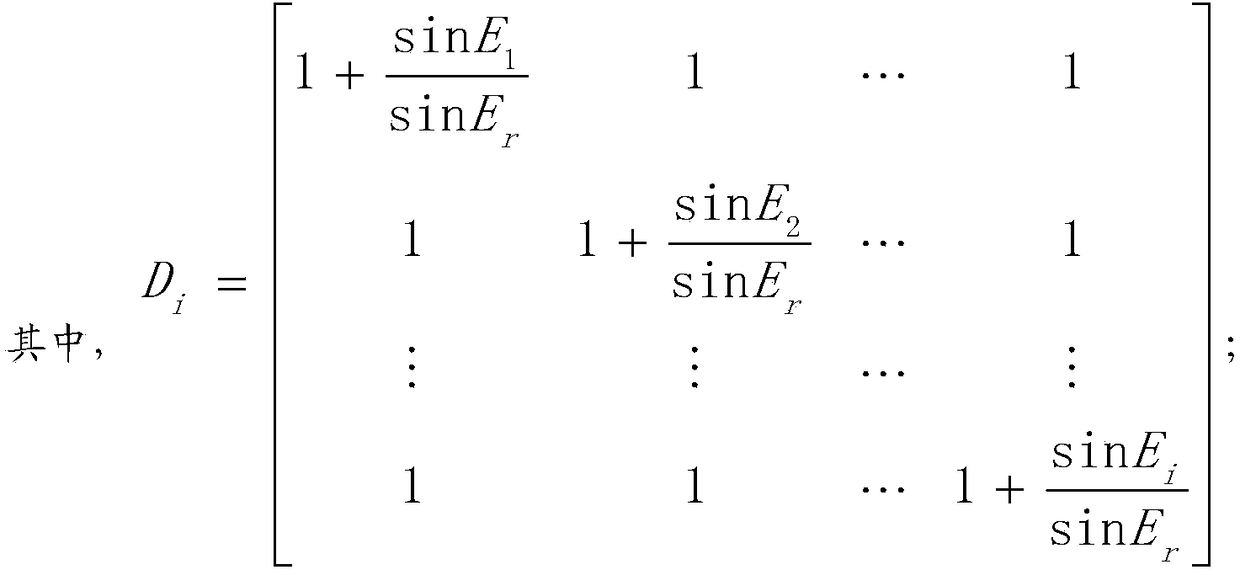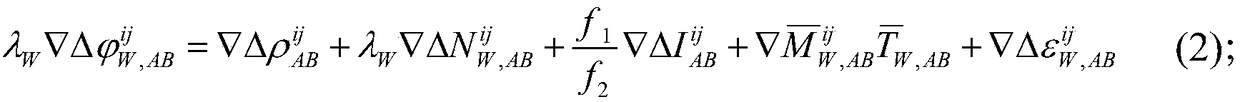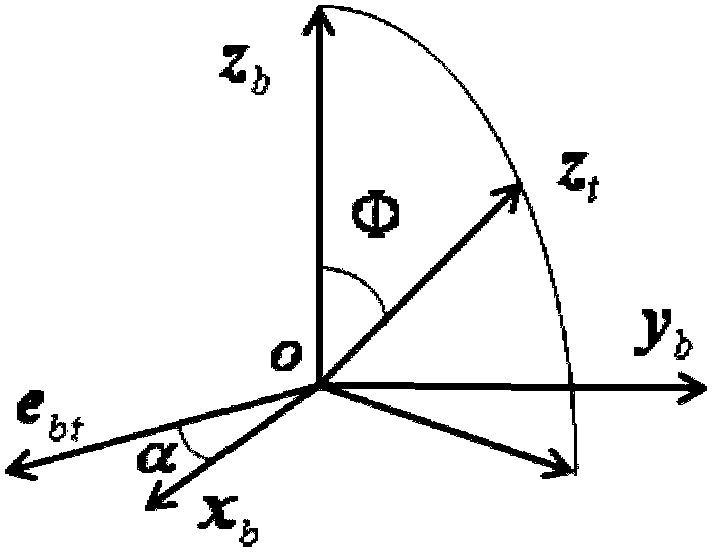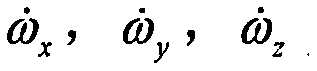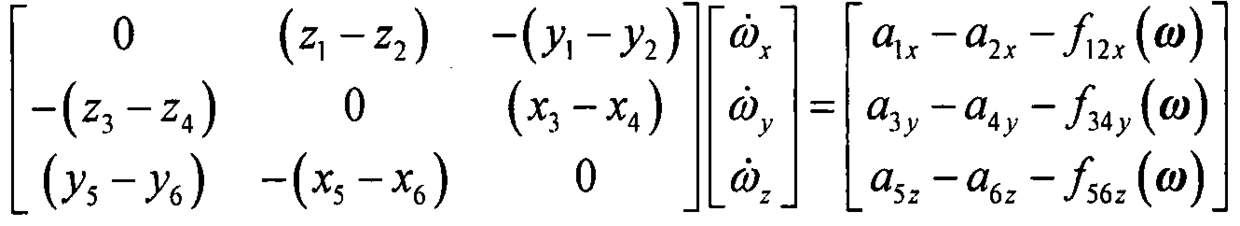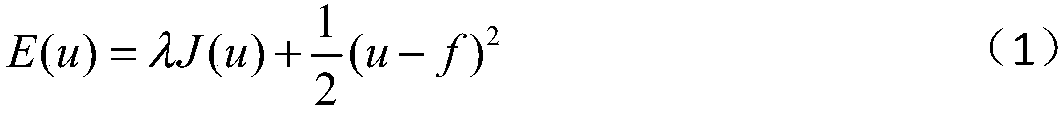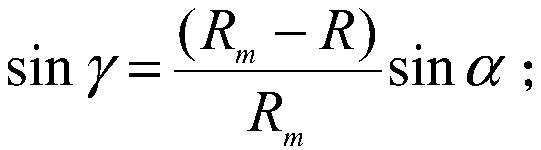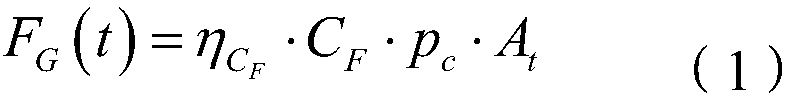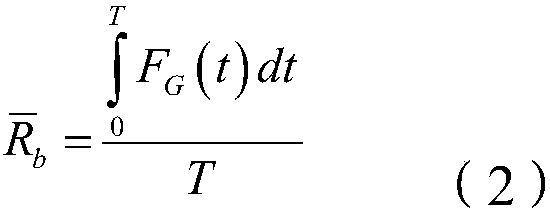Patents
Literature
125 results about "Equation of the center" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In two-body, Keplerian orbital mechanics, the equation of the center is the angular difference between the actual position of a body in its elliptical orbit and the position it would occupy if its motion were uniform, in a circular orbit of the same period. It is defined as the difference true anomaly, ν, minus mean anomaly, M, and is typically expressed a function of mean anomaly, M, and orbital eccentricity, e.
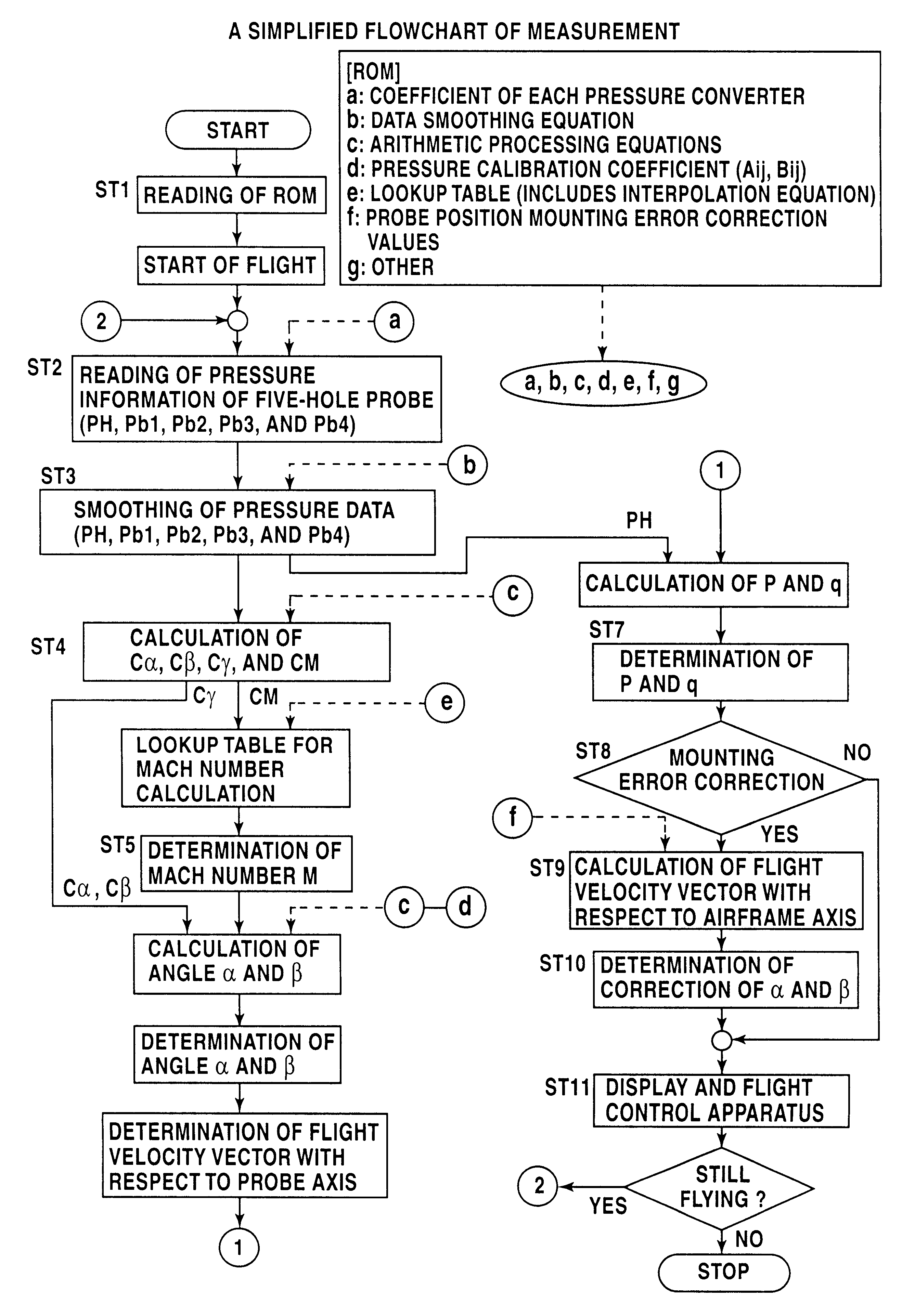
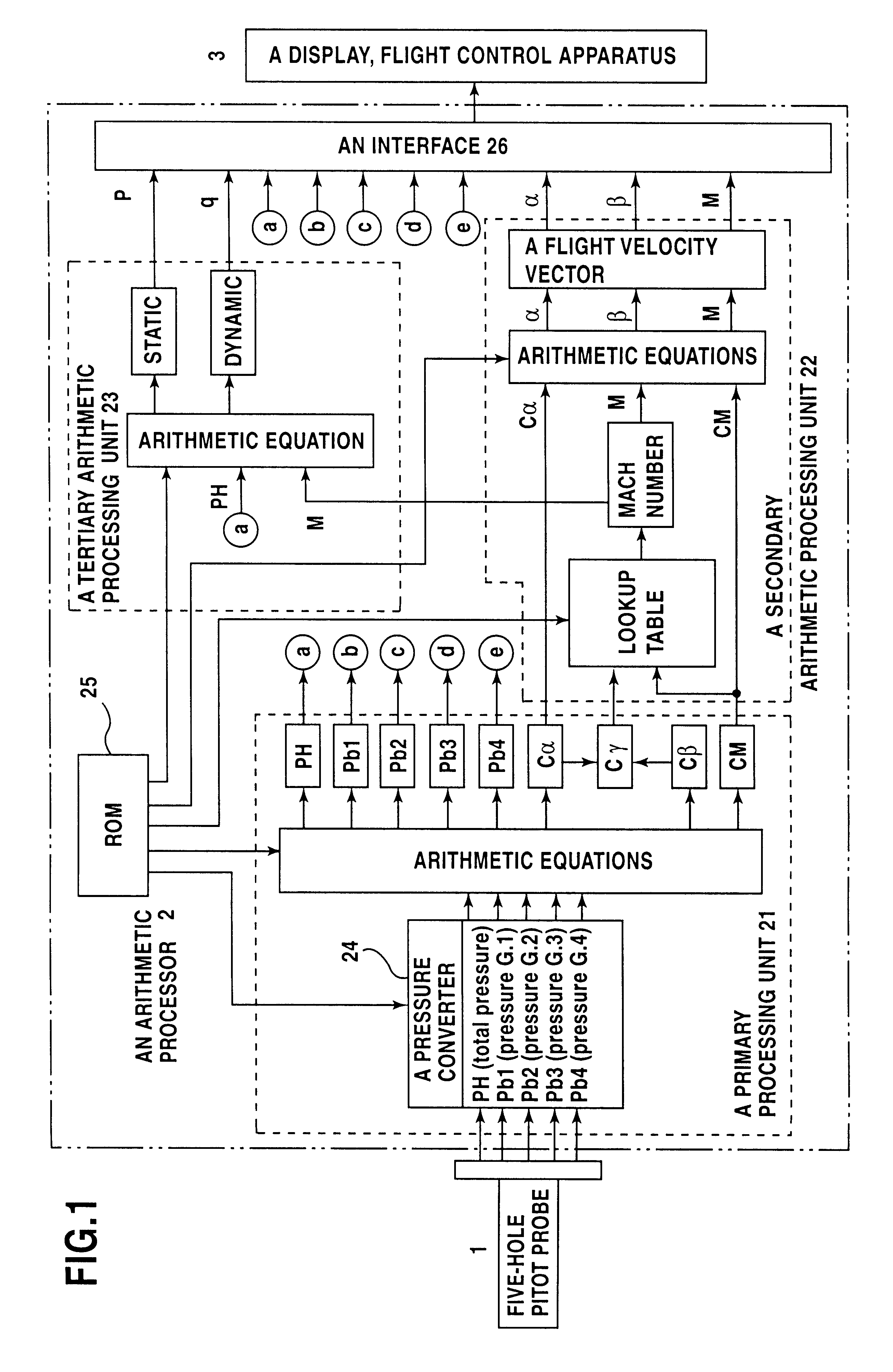
Arithmetic processing method and system in a wide velocity range flight velocity vector measurement system using a square truncated pyramid-shape five-hole pitot probe
InactiveUS6336060B1Digital data processing detailsVolume/mass flow measurementTime responseEquation of the center
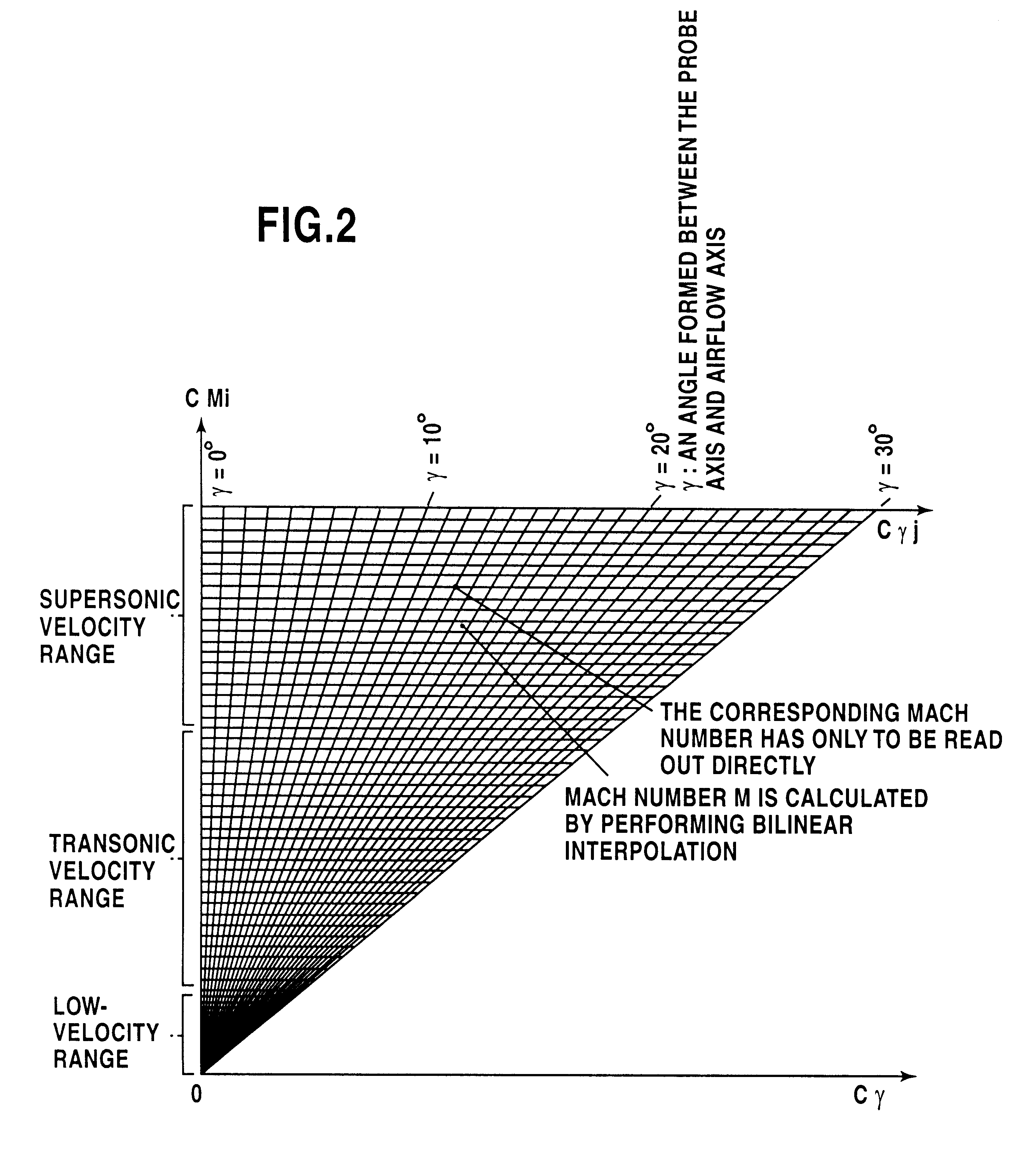
An arithmetic processing method and system in a wide velocity range flight velocity vector measurement system using a square truncated pyramid-shape five-hole Pitot probe. Approximation equations that determine attack angle alpha and sideslip angle beta in the form of third-order equations concerning attack angle pressure coefficient Calpha and sideslip angle pressure coefficient Cbeta, which are known numbers, are expressed in the form of a polynomial equation concerning Mach number M, where the coefficients are obtained from a lookup table. Coefficient calculations in the polynomial equation, and attack angle a and sideslip angle beta, calculations may be performed as simple calculations by specifying and applying known numbers into the approximation equation without solving third-order equations, with calibration coefficients that form the basis of coefficient calculation with the polynomial equation first being stored in memory in advance as a table for each wide velocity range on the basis of wind tunnel testing. A Mach number may be calculated instantly from a lookup table by specifying Mach pressure coefficient CM and angle to airflow pressure coefficient Cgamma. Wide velocity range flight velocity vector measurement with a high update rate which is capable of real time response in flight control as demanded by aircraft is obtained.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY
Spacecraft attitude tracking control method based on discontinuous adaptive control
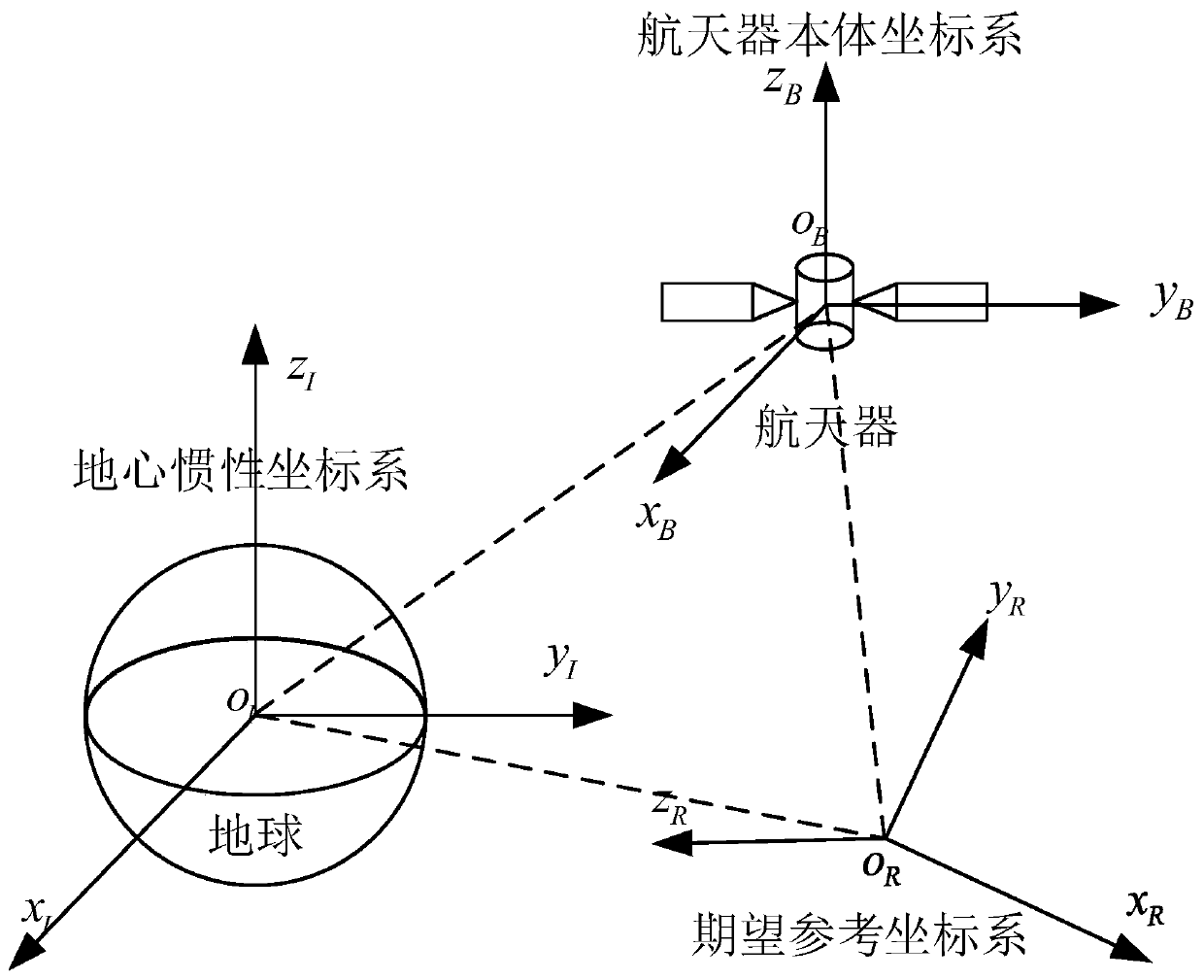
ActiveCN110347173AImplement trackingHigh steady-state control accuracyAttitude controlAdaptive controlKinematics equationsInertial coordinate system
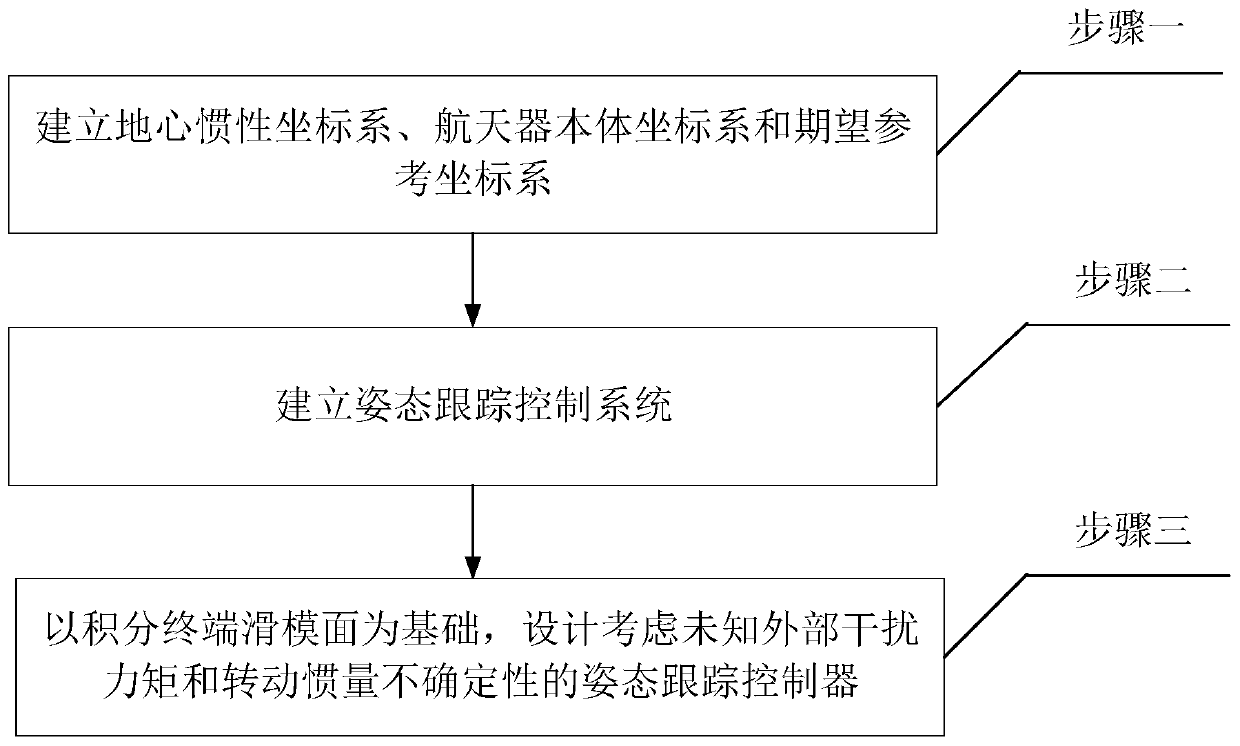
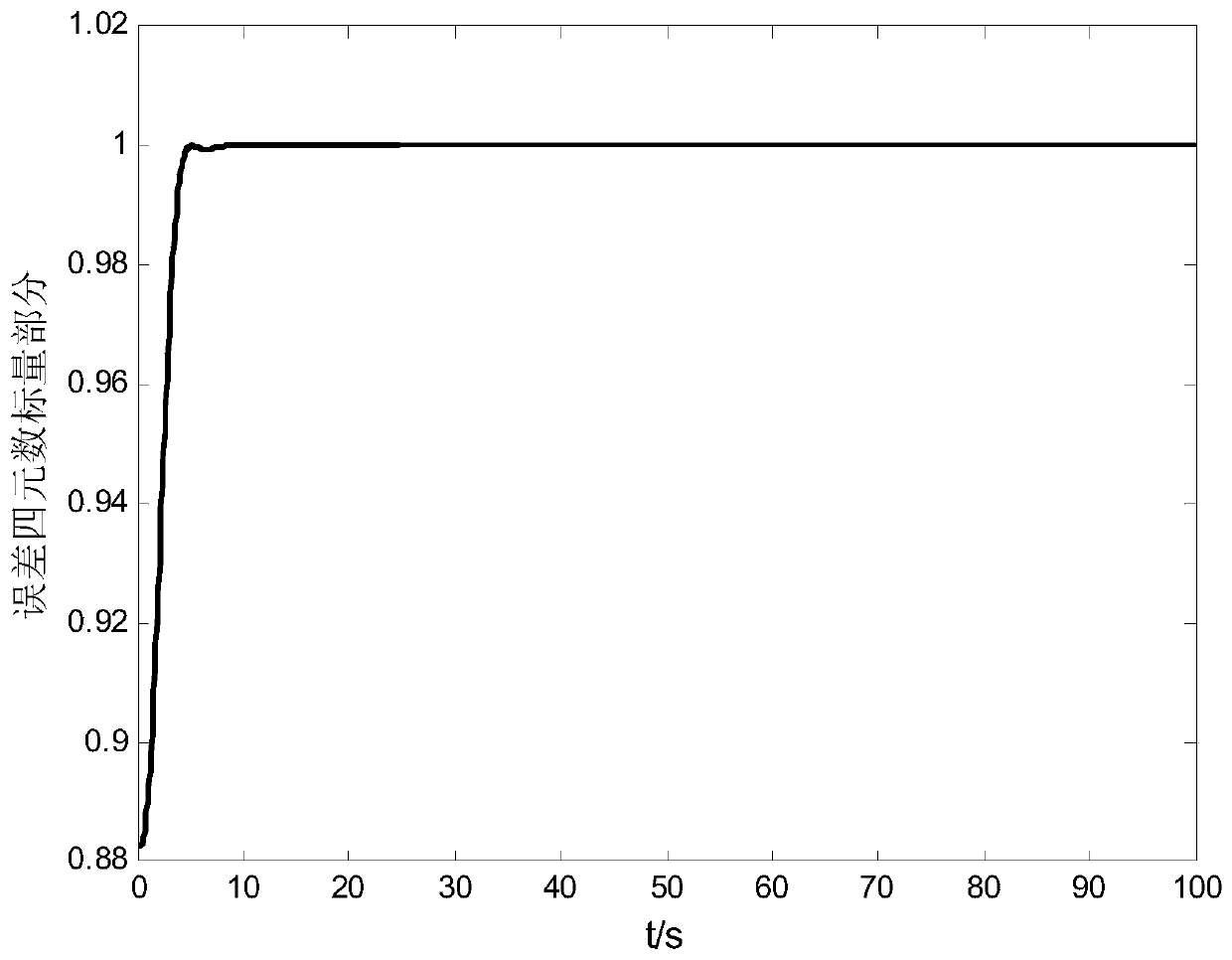
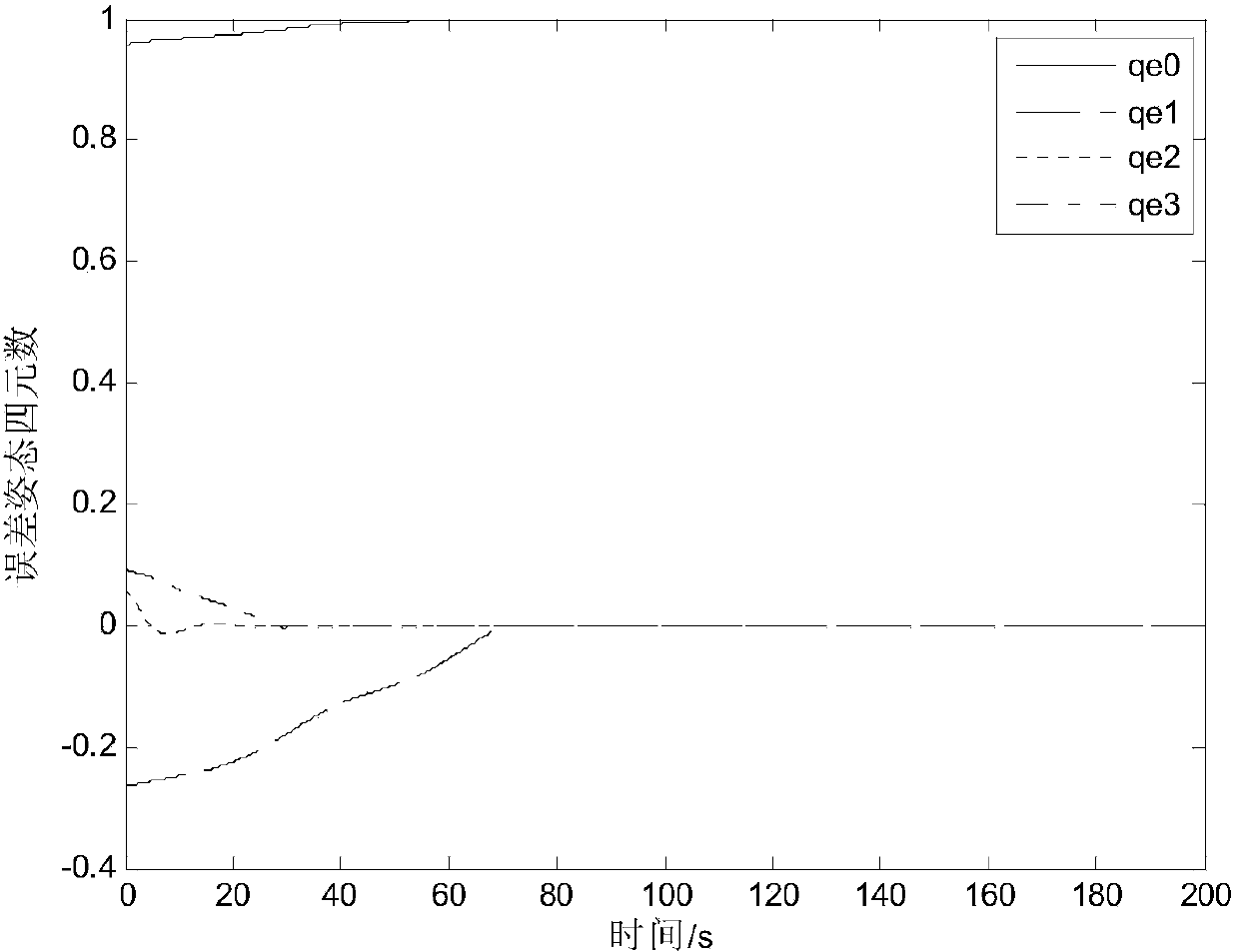
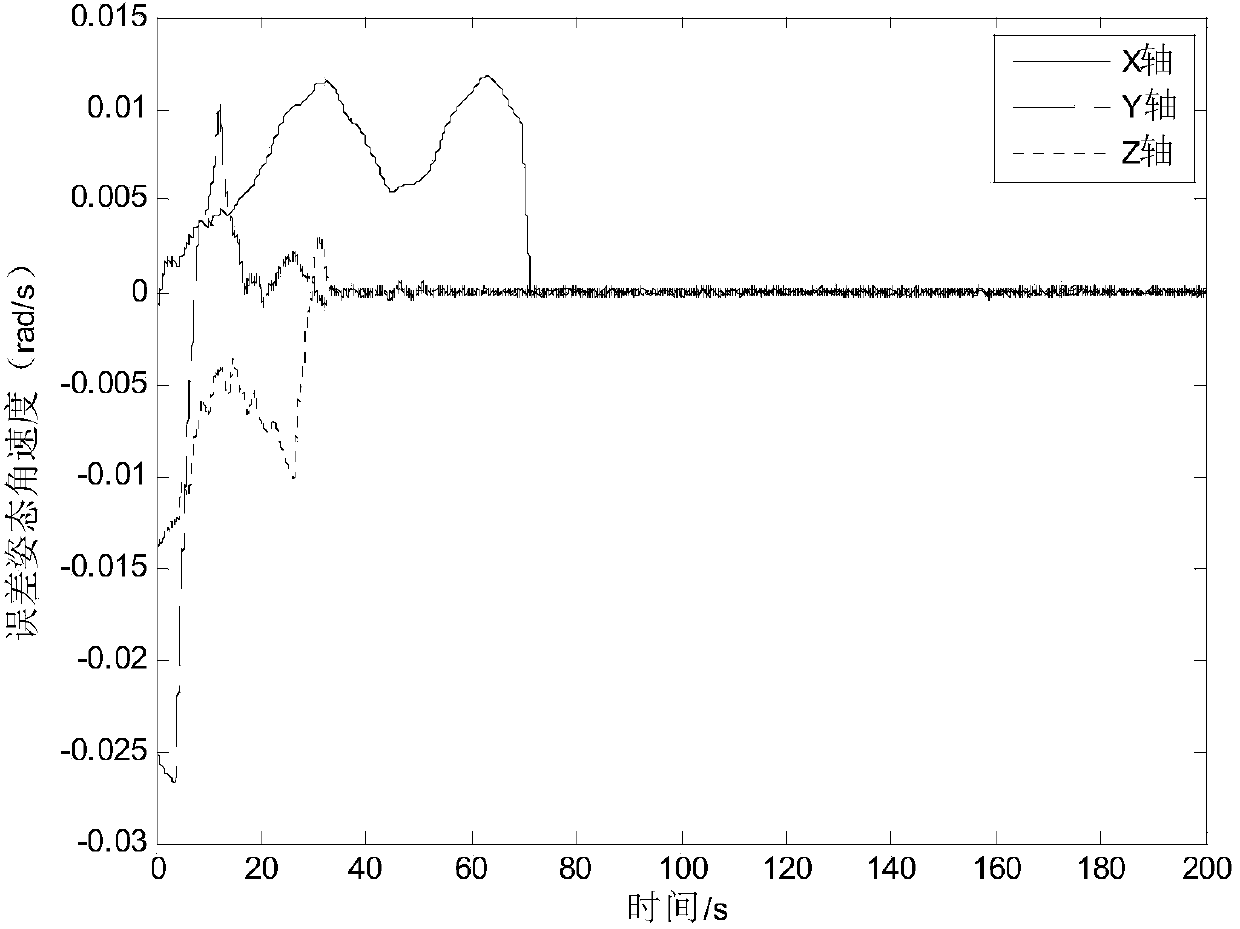
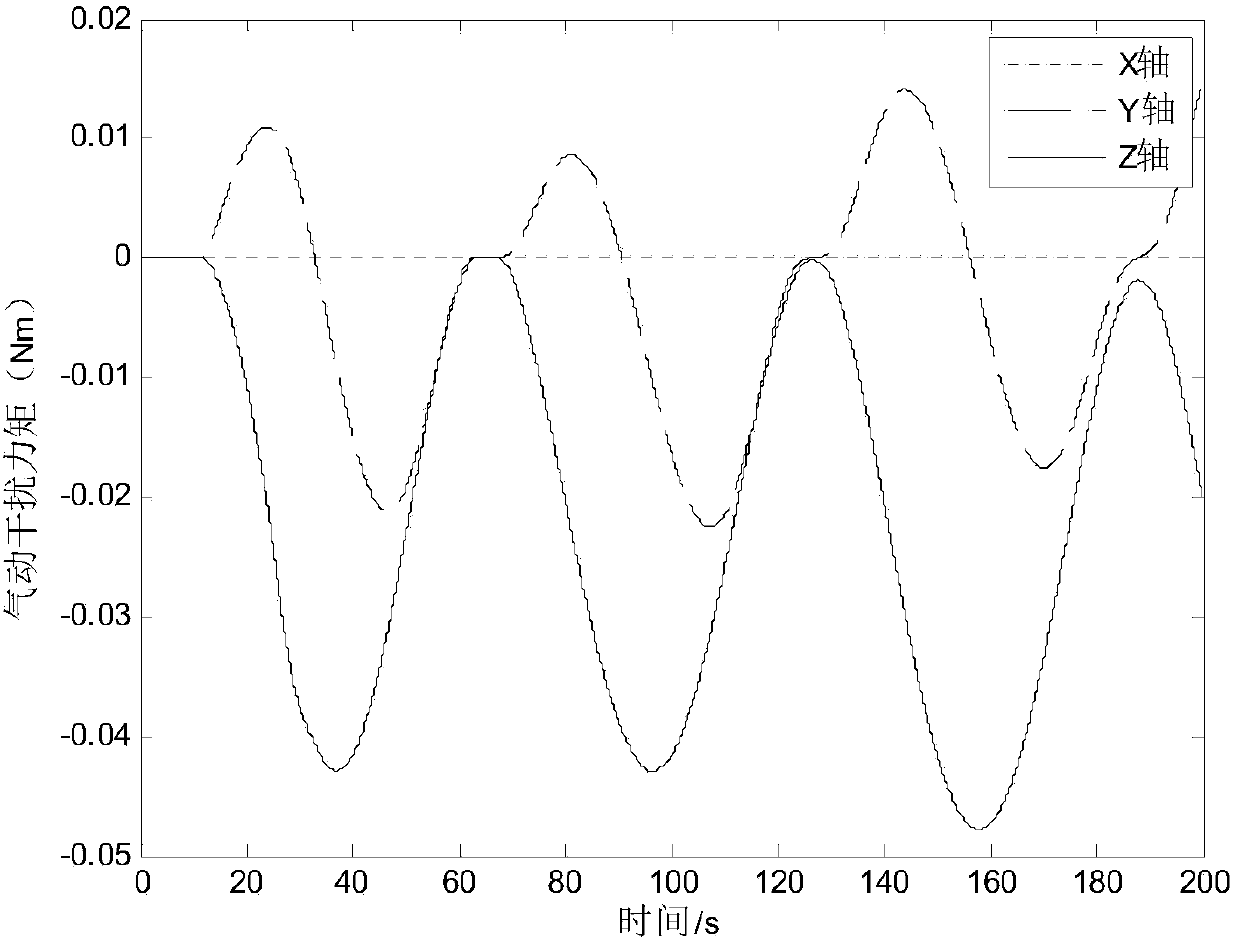
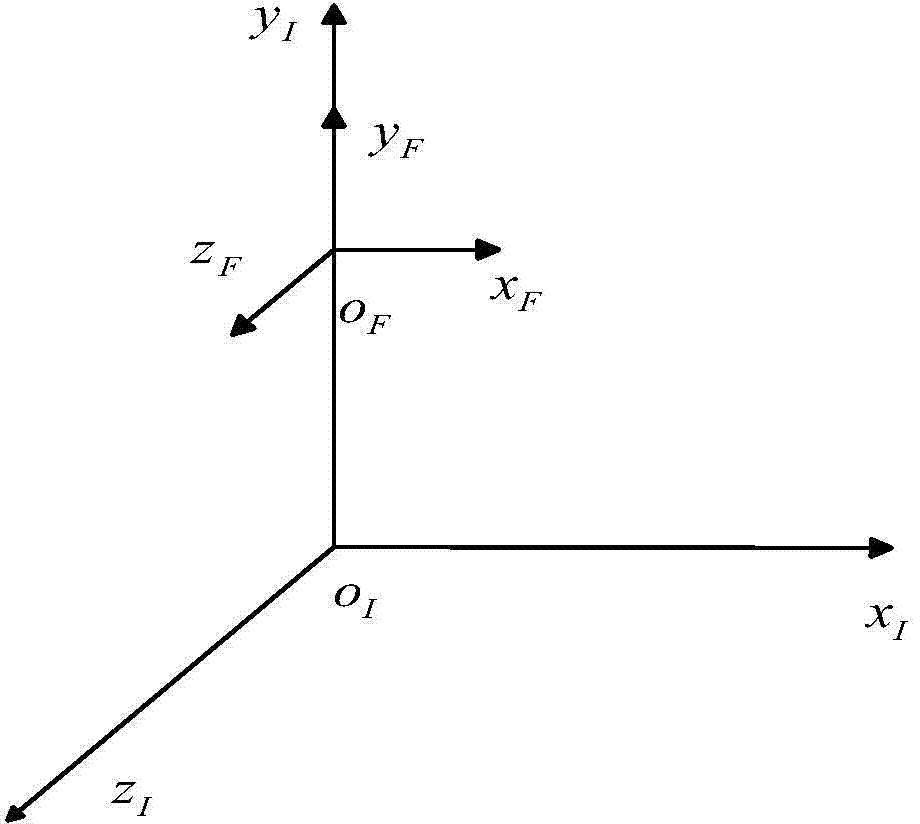
The invention provides a spacecraft attitude tracking control method based on discontinuous adaptive control, belongs to the technical field of spacecraft attitude tracking control, and solves the problem that a spacecraft attitude tracking control system is poor in robustness so that a spacecraft attitude tracking control effect is poor in the case of modeling uncertainty, external disturbances and input saturation effects. The spacecraft attitude tracking control method comprises the following specific steps of step 1, establishing an earth centered inertial oIxIyIzI, a spacecraft body coordinate system oBxByBzB and an expected reference coordinate system oRxRyRzR; step 2, according to the coordinate systems established in step 1, obtaining the spacecraft attitude kinematics and a kinetic equation described by using an attitude quaternion, and a spacecraft error attitude kinematics equation and the kinetic equation, namely the attitude tracking control system; and step 3, based on the step 2, based on a sliding mode surface of an integral terminal, designing an attitude tracking controller considering an unknown external disturbance torque and the rotational inertia uncertainty.The spacecraft attitude tracking control method based on the discontinuous adaptive control provided by the invention can be applied to spacecraft attitude tracking control.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Automobile driving state estimation method with influence of rolling considered
InactiveCN106250591AOvercoming the Effects of Measurement NoiseAccurate estimateDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsCar drivingThree degrees of freedom
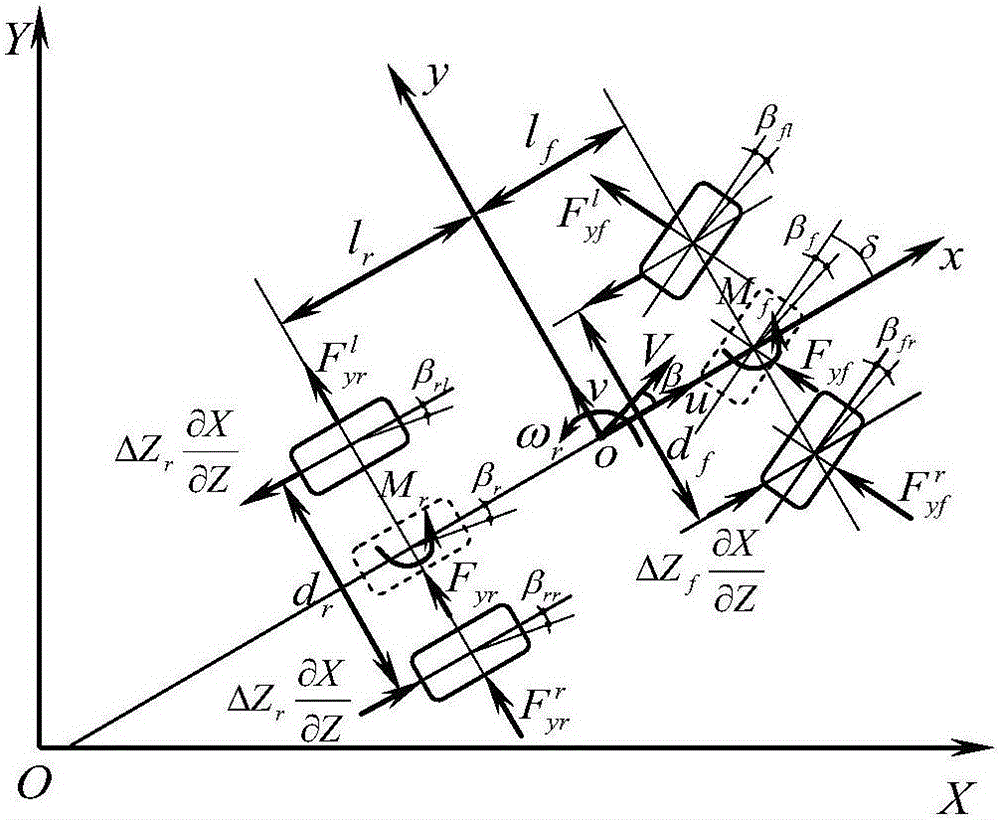
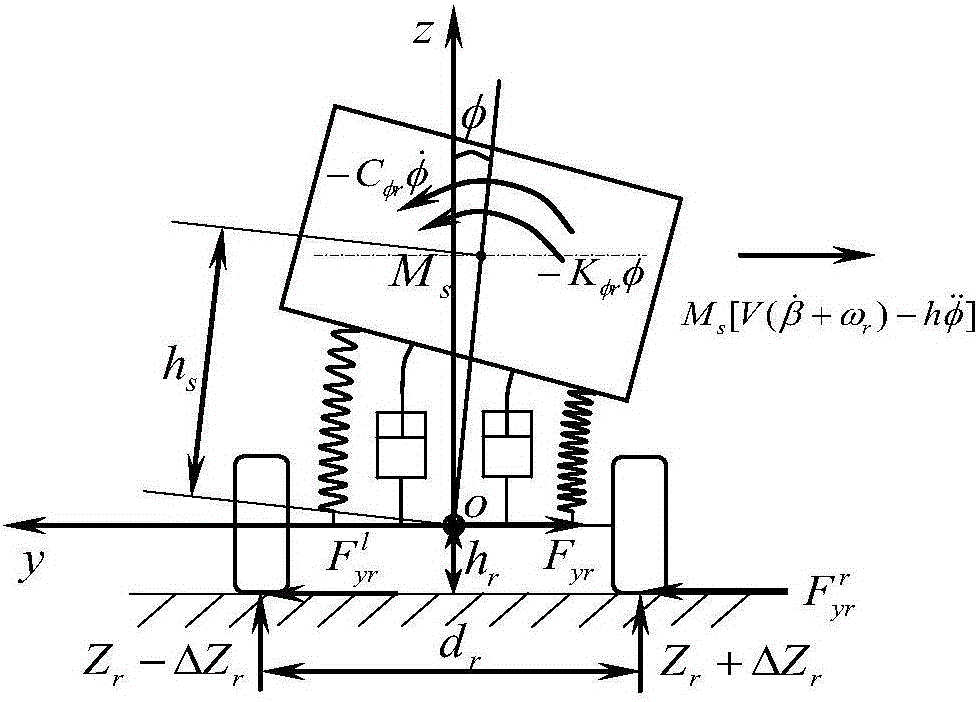
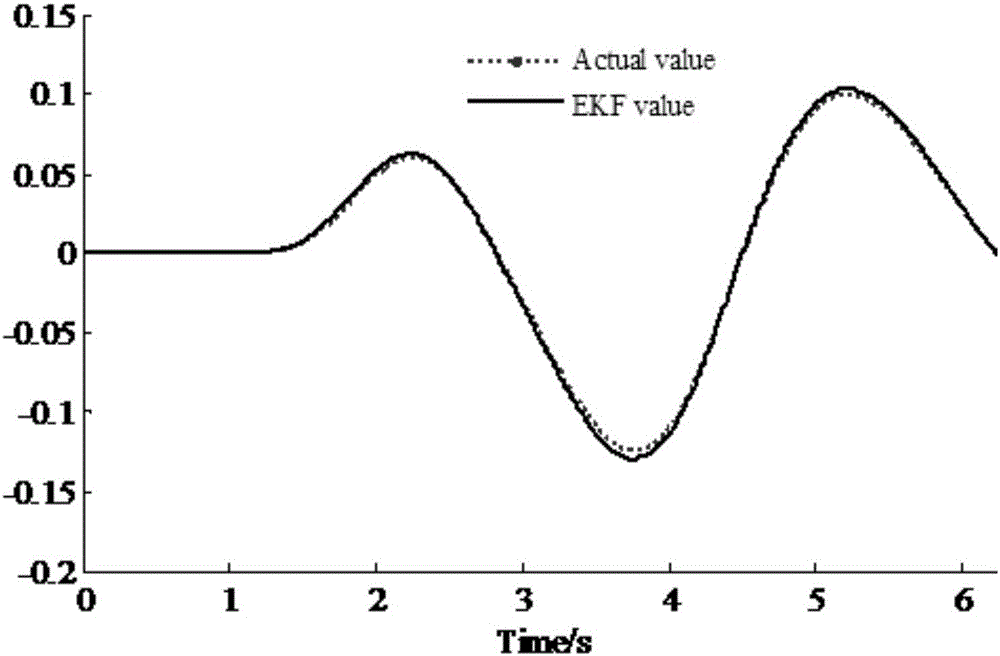
The invention discloses an automobile driving state estimation method with the influence of rolling considered. The method includes the steps that with the influence of automobile rolling motion considered, a three-degree-of-freedom motion differential equation which includes automobile mass center deviation, yawing motion and rolling motion and has nonlinear characteristics is established; the nonlinear three-degree-of-freedom motion differential equation is linearized; a state equation about the mass center deviation angle and the yaw velocity and a measurement equation are established, the mass center deviation angle and the yaw velocity are linearized and iterated into an extended Kalman filtering equation to obtain optimal estimated values of the mass center deviation angle and the yaw velocity, and meanwhile the mass center deviation angle and the yaw velocity of the nonlinear three-degree-of-freedom motion differential equation are input into an extended Kalman filtering model. Thus, comparison of the estimated values and actual values can be verified.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Inertial system spacecraft attitude control/angular momentum management method
