Patents
Literature
122 results about "Stochastic distribution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
"Stochastic" means being or having a random variable. A stochastic model is a tool for estimating probability distributions of potential outcomes by allowing for random variation in one or more inputs over time.
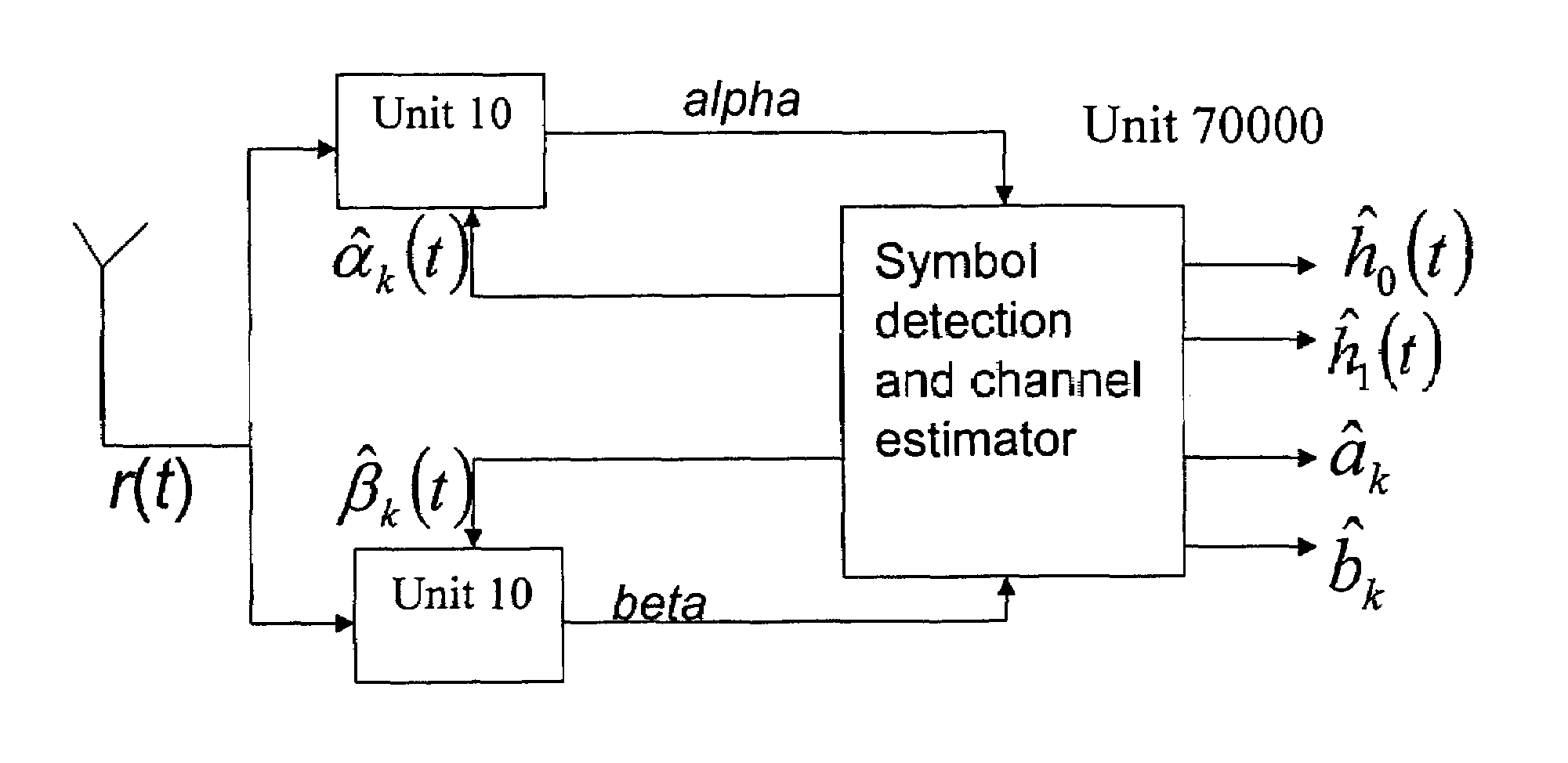
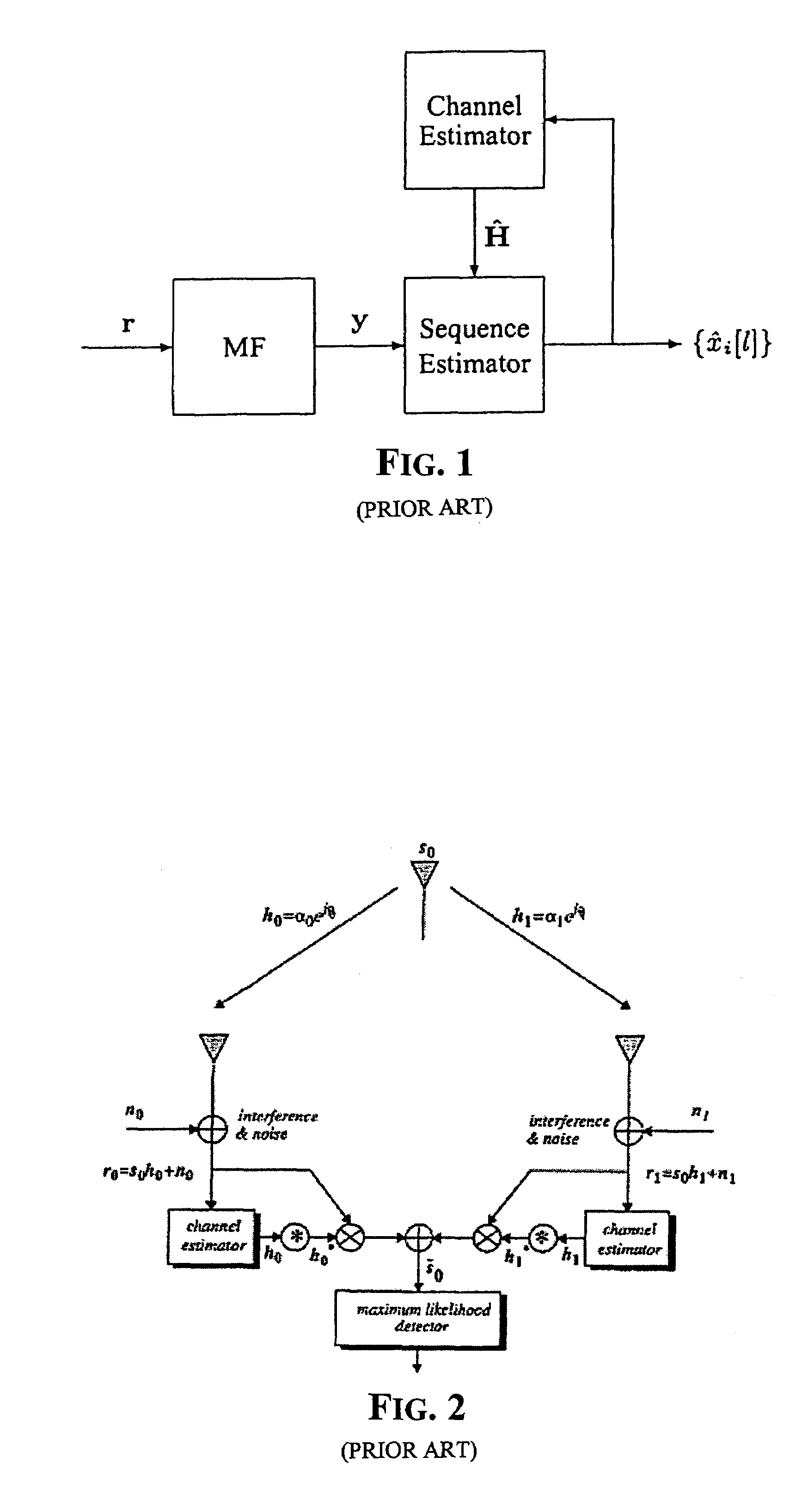
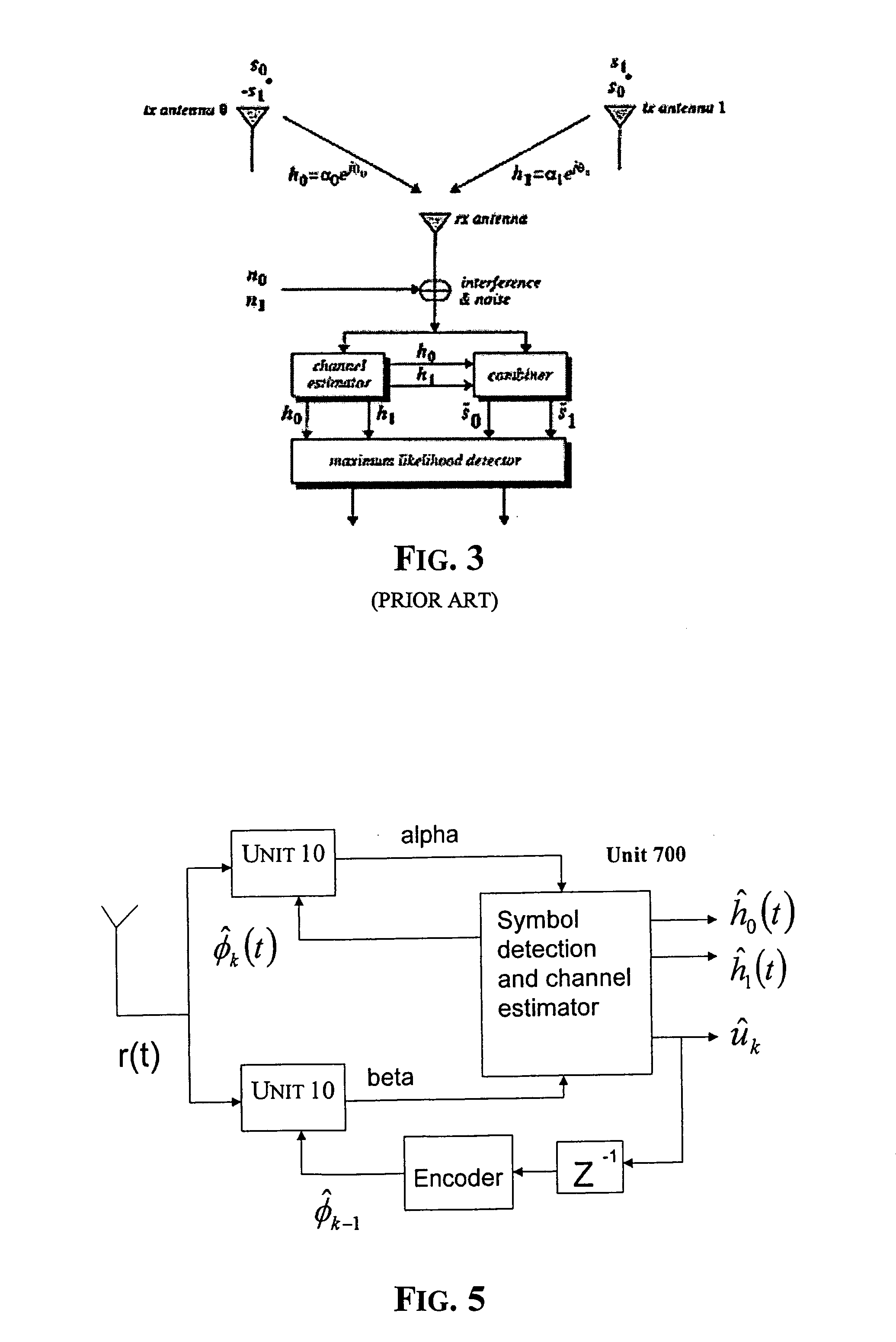
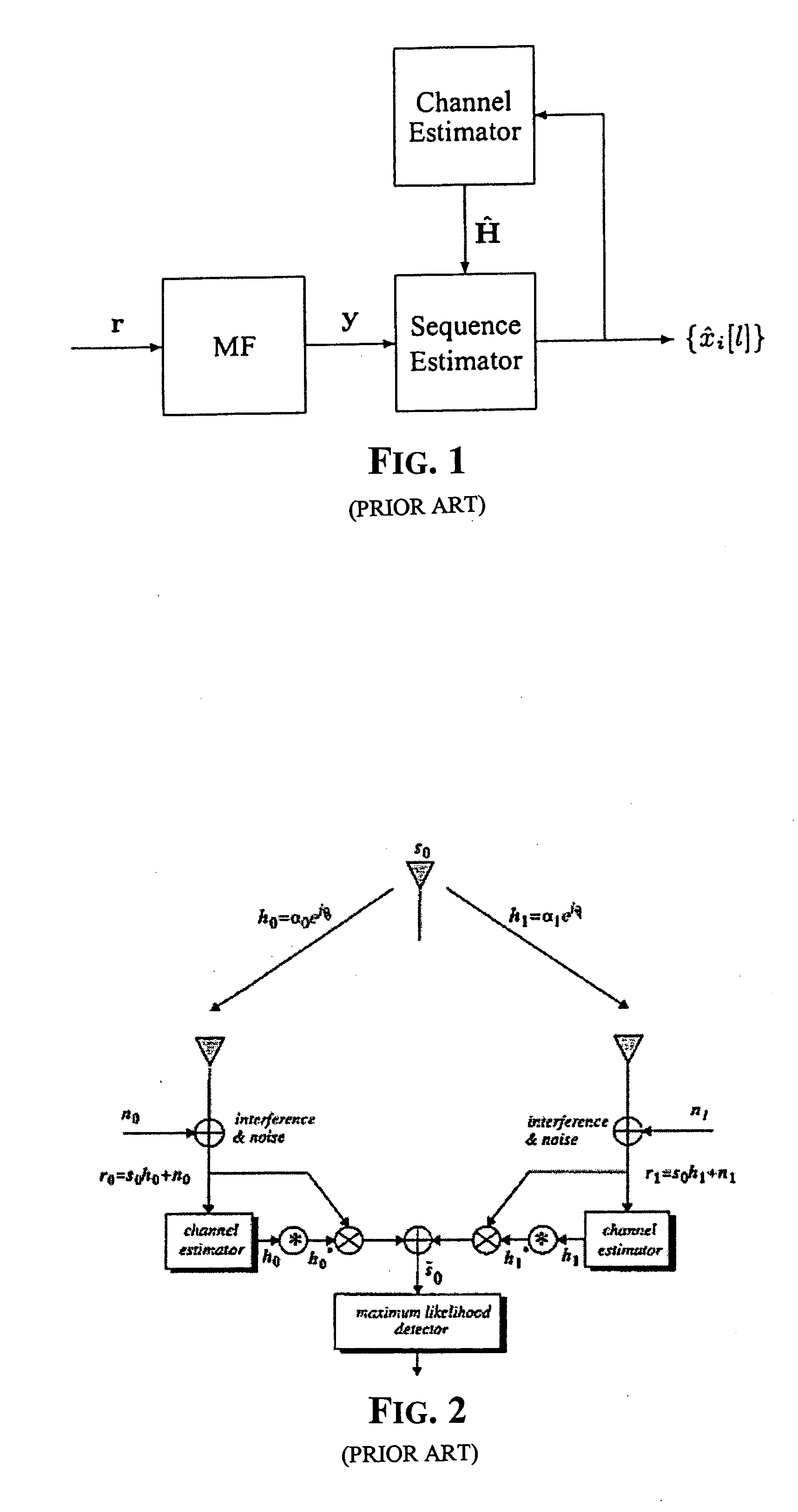
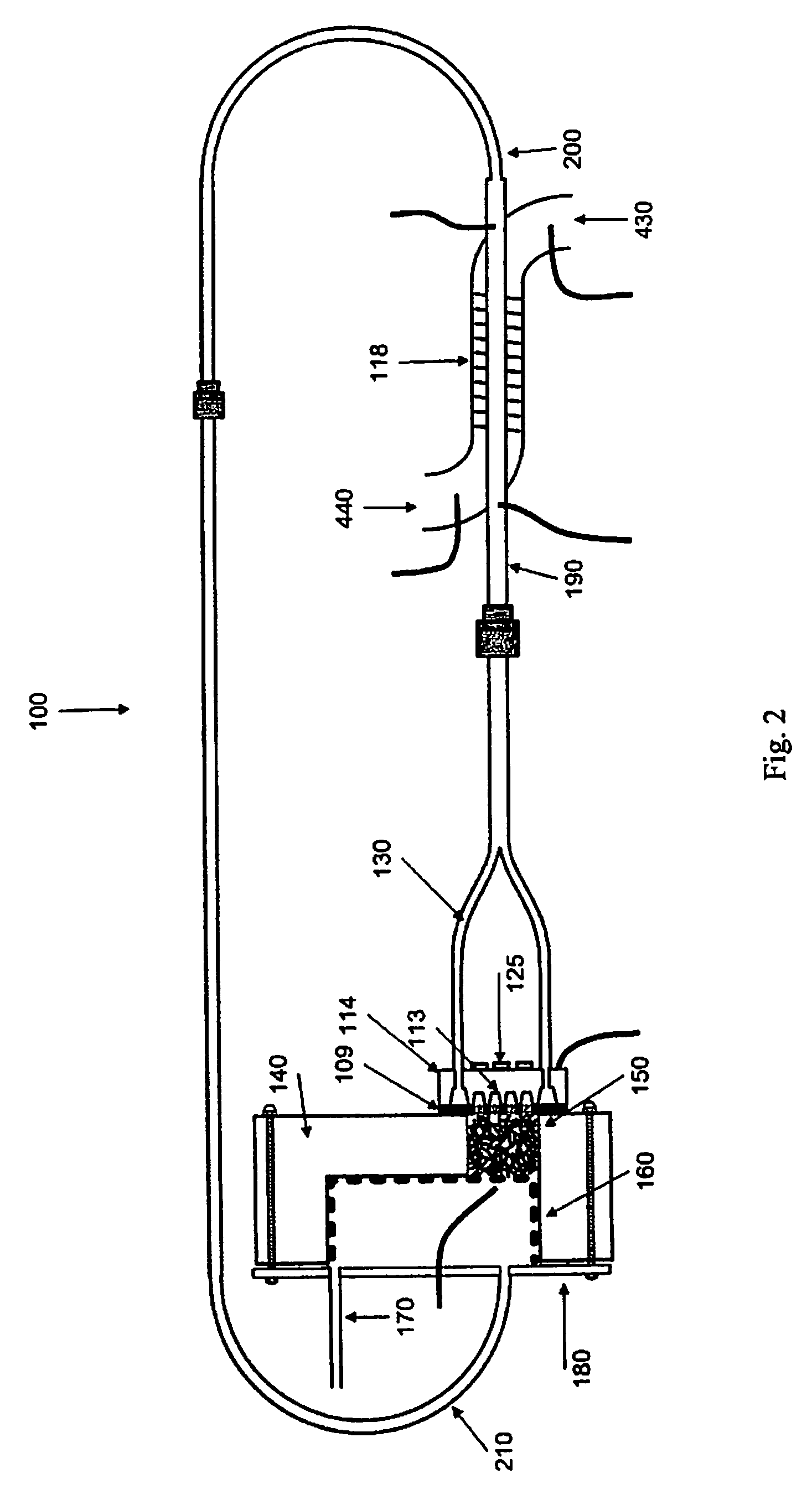
Method of estimating fading coefficients of channels and of receiving symbols and related single or multi-antenna receiver and transmitter
The method is for estimating the fading coefficients of a plurality of transmission channels on which signals to be sent, generated as a function of a sequence of symbols, are transmitted according to a particular modulation, e.g. AM-PSK modulation. The fading coefficients are estimated by using estimations of the transmitted symbols obtained in advance, thus obtaining DC components of the received signal by coherent demodulation locked to the phases of the transmitted AM-PSK signals, and processing these DC components. The method may not require the choice of a stochastic distribution model of the channel fading, thus it remains efficient even when the channel characteristics vary significantly. Moreover, the method works correctly even if the received stream is disturbed by inter-symbolic interference (ISI) and / or by multi-path fading.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
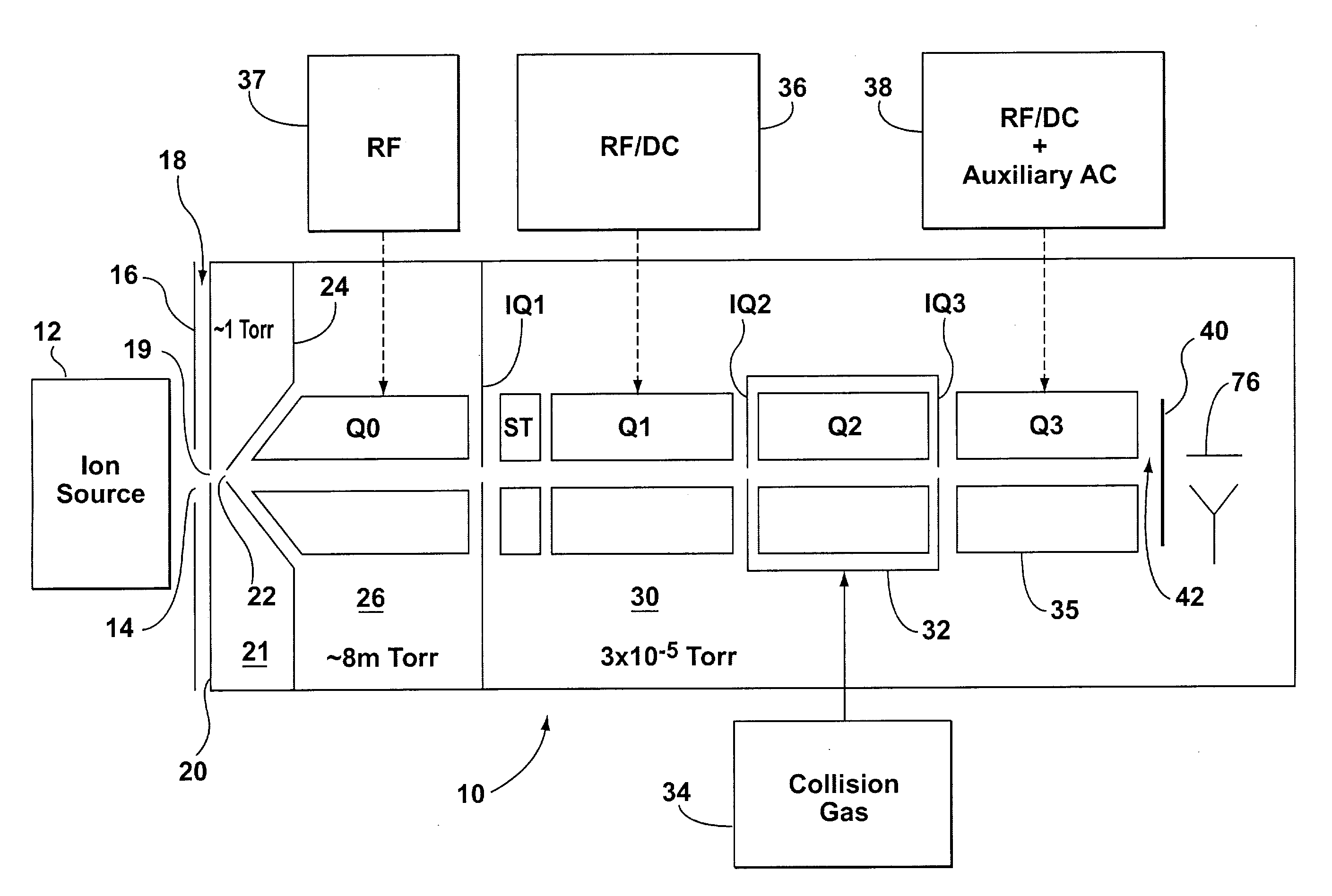
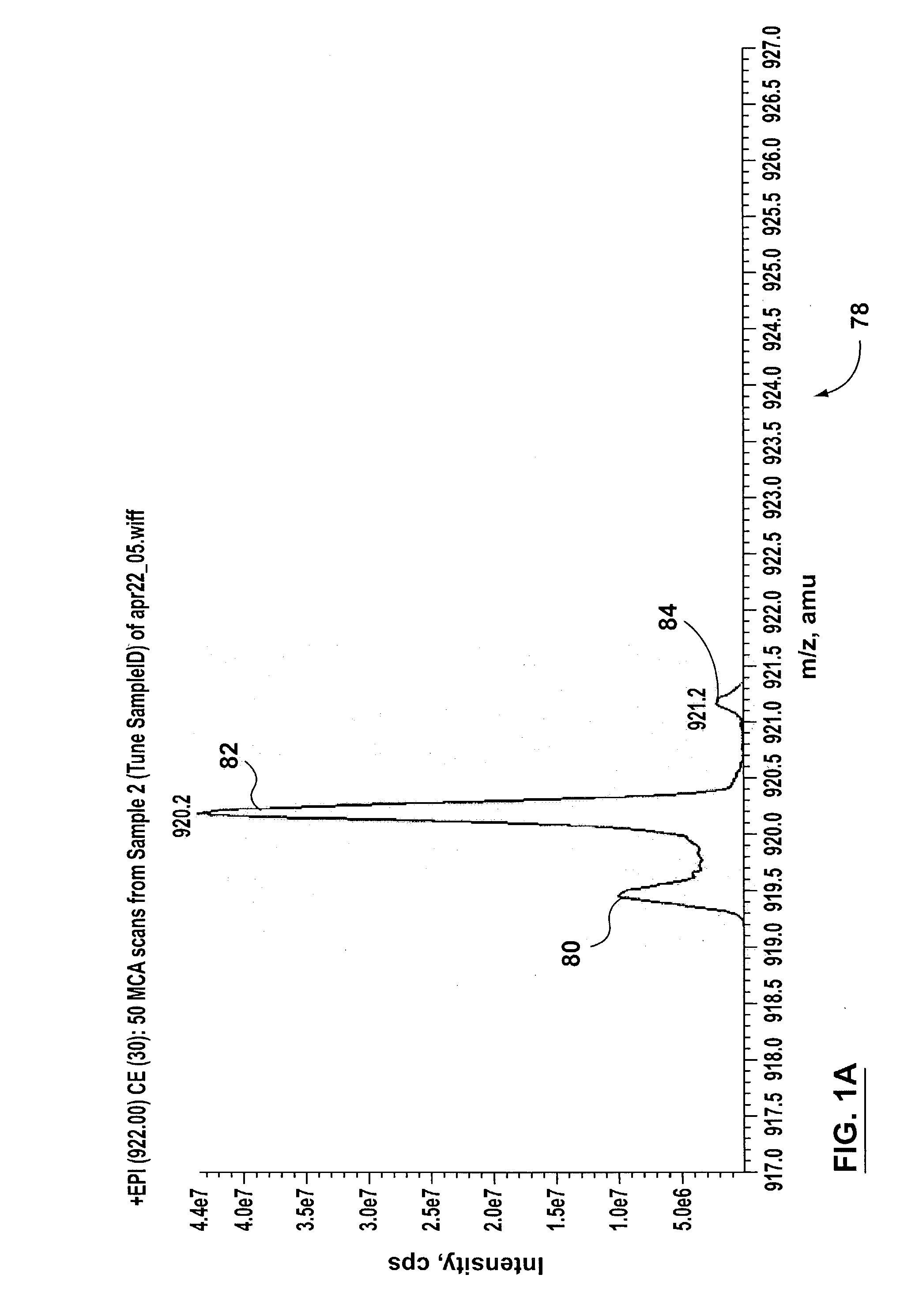
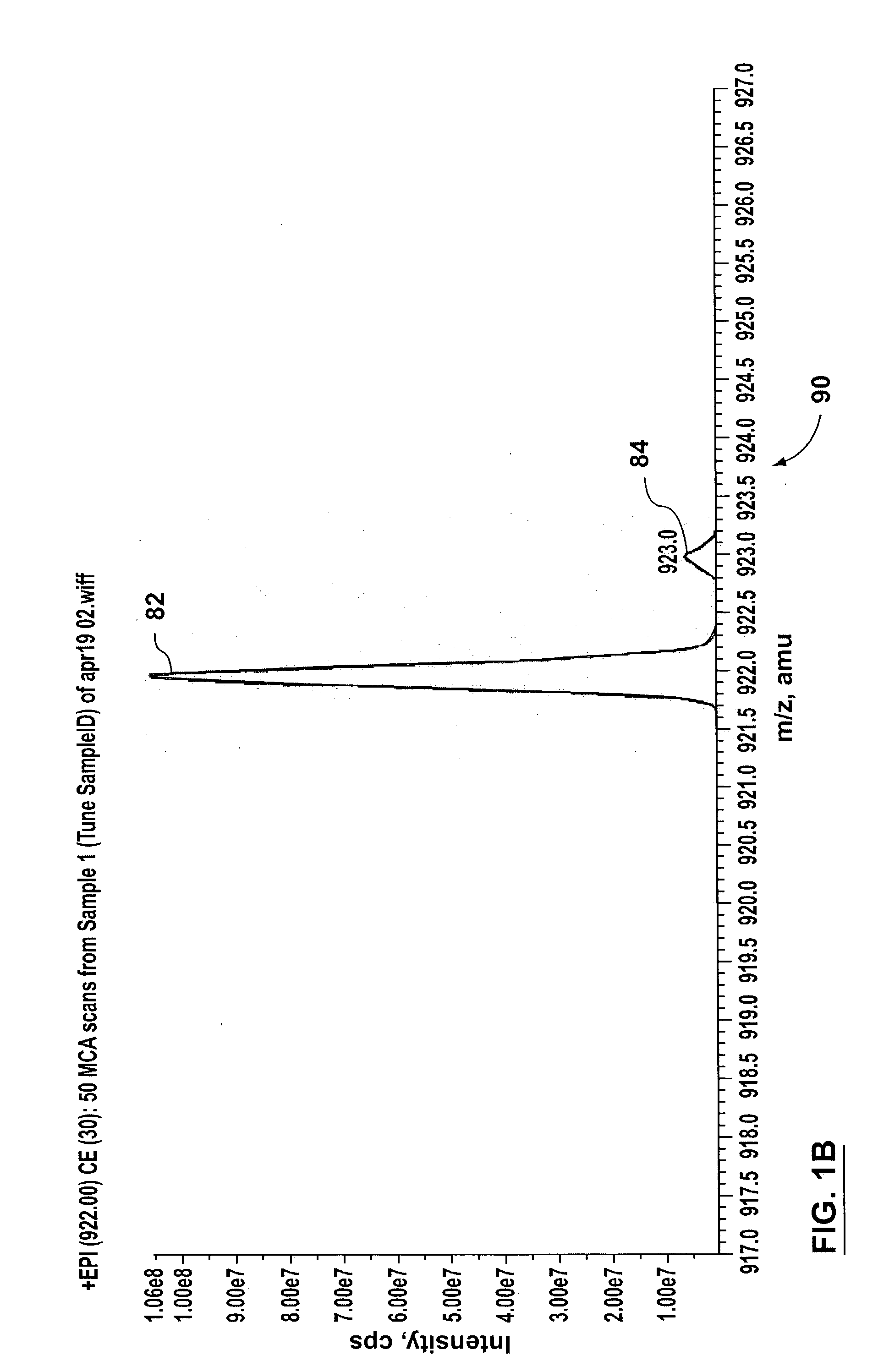
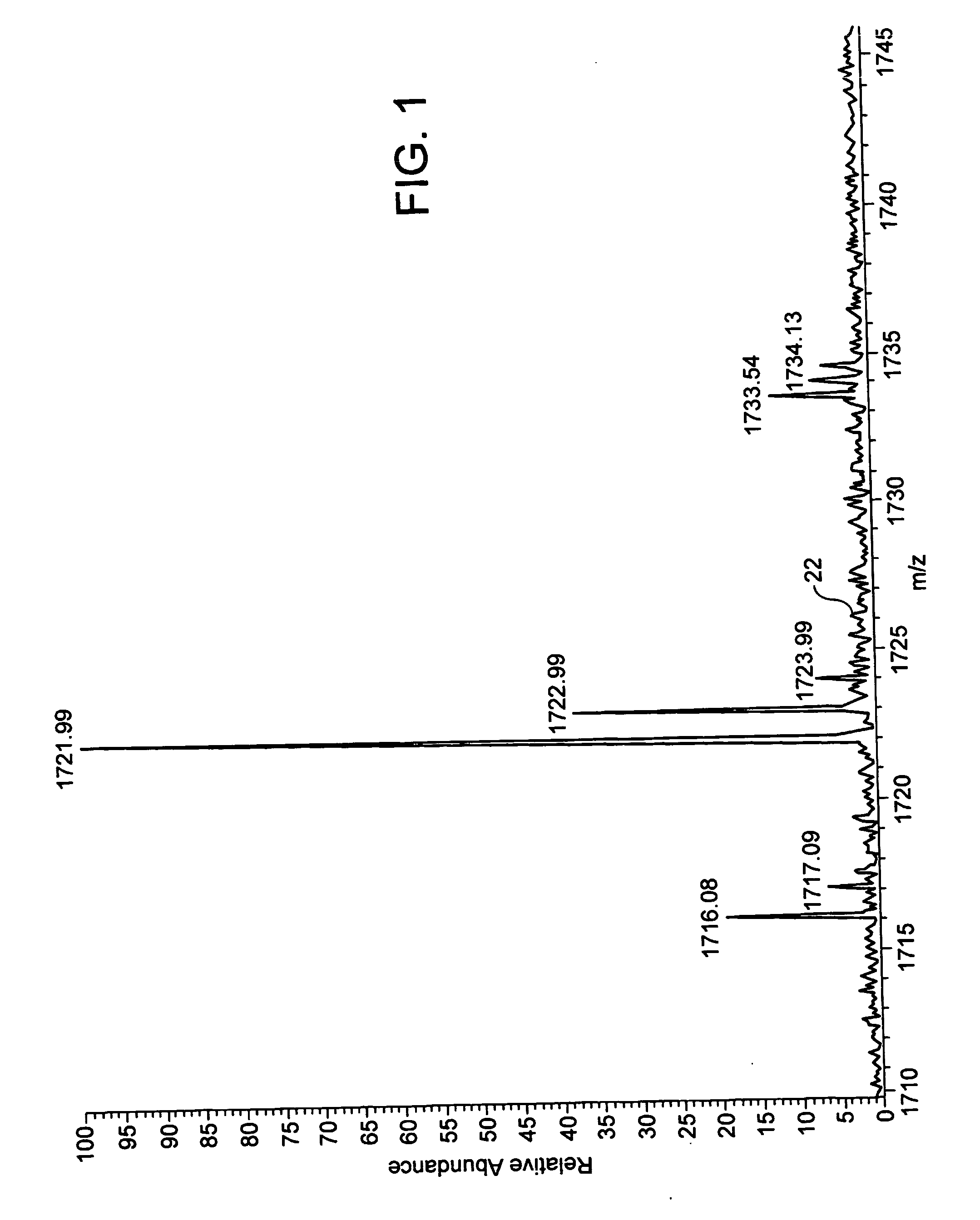
Methods and apparatus for reducing artifacts in mass spectrometers
InactiveUS20040011956A1Excellent characteristicsImprove propertiesStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansVoltage gradientMass analysis
The invention solves the problem of artifact ghost peaks which can sometimes arise in mass spectrometers that employ a quadrupole rod set for both trapping and mass analyzing the trapped ions. The problem arises as a result of randomly distributed voltage gradients along the length of the rods. Three solutions are presented. The first approach involves improving the conduction characteristics of the rod sets. The second approach involves the application of at least one continuous axial DC field to the trapping quadrupole rod set in order to urge ions towards a pre-determined region of the trap, thereby avoiding voltage gradients. The third approach involves the application of one or more discrete axial fields to create one or more potential barriers along the axial dimension of the trap (in addition to the barriers used to initially trap the ions). These barriers prevent ions of differing voltage gradients from equilibrating with one another.
