Patents
Literature
353 results about "Articularis genus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
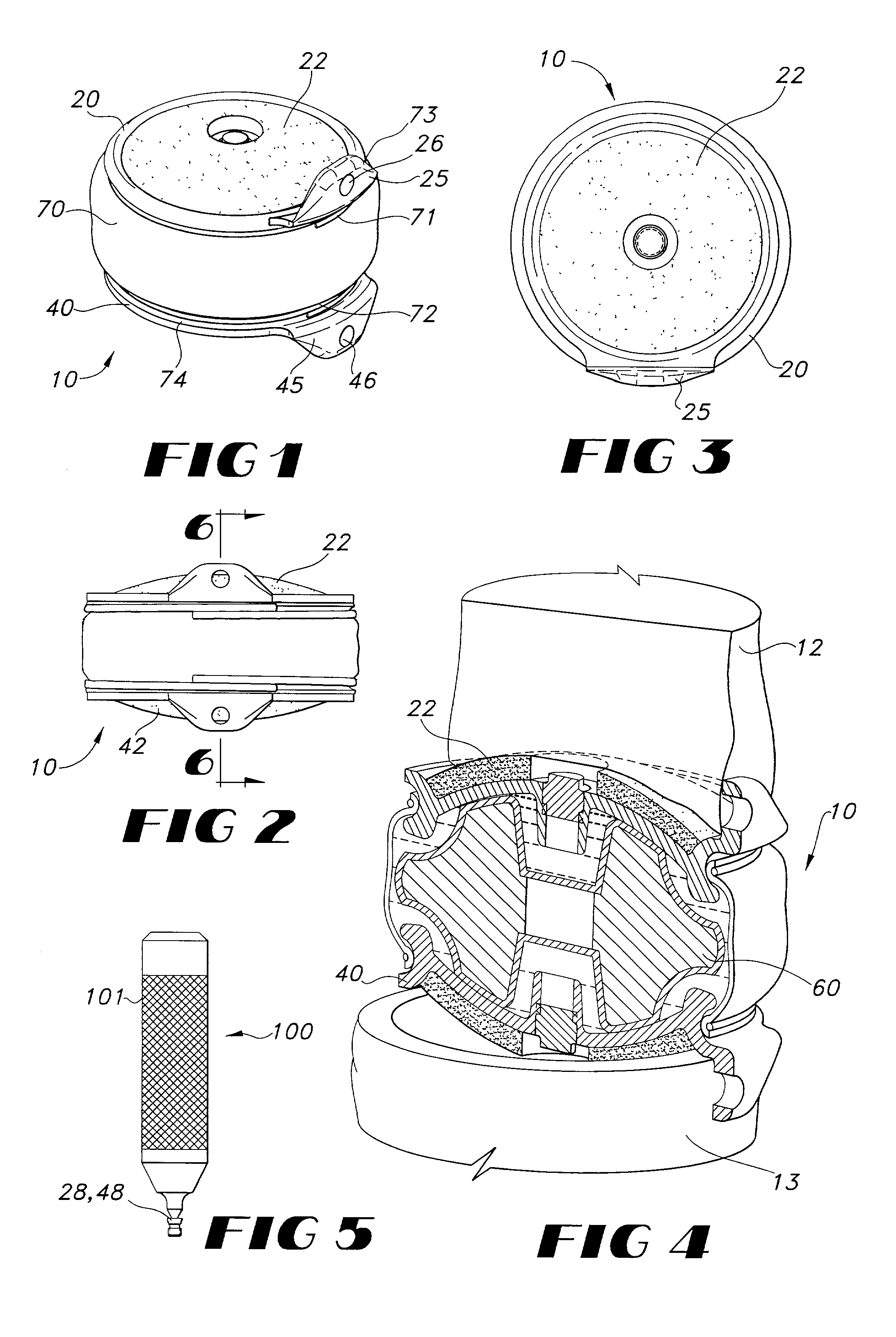
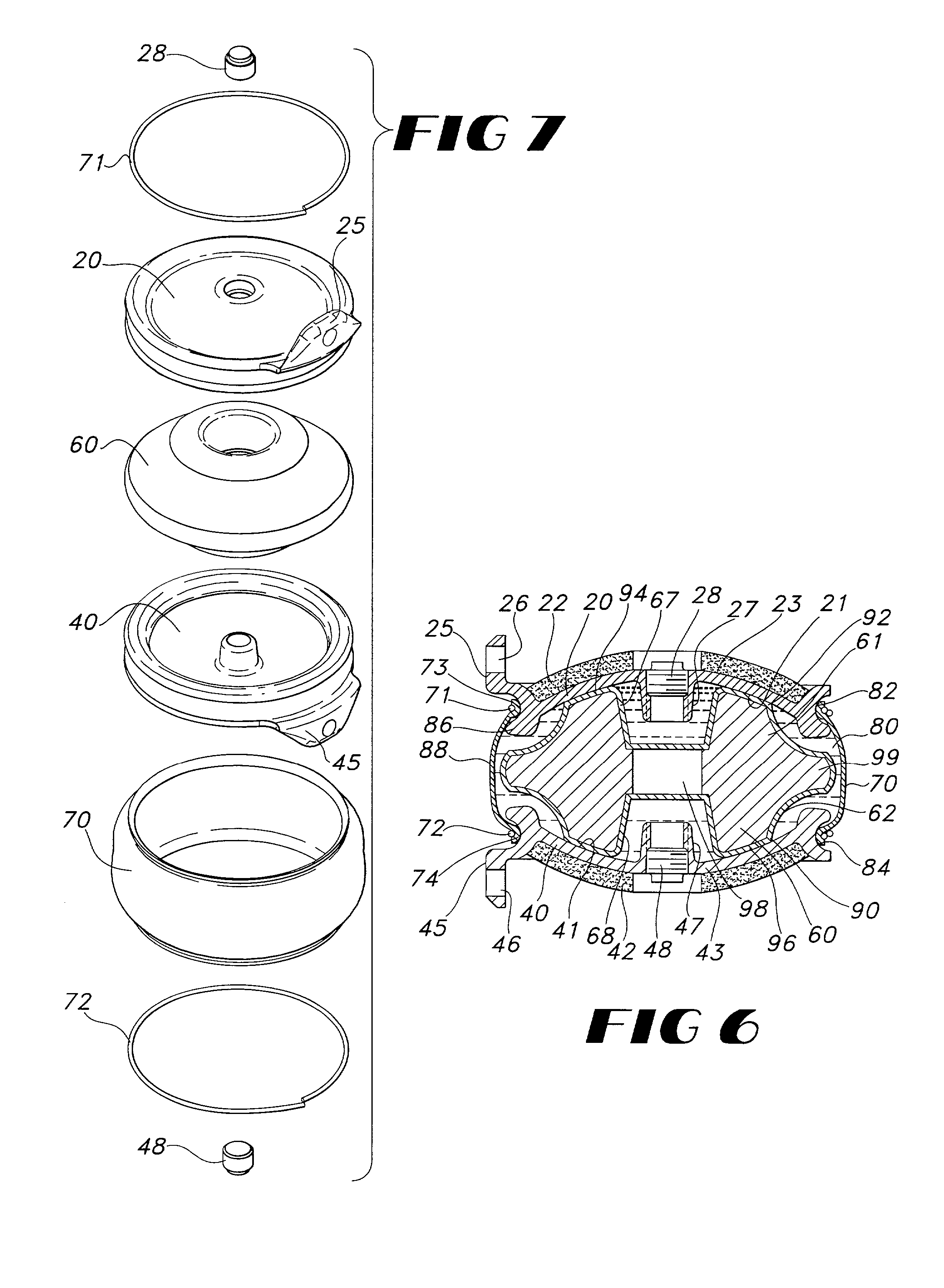
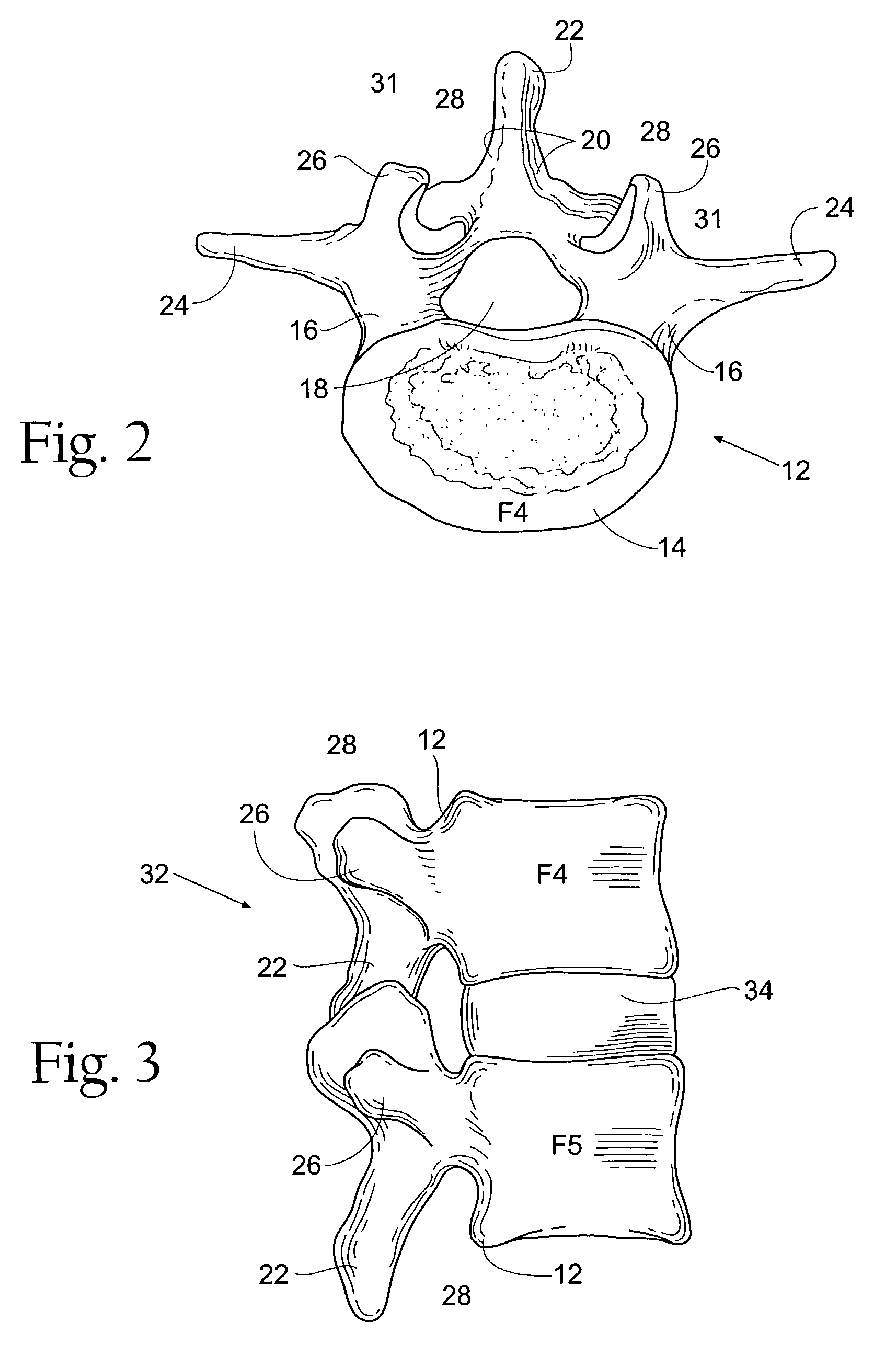
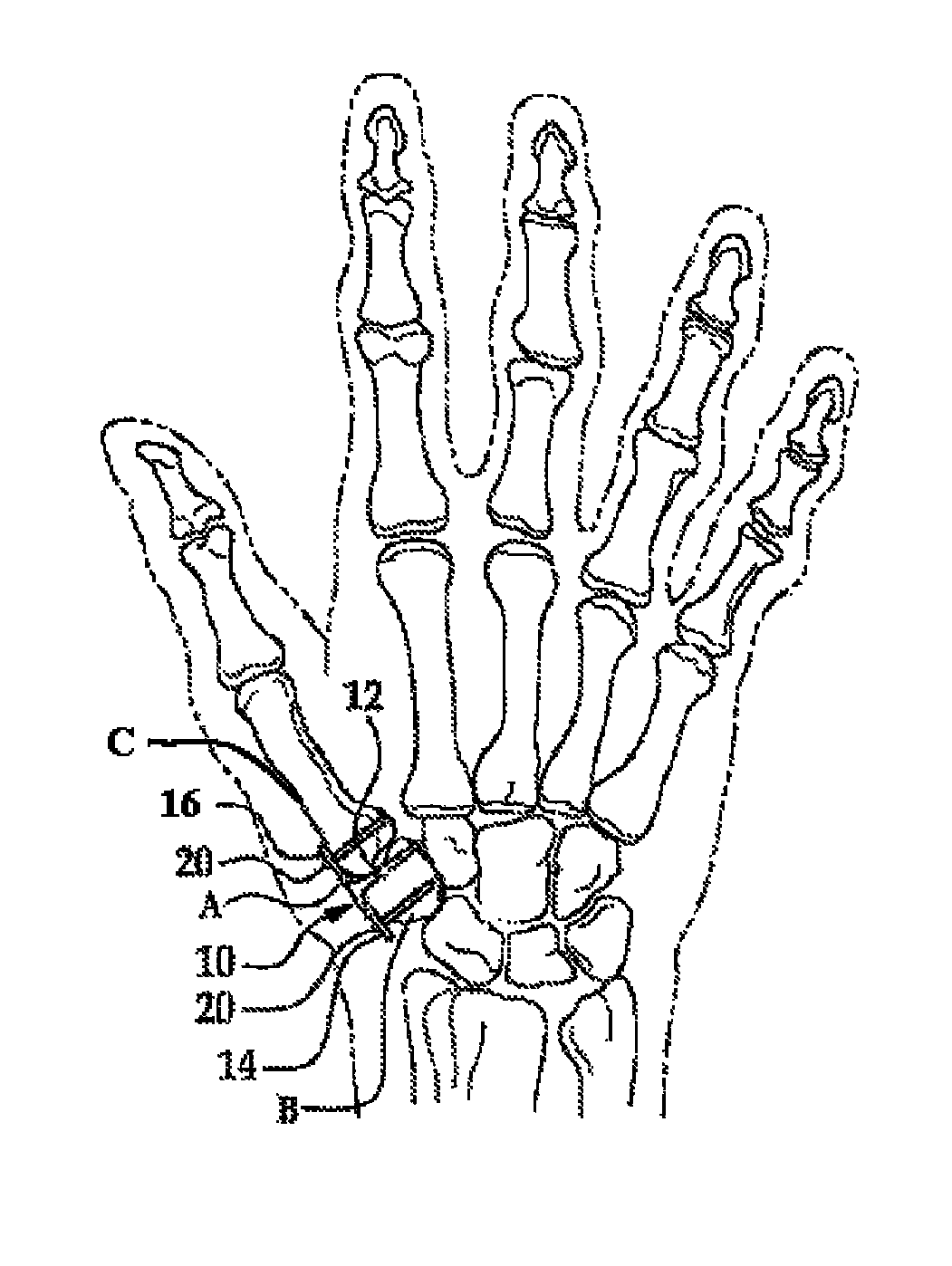
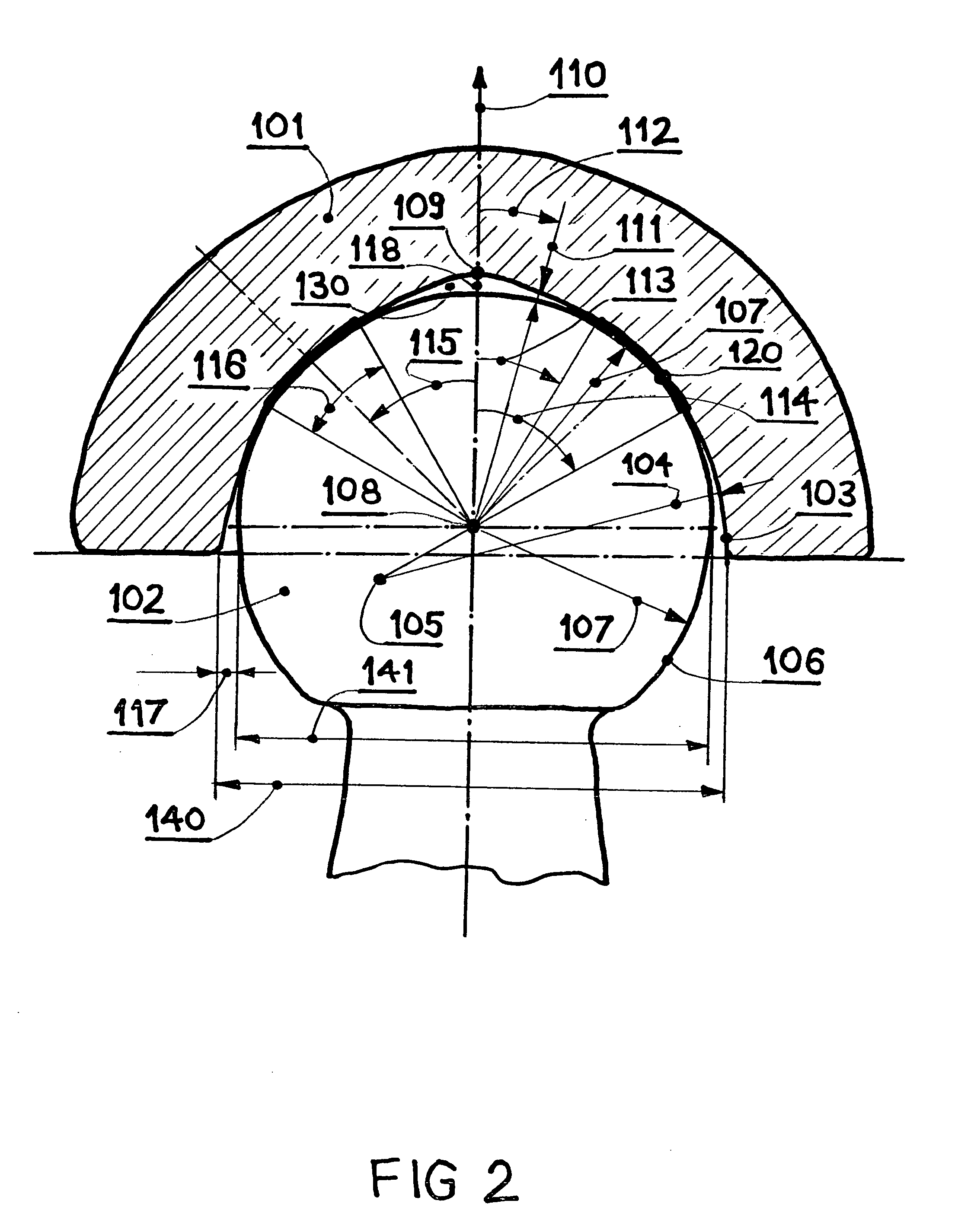
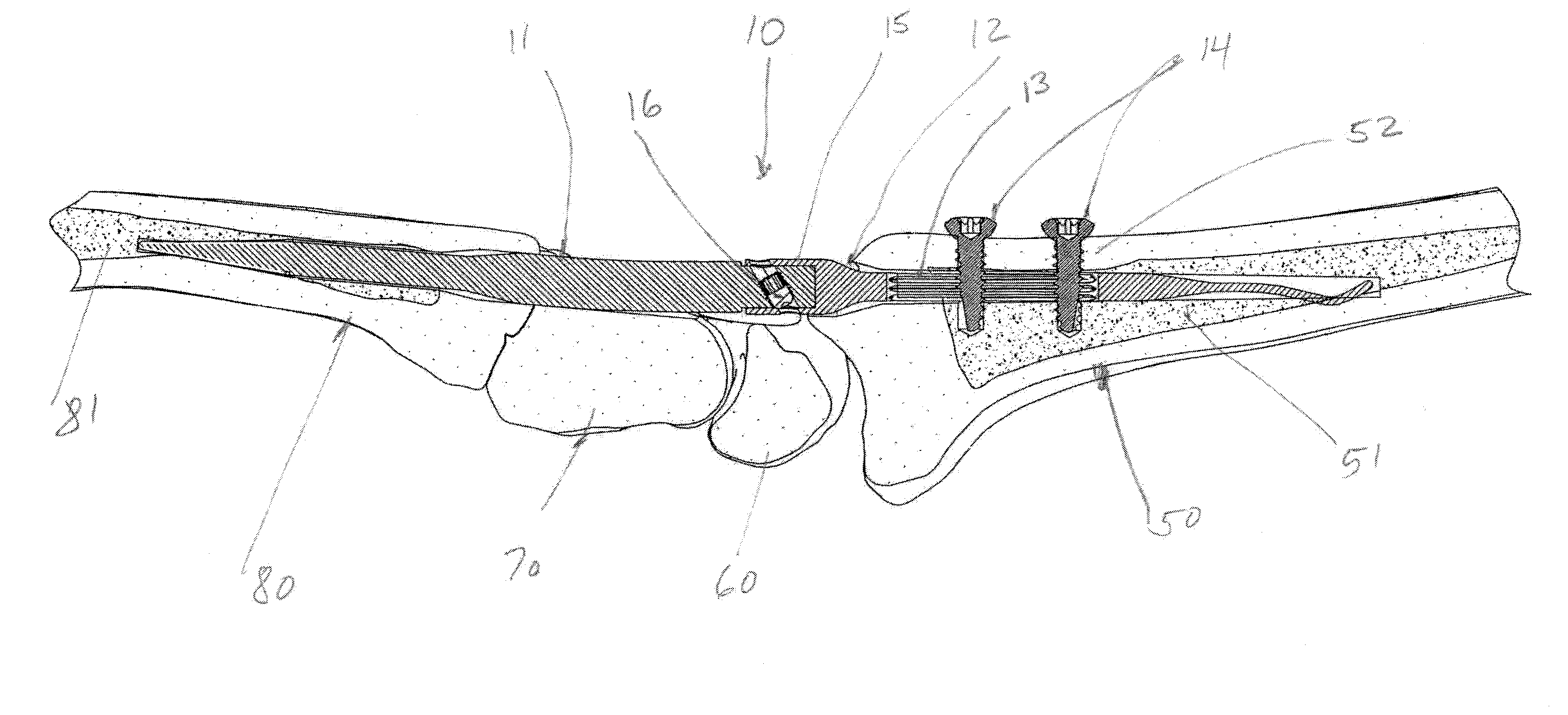
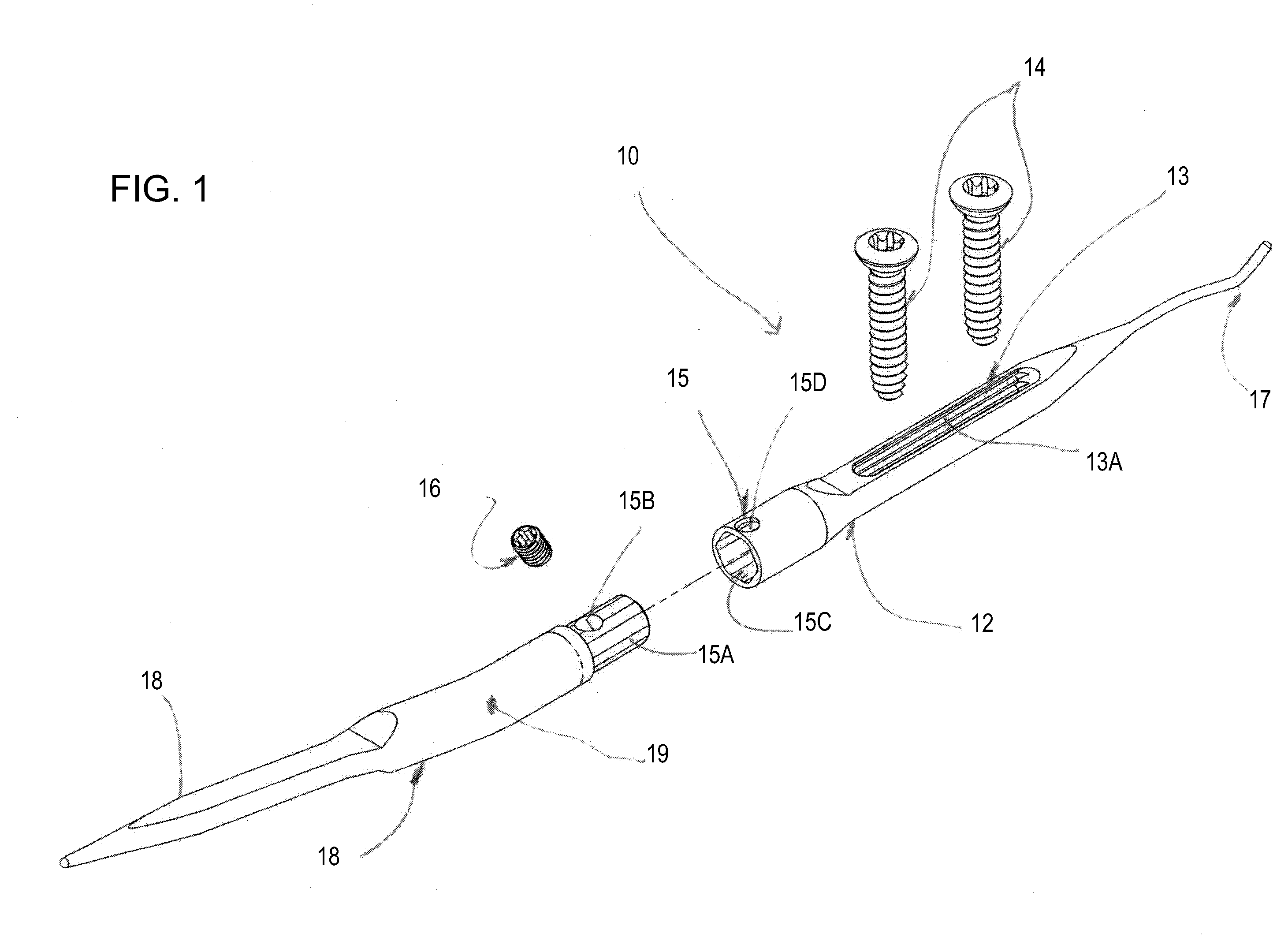
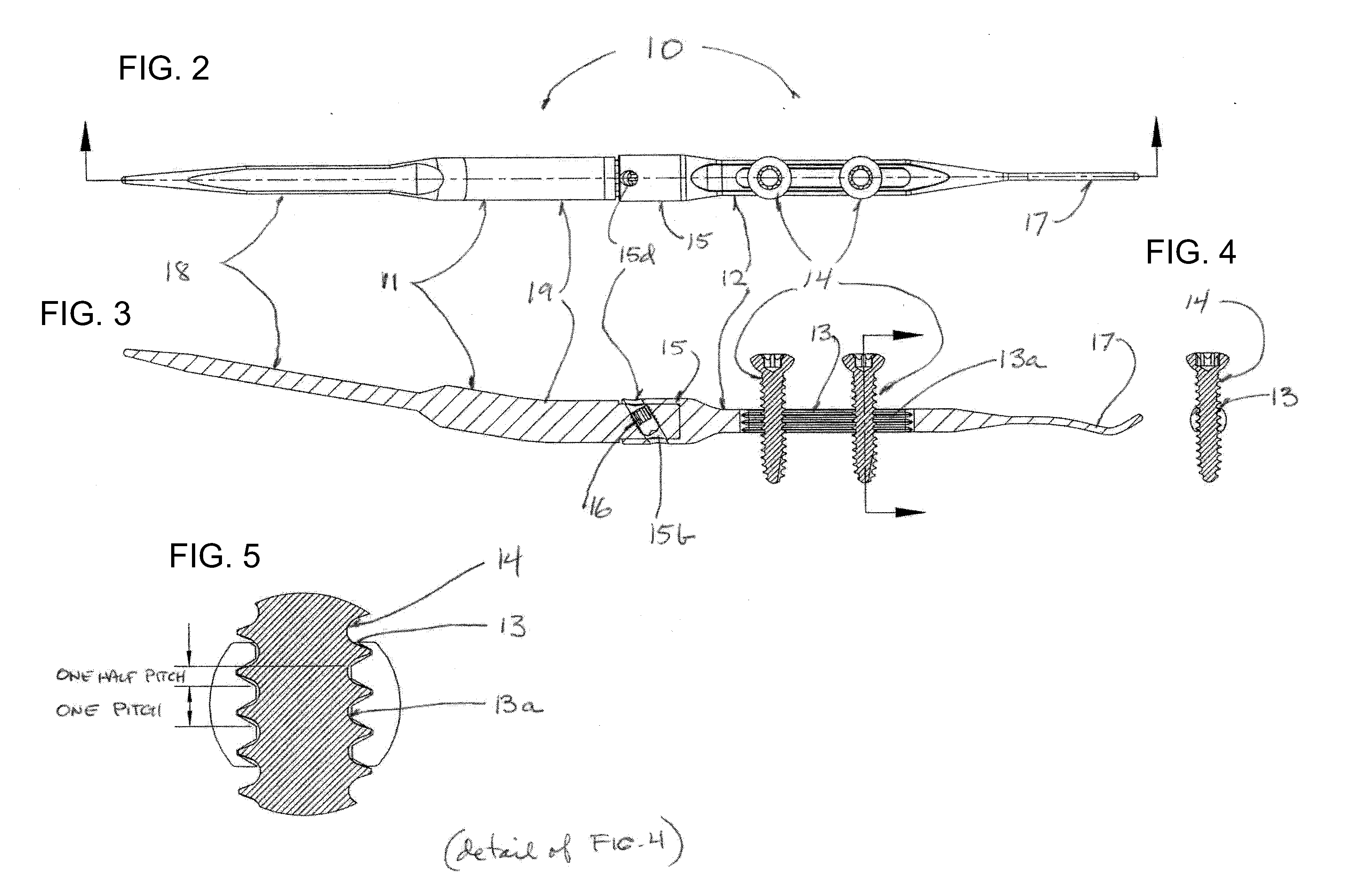
Implantable joint prosthesis
InactiveUS20020035400A1Improve wear resistanceImprove tribological propertiesDiagnosticsJoint implantsRange of motionIntervertebral disc
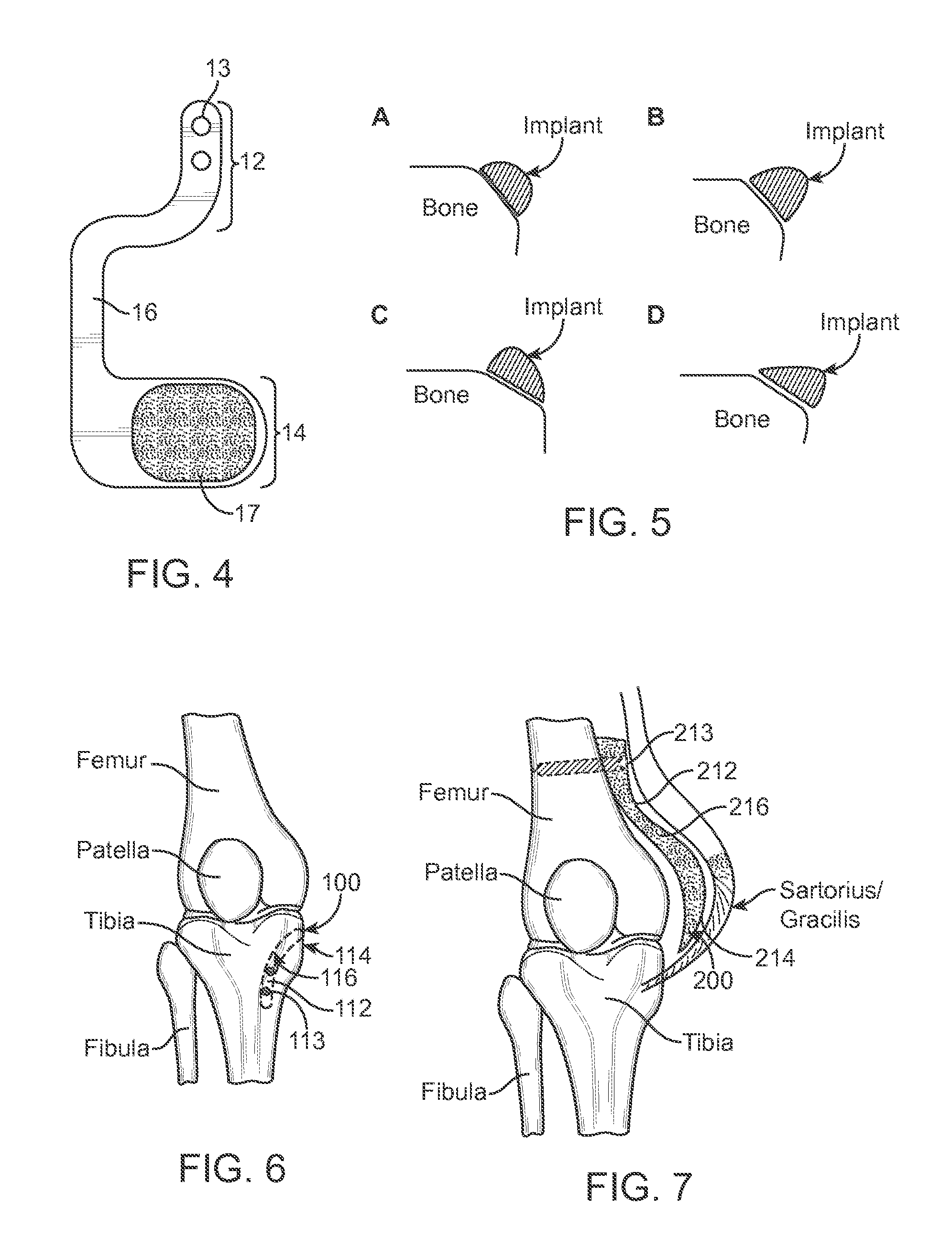
The invention relates to a surgical implant that provides an artificial diarthroidal-like joint, suitable for use in replacing any joint, but particularly suitable for use as an intervertebral disc endoprosthesis. The invention contains two rigid opposing shells, each having an outer surface adapted to engage the surfaces of the bones of a joint in such a way that the shells are immobilized by friction between their outer surfaces and the surfaces of the bone. These outer surfaces are sufficiently rough that large frictional forces strongly resist any slippage between the outer surface and the bone surfaces in the joint. They may be convex, and when inserted into a milled concavity, are immediately mechanically stable. Desirably, the outer surfaces of the shells are adapted to allow for bony ingrowth, which further stabilizes the shells in place. The inner surfaces of the shells are relatively smooth, and adapted to slide easily across a portion of the outer surface of a central body disposed between the shells. The central body has a shape that cooperates with the shape of the inner surface of the shell so as to provide a range of motion similar to that provided by a healthy joint. A flexible sheath extends between edges of the opposing shells. The inner surface of this sheath, together with the inner surfaces of the rigid shells, defines a cavity encasing the central body. At least a portion of this cavity is filled with a fluid lubricant, further decreasing the frictional force between inner surfaces of the shell and the surface of the central body.
