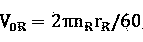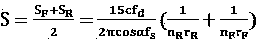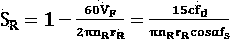Patents
Literature
45 results about "Translational velocity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Translational velocity just means ordinary velocity, measured in metres per second. tangential velocity is the component of ordinary (translational) velocity in the tangential direction.
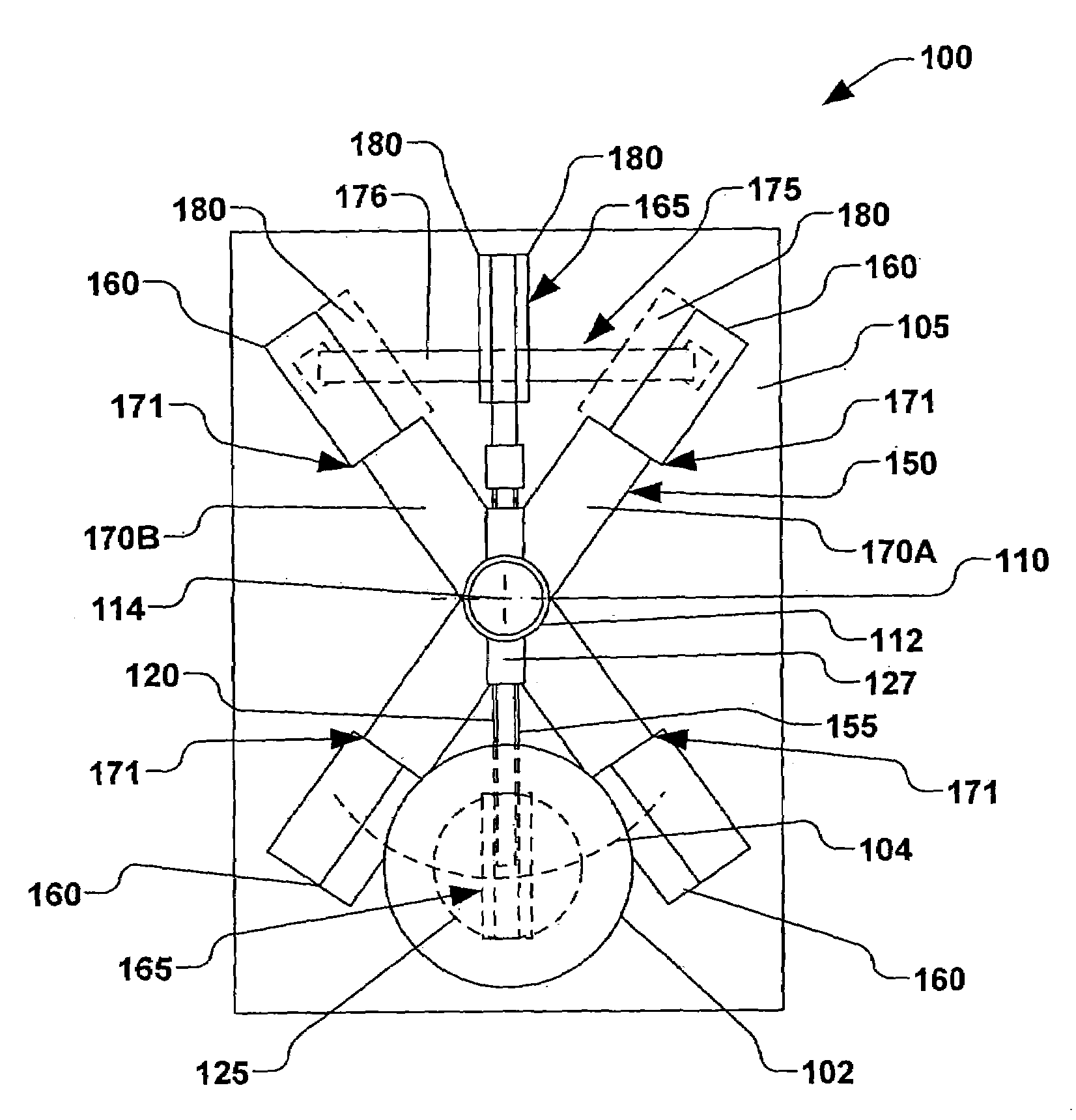
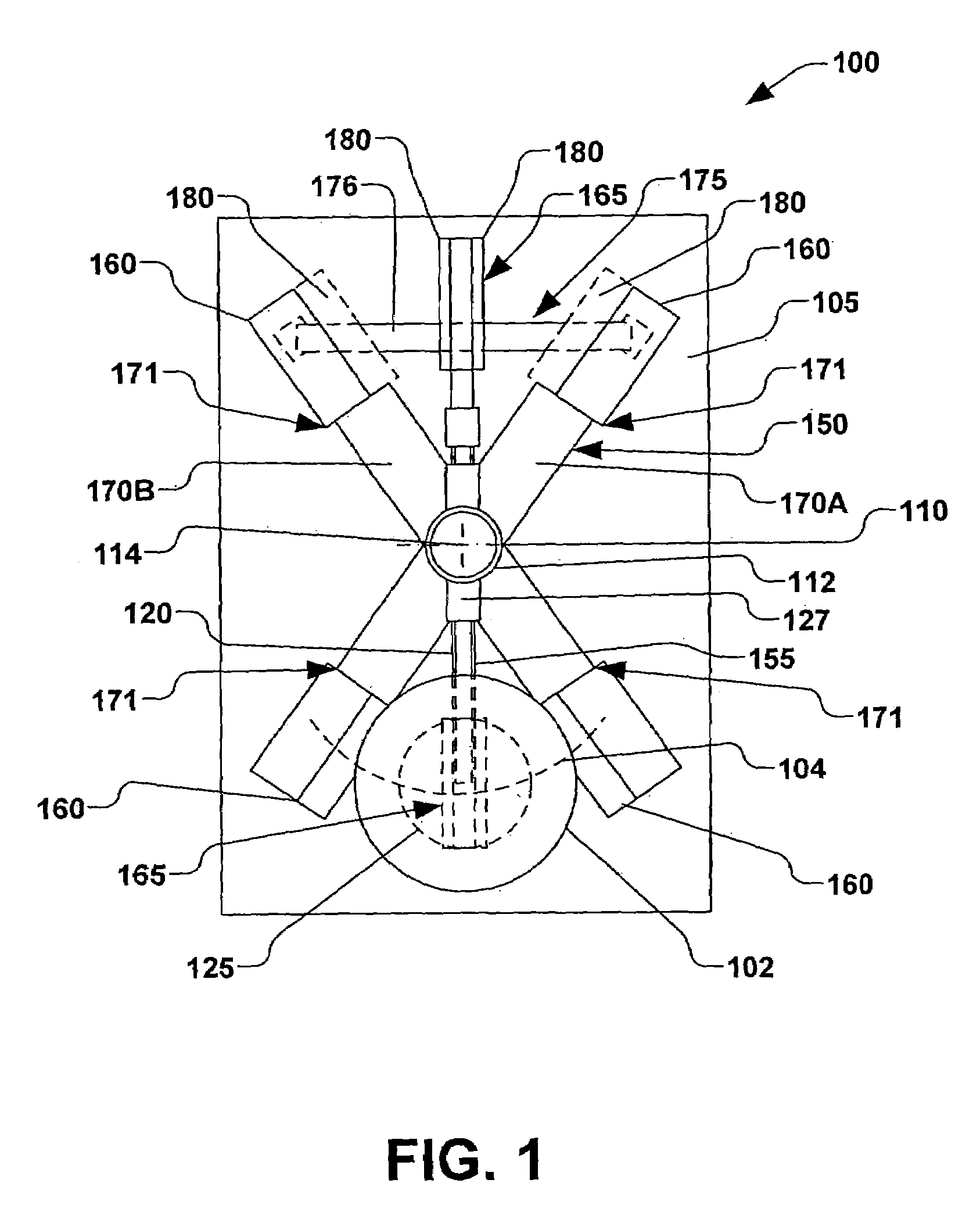
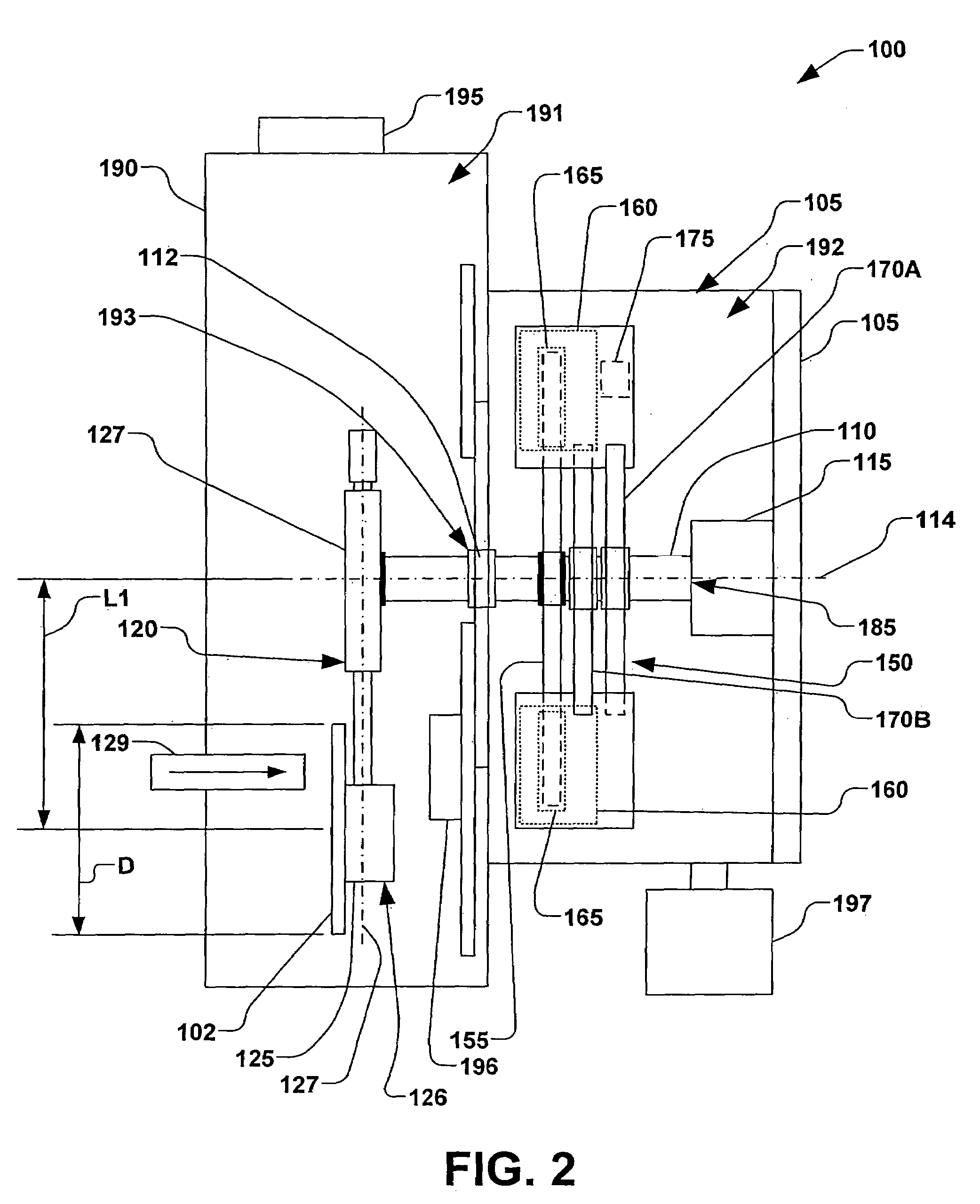
Method of producing quartz glass bodies
InactiveUS6047564AImprove the usefulnessIncrease surface temperatureBlowing machine gearingsGlass deposition burnersVitreous BodiesEngineering
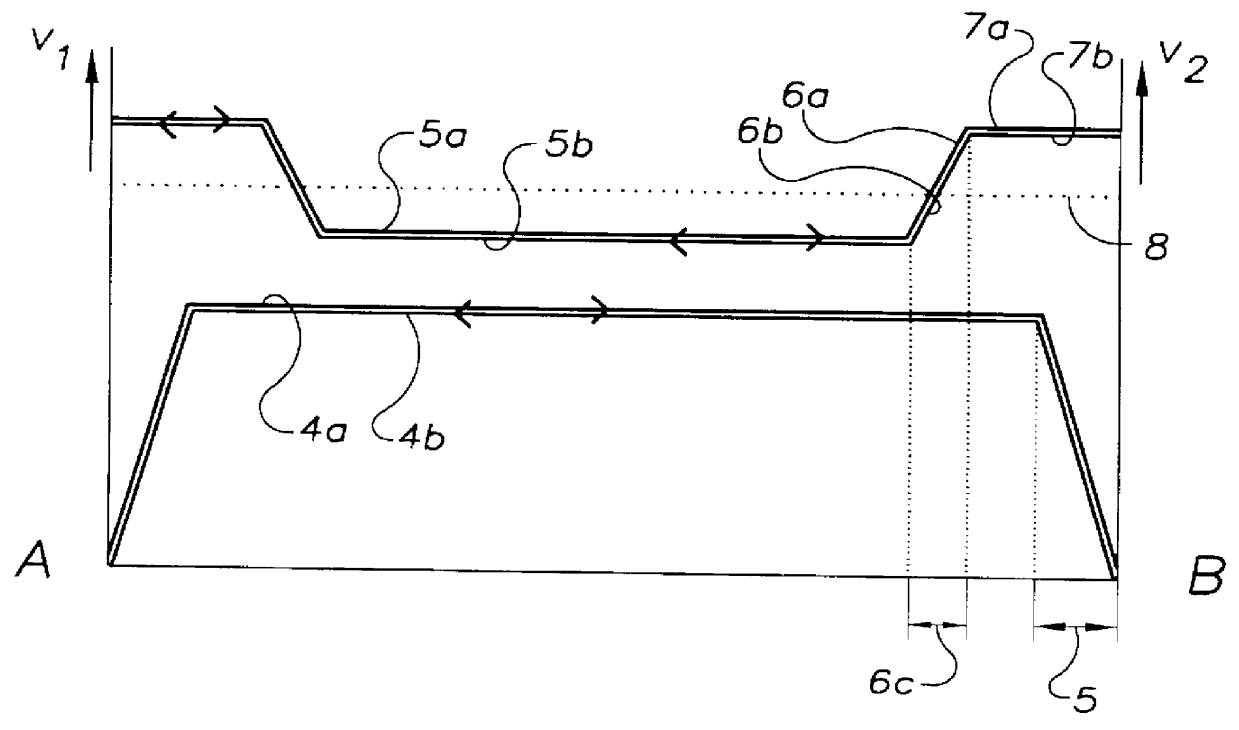
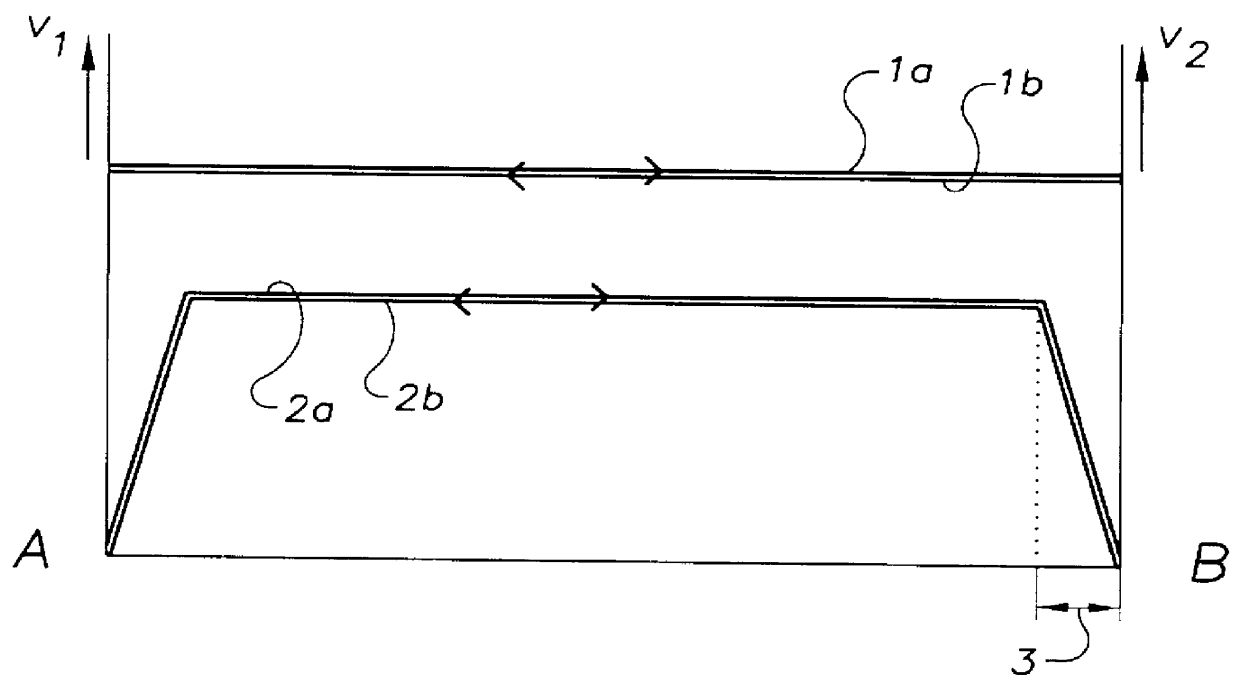
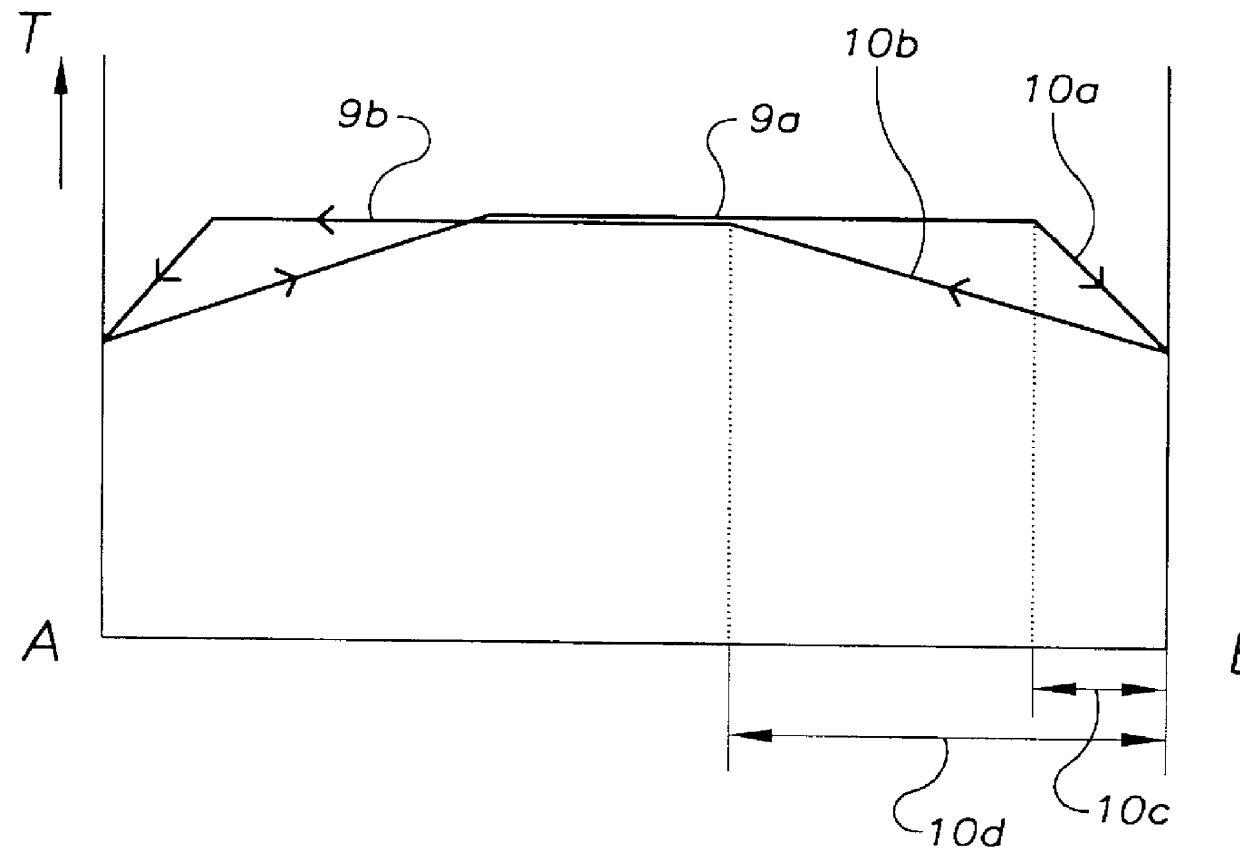
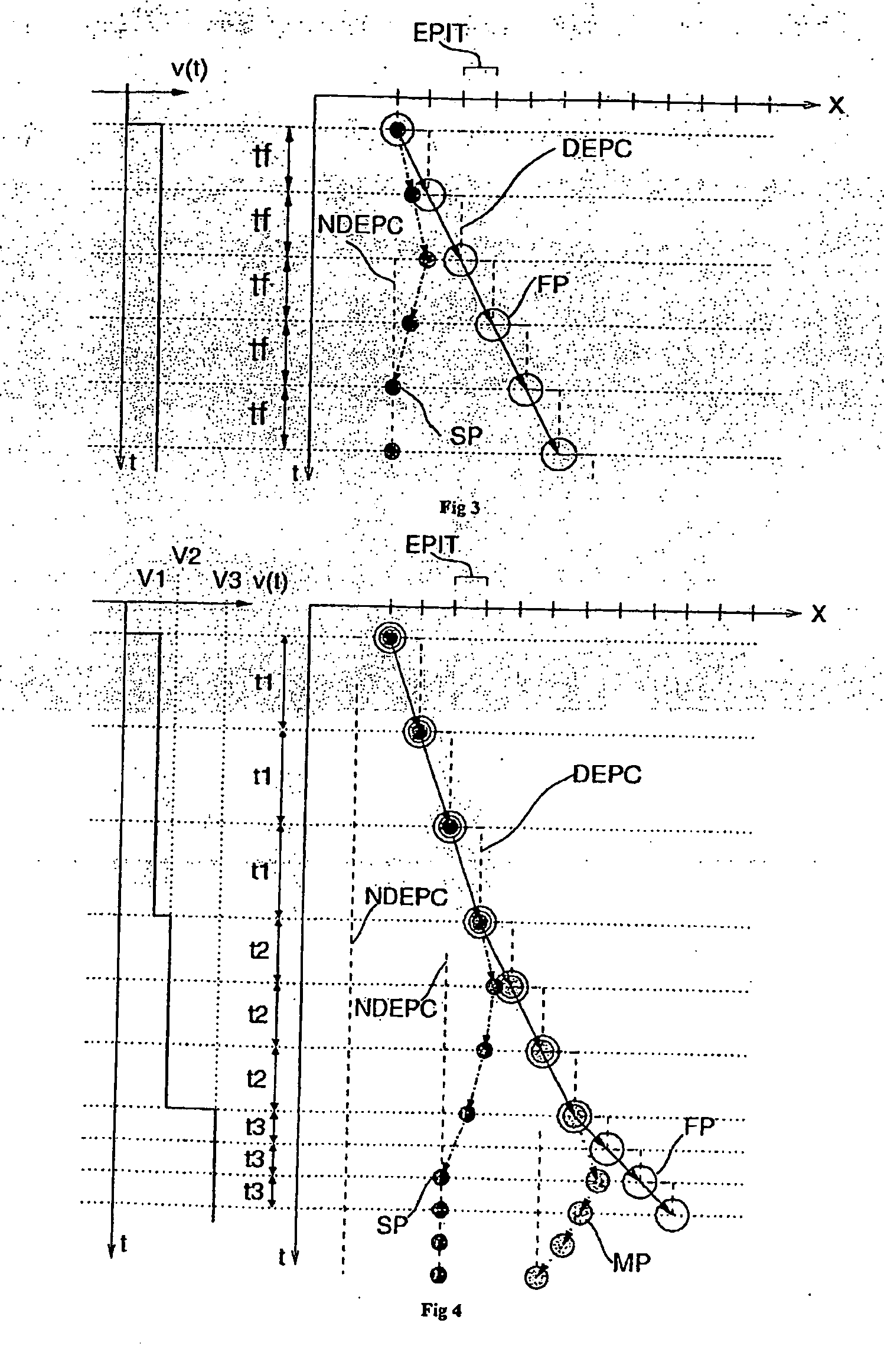
PCT No. PCT / EP97 / 03818 Sec. 371 Date Mar. 3, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Mar. 3, 1998 PCT Filed Jul. 17, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 03440 PCT Pub. Date Jan. 29, 1998In a known process for the production of quartz