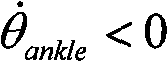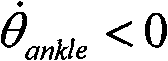Patents
Literature
111 results about "Toe Joints" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
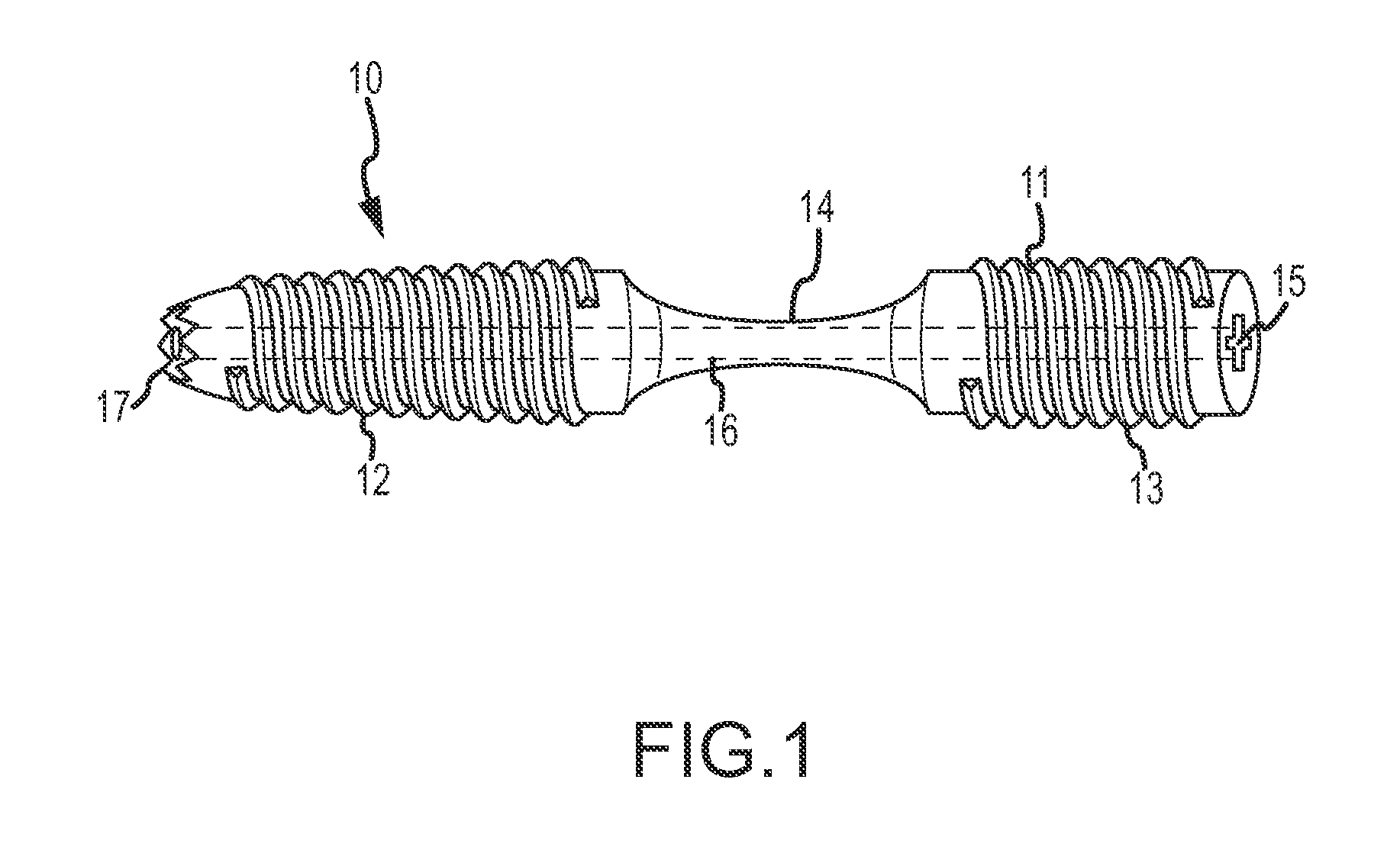
Joint fusion device
A device and method are disclosed for the fusion of joints (particularly finger joints or toe joints) in a bent (or angled) position. In certain embodiments, a device for the fusion of joints preferably allows for one or more of various angled positions, and the particular angle may differ for different joints. The device is preferably a bendable implant device for fusing together bones or a joint.
Owner:EXSOMED CORP
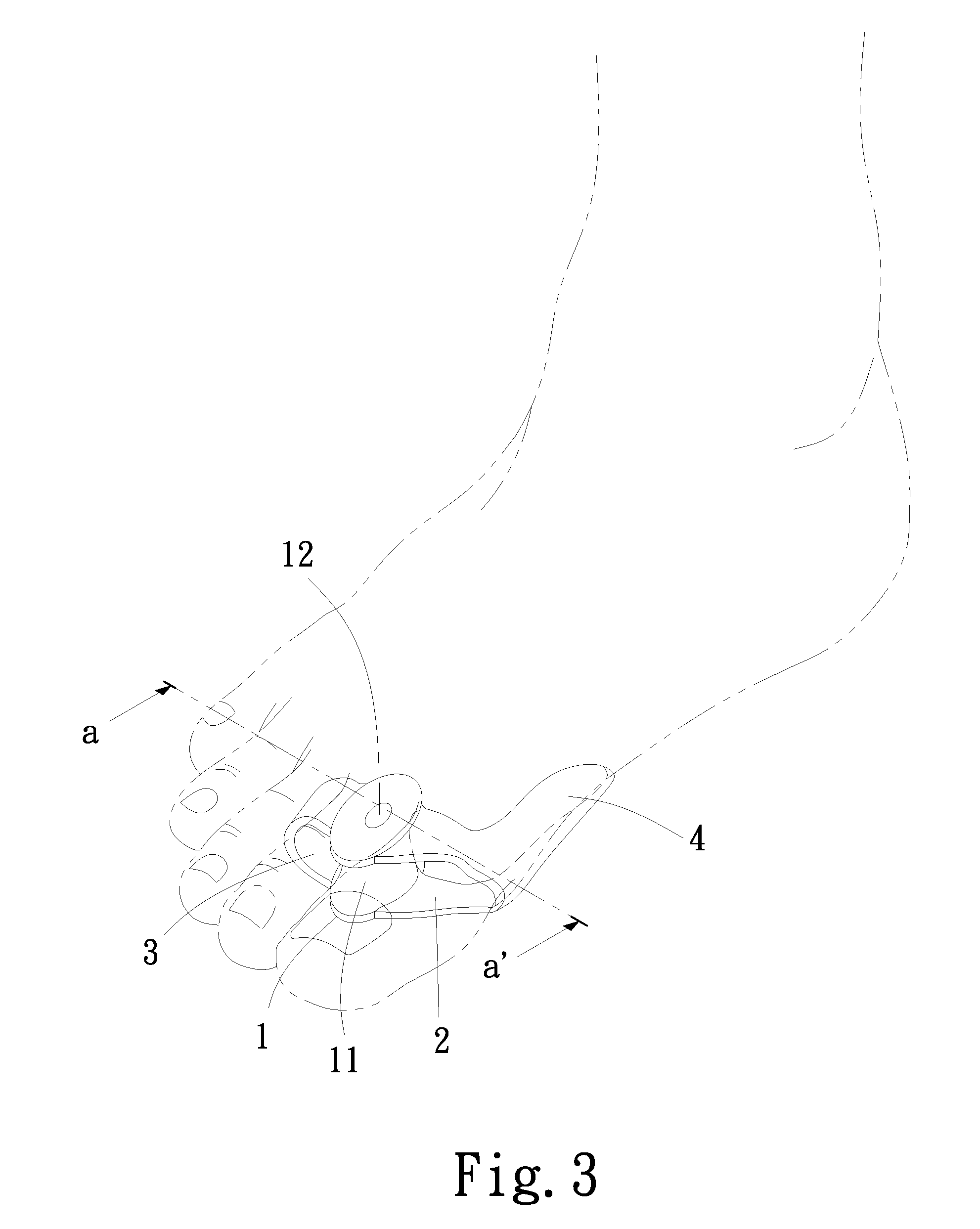
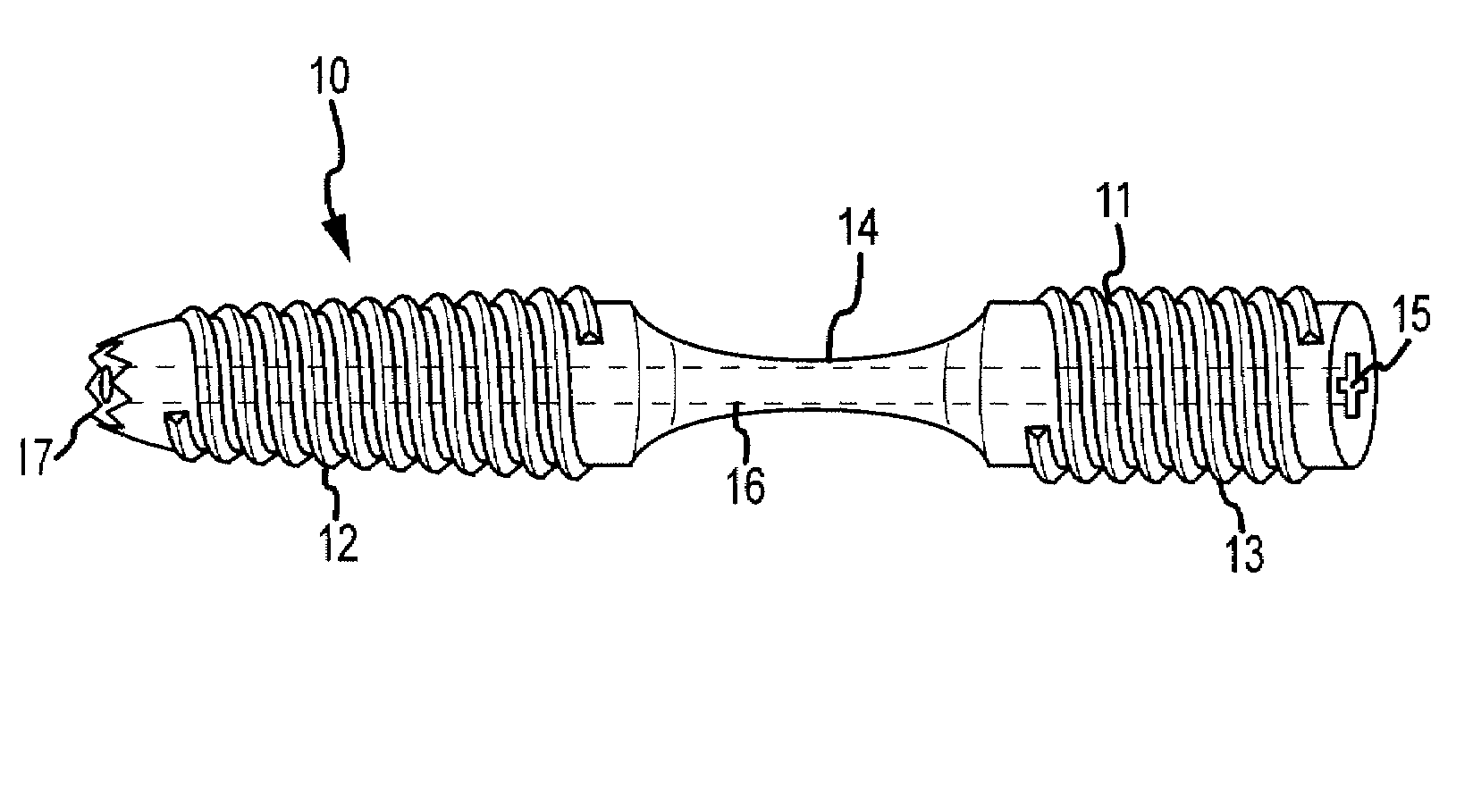
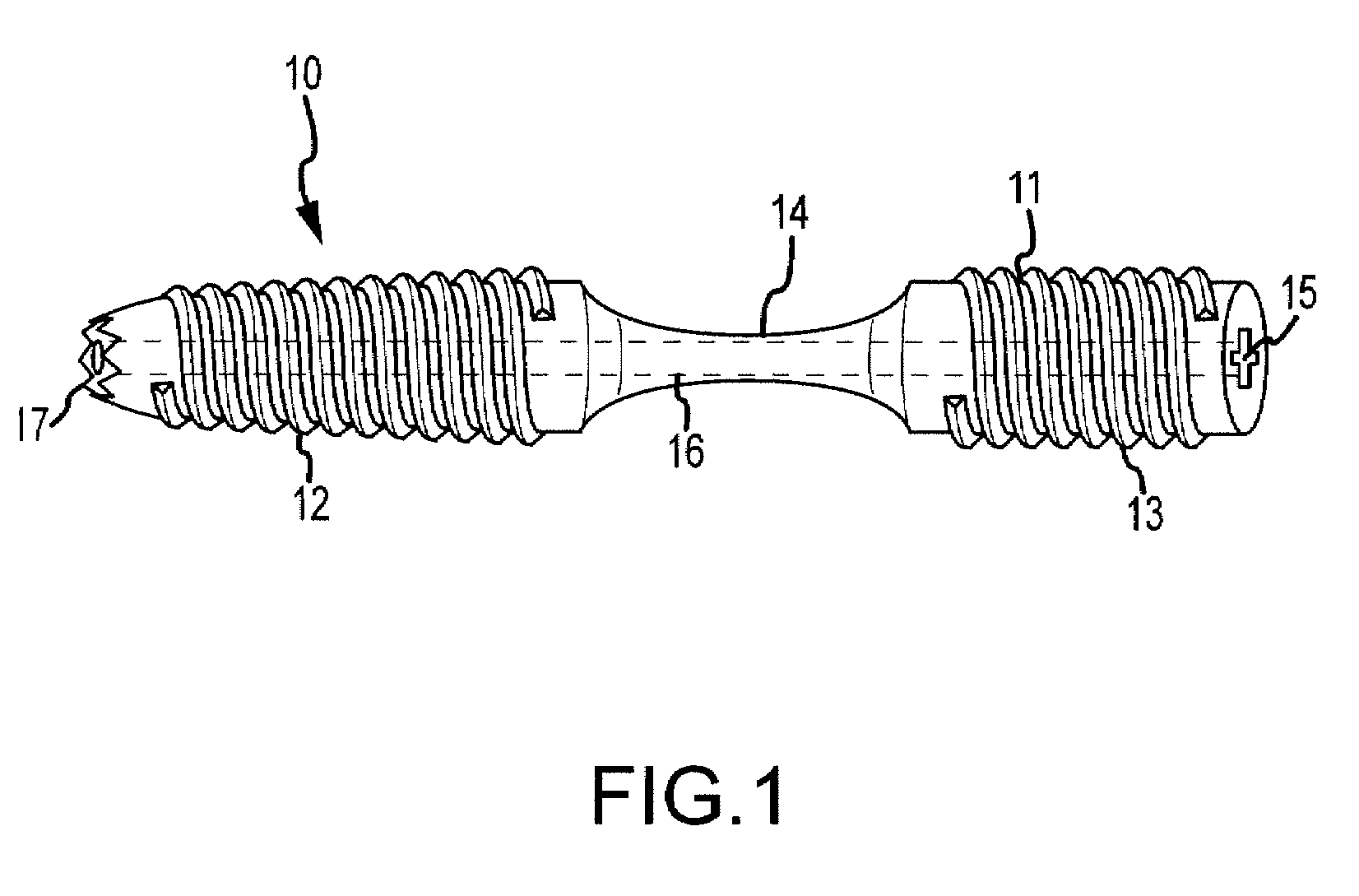
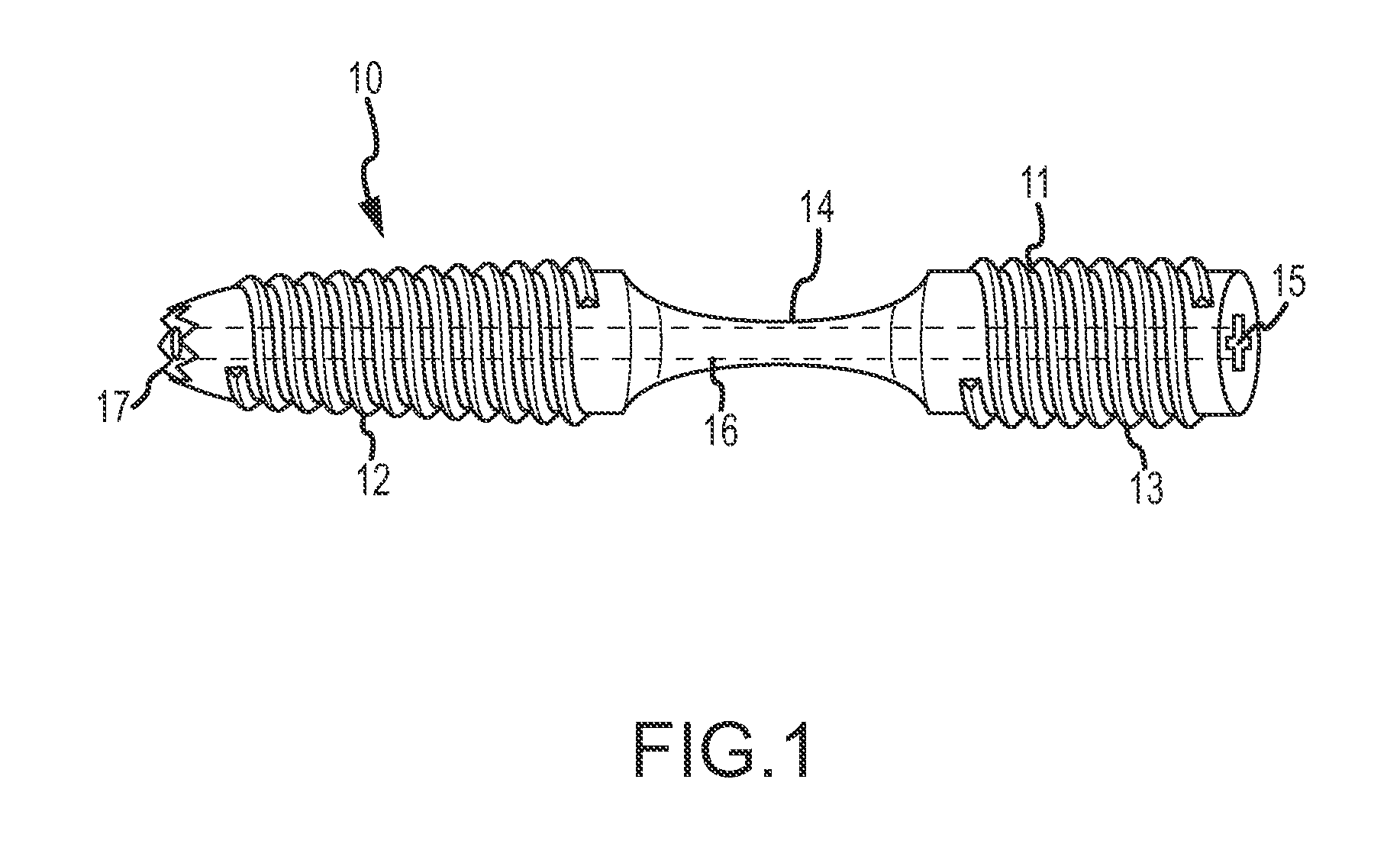
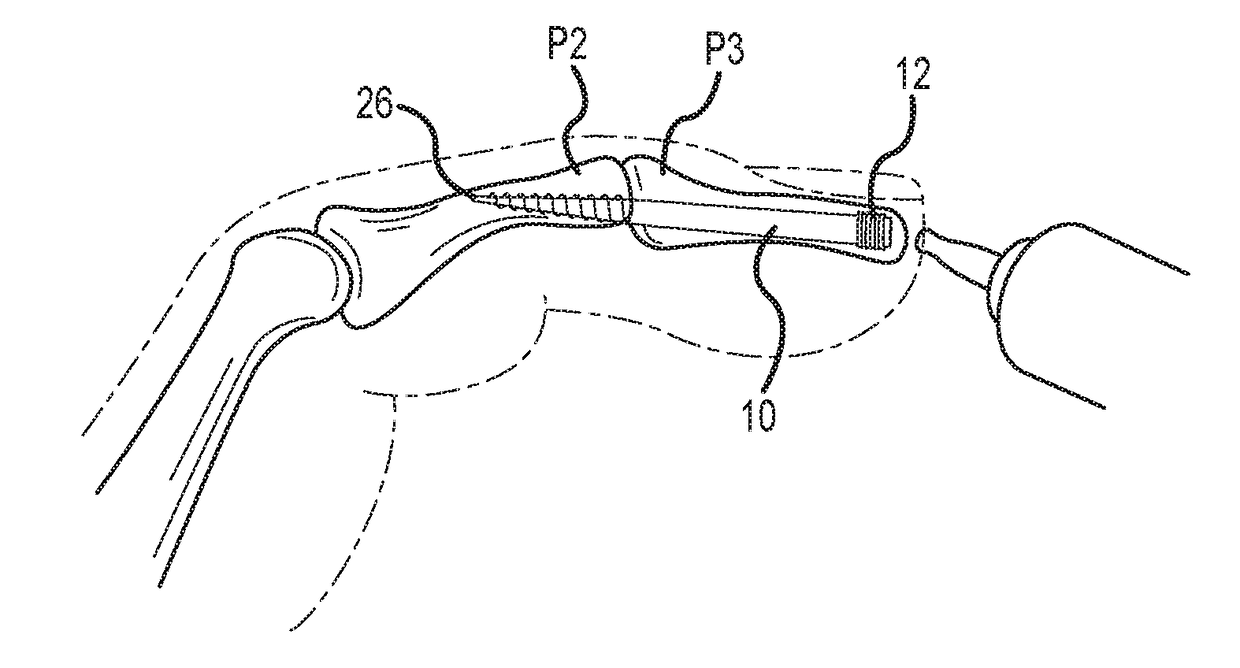
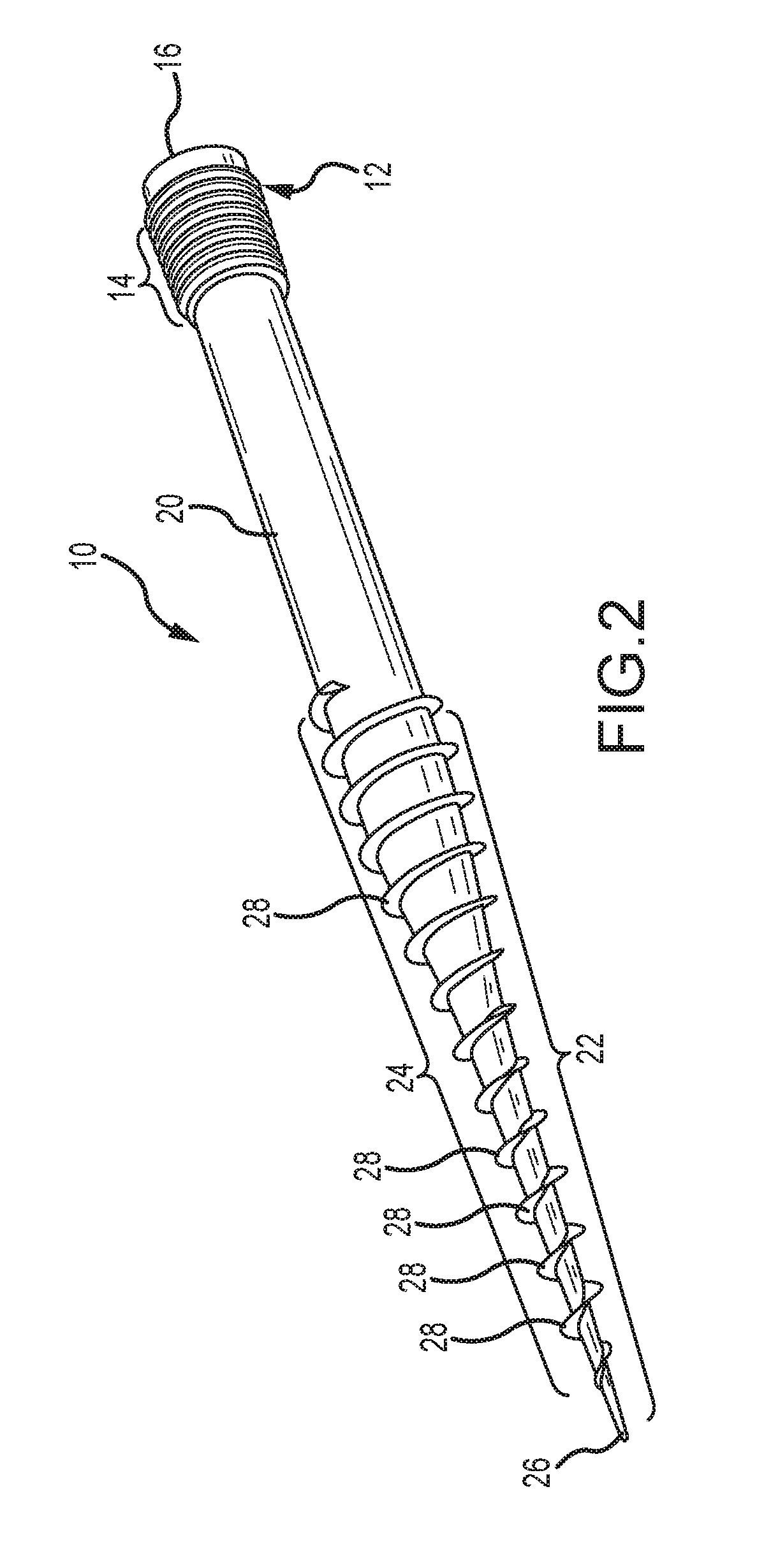
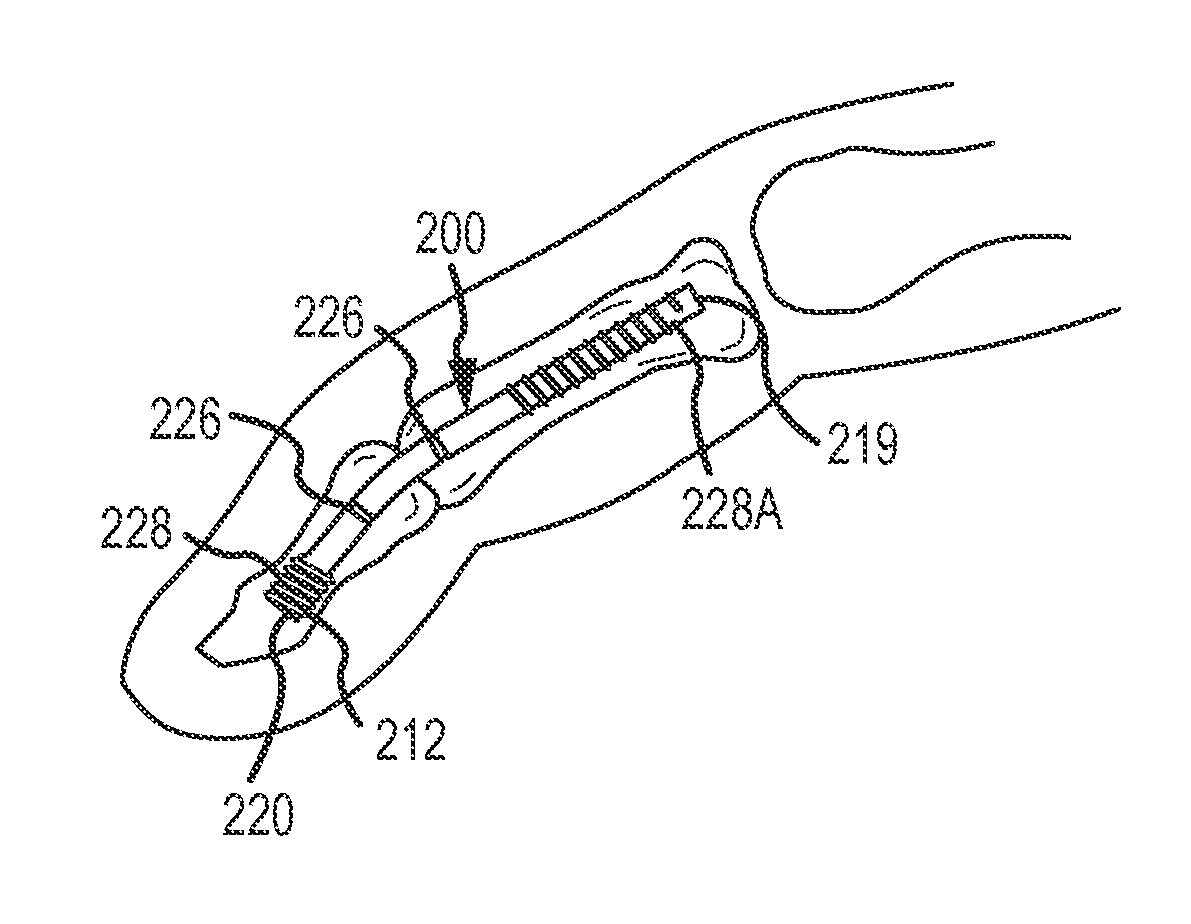