ActiveCN105159310AEasy to implementReduce the burden onAttitude controlMassive gravitySpacecraft attitude control
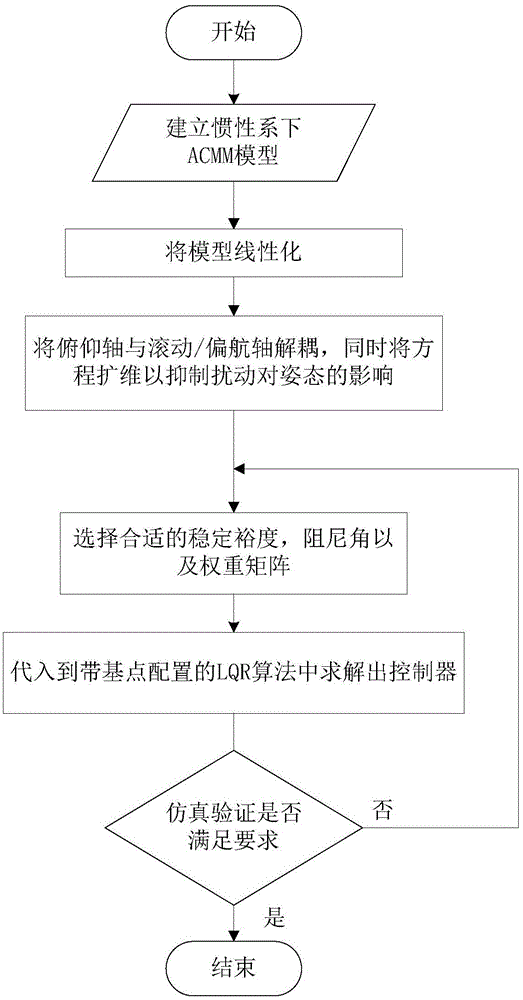
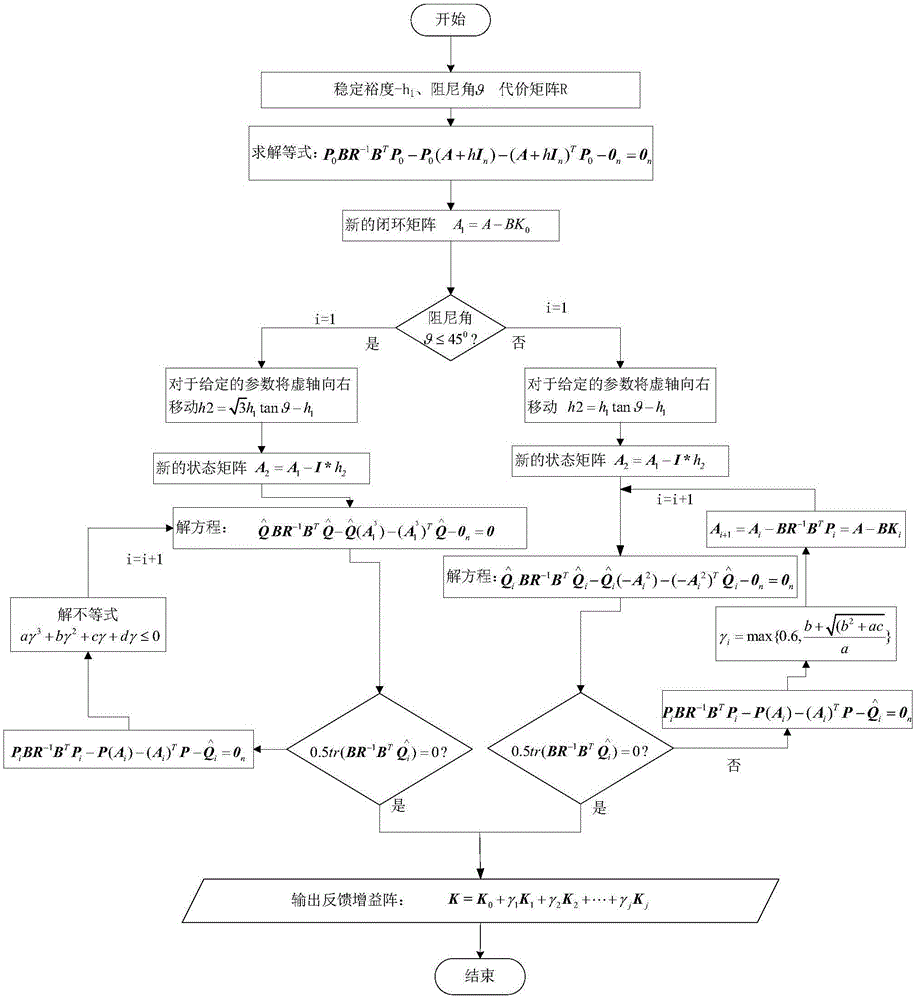
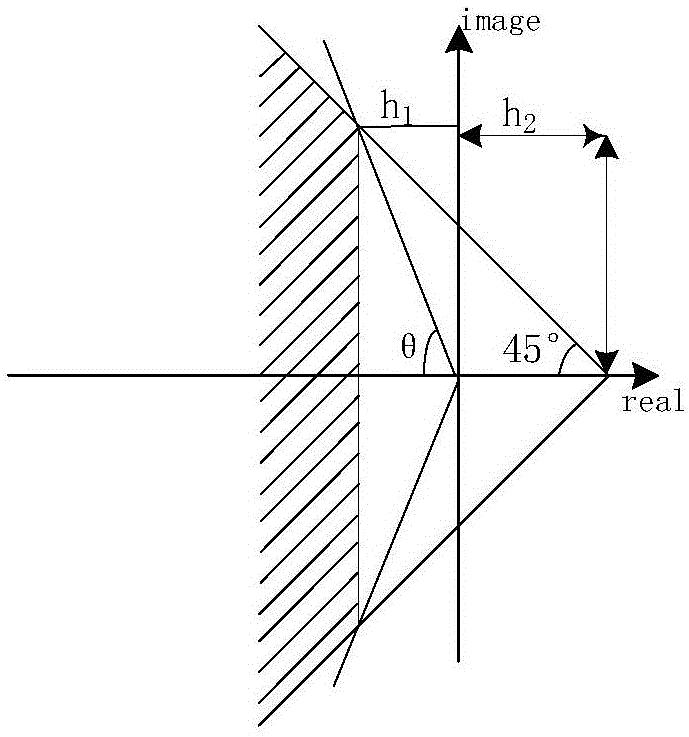
The invention provides an inertial system spacecraft attitude control / angular momentum management method including four steps. The invention aims to solve the problems of control moment gyro angular momentum accumulation caused by gravitation gradient moment and other interference moments in an inertial system, the gravitation gradient moment is adopted to balance the gestures, and a space station angular momentum management controller based on pole assignment is designed. A space station linear model is established under the inertial system, the infeasibility of the inertial system angular momentum management in the pitch axis direction is analyzed, the pitch axis is decoupled from a rolling / yaw axis, and the CMG angular momentum in the pitch axis direction is not restrained, constant disturbance, disturbance being one-time of the track frequency, and disturbance being twice of the track frequency are brought into a state equation to suppress the influence to the pitch axis gestures, and a linear quadratic algorithm based on pole assignment is adopted to solve a feedback gain matrix. The algorithm prevents the selection of cost matrix Q, and based on the requirement of the system performance, the closed-loop poles can be configured to a specified area at the left side of a complex plane imaginary axis, and at the end, the feasibility of the algorithm is verified by the simulation results.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
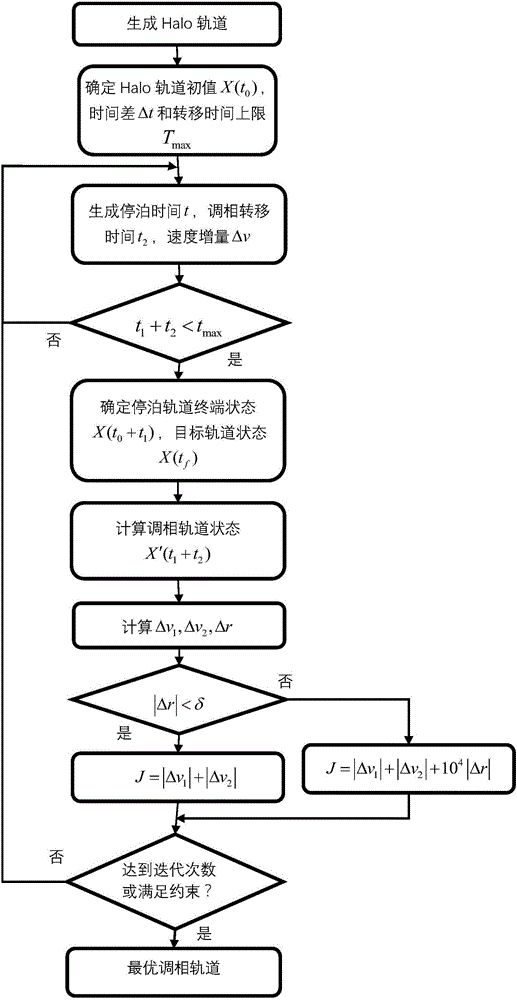
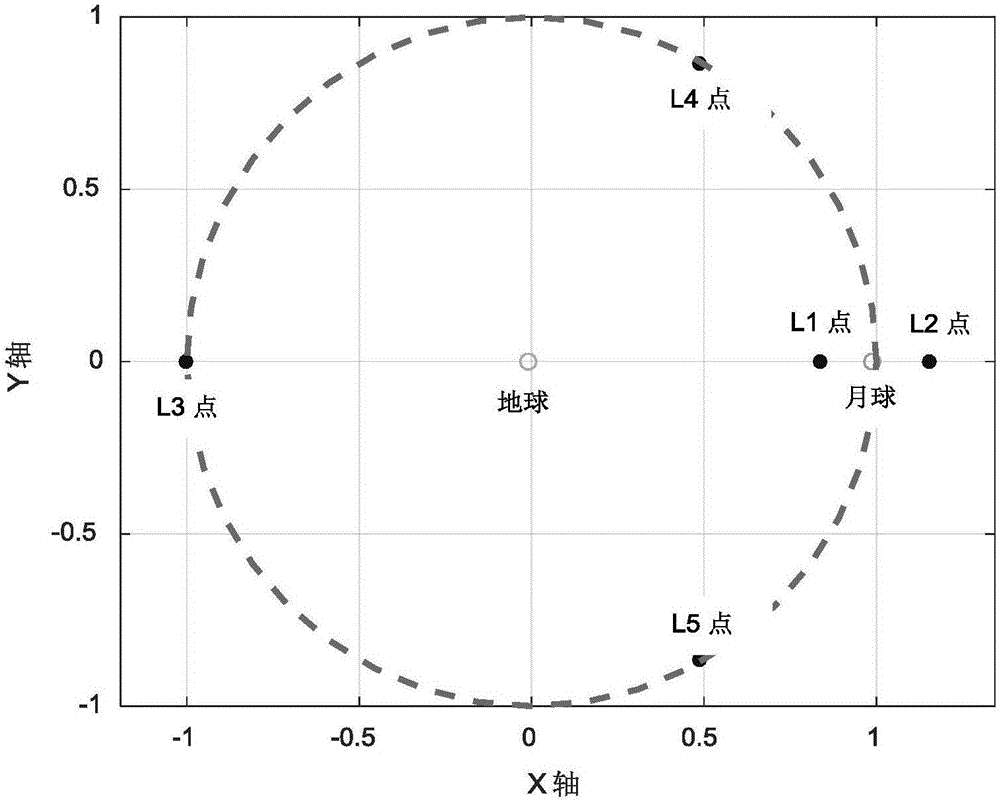
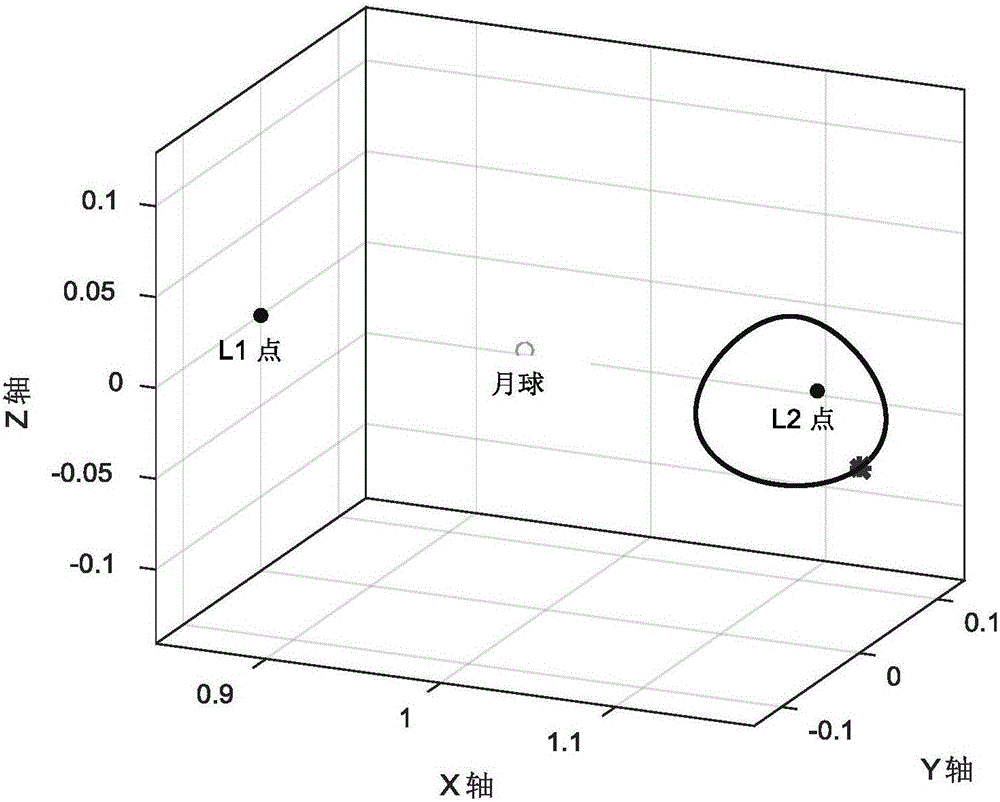
Balance point Halo orbit phasing orbit transfer method taking time constraint into consideration
ActiveCN106672266AFast convergenceIncrease fuel consumptionCosmonautic vehiclesSpecial data processing applicationsAviationDynamic equation
The invention discloses a balance point Halo orbit phasing orbit transfer method taking the time constraint into consideration, relates to a Halo orbit phasing orbit transfer method based on an earth-moon three-body dynamic model and belongs to the technical field of aerospace. According to the method, a dynamic equation is established under a restrictive three-body model formed by the earth, the moon and the star, and a Halo orbit near the point L2 is generated under an earth-moon rotation system; the Halo orbit initial phase position of a detector and the phase position difference needing to be changed are determined, and the optimal fuel phasing orbit meeting the phase position constraint condition and the transfer time constraint condition is obtained through an optimization algorithm with the initial anchoring time and transfer time as optimization variables; and the time difference delta t, the task Halo orbit or the upper limit tmax of the transfer time are adjusted according to the task which the detector needs to fulfill, and the orbit shadow detection avoiding task or the spatial intersection detection task of the detector on the Halo orbit is fulfilled. The method can obtain the optimal fuel phasing orbit meeting the phase position constraint condition and the transfer time constraint condition, and has the advantages of good convergence, high flexibility and the like.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
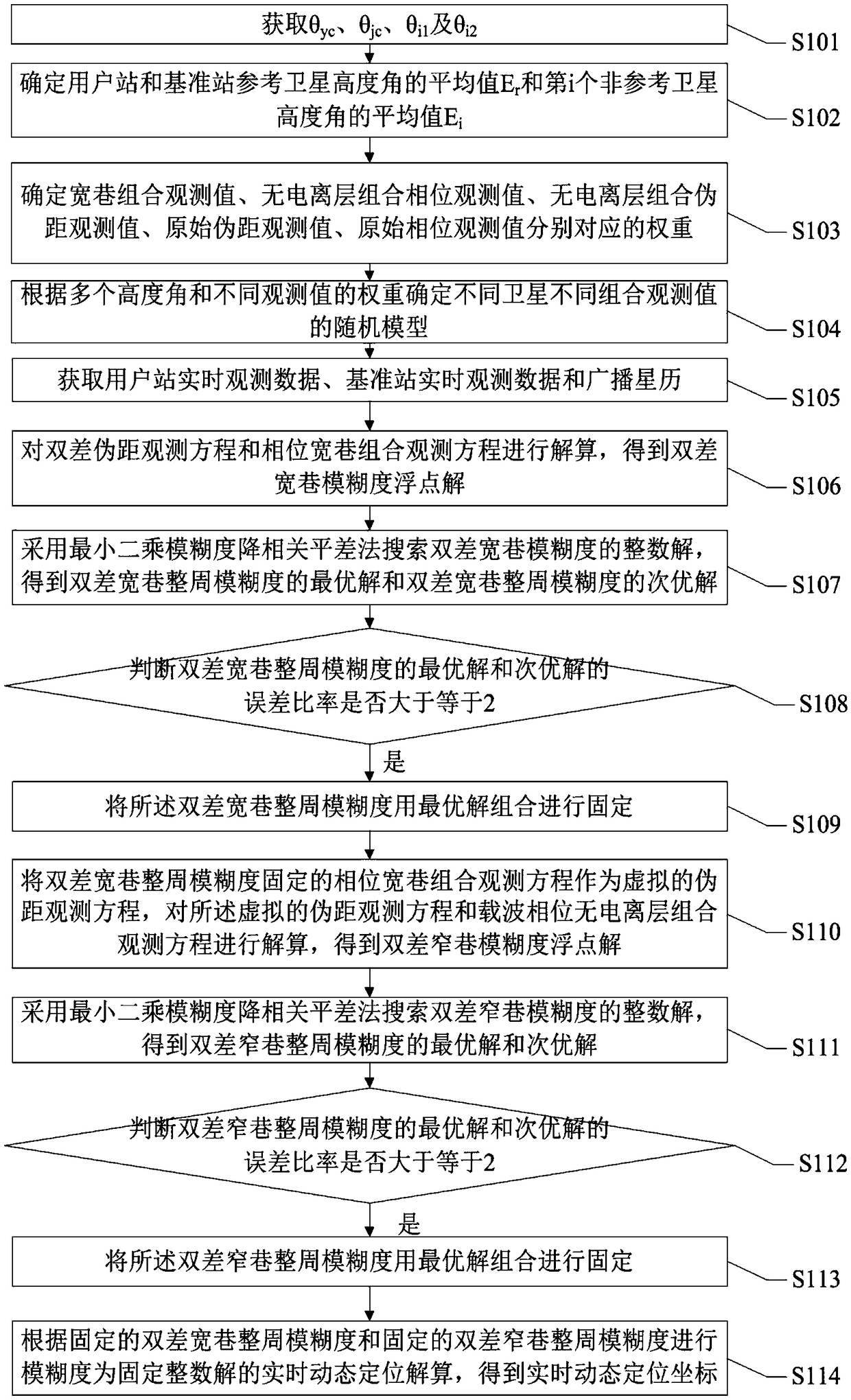
Real-time dynamic positioning method for baselines with different lengths
ActiveCN109116394AAchieve seamless connectionWeaken residual effectsSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceElevation angle
The invention discloses a real-time dynamic positioning method for baselines with different lengths. Elevation angles and observation weights of different satellites are determined to obtain a stochastic model of different combined observation values; a double-difference wide-lane combination equation is formed, a phase wide-lane combination observation equation after double-difference wide-lane whole-cycle ambiguity fixation is used as a virtual pseudo-range observation equation, and a virtual double-difference pseudo-range observation equation and a carrier phase ionospheric-free combinationobservation equation are calculated; and according a fixed double-difference wide lane and narrow-lane whole-cycle ambiguity, real-time dynamic positioning calculation with the ambiguity being an integer solution is carried out to obtain a real-time dynamic positioning coordinate. According to the method disclosed by the invention, with the phase wide-lane combination observation equation after double-difference wide-lane whole-cycle ambiguity fixation as the virtual pseudo-range observation equation, the ionospheric residual influence is weakened and the pseudo-range observation precision isimproved, so that seamless connection of real-time dynamic positioning of baselines with different lengths is realized.
Owner:NAT TIME SERVICE CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
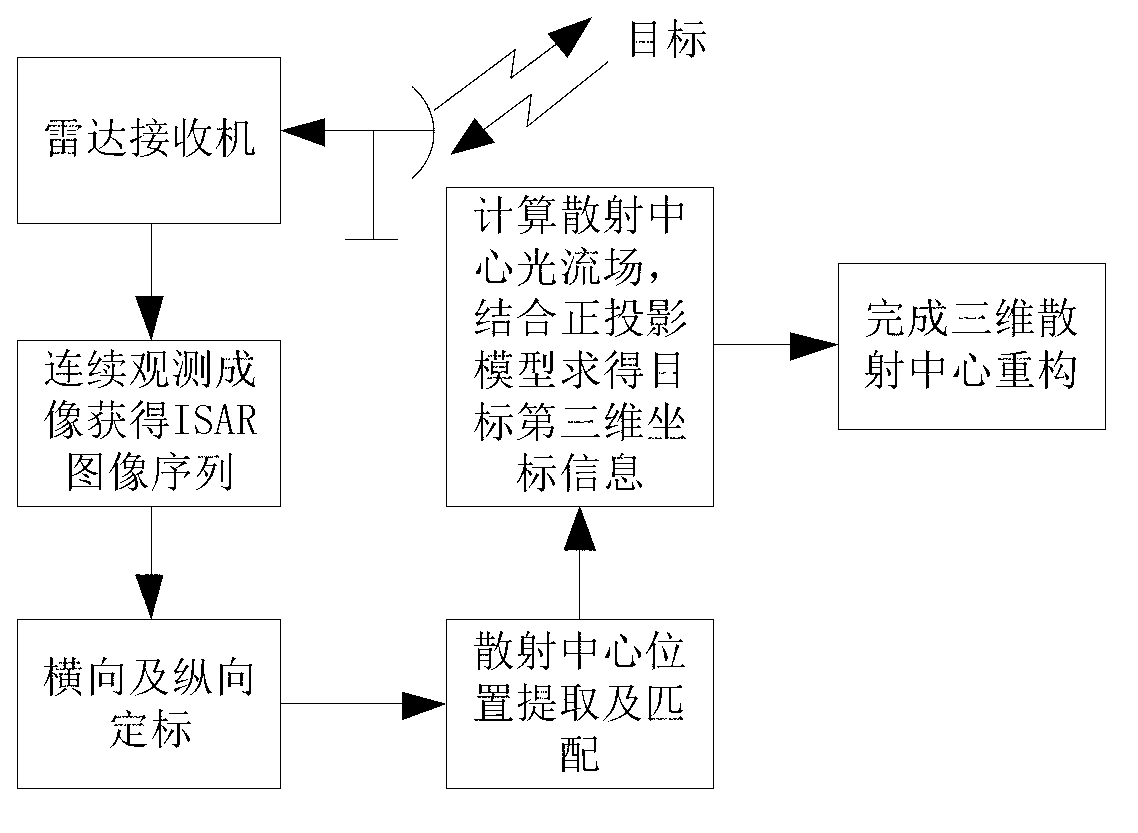
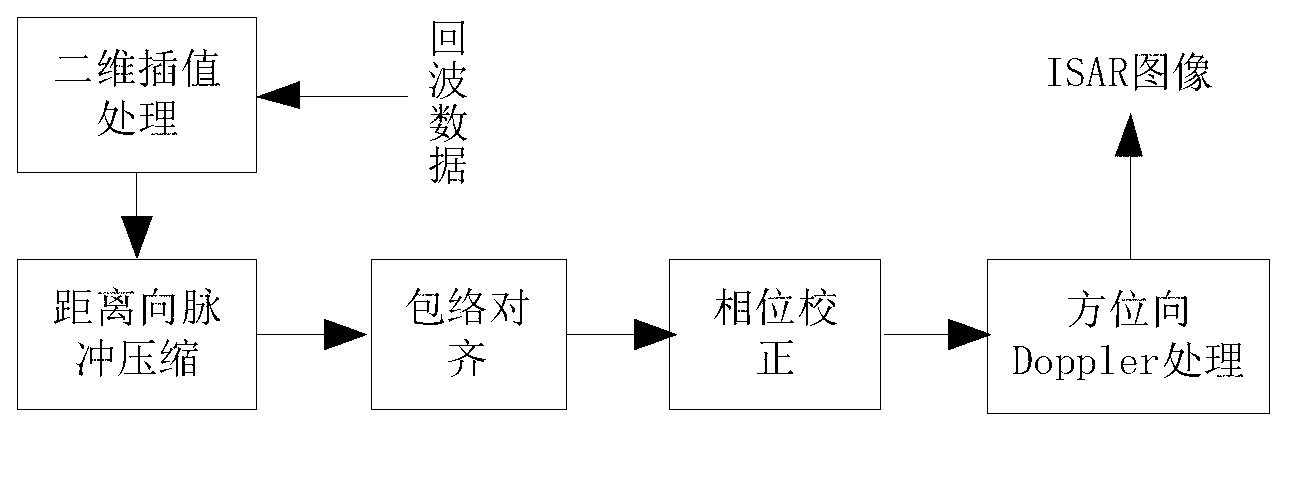
Method for reconstructing target three-dimensional scattering center of inverse synthetic aperture radar
InactiveCN103217674AResolve mismatchSmall amount of calculationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarInverse synthetic aperture radar
