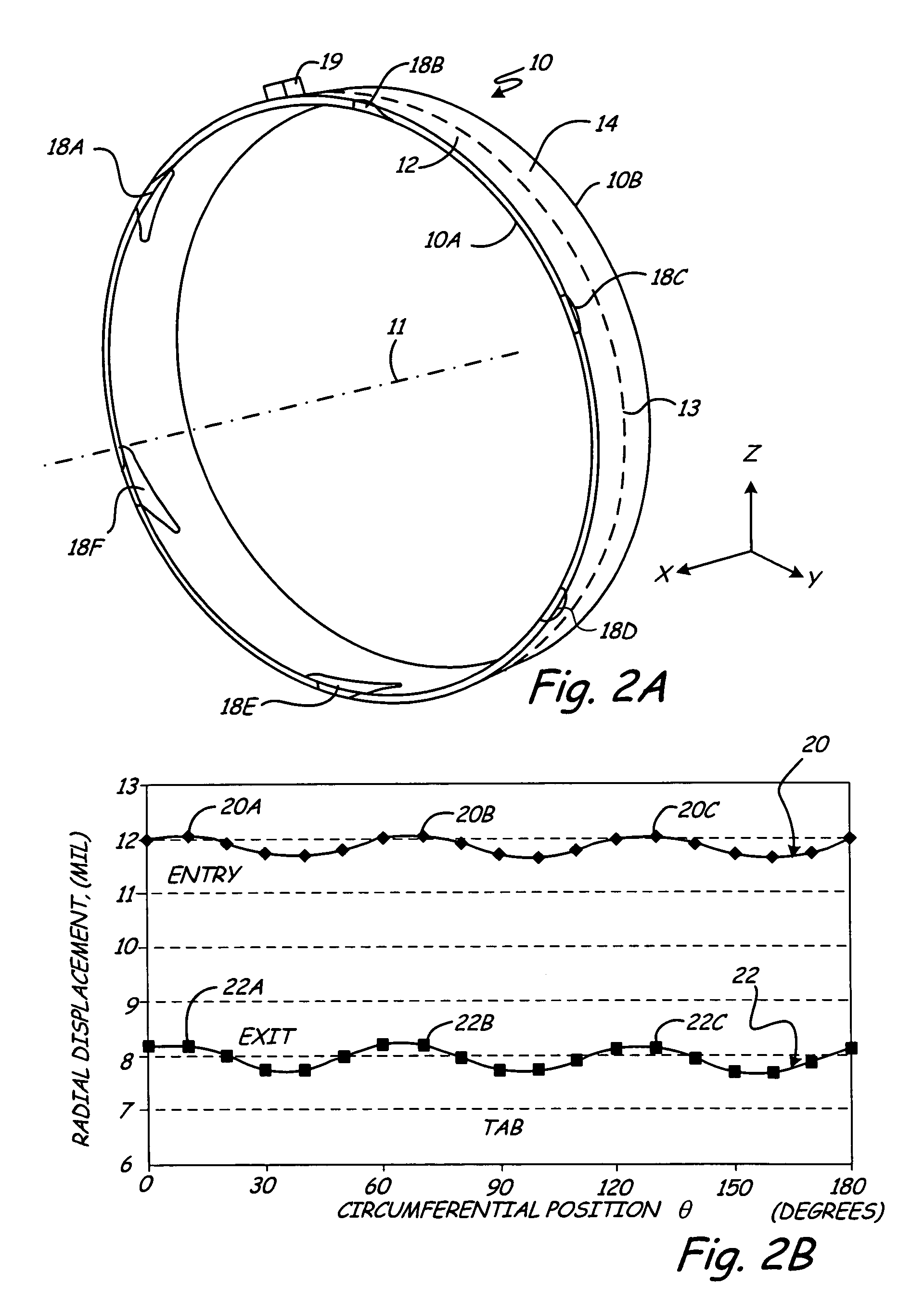
Turbine shroud thermal distortion control
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
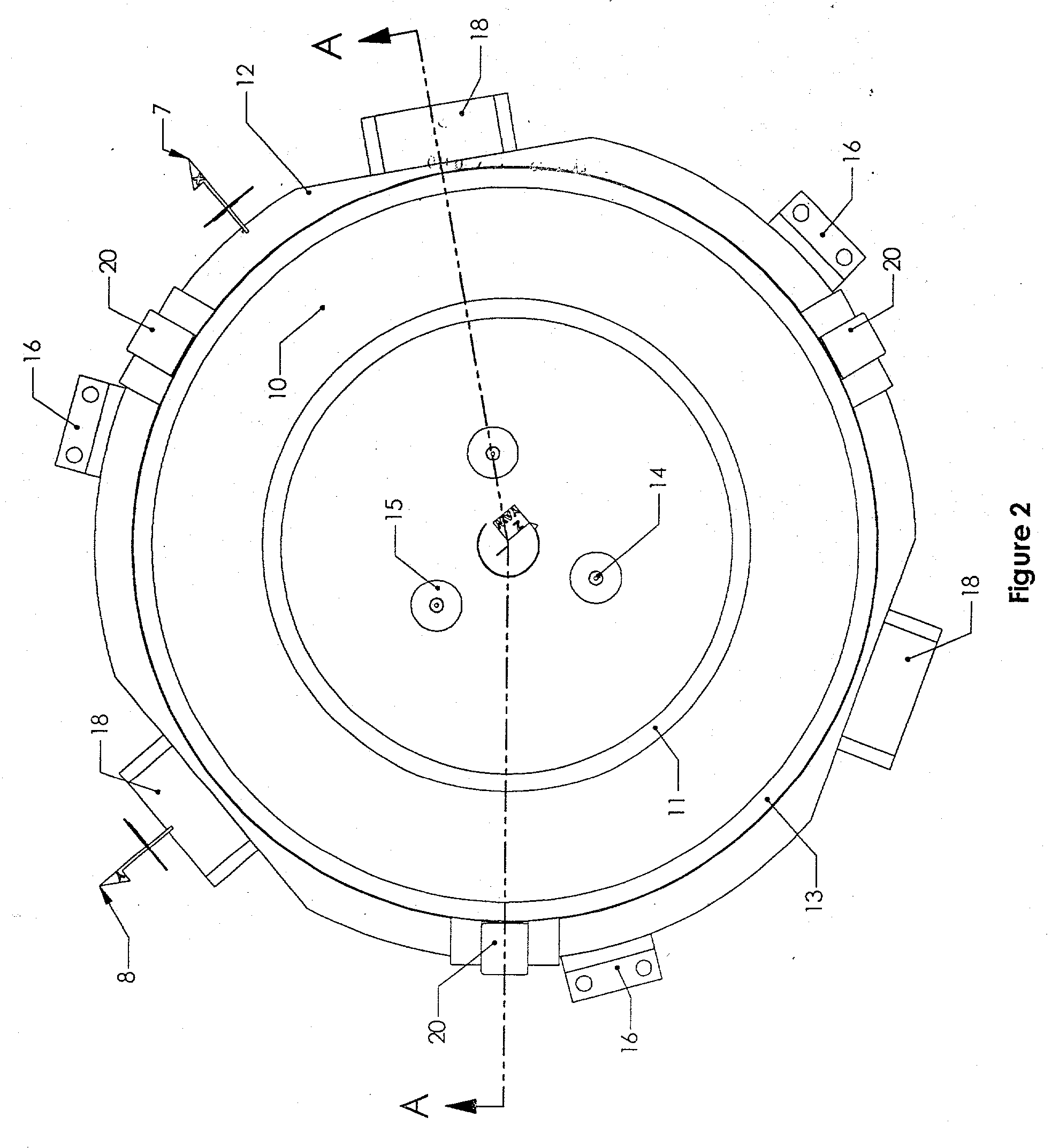
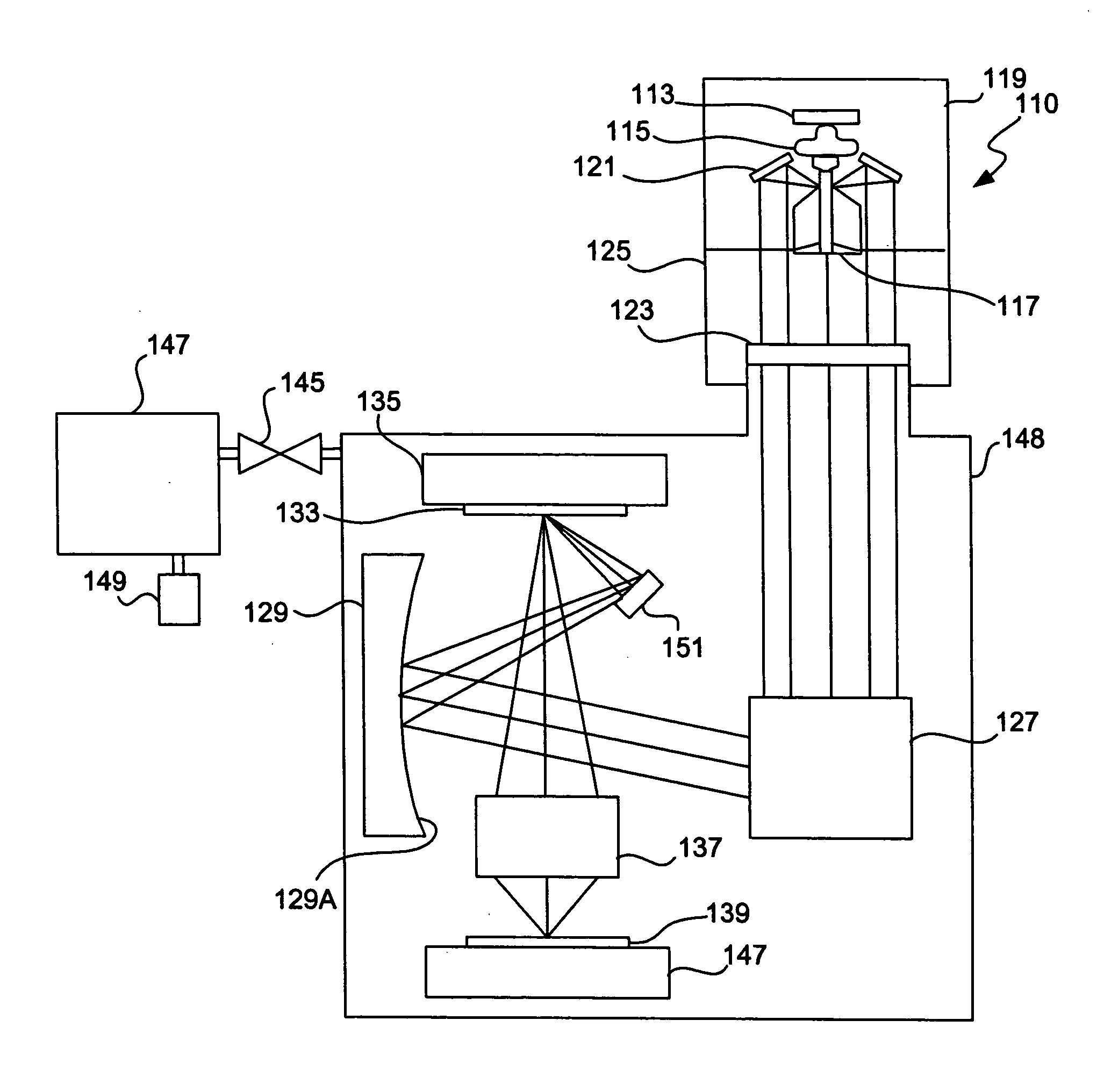
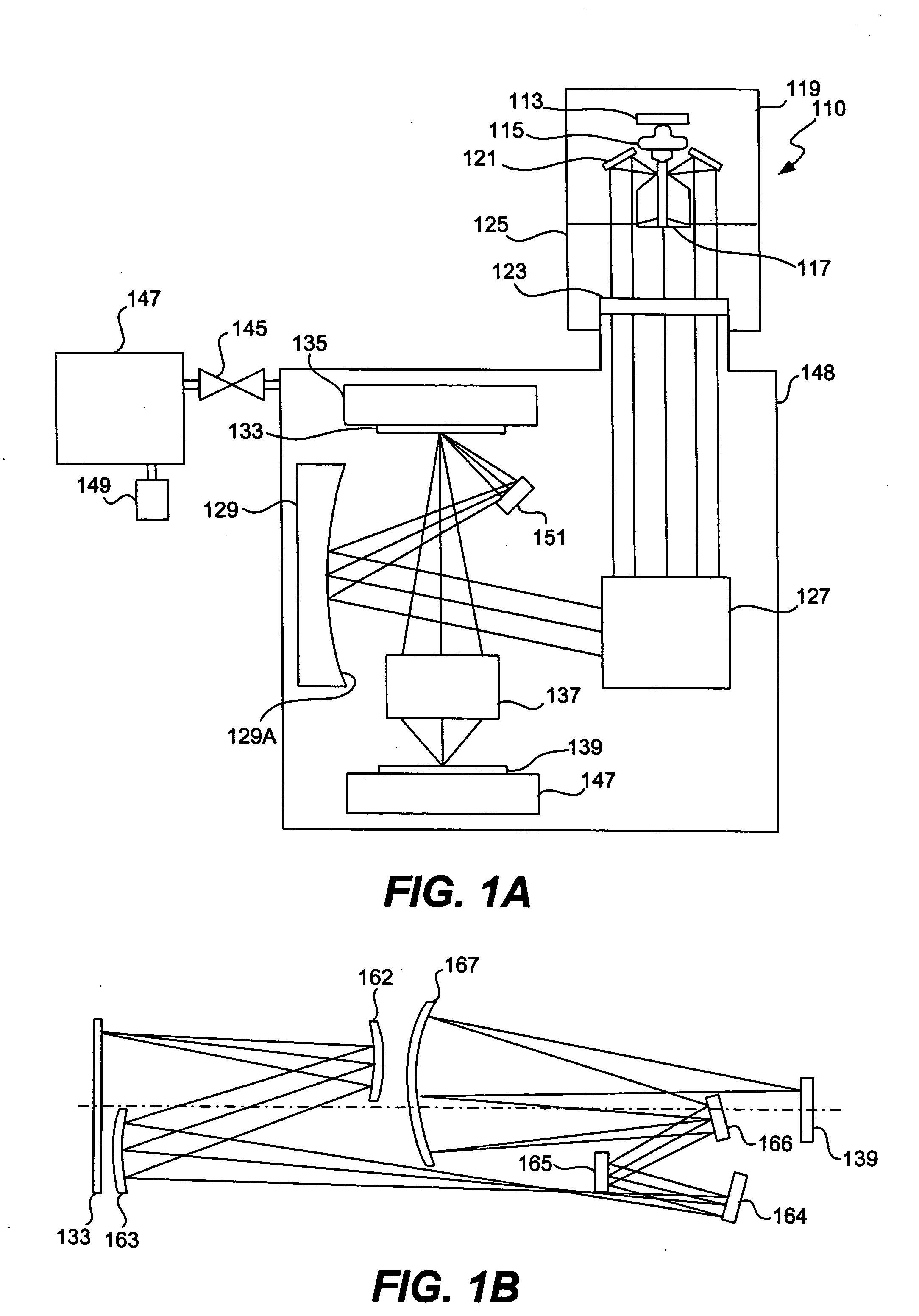
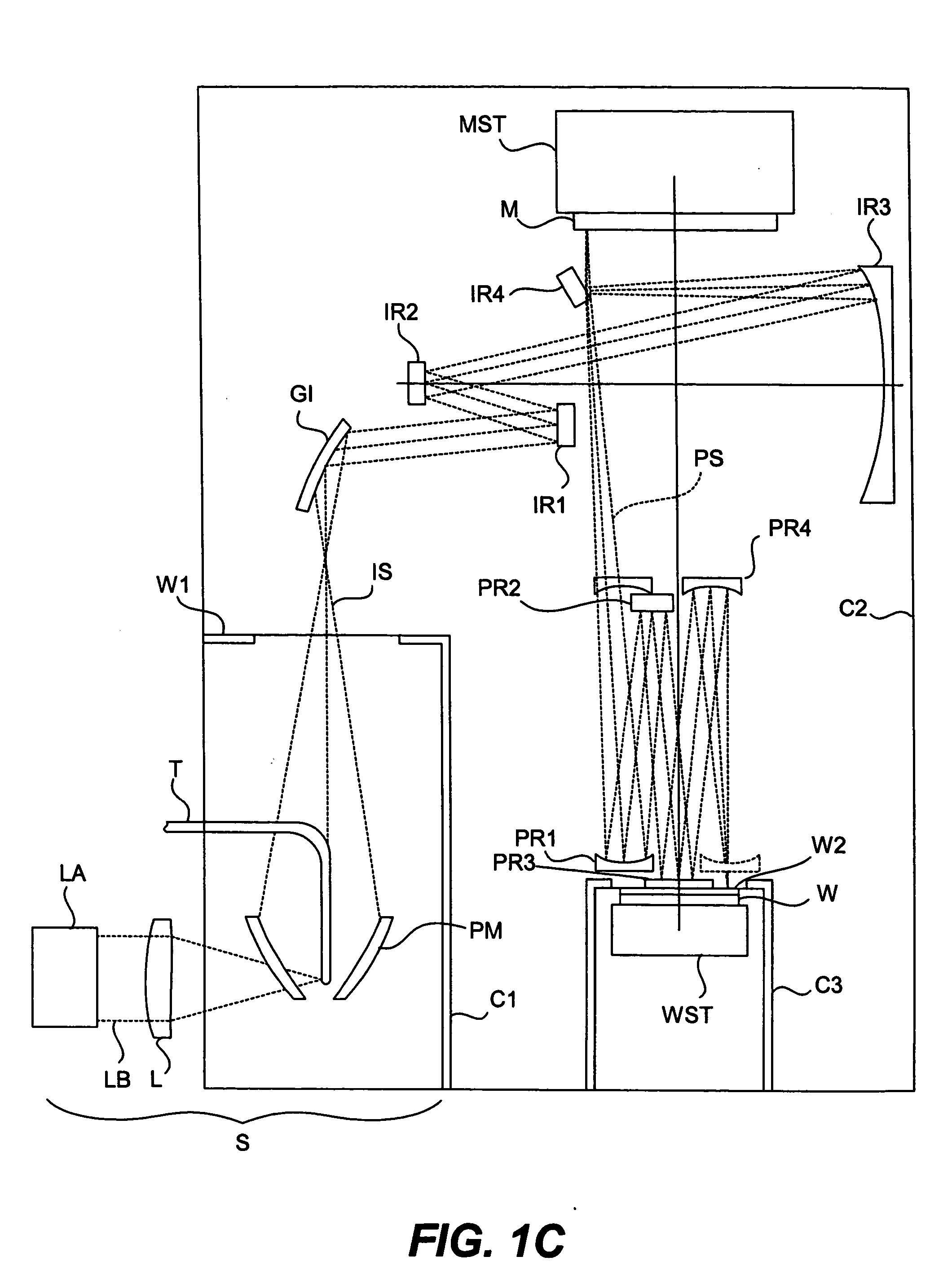
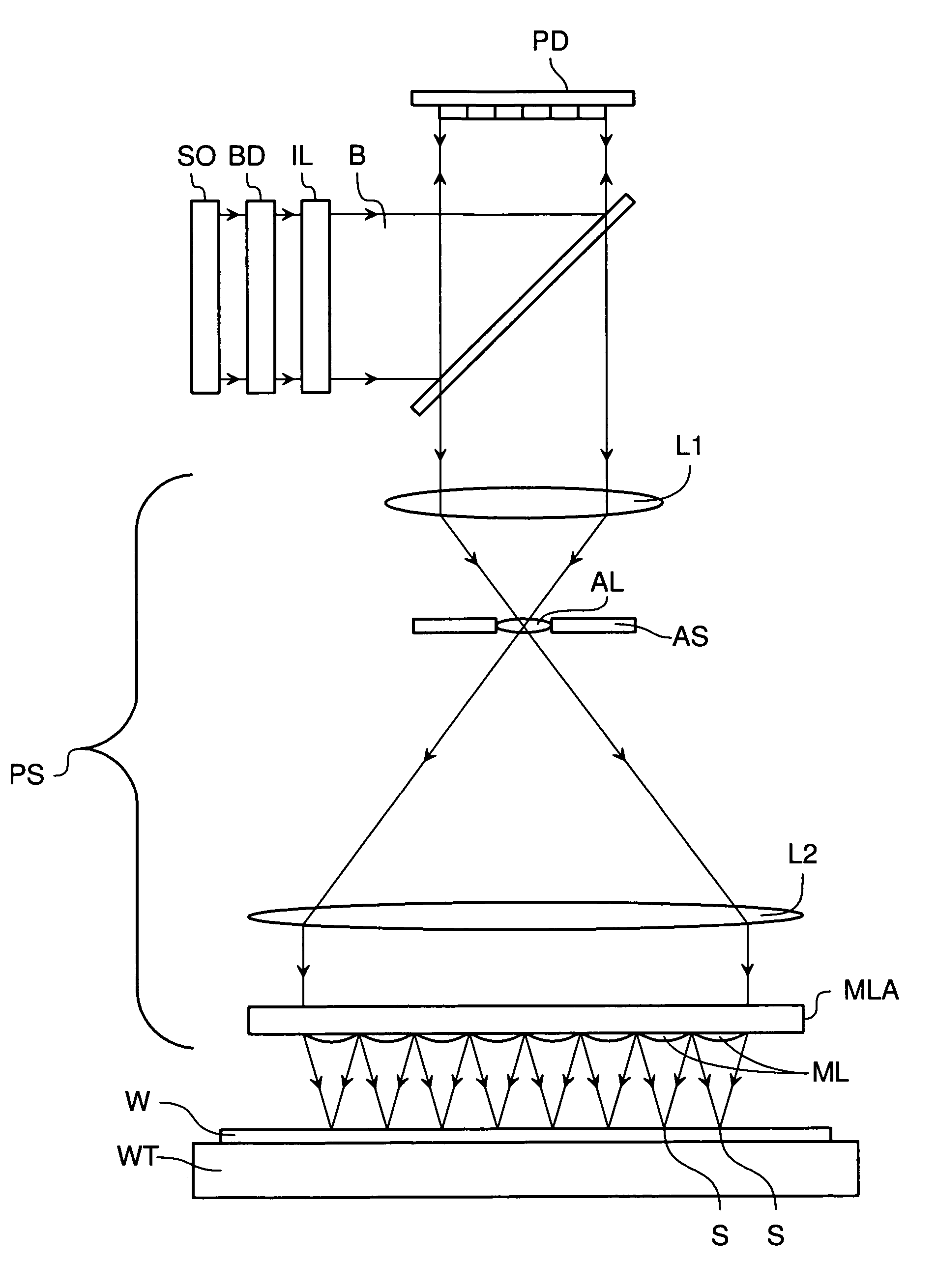
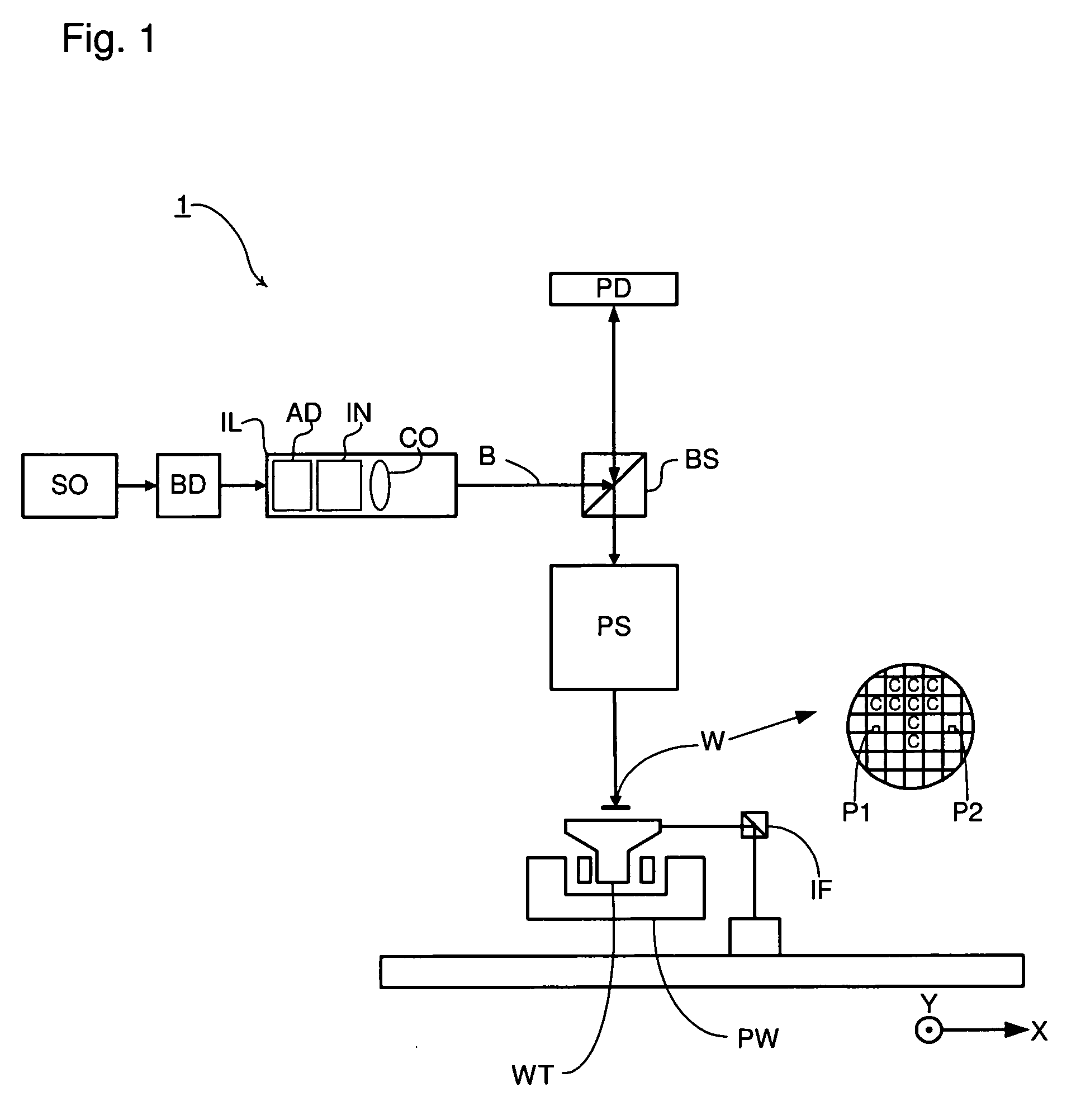
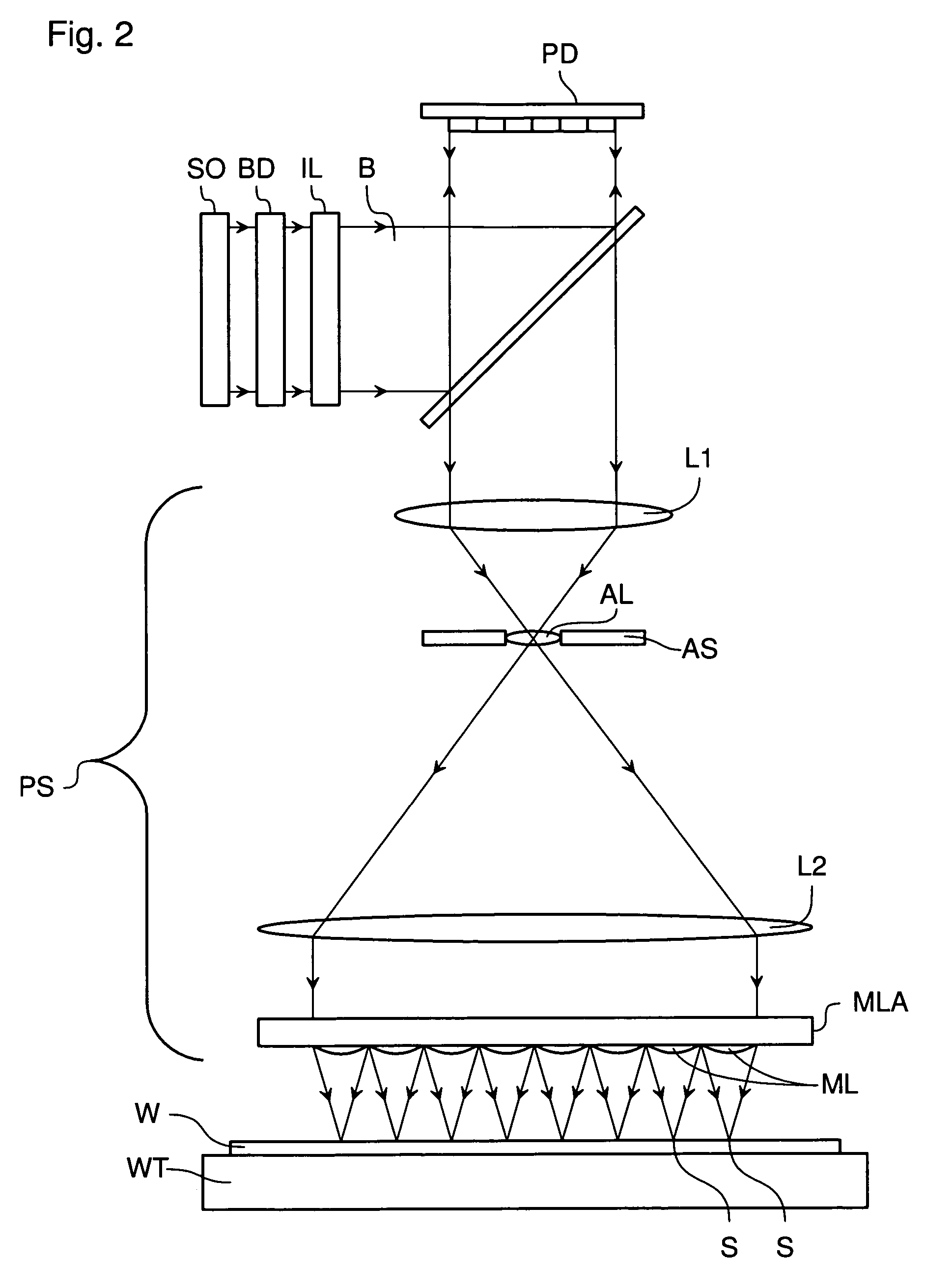
System and method for compensating for radiation induced thermal distortions
ActiveUS20070076180A1Distortion of can arisePhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingProjection systemThermal effect
A system and method are used to compensate for thermal effect on a lithographic apparatus. The system comprises a patterning device, a projection system, a substrate position controller, and a substrate-position-based expansion-compensator. The patterning device modulates a radiation beam. The projection system projects the modulated radiation beam onto a target portion of a substrate. The substrate position controller moves the substrate relative to the projection system sequentially through a plurality of exposure positions. The substrate-position-based expansion-compensator interacts with the substrate position controller to modify the exposure positions in order at least partially to compensate for thermally-induced geometrical changes of at least one of the substrate and projection system.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
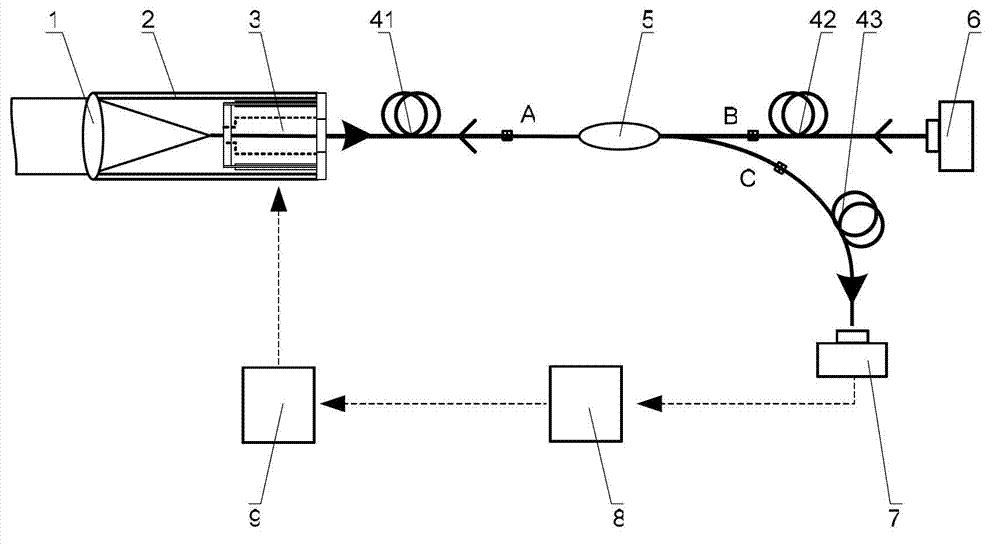