Owner:MDS CO LTD +2
Three-dimensional imaging method and device utilizing planar lightwave circuit
ActiveCN103207458ASmear suppressionRealize regulationHolographic optical componentsActive addressable light modulatorVisual perceptionLightness
The invention discloses a three-dimensional imaging method and a device utilizing a planar lightwave circuit. The three-dimensional imaging method includes that coherent light emitted from coherent light source is converted into a two dimensional point light source array; the position of every point light source in the two dimensional point light source array is randomly distributed; three-dimensional images are discretized into a large amount of vexel; the vexel is divided into a plurality of groups from high to low according to the brightness; a phase regulating amplitude of the point light source is calculated according to the distance between every point light source and every vexel of every group to enable the lightwave from every point light source to be in the same phase when reaches the vexel; every point light source is accumulated as a complex amplitude regulation amplitude for generating every vexel; and an amplitude regulator and a phase regulator of every point light source are driven to generate every group of vexel based on constructive interference. The imaging device is formed by coherent light source, the planar lightwave circuit, a conductive glass front panel and a back driving circuit. The three-dimensional imaging method and the device utilizing the planar lightwave circuit are capable of being widely applied to the fields of three-dimensional display of a computer and a television, three-dimensional human-machine exchange, robot vision and the like.
Owner:李志扬
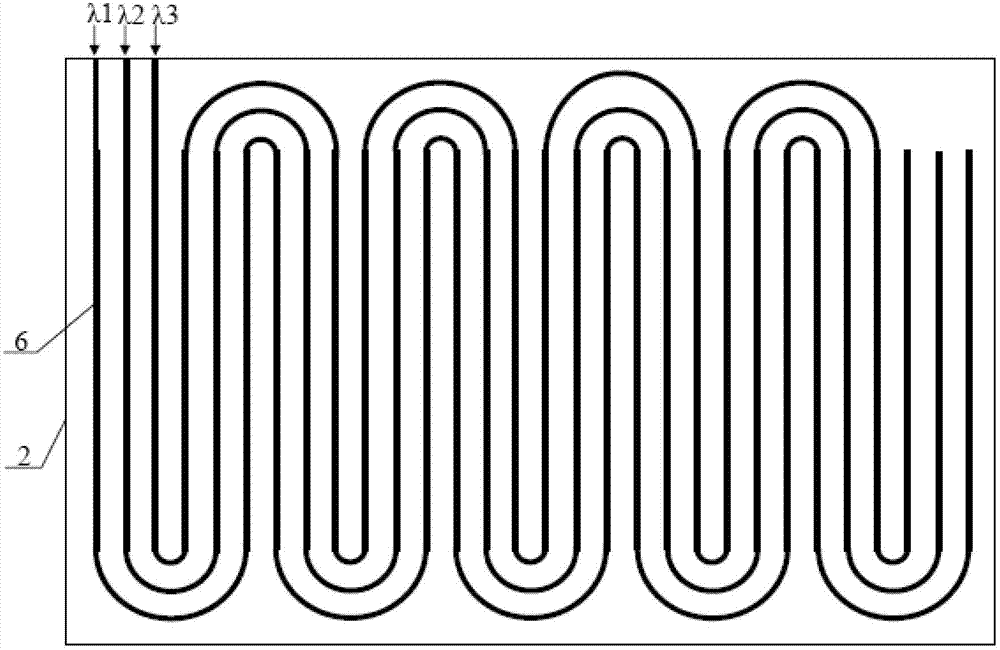
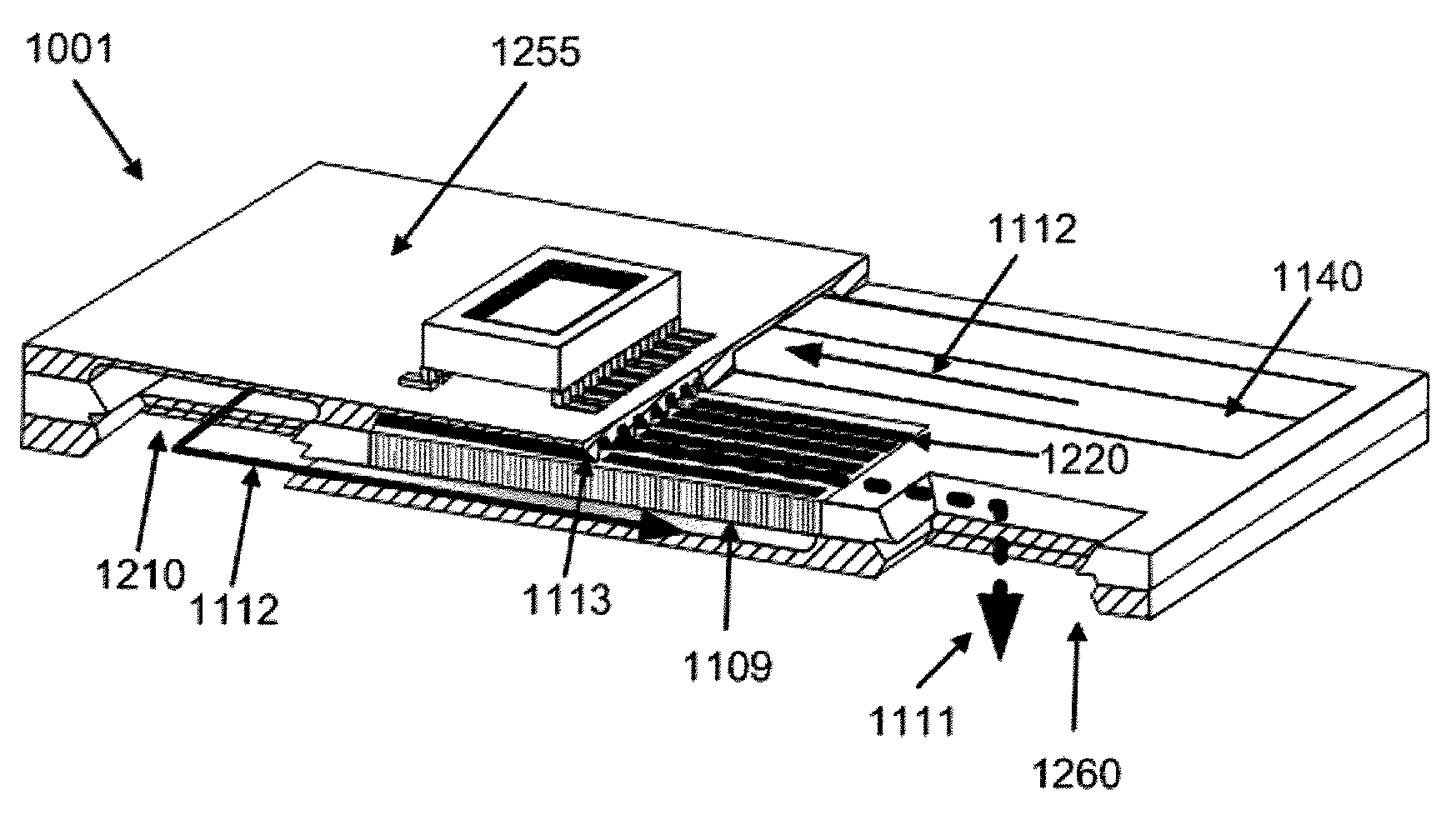
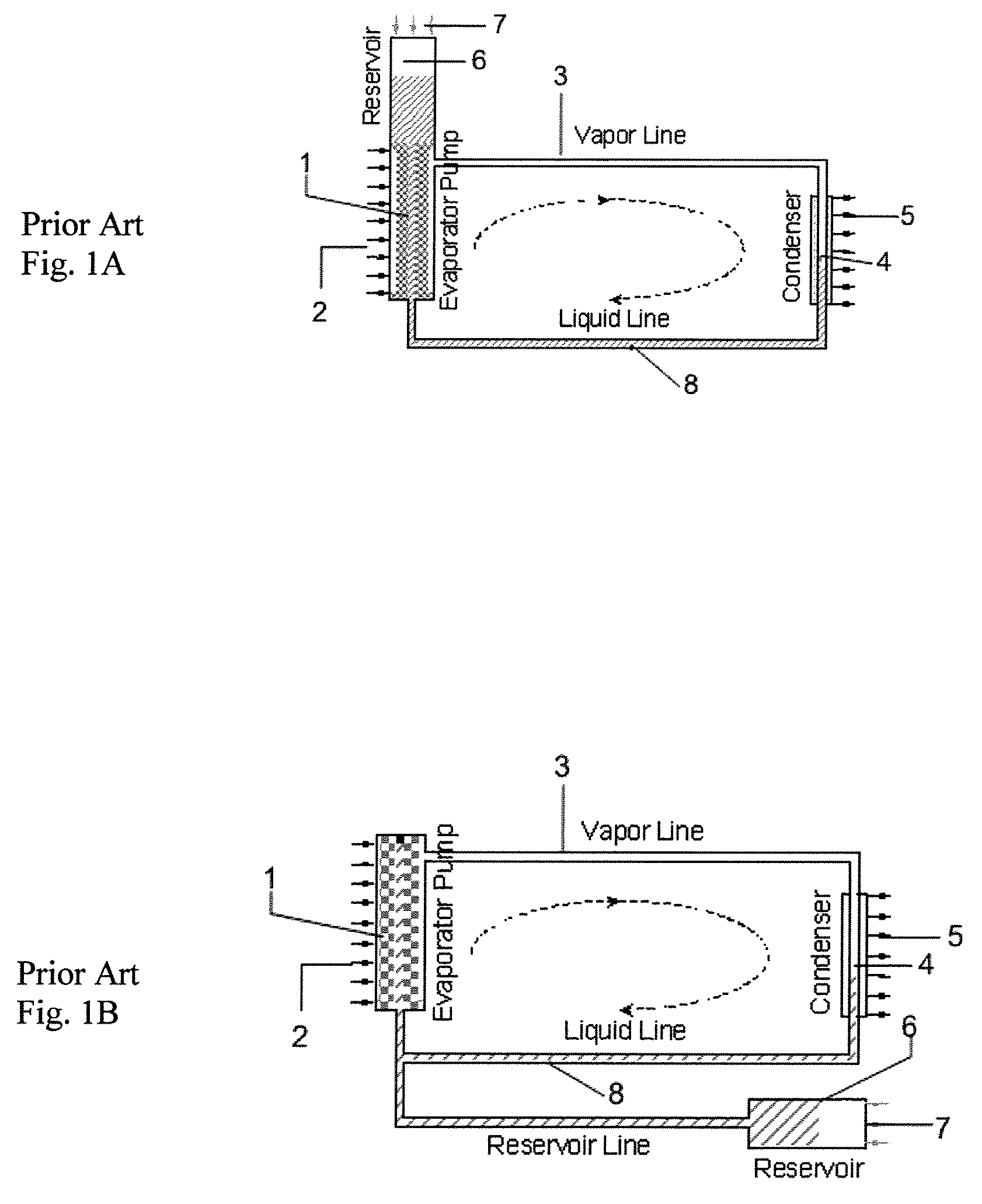
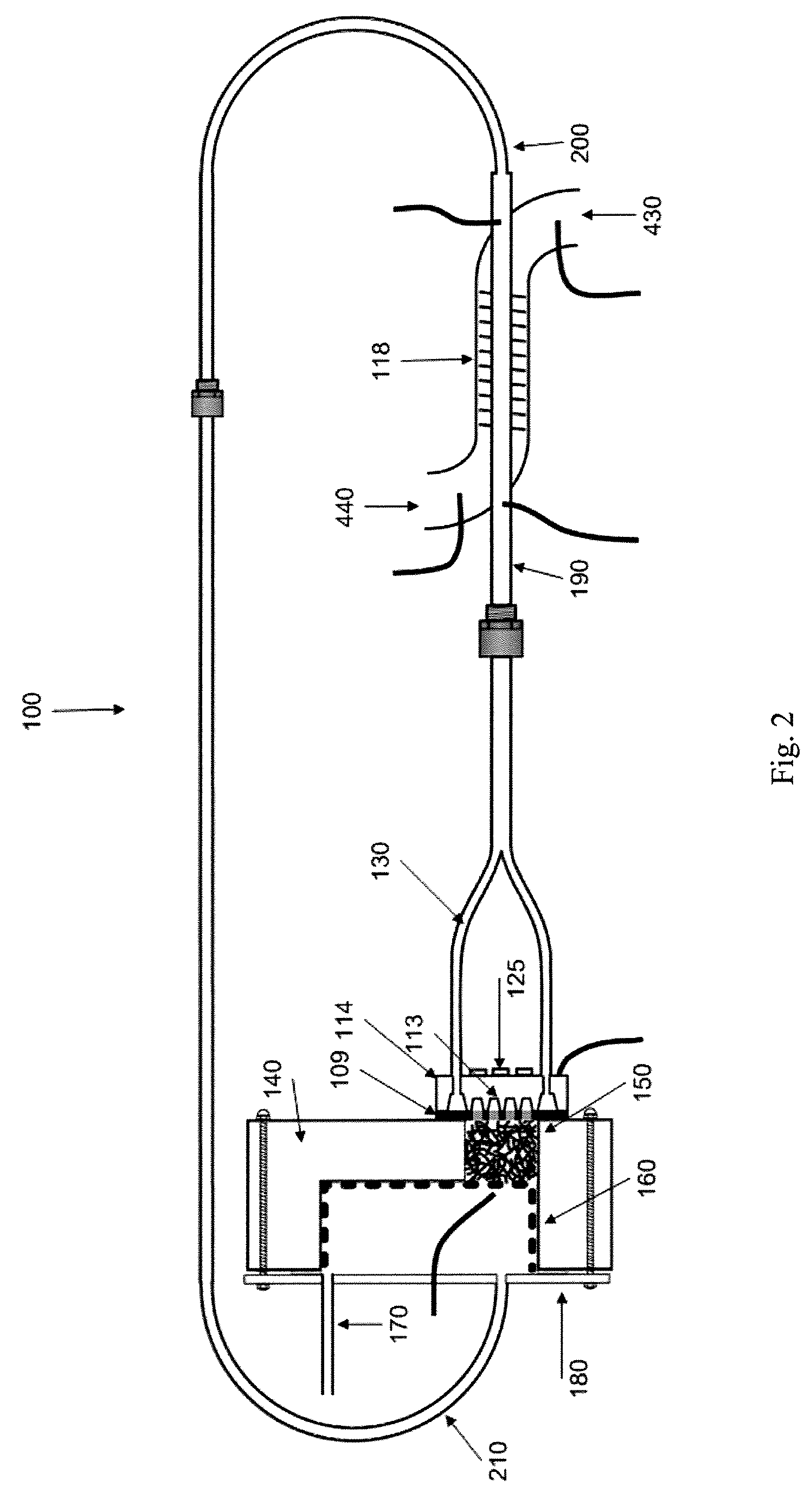
Silicon MEMS based two-phase heat transfer device
InactiveUS20070095507A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMicron scaleVolumetric Mass Density
The present invention is a MEMS-based two-phase LHP (loop heat pipe) and CPL (capillary pumped loop) using semiconductor grade silicon and microlithographic / anisotrophic etching techniques to achieve a planar configuration. The principal working material is silicon (and compatible borosilicate glass where necessary), particularly compatible with the cooling needs for electronic and computer chips and package cooling. The microloop heat pipes (μLHP™) utilize cutting edge microfabrication techniques. The device has no pump or moving parts, and is capable of moving heat at high power densities, using revolutionary coherent porous silicon (CPS) wicks. The CPS wicks minimize packaging thermal mismatch stress and improves strength-to-weight ratio. Also burst-through pressures can be controlled as the diameter of the coherent pores can be controlled on a sub-micron scale. The two phase planar operation provides extremely low specific thermal resistance (20-60W / cm2). The operation is dependent upon a unique micropatterened CPS wick which contains up to millions per square centimeter of stacked uniform micro-through-capillaries in semiconductor-grade silicon, which serve as the capillary “engine,” as opposed to the stochastic distribution of pores in the typical heat pipe wick. As with all heat pipes, cooling occurs by virtue of the extraction of heat by the latent heat of phase change of the operating fluid into vapor. In the cooling of a laptop computer processor the device could be attached to the processor during laptop assembly. Consistent with efforts to miniaturize electronics components, the current invention can be directly integrated with a unpackaged chip. For applications requiring larger cooling surface areas, the planar evaporators can be spread out in a matrix and integrally connected through properly sized manifold systems.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
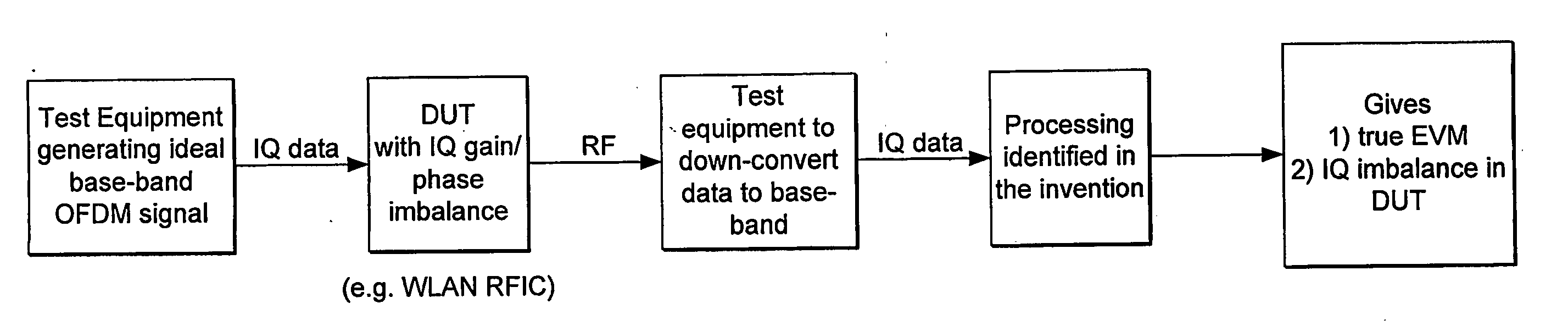
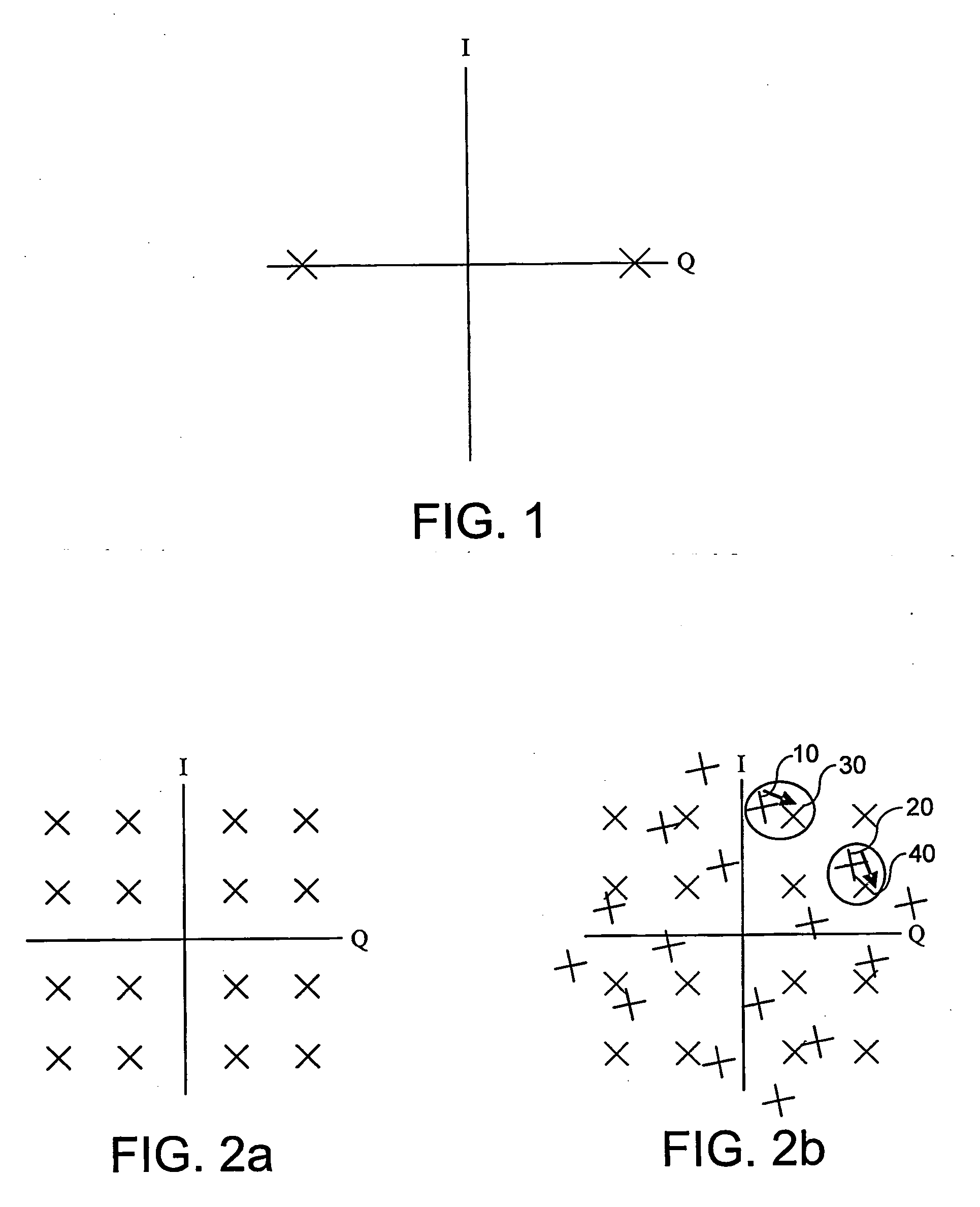
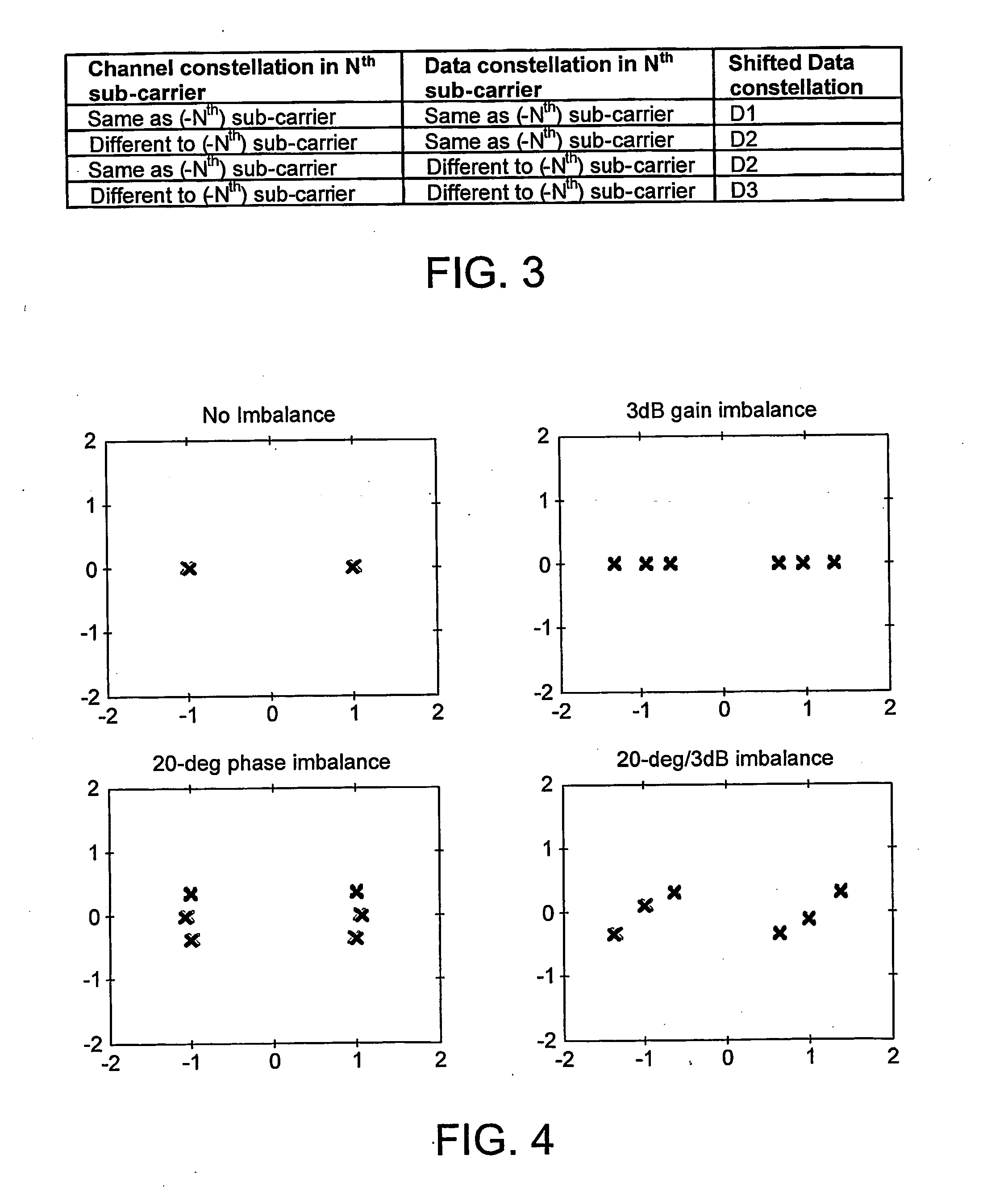
Method of Determining True Error Vector Magnitude in a Wireless Lan
InactiveUS20090316589A1Measurement is faster and cheapNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementCorrect operation testingPhase noiseError vector magnitude
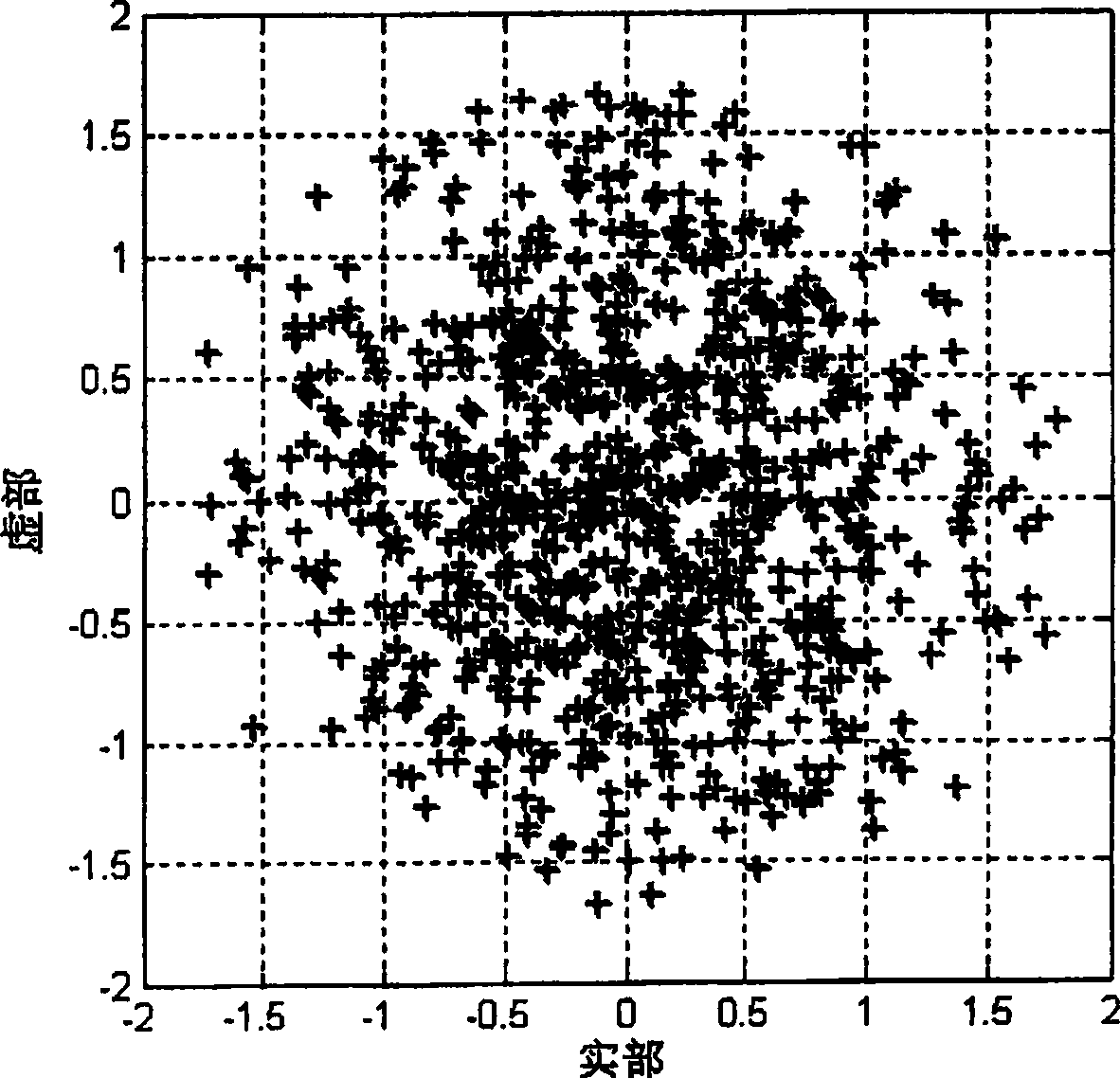
Systematic transmit IQ phase and amplitude imbalances in the transmit chain of a wireless local area network (WLAN) cause a corresponding systematic shift in the roots of a constellation diagram. Additional random phase noise in the transmit chain will cause a further Gaussian distribution of points in the constellation diagram about the systematically shifted roots. This random distribution represents a true error vector magnitude (EVM). By transmitting a known training sequence through the transmit chain, which it is known will be shifted to all of the systematically shifted roots in the constellation diagram, the Gaussian spread around those shifted roots can be analysed to determine the true EVM.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
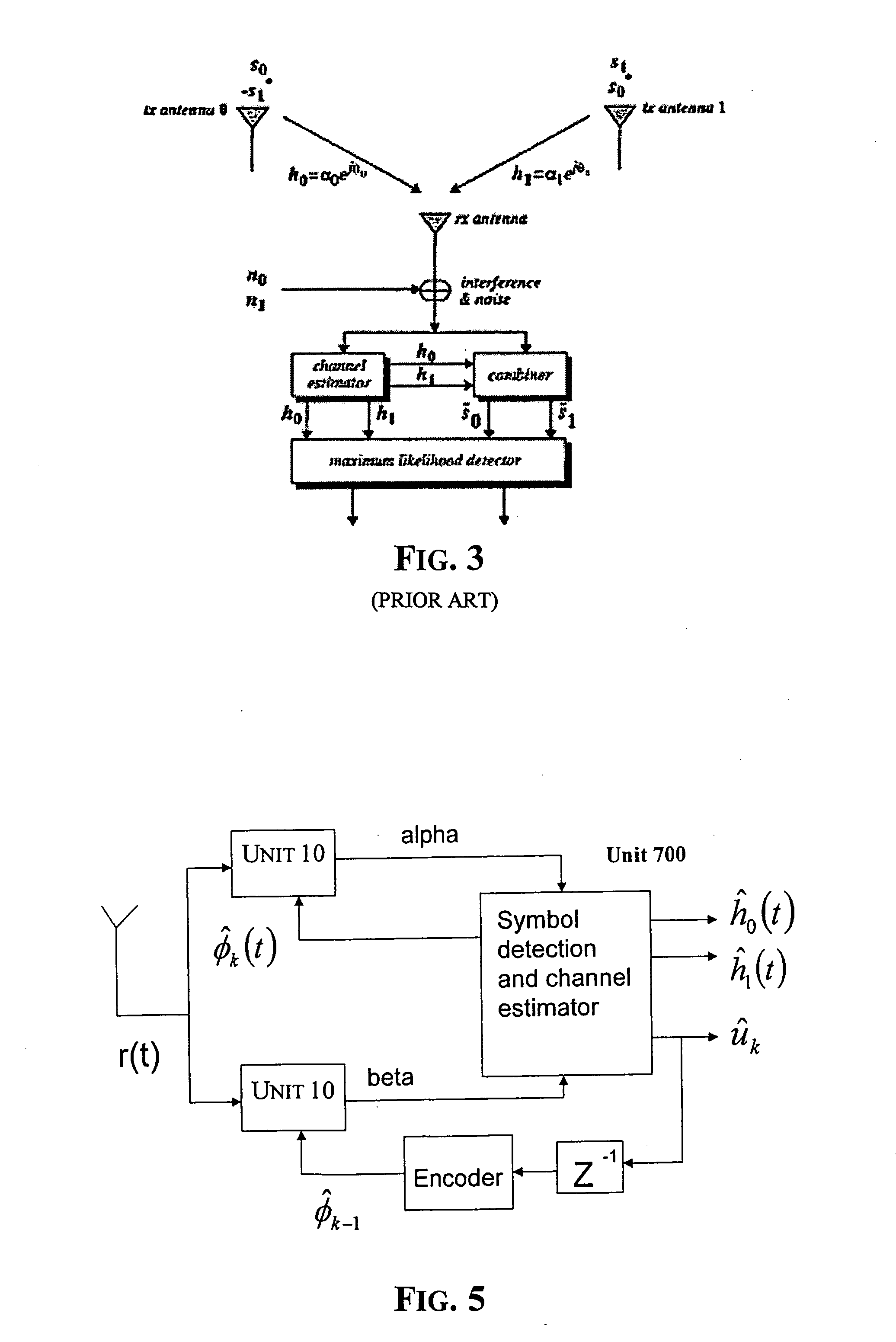
Method of estimating fading coefficients of channels and of receiving symbols and related single or multi-antenna receiver and transmitter
ActiveUS20060120486A1Efficient methodError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionTransmission channelMulti path
The method is for estimating the fading coefficients of a plurality of transmission channels on which signals to be sent, generated as a function of a sequence of symbols, are transmitted according to a particular modulation, e.g. AM-PSK modulation. The fading coefficients are estimated by using estimations of the transmitted symbols obtained in advance, thus obtaining DC components of the received signal by coherent demodulation locked to the phases of the transmitted AM-PSK signals, and processing these DC components. The method may not require the choice of a stochastic distribution model of the channel fading, thus it remains efficient even when the channel characteristics vary significantly. Moreover, the method works correctly even if the received stream is disturbed by inter-symbolic interference (ISI) and / or by multi-path fading.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Electrical pulse generator using pseudo-random pole distribution
InactiveCN1615573ALow power outputElectrical output does not generateElectric ignition installationMachines/enginesHigh energyElectrical polarity
A multi-pole electric pulse generator containing magnetic poles having a pseudo-random distribution. Preferably, the magnetic poles are equal in size and interval, and the polarity conforms to a pseudo-noise binary sequence, which sequence is specifically a primitive polynomial m-sequence. At one position in the rotor rotation, all rotor poles are aligned with corresponding stator poles to provide maximum net magnetic flux through the armature windings. At all other rotor positions, the poles are misaligned and the net magnetic flux through the armature windings is small. In operation, rotation through these misaligned rotor positions produces substantially no change in magnetic flux and thus no electrical energy. When the rotor reaches this alignment position, a sudden, large change in magnetic flux produces a high-energy electrical pulse. An exemplary application is for generating an ignition spark for an internal combustion engine.
