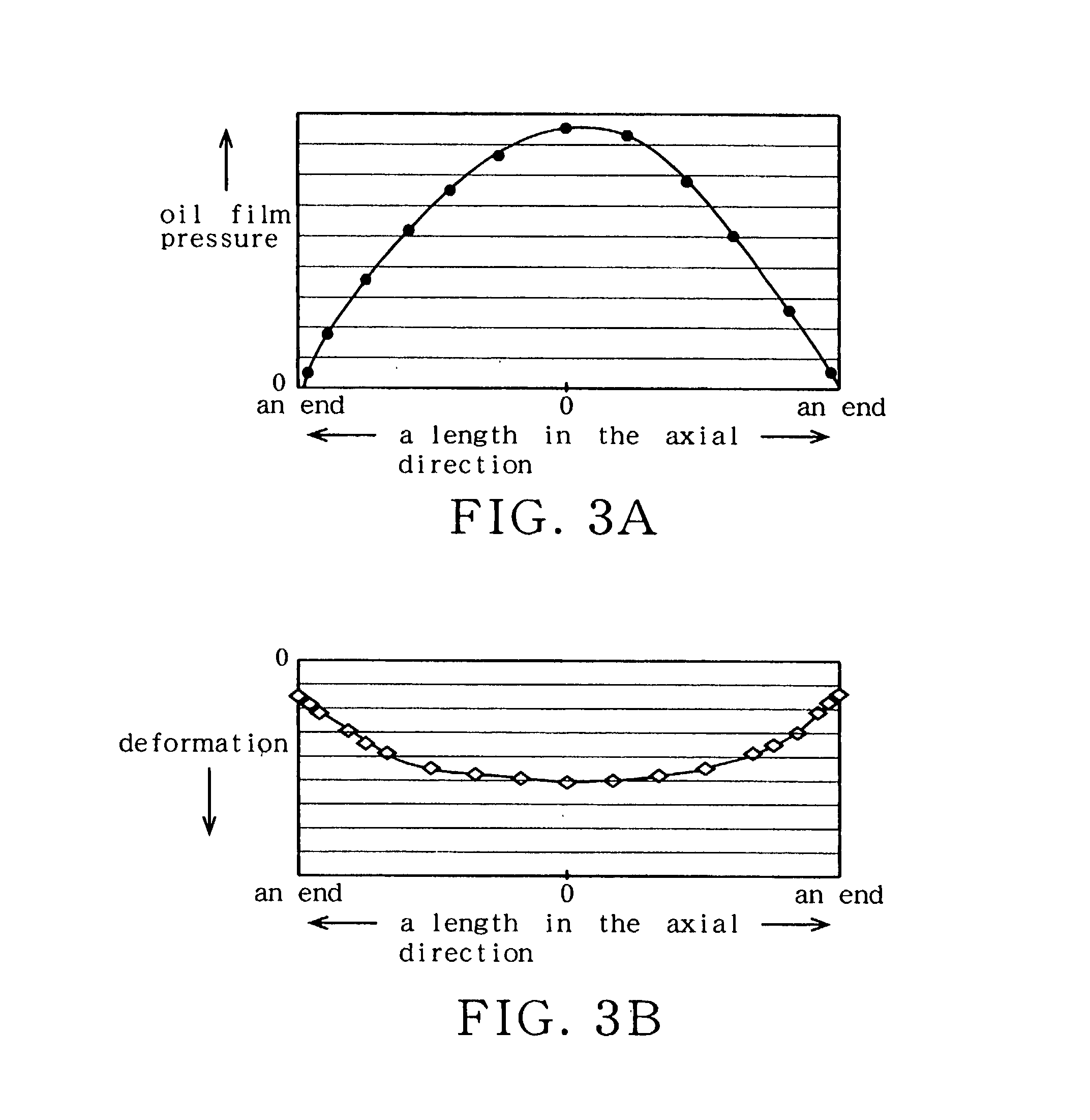
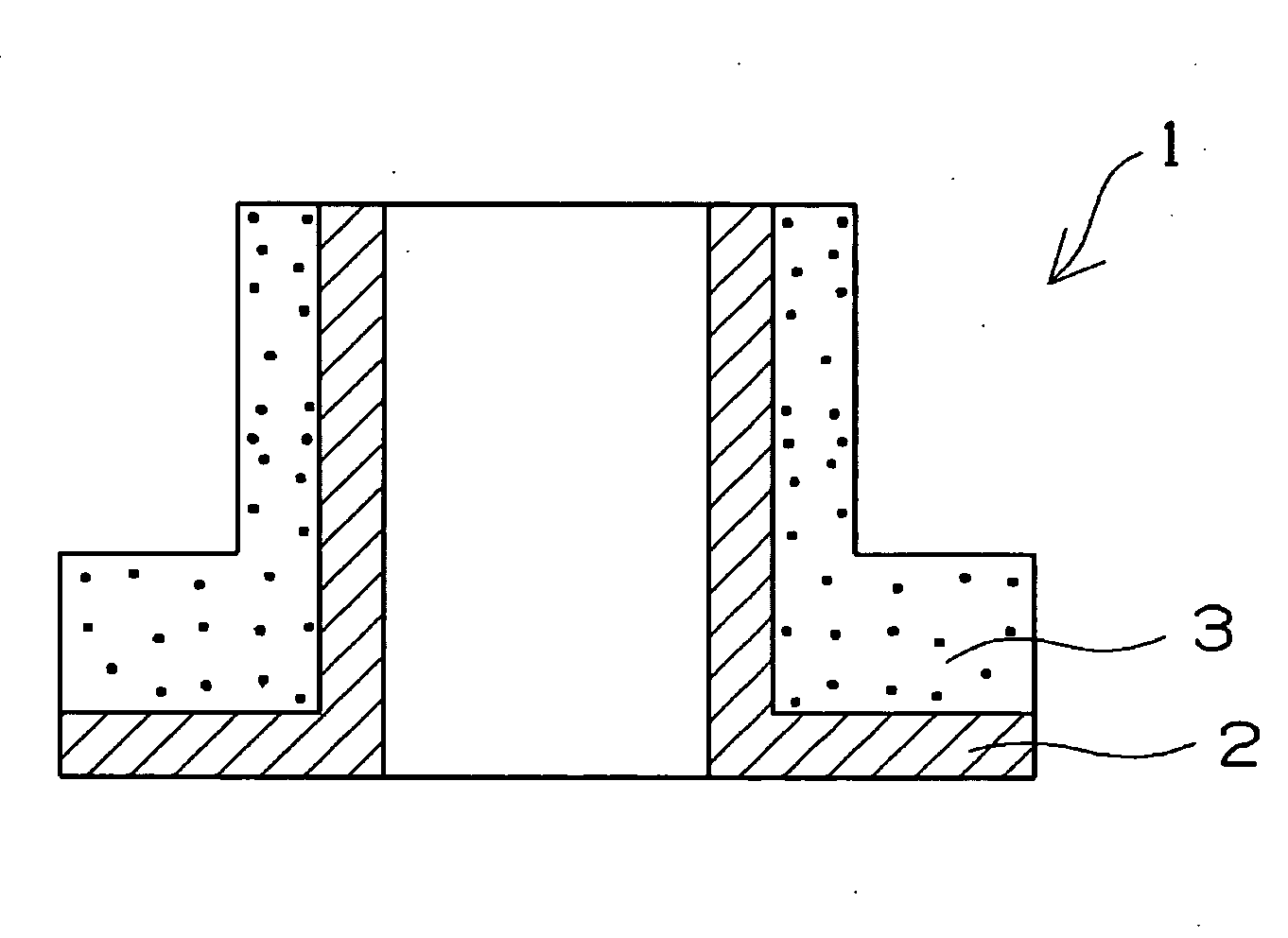
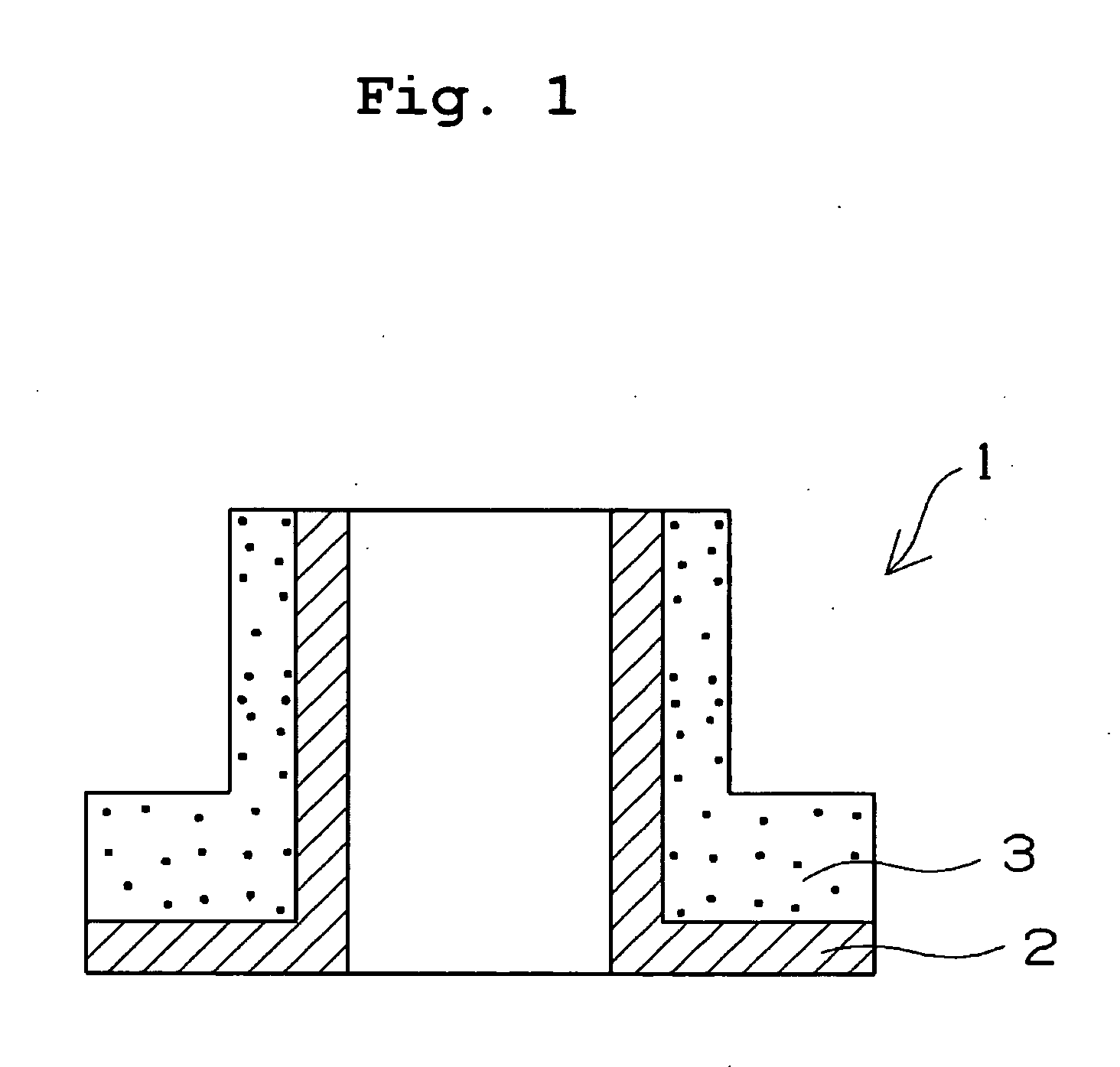
Patents
Literature
3159 results about "Plain bearing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A plain bearing, or more commonly sliding bearing and slide bearing (in railroading sometimes called a solid bearing or friction bearing), is the simplest type of bearing, comprising just a bearing surface and no rolling elements. Therefore, the journal (i.e., the part of the shaft in contact with the bearing) slides over the bearing surface. The simplest example of a plain bearing is a shaft rotating in a hole. A simple linear bearing can be a pair of flat surfaces designed to allow motion; e.g., a drawer and the slides it rests on or the ways on the bed of a lathe.
Torque tool
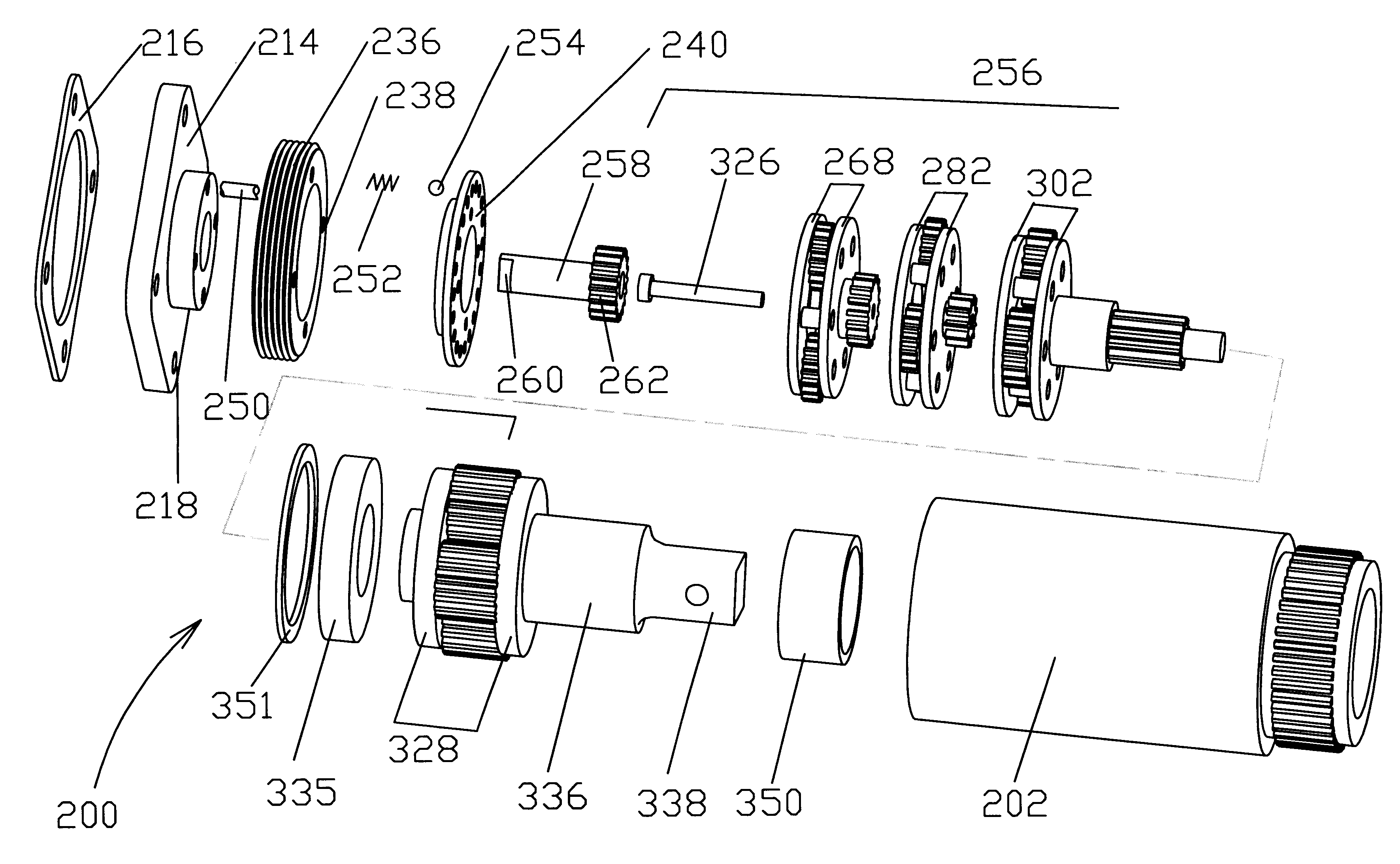
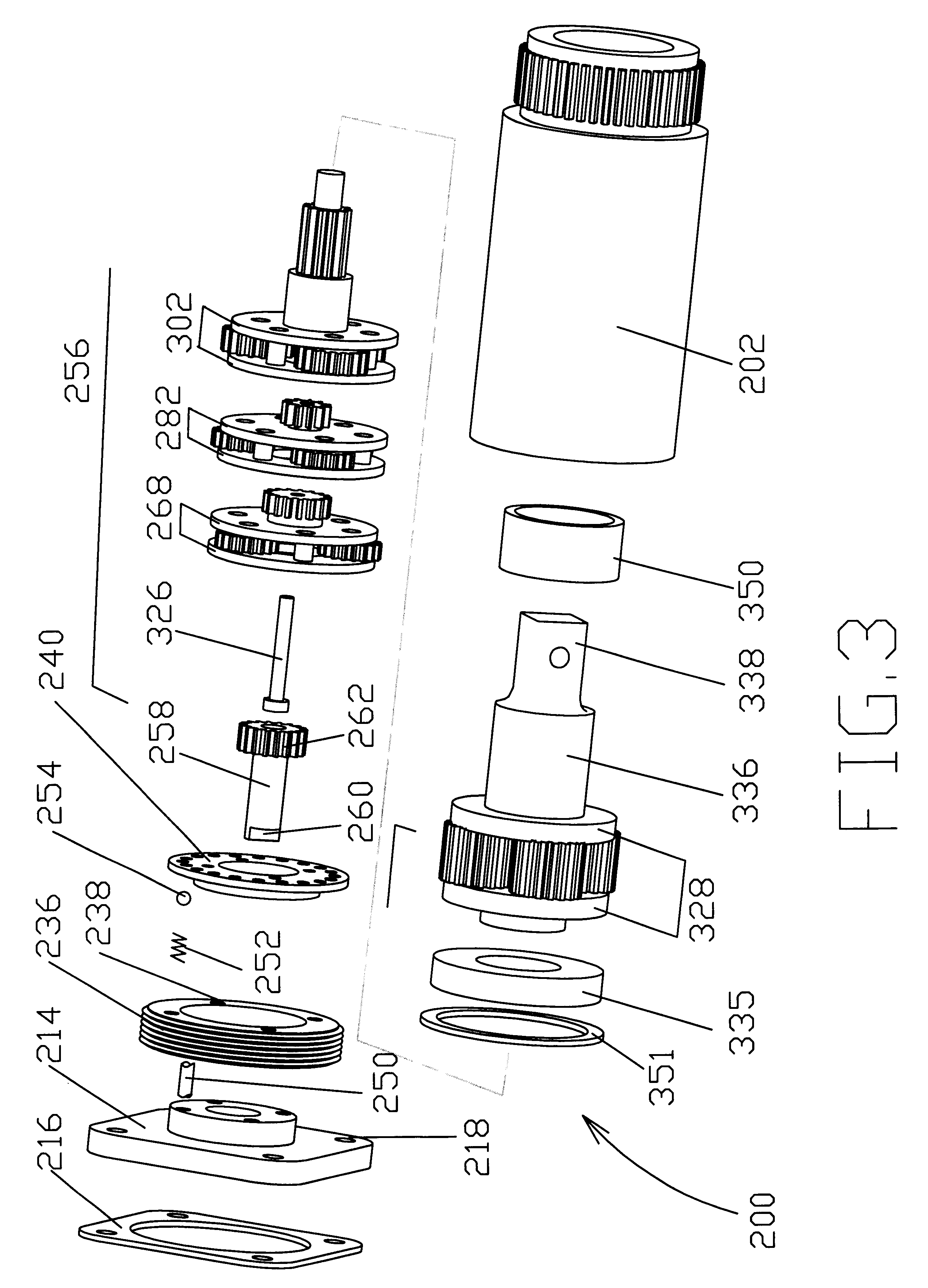
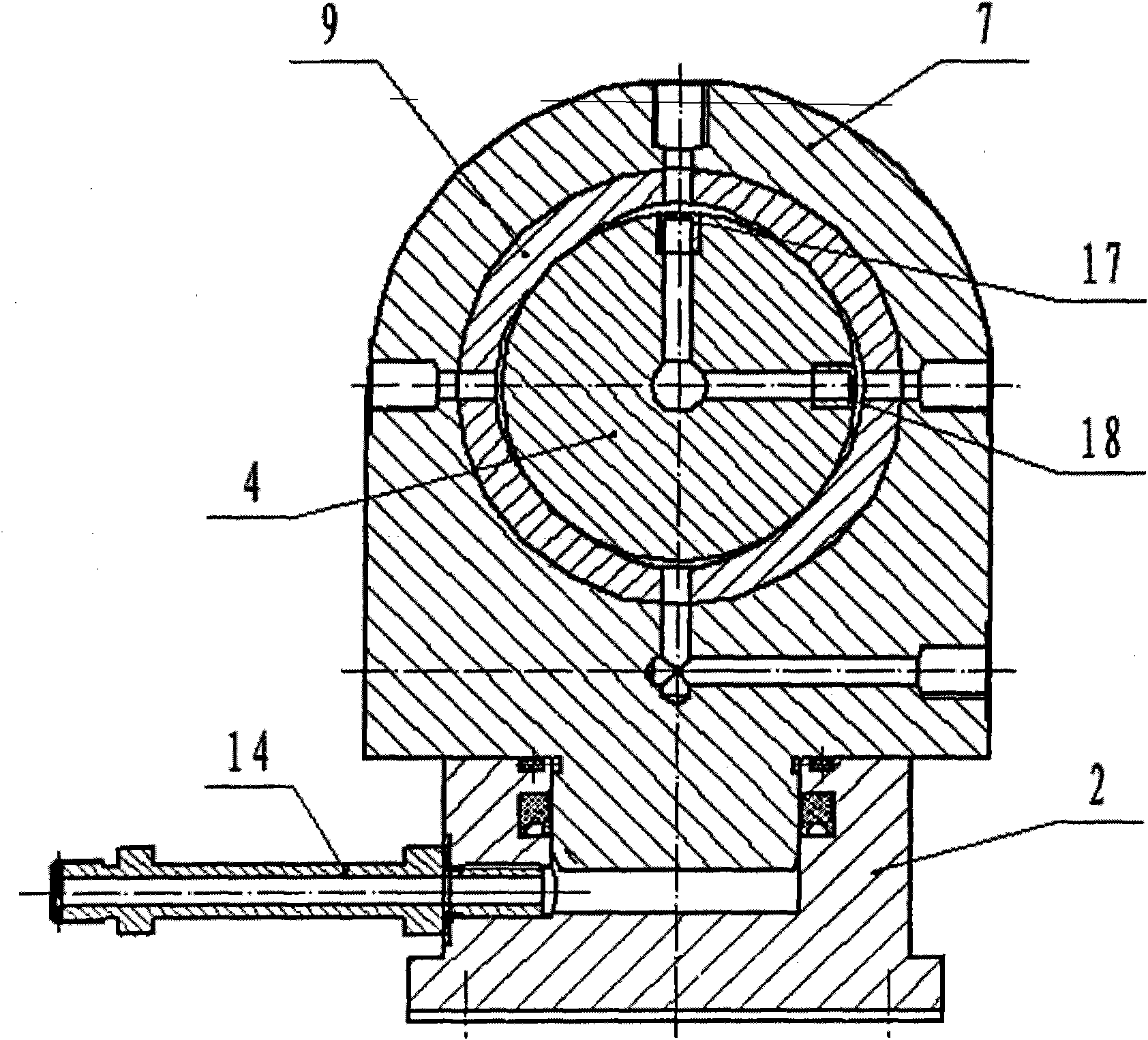
The torque tool comprises a torque converter including three planet carriers which encase three planetary gears. Each of the three planetary gears includes a sun gear and three planet pinions. Each of the three planet carriers has an input disc-shaped plate, directed towards an input shaft of the torque tool and an output disc-shaped plate directed towards an output shaft of the torque tool. The input and output shafts constitute the main shafts of the torque tool. Two of the three planet carriers, which are next to the input shaft, have their output disc-shaped plates extending into sun gears with which they form unitary structures. A stepped pin is centrally disposed in a needle bearing of a first sun gear adjacent the input shaft and extends through sliding bearings located in the following sun gears. A first large diameter of the stepped pin is commensurate with an interior diameter of the needle bearing and a second small diameter of the stepped pin is commensurate with interior equal diameters of the sliding bearings inserted in the following sun gears. The planet pinions of one of the three planet gears, which is adjacent to the output gear, arc each provided with a multiplicity of roll needles closely spaced together, the multiplicity of roll needles being inserted between each of the at least three planet gears and an axle for supporting.