Self-adaptive optical fiber coupler or collimator control system capable of bilaterally receiving and transmitting laser beams
ActiveCN103311790ARealize two-way sending and receivingAchieving Synchronous Adaptive CorrectionLaser output parameters controlActive medium shape and constructionOptical fiber couplerHigh pressure
The invention discloses a self-adaptive optical fiber coupler or collimator control system capable of bilaterally receiving and transmitting laser beams. The self-adaptive optical fiber coupler or collimator control system comprises a coupling or collimating lens, a connecting sleeve, an optical fiber end face positioner, a first optical fiber, a three-port optical fiber circulator, a second optical fiber, a third optical fiber, a laser, a photoelectric detector, a control platform and a high-voltage amplifier, wherein the optical fiber end face positioner comprises a flexible crossed beam, a bimorph driver, a damping material, a boss and a fixed seat. Due to the adoption of the self-adaptive optical fiber coupler or collimator control system, the light beam arriving angle errors caused by factors such as atmosphere turbulence, mechanical vibration, thermal distortion and the like can be corrected adaptively; and meanwhile, according to the reversibility principle of a light path, the transmitting angle correction of emitted collimating light beams is also realized. The self-adaptive optical fiber coupler or collimator control system has an important application prospect in the field of optical fiber-based laser space application, such as free space laser communication, laser precise positioning and laser radar.