The invention provides a method for reconstructing target three-dimensional scattering center inverse synthetic aperture radar. The method for reconstructing the target three-dimensional scattering center of the inverse synthetic aperture radar comprises the following steps: conducting continuous image formation on echo data after motion compensation so as to obtain an ISAR two-dimensional image sequence; respectively conducting horizontal scaling and vertical scaling on the information storage and retrieval (ISAR) two-dimensional image sequence so as to obtain a position coordinate of the scattering center; and respectively extracting a position coordinate of the scattering center in an ISAR two-dimensional image of each frame, calculating a displacement velocity field of every two adjacent frames of the scattering center of the ISAR two-dimensional image, combining projection equation and target motion equation of an orthographic projection model so as to obtain estimated values of a third dimension coordinate by combining a projection equation and a target motion equation of an orthographic projection model, and averaging multiple estimated values to obtain the final third dimension coordinate. Therefore, reconstruction of the target three-dimensional scattering center is completed directly. The method for reconstructing the target three-dimensional scattering center of the inverse synthetic aperture radar does not need cost of extra system hardware, can distinguish scattering centers with different heights in the same distance and position resolution unit, does not need to utilize prior information such as observation perspective of the radar, and has relatively small calculating amount.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
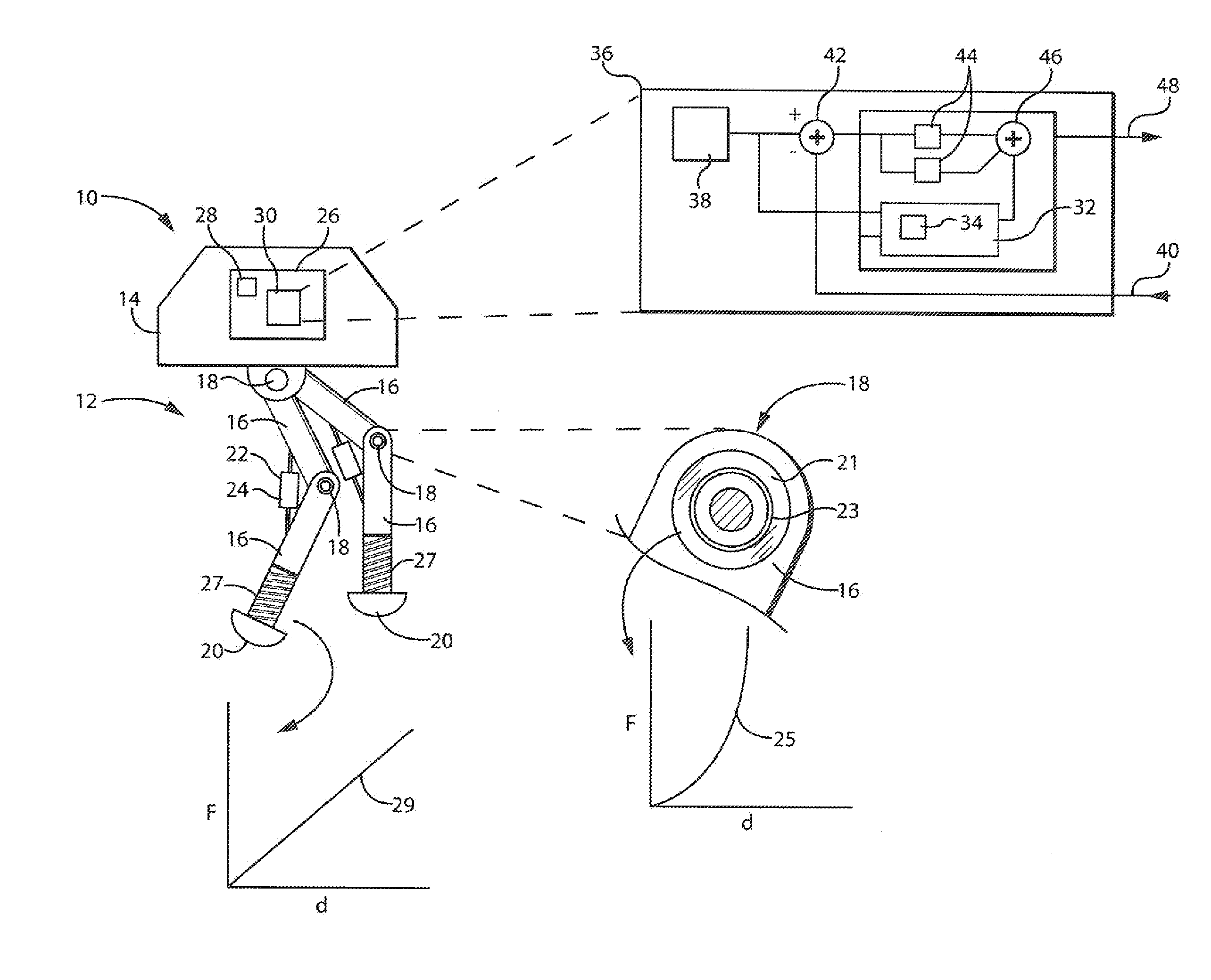
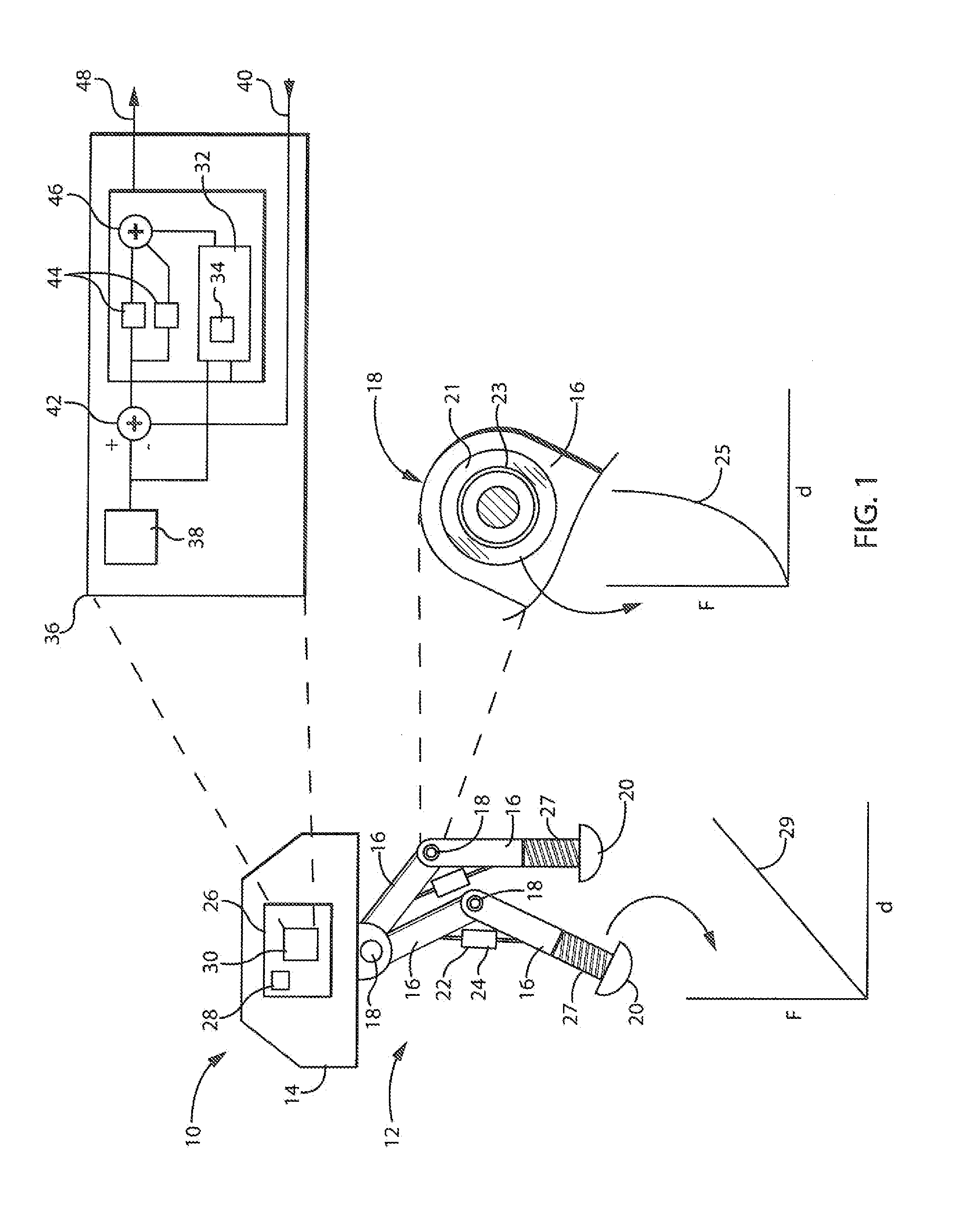
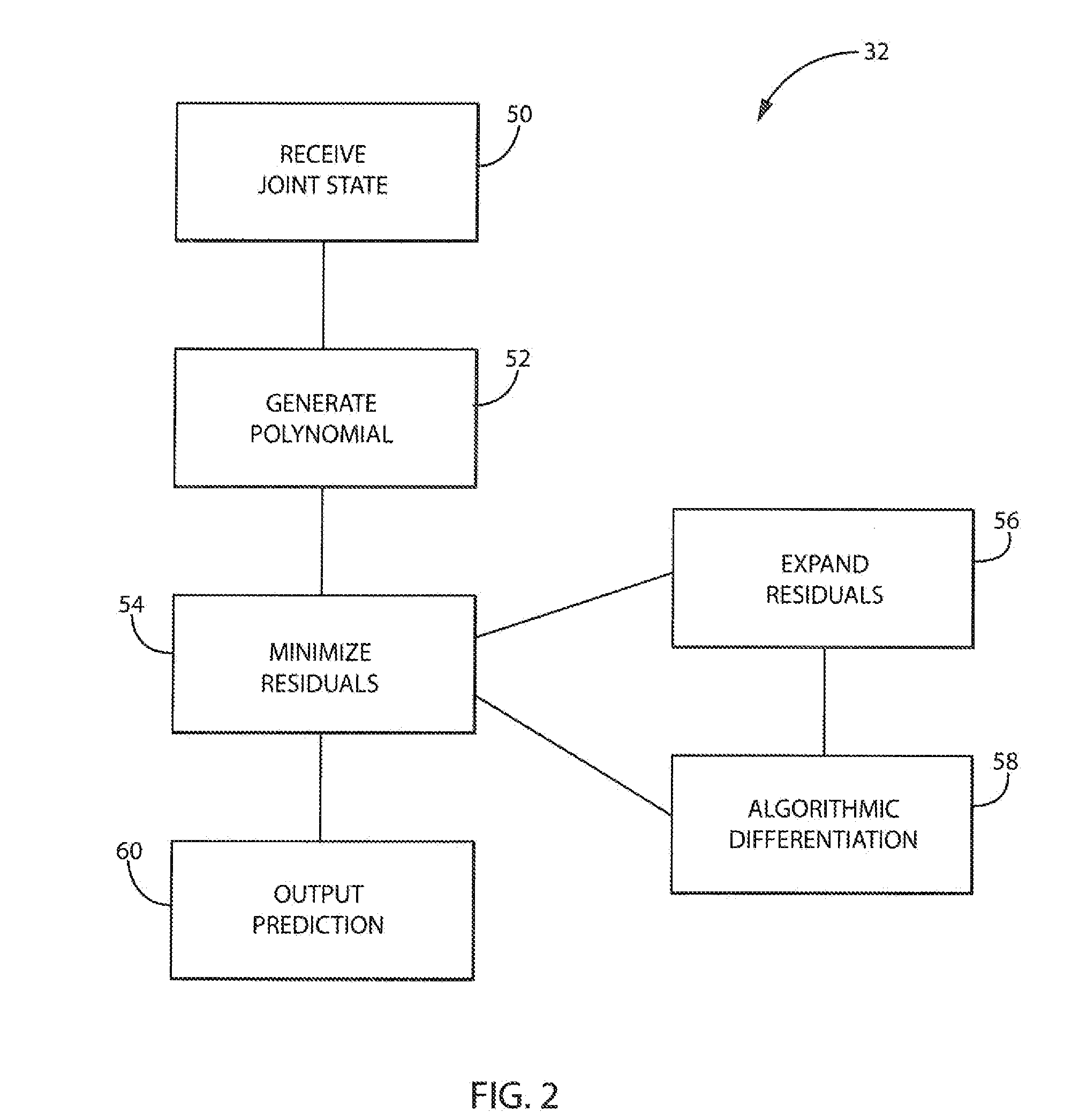
Dynamic Predictor for Articulated Mechanisms
ActiveUS20150005941A1Stable and accurate solutionImproved polynomial approximationProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorEquation of the centerEngineering
A dynamic predictor usable for rapid and accurate calculation of joint commands of an articulated dynamical mechanism describes the relationship between the joints in the form of a differential equation. The predictor solves this differential equation for predicted joint states by fitting a polynomial equation having free parameters describing the predicted joint states to the differential equations by minimizing the differential equation residuals. This minimization employs a series expansion allowing algorithmic differentiation.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Low-orbit flexible satellite attitude tracking control method based on sliding-mode observer
ActiveCN104483973AIncrease factor valueImprove robustnessAttitude controlAdaptive controlTracking modelMode control
The invention discloses a low-orbit flexible satellite attitude tracking control method based on a sliding-mode observer, relates to a low-orbit flexible satellite attitude tracking control method based on a sliding-mode observer, and aims at solving the problems that an existing low-orbit flexible satellite is low in satellite attitude tracking control accuracy due to relatively large aerodynamic interference torque and vibration of flexile components. The low-orbit flexible satellite attitude tracking control method based on the sliding-mode observer comprises the following steps: building a geocentric inertial coordinate system and a satellite body coordinate system; building a state space expression, and determining an upper bound of an interference signal received by the observer; solving a gain matrix of the observer, a matching matrix of the observer and a Lyapunov equation matrix variable; observing to obtain an estimated mode vibration velocity value of the sliding-mode observer and an estimated mode vibration state value of the sliding-mode observer; rewriting a kinetic equation of a flexible satellite attitude into an error attitude tracking control model; determining a sliding-mode term gain of the control law, and carrying out tracking control on the error attitude tracking model by adopting the siding-mode control law according to measured satellite attitude quaternion, attitude angular velocity information and estimated mode quantity value. The low-orbit flexible satellite attitude tracking control method is applied to satellite attitude tracking control.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for predicting skipping trajectory of hypersonic glide warhead in near space
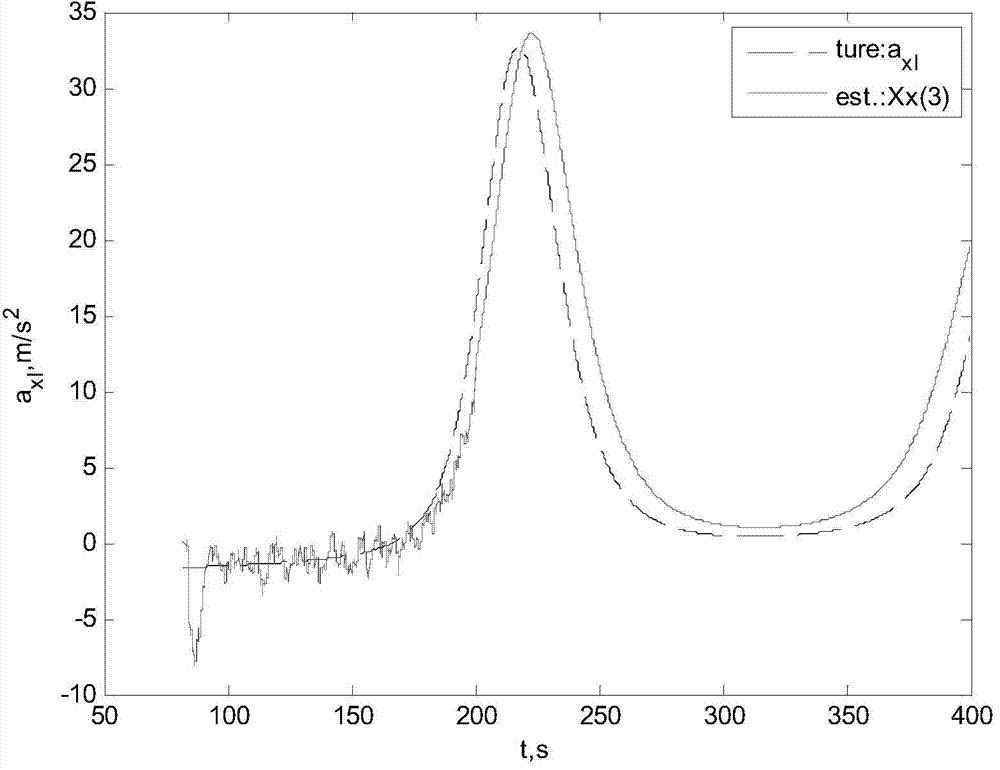
ActiveCN104778376AReduce forecast errorImprove forecast accuracySustainable transportationSpecial data processing applicationsKaiman filterEquation of the center
The invention relates to an aircraft trajectory predicting method, in particular to a method for predicting a skipping trajectory of a hypersonic glide warhead in near space and belongs to the technical field of target tracking. The method aims to solve the problem that by the adoption of an existing method, the prediction precision of the trajectory of a maneuvering target is low. The method comprises the steps that firstly, a trajectory equation of the hypersonic glide warhead is established; secondly, a kalman filter tracking the movement curve of the hypersonic glide warhead is designed; thirdly, according to the position, the speed and the acceleration of the hypersonic glide warhead at the tracking end moment and the trajectory equation, the attack angle and the roll angle of the hypersonic glide warhead in fight are estimated, the hypersonic glide warhead in the near space flies by a constant attack angle and a constant roll angle in a subsequent flight time period, recursive calculation for the trajectory at a next moment is conducted through the trajectory equation, and then a trajectory prediction value of the hypersonic glide warhead after a time period is obtained.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method of detecting compound motion target based on orbital angular momentum