Owner:SPINAL DYNAMICS CORP
Implantable joint prosthesis
ActiveUS20020128715A1Increased durabilityImprove stabilityDiagnosticsJoint implantsIntervertebral discSurgical implant
The invention relates to a surgical implant that provides an artificial diarthroidal-like joint, suitable for use in replacing any joint, but particularly suitable for use as an intervertebral disc endoprosthesis. The invention contains two rigid opposing shells, each having an outer surface adapted to engage the surfaces of the bones of a joint in such a way that the shells are immobilized by friction between their outer surfaces and the surfaces of the bone. These outer surfaces are sufficiently rough that large frictional forces strongly resist any slippage between the outer surface and the bone surfaces in the joint. They may be convex, and when inserted into a milled concavity, are immediately mechanically stable. Desirably, the outer surfaces of the shells are adapted to allow for bony ingrowth, which further stabilizes the shells in place. The inner surfaces of the shells are relatively smooth, and adapted to slide easily across a portion of the outer surface of a central body disposed between the shells. The central body has a shape that cooperates with the shape of the inner surface of the shell so as to provide a range of motion similar to that provided by a healthy joint. A flexible sheath extends between edges of the opposing shells. The inner surface of this sheath, together with the inner surfaces of the rigid shells, defines a cavity encasing the central body. At least a portion of this cavity is filled with a fluid lubricant, further decreasing the frictional force between inner surfaces of the shell and the surface of the central body.
Owner:COMPANION SPINE LLC
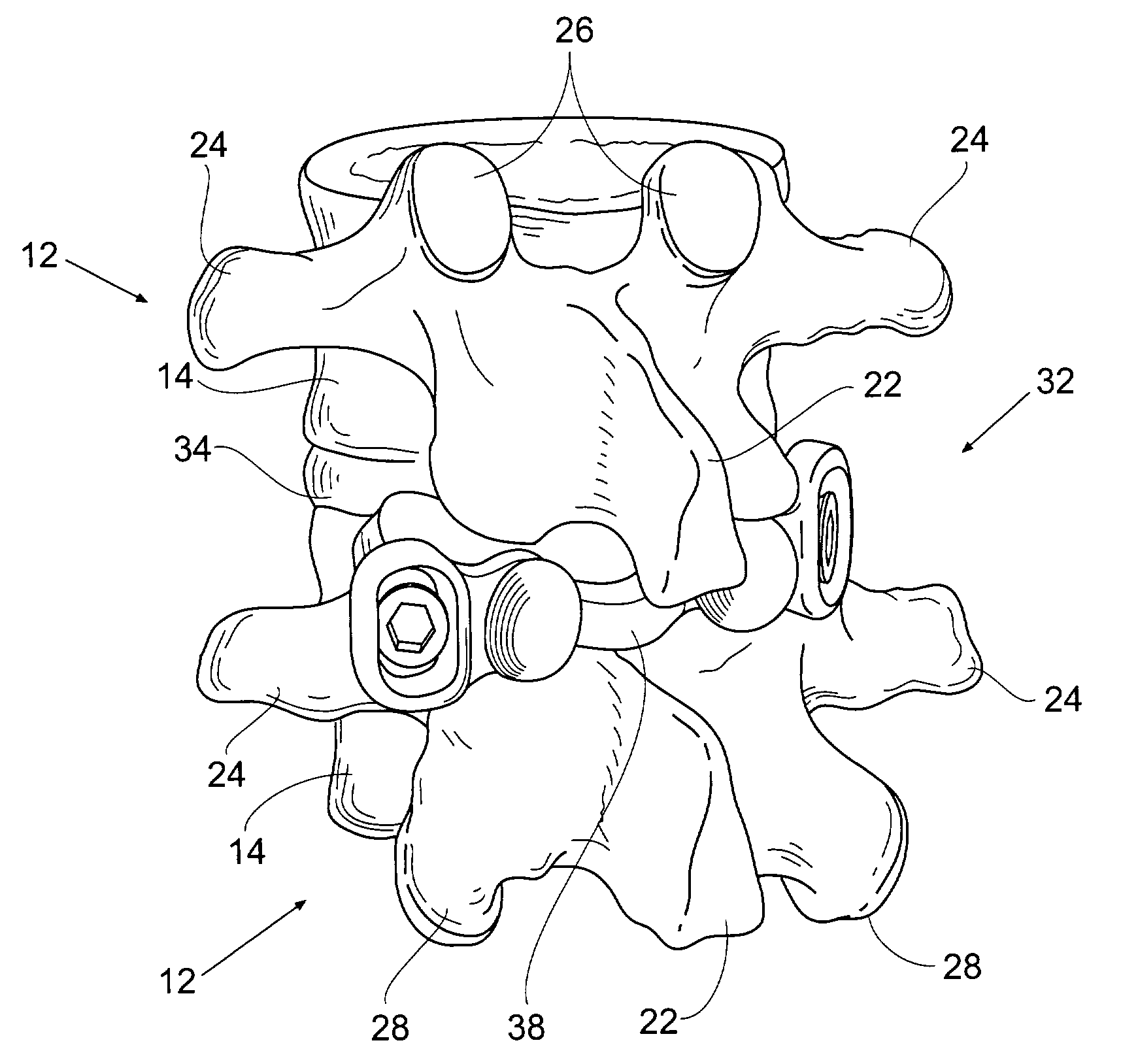
Prostheses, systems and methods for replacement of natural facet joints with artificial facet joint surfaces
InactiveUS6974478B2Desired range of mobilityLessen and alleviate spinal painSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisArticular surfacesSpinal column
Cephalad and caudal vertebral facet joint prostheses and methods of use are provided. The prostheses provide an artificial facet joint structure including an artificial articular configuration unlike the preexisting articular configuration. The radii and material stress values of the prostheses are configured to sustain contact stress. The cephalad prosthesis provides for posterior-anterior adjustment. Both prostheses permit lateral adjustment and adjustment to accomodate interpedicle distance. Further, the prostheses may be customized to provide a pre-defined lordotic angle and a pre-defined pedicle entry angle.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Modular knee prosthesis
A modular prosthetic knee system used to replace the natural knee. The system includes a femoral knee prosthesis and a tibial knee prosthesis. Both prostheses are formed of modular components that are connectable in-vivo to form the prosthetic knee system. The femoral knee prosthesis includes two separate components, a lateral condyle and medial condyle; and the tibial knee prosthesis includes a multiple separate components, a medial baseplate, a lateral baseplate, a medial insert, and a lateral insert. The medial and lateral baseplate are connectable to form a complete baseplate with the medial and lateral inserts connectable to the complete baseplate.
Owner:ZIMMER TECH INC
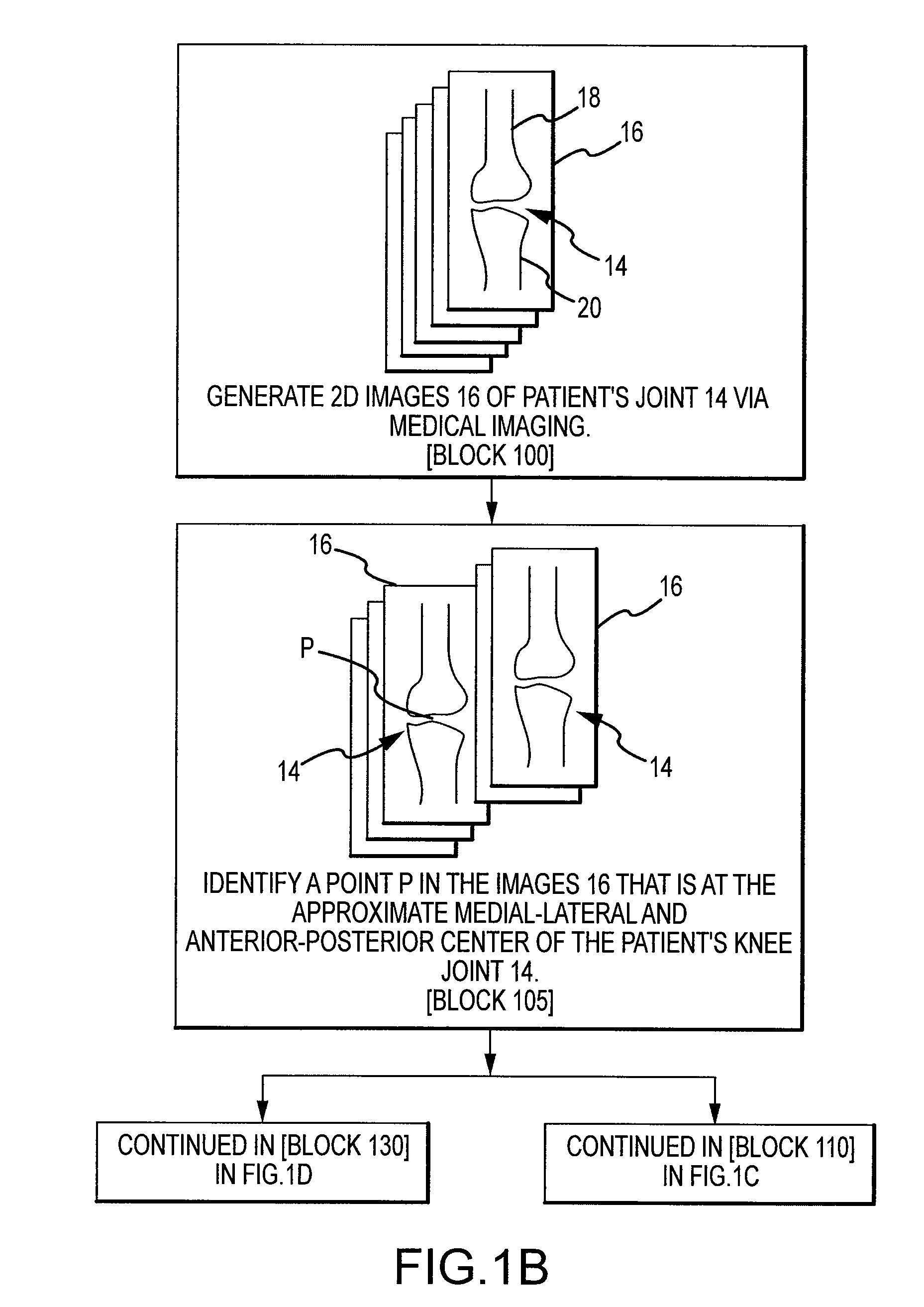
System and method for manufacturing arthroplasty jigs
ActiveUS20090157083A1Facilitate arthroplasty implantsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputerised tomographsBone formingSacroiliac joint
Disclosed herein is a method of computer generating a three-dimensional surface model of an arthroplasty target region of a bone forming a joint. The method may include: generating two-dimensional images of at least a portion of the bone; generating an open-loop contour line along the arthroplasty target region in at least some of the two-dimensional images; and generating the three-dimensional model of the arthroplasty target region from the open-loop contour lines.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Methods of stabilizing the sacroiliac joint
ActiveUS20090099610A1Not easy to relative displacementPermit fusionSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSacrum boneSacro-iliac joint
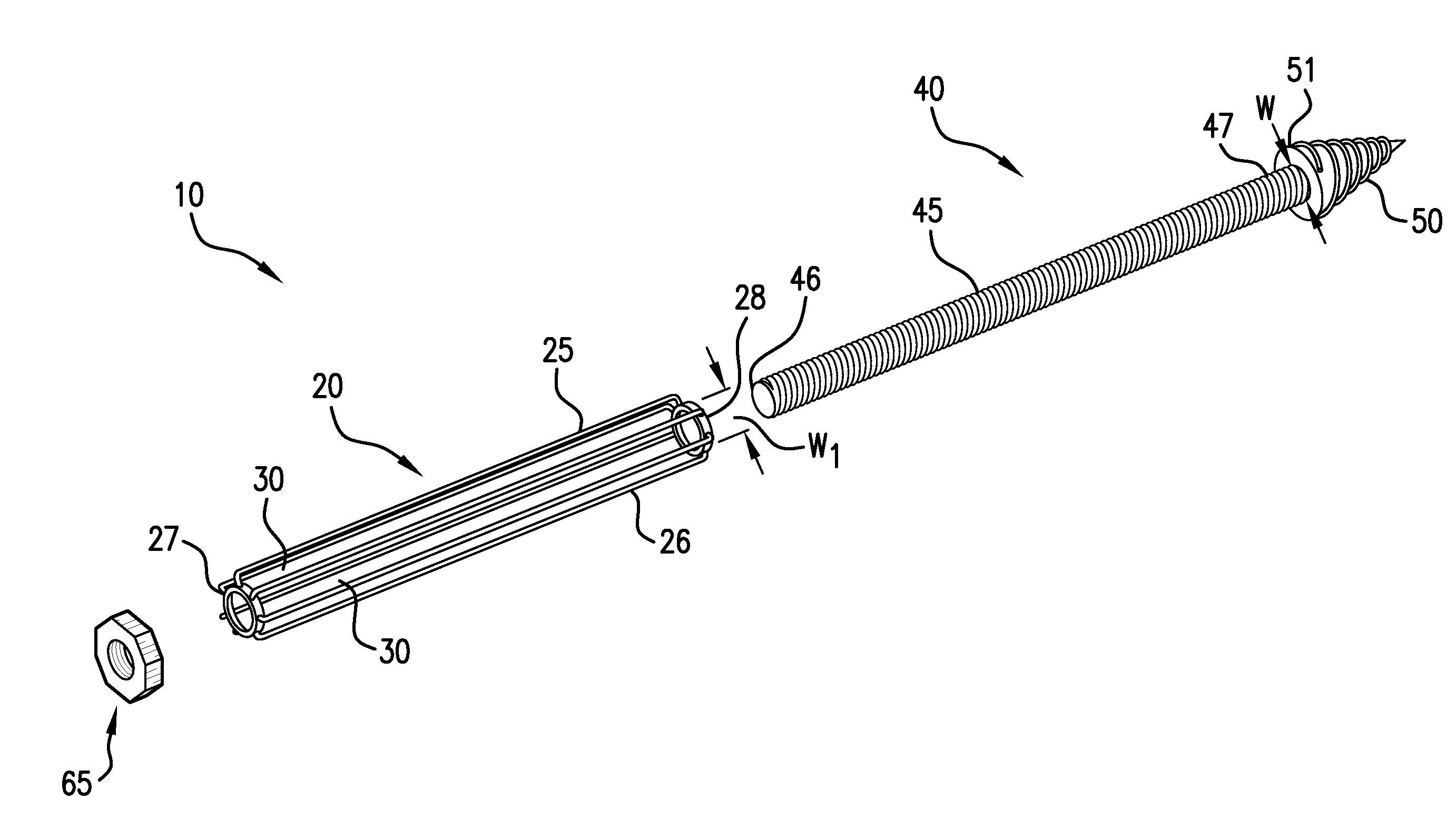
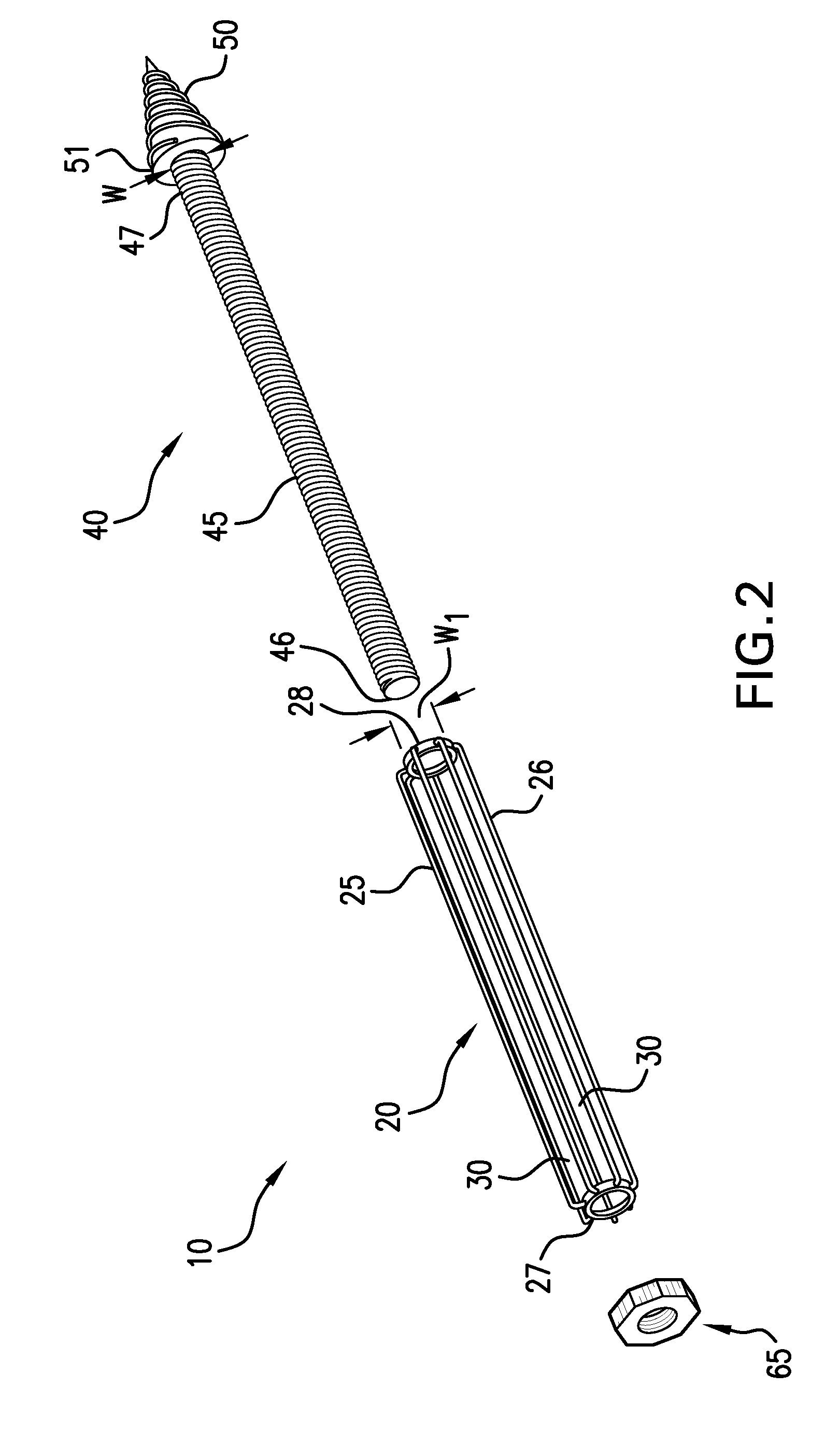
Methods of stabilizing the sacroiliac joint by placing an expandable device in the joint to generate laterally opposing forces against the iliac and sacral surfaces of the SI joint to securely seat the device in a plane generally parallel to the SI joint. The expandable device is coated with or otherwise contains a bone material to promote fusion of the joint. The expandable device used in methods of the present invention can be, for example, an expandable cage, a balloon, a balloon-expandable stent or a self-expanding stent.
