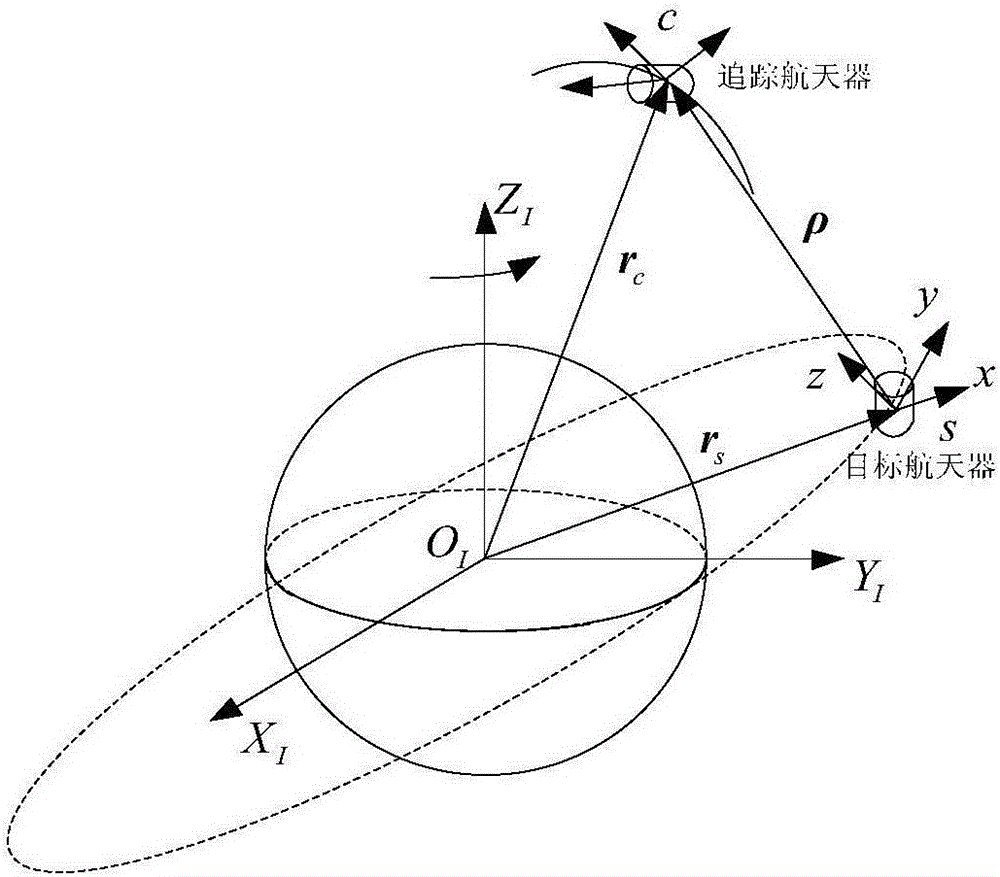
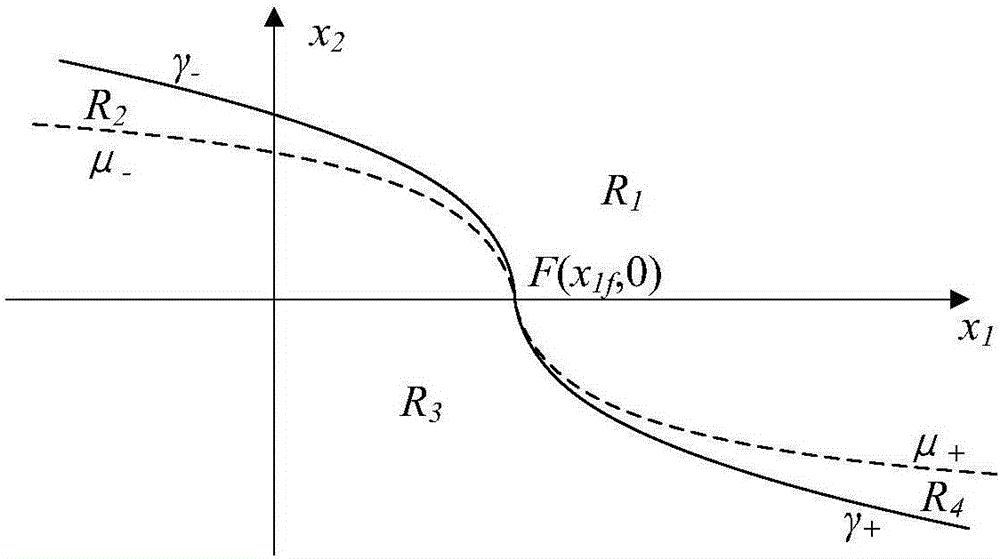
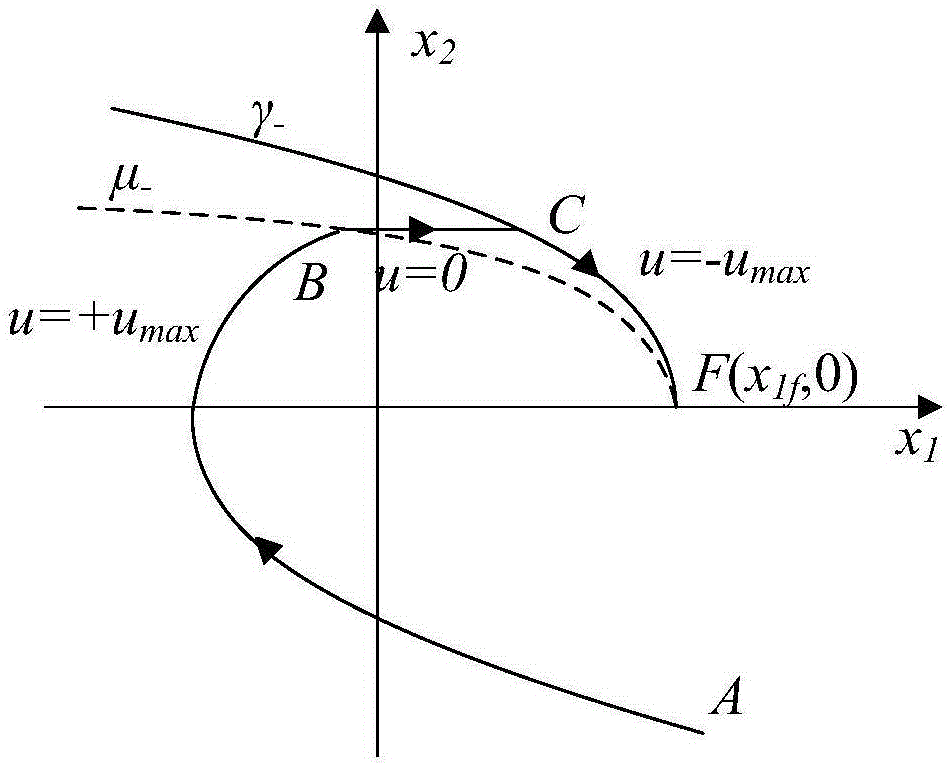
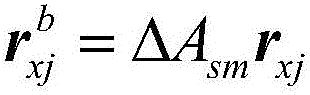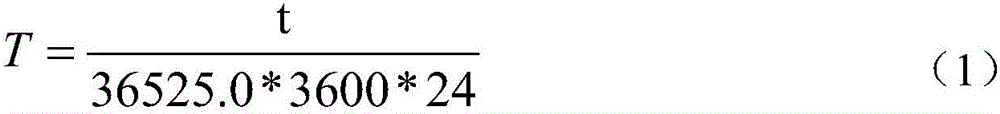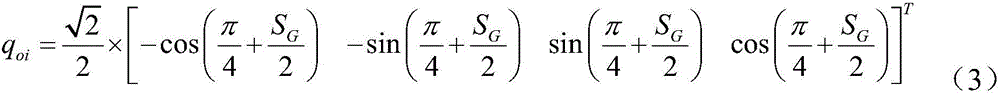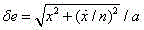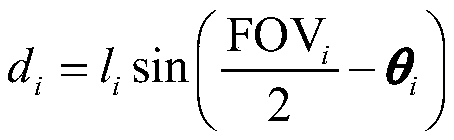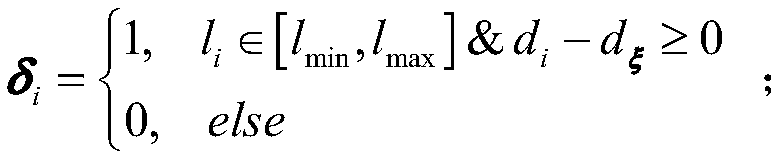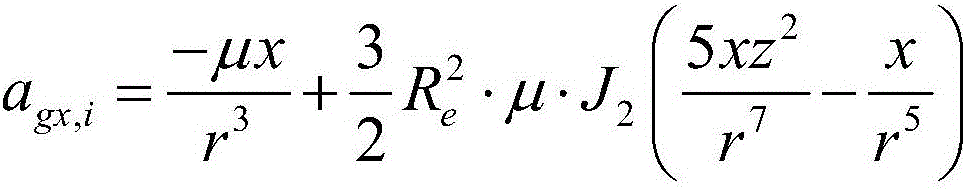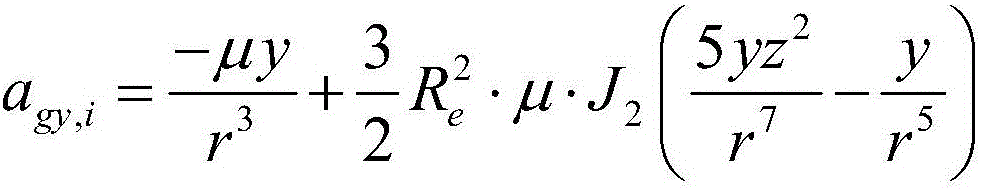Patents
Literature
102 results about "Relative orbit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Relative orbit. [′rel·əd·iv ′ȯr·bət] (astronomy) The closed path described by the apparent position of the fainter member of a binary system relative to the brighter member.
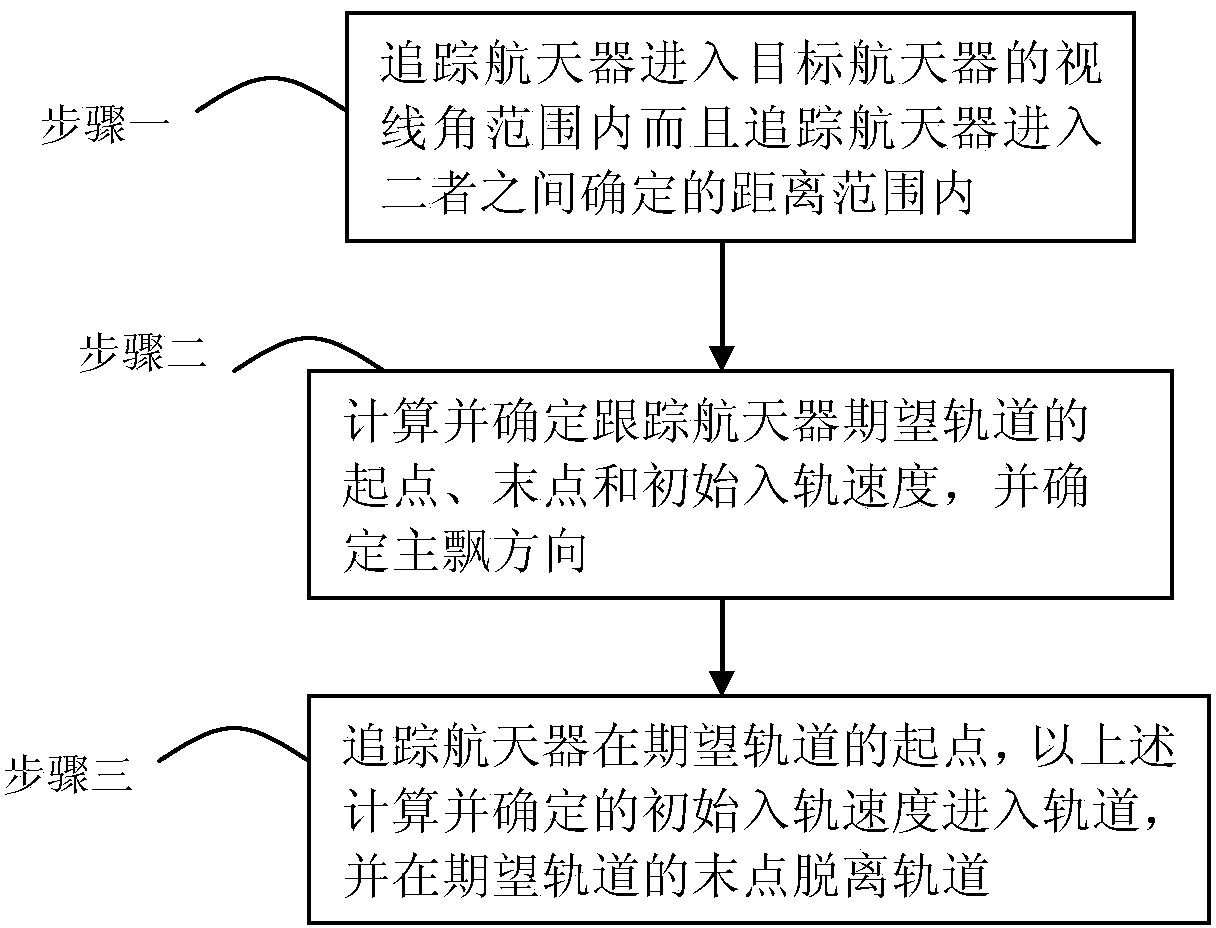
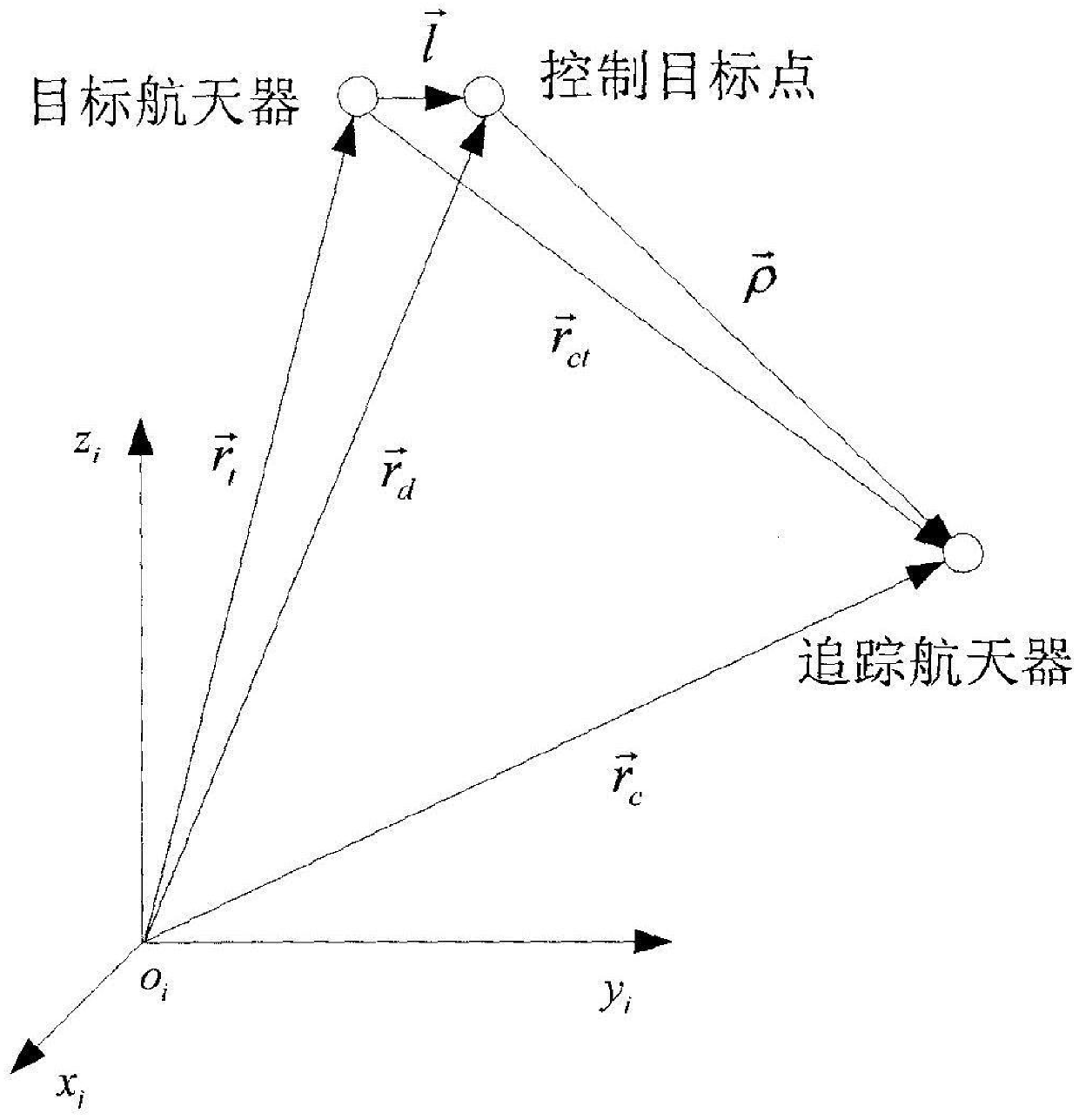
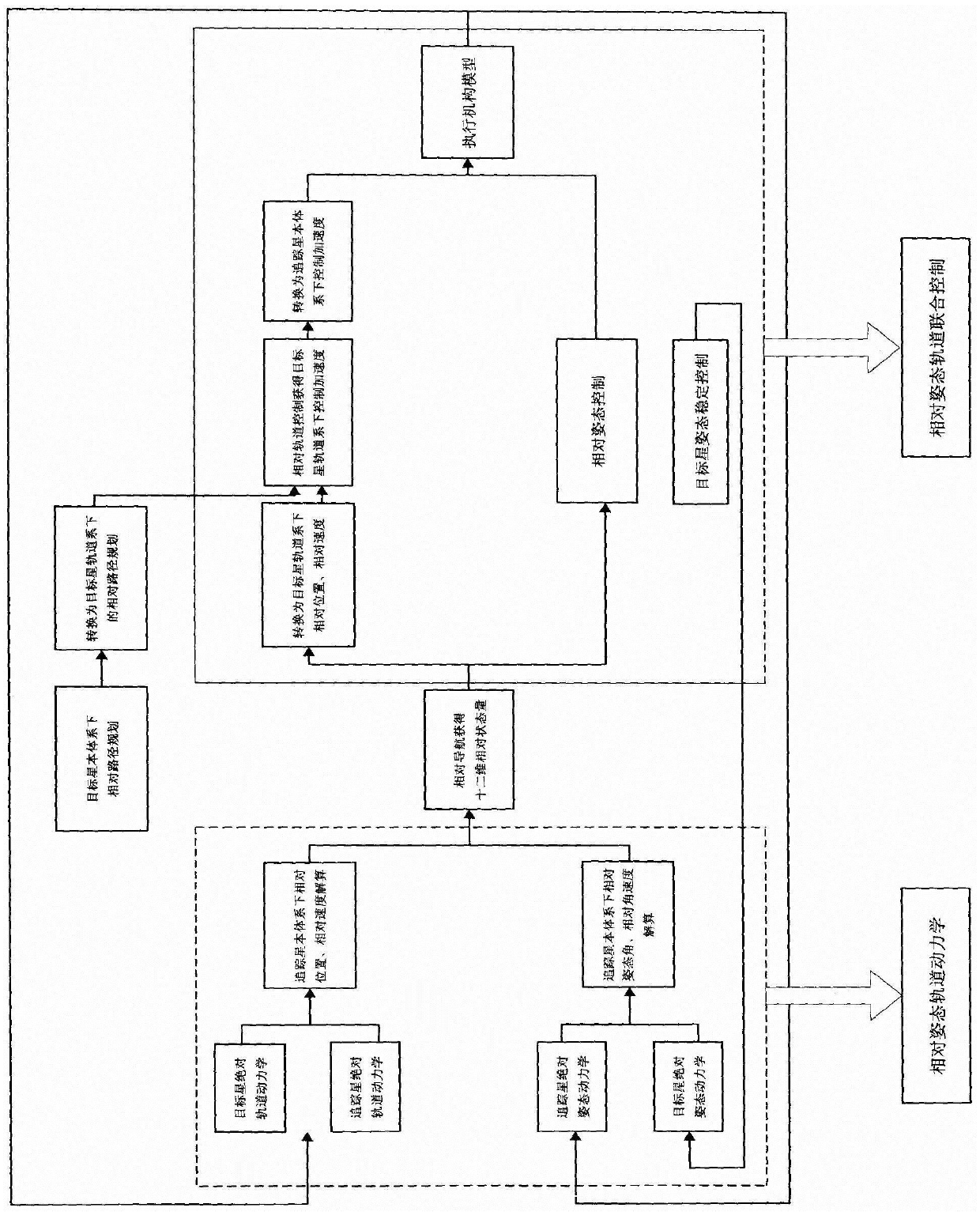
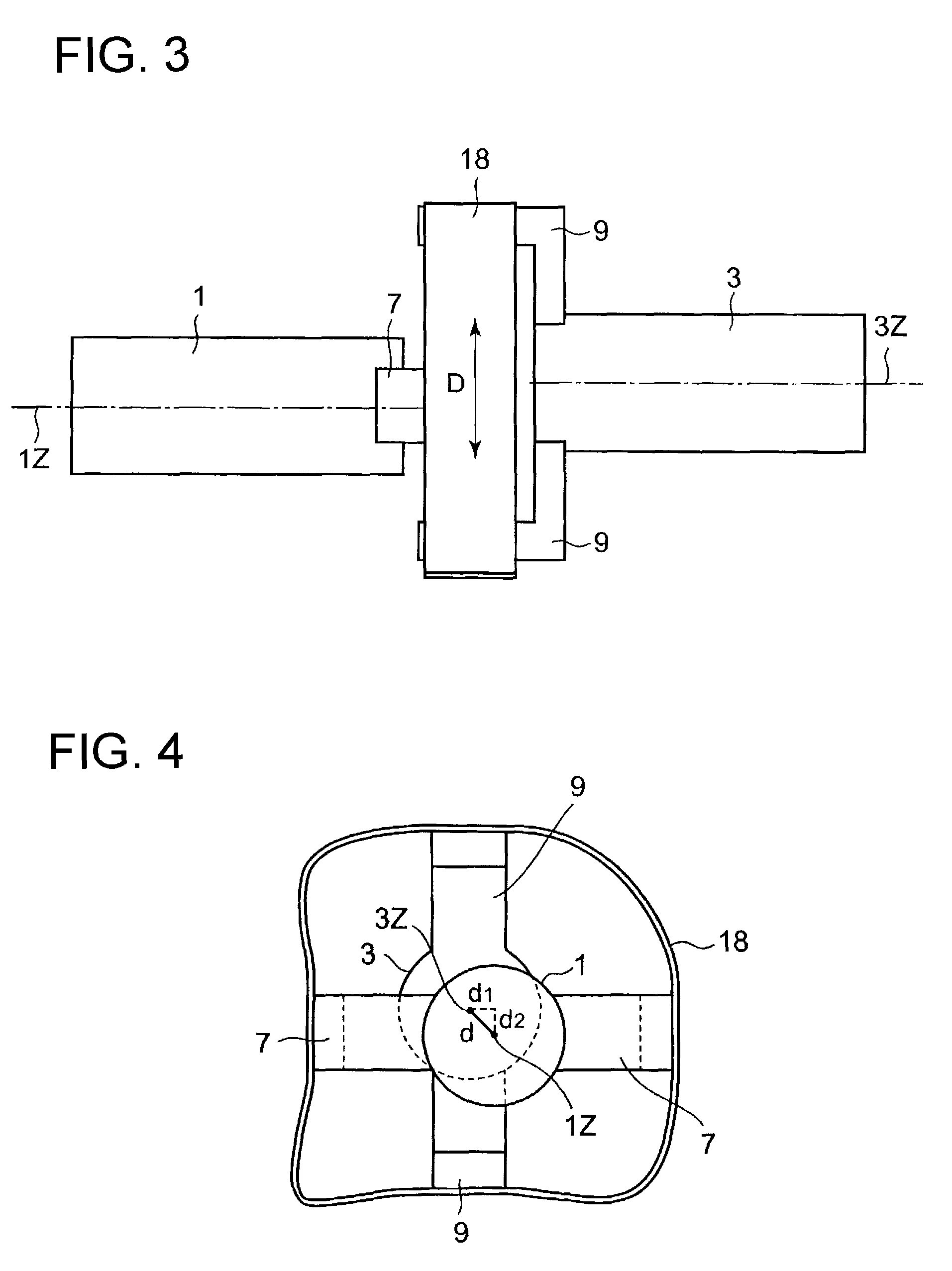
Spacecraft relative orbit control method
ActiveCN103728980AAvoid coupled controlSimple analysis ideasPosition/course control in three dimensionsRelative orbitAttitude control
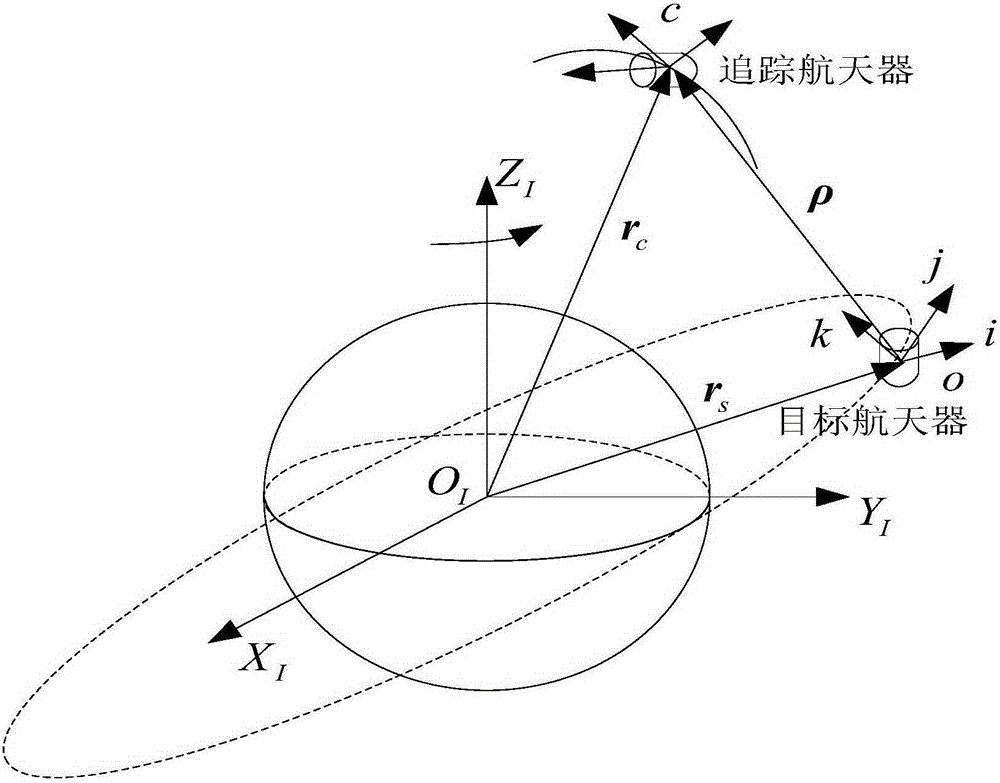
The invention relates to a spacecraft relative orbit control method which relates to a spacecraft close range relative orbit control method to achieve a hedgehop flying mode of a spacecraft, namely a tracking spacecraft runs according to the self orbit after entering the designated space range relevant to a target spacecraft, and only gesture control is required. The problems of complex calculation, poor pointing accuracy caused by pose orbit control coupling, easiness in identity exposure, difficulty in time maintaining and the like in the traditional methods of hovering, accompanying flying, diversion and the like are solved. The method includes the following steps that 1 the tracking spacecraft enters a sight angle range of the target spacecraft and enters the determined distance range between the tracking spacecraft and the target spacecraft; 2 the starting point, the end point and the initial orbit entering speed of an expected orbit of the target spacecraft are calculated, and the main wave direction is determined; 3 the tracking spacecraft enters the orbit with the calculated determined initial orbit entering speed from the starting point of the expected orbit and breaks away from the orbit at the end point of the expected orbit.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
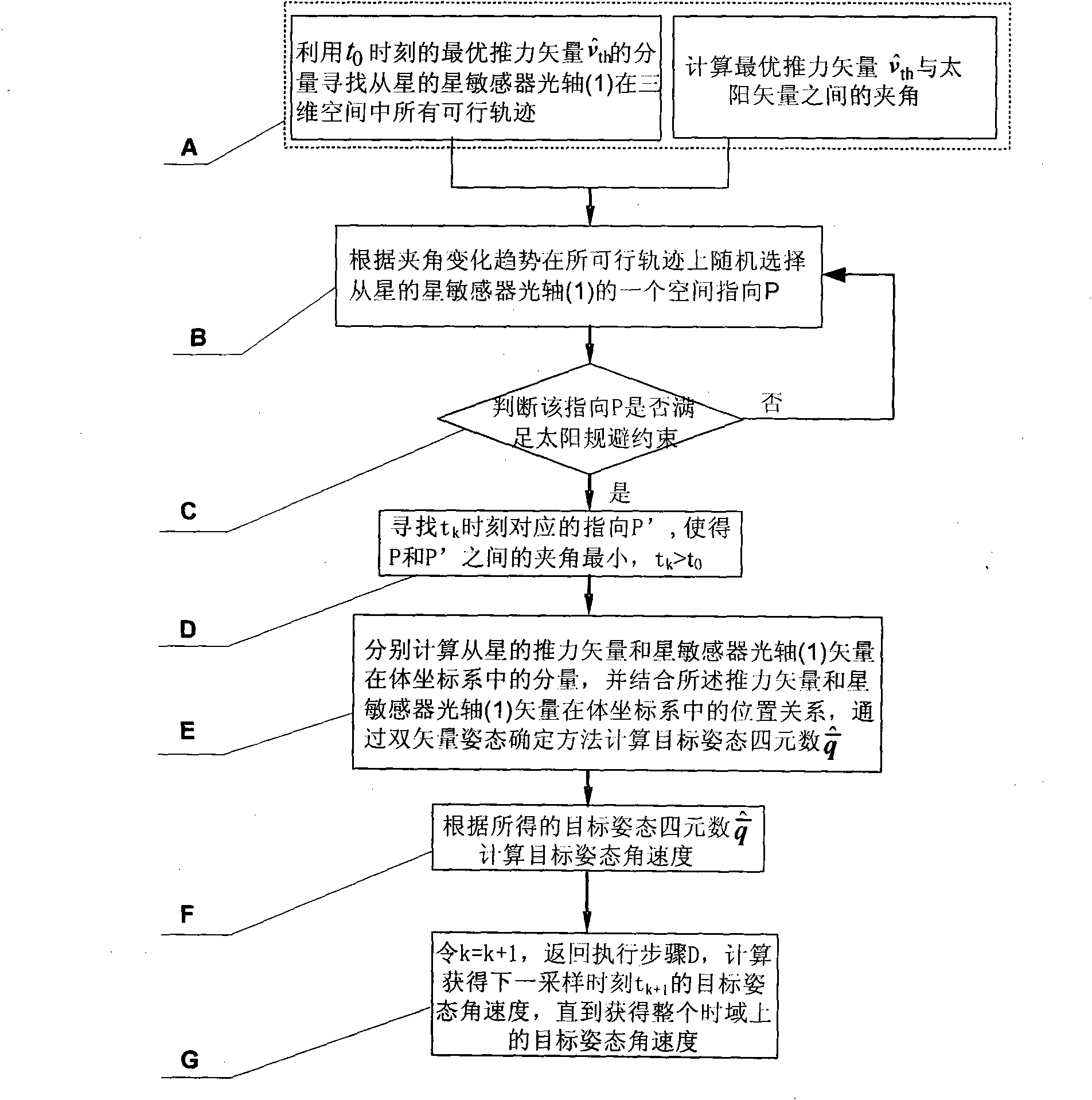
Decoupling control method for relative orbits and attitudes of formation satellites
InactiveCN101794154AReduce the control dimensionImprove solution efficiencyAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsRelative orbitAttitude control
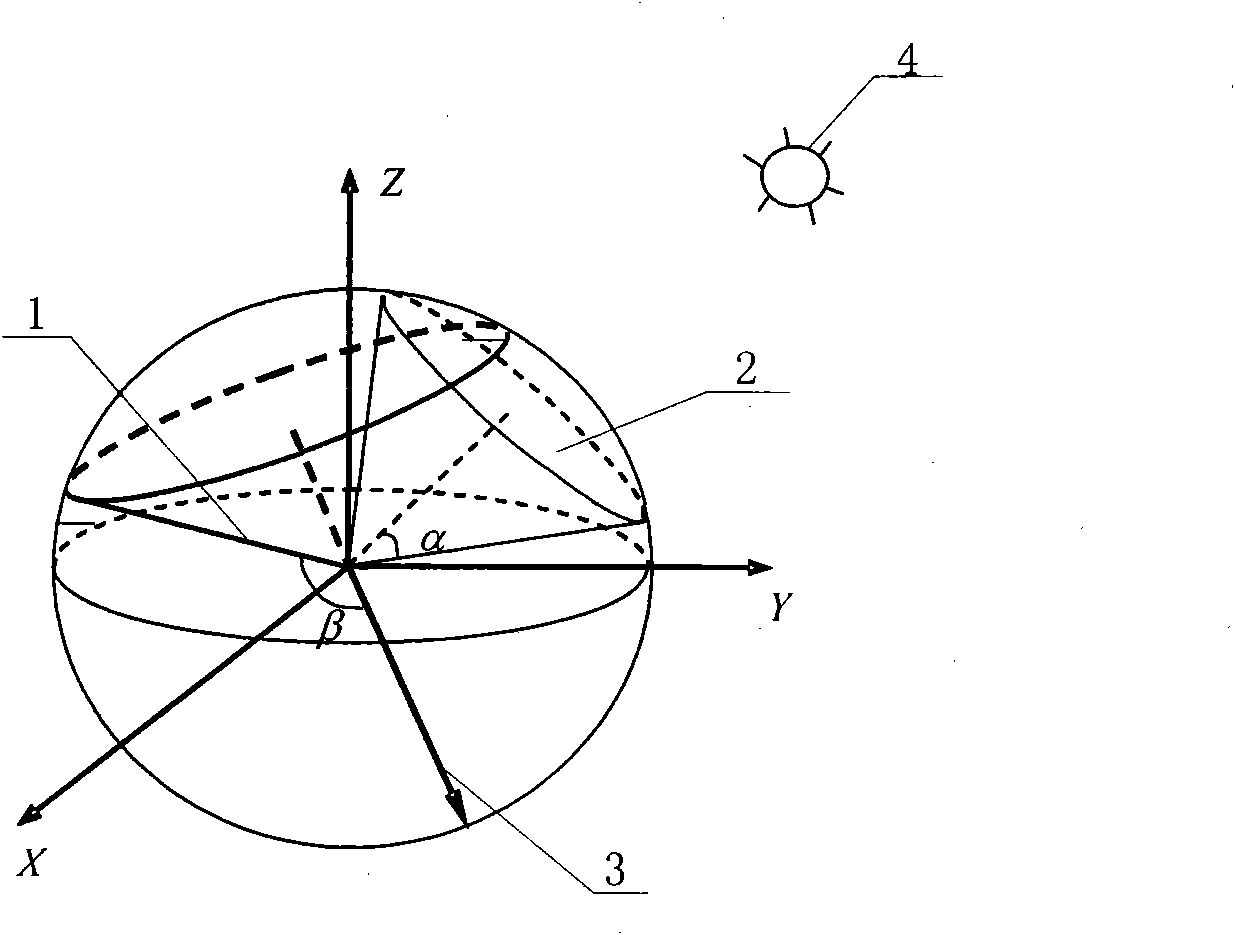
The invention discloses a decoupling control method for relative orbits and attitudes of formation satellites, relates to the technical field of the control of the orbits and attitudes of a spacecraft formation, and solves the problems of large satellite calculation amount and low orbit solving efficiency caused by high control dimension of the formation satellites due to serious coupling of the relative orbits and the attitudes of the formation satellites. The method gives two decoupling conditions at first, so that the control of the relative orbits and the attitudes can be designed independently; a thrust vector mobility decoupling constraint condition is introduced to the initialization control of the relative orbits according to satellite attitude mobility constraints indirectly; and during the optimal thrust vector attitude tracking, the possible orientation in space, which meets solar avoidance constraints, of a star sensor optical axis (1) is sought by using a geometric method, and the optimal attitude quaternion and attitude angular velocity are calculated finally by using a double-vector attitude determination algorithm. The method provides important reference value for the control of the orbits and the attitudes of the spacecraft formation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Relative orbit design and high-precision posture pointing control method aiming at space non-cooperative target
ActiveCN104656666ASimple parameter designNot easy to exposeAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsRelative orbitAttitude control
The invention discloses a relative orbit design and high-precision posture pointing control method aiming at a space non-cooperative target, and relates to a relative orbit design and a high-precision posture pointing control method. The problems that the orbit control is difficult and the posture pointing precision is influenced in orbit posture coupling control when the track position is limited in the prior art are solved. The method comprises the following steps: tracking a flying over track design of a relative space non-cooperative target spacecraft of a spacecraft; tracking a shifting track design of the relative space non-cooperative target spacecraft of the spacecraft; and tracking a posture controller design of the relative space non-cooperative target spacecraft of the spacecraft, namely, finishing the relative orbit design and the high-precision posture pointing control method aiming at the space non-cooperative target. The method disclosed by the invention is applied to the field of the space spacecrafts.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Autonomous formation flight control method for satellites
ActiveCN104142686ALong-term change controlDrift speed is smallAttitude controlRelative orbitRelative motion
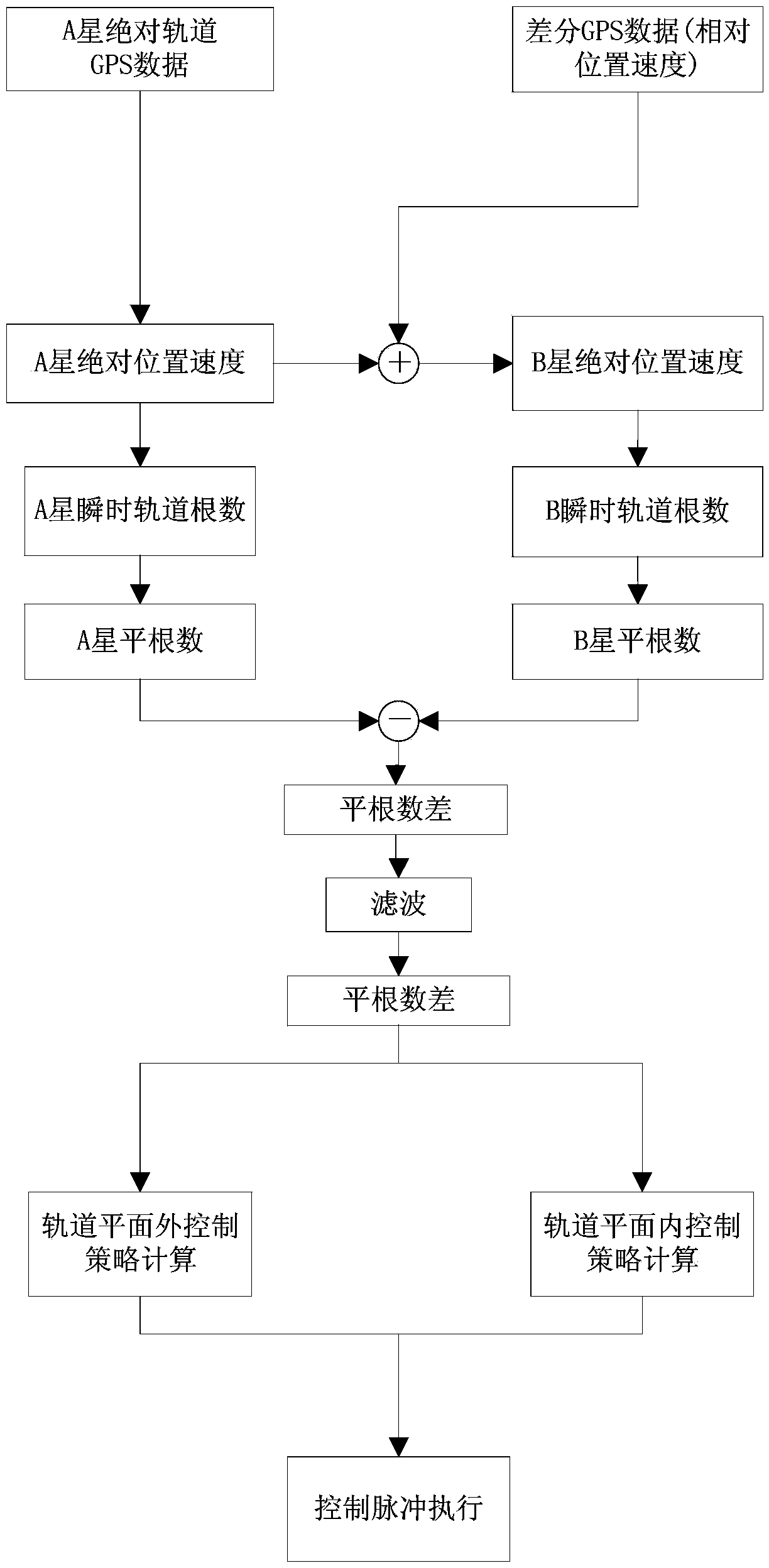