glass bodies, SiO2 particles are deposited of the mantle surface of a cylindrical carrier rotating about its longitudinal axis, forming an elongated, porous preform, where the SiO2 particles are formed in a plurality of flame hydrolysis burners which are arranged in at least one burner row parallel to the longitudinal axis of the carrier and are moved at a preset translational speed forward and back between turnaround points at which points their direction of movement is reversed, and in which process the preform is sintered. In order to make available on this basis an easily accomplished process that makes it possible to manufacture a preform which is largely free of localized density variations, the invention proposes on the one hand that the base value of the surface temperature of the preform being formed be kept in a range between 1,050 DEG C. and 1,350 DEG C., that the average peripheral velocity of the preform be kept in the range between 8 m / min and 15 m / min and the average translational velocity of the burner row be kept in a range between 300 mm / min and 800 mm / min. On the other hand, the object is also accomplished according to the invention and on the basis of the known process in that in the area of the turnaround points (A, B) the peripheral velocity of the preform being formed is increased and / or the flame temperature is lowered and / or the distance of the burners from the preform surface is changed.
Owner:HERAEUS QUARZGLAS
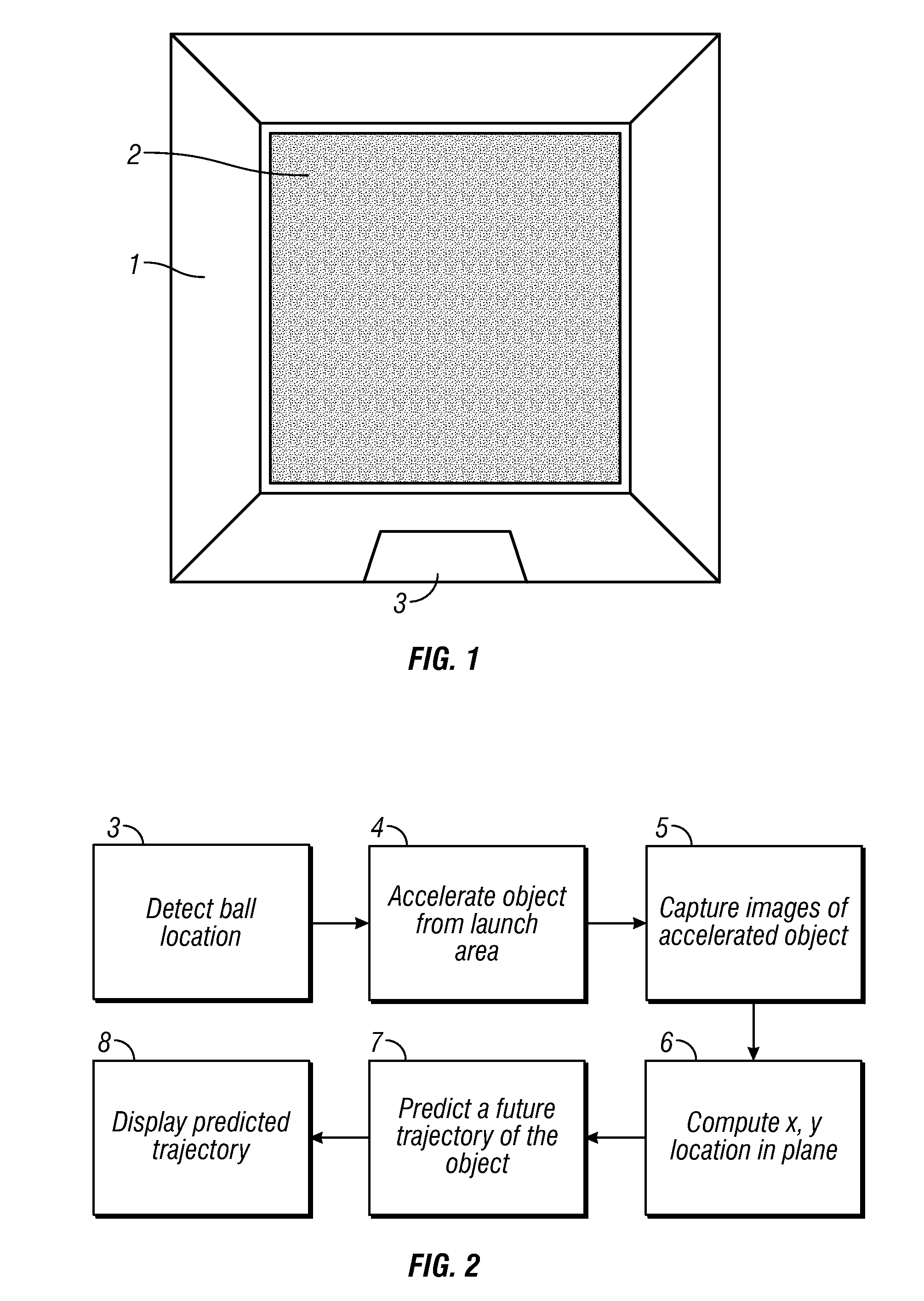
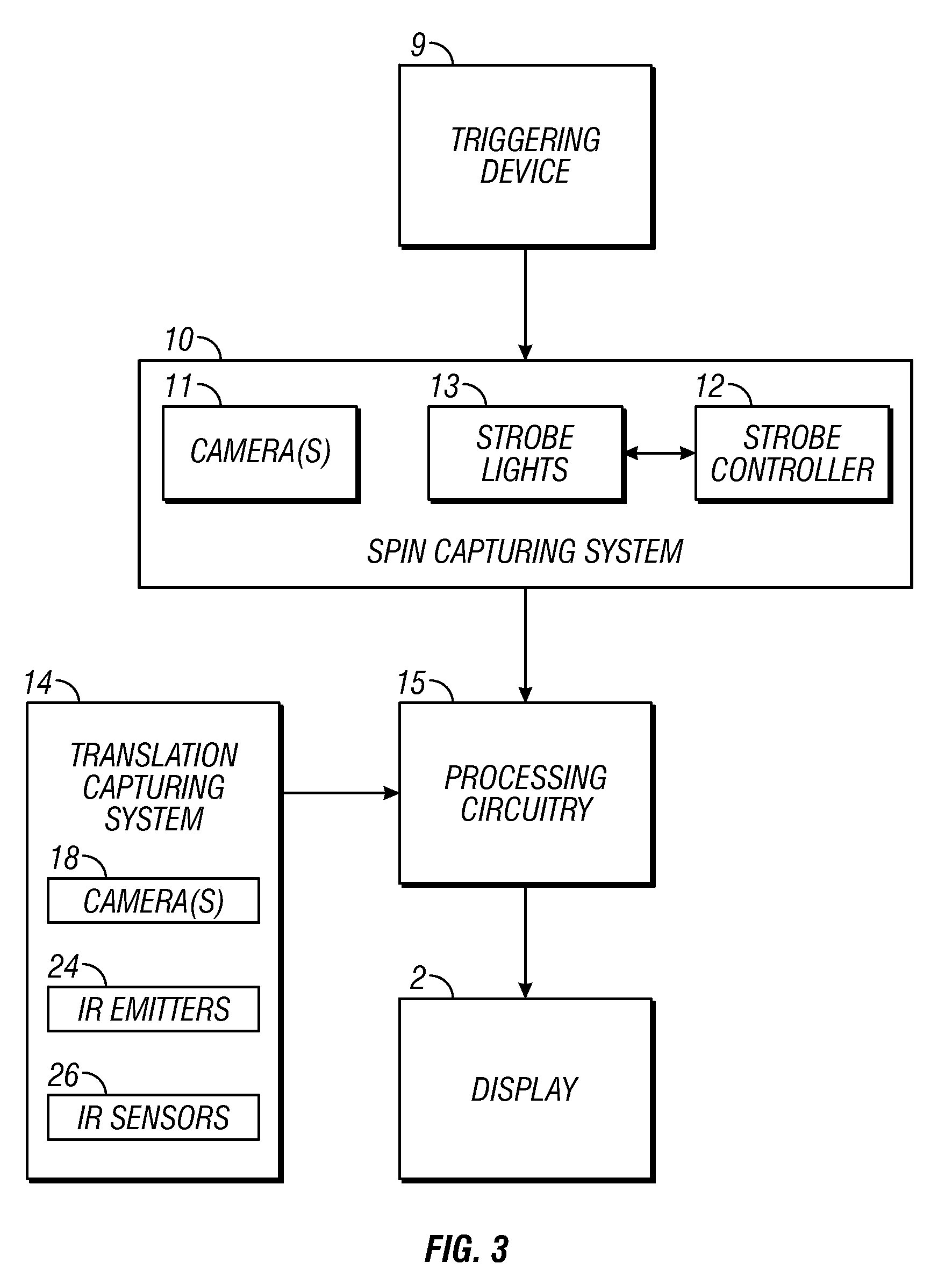
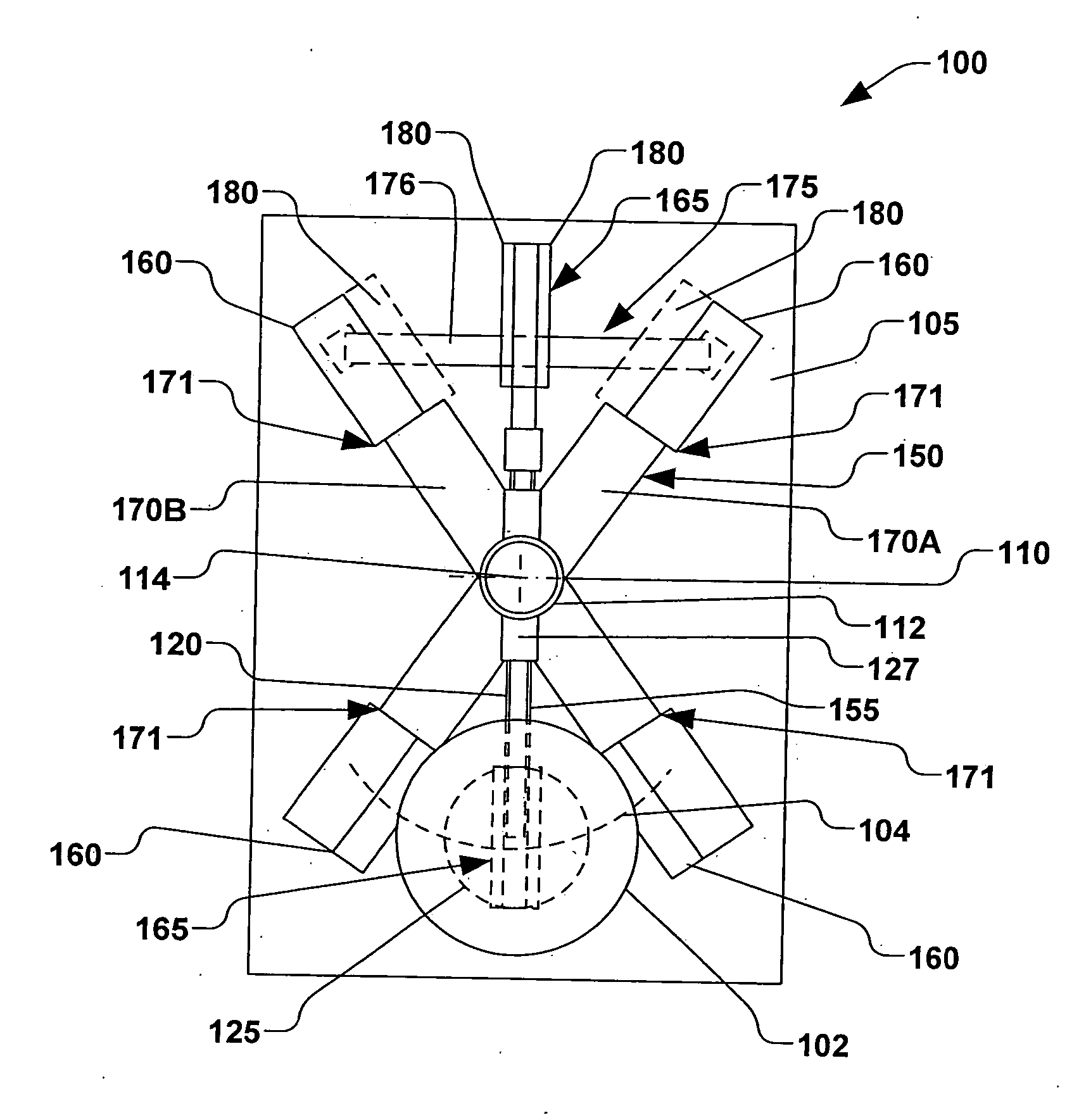
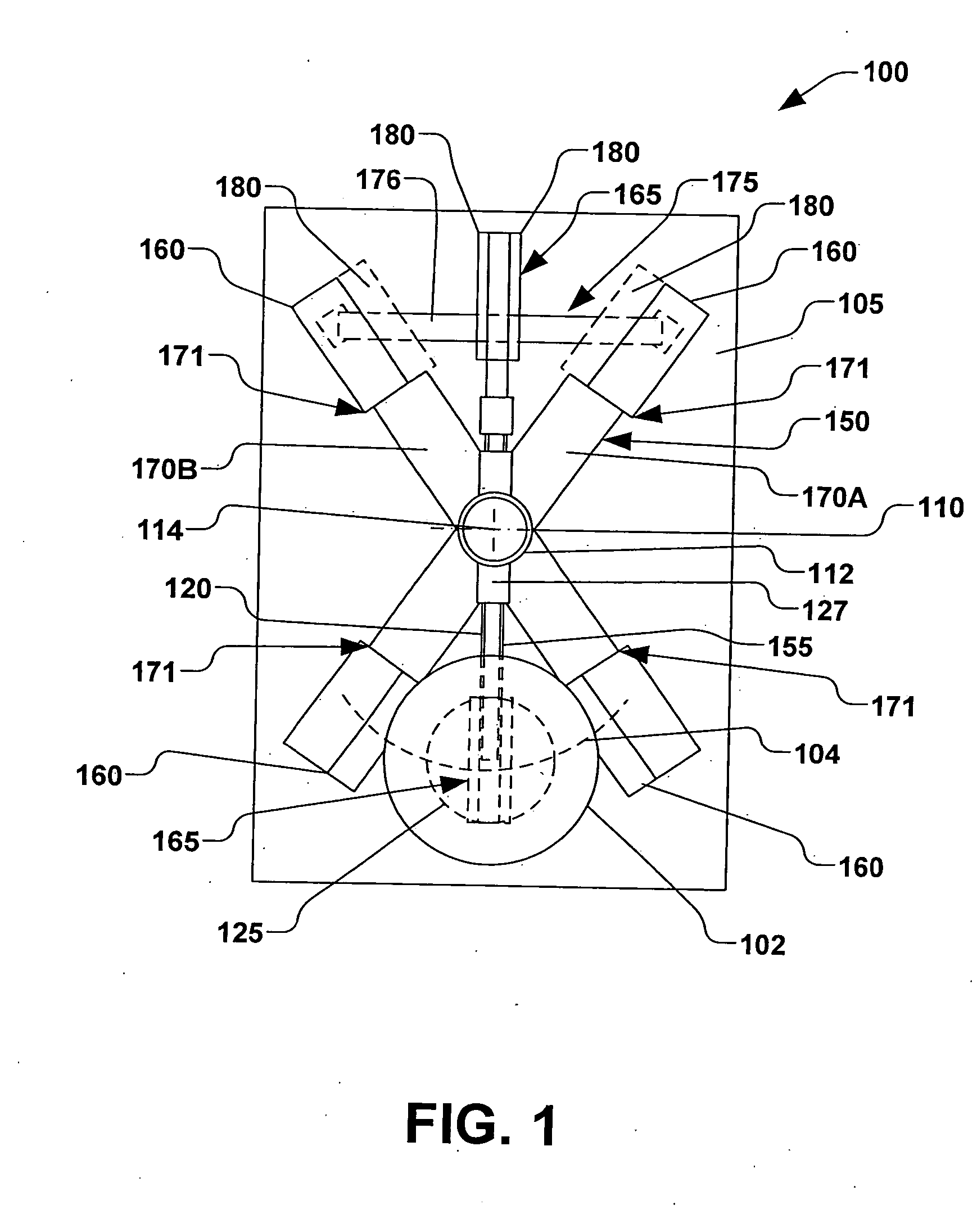
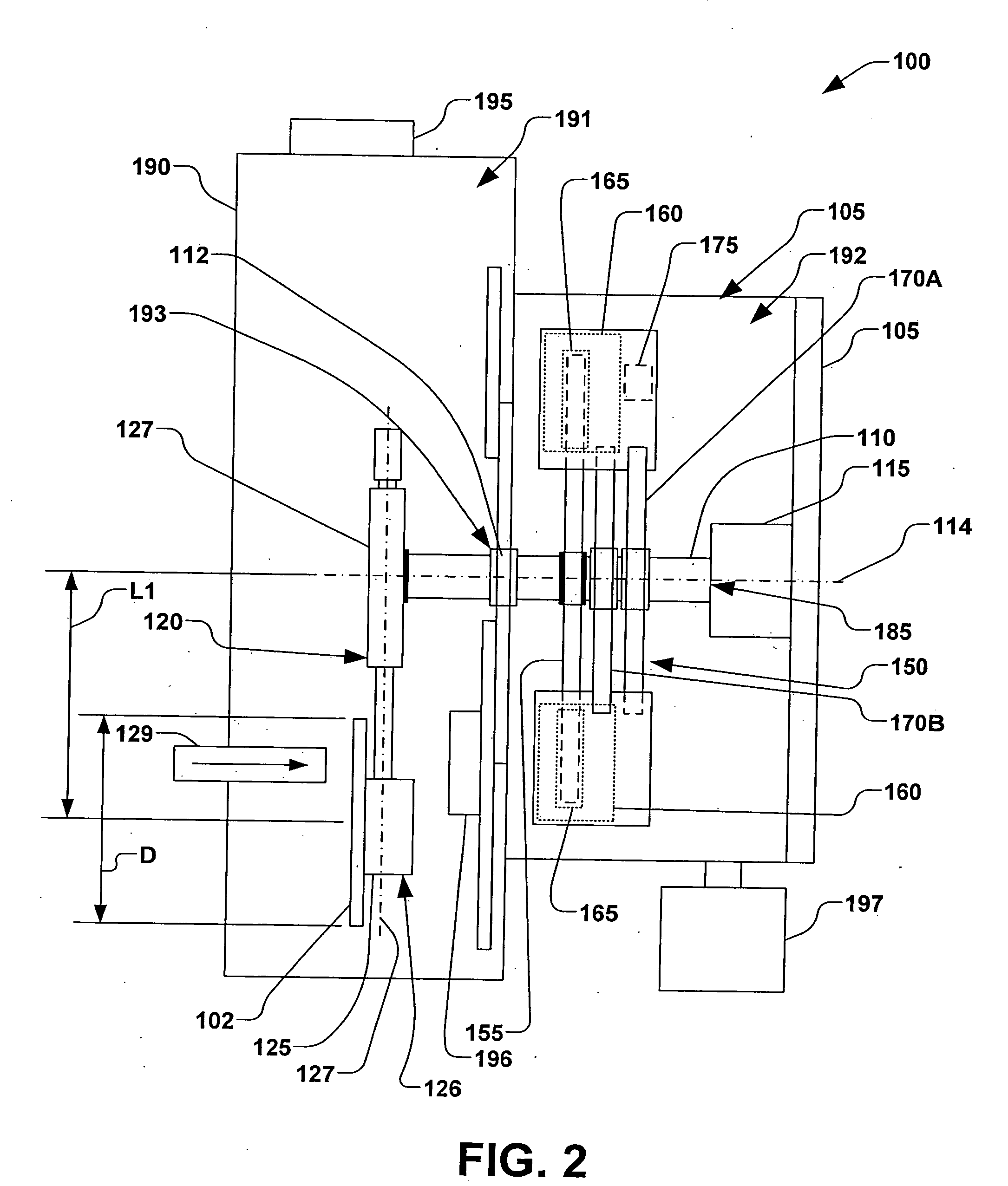
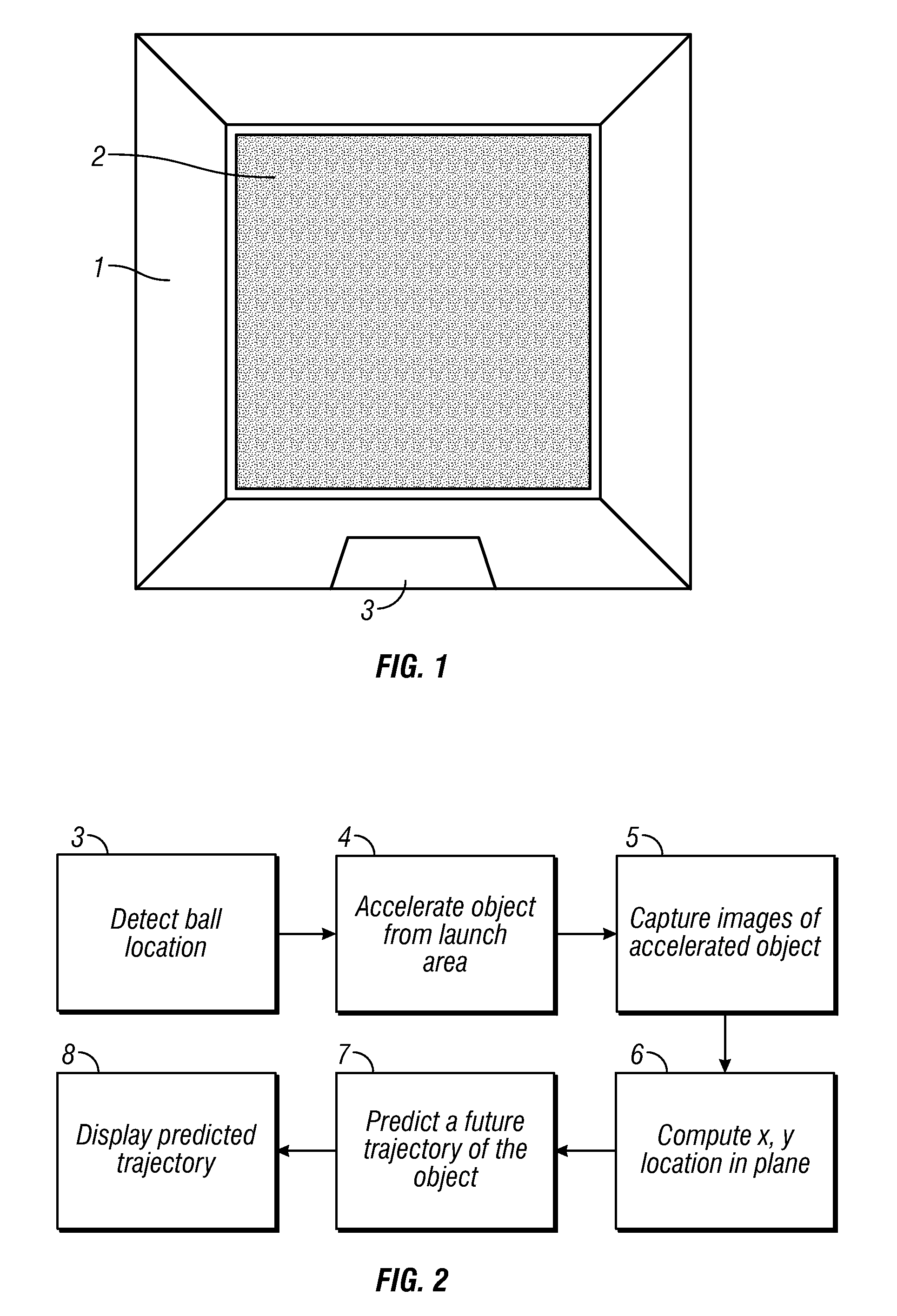
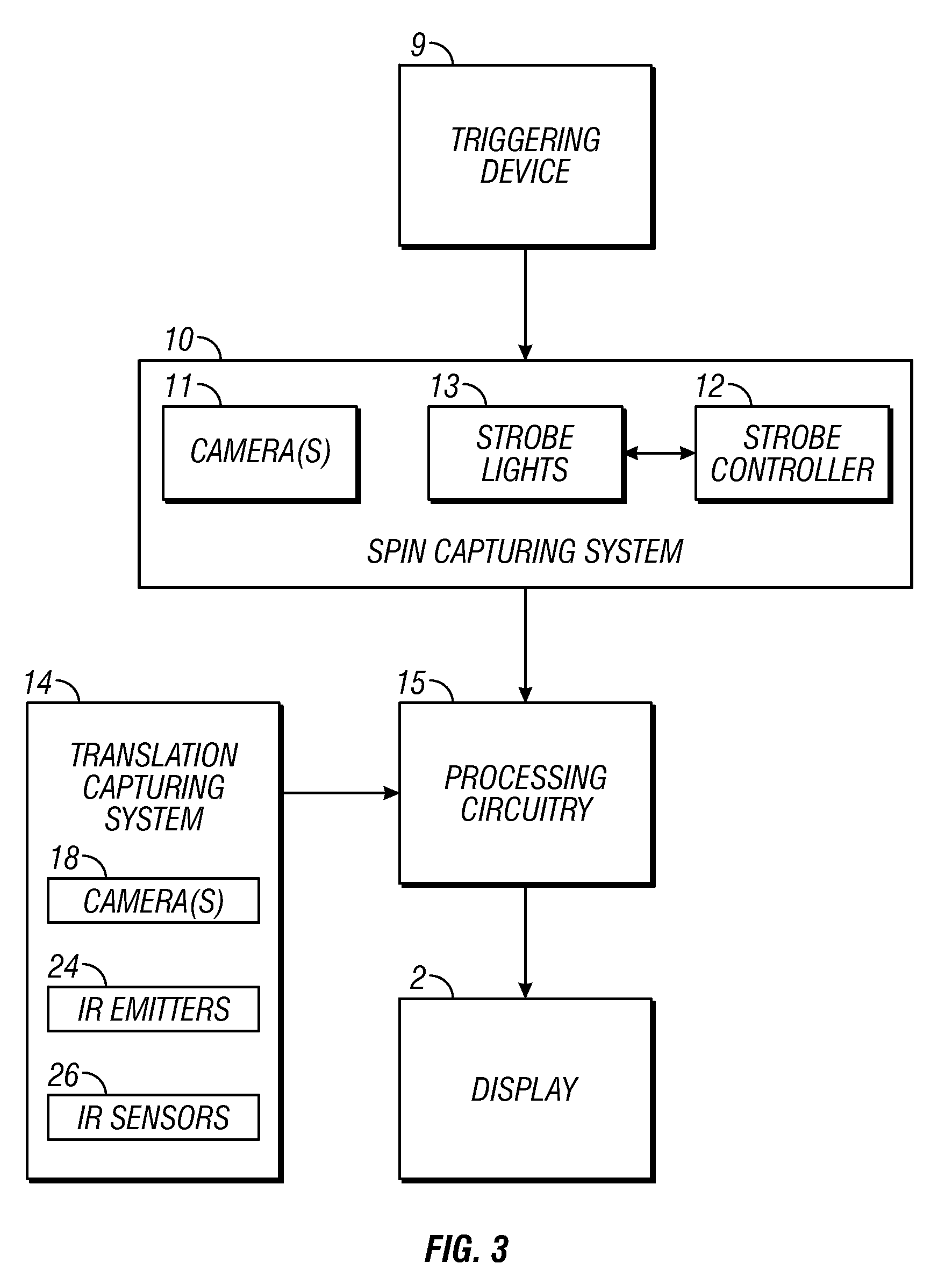
Methods and systems for sports simulation
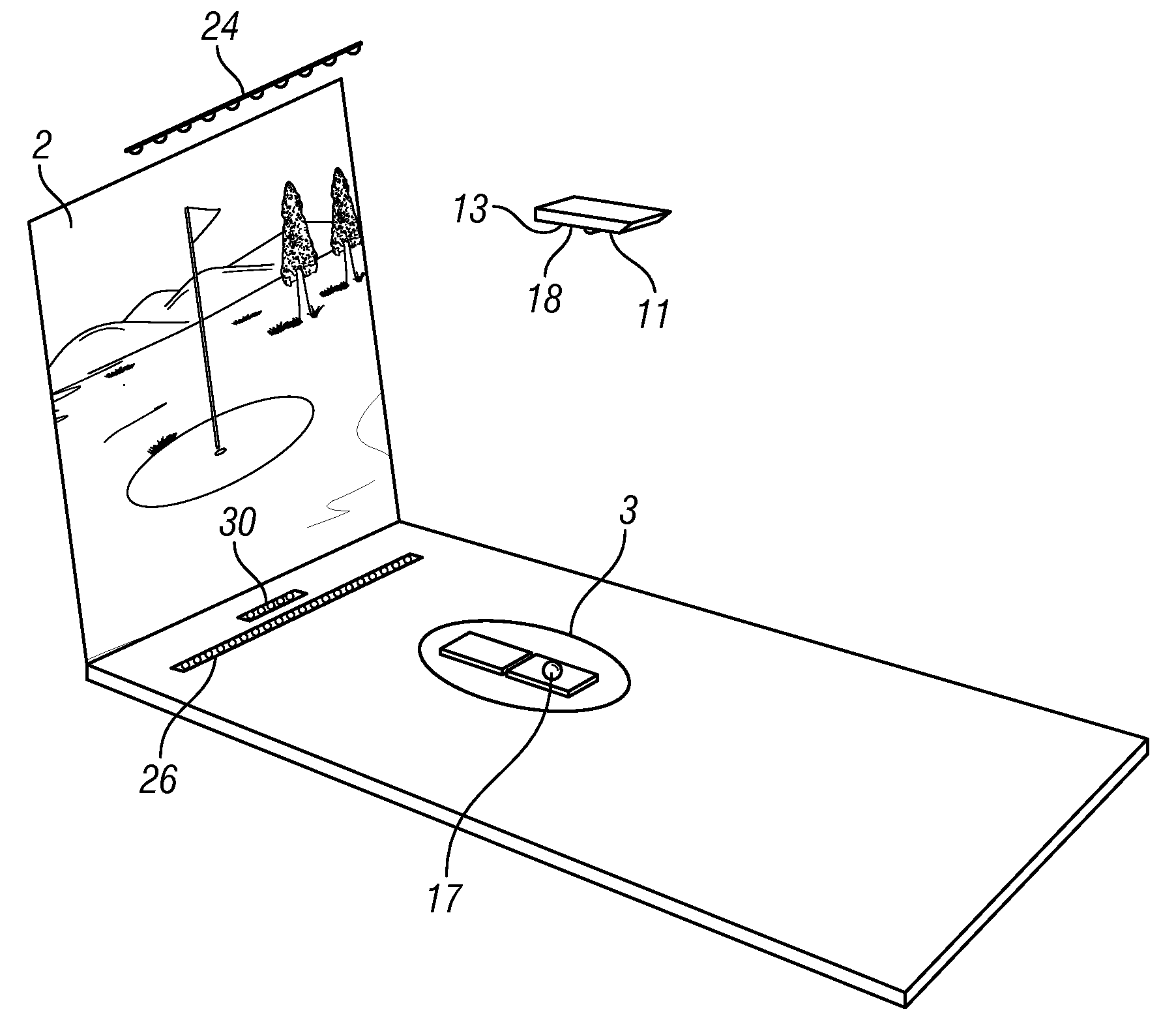
A sports simulator calculates the rotational and translational velocity of a sports object. The rotational velocity is calculated using image analysis. The translational velocity is calculated using image analysis and a set of emitters and sensors. The simulator then computes the future trajectory of the sports object based on the rotational and translational velocity. In one embodiment, the sports object is a golf ball and the sports simulator simulates golf.