Owner:SPINAL INNOVATIONS +1
Minimally Invasive Spine Restoration Systems, Devices, Methods and Kits
InactiveUS20070088358A1Restore qualityRestore stateInternal osteosythesisBone implantArticular surfacesRestoration device
The invention discloses methods and devices for repairing, replacing and / or augmenting natural facet joint surfaces and / or facet capsules. A facet joint restoration device of the invention for use in a restoring a facet joint surface comprises: a cephalad facet joint element comprising a flexible member adapted to engage a first vertebrae and an artificial cephalad joint; and a caudad facet joint element comprising a connector adapted for fixation to a second vertebrae and an artificial caudad joint adapted to engage the cephalad facet joint. In another embodiment, the invention discloses a facet joint replacement device for use in replacing all or a portion of a natural facet joint between a first vertebrae and a second vertebrae comprising: a first cephalad facet joint element having a fixation member adapted to engage a lamina or spinous process of the first vertebrae and a first caudad facet joint element, the first caudad facet joint element comprising a first caudad connector adapted to fixate to the second vertebral body and an artificial caudad facet surface adapted to engage with the cephalad facet joint element.
Owner:FACET SOLUTIONS
Sacro-iliac joint implant system and method
An orthopedic implant includes at least one circular body. The at least one circular body defining an outer surface configured to engage at least one articular surface of a sacro-iliac joint along a plane substantially parallel to the articular surface.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
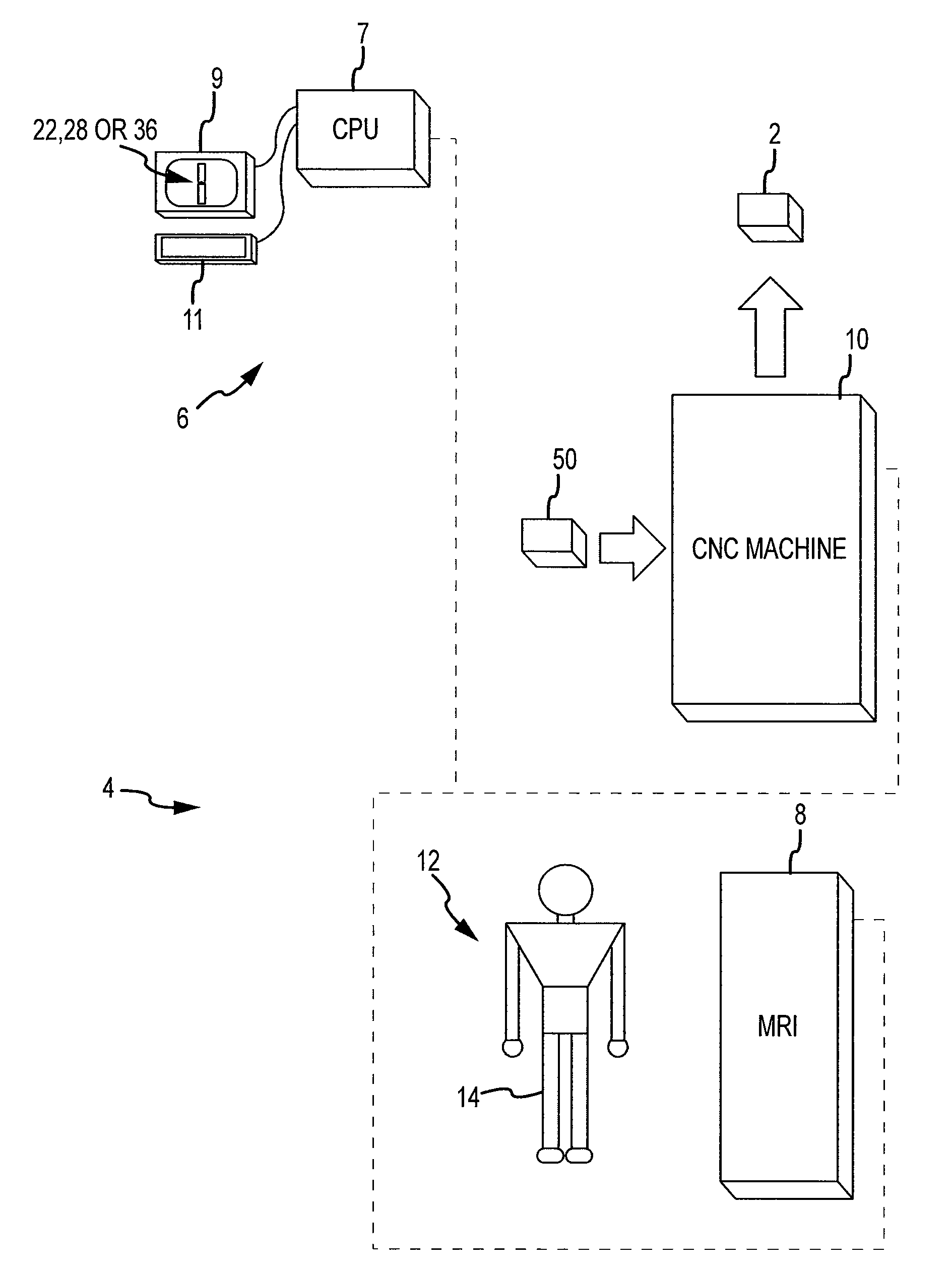
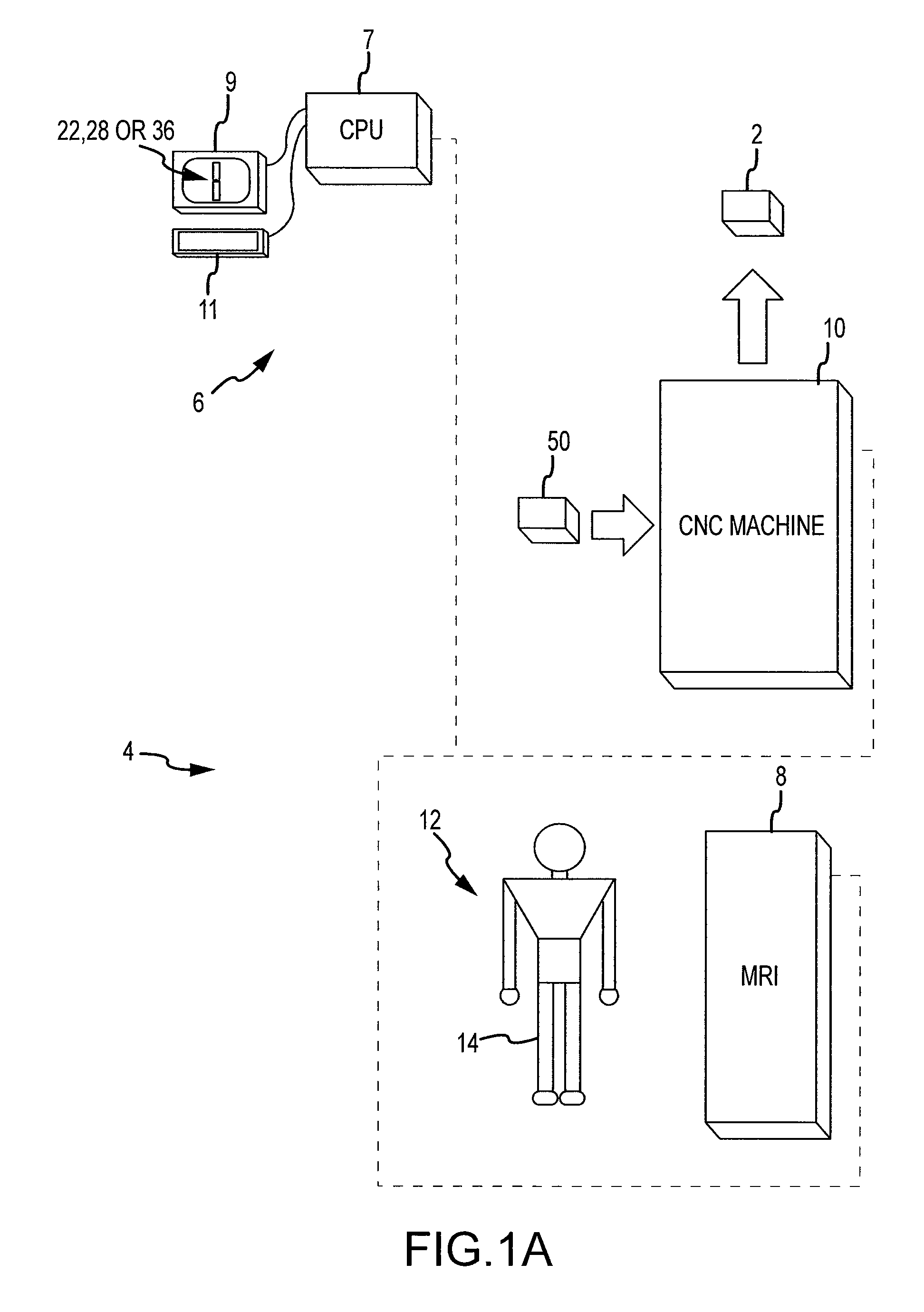
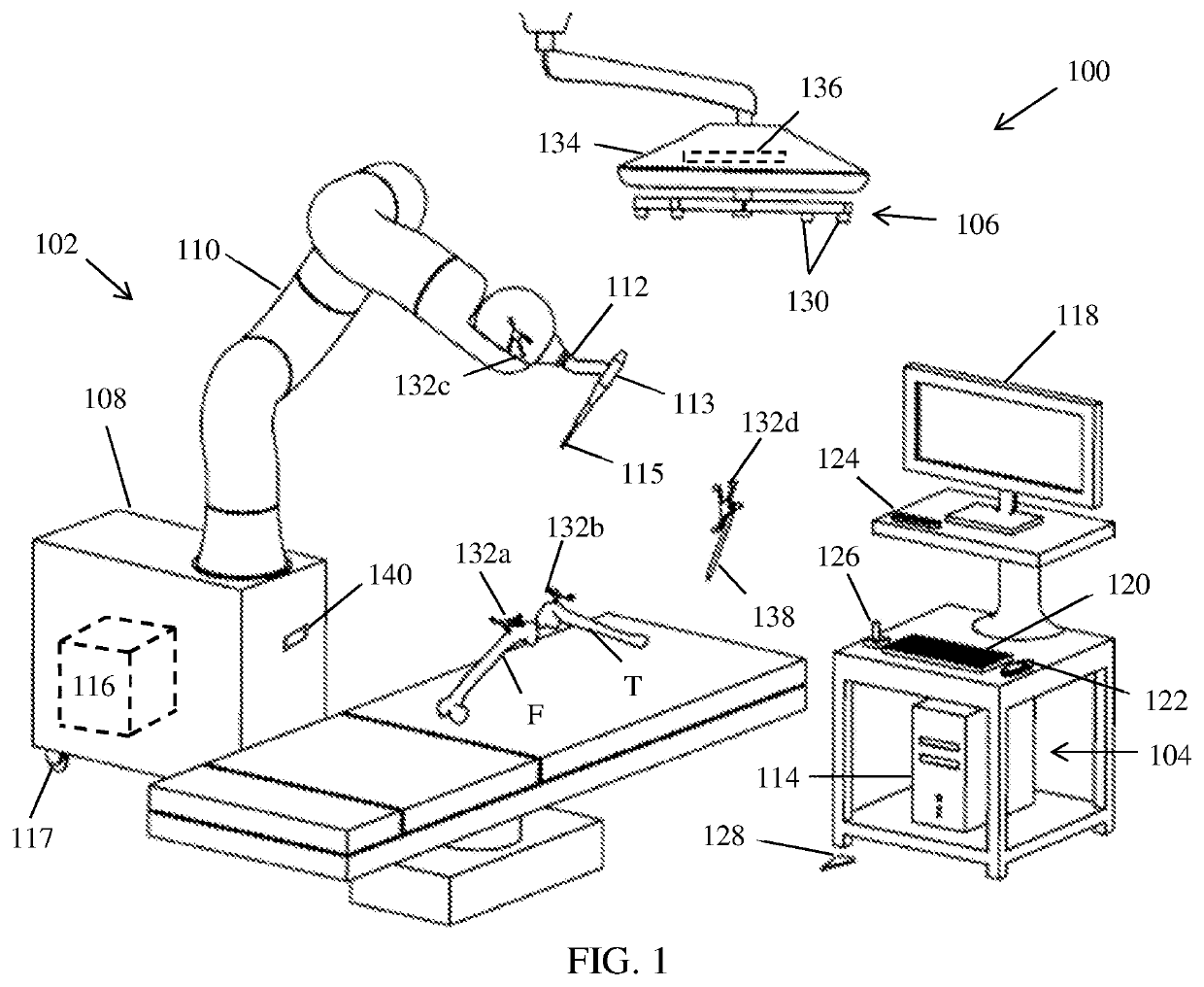
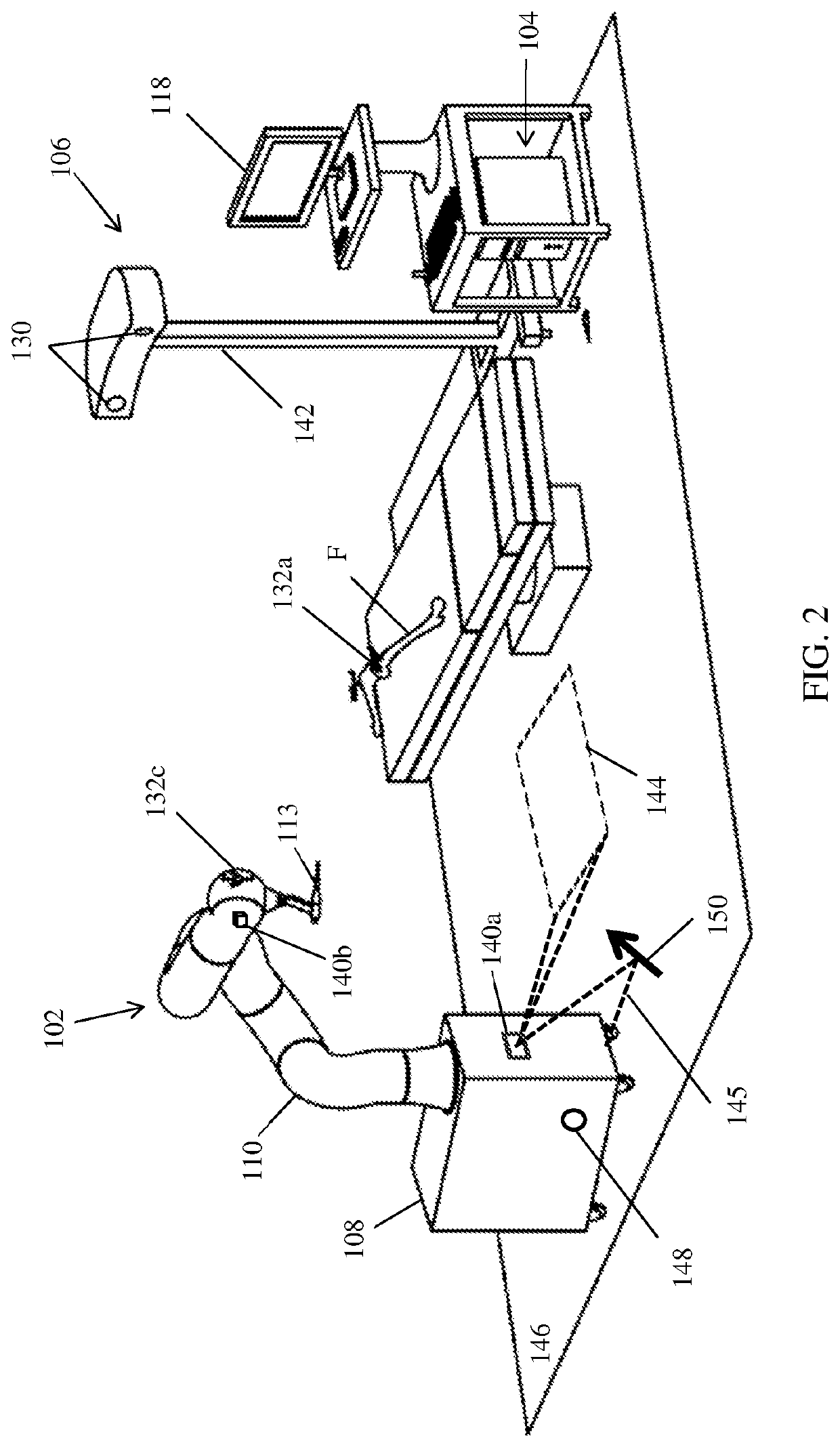
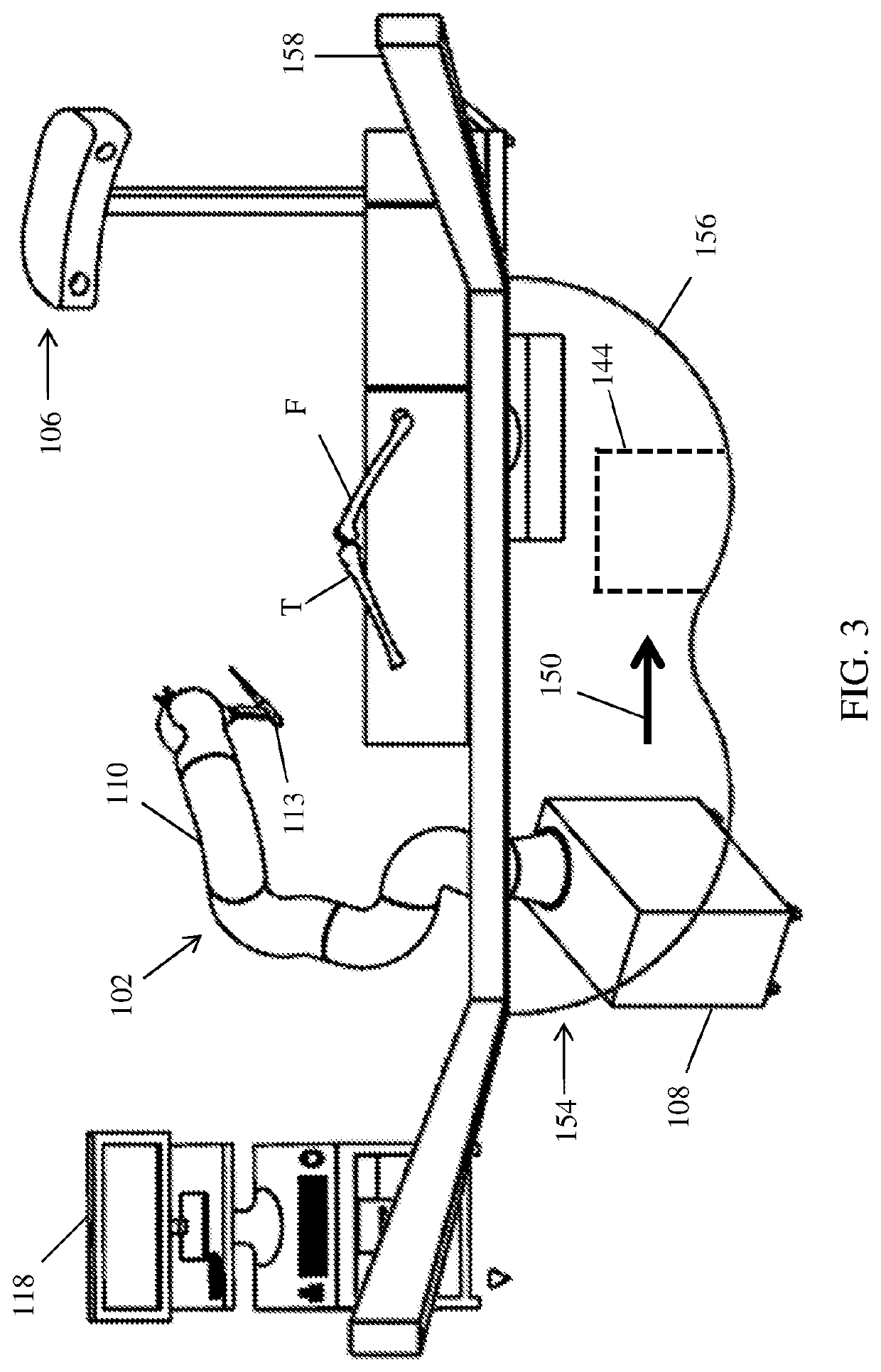
Method and system for guiding user positioning of a robot
ActiveUS10864050B2Surgical navigation systemsSurgical systems user interfaceSpinal columnAnatomical structures
A system and process is provided for dynamically positioning or repositioning a robot in a surgical context based on workspace and task requirements, manipulator requirements, or user preferences to execute a surgical plan. The system and method accurately determines and indicates an optimal position for a robot with respect to a patient's anatomy before or during a surgical procedure. Optimal positions for a robot are intuitively indicated to a user, surgical procedures can illustratively include surgery to the knee joint, hip joint, spine, shoulder joint, elbow joint, ankle joint, jaw, a tumor site, joints of the hand or foot, and other appropriate surgical sites.
Owner:THINK SURGICAL
Surgical technique using a contoured allograft cartilage as a spacer of the carpo-metacarpal joint of the thumb or tarso-metatarsal joint of the toe
A spacer for implantation into a subject is provided that includes a sterilized piece of cartilaginous allograft tissue. The piece forms a Y-shape with a base adapted to insert within a first carpo-metacarpal joint or carpo-metatarsal joint of the subject, and has a first arm adapted to secure to a trapezium bone adjoining the joint, and a second arm adapted to secure to a proximal metacarpal or metatarsal bone adjoining the joint. A procedure for implanting the spacer includes exposing a target joint and abrading a bone surface interior to the joint to induce surface bleeding. The spacer base is then inserted into the joint. The spacer first arm is adhered to the first bone of the joint and the spacer second arm is adhered to the second bone of the joint. A kit is also provided for surgical implantation of the spacer.
Owner:SHAPIRO PAUL S
Patellar alignment device
InactiveUS6589248B1Accurately locate proper positionReduce performanceDiagnosticsJoint implantsPatella prosthesisEngineering
A patellar alignment device for determining the position of a patella prosthesis. The device comprises two components-a baseplate and a mobile component which is preferably magnetically attached to the baseplate. During a surgical procedure to replace the knee, the baseplate is temporarily attached to the back of the patella. The baseplate may contain spikes or prongs to secure it to the patella. The baseplate further includes a series of slots for marking the patella. The mobile component resembles a patella and is placed on the baseplate. The patella with the alignment device in place is then placed in position on the knee and trialed. Because the mobile component is free to move on the baseplate, it finds the position that is most amenable to a natural knee movement. The alignment device is then exposed and the patella is marked at the position of the mobile component. Since the baseplate contains a series of slots, the patella can be easily marked at several locations around the mobile component. The entire patella alignment assembly is then removed and the final prosthetic device can be inserted at the marked location.