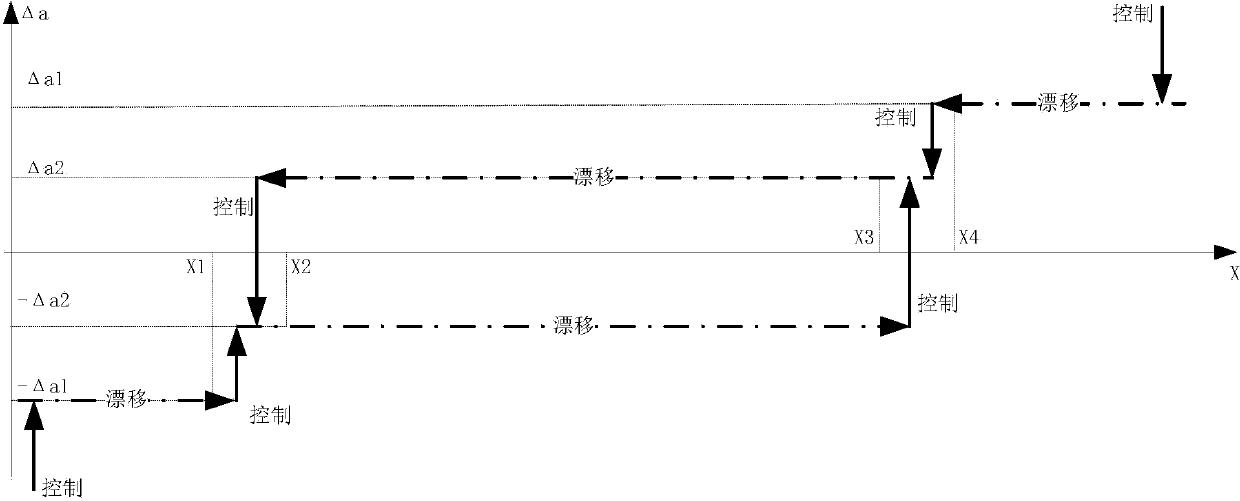
The invention discloses an autonomous formation flight control method for satellites. Formation flight control is carried out through relative orbit mean elements, and due to the fact that a long-term trend of relative movement between the satellites is accurately reflected through the relative orbit mean elements, long-term changes of the relative movement can be well controlled with the method. The autonomous formation flight control method is characterized in that a mean semi-major axis difference control strategy in an orbital plane is designed, the mode that control targets are set in a partitioned mode is adopted, and it is guaranteed that the drift speeds within control zones are low; when outside the control zones, the control targets can return to the control zones at high speeds. According to the autonomous formation flight control method, due to the mode that small-pulse air injecting is used for orbit control multiple times, and a momentum wheel is used for posture control, influences of posture air injection control on orbits are reduced, and the orbit control execution accuracy is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Formation satellite finite-time configuration containment control method
ActiveCN104898691AIncrease speedReliable controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsRelative orbitDirected graph
The invention relates to a formation satellite configuration containment control method, in particular, a formation satellite finite-time configuration containment control method. The objective of the invention is to solve the problem of low robustness of an existing multiple-satellite system formation control method and the problem of incapability of completely adapting to a practical application environment which is caused by a situation that inter-satellite communication topology is an undirected graph in the existing multiple-satellite system formation control method. The formation satellite finite-time configuration containment control method includes the following steps that: a relative orbit dynamic model of formation satellites i of a satellite formation system and relative reference points is established according to an established relative motion dynamic equation of reference satellites and accompanying satellites, and is simplified as an expression described in the descriptions; a weighted adjacent matrix A and a Laplacian matrix in the graph theory of a directed graph in the satellite formation system are provided according to the formation types of the formation satellites i; and a distributed finite-time configuration containment control laws of the multi-dynamic-pilot-satellite satellite formation system are designed, and therefore, each following satellite can achieve at a configuration convex hull formed by pilot satellites in finite time, and formation satellite finite-time configuration containment control can be realized. The formation satellite finite-time configuration containment control method of the invention is applicable to the control field of formation satellite configuration.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
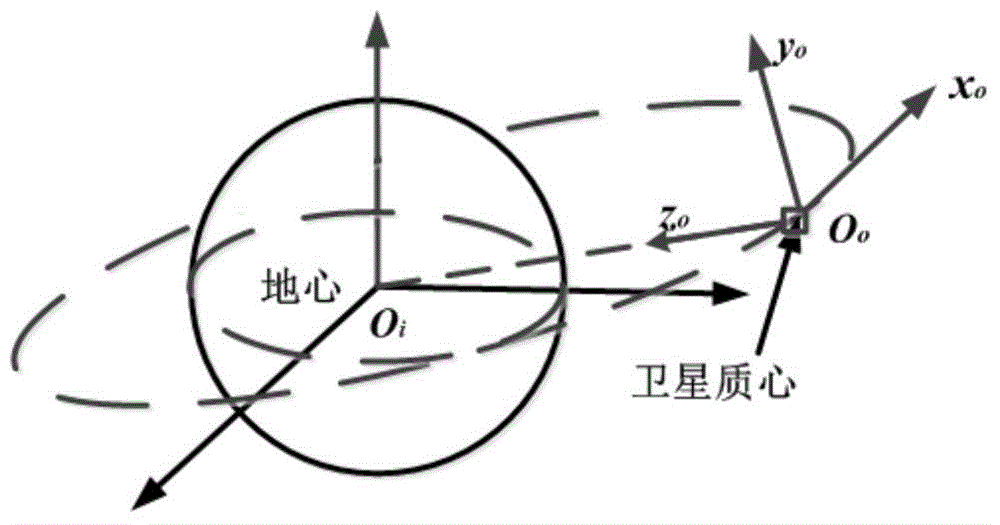
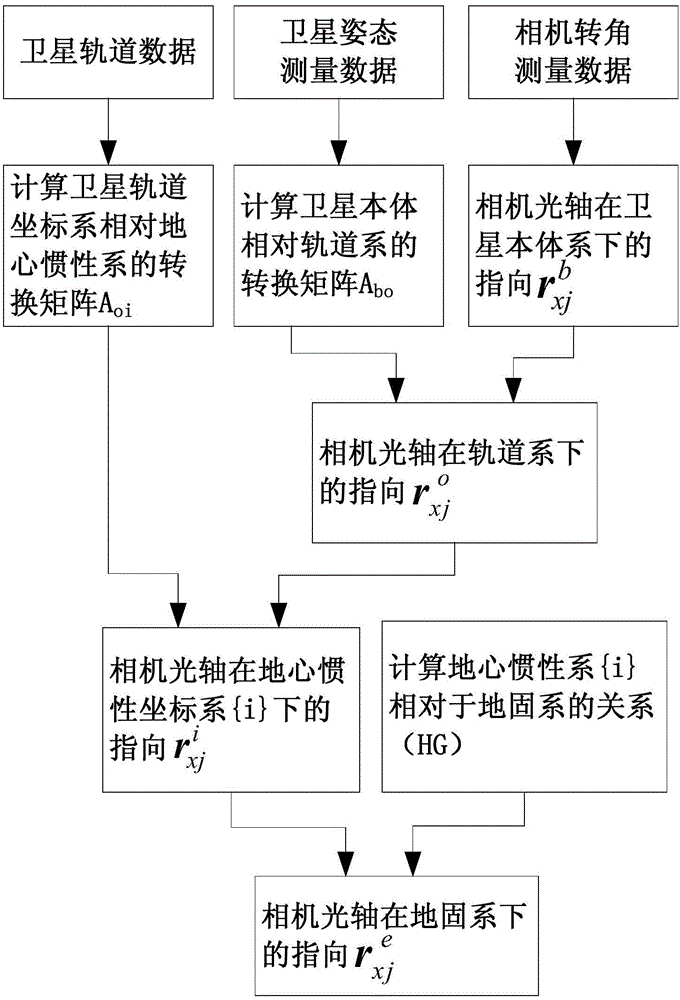
Camera optical axis direction calculation method based on high-precision posture information
ActiveCN106124170AEasy accessImprove imaging effectTesting optical propertiesRelative orbitOptical axis
The invention provides a camera optical axis direction calculation method based on high-precision posture information, and the method comprises the steps: calculating the orientation (shown in the description) of a camera optical axis in a rail coordinate system according to the orientation (shown in the description) of a scanning camera optical axis in a satellite system {b} and the conversion matrix Abo of the satellite system {b} relative to the rail coordinate system {o}; calculating the orientation (shown in the description) of the camera optical axis in an inertial coordinate system {i} according to the orientation (shown in the description) of the camera optical axis in the rail coordinate system {o} and a conversion matrix Aoi of the rail coordinate system {o} relative to the inertial coordinate system {i}; calculating the orientation (shown in the description) of the camera optical axis in an earth-fixed reference coordinate system according to the orientation (shown in the description) of the camera optical axis in the inertial coordinate system {i} and a conversion matrix (HG) of the inertial coordinate system {i} relative to the earth-fixed reference coordinate system. The method can achieve the real-time calculation on the ground and correct the orientation of the optical axis, also can enable the information of a rail and the earth-fixed reference coordinate system on the ground to be stored on a satellite in advance so as to autonomously carry out real-time calculation and correct the orientation of the optical axis, and can improve the imaging capability of the satellite in a simple mode.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
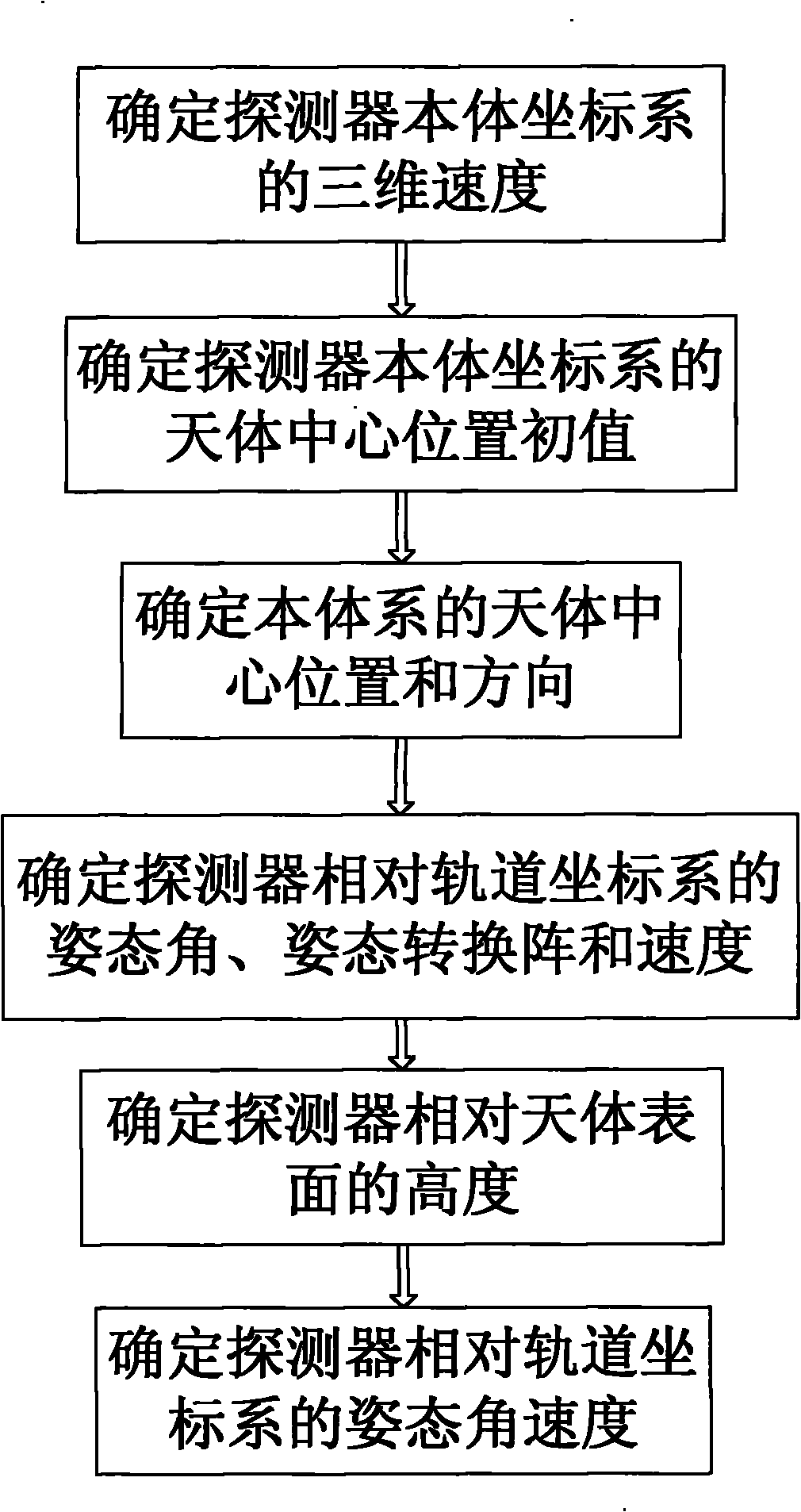
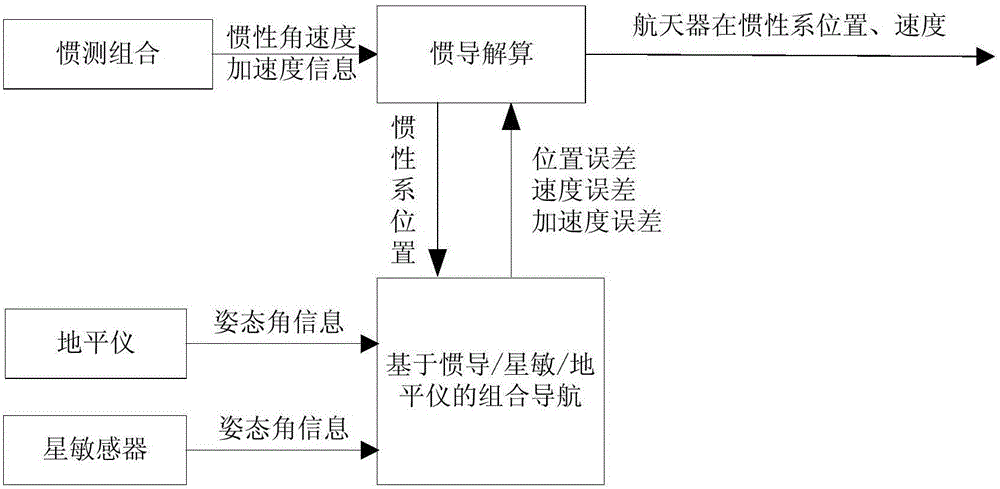
High-precision navigation method for landed or attached deep sky celestial body detector