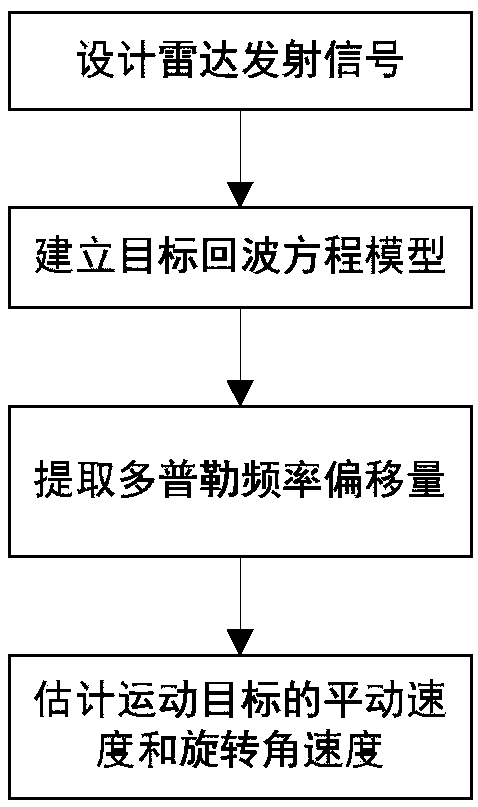
ActiveCN108594198AEffective detectionEfficient separationWave based measurement systemsMomentumEquation of the center
The invention belongs to the field of radar detection and Doppler detection of moving targets and particularly relates to a method of detecting a compound motion target based on orbital angular momentum. The method comprises the steps: designing a radar emission signal, and establishing an emission signal model; setting target motion parameters, acquiring a target echo equation by deduction, and analyzing with the target echo equation to obtain internal relations of Doppler frequency offset to target translational velocity and rotational angular velocity; providing a detection and separation method of translational Doppler frequency offset and rotational Doppler frequency offset; finally, implementing detection of the compound motion target based on the detection results of Doppler frequency offset. orbital angular momentum information carried by vortex electromagnetic wave can be utilized herein to provide effective detection and separation for translational Doppler and rotational Doppler, so that the detection of the compound motion target is implemented; references are provided for the development of radar detection techniques and target recognition techniques based on orbital angular momentum.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
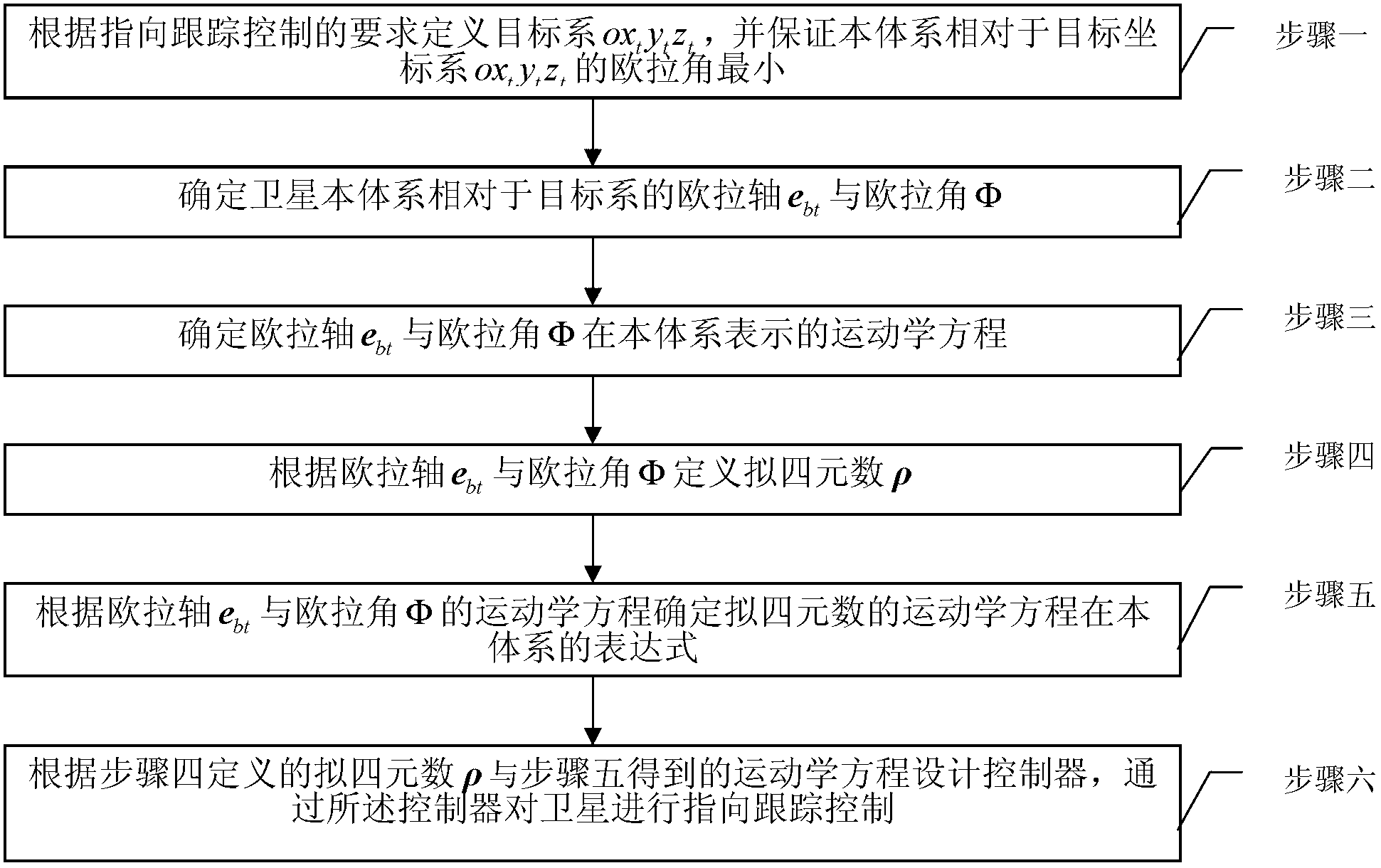
Satellite pointing tracking control method based on quasi-quaternion and quasi-quaternion kinematical equation
ActiveCN103268067AEasy accessShort path of motionAdaptive controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsKinematicsKinematics equations
The invention provides a satellite pointing tracking control method based on a quasi-quaternion and a quasi-quaternion kinematical equation. The satellite pointing tracking control method aims to solve the problems that kinematical parameters used in an existing satellite pointing tracking controller are unreasonable in design and can not guarantee the shortest tracking path of a satellite, and a uniform kinematical equation applied to pointing tracking control does not exist. The satellite pointing tracking control method includes the steps of defining a target system according to demands of the pointing tracking control and guaranteeing that the eulerian angle of the system is the smallest relative to that of the target system, determining the eulerian angle and the eulerian shaft of the satellite system relative to those of the target system and the kinematical equation of the eulerian angle and the kinematical equation of the eulerian shaft in the system, determining the quasi-quaternion and the kinematical equation of the quasi-quaternion in the system, and designing the controller to enable satellite gestures to be capable of tracking target gestures. The satellite pointing tracking control method based on the quasi-quaternion and the quasi-quaternion kinematical equation can be widely used in satellite pointing tracking control systems.
Owner:哈尔滨工大卫星技术有限公司
Accurate curvature estimation algorithm for path planning of autonomous driving vehicle
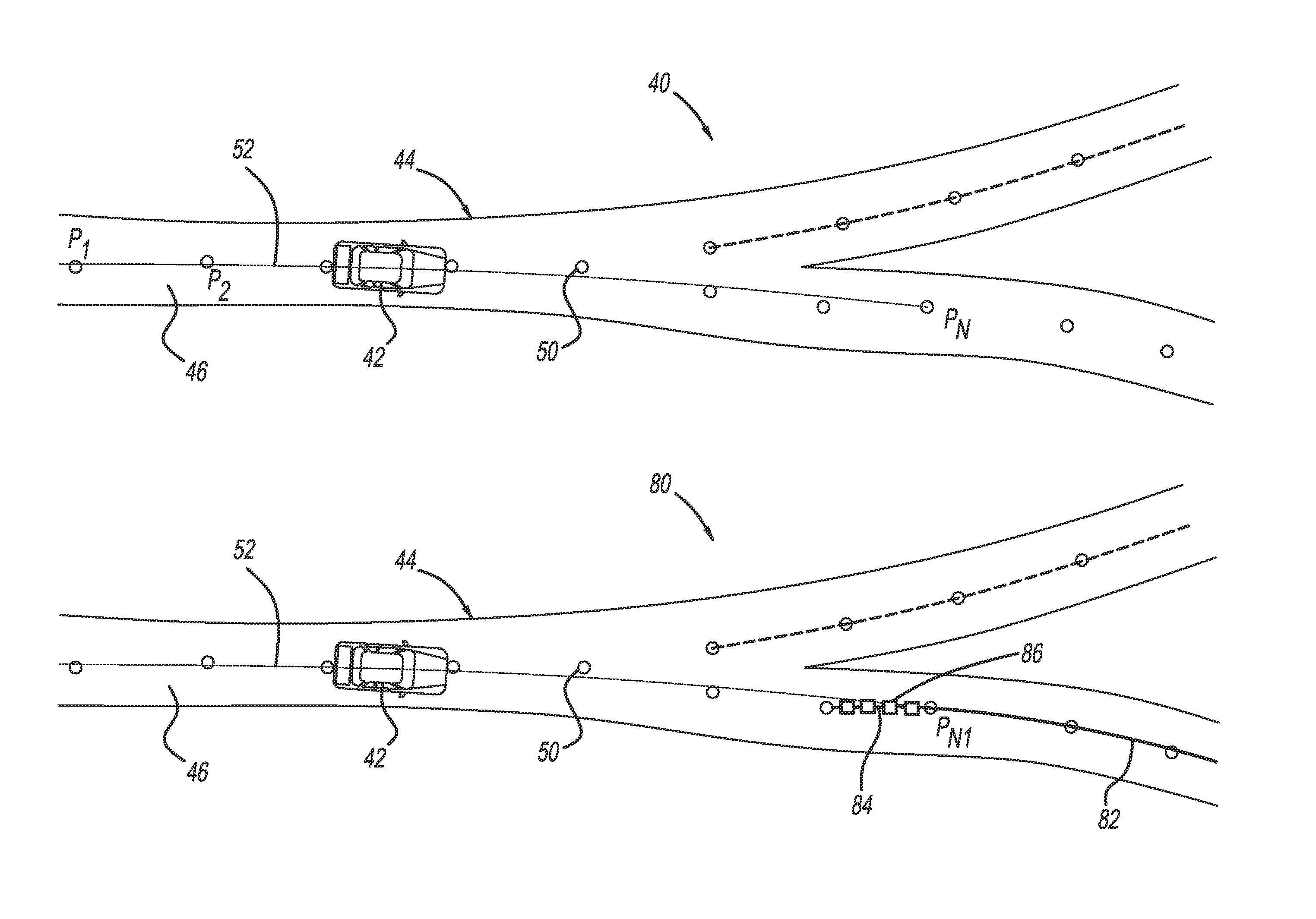
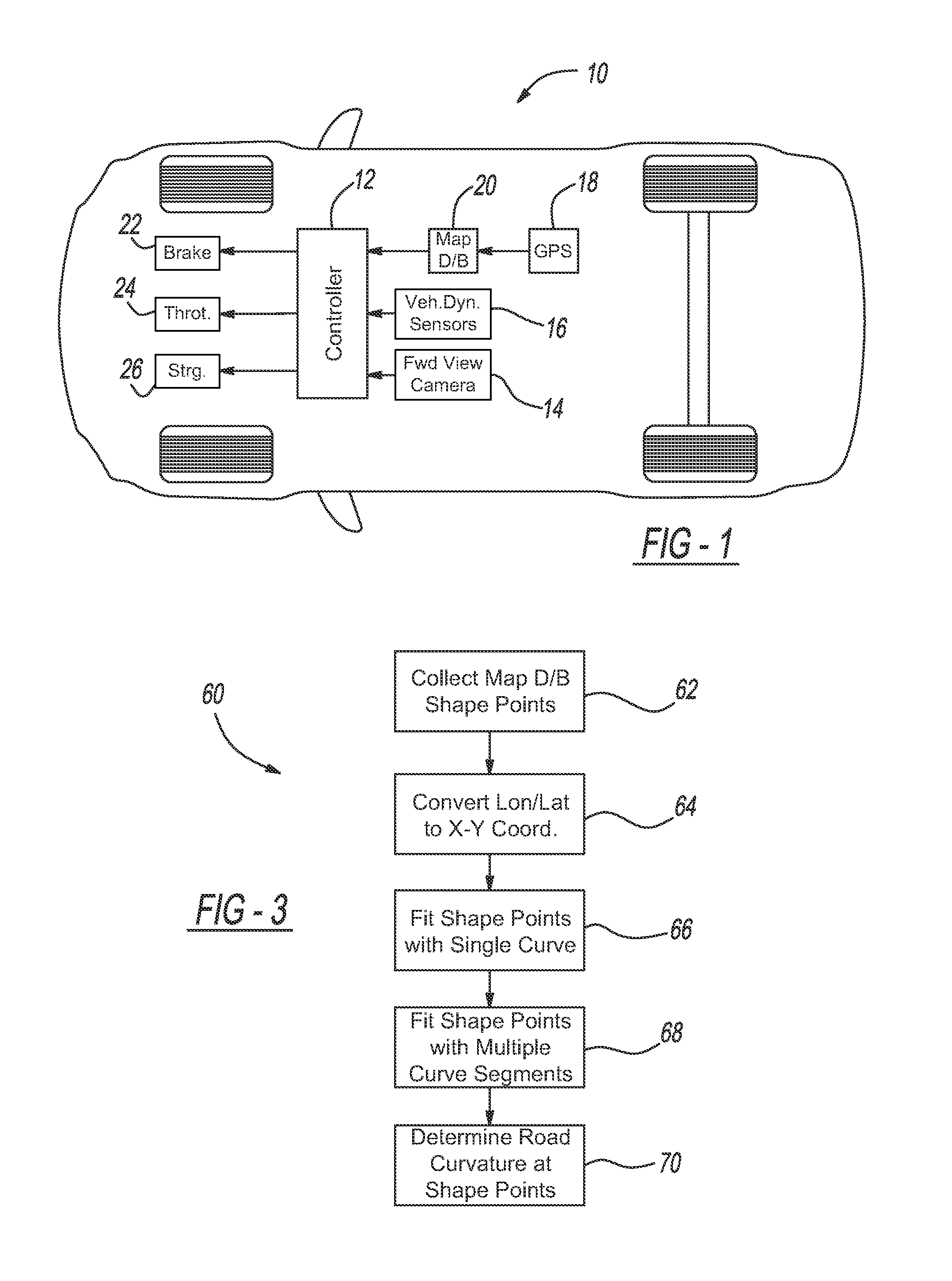
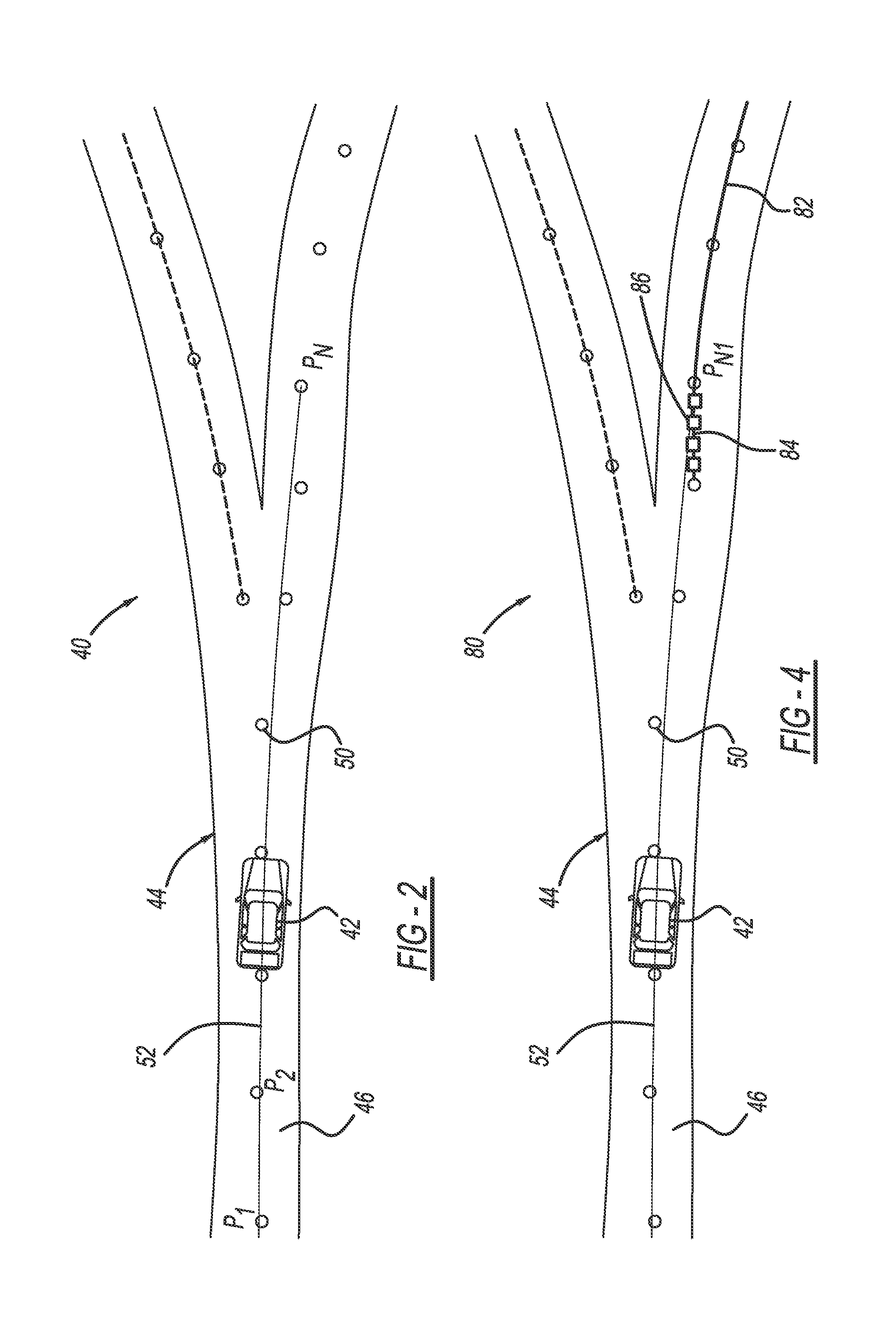
InactiveUS9283967B2Instruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsEquation of the centerAlgorithm
A method for identifying roadway curvature that includes determining a range of interest and collecting shape points from a map database from a current position of the vehicle to an end of the range of interest that define the location of the roadway. The method converts the shape points from World Geodetic System 84 (WGS84) coordinates to UTM coordinates, and then fits a single set of polynomial equations to define a curve using the converted shape points. The method determines whether the single set of polynomial equations exceeds a predetermined curvature accuracy threshold, and if so, fits multiple sets of polynomial equations to multiple roadway segments over the range of interest using the converted shape points. The method then determines the roadway curvature at any roadway location using solutions to the multiple sets of polynomial equations.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
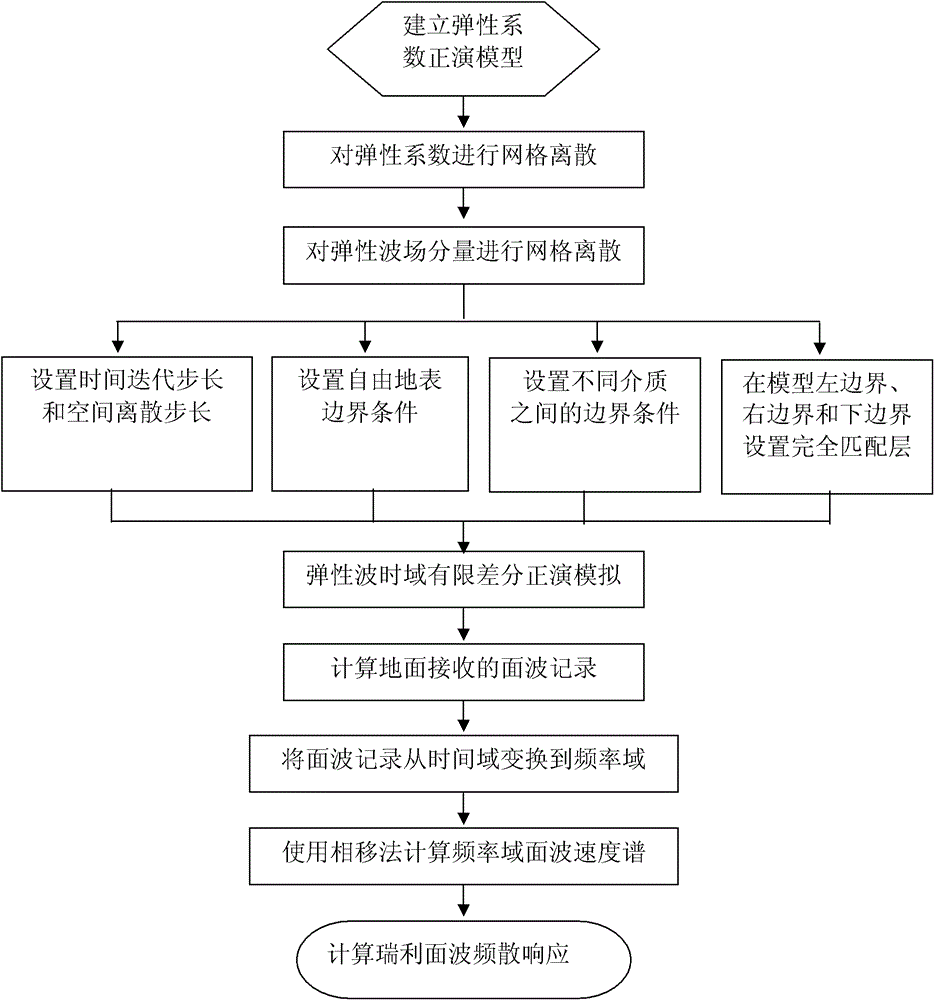
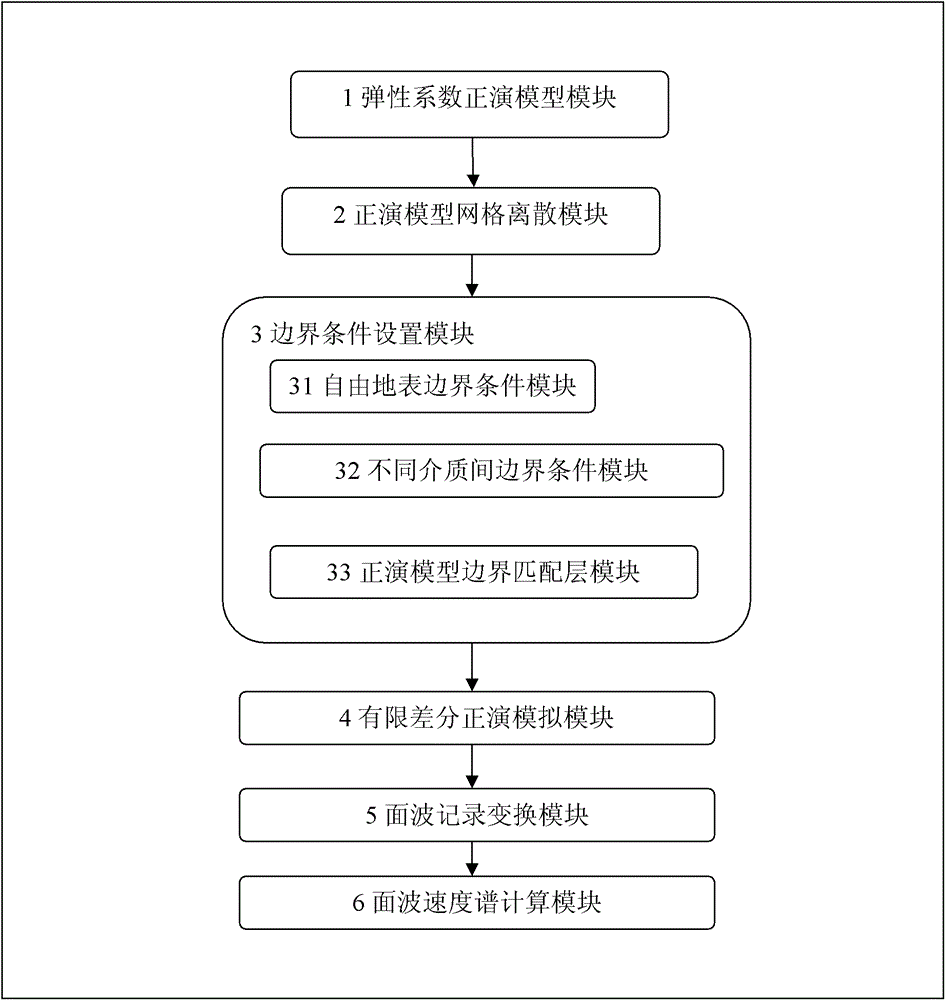
Method and device for calculating Rayleigh surface wave dispersion response by forward modeling of wave equation
ActiveCN102749643AExplain correctnessExplain credibilitySeismic signal processingTime domainWave equation
The invention discloses a method and device for calculating Rayleigh surface wave dispersion response by forward modeling of a wave equation. A phase velocity spectrum of a surface wave, namely, the dispersion response of a Rayleigh surface wave in a frequency domain, is calculated by adopting high-precision higher-order finite difference, rationally setting boundary conditions of a free surface, effectively suppressing false reflection of an external boundary of a model and adopting a Radon transformation method. According to the method and the device disclosed by the invention, Rayleigh surface wave dispersion response characteristics are calculated by forward modeling simulation of finite time-domain difference based on an anisotropic elastic wave equation, wherein the geological model can be an anisotropic and non-horizontal layered medium, and the free surface can be a freely-fluctuated surface. The method and the device can be used for researching the Rayleigh surface wave dispersion response characteristics of complex media.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