Owner:成都芯智锐光科技有限公司
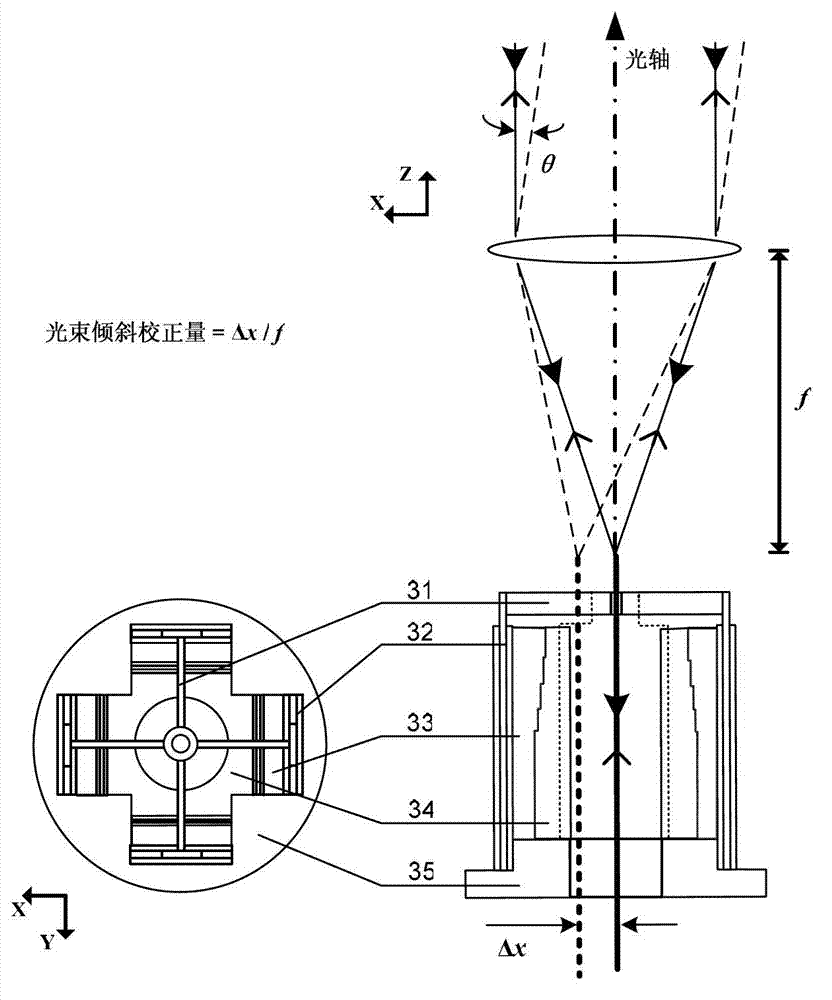
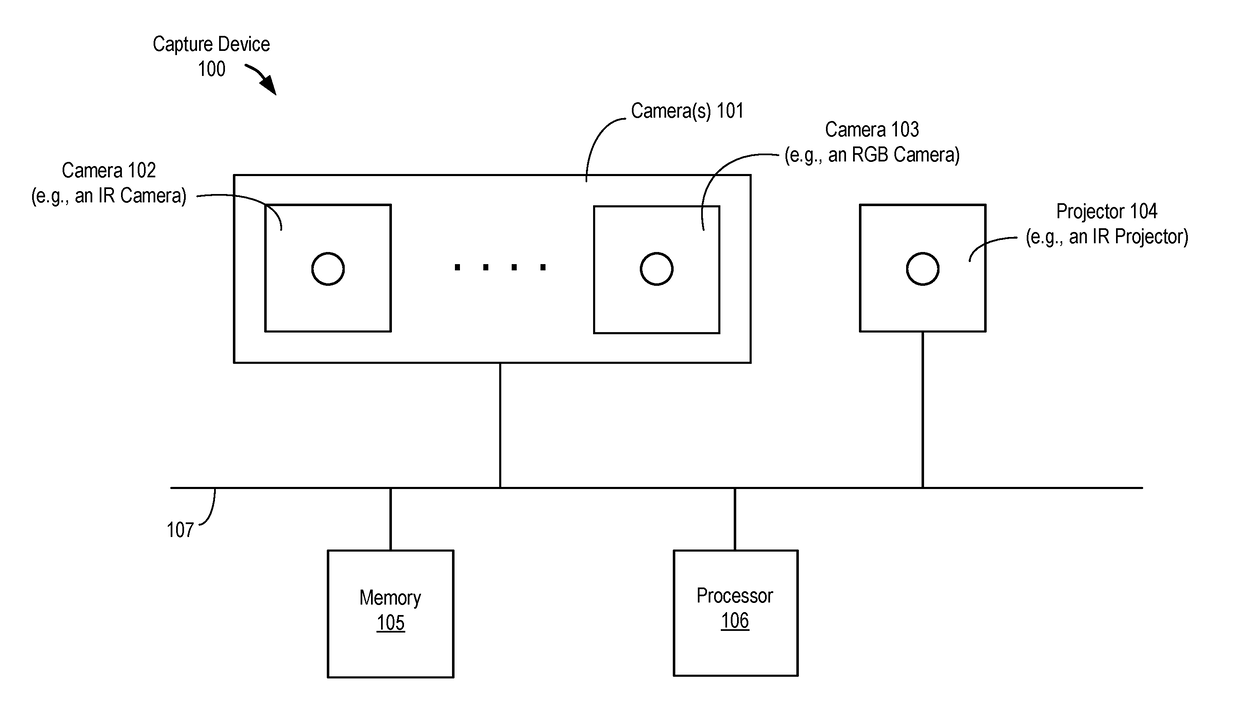
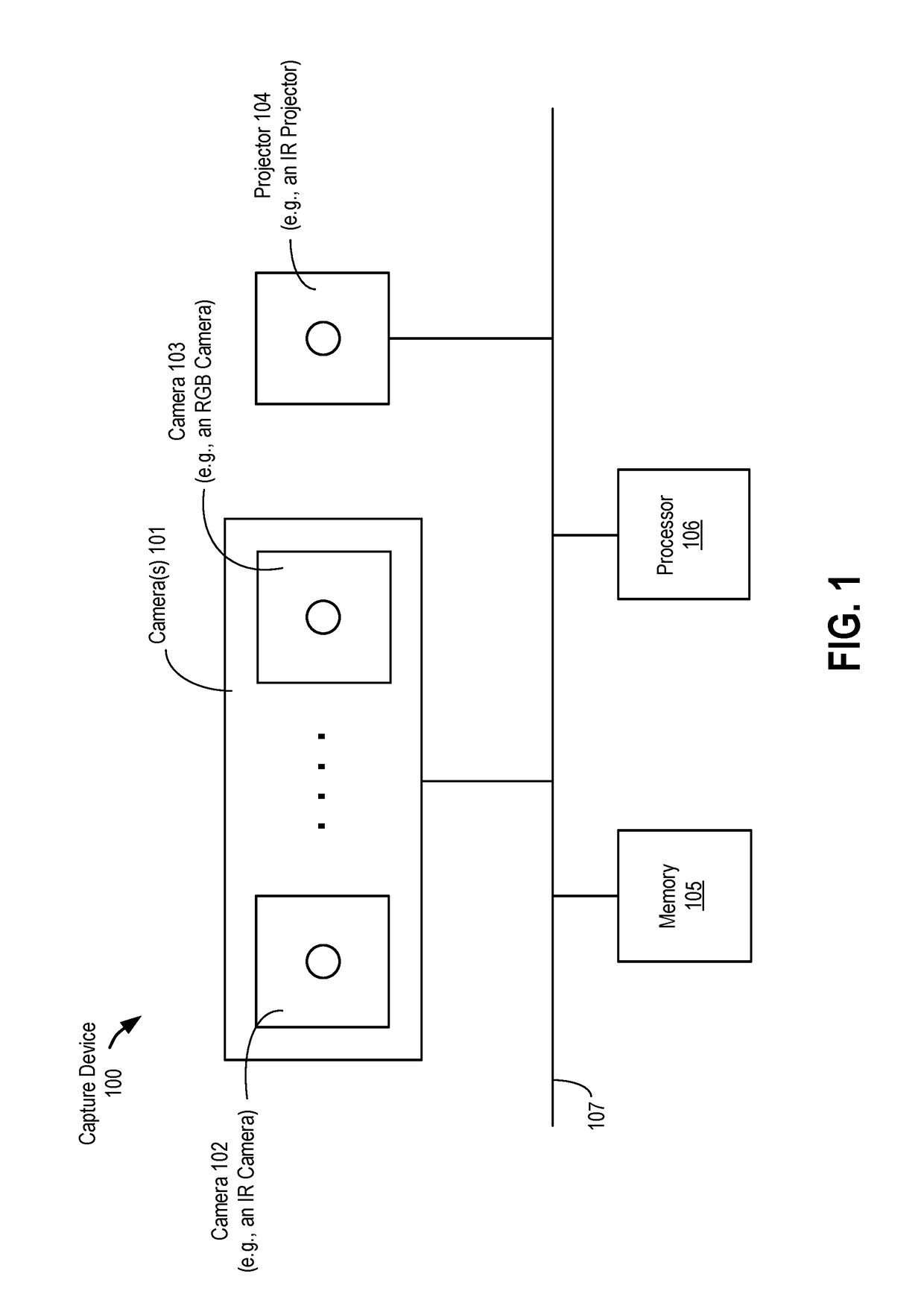
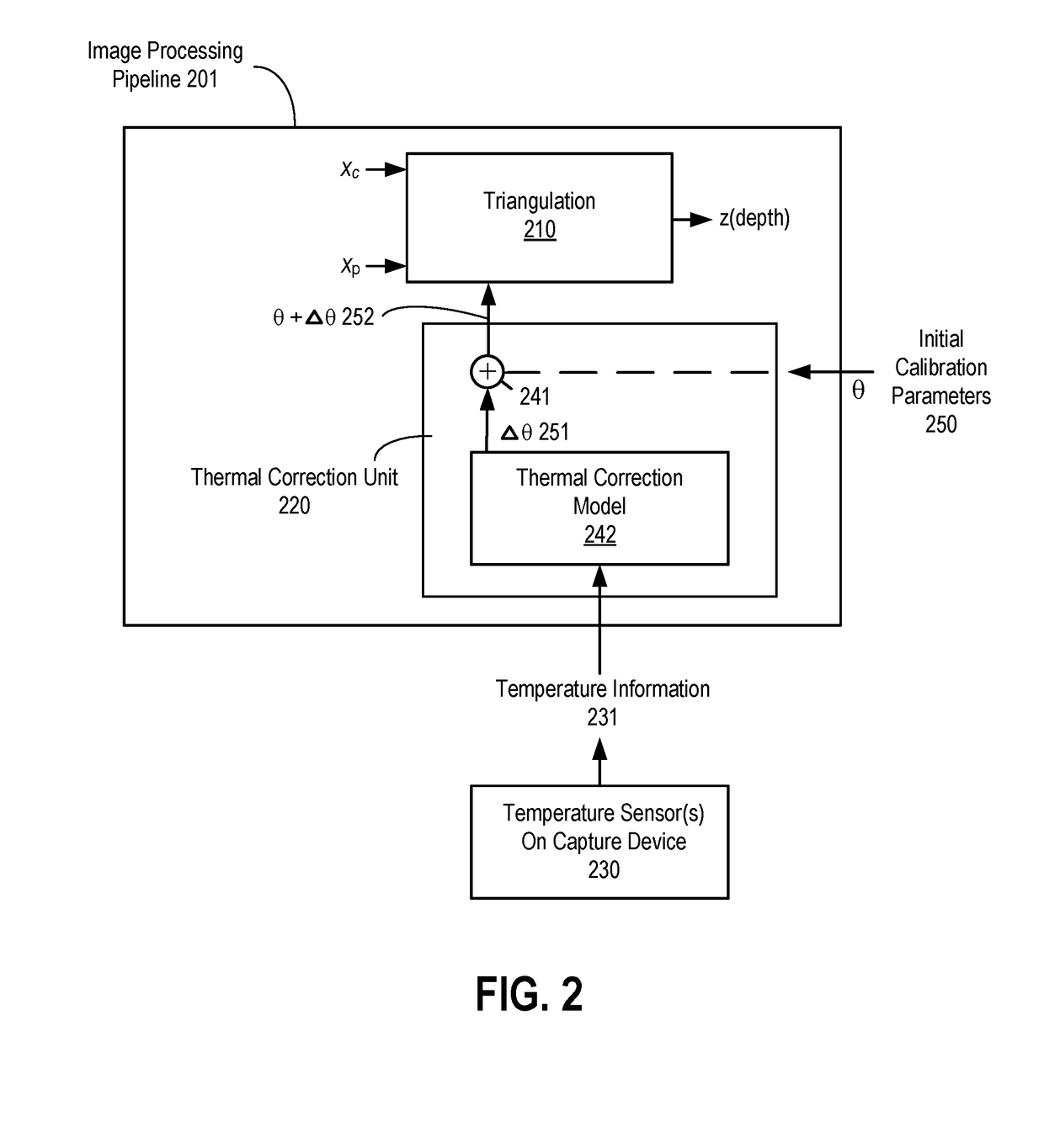
Online compensation of thermal distortions in a stereo depth camera
A method and apparatus for performing temperature compensation for thermal distortions in a camera system. In one embodiment, the system comprises a first camera configured to capture a sequence of images of the object; a second device; a processing unit to receive the sequence of images and determine depth information in response to parameters of the camera and the second device; one or more temperature sensors; and a thermal correction unit responsive to temperature information from the one or more temperature sensors to adjust one or more of the calibration parameters of the first camera and the second device.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method of forming light-emitting element
InactiveUS7550305B2Low costInhibit deteriorationDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsEngineeringThermal distortion
An object of the present invention is to provide a method of forming a light-emitting element at a lower cost than a conventional cost with suppressing the deterioration of the substrate due to thermal distortion in comparison with a conventional method of recycling a substrate and further having an effect equal to that of the method of recycling a substrate. The method of forming a light-emitting element by growing a separation layer and a light-emitting layer in this order on a first substrate, bonding the light-emitting layer onto a second substrate, and removing the separation layer to form the light-emitting layer on the second substrate, includes growing a plurality of groups each containing the separation layer and light-emitting layer on the first substrate; patterning the light-emitting layer existing as a uppermost layer into an island shape, and then bonding the light-emitting layer onto the second substrate, and etching the separation layer adjacent to the light-emitting layer patterned into the island shape to form the light-emitting layer patterned into the island shape on the second substrate.