The invention belongs to the technical field of guidance, navigation and control of deep sky detectors, and particularly discloses a high-precision navigation method for a landed or attached deep sky celestial body detector. The method comprises the following steps: (1) determining the three-dimensional speed of a coordinate system of a detector body; (2) determining initial value of the center position of a celestial body in the coordinate system of the detector body; (3) determining the position and the direction of the celestial body in the body system; (4) determining the attitude angle and the speed of the detector relative to the coordinate system of an orbit; (5) determining the height of the detector relative to the surface of the celestial body; and (6) determining the angular speed of the detector relative to the coordinate system of the orbit. The method is not affected by the situation that inertial navigation error is constantly increased along the time, thereby effectively improving the precision of key navigation parameters for autonomous navigation of the landed or attached detector, and meeting the demands on navigation and control of the high-precision landed or attached deep sky celestial body detector.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Optimization method of relative orbit transfer path of spacecraft based on time-fuel optimum control
The invention provides an optimization method of a relative orbit transfer path of a spacecraft based on time-fuel optimum control and relates to the optimization method of the relative orbit transfer path of the spacecraft. The optimization method of the relative orbit transfer path of the spacecraft is used for solving the problem that the finite thrust amplitude is not considered in the existing method and the problem that only time optimum or only the fuel consumption is considered in the existing method when a tracking spacecraft is in a relative orbit coordinate system. The optimization method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a kinematics and dynamics model as shown in the specification of the relative orbit, and designing control quantities ux, uy and uz applied along three axes respectively; secondly, decoupling the kinematics and dynamics model of the relative orbit into three subsystems; after decoupling into three subsystems, transforming the total performance index as shown in the specification considering transfer time and fuel consumption of the tracking spacecraft into monoaxial performance index as shown in the specification of each axis, and finally obtaining the time-fuel optimal control law as shown in the specification for controlling the tracking spacecraft. The optimization method is suitable for optimizing the relative orbit transfer path of the spacecraft.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Satellite formation relative orbit adaptive neural network configuration containment control method
ActiveCN105068546AVerify validityGet speed informationAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsRelative orbitNerve network
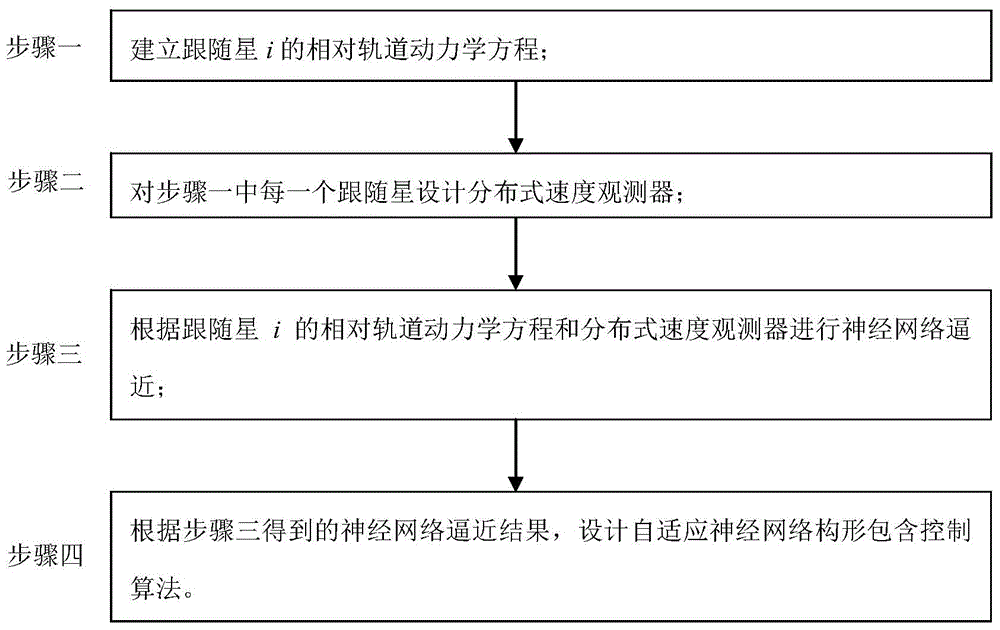
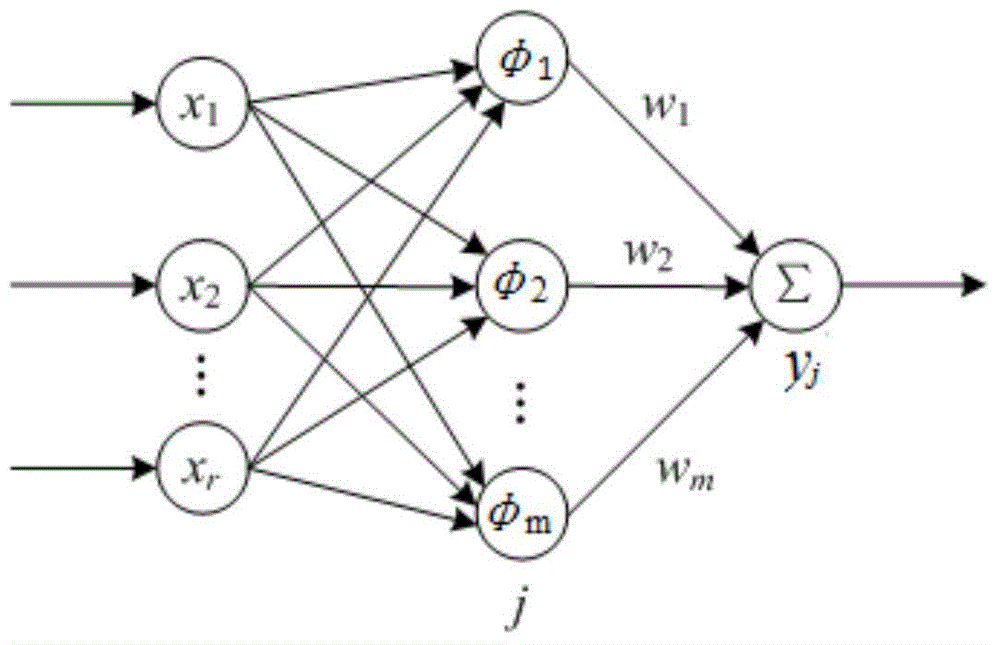
The present invention relates to a satellite formation relative orbit adaptive neural network configuration containment control method, and aims to solve the communication burden problems in the prior art brought by not considering the situations that a system exists the non-linear uncertainty and the external disturbance, not considering the situation that a satellite formation system kinetics exists the generalized interference, not considering a chattering phenomena and the known global information. The method of the present invention is realized by the following technical schemes of a step 1 of establishing a relative orbit kinetic equation of a following satellite i; a step 2 of designing a distributed speed observer for each following satellite in the step 1; a step 3 of carrying out the neural network approximation according to the relative orbit kinetic equation and the distributed speed observer of the following satellite i; a step 4 of designing an adaptive neural network configuration containment control algorithm according to a neural network approximation result obtained in the step 3. The satellite formation relative orbit adaptive neural network configuration containment control method of the present invention is applied to the satellite field.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Relative orbit attitude finite time control method for non-cooperative target spacecraft
ActiveCN105353763AWell formedSmall amount of calculationCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsRelative orbitAviation
The invention discloses a relative orbit attitude finite time control method for a non-cooperative target spacecraft, and relates to the field of aerospace. The method solves the problems in present relative orbit attitude joint control of non-cooperative target spacecrafts. The relative orbit attitude finite time control method for the non-cooperative target spacecraft comprises the following steps: 1, projecting a relative orbit dynamics model expressed by an inertial system to a sight system, and describing the relative orbit dynamics model of the spacecraft by adopting the sight system; 2, establishing an attitude dynamics model and an attitude kinematics model; 3, performing state space representation on the relative orbit dynamics model, the attitude dynamics model and the attitude kinematics model to obtain a relative orbit attitude dynamics model; and 4, obtaining a finite time continuous controller according to the relative orbit attitude dynamics model and the finite time control theory. The method is suitable for relative orbit attitude joint control of non-cooperative target spacecrafts.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
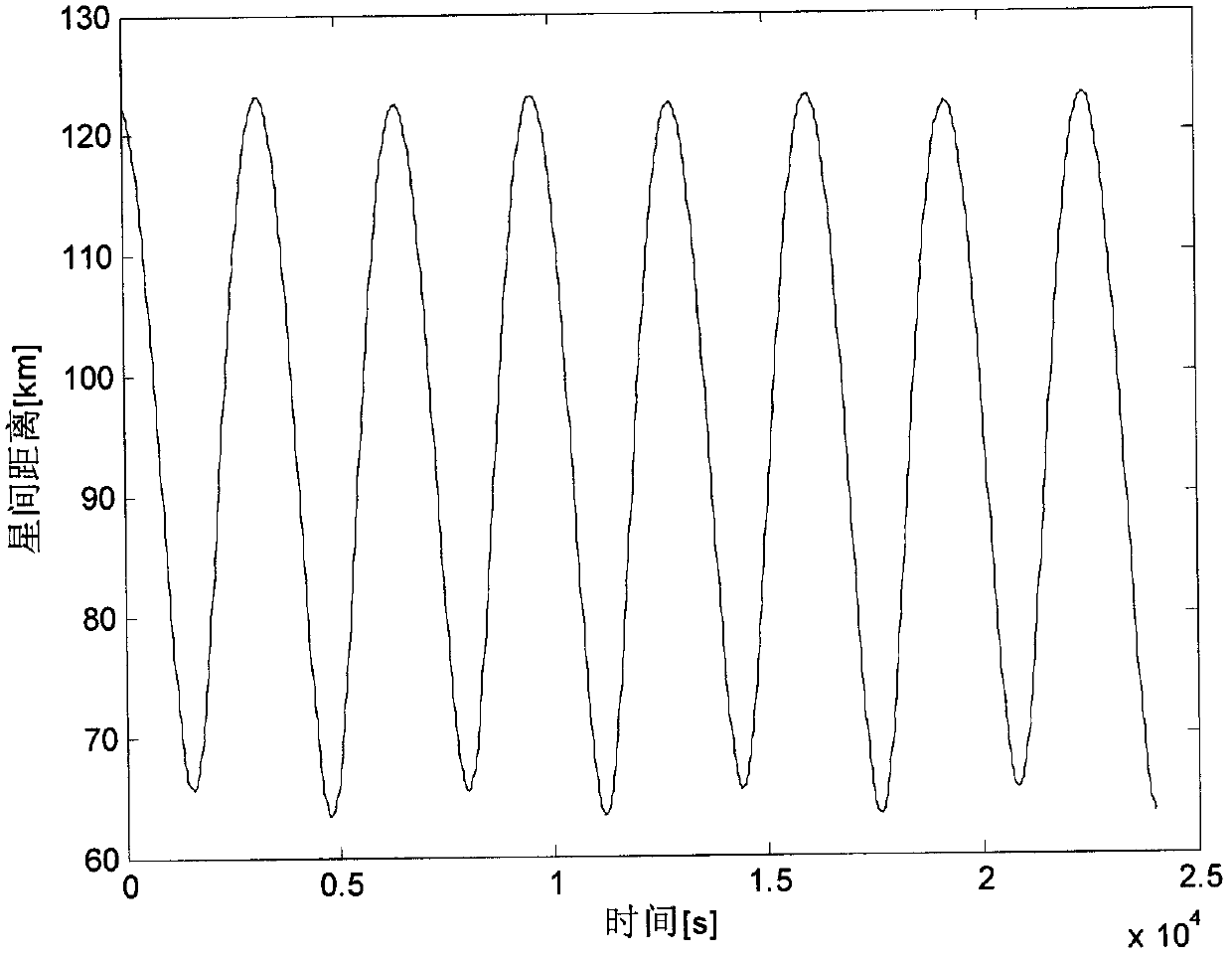