Owner:HUGHES JOE L
Methods and apparatus for improved cutting tools for resection
ActiveUS20060015109A1Facilitating intraoperativeFacilitating postoperative efficacyJoint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesTibiaSacroiliac joint
A cutting tool is provided with an arcuate cutting blade that preferably engages a guide tool to create a curved resected surface during an arthorplasty procedure. In one embodiment, a depth of the cutting blade is sufficient to permit the simultaneous creation of resected surfaces on two bones that articulate, such as both the femor and the tibia for a given condyle, without the need to reposition the guide or the leg. In another embodiment, a cutting member has a generally rectangular cross-section along a longitudinal axis with a first and second surface having cutting teeth defined thereon and a third and fourth surface adapted to interface with a cutting guide positioned proximate the bone. In this embodiment, the cutting tool can resect the bone in two different directions without reorienting the cutting member.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Activating and rotating surgical end effectors
Various surgical tools are provided with multi-axis articulation joints and with the ability to rotate distal to the joint. In one embodiment, a surgical tool is provided having an elongate shaft with an end effector disposed at a distal end of the elongate shaft. The end effector can have first and second jaws configured to grasp tissue and a sled or cutting element configured to advance through the jaws and cut tissue therein. A multi-axis articulation joint can be formed on the shaft or between the shaft and the end effector. The joint can allow articulation of the end effector in multiple directions. The end effector can be configured to rotate distal to the multi-axis articulation joint about a longitudinal axis of the elongate shaft. Methods for allowing rotation and articulation of the end effector are also provided.
Owner:ETHICON LLC
Surface guided knee replacement
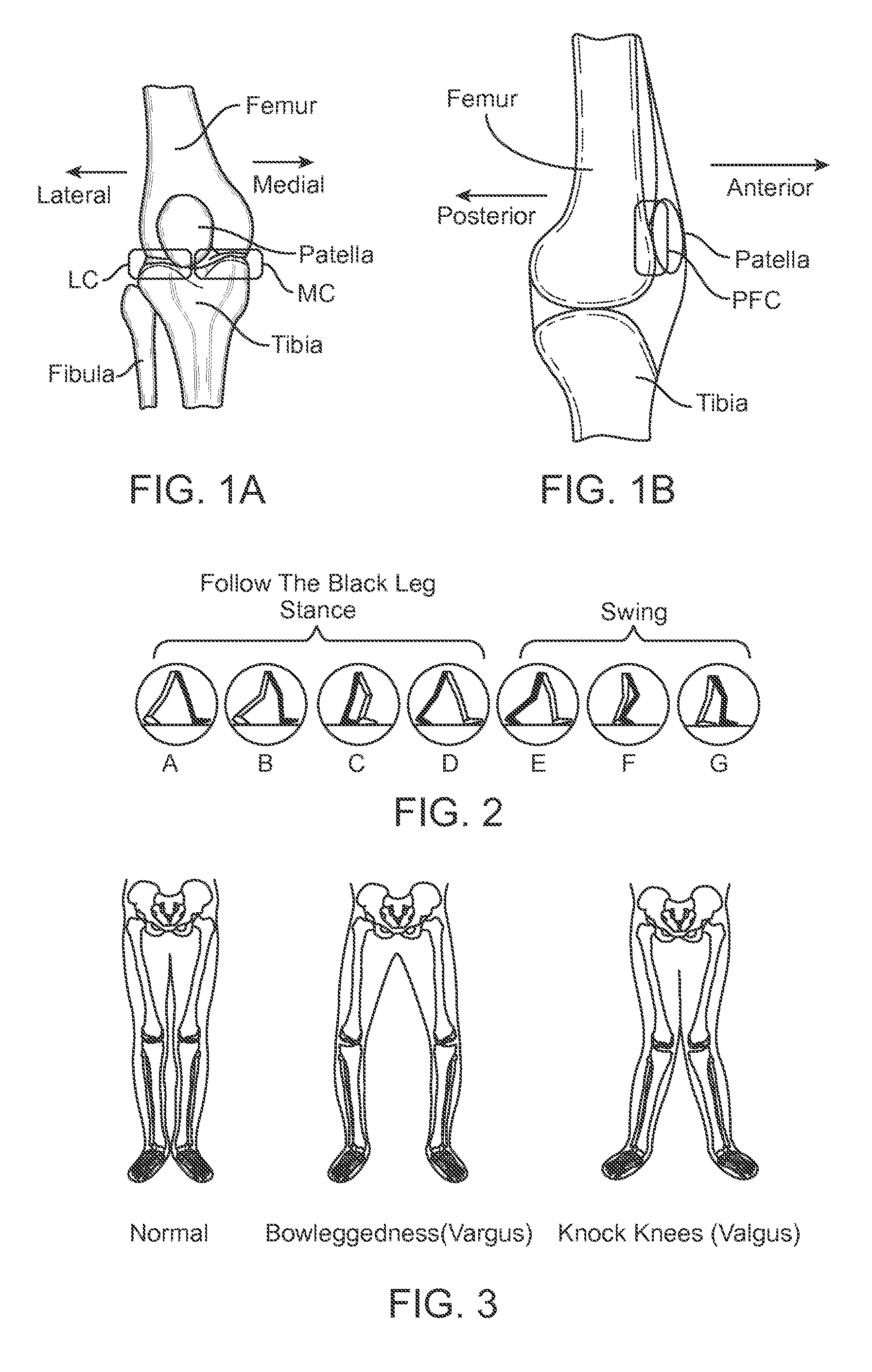
InactiveUS20070135925A1Reduce consistencyAvoid large displacementJoint implantsKnee jointsGonial angleTibial surface
An artificial knee joint that includes a femoral component with a specially shaped bearing surface and a tibial component, whose surface interacts with the femoral surfaces. The interaction provides for the motion and stability characteristics of the anatomic knee. The interaction between the femoral and tibial surfaces is such that as the knee is flexed to maximum, the femoral component moves posteriorly on the tibial surface, more so on the lateral side than on the medial side. This is accomplished by the interaction of a projecting tibial post inside a cupola in the center of the femoral component, and by the saggital radius on the medial side being smaller than that on the lateral side. The prevention of anterior sliding of the femur on the tibia in early flexion is accomplished by the interaction between a distal-anterior recess on the medial side of the femur and an apposing raised pad on the tibial surface. Rotational laxity at all angles is allowed by the presence of only one recess pad and by non-conforming femoral-tibial surfaces on the lateral side.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Systems and methods for providing deeper knee flexion capabilities for knee prosthesis patients
InactiveUS20090306786A1Deep knee flexion capabilityClosely replicate physiologic loadingJoint implantsKnee jointsSacroiliac jointFemoral bone
Systems and methods for providing deeper knee flexion capabilities, more physiologic load bearing and improved patellar tracking for knee prosthesis patients. Such systems and methods include (i) adding more articular surface to the antero-proximal posterior condyles of a femoral component, including methods to achieve that result, (ii) modifications to the internal geometry of the femoral component and the associated femoral bone cuts with methods of implantation, (iii) asymmetrical tibial components that have an unique articular surface that allows for deeper knee flexion than has previously been available, (iv) asymmetrical femoral condyles that result in more physiologic loading of the joint and improved patellar tracking and (v) modifying an articulation surface of the tibial component to include an articulation feature whereby the articulation pathway of the femoral component is directed or guided by articulation feature.