Owner:IBM CORP
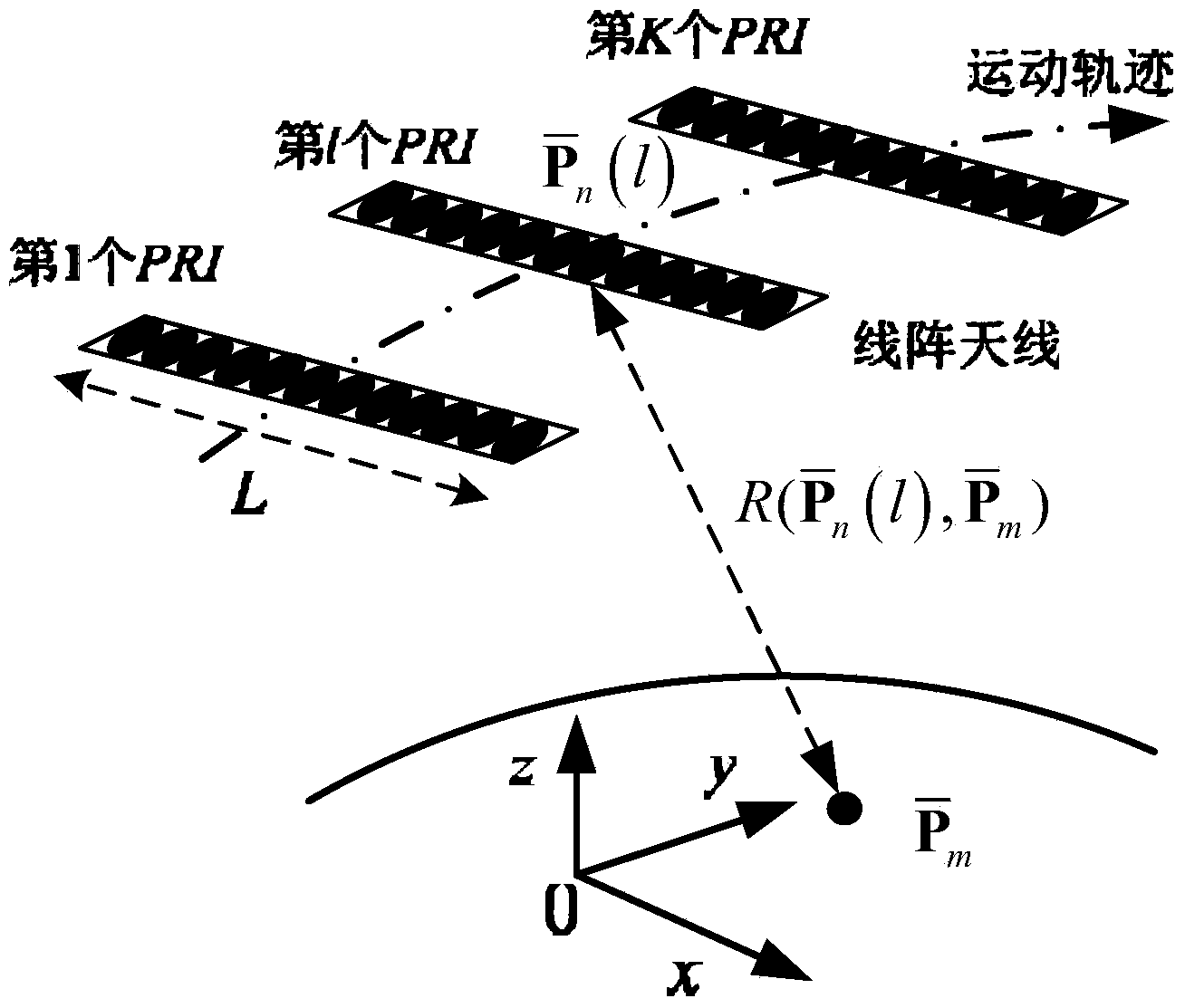
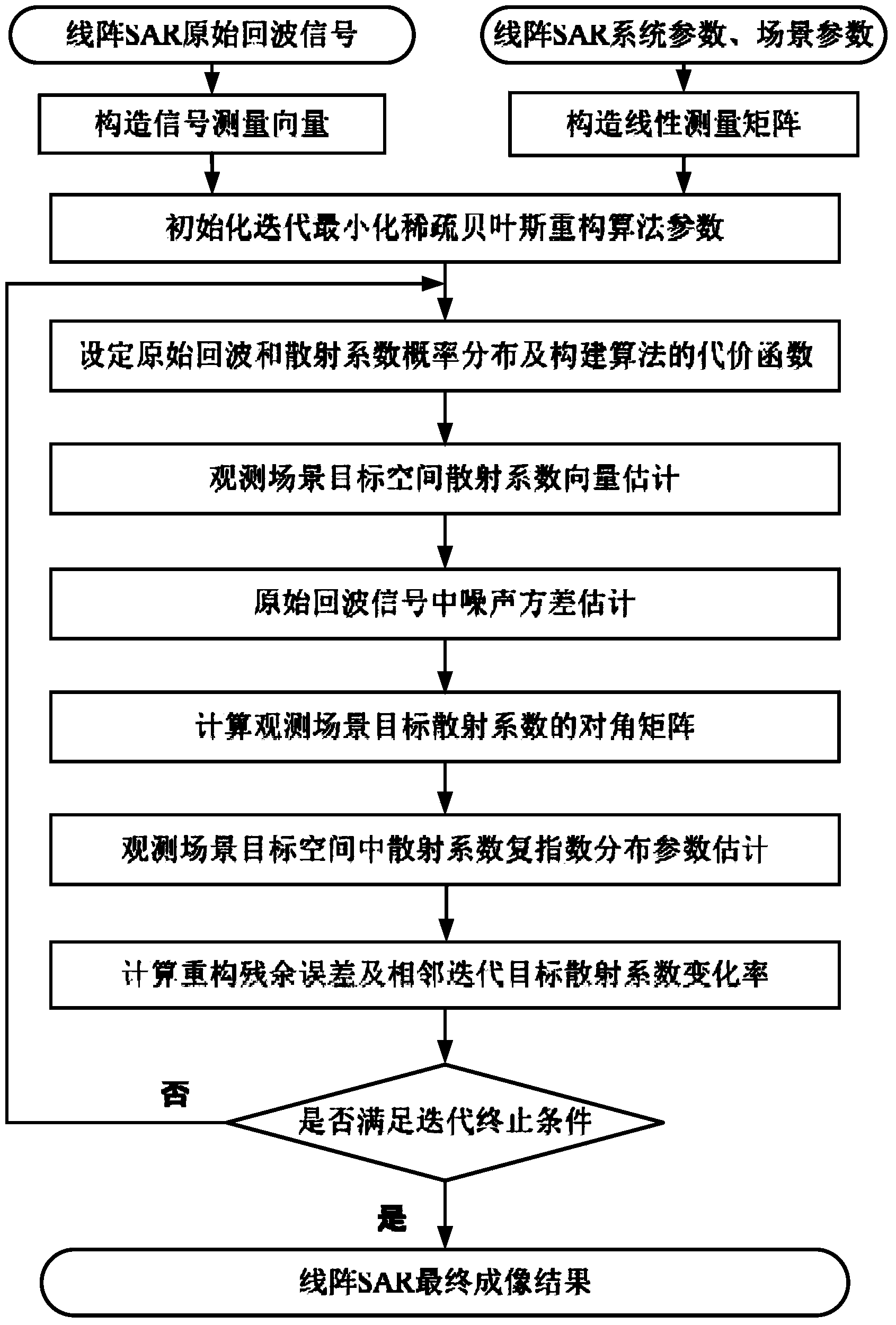
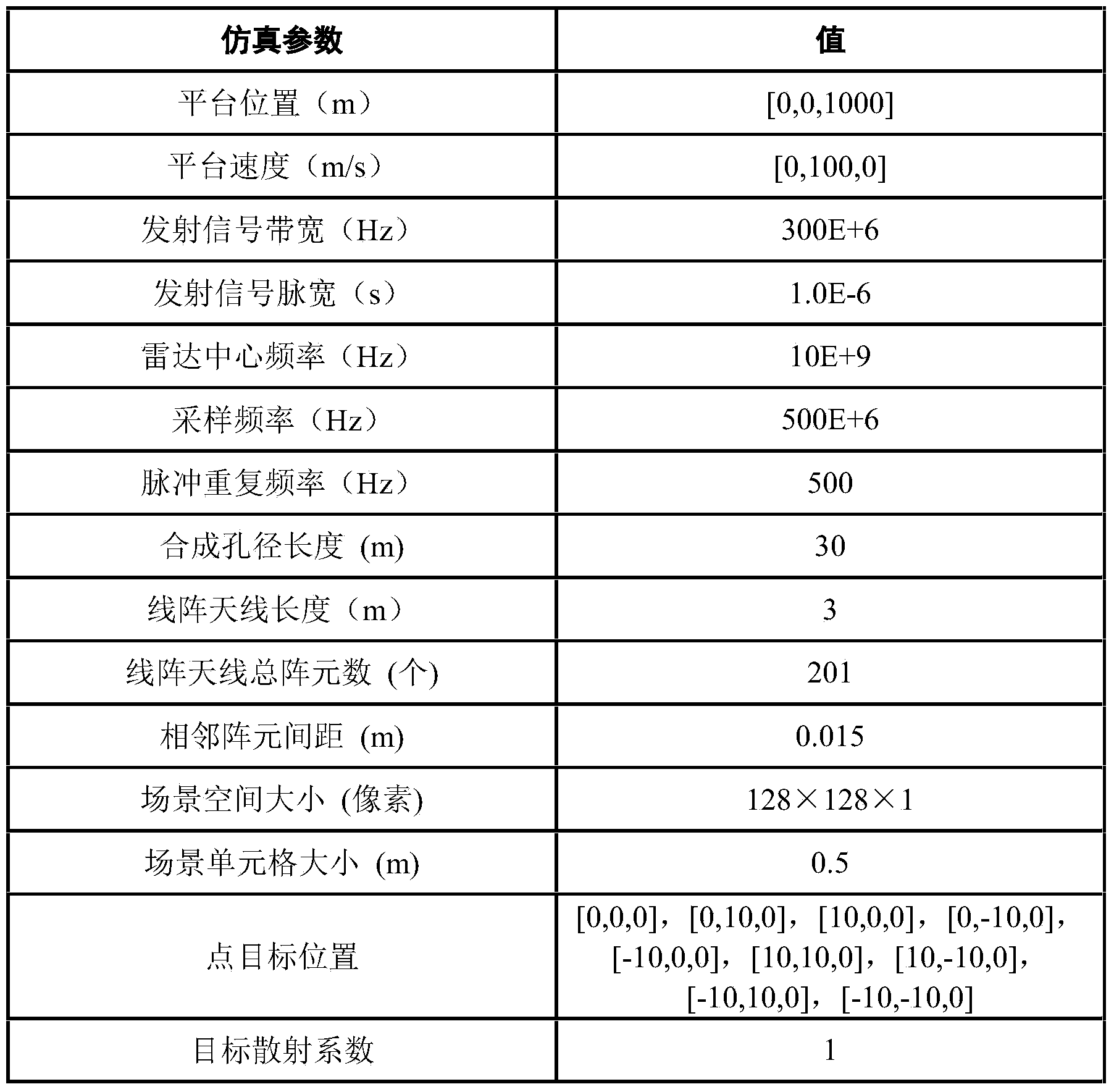
Linear array SAR imaging method based on iterative minimization sparse Bayesian reconstitution
InactiveCN103713288AImproving Performance for Sparse ImagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionHypothesisRadar
The invention provides a linear array SAR imaging method based on iterative minimization sparse Bayesian reconstitution. The method is prior distributional hypothesis based on a linear array SAR original echo signal measurement model, it is assumed that a prior probability density function of a scattering coefficient in a linear array SAR observation scene target space complies with complex exponential prior distribution, it is also assumed that a posterior probability density function of a linear array SAR original echo signal complies with Gaussian stochastic distribution, a reconstitution cost function of the scattering coefficient in the linear array SAR observation scene target space is set up through the Bayesian criterion, sparse reconstitution of the scattering coefficient in the linear array SAR observation scene target space is achieved through complex exponential distribution parametric optimization estimation and the iterative minimization constitution cost function, and therefore performance of linear array SAR sparse imaging is improved. The linear array SAR imaging method can be applied to the synthetic aperture radar imaging field, the global remote sensing field and other fields.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
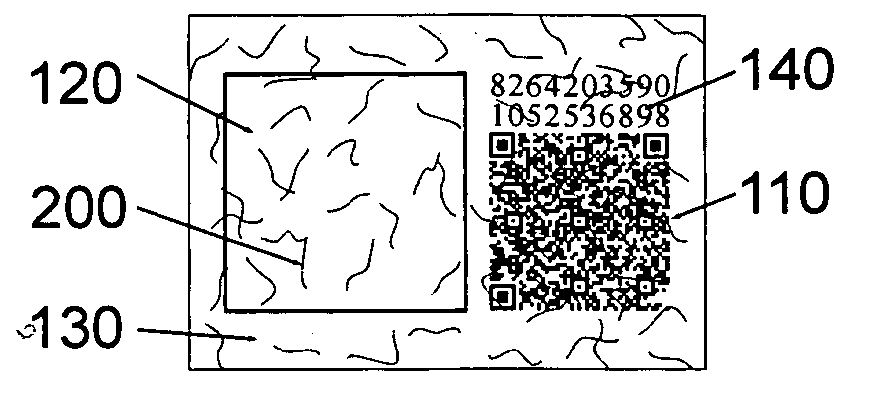
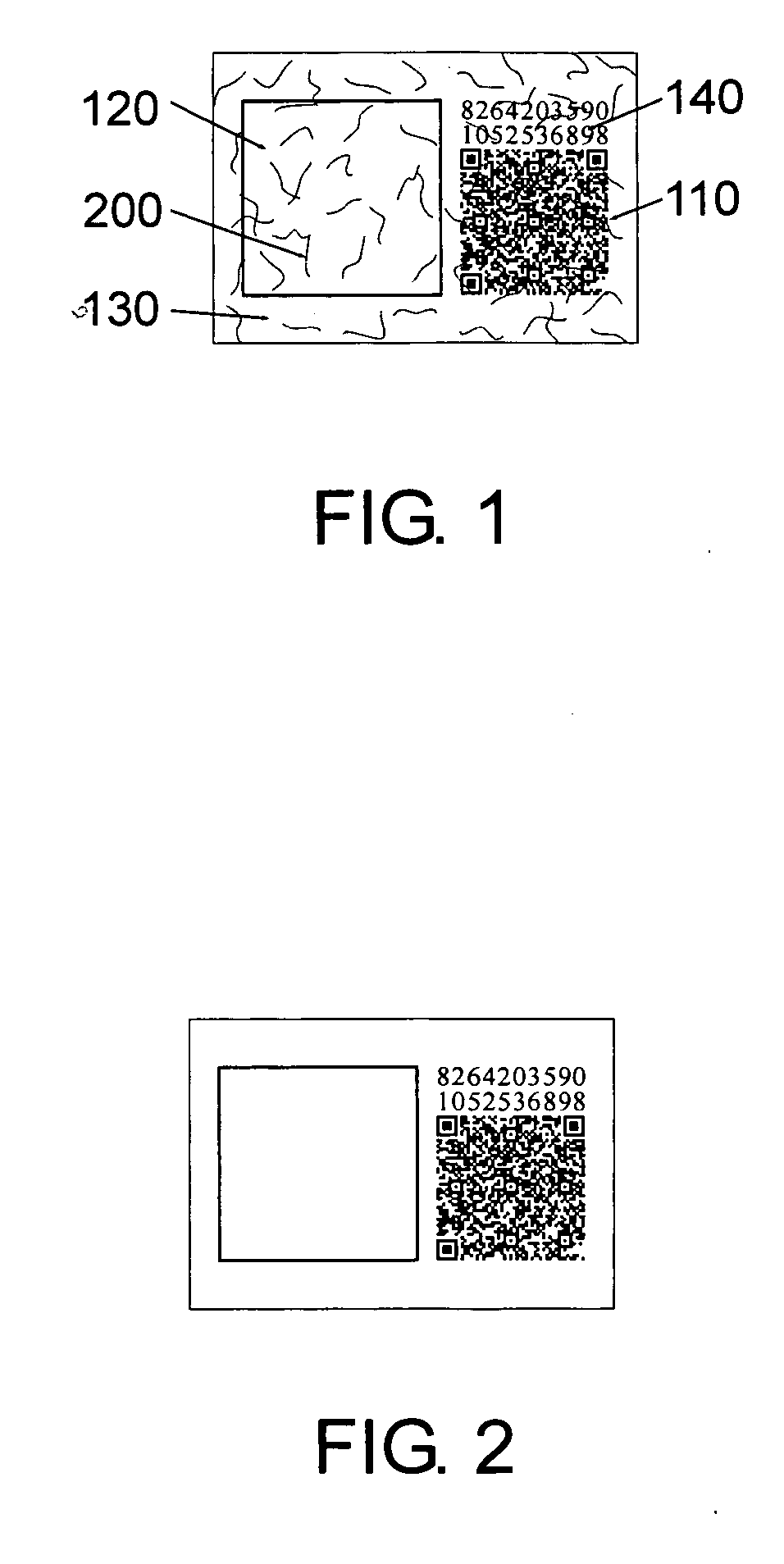
Texture coding label
InactiveUS20060244253A1Good anti-counterfeiting functionGuaranteed normal processingStampsOther printing matterPattern recognitionFiber
The present invention discloses a texture coding label for certificating authentification of a genuine commodity, wherein the texture coding label comprises a fabric texture portion having a plurality of fiber threads randomly distributed therein to form a fiber image, and a two-dimensional bar code portion for recording a two-dimensional bar code generated by calculating the fiber image and a serial number of the commodity through a first predetermined algorithm. Since the texture coding label combines the texture coding technology, two-dimensional bar code technology and digital encryption technology, a uniqueness could be ensure for the commodity so as to enhance the anti-counterfeiting function.