Method for determining absolute orbit and relative orbit of formation flight satellite
The invention discloses a method for determining an absolute orbit and a relative orbit of a formation flight satellite. According to the method, aiming at a formation flight task of equipment for measuring interstellar relative distance, an absolute orbit number and a relative orbit number of two formation satellites are obtained by resolving a relative measure value of the interstellar distance. The measure value of relative distance is only needed in the resolving process and a third-party signal source is avoided, so that a receiving party of the interstellar distance can separately determine the absolute orbit number and the relative orbit number of the formation flight task without support of a ground tracking telemetry and command station, a GPS (Global Position System) and other auxiliary equipment.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
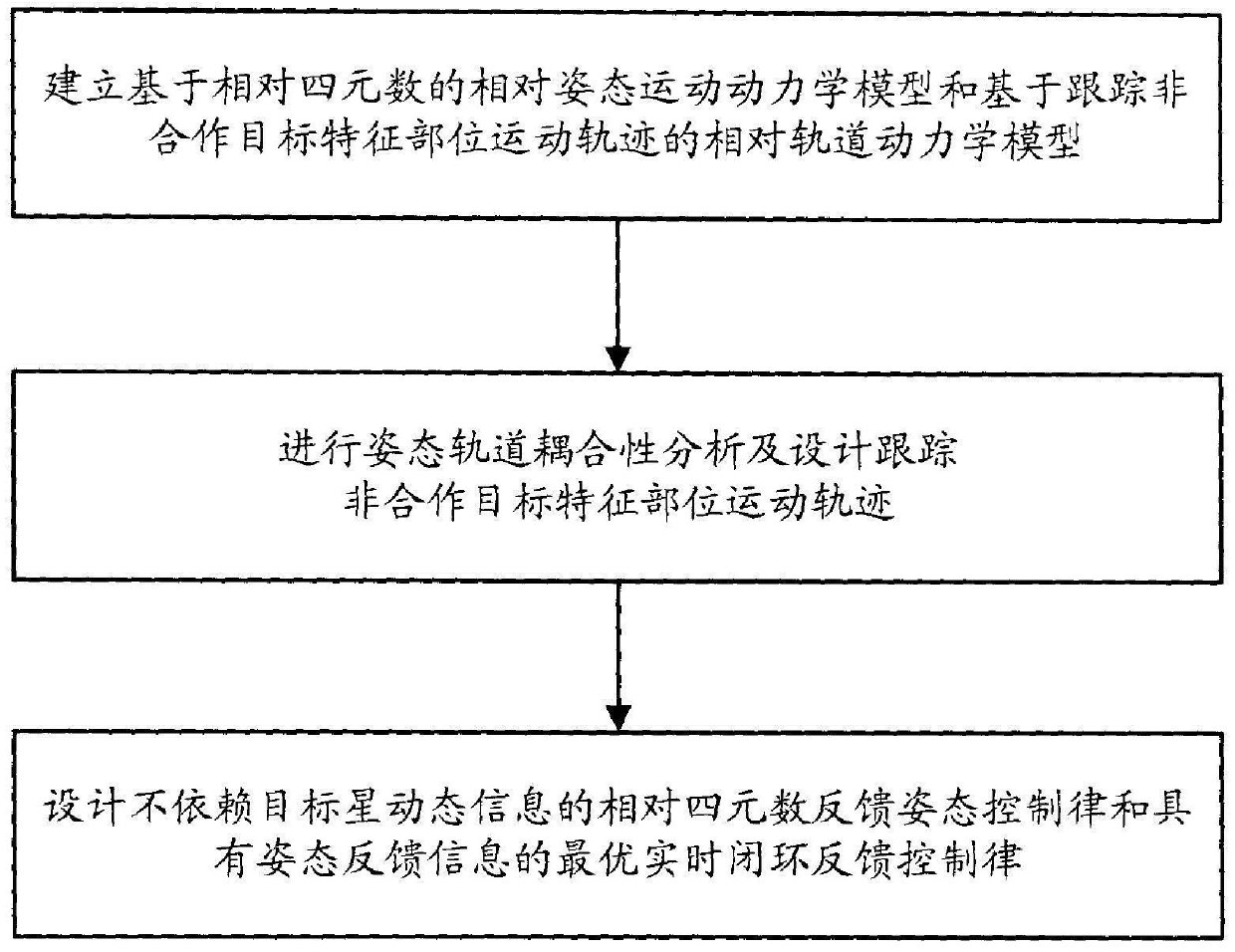
An attitude-orbit coupling control method for tracking the characteristic parts of non-cooperative targets
ActiveCN107529389BImprove control accuracyImprove robustnessSpacecraft guiding apparatusPosition/course control in three dimensionsRelative orbitDynamic models
The invention provides an attitude-orbit coupling control method for tracking the characteristic parts of non-cooperative targets. The steps include: establishing a relative attitude motion dynamics model based on relative quaternions and a relative orbital dynamics based on tracking the motion trajectory of the characteristic parts of non-cooperative targets Model; conduct attitude-orbit coupling analysis and design and track the trajectory of non-cooperative target feature parts; design a relative quaternion feedback attitude control law that does not depend on the dynamic information of the target star and an optimal real-time closed-loop feedback control law with attitude feedback information. The attitude-orbit coupling control method does not need the dynamic information of the target spacecraft, which is in line with the characteristics of non-cooperative targets; it is suitable for the target spacecraft in a three-axis stable state or a slow rotation state; it can enable the tracking spacecraft to track the characteristic parts of the target spacecraft Capability, good control accuracy, robustness and safety, and easy engineering implementation, so as to carry out reliable and effective capture tasks.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINYUE METER FACTORY
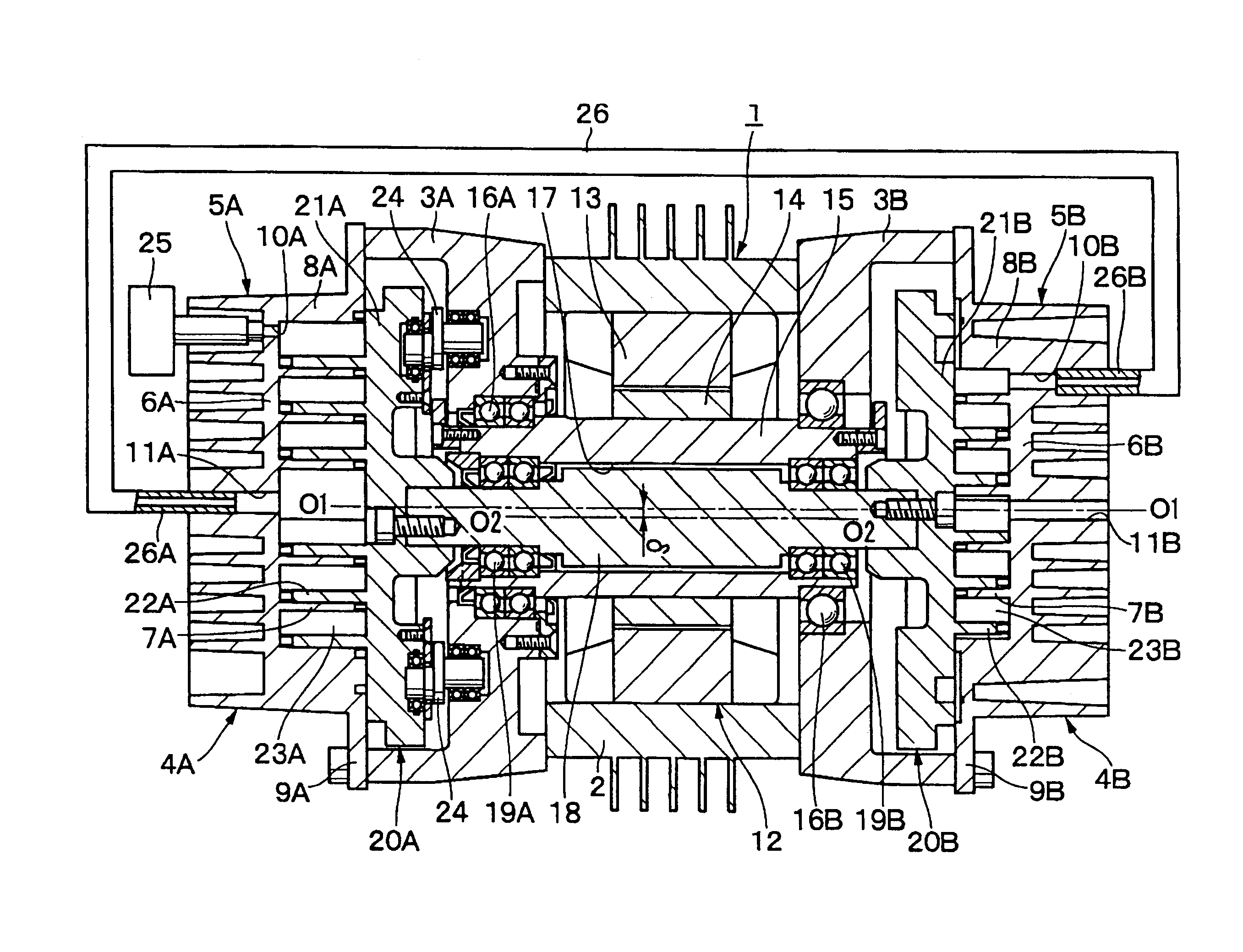
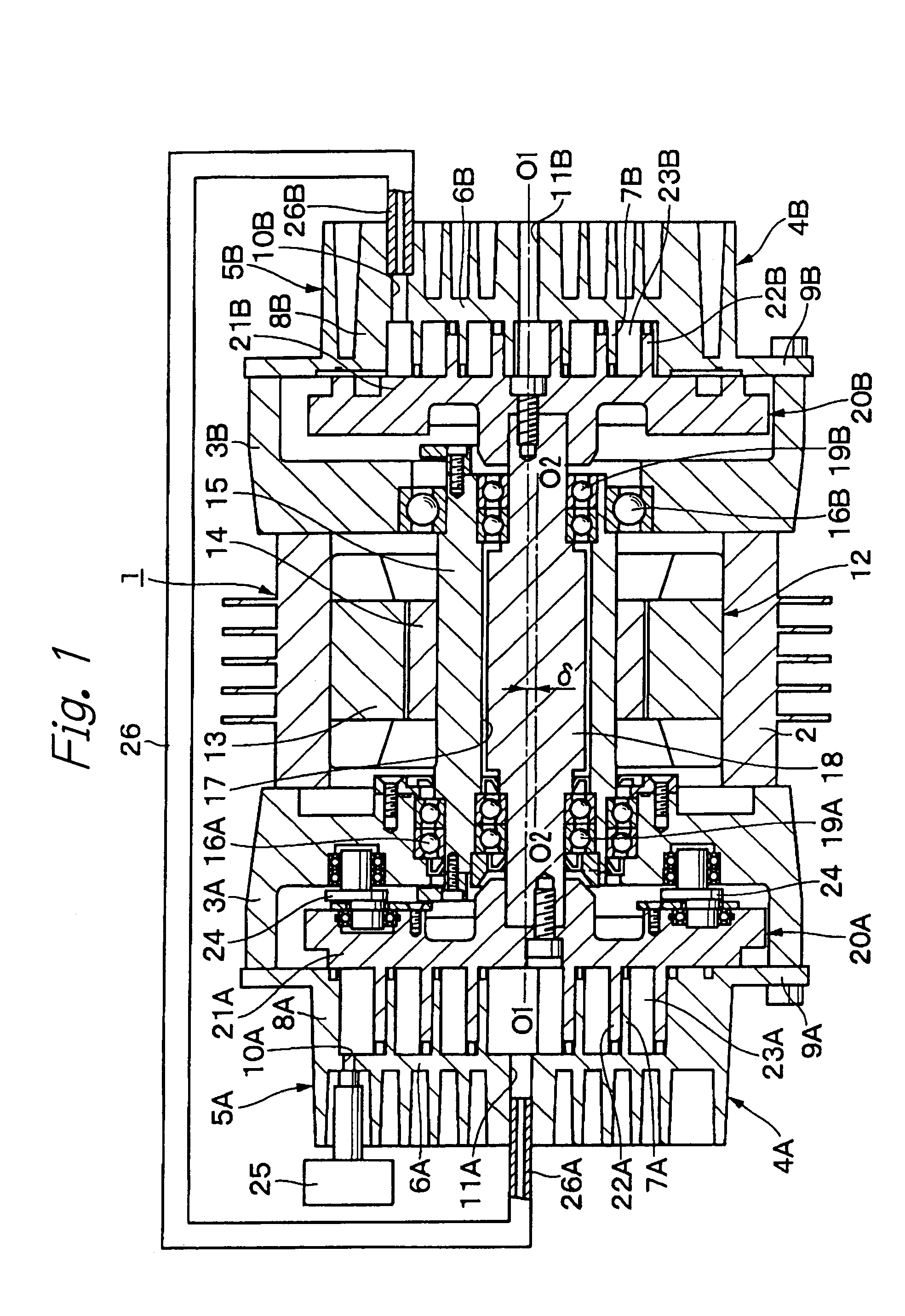
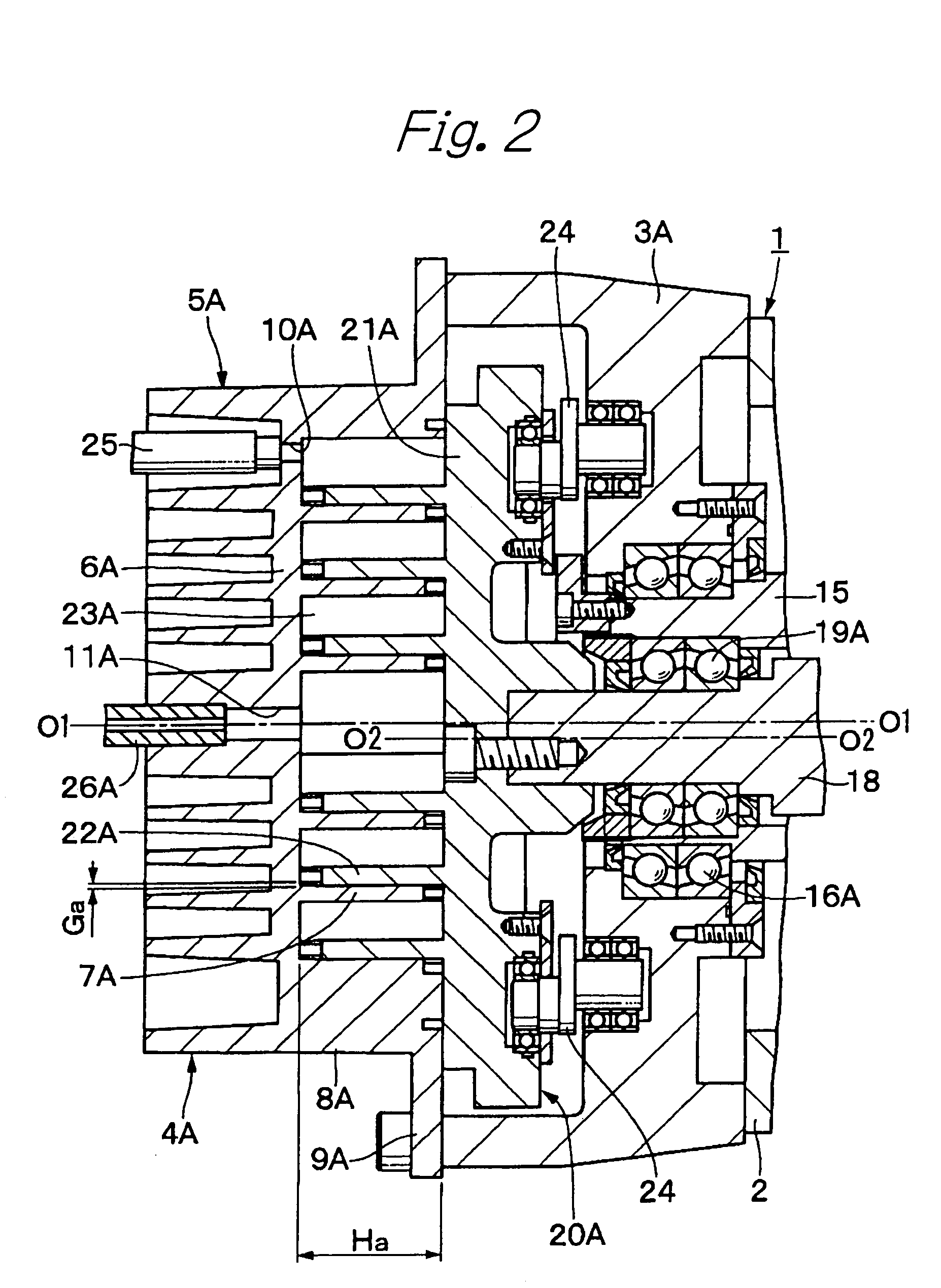
Scroll fluid machine having a coupling mechanism to allow relative orbiting movement of scrolls
InactiveUS8007260B2Reduce the required powerReduce noiseYielding couplingEngine of arcuate-engagement typeRelative orbitCoupling
A scroll fluid machine has a stationary scroll having a stationary scroll lap fixed to a scroll casing and an orbiting scroll having an orbiting scroll lap that orbits relative to the stationary scroll lap. The stationary and orbiting scrolls are connected via a coupling mechanism other than an Oldham coupling or pin crank type mechanism having sliding parts. The coupling mechanism includes plate springs that connect the stationary scroll to the orbiting scroll. The orbiting scroll lap engages with the stationary scroll lap to form a closed compression chamber.
Owner:ANEST IWATA CORP
Satellite gravity inversion method based on two-star energy interpolation principle
InactiveCN102393535AGood for error analysisClear physical meaningGravitational wave measurementRelative orbitMeasuring instrument
The invention relates to the field of interleaving techniques such as satellite geodesy, geophysics, space science and the like, and provides a satellite gravity inversion method based on a two-star energy interpolation principle. In the method, the global gravity field is accurately and rapidly inverted by introducing high-accuracy inter-satellite distance interpolation of a satellite-loaded K waveband measuring instrument into two-star relative orbits kinetic energy and further establishing a two-star energy interpolation observation equation. The method has the advantages of high satellitegravity inversion accuracy, definite physical meanings of the observation equation, contribution to error analysis of a gravity satellite system, easiness for sensing high-frequency gravity field signals and low requirement on the computer performance. The sensing accuracy of a 120-step GRACE earth gravity field can be increased substantively, so that the two-star energy interpolation principle method provided by the invention is an effective method for establishing a new generation high-accuracy and high-space-resolution global gravity field model.
Owner:INST OF GEODESY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
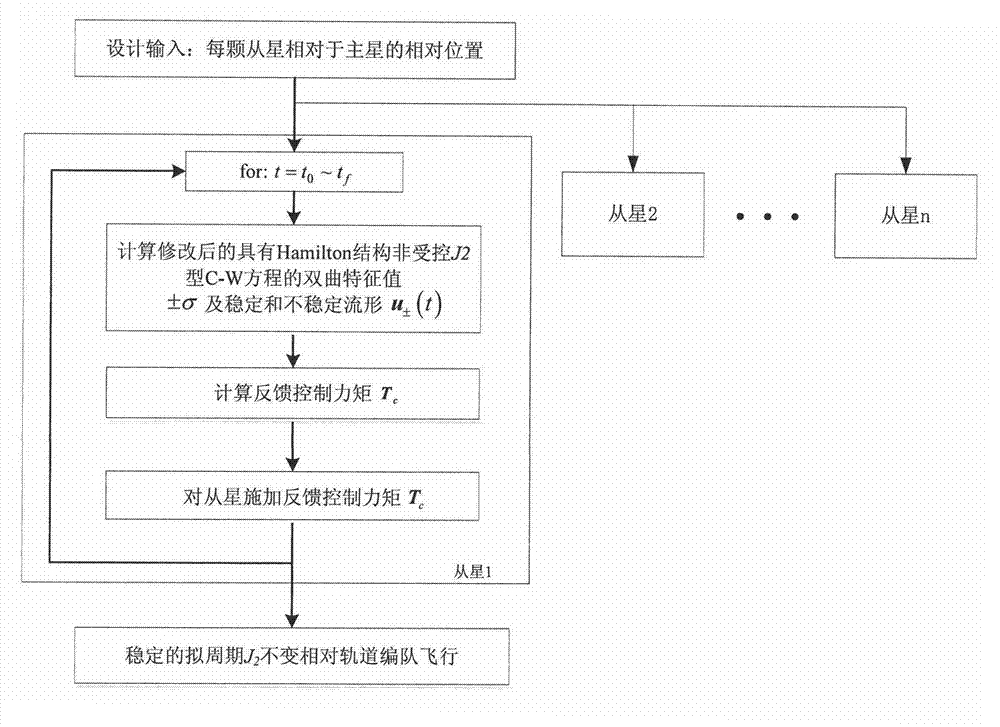
Formation flight control method of relative orbit with fixed quasi periodicity J2
ActiveCN102819266AReduce consumptionSmall control ratePosition/course control in three dimensionsRelative orbitInitial rate