Owner:NEW WORLD TECH
Planetary gear mechanism for a wind power plant
ActiveUS20120108380A1Effective lubricationCost-effective manufacturingEngine fuctionsShaftsEngineeringMechanical engineering
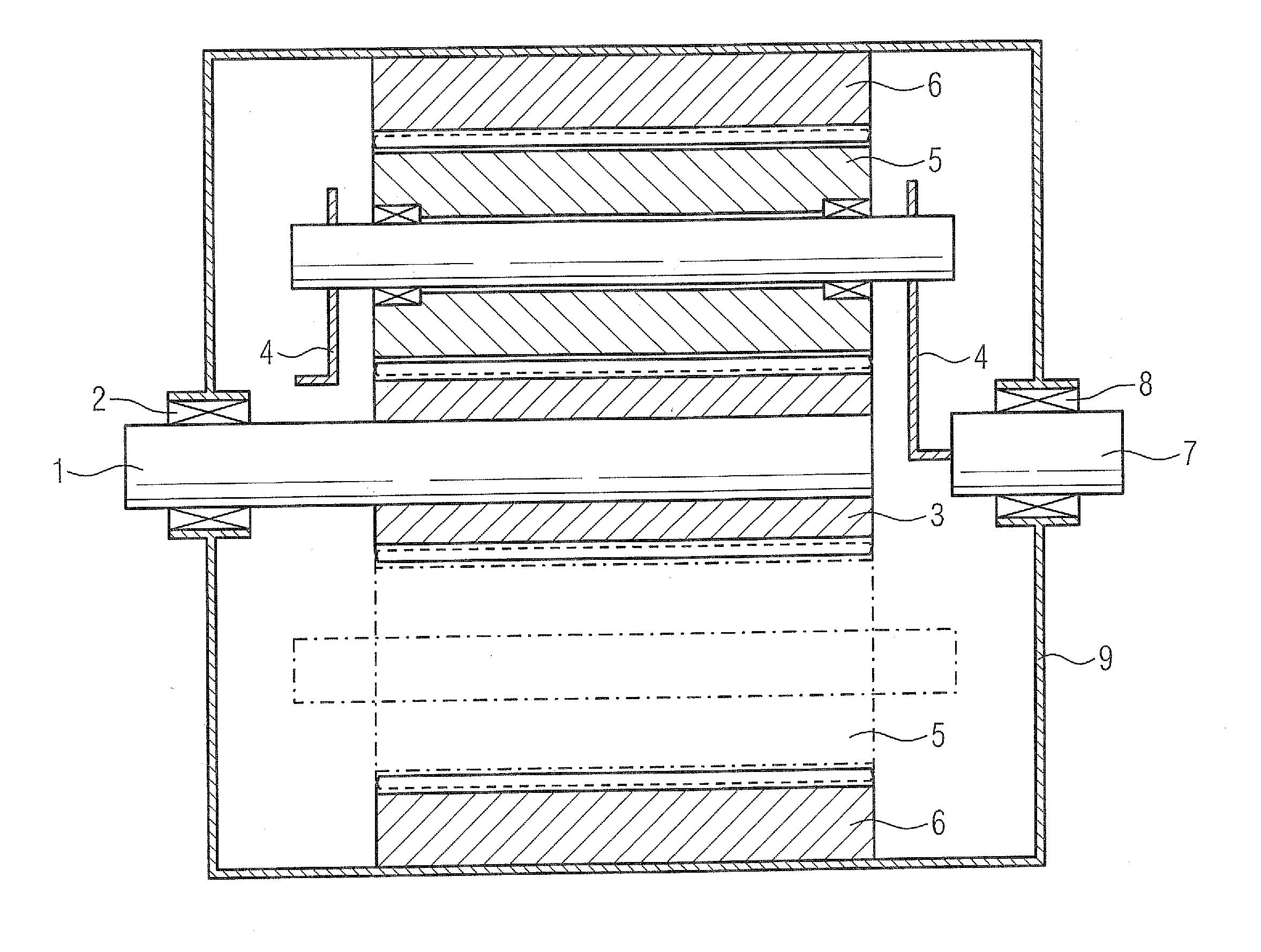
A planetary gear mechanism for a wind power plant includes a sun gear, an internal gear and a planetary carrier with planetary gears supported by radial and axial slide bearings. The radial slide bearings include a sleeve made of a slide bearing material and attached as an inner ring to a planetary gear shaft or mounted as an outer ring in a bore in a planetary gear. An outer bearing ring cooperating with the inner ring is formed by the bore in the planetary gear, or an inner bearing ring cooperating with the outer ring is formed by the planetary gear shaft. A slide bearing material of a first bearing element of the axial slide bearings is applied between a planetary carrier cheek and an end side of a planetary gear. The end side of the planetary gear or the planetary carrier cheek forms a corresponding cooperating second bearing element.
Owner:FLENDER GMBH
On-line measuring and testing machine for radial sliding bearing friction and wearing
InactiveCN1828264AProtection of transient contact surface statesMachine bearings testingUsing mechanical meansTested timeEngineering
The tester comprises: a clamp (22) to fix the upper sample (23) on its arc groove above the lower sample (25) connected to the middle of supporting shaft (37) by a flat key, a oil bath (26) to accommodate part (25), and a pressure bearing (20) with outside circle contacted to the upper arc surface of (22). This invention can protect the failure condition, and cuts wear test time.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Bearing and hinge mechanism
A spherical plain bearing has an outer ring having a concave first bearing surface and an inner ring having a convex second bearing surface slidably disposed to the first bearing surface. The inner ring member also has a third bearing surface for engaging a pin to be mounted in the bearing. At least one bearing surface has a lubrication groove, and one of the outer ring and the inner ring is made from 440 stainless steel while the other is made from a precipitation-hardened martensitic stainless steel. Alternatively, the outer ring and the inner ring may be made from steel and a copper-beryllium alloy. In yet another alternative, the bearing need not have a lubrication groove, but may have a lubrication liner on the third bearing surface. A dropped hinge mechanism for a flap on a fixed wing aircraft has a hinge that includes such a bearing.
Owner:ROLLER BEARING OF AMERICA
Sliding structure for automotive engine
InactiveUS6886521B2Preventing cracking and separationReduce coefficient of frictionPiston ringsMolten spray coatingCarbon filmPiston ring
A sliding structure for an automotive engine includes a sliding member with a sliding portion and a lubricant applied to the sliding portion so that the sliding portion can make sliding contact with a counterpart member via the lubricant. The sliding member is either of a piston ring, a piston pin, a cam lobe, a cam journal, a plain bearing, a rotary vane and a timing chain. The sliding portion has a base made of a steel or aluminum material and a hard carbon film formed on the base to coat the sliding portion. The hard carbon film has a thickness of 0.3 to 2.0 mum, a Knoop hardness of 1500 to 4500 kg / mm2, a surface roughness Ry (mum) satisfying the following equation: Ry<{(0.75-Hk / 8000)xh+0.07 / 0.8}, where h is the thickness (mum) of the film; and Hk is the Knoop hardness (kg / mm2) of the film.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Sliding bearing and bearing mechanism having the same
ActiveUS7220056B2Cancel noiseReduce linear-motion frictional resistanceLinear bearingsShaftsSteering columnEngineering
A sliding bearing for a steering column includes: a cylindrical bearing body; flat surfaces formed integrally on an inner peripheral surface of the bearing body; first slits extending from one end face of the bearing body to this side of the other end face of the bearing body; second slits extending from this side of the other end face of the bearing body to the one end face of the bearing body; grooves formed in an outer peripheral surface of the bearing body; and elastic rings which are respectively fitted in the grooves in such a manner as to project from the outer peripheral surface of the bearing body and to reduce the diameter of the bearing body.
Owner:OILES CORP
Composite multilayer bearing material
InactiveUS6194087B1Reduce hardnessImprove carrying capacityElectrolytic coatingsShaftsDiffusion barrierCobalt
A composite material for plain bearings comprises a backing layer, a bearing metal layer consisting of a copper alloy with a copper content of from 50 to 95 wt. % or an aluminum alloy with an aluminum content of from 60 to 95 wt. %, a diffusion barrier layer and an overlay, applied by electroplating, consisting of a lead-free, tin and copper-containing alloy. The invention provides a composite multilayer material whose overlay, applied by electroplating, does not exhibit any embrittlement even at relatively high temperatures, irrespective of the copper content. The overlay preferably comprises from 8 to 30 wt. % copper, 60 to 97 wt. % tin and 0.5-19 wt. % cobalt.
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL WIESBADEN
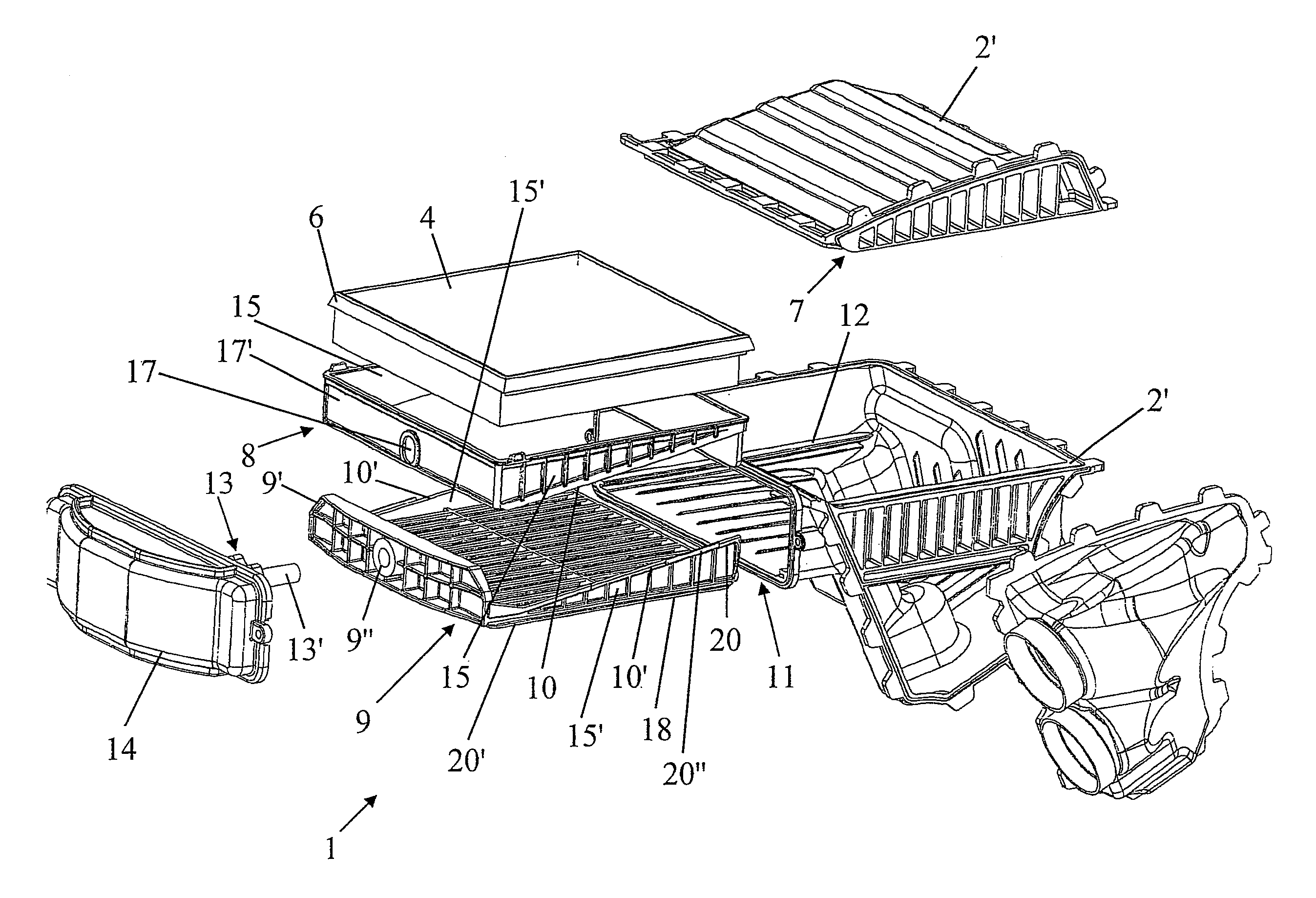
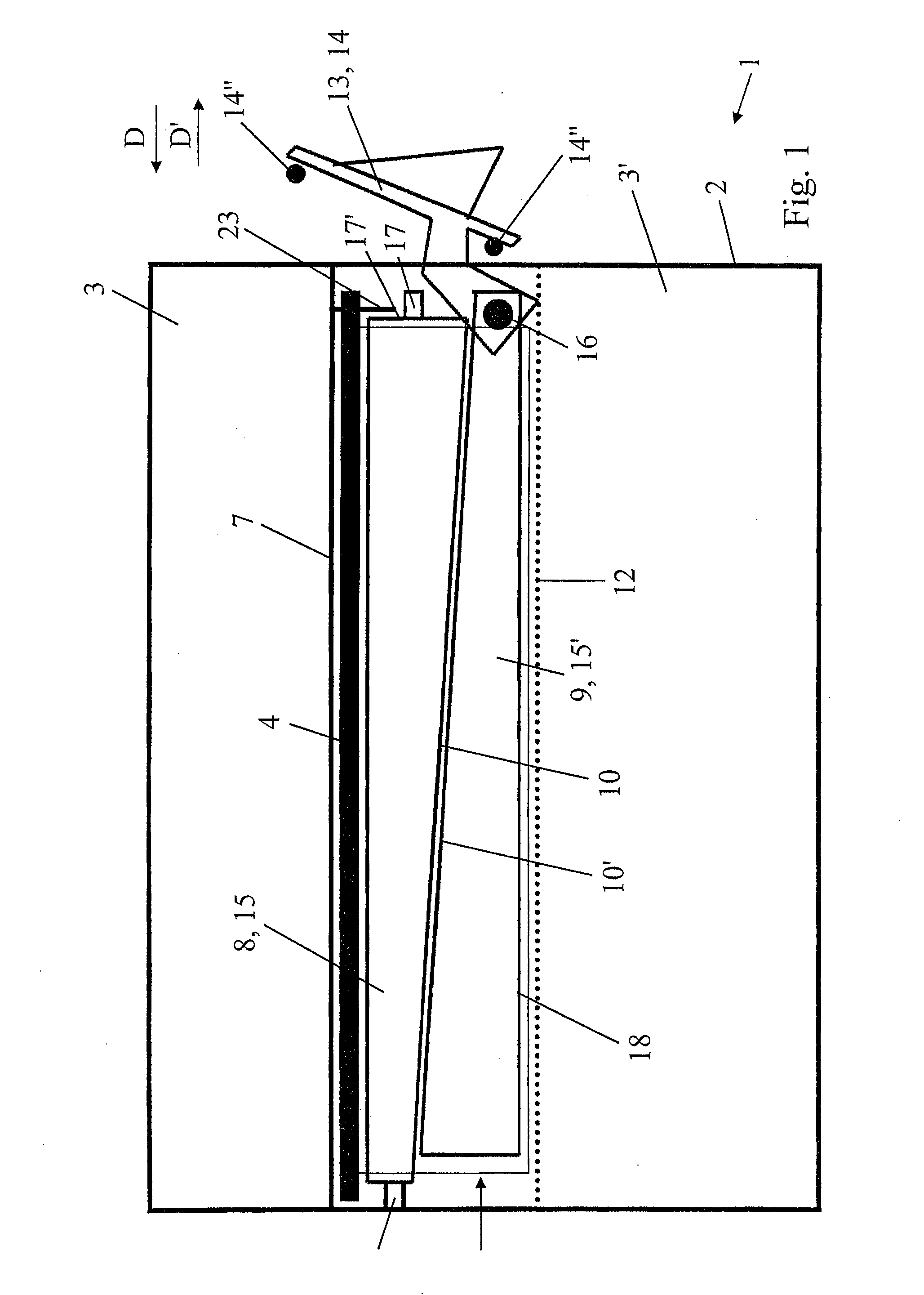
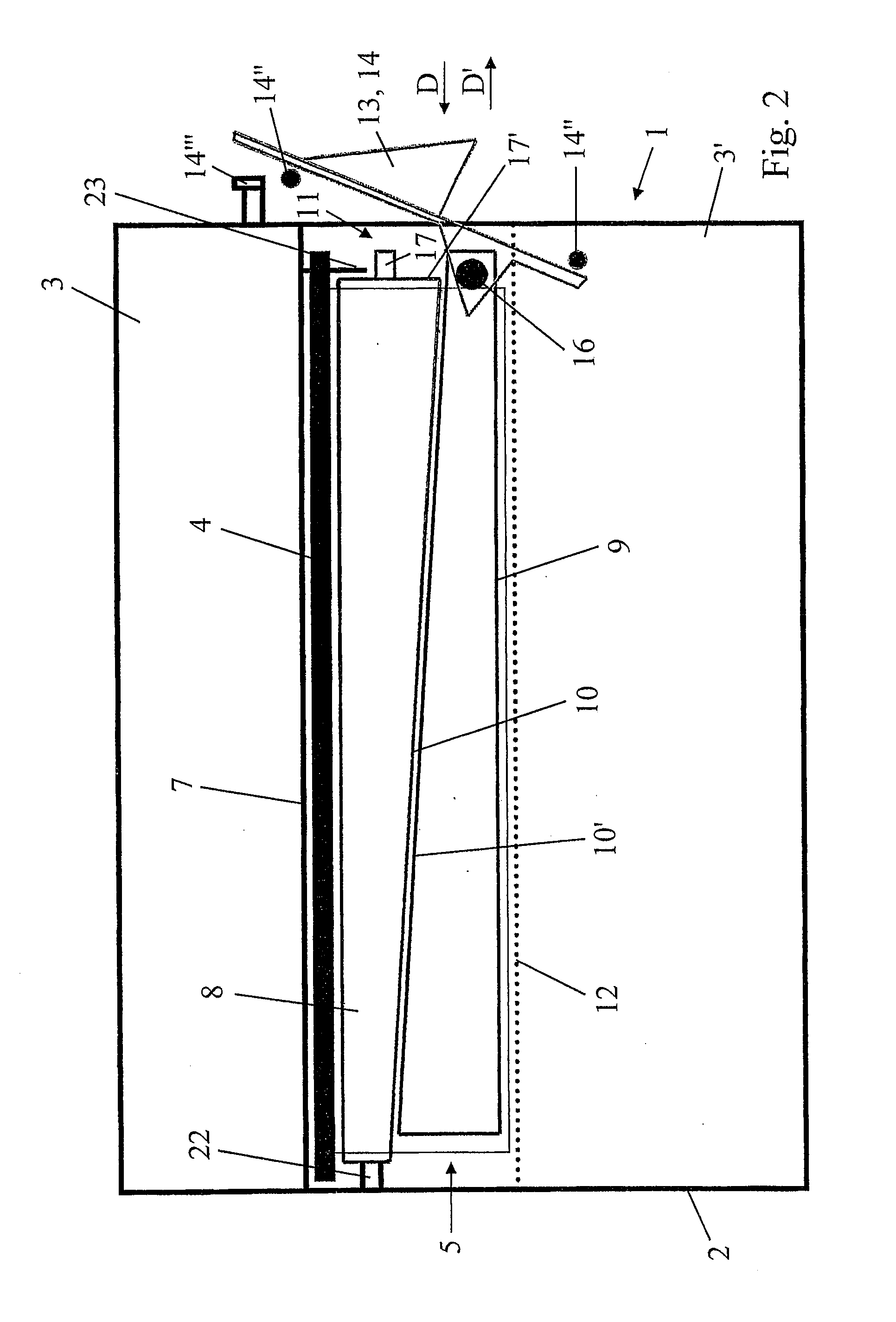
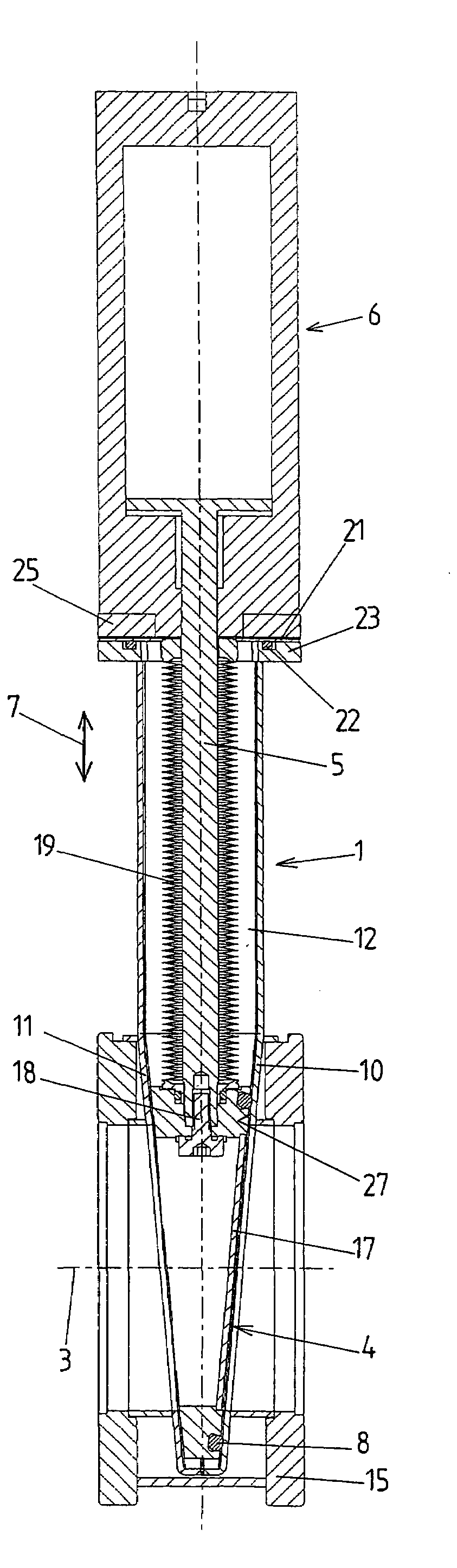
Drawer air-filter device and inlet assembly having such a device
Owner:MARK IV SYST MOTEURS USA
Vacuum valve
Owner:VAT HLDG AG
Substrate or sheet surface cleaning apparatus
InactiveUS6237176B1Efficient captureEfficient removalLiquid processingCarpet cleanersFixed bearingSurface cleaning
A substrate or sheet surface cleaning apparatus is provided with at least one tacky rubber roller and at least one adhesive tape roll which is brought into close contact with the tacky rubber roller. The roller and roll are rotatably supported at opposite ends of their shafts by bearings which are slidable in a vertical direction. Pressed rods are arranged integrally on the slidable bearings for the roll. By urging the pressed rods with pressing rods driven by d.c. motors via gear trains while controlling the d.c. motors by a position sensor, the pressure between the roll and the roller and the pressure between the roller and the substrate or sheet are optimized so that dirt or particles can be efficiently removed from an opposing surface of the substrate or sheet. Another substrate or sheet surface cleaning apparatus is provided two tacky rubber rollers arranged in an up-and-down parallel relationship and two adhesive tape rolls arranged above the upper roller and below the lower roller, respectively. Position adjusters with one or more springs disposed therein are arranged between slidable bearings supporting the upper roller and fixed bearings supporting the lower roller to correct tilting, if any, of the upper roller.
