Genetic-algorithm-based trajectory planning optimization method for mobile mechanical arm
A technology for mobile robotic arms, trajectory planning, and applications in instrumentation, adaptive control, control/regulation systems, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
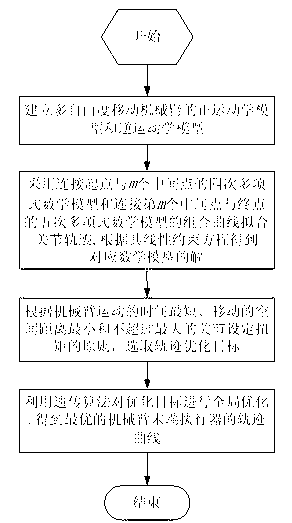
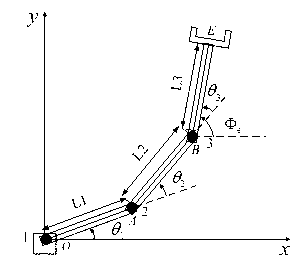
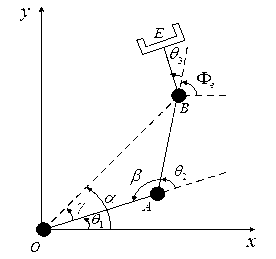
[0134] An optimization method for trajectory planning of mobile manipulator based on genetic algorithm. This example figure 2 Shown is a three-degree-of-freedom mobile robotic arm consisting of a fixed link and three movable links that move in a plane. All connecting rods are connected by rotating joints, and the joint axes are perpendicular to the plane of the connecting rods.
[0135] Since the mobile robot performs tasks by moving the point E of the end effector, in order to describe the position, a coordinate system xoy is introduced, where the x axis is parallel to the base connecting rod, the coordinate origin coincides with the first joint, and the position of the end effector is represented by Coordinates (x e ,y e )express. For the convenience of description, the length of the connecting rod is specified, that is, the distance between adjacent joint axes, expressed as L 1 , L 2 and L 3 , point O, point A and point B are located on the three joint axes respecti...
Embodiment 2
[0254] An optimization method for trajectory planning of mobile manipulator based on genetic algorithm. This embodiment is a mobile mechanical arm with one degree of freedom, which is composed of a fixed link and a movable link moving in a plane. All connecting rods are connected by rotating joints, and the joint axes are perpendicular to the plane of the connecting rods.
[0255] Since the mobile robot performs tasks by moving the point E of the end effector, in order to describe the position, a coordinate system xoy is introduced, where the x axis is parallel to the base connecting rod, the origin of the coordinates coincides with the first joint, and the position of the end effector is represented by Coordinates (x e ,y e )express. For the convenience of description, the length of the connecting rod is specified as the distance between adjacent joint axes, expressed as L 1 , assuming that the connecting rod 1 fixed on the base connecting rod (connecting rod 0) is driven...
Embodiment 3
[0282] An optimization method for trajectory planning of mobile manipulator based on genetic algorithm. This embodiment is an eight-degree-of-freedom mobile robot arm, which is composed of a fixed link and eight movable links moving in a plane. All connecting rods are connected by rotating joints, and the joint axes are perpendicular to the plane of the connecting rods.
[0283] Since the mobile robot performs tasks by moving the point E of the end effector, in order to describe the position, a coordinate system xoy is introduced, where the x axis is parallel to the base connecting rod, the origin of the coordinates coincides with the first joint, and the position of the end effector is represented by Coordinates (x e ,y e )express. For the convenience of description, the length of the connecting rod is specified, that is, the distance between adjacent joint axes, expressed as L and L respectively 2 ,...,L 8 , assuming that the connecting rod 1 fixed on the base connectin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com