Owner:SHENZHEN SINOSUN TECH
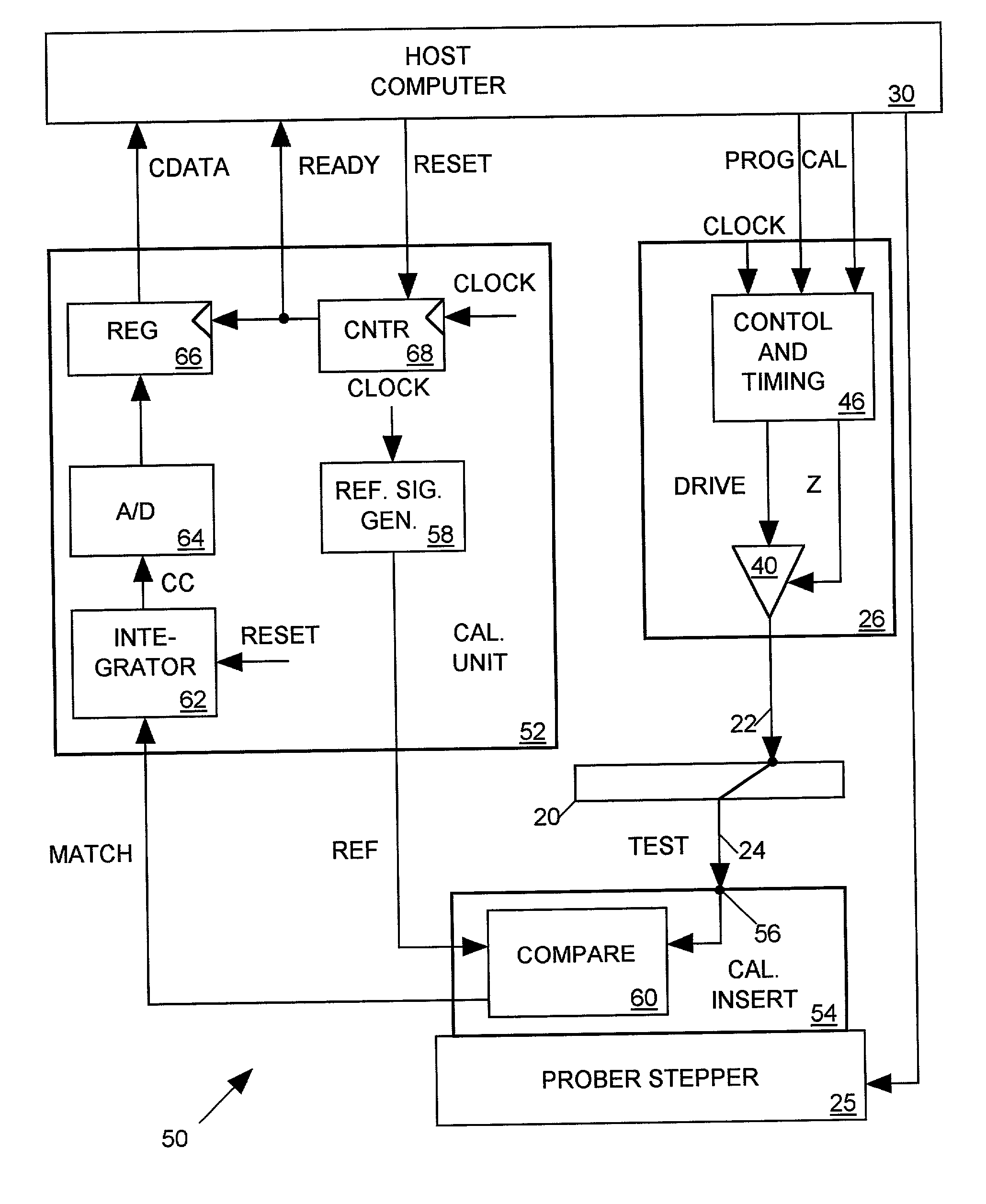
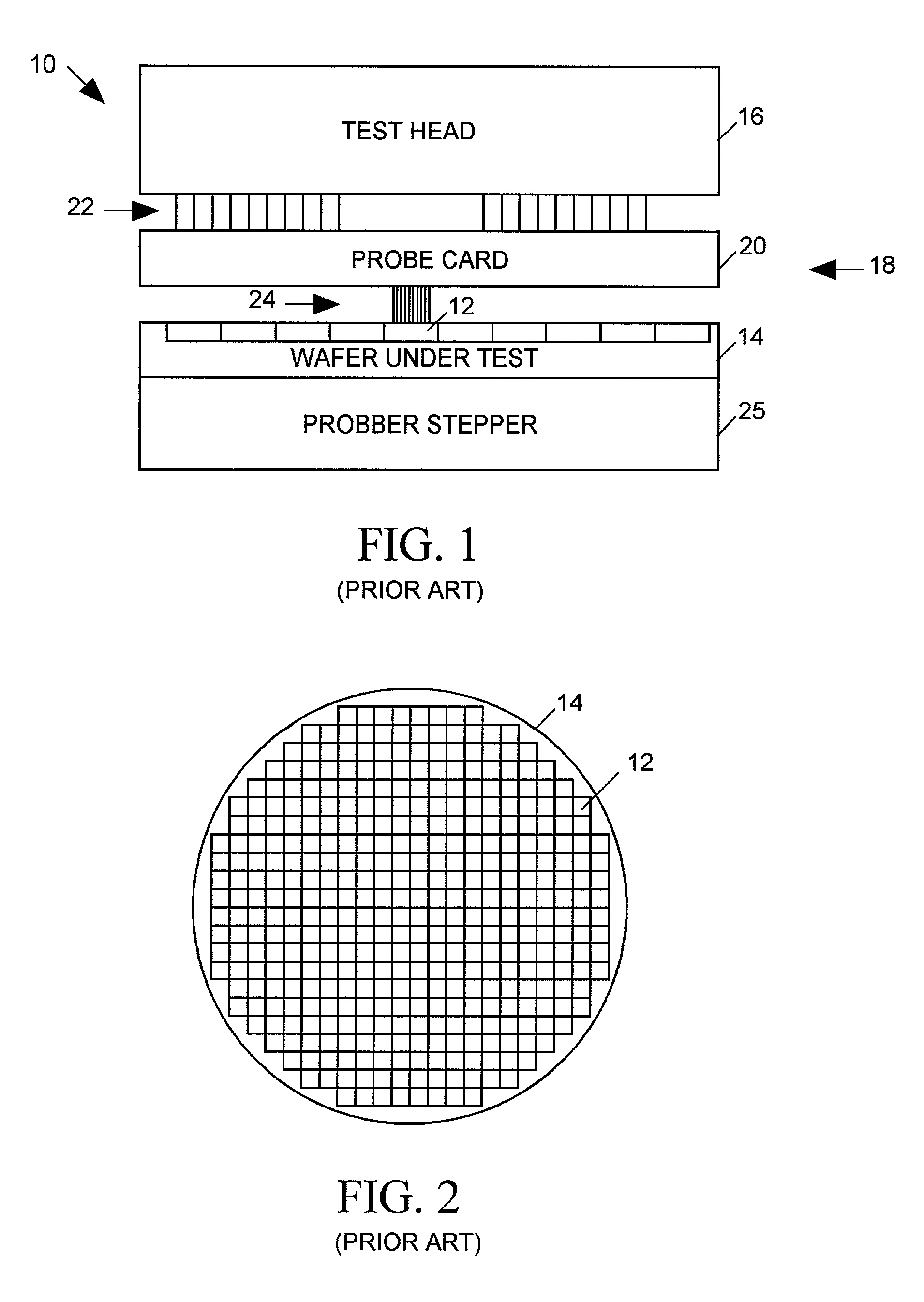
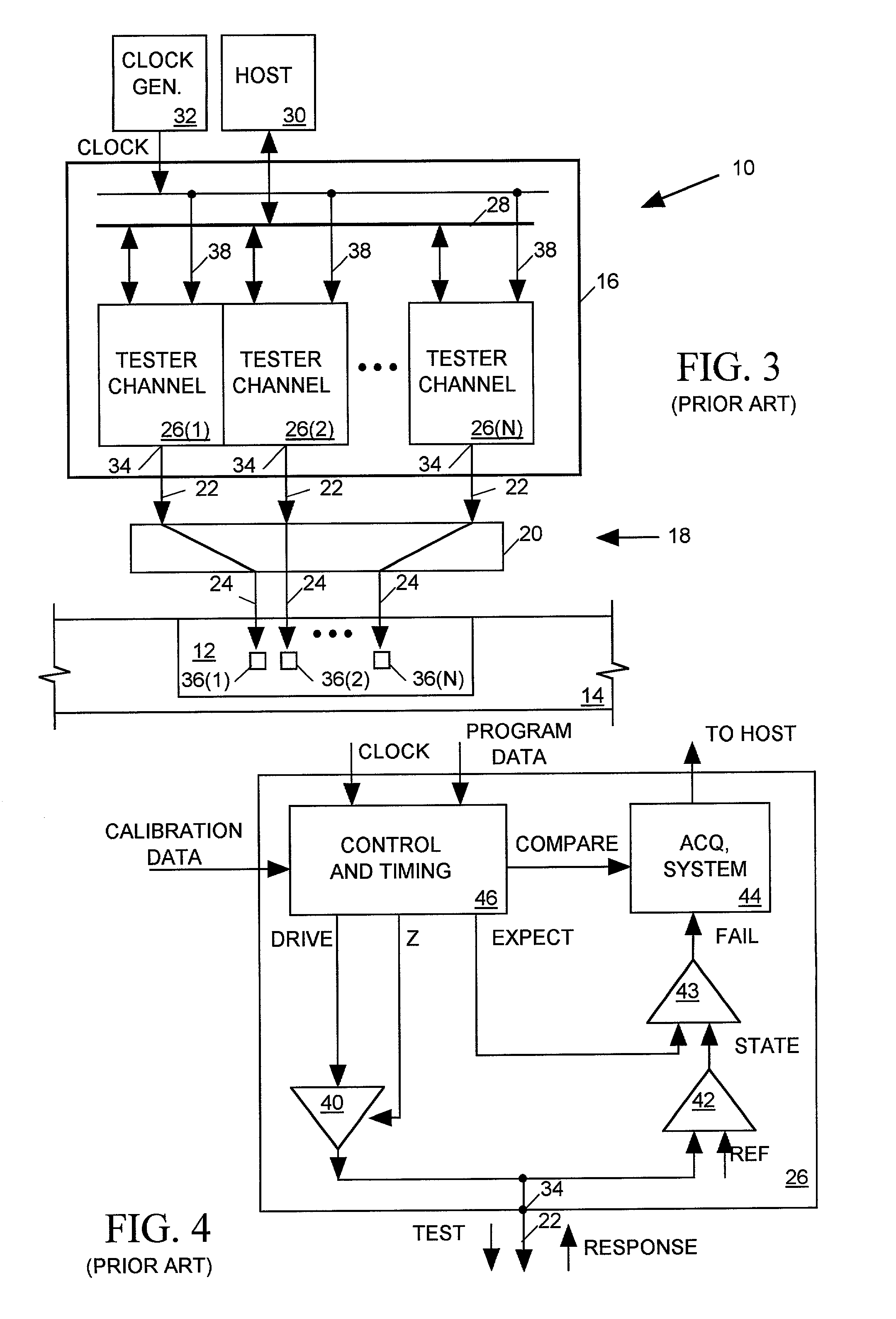
Cross-correlation timing calibration for wafer-level IC tester interconnect systems
InactiveUS20020049554A1Easy accessDigital circuit testingTesting/calibration apparatusContact padTester device
A timing calibration system for a wafer level integrated circuit (IC) tester is disclosed. The tester includes a set of probes for contacting pads on a surface of an IC and having a plurality of tester channels. Each channel generates a TEST signal at a tip of a corresponding probe in response to a periodic CLOCK signal with a delay adjusted by drive calibration data supplied as input to the tester channel. The TEST signal produced by each channel includes edges occurring in a timing pattern controlled by programming data provided as input to each tester channel. To calibrate test signal timing of all channels, each channel is programmed to generate a test signal having the same repetitive edge timing pattern at the tester channel's corresponding probe tip. The test signal produced at each probe tip is then cross-correlated to a periodic reference signal having the same repetitive edge timing pattern. The drive calibration data of each channel is then iteratively adjusted to determine a value which maximizes the cross-correlation between its output test signal and the reference signal. To maximize the accuracy of the timing calibration, each repetition of the test and reference signal edge pattern provides pseudo-randomly distributed time intervals between successive signal edges.
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
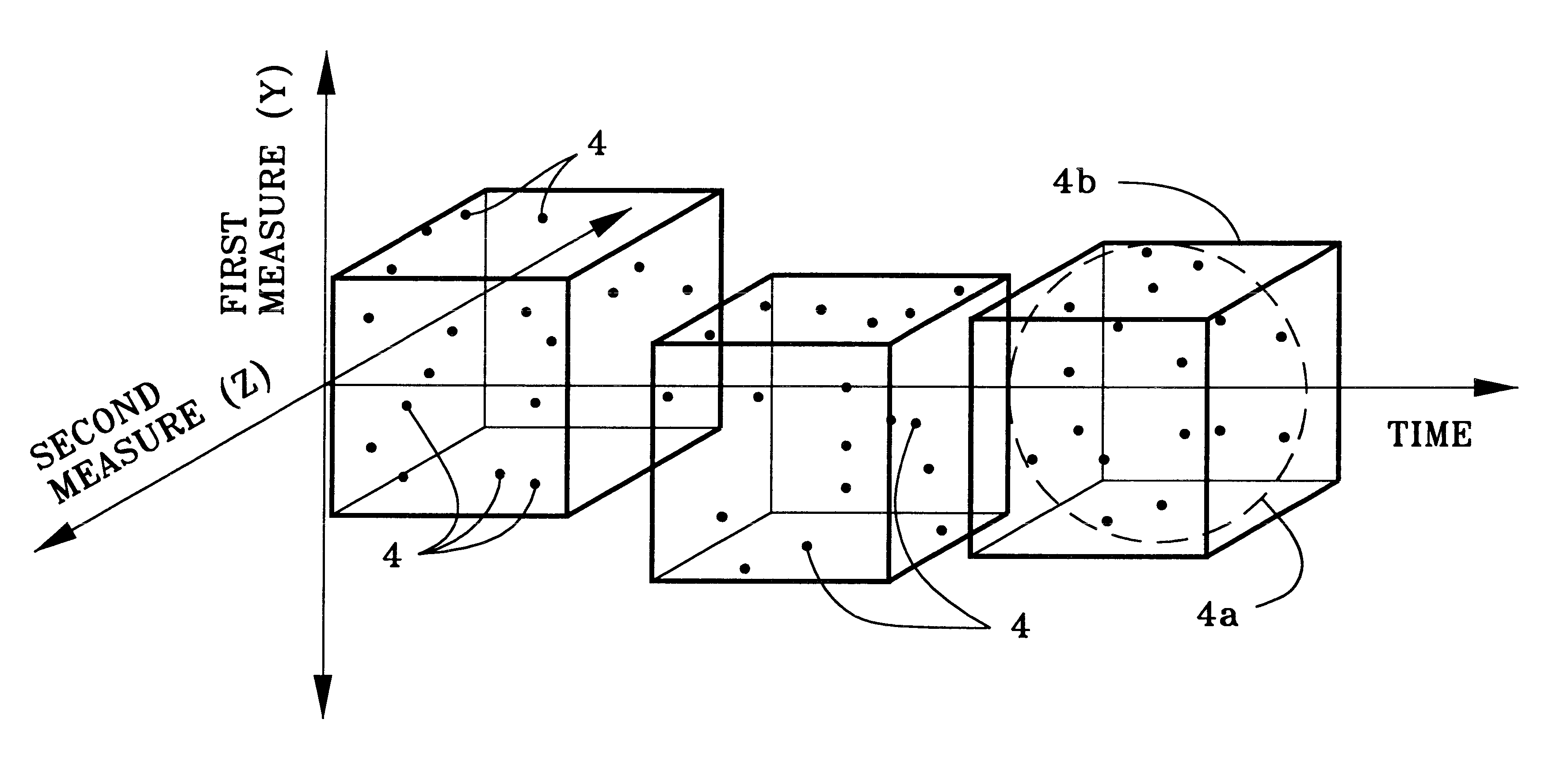
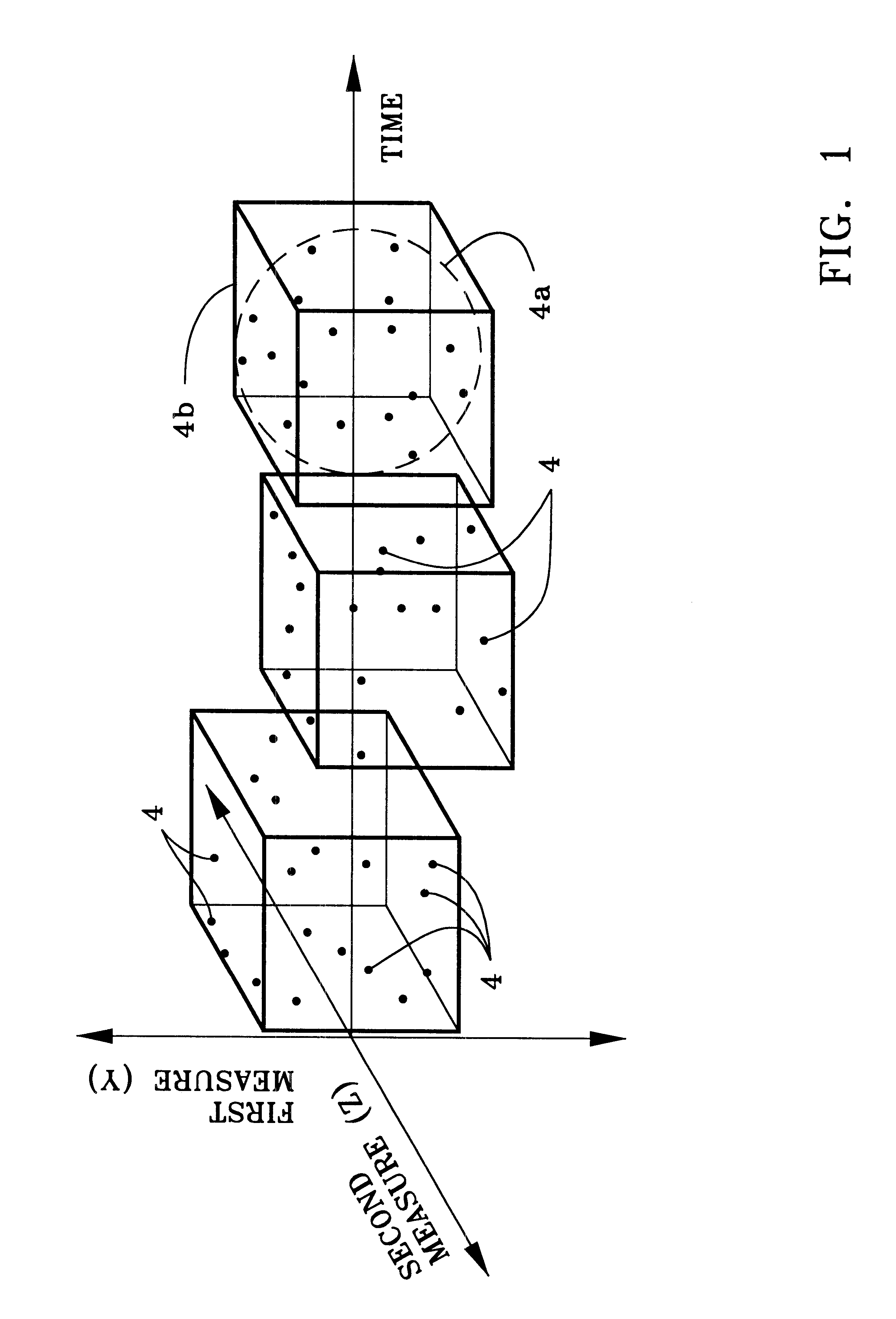
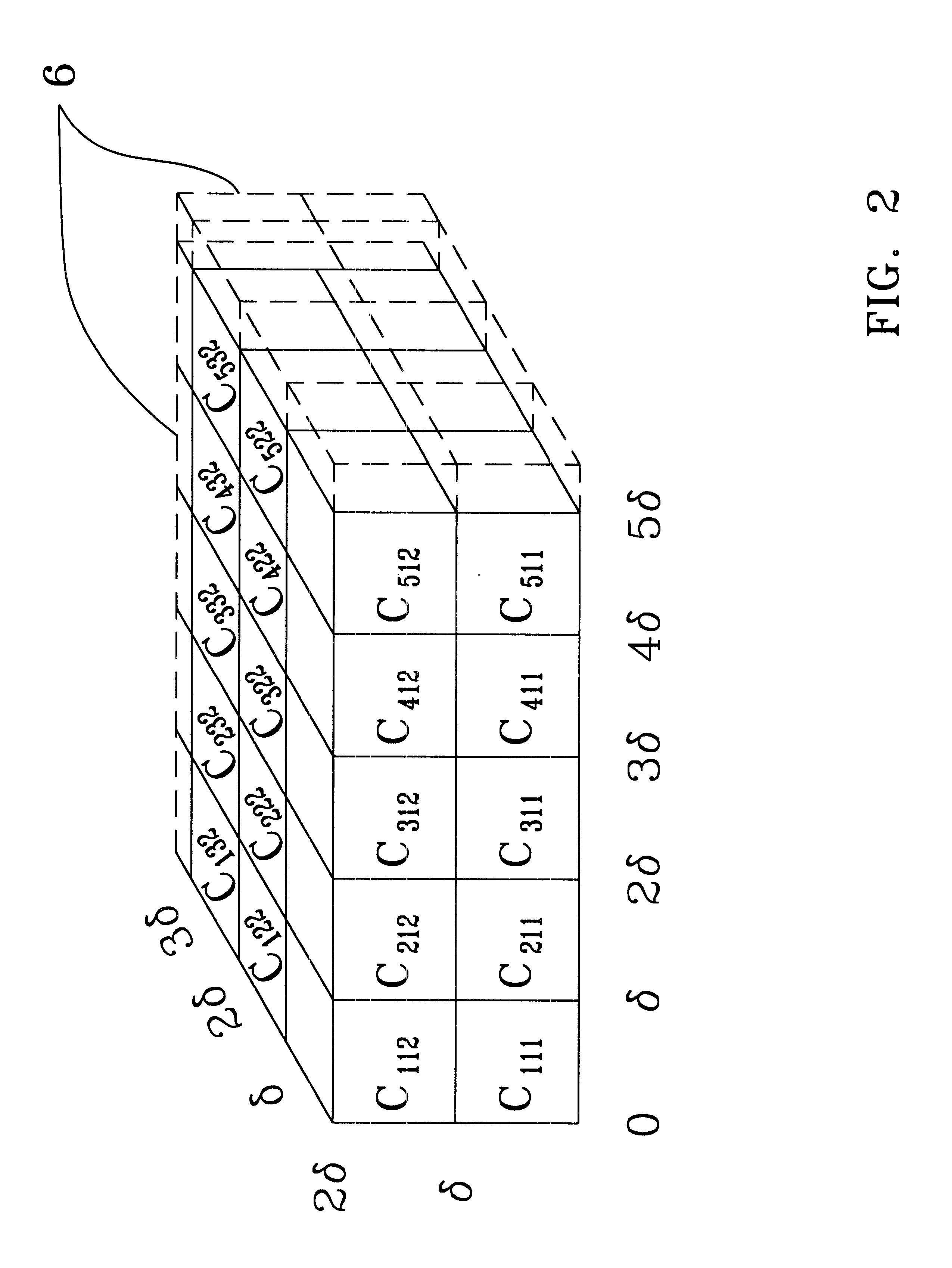
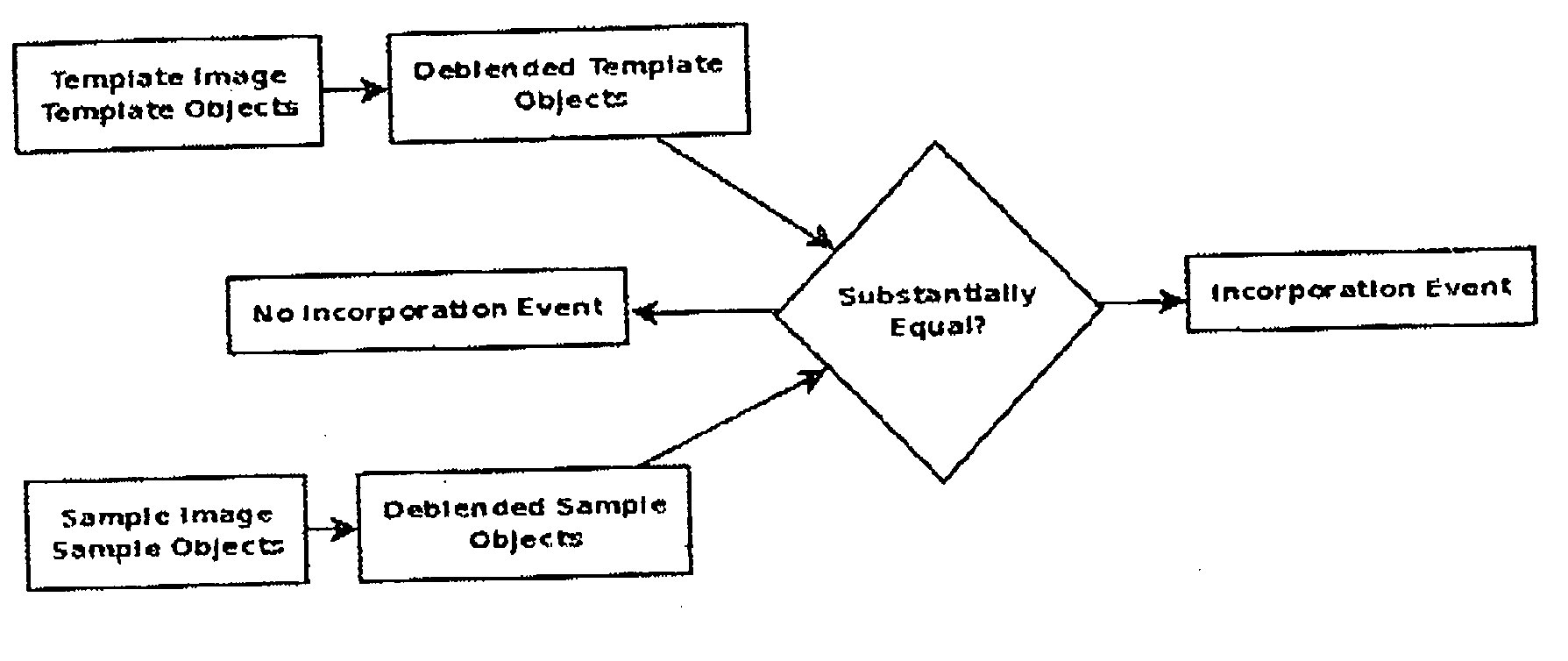
System and apparatus for the detection of randomness in three dimensional time series distributions made up of sparse data sets
InactiveUS6466516B1High sensitivityAppropriate detectionSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionDigital computer detailsData processing systemComputer science
A method and apparatus are provided for automatically characterizing the spatial arrangement among the data points of a three-dimensional time series distribution in a data processing system wherein the classification of said time series distribution is required. The method and apparatus utilize grids in Cartesian coordinates to determine (1) the number of cubes in the grids containing at least one input data point of the time series distribution; (2) the expected number of cubes which would contain at least one data point in a random distribution in said grids; and (3) an upper and lower probability of false alarm above and below said expected value utilizing a discrete binomial probability relationship in order to analyze the randomness characteristic of the input time series distribution. A labeling device also is provided to label the time series distribution as either random or nonrandom, and / or random or nonrandom within what probability, prior to its output from the invention to the remainder of the data processing system for further analysis.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
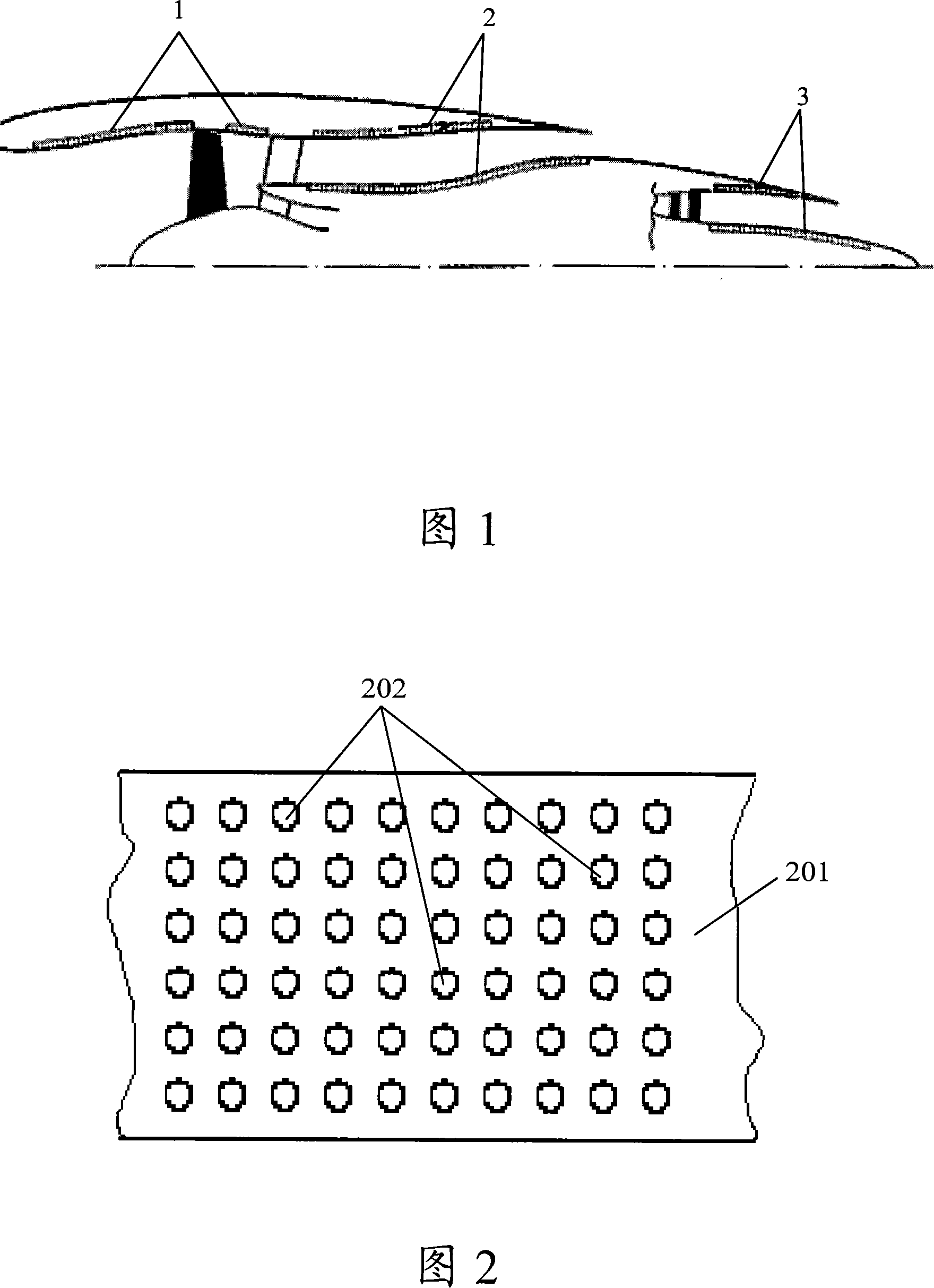
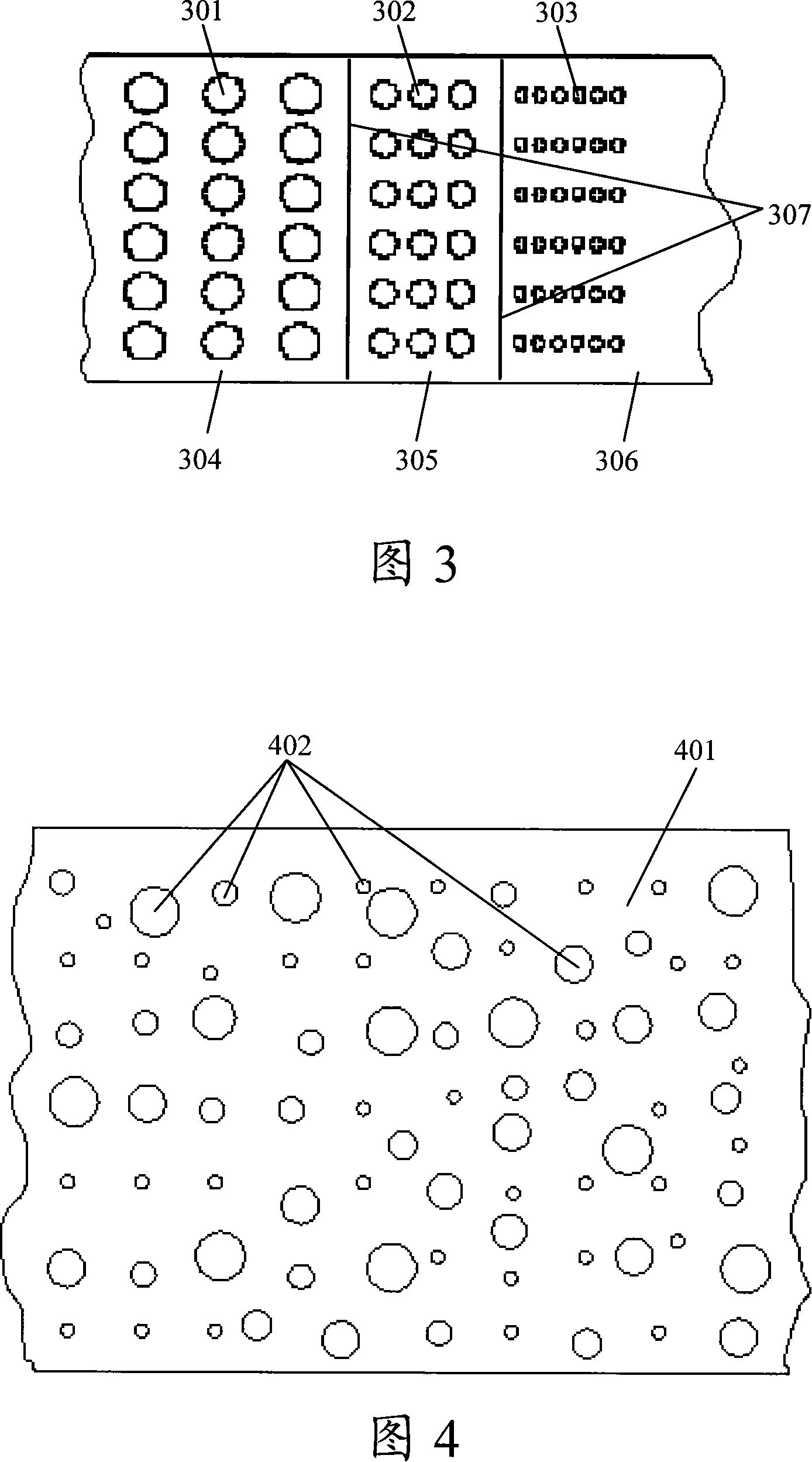
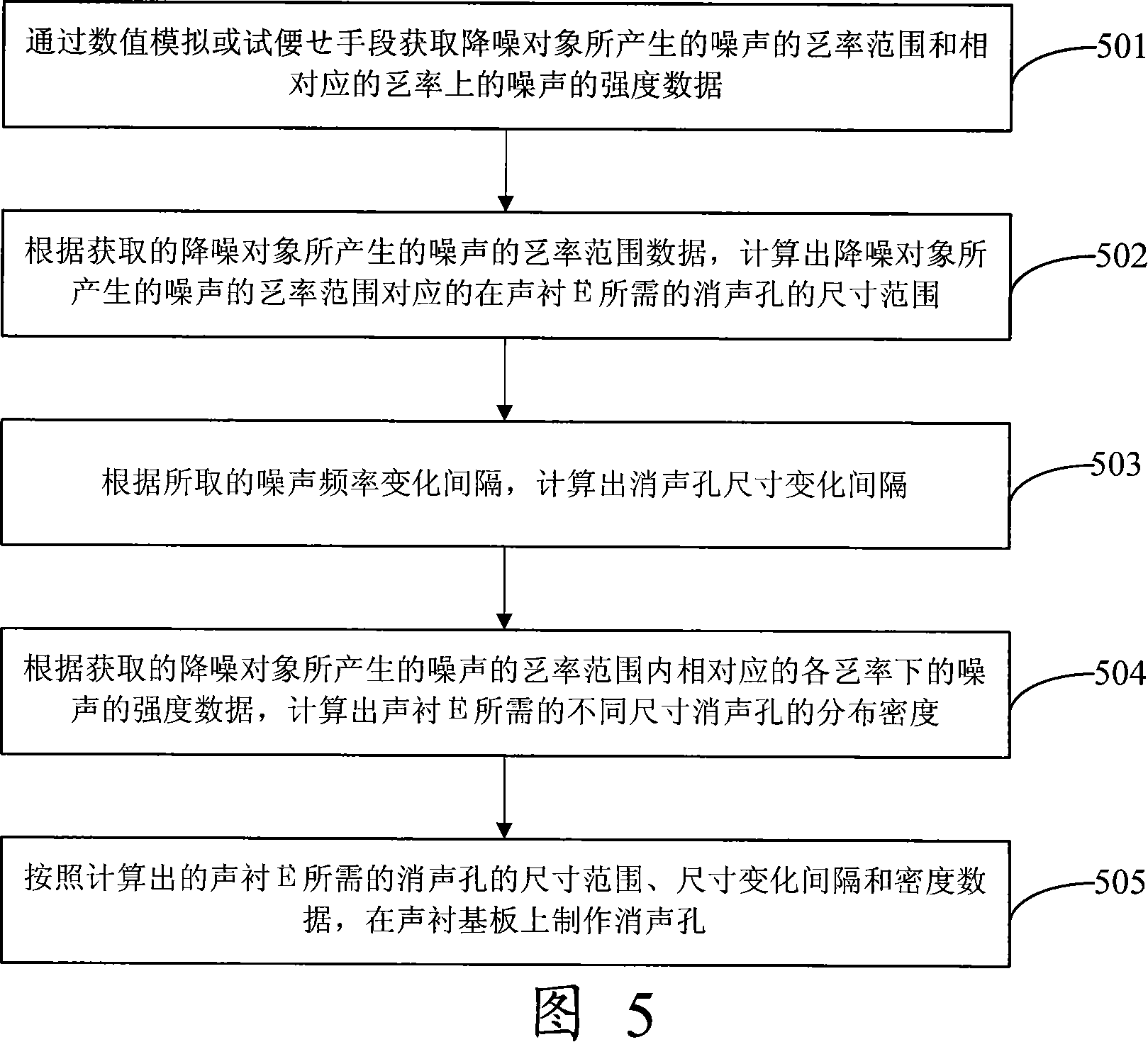
Broad-band noise-reducing acoustic liner and its manufacture method
InactiveCN101149296AEffective noise reductionPump componentsThermometers using physical/chemical changesBroadbandEngineering