Owner:RAYON IND
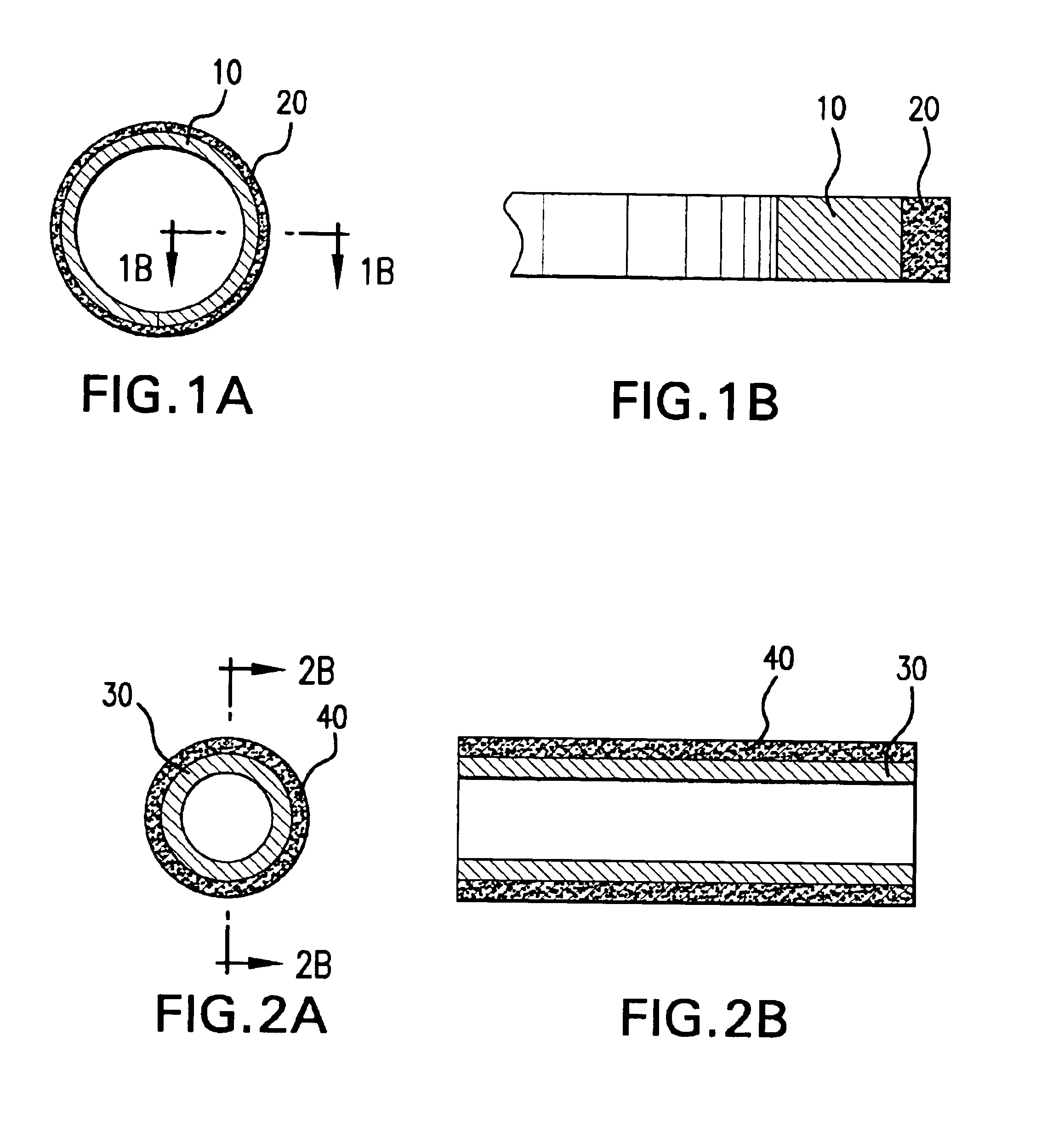
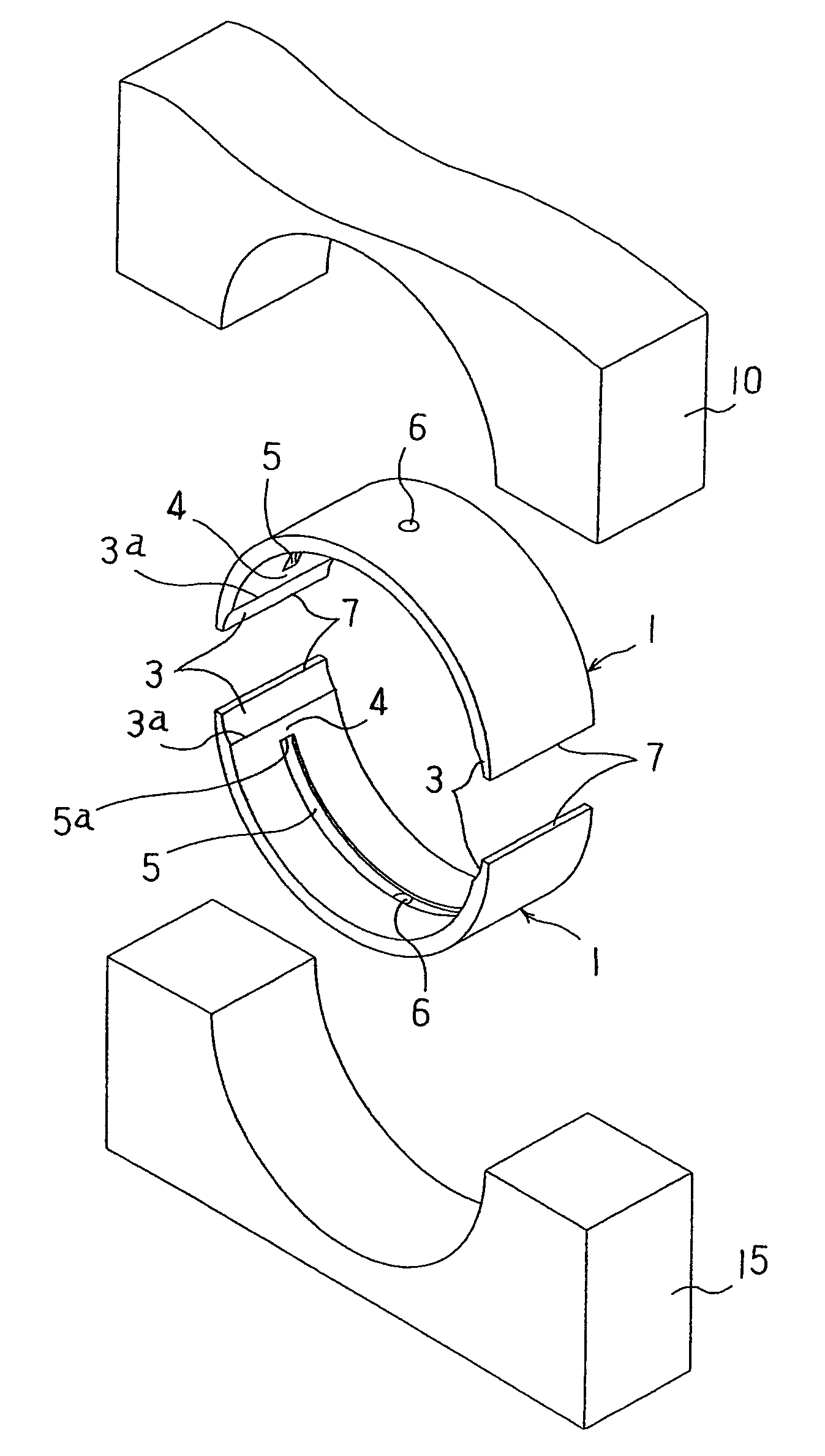
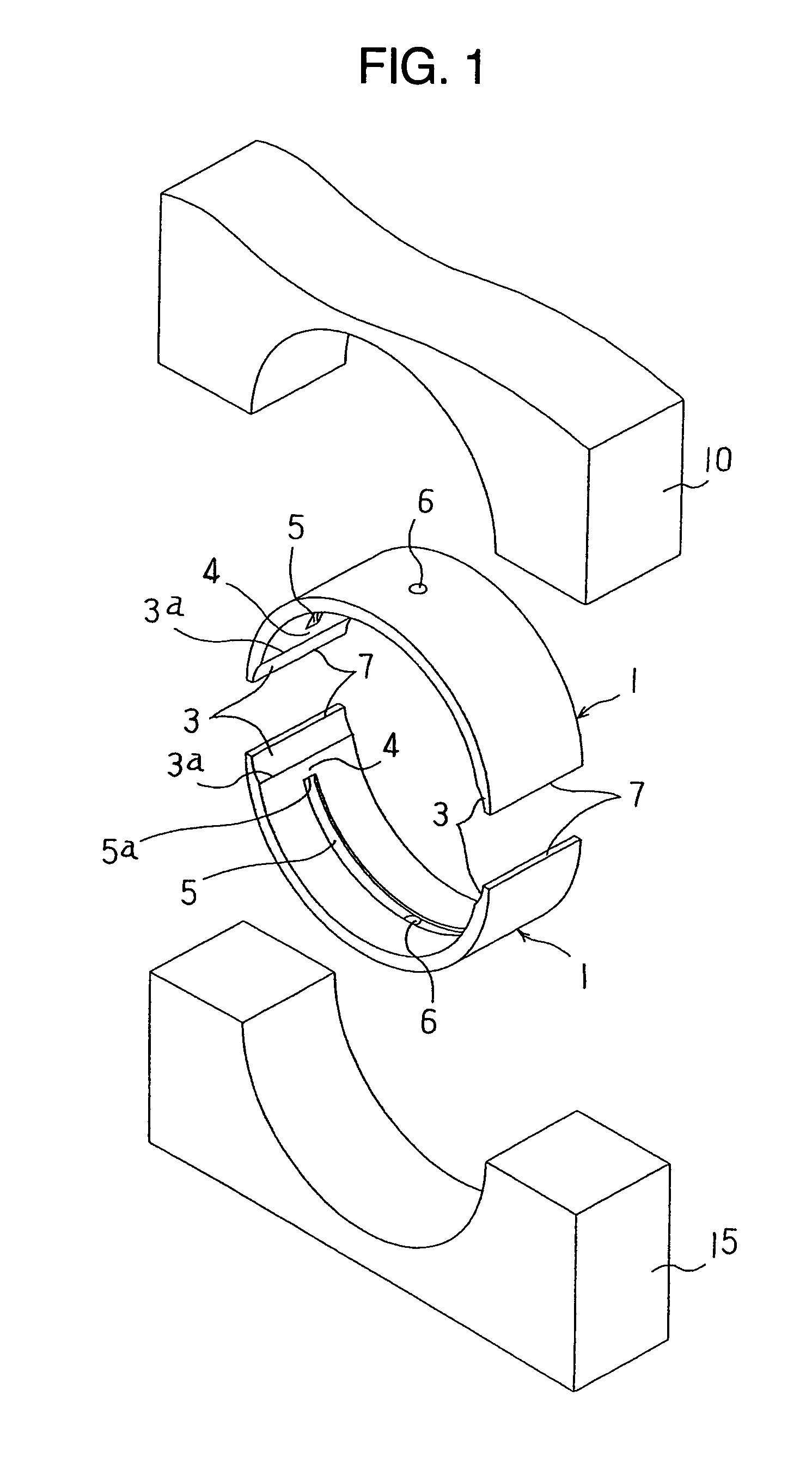
Multi-layer plain bearing having an anti-fretting layer
The invention relates to a multi-layer plain bearing (1) that has a front side (4) that can face the element to be supported and a rear side (6) opposite the front side, comprising a supporting layer (2), a sliding layer (3) arranged on the front side (4), and an anti-fretting layer (5) arranged on the rear side (6), wherein the anti-fretting layer (5) is made of a copper-based alloy having copper mixed-crystal grains. The copper-based alloy of the anti-fretting layer (5) is formed by a binary alloy having an alloying element from the group comprising aluminum, zinc, indium, silicon, germanium, and antimony or by an at least ternary alloy having one alloying element from the group comprising aluminum, zinc, indium, silicon, germanium, tin, and antimony and at least one further element from said group and / or the further group comprising nickel, cobalt, iron, manganese, bismuth, lead, silver, and phosphorus, possibly with unavoidable impurities originating from production, wherein the total fraction of said alloying elements is at least 1 wt % and at most 30 wt %.
Owner:MIBA SINTER AUSTRIA
Quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolator with annular permanent magnets used for generating negative stiffness
InactiveCN104455181ALarge negative stiffnessImprove uniformityMagnetic springsShock absorbersDynamic stiffnessNegative stiffness
A quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolator with annular permanent magnets used for generating negative stiffness comprises a base and an outer cylinder connected with the base, the outer permanent magnet is arranged in a top notch of the outer cylinder, an upper cover is connected with the outer cylinder, a sliding bearing is combined with a central hole of the upper cover in a sleeved mode, and a central shaft is sleeved with the sliding bearing and is in clearance fit with the sliding bearing. A sleeve and an adjusting sleeve are sequentially connected to the position, located on the lower portion of the sliding bearing, of the central shaft, and the inner permanent magnet is installed in the sleeve. A spring is arranged at the bottom of the central shaft in a sleeving mode, the bottom end of the spring is fixed to the base, and the top end of the spring is fixed to the adjusting sleeve. A mark line on the central shaft is used for representing the position of the inner permanent magnet relative to the outer permanent magnet. When the mark line coincides with the upper end face of the sliding bearing, the inner permanent magnet exactly faces the outer permanent magnet, and the isolator is in a normal working state. The quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolator has the advantages of being high in static stiffness and low in dynamic stiffness, basic stimulation with large amplitude can be isolated, and the mass of a vibration-isolated objected can be adjusted.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
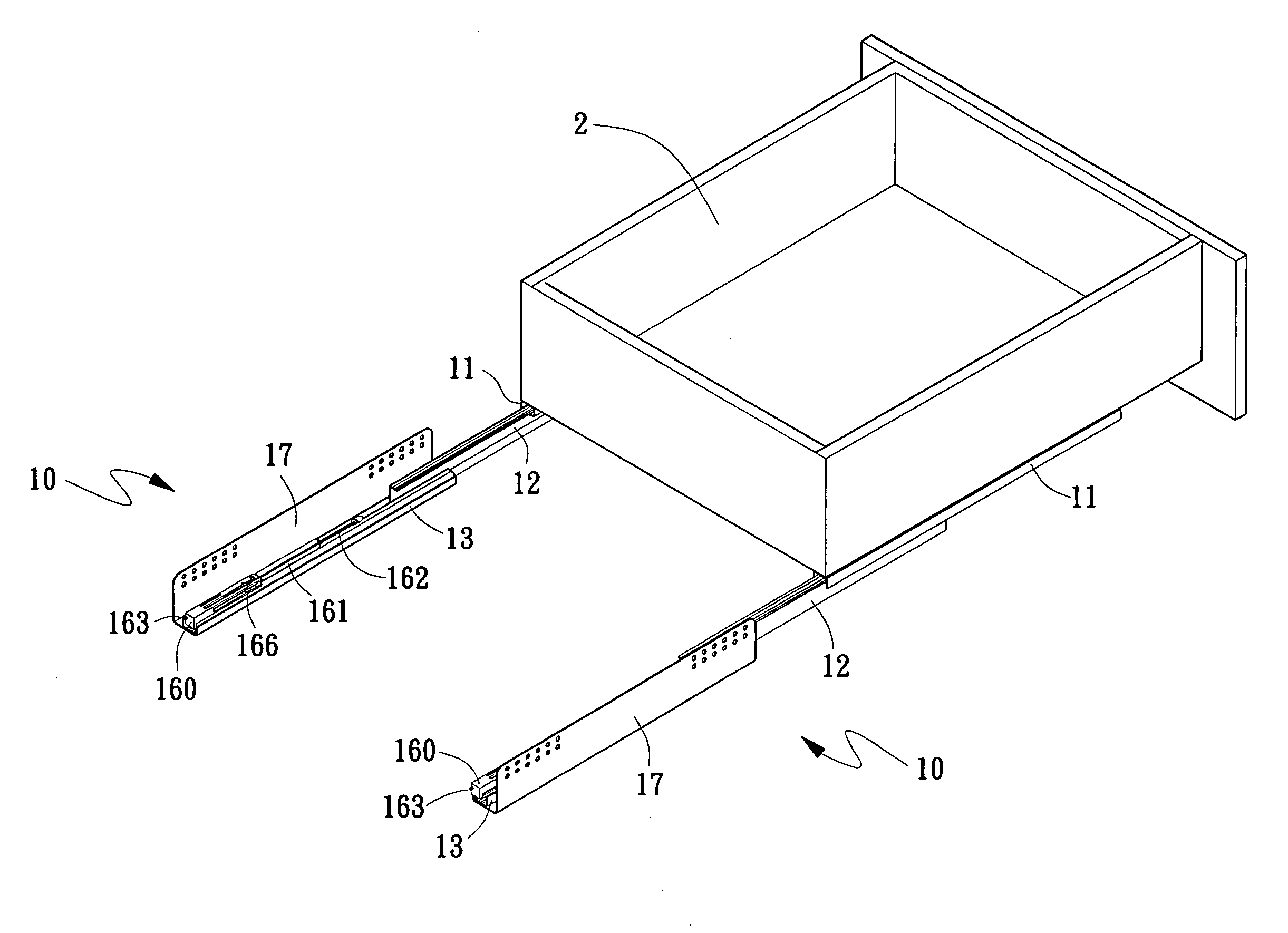
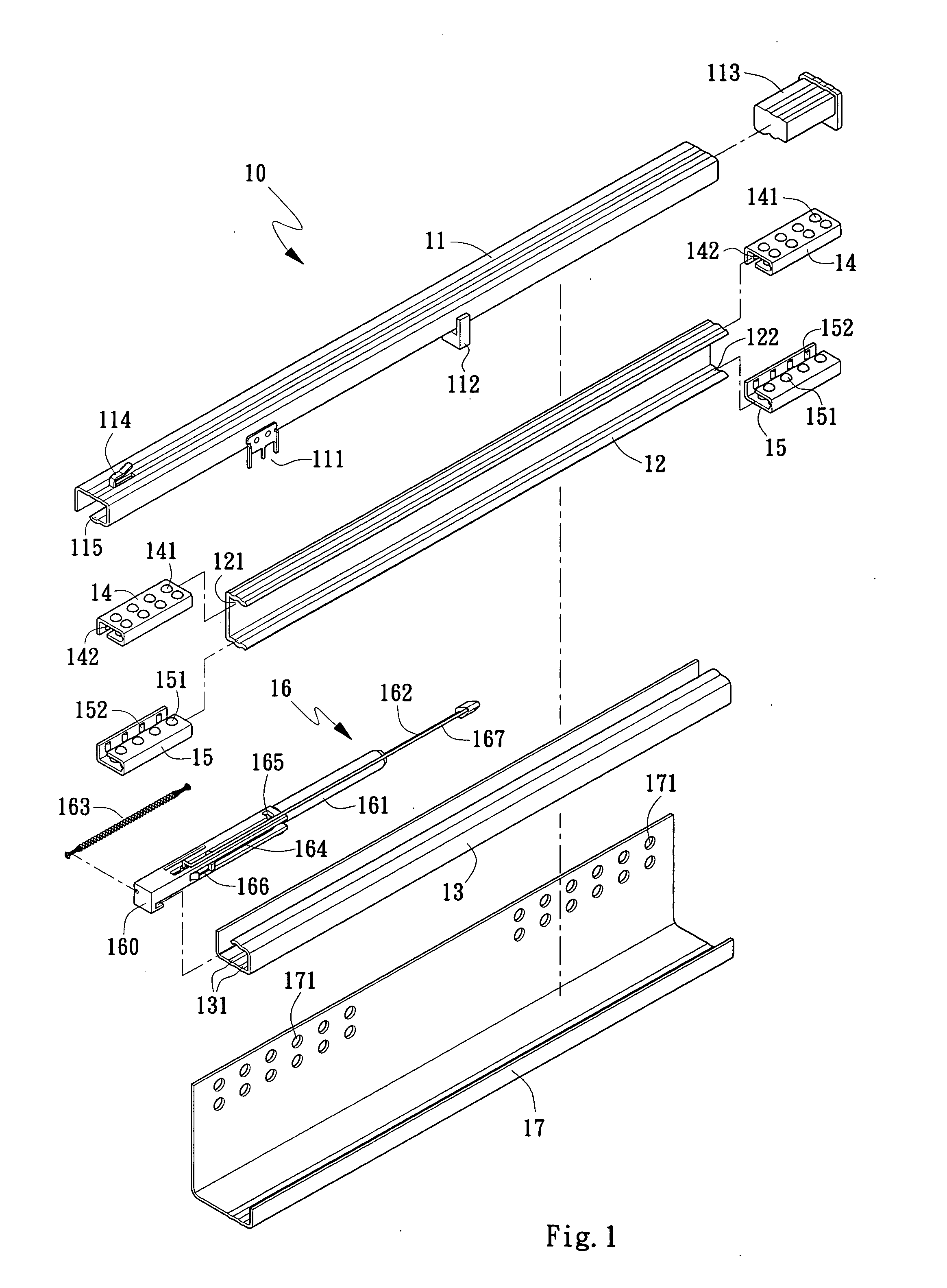
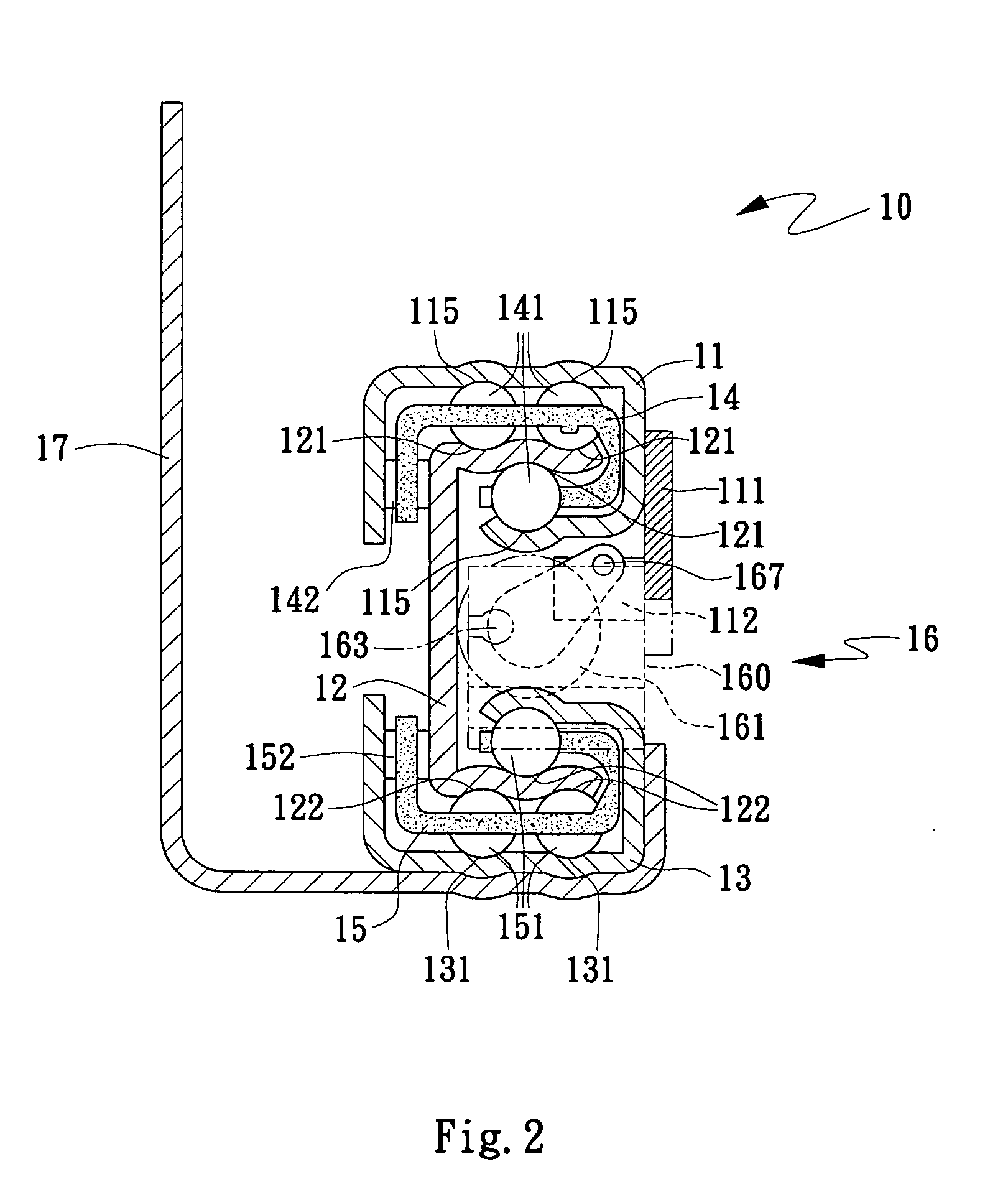
Drawer slide assembly
InactiveUS20080157643A1Smooth and stable openingSmooth and stable and closingDrawersEngineeringFixed position