Owner:SAMUELSON KENT M +1
Method and Apparatus for Altering Biomechanics of the Articular Joints
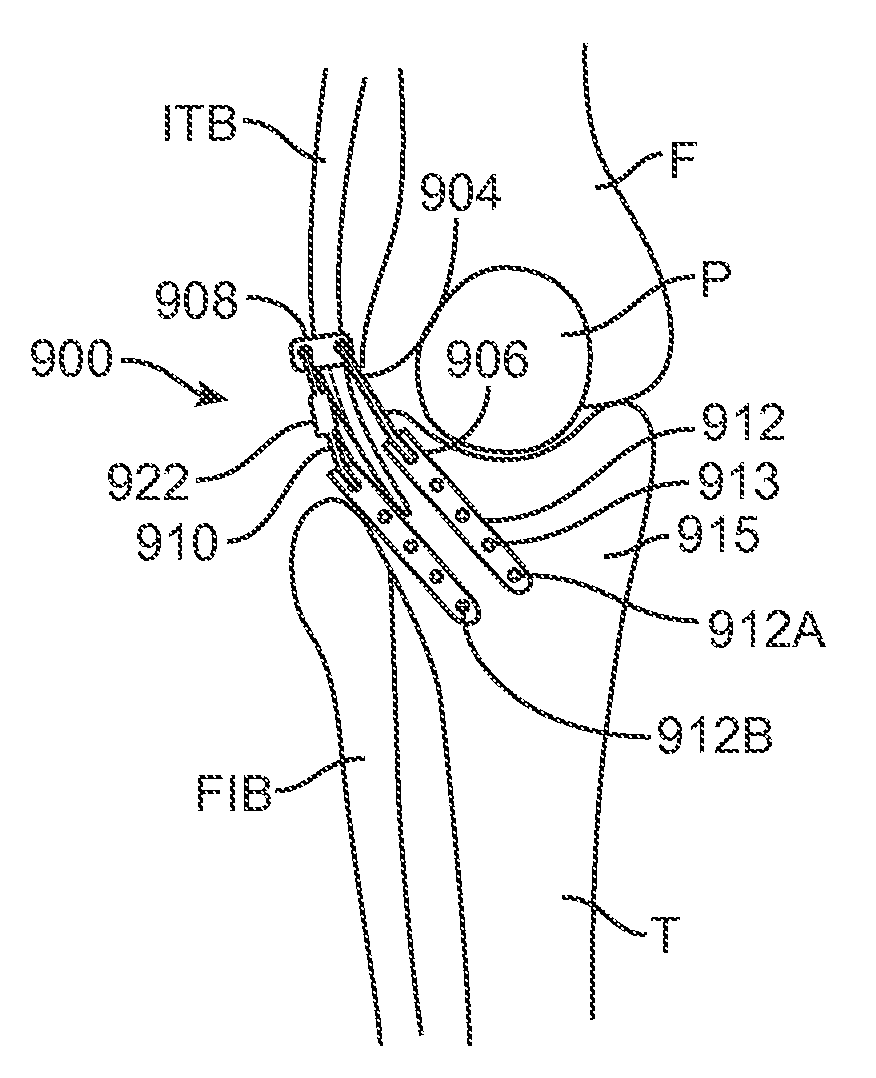
ActiveUS20130211521A1Redistributing loading in the jointReduce loadLigamentsJoint implantsBiomechanicsKnee Joint
Pathology of the human knee can arise from excessive and / or uneven loading of regions within the joint. Methods and apparatus are disclosed that enable displacement of soft tissue around the knee, without displacing or severing bone thereby altering the mechanical load distribution within the joint in a less invasive manner than previous techniques.
Owner:THE FOUNDY LLC
Facet joint prosthesis
A prosthetic implant for replacing a facet joint of a spinal motion segment includes a generally conical superior component adapted to be implanted at a surgically prepared site on a lower articular process of a cephalad vertebra of a spinal motion segment, and a cup-shaped inferior component adapted to be implanted at a surgically prepared site on a superior articular process of a caudad vertebra of the spinal motion segment.
Owner:RE SPINE
Arthroplasty system and related methods
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Lift assist device and method
InactiveUS20050130815A1Increase valueSmall valueDumb-bellsResilient force resistorsEngineeringSacroiliac joint
The invention relates to a device and method for assisting a subject to perform a motion such as a lift. The invention comprises a first anchor attachable to a first side of a joint of the subject's body, a second anchor attachable to a second side of the joint; and an elastic member connecting the first anchor and the second anchor, such that articulation of the joint in a first direction causes deformation of the elastic member and storing of energy, and articulation of the joint in a second direction causes relaxation of the elastic member wherein the energy is released and assists the subject to perform a motion in said second direction. The invention may be used at a subject's waist, ankle, wrist, knee, hip, elbow, shoulder, and / or at least one joint of the back and / or neck.
Owner:QUEENS UNIV OF KINGSTON
Methods of stabilizing the sacroiliac joint
ActiveUS8551171B2Stability in the SI jointResistance to and loadingSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSacrum boneSacro-iliac joint
Methods of stabilizing the sacroiliac joint by placing an expandable device in the joint to generate laterally opposing forces against the iliac and sacral surfaces of the SI joint to securely seat the device in a plane generally parallel to the SI joint. The expandable device is coated with or otherwise contains a bone material to promote fusion of the joint. The expandable device used in methods of the present invention can be, for example, an expandable cage, a balloon, a balloon-expandable stent or a self-expanding stent.
Owner:SPINAL INNOVATIONS +1
Prosthetic implant and surgical tool
InactiveUS20020177854A1Promote ingrowthCompromise integrityJoint implantsCoatingsBone chamberSacroiliac joint
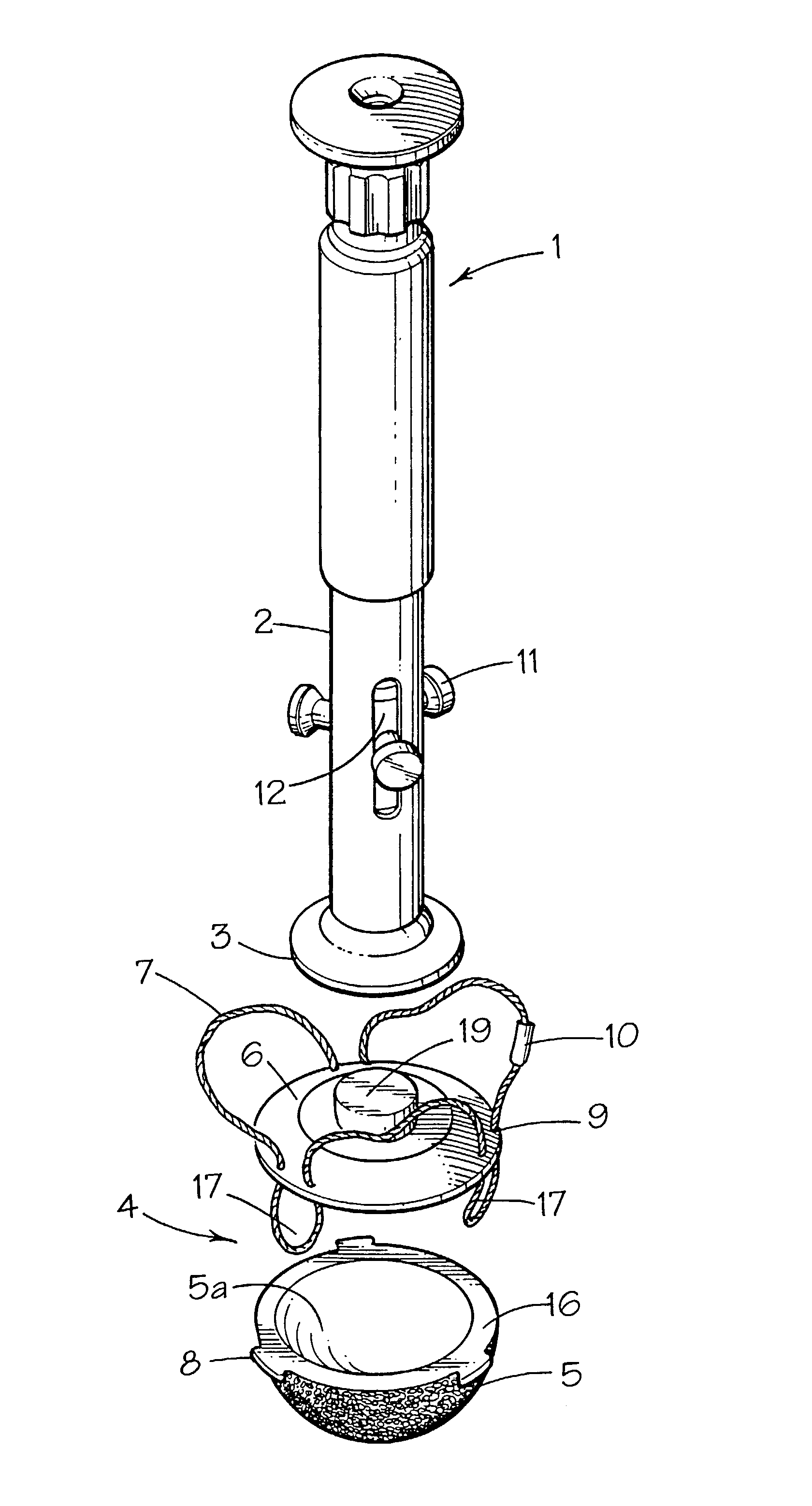
The invention relates to a prosthetic implant comprising a main body portion having a first surface for presentation to a receptive bone surface or into a bone cavity and a second surface for receipt of an articulating joint, and means on the implant adapted for attachment of a filamentary member, such as a cable. The invention also relates to a surgical tool for gripping the implant, comprising an elongate body having a first end surface for bearing on the prosthetic implant and means for attachment of the tool to the implant, directly or indirectly by means of the cable.
Owner:T J SMITH & NEPHEW
Wear-reducing geometry of articulations in total joint replacements
ActiveUS20100063589A1Improve stabilityImprove wearing rateFinger jointsWrist jointsHip joint simulatorClassical mechanics
The invention reduces wear in total joint articulations by modifications of the shape of either component of the kinematic pair, so as to result in an annular surface contact between the two components. Fluid trapped between the two components within the inner contour of the annular contact area is pressurized under load due to elastic deformation of the components and exuded out through inter-articular gap over the surface of contact, aiding in lubrication and reducing the wear. Reduced to practice for a total hip joint with UHMWPE-metal pair, the wear rate tested in a hip joint simulator up to five million cycles was reduced by factor seven to fifteen compared to conventionally shaped components.
Owner:SCYON ORTHOPAEDICS
Prosthetic implant and surgical tool
InactiveUS20010051830A1Improve visibilityReduce risk of damageJoint implantsCoatingsBone chamberSacroiliac joint
The invention relates to a prosthetic implant comprising a main body portion having a first surface for presentation to a receptive bone surface or into a bone cavity and a second surface for receipt of an articulating joint, and means on the implant adapted for attachment of a filamentary member, such as a cable. The invention also relates to a surgical tool for gripping the implant, comprising an elongate body having a first end surface for bearing on the prosthetic implant and means for attachment of the tool to the implant, directly or indirectly by means of the cable.
Owner:T J SMITH & NEPHEW
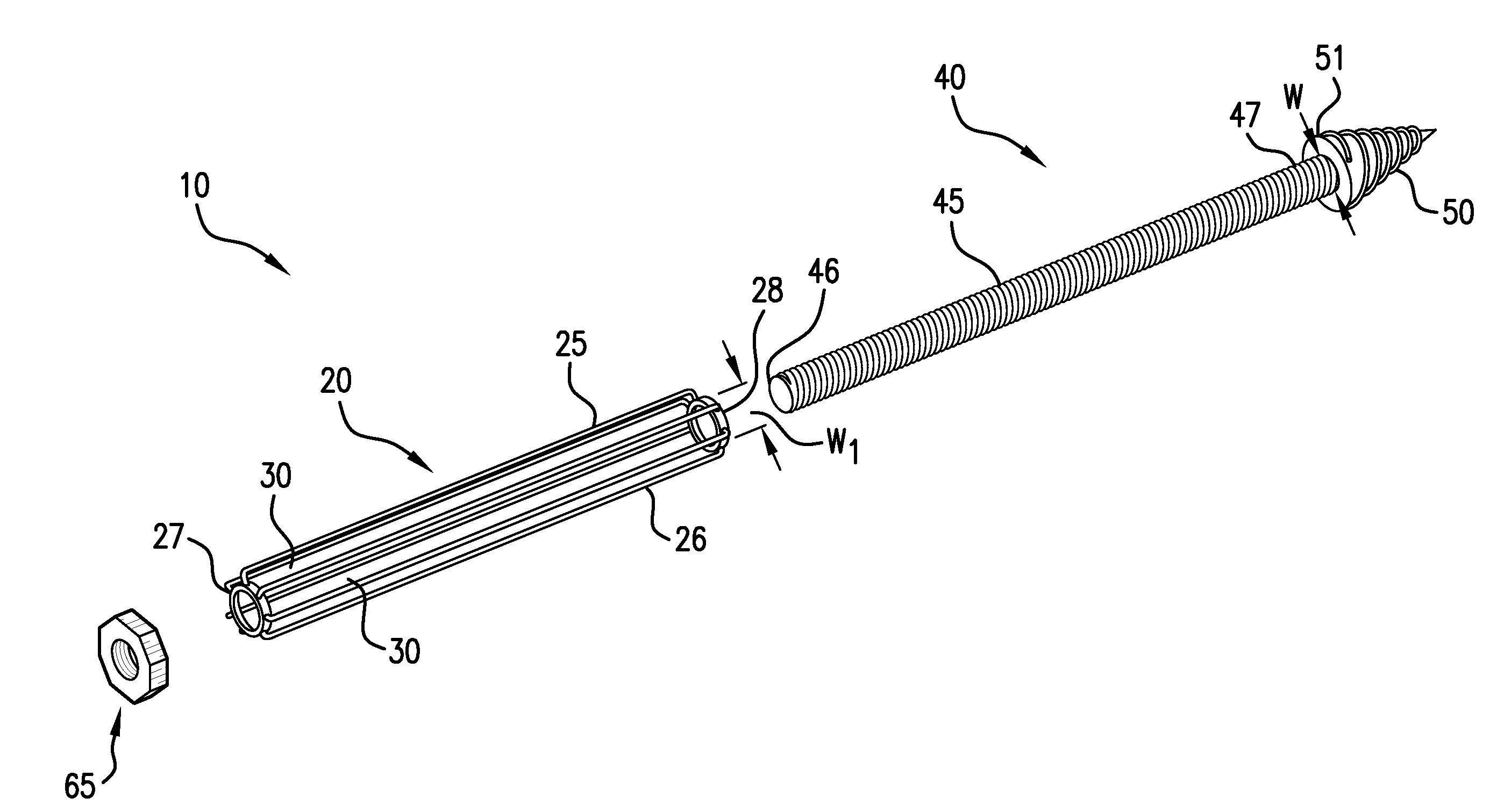
Intramedullary Arthrodesis Nail and Method of Use
ActiveUS20100130978A1Minimize excessive bone resectionMinimize tendon damageWrist jointsInternal osteosythesisJoint arthrodesisPost operative
A device is provided including a distal nail portion and a proximal nail portion that can be connected to each other to attain a rigid configuration. The device is to be placed internally within the medullary cavities of at least two bones forming a joint to accomplish arthrodesis of the joint. The device is placed intramedullarily in order to minimize incision size, excessive bone resection and post-operative tendon damage and tenderness. Additionally, one particular method for using the device is provided that includes placing and affixing the distal nail in a bone of a joint, placing the proximal nail in another bone of a joint, connecting the distal nail to the proximal nail, doing the desired geometrical adjustments, affixing the proximal nail to the distal nail by tightening the connection and affixing the proximal nail to the other bone of the joint to attain a rigid configuration.