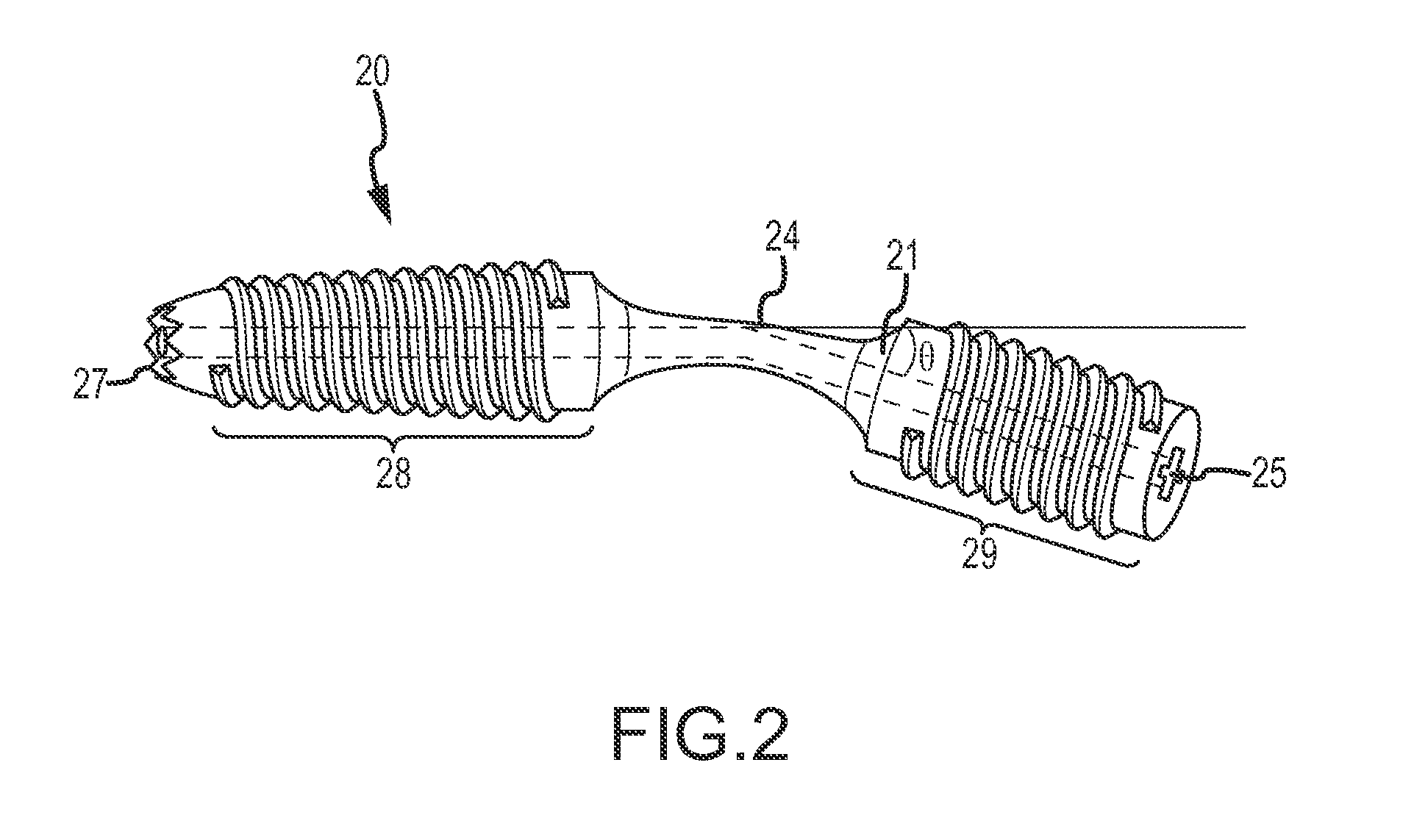
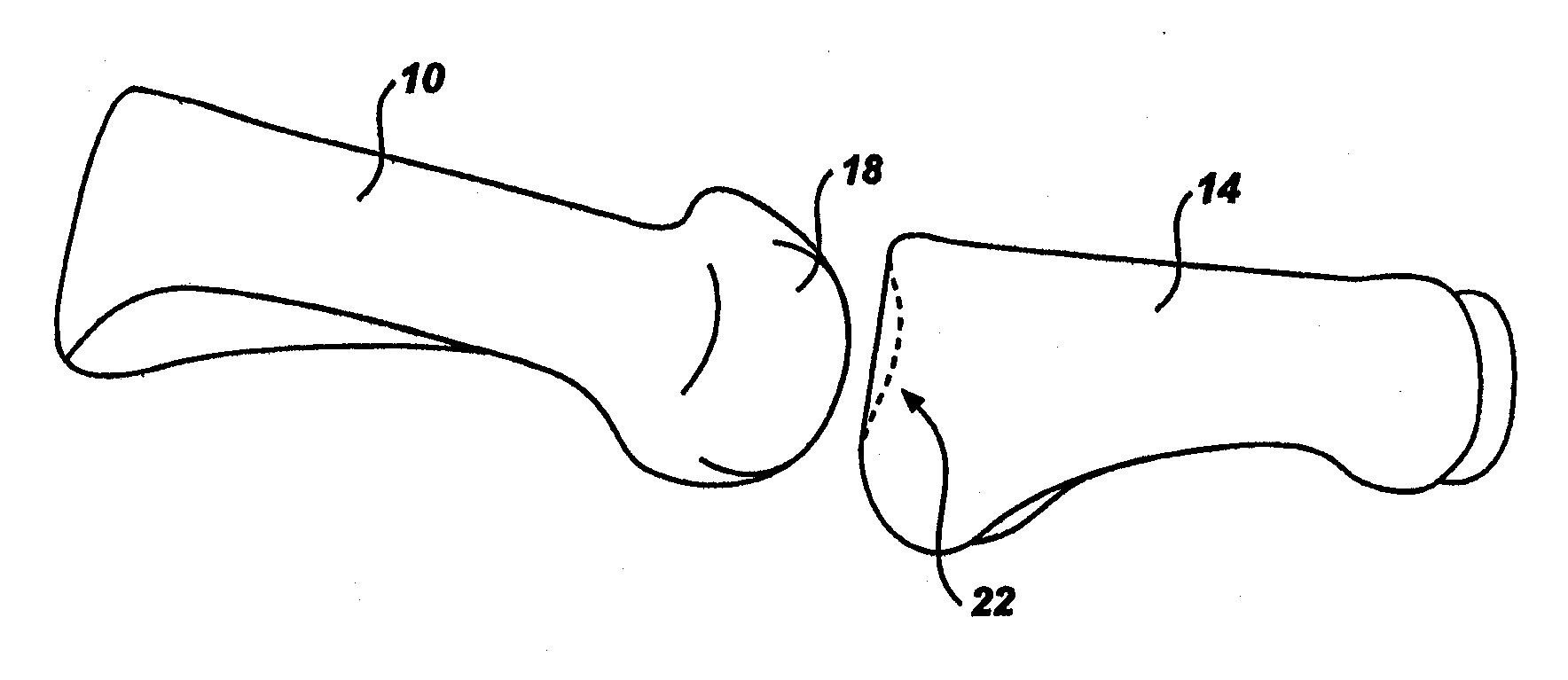
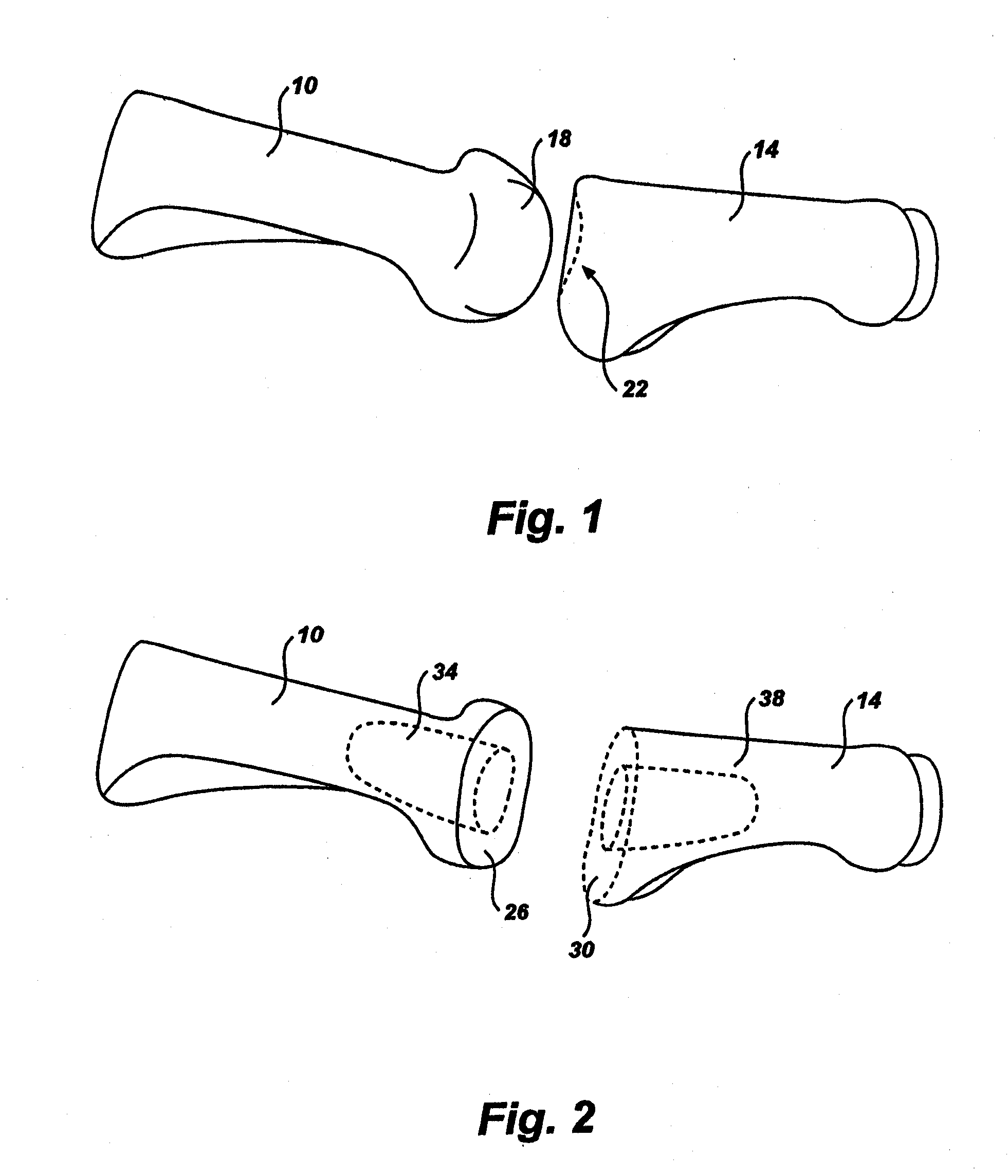
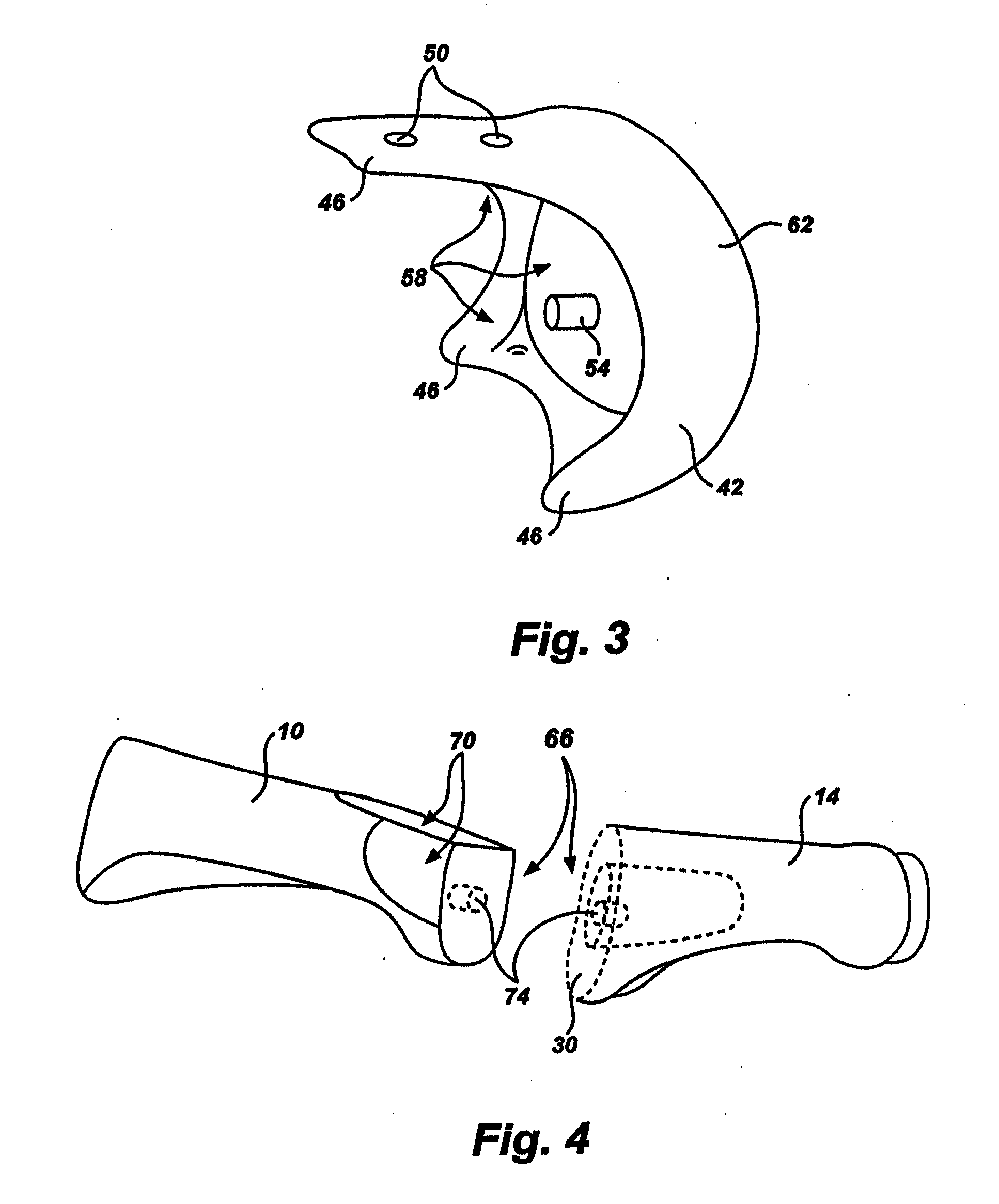
Bent dip fusion screw
Devices and methods are disclosed for the fusion of joints (particularly finger joints or toe joints) in a bent (or angled) position. In certain embodiments, the device is pre-bent and inserted into the joint in its pre-bent configuration. Alternatively, the device may be configured to have a first position wherein it is bent and a second position wherein it is straight. In that case, the device is preferably straightened by inserting a K-wire through a cannula in the device, and the device can be inserted into the joint in its straight position. Once inserted, the device is permitted to move to its bent position, which moves the joint to a bent position. In one embodiment the device moves to its bent position when the K-wire is removed.