The invention discloses a formation flight control method of a relative orbit with fixed quasi periodicity J2. The method comprises the steps of: taking a satellite flying on a nominal orbit in a formation flight satellite as a reference layer; exerting control torque Tc on the satellite which does not fly on the nominal orbit in the formation flight satellite to adjust; as for each moment, after giving an initial value of a relative position, calculating a hyperbolic characteristic value with Hamiltonian structure non-controlled J2-type C-W equation and stable and unstable manifolds; and selecting proper control gain, and finally calculating a feedback control torque Tc. According to the method, the control law is obtained on the basis of a more accurate model; just relative position feedback information between two satellites is required; no constraint is generated on the initial value of the relative position, the calculated quantity is small, the fuel consumption is low and a project is easy to realize.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
Spatial non-cooperation target autonomous visual line rendezvous no-model preset performance control method
ActiveCN106970530AImprove securityStrong engineering application valueAdaptive controlRelative orbitSimulation
The invention discloses a spatial non-cooperation target autonomous visual line rendezvous no-model preset performance control method, and the method comprises the following steps: 1), building a non-cooperation target autonomous visual line rendezvous relative orbit motion model in a visual line coordinate system; 2), defining a relative orbit control state quantity, and converting the relative orbit motion model into an affine form; 3), taking the exponential convergence speed, overshoot and steady-state error boundary as the constraints, and building a preset performance boundary function; 4), designing a relative orbit no-model preset performance controller; 5), designing a relative posture no-model preset performance controller. The method achieves the autonomous rendezvous control of a non-cooperation target with spinning and unknown maneuver. The method can achieve the high-precision and high-robustness autonomous rendezvous control of the non-cooperation target without the specific parameters of the model, and is higher in theoretical significance and engineering application value. In addition, the method greatly improves the safety of a rendezvous task of the non-cooperation target.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
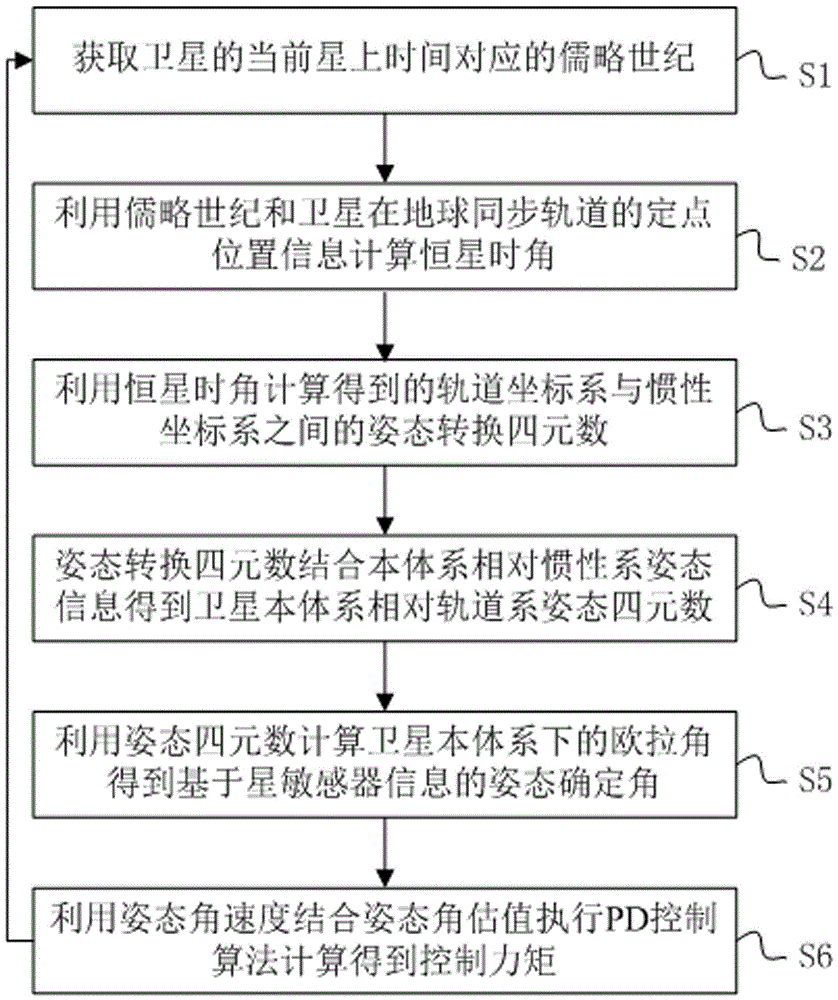
Sidereal hour angle based attitude control method and system
ActiveCN106292677AAchieve self-managementImprove reliabilityCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsRelative orbitNatural satellite
The invention discloses a sidereal hour angle based attitude control method. The method comprises S1) a Julian century corresponding to present onboard time of a satellite is obtained; S2) a sidereal hour angle is calculated; S3) an attitude conversion quaternion between a track coordinate system and an inertia coordinate system is obtained by calculation; S4) an attitude quaternion, relative to a track system, of a satellite body system is obtained by calculation; S5) an Euler angle of the satellite body system in a pitching-rolling-yawing turn order is calculated, and an attitude determining angle based on star sensor information is obtained; S6) a PD control algorithm is executed, and a control moment is obtained by calculation; and the steps S1) to S6) are repeated to realize autonomous continuous navigation and attitude control of the satellite. According to the invention, autonomous navigation and attitude control for the aircraft position are carried out only by calculating the sidereal hour angle, the problem that ground or GNSS measuring track information cannot be obtained in an abnormal state is solved, autonomous management of the satellite is realized, and the reliability and survival capability of the satellite are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Spatial non-cooperative target autonomous relative navigation in-orbit validation system based on image information
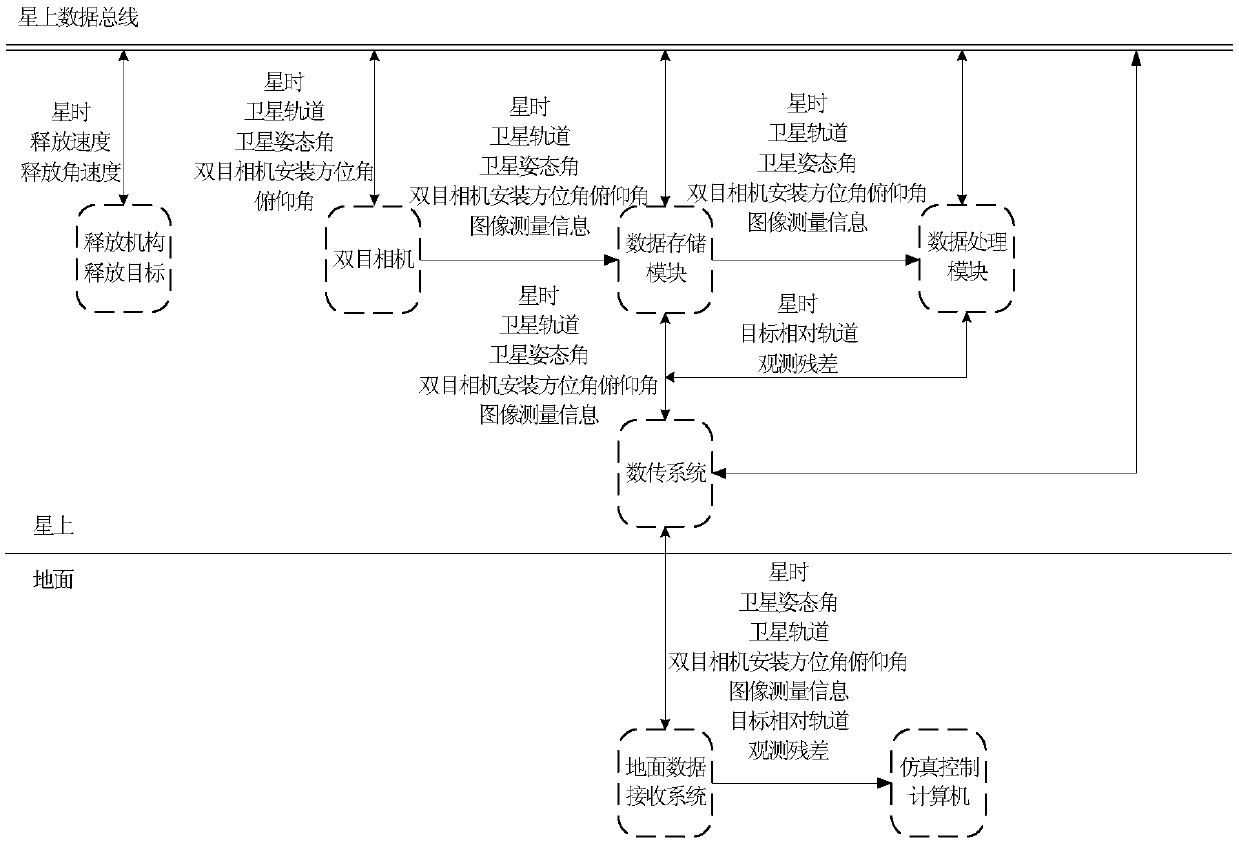
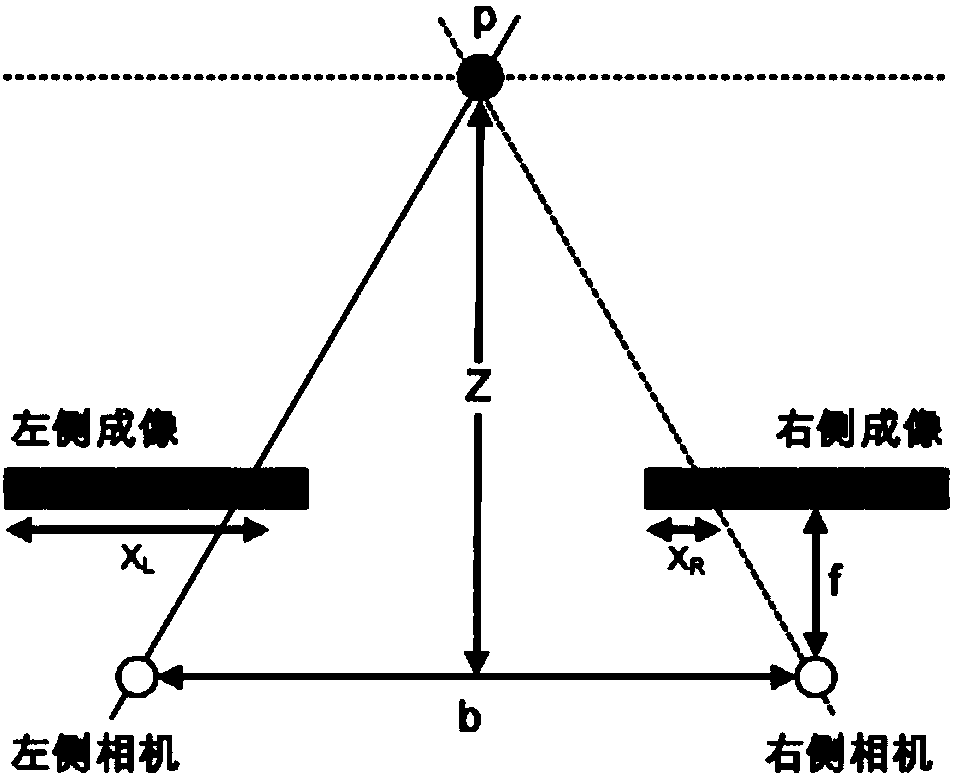
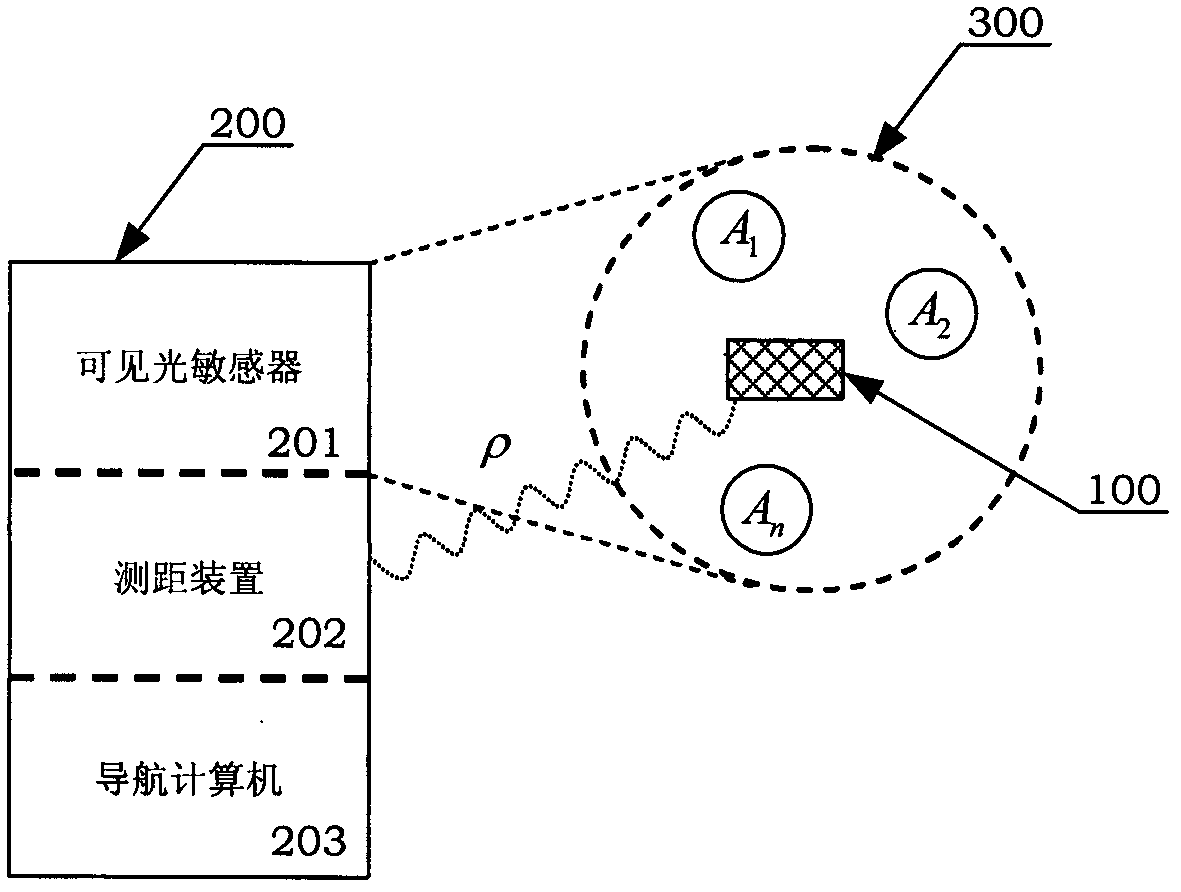
ActiveCN108519110AFix implementation issuesFully and effectively completedMeasurement devicesRelative orbitOn board
A spatial non-cooperative target autonomous relative navigation in-orbit validation system based on image information is disclosed. A target release mechanism receives an instruction from an on-boarddata bus to release a space-borne target, and the space-borne target has spatial non-cooperative target characteristics and enters the measurement range of a binocular camera; the binocular camera carries out stereoimaging and transmits sidereal time, satellite orbit, satellite attitude angle, binocular camera installation azimuth and pitch angle information to a data memory module; a data processing module carries out autonomous relative navigation calculation in real time, and calculated corresponding sidereal time and calculation results are sent to a ground data receiving system through adata transmission system; and the ground data receiving system stores the received data and carries out relative navigation calculation to obtain relative orbit and observation residual error of the non-cooperative target, and the calculation results are compared with the calculation results downloaded by the data transmission system so as to validate the on-board autonomous relative navigation.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
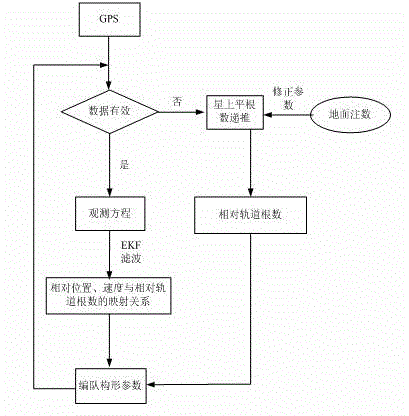
Mean orbit element-based relative navigation robust filtering method
ActiveCN105737834AGuaranteed filtering effectGuaranteed accuracyInstruments for comonautical navigationRelative orbitKinematics
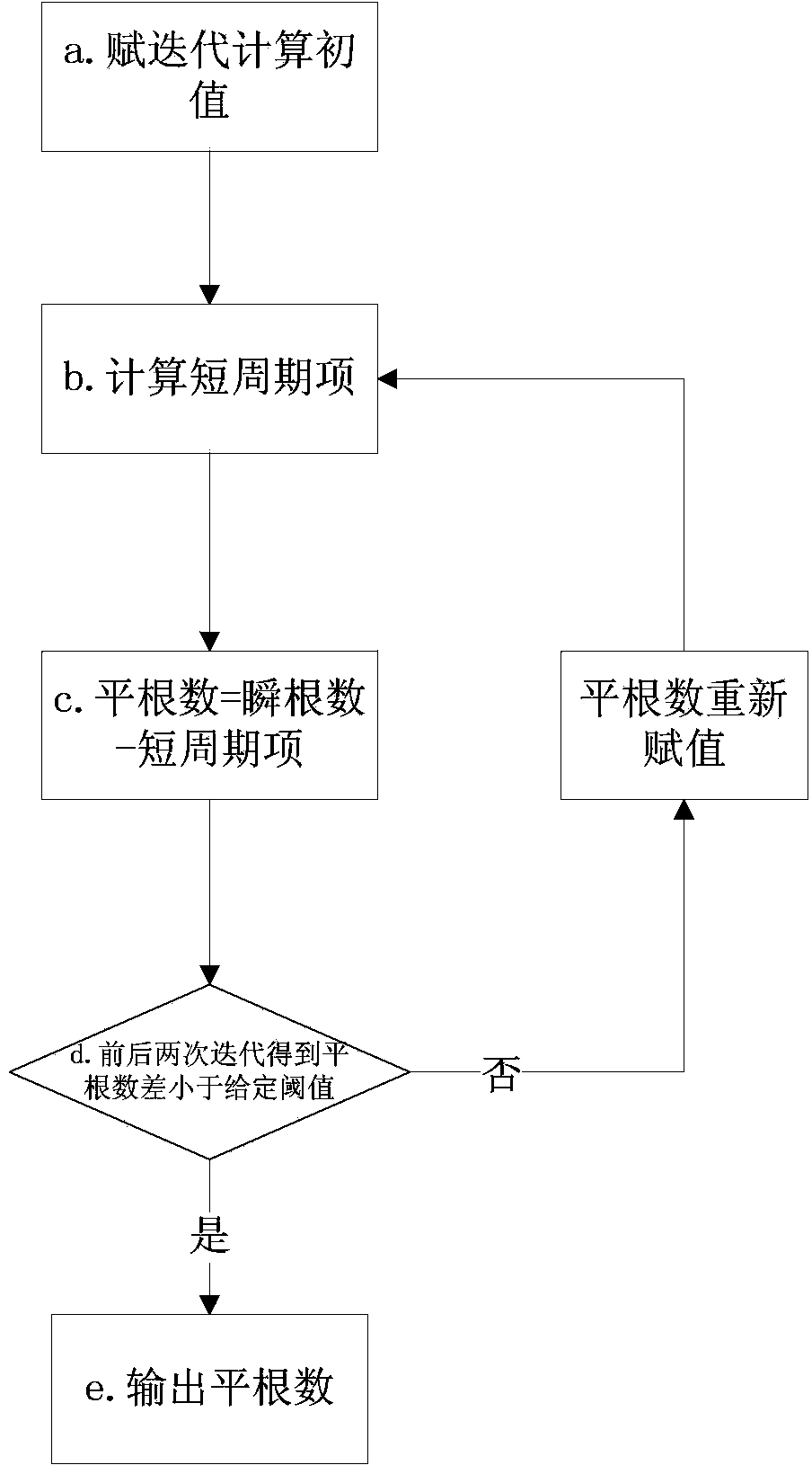