A drawer slide assembly includes an upper slide; an inner slide having a buffer unit located therein; at least two upper sliding guides being provided on top and bottom with first sliding bearings to bear against upper inner and lower inner surfaces of the upper slide and upper inner and upper outer surface of the inner slide, and on a lateral wall with second sliding bearings to bear against a lateral inner surface of the upper slide and a lateral upper outer surface of the inner slide, so that the upper slide and the inner slide are mutually slidably assembled to each other; and a mounting plate for holding the assembled upper slide and inner slide to a fixed place. With the sliding bearings so arranged, the drawer slide assembly provides a buffering effect to enable smooth and stable opening and closing of a drawer box.
Owner:CHEN KUO CHEN
Sliding bearing for internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20110058761A1Reduced conformabilityIncrease load capacityCrankshaft bearingsShaftsEngineeringInternal combustion engine
Disclosed is a sliding bearing for an internal combustion engine for supporting a crankshaft including a pair of semi-cylindrical bearings combined with each other into a cylindrical body. Each of inner circumferential surfaces of the respective semi-cylindrical bearings includes first and second curved surfaces following two kinds of arcs with different curvatures. The first curved surface is in a region including a circumferential central portion of the inner circumferential surface. The second curved surfaces are in remaining two regions of the inner circumferential surface. The circumferential oil groove and the axial groove communicate with each other. The circumferential grooves of the second curved surfaces and the axial groove communicate with each other. The groove bottoms of the circumferential grooves of the second curved surfaces are displaced to a side of the bearing inner circumferential surface from a groove bottom of the axial groove.
Owner:DAIDO METAL CO LTD
Large-allowance capturing mechanism for end effector of spatial large manipulator
ActiveCN103331759AImprove toleranceHigh Tolerance Capability for Large Arm End EffectorsGripping headsToolsControl systemBall screw
The invention provides a large-allowance capturing mechanism for an end effector of a spatial large manipulator, relating to a large-allowance capturing mechanism. By the adoption of the large-allowance capturing mechanism for the end effector of the spatial large manipulator, the problems that an end effector mechanism and a control system of an existing spatial large manipulator are complicated and the reliability of space application is lowered are solved. A linear sliding bearing is installed on each linear sliding bearing guide rod in a penetration way; a finger installation platform is connected with the three linear sliding bearing guide rods in a sliding way through the three linear sliding bearings; a nut floating spring is sheathed on the outer wall of a ball screw nut; the center of the finger installation platform is elastically connected with the ball screw nut in a micro floating way through the nut floating spring; one end of each main connecting rod is rotationally connected with the finger installation platform; the other end of each main connecting rod is rotationally connected with a finger; one end of each auxiliary connecting is rotationally connected with the finger installation platform; and the other end of each auxiliary connecting rod is rotationally connected with the finger. The large-allowance capturing mechanism provided by the invention is used for the spatial in-orbit end effector.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