The invention discloses a line to decrease noise for Broad Band and manufacture method. The sound line has the noise elimination hole which is distributed randomly and the size is changed continuously. So it can decrease the noise of broad frequency noise. Because of whole forming, it can not generate the noise dispersion phenomena caused by the sound line joint to influence the noise decreasing effect. In process of Broad Band noise decreasing line, it can get the noise frequency and corresponding noise intension by value simulation of test and get the size range, changing interface and density of noise elimination hole; also it distributes the hole on the sound line basal board to have the good noise decreasing effect.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
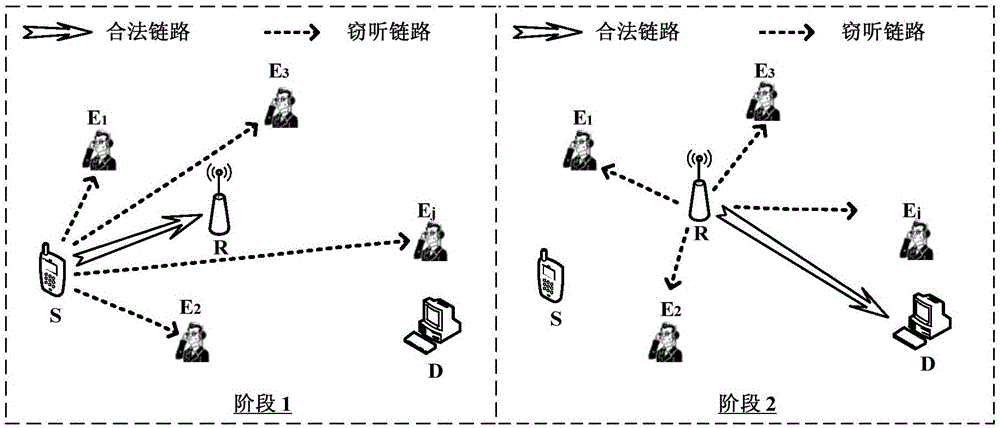
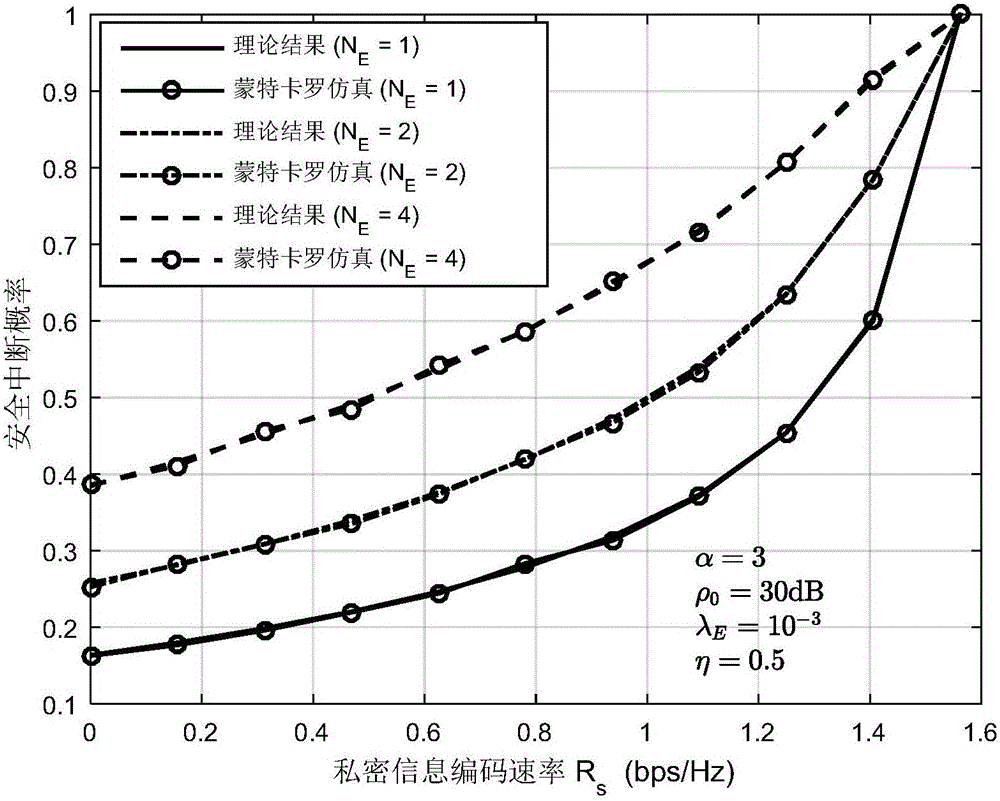
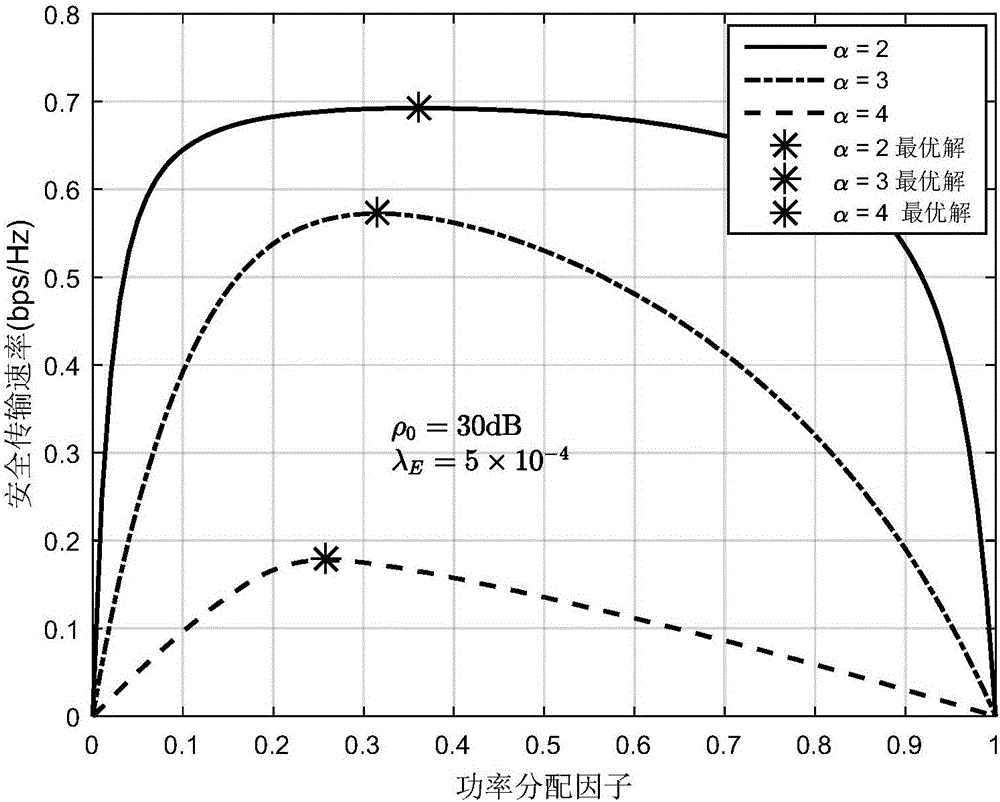
Relay transmission method based on physical layer safety in eavesdropping user randomly distributed scene
ActiveCN106131823AMaximize safe transfer rateEasy to implementTransmission monitoringSecurity arrangementTransmitted powerEavesdropping
The invention discloses a relay transmission method based on physical layer safety in an eavesdropping user randomly distributed scene. The method comprises the steps of 1), obtaining a safe interruption probability of two-hop relay transmission after two times of independent eavesdropping coding is carried out in the eavesdropping user randomly distributed scene based on a random geometric theory; 2), establishing an optimization problem of maximizing a safe transmission speed under the condition that the total transmitting power of a source node and a relay node is limited; and 3), obtaining a relay transmission method capable of maximizing the safe transmission speed through solution of the established optimization problem, wherein the method comprises two parts of power distribution and codebook rate design. According to the method, under the condition that the specific locations of the eavesdropping users are unknown, the communication reliability and safety are taken into comprehensive consideration, the safe interruption probability constraint is satisfied, and moreover, the safe transmission speed is maximized.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
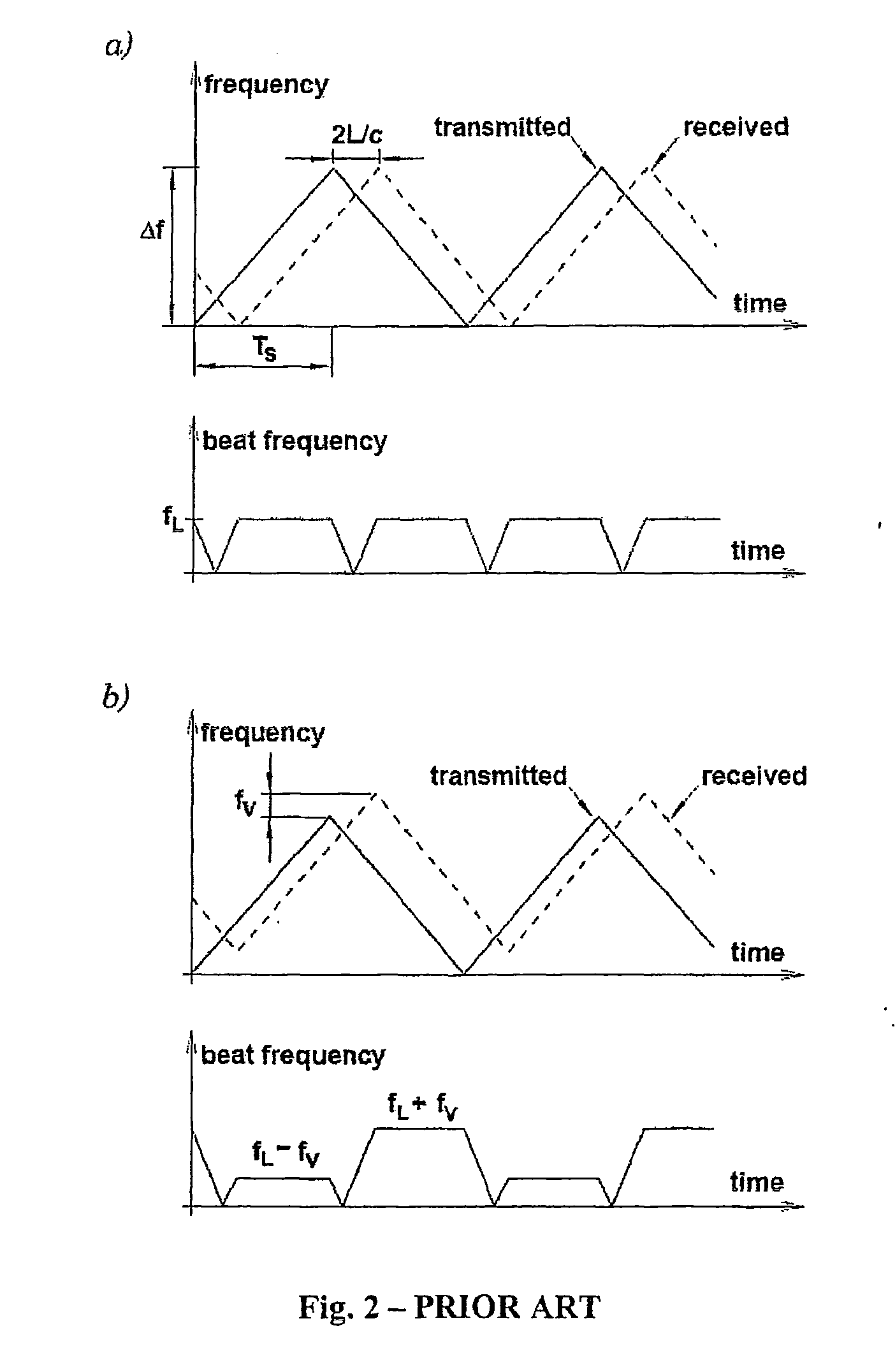
Object detection
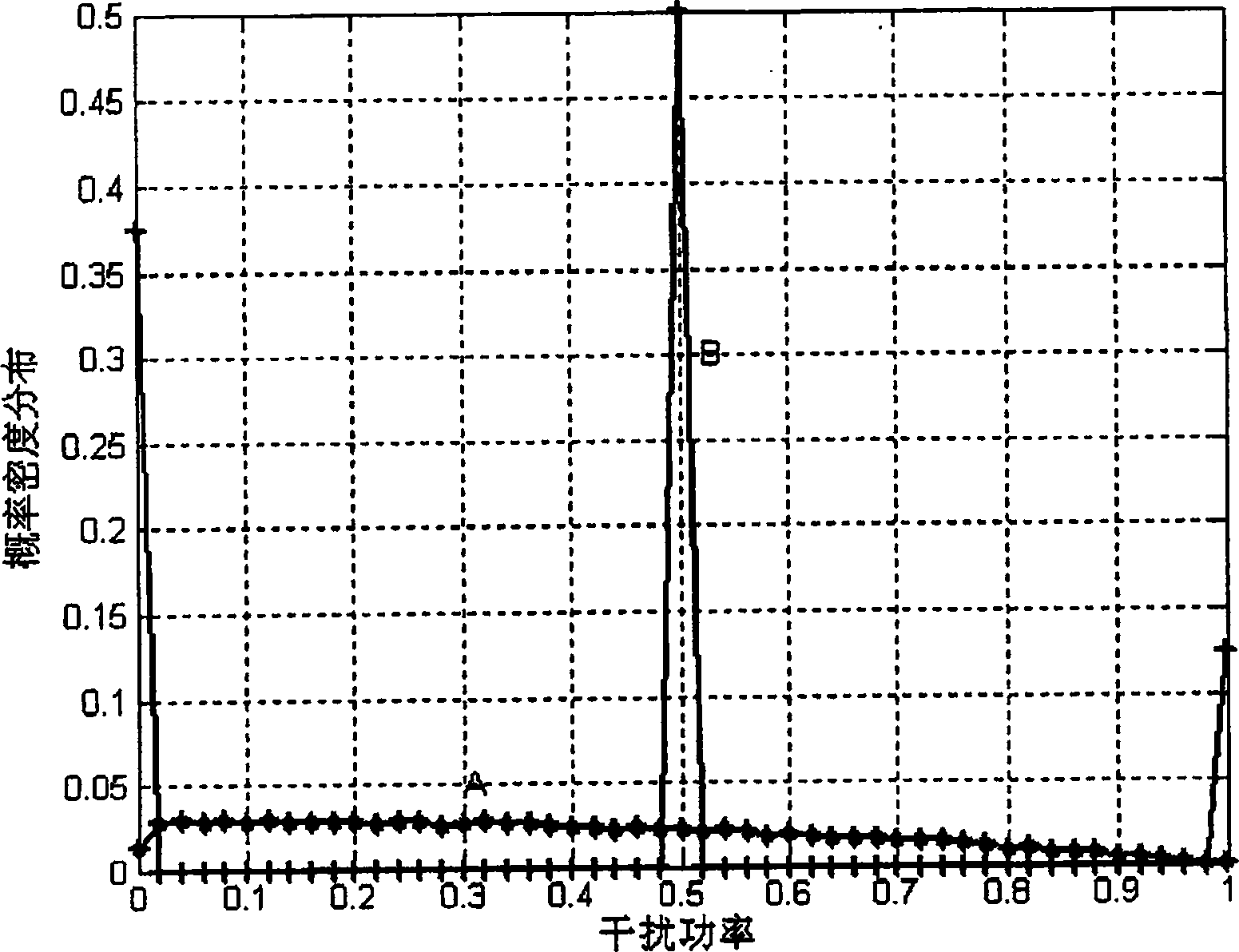
InactiveUS20100245154A1Improve the immunityLimited bandwidthRadio wave reradiation/reflectionComputer scienceStochastic distribution
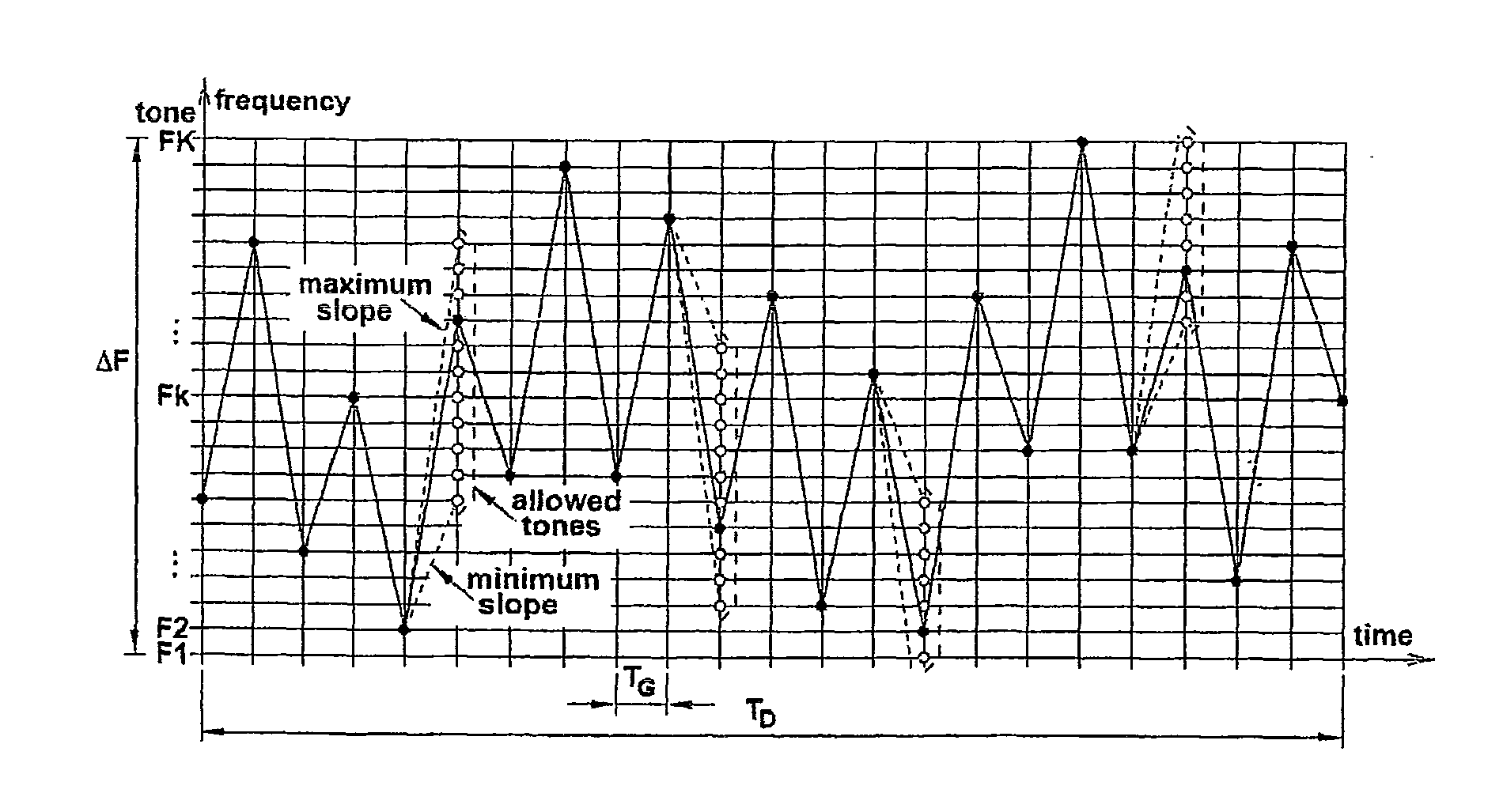
An object ranging system operates by transmitting alternating up and down frequency sweeps which have randomly distributed slopes as a result of random selection of local frequency peaks and valleys according to predetermined probability tables, and determining the beat frequency obtained when combining the transmitted signal with its reflection from an object.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Random grain anti-fake method
InactiveCN1349186AReduce storageIdentify carefullyStampsSpecial data processing applicationsFiberComputer science
The invention discloses an anti false method by using texture. The features are as follows. There are a lot of fibers in selected area; all fibers possess character of random distribution. Only one or few characters of random distribution are chosen as a carrier of anti false informatino to be stored on computer data for user to query through comunication method, so as to confirm whether the product is true or false. The characters chosen can be coordinate of an end point of one fiber or quantity of fibers in any local area for example. Although only one or few characters are chosen, since not knowing which one being chosen, falsifier must copy all distributed fibers in selected area accurately.