Owner:SKELETAL DYNAMICS INC
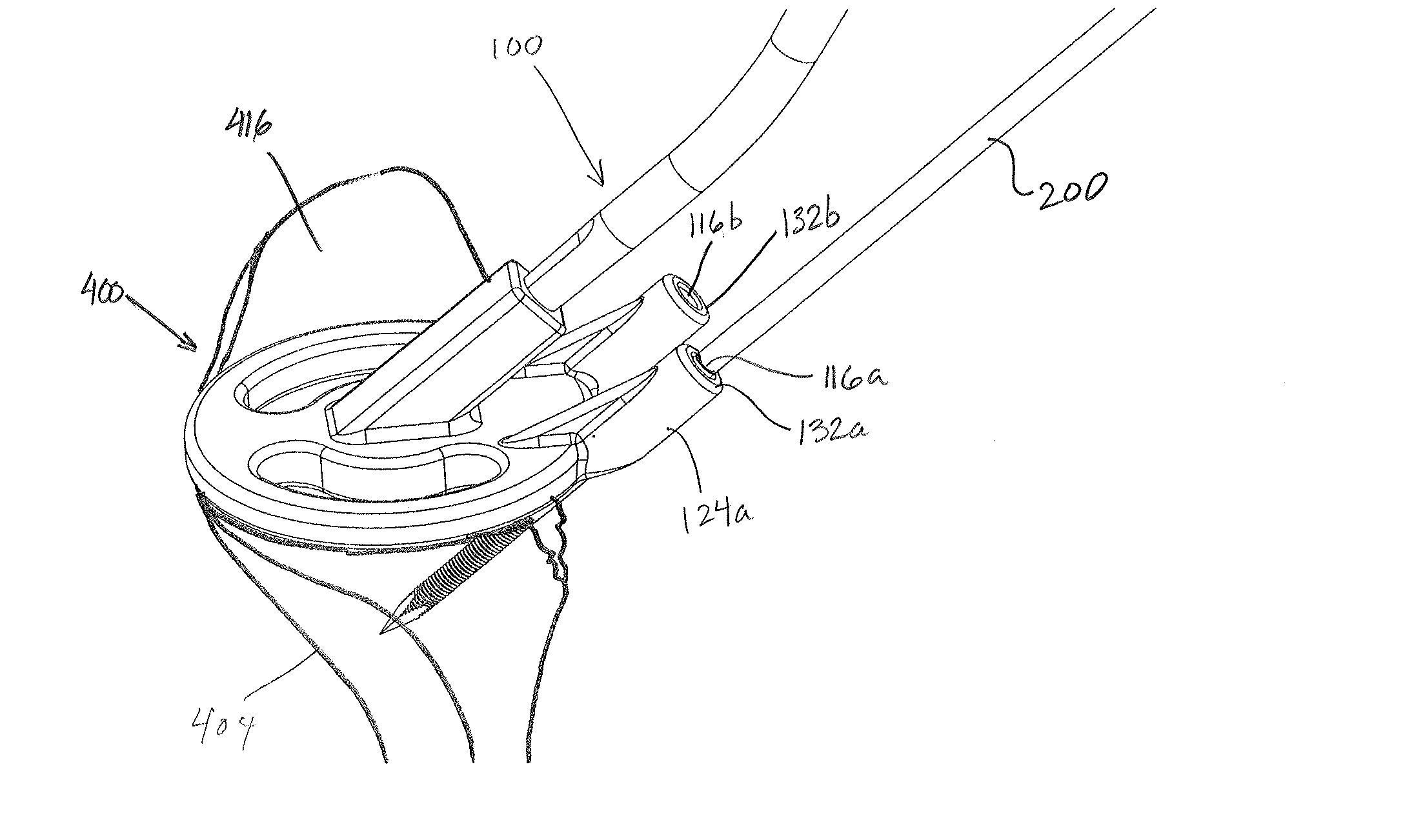
Devices, apparatuses, kits, and methods for repair of articular surface and/or articular rim
Embodiments of devices, apparatuses, kits, and methods for repairing and / or augmenting the articular surface and / or articular rim of a joint (e.g., repairing the anterior glenoid rim after an anterior shoulder dislocation).
Owner:ARTHROSURFACE
Injection systems for delivery of fluids to joints
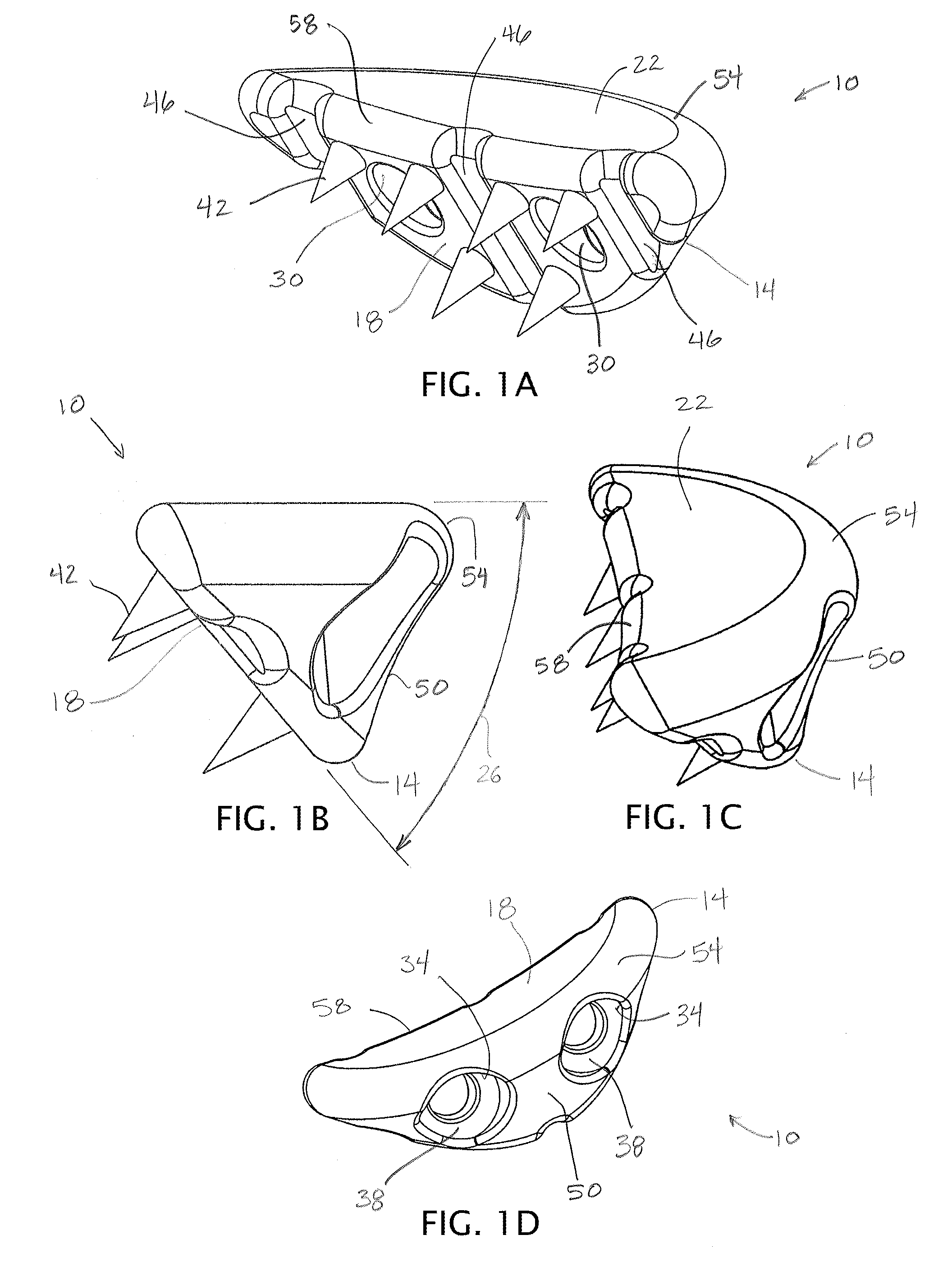
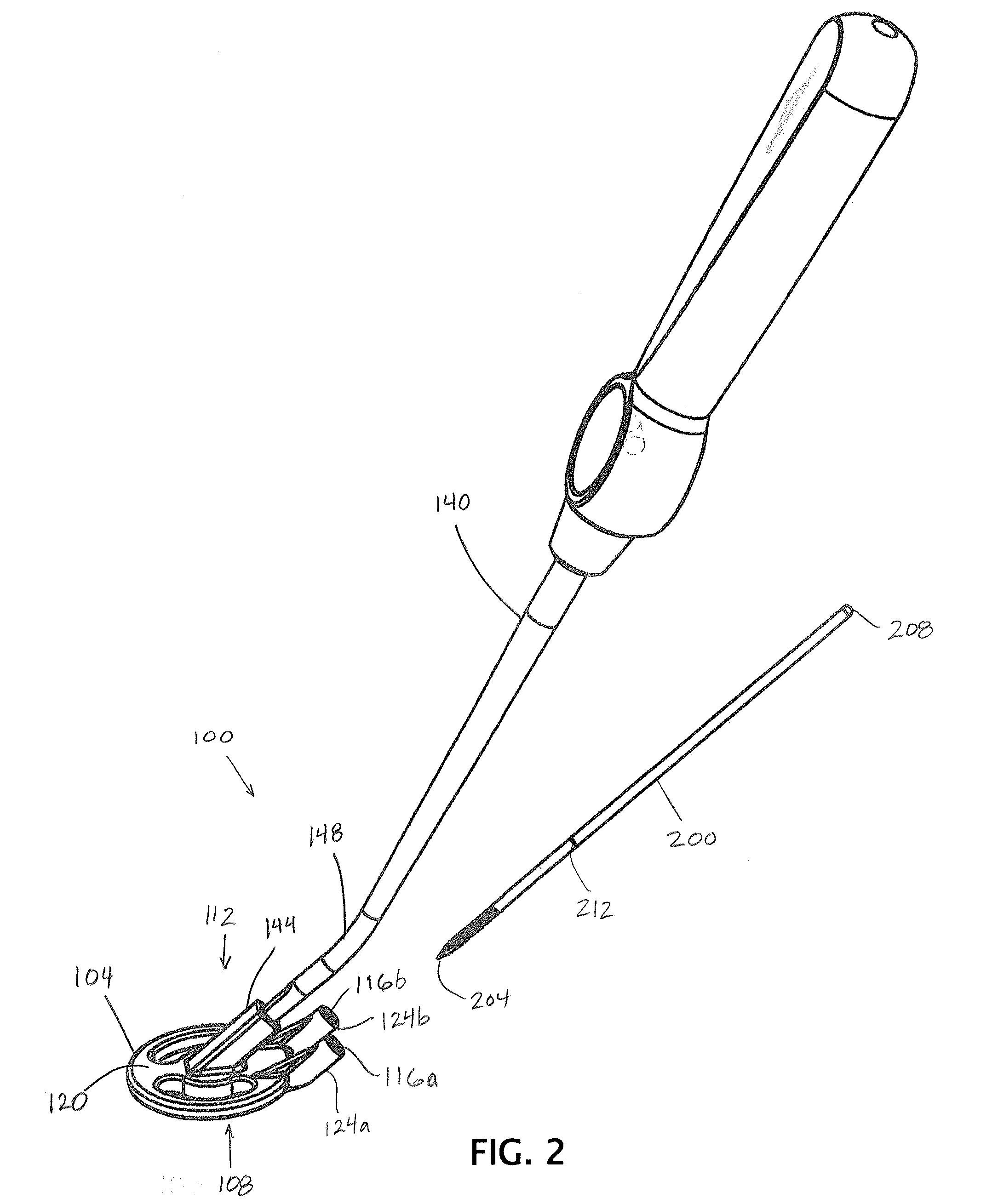
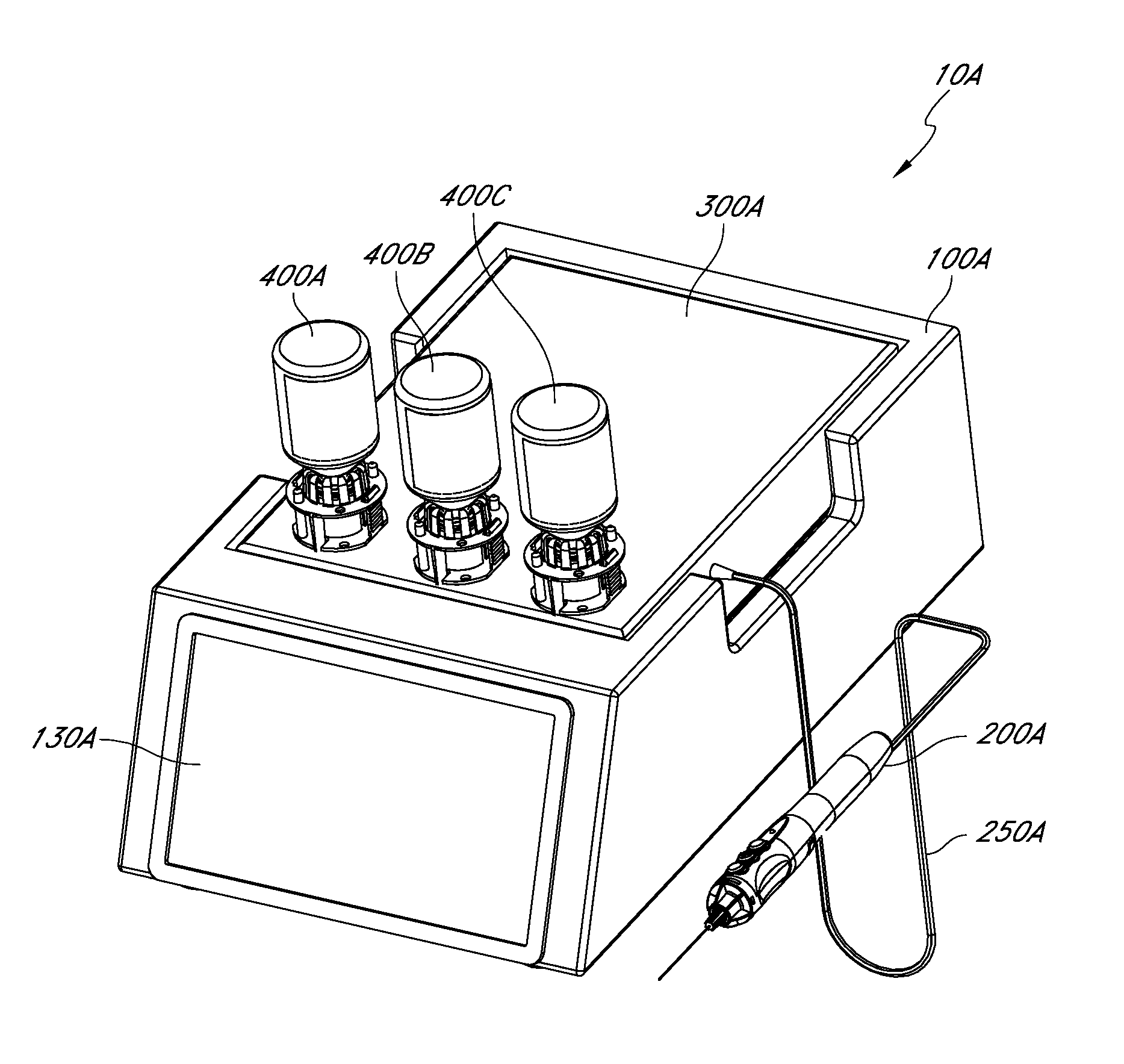
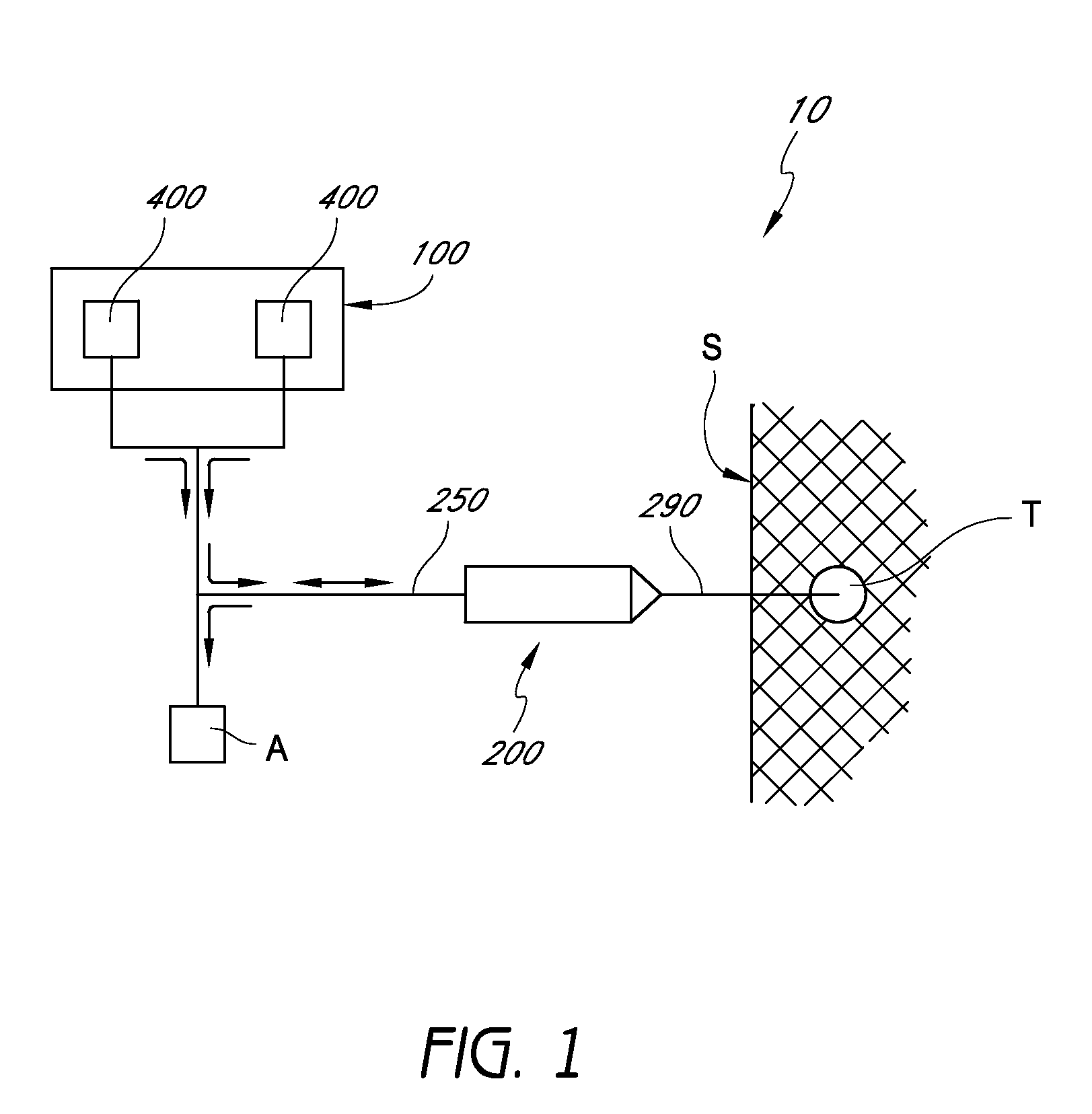
InactiveUS8002736B2Precise deliveryPatient benefitUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAutomatic syringesAnatomical structuresCatheter
Systems for injecting fluids and / or other materials into a targeted anatomical location, in particular, an intra-articular space, include a handpiece assembly having a proximal end and a distal end, a needle extending from the distal end of the handpiece assembly, a fluid delivery module comprising a cassette and a fluid transfer device. A conduit is generally configured to place the fluid delivery module in fluid communication with the handpiece assembly. Medications, formulations and / or other fluids or materials contained within vials that are secured to the fluid delivery module can be selectively delivered into an anatomy through a needle located at the distal end of the handpiece assembly. In some embodiments, ultrasound or other imaging technologies can be used to locate a joint or other targeted anatomical location.