Owner:EXSOMED CORP
Dynamic below-knee artificial limb containing flexible dynamic ankle joints and toe joints
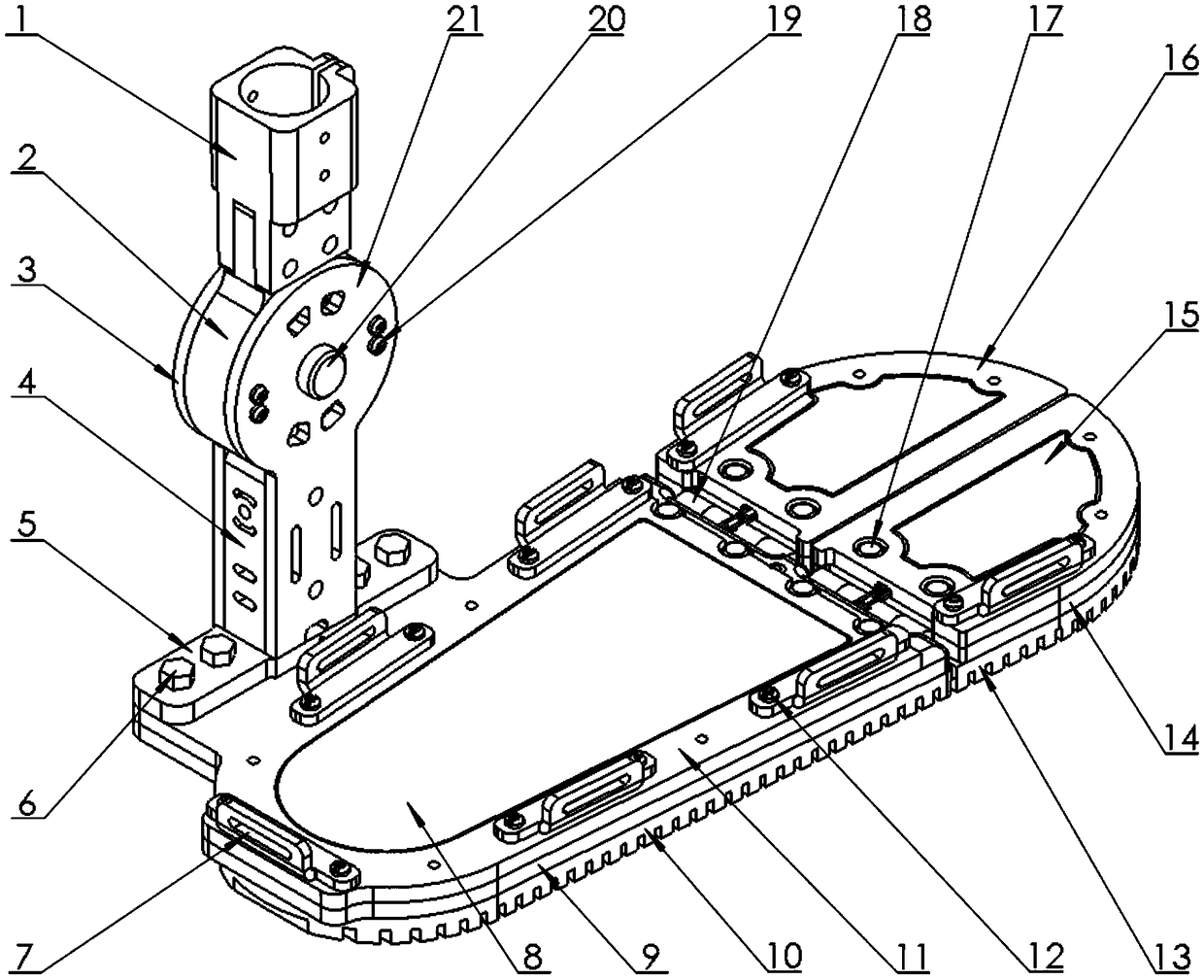
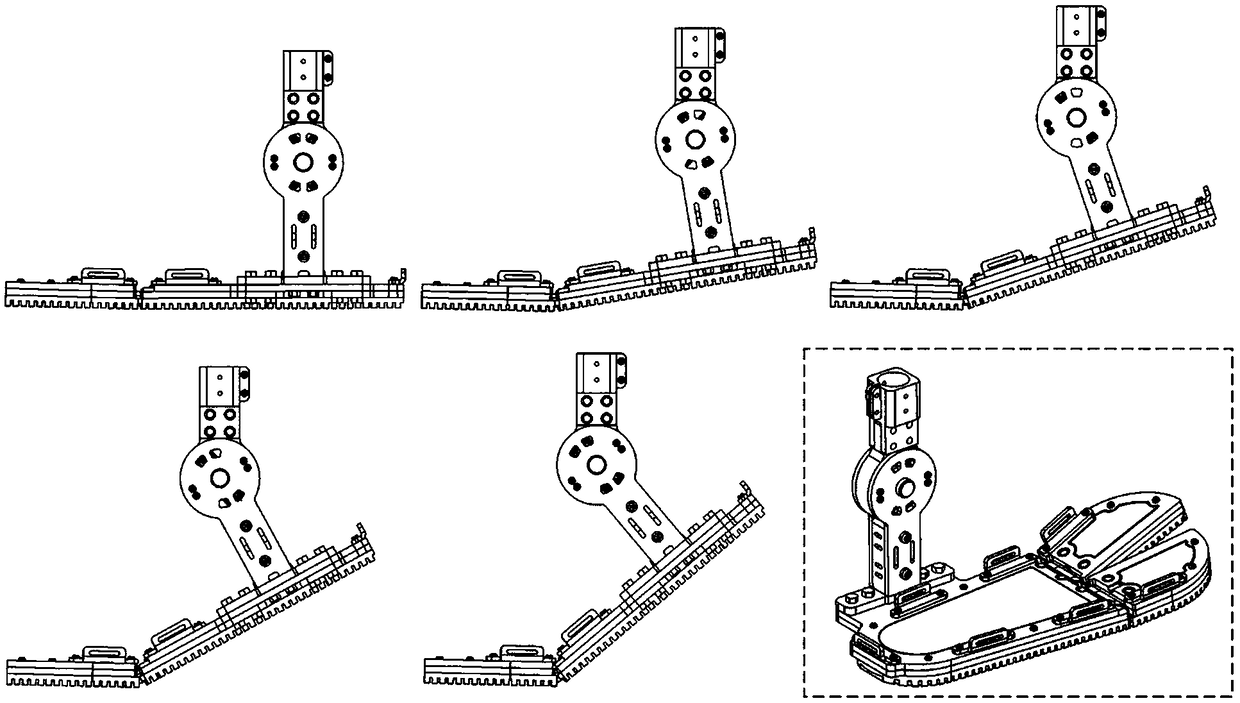
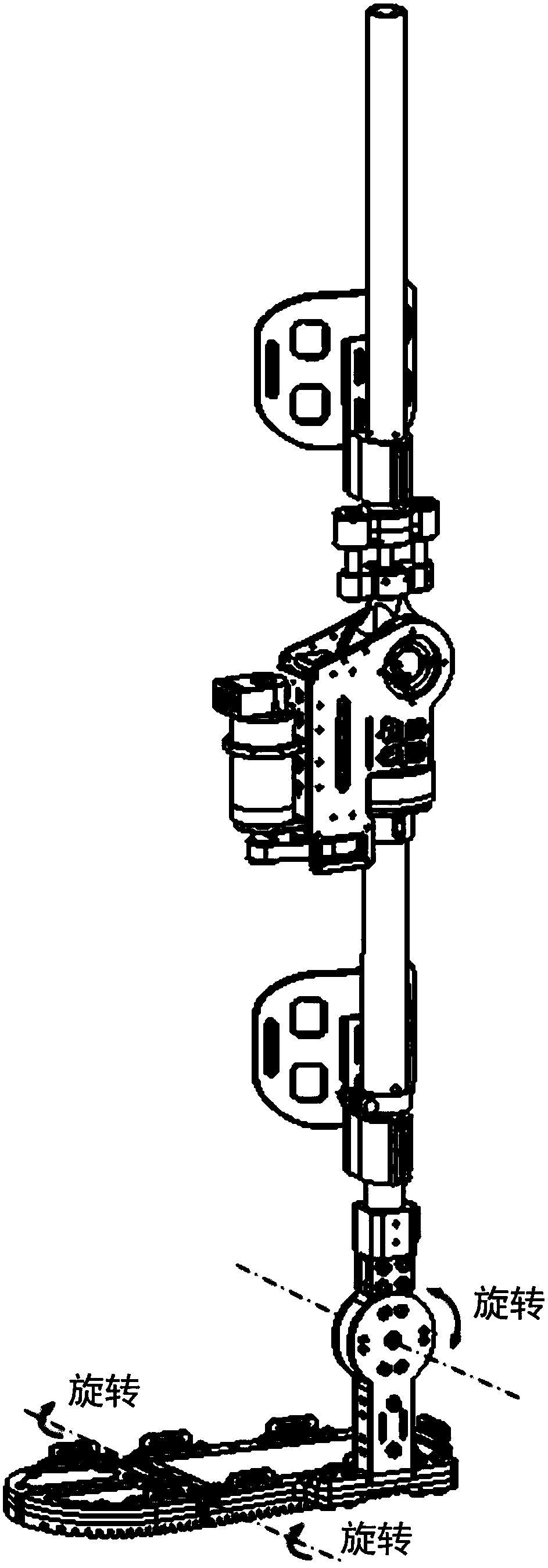
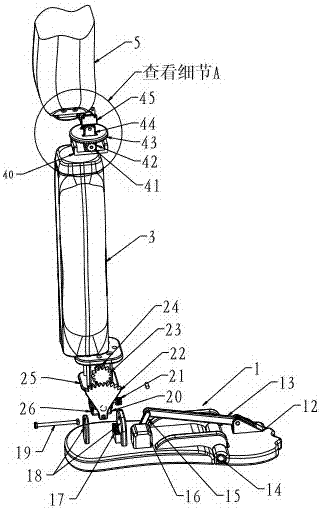
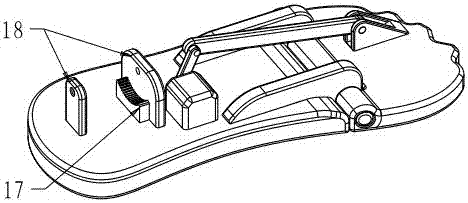
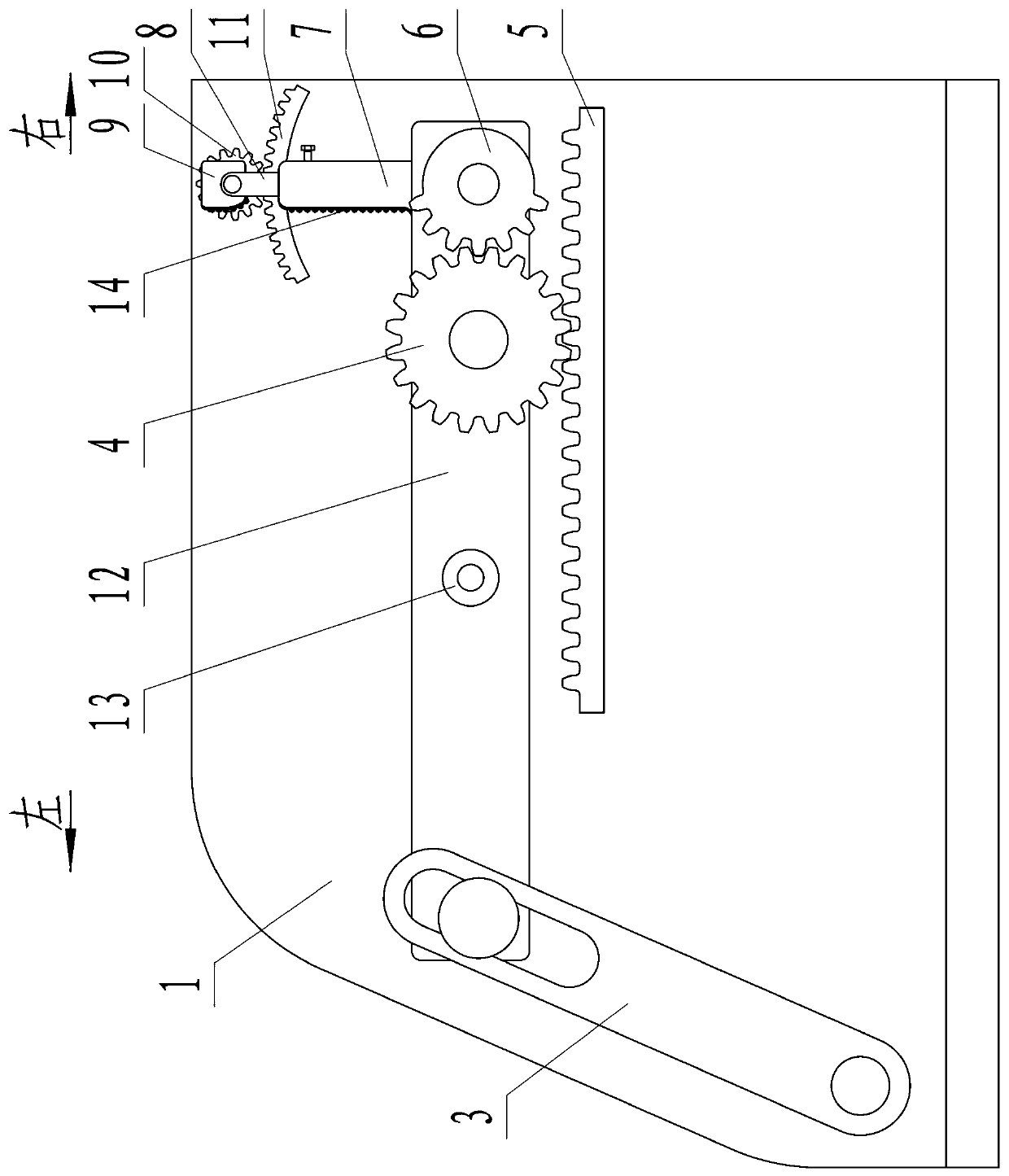
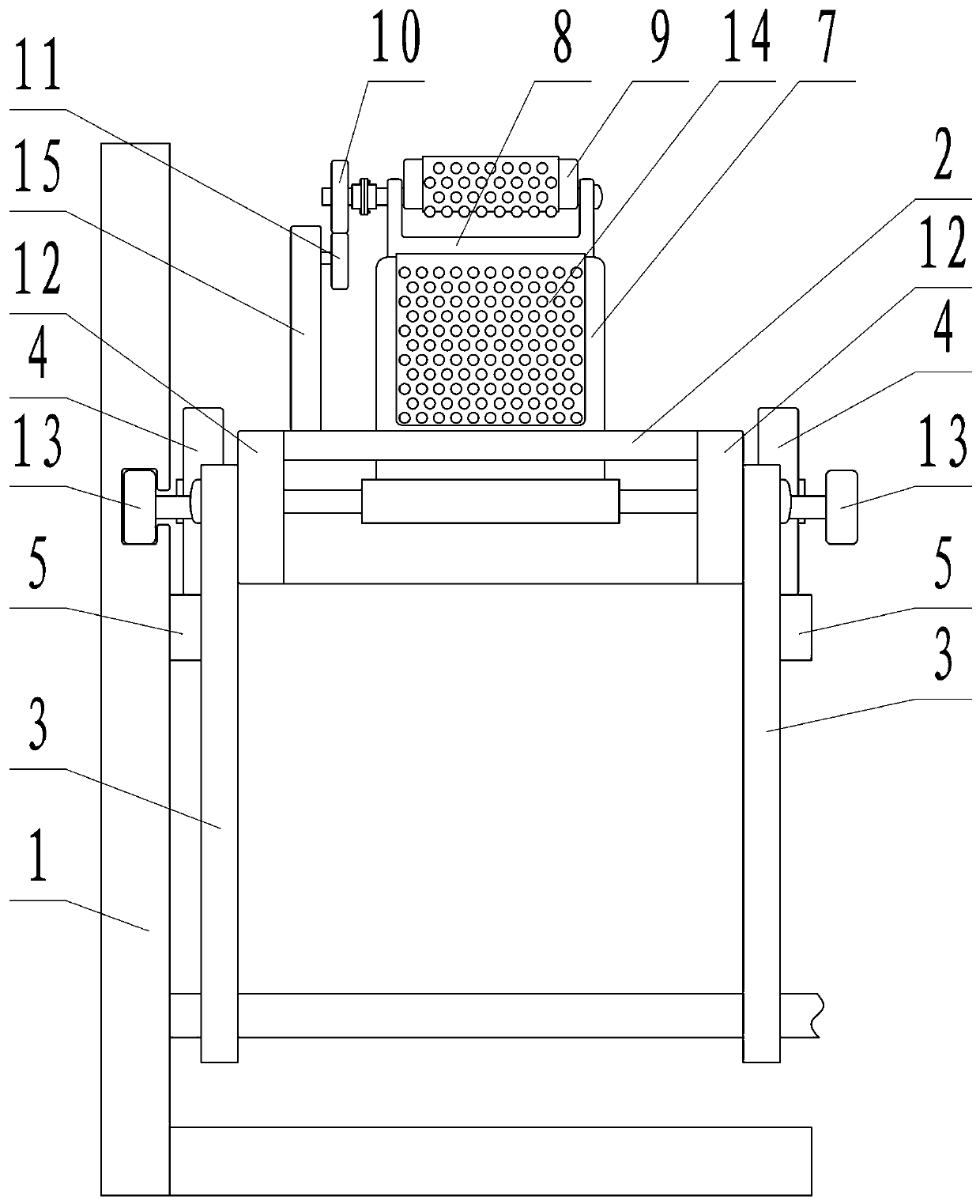
The invention relates to a dynamic below-knee artificial limb containing flexible dynamic ankle joints and toe joints, which is characterized by comprising an ankle joint moving mechanism and a toe joint moving mechanism, wherein the ankle joint moving mechanism comprises a back sole, an ankle joint supporting frame, shank baffle plates and an ankle joint motor; the ankle joint supporting frame is fixed at the upper part of the back sole, and the upper end of the ankle joint supporting frame is articulated with an ankle joint shaft connecting frame connected between two shank baffle plates; the ankle joint motor is fixedly connected between the two shank baffle plates, the output end of the ankle joint motor is fixedly connected with one end of an ankle joint screw through a shaft coupling, and the other end of the screw is connected with the back sole through an ankle joint spring mechanism; the toe joint moving mechanism comprises a front sole and a toe joint motor, wherein the front sole is articulated with the back sole, and the toe joint motor is fixedly connected with the back sole; an output shaft of the toe joint motor is fixedly connected with one end of a toe joint screw through a shaft coupling, and the other end of the screw is articulated with a toe joint screw fixing frame; and the toe joint screw is connected with the front sole through a toe joint spring mechanism. The dynamic below-knee artificial limb can be widely applied to the researches on the flexible dynamic joints of artificial limbs and serves the handicapped.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
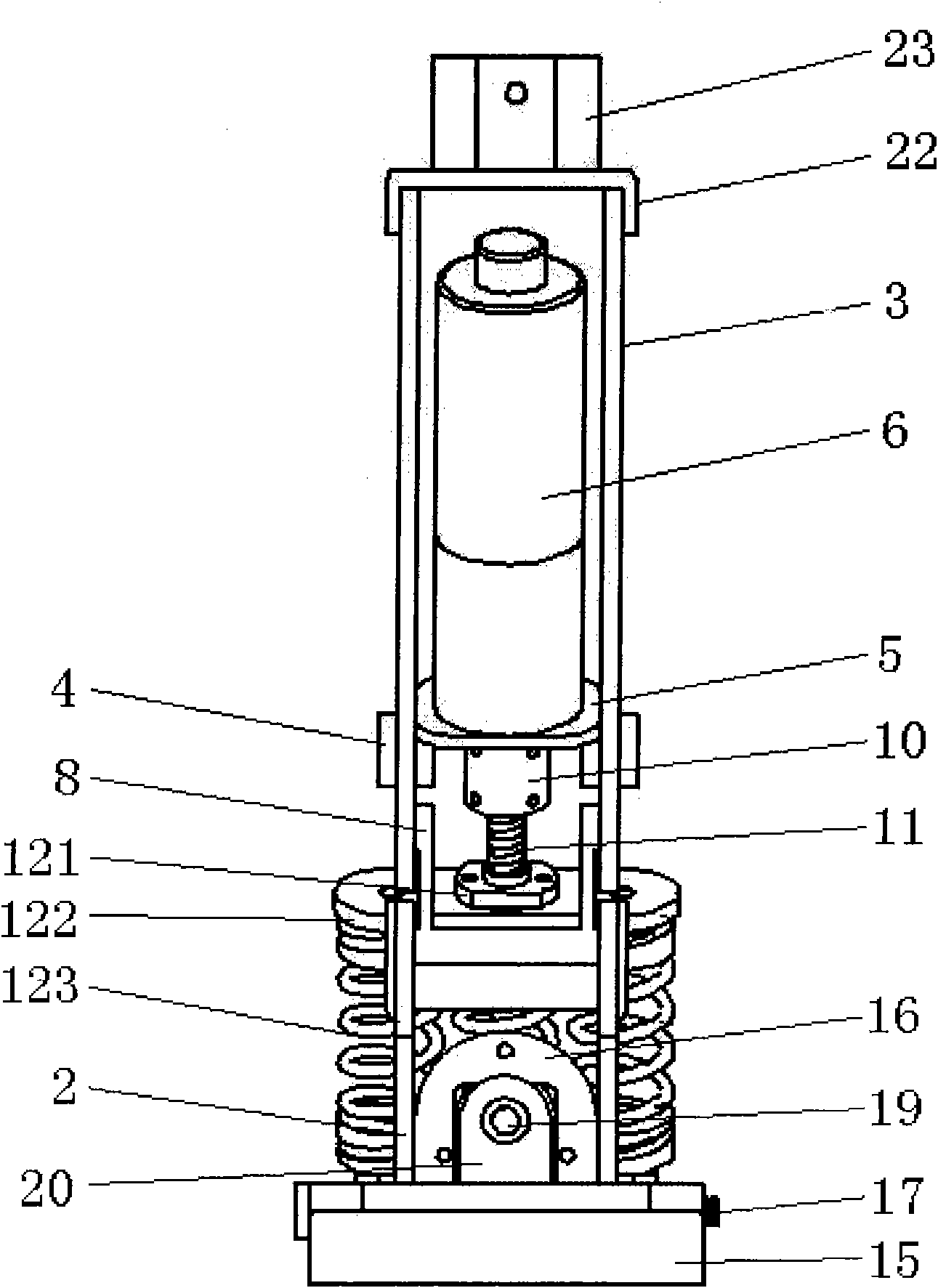
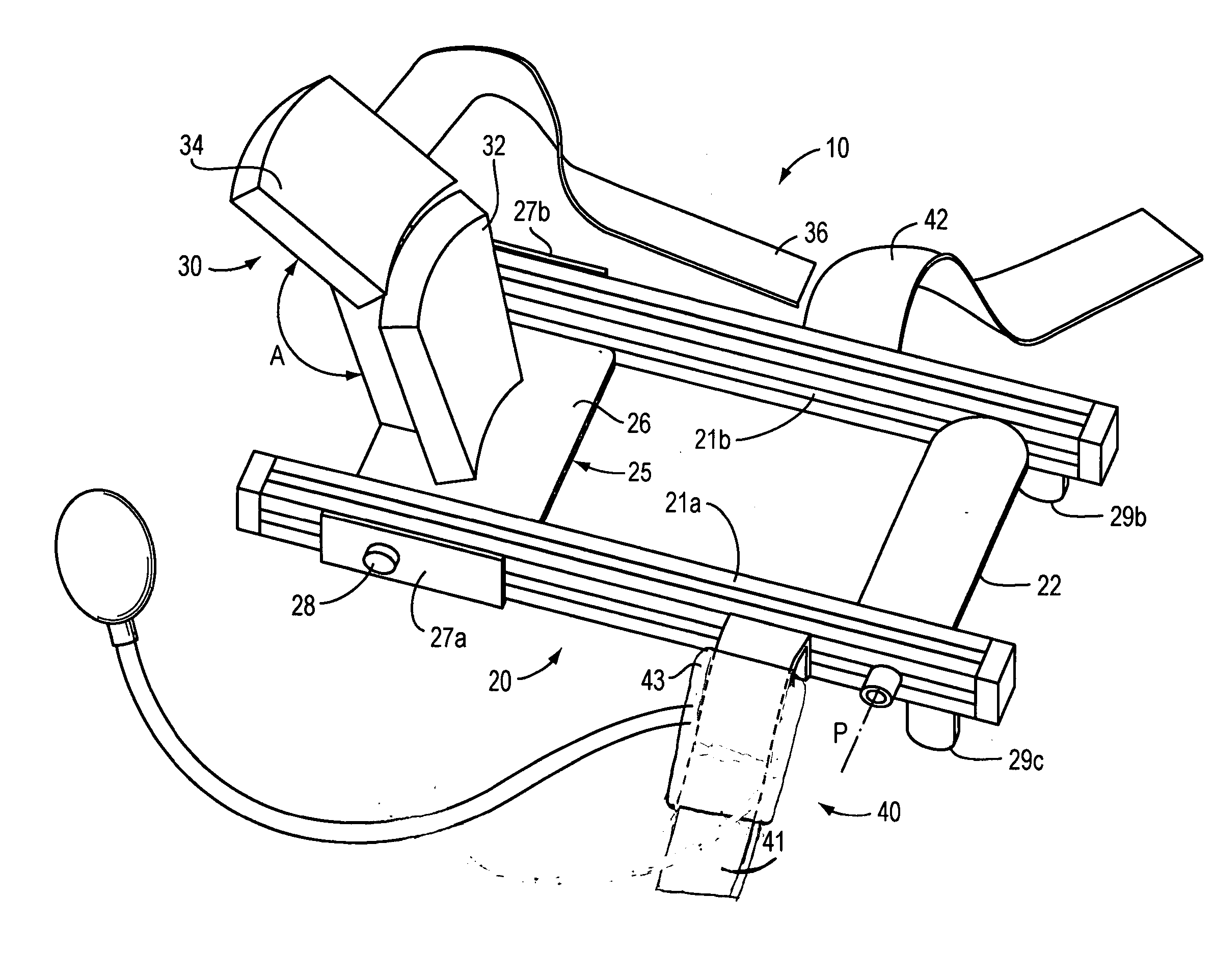
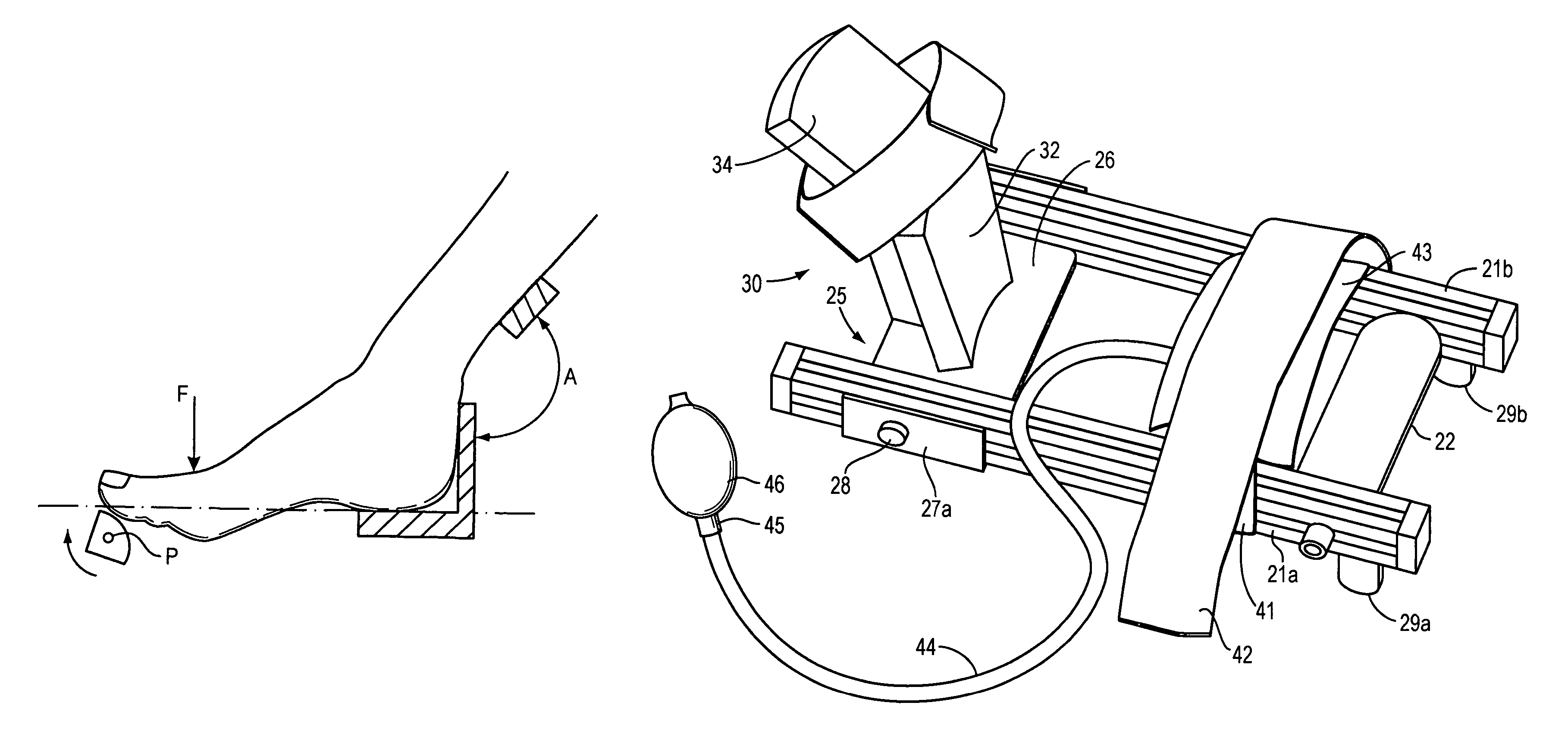
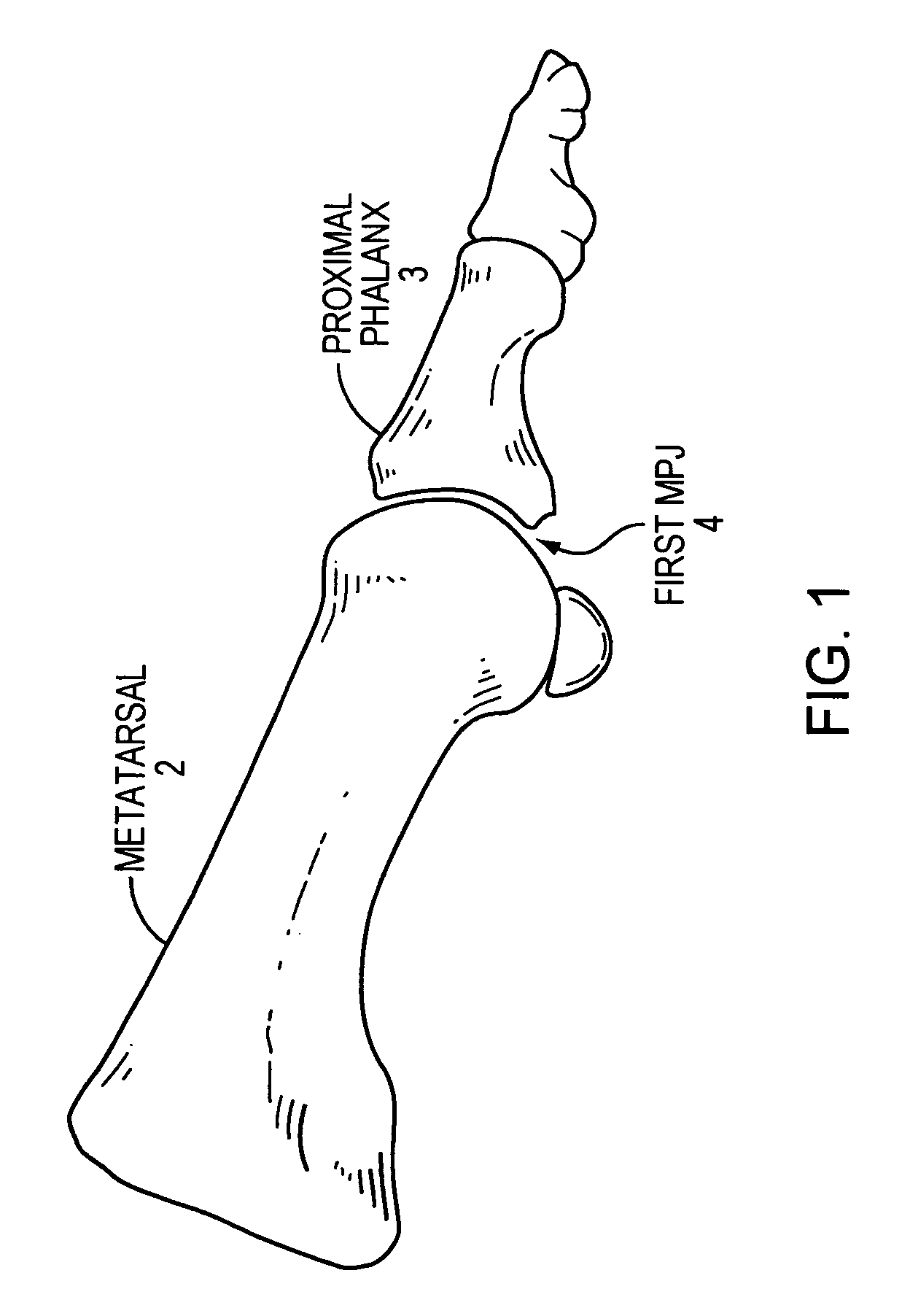
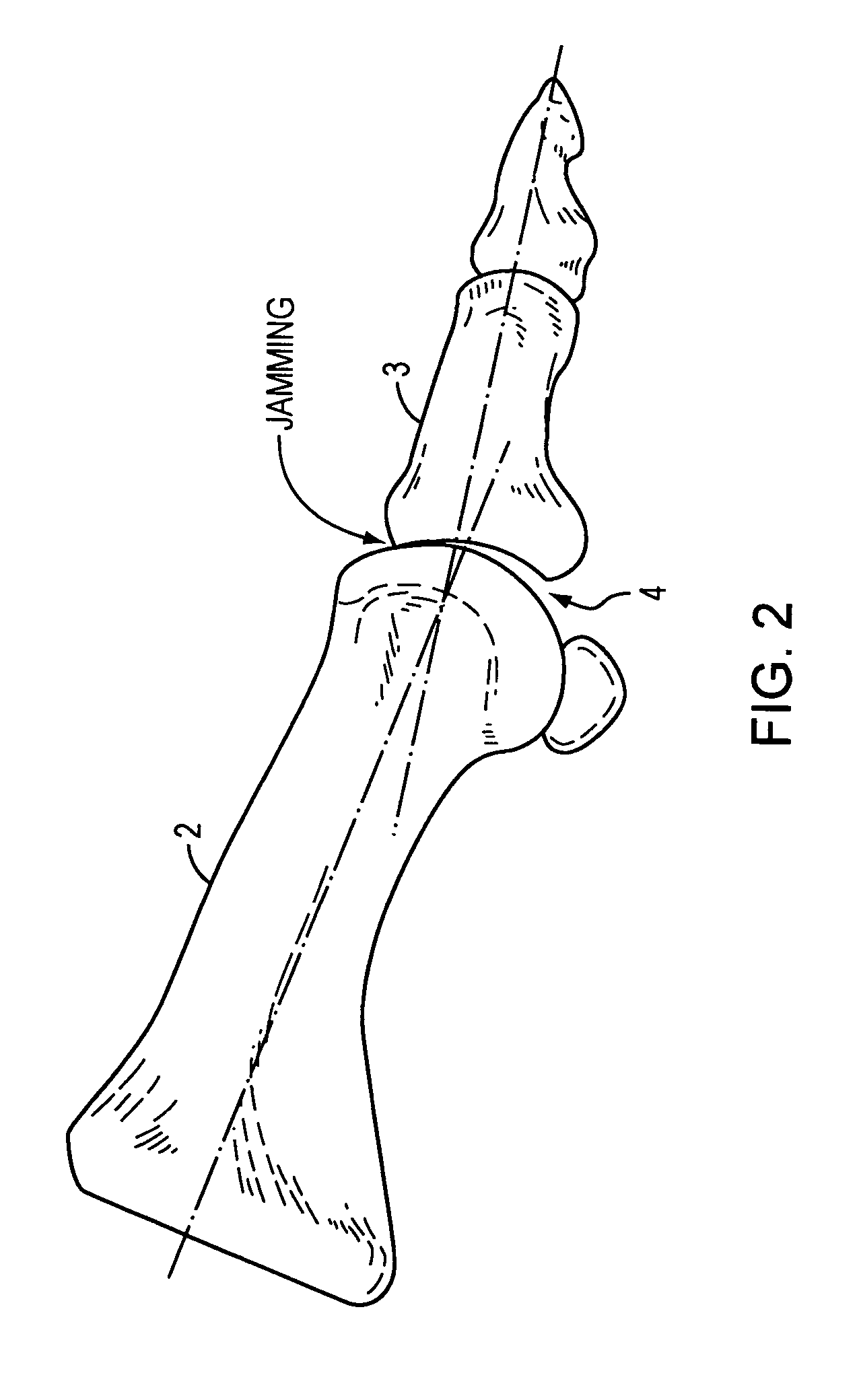
Method and apparatus for manipulating a toe joint