The invention discloses a mean orbit element-based relative navigation robust filtering method. The method comprises the following steps: 1, deriving a relative navigation state equation according to relative kinematics of formation flying satellites, measuring the intersatellite real-time relative positions and speeds through using CDGPS, and filtering measured data through an EKF algorithm to obtain a relative mean orbit element; 2, outputting formation configuration parameters after filtering is stable; and 3, carrying out prediction and recursion according to a relationship among the relative positions, the relative speeds and the configuration parameters in order to obtain intersatellite relative positions.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINYUE METER FACTORY
Space multi-robot autonomous navigation method for geostationary orbit target action
ActiveCN106595673ASolve the problem of only passive observationImprove continuous observation efficiencyNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationRelative orbitImaging condition
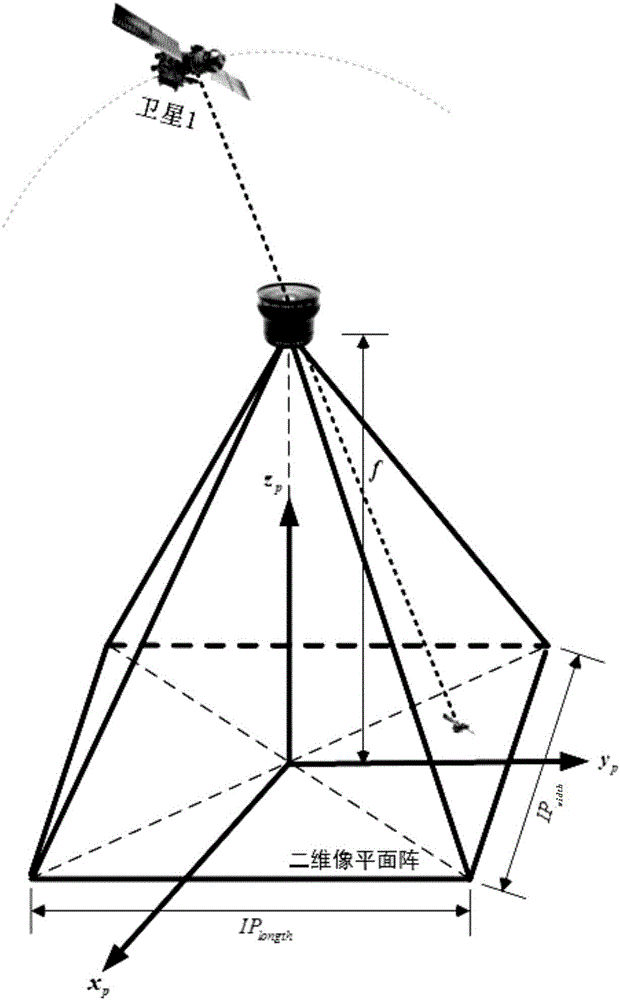
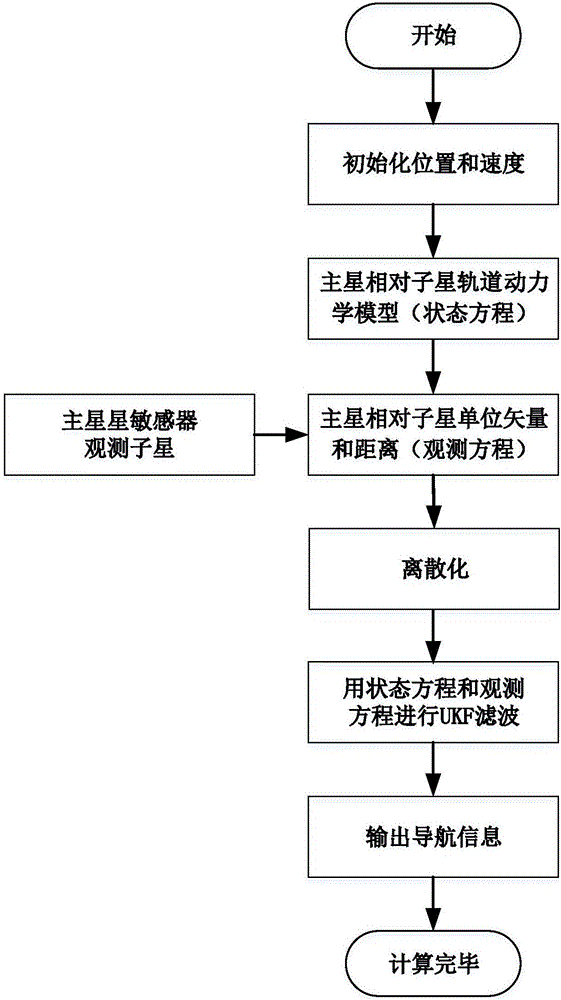
The invention discloses a space multi-robot autonomous navigation method for geostationary orbit target action. The method comprises the following steps: designing the formation flight configuration and the orbit parameters of two space robots (set as a primary star and a component star) by adopting a GEO target satellite as an on-orbit service target, and establishing an autonomous navigation system state model according to a relative orbit dynamic model of the satellite in an earth's core inertia coordinate system; providing theoretic illumination conditions and imaging conditions needed by observation of the component star by a primary star sensor; calculating the theoretic azimuth and the theoretic pitch angle of the component star to the primary star, adjusting the direction of a true star sensor optical axis to be consistent with a theoretic direction, truly observing the component star, and establishing an observation equation adopting relative unit direction vector and distance as observations; and establishing the relative position and speed of the primary star by using Unscented Kalman filtering. The method belongs to the technical field of space navigation, provides high-precision navigation information for GEO formation flight of the satellite, and provides references for design of an autonomous navigation system.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
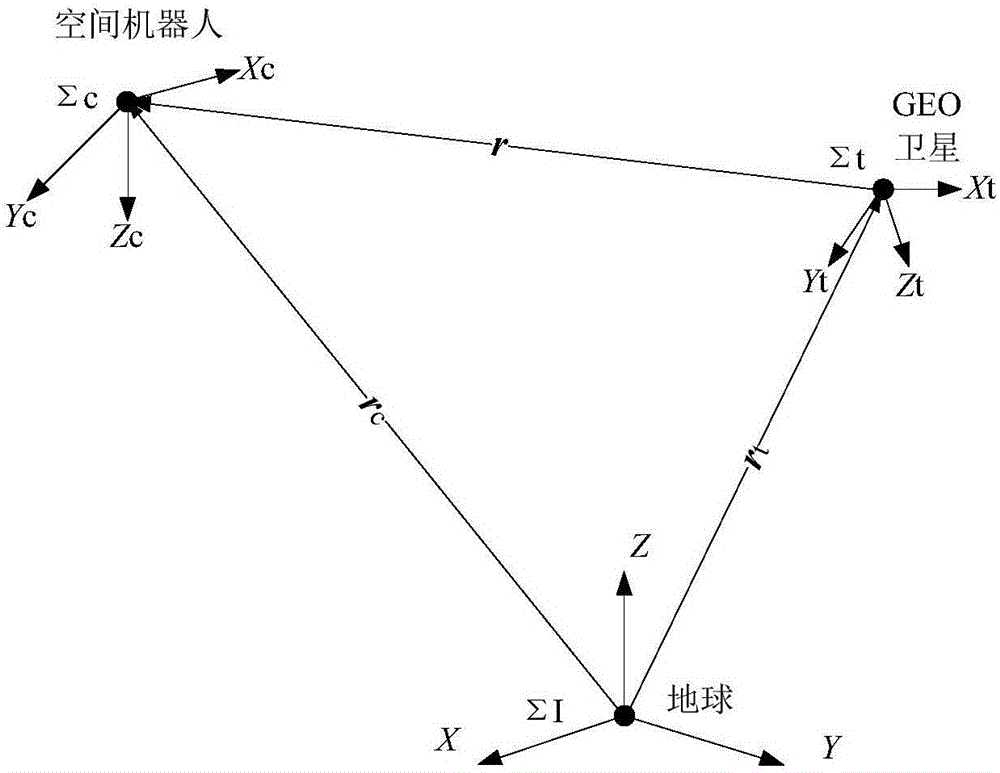
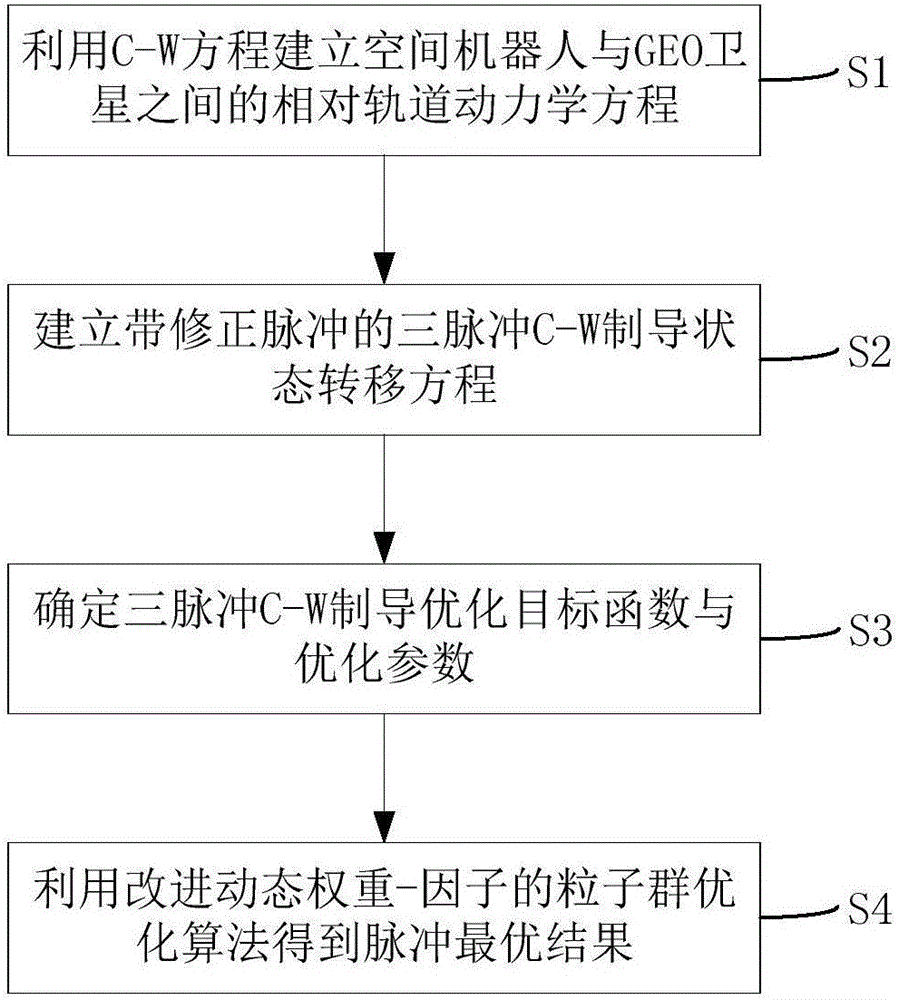
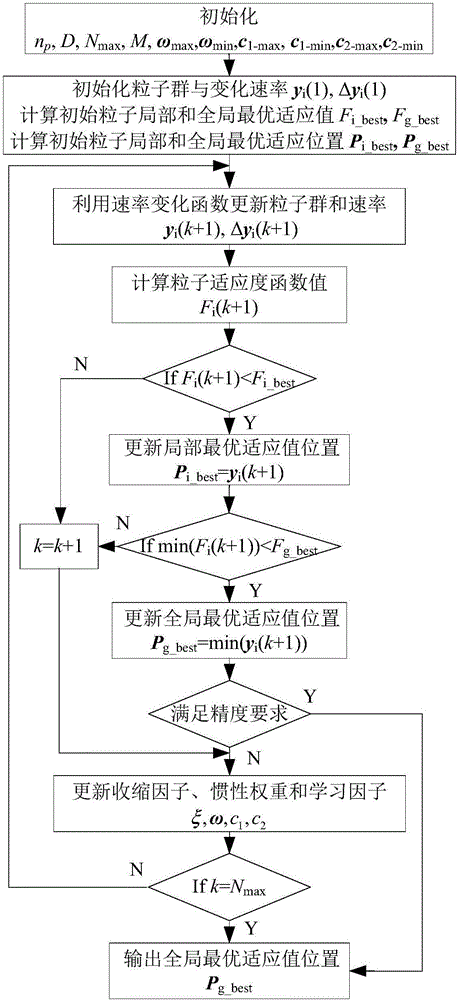
Three-pulse intersection approaching guidance method
ActiveCN105930305AImprove final position accuracyImprove search capabilitiesComplex mathematical operationsRelative orbitEngineering
The invention discloses a three-pulse intersection approaching guidance method. The method comprises following steps: a relative orbit kinetic equation between a space robot and a GEO satellite is established by means of the C-W equation; a three-pulse C-W guidance status transition equation with revised pulses is established by means of the relative orbit kinetic equation; an optimized objective function for minimum fuel consumption and guidance precision is established according to the status transition equation, the pulse size, direction and time are determined as optimizing parameters; optimized results are obtained according to the optimized objective function. According to the three-pulse intersection approaching guidance method, a revised pulse is added between an inceptive pulse and a final pulse approaching the intersection for increasing guidance precision.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
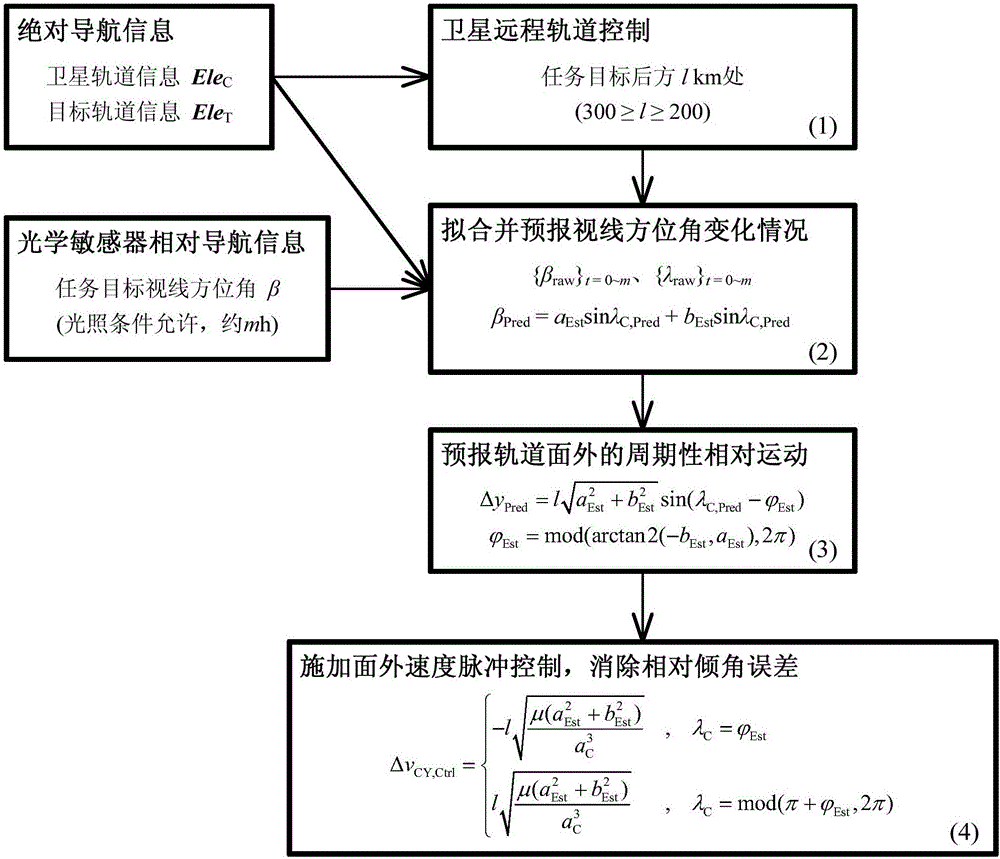
Synchronous orbit satellite relative dip angle remote correcting method based on line-of-sight measurement
ActiveCN106564622ACircumventing Observability ShortcomingsArtificial satellitesSpacecraft guiding apparatusRelative orbitRelative motion
The invention discloses a synchronous orbit satellite relative dip angle remote correcting method based on line-of-sight measurement. The method comprises the following steps: at first, carrying out remote orbit control on a synchronous orbit satellite through absolute navigation information provided by a ground measurement and control system, and directing the synchronous orbit satellite to a remote mooring point in the rear of a task object; then, through relative navigation information of an optical sensor and the absolute navigation information provided by the ground measurement and control system, and in combination with typical motion features of the relative orbit of a spacecraft, adopting the Least Squares method to fit and forecast variation of a line-of-sight azimuth angle; further, forecasting the periodic relative motion outside an orbital plane between the satellite and task object in combination with the nominal distance at the mooring point; and finally, carrying out velocity pulse control outside of the orbital plane on the operating satellite at the mooring point to eliminate relative position error outside of the orbital plane caused by the relative dip angle to avoid the situation that the task object is lost because the task object is beyond the field of view of the optical sensor, so that the satellite can rapidly and accurately approach the task object.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
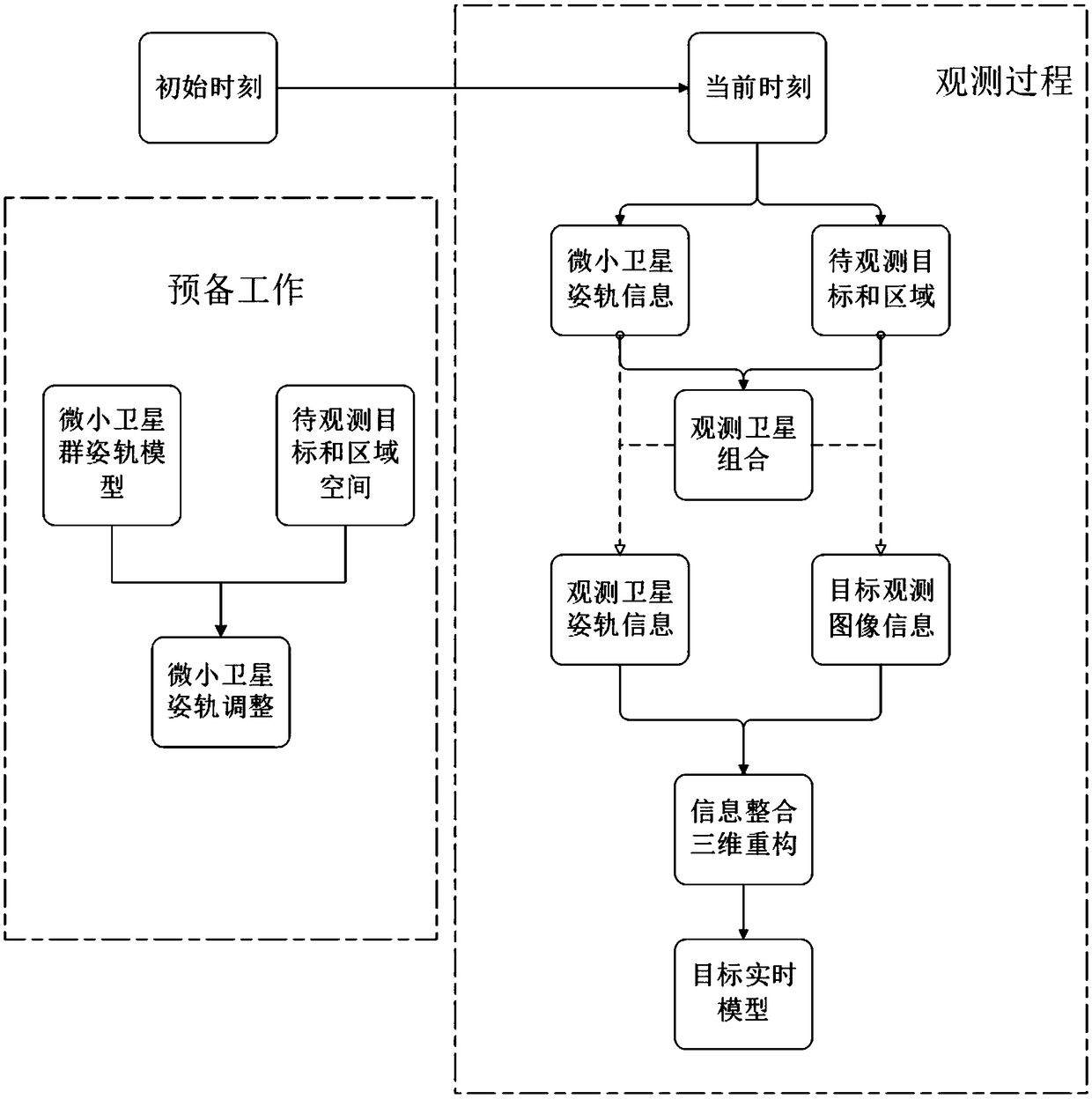
A method for acquiring three-dimensional image information of an object based on a micro satellite constellation