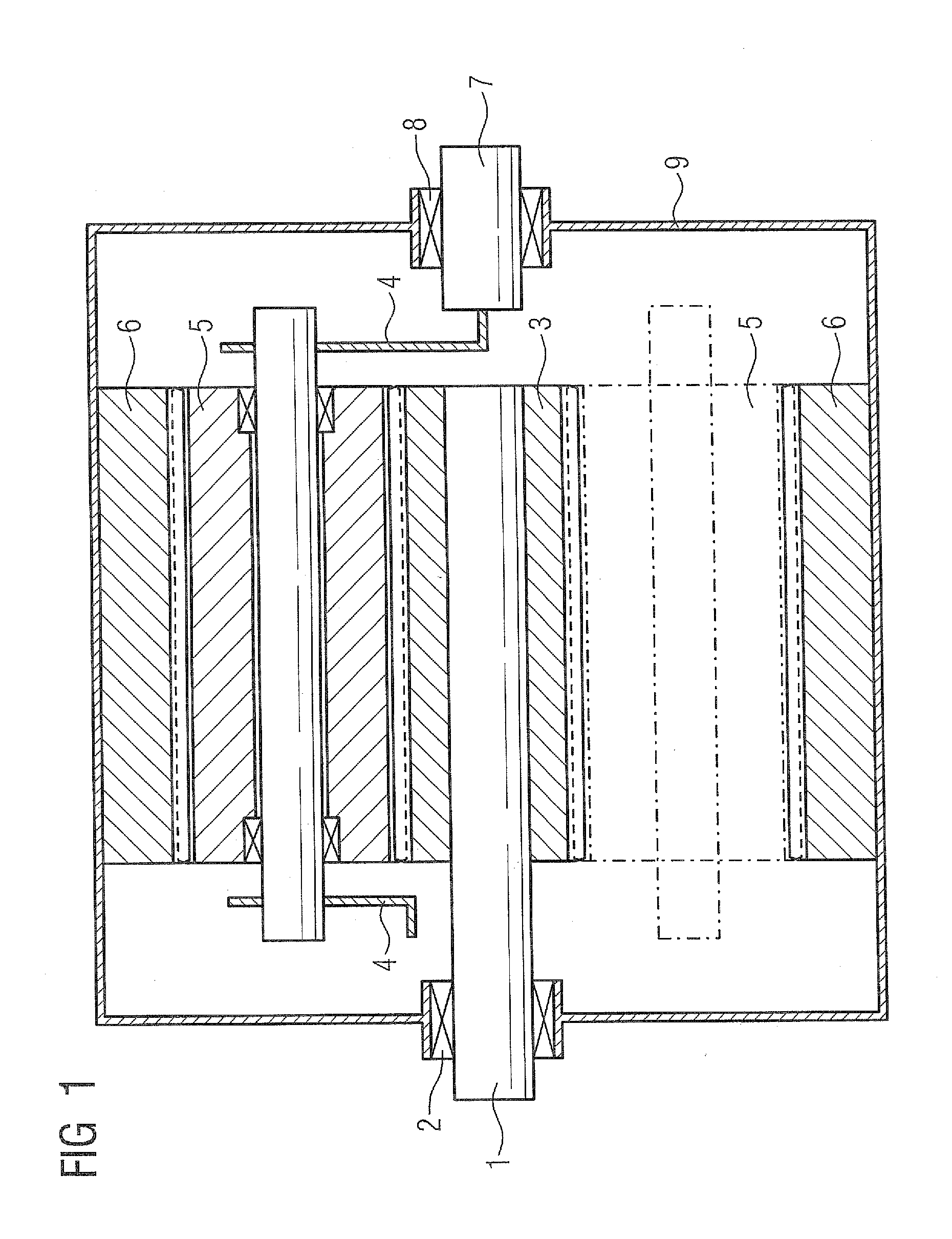
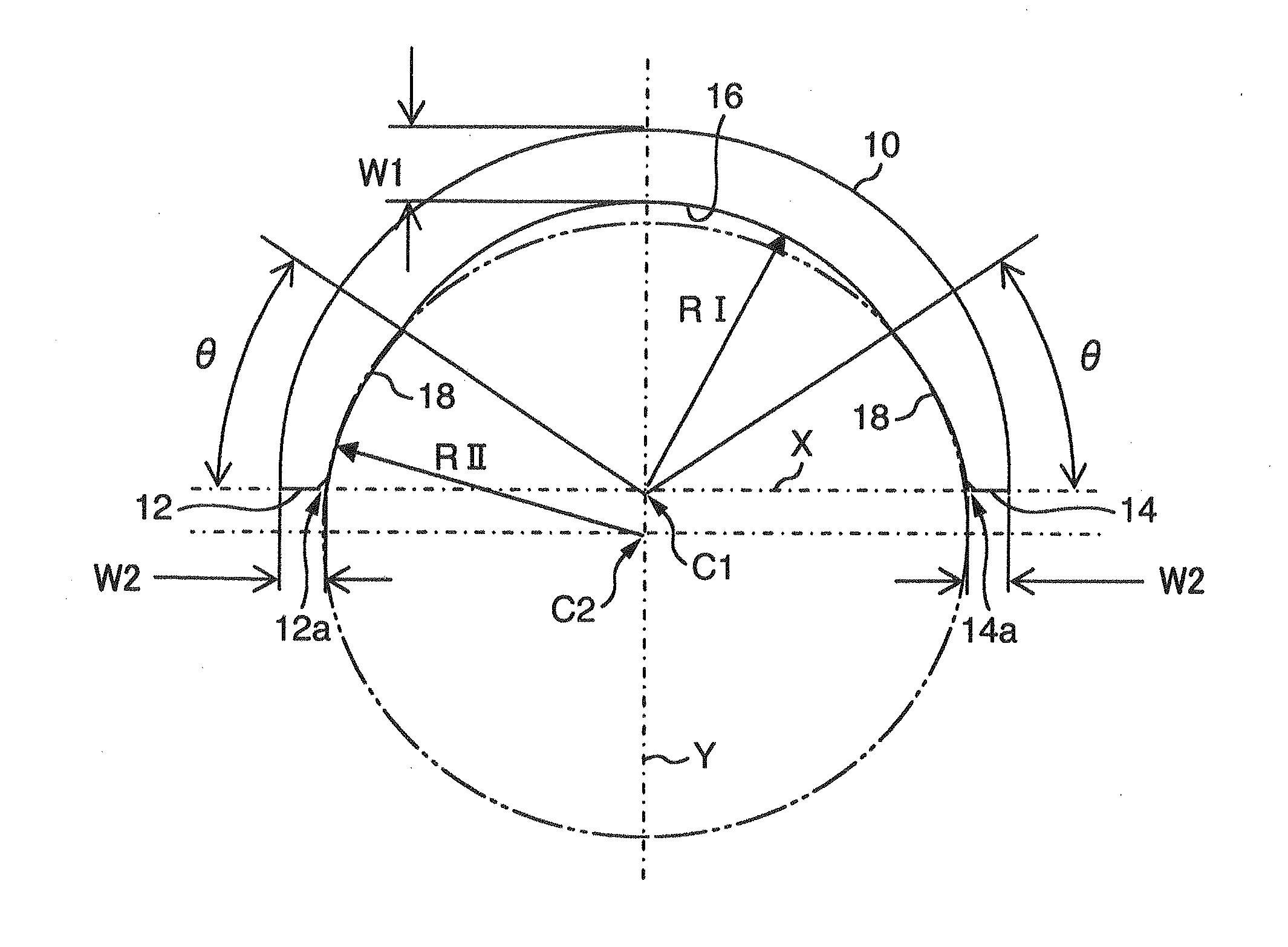
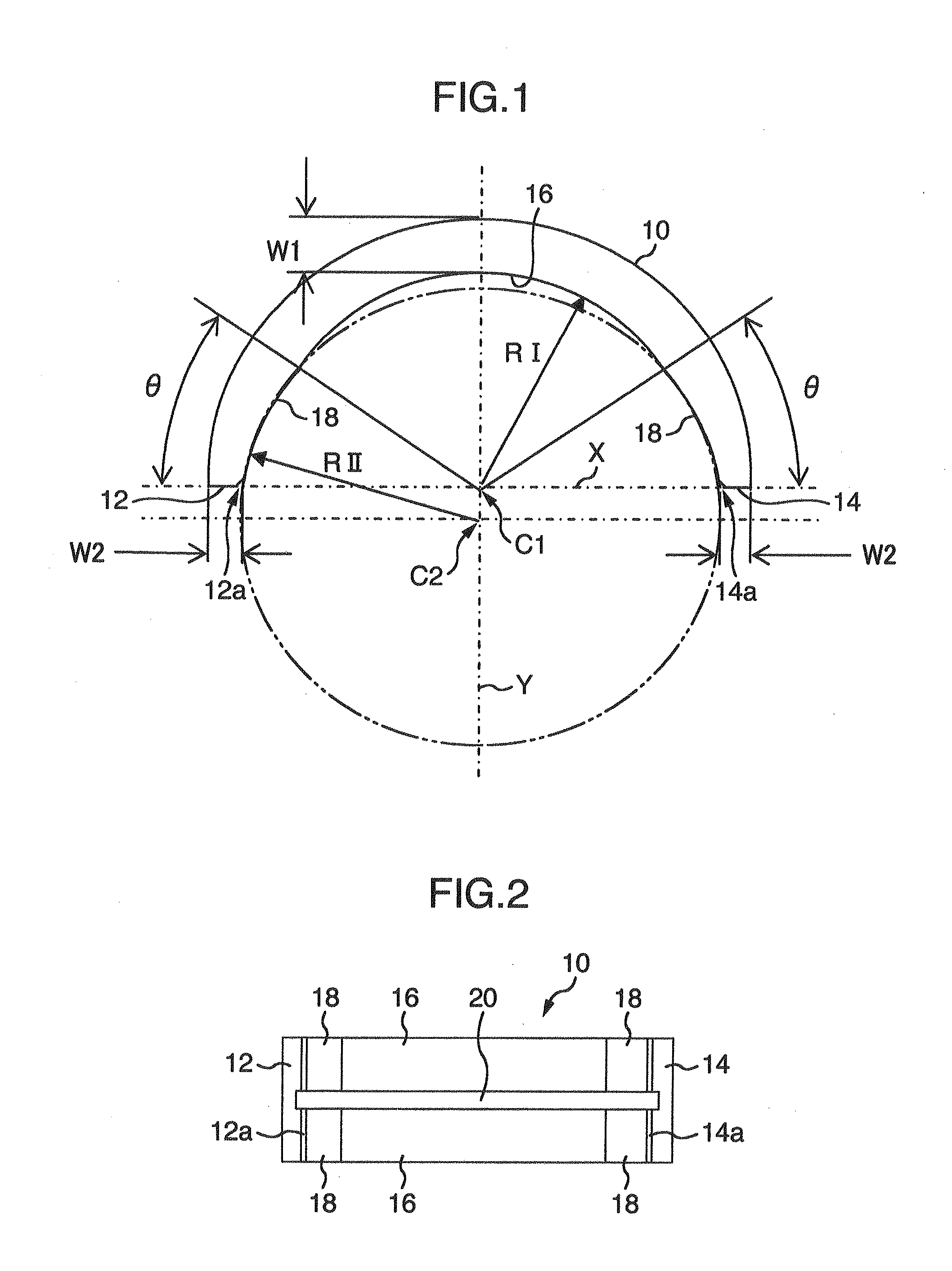
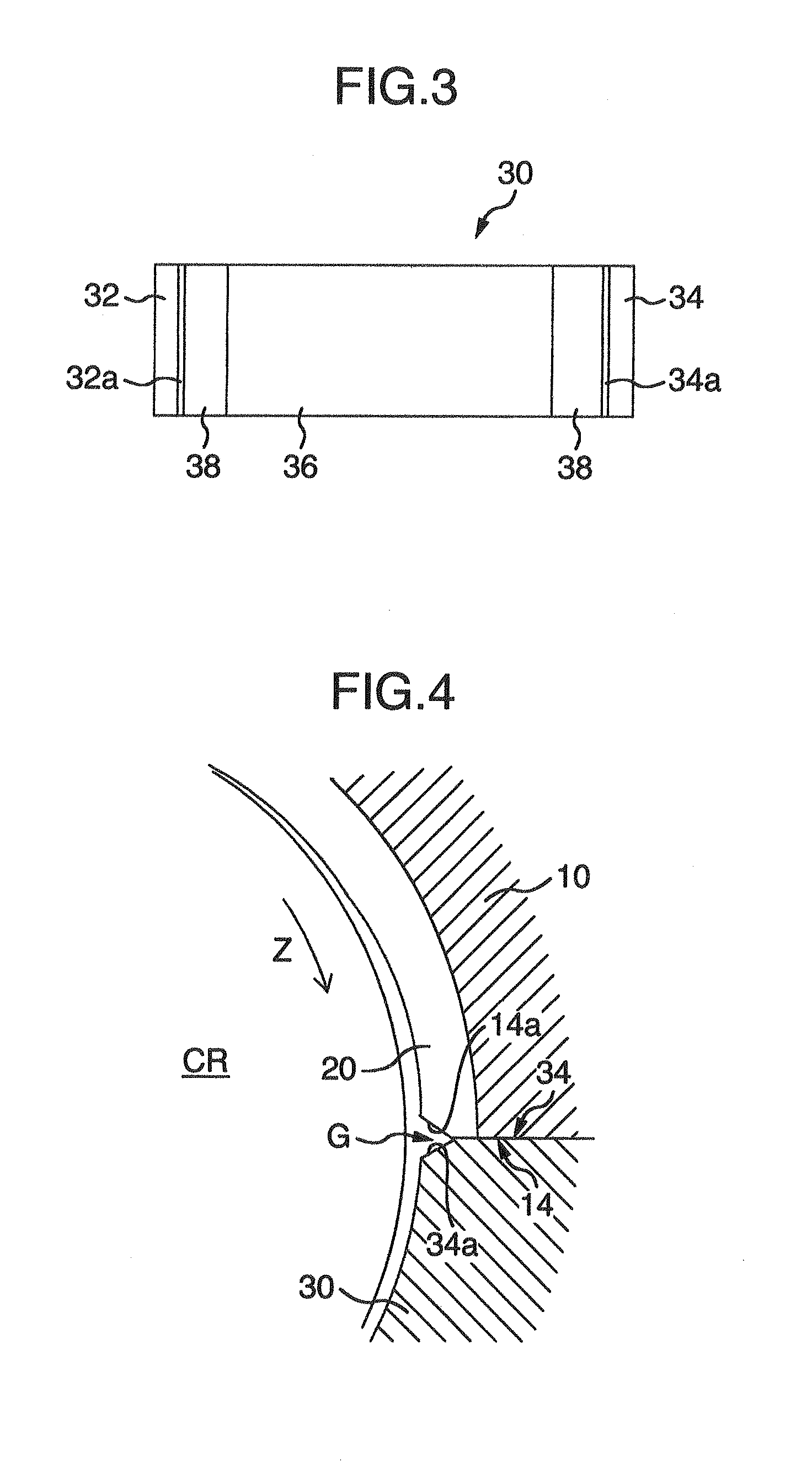
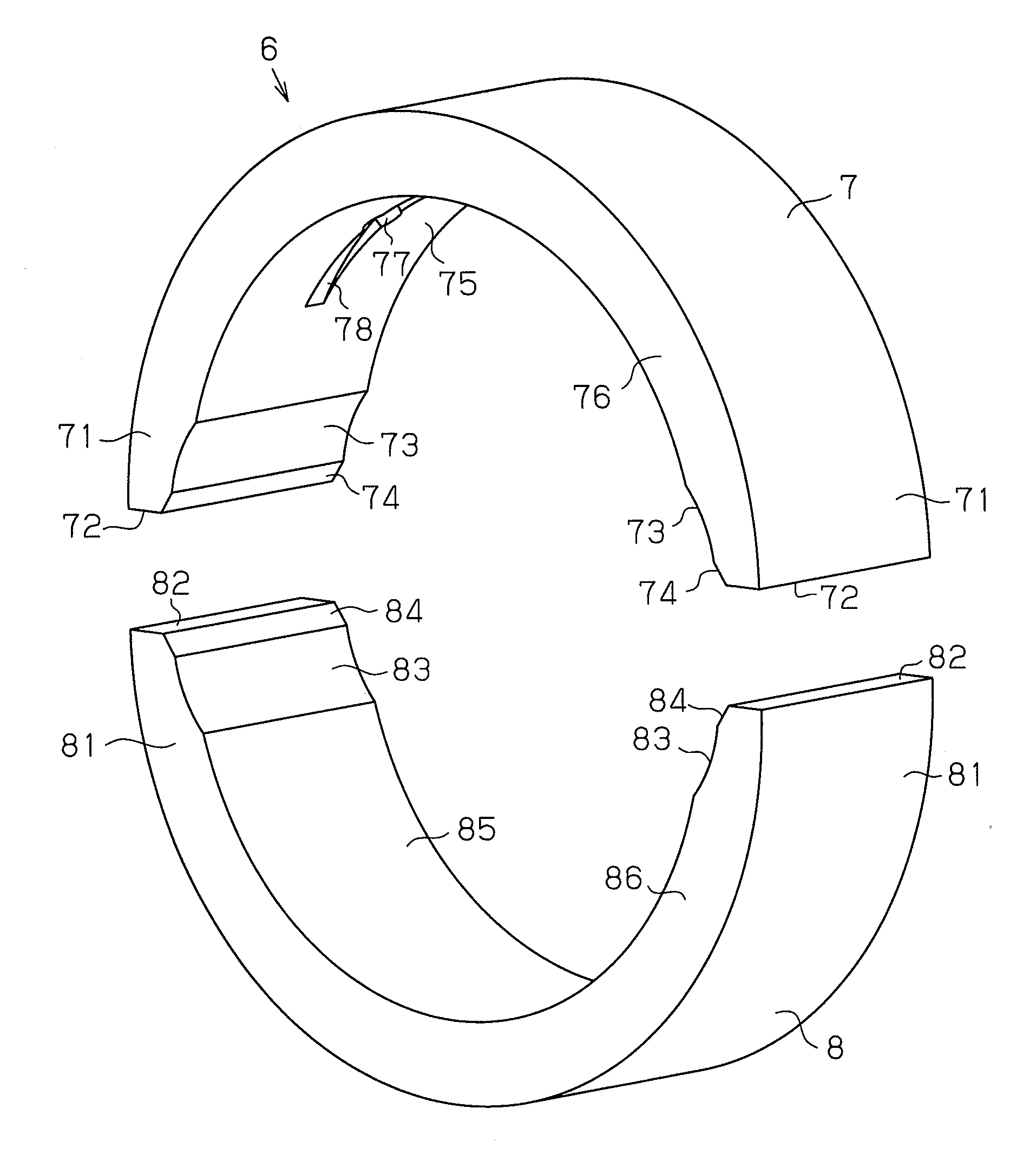
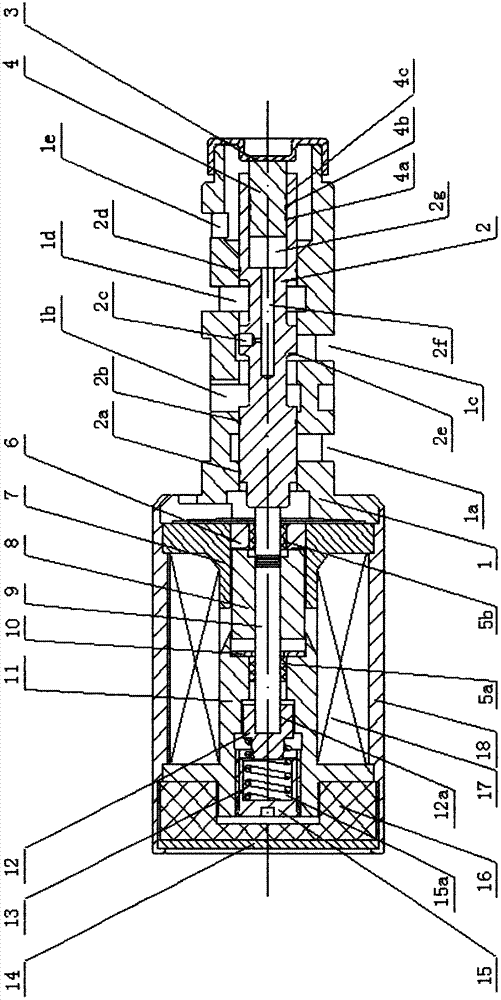
Plain bearing
InactiveUS20020126924A1Area minimizationSuppressing decrease in load capacityConnecting rod bearingsRolling contact bearingsEngineeringAlloy
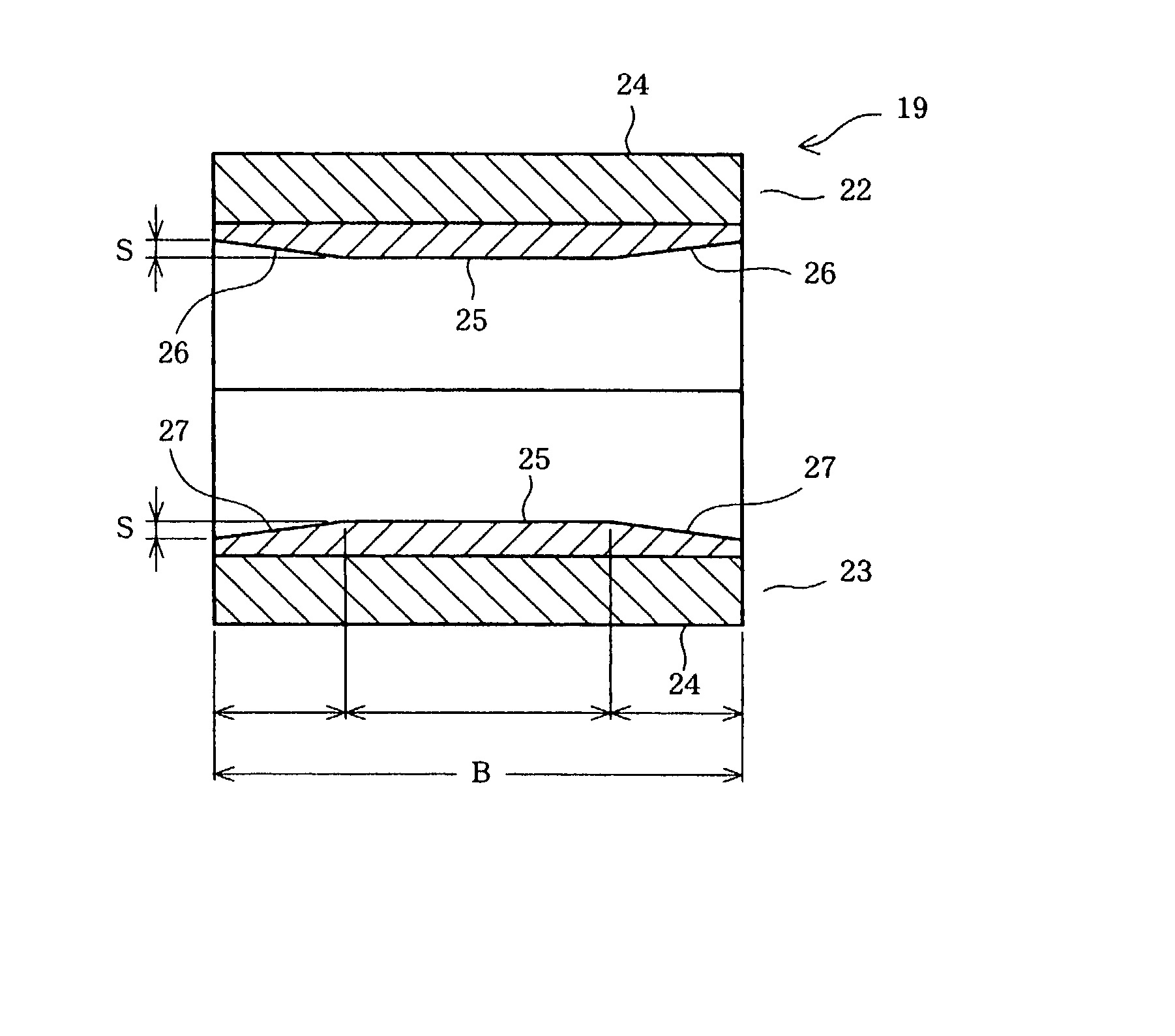
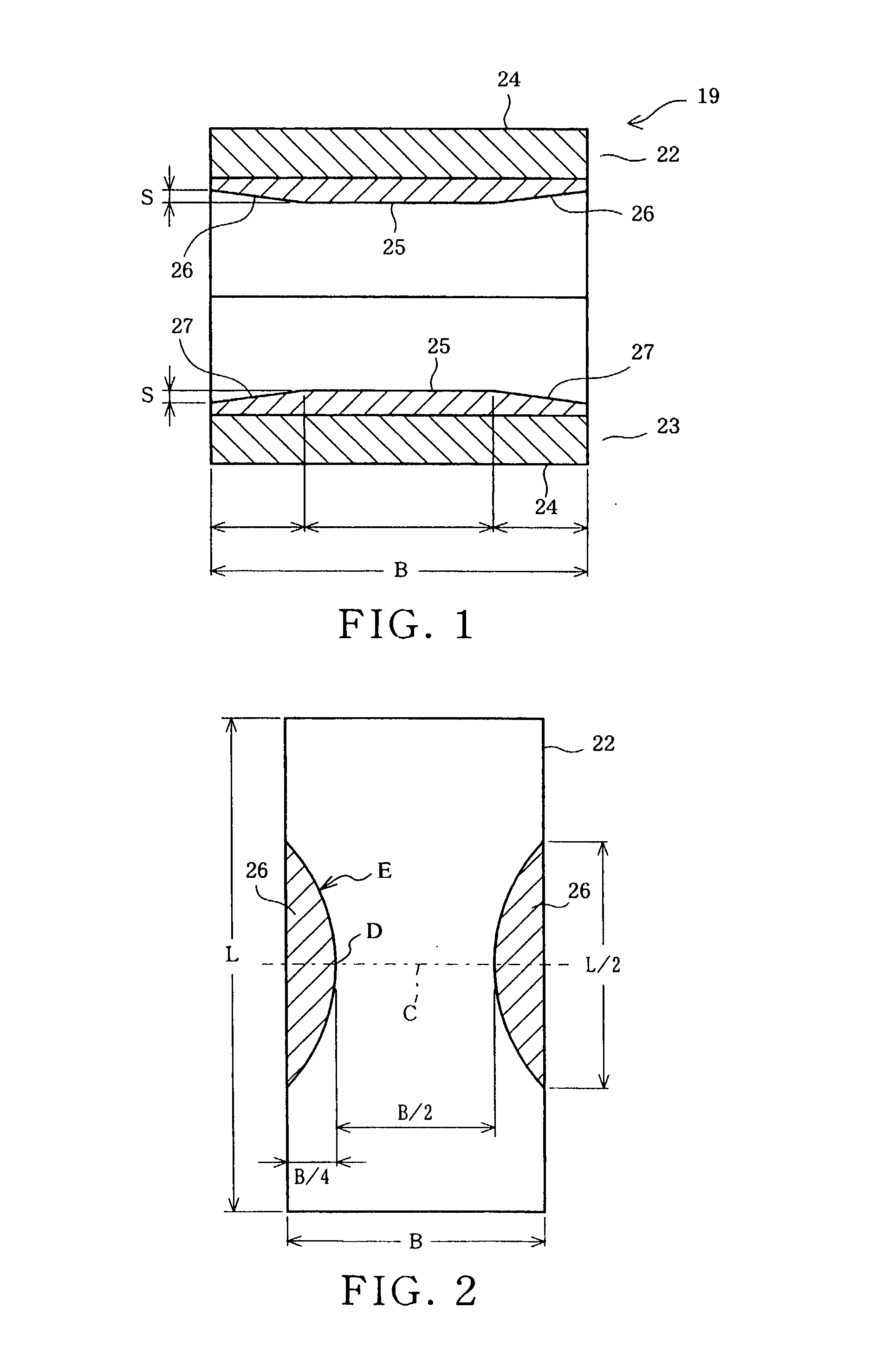
There is disclosed a plain bearing comprising: a back metal; and a bearing alloy layer bonded onto the back metal which bearing alloy layer is provided at a surface side thereof with a cylindrical bearing face extended in the direction of the axis of the plain bearing, the bearing alloy face being provided at each of axial terminal portions thereof with an inclination face inclined radially outwardly from a location defined between both of axially terminal ends of said bearing face toward said axially terminal ends thereof, the inclination face having an axial length varying along the circumference of the inclination face.
Owner:DAIDO METAL CO LTD
Sliding Material and Sliding Bearing
InactiveUS20070232502A1High strengthReduce coefficient of frictionBearing componentsBase-materialsPorosityShell molding
A sliding material including a resinous porous article having an interconnected hole porosity of not less than 30% and a lubricating oil which impregnates the resinous porous article is disclosed. The resinous porous article has an interconnected hole formed by molding a resin mixed with a pore-forming substance into said resin, and extracting said pore-forming substance from said molded article with a solvent which dissolves said pore-forming substance and does not dissolve said resin. A sliding bearing composed of a sliding material having a sliding surface which slides on a mating member and a lubricating oil supply layer which supports the sliding material and supplies the sliding surface with the lubricating oil.
Owner:NTN CORP
Self-lubricating bearing material and plain bearing of such a bearing material
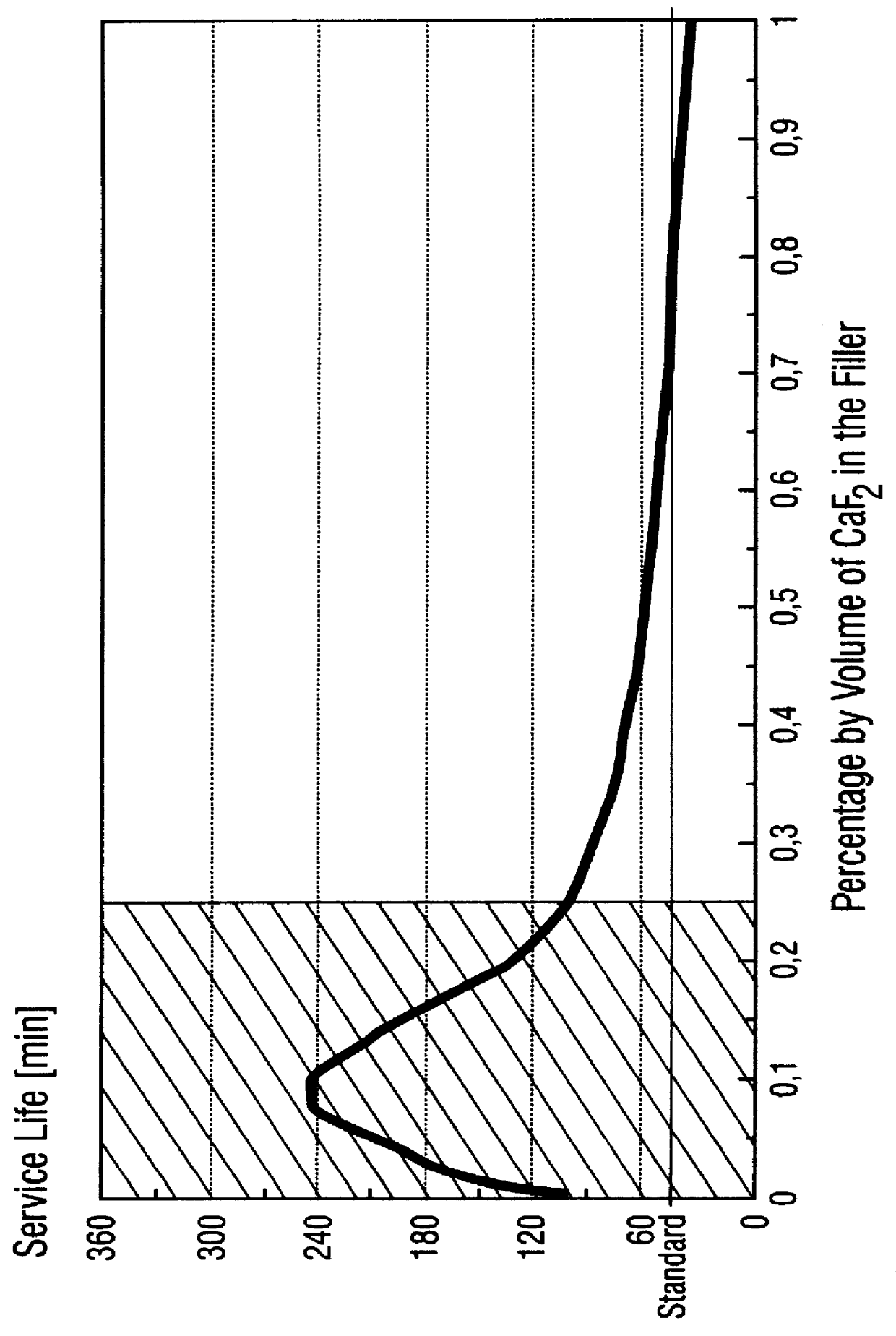
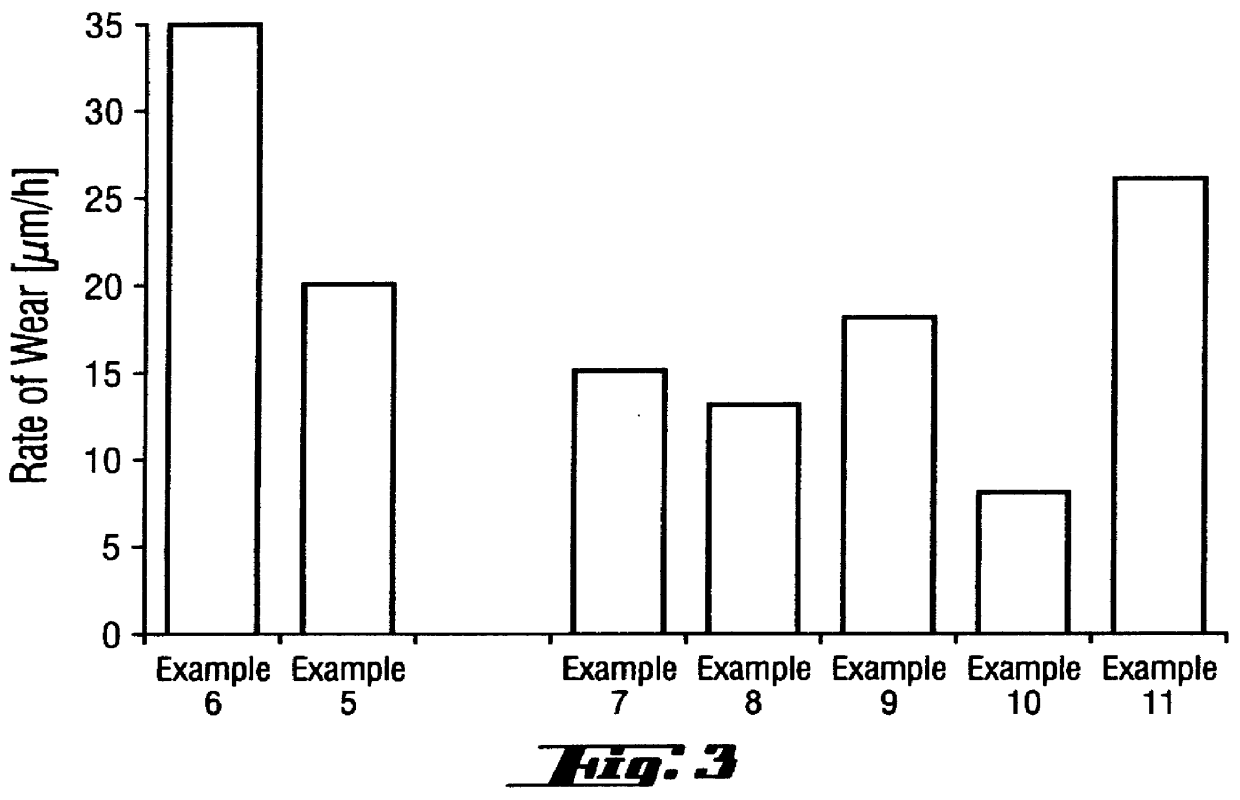
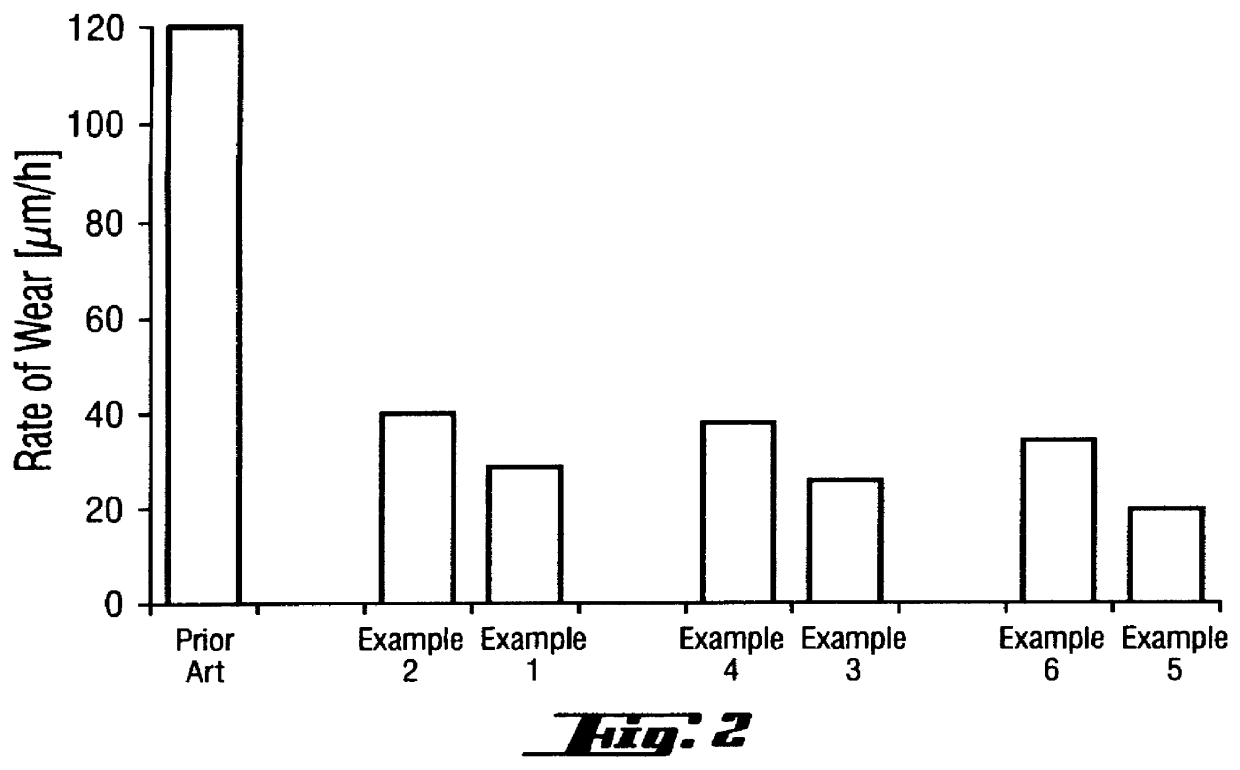
PCT No. PCT / DE96 / 00244 Sec. 371 Date Aug. 25, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Aug. 25, 1997 PCT Filed Feb. 14, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 26975 PCT Pub. Date Sep. 6, 1996A self-lubricating bearing material is described, as well as a plain bearing of such a bearing material, the performance of which, under lubricant-free conditions, is so markedly improved that pv values of up to 6 MPa / m / s are achieved in an average load and speed range. The self-lubricating bearing material comprises a PTFE-containing polymer matrix with fillers comprising PbO and at least one metal fluoride. The PbO content is from 15-55 vol. % and the metal fluoride content is from 0.1-14 vol. %. Preferred metal fluorides are CaF2, PbF2 and MgF2. The addition of further fillers such as hard materials, pigments or fibrous material is possible. The proportion of further additives may amount to up to 40 vol. % of the PbO / metal fluoride fillers.