Owner:CANON KK
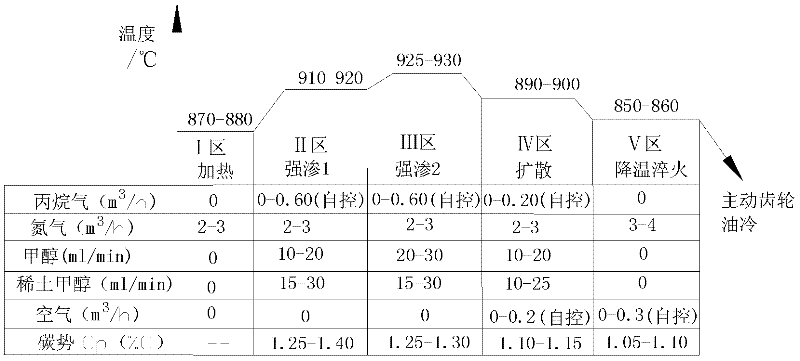
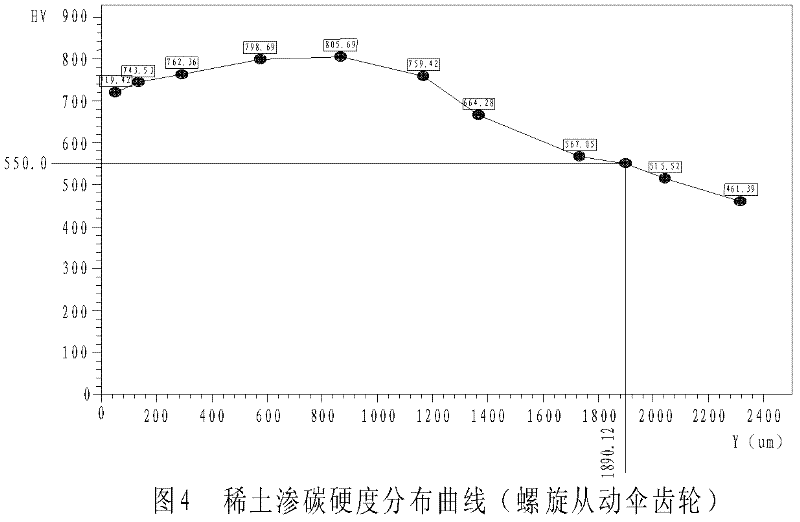
Heat treatment method of spiral bevel gear of cargo truck on double-row rare earth carburization equipment
ActiveCN102373400AEmission reductionIncrease carburizing speedSolid state diffusion coatingCarbon potentialRare earth
The invention provides a heat treatment method of a spiral bevel gear of a cargo truck on double-row rare earth carburization equipment, and relates to a carburization heat treatment technological process of the spiral bevel gear of the cargo truck. The invention solves the problems that energy consumption of carburization heat treatment is high, production cost of a product is high and carburization quenching and gear thermal distortion still exist in a carburization process. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: taking a preheating zone as a strong leakage region 1 and taking a carburizing region as a strong leakage region 2, namely taking a region II and a region III as a carburizing speed main control region and taking a region IV and a region V as a metallographic structure main control region, carrying out temperature control in the regions I, II, III, IV and V, carrying out carbon potential control in the regions II, III, IV and V, and inputtingcarburizing medium propane gas, rare earth methanol penetrating agent, nitrogen, methanol and air into a furnace, thus the heat treatment method is realized. The metallographic structure and surface hardness of the spiral bevel gear subjected to the heat treatment method provided by the invention are all optimized, and heat treatment quality of the spiral bevel gear is improved; meanwhile, capacity is improved by 23%, heat treatment production cost is reduced by 18.9%, and pollution of exhaust emission to the environment is reduced.
Owner:哈尔滨汇隆汽车箱桥有限公司 +3
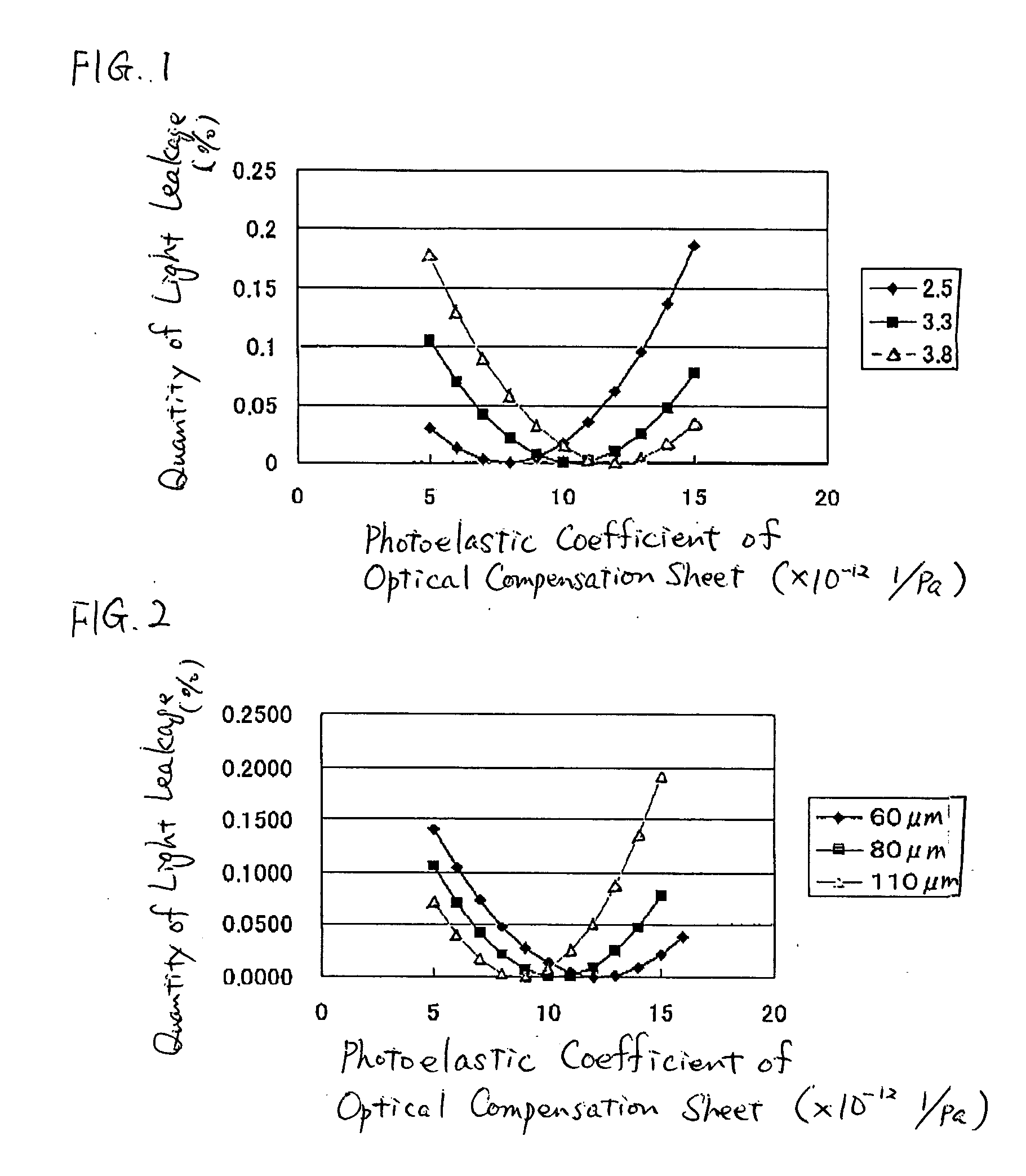
Optical compensation sheet, polarizing plate and liquid crystal display
InactiveUS20050105027A1Improve display qualityAvoid it happening againPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsEngineeringPolarizer
To provide a high-display-quality optical compensation sheet and a liquid crystal display having the optical member without inducing a problem, such as light leakage due to thermal distortion, the optical compensation sheet for a liquid crystal display, the liquid crystal display containing: a liquid crystal cell having a glass plate; and a polarizing plate having the optical compensation film faced to the glass plate, wherein a thickness of the optical compensation sheet, a photoelastic coefficient of the optical compensation and a photoelastic coefficient of the glass plate satisfy the condition specified in the specification.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Optical film and frame with high resistance to thermal distortion
InactiveUS20070127144A1Eliminates and reduces thermal bucklingReduce distortionPlanar/plate-like light guidesMountingsHigh resistanceEngineering
This invention relates to an optical film / frame combination wherein the optical film comprises a viewing portion and wherein either the film or the frame comprises a compression reducing mechanism for allowing the film to expand within the frame without distortion of the viewing portion of the film.
Owner:SKC HAAS DISPLAY FILMS CO LTD
Quartz glass crucible, process for producing the same, and use
InactiveCN101316953APromote crystallizationHigh mechanical strengthPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltSusceptorSingle crystal
A crucible has a structure where a layer containing a crystallization accelerating component such as aluminum or the like (a crystallization accelerating layer) is inserted inside a quartz glass layer of a crucible straight body part excepting a crucible bottom part. The crucible does not deform and fall inwardly at the straight body part since a part containing a crystallization accelerating component advances to crystallize so as to increase strength at a high temperature when the crucible is used in pulling up silicon single crystal. Therefore, a single crystallization rate can be increased. Further, since the crystallization accelerating layer is inserted inside the quartz glass layer, the crystallization accelerating component, such as aluminum or barium, does not contact with silicon melt or a carbon susceptor, contamination by eluting these metals does not occurs. Further, since the crystallization accelerating layer is not provided at the crucible bottom part, there is no danger to crack due to thermal distortion at a time of pulling up silicon single crystal and melt leakage does not occur.
Owner:JAPAN SUPER QUARTZ CORP
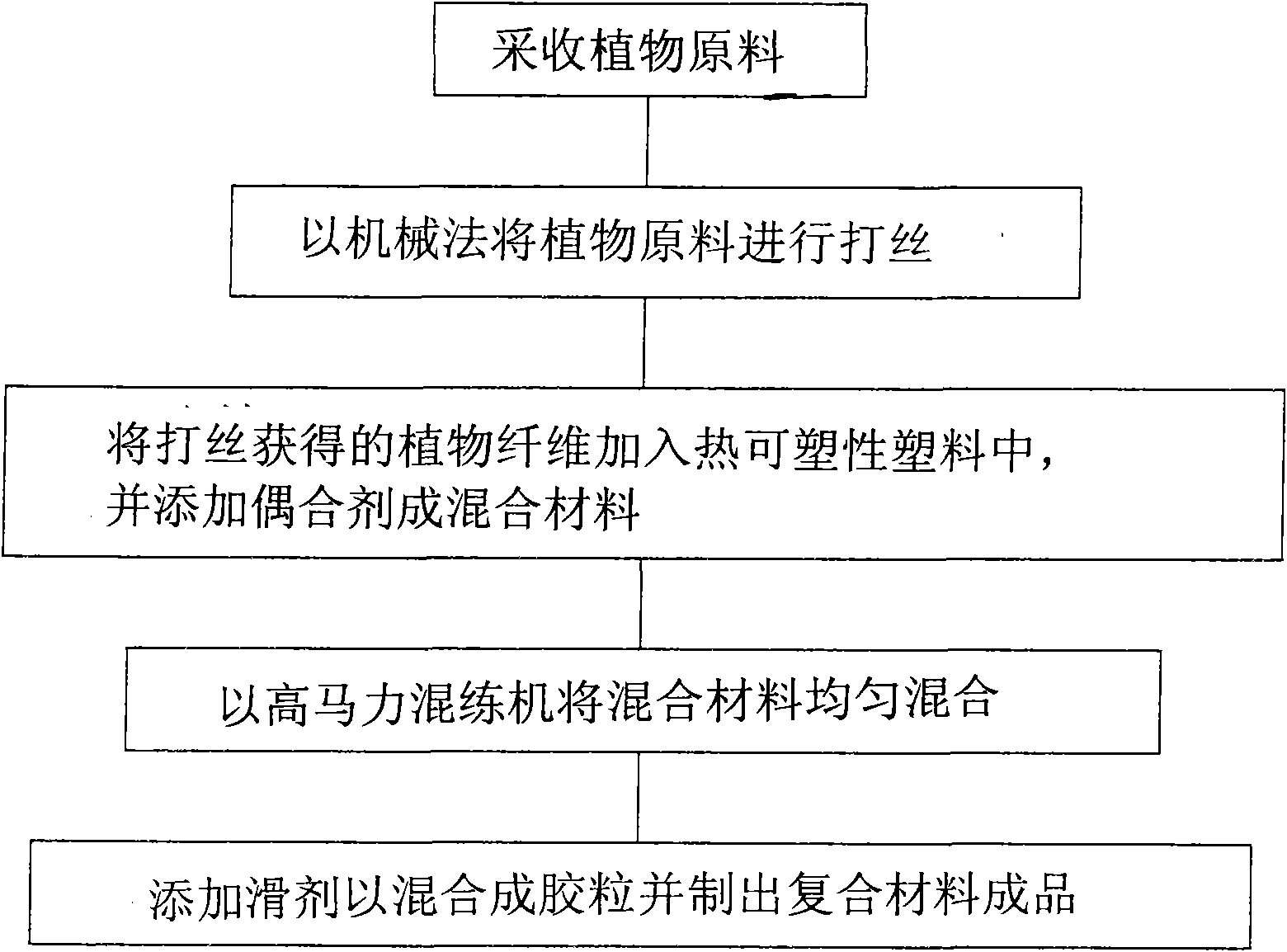
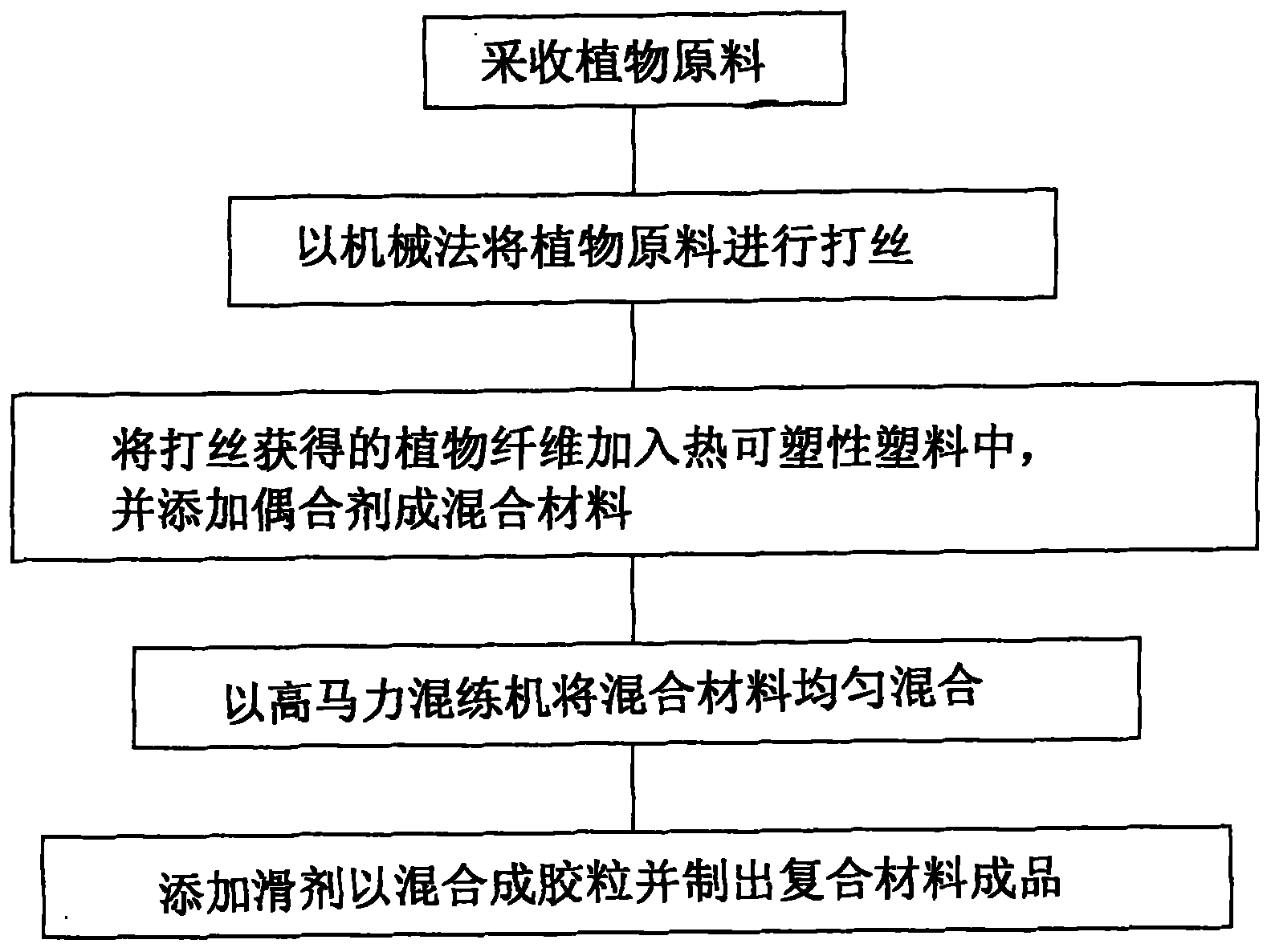
Preparation process of plant fiber composite materials
InactiveCN101781472AImprove flexural strengthReduce weightMechanical fibre separationManufacturing cost reductionFiber
The invention provides a preparation process of plant fiber composite materials, which comprises the following steps: collecting plant raw materials; using a mechanical method for cutting the plant raw materials into threads; adding the plant fiber obtained after the thread cutting into thermoplastic plastics and adding coupling agents to obtain mixed materials; using a high-horsepower calendaring machine for uniformly mixing the mixed materials; and adding lubricating agents to be mixed into colloidal particles and preparing finished products of composite materials. Because of the plant fiber composite materials, the prepared finished products have the characteristics of high bending resistance intensity, weight reduction, difficult thermal distortion, small thermal contraction force, manufacture cost reduction and the like.