A Method for Estimating the Position of Spacecraft's Center of Mass in Orbit
InactiveCN108401561BReduced measurement accuracySmall estimated absolute errorStatic/dynamic balance measurementComplex mathematical operationsAccelerometerKinematics equations
The invention relates to a method for estimating the position of the center of mass of a spacecraft, in particular to a method for quickly estimating the position of the center of mass of the spacecraft. The technical feature is that: based on attitude kinematics equations, the center of mass position estimation equation is established by using the least square method. Two accelerometers are installed in the three-axis direction of the spacecraft body, combined with the gyro information, the angular acceleration at each time is calculated, which avoids the calculation error caused by the direct differentiation of the angular velocity to obtain the angular acceleration, and greatly reduces the estimation algorithm. measurement accuracy requirements. The new method for estimating the center of mass of the spacecraft does not need to know the information of the moment of inertia and control moment of the spacecraft, and the algorithm is simple, which can ensure that the absolute error of the estimation of the center of mass of the spacecraft is less than 10 mm.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method for measuring and calculating inertial parameter of non-contact-type tumbling spacecraft
ActiveCN106468554AReduce mistakesImprove estimation accuracyInstruments for comonautical navigationStatic/dynamic balance measurementAngular velocitySpaceflight
The invention discloses a method for measuring and calculating an inertial parameter of a non-contact-type tumbling spacecraft, and relates to the technology of attitude as well as inertia moment measurement of the tumbling spacecraft under a space on-orbit-servicing technology belonging to the field of spaceflight. A principle is characterized in that an analytical solution of an attitude quaternion kinetic equation of the tumbling spacecraft is employed, and the attitude quaternion is expressed as an equation having a linear form and containing the undetermined parameters; then the undetermined parameters of the constant values substitute the inertia parameter, angular velocity and attitude angle for being as a state quantity of a system, and a Kalman filter is used for estimation. The observed quantity obtained by employing the Kalman filter is the measured value of the attitude quaternion of the tumbling spacecraft obtained by a current observation technology. Following with the increasing observation data, the estimated value of the constant parameter is more and more accurate, by using the estimated value of the undetermined parameters, the ratio of the main inertia moments of the tumbling spacecraft can be directly reckoned.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Singularity Escape and Avoidance Using A Virtual Array Rotation
ActiveUS20080251646A1Improving reliability and operationMechanical apparatusCosmonautic vehiclesEquation of the centerVirtual array
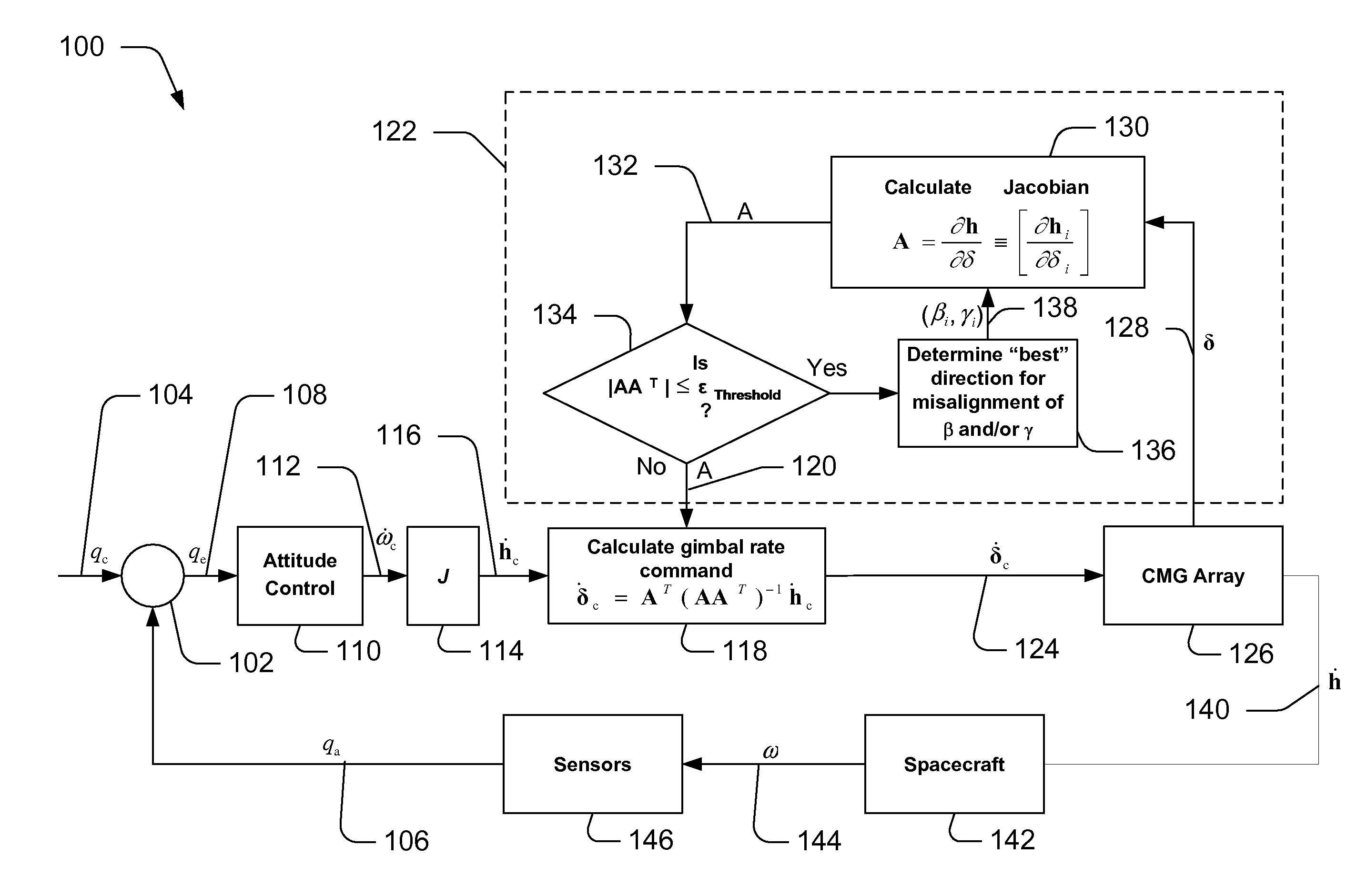
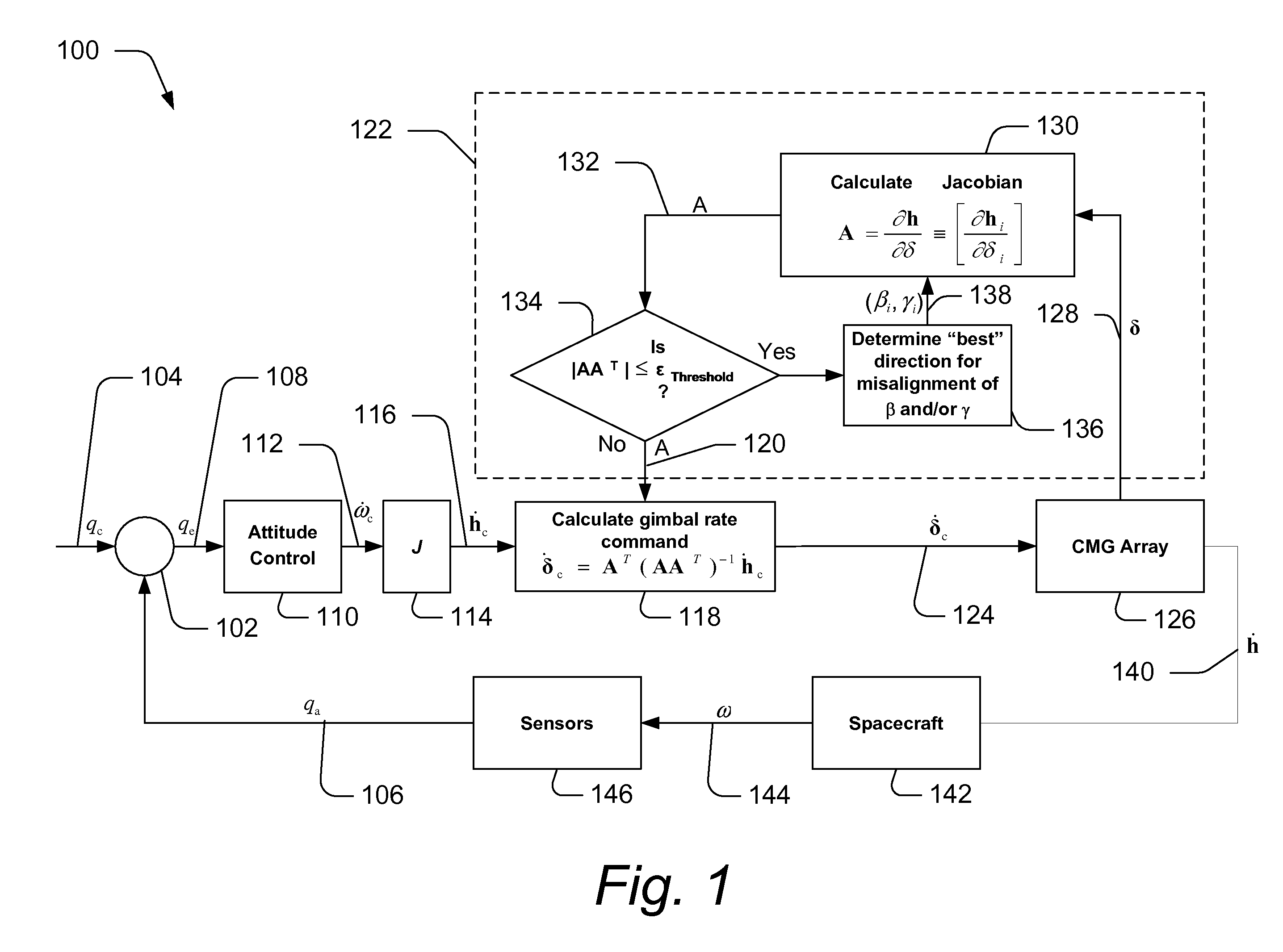
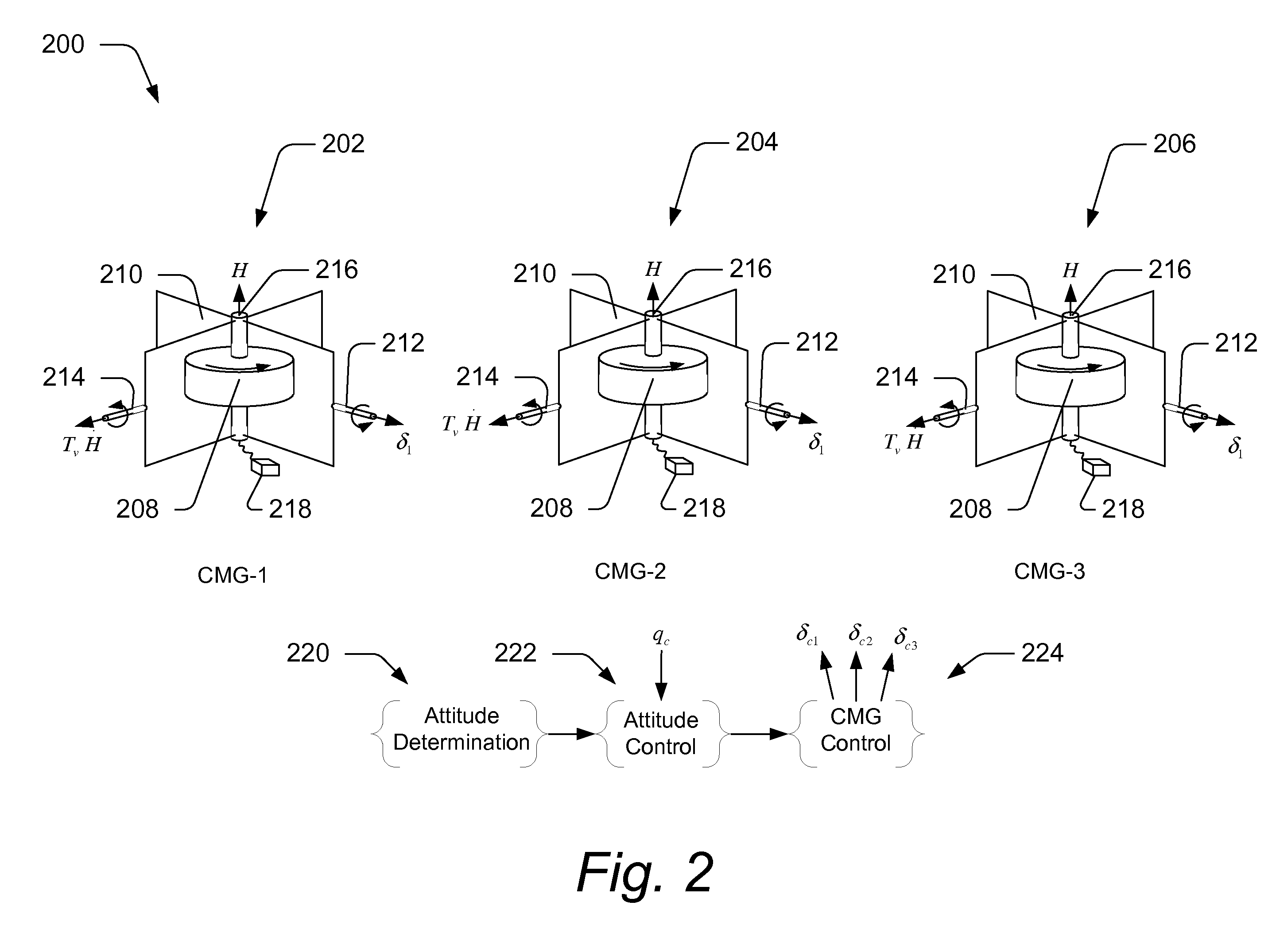
Techniques for providing singularity escape and avoidance are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method for providing control moment gyroscope (CMG) attitude control singularity escape includes calculating a Jacobian A of a set of control equations, calculating a measure of closeness to a singularity, and comparing the calculated closeness to a threshold value, when the calculated closeness is less than or equal to the threshold value, recalculating the Jacobian A. Recalculating may include determining a new direction of virtual misalignment of β and γ, recalculating the Jacobian inputting the new direction of the virtual misalignment, recalculating the measure of closeness to a singularity, and comparing the measure of closeness to the threshold value. Further, the method may include calculating a gimbal rate command if the of closeness is greater than the threshold value and generating a torque from the gimbal rate command to control the attitude of a satellite.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Near-real time earthquake source position positioning method
InactiveCN105759311AHigh positioning accuracyImproving the accuracy of earthquake locationSeismic signal processingEquation of the centerGeophysics
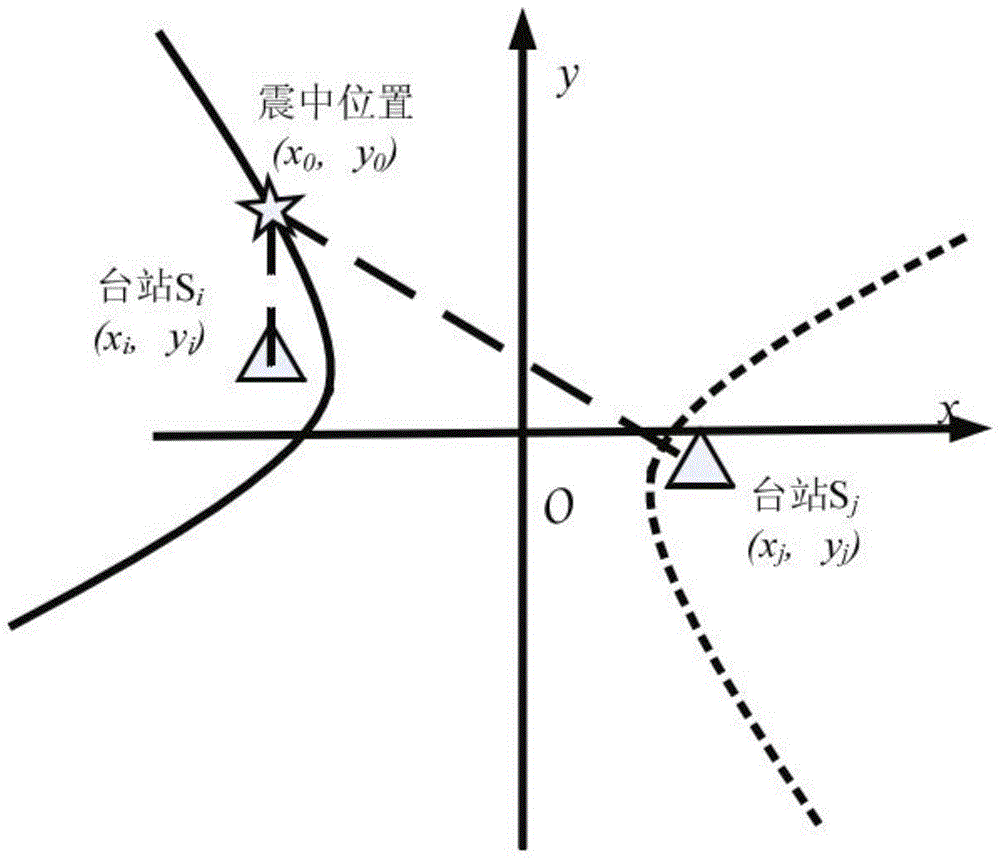
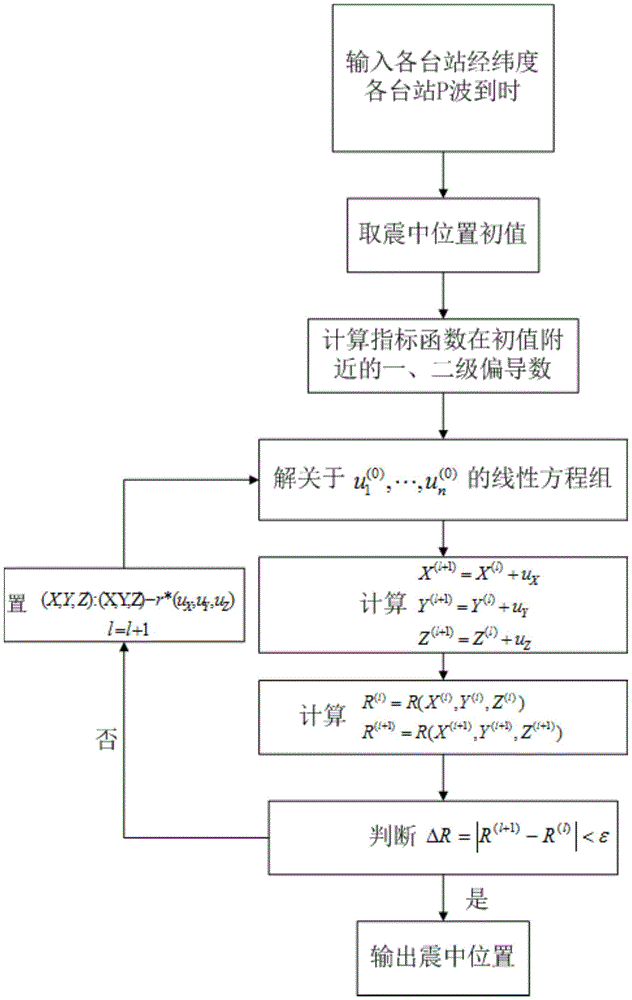
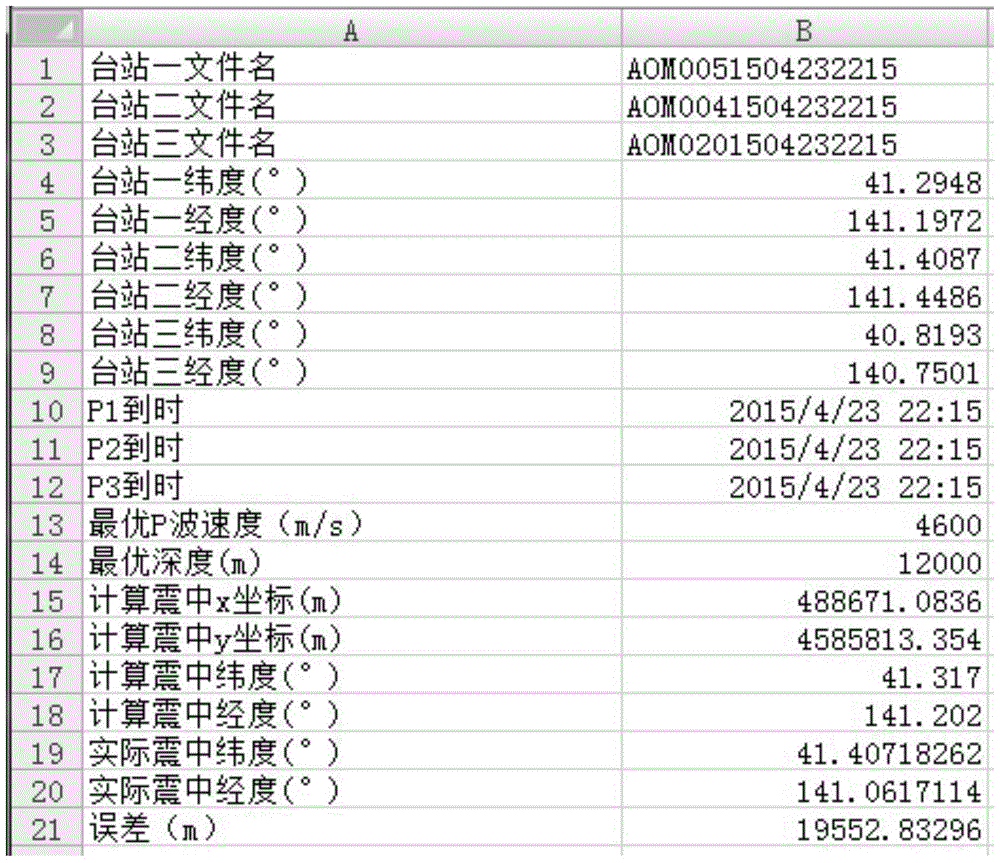
The invention discloses a near-real time earthquake source position positioning method. The method comprises the following steps: after an earthquake happens, numbers and geographical coordinates of three stations firstly acquiring P wave arrival time are read, the P wave arrival time is recognized, arrival time differences are solved pairwisely, and latitude and longitude coordinate data of earthquake stations are subjected to projection transformation and converted into plane rectangular coordinates; as for any two stations, hyperbolic curves meeting the arrival time differences are drawn, the epicenter is close to the one of the early-arrival station, and any two of the three hyperbolic curves are intersected; according to a triangle formed by coordinates of the intersected points, the gravity center of the triangle is calculated, and the coordinates of the gravity center are the initial value of the epicenter position; the earthquake source position is revised further; variable reduction processing is carried out on an observation equation and an index function; a partial derivative is solved until the requirements are met; and the final calculation result is converted into geographic coordinates, and the coordinates are the final result. Through eliminating errors for the epicenter azimuth and earthquake magnitude estimation, the earthquake positioning precision and the positioning speed are improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Method of estimating floor reaction of bipedal movable body