Embodiments of the present invention are generally related to the manipulation of a joint to provide therapy. More specifically, some embodiments of the present invention use inflatable members and a three point bending concept to cause flexion in a toe joint for the purpose of increasing the range of motion of the toe joint. In one embodiment, a user's foot is placed in a frame with at least one toe atop a toe bar. An inflatable member is positioned atop the user's foot and held in position with a strap attached relative to the frame. As the inflatable member is inflated, the strap increases in tension urging the toe toward the toe bar and causing actuation of the joint at the base of the toe.
Owner:ERMI
Method and apparatus for manipulating a toe joint
Embodiments of the present invention are generally related to the manipulation of a joint to provide therapy. More specifically, some embodiments of the present invention use inflatable members and a three point bending concept to cause flexion in a toe joint for the purpose of increasing the range of motion of the toe joint. In one embodiment, a user's foot is placed in a frame with at least one toe atop a toe bar. An inflatable member is positioned atop the user's foot and held in position with a strap attached relative to the frame. As the inflatable member is inflated, the strap increases in tension urging the toe toward the toe bar and causing actuation of the joint at the base of the toe.
Owner:ERMI
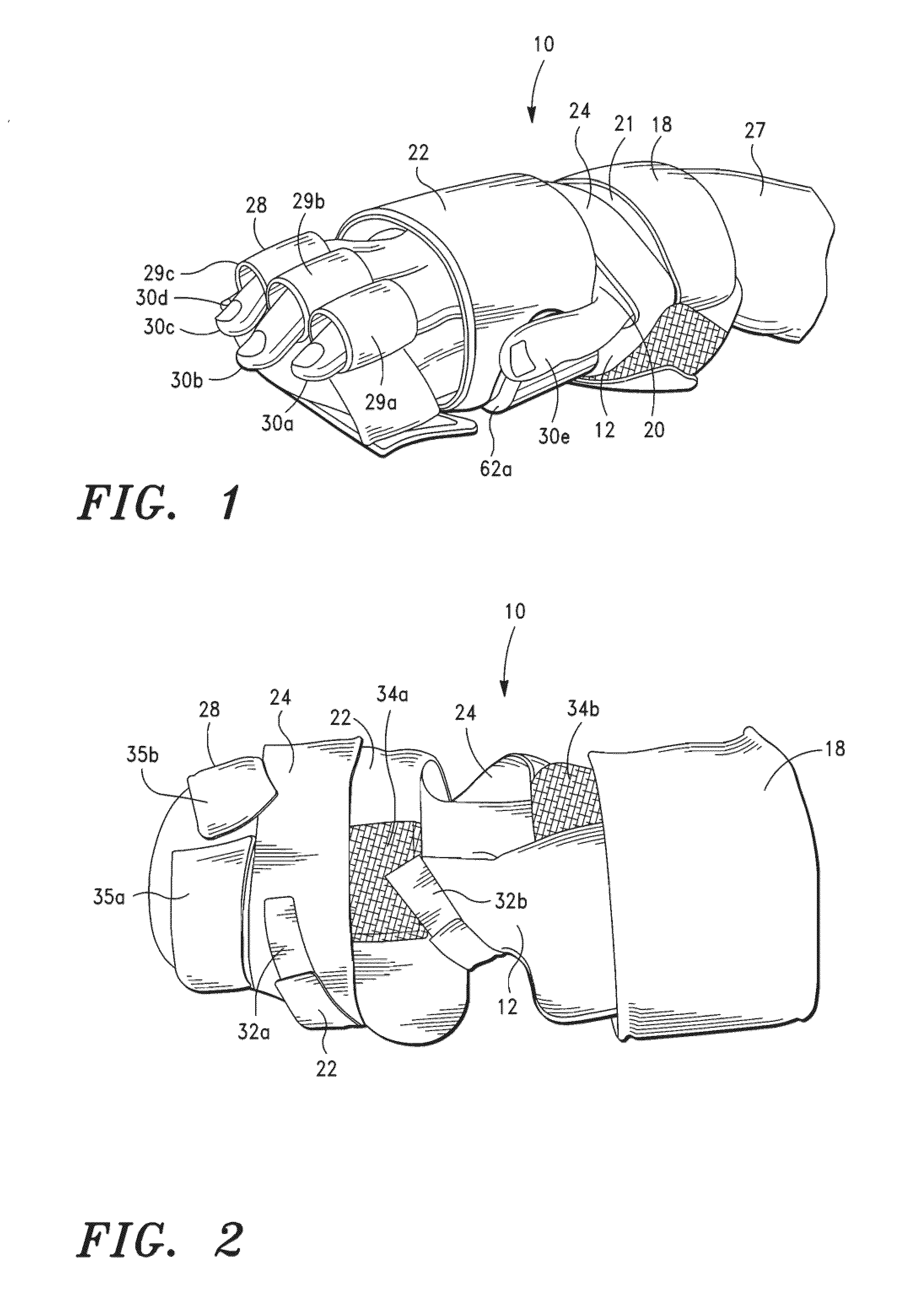
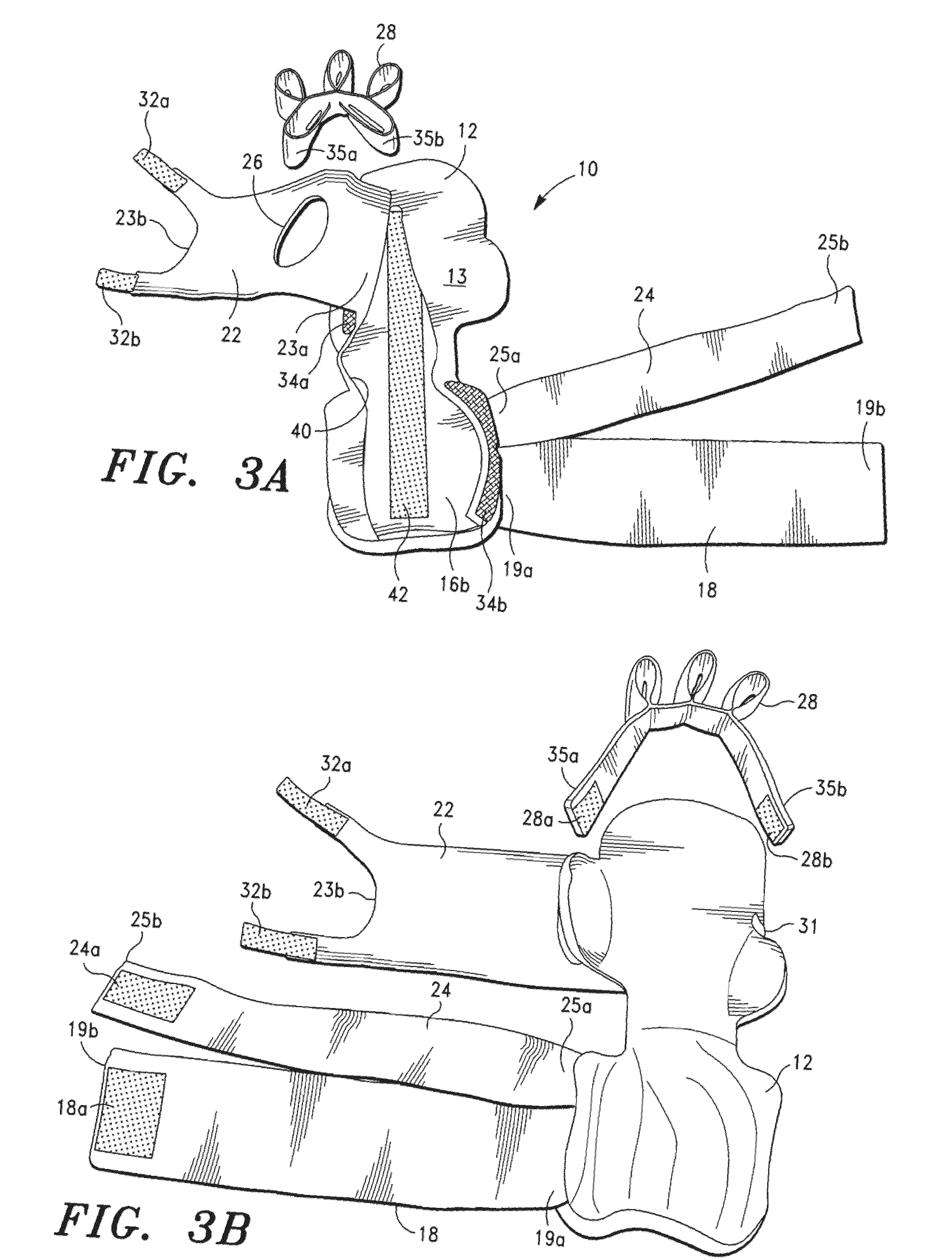
Orthosis
ActiveUS20110066095A1Hindering joint movementPreventing loss of range of motionResilient force resistorsFractureMuscle contractionFinger joint
An orthosis comprising a dynamic, flexible, elastic stiffener that is configured to extend across a joint. The stiffener is configured to extend across a joint in a first configuration, wherein the stiffener is preferably substantially planar, and a second configuration when a patient's muscle is under contraction such that the stiffener allows some joint movement but resists flexion of the joint to impede joint movement. The stiffener rebounds to its first configuration after the muscle contraction has terminated. The orthosis may be used to impede the movement of any joint, including a wrist joint and finger joints, an elbow joint, a knee joint, and an ankle joint and toe joints. Preferably, the flexible stiffener is made from a heat treated and tempered spring steel so that is has desirable dynamic and elastic properties.