Owner:詹德威
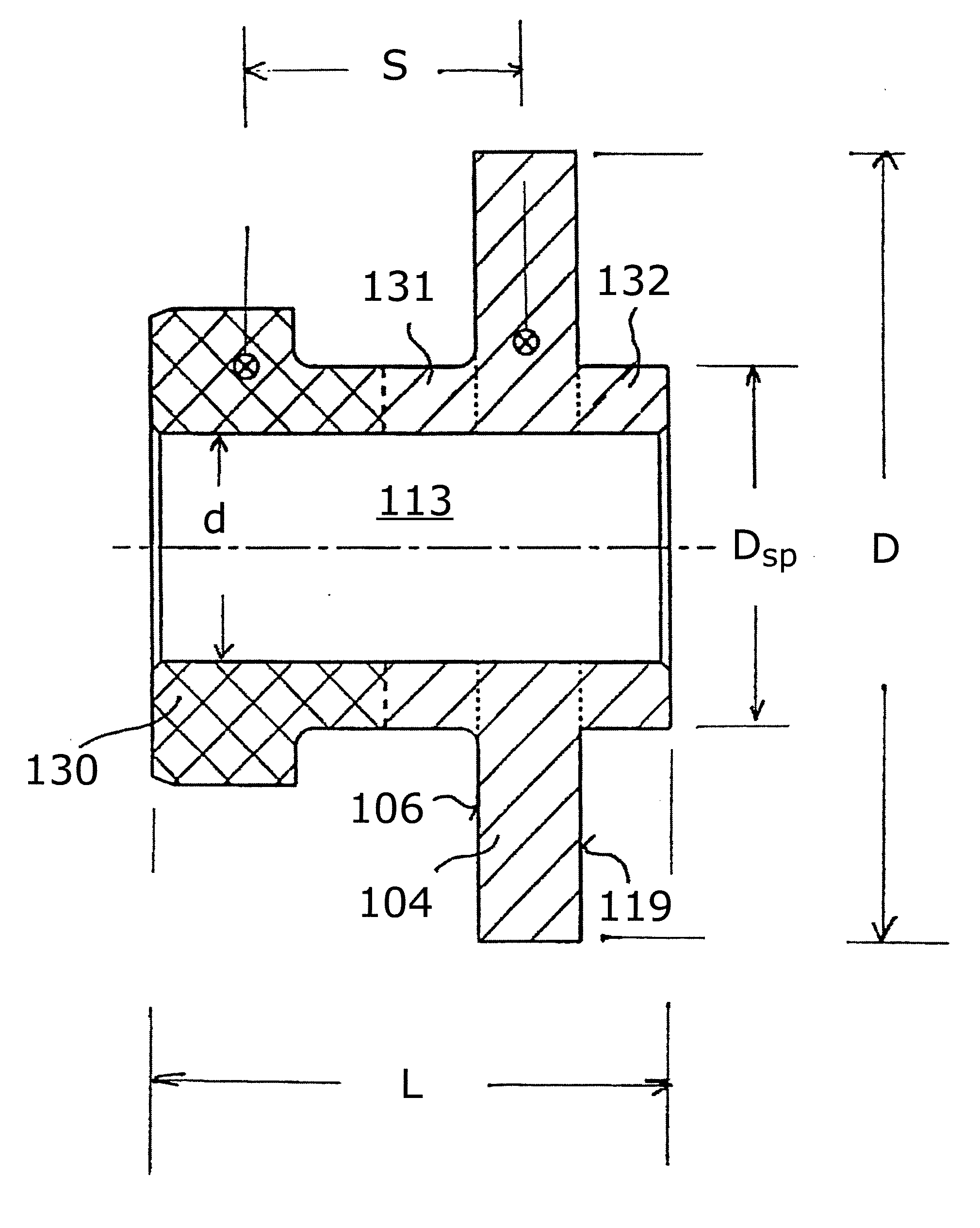
Axial plain bearing assembly
ActiveUS20080181546A1Highly effectiveReduce component countEngine sealsShaftsThrust bearingEngineering
An axial plain bearing assembly includes a thrust ring provided for common rotation with a rotary component. The thrust ring has a radial seal face on an end face thereof for co-operating with a radial seal face of a non-rotational seal ring of a gas-lubricated mechanical face seal assembly for sealing said rotary and stationary components against each other. A plurality of peripherally spaced gas-pumping grooves is formed in at least one of the radial seal faces of the thrust and non-rotational seal rings. A mass ring connected with the thrust ring is provided at an axial distance from the thrust ring. The mass ring is configured and adapted to exert a balancing force on the thrust ring under centrifugal forces acting on the mass ring during common rotation of the mass and thrust rings to compensate for thermal distortion of the thrust ring during operation.
Owner:CARL FREUDENBERG KG
CTE compensation of semiconductor laser bars
InactiveUS6895027B2Limited useful lifeSemiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor laser structural detailsThermal expansionCopper
A laser bar is soldered to a conventional microchannel copper heat sink whose coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) is locally modified in the area where the laser bar is soldered to better match the CTE of the laser bar. A strip of ceramic material having a CTE lower than that each of the laser bar and of the copper heat sink is soldered to portions of the metallic heat sink located adjacently to the surface area on which the laser bar is located. The inclusion of the ceramic strips enables a laser bar having a nominal CTE of 6.6×10−6 / K, to be soldered directly to a copper heat sink having a nominal CTE of 16.5×10−6 / K without incurring thermal distortions at the interface that would limit the useful life of the laser bar.
Owner:SPECTRA PHYSICS SEMICON LASERS
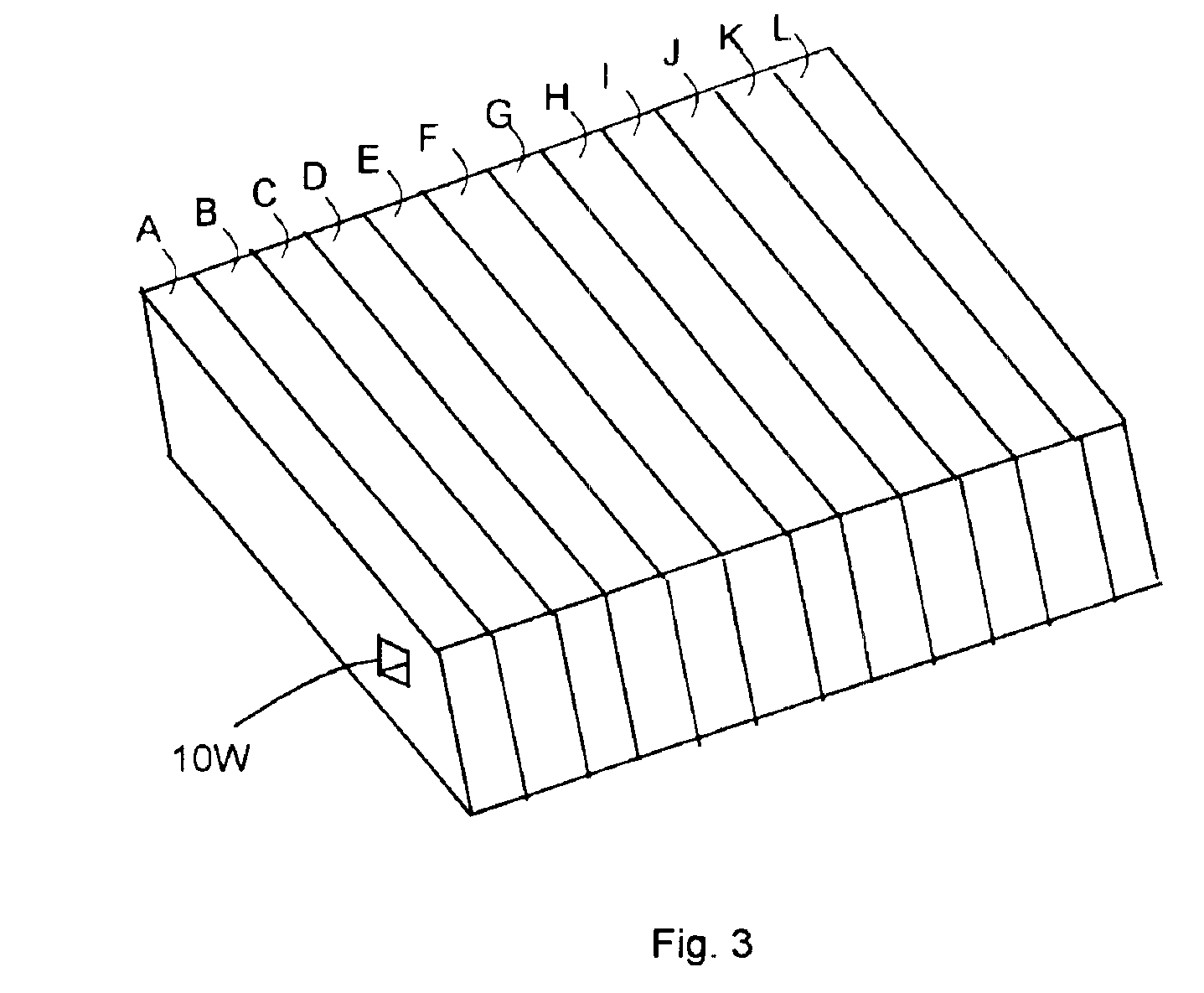
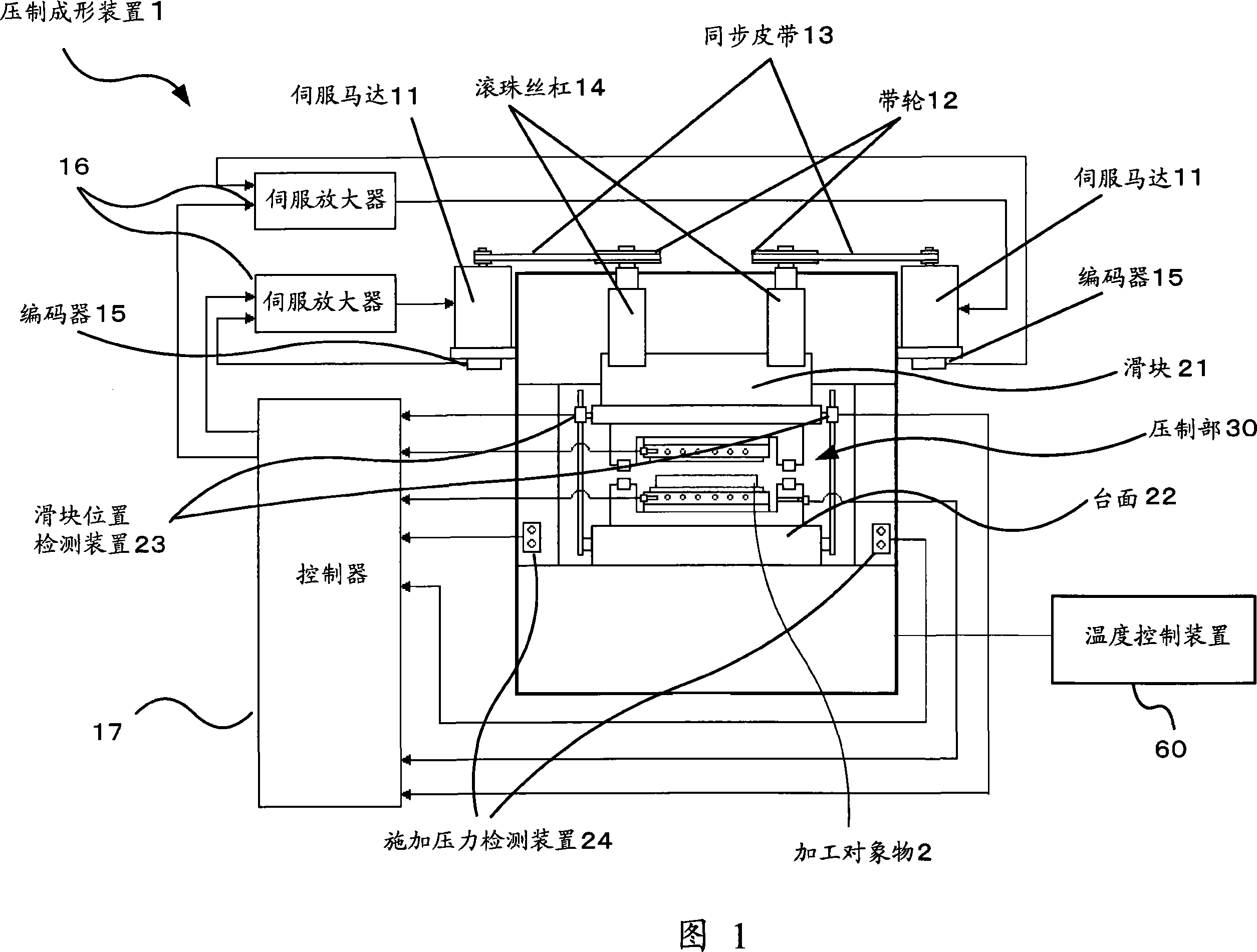
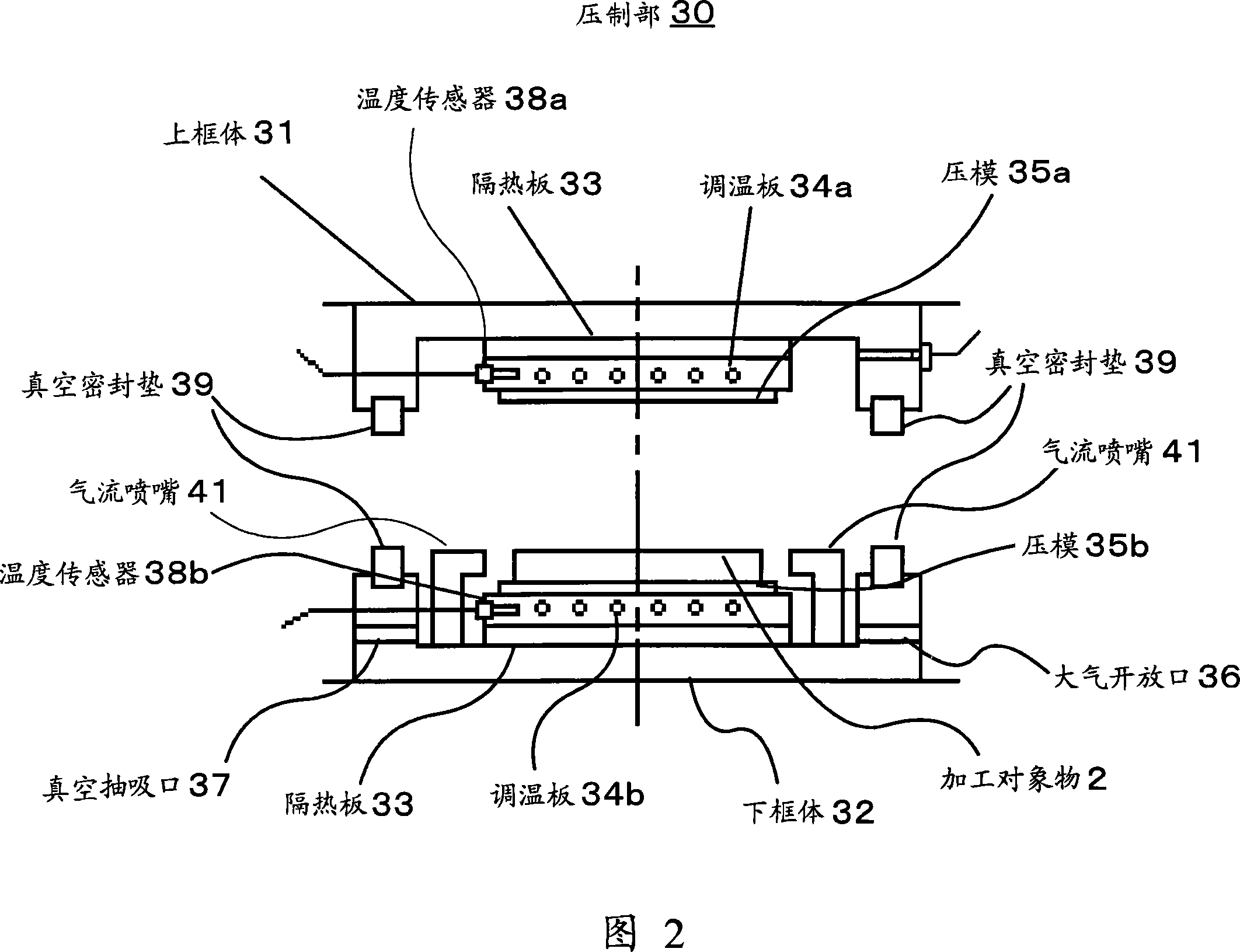
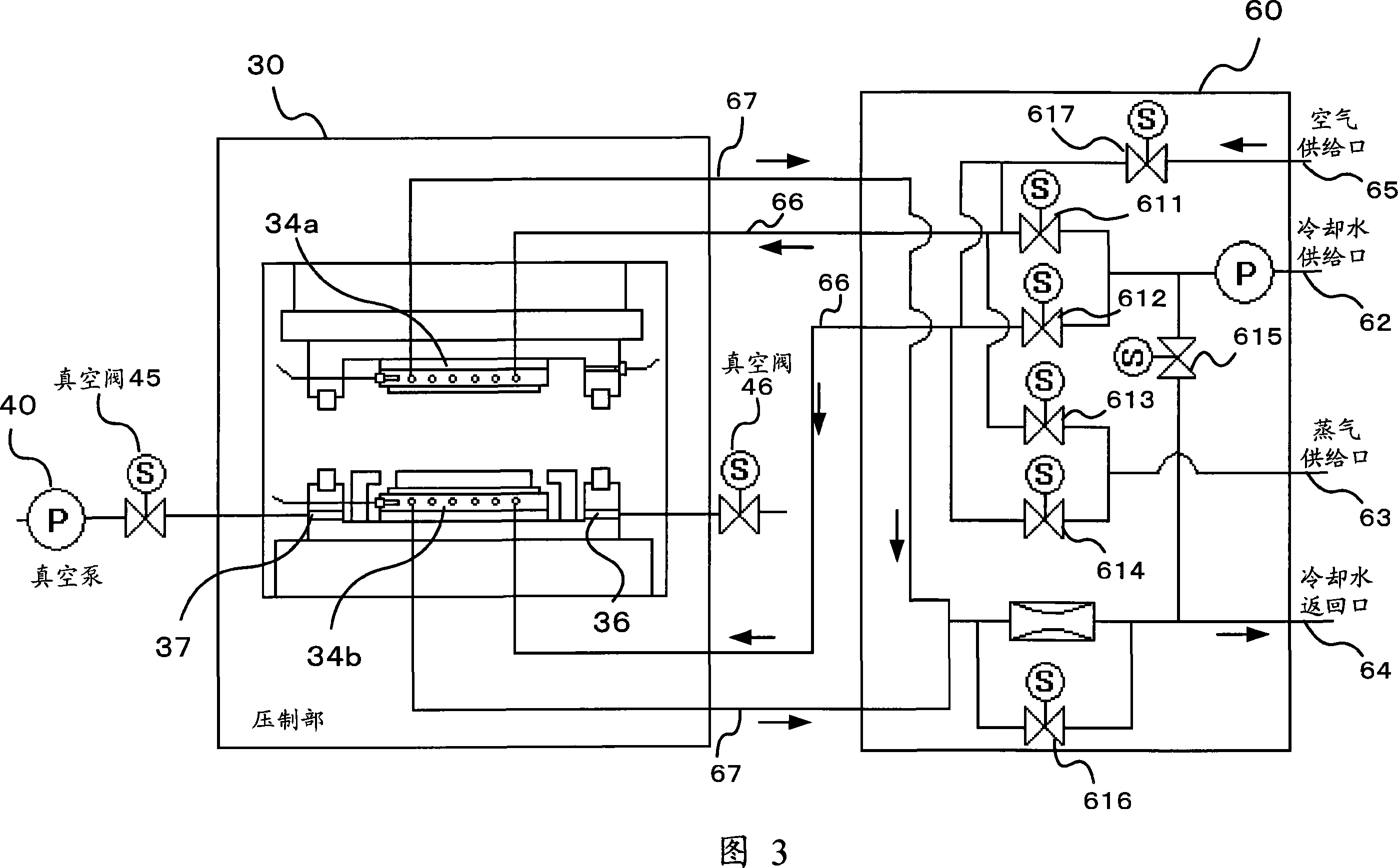
Pressing forming device and method thereof
In a pressing shaped device, a die is easy to be taken off from a machining object when finishing transfer printing pattern. The pressing shaped device (1) comprises: upper and lower dies (35a, 35b); regulating temperature boards (34a, 34b) for heating and cooling the upper and lower dies (35a, 35b); and an air current nozzle (41). To heat the regulating temperature boards (34a, 34b) until its temperature is above the softening temperature of the machining object (2), under the vacuum or decompression state, pressing the dies (35a, 35b) on the two surfaces of the machining object (2) to press shaped. After figuration, cooling the regulating temperature boards (34a, 34b) to various temperatures, so as to enlarge the distance of the dies (35a, 35b) with Delta H only. Opening the vacuum chamber, and wafting the air current to the gap between the dies (35a, 35b) generated by thermal distortion and the machining object (2).