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL WIESBADEN
Multifunctional width adjustable conveying device
InactiveCN104401644AAdjustable distanceAchieve cleaningCharge manipulationConveyor partsLinear motionDrive shaft
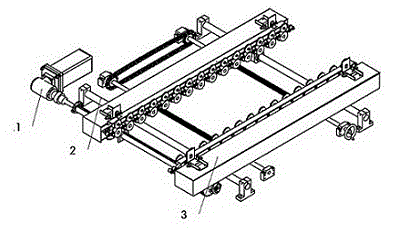
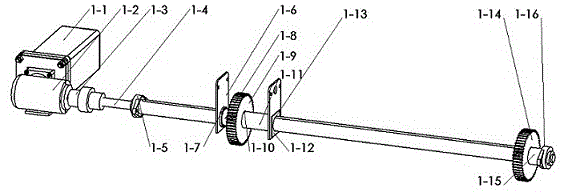
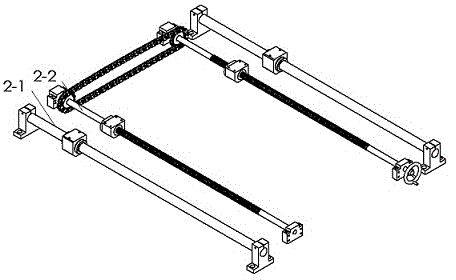
The invention discloses a multifunctional width adjustable conveying device of a PCB (printed circuit board) and machined component washing device, which is a core part of the washing device. The multifunctional width adjustable conveying device consists of a power input device (1), a supporting width adjusting device (2) and a conveying guide rail compression device (3), wherein a motor (1-1) drives a gear of a conveying guide rail (3-1) to rotate through a transmission shaft (1-4), a gear (1-9) and a gear (1-14), and a chain of the conveying guide rail (3-1) drives a large roller and a small roller to rotate together so as to realize the online washing of a PCB; a groove body of the conveying guide rail (3-1) is connected with a slide bearing sleeve and a nut seat of the supporting width adjusting device (2-1), a handle of a ball screw width adjusting device (2-2) is rotated so as to drive a ball screw to rotate through a chain wheel and the chain, the conveying guide rail (3-1) is driven by the linear motion of the nut seat to make linear movement along the axis direction so as to realize the width adjustment of the conveying guide rail, and the online washing of PCBs in different widths can be satisfied.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
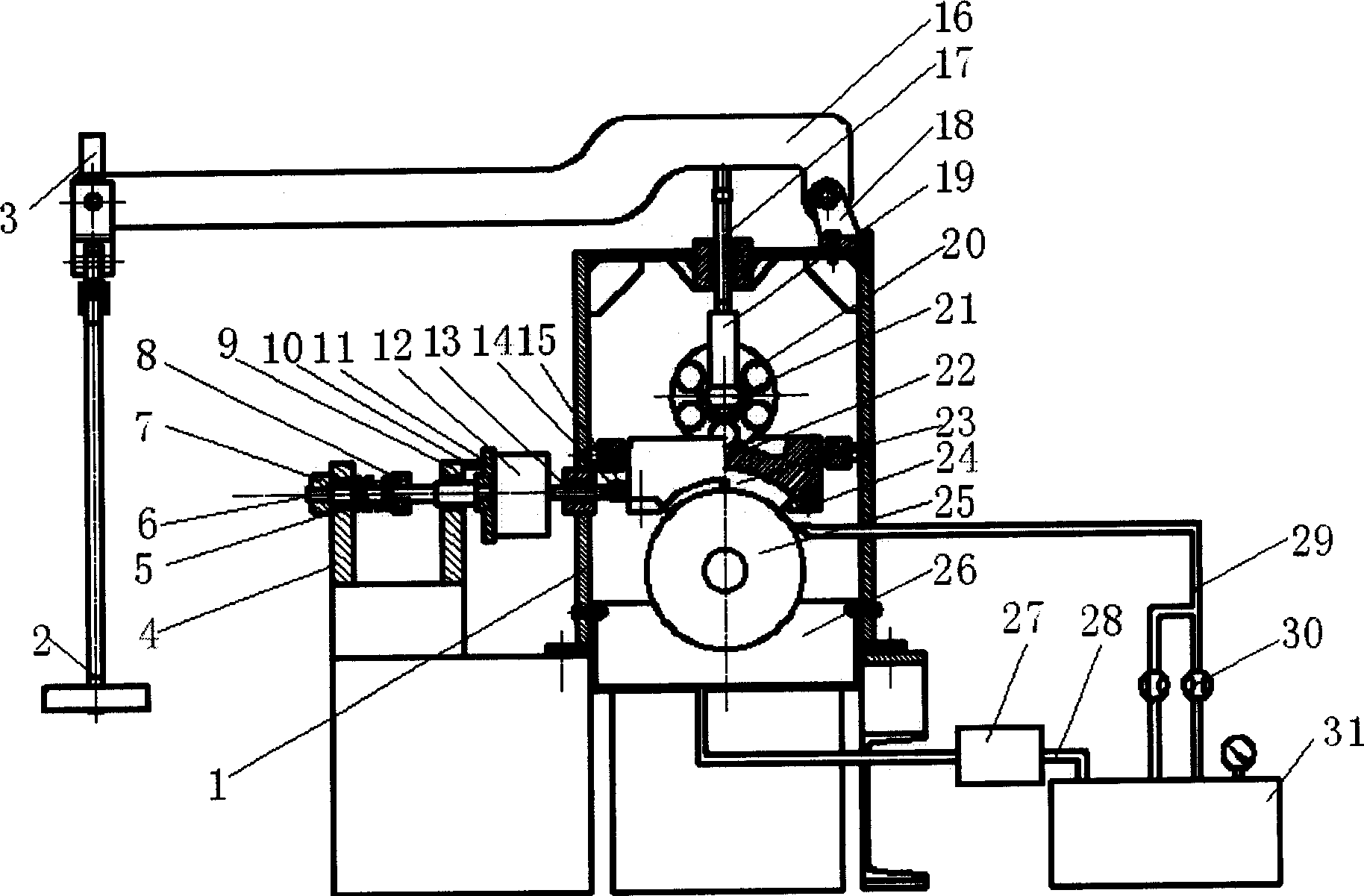
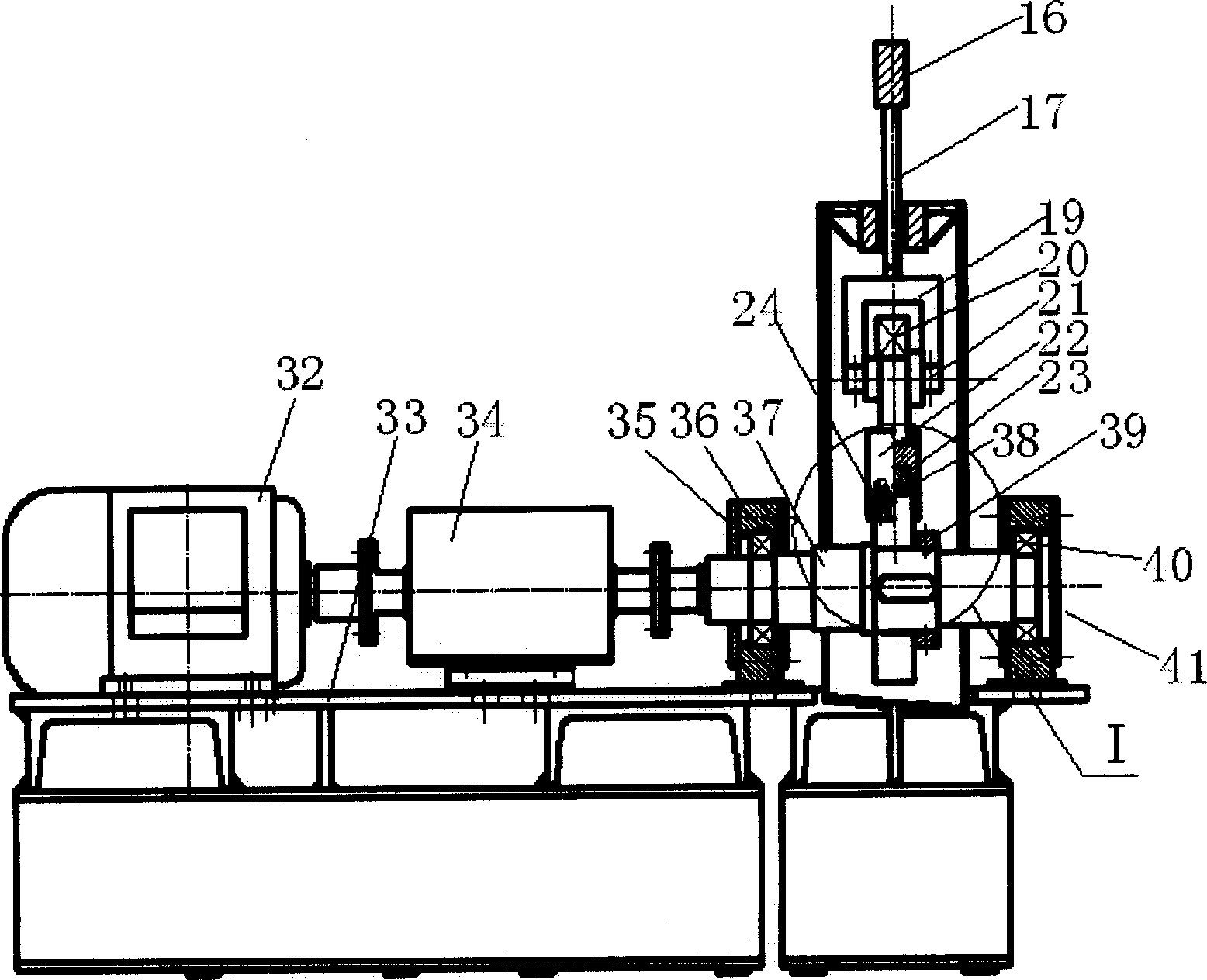
Comprehensive performance test table for water-lubricated dynamic-static pressure radial sliding bearing
InactiveCN101876590APerformance TestingSimple structureMachine bearings testingAxial displacementHydraulic pump
The invention provides a comprehensive performance test table for a water-lubricated dynamic-static pressure radial sliding bearing, comprising a box and main shaft. The main shaft penetrates through the box; a radial sliding bearing is sleeved on the part of the main shaft, which is in the box; the radial sliding bearing is fixed in a radial sliding bearing pedestal; the radial sliding bearing pedestal is arranged in a loading cylinder which is fixed at the bottom of the box; a static-pressure water cavity is formed in the gap between the radial sliding bearing pedestal and the loading cylinder, and the static-pressure water cavity is communicated with a loading connection pipe; the gap between the main shaft and the radial sliding bearing is communicated with a water inlet pipe; the side wall of the box is provided with a drain pipe; a displacement sensor which is used for measuring the horizontal displacement and the vertical displacement of the main shaft is arranged near the main shaft; a pressure sensor and a temperature sensor are arranged on the matching surface of the main shaft and the radial sliding bearing; and a rotation torque and speed sensor is arranged on the input end of the main shaft. The comprehensive performance test table adopts the pure water lubrication and can simulate various working conditions and test the pressure, the temperature, the thickness, the friction coefficient, the axial displacement, the deviation angle and other parameters of the water film to provide valuable basis for the design of the radial sliding bearing which is used for the water hydraulic pump, the motor and related water-lubricated machinery.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Thrust bearing applying interface sliding technology
InactiveCN101265942AWith carrying capacityExcellent friction reductionBearing componentsSliding contact bearingsCarrying capacityThrust bearing
The invention is a thrust bearing using the interface slippage technology, and is characterized in that the bearing comprises a static and a moving flat panels that are parallel to each other; the gap between the static and the moving flat panels is filled with fluid lubricating oil; a coating layer II is arranged on part of the static flat panel; a coating layer I is arranged on the rest partof the static flat panel; a coating layer III is arranged on the surface of the moving flat panel, Therefore, a thrust bearing is formed by the two flat panels through a certain relative moving between the static flat panel and the moving flat panel, the coating layer I is a fluorocarbon coating layer, and the coating layer II and III are coatings of mica powder modified by silane coupling agents. The thrust bearing is simple in the bearing forming and has a certain carrying capacity, good anti-friction and wear-resistance without the need of processing the matching surface into a geometric shape. With simple and compact structure and small size and low production cost, the thrust bearing can replace the traditional fluid motive power lubrication thrust bearing for bearing purpose.
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH
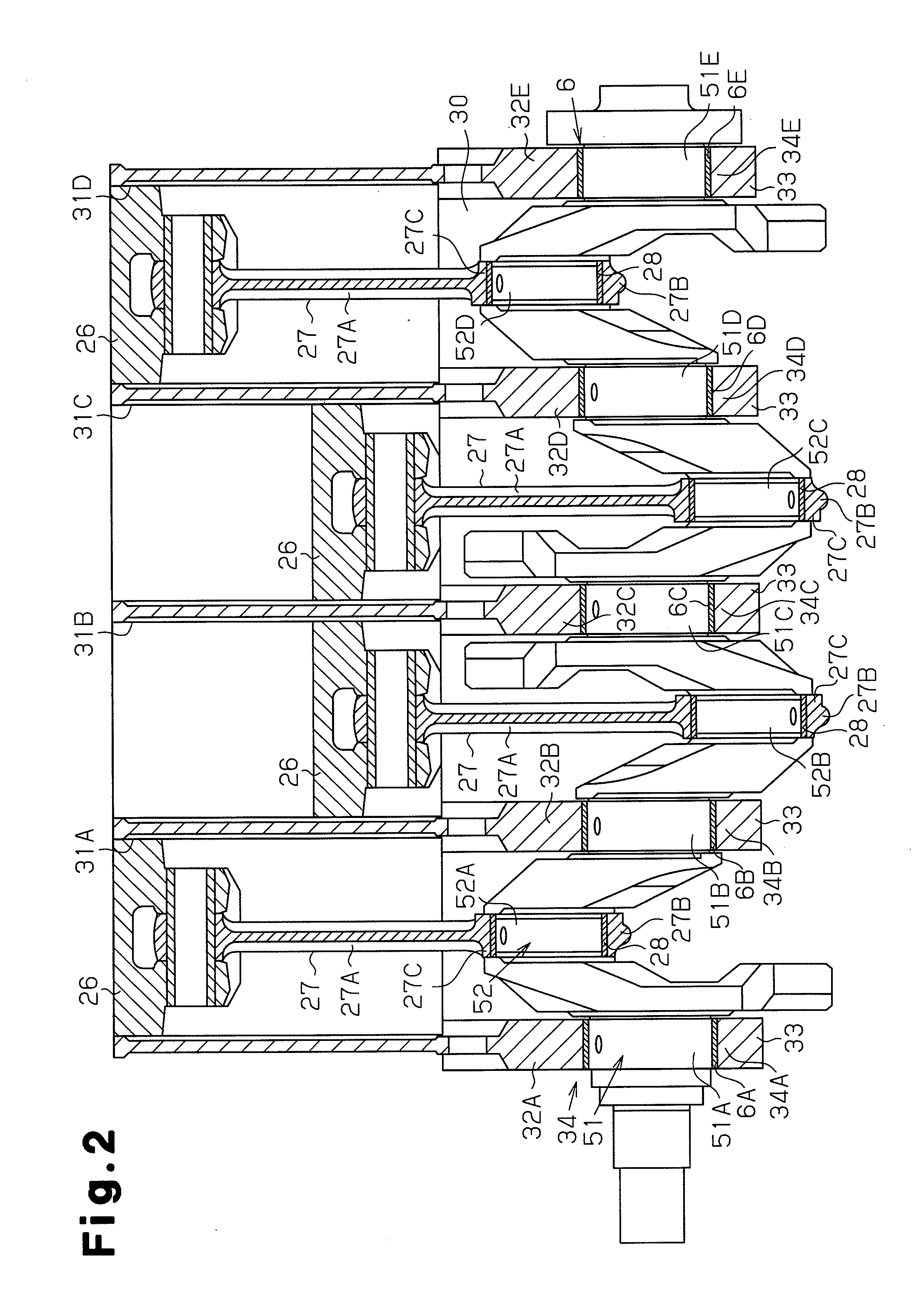
Slide bearing
ActiveUS20100046869A1Reduces amount of lubricantAvoid damageCrankshaftsConnecting rod bearingsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A crank bearing is disclosed that includes a semicircular upper bearing and a semicircular lower bearing, which can be split from each other. The upper bearing includes a first oil passage for introducing engine oil from the outside to a gap between the crank bearing and a crank journal, and a second oil passage for permitting the engine oil to flow in the circumferential direction of the crank bearing. The first oil passage includes an inner circumference opening, which is open to the inner circumference of the main bearing. The upper bearing includes a non-undercut portion in which no oil passage is formed on the trailing side of the inner circumference opening in the rotational direction of the crank journal. A chamfer oil passage for discharging the engine oil in the second oil passage to the outside from the axial direction of the crank bearing is provided in at least one of the lower bearing and a region on the proceeding side of the circumference opening in the rotational direction of the crank journal.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method and device for measuring friction force of bearing under tiny load
InactiveCN1687728AAccurate measurementStudy opening and closing characteristicsWork measurementTorque measurementPull forceRolling-element bearing
The invention discloses the bearing micro-load friction measuring method and the equipment. The measuring frame comprises the extruding arm, the measuring dial, the loading bolt, the measured bearing and the baffle. Equip the measured bearing in the hole of the measuring dial; add the force on the measuring frame from the top by the upward force and realize the micro-load measuring through the gravity of the measuring frame paralleled floating above the spin axis. The angle produced by the parallel of the friction and the pull force of the deviation is amplified into the vertical displacement of the extruding arm end. The non-contacting sensor realizes the precise measurement of the friction and the frictions coefficients of the sliding bearing and rolling bearing.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
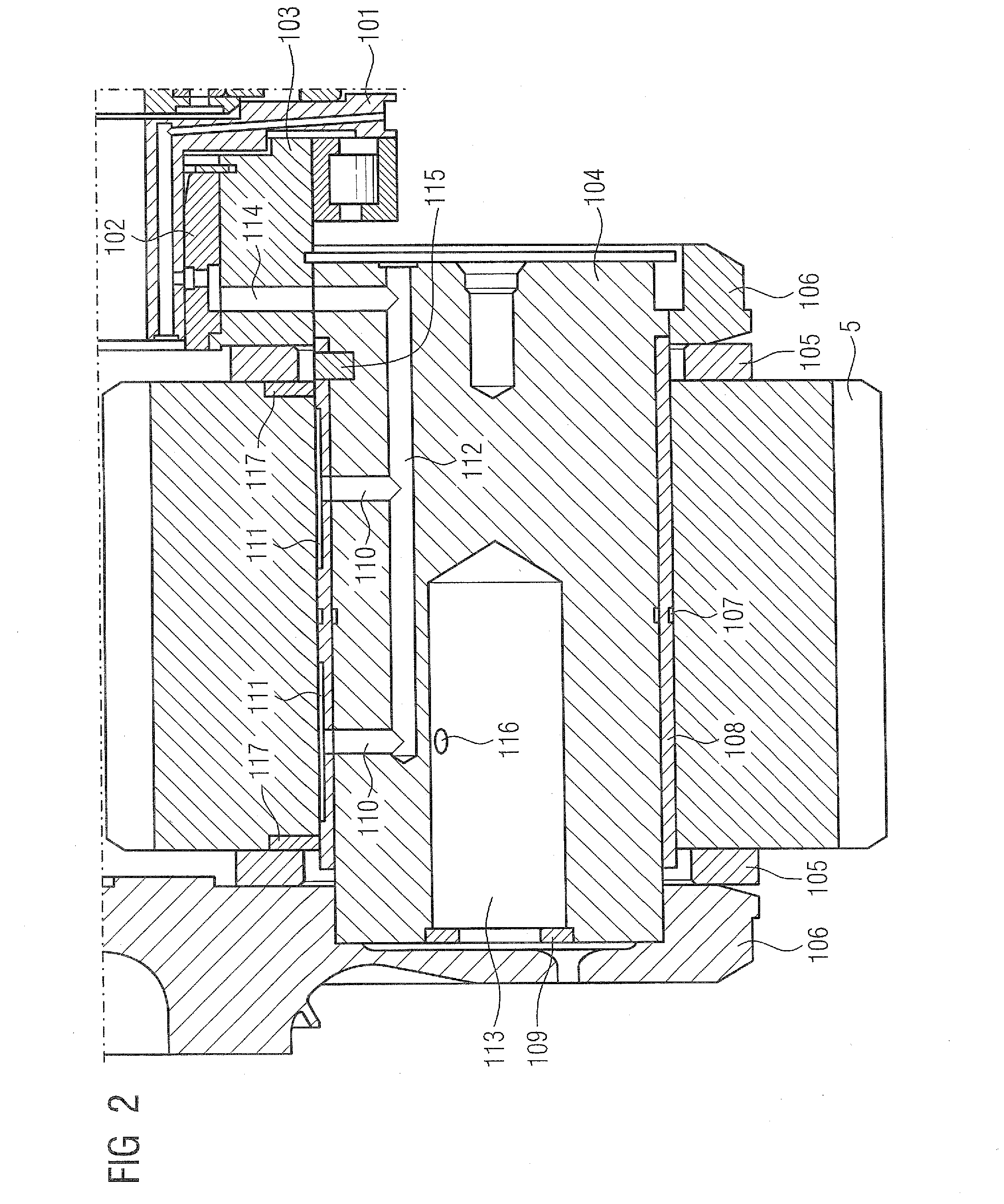
Plain bearing
Owner:DAIDO METAL CO LTD
Sliding rail coupling structure for hidden sliding track assembly
A sliding rail coupling structure includes an outer rail, an intermediate sliding rail slidable in and out of the outer rail and having two longitudinal sliding grooves at two sides, sliding bearing bushes coupled to and movable along the intermediate sliding rail, each sliding bearing bush holding a plurality of roller cylinders that are kept in contact between the top wall of the intermediate sliding rail and the top wall of the outer sliding rail and a plurality of rolling balls that are respectively kept in contact between the longitudinal sliding grooves of the intermediate sliding rail and the sidewalls of the outer sliding rail, a roller holder affixed to the intermediate sliding rail to support two support rollers that are respectively in contact with two bottom flanges of the outer sliding rail.