Owner:孙显林
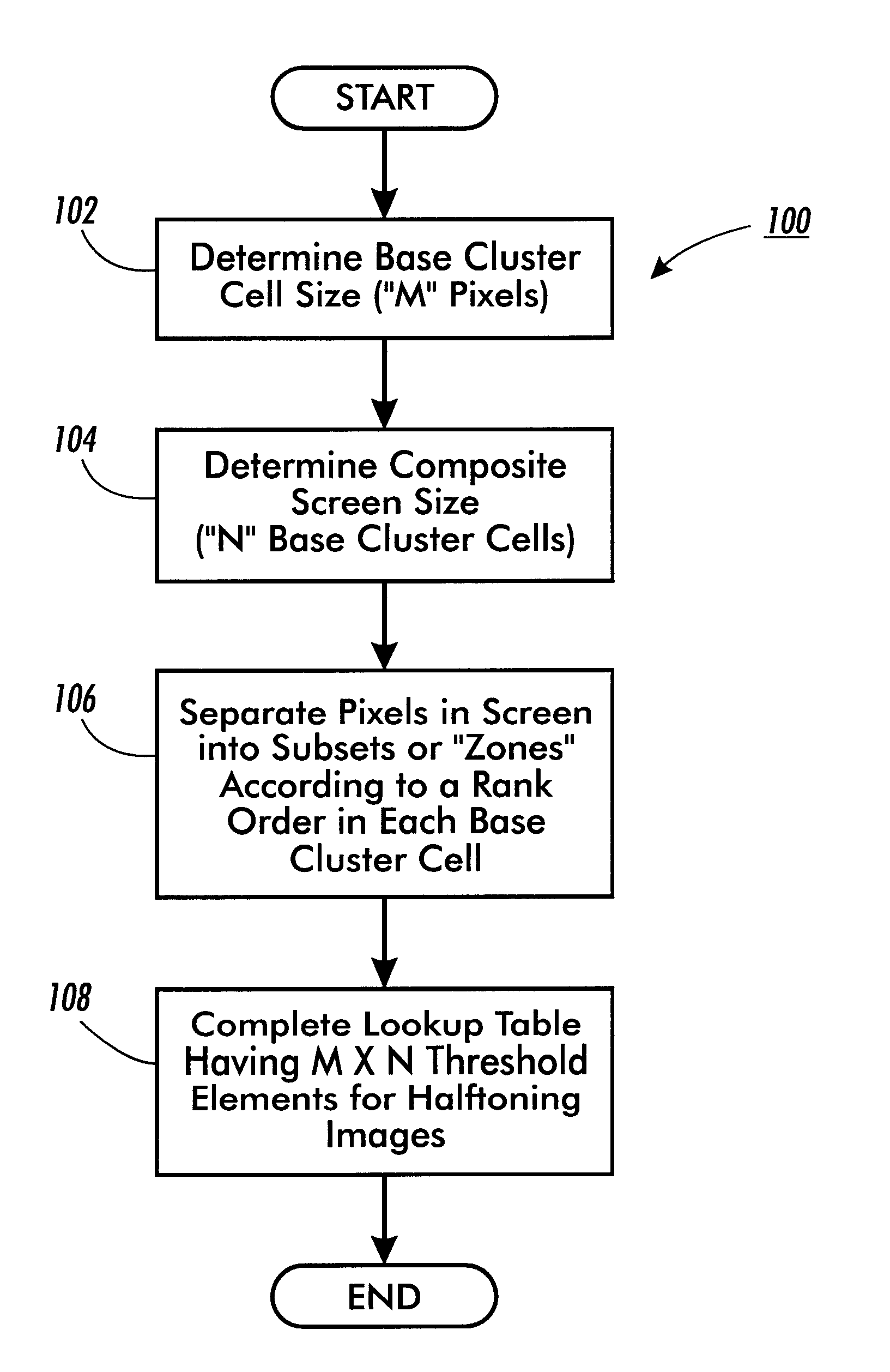
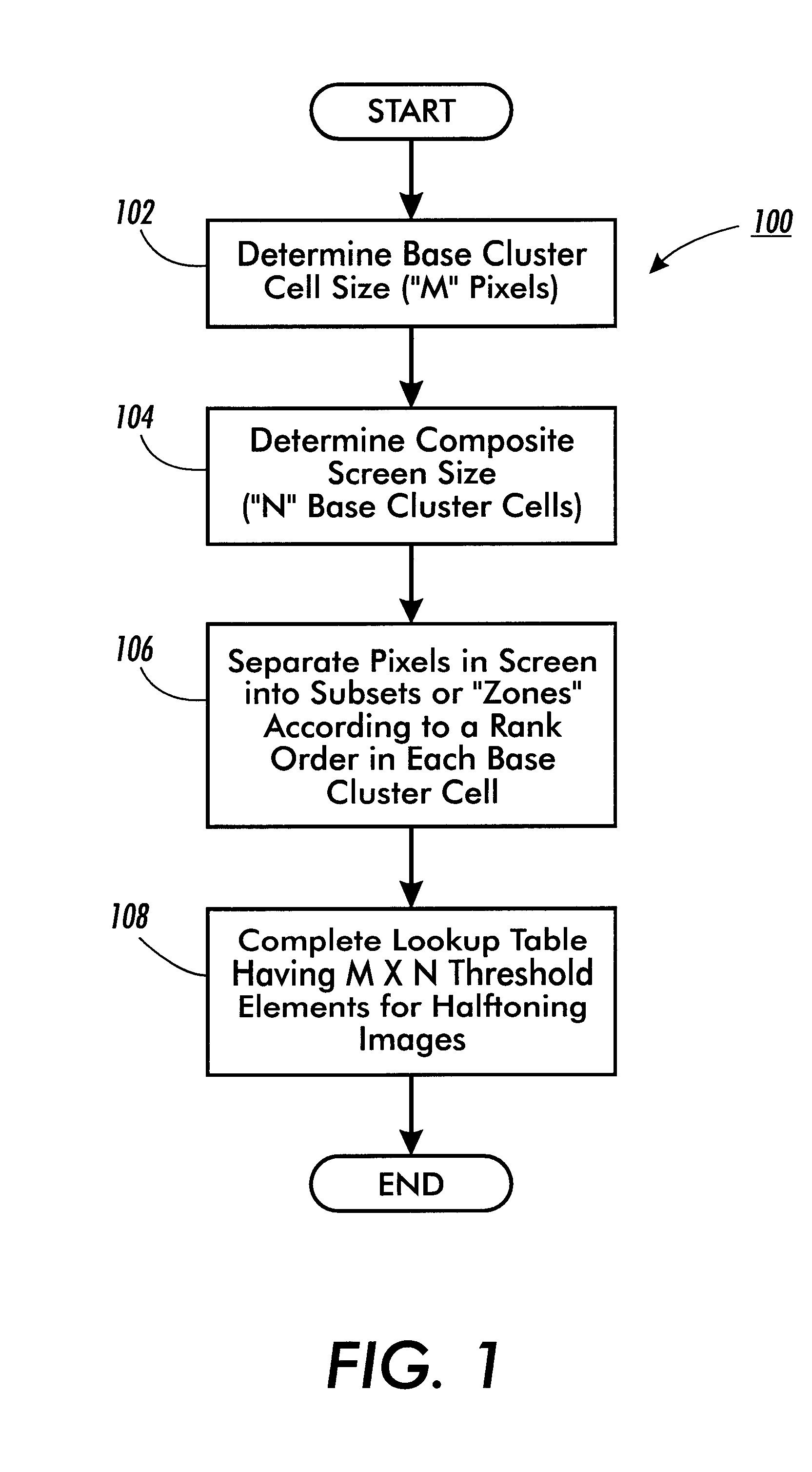
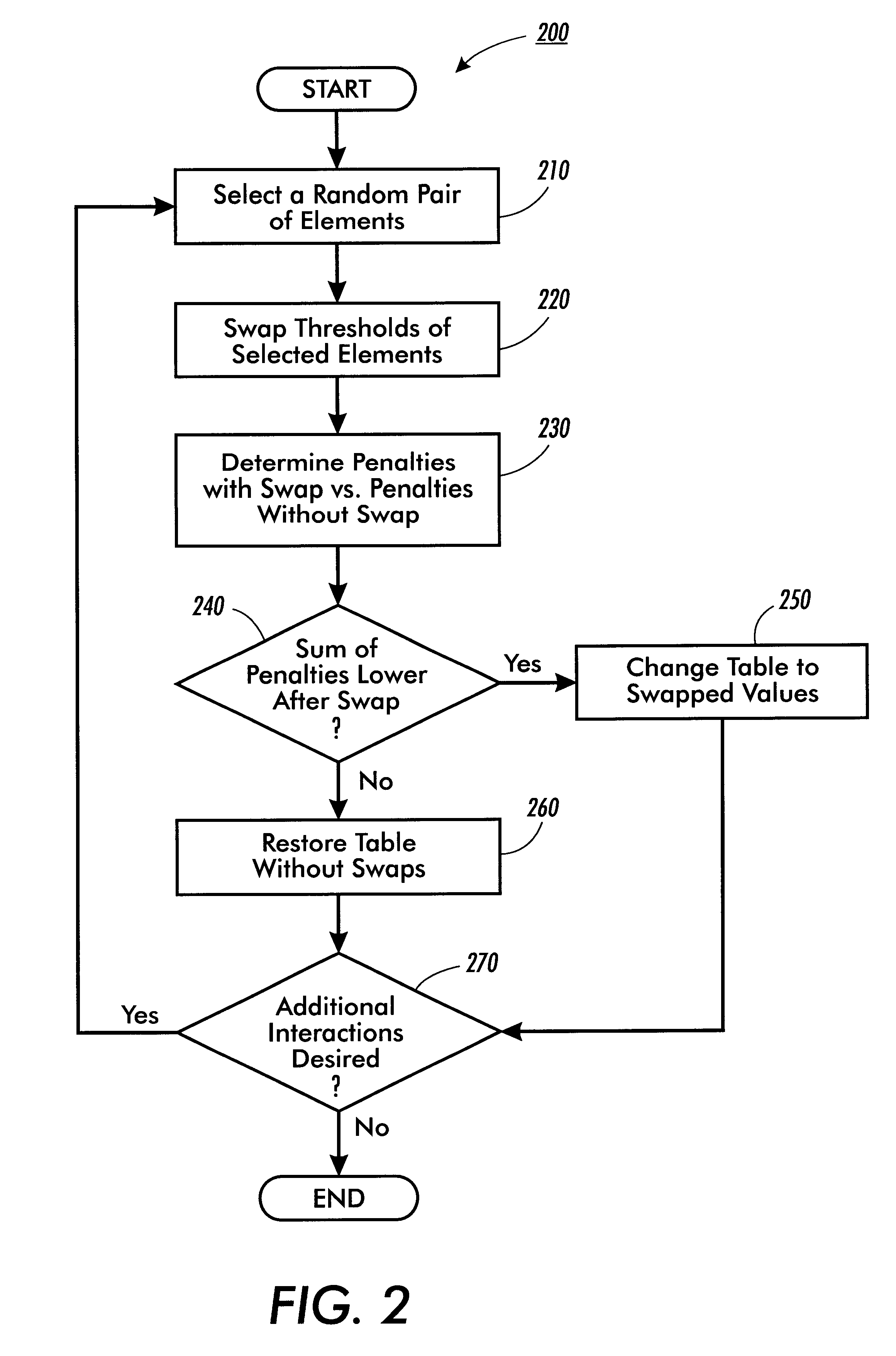
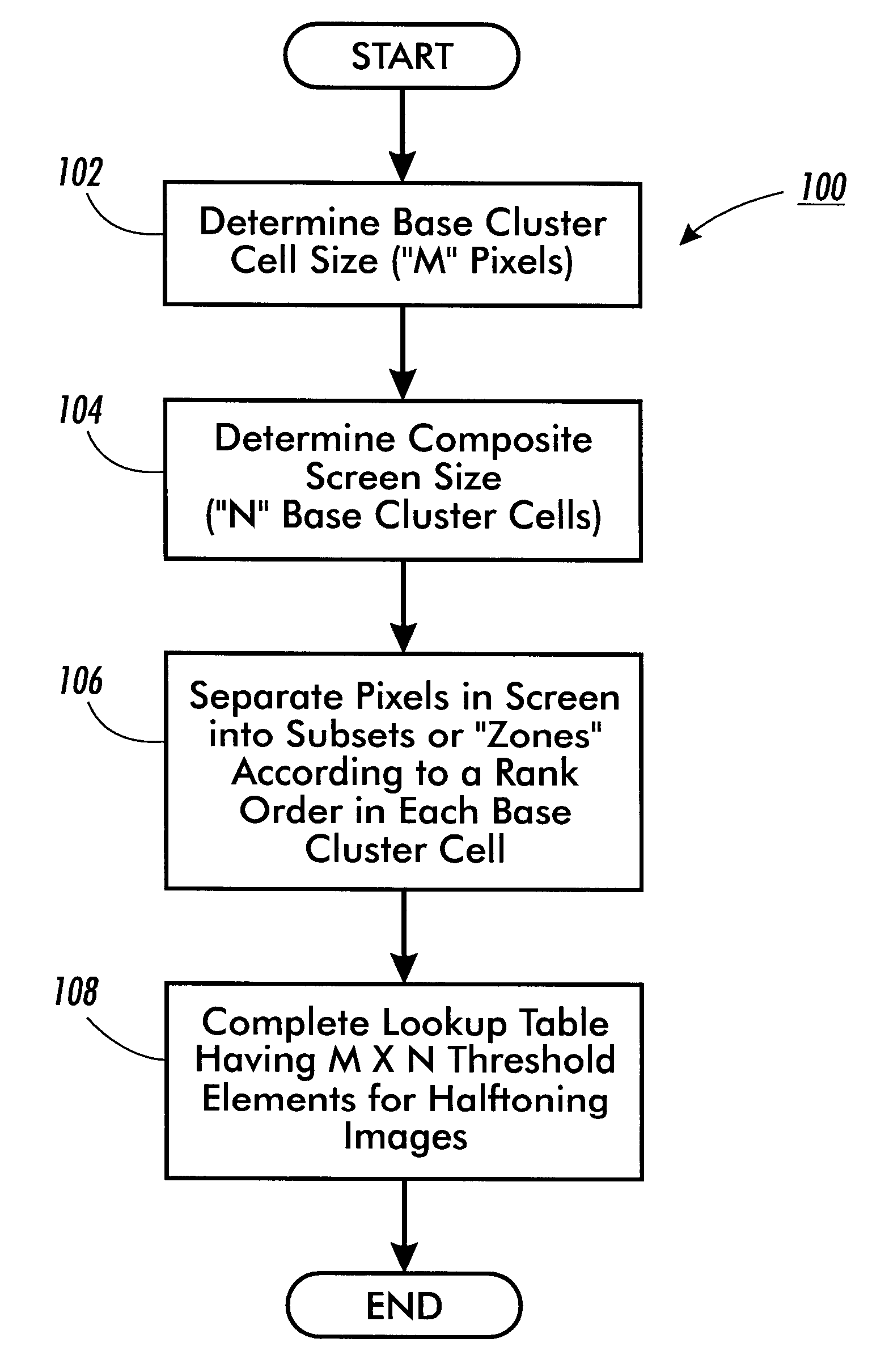
Composite halftone screens with stochastically distributed clusters or lines
InactiveUS6917443B1Lower Level RequirementsDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsSingle levelHue
A method and system of designing a digital halftoning screen for forming images on output sheets according to a set of image signals. The method generates a halftone line screen having multiple levels, each level having multiple line segments, each line segment having an equal pre-determined number of elements. The method stochastically assigns threshold values to pixels corresponding to a first element within the multiple line segments of a first level and assigns a same threshold value to a pixel corresponding to a single level to create a first element stochastic fill sequence. The method then assigns threshold values to pixels corresponding to a first element within the multiple line segments of the remaining levels of the halftone line screen according to the first element stochastic fill sequence.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method for transferring images with incoherent randomly arranged fiber optical bundle and for displaying images with randomly arranged pixels
A method and means to use randomly arranged fibers assembled together in a bundle that is capable of conveying images from an inaccessible location to a more accessible, convenient or safe location for viewing. Allows for mixing fibers of different diameters. Random distribution of fibers decreases the packing fraction, offering in exchange easiness of manufacturing and decrease in production cost. System can be also used for display units, including computer monitors, home TV, movie theatres, public display announcement boards, as airport, trains stations, highway instructions and billboard advertising. As display units, random assembled fibers are organized at the display end at the display shape, usually rectangular, from where light is emitted towards the viewer. At the illuminating end, light enters the individual fibers from multicolored lasers or other light sources which are controlled by single or multiple video boards and computers.
Owner:MONTEIRO SERGIO LARA PEREIRA
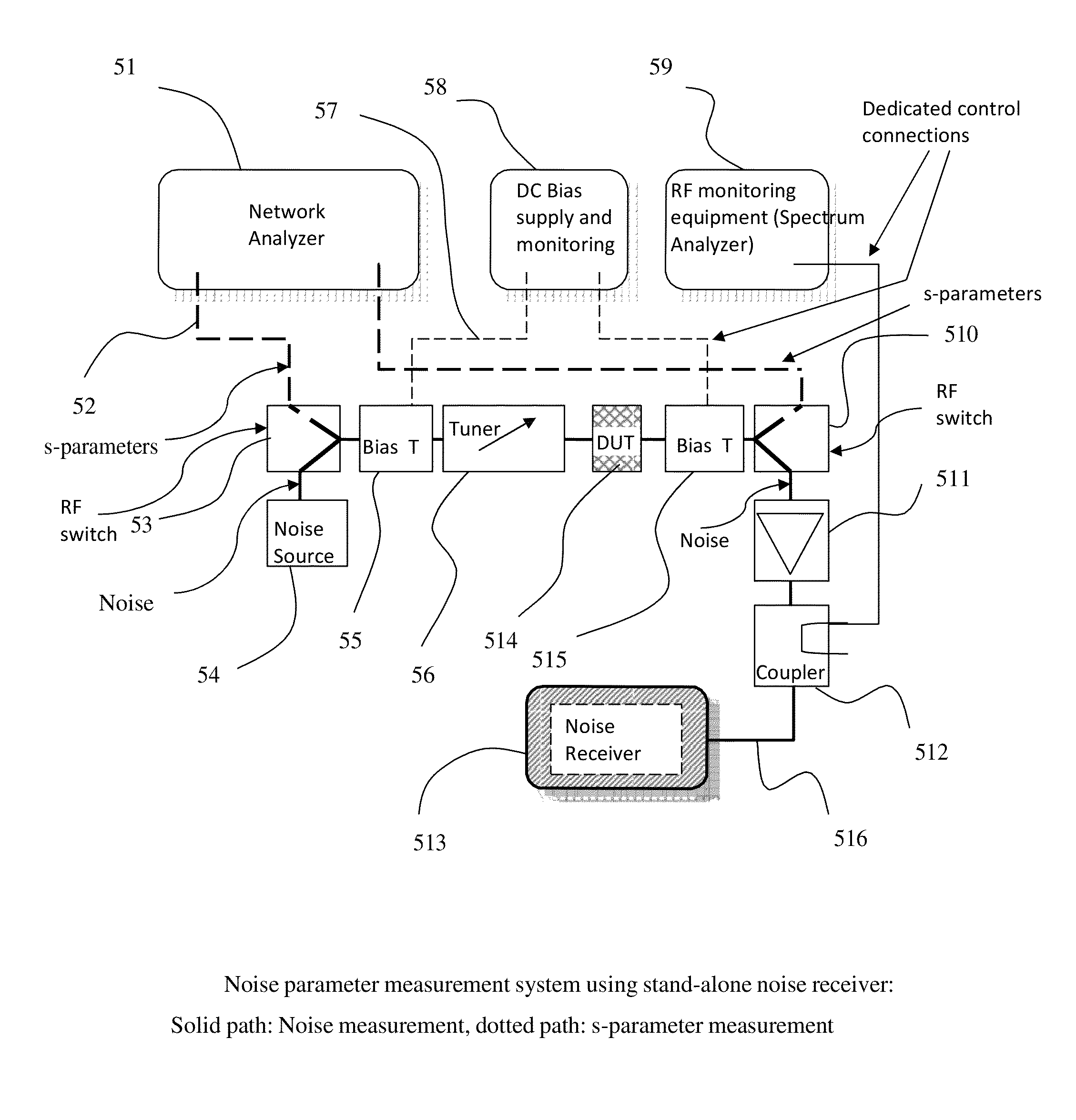
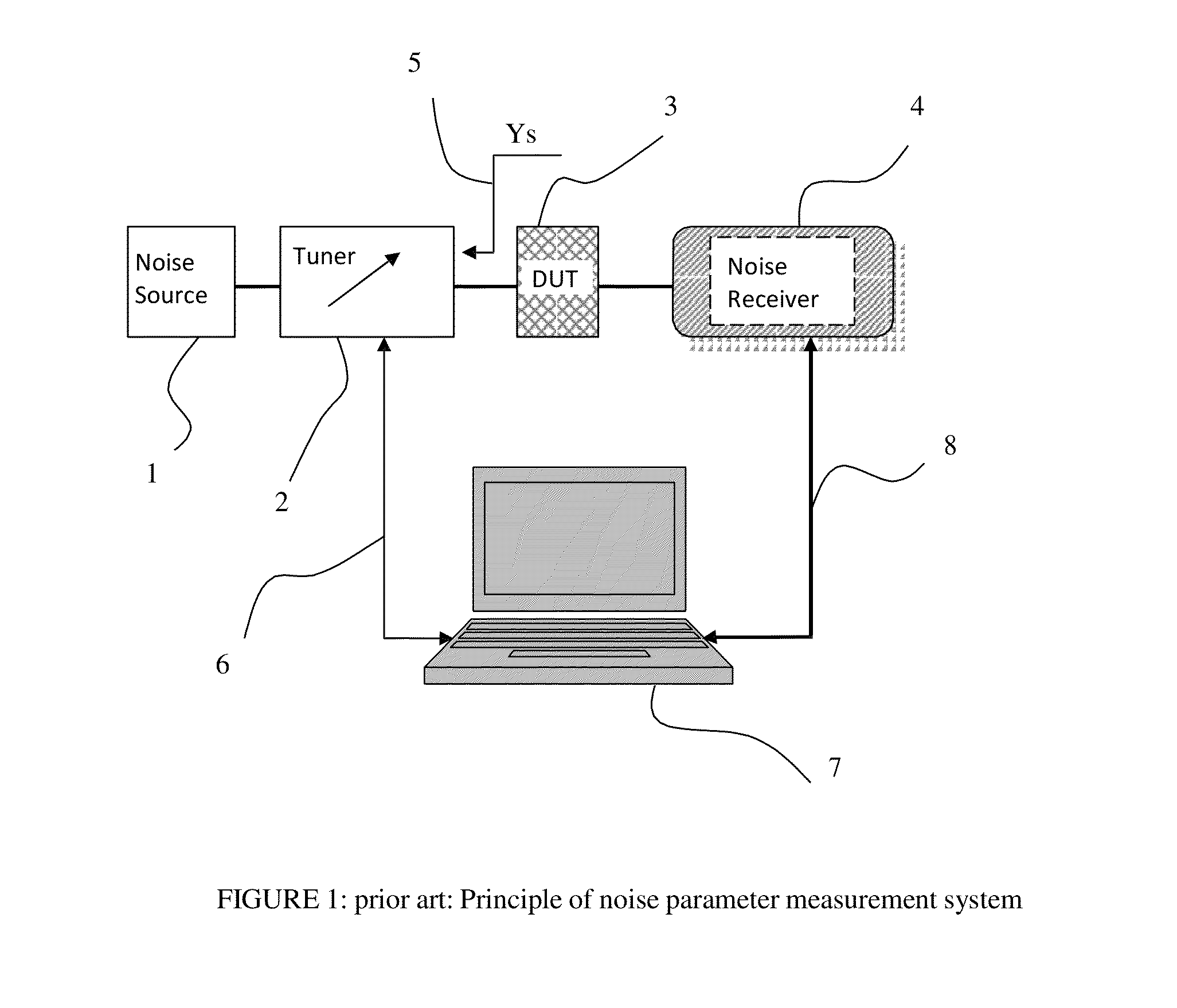
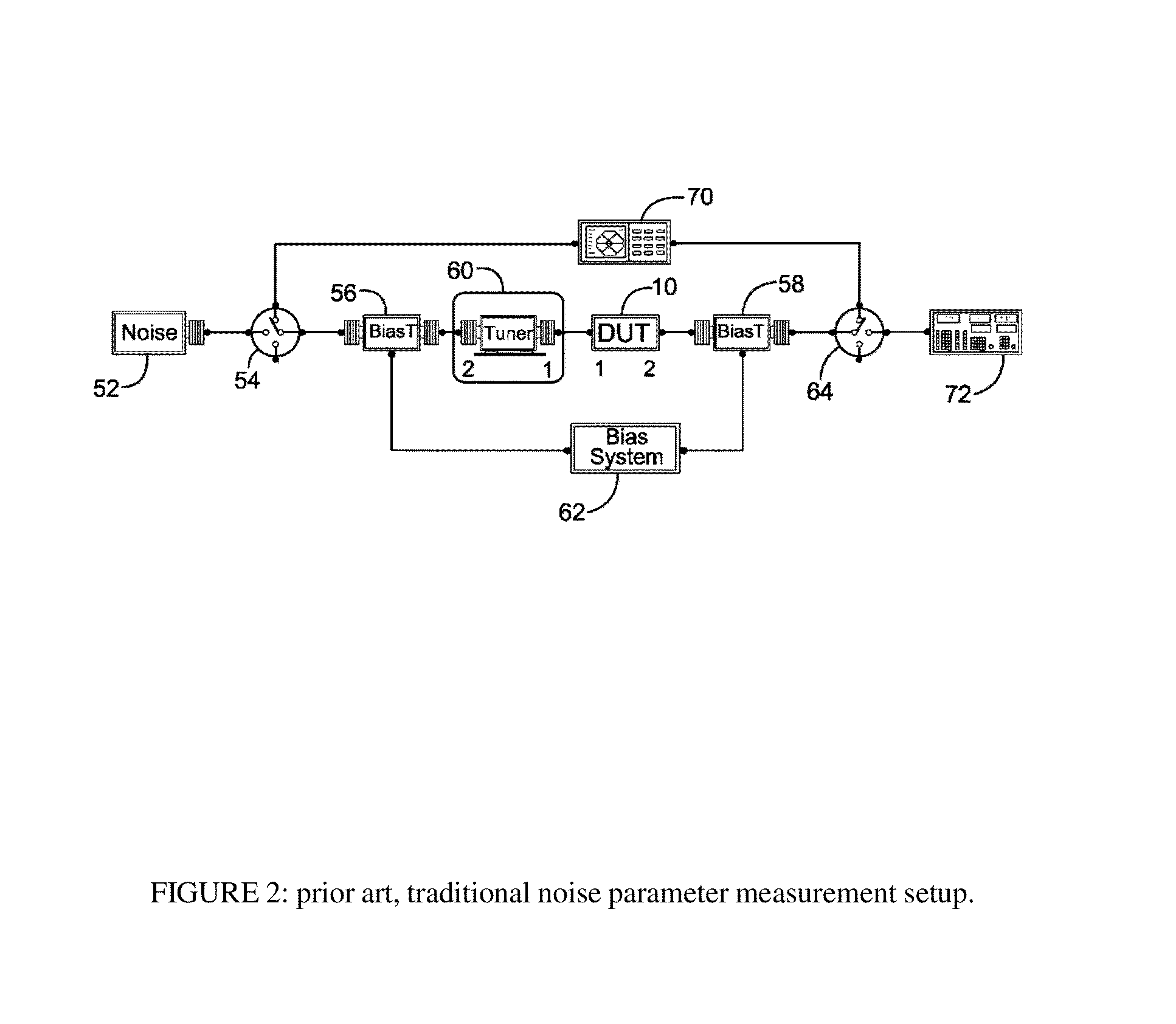
Noise parameter measurement system and method
InactiveUS8786293B1Noise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceBroadband noiseLow noise
A wideband four noise parameter measurement system and method uses electro-mechanical wideband tuners and fast noise and small signal receivers (network analyzers) to collect noise data in fast frequency sweeps over a large number of randomly distributed source tuner states; because of the random nature of source impedances, additional monitoring equipment allow evaluating critical device parameters in view of output mismatch and instabilities in order to validate the measured data. Multiple noise parameter extractions for all possible cross-combinations of source impedance states at each measured frequency allows reliable and physically meaningful generation of wideband noise parameters, even for very low noise and potentially unstable DUT's.
Owner:TSIRONIS CHRISTOS
Composite halftone screens with stochastically distributed clusters or lines
InactiveUS6304340B1Reduce in quantityThe relative position is appropriateDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsSingle levelHue
A method and system of designing a digital halftoning screen for forming images on output sheets according to a set of image signals. The method generates a halftone line screen having multiple levels, each level having multiple line segments, each line segment having an equal pre-determined number of elements. The method stochastically assigns threshold values to pixels corresponding to a first element within the multiple line segments of a first level and assigns a same threshold value to a pixel corresponding to a single level to create a first element stochastic fill sequence. The method then assigns threshold values to pixels corresponding to a first element within the multiple line segments of the remaining levels of the halftone line screen according to the first element stochastic fill sequence.
Owner:XEROX CORP
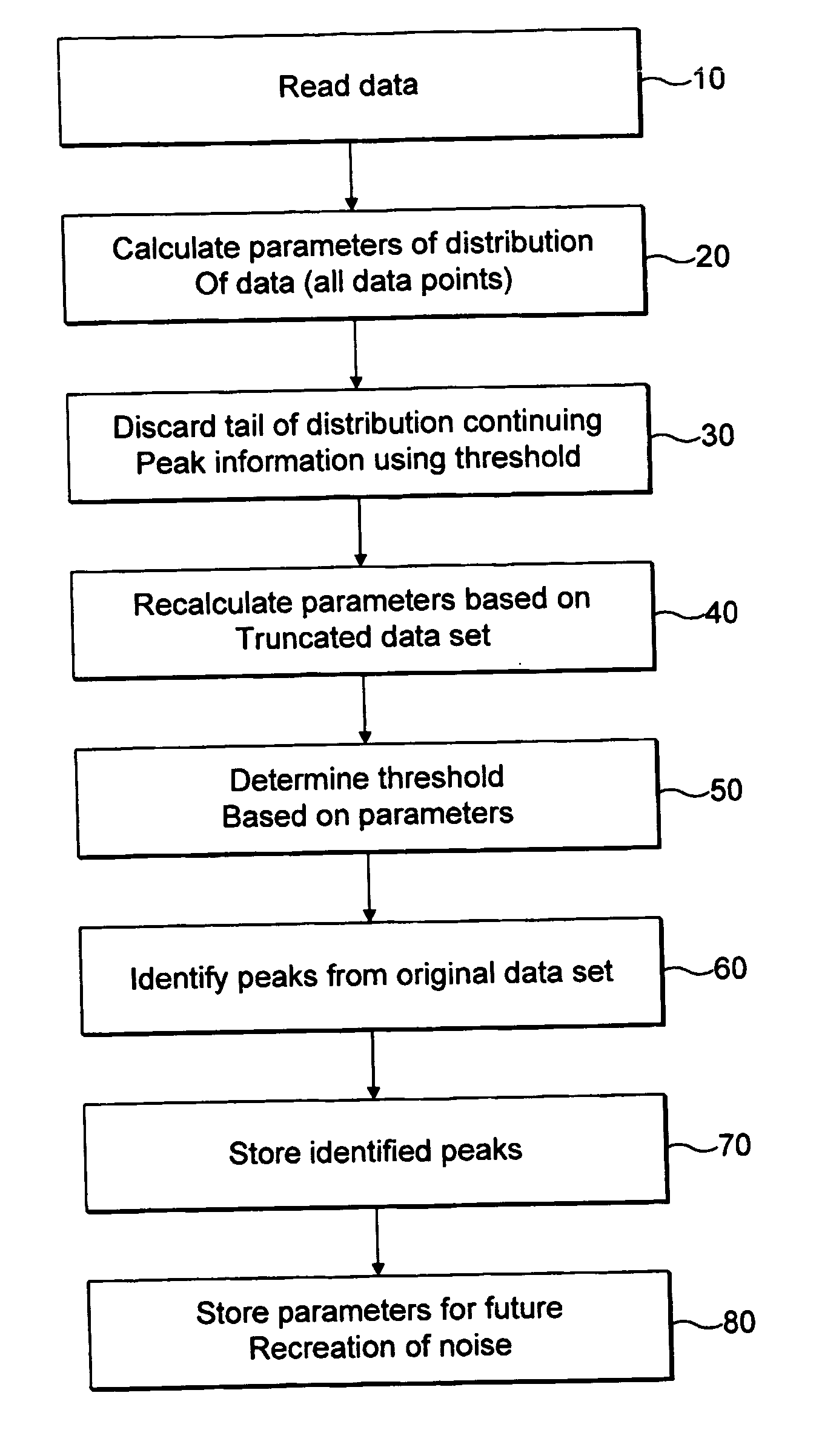
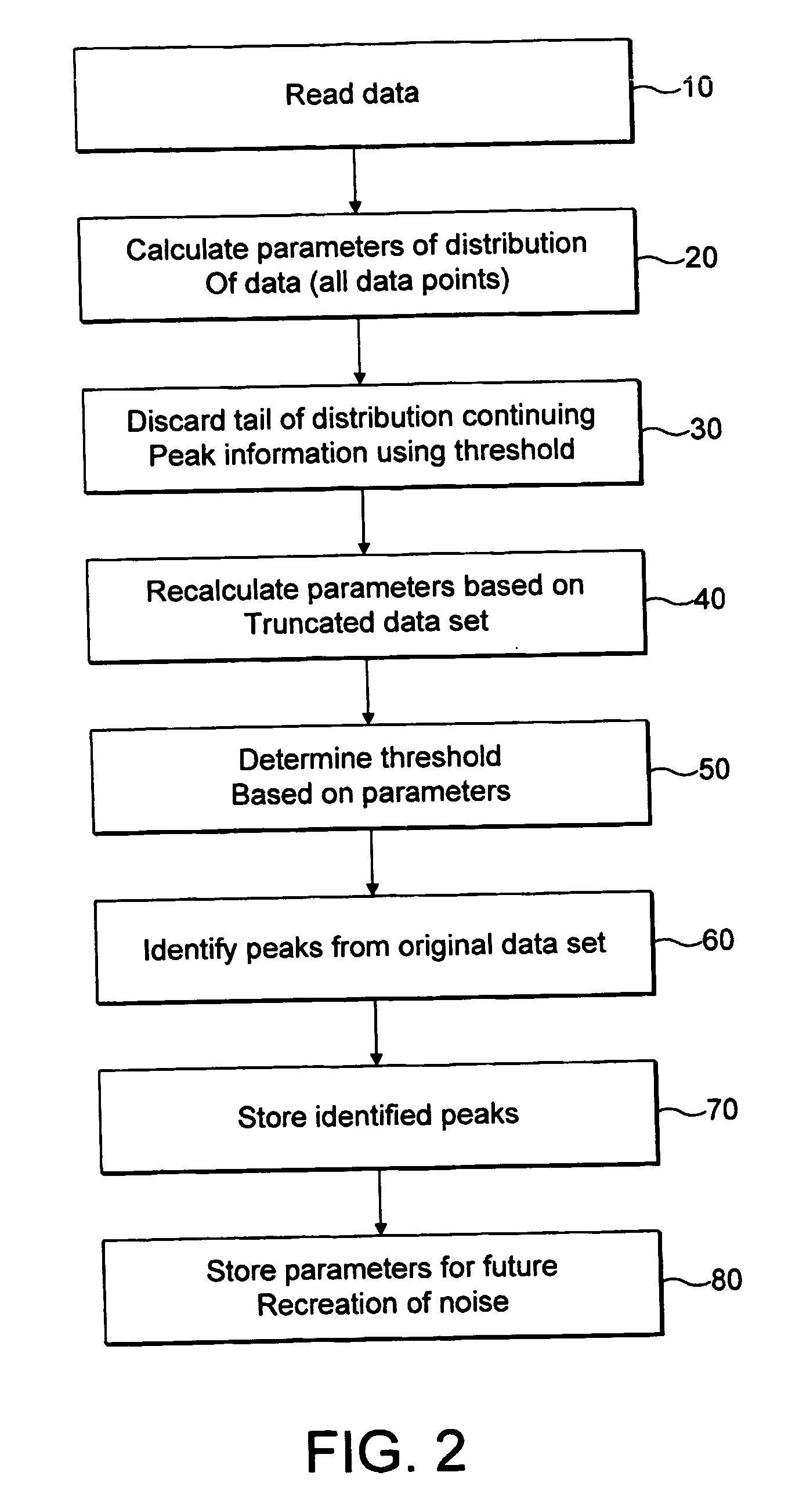
Method of processing and storing mass spectrometry data
ActiveUS20070143319A1Spectral/fourier analysisDigital data processing detailsData compressionFrequency spectrum
A data compression technique is disclosed for Fourier Transform Mass Spectrometry (FTMS). A statistical analysis is applied to the data in the frequency domain since most of this data is a result of randomly distributed electronic noise. A fit of the whole frequency dataset to the distribution is made to determine preliminary moments of the distribution. The data in the tail of that distribution (which is mainly the peak data) is then removed and the remaining data points are re-fitted to the distribution, to identify the moments of distribution of that remaining noise data. A noise threshold for the mass spectrum is then applied using the calculated moments. The data above the threshold is kept. The whole spectrum can be reconstituted by storing the moments of distribution along with the peak data and then regenerating the noise from those moments and adding it to the peak data
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Anti-fake label with electronic grains
InactiveCN1417732AEasy to identifyImprove accuracyStampsSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionGraphics
The present invention relates to one kind of product anti-fake label made of material with some texture characteristics. The randomly formed figure, color and amount in the marker are used as the anti-fake information and coded as the anti-fake data stored in the data base of computerized identification system while being printed in anti-fake marker. The consumer can chedk the figure and color inthe label via comparison with the code to verify the truth of the commodity and may also check the codes in the marker via comparison with those in computer data base to verify the truth of the commodity through modern communication means.