The invention discloses a method for obtaining three-dimensional image information of an object based on a micro satellite group, which comprises the following steps: step S1, each micro satellite inthe micro satellite group carries out observation work according to a preset working time sequence, and obtains image information of the object; step S2, a satellite observation combination is obtained according to the relative orbit and attitude relationship between the observation area of the micro satellite and the target; step S3, each satellite observation combination obtains the image information of the target, and constructs the three-dimensional image information of the target, and constructs the real-time model of the target in the space environment. By synthesizing the images acquired by a large number of micro-satellites, analyzing and integrating the image information about the target and its space, the corresponding three-dimensional model of the target and space environment is constructed, which overcomes the shortcoming of limited and useless image information acquired by single micro-satellite.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
A trajectory optimization method for spacecraft relative orbit transfer based on time-fuel optimal control
The invention provides an optimization method of a relative orbit transfer path of a spacecraft based on time-fuel optimum control and relates to the optimization method of the relative orbit transfer path of the spacecraft. The optimization method of the relative orbit transfer path of the spacecraft is used for solving the problem that the finite thrust amplitude is not considered in the existing method and the problem that only time optimum or only the fuel consumption is considered in the existing method when a tracking spacecraft is in a relative orbit coordinate system. The optimization method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a kinematics and dynamics model as shown in the specification of the relative orbit, and designing control quantities ux, uy and uz applied along three axes respectively; secondly, decoupling the kinematics and dynamics model of the relative orbit into three subsystems; after decoupling into three subsystems, transforming the total performance index as shown in the specification considering transfer time and fuel consumption of the tracking spacecraft into monoaxial performance index as shown in the specification of each axis, and finally obtaining the time-fuel optimal control law as shown in the specification for controlling the tracking spacecraft. The optimization method is suitable for optimizing the relative orbit transfer path of the spacecraft.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Spacecraft cluster only-ranging relative navigation method based on consistency filtering
PendingCN110186463AImplement relative orbit distribution estimationResolving Relative Orbital AmbiguityNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationRelative orbitKaiman filter
The invention discloses a spacecraft cluster only-ranging relative navigation method based on consistency filtering. According to the method, measurement sensors are not added to members of the spacecraft cluster, and related orbital maneuvers are not performed. Under the condition that the absolute orbit is unknown, only only-ranging relative navigation of the spacecraft cluster can be realized by constructing the consistency expansion Kalman filter only by relying on the lever arm effect of the communication receiver antenna which is installed to deviate from the spacecraft mass center and the geometric topological constraint between cluster members. The method comprises: performing evolution of a relative orbit by taking a relative orbit motion equation among members of a spacecraft cluster as a navigation state equation; taking relative distance information measured in a receiver TOA mode installed in a manner of deviating from the mass center of the spacecraft as a measurement quantity; introducing geometric topology information among the members of the cluster as a consistency constraint; and designing a consistency-based extended Kalman filter to finish only-ranging relativenavigation of the spacecraft cluster.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Scroll fluid machine
ActiveUS7201568B2Minimize fluid leakageLeakage of fluid can be satisfactorilyRotary/oscillating piston combinations for elastic fluidsEngine of arcuate-engagement typeRelative orbitHigh pressure
A scroll fluid machine has a low-pressure stage compression part for compressing a fluid sucked in from the outside between mutually overlapping wrap portions of two scroll members performing a relative orbiting motion and a high-pressure stage compression part for compressing the fluid sucked in from the low-pressure stage compression part between mutually overlapping wrap portions of two scroll members performing a relative orbiting motion. The scroll members in the low-pressure stage compression part have a larger radial gap between the wrap portions than that of the scroll members in the high-pressure stage compression part.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Spacecraft combination navigation method
ActiveCN106153051AEasy to implementInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsRelative orbitHorizon