Owner:GSLIDE
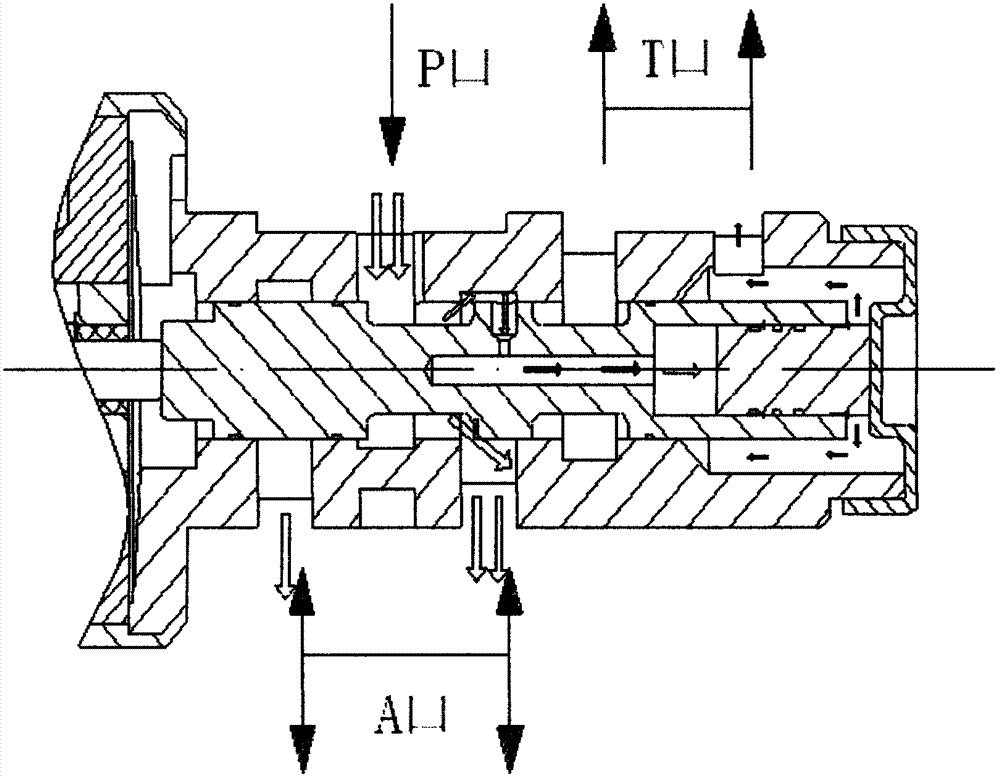
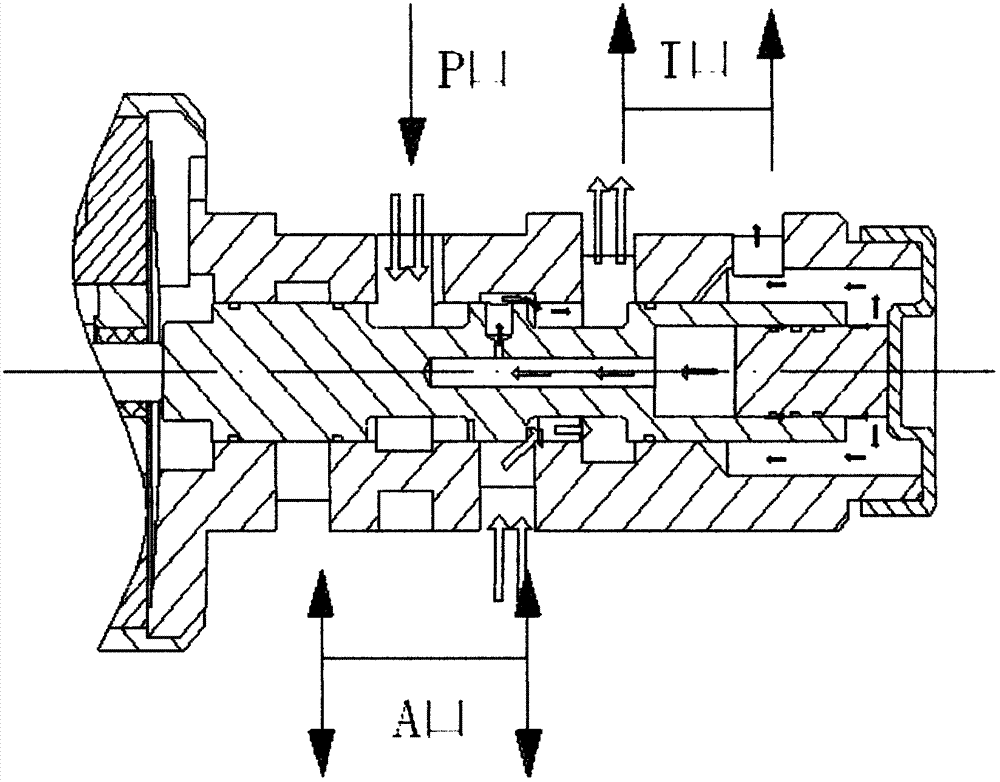
Two-position three-way inverse proportion decompression electromagnetic valve for AT (Automatic Transmission)
InactiveCN103032619ALight in massQuick responseOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMultiple way valvesAutomatic transmissionEngineering
The invention relates to a two-position three-way inverse proportion decompression electromagnetic valve for an AT (Automatic Transmission). The two-position three-way inverse proportion decompression electromagnetic valve is mainly formed by a main valve and a proportion electromagnet, wherein the main valve is formed by a valve body, a valve core which is positioned at the inner part of the valve body, a valve seat which is sleeved on the valve body and an inner valve core which is positioned at the inner part of the valve core and close to one side of the valve seat, and the proportion electromagnet is formed by a sliding bearing, a bearing seat, a pole shoe, an armature, a top rod, a stroke gasket, a stop iron, a spring seat, a regulating spring, a baffle plate, a regulating screw, a baffle plate cushion, a coil and a yoke iron. According to the two-position three-way inverse proportion decompression electromagnetic valve disclosed by the invention, the problems such as lower response speed, larger pressure fluctuation, short service life, large leakage rate and high manufacturing cost of an existing inverse proportion decompression electromagnetic valve for the AT are solved, and the two-position three-way inverse proportion decompression electromagnetic valve disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high response speed, small pressure fluctuation, long service life , small leakage rate, lower manufacturing cost and the like.
Owner:兰溪市中元贸易有限公司
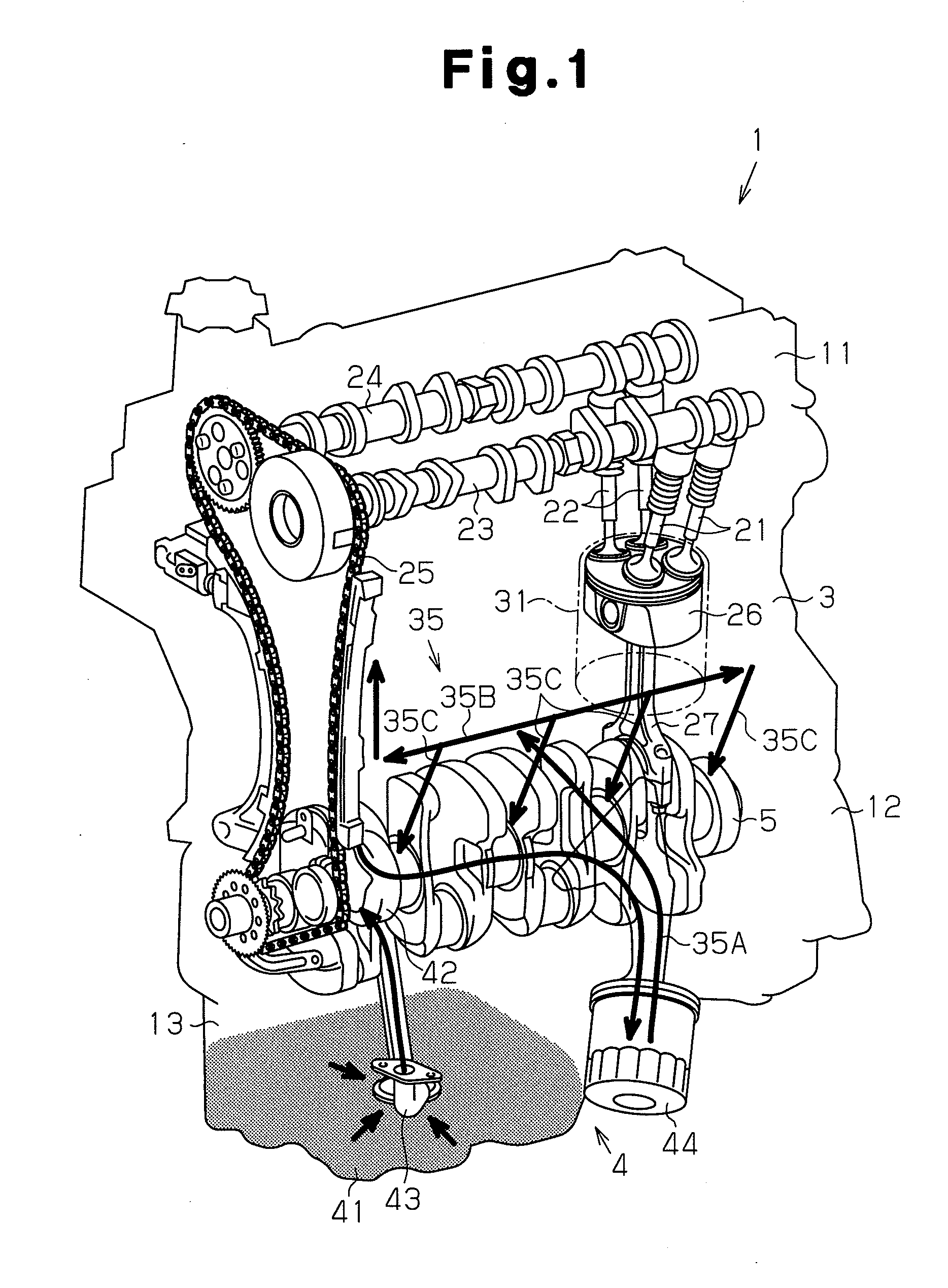
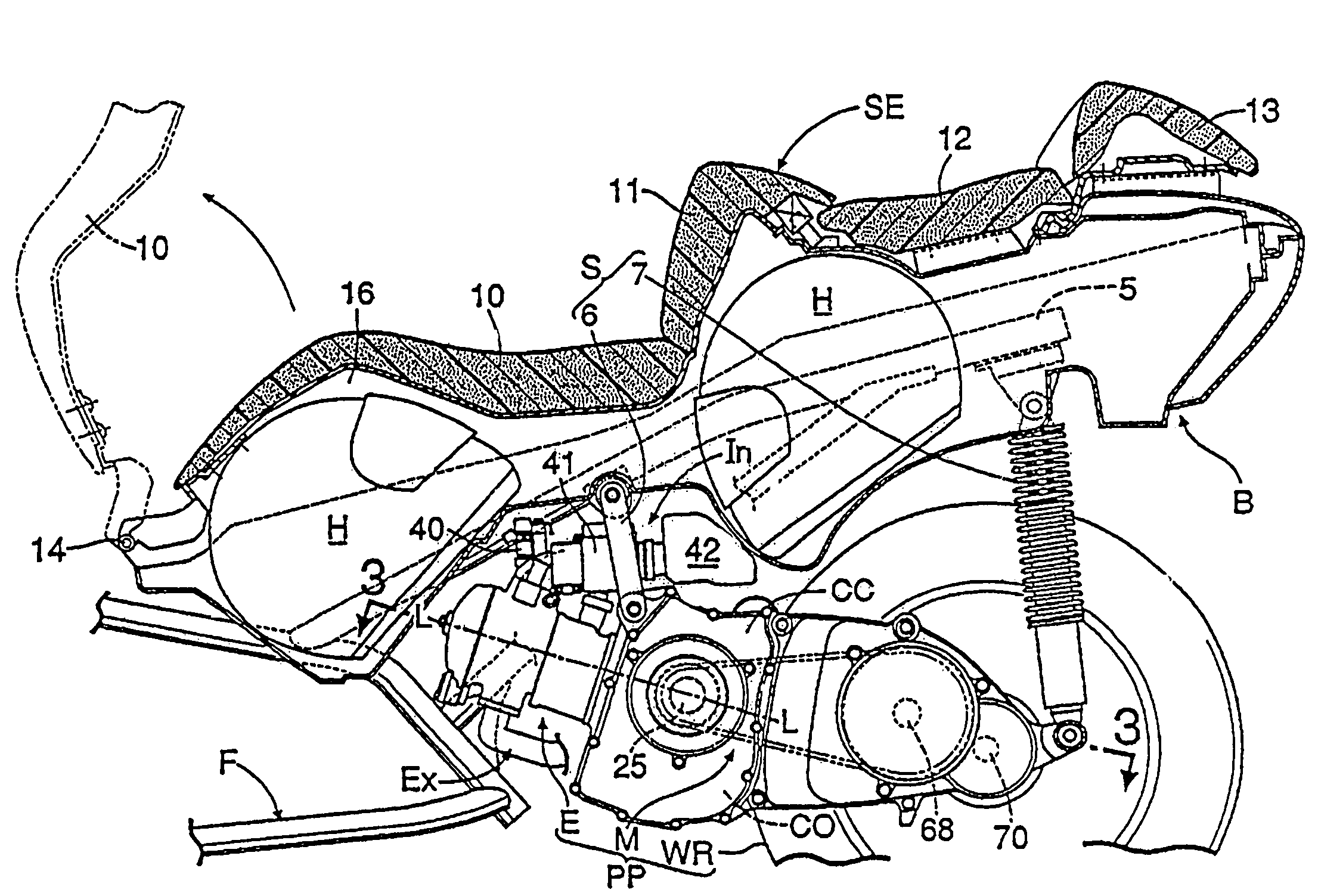
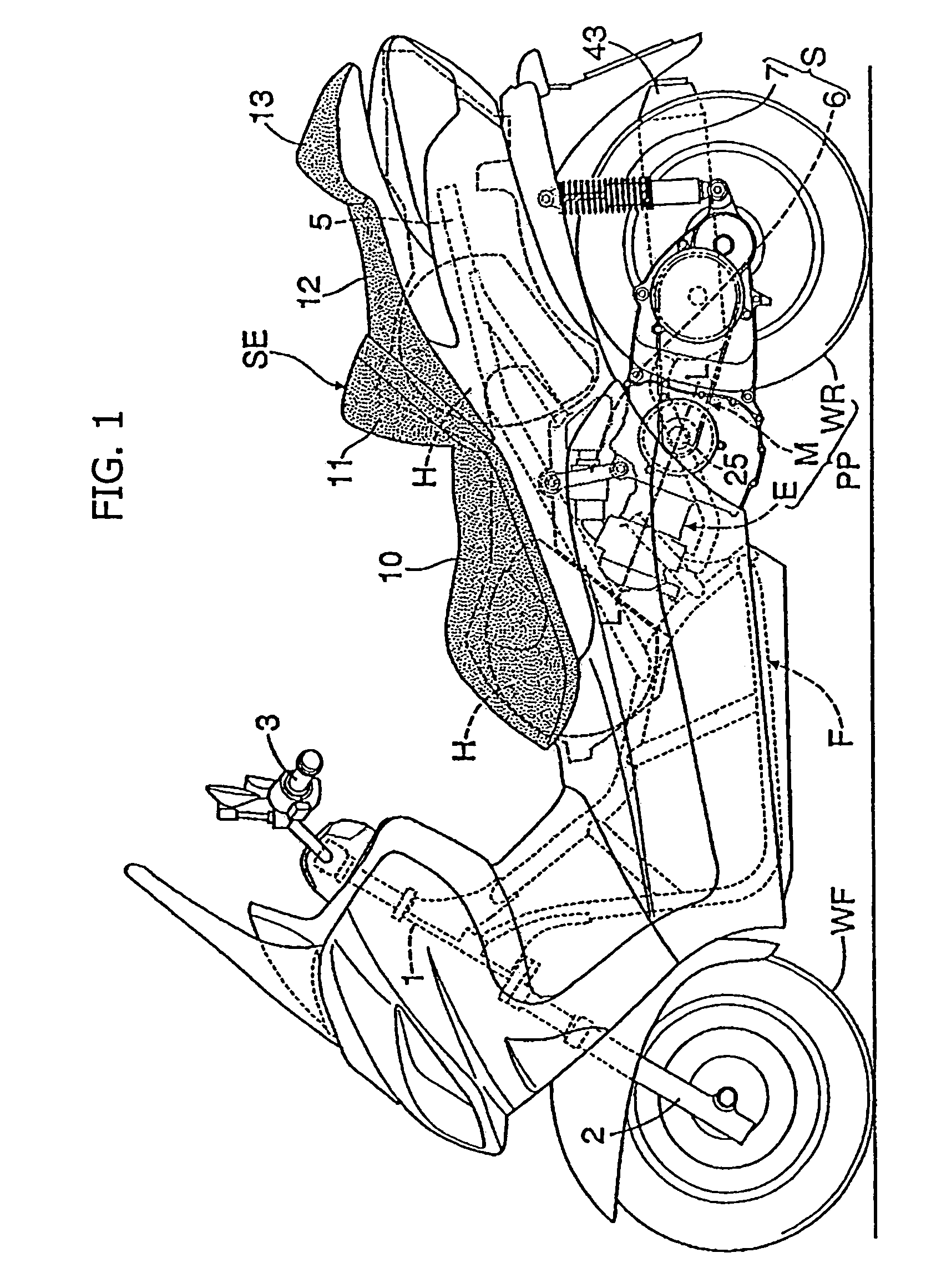
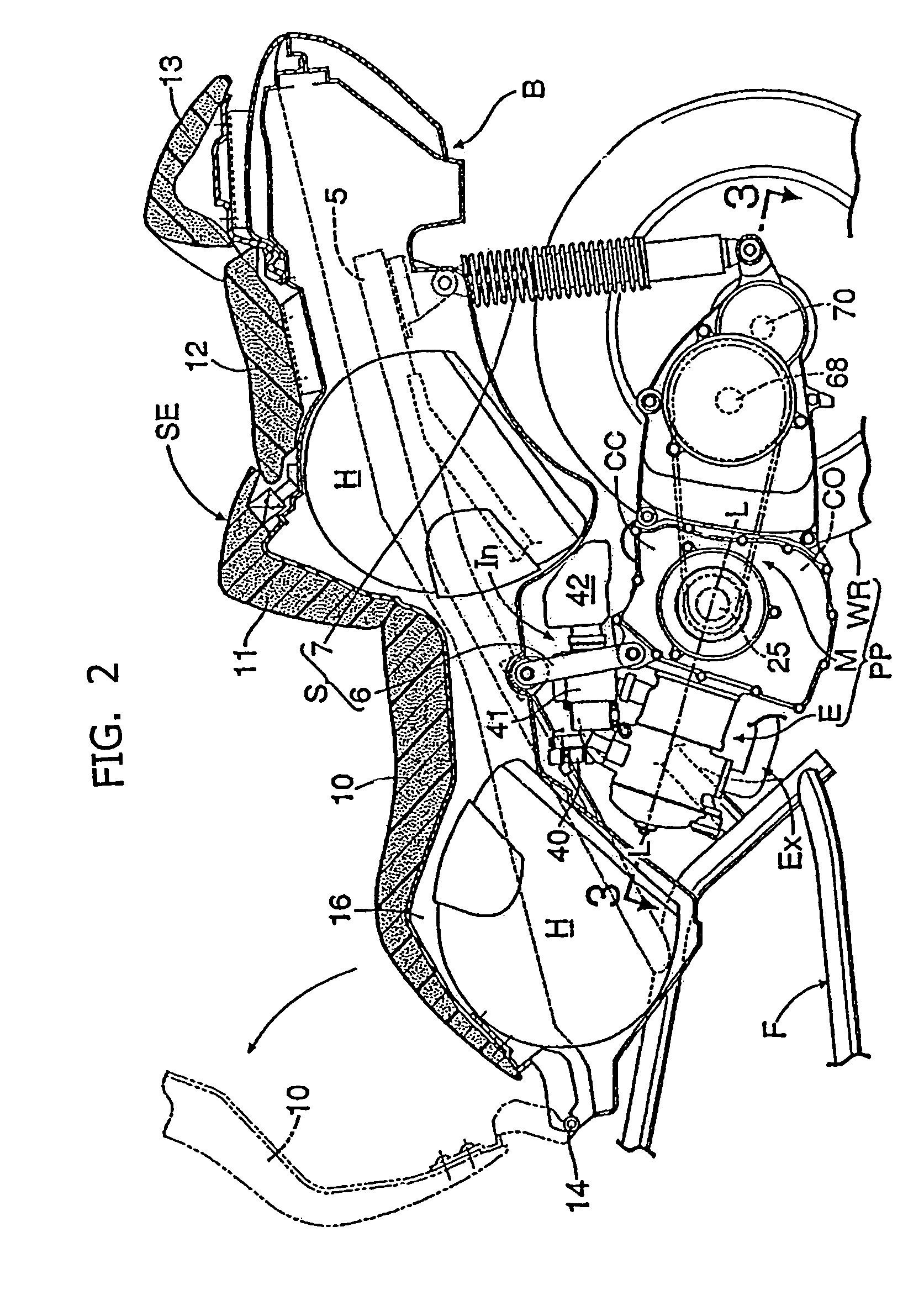
Engine configuration for a motorcycle
ActiveUS7334556B2Prevention of entrance of the lubricating oilEasy to processCasingsLubrication of auxillariesCrankcaseLubrication
A motorcycle is provided in which a seat and a storage box are arranged so as to be vertically stacked on each other in a rear portion of a body frame, and a pivotally mounted powertrain unit is suspended from the body frame under the storage box. The powertrain unit extends in the fore-and-aft direction of the body frame, and the engine has a crank chamber and a lubricant oil chamber provided separately from each other. A lubrication-oil passage structure for the engine is provided between each of a pair of journal bearing portions of a crankcase. The crankcase has an enclosed crank chamber and a crankshaft which is freely rotatably supported by the journal bearing portions with plain bearings. The journal bearing portions are provided with protrusion bosses for resisting entry of lubricating oil into the crank chamber from outside of the crankcase.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