Owner:TIANJIAN ANTI FORGERY SCI & TECH
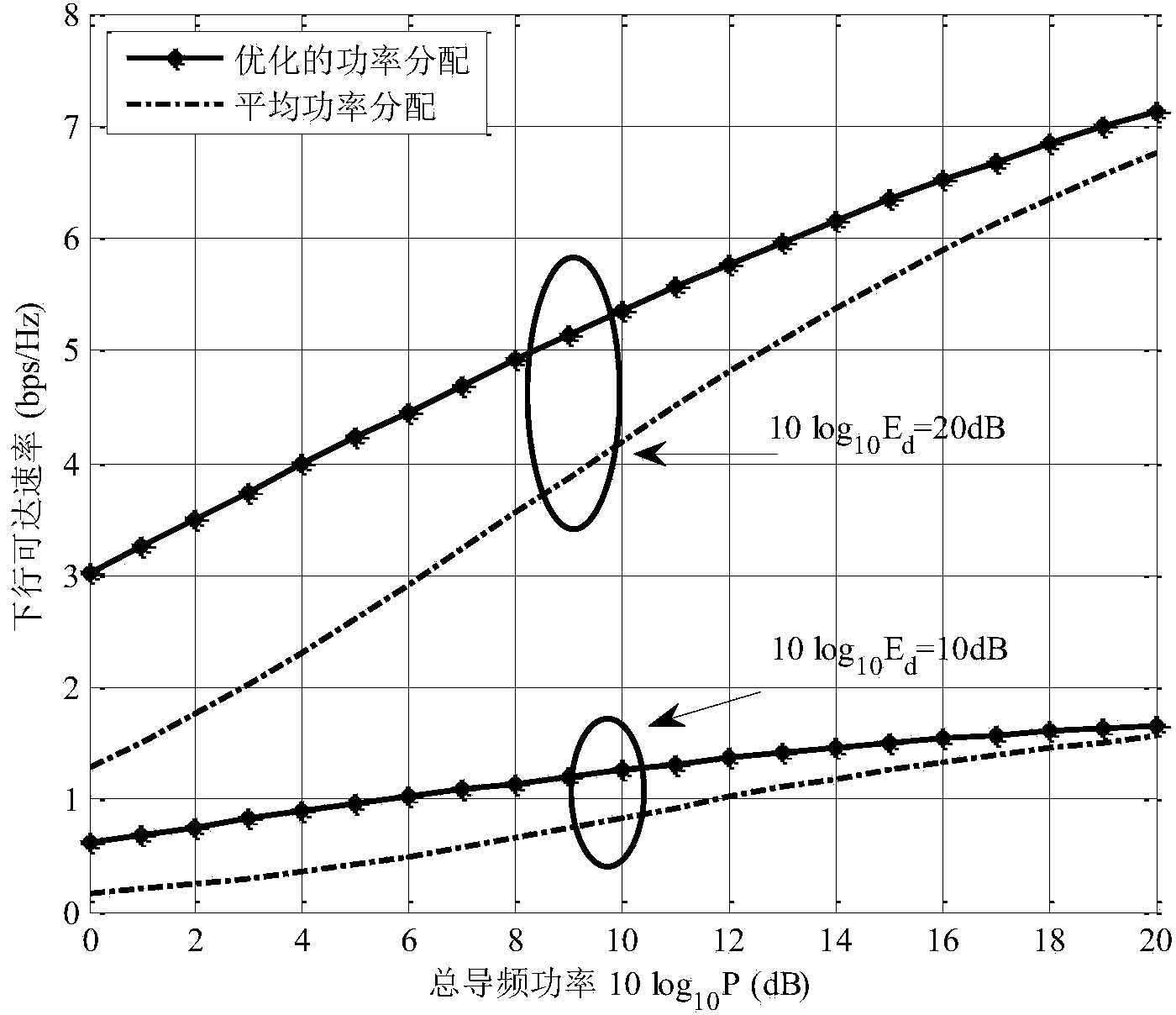
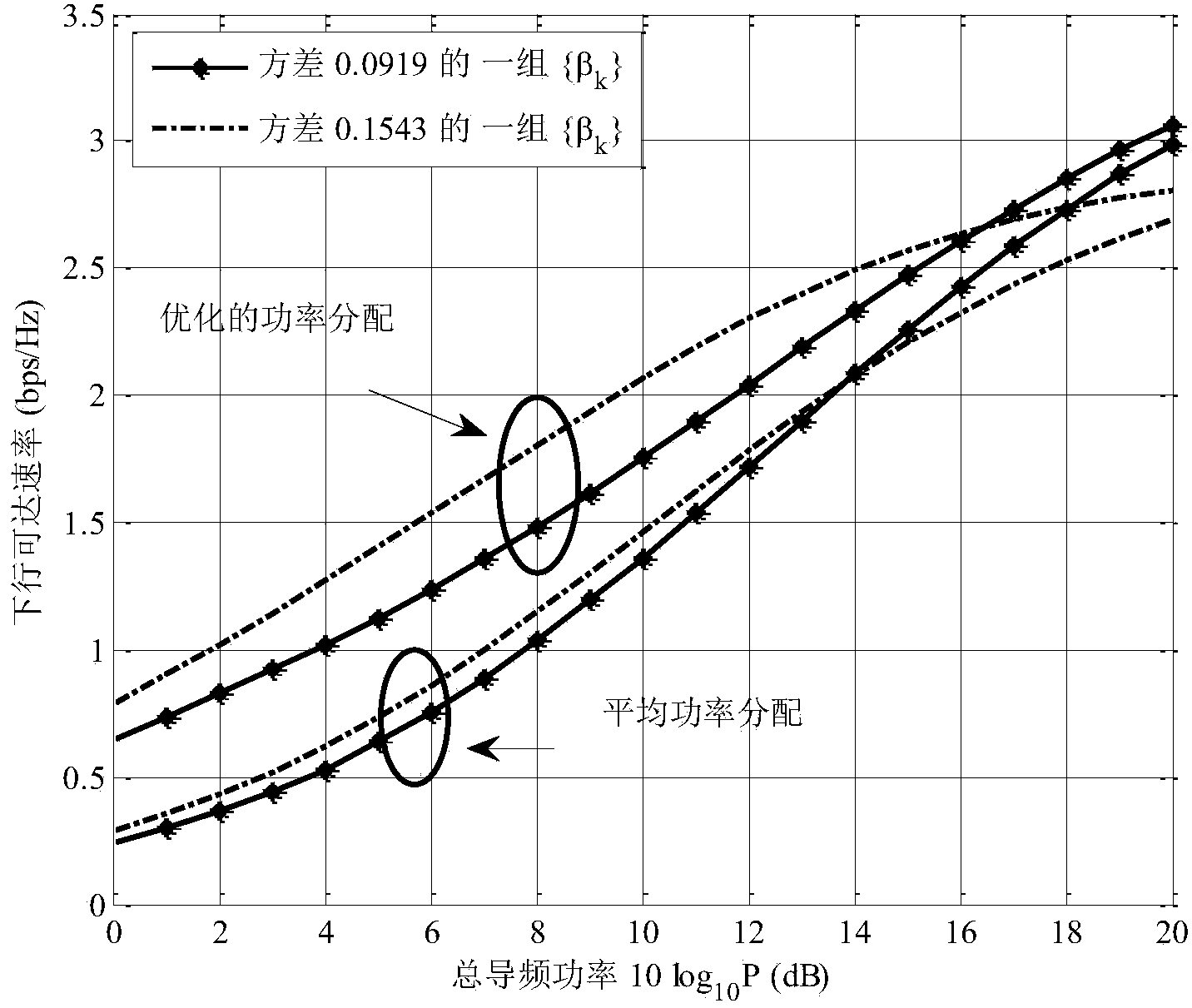
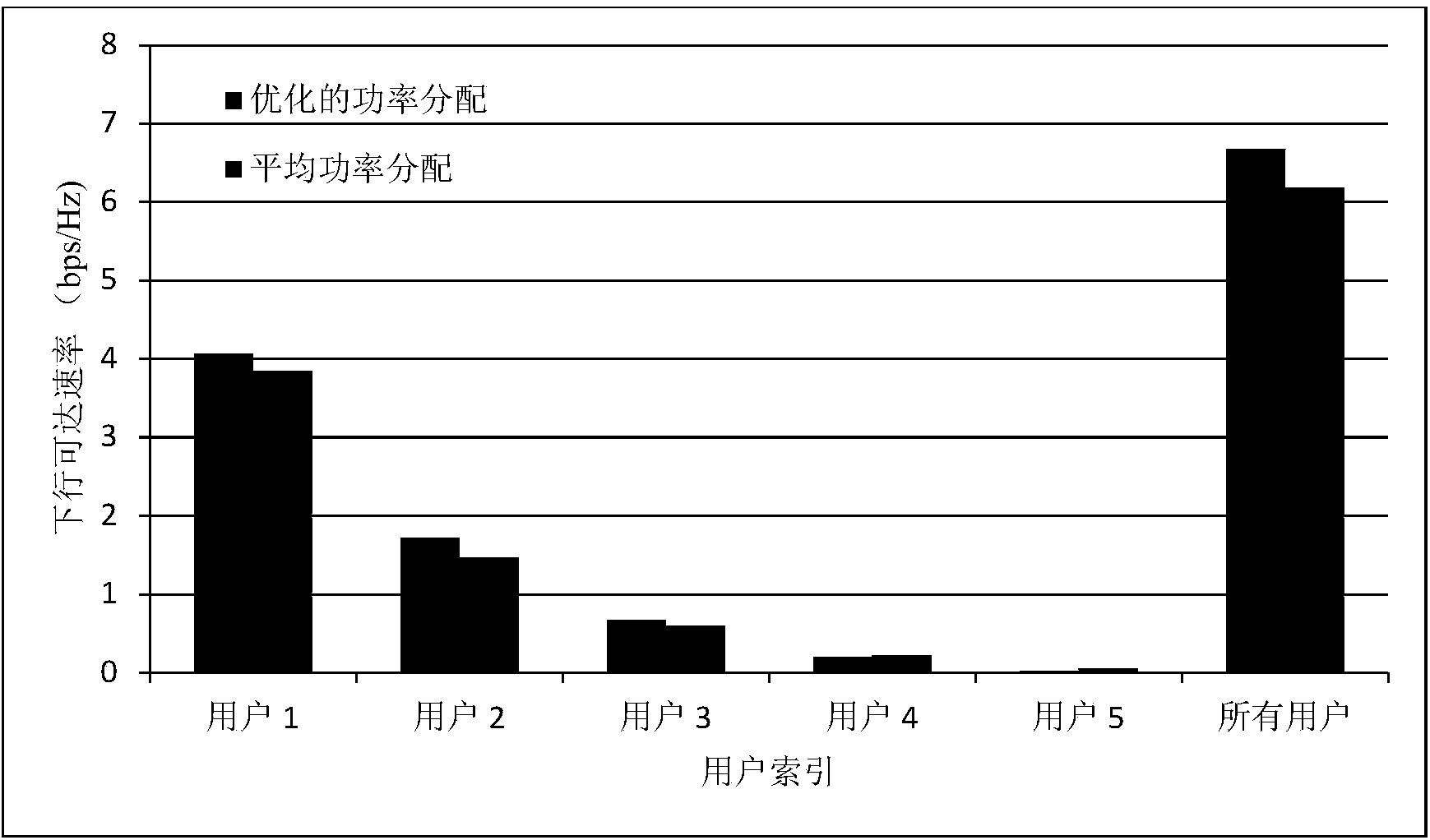
Method for heterogeneous user pilot frequency power optimal distribution in large-scale multi-input multi-output system
InactiveCN104039004AImprove data transfer performancePracticalPower managementMulti inputDistribution method
The invention discloses a method for heterogeneous user pilot frequency power optimal distribution in a large-scale multi-input multi-output system. The method comprises a first step of generating a group of randomly distributed heterogeneous users, enabling each user to undergo independent channel information, and calculating a system downlink achievable speed; a second step of forming a Lagrangian function L by the system downlink achievable speed and total power constraint conditions; a third step of assuming lambda to be a Lagrangian multiplier, performing derivation of L on pilot frequency power rhok and lambda to obtain an expression of rhok related to the lambda and the channel information; a fourth step of obtaining the value range of lambda based on the expression obtained in the third step according to the restrictions that rhok is larger than 0 and smaller than the total power; a fifth step of performing binary search according to the value range of lambda obtained in the fourth step, and obtaining an optimal pilot frequency power distribution value. According to the method, different channel information of the heterogeneous user is utilized to achieve optimal distribution of pilot frequency power, and the overall data transmission performance of the system is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
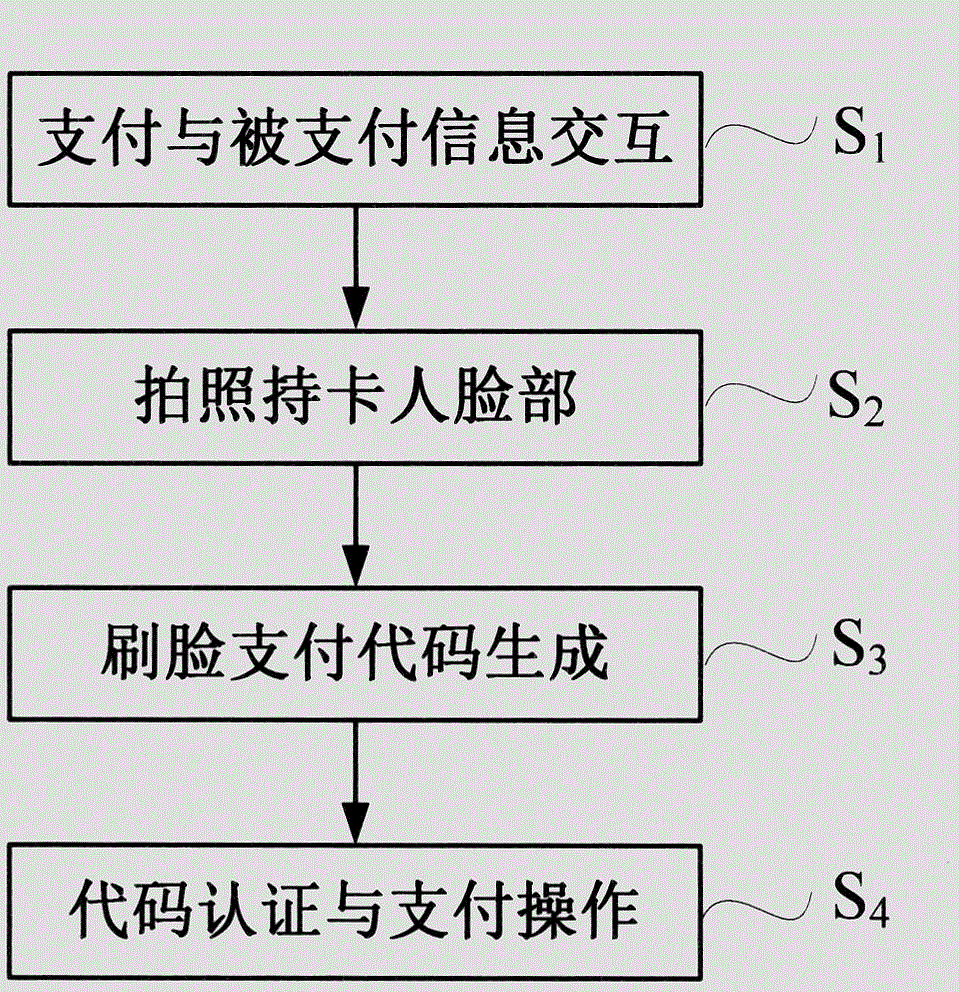
Composition of mobile phone face-scanning payment system
The invention relates to a composition of a mobile phone face-scanning payment system in the field of image processing. The composition of the mobile phone face-scanning payment system is characterized in that in a payment and paid information interaction step, a mobile phone receives payment information from a POS machine or a network through wireless Wi-Fi or a network, and automatically sends paid information; in a card holder face image taking step, the mobile phone or the camera of the POS machine takes out the face image of the card holder; in a face-scanning payment code generation step, the five-organ position information in stochastic distribution of the face-scanning image is converted into an adaptive feature vector of a probability measure distance space, the adaptive feature vector is numerically processed through a membership function according to a method of human intervention, and then, a face-scanning payment code is obtained through an adaptive feature vector learning method; and in a code authentication and payment operation step, the face-scanning payment code is sent to a network server of a bank to carry out face-scanning payment code authentication and payment. With the system, a very stable face-scanning payment code can be obtained in a complex shooting environment of a mobile phone.
Owner:顾泽苍
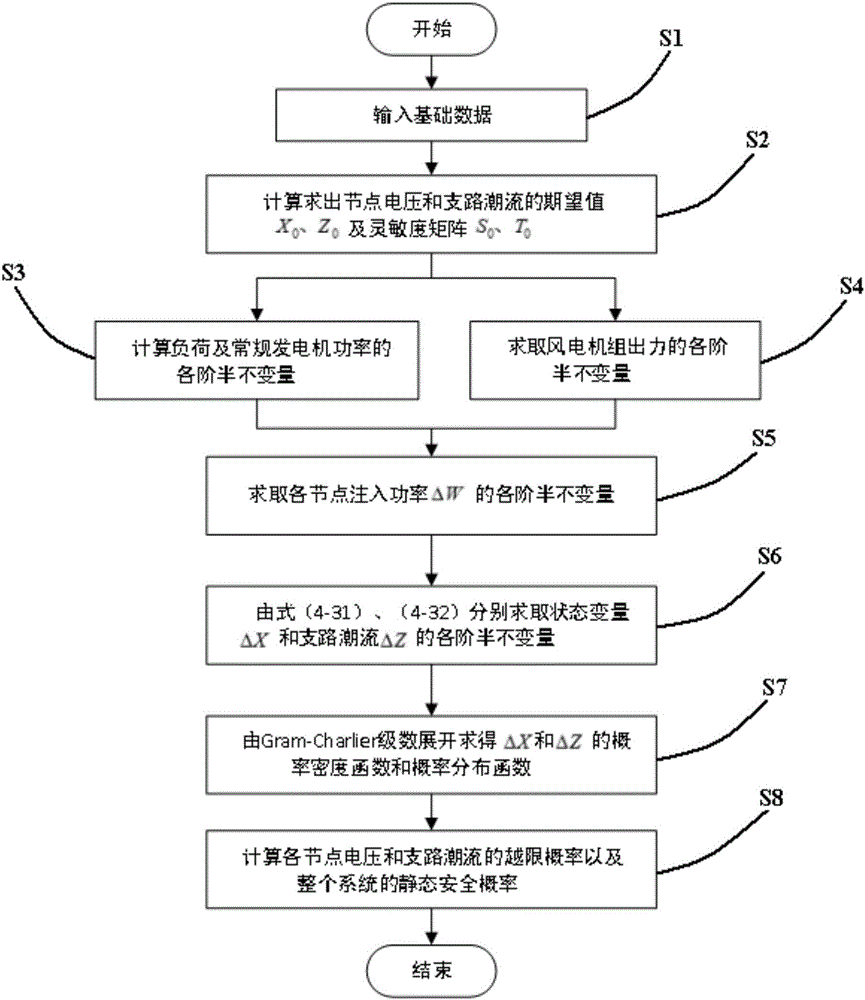
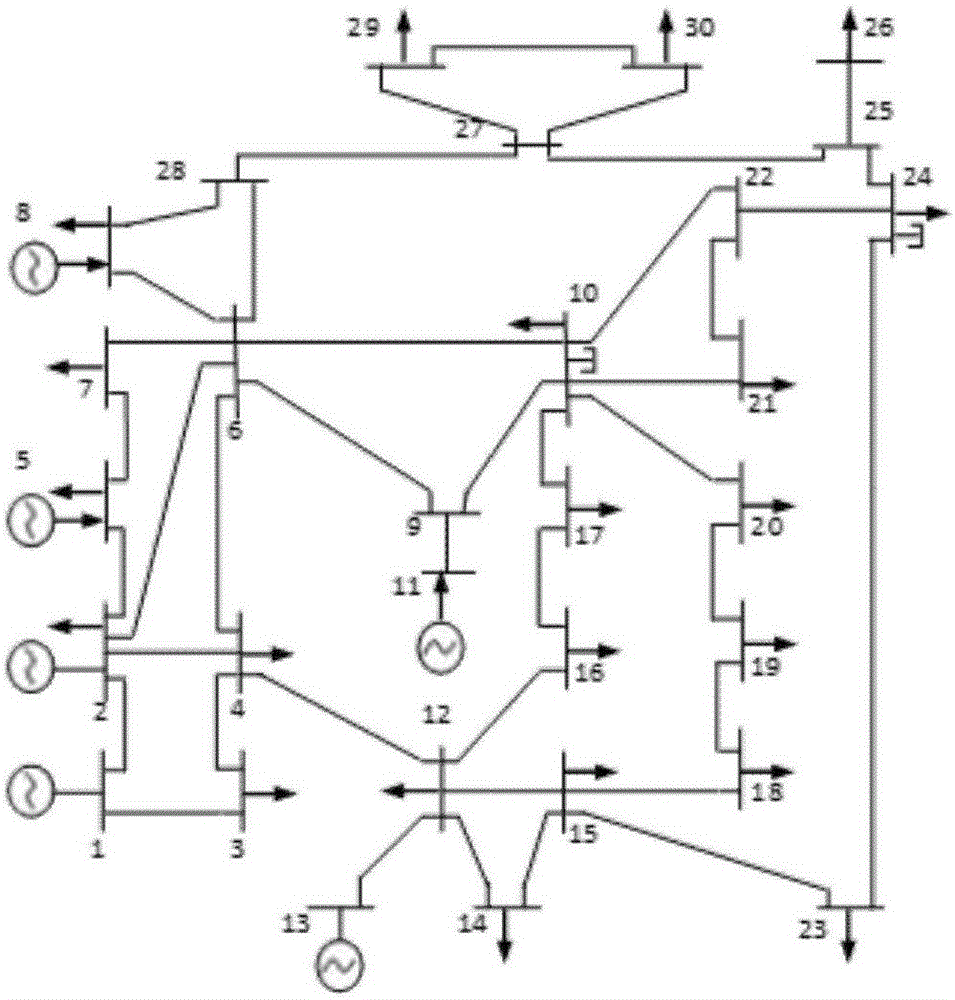
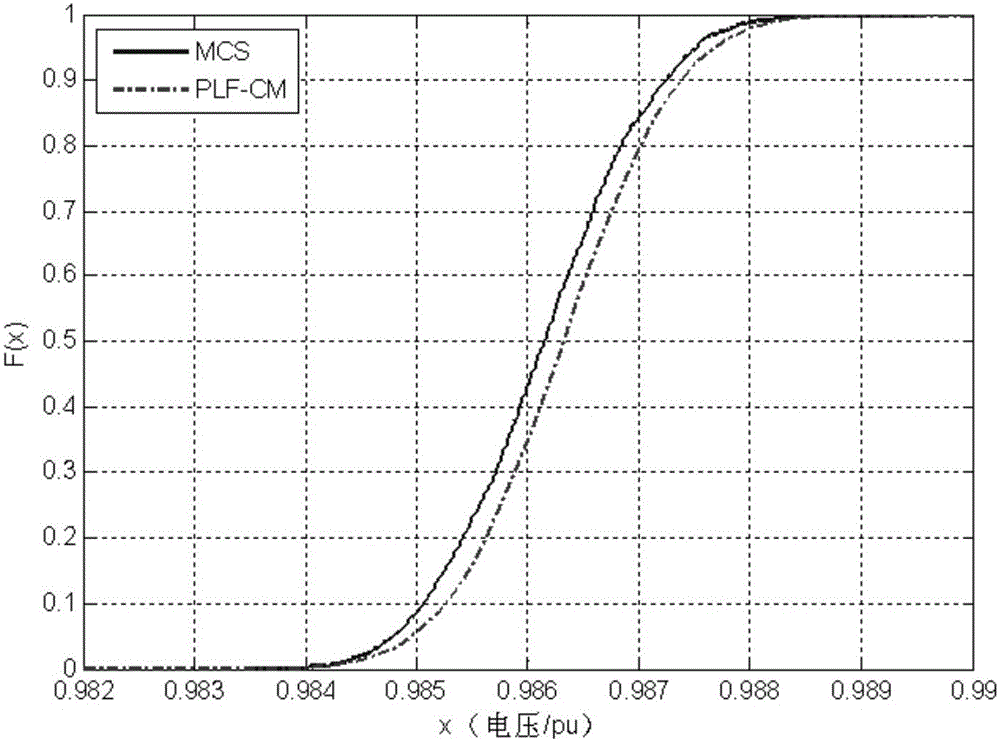
Probabilistic load flow algorithm based on semi invariant and series expansion method
ActiveCN105811403AAvoid complexityAvoid calculationAc networks with different sources same frequencyElectricityNew energy
The invention discloses a probabilistic load flow algorithm based on a semi invariant and series expansion method. By the probabilistic load flow algorithm, the uncertainty of a system under access of large-scale new energy sources can be reflected, a Monte Carlo sampling technology is introduced based on the analysis of a traditional semi invariant method to calculate the output of a wind power generator set, complicated mathematical analysis and calculation are prevented, and the probabilistic load flow algorithm can be applicable to a new energy output model with arbitrary random distribution; and relatively high adaptability and favorable convergence can be achieved when photovoltaic or other new energy sources are accessed to the system except wind and power.
Owner:JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +3
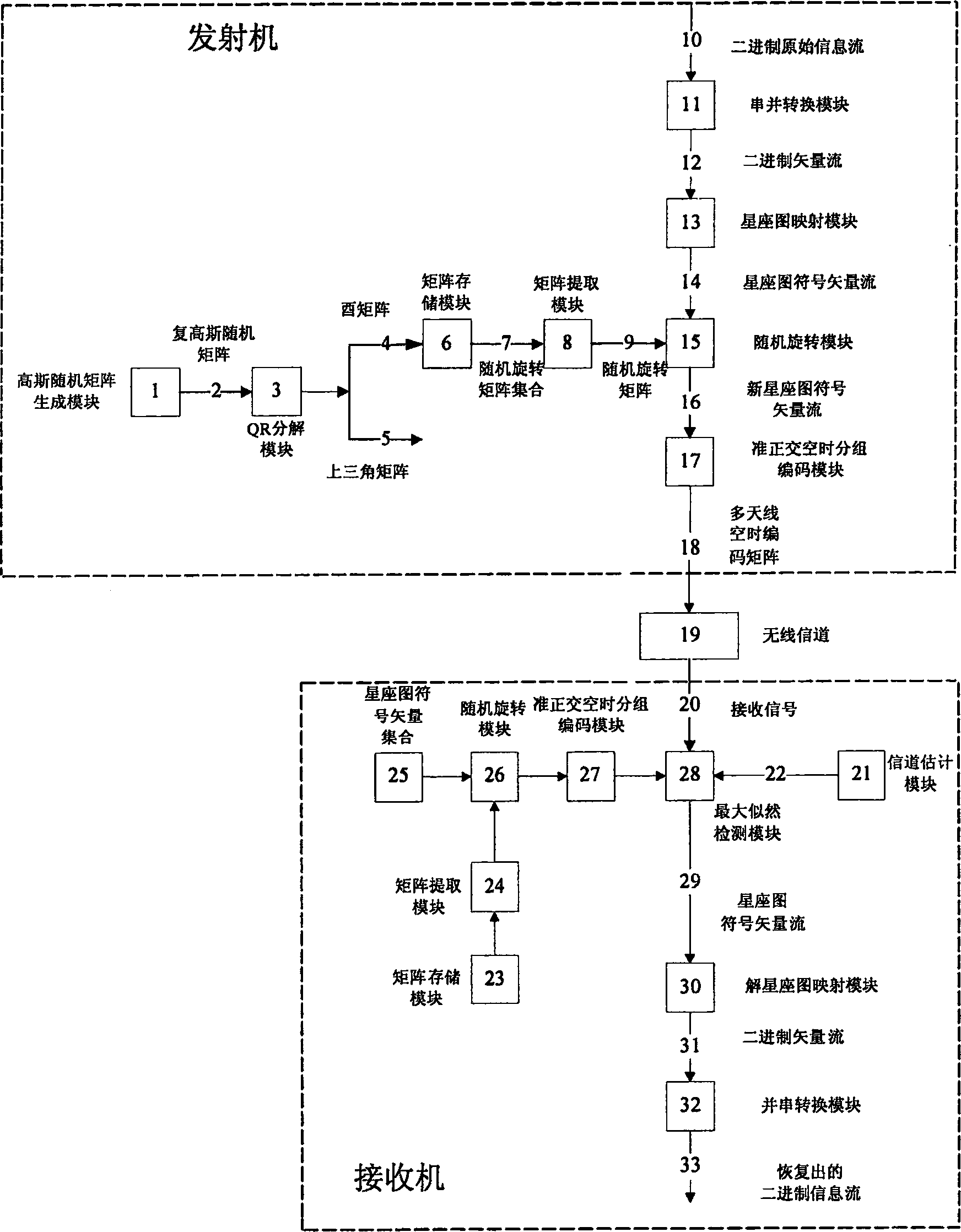
Method for transmitting and receiving quasi-orthogonal time space group code, transmitter and receiver, and communication system
InactiveCN1874210AIncrease freedomOvercoming the disadvantages of fixed constellation diagram distributionError preventionSignal-to-quantization-noise ratioTransmitter
The invention is related to transmitting / receiving method in quasi-orthogonal time space group code, receiver and transmitter and corresponding comm. system. Random rotation matrix is obtained through Graham-Schmitt orthogonalized decomposing plural gauss random square matrix. After using multiplication between random rotation matrix and symbolic vector of planisphere, the transmitting terminal carries out encoding quasi-orthogonal time space group code so as to make new planisphere possess characteristic of random distribution. Thus, interferences among multiple antenna symbols at transmitting end are distributed evenly. Moreover, distribution of probability density in high power interference segment is smaller relatively so as to raise performance of system in high SNR. Accordingly, all possible symbolic vectors of planisphere at receiving end are carried out rotation same as transmitting end randomly and then maximum likelihood decoding is carried out.
