Relative orbit design and high-precision posture pointing control method aiming at space non-cooperative target
A non-cooperative target, relative orbit technology, applied in the field of relative orbit design and high-precision attitude pointing control, can solve the problems of difficult orbit control, affecting attitude pointing accuracy, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0043] Specific implementation mode one: the relative orbit design and the high-precision attitude pointing control method for space non-cooperative target spacecraft of the present embodiment, it is realized according to the following steps:
[0044] 1. The design of the skimming trajectory of the tracking spacecraft relative to the non-cooperative target spacecraft in space;
[0045] 2. The design of the transfer trajectory of the tracking spacecraft relative to the non-cooperative target spacecraft in space;
[0046] 3. The attitude controller design of the tracking spacecraft relative to the space non-cooperative target spacecraft, that is, the relative orbit design and high-precision attitude pointing control method for space non-cooperative targets have been completed.
[0047]x, y, z: position components in the relative orbital coordinate system;
[0048] the velocity component in the relative orbital coordinate system;
[0049] r 0 : The relative position of the e...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0062] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the design of the flying trajectory in the step one is specifically:
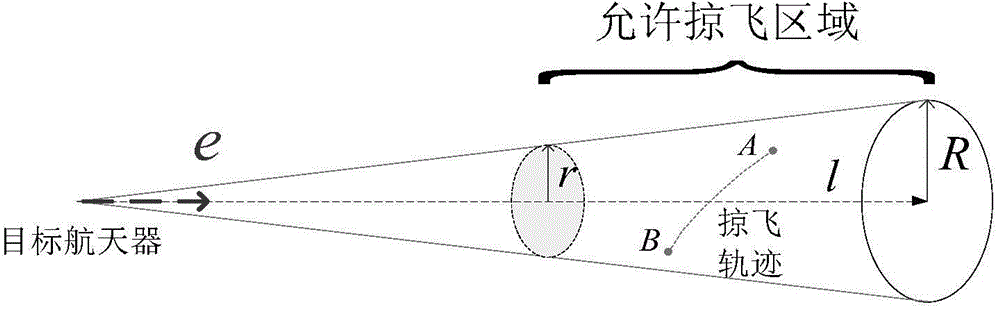
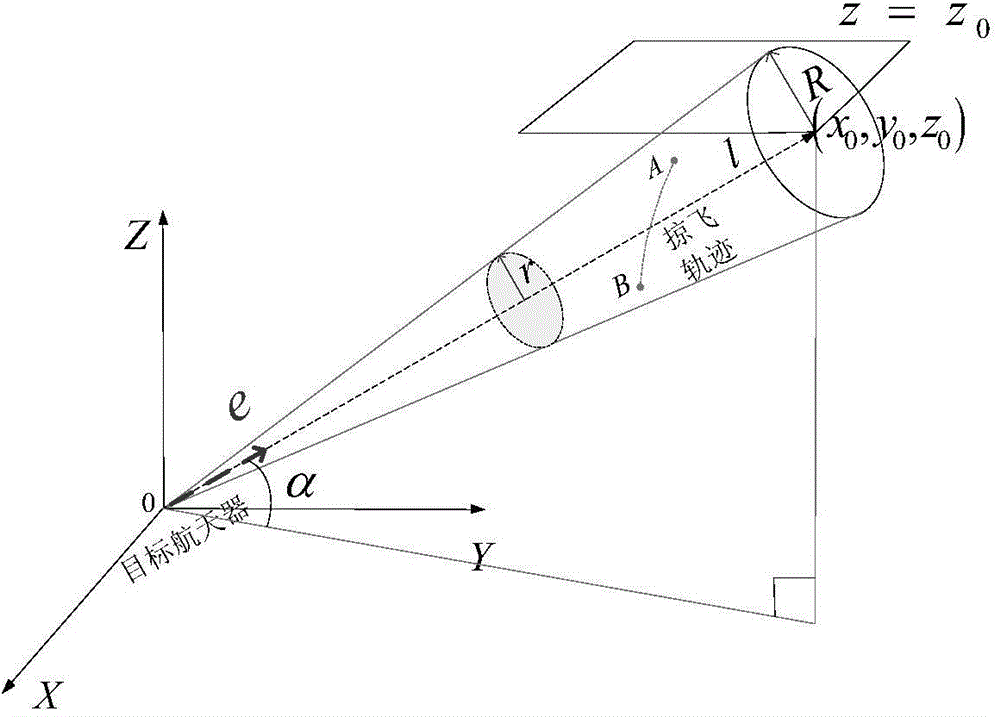
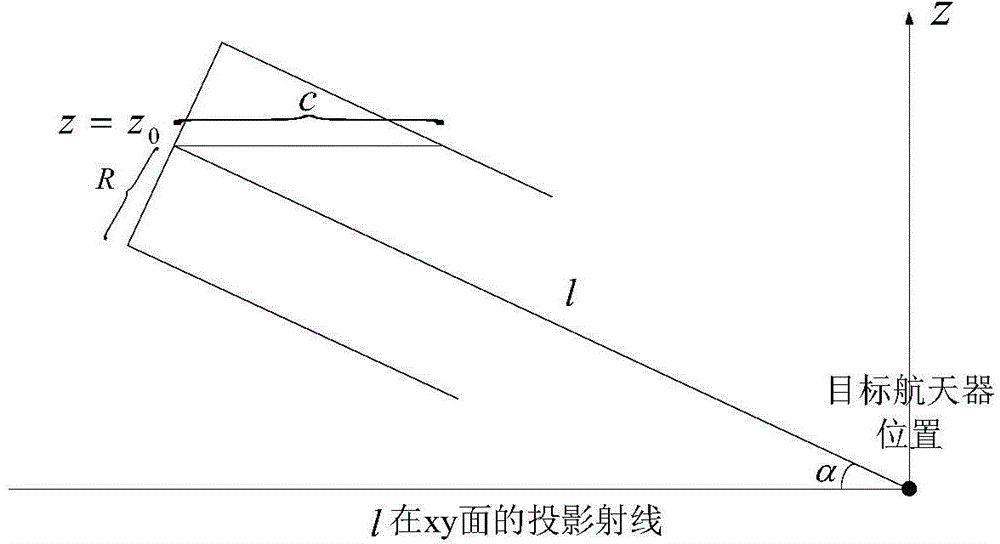
[0063] 1. Establish the relative position relationship between space non-cooperative targets and the spacecraft in the relative motion coordinate system of the Hill equation. Based on the relative motion coordinate system of the Hill equation, select the appropriate entry point A information and departure point B information of the spacecraft in the relative motion based on the Hill equation. In the motion coordinate system, such as figure 1 Shown e=[e 1 ; e 2 ; e 3 ] is the sight direction vector e of the non-cooperative target hill The unit vector of e i (i=1,2,3) is the component in the relative motion coordinate system of the hill equation; the line of sight direction e hill The range of distance between the target spacecraft and the tracking spacecraft determines the allowable skimming range of t...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0100] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is:
[0101] Orbit Transfer Optimization Algorithm
[0102] 1. Transformation of nonlinear programming problems
[0103] Assuming that there are N speed pulse points in the whole orbital transfer process (the start point and the end point are two fixed pulse points), define △t i is the time interval between the i-th speed pulse point and the i+1-th speed pulse point, t f is the total transfer time.
[0104] From the previous analysis, the following expression can be obtained:
[0105] r · ti - = Φ 21 ( Δt i ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com