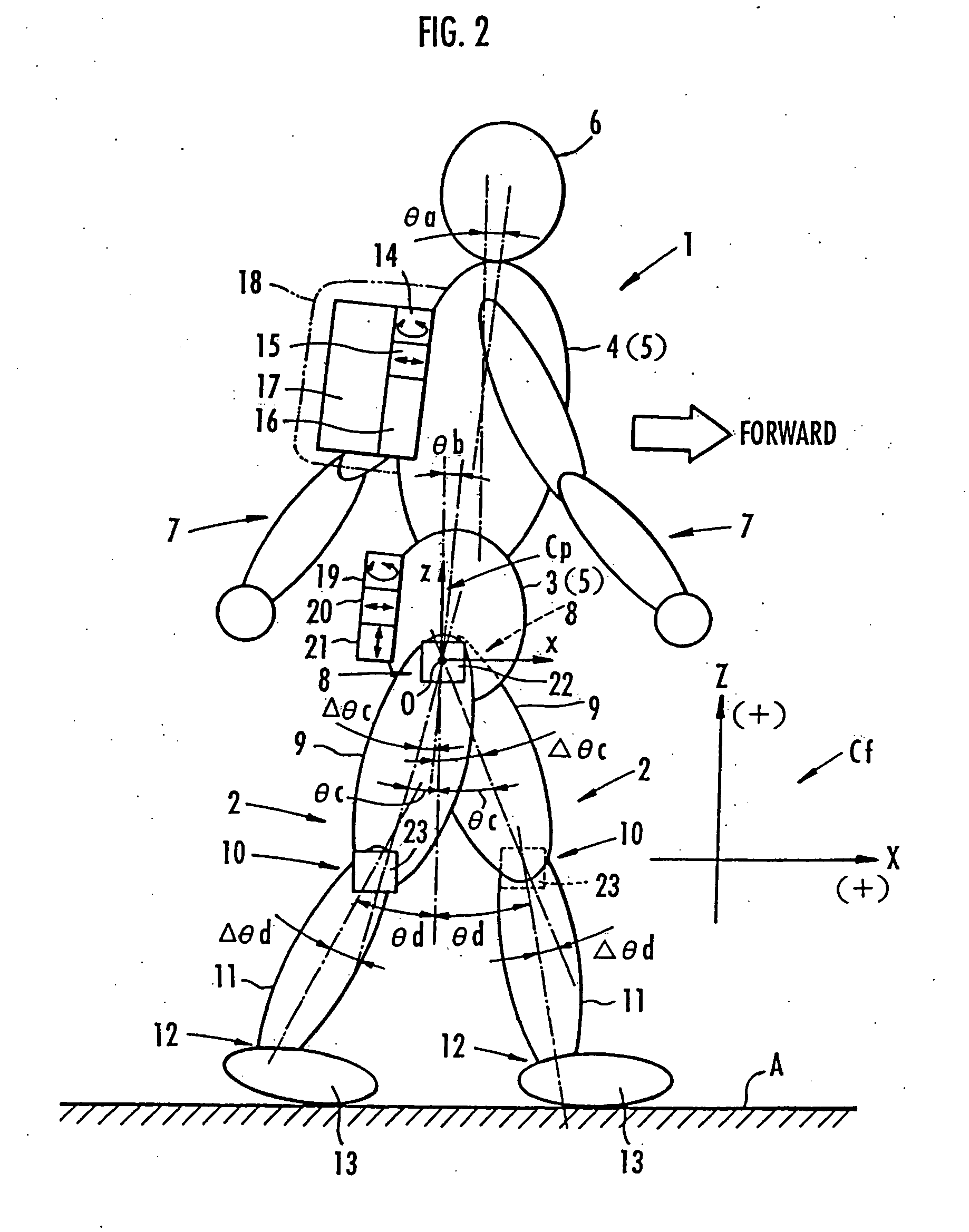
InactiveUS20050080590A1Easy to installSimple processDigital computer detailsAcceleration measurementEquation of the centerEngineering
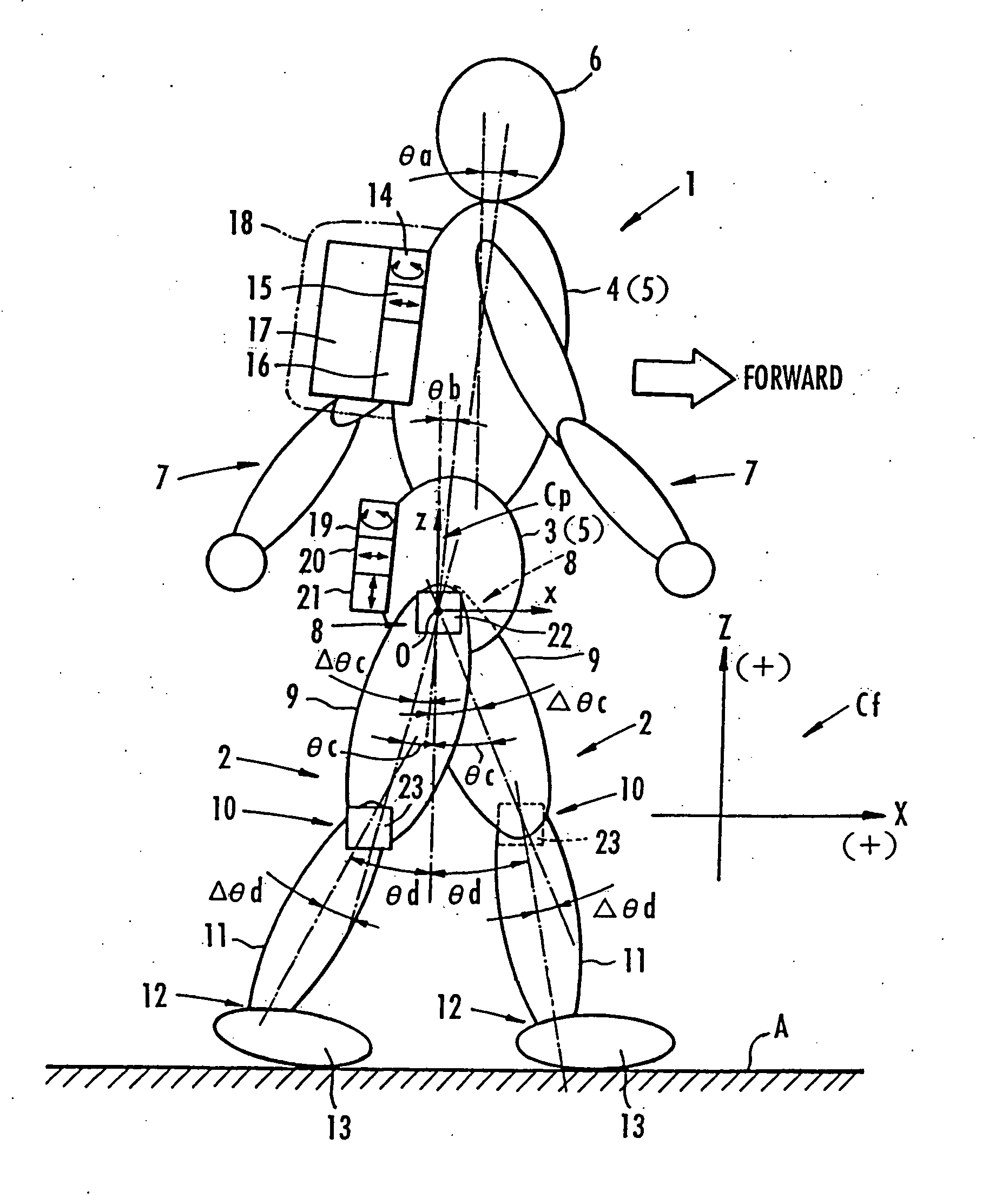
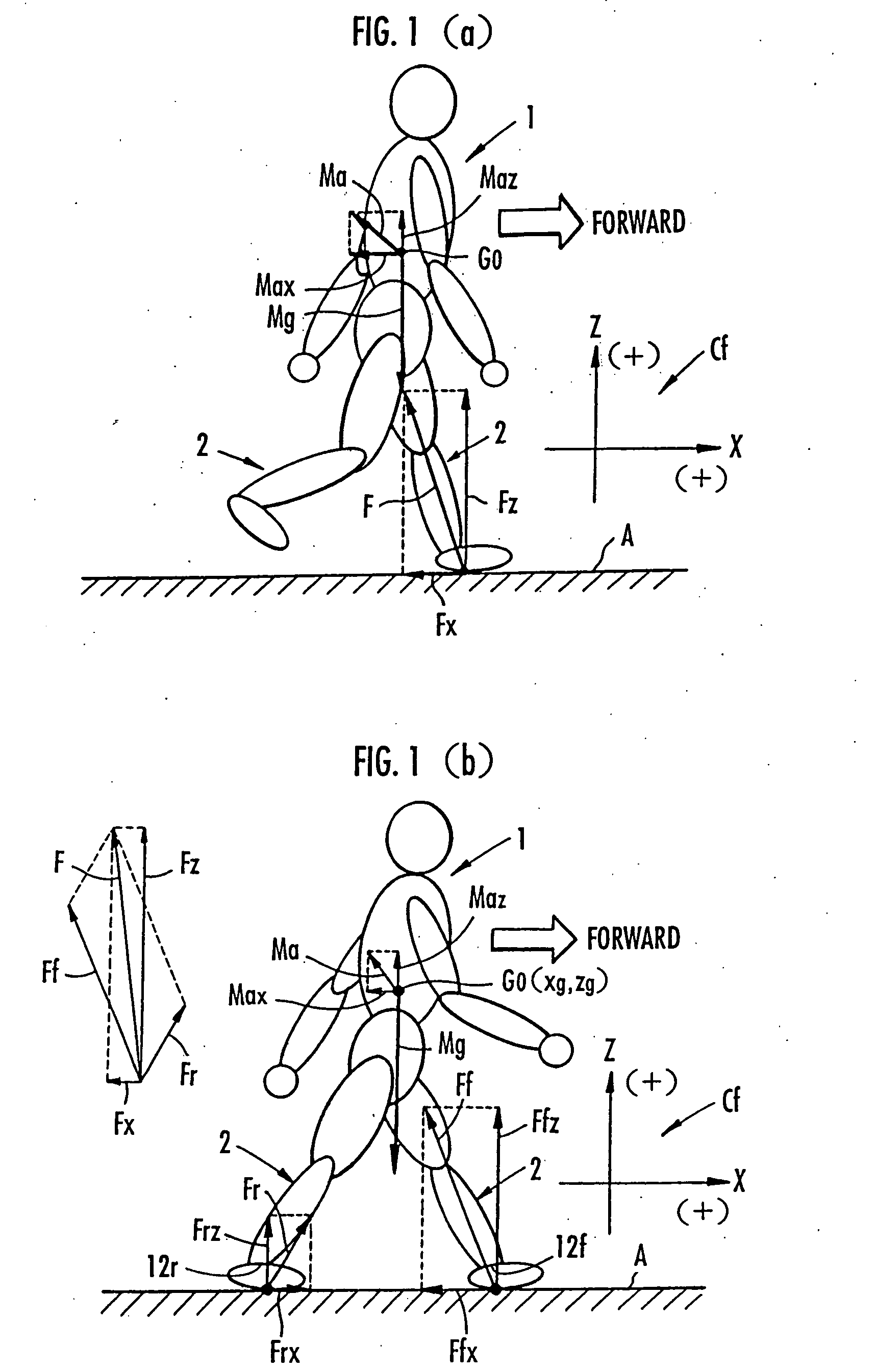
It is determined whether the motion state of legs 2, 2 is a one-leg supporting state or a two-leg supporting state, and a total floor reaction force is estimated based on a motion equation of the center of gravity of a bipedal movable body 1. If the motion state of legs 2, 2 is the one-leg supporting state, the estimated value of the total floor reaction force is used as an estimated value of the floor reaction force on the leg 2 which is landed. When the motion state changes to the two-leg supporting state, a vertical component of the floor reaction force on the rear leg is estimated from the MP height of the front leg based on a predetermined correlation between the MP height of the front leg and the vertical component of the floor reaction force on the leg.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
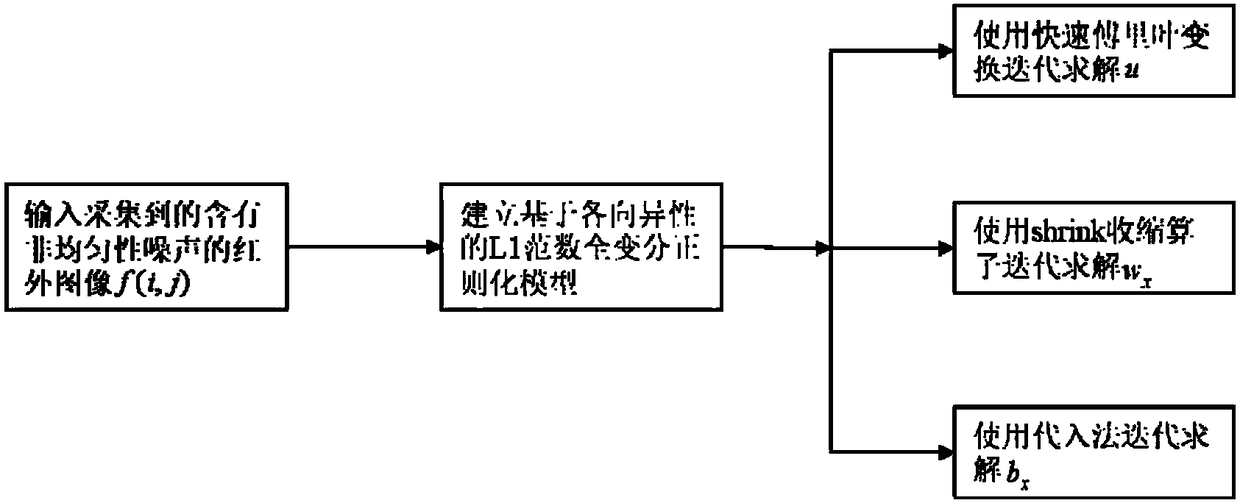
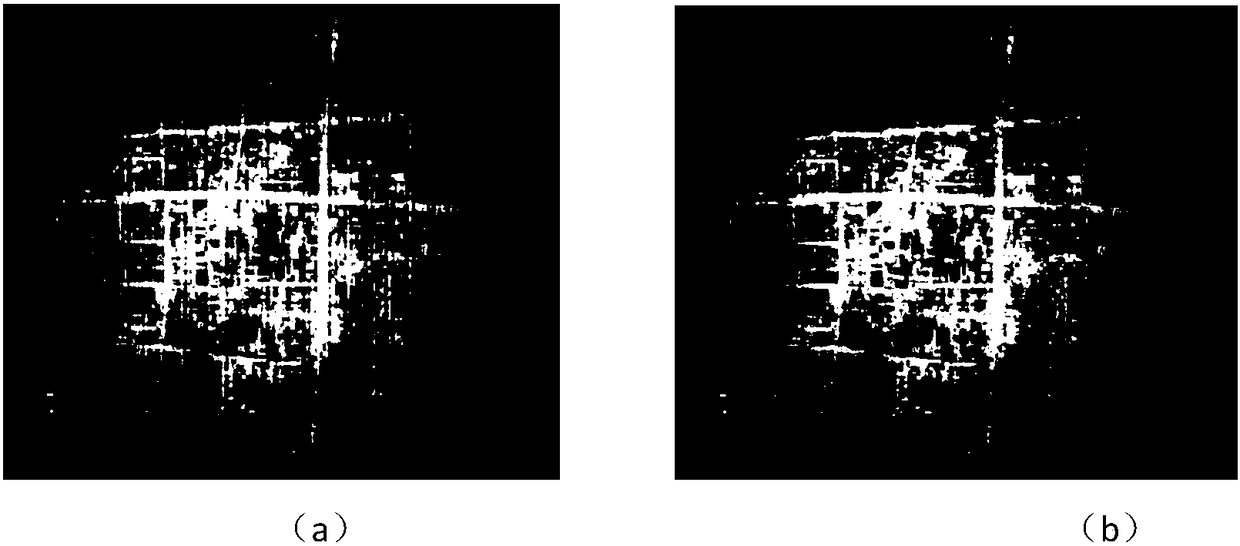
L1 norm total variation regularization heterogeneity correction method based on anisotropy
ActiveCN108230249AImprove denoising processing speedKeep detailsImage enhancementImage analysisEquation of the centerSingle image
The invention discloses an L1 norm total variation regularization heterogeneity correction method based on anisotropy. The method comprises the following steps that: establishing anisotropy total variation regularization model based on a single image, converting a problem of removing infrared image heterogeneity stripe noise into a minimized total variation problem, then, adopting a separated Bragg iteration method to carry out optimization to obtain an optimal solution, and taking a last iteration result as a corrected infrared image. The method has an innovation point that a traditional total variation model aims at a structural feature improvement equation that the horizontal direction total variation of heterogeneity stripe noise is far greater than vertical direction total variation,a regularized constraint based on the L1 norm can be used to enable the method to be suitable for the heterogeneity correction of the infrared image, the separated Bragg iteration method replaces a steepest gradient descent method to carry out the optimal processing of the equation, processing speed is greatly improved, and the edge information of an object is kept to a maximum degree.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
WSN node positioning method based on combination of PSO and UKF
InactiveCN104023390AImprove environmental adaptabilityFast convergenceNetwork topologiesEquation of the centerEquation of state
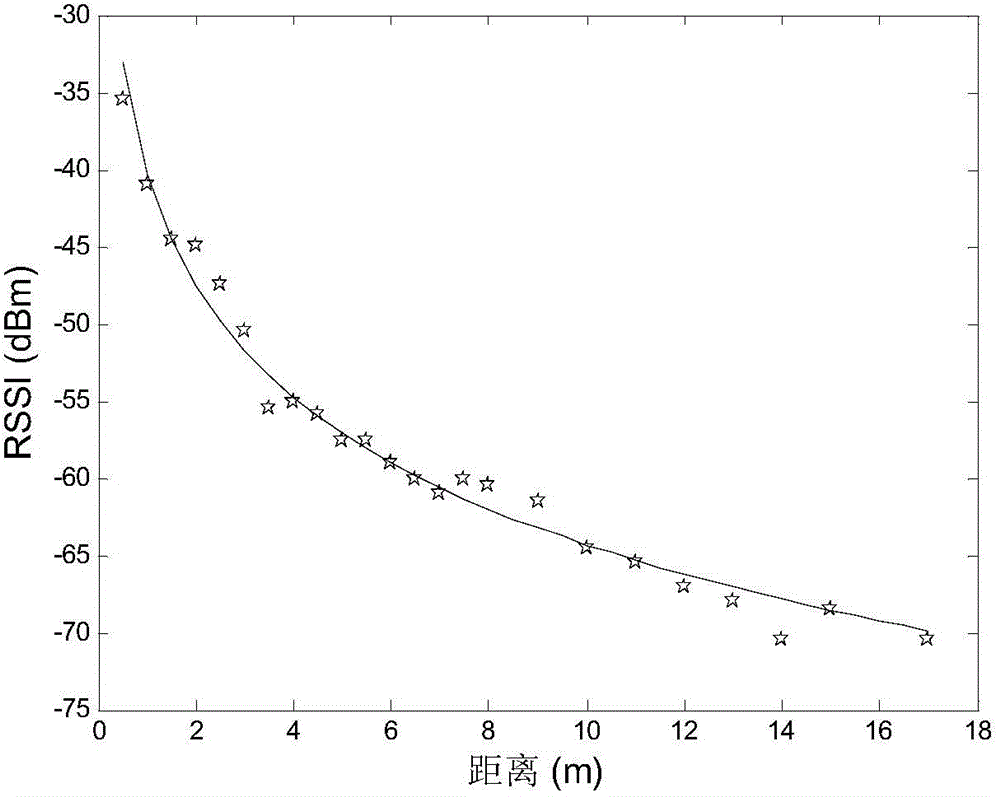
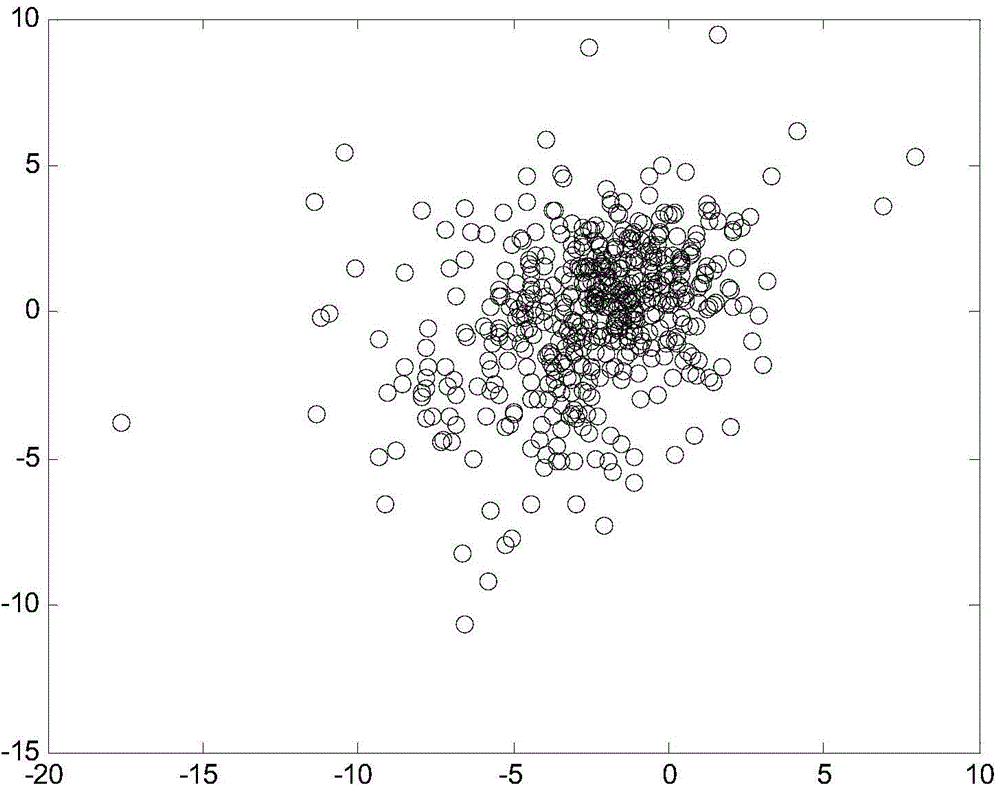
The invention relates to a WSN node positioning method based on combination of PSO and UKF. The PSO is utilized to carry out preliminary positioning, and the acquired coordinate figure is taken as an initial value of the UKF; a state equation and a measurement equation of the positioning system are established, an RSSI value is taken as observed quantity, a coordinate estimate of an unknown node is acquired, and multitime iteration is carried out; a mass center algorithm principle is utilized, and a polygon mass center coordinate is taken as the final estimate coordinate of the unknown node. Compared with a traditional positioning algorithm, the WSN node positioning method has advantages of higher positioning precision, stronger reliability and relatively strong practical value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Double-Doppler radar three-dimensional wind field retrieval method
ActiveCN107843895AImprove accuracyFacilitate network analysisRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationRadar observationsEquation of the center
The invention relates to a double-Doppler radar three-dimensional wind field retrieval method. The method comprises the following steps that: a dynamic earth coordinate system is determined; a grid which is corresponding to the dynamic earth coordinate system and is equal to the dynamic earth coordinate system in longitude, latitude and altitude is adopted as a retrieval grid; the influence of atmospheric refraction on wind field retrieval is analyzed, so that an included angle between a radar beam at a target point and the horizontal plane of the target point is obtained; by means of the included angle between the radar beam at the target point and the horizontal plane of the target point, radial velocity with the influence of standard atmospheric refraction on vertical wind velocity projection considered is obtained; radial velocities observed by two radars on the same grid point, are approximated as horizontal wind vectors, and are synthesized, so that a resultant wind velocity is generated; and by means of a mass continuous equation and the falling velocity empirical formula of precipitation particles, iterative calculation is performed until the error of two iterations is smaller than a preset value, and finally the three-dimensional wind field of a precipitation echo region is obtained. According to the method of the invention, the influence of the standard atmospheric refraction on the double-radar wind field retrieval is considered, and the accuracy of the wind field retrieval can be improved.