Owner:KOMATSU SANKI
Turbine shroud thermal distortion control
InactiveUS20090272122A1Uniform growthImprove efficiencyPropellersPump componentsThermal growthTurbine
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
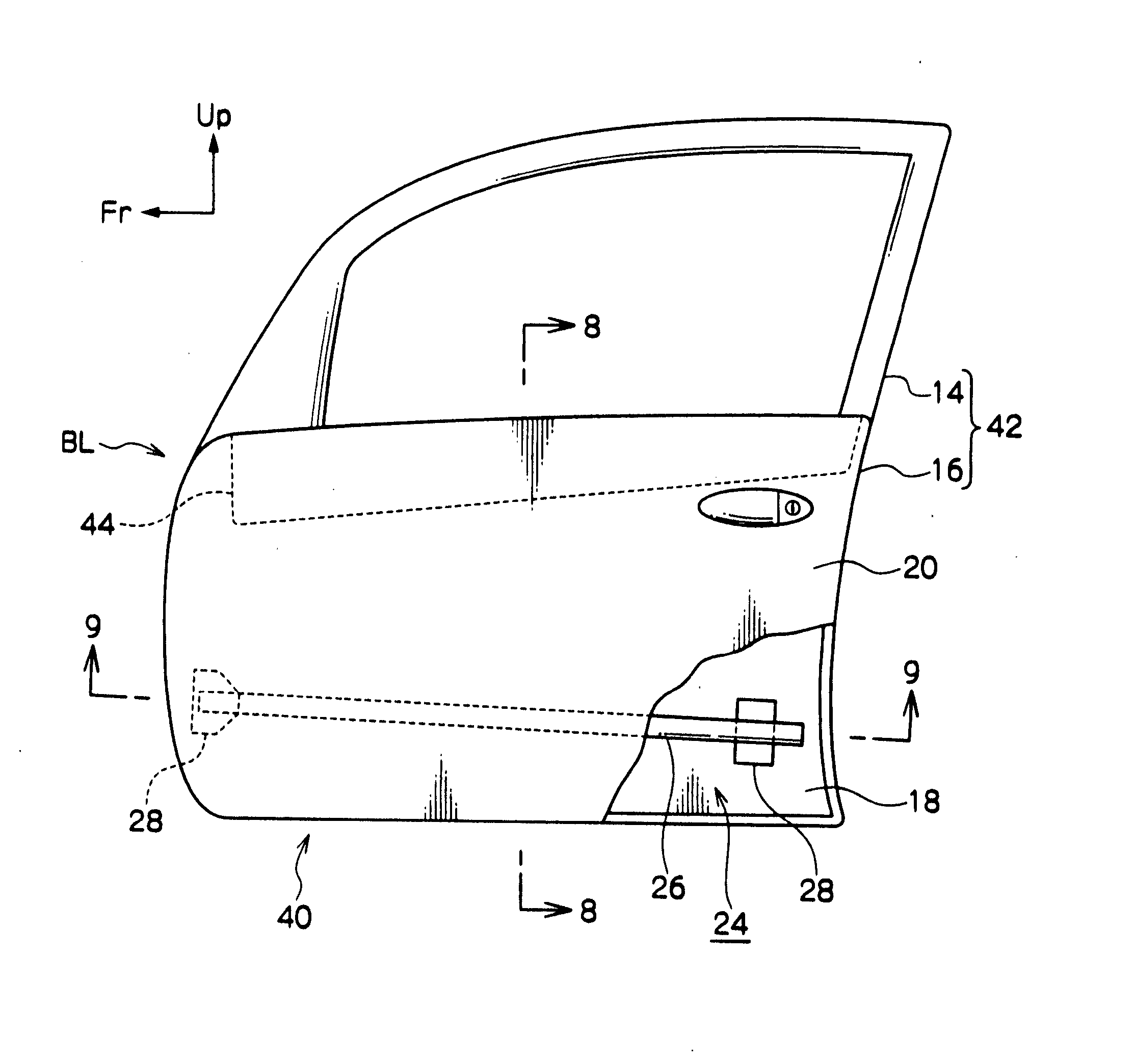
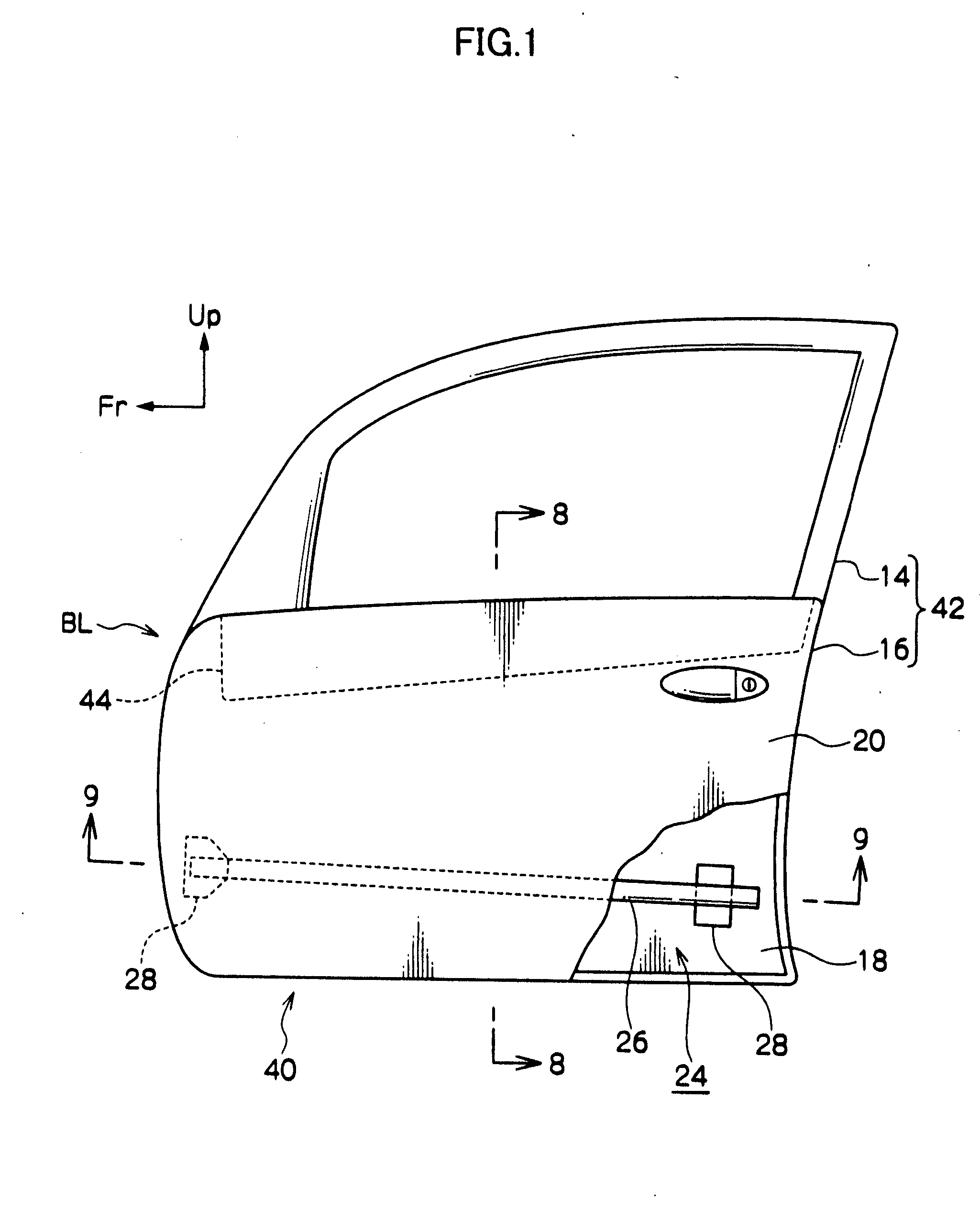
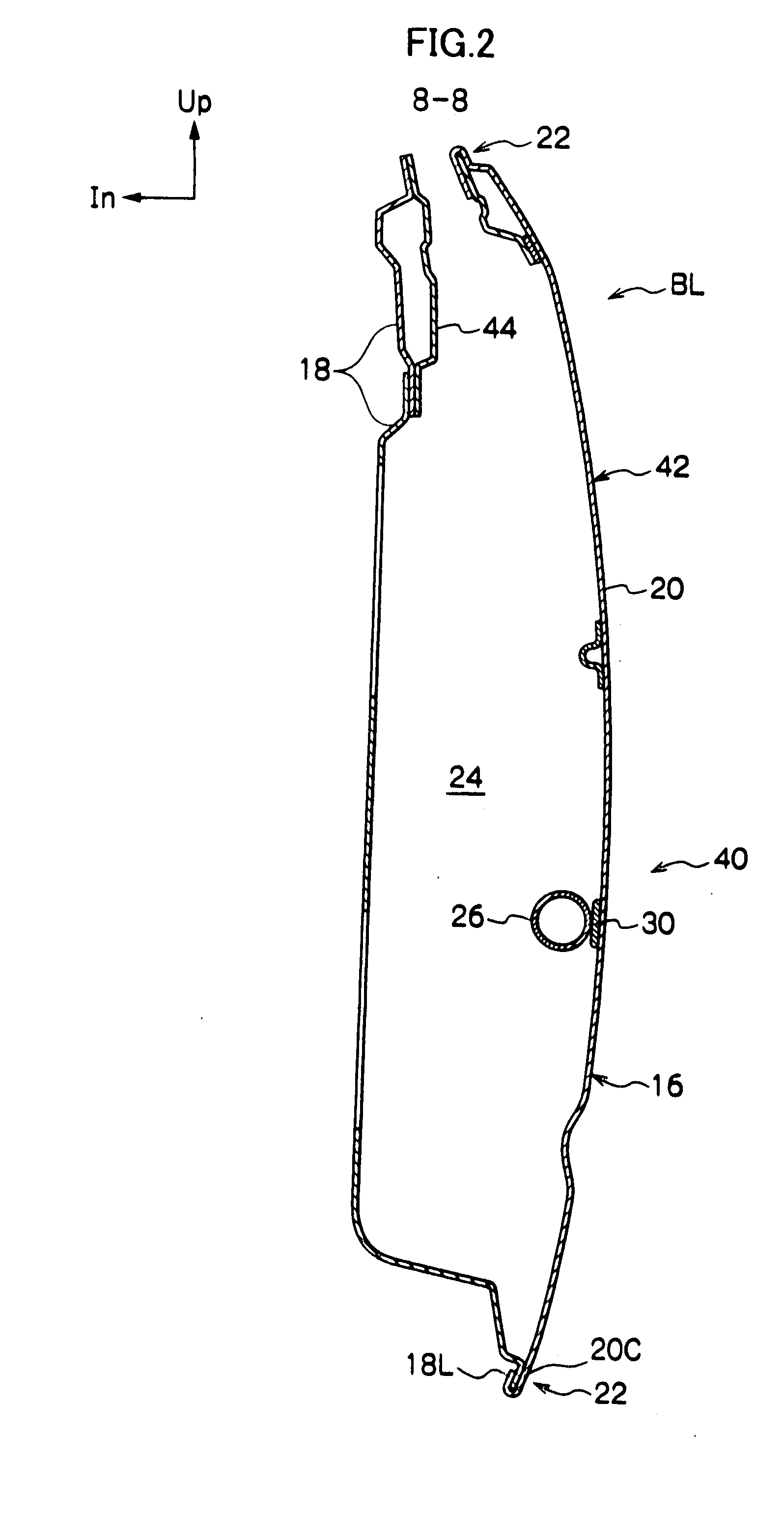
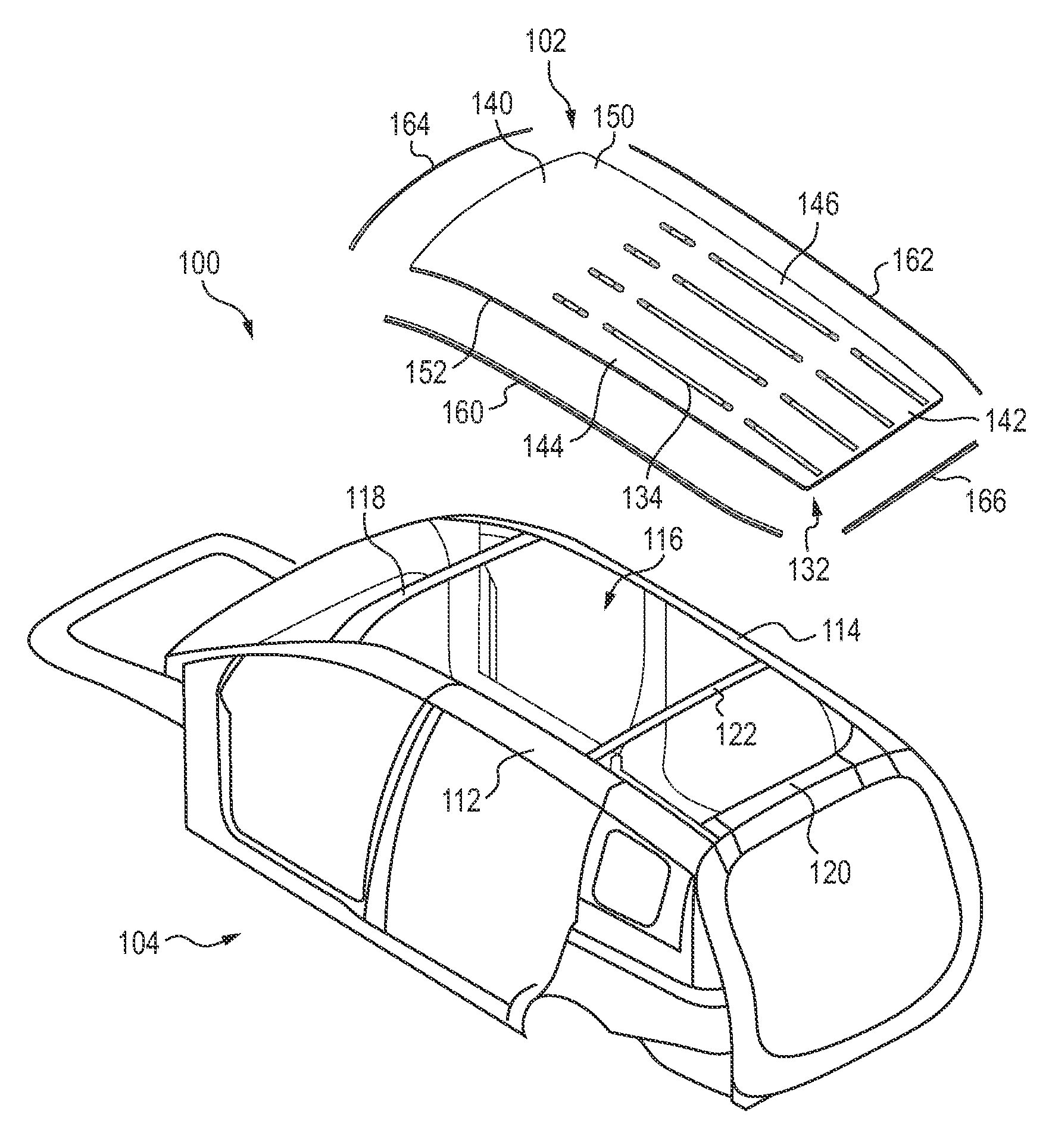
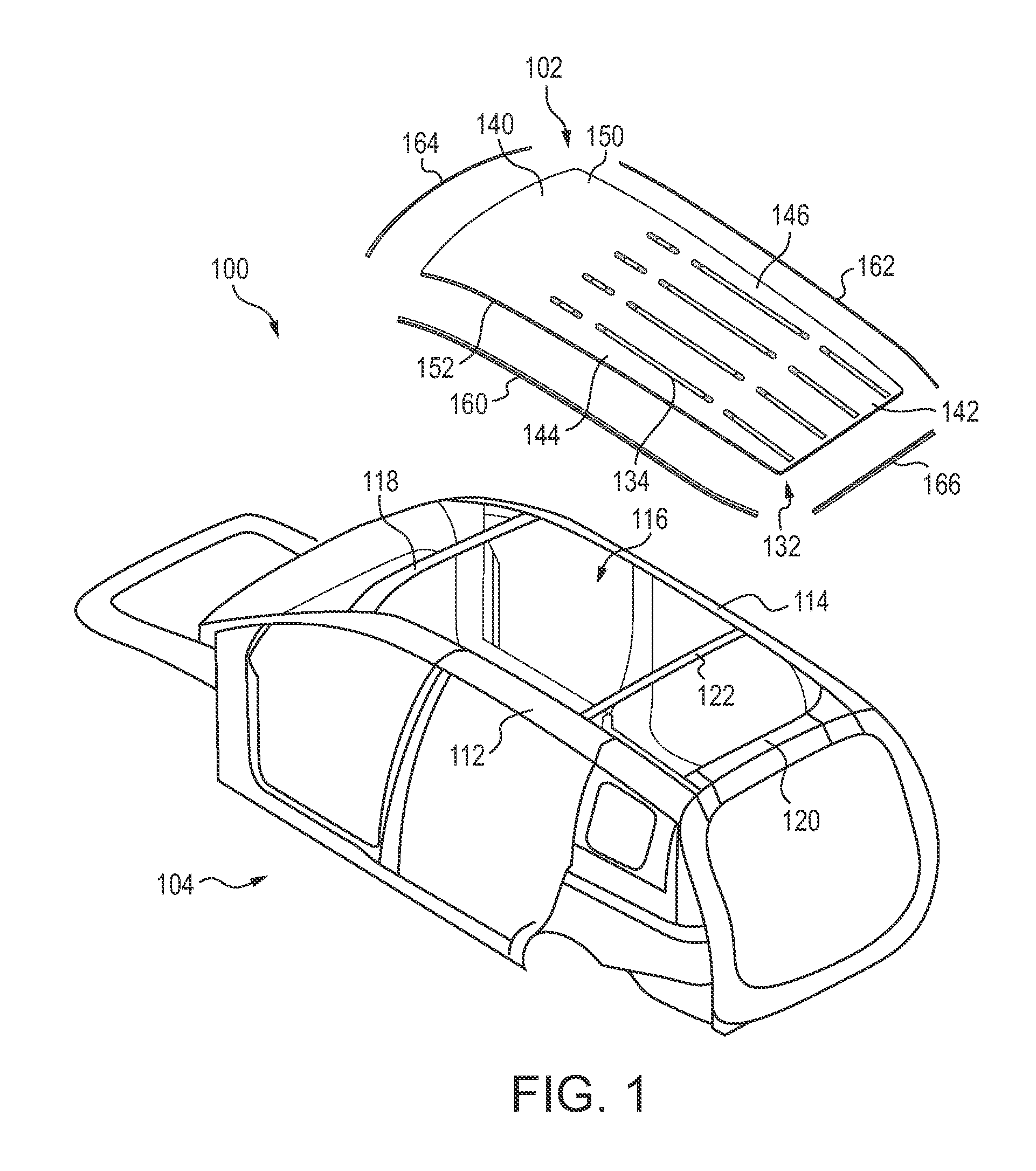
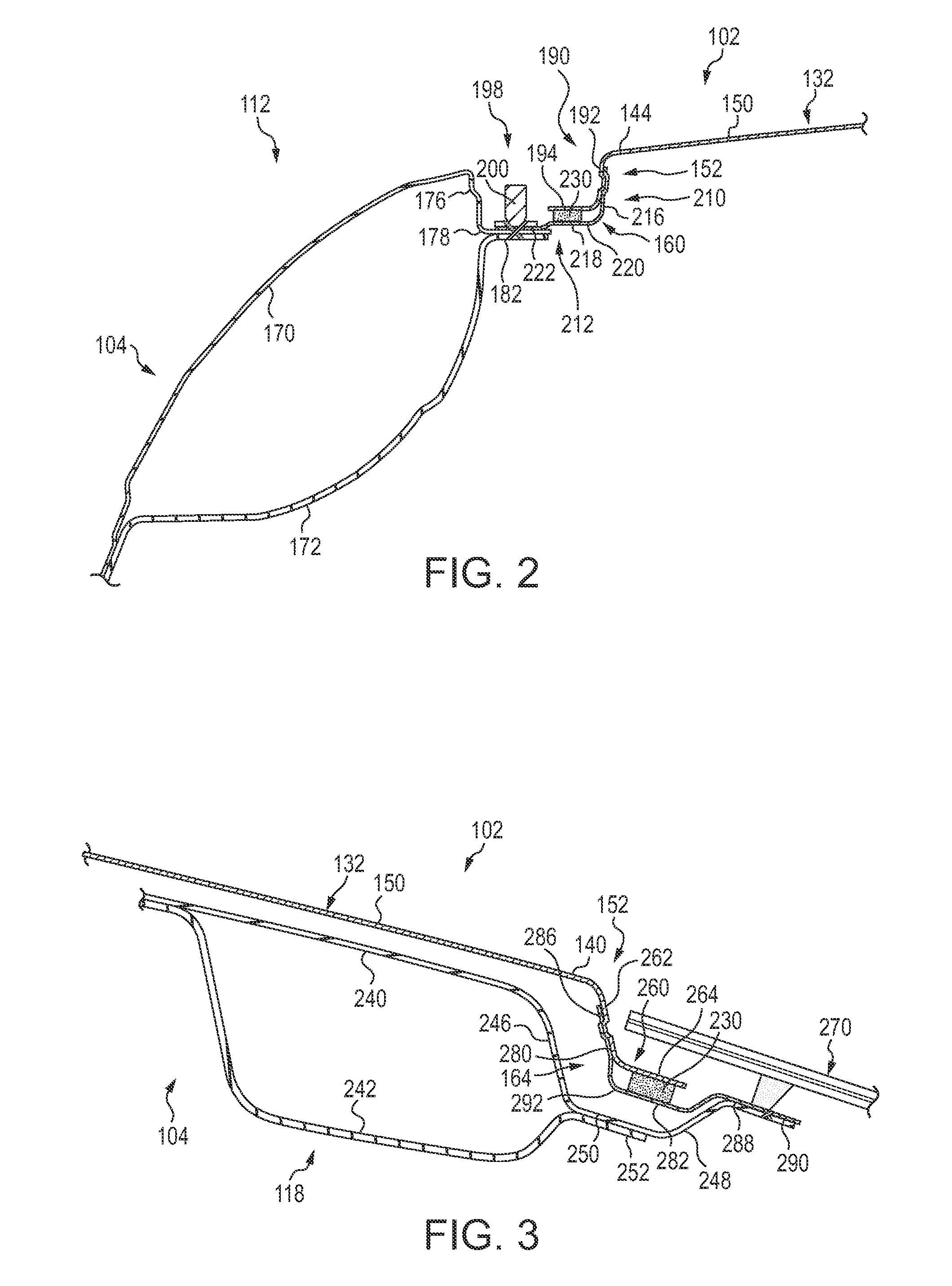
Vehicle door structure
ActiveUS20080007087A1Suppression of deformationAccelerate buildingVehicle seatsDashboardsThermal expansionThermal distortion
A vehicle door structure for suppressing permanent deformation due to thermal distortion of a door is described. A door inner panel 18 and a door outer panel 20 are configured in aluminum alloy or the like. An impact beam 26 and a belt line inner reinforcement 44 are joined to the door inner panel 18. The impact beam 26 and the belt line inner reinforcement 44 are configured from a material, such as steel, with a smaller linear expansion coefficient than the door outer panel 20. Therefore, even if the door 42 as a whole is, for example, placed in a high temperature environment such as a bake oven in electrophoretic coating, the door inner panel 18 side and the door outer panel 20 side are restrained, respectively, by the belt line inner reinforcement 44 and the impact beam 26. Thus, permanent deformation due to thermal distortion at the door outer panel 20 side, due to a difference in the thermal expansion conditions of the door inner panel 18 side and the door outer panel 20 side, may be suppressed.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Base material of self-adhesive water-proof coiled material and self-adhesive water-proof coiled material manufactured by the same
InactiveCN1919958AReduce volatilityImprove migration resistanceOther chemical processesRoof covering using flexible materialsPolyesterThermal distortion
The invention discloses the base material and self-adhering water-proofing coiled material made with the base material. The base material is made by the modified PVC material, comprising PVC, polyester plasticity agent, modifier, filling agent, stabilizer, lubricating agent and antiaging agent. On the surface of base material add creep rubber bitumen self-adhering layer and non-stick coating to get self-adhering water-proofing coiled material. The self-adhering water-proofing coiled material has good physical-mechanical properties, thermal distortion property, elasticity, cold-resistant, flame-proof, abrasion-proof and resistance to chemical attack; it also has low volatility and long life.