Owner:UT STARCOM (CHINA) CO LTD +1
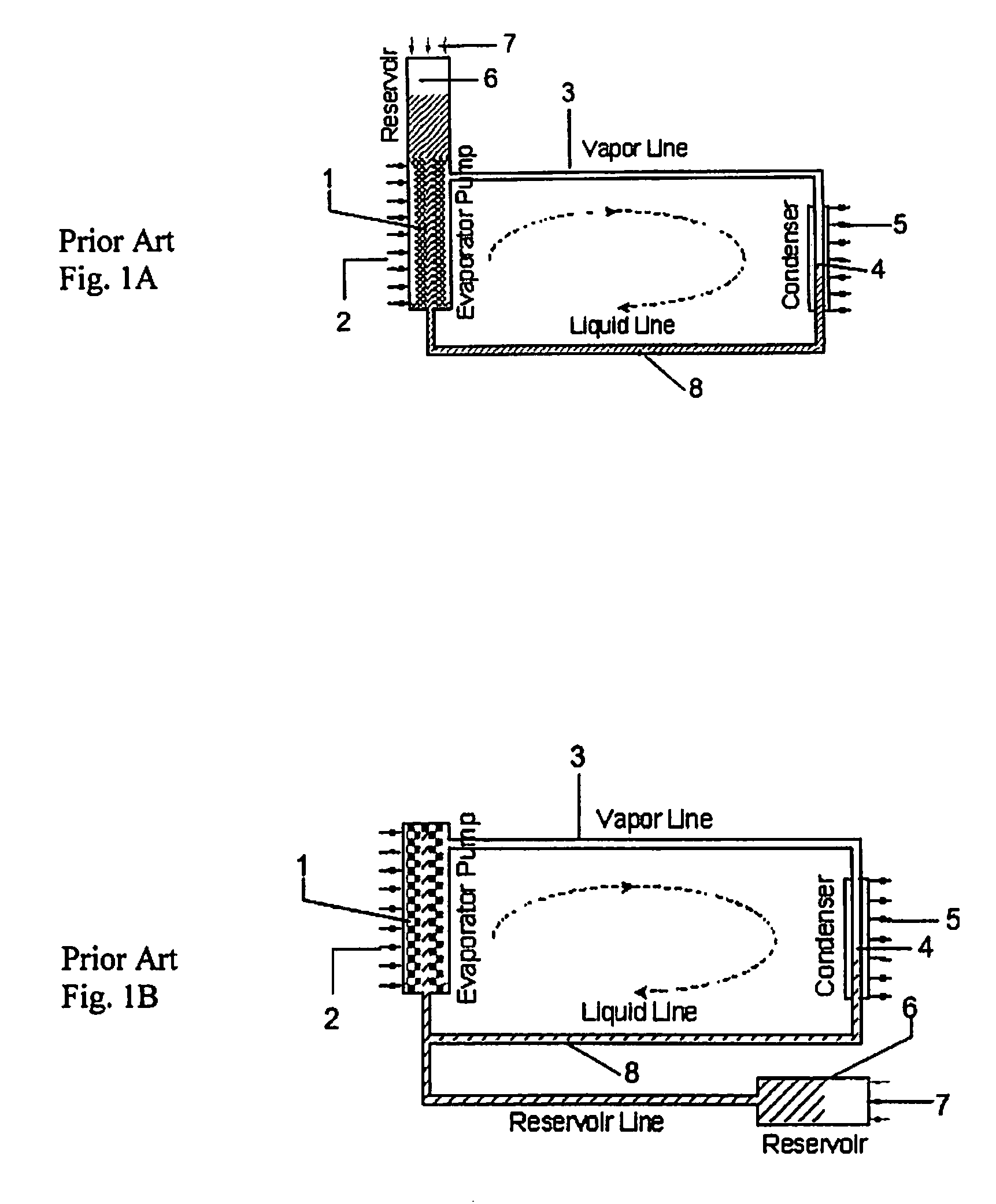
System and method of a heat transfer system and a condensor
InactiveUS20080110598A1Level controlSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMicron scaleWorking fluid
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
Point source detection
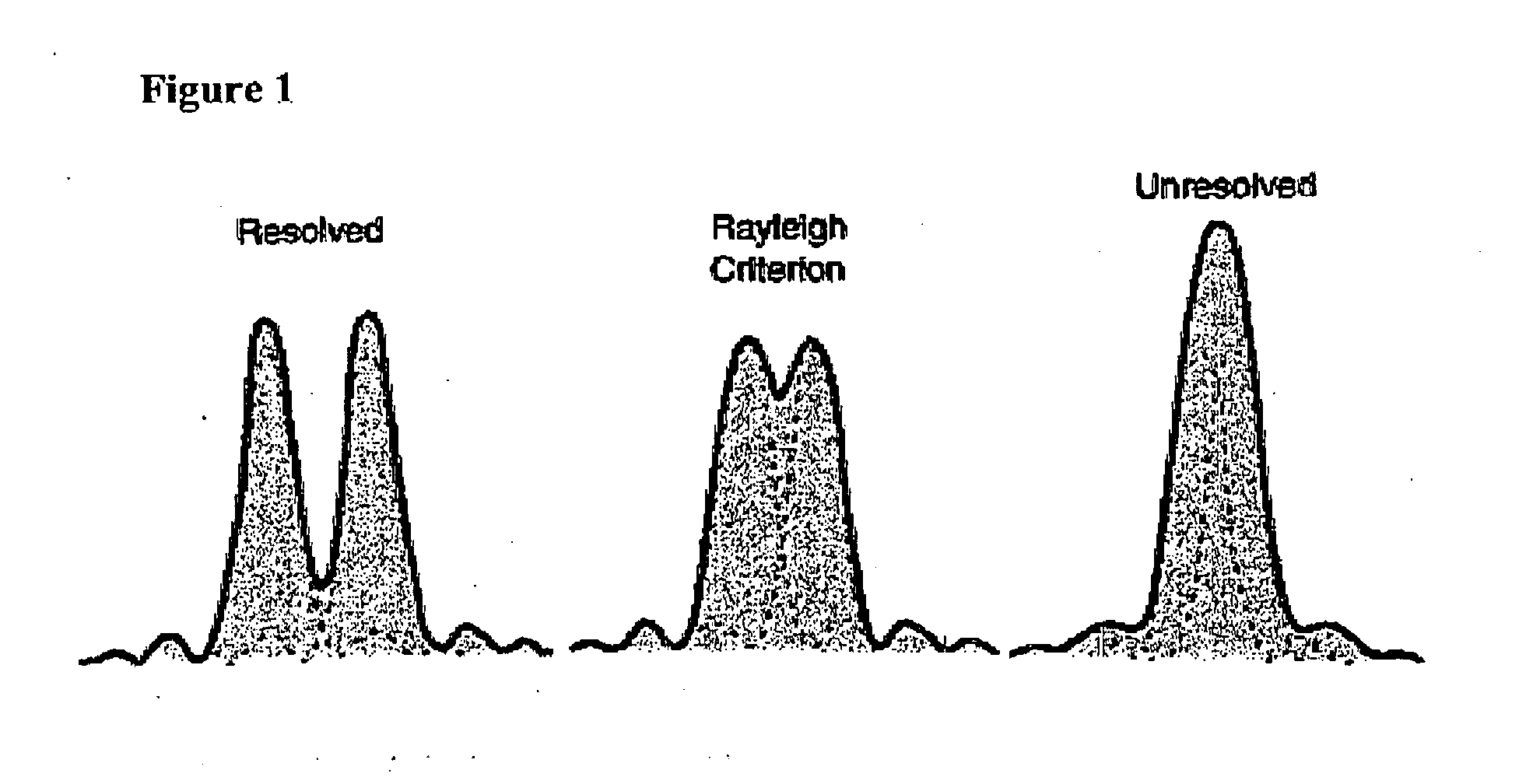
InactiveUS20110254969A1Minimize and eliminate artifactImprove accuracyTelevision system detailsImage enhancementNucleotideFluorescence
The invention provides a technique for accurate detection of objects appearing in the image, such as single fluorescent molecules, cells, microorganisms, nucleotides, DNA strands, or stars in celestial images. The method allows to differentiate between two combined point sources even if they are closer to each other than the optical resolution of the system. The procedure involves computing several coefficients representing decomposition of the intensity data in the basis of Hermit functions. In the case when the objects are distributed randomly and higher yield of accurately detected objects is desired, the method allows for a tenfold increase in such yield.
Owner:ANASTASIA TYURINA
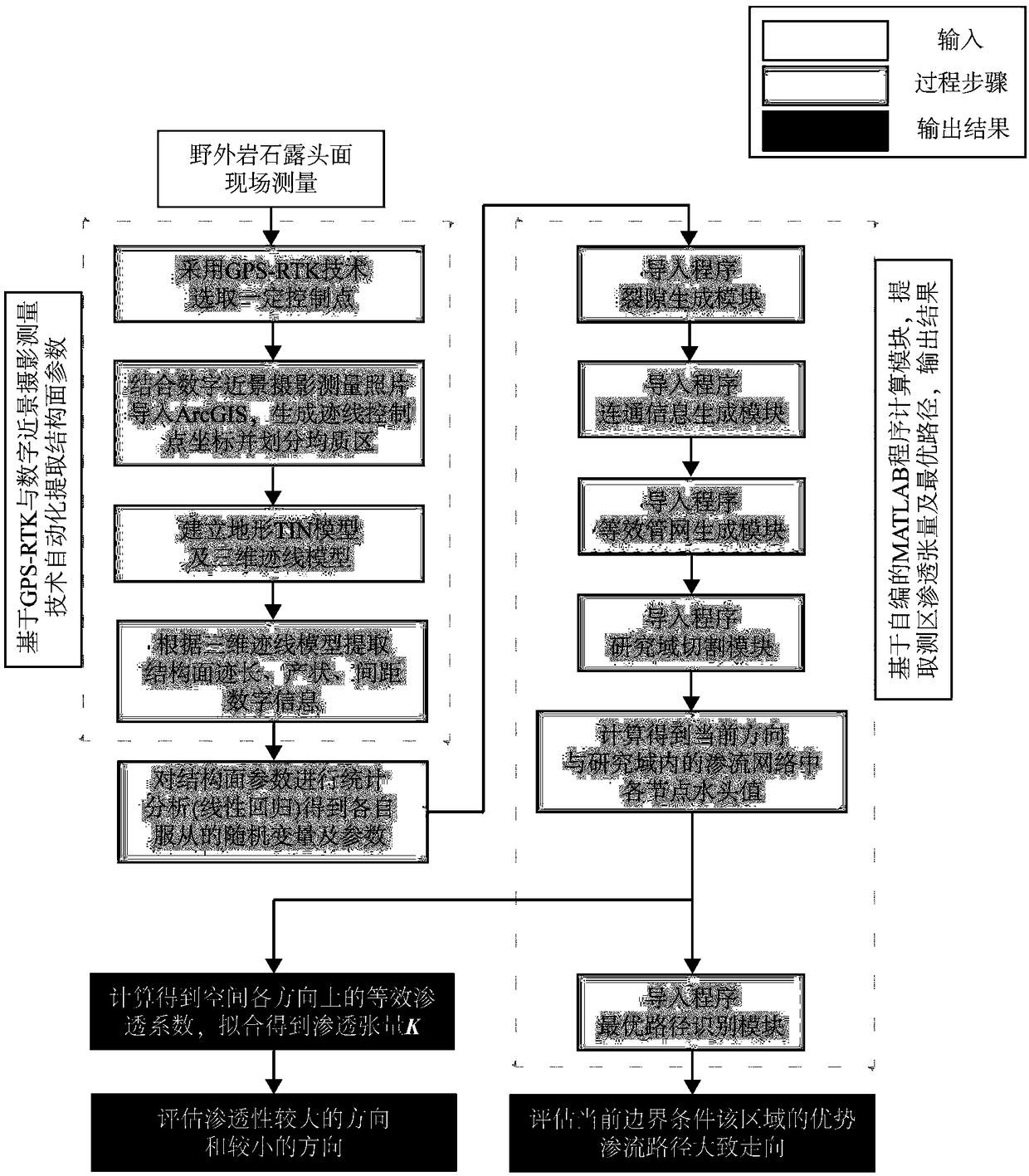
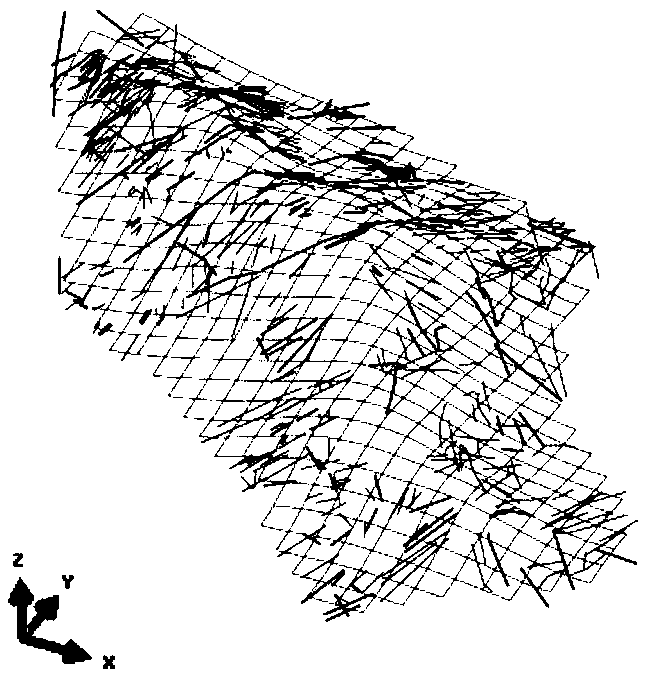
A method for calculating permeability tensor of fractured rock mass based on measured structural plane parameters
ActiveCN109033538AImprove processing efficiencyImprove accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationPermeability/surface area analysisInformation processingOutcrop
The invention discloses a method for calculating and optimizing the permeability tensor of fractured rock mass based on measured structural plane parameters, which marks control points on the rock outcrop surface and takes pictures of the rock outcrop surface from different angles at the same time. The three-dimensional coordinates of the control points of the structural plane traces on the photographs are located according to the coordinates of the marked control points, and the homogeneous regions are divided according to the clustering degree of the control points on the structural plane traces. According to the coordinates of the control points of the structural plane traces, a three-dimensional model of the structural plane traces in the homogeneous region to be measured is established. According to the three-dimensional model of structural plane traces, the information of structural plane traces length, occurrence and spacing is extracted. Statistical analysis of trace length, occurrence and spacing of structural planes is carried out to determine the random distribution types and parameters obeyed by them. According to the type and parameter of random distribution, the permeability tensor of the homogeneous area to be measured is calculated. The invention improves the accuracy and efficiency of the structural plane information processing, and simultaneously improves thecalculation efficiency of the infiltration tensor and the optimal path identification in the calculation module.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
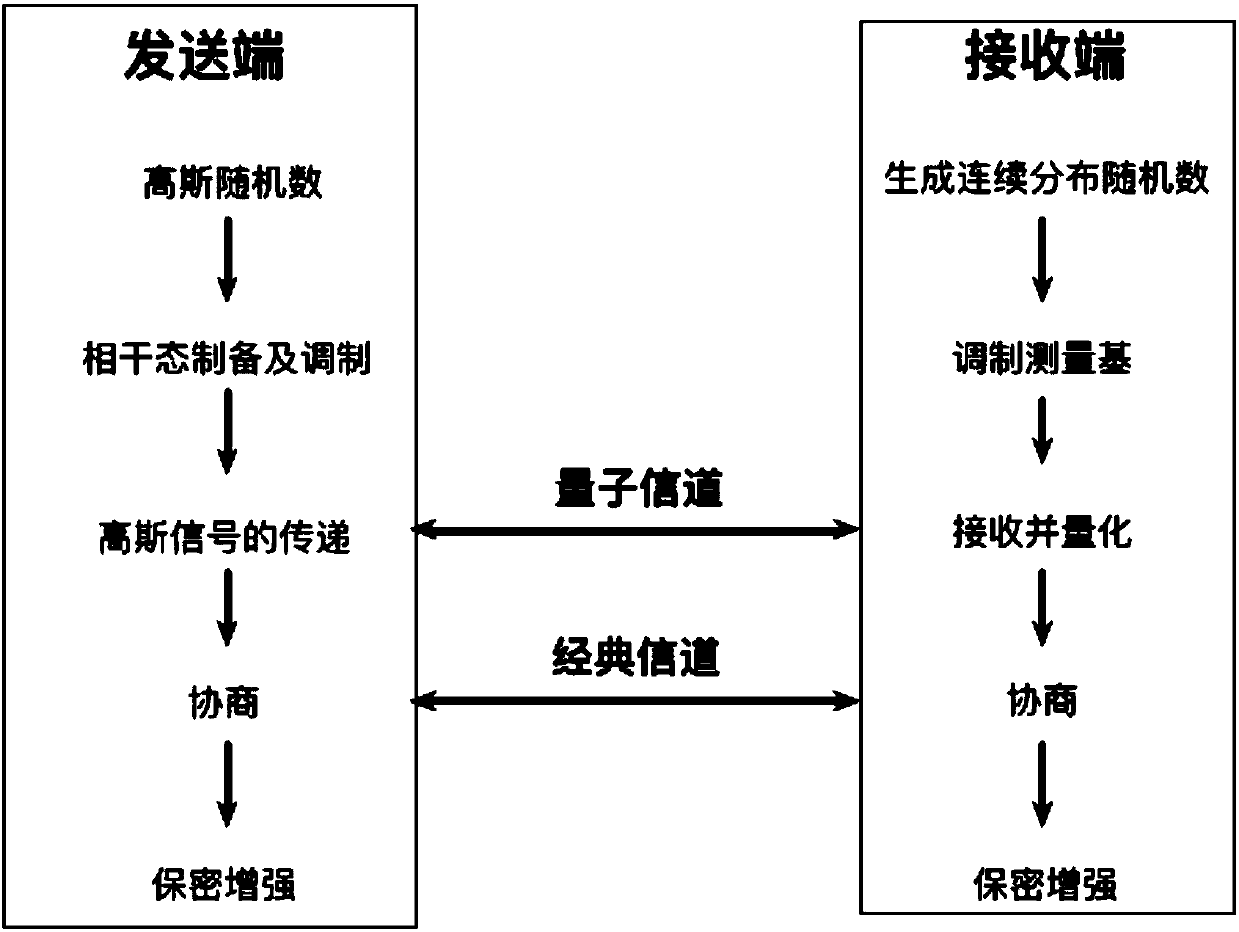
Continuous random measurement matrix-based continuous variable quantum key distribution method
ActiveCN107733640AEnsure safetyReduce complexityKey distribution for secure communicationDigital analog converterCoherent states
The invention provides a continuous random measurement matrix-based continuous variable quantum key distribution method. The method comprises the following steps of first, Gaussian modulation of a coherent state by a sending end, wherein the sending end prepares true random numbers of Gaussian distribution and prepares the coherent state, and encodes the coherent state through strength and a phasemodulator according to an element of a Gaussian random number set; second, transmission of a Gaussian signal, wherein the sending end transmits the encoded coherent state signal to a receiving end through a quantum channel; third, demodulation of a continuous random measurement matrix by the receiving end, wherein the receiving end prepares a plurality of binary variables that are distributed continuously and randomly; and fourth, data consultation and privacy amplification. Through adoption of the method, matrix comparison is prevented so that some original data strings are not discarded, further, the method is easy to realize in the prior art. Due to use of continuously distributed phase angles, requirements on performance of a digital-analog converter and a phase modulator are relatively lowered, so that engineering is easy to realize.
Owner:上海循态量子科技有限公司
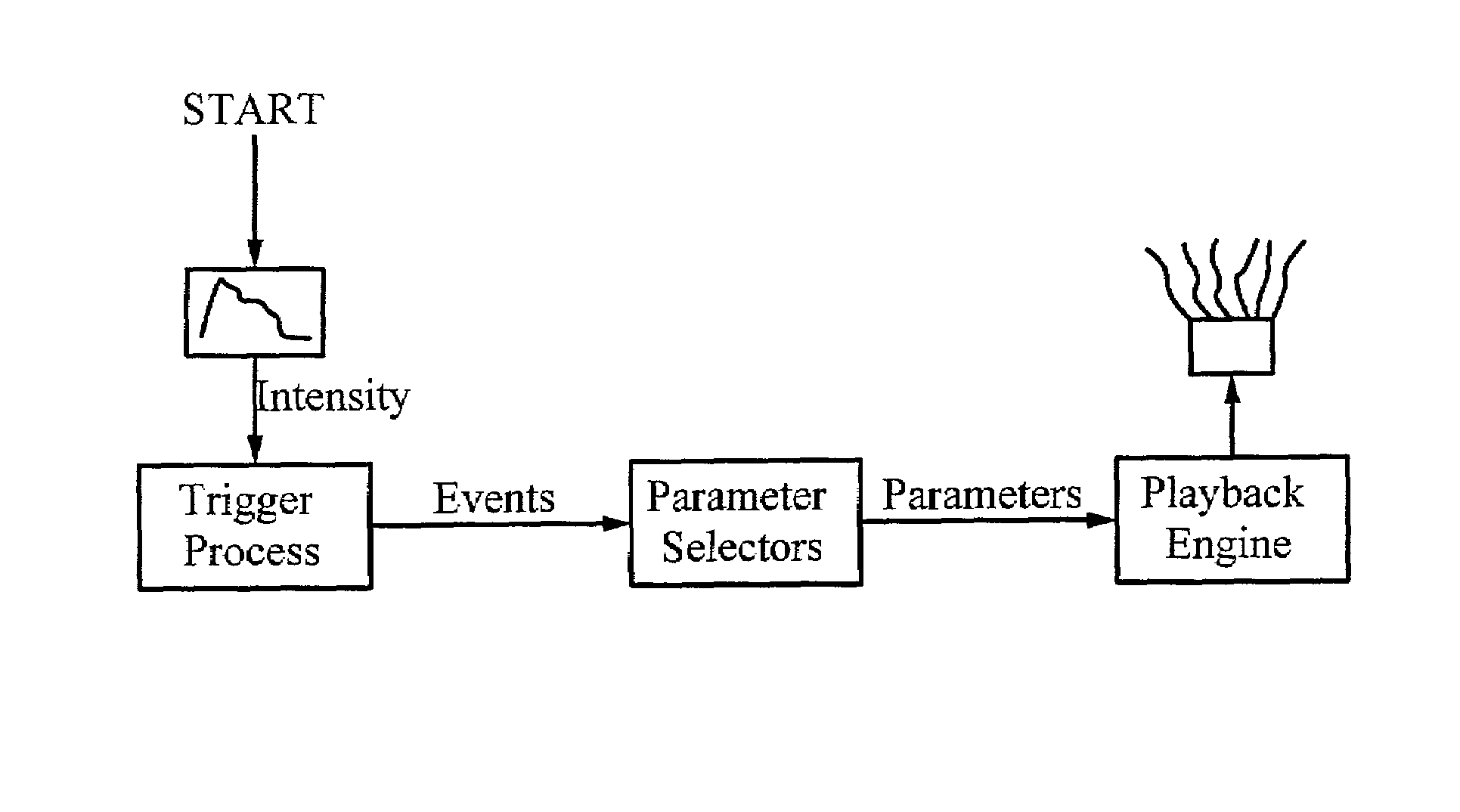
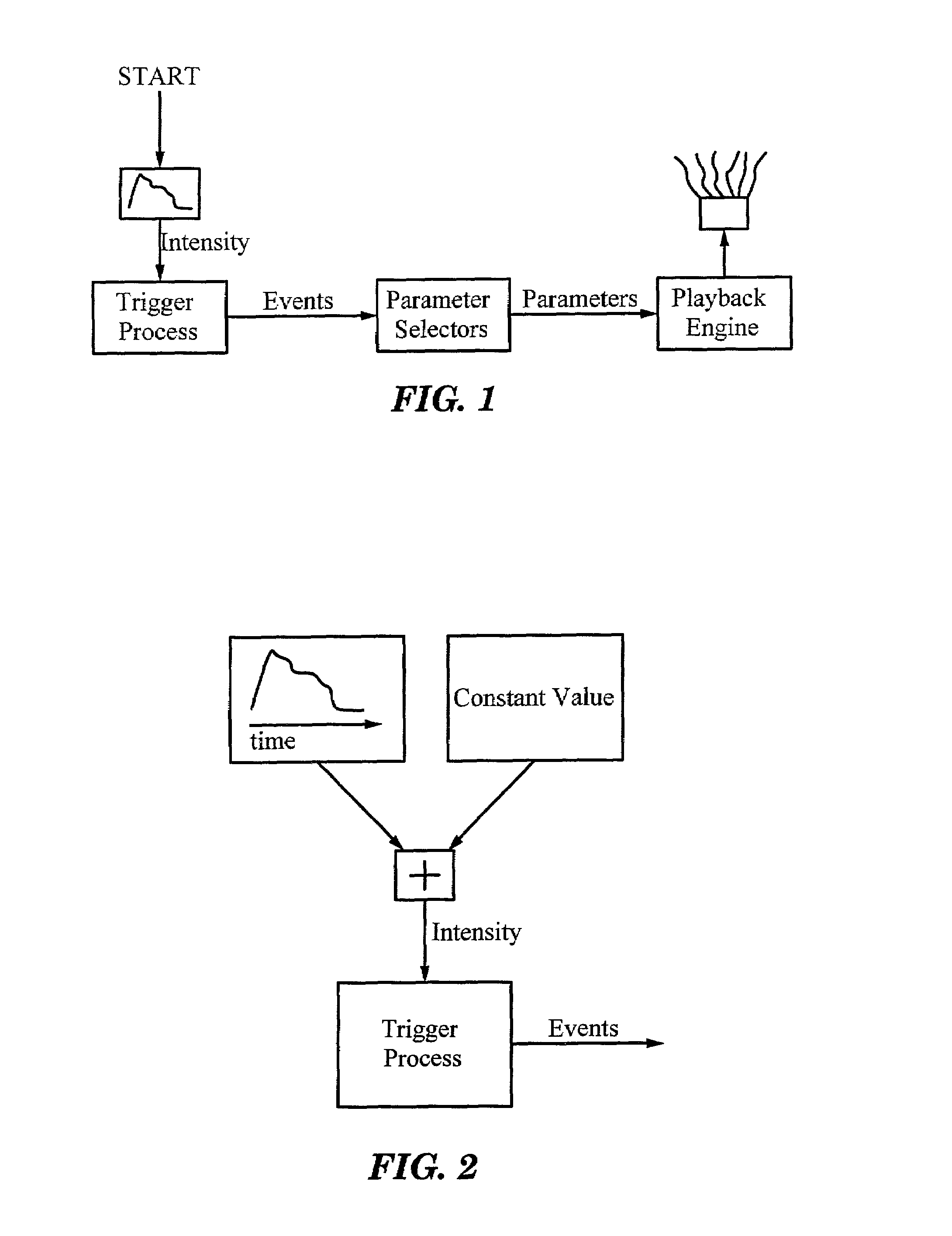
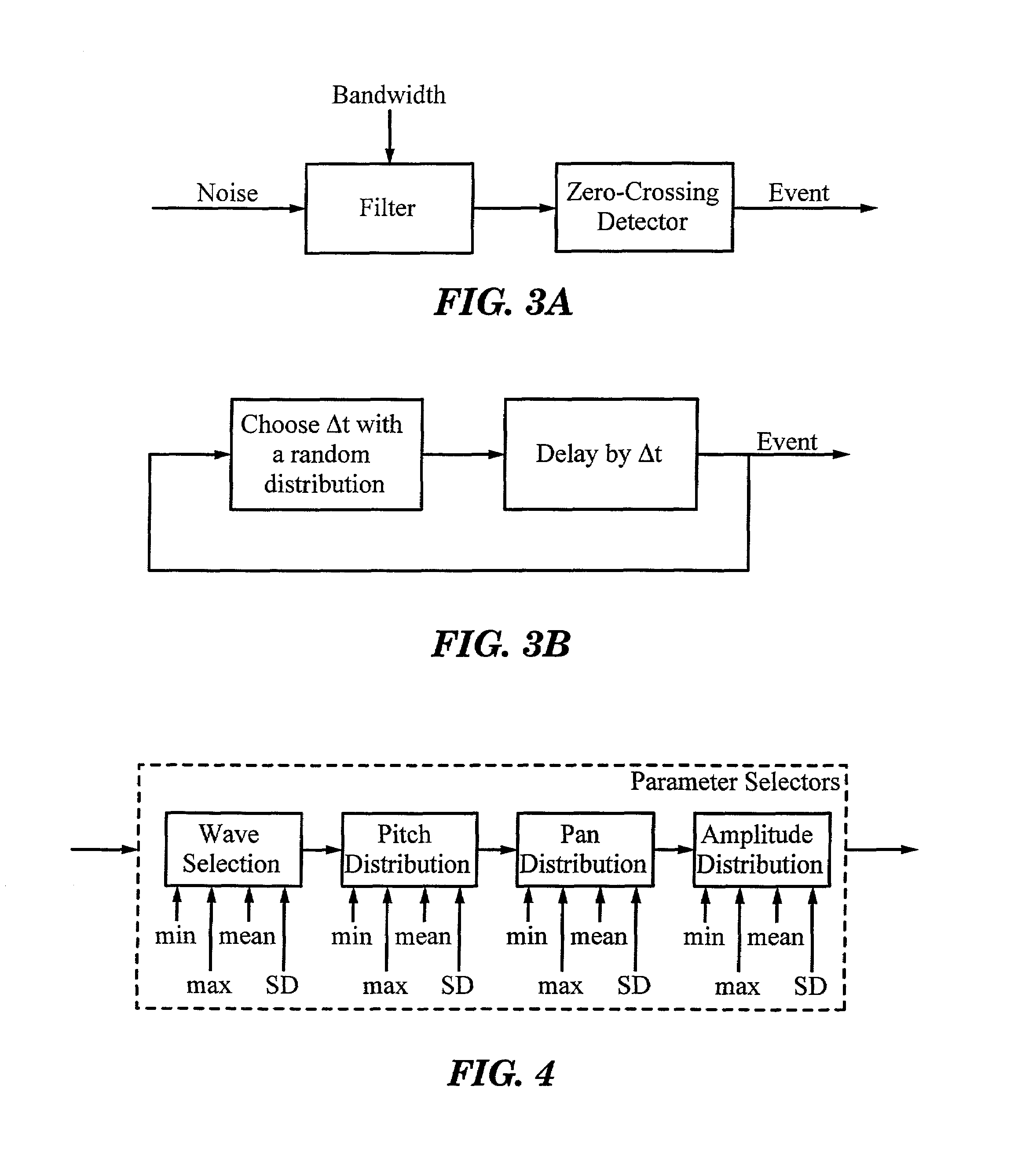
Statistical sound event modeling system and methods
Complex sound events are created by generating multiple different kinds of simpler sounds with randomly varying repetition rates. The average repetition rate can also be variable. The values of sound parameters such as wave selection, pitch distribution, pan distribution and amplitude distribution can have random distributions, as determined by various control inputs, some of which have their own random distributions.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com