Owner:BLAKE MFG
Power below-knee prosthesis-based gait recognition method
The invention relates to a power below-knee prosthesis-based gait recognition method. The method comprises the following steps that: 1) a sensor is arranged at a corresponding position of a power below-knee prosthesis; 2) when H is equal to 1, and simultaneously FH is greater than FPH and the derivative of theta ankle is less than 0, an ankle joint enters a passive plantar flexion stage; 3) when T is equal to 1, the passive plantar flexion stage is finished; the ankle joint enters a passive dorsiflexion stage, and simultaneously the ankle joint rotates forwards until the ankle joint reaches amaximal forward angle or H is equal to 0; 4) when H is equal to 0, Tankle is greater than tau pp, and the derivative of the theta ankle is less than 0, the ankle joint enters an active plantar flexion stage; 5) when theta toe is less than 0, a toe joint enters an active dorsiflexion stage; 6) when FT is greater than FPT, the toe joint enters the active plantar flexion stage and simultaneously thetoe joint starts to rotate downwards; and 7) when the ankle joint and the toe joint reach a specified angle or T is equal to 0, the active plantar flexion stage is finished, and a foot leaves the ground to enter a swinging stage; and in the swinging stage, the ankle joint and the toe joint recover to a balance state respectively. The invention provides a new gait recognition method in which a power ankle joint and a power toe joint are involved at the same time.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
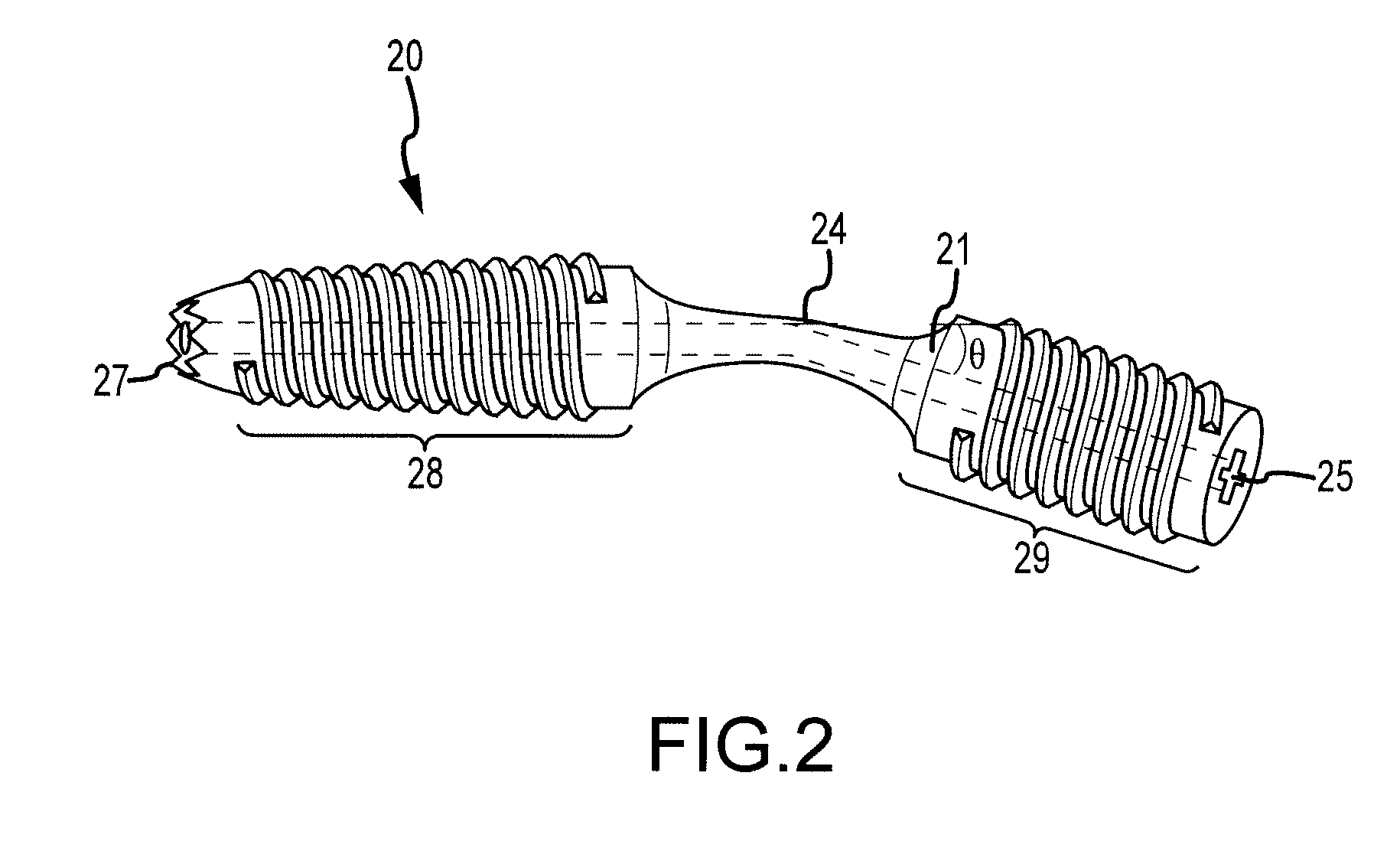
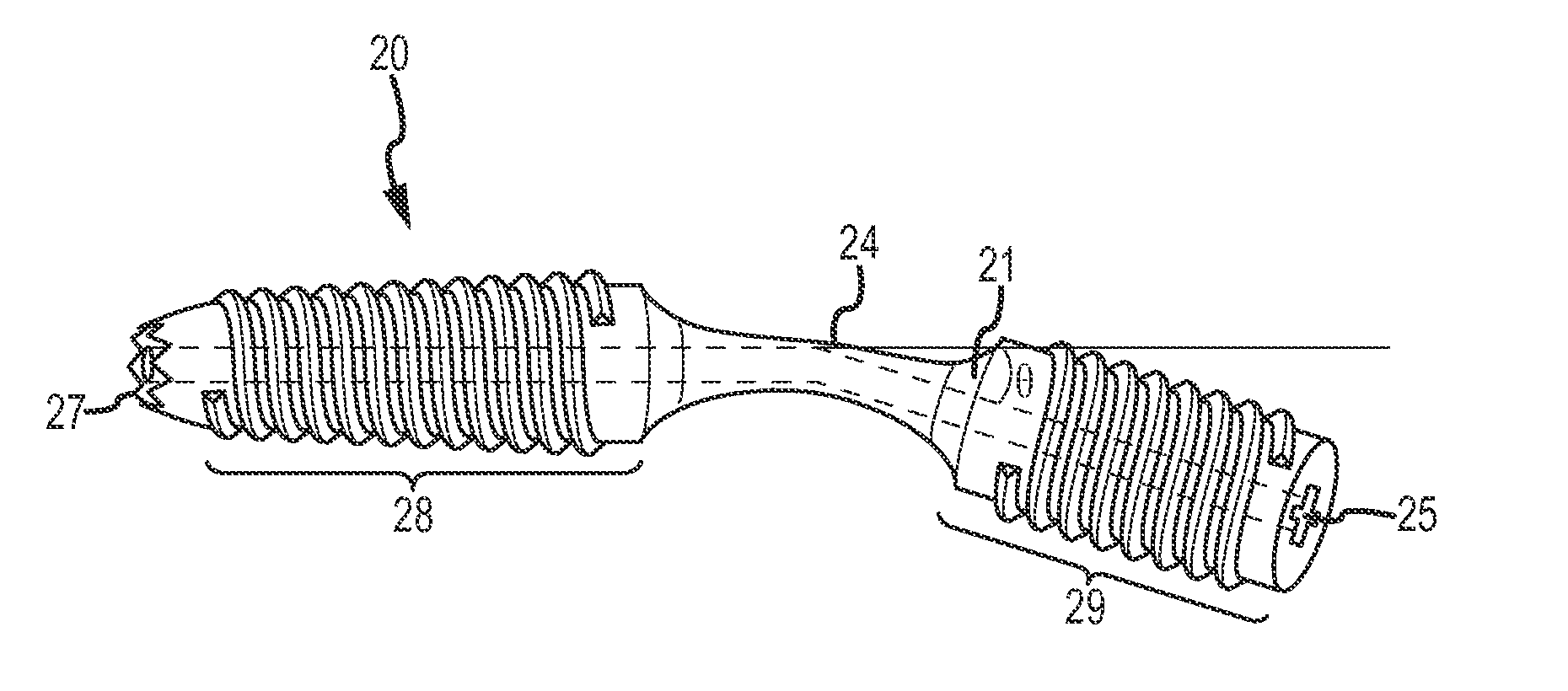
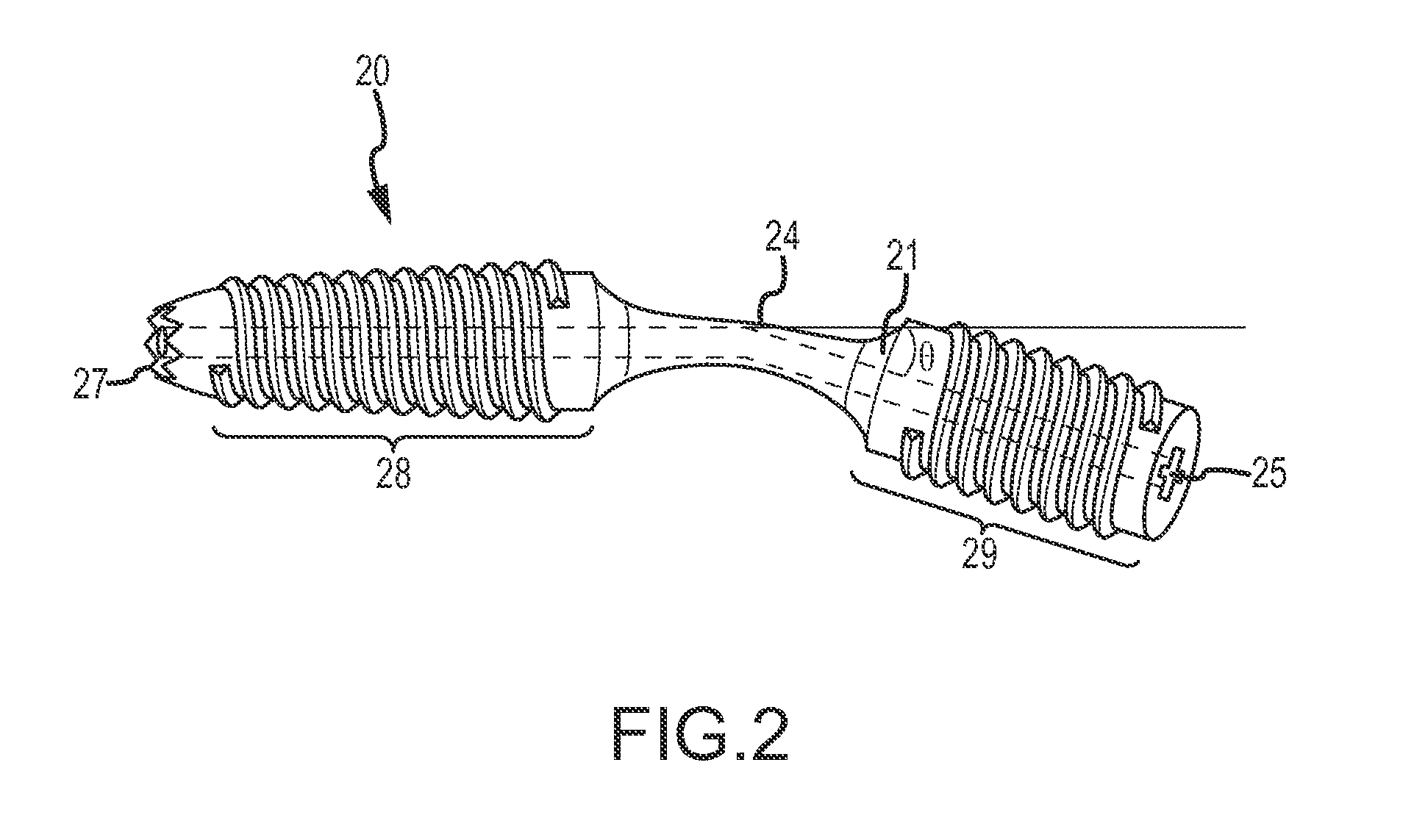
Dip fusion spike screw
ActiveUS20170189090A1Easy to placeAvoid insufficient thicknessInternal osteosythesisFastenersFinger jointTarsal Joint
Devices and methods are disclosed for the fusion of joints (particularly finger joints or toe joints) in a bent (or angled) position. The device is not cannulated, straight and inserted into the joint in its straight configuration. The device is configured to have a thicker portion at its proximal end than at its distal end. The device is preferably inserted into a finger joint that is already bent at an angle, and the thin, distal end is configured to screw into and attach to the bone of second joint thereby fusing the first joint to the second joint.
Owner:EXSOMED CORP
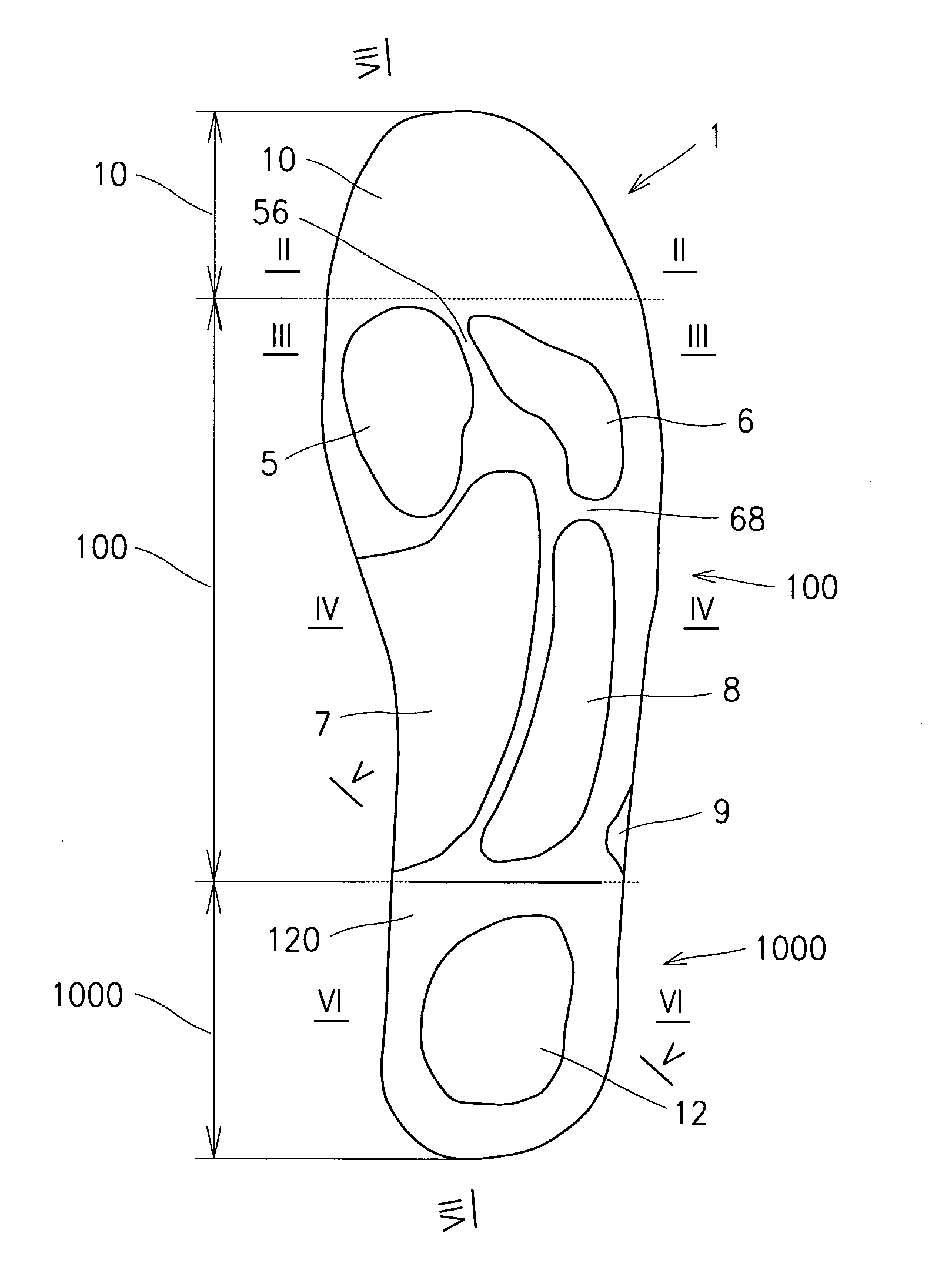
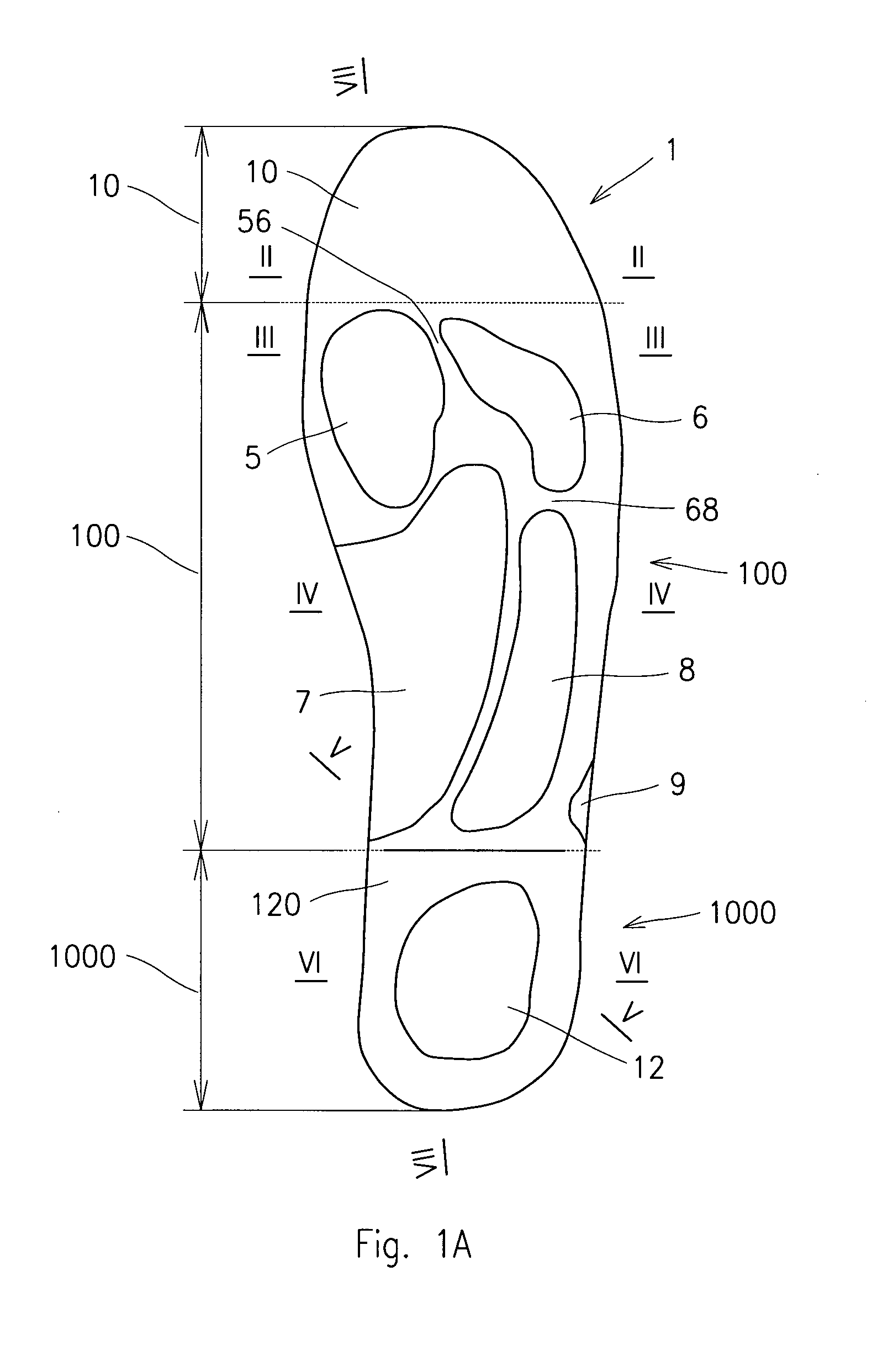
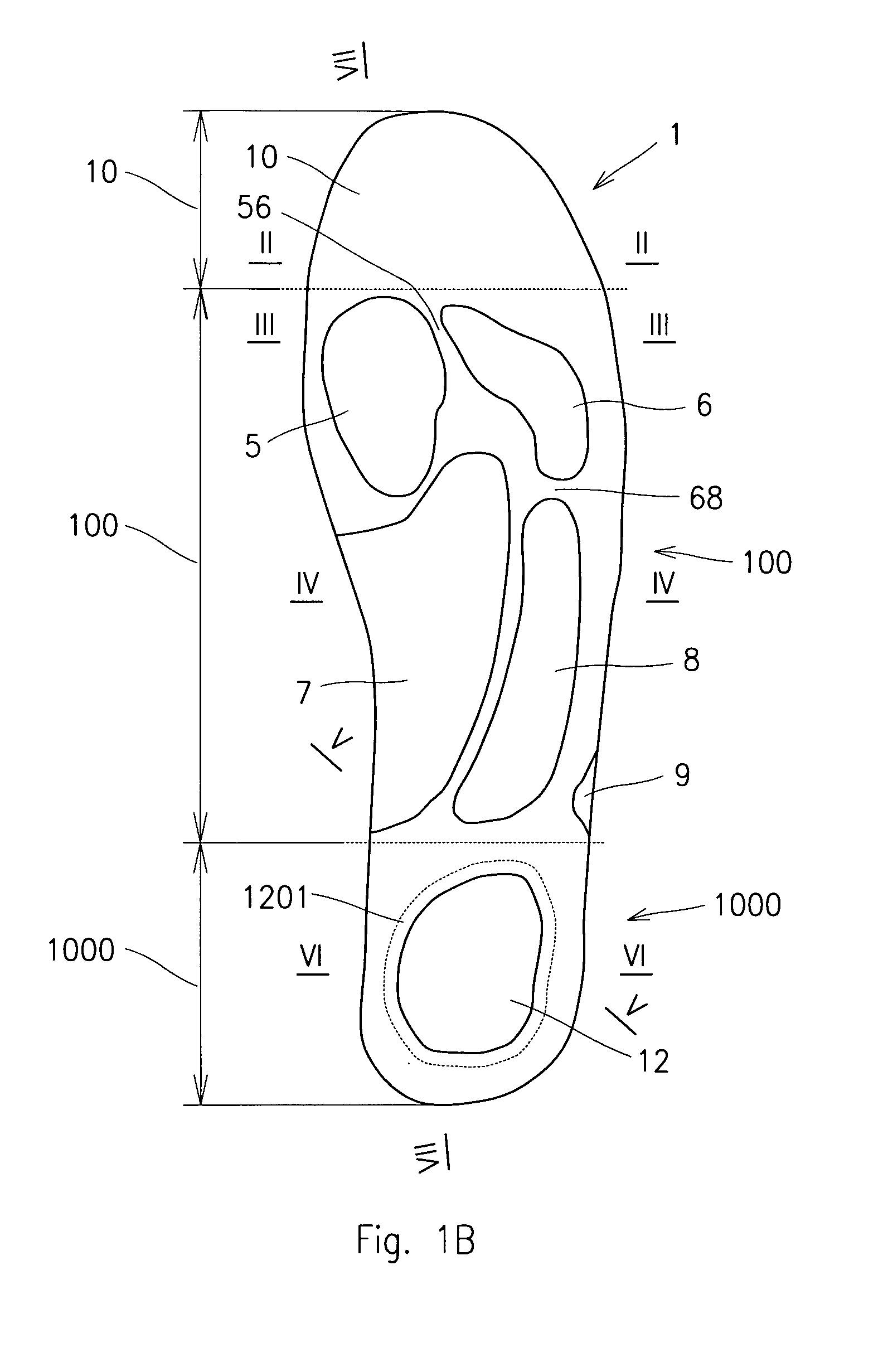
Insole
The insole (1) from the upper side provided with shaping corresponding to the form of impression of bottom part of a human foot sole with recess (5) for the big toe joint with smooth toe section (10), and from the bottom side with shaping corresponding to the bottom part of a human foot sole with smooth toe section (10), while it in a flexible manner supports all parts of the foot sole between the toe section (10) and the heel section (1000). In the heel section (1000) there is performed recess (1201) or depression (120), in which the heel recession (12) is performed.