The invention relates to a spacecraft combination navigation method. The problem that as drifting exists on the earth surface, the orbital parameter cannot be calculated based on the positions / speeds output based on inertial navigation for a long time is solved through satellite sensor / horizon sensor / inertia automatic astronomy combination navigation based on PI filtering. The positions and the speeds output by inertial navigation are corrected based on the earth core pointing error determined by a satellite sensor and a horizon sensor, the inertial navigation accumulative error can be restrained through the inertia / astronomy combination navigation. According to the spacecraft combination navigation method, under the abnormal situations that a satellite GNSS compatible machine becomes abnormal and ground orbital parameters are not transmitted in real time, corresponding orbital parameters are calculated through the positions / speeds output by the satellite sensor and horizon sensor inertia-astronomy combination navigation, and the posture, determined based on a satellite sensor, of a body relative orbit system can be ensured. Compared with the prior art, the spacecraft combination navigation method has the advantages that the algorithm is simple and effective and engineering achievement is easy.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
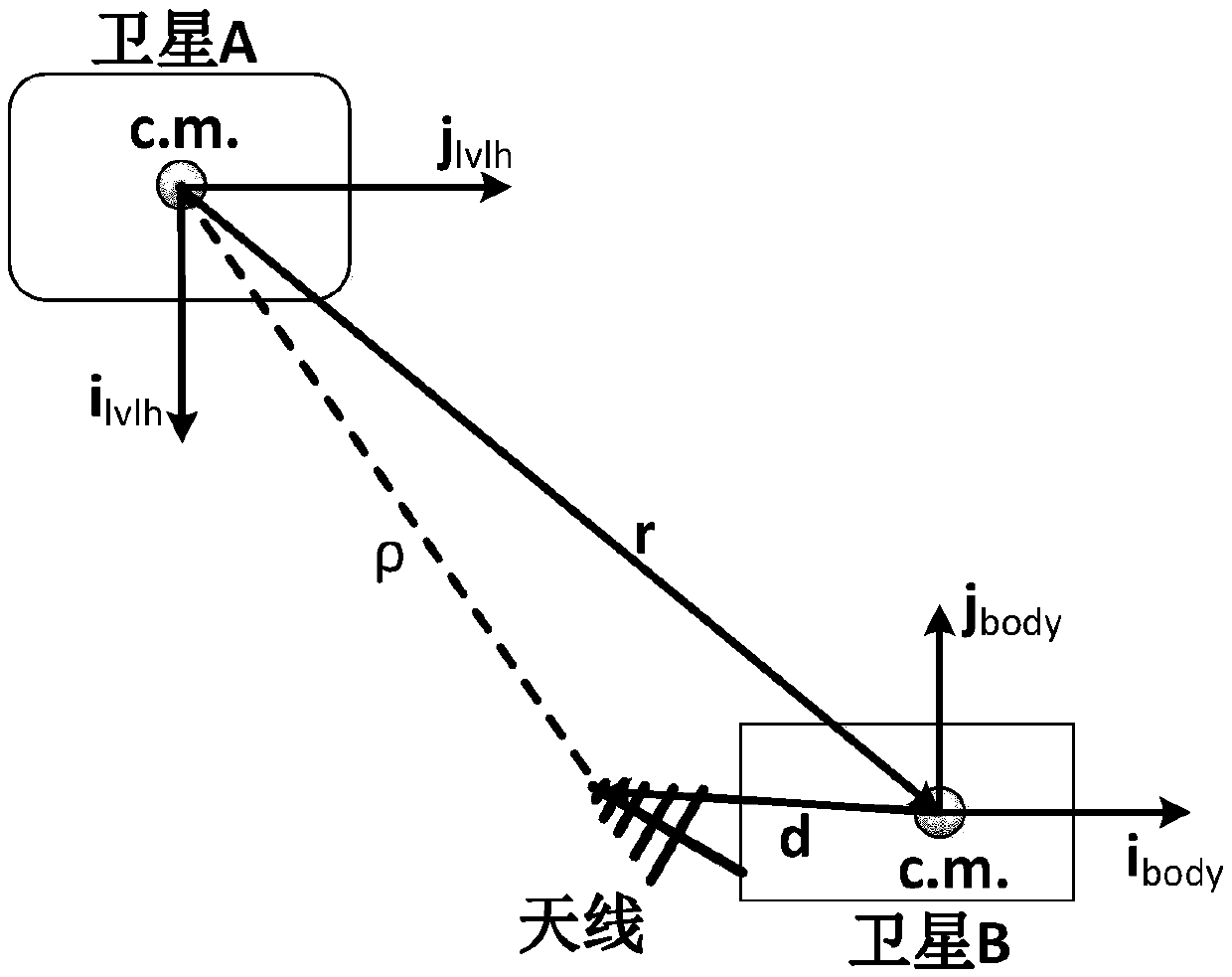
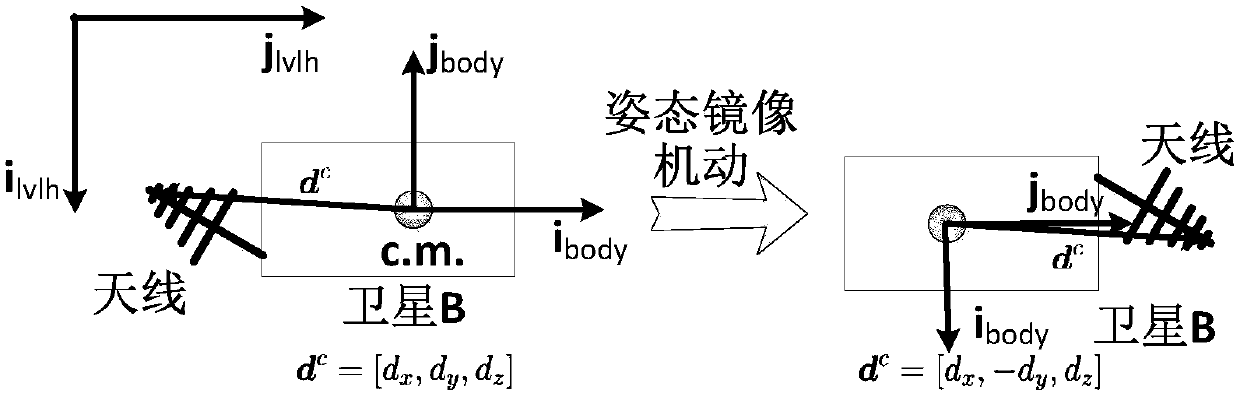
Ranging only relative navigation analysis method for double-satellite formation periodic relative motion
ActiveCN108957509AGain observabilityNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingRelative orbitEquation of the center
The invention relates to a ranging only relative navigation analysis method for double-satellite formation periodic relative motion. The analytical autonomous relative navigation of periodic relativemotion formation double satellites can be achieved only depend on off-centroid installation of an antenna receiver and an attitude mirror image maneuvering aid in the case that satellites do not perform special orbit maneuvering or a satellite-borne data link receiving antenna is not increased. A relative orbital motion equation of the double satellites in a double-satellite formation is taken asa navigational state equation to evolve a relative orbit, a relative position and a relative speed are calculated with relative distance information before and after attitude mirror image maneuveringmeasured by a satellite-borne data link antenna receiver installed in a way deviating from a satellite centroid, and the ranging only relative navigation of the periodic relative motion formation double satellites is completed. By introducing an eccentric effect of the off-centroid installation of the antenna receiver, the observable ability of a ranging only relative navigation solution is obtained, and the relative position and speed are analyzed, solved and obtained by using the attitude mirror image maneuvering aid.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Spacecraft relative orbit finite time anti-saturation control method with respect to non-cooperative target
ActiveCN105242680ASimple designDoes not require complex solution processAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsRelative orbitSystems design
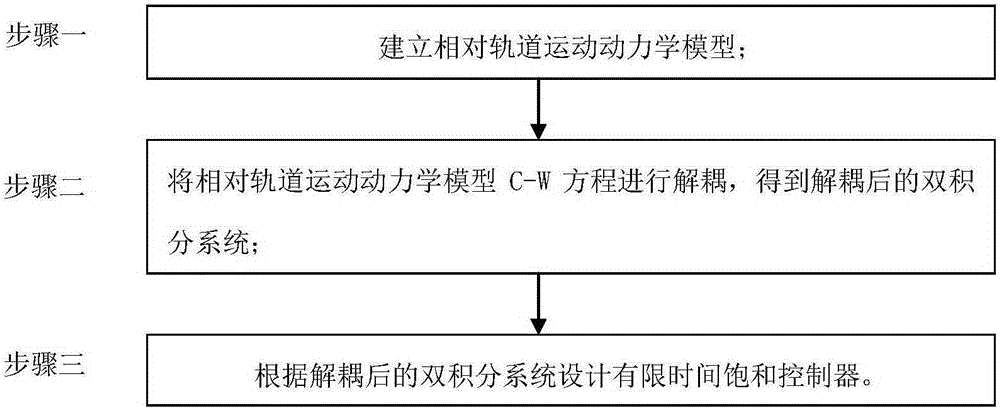
The invention relates to a spacecraft relative orbit finite time anti-saturation control method with respect to a non-cooperative target, and is to solve the problems that in an existing control scheme, the design of a controller is complex, the solving process is troublesome, system buffets due to frequent switching of the controller since sliding-mode control is adopted for the weak strain capacity for unknown factors of the spacecraft relative orbit transfer process under pulse control, and since an existing method fails to consider saturation of the controller in the practical engineering, expected value cannot be converged in the finite time and a certain limitation exists in the practical engineering application. The method comprises the following specific steps: establishing a relative orbit motion dynamics model; carrying out decoupling on a relative orbit motion dynamics model C-W equation to obtain a decoupled double-integral system; and designing a finite time saturation controller according to the decoupled double-integral system. The method is applied to the spaceflight field.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
System for performing relative navigation on spacecraft based on background astronomical information
InactiveCN102607563AReduce mistakesThe calculation process is simpleInstruments for comonautical navigationRelative orbitCelestial body
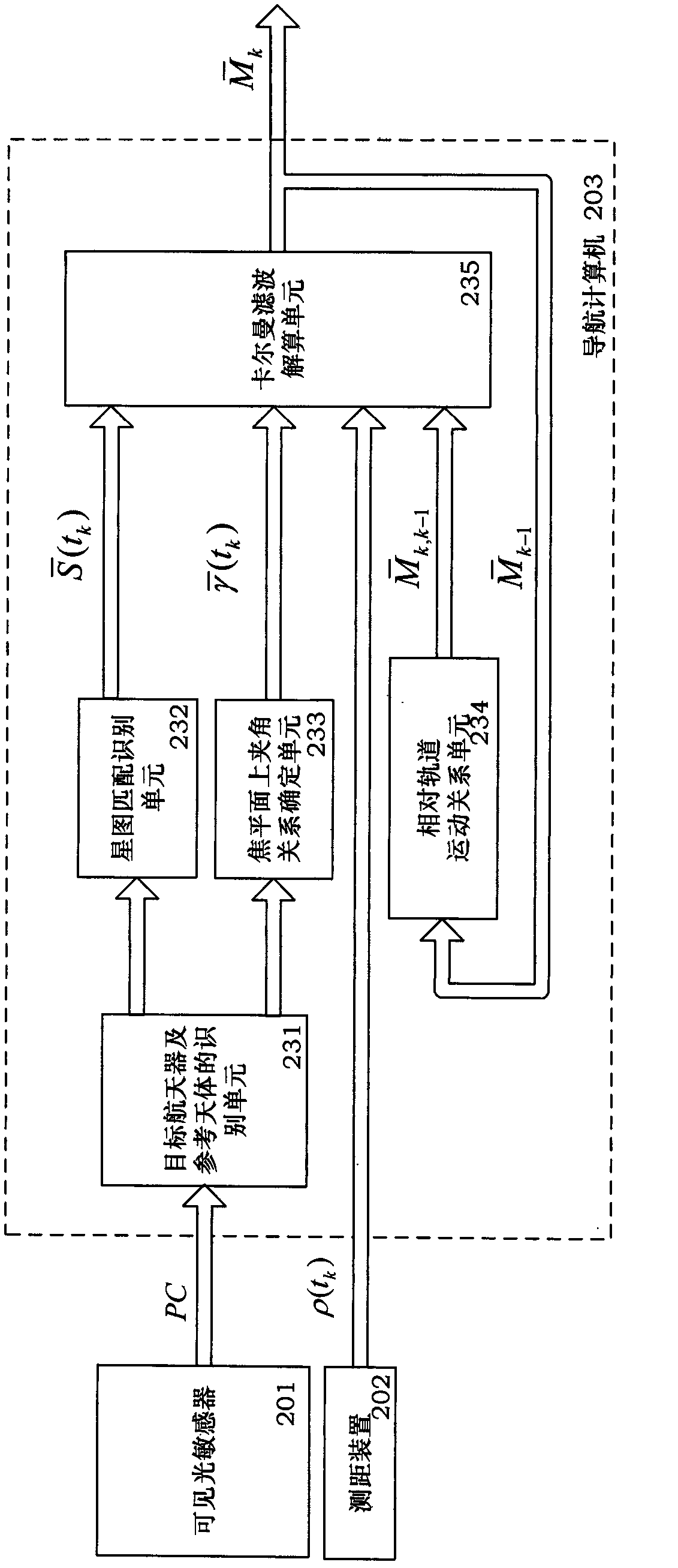
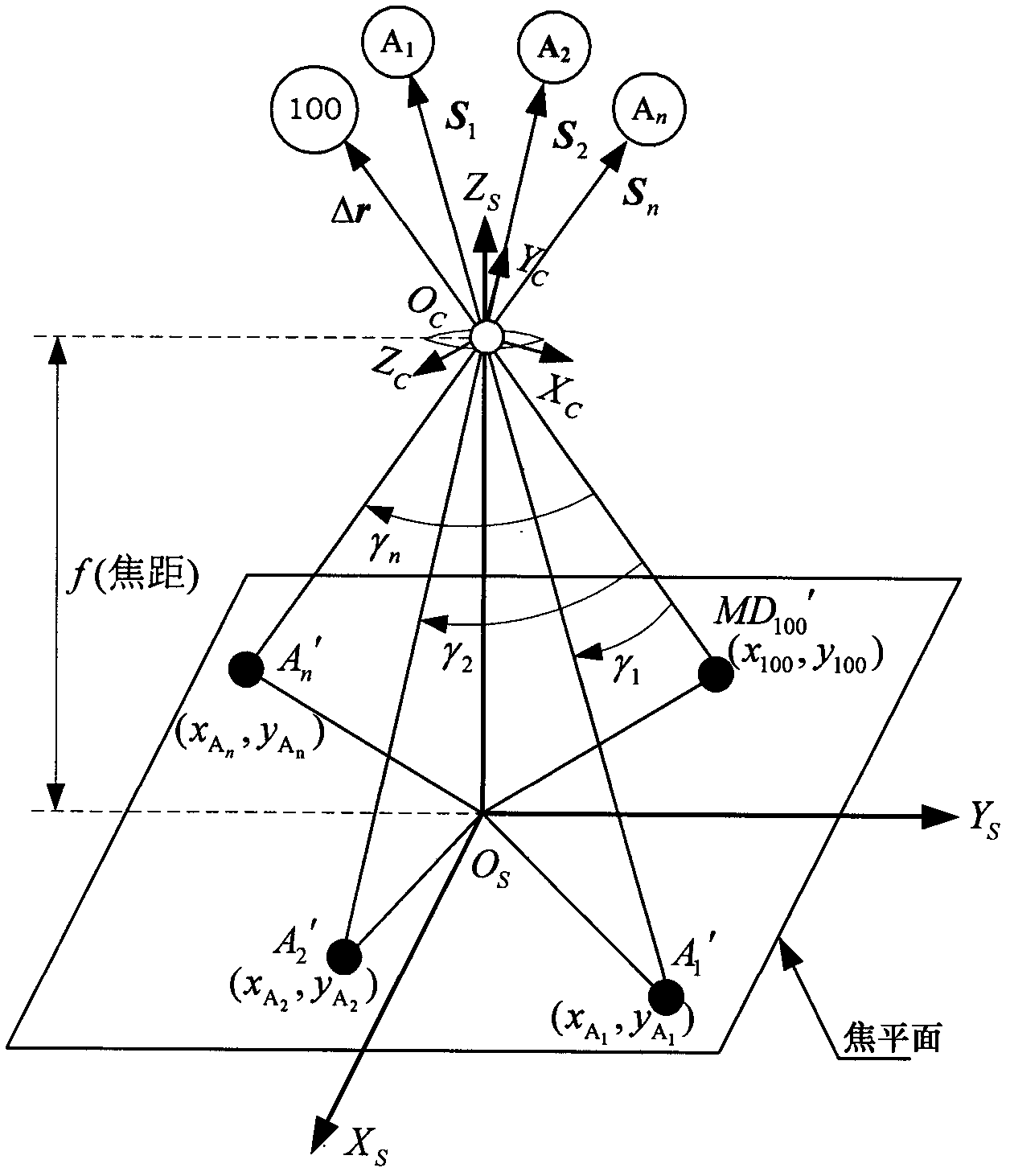
The invention discloses a system for performing relative navigation on a spacecraft based on background astronomical information. The system comprises a target spacecraft and reference celestial body recognition unit, a star map matching recognition unit, a determining unit for relationship between a focal plane and an upper included angle, a relative orbital motion relationship unit and a Kalman filtering resolving unit. The system is kept in a processor of a navigational computer. According to the system, by means of a hardware platform of a tracing spacecraft, in reference to the information of the target astronomical background and according to the distance between the target spacecraft and the tracing spacecraft, the relative motion state of the target spacecraft under the inertial frame OCXCYCZC of the tracing spacecraft is calculated by using a filtering method, and the target spacecraft is finally traced and positioned.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com