Owner:厦门市气象灾害防御技术中心(海峡气象开放实验室 +3
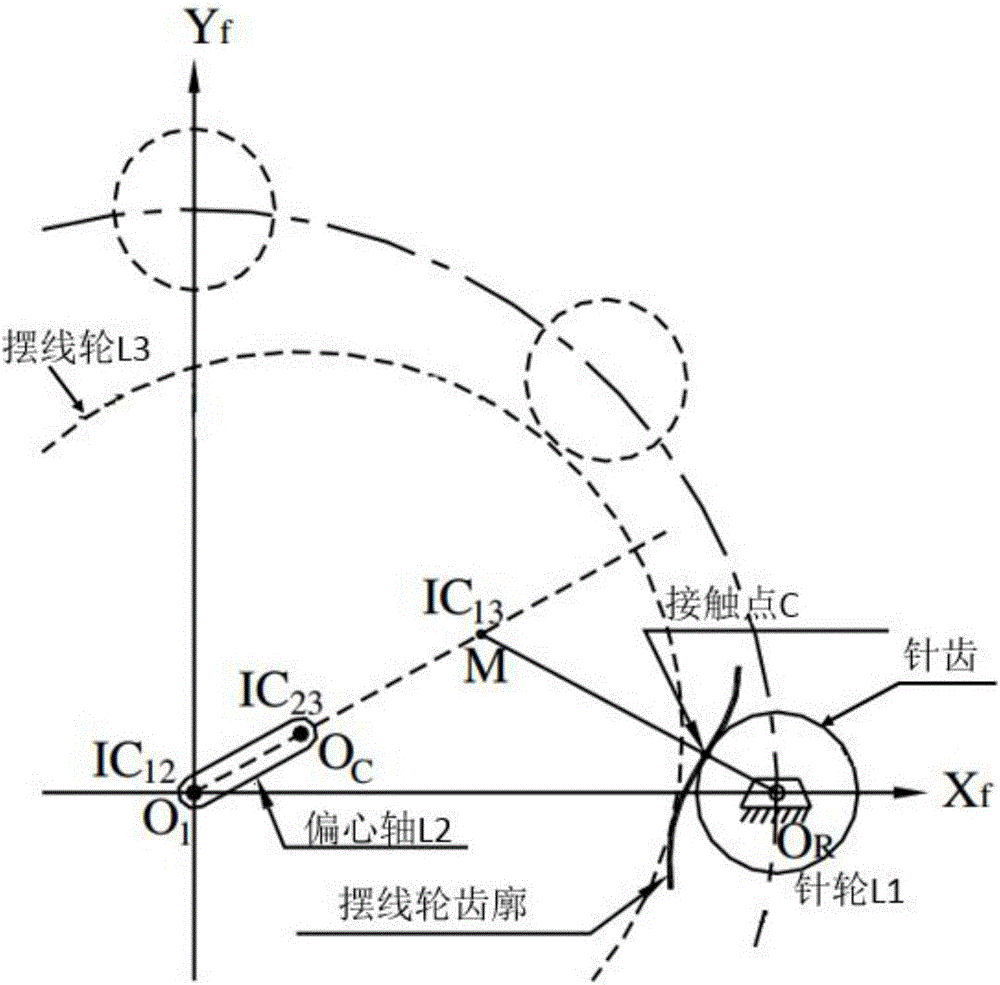
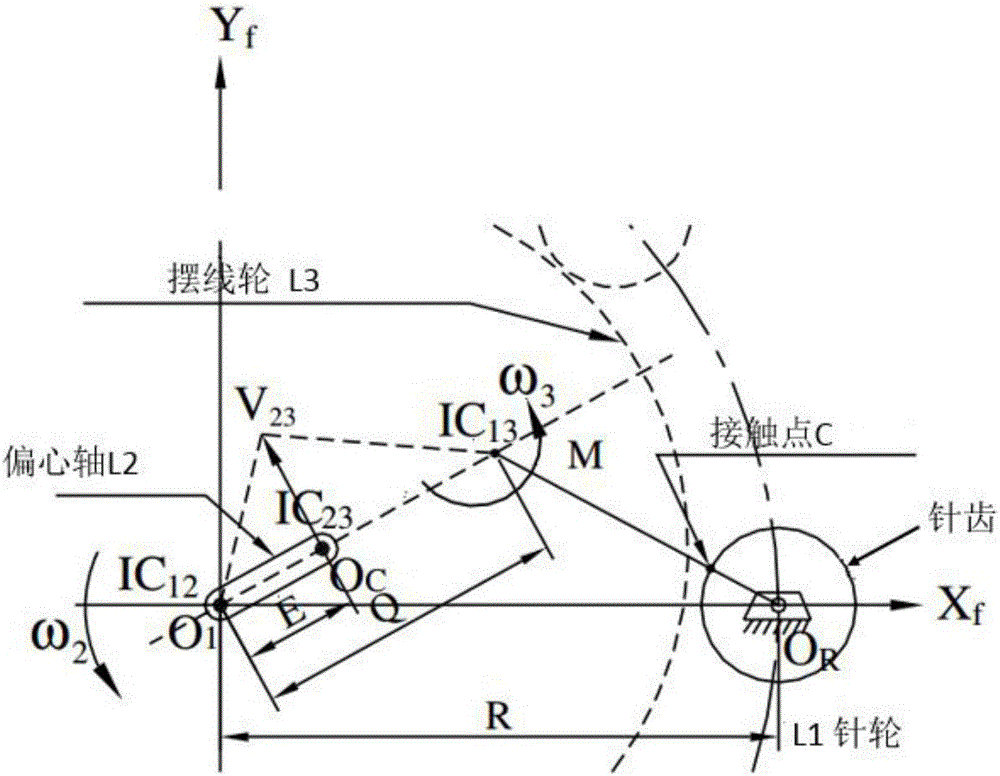
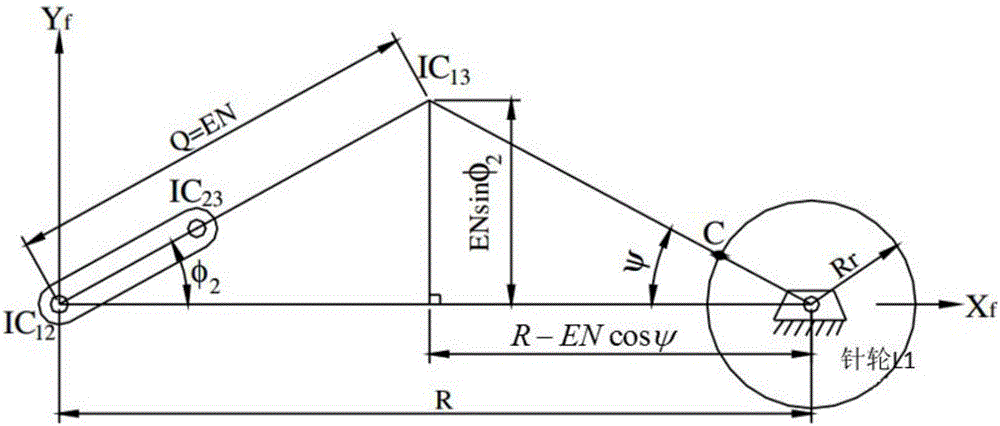
Design method for tooth profile equation of cycloidal gear based on instantaneous velocity center method
The invention discloses a design method for a tooth profile equation of a cycloidal gear based on the instantaneous velocity center method. The design method comprises the steps of 1, determining the correspondence relation between the instantaneous velocity center and the turning angle of a cycloidal pin gear speed reducer, wherein for determining the position relation of the instantaneous velocity center of the cycloidal pin gear, the eccentric distance is recorded as E, the number of teeth of the pin gear is recorded as N, the radius of pin teeth is recorded as Rr, the radius of the center circle of the pin gear is recorded as R, and the distance length is recorded as Q; and 2, obtaining the tooth profile equation of the cycloidal gear through the homogeneous coordinate transformation technology. The design method for the tooth profile equation of the cycloidal gear based on the instantaneous velocity center method is obtained through the instantaneous velocity center method and the homogeneous coordinate transformation technology, and theoretical bases can be provided for quickly and conveniently obtaining the tooth profile equation of the cycloidal pin gear.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
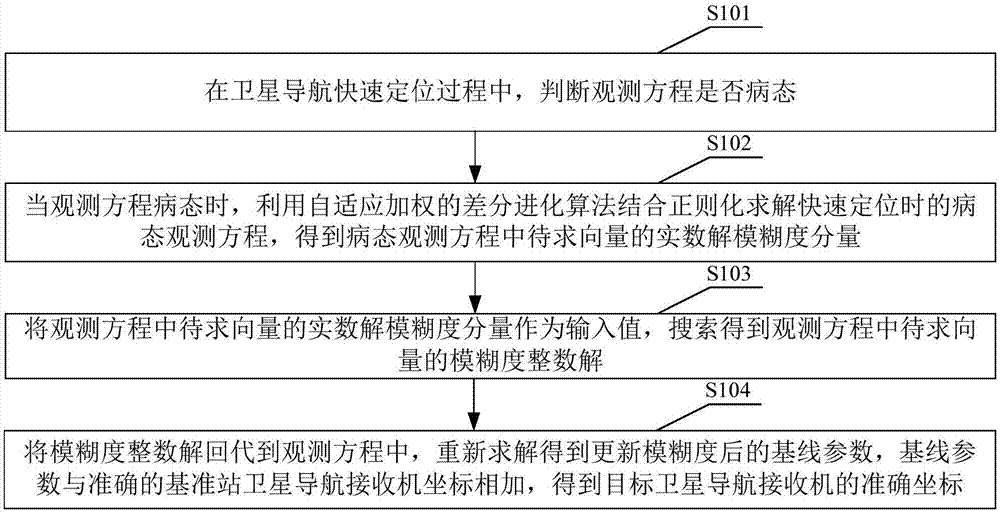
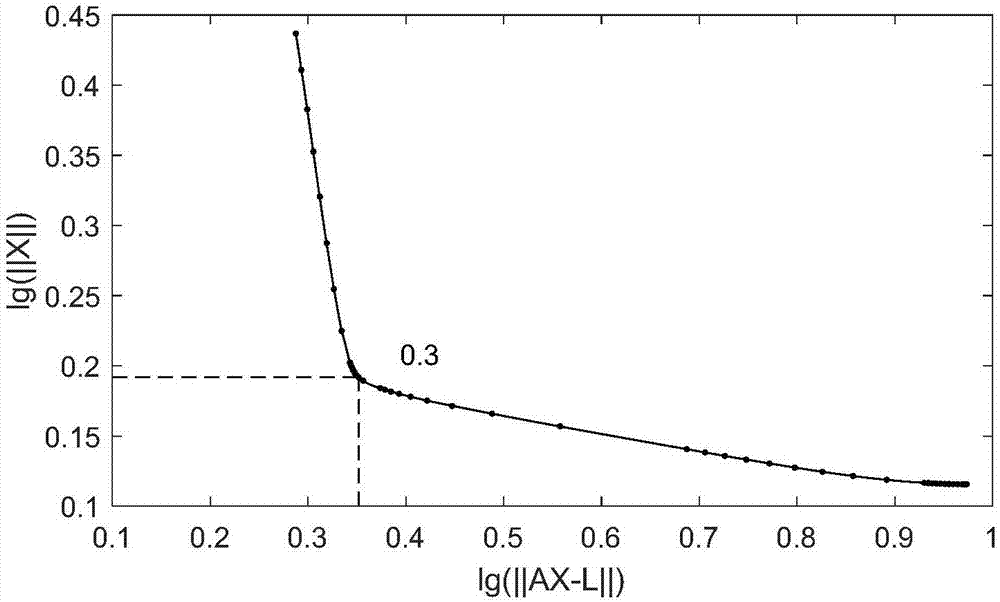
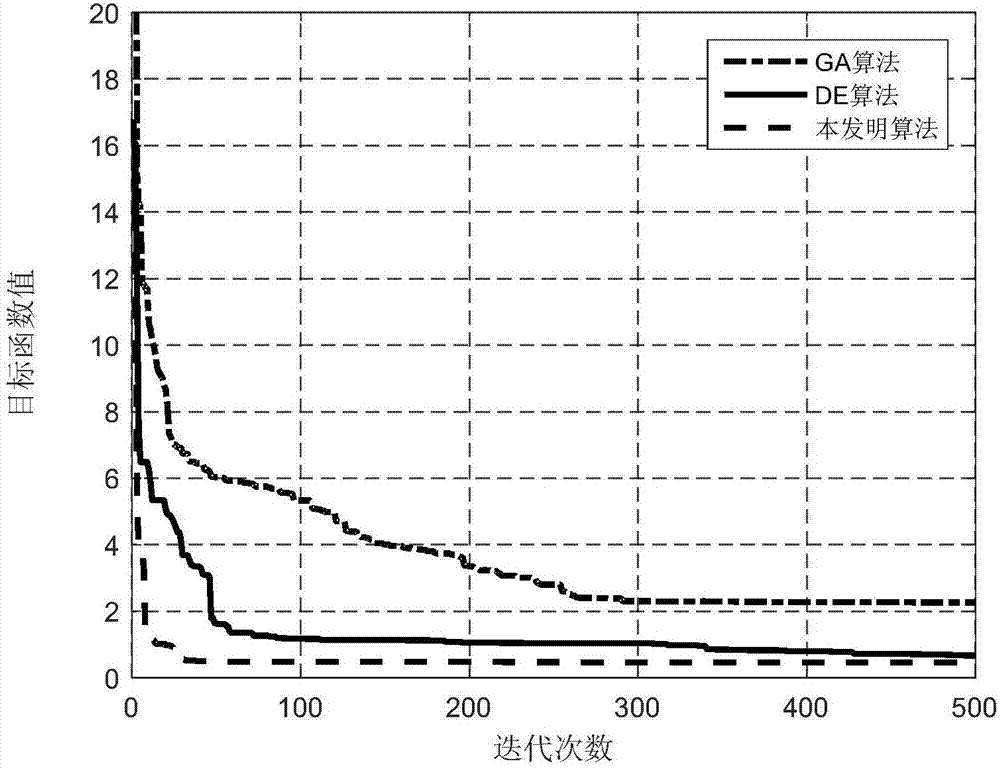
Satellite navigation fast positioning method and device and satellite navigation receiver
ActiveCN107490800AFast convergenceWide range of searchSatellite radio beaconingAdaptive weightingEquation of the center
The present invention is applicable to the field of satellite navigation and provides a satellite navigation fast positioning method and device and a satellite navigation receiver. The method comprises the following steps of: judging whether an observation equation is sick or not; solving an ill observation equation in fast positioning with the combination of regularization by using a differential evolutionary algorithm with adaptive weighting when the observation equation is ill, and obtaining a real number solution ambiguity component of the vector to be solved in the ill observation equation; taking the real number solution ambiguity component of the vector to be solved in the observation equation as an input value and searching to obtain an ambiguity integer solution of the vector to be solved in the observation equation; substituting the ambiguity integer solution into the observation equation, carrying out solution again to obtain baseline parameters with updated ambiguity, adding the baseline parameters and accurate reference station satellite navigation receiver coordinates, and obtaining accurate coordinates of a target satellite navigation receiver. According to the satellite navigation fast positioning method and device and the satellite navigation receiver, a global optimal solution is more easily obtained, the solution precision and speed are improved, ill conditions can be reduced, the gross error influence brought by noise and an observation error is suppressed, and the robustness is improved.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Glide trajectory error propagation analysis method based on perturbation theory
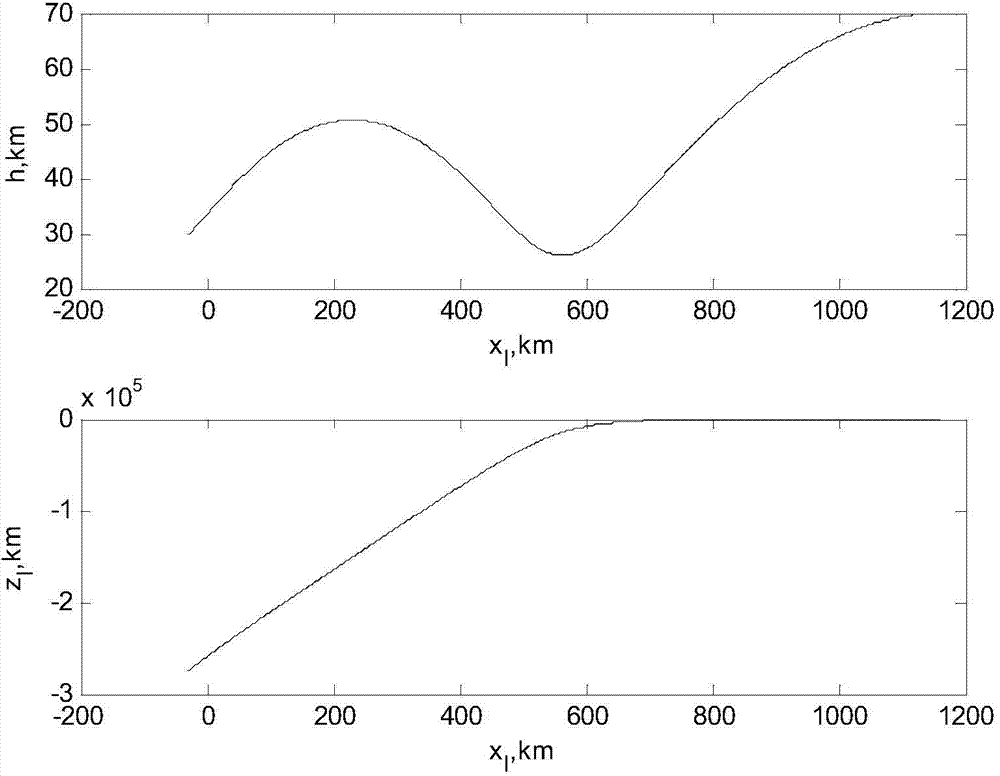
ActiveCN105138808AGain and deepen mechanistic understandingQuick fixSpecial data processing applicationsLongitudinal planePropagation of uncertainty
The invention relates to a glide trajectory error propagation analysis method based on the perturbation theory. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a pole-changing coordinate system by adopting a glide trajectory reentry longitudinal plane as a pole-changing equatorial plane; establishing an aircraft kinetic model in the pole-changing coordinate system and a motion perturbation equation; solving a state-transition matrix to obtain the analytic solution of the perturbation equation; and establishing an error propagation module in a common coordinate system based on the coordinate change. The glide trajectory error propagation analysis method provided by the method strives for filling up the blank of a glide trajectory perturbation factor influence mechanism analysis method of a hypersonic velocity glide aircraft, and lays a foundation and a method support for deepening the error propagation mechanism acquaintance and establishing a trajectory rapid correction method.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Ephemeris model-based method for analyzing shade of earth-moon L2 point Halo orbit
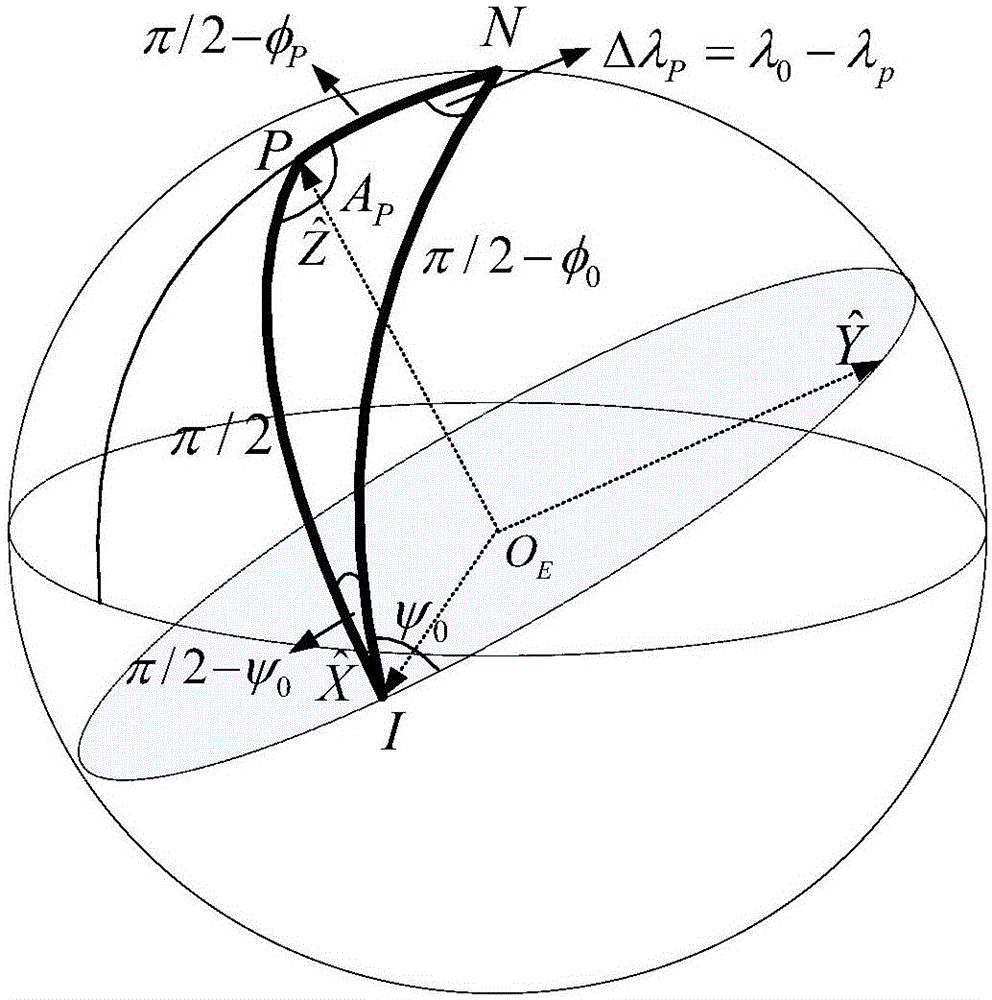
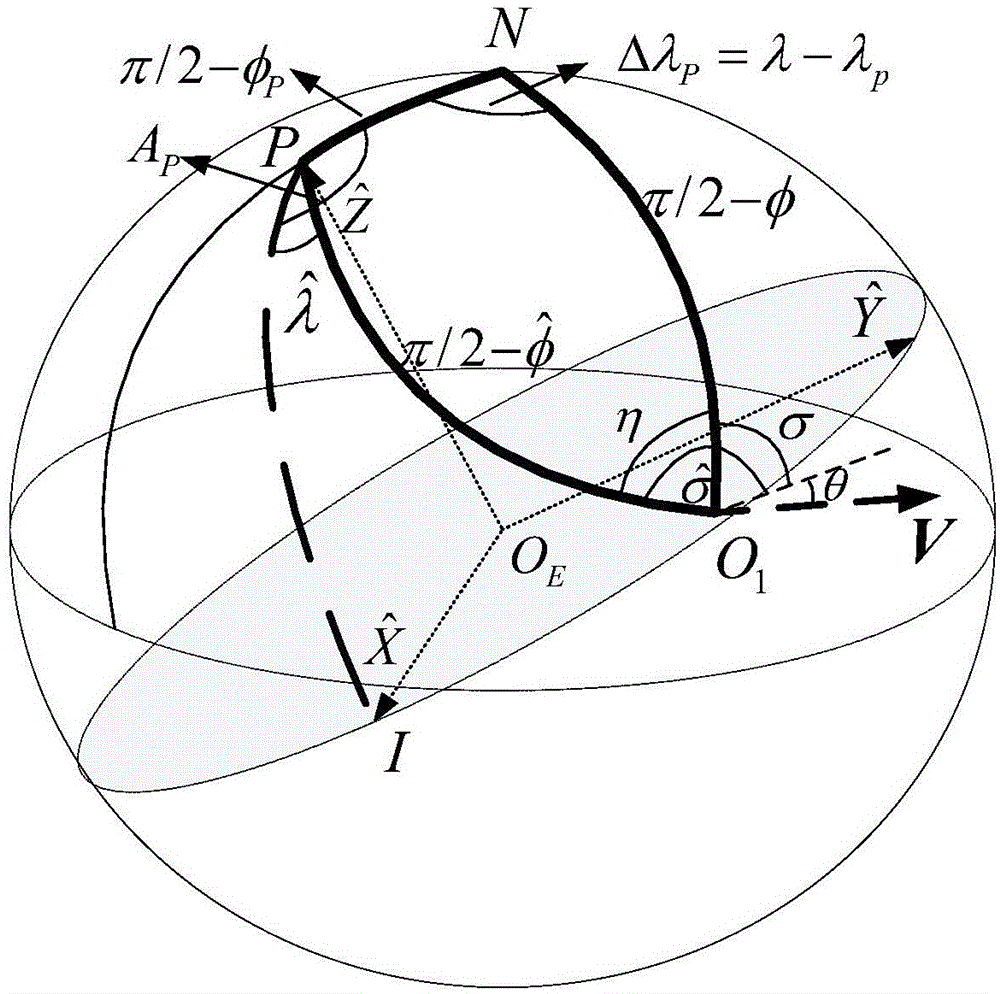
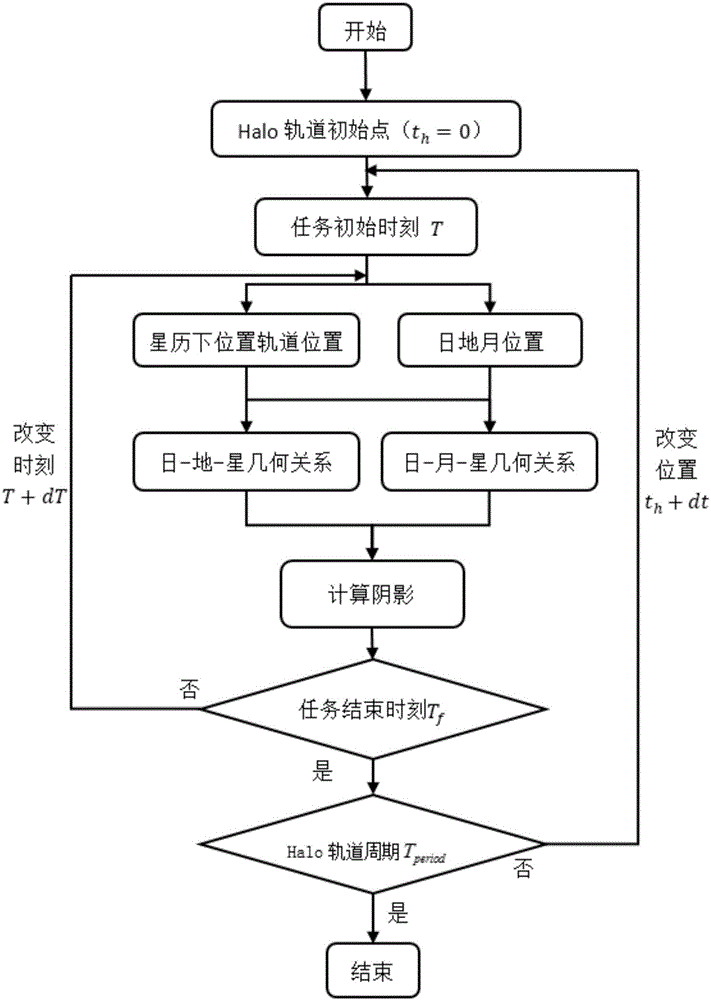
InactiveCN106679674AIncrease the degree of realismShadow Analysis Considers the Whole SituationInstruments for comonautical navigationNatural satelliteEquation of the center
The invention discloses an ephemeris model-based method for analyzing the shade of an earth-moon L2 point Halo orbit, and belongs to the technical field of aerospace. The method comprises the steps of building a kinetic equation under a restricted three-body model formed by the earth, the moon and the planet and generating the Halo orbit near an L2 point under an earth-moon rotation system; selecting on-orbit time th and a corresponding task moment T within a Halo orbit period and converting the Halo orbit under a rotary coordinate system into an inertia system; judging the shielding conditions of the earth and the planet on the satellite by using a conical shadow model according to the sun-earth-planet relative position and the sun-moon-planet relative position under an inertia coordinate system; changing the task moment T, and calculating the sun-earth-planet relative position and the sun-moon-planet relative position, carrying out shadow analysis by using the conical shadow model again until the orbit is completed; and changing the on-orbit time th of the Halo orbit, repeating the analysis, and calculating the shadow distribution conditions at different positions. The real degree is high, and the shadow analysis consideration is more comprehensive.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for simulating deviation of guidance of solid rocket launch vehicle
ActiveCN107562999ASimple calculationPracticalSpecial data processing applicationsWork periodGuidance system