Owner:BOTY J HANAK R
Ergonomic swim fin apparatus
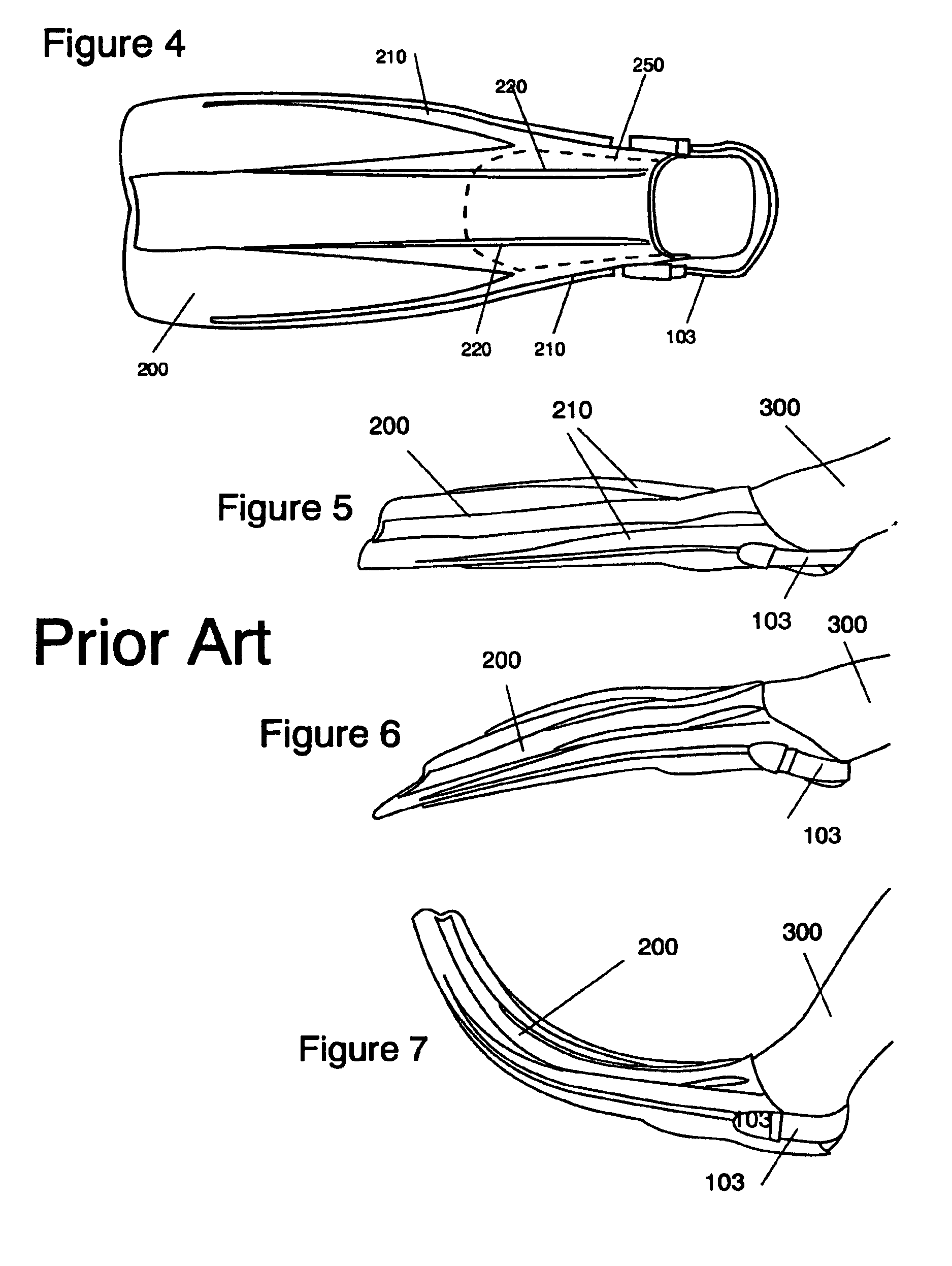
The ergonomic swim fin apparatus comprises a foot-pocket sized to fit about a user's foot, channeling scoops are positioned on opposite sides of the footpocket, and a flexible blade extends from the foot-pocket to a trailing edge. A “wing shaped” tail fin is secured to the trailing edge of the flexible blade. The channeling scoops are rounded to channel the water displaced by the user's foot over the flexible blade and tail fin. The flexible blade and wing like tail fin channel water while enhancing lift and thrust. At least one securing strap is used to secure the user's foot to the foot-pocket. The tail fin is preferably selectively attachable and removable from the distal end of the flexible blade. The flow of water across the foot is converted by the channeling scoops into a propulsion stroke in both the up and down strokes, while allowing the foot the freedom to flex naturally at the ankle and toe joints.
Owner:MELIUS JOHN DAVID
Walking Stilts with Separate Heel and Toe Sections
A walking stilt includes a shoe platform and a floor platform connected by a support. The floor platform includes a heel section pivotally attached to the support and a separate and independently pivotable toe section pivotally attached to the support. The construction mimics an ankle joint and toe joints to provide a smooth rolling action while walking.
Owner:SINGLETON ROBERT P
Human vola-emulated mechanism with force-sensing ability
InactiveCN1966338AAchieve rotationSimple structureSelf-moving toy figuresProsthesisPolyesterReduction drive
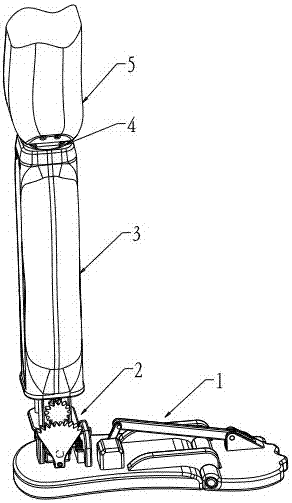
The invention relates to a simulated sole with toe joint, which can detect the vertical pressure of sole, with simple structure, wherein it comprises front sole, back sole, sensitive detector, rotation axle connecting front and back soles, and relative transmitters. Each sensitive detector comprises one suspension beam, two stress plates, two bolts, one adjustable nut, one muffle, one guide block, one anti-impact polyester rubber block. The rotation axle and transmitters comprise rotation axle, bearing, bearing base, axial base, motor base, gear, synchronous tooth band, bolt, direct-current motor, speed reducer, and coder. The invention can simulate the toe motion of human, with small volume, light weight, and compact structure.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Lower limb rehabilitation training device for neurology department
InactiveCN107736992ARealize autonomous rotationAchieve trainingChiropractic devicesMovement coordination devicesNeurology departmentKnee Joint
The invention discloses a lower limb rehabilitation training device for the neurology department, and belongs to the field of medical care equipment. A central rotating shaft of the device is arrangedon a motor connected with a transmission, and a binding tape for fixing the foot of a patient is arranged on a pedal; a toe joint training component is arranged in the pedal and is driven by a concave-convex wheel, so that a rotating shaft top pillar pushes one end of a rotating sleeve rod up or down, and the other end of the rotating sleeve rod is pushed down or up by using a lever mechanism; atoe sleeve piece is driven by a moving rod to move up and down, so that the toe of the patient is upturned or bent down; a transverse direction training component is arranged on the pedal, the patientfreely controls a pedal panel and the toe sleeve piece to deflect together, and the related structure can satisfy the rotation requirement without affecting other actions. The lower limb rehabilitation training device provided by the invention has the functions of simultaneously training the hip joint, the knee joint, the ankle joint and the toe joint, can meet the exercise training of the jointsin the longitudinal and transverse directions, can carry out the active training and the passive training, has relatively comprehensive training functions and is easy to control.
Owner:张海玉
Bent dip fusion screw
Devices and methods are disclosed for the fusion of joints (particularly finger joints or toe joints) in a bent (or angled) position. In certain embodiments, the device is pre-bent and inserted into the joint in its pre-bent configuration. Alternatively, the device may be configured to have a first position wherein it is bent and a second position wherein it is straight. In that case, the device is preferably straightened by inserting a K-wire through a cannula in the device, and the device can be inserted into the joint in its straight position. Once inserted, the device is permitted to move to its bent position, which moves the joint to a bent position. In one embodiment the device moves to its bent position when the K-wire is removed.
Owner:EXSOMED CORP
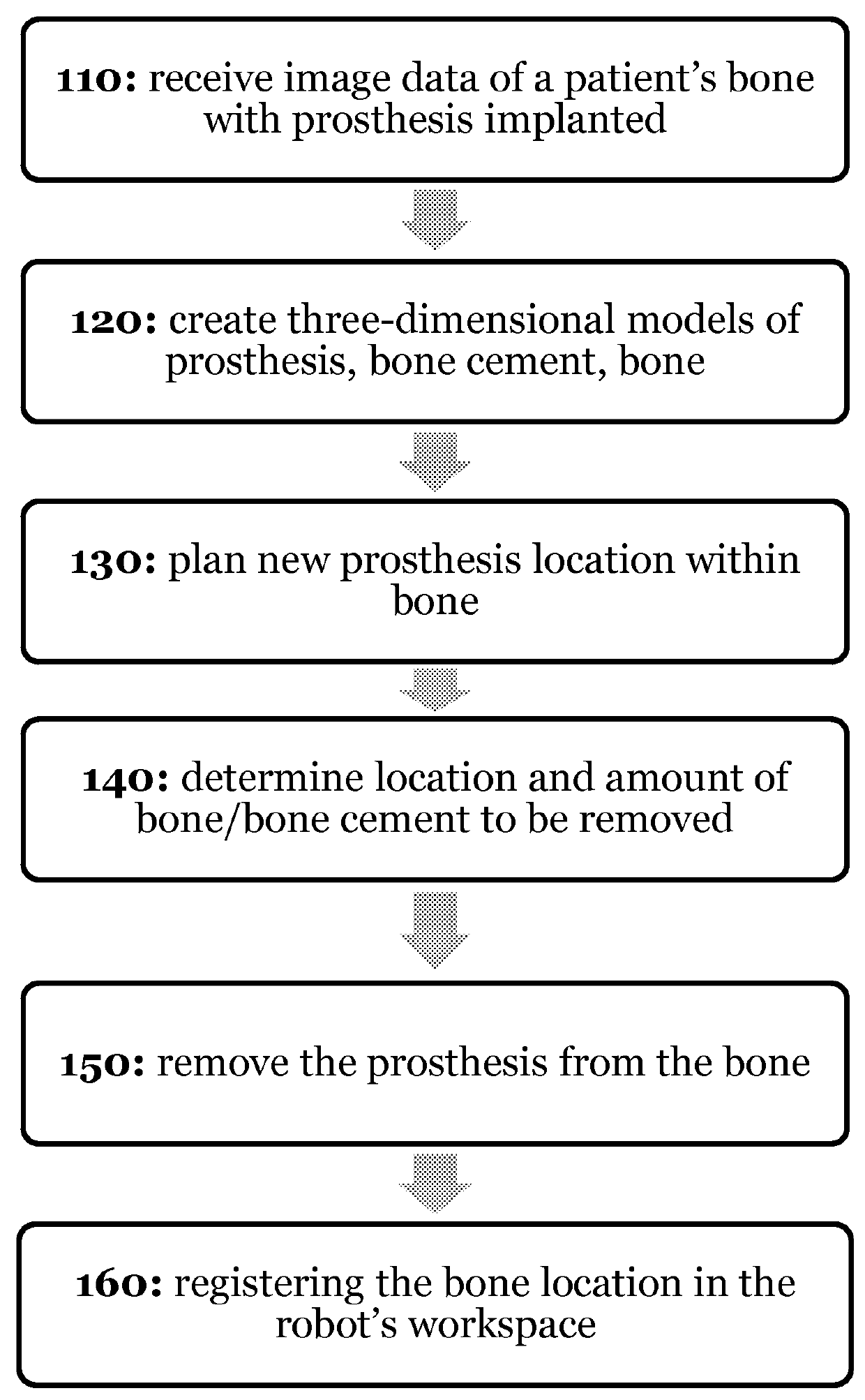
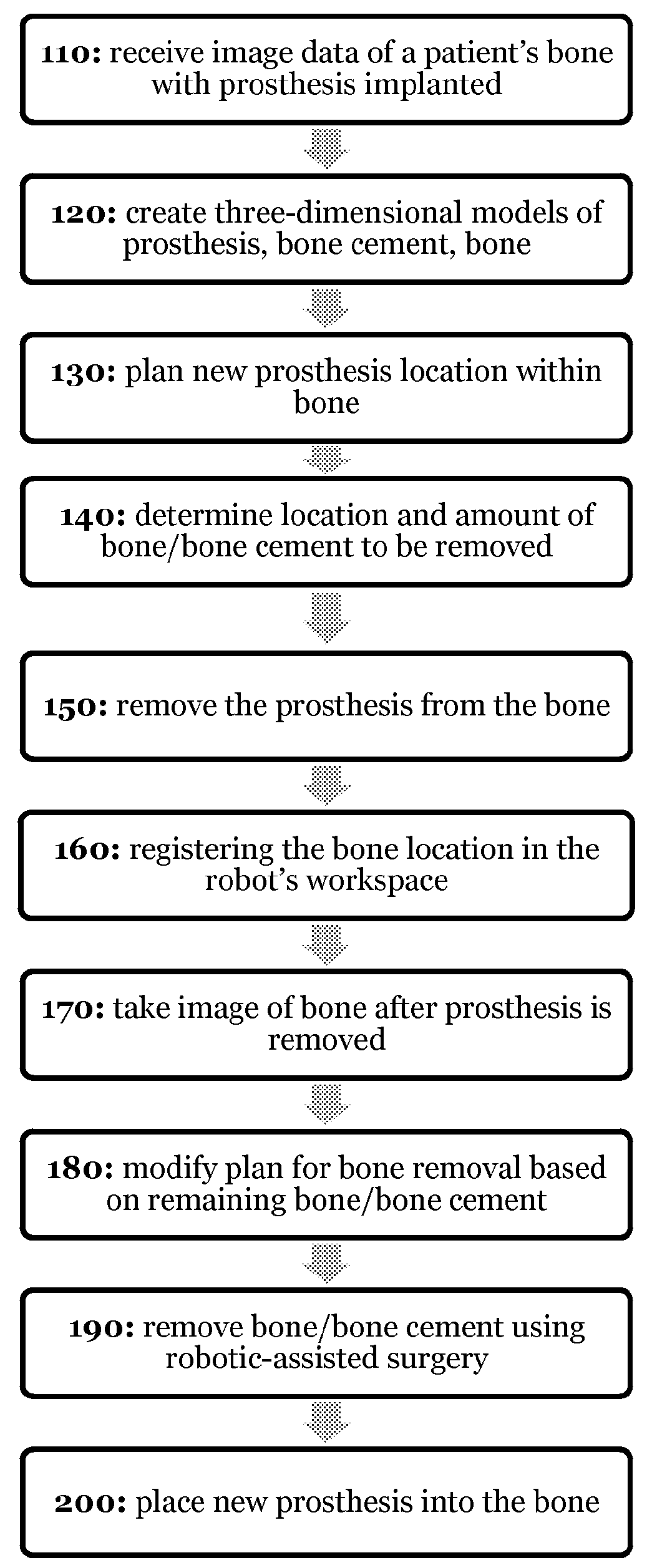
Systems and processes for revision total joint arthroplasty
A process and system for performing orthopaedic surgery with the use of computer systems and robotic assistance to remove bone, bone cement, and a bone prosthesis, typically a bone prosthesis used in hip replacement surgery, knee replacement surgery, and the like. The process for replacing one or more bone prostheses using a robotic system includes receiving image data comprising an image of each bone, including at least one prosthesis implanted within each bone; creating three-dimensional models of the prosthesis, and the bone; creating a plan for positioning new prostheses within the bone; determining the location and amount of bone and any non-bone material to be removed for the new prostheses; and removing the bone prosthesis from the bone. The inventive process may be used for the replacement of hip joints, shoulder joints, ankle joints, wrist joints, finger joints, toe joints, or other joints.
Owner:THINK SURGICAL
Training device for human walking movement
ActiveUS20140371640A1Meet convenient maintenanceConvenient repairChiropractic devicesWalking aidsAthletic trainingEngineering
A walking movement device is provided for producing a walking movement of a human being with two controlled foot guiding units, each having a foot plate for placing a foot thereon. The foot plates are alternately movable forward and backwards in opposite directions to stimulate the walking movement. The foot plates are coupled with at least one drive unit, via which drive unit the walking movement of the foot plates can be produced, and have a suspension unit for easing the weight on the human being. The foot plates each have a front and a rear partial area with the at least one drive unit being configured to move the rear partial area out of the common plane with respect to the front partial area and back again during the walking movement of the foot plates, in order to enable bending of the midfoot toe joint during the movement process.
Owner:BTL MEDICAL DEV AS
Toe Extroversion Correction Device
ActiveUS20110046531A1Reduce frictionNon-surgical orthopedic devicesFootwearEngineeringSoft materials
A toe extroversion correction device includes a support portion integrally formed and made of a soft material, a first toe sheath portion disposed on a lateral side of the support portion, a second toe sheath portion disposed on another lateral side of the support portion, and a protection pad portion protruded from a lateral side of the first toe sheath portion, such that the first toe sheath portion is sheathed on big toe, and the second toe sheath portion is sheathed on the second toe, and the support portion is clipped between the big toe and the second toe to produce an action force to push away the big toe, and the protection pad portion can be attached onto an internal side of a first toe joint of the big toe to prevent the protruding first toe joint of the extroverted big toe from being rubbed with a shoe.
Owner:DR FOOT TECH
Assistance external skeleton segment-type foot structure of lower limb
ActiveCN109262595AReduce constraintsHigh dynamicProgramme-controlled manipulatorRoad surfaceEngineering
The invention discloses an assistance external skeleton segment-type foot structure of the lower limb. Elastic disc-type structures which are turnable and returnable through torsion are adopted as theankle joints of the feet, when the ankle joints of the human body move, the ankle joints of the feet of the external skeleton can move along with the ankle joints of the human body, and through deformation of a spring, the dynamic performance and flexibility of an external skeleton system are improved; separated hinge design is adopted for the toe joints of the feet of the external skeleton, thefront soles of the feet of the external skeleton are separated from the rear soles, each front sole is divided into the left and right parts, the toe joints of the feet of the external skeleton can follow to move in the gait of the human body, and the constraint of the external skeleton to movement of the feet of the human body is reduced; when the external skeleton is worn, the structure can adapt to the uneven road, the maximum contact area of the feet of the external skeleton and the ground is increased, and the external skeleton can be relatively stably supported at the support phase. By adopting the multi-segment rigid and flexible composite feet, the movement gesture of the feet of the human body can be fitted to the higher degree, and the flexibility and movement follow-up performance of the human body when the assistance external skeleton is worn are improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
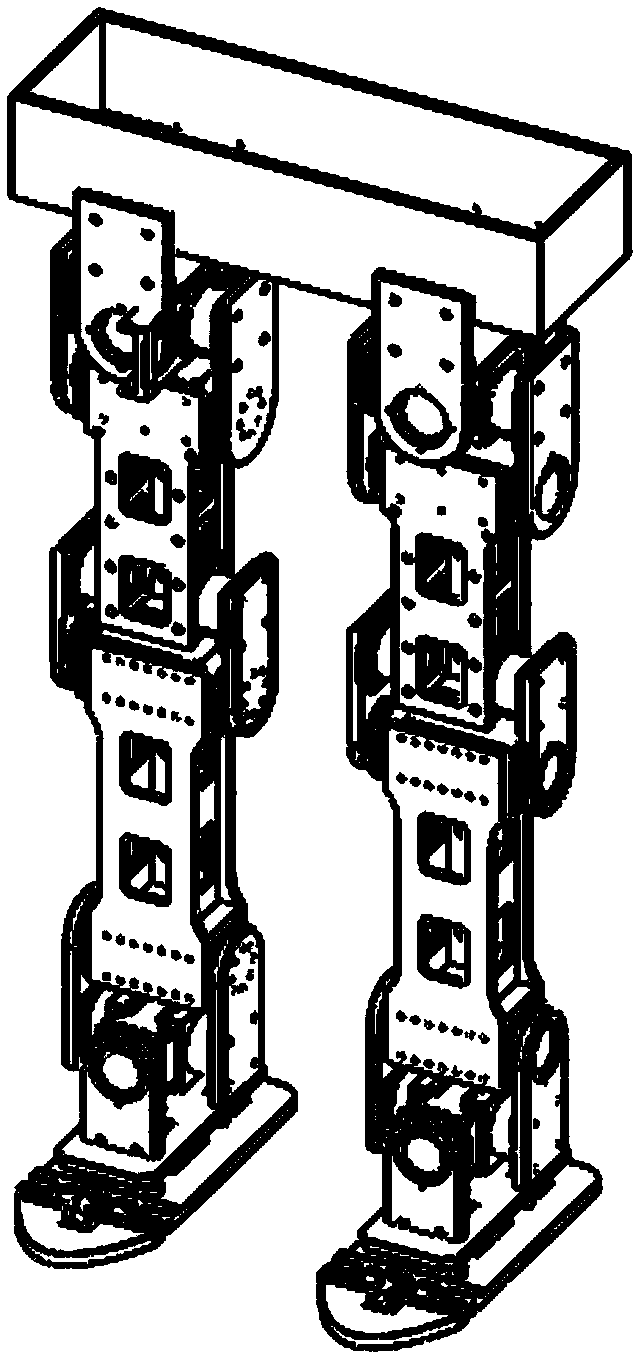
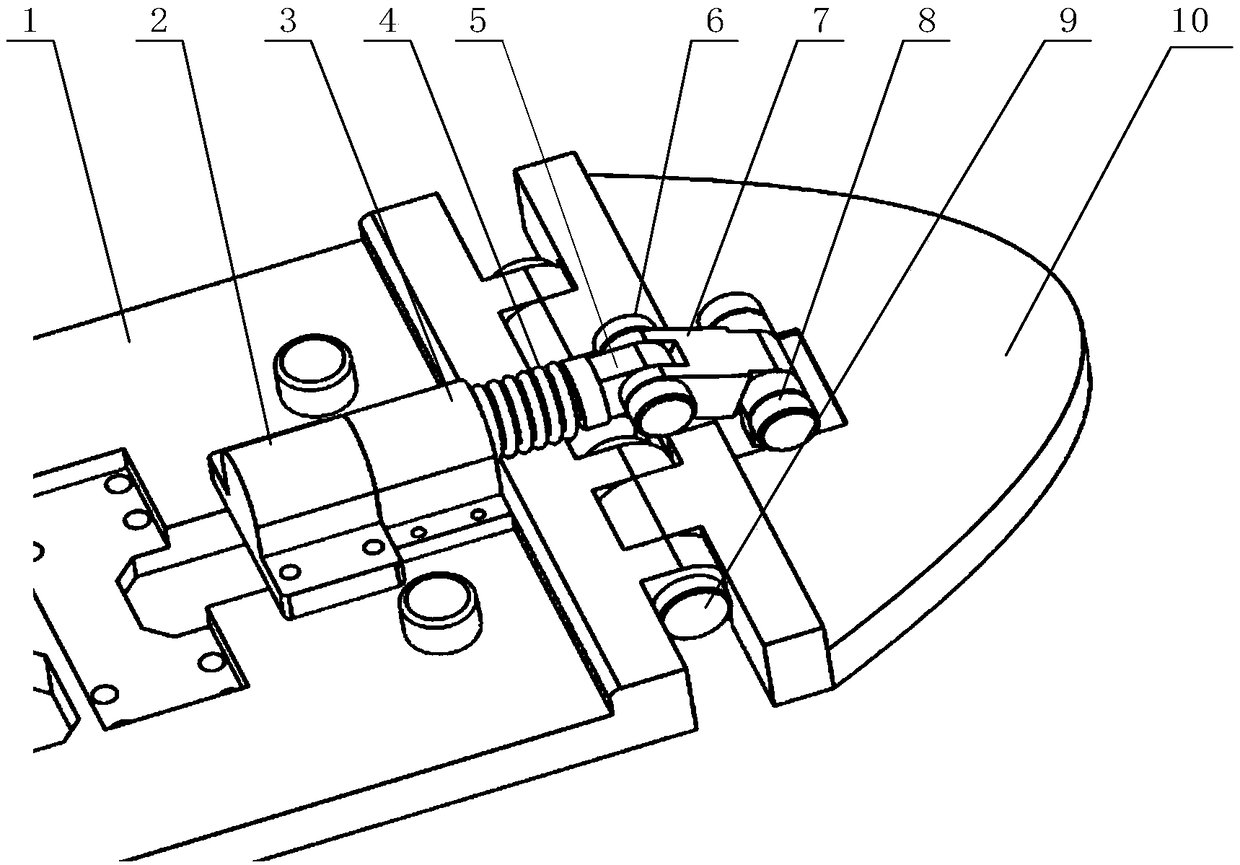
Multi-joint leg structure of biped walking robot
The invention relates to a multi-joint leg structure of a biped walking robot. The multi-joint leg structure comprises a foot sole movement mechanism, an ankle joint movement mechanism and a leg joint movement mechanism; toe joints are hinged with a foot sole by shafts; a shank lower joint support is hinged with an inner support by a shaft; the inner support is hinged with an ankle joint support plate; the foot sole movement mechanism can be used for controlling the toe joints to make a movement of lifting toes around the shafts through which the toe joints are hinged with the foot sole, so that the movement of lifting the toes is realized; the ankle joint movement mechanism can be used for controlling the foot sole to make a foot swing movement to the left or to the right, and also can be used for controlling the foot sole to move forwards or backwards, so that a foot sole joint of the robot can move in multiple degrees of freedom; the leg joint movement mechanism can be used for controlling the joints of the shank to realize a clockwise or anticlockwise leg raising movement, and also can be used for controlling the shank to make a rotational motion around the thigh. Therefore, after the multi-joint leg structure of the biped walking robot is adopted, the robot can make a biped walking movement since the leg raising movement is realized in the multiple degrees of freedom by the joints of the leg of the robot, and the biped walking of the humanoid robot is more flexible.