Owner:FULL SWING GOLF
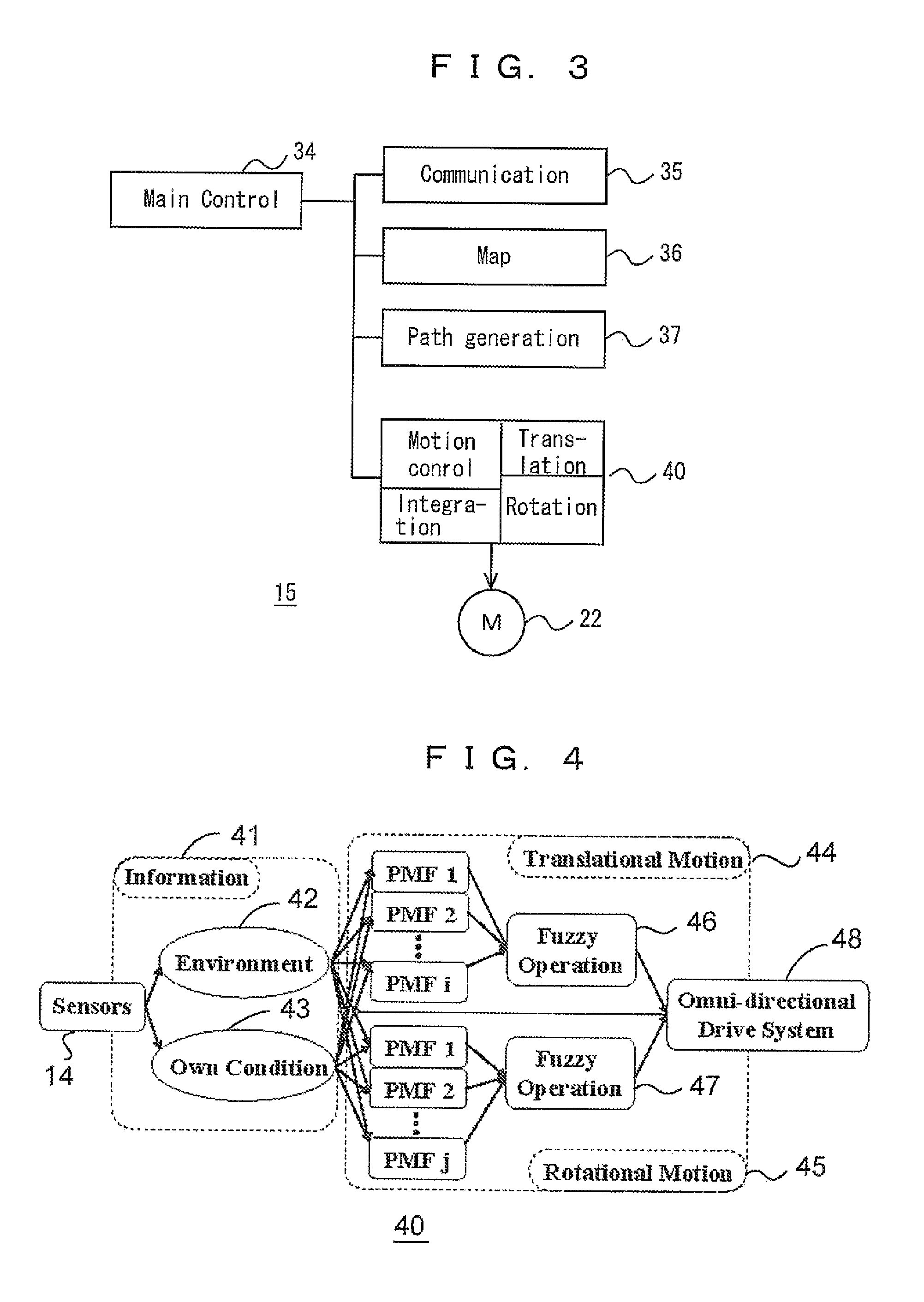
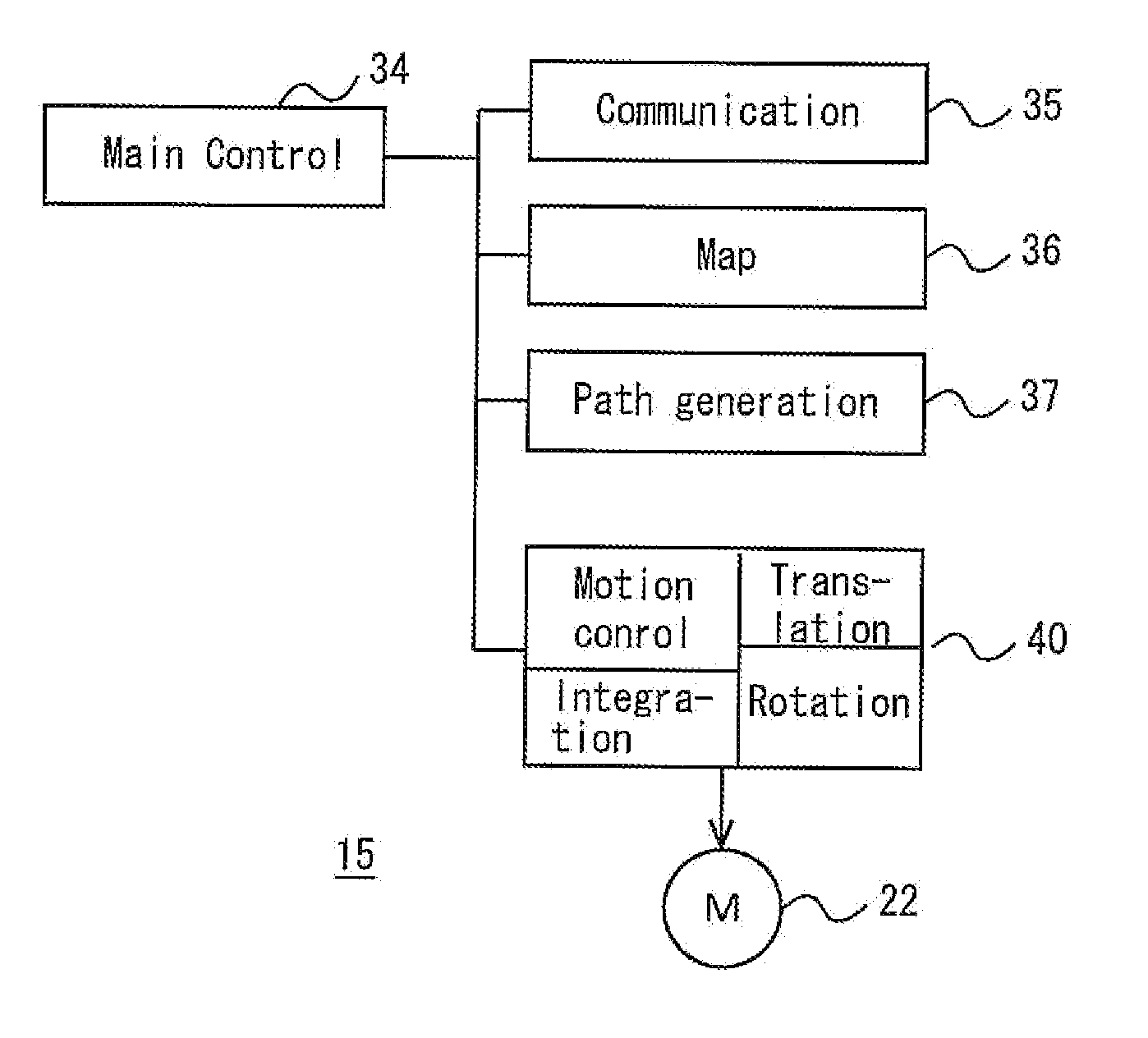
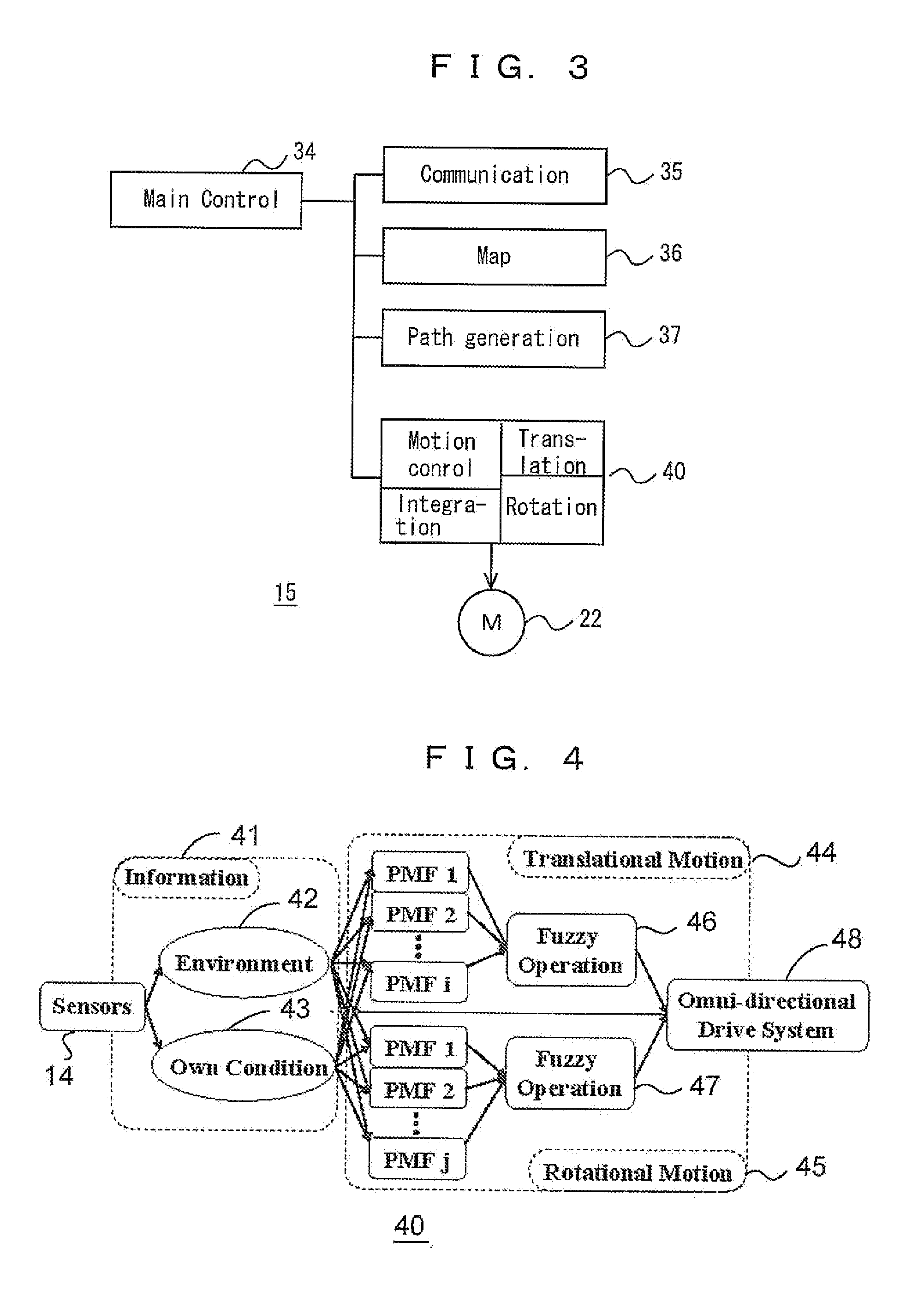
Autonomous mobile body and control method of same
An autonomous mobile body is configured to flexibly avoid obstacles. The mobile body has a movement mechanism configured to translate in a horizontal plane and rotate around a vertical axis, and the distance to an obstacle is derived for each directional angle using an obstacle sensor. A translational potential of the mobile body and a rotational potential of the mobile body for avoiding interference with the obstacle are generated, based on the distance from the autonomous mobile body to the obstacle at each directional angle. An amount of control relating to a translational direction and a translational velocity of the mobile body and an amount of control relating to a rotational direction and an angular velocity of the mobile body are generated based on the generated potentials, and the movement mechanism is driven.
Owner:MURATA MASCH LTD
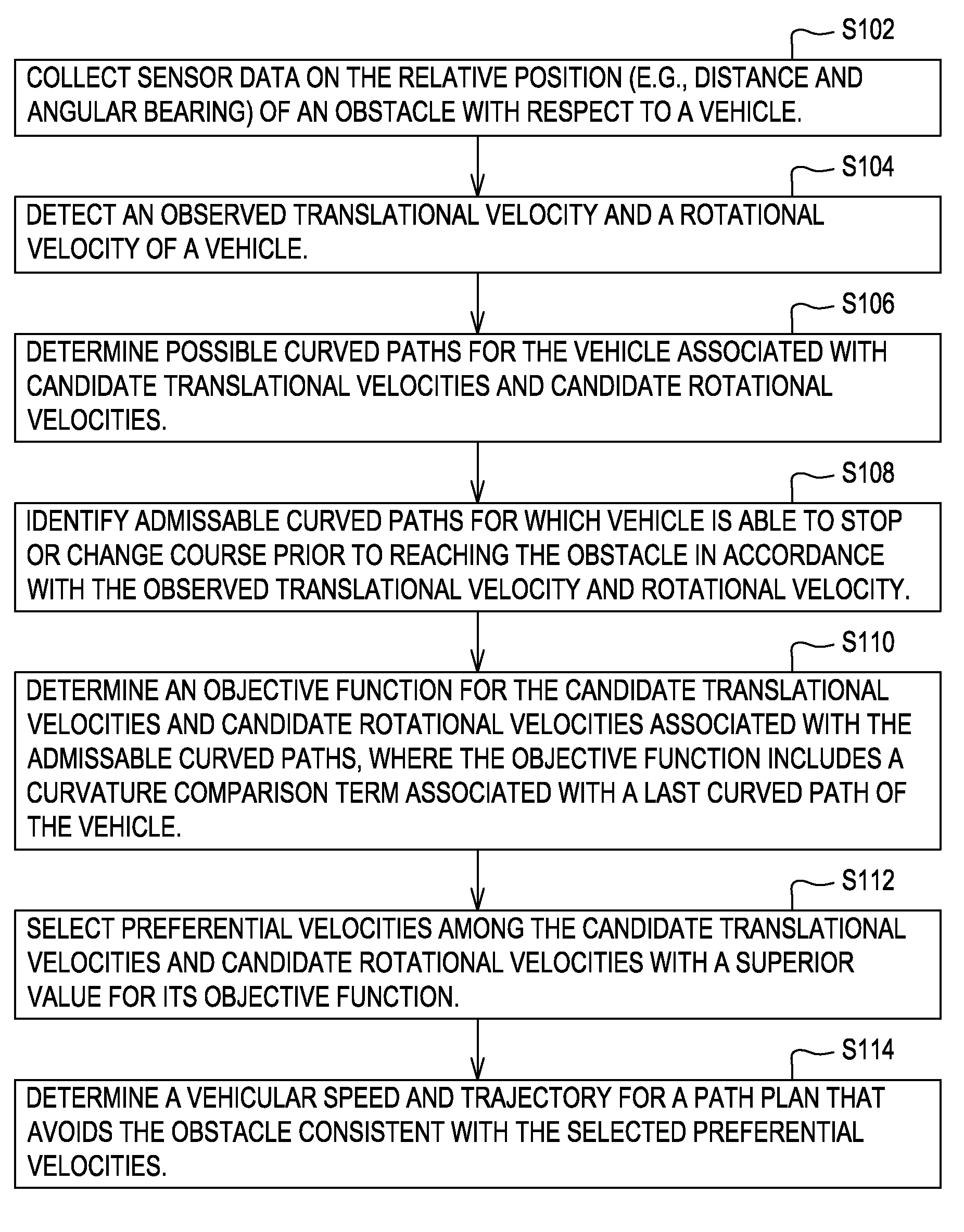
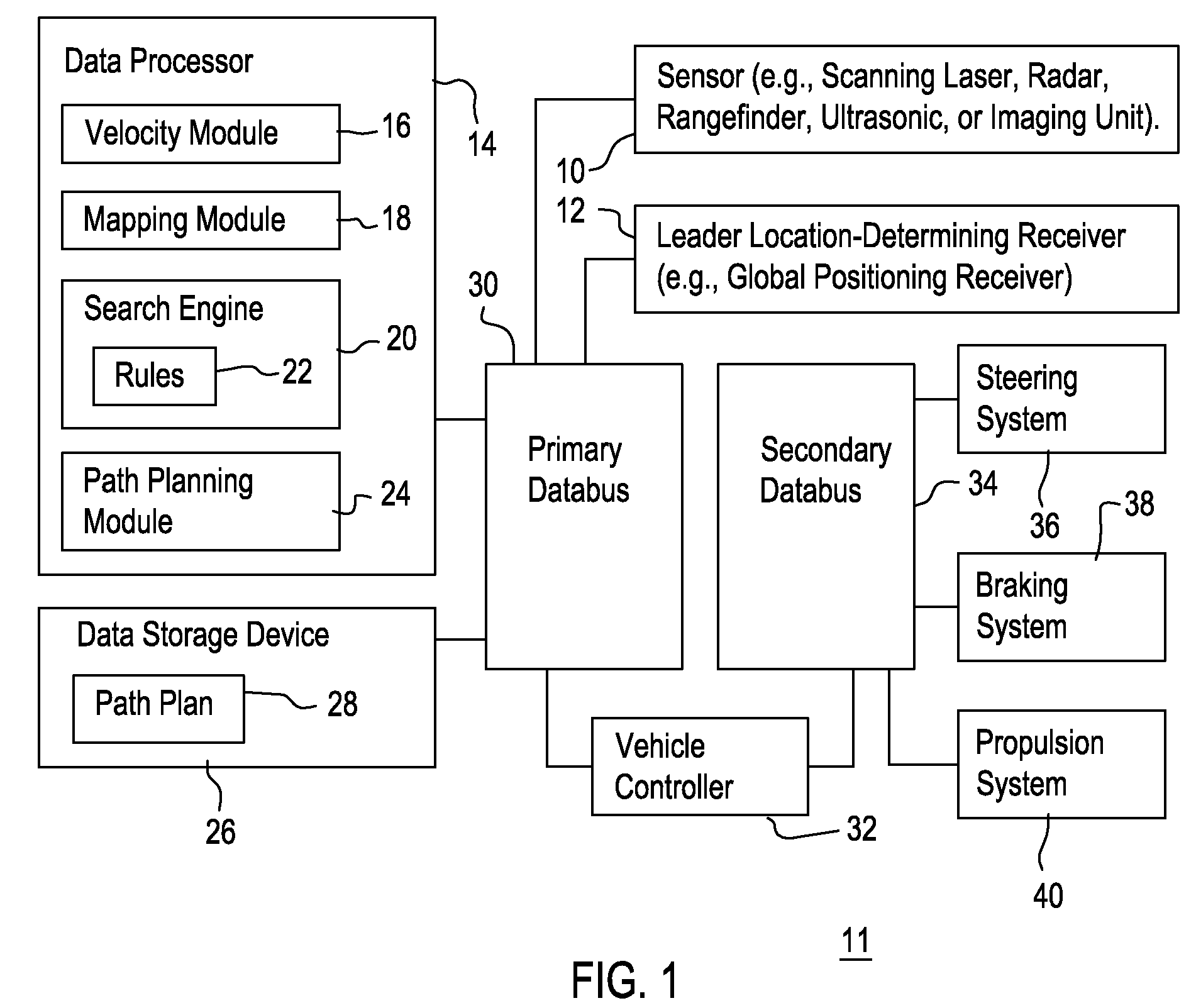
Method and system for obstacle avoidance for a vehicle
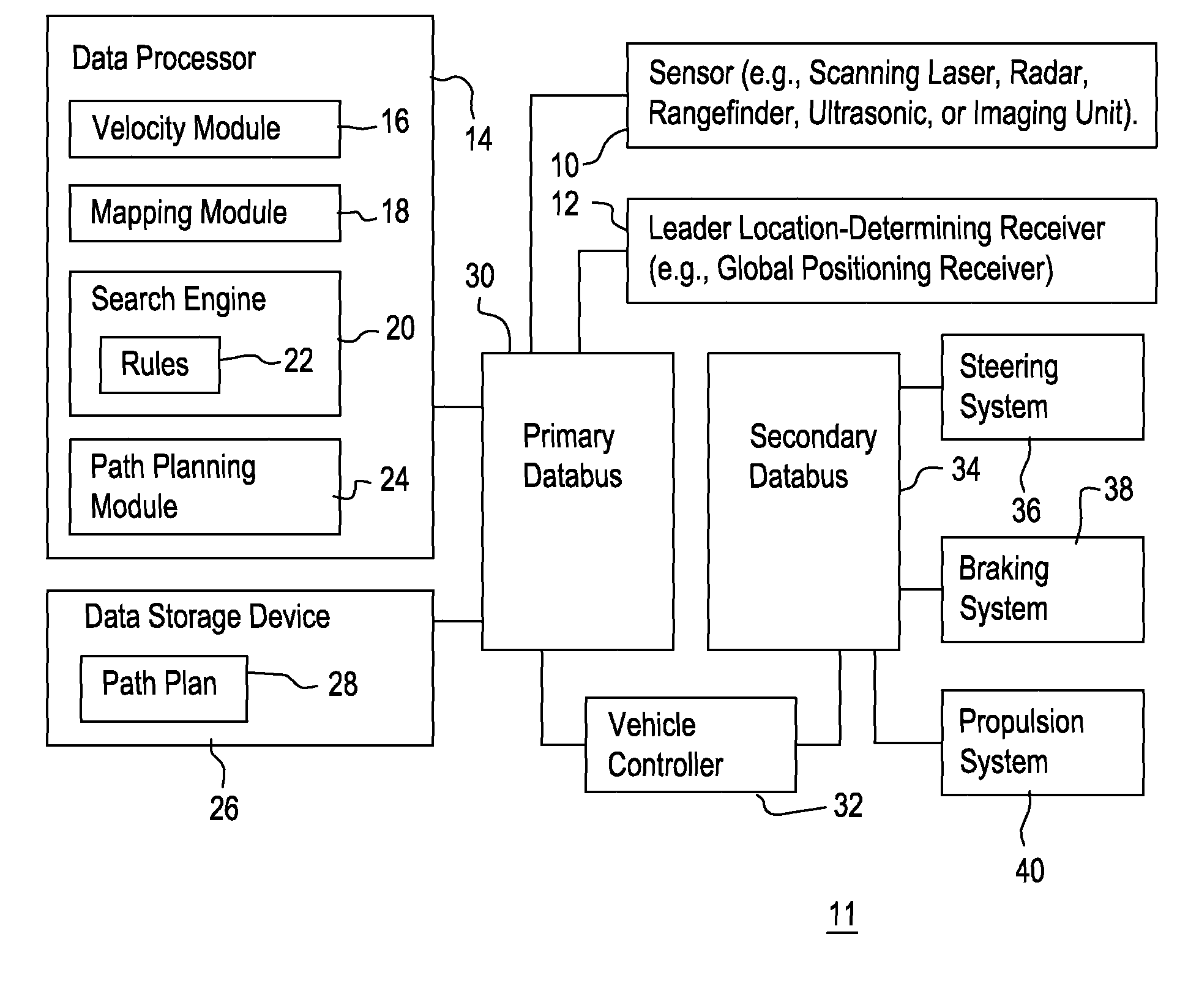
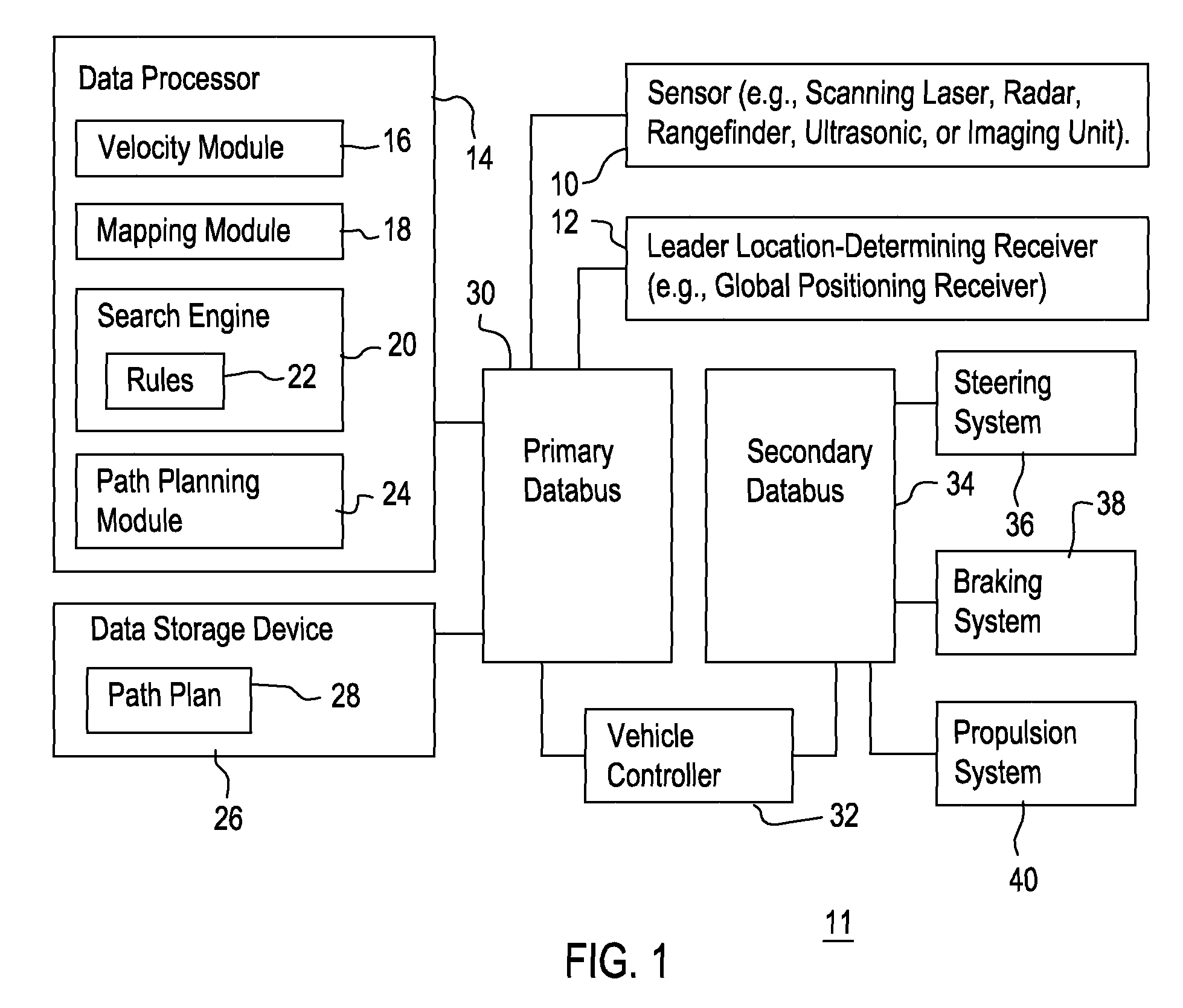
InactiveUS20090093960A1Instruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsRotation velocityEngineering
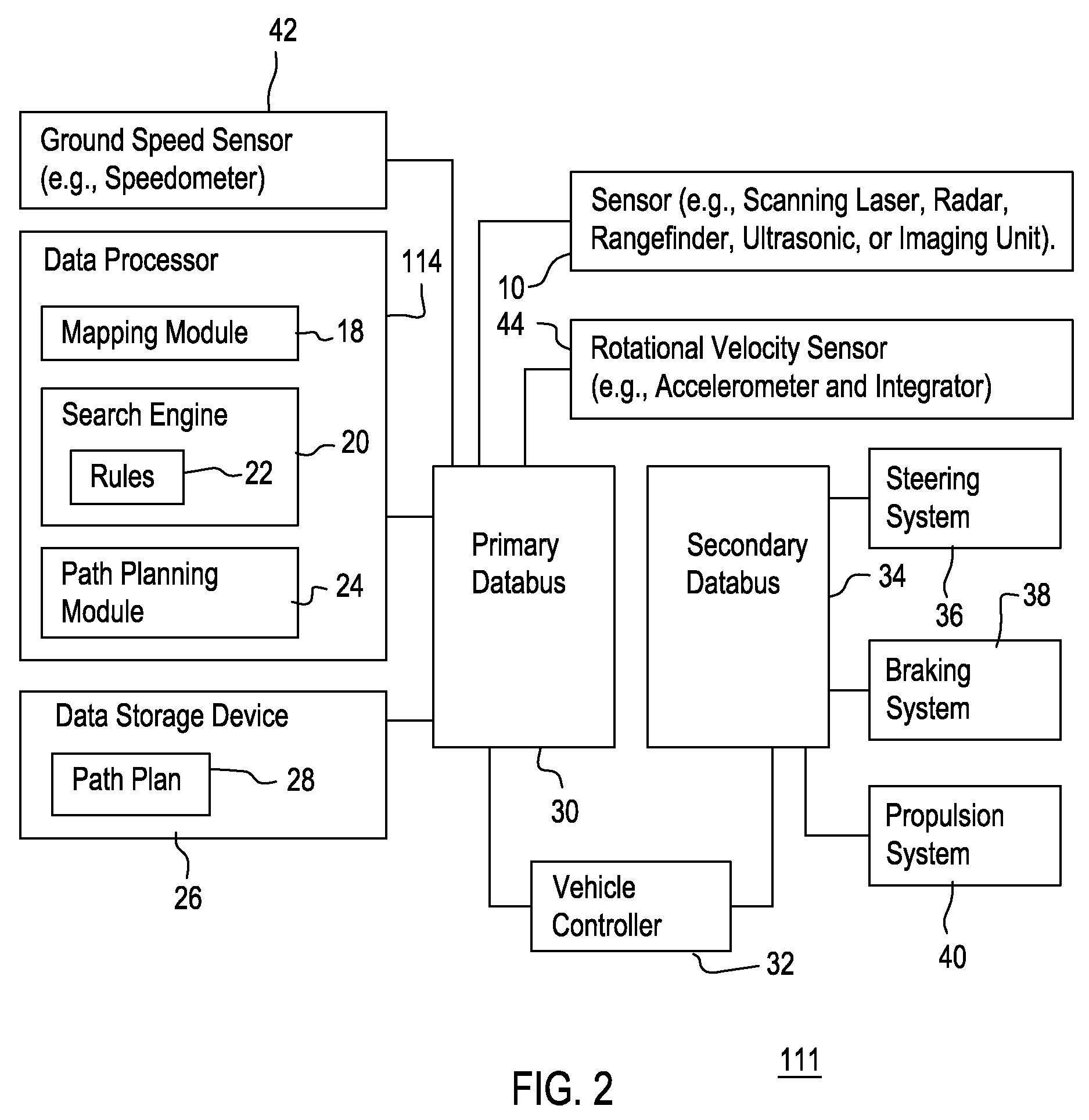