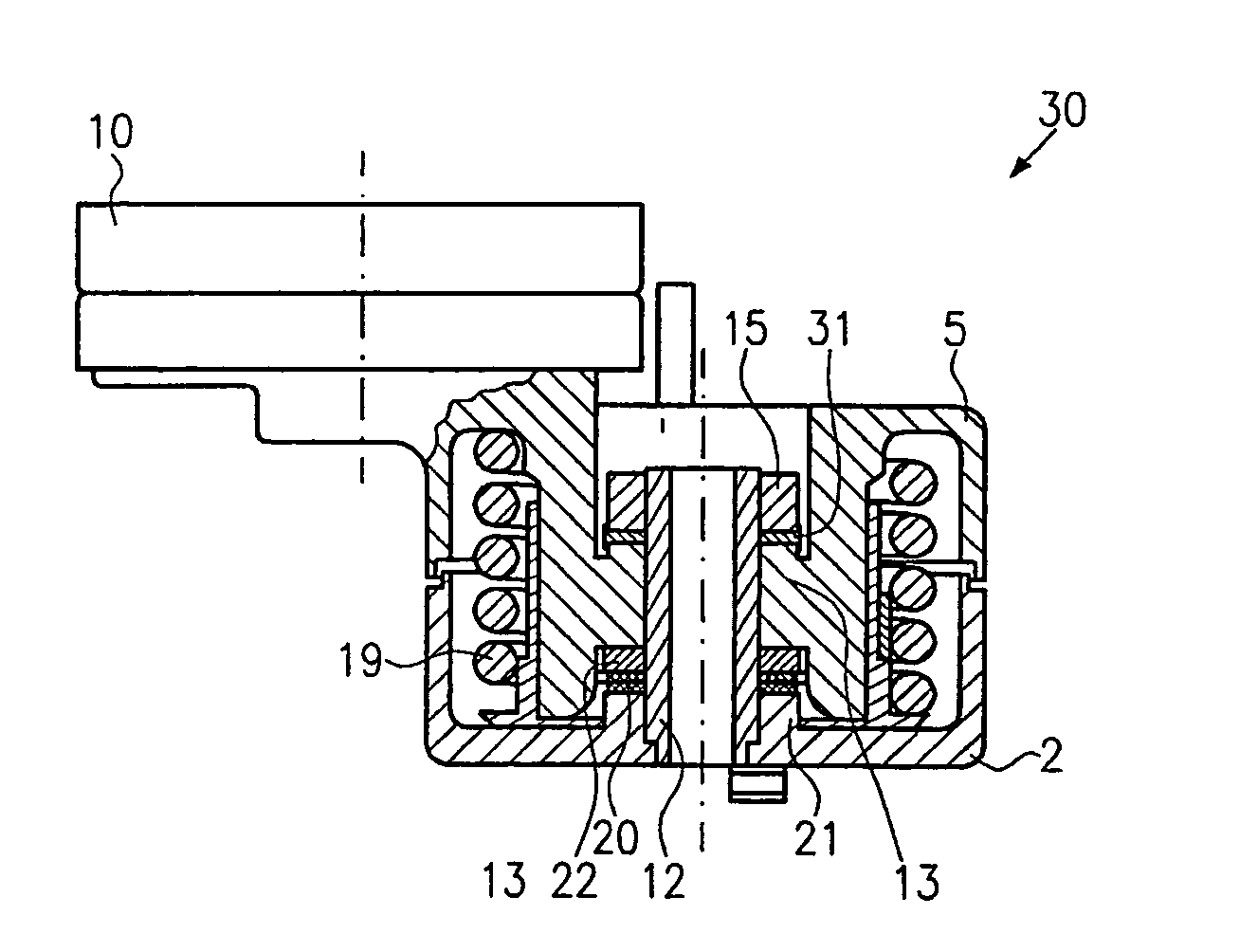
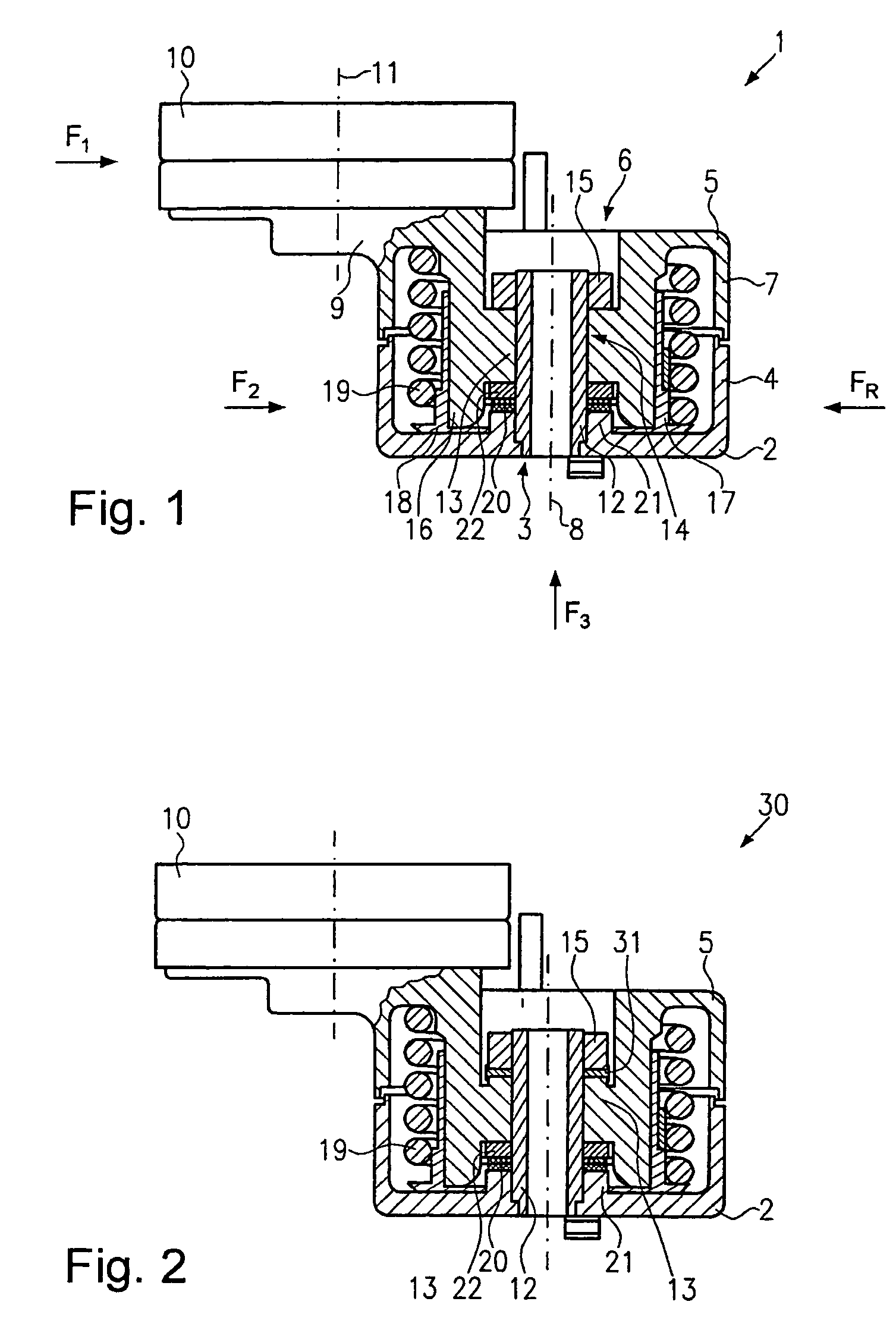
Belt tensioner
A belt tensioner with a retainer can be brought into contact with a belt via a belt support for applying a tensile force. The retainer is joined at a distance from the belt support to a radial plain bearing and it can be swivelled about the axis of rotation of the radial plain bearing, whereby the tensioning and swivel movements of the belt support occur under the action of a coil spring. For a belt tensioner of this type, which with a compact construction runs essentially wear-free, it is suggested that the retainer is subject to the action of a spring, which exerts a force (F3) essentially parallel to the axis of rotation on the retainer, the said force (F3) counteracting the force (F1) exerted by the belt on the retainer.
Owner:LITENS AUTOMOTIVE GMBH
Sliding structure for automotive engine
InactiveUS20050188942A1Reduce coefficient of frictionIncreased durabilityMolten spray coatingPiston ringsCarbon filmPiston ring
A sliding structure for an automotive engine includes a sliding member with a sliding portion and a lubricant applied to the sliding portion so that the sliding portion can make sliding contact with a counterpart member via the lubricant. The sliding member is either of a piston ring, a piston pin, a cam lobe, a cam journal, a plain bearing, a rotary vane and a timing chain. The sliding portion has a base made of a steel or aluminum material and a hard carbon film formed on the base to coat the sliding portion. The hard carbon film has a thickness of 0.3 to 2.0 μm, a Knoop hardness of 1500 to 4500 kg / mm2, a surface roughness Ry (μm) satisfying the following equation: Ry<{(0.75−Hk / 8000)×h+0.07 / 0.8}, where h is the thickness (μm) of the film; and Hk is the Knoop hardness (kg / mm2) of the film.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
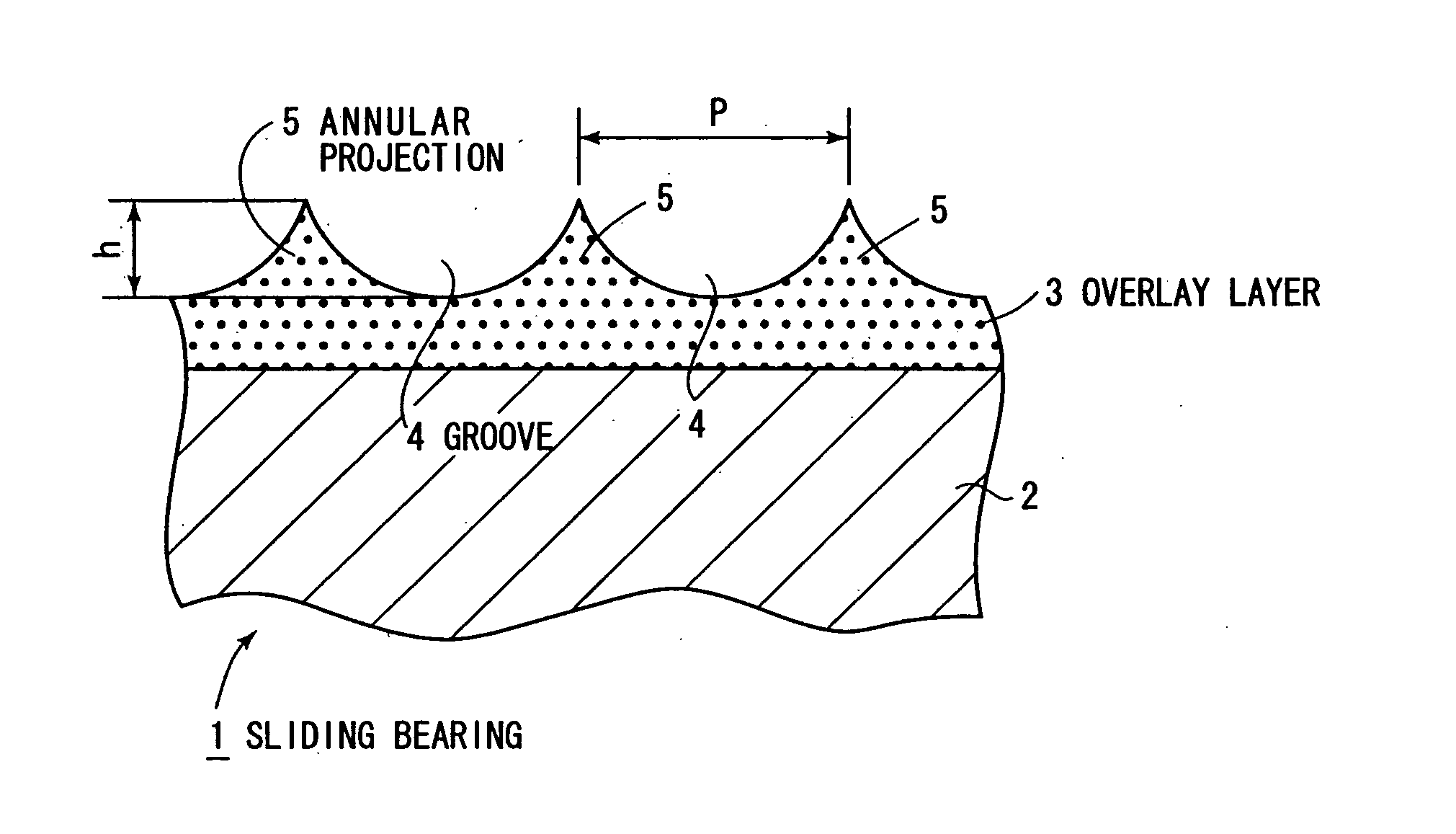
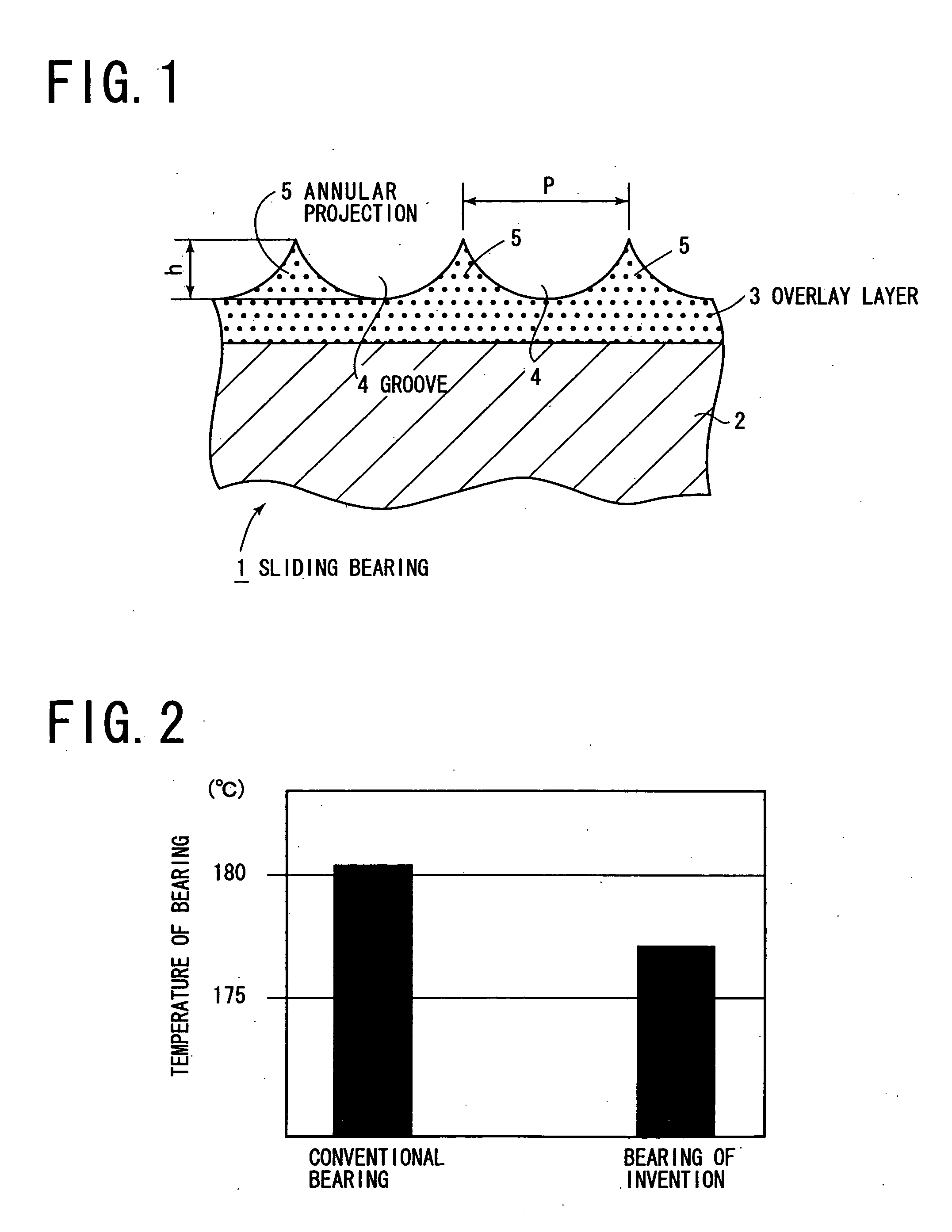
Sliding bearing
InactiveUS20060083451A1Good anti-occlusion performanceIncrease roughnessShaftsBearing componentsEngineeringAlloy
An overlay layer 3 comprising MoS2 as a solid lubricant and PAI resin as a binder resin is formed on a flattened surface of a bearing alloy layer 2, and a helical groove 4 and annular projections 5 are formed as an uneven configuration in and on the surface of the overlay layer. In accordance with the invention, a regular uneven configuration is formed on the surface of the overlay layer to allow a lubricant oil to be secured in recesses of the uneven configuration, allowing a seizure resistance to be improved. The bearing alloy layer is machined to have a flat surface having a fine roughness on its surface which represents a boundary with an overlay layer, whereby individual convex areas of the overlay layer are evenly subject to a plastic deformation, allowing the fitting property response of the sliding bearing to be improved.
Owner:TAIHO INDUSTRIES CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com