Owner:江门市华彬科技有限公司
Rehabilitation exercise device for patient
ActiveCN110859734ARehabilitation is goodPromote blood circulationDevices for pressing relfex pointsChiropractic devicesKnee JointEngineering
The invention relates to a rehabilitation exercise device for a patient, and effectively solves the problems that movement of lower limb joints cannot be carried out in one step, and the lower limb joints of a patient can be subjected to secondary damage when the joints are moved. According to the technical scheme, the device comprises a support plate for supporting a lower leg of the patient andan L-shaped plate for supporting a foot of the patient; and the upper end of a vertical plate of the L-shaped plate is hinged with a pressing block. When the supporting plate moves left and right horizontally, a hip joint and a knee joint of the patient are moved; when the supporting plate moves left and right horizontally, the L-shaped plate is driven to swing left and right through first gears and incomplete gears, so that an ankle joint of the patient is moved; and when the L-shaped plate swings left and right, the pressing block is driven to swing left and right, so that toe joints of thepatient are moved. The L-shaped plate and the pressing block are respectively and fixedly provided with finger pressing plates, so that when the ankle joint and the toe joints of the patient are moved, the finger pressing plates are used for massaging a sole of the patient, blood circulation of the foot of the patient is promoted, and good help for rehabilitation exercise of the patient is facilitated.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU RAILWAY VOCATIONAL & TECH COLLEGE
Multifunctional comfortable sports shoe sole
The invention provides a multifunctional comfortable sports shoe sole. The multifunctional comfortable sports shoe sole is provided with a shoe sole body, a shock absorption column arranged on the big toe joint of the shoe sole body, a first breathable pad covering the toes of the shoe sole body, and a second breathable pad covering the heel of the shoe sole body in a sealing mode. A first containing cavity and a second containing cavity are formed in the positions, on the toes and the heel, of the shoe sole body respectively, vent holes are formed in the left side and the right side of the first containing cavity, multiple first breathable vertical columns and multiple breathable outer pipes are arranged in the first containing cavity and the second containing cavity respectively, trapezoidal grooves are formed in the upper ends of the first breathable vertical columns, the lower ends of the interiors of the breathable outer pipes are fixedly connected with elastic air bags, and openings of the elastic air bags are formed upwards. The shock absorption effect is achieved through the shock absorption column, and ventilation between the shoe sole and the exterior is accelerated through the breathable pads.
Owner:LIMING VOCATIONAL UNIV
Foot sliding prevention product
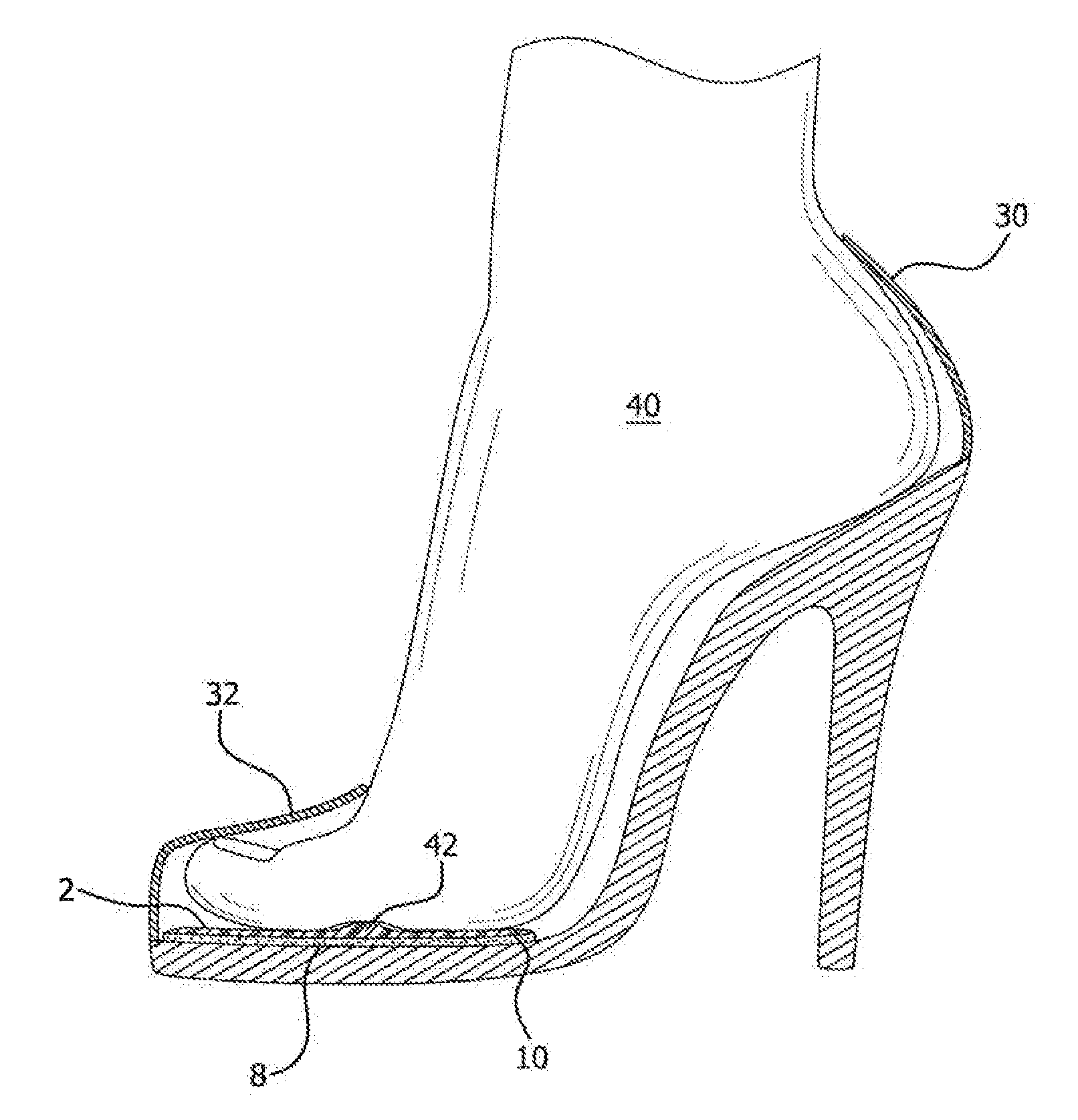
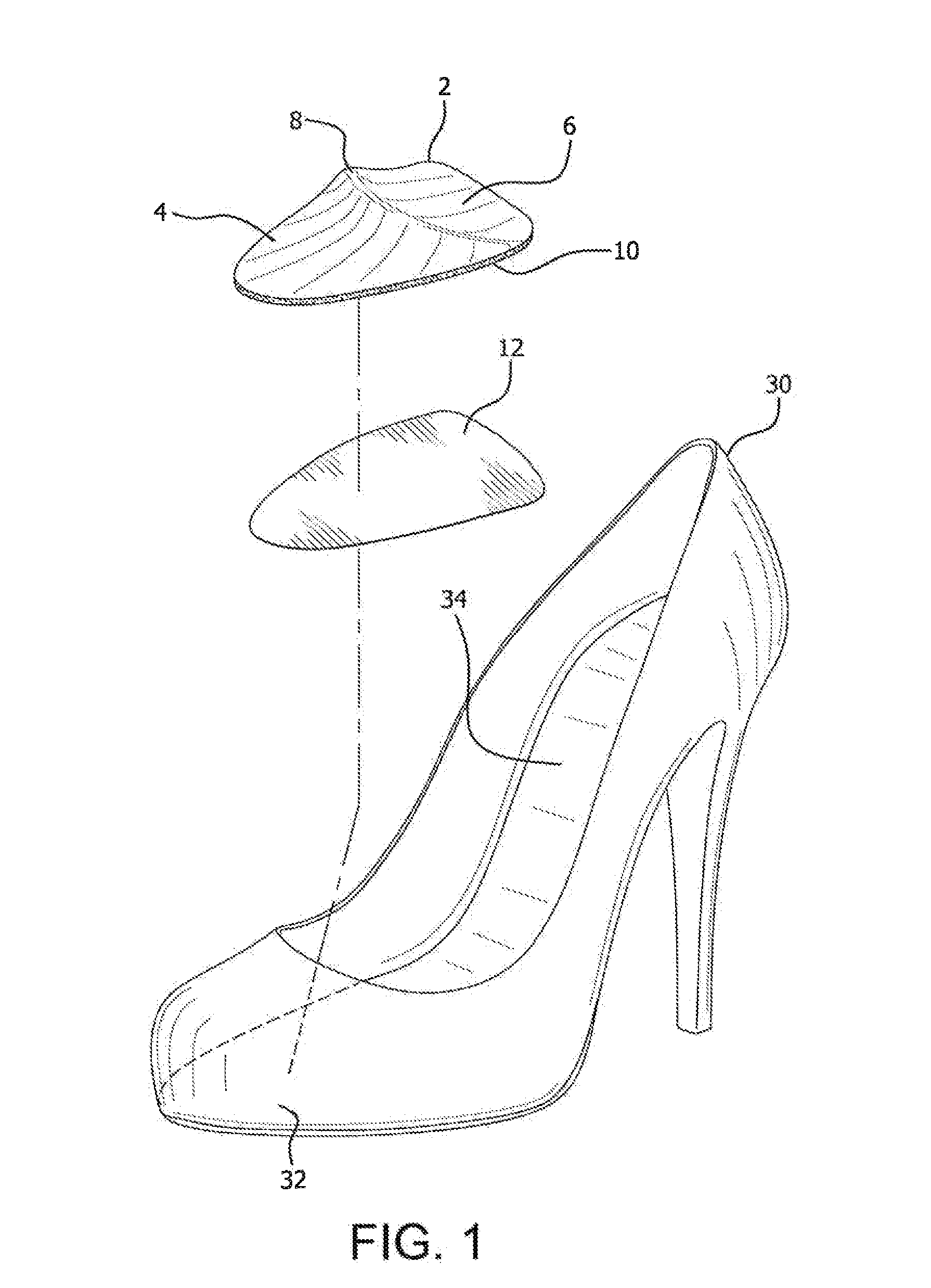
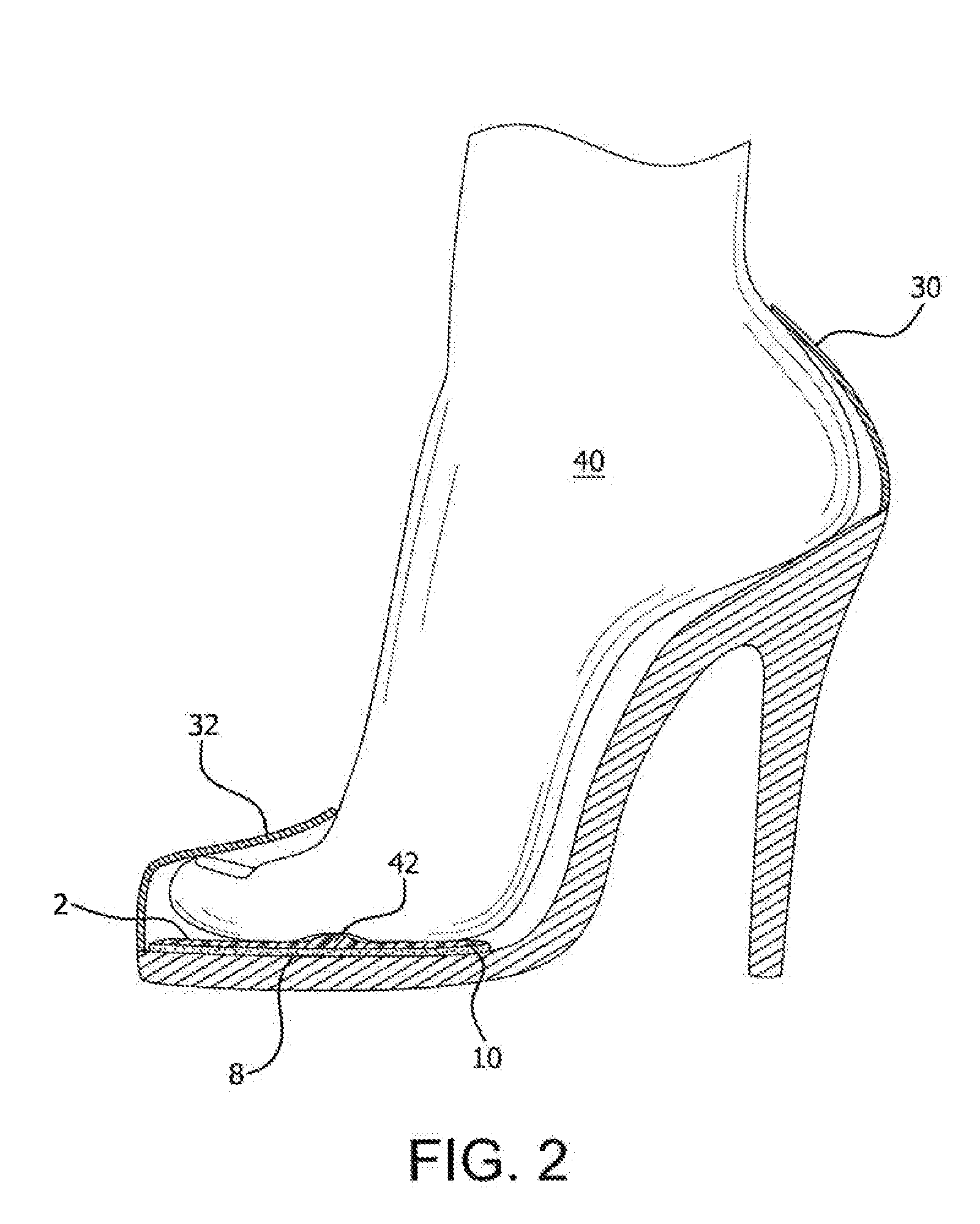
InactiveUS20130318826A1Address and prevents problemAddress and prevents and injuryInsolesHigh heelSacroiliac joint
A foot sliding prevention product utilizes a unitary pad shaped to conform with the tapered toe section of a shoe, particularly a women's high heel shoe. The pad is sized to extend from the toe section of the shoe to an area short of the shoe's arch section. An arcuate shaped ridge member extends from one side of the pad to the other side. The ridge member is configured to be positioned within the toe joints of the wearer to prevent the foot from sliding down and forward in the shoe.
Owner:NATHANIEL MICHELE E
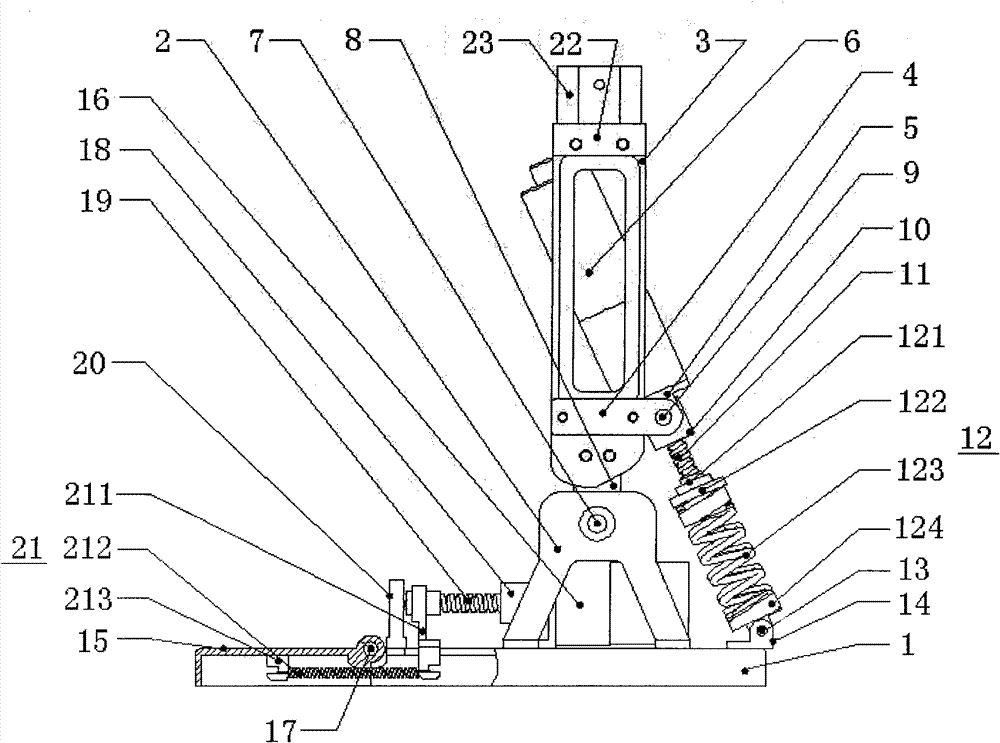
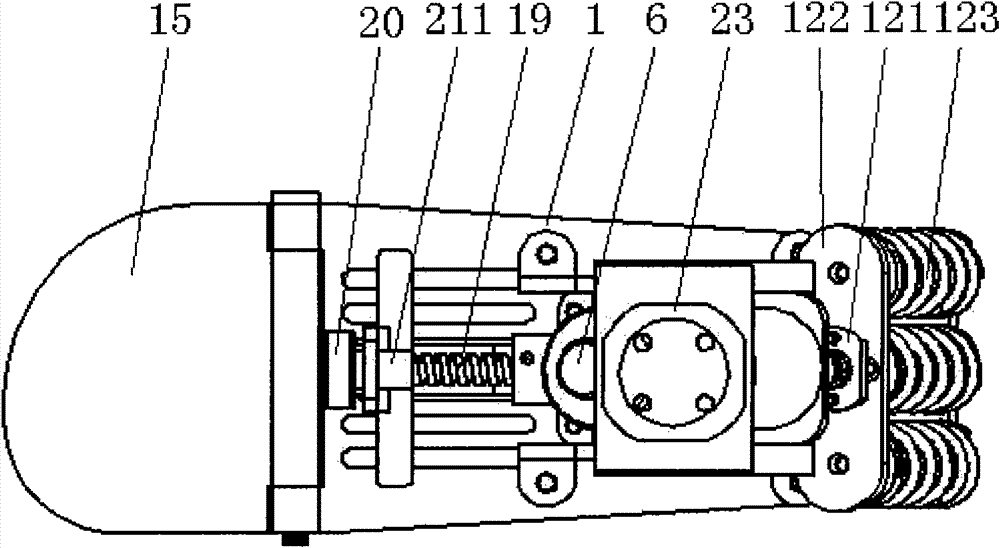
Humanoid robot two-freedom-degree parallel-connection shock absorption mechanical foot
The invention discloses a humanoid robot two-freedom-degree parallel-connection shock absorption mechanical foot, and belongs to the field of humanoid robots. The mechanical foot comprises an upper metatarsal bone, an ankle shaft arranged on the upper metatarsal bone, a lower metatarsal bone, four shock absorption guide columns, a toe joint shaft, a big toe, a second toe, a third toe, a fourth toe, a small toe, a tensile spring A, a tensile spring B, and a toe spring for connecting the toe joint shaft with the lower metatarsal bone. A shank rod is arranged on the ankle shaft. The tensile spring A and the tensile spring B are symmetrically arranged on the two sides of the shank rod. The four shock absorption guide columns are of the same structure and each comprises a universal joint arranged on the upper metatarsal bone, a connecting rod, a sleeve arranged on the lower metatarsal bone, a tensile spring arranged in the sleeve, and a slide block. The initial state of the shank rod is vertical, and accordingly the tensile spring A and the tensile spring B are in a zero-force state. The humanoid robot foot is simple in structure and has two movement freedom degrees, a shock absorption function and a parallel-connection mode.