Owner:CARTICEPT MEDICAL
Orthopaedic stem with protrusion and associated surgical procedure
ActiveUS20080177393A1Reducing the bone fragments onto the humerusPromote bone fracture healing and unionJoint implantsKnee jointsJoint arthroplastyProsthesis
A first articulating member for use with a second articulating member to form a prosthesis for use in joint arthroplasty for a joint formed between adjacent first and second bones in which a bone fragment having an exterior surface has separated from the first bone is provided. The first articulating member includes an articulating portion having an articulation surface for articulation with the second articulating member and an attaching portion connected to the articulating portion for attachment to the first bone. The first articulating member also includes a fragment portion connected to at least one of the articulating portion and the insertion portion. The fragment portion includes a surface for contact with the external periphery of the bone fragment.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation of the knee
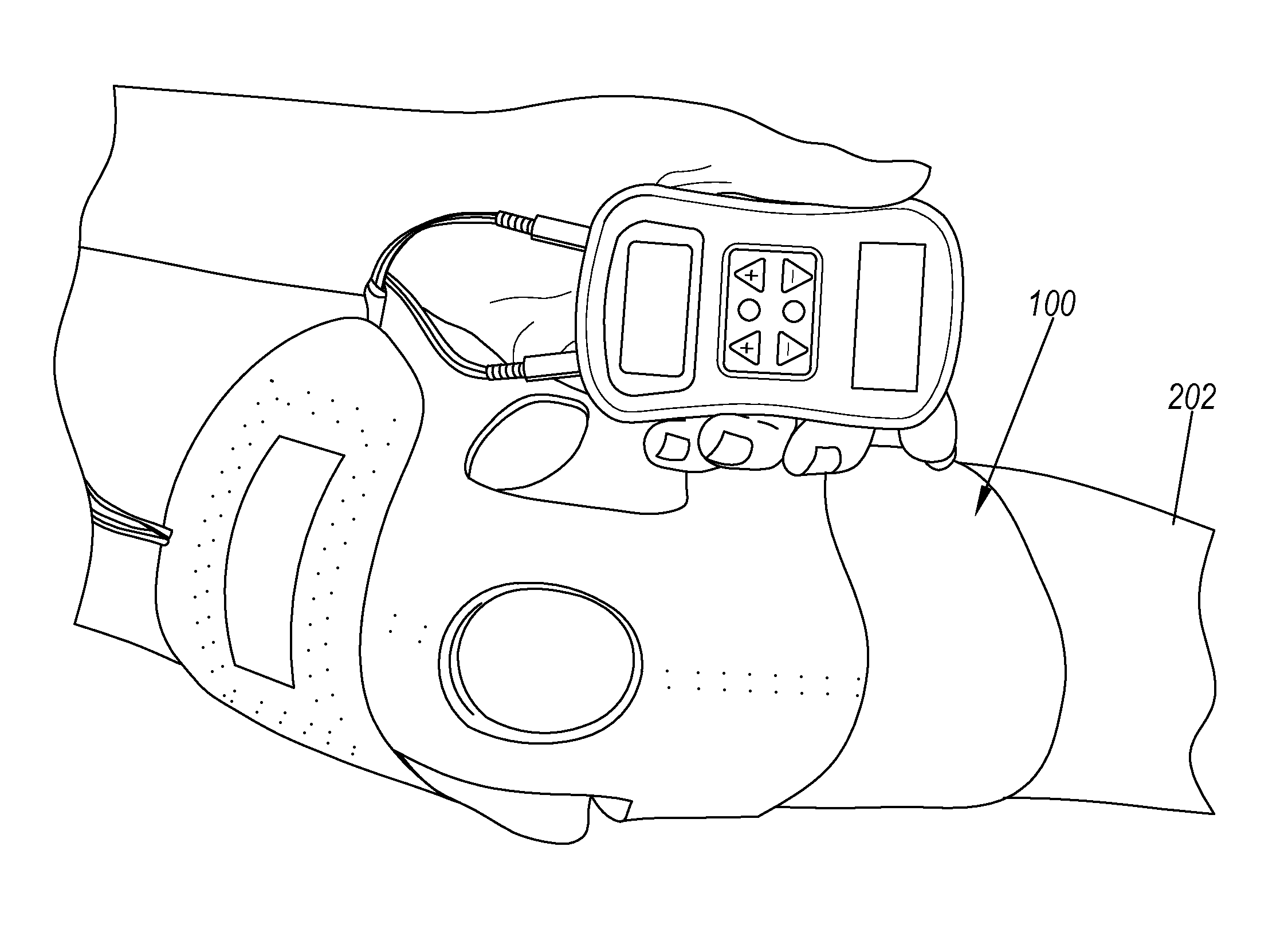
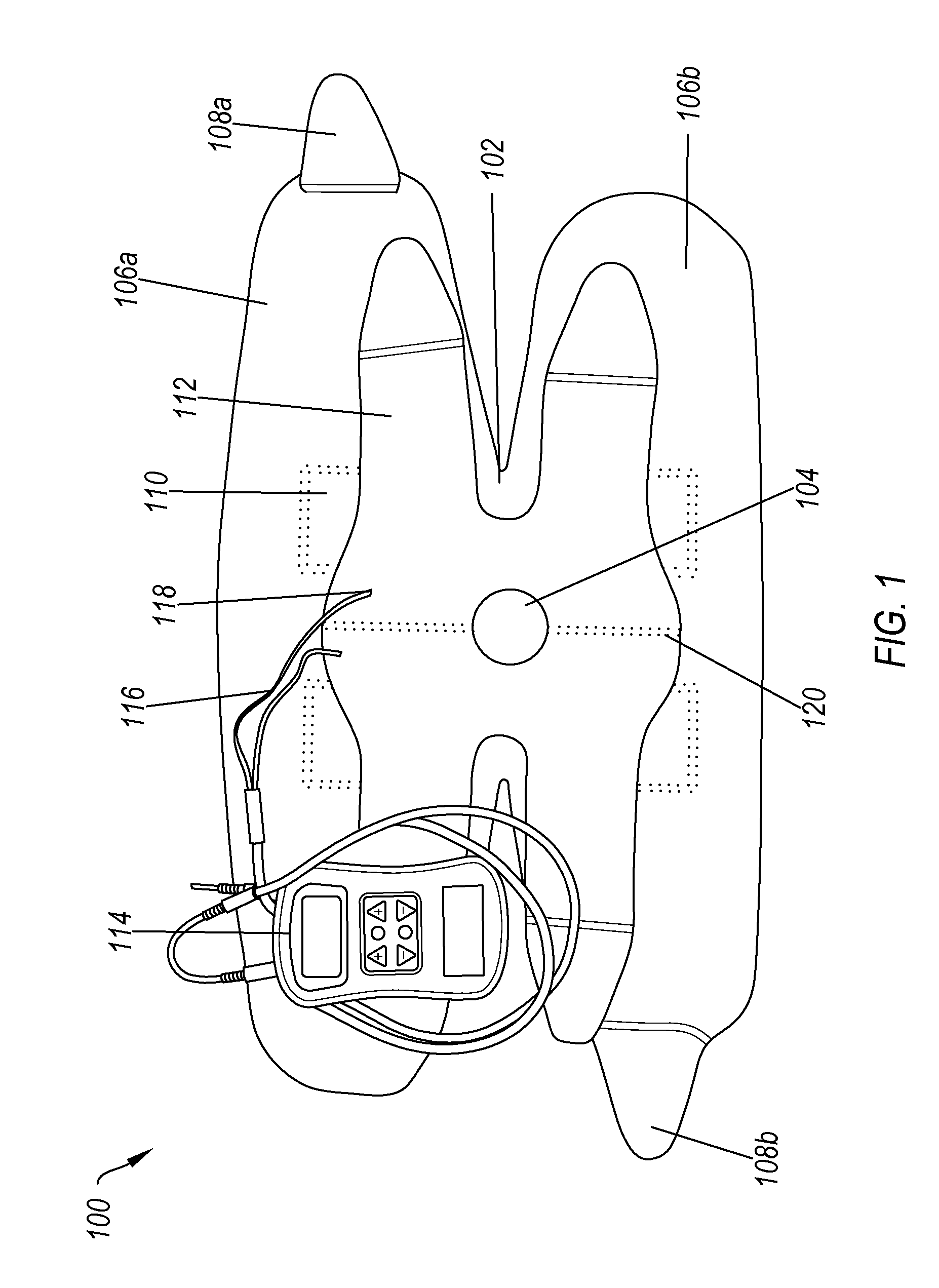
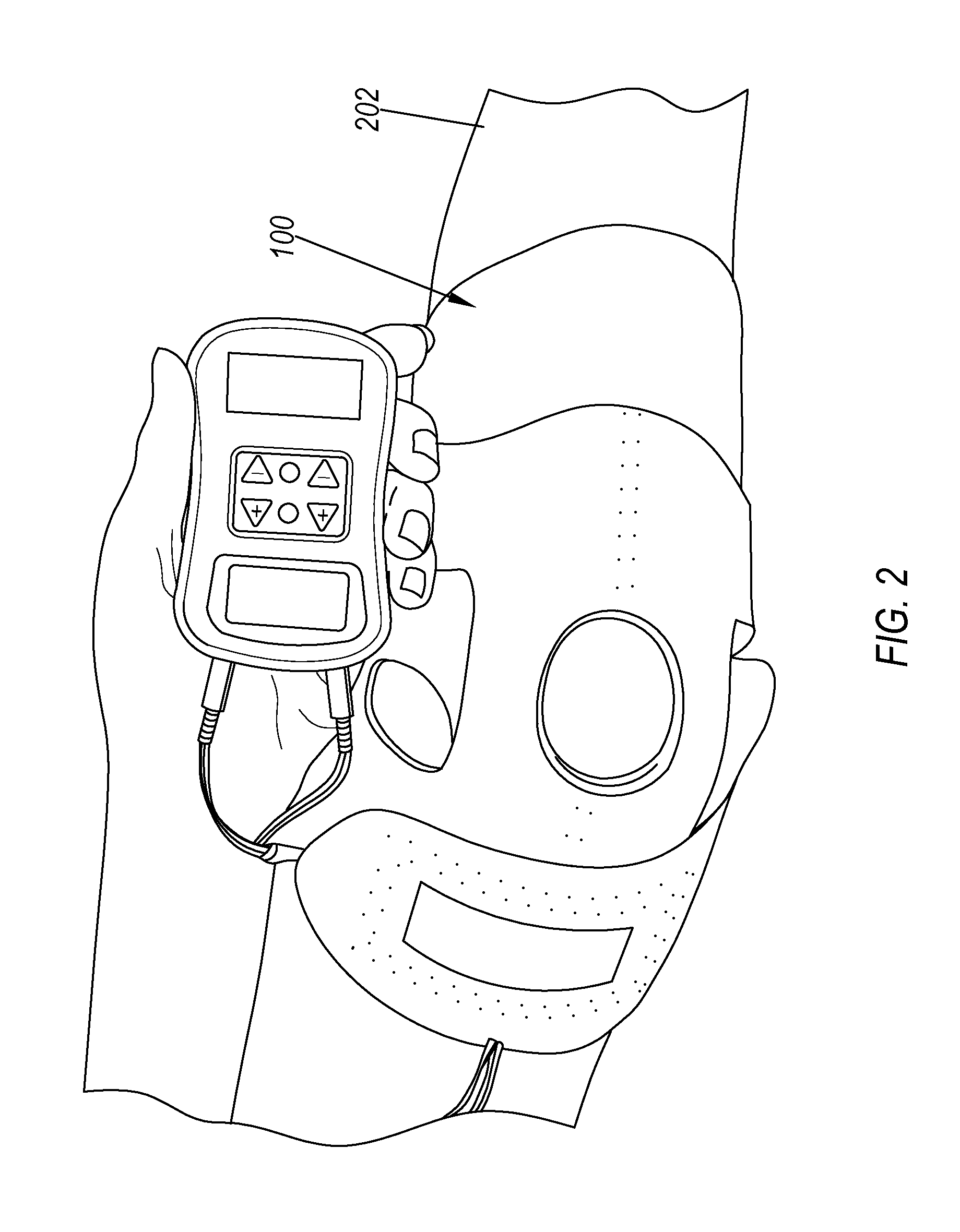
A system for providing electrical stimulation of a joint. The system includes a wrap. The wrap includes a body, wherein the body is configured to be placed over the joint. The wrap also includes a first arm configured to be placed on a first side of the joint and attached to the body. The wrap further includes a second arm configured to be placed on a second side of the joint and attached to the body opposite the first arm. The wrap also includes a set of electrode locators. The set of electrode locators includes a first electrode locator, configured to receive a first electrode, a second electrode locator, configured to receive a second electrode, a third electrode locator, configured to receive a third electrode and a fourth electrode locator, configured to receive a fourth electrode.
Owner:BROWN MARTIN
Method and Apparatus for Altering Biomechanics of the Articular Joints
ActiveUS20140156004A1Redistributing loading in the jointReduce loadLigamentsJoint implantsBiomechanicsLess invasive
Owner:THE FOUNDY LLC
Modular apparatus and method for sculpting the surface of a joint
The present invention provides a modular device for restoring individual joint kinematics using minimally invasive surgical procedures. The modular implants include distinct components that include interconnection means and tethering means. The modular implants provide intraoperative surgical options for articular constraint and facilitate proper alignment and orientation of the joint to restore kinematics as defined by the individual patient anatomy.
Owner:CAYENNE MEDICAL INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com