Owner:GUANGDONG PSYLIC WATERPROOF MATERIAL +1
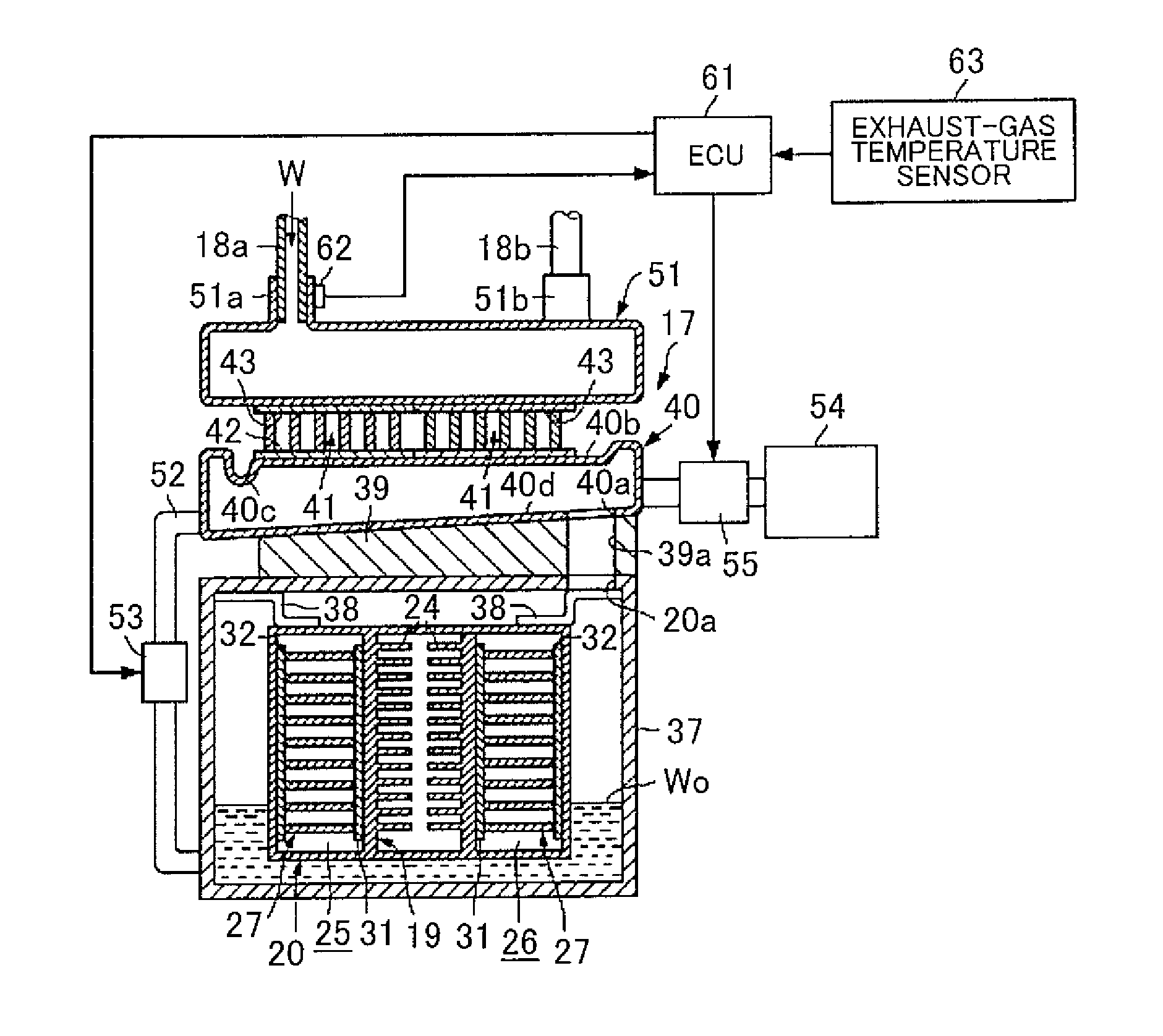
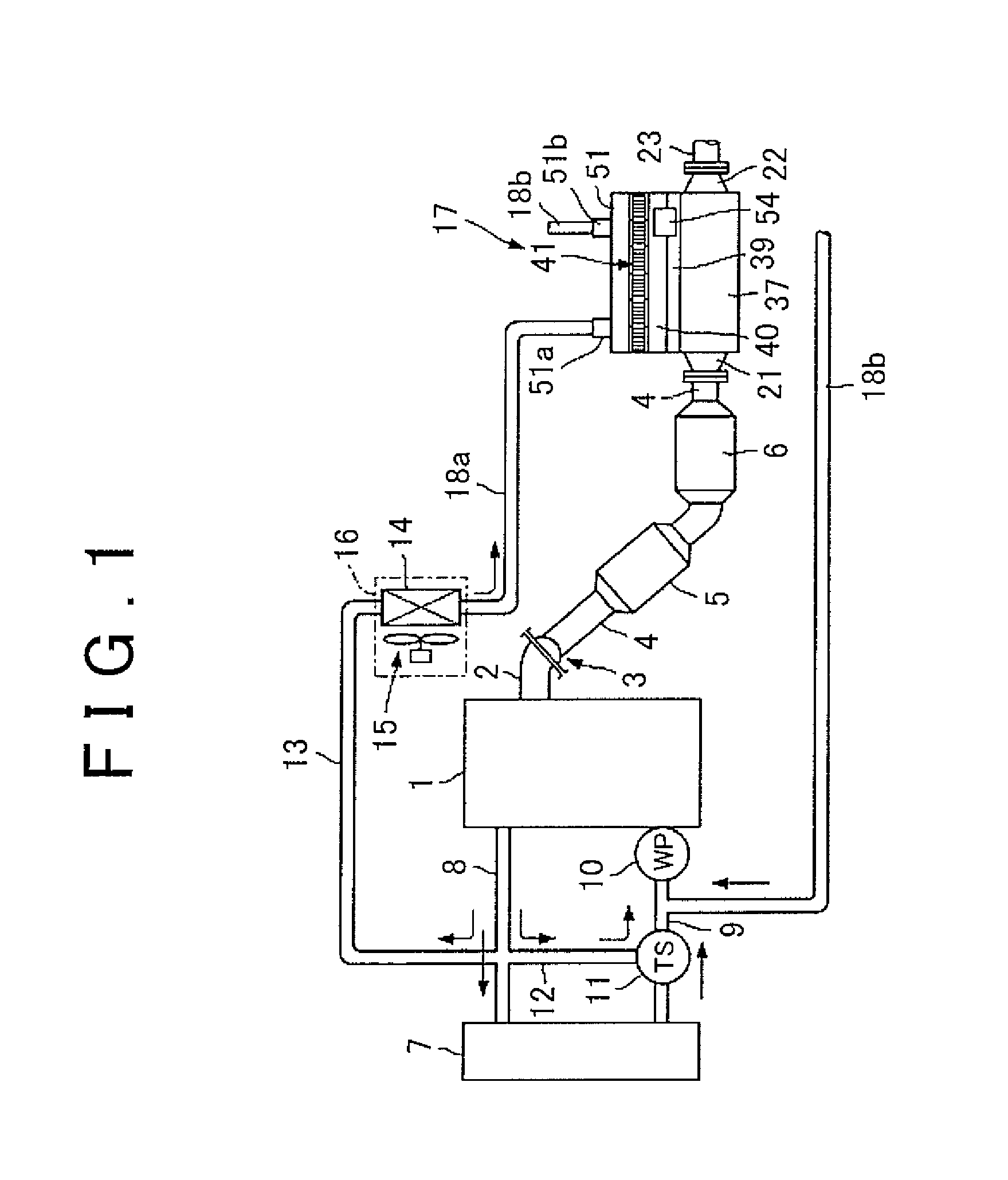
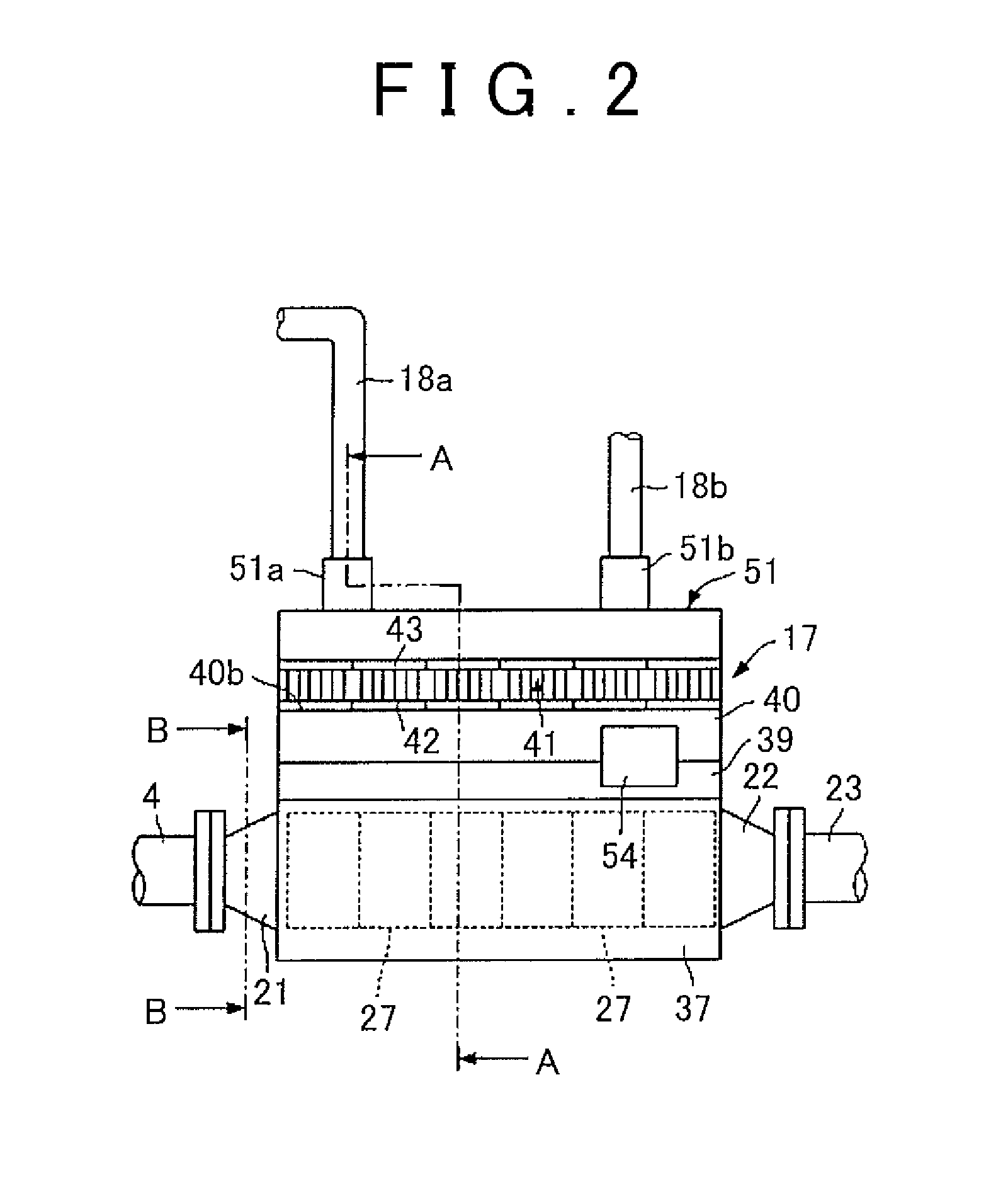
Thermoelectric power generating device
InactiveUS20150068575A1Reduce thermal deformationEasy to operateInternal combustion piston enginesThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectManufacturing cost reductionEngineering
[Object] Provided is a thermoelectric power generating device that is able to decrease thermal distortion of thermoelectric conversion modules and to upsize the thermoelectric conversion modules, thereby making it possible to simplify a manufacturing operation and to decrease a manufacturing cost. A thermoelectric power generating device (17) is configured to include: a body case (20) accommodating therein thermoelectric conversion modules (27); an exhaust-pipe portion (19) provided in the body case (20) so as to be opposed to heat-receiving substrates (31) of the thermoelectric conversion modules (27); a steam tank (37) attached to an outer side of the body case (20) so as to be opposed to heat-dissipation substrates (32) of the thermoelectric conversion modules (27); a steam tank (40) provided above the body case (20); thermoelectric conversion modules (41) provided above the steam tank (40) so that heat-dissipation substrates (43) thereof are opposed to the steam tank (40); and a cooling water tank (51) provided above the thermoelectric conversion modules (41) so as to be opposed to heat-receiving substrates (42) of the thermoelectric conversion modules (41).
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Vehicle roof structure
InactiveUS20150217812A1Prevent galvanic corrosionReduce thermal deformationSoldering apparatusSuperstructure subunitsAdhesiveAlloy
A vehicle assembly includes a roof structure having a roof panel formed of aluminum or an aluminum-based alloy and a vehicle body formed of steel or a steel alloy supporting the roof structure. The vehicle body includes a pair of laterally spaced side panels, a front roof rail and a rear roof rail. A bracket formed of steel or a steel alloy secures the roof structure to the vehicle body. The bracket has a first portion fastened to the roof panel and a second portion extending away from the roof structure and welded to the vehicle body. An adhesive located inward of the connection of the vehicle body and second portion of the bracket bonds the second portion to the vehicle body. The adhesive seals the connection of the roof panel and bracket first portion and reduces thermal distortion of the attached roof panel relative to the vehicle body.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
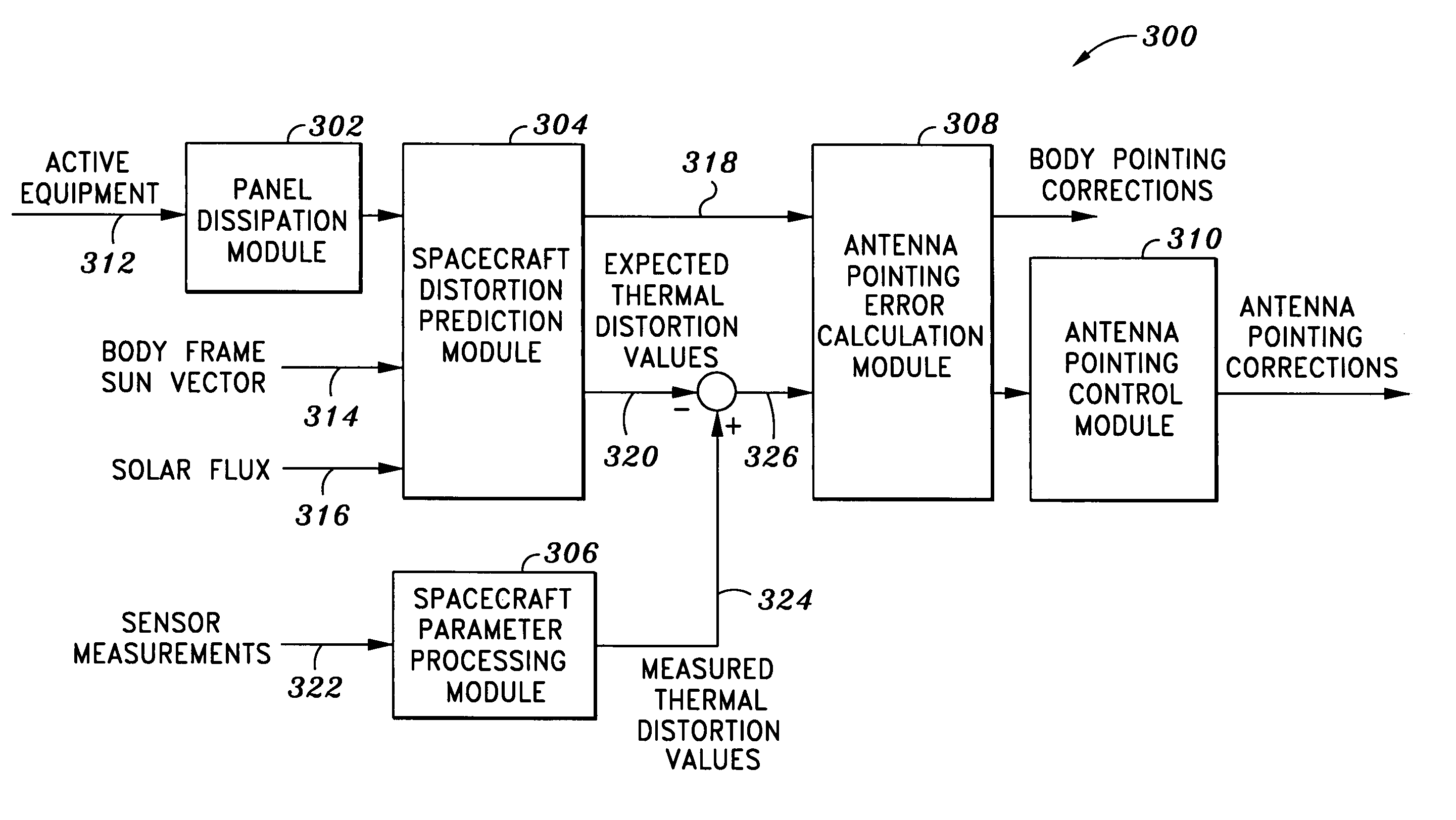
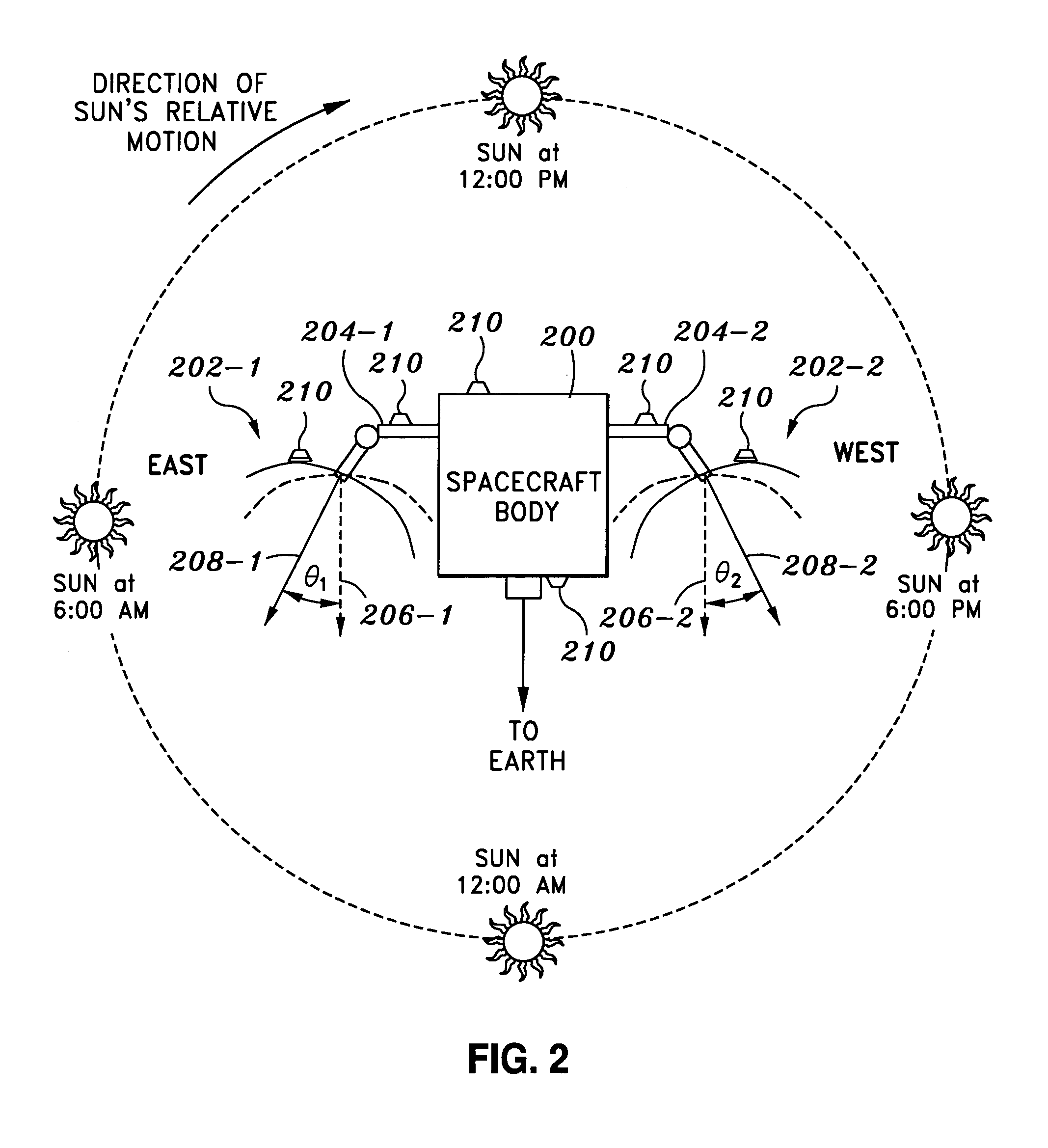
Systems and methods for correcting thermal distortion pointing errors
One embodiment of the present invention relates to a system for correcting spacecraft thermal distortion pointing errors. The system comprises one or more spacecraft sensors located at positions on a spacecraft and which are adapted to measure spacecraft parameters at those positions. The system also includes a spacecraft distortion prediction module, which is adapted to generate expected spacecraft thermal distortion parameter values and expected antenna thermal distortion pointing errors. Further, the system includes a spacecraft parameter processing module adapted to generate measured spacecraft thermal distortion parameter values from the measured spacecraft parameters, and an antenna pointing error calculation module adapted to calculate antenna pointing error correction commands. Finally, the system includes an antenna pointing control module adapted to receive the antenna pointing correction commands and control the adjustment of the antenna pointing using the correction commands.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com