Owner:CHANGZHOU XIAOGUO INFORMATION SERVICES
Road Roller Skates
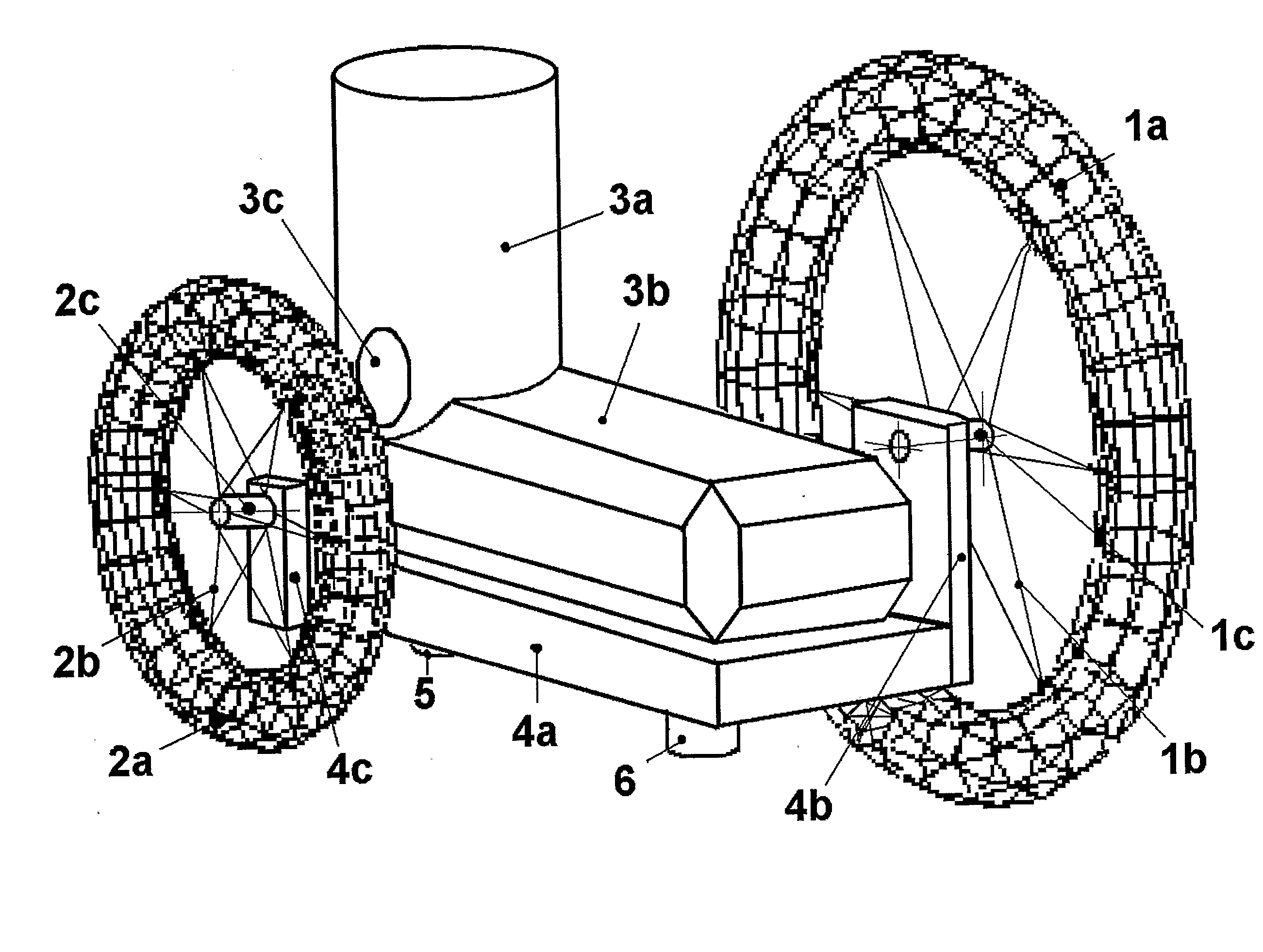
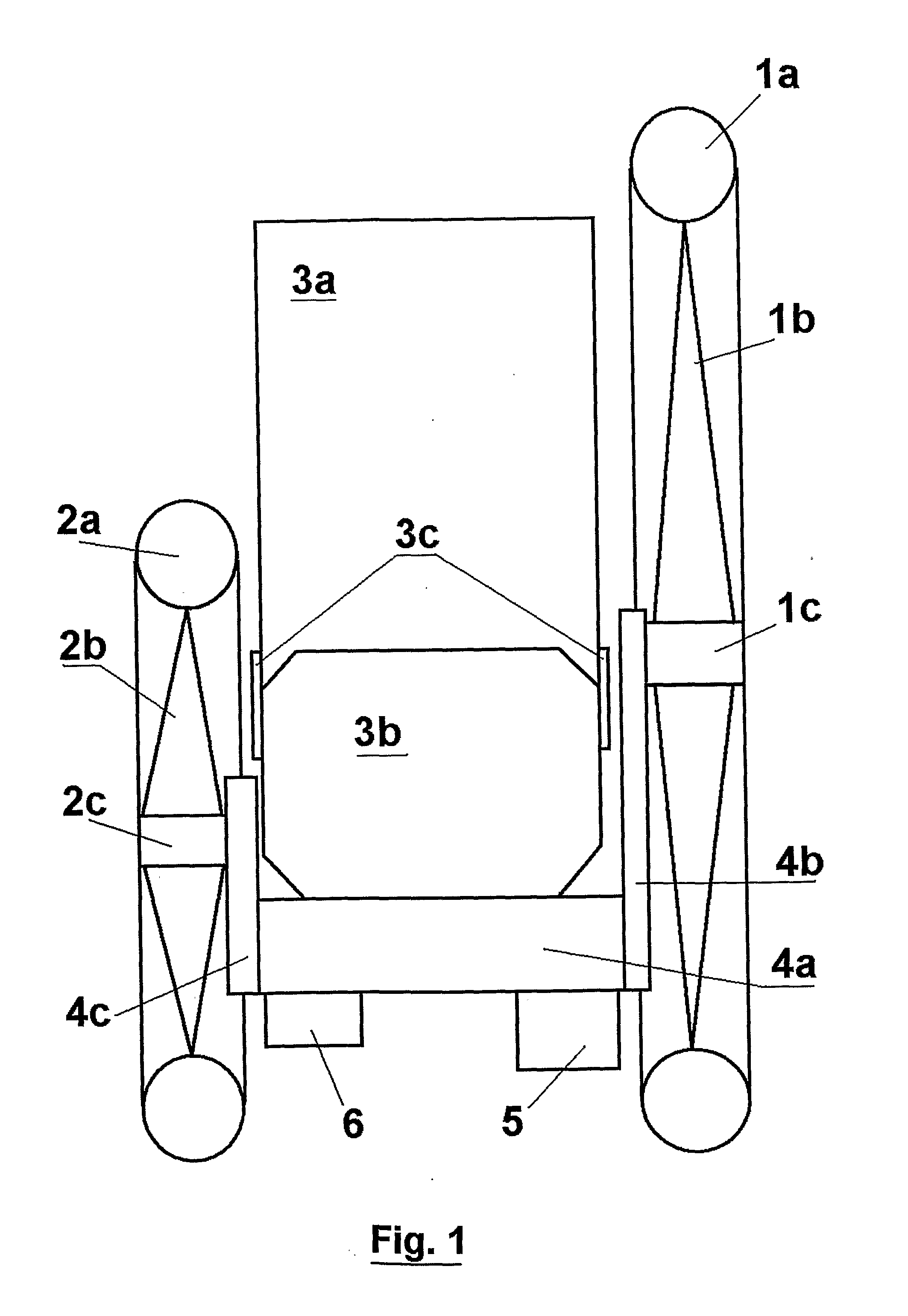
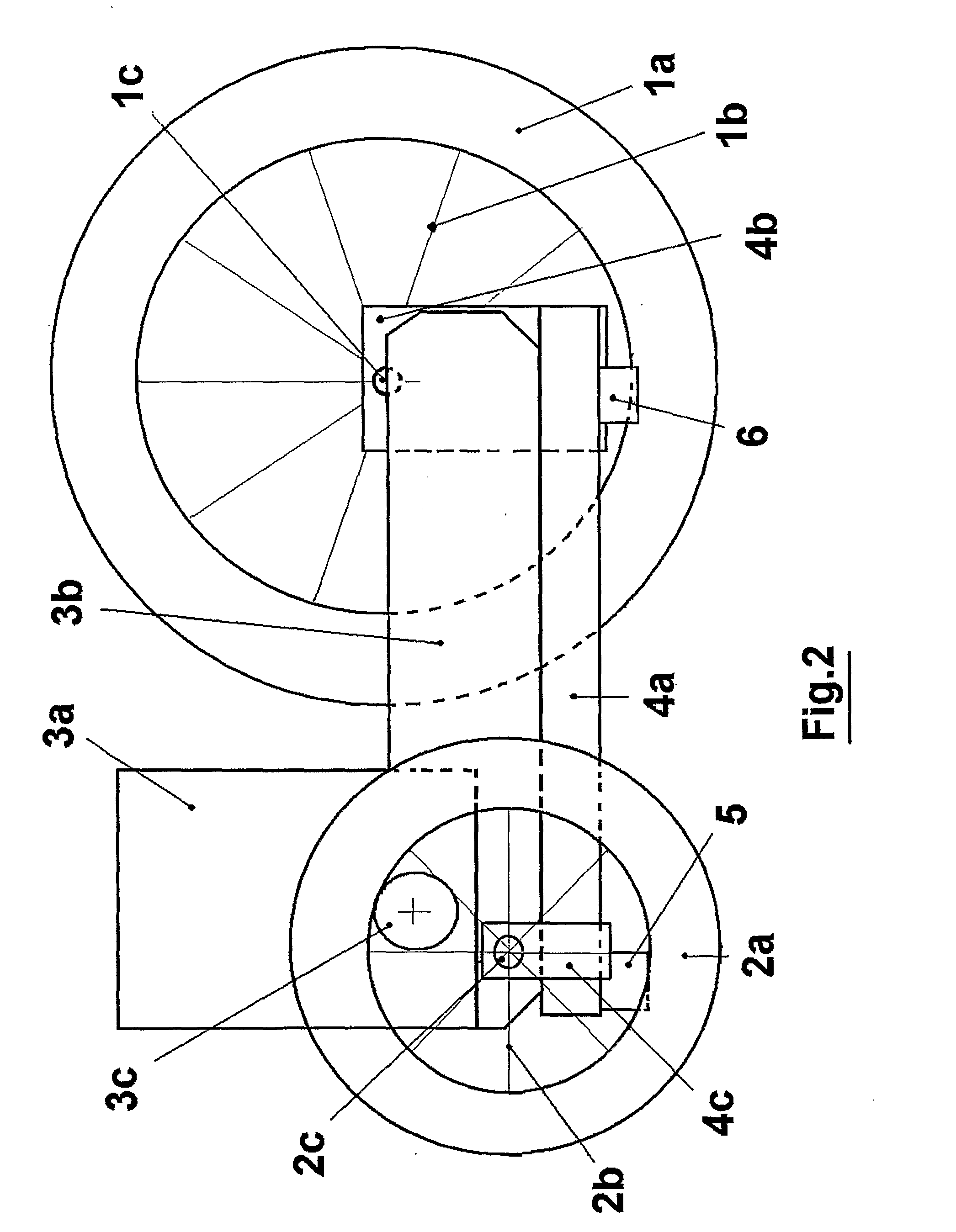
The invention relates to road roller skates for travelling on average quality roads, comprised of a semi-rigid high-top-shoe (3) fixed to a supporting sole (4) at a height of 50 mm above the ground and fitted with angle brackets (4b and 4c) to which the rotation axis of a front wheel (1) is fixed, this front wheel having a large diameter (150 to 300 mm) and being situated to the outside of the foot next to the toe joints, and to which the rotation axis of a rear wheel (2) is fixed, this rear wheel having a medium diameter (100 to 150 mm) and being situated to the inside of the foot next to the heel. The large diameter of the wheels makes it possible to handle defects in the terrain. This arrangement confers its stability to the skate, and front and rear rubber blocks (6, 5) placed under the sole (4) can be pressed against the ground by rotating the knees. Optionally, the front wheel (1) can be slightly tilted underneath the sole (4), the assembly can be adapted to a purchased in-line skate whose wheels have been removed, the characteristics of the diameter and material of the wheels being adjustable.
Owner:BIESSE PHILIPPE
A flexible passive foot system based on bionics
The invention relates to a flexible passive foot system based on bionics, comprising a flexible toe joint and a lateral cushioning shock absorbing layer, which enables the foot to have the functions of stable support, cushioning shock absorbing and energy storage. The flexibility of the toe joint is provided by a compression spring parallel to the sole of the foot, and the toe portion is connectedto the sole of the foot by a crank linkage mechanism. The shock-absorbing springs are symmetrically distributed in the upper and lower layers of the foot, which is helpful to enhance the stability ofthe robot when walking on uneven ground, and can effectively eliminate the impact of the ground on the foot when walking. The invention realizes the degree of freedom of flexion and extension of thetoe joint and the lateral passive degree of freedom of the foot through the compression and extension functions of the compression spring, and simultaneously utilizes the energy storage characteristics of the spring to enable the foot to have the functions of cushioning, shock absorption and energy saving, so that the walking stability of the robot can be improved and the energy loss can be reduced. Compared with the foot structure of the traditional robot, the invention has the advantages of good imitation of human nature, high walking stability, high energy efficiency, compact structure andgood adaptability.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Dynamic below-knee artificial limb containing flexible dynamic ankle joints and toe joints
The invention relates to a dynamic below-knee artificial limb containing flexible dynamic ankle joints and toe joints, which is characterized by comprising an ankle joint moving mechanism and a toe joint moving mechanism, wherein the ankle joint moving mechanism comprises a back sole, an ankle joint supporting frame, shank baffle plates and an ankle joint motor; the ankle joint supporting frame is fixed at the upper part of the back sole, and the upper end of the ankle joint supporting frame is articulated with an ankle joint shaft connecting frame connected between two shank baffle plates; the ankle joint motor is fixedly connected between the two shank baffle plates, the output end of the ankle joint motor is fixedly connected with one end of an ankle joint screw through a shaft coupling, and the other end of the screw is connected with the back sole through an ankle joint spring mechanism; the toe joint moving mechanism comprises a front sole and a toe joint motor, wherein the front sole is articulated with the back sole, and the toe joint motor is fixedly connected with the back sole; an output shaft of the toe joint motor is fixedly connected with one end of a toe joint screwthrough a shaft coupling, and the other end of the screw is articulated with a toe joint screw fixing frame; and the toe joint screw is connected with the front sole through a toe joint spring mechanism. The dynamic below-knee artificial limb can be widely applied to the researches on the flexible dynamic joints of artificial limbs and serves the handicapped.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Shoe appliance with an orthopedic device
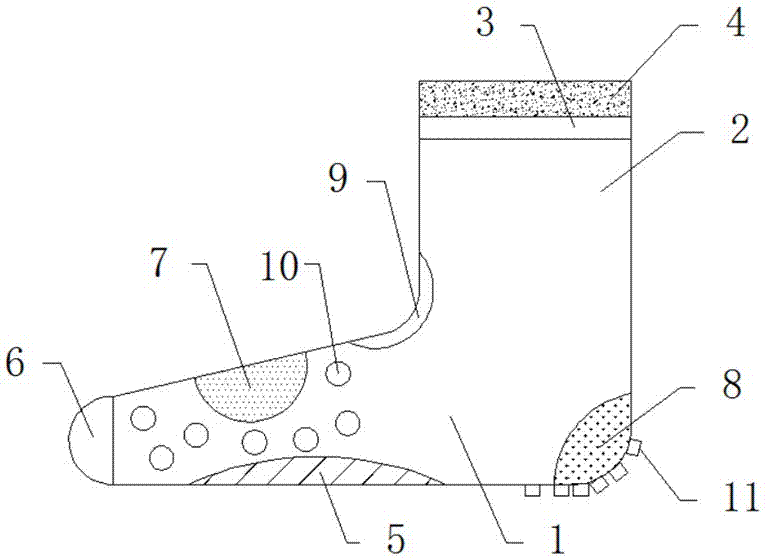
An orthopedic shoe appliance includes an insole, midsole or outersole of footwear; and one or more orthopedic devices disposed on the insole, midsole or outersole at one or more locations selected from the group consisting of a location under a big toe, a location under a medial longitudinal arch, a location under a lateral longitudinal arch, a location under a transverse metatarsal arch, and a location under and / or around a heel. Small wings may be attached to a part of the insole that will wrap around the medial and lateral aspects of the foot. A slit and hinge as well as changes in the flexibility of the materials allow the big toe joint to move independently of the other toes. Other pads may be applied to the top of the insole to allow for other corrections.
Owner:CLOUGH JAMES G
Toe rehabilitation training device for medical orthopedics department
InactiveCN111530031ARegulating pressureAdjust training intensityMuscle exercising devicesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationHeel strike
The invention discloses a toe rehabilitation training device for the medical orthopedics department, and relates to the technical field of medical orthopedics. The device comprises a main frame, a support frame fixedly mounted on the left side of the upper surface of the main frame, a pedal mechanism fixedly mounted on the left side in the main frame, a fixing frame fixedly mounted on the right side surface of the main frame, an adjusting mechanism mounted in the fixing frame and a toe pressure mechanism fixedly mounted on the right side in the main frame. According to the toe rehabilitation training device for the medical orthopedics department, an operator can adjust according to the training intensity, the finger joint flexibility and the bearing capacity can be effectively trained, andthe device is suitable for rehabilitation training after toe joint injury in orthopedics department. The heel is pressed downwards, the left end of the pedal is pressed to rotate downwards, in the gradual downward moving process of the left end of the pedal, the state of the foot sole is changed till the foot sole is pressed downwards to the limit position, toes are in a downward inclining staterelative to the foot sole at the moment, and the effect of passive upward and downward overturning training on the finger joints is achieved through reciprocating downward pressing.
Owner:JILIN UNIV FIRST HOSPITAL
Anti-corrosion thickening sock
InactiveCN107173860AExtended service lifeWear dryHandkerchiefsBaby linensWear resistantMoisture absorption
The invention discloses an anti-corrosion thickening sock which comprises a sock body and a sock leg, wherein the sock body meets the shape of a foot; the sock leg is integrally woven with the sock body; a wear-resistant layer covering toe joints in an annular manner is woven at the toe part of the sock body; a moisture absorption layer covering sole joints in the annular manner is woven in the middle of the sole part of the sock body; vent holes covering the sole joints in the annular manner are formed in the sole part of the sock body; an antibacterial additive is fixedly connected with a part covering the back part of the sock body; an ankle elastic ribbon covering an ankle joint in the annular manner is woven at the connecting part of the sock body and the sock leg; an elastic ribbon is woven at the tail end at the upper part of the sock leg; a withdrawing hole is woven at the upper part of the elastic ribbon; the heal part of the sock body is covered by a heal wear-resistant device; and anti-sliding convex points are fixedly connected below the heal wear-resistant device. The anti-corrosion thickening sock is scientific and reasonable in design, the service life of the sock is prolonged, and relatively high market popularization values are achieved.
Owner:HAINING RANDY SOCKS
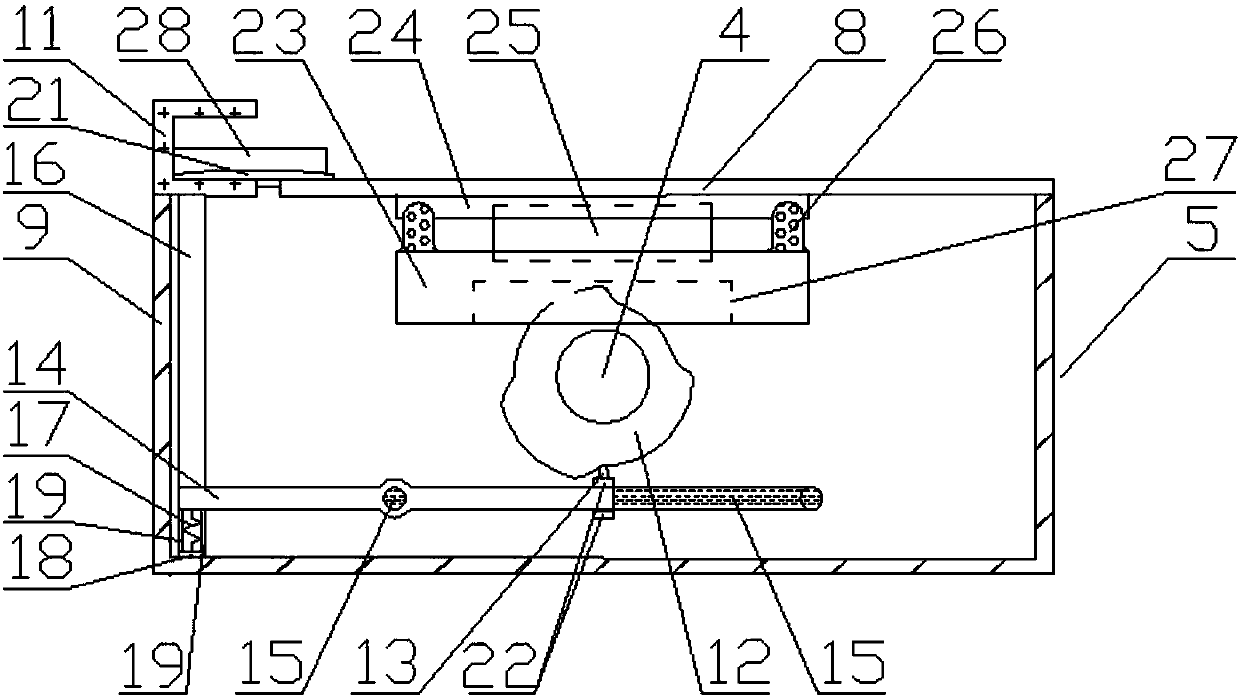
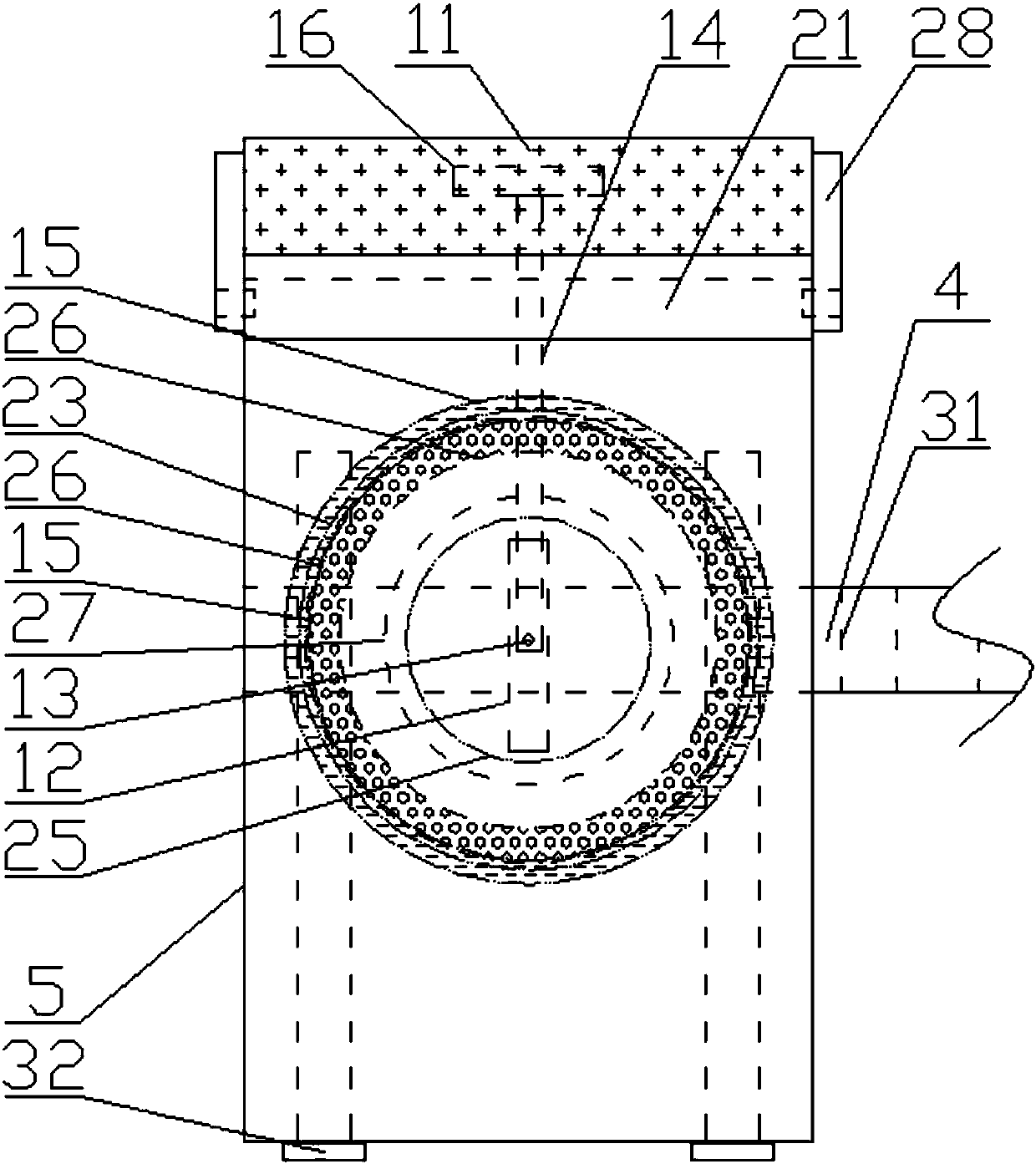
Artificial toe joint
InactiveUS20110087334A1Long-term successStable structureAnkle jointsToe jointsArtificial jointsEngineering
An artificial toe joint utilizes a ball in socket joint structure and arms or side walls which are exterior to the bone. The resulting joint provides improved strength and durability, and may be used to repair joints which are not suitable for installation of a prior art artificial joint.
Owner:MORTON BALLARD ARTHROTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com