The present invention provides a method for simulating the deviation of guidance of a solid rocket launch vehicle. The method comprises the following steps: S1: calculating a theoretical average specific impulse and a theoretical total charge according to a nominal internal ballistic parameter of a solid engine; S2: according to the theoretical average specific impulse, theoretical total charge, the average specific impulse deviation, and the total charge deviation, calculating the total impulse of the solid engine in the deviation state; S3: according the theoretical total charge, the total charge deviation, the rated working time, and the working time deviation, calculating the average second consumption, and calculating the average thrust according to the total impulse, the rated working time and the working time deviation; and S4: calculating the equation of the center of mass motion of the guidance system by using the average second consumption and the average thrust so as to carry out simulation analysis of the deviation of the solid engine on the guidance system. The method provided by the present invention is simple in calculation and strong in practicability, and has strong engineering application value for the launch vehicle guidance system to carry out Monte Carlo simulation analysis on the influence of the deviation of the solid engine.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE SYST ENG INST
Planetary landing image and distance measurement fusion relative navigation method
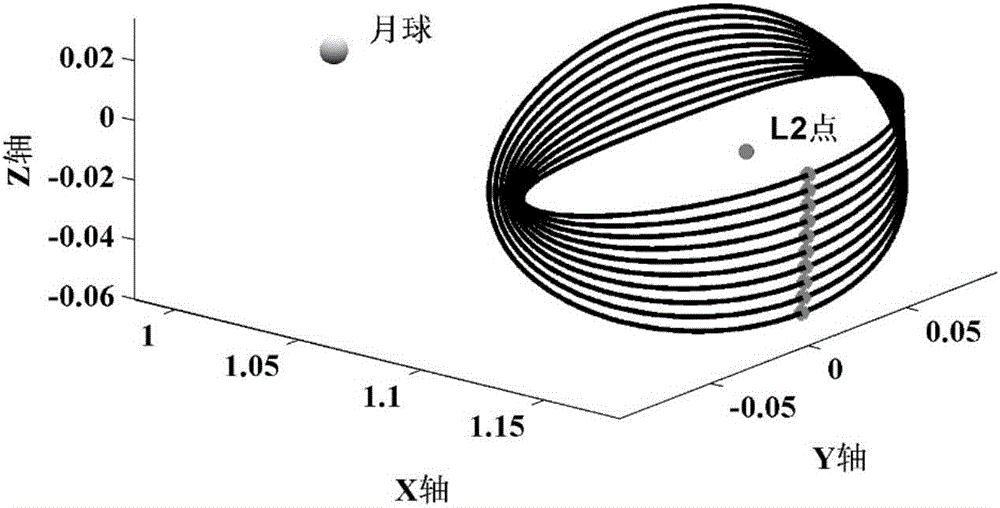
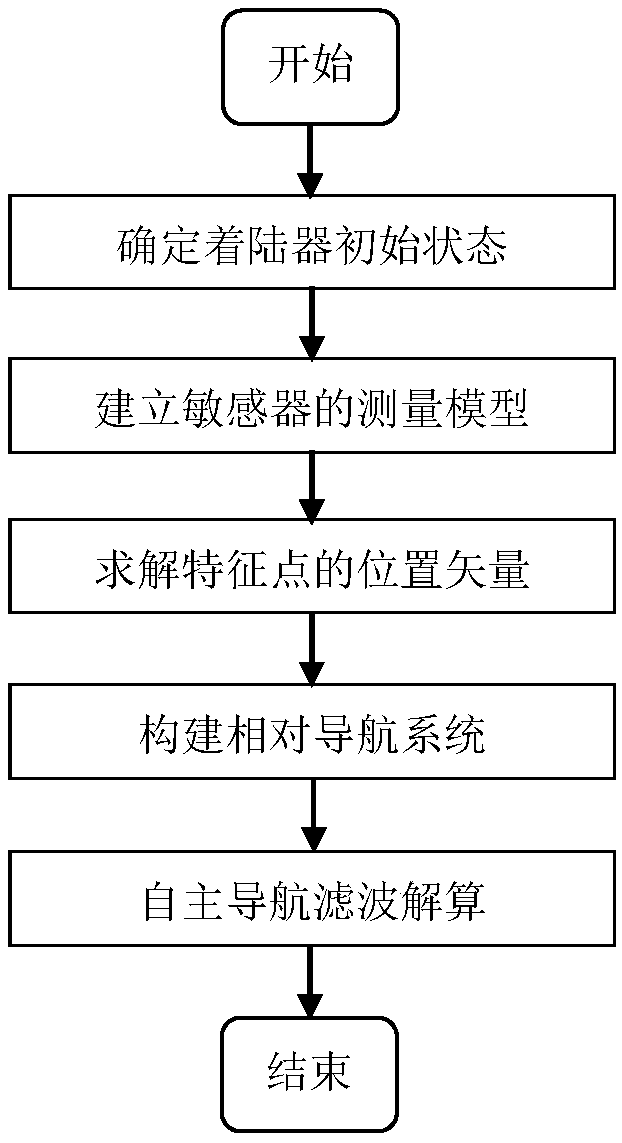
ActiveCN109269512AAvoid dependenceMeet the needs of precision landing missionsInstruments for comonautical navigationTerrainEquation of the center
The invention discloses a planetary landing image and distance measurement fusion relative navigation method, and belongs to the technical field of deep space exploration. The planetary landing imageand distance measurement fusion relative navigation method comprises the following steps: establishing a measurement model of a sensor; solving the position vector of a feature point according to an optical camera in the measurement model and observed quantity of a range finder; and constructing a relative navigation system by taking the solved position vector of the feature point as a navigationsystem, inputting a state equation and an observation equation in the relative navigation system into a navigation filter to obtain the position, speed and attitude information of a planetary landingdevice relative to a target landing point, and then implementing relative optical navigation of planetary landing. Dependence of optical navigation to a planetary terrain database can be avoided, furthermore, state information of the planetary landing device relative to the target landing point can be obtained, and then relative optical navigation of planetary landing is realized. Technical support and reference can be provided for a planetary accurate soft landing task navigation scheme design, and related engineering problems are solved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Dual-satellite formation only-ranging relative navigation method
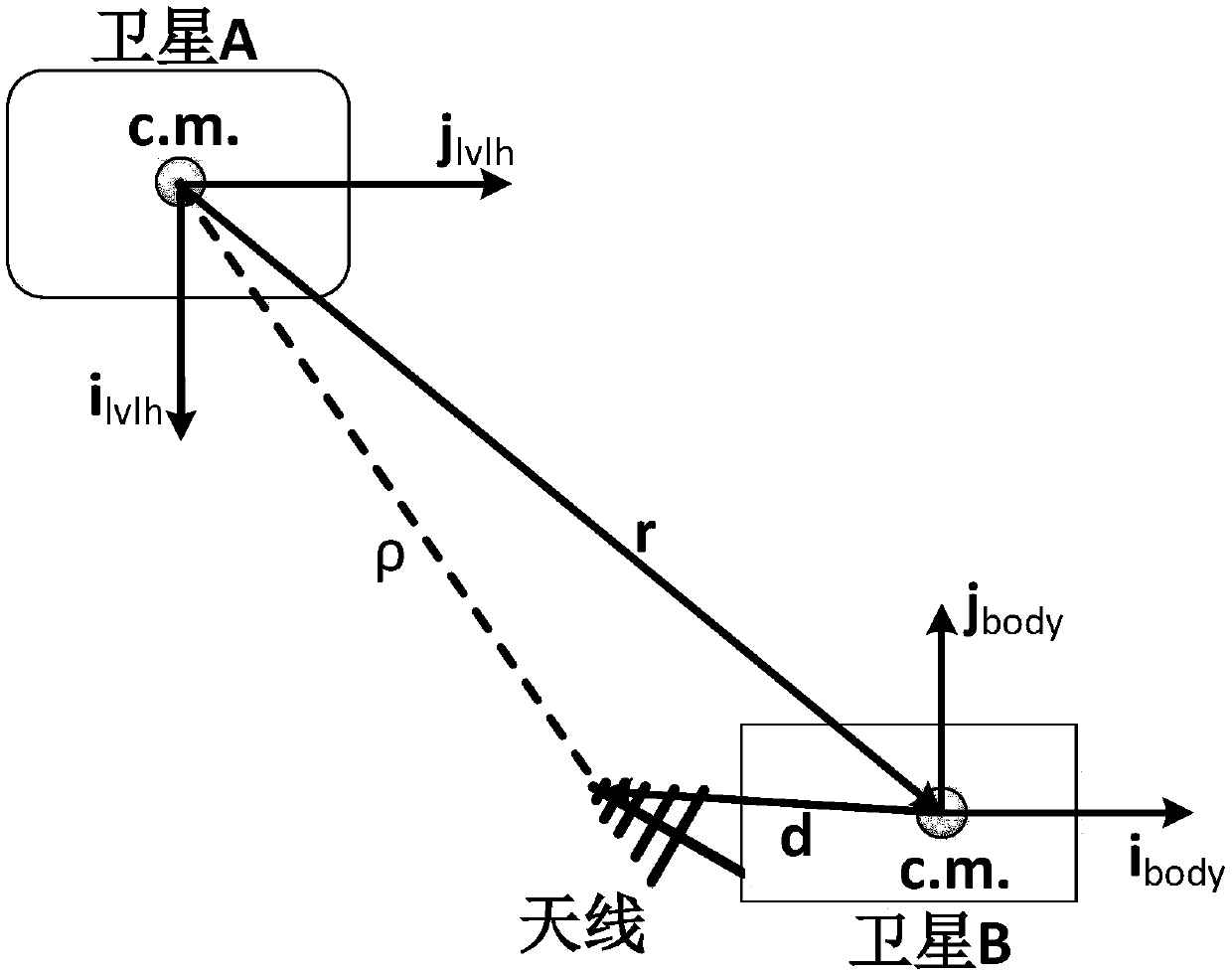
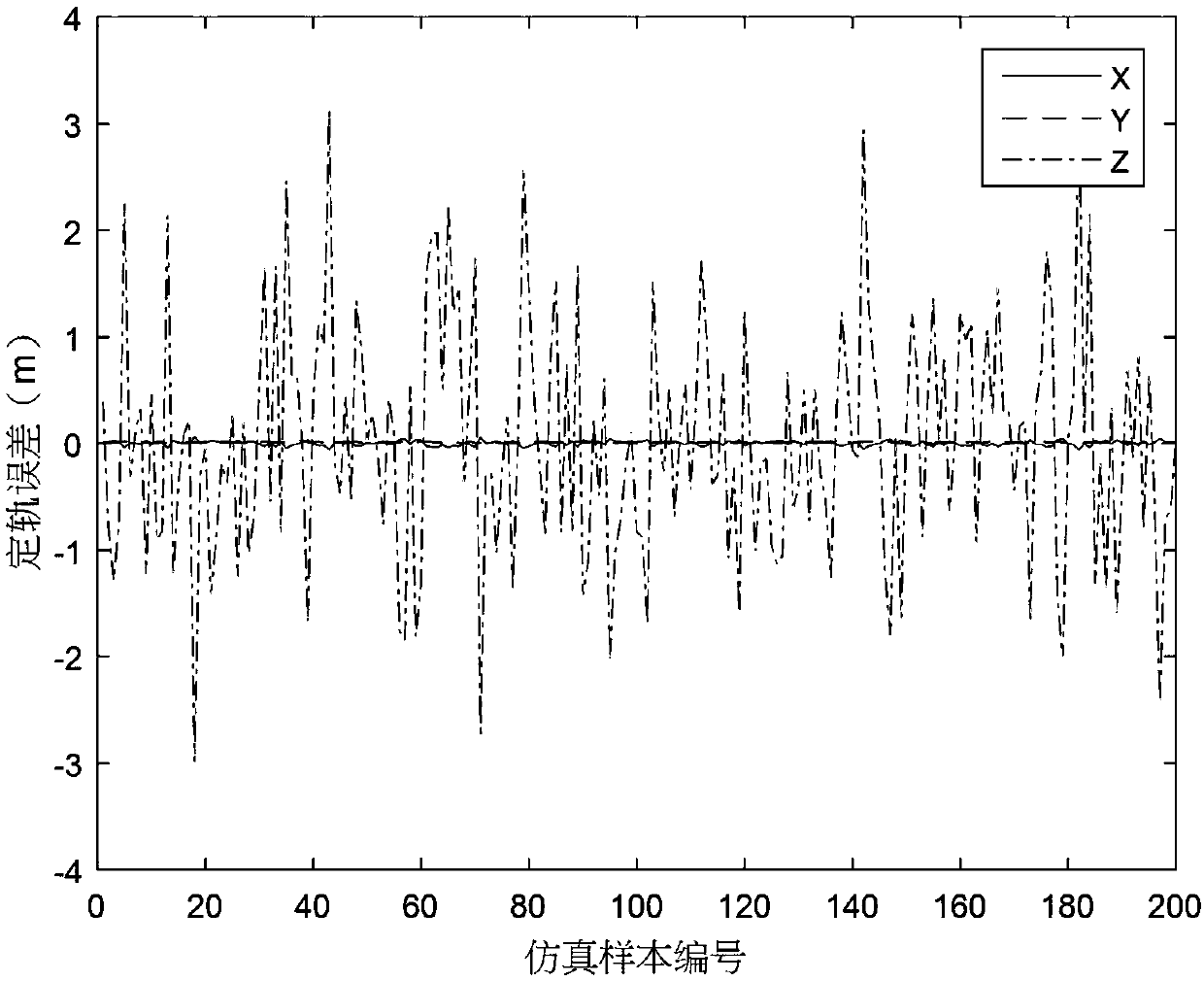
ActiveCN108917764ARealize multi-directional distance measurement and orbit determination navigationImprove ObservabilityNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationOn boardObservability
The invention relates to a dual-satellite formation only-ranging relative navigation method. The dual-satellite formation only-ranging relative navigation method can only rely on off-mass-center installation and attitude maneuvering assistance of an antenna receiver to realize dual-satellite formation autonomous relative navigation without special orbit maneuvering of satellites or increase of on-board data link receiving antennas. Relative orbital evolution is performed by use of a relative orbital motion equation of dual satellites in the dual-satellite formation as a navigational state equation, and dual-satellite formation only-ranging relative navigation can be completed by use of an iterative algorithm to solve relative position and relative velocity according to relative distance information measured by the on-board data link receiving antenna receiver installed in the manner of deviated from centers of mass of the satellites. By introducing of the eccentricity effect of the antenna receiver installed in the manner deviated from the centers of mass of the satellites, the observable ability of the only-ranging relative navigation solution is obtained. The attitude maneuveringassistance is used to improve the observability, and the relative position and the velocity are obtained by the iterative solution method.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Ranging only relative navigation analysis method for double-satellite formation periodic relative motion
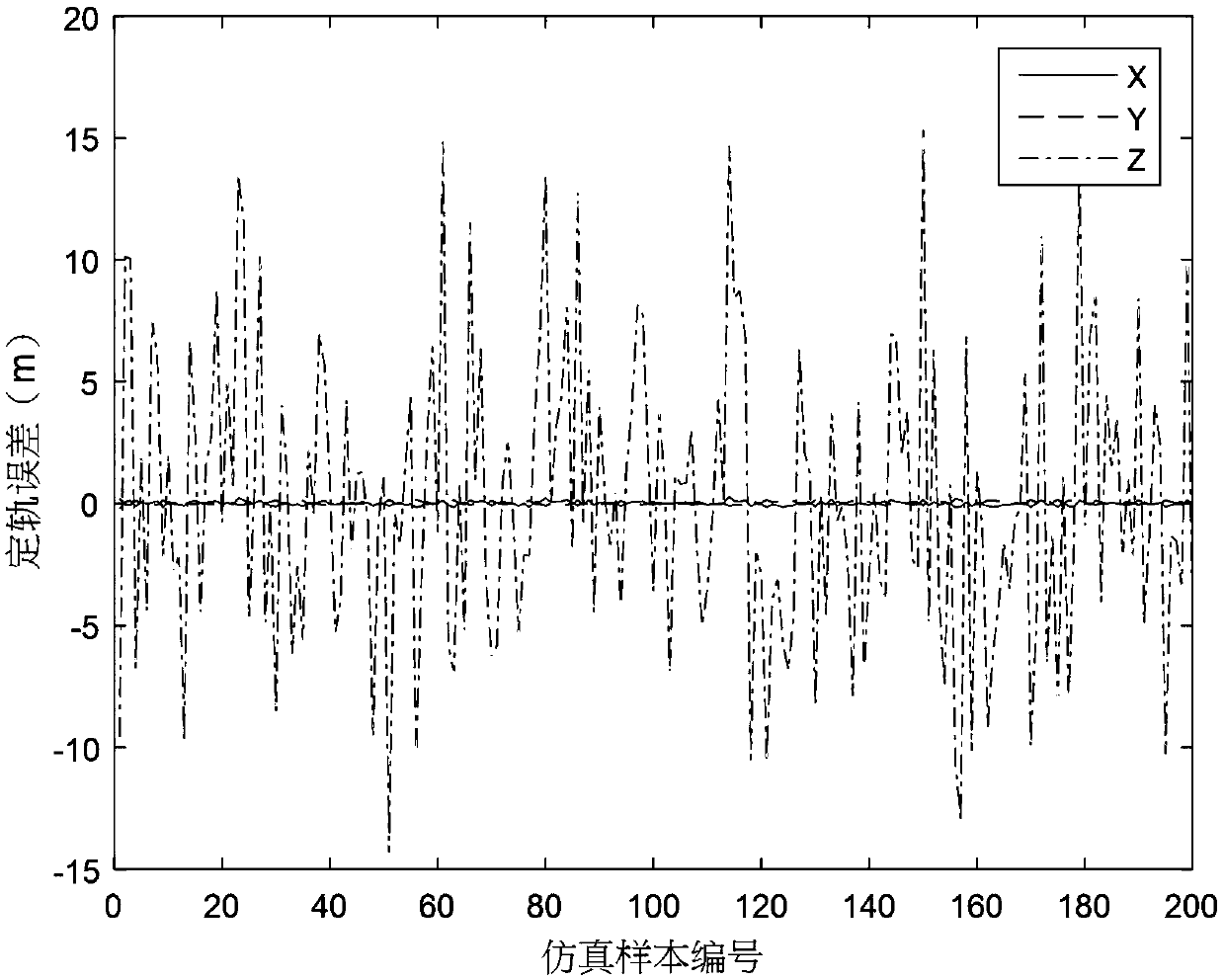
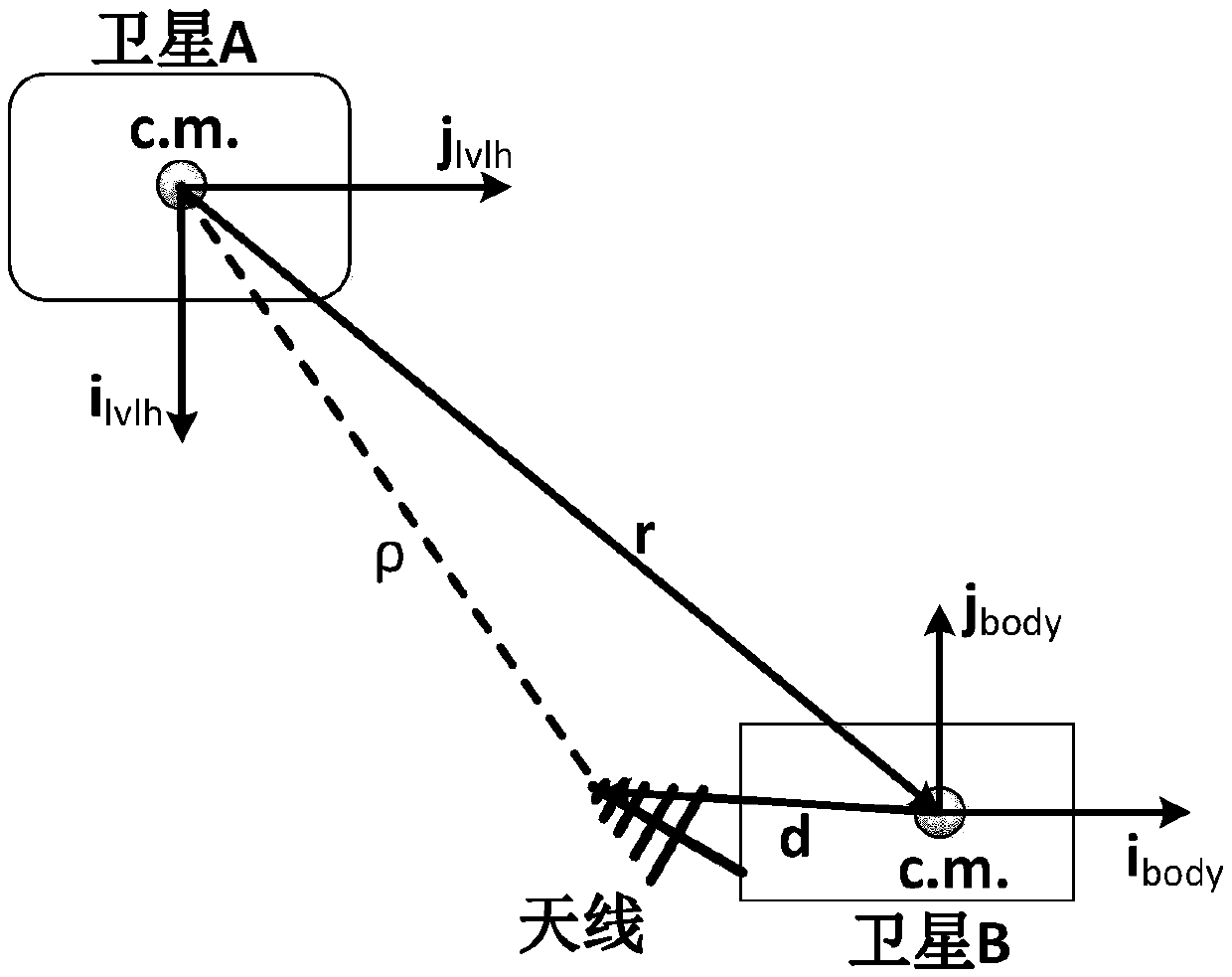
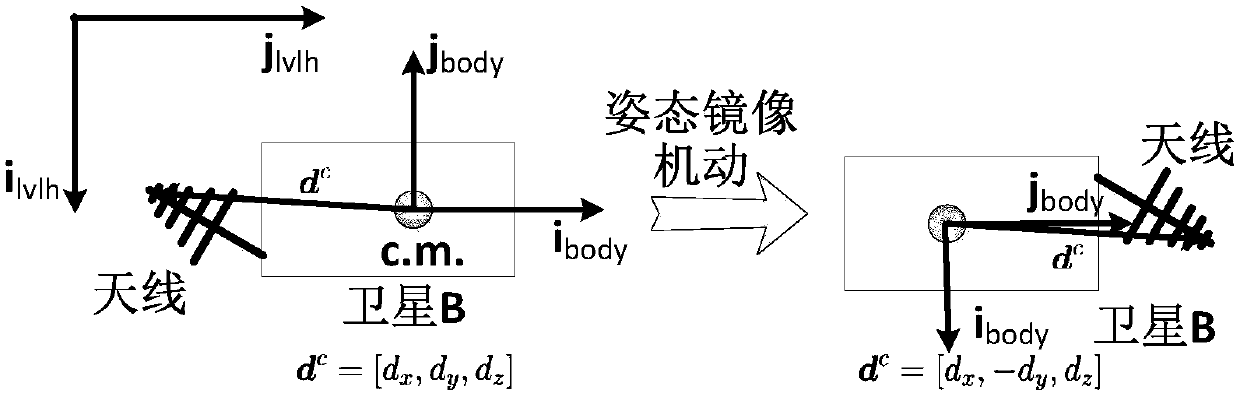
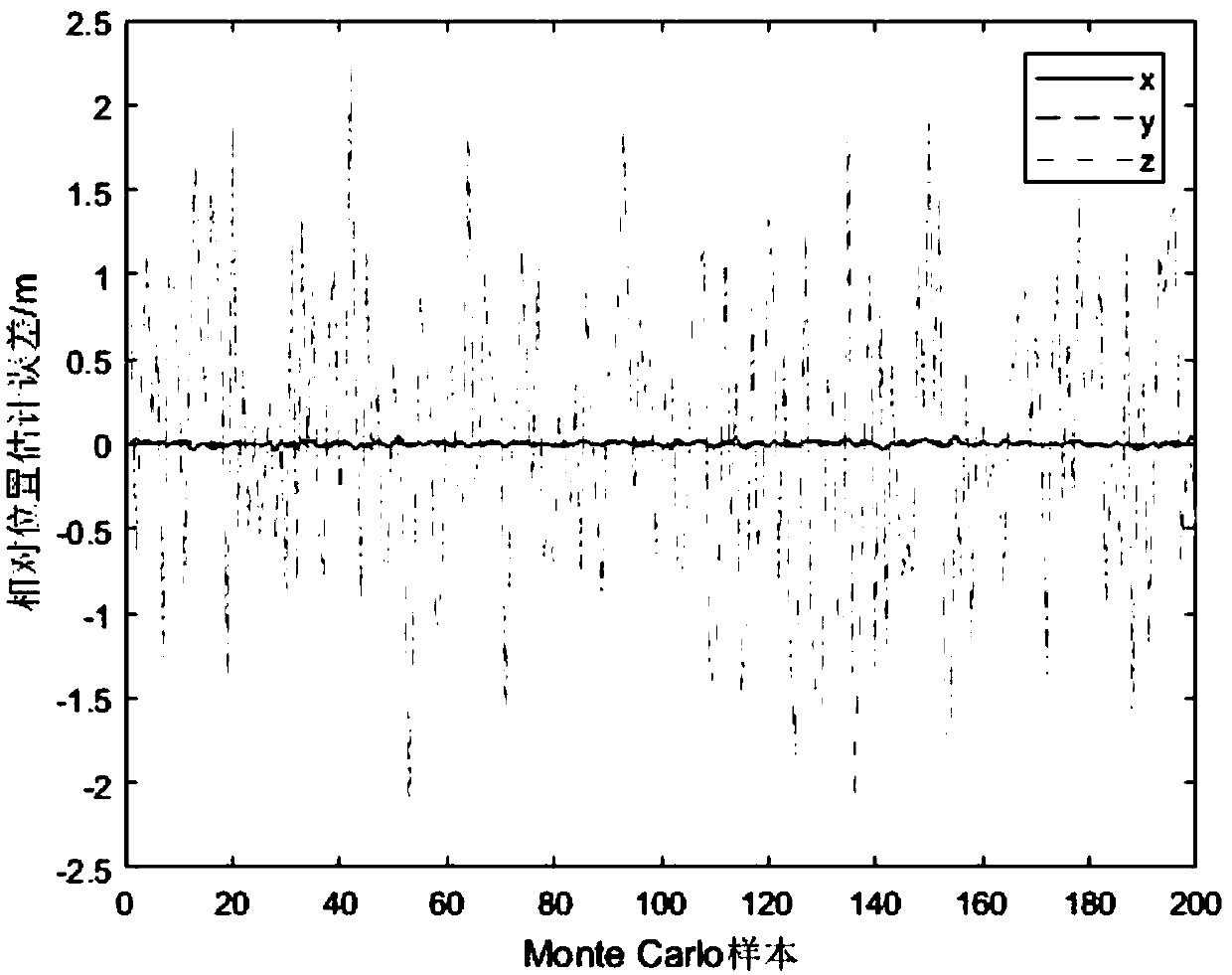
ActiveCN108957509AGain observabilityNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingRelative orbitEquation of the center
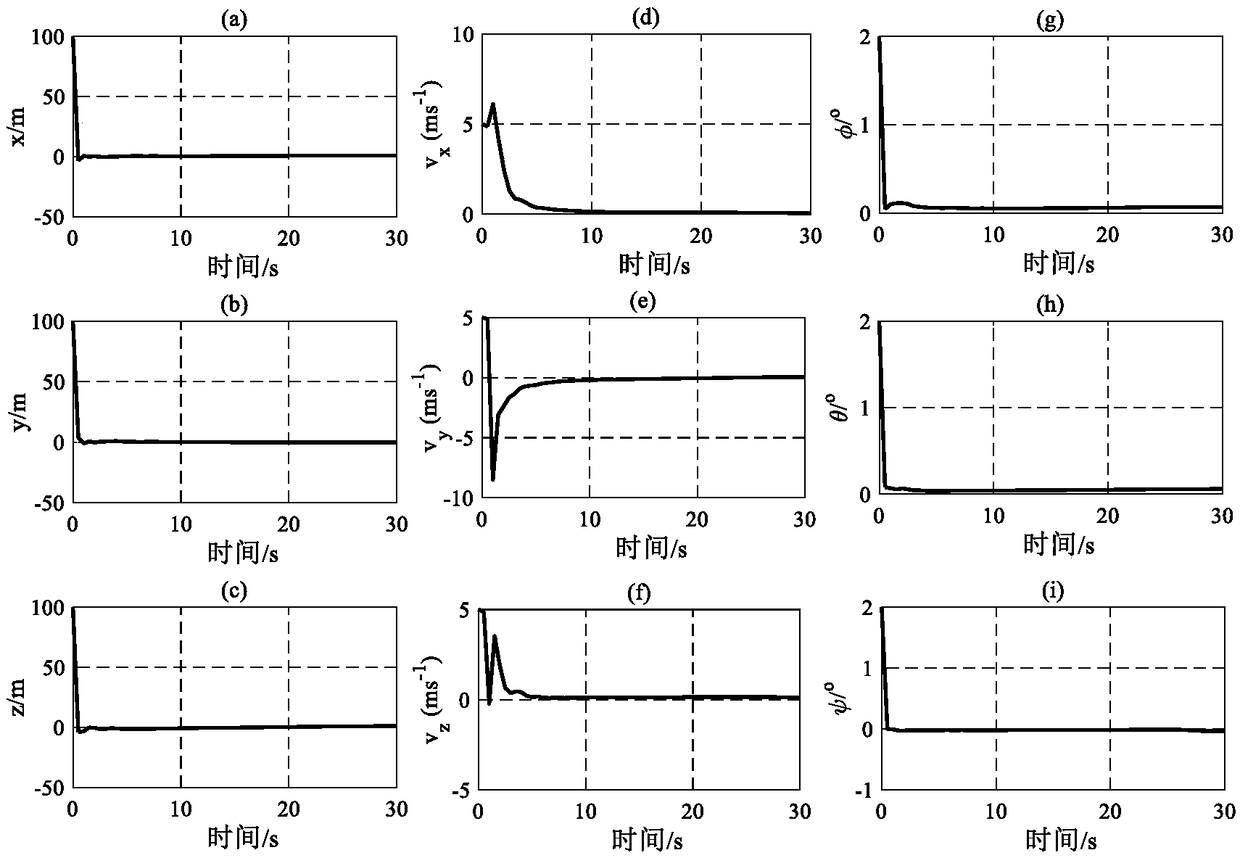
The invention relates to a ranging only relative navigation analysis method for double-satellite formation periodic relative motion. The analytical autonomous relative navigation of periodic relativemotion formation double satellites can be achieved only depend on off-centroid installation of an antenna receiver and an attitude mirror image maneuvering aid in the case that satellites do not perform special orbit maneuvering or a satellite-borne data link receiving antenna is not increased. A relative orbital motion equation of the double satellites in a double-satellite formation is taken asa navigational state equation to evolve a relative orbit, a relative position and a relative speed are calculated with relative distance information before and after attitude mirror image maneuveringmeasured by a satellite-borne data link antenna receiver installed in a way deviating from a satellite centroid, and the ranging only relative navigation of the periodic relative motion formation double satellites is completed. By introducing an eccentric effect of the off-centroid installation of the antenna receiver, the observable ability of a ranging only relative navigation solution is obtained, and the relative position and speed are analyzed, solved and obtained by using the attitude mirror image maneuvering aid.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com