A mapping module or path filtering module is arranged to identify admissible curved paths for which the vehicle is able to stop prior to reaching a detected obstacle in accordance with an observed translational velocity and an observed rotational velocity. A data processor determines a respective objective function for the candidate translational velocities and candidate rotational velocities associated with the admissible curved paths, where the objective function includes a curvature comparison term associated with the last curved path of the vehicle. A search engine or data processor selects preferential velocities, among the candidate translational velocities and candidate rotational velocities, with a superior value for its corresponding objective function. A path planning module or data processor determines the vehicular speed and trajectory for a path plan that avoids the obstacle consistent with the selected preferential velocities.
Owner:DEERE & CO
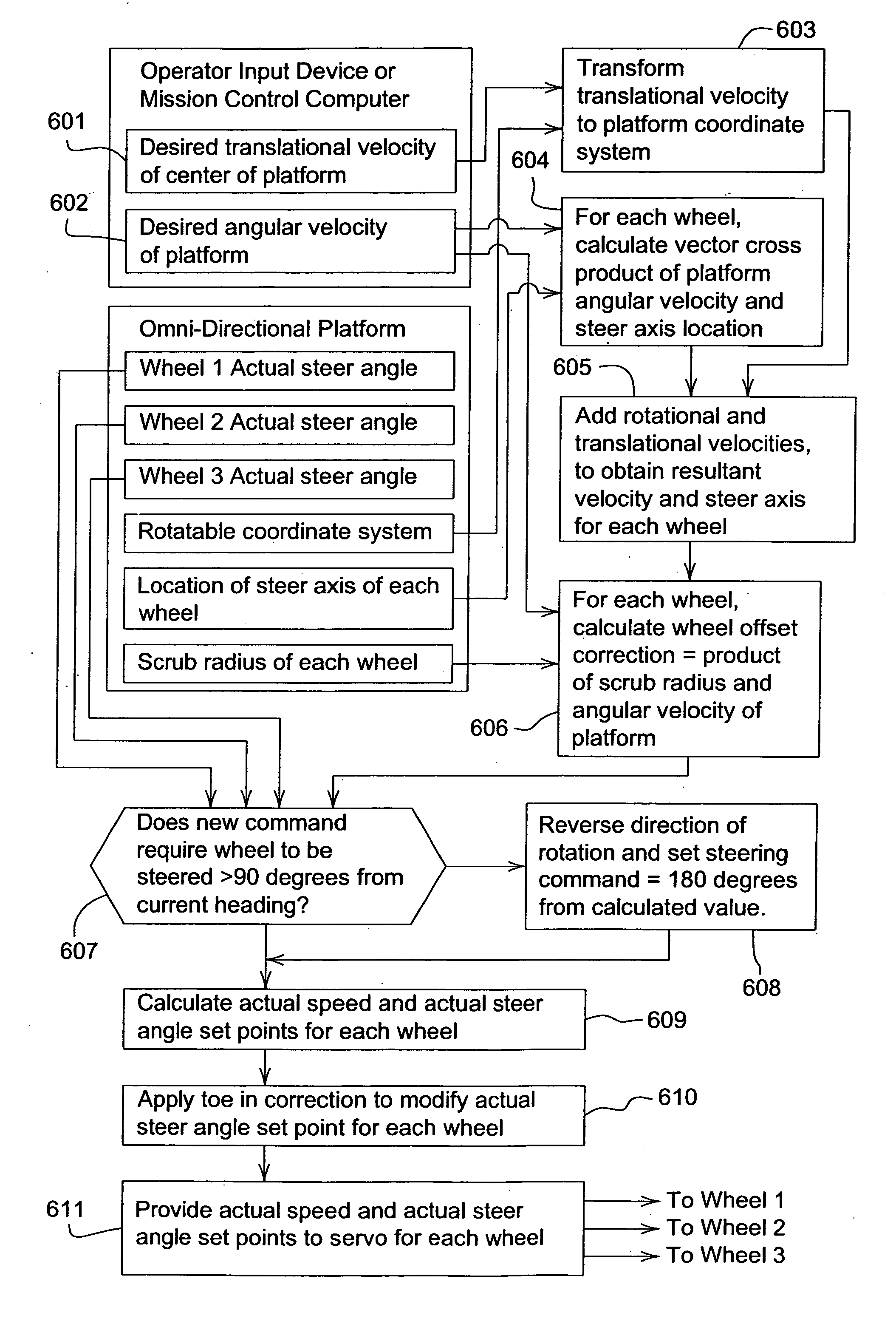
Steering logic for self-propelled mower
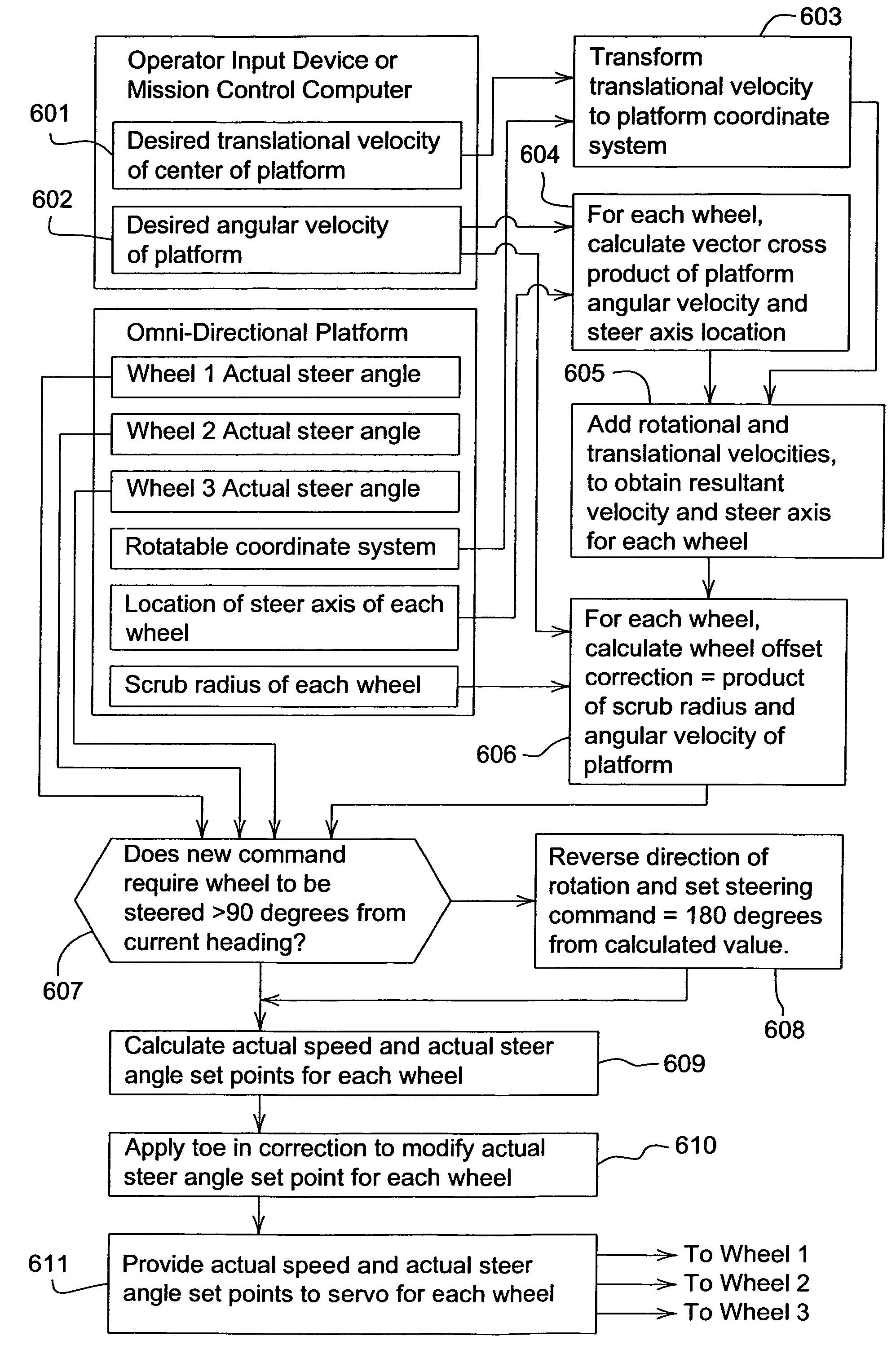
ActiveUS7418328B2Prevents scuffing and damagePerformance maximizationSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsSteering angleAngular velocity
Steering logic for a self-propelled vehicle having a plurality of wheels includes the steps of receiving translational velocity and angular velocity commands, determining the resultant velocity and steer angle of each wheel, and determining the wheel offset correction for each wheel based on the scrub radius of each wheel and the angular velocity command.
Owner:DEERE & CO
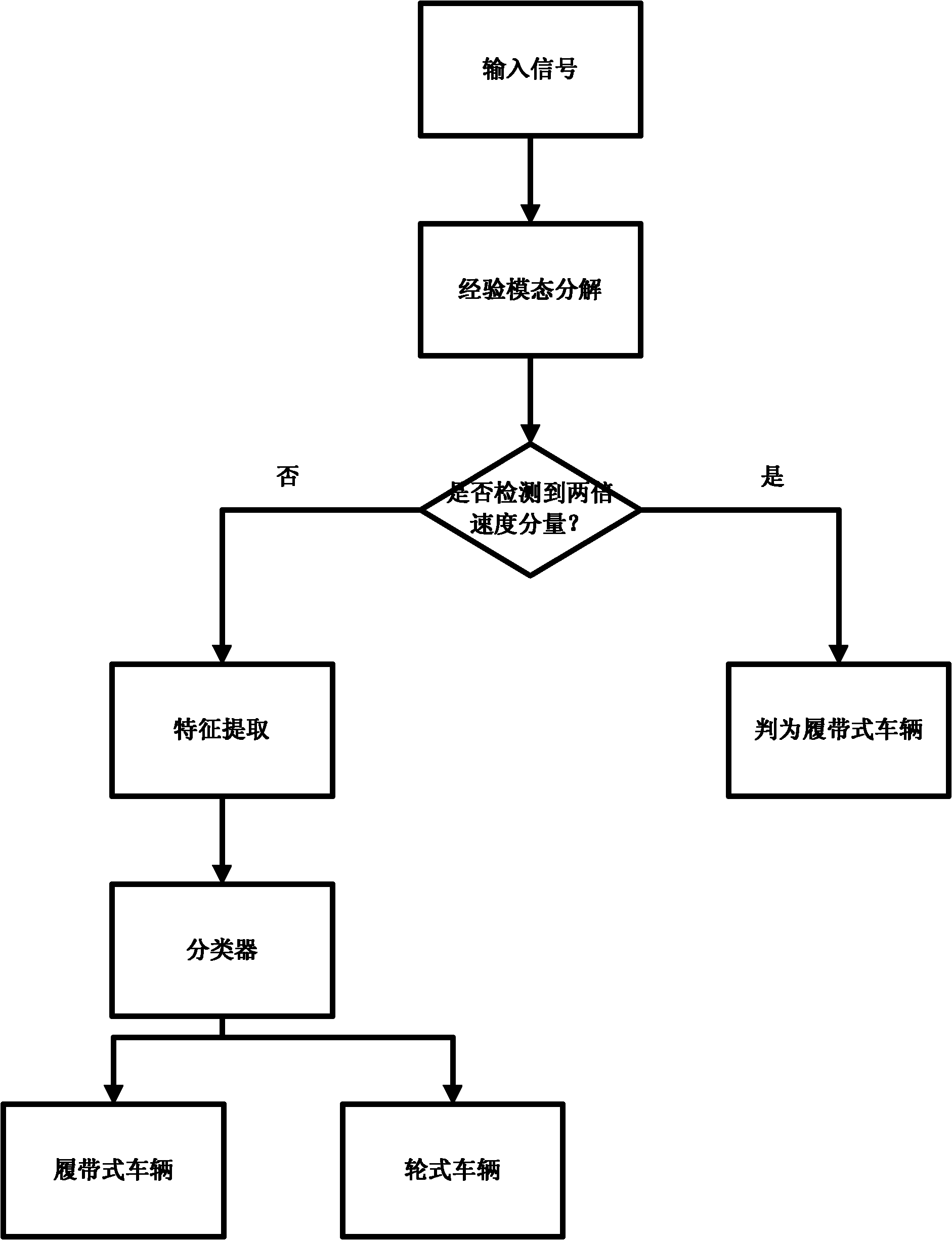
Empirical mode decomposition based moving vehicle target classification method
InactiveCN102184382AEliminate the effect of target Doppler spectral widthCharacter and pattern recognitionMobile vehicleDecomposition
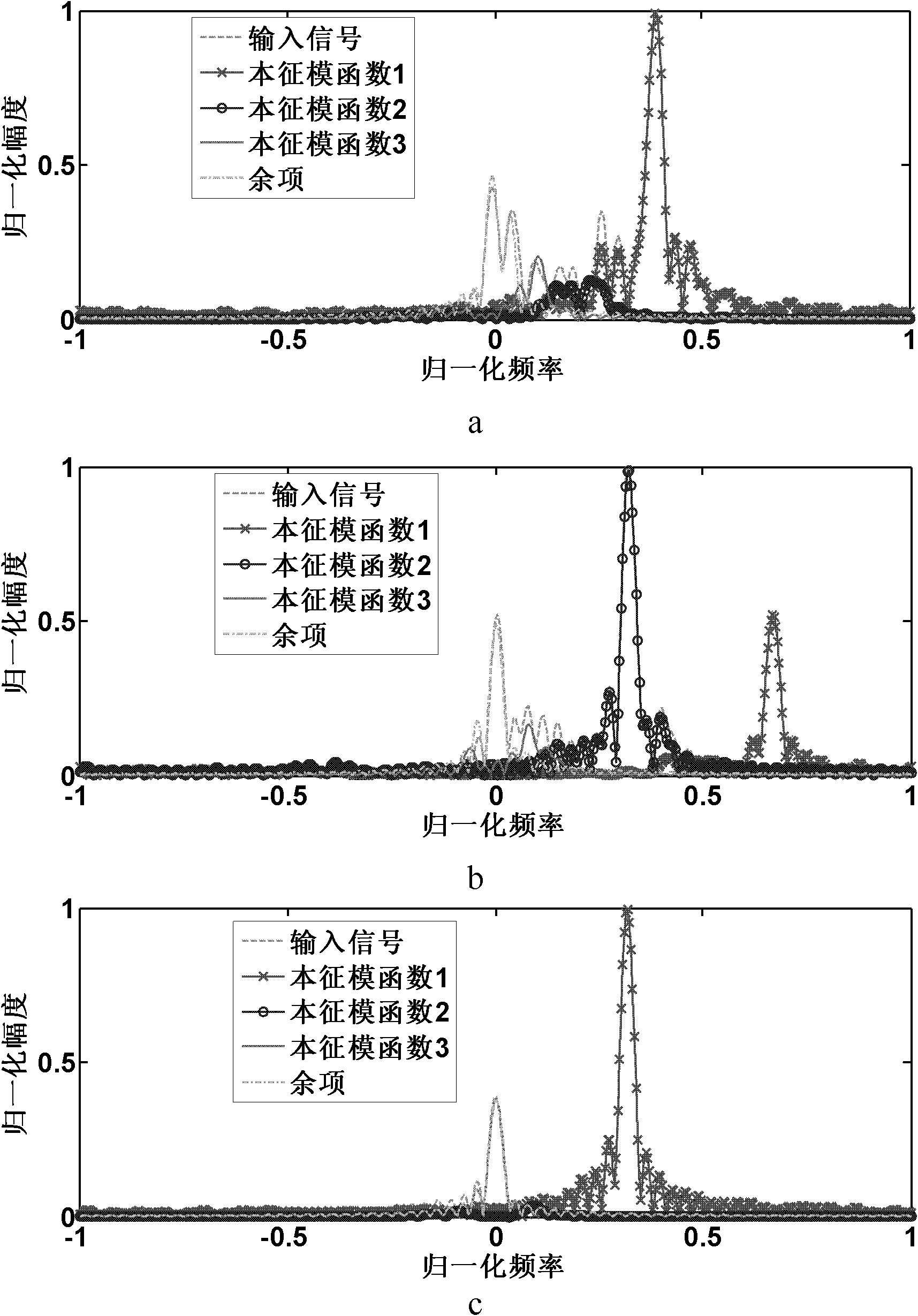
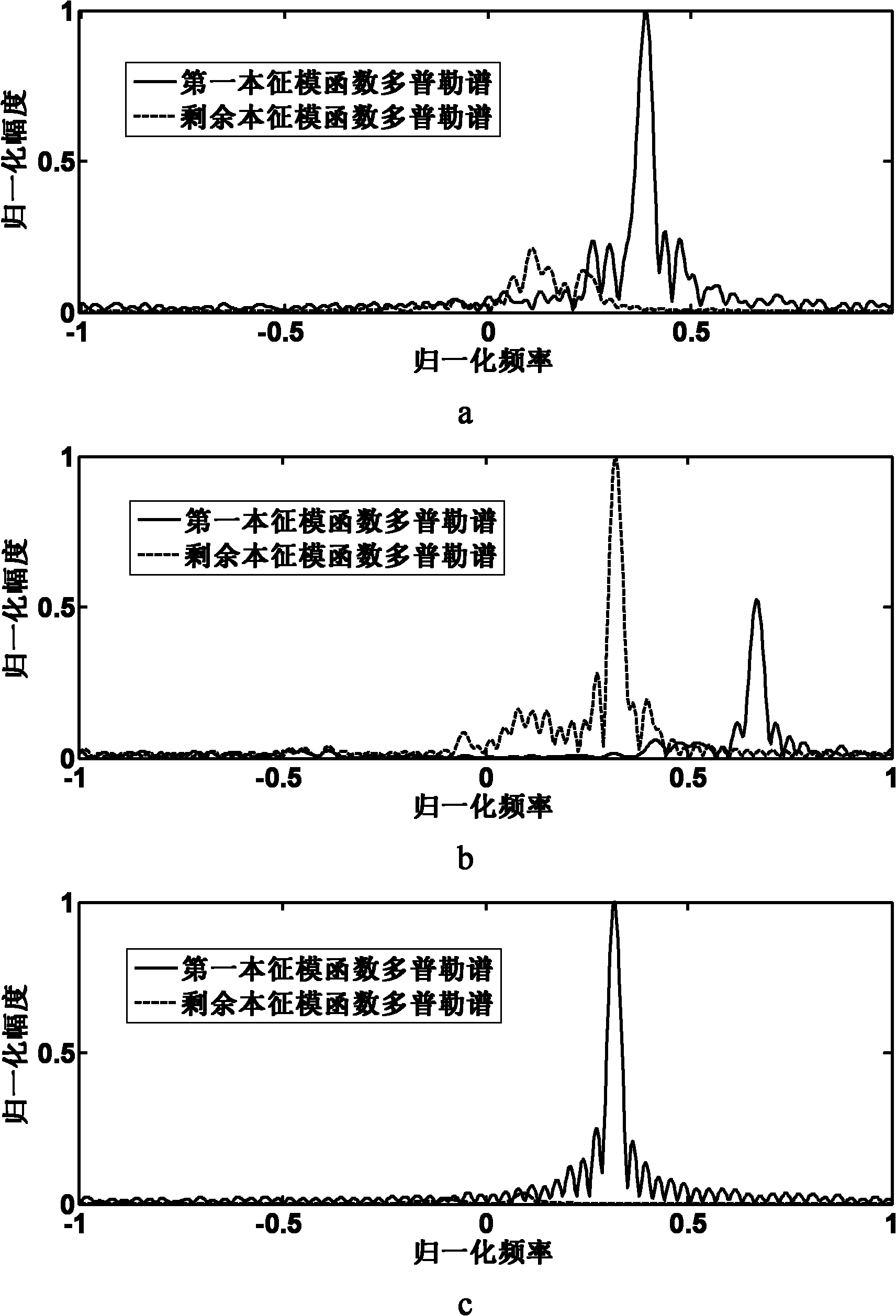
The invention discloses an empirical mode decomposition based moving vehicle target classification method which is used for mainly solving the problems that the conventional similar methods are sensitive to variation in translational velocities of targets, extra clutter suppression is required and special structural information of the target cannot be utilized. A realization process of the methodcomprises the following steps of: performing empirical mode decomposition on a Doppler echo signal; finishing clutter suppression by rejecting a remainder; defining a Doppler spectrum of a first intrinsic modular function and Doppler spectrums of remaining intrinsic modular functions by using a decomposition result; judging whether doubling translation micro-Doppler components exist according to the defined spectrums and preliminarily discriminating a track-laying vehicle; if the discrimination fails, extracting characteristics of the intrinsic modular functions and the defined spectrums; andclassifying the extracted characteristics by using a classifier. By adopting the method, influence of variation in the translational velocities of the targets on positions and widths of the Doppler spectrums of the targets can be eliminated, the clutter suppression is automatically performed, and the method can be used for classifying moving vehicle targets with maneuvering parts by using the special structural information of a track.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
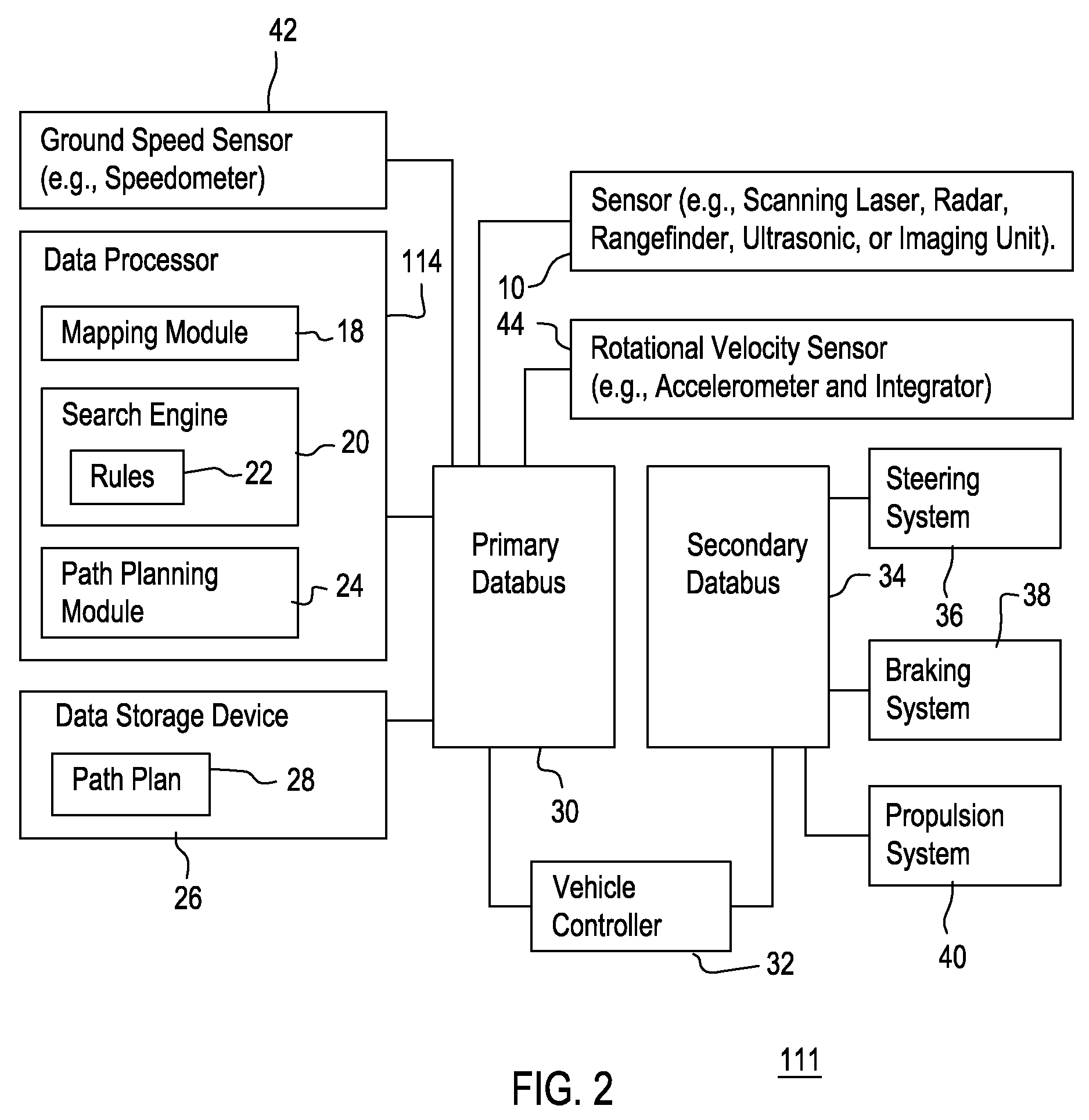
Method and system for obstacle avoidance for a vehicle
InactiveUS8060306B2Instruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsProgram planningRotation velocity
A mapping module or path filtering module is arranged to identify admissible curved paths for which the vehicle is able to stop prior to reaching a detected obstacle in accordance with an observed translational velocity and an observed rotational velocity. A data processor determines a respective objective function for the candidate translational velocities and candidate rotational velocities associated with the admissible curved paths, where the objective function includes a curvature comparison term associated with the last curved path of the vehicle. A search engine or data processor selects preferential velocities, among the candidate translational velocities and candidate rotational velocities, with a superior value for its corresponding objective function. A path planning module or data processor determines the vehicular speed and trajectory for a path plan that avoids the obstacle consistent with the selected preferential velocities.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Pitot tube velocimeter system
ActiveUS20140130608A1Improve overall utilizationFluid speed measurement using pressure differenceMechanical clearance measurementsMechanical engineeringStress sensors
An apparatus and method for sensing position according to flow velocity includes at least two pitot tubes each defining a central axis is along mutually orthogonal axes. Each of at least two pressure sensors is positioned in fluid communication with a corresponding one of the at least two pitot tubes. A controller receives outputs from the at least two pressure sensors and analyzes to determine at least one of an angular and translational velocity according to the outputs. A distance traveled is then determined according to the at least one of an angular and translational velocity. Corresponding methods of use and calibration are also disclosed.
Owner:ADAMS PHILLIP M
Steering logic for self-propelled mower
ActiveUS20070260370A1Avoid scuffingAvoid damageSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsSteering angleAngular velocity
Steering logic for a self-propelled vehicle having a plurality of wheels includes the steps of receiving translational velocity and angular velocity commands, determining the resultant velocity and steer angle of each wheel, and determining the wheel offset correction for each wheel based on the scrub radius of each wheel and the angular velocity command.
Owner:DEERE & CO
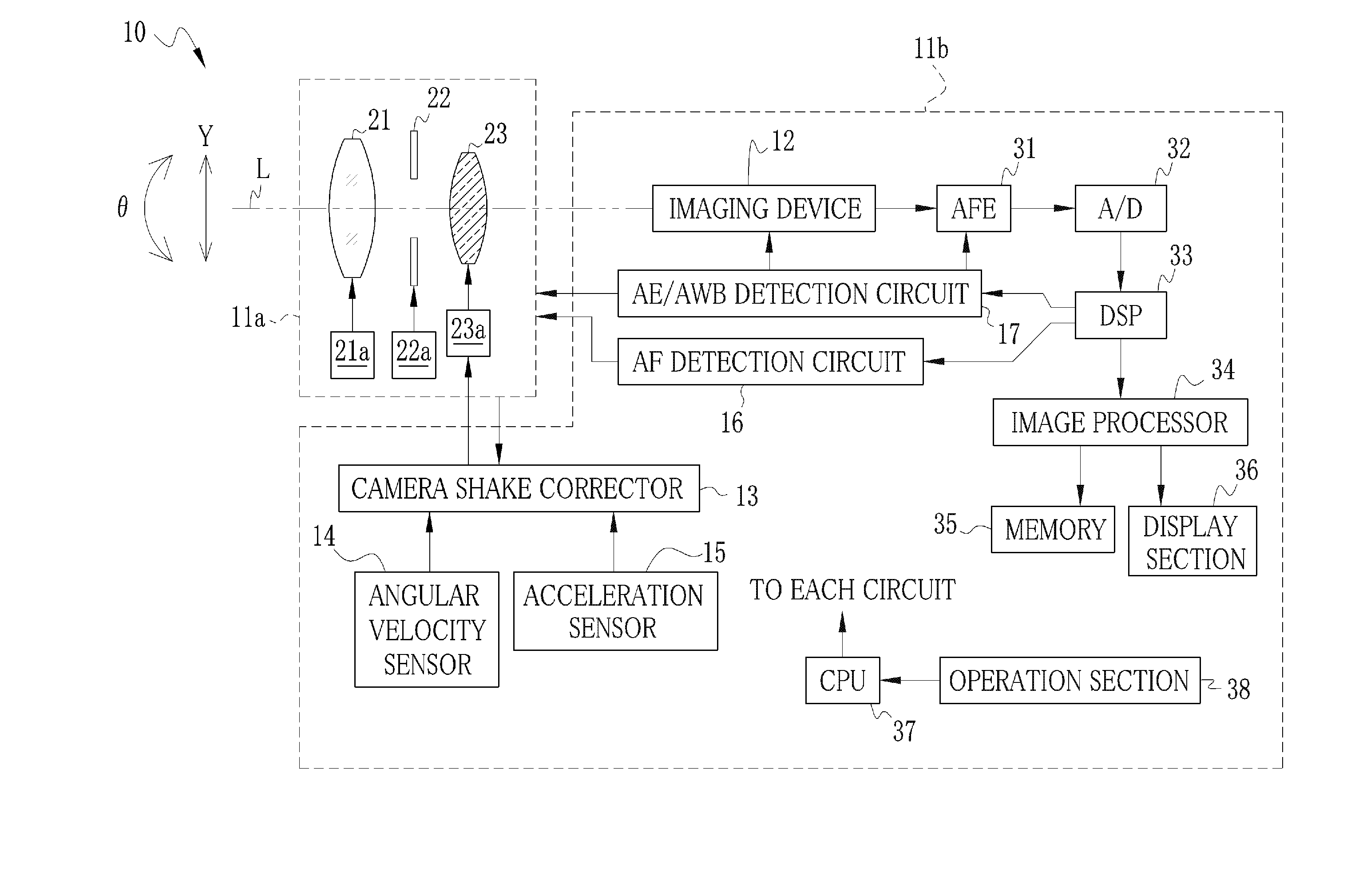
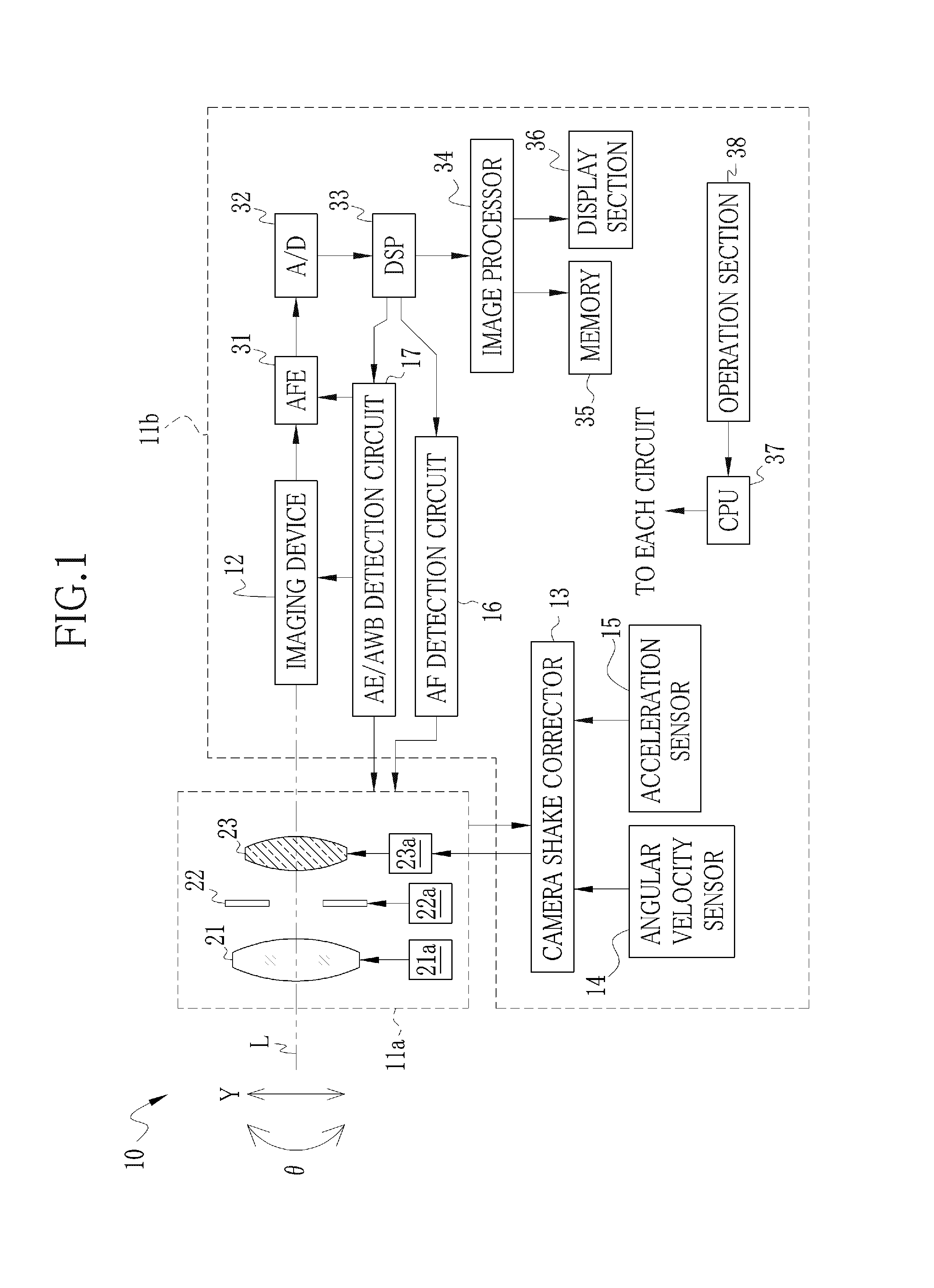
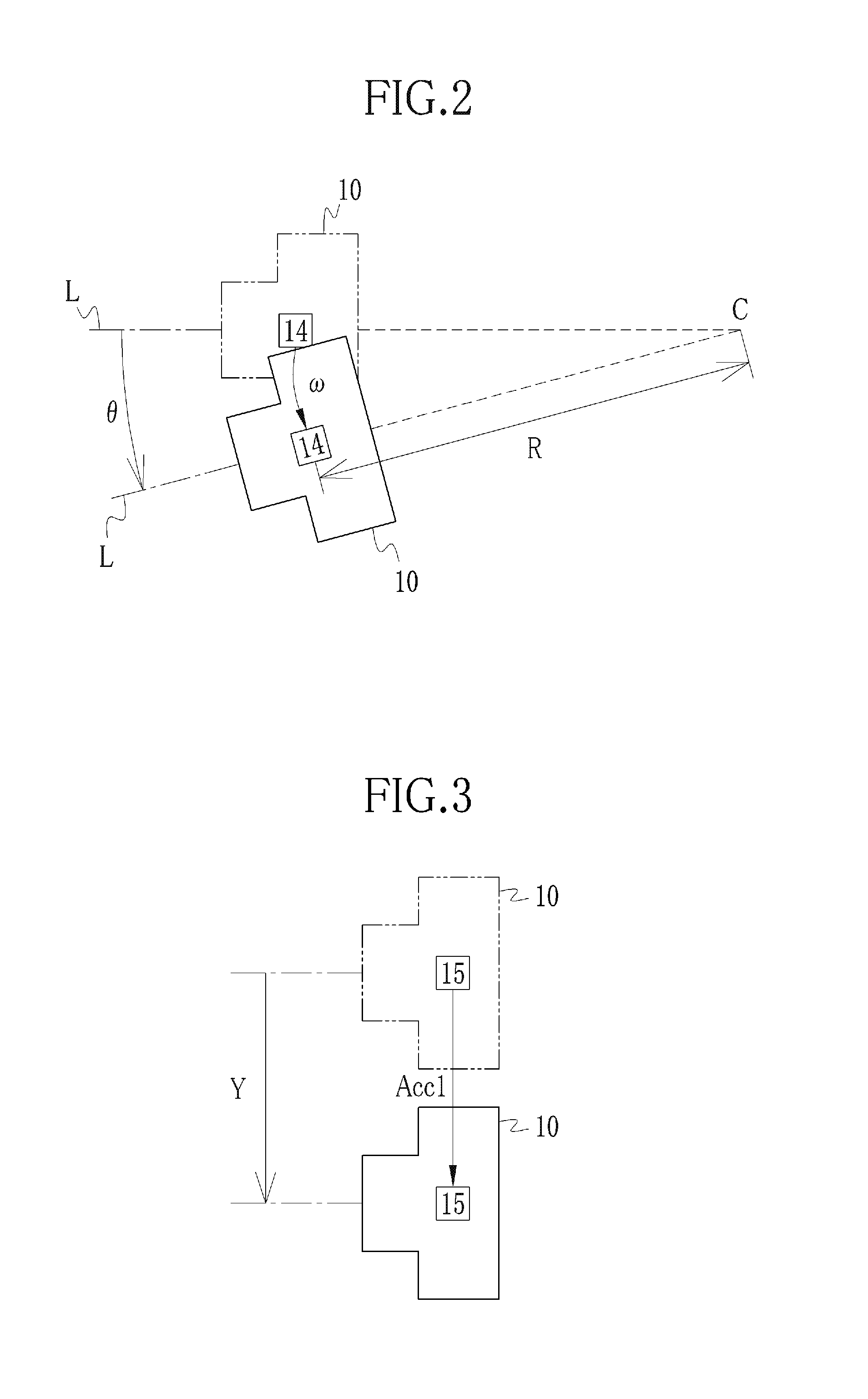
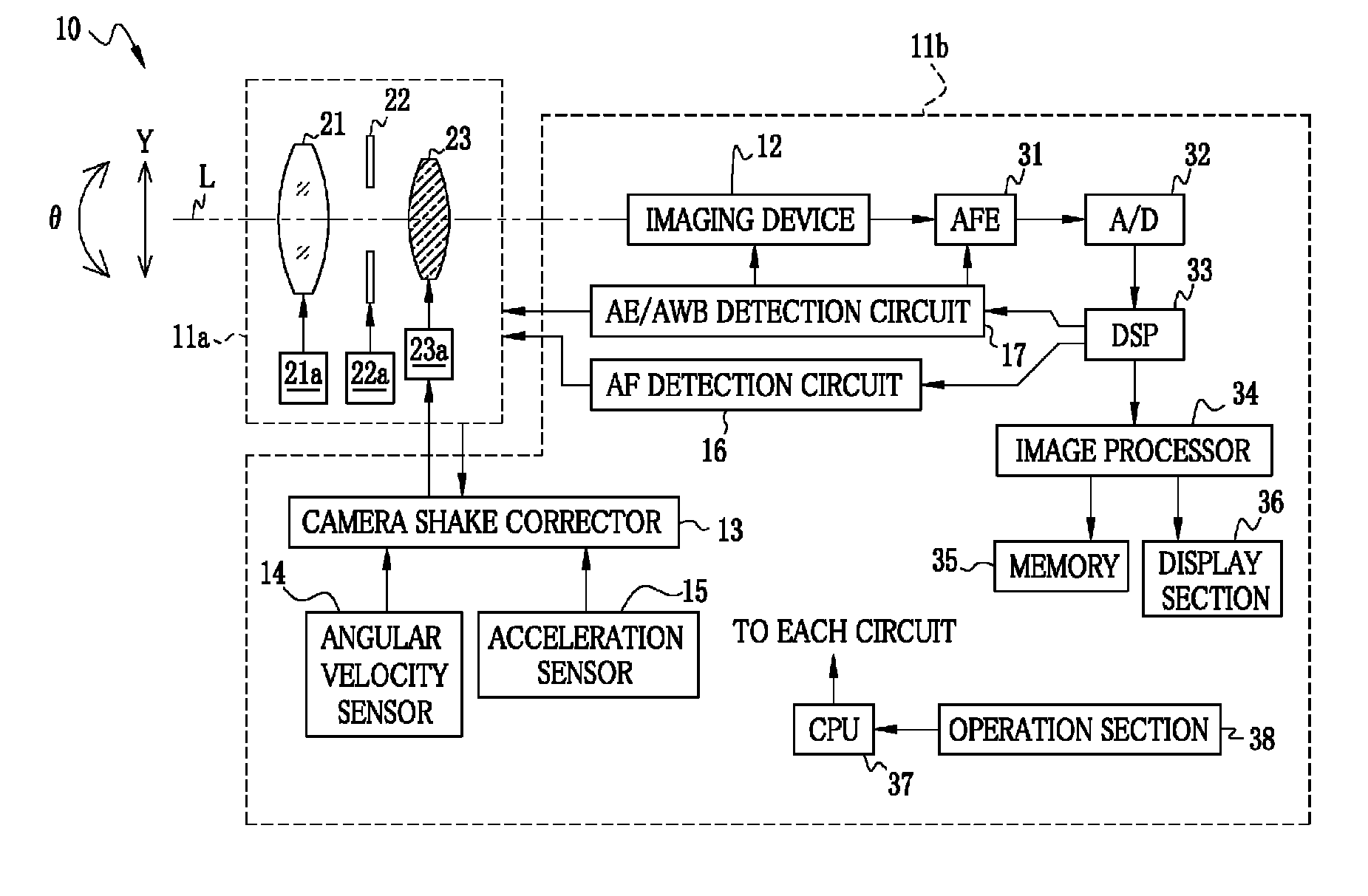
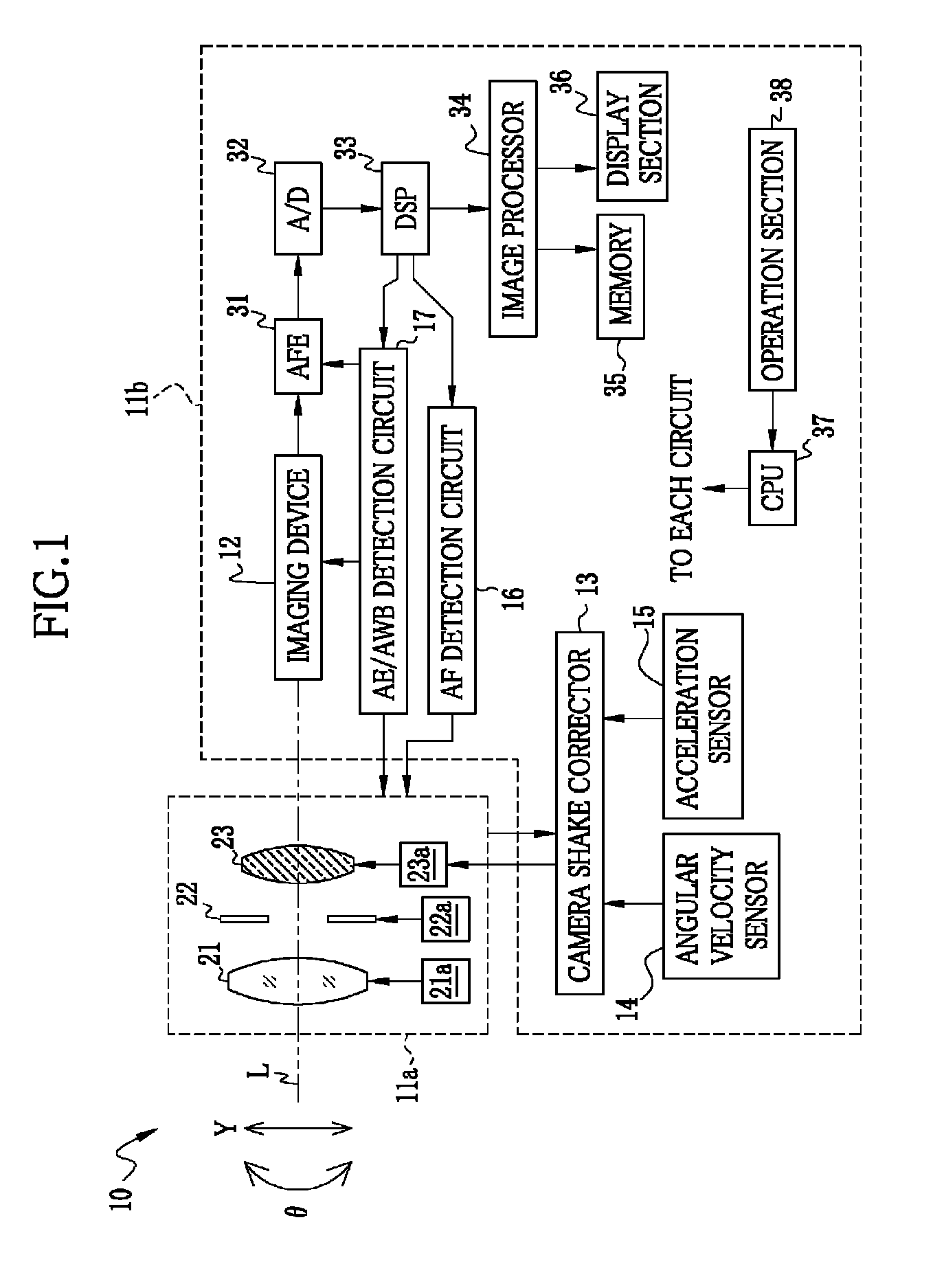
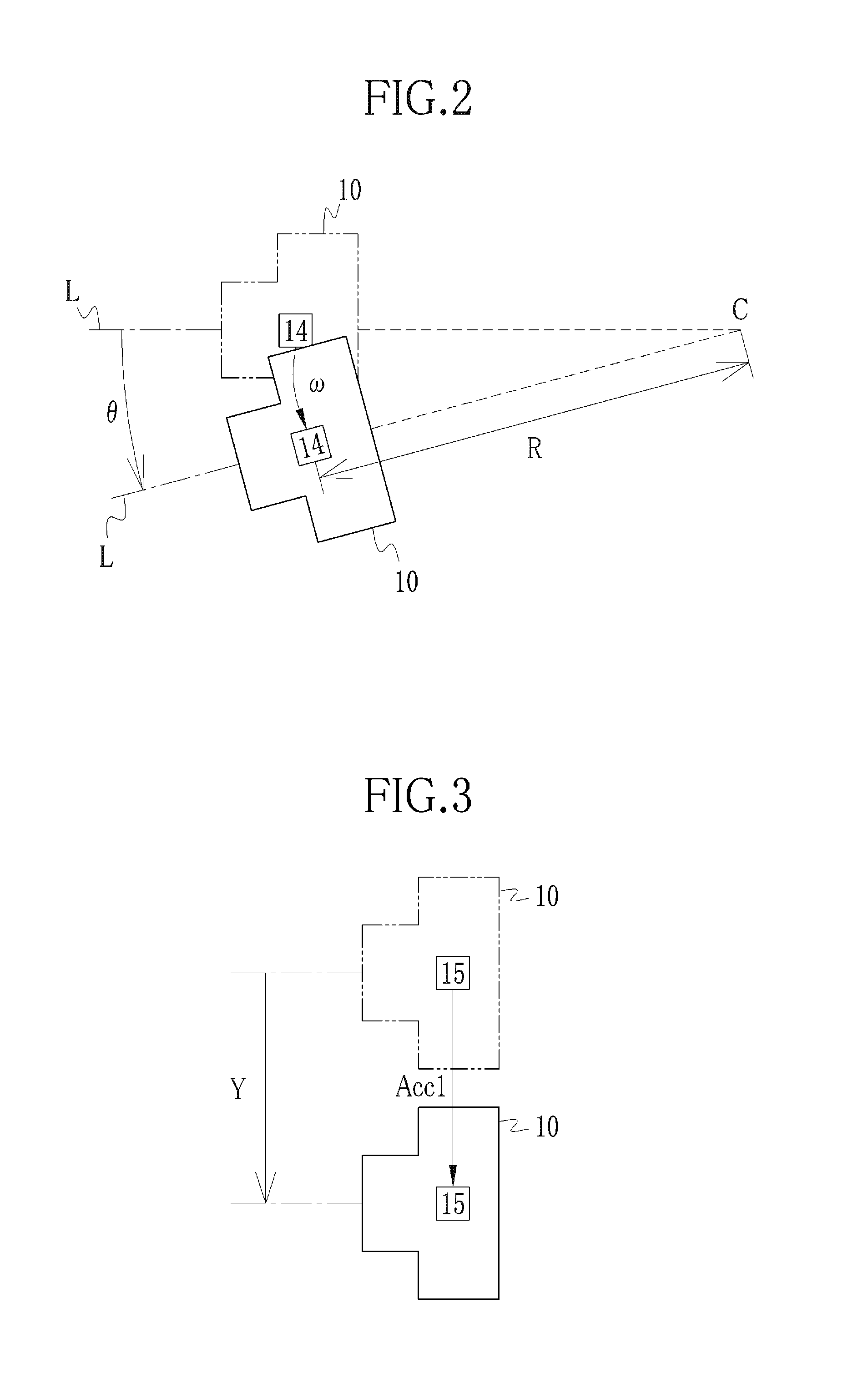
Image pickup apparatus
ActiveUS20140036101A1Ensure correct executionTelevision system detailsPrintersAngular velocityActuator
At the time of occurrence of camera shake, an angular velocity sensor detects an angular velocity. A rotation angle calculator integrates the angular velocity to calculate angle camera shake. A translational acceleration calculator subtracts an internal acceleration caused during operation of a lens unit from a first translational acceleration detected by an acceleration sensor, so as to calculate a second translational acceleration. A translational velocity calculator integrates the second translational acceleration to calculate a translational velocity. A rotation radius calculator calculates a rotation radius based on the angular velocity and the translational velocity. A shake amount calculator calculates a camera shake amount based on the angle camera shake and the rotation radius. An actuator drives a camera shake correction lens in a direction for canceling the camera shake amount.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
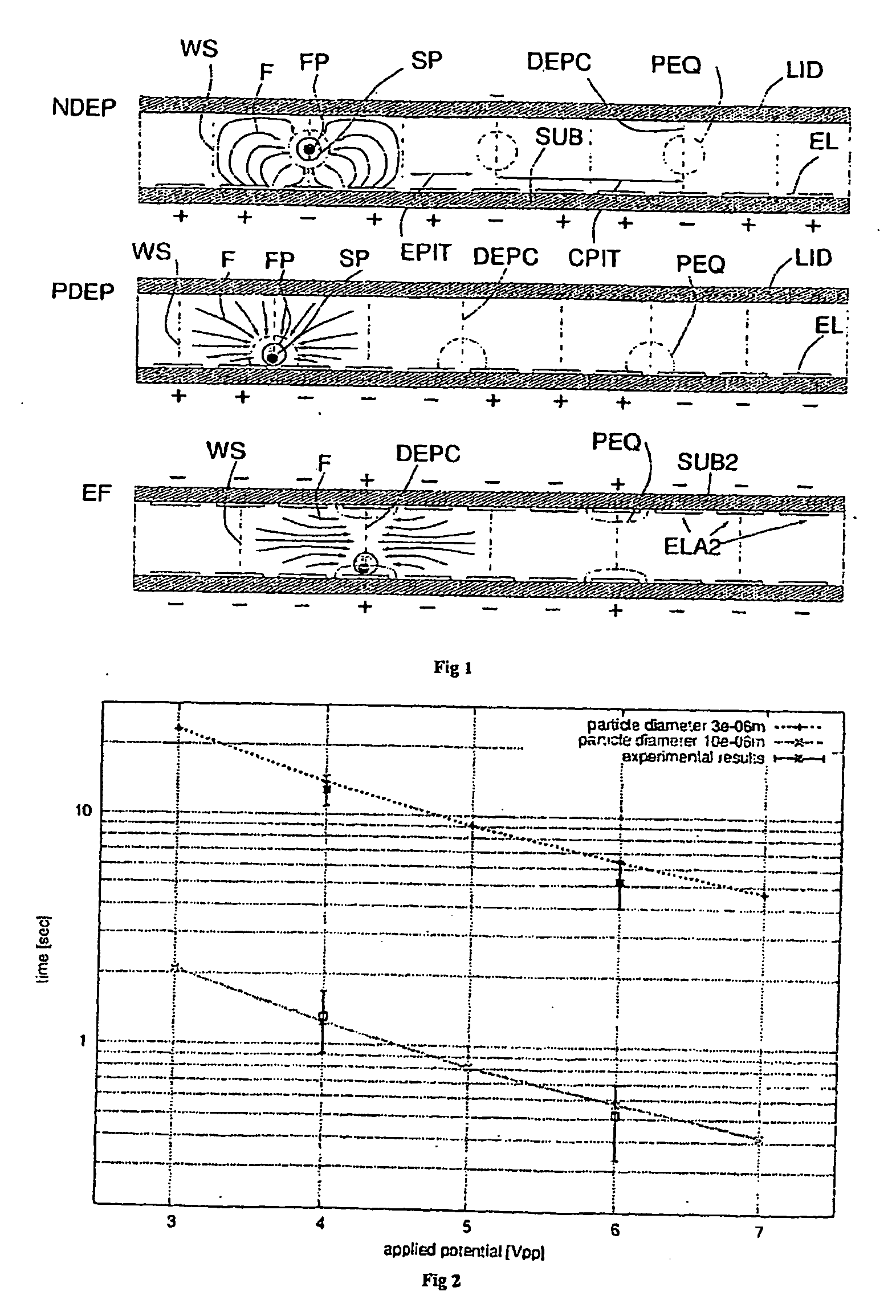
Method and apparatus for the separation and quantification of particles
The invention pertains to a method and apparatus to separate and quantify particles using time-variable force fields. The force fields can be for dielectrophoresis (positive or negative), electrophoresis or electrohydrodinamic. In a first aspect of the method, the fields are translated and / or modified in space at a speed substantially comparable to the speed of translation of the fastest particles in the sample so that only these follow by changing position, while the slowest particles are not affected.According to the invention the translation and / or modification of the force field can also occur with varying speed, which is especially useful when this happens with periodic law on a field with spatial periodicity. In one aspect of the method, a force field with spatial periodicity is translated and / or modified in a first direction at high speed, for such a period of time as to cause a movement equal to the spatial period of the field, and at low speed in a second direction, opposite to the first one, for such a period of time as to cancel the overall movement of the field, causing the translation of the slowest particles in the second direction and no movement of the fastest particles.In an additional aspect of the method, the field is translated and / or modified in a first direction at high speed, for such a period of time as to cause a movement equal to the spatial period of the field minus a quantity corresponding to the period of the electrodes generating it, causing the translation of the fastest particles in the first direction and of the slowest particles in the opposite direction.In another aspect of the method, the quantity or size of the particles is determined by an indirect measurement of the speed of movement after varying the force field by means of a relationship between the speed of movement and the volume of the particles.This invention also pertains to an apparatus to produce appropriate field configurations that are necessary for the selective movement of particles
Owner:MENARINI SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA
Method of detecting compound motion target based on orbital angular momentum
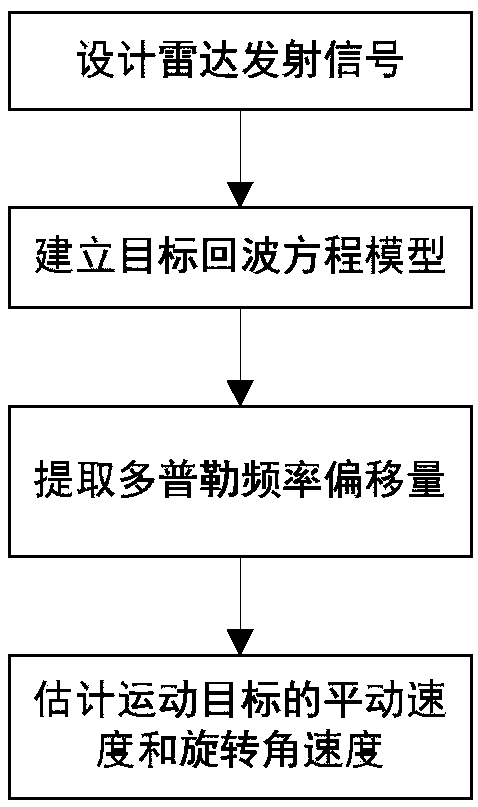
ActiveCN108594198AEffective detectionEfficient separationWave based measurement systemsMomentumEquation of the center
The invention belongs to the field of radar detection and Doppler detection of moving targets and particularly relates to a method of detecting a compound motion target based on orbital angular momentum. The method comprises the steps: designing a radar emission signal, and establishing an emission signal model; setting target motion parameters, acquiring a target echo equation by deduction, and analyzing with the target echo equation to obtain internal relations of Doppler frequency offset to target translational velocity and rotational angular velocity; providing a detection and separation method of translational Doppler frequency offset and rotational Doppler frequency offset; finally, implementing detection of the compound motion target based on the detection results of Doppler frequency offset. orbital angular momentum information carried by vortex electromagnetic wave can be utilized herein to provide effective detection and separation for translational Doppler and rotational Doppler, so that the detection of the compound motion target is implemented; references are provided for the development of radar detection techniques and target recognition techniques based on orbital angular momentum.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Wafer scanning system with reciprocating rotary motion utilizing springs and counterweights
InactiveUS20050254932A1Constant movementThermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsEngineeringActuator
The present invention is directed to a scanning apparatus and method for processing a workpiece, wherein the scanning apparatus comprises a wafer arm and moving arm fixedly coupled to one another, wherein the wafer arm and moving arm are operable to rotate about a first axis. An end effector, whereon the workpiece resides, is coupled to the wafer arm. A rotational shaft couples the wafer arm and moving arm to a first actuator, wherein the first actuator provides a rotational force to the shaft. A momentum balance mechanism is coupled to the shaft and is operable to generally reverse the rotational direction of the shaft. The momentum balance mechanism comprises one or more fixed spring elements operable to provide a force to a moving spring element coupled to the moving arm. A controller is further operable to maintain a generally constant translational velocity of the end effector within a predetermined scanning range.
Owner:AXCELIS TECHNOLOGIES
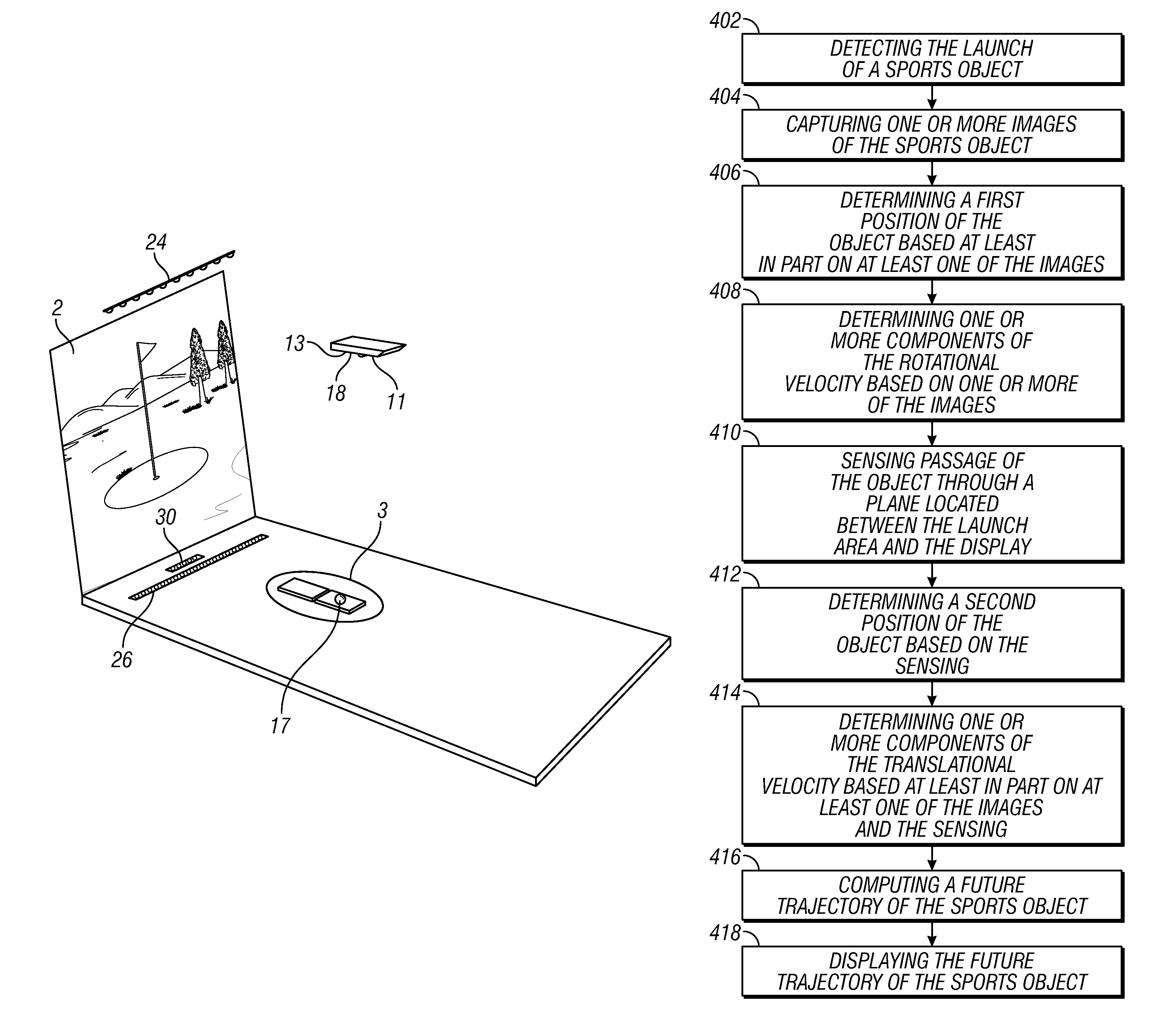
Methods and systems for sports simulation
A sports simulator calculates the rotational and translational velocity of a sports object. The rotational velocity is calculated using image analysis. The translational velocity is calculated using image analysis and a set of emitters and sensors. The simulator then computes the future trajectory of the sports object based on the rotational and translational velocity. In one embodiment, the sports object is a golf ball and the sports simulator simulates golf.
Owner:FULL SWING GOLF
Test method of slippage rate of tractor
ActiveCN104198200AImprove accuracyImprove measurement efficiencyVehicle wheel testingElectricityLow speed
The invention provides a test method of slippage rate of a tractor. The method comprises the following steps: 1) measuring the rotating speeds of a front wheel and a rear wheel which are at the same side through an optical-electricity encoder; 2) measuring a translational velocity of a vehicle through a low-speed radar sensor; 3) calculating to obtain the slippage rate of the whole tractor; 4) measuring various parameter values respectively according to different tilling depth during working in a farmland; 5) measuring traction force as the parameter value of the transportation condition during transportation; 6) processing the experimental data, wherein the measurement above is performed by groups, each group is subjected to at least three measurements to remove abnormal data, and effective test results are selected and sorted summed up. The test method of the slippage rate of the tractor has the beneficial effects that 1, two different working conditions of the tractor, namely, working in the farmland and transporting can be completely simulated, and thus the accuracy of the measured data is improved; 2, various measuring devices are used to further improve the accuracy of the measured data; 3, various traction force values are provided according to the application of a load trolley, so as to improve the measuring efficiency.
Owner:江阴智产汇知识产权运营有限公司
Autonomous mobile body and control method of same
ActiveUS20130131910A1Avoid interferencePromote generationRobotManipulatorAngular velocityAngular degrees
An autonomous mobile body is configured to flexibly avoid obstacles. The mobile body has a movement mechanism configured to translate in a horizontal plane and rotate around a vertical axis, and the distance to an obstacle is derived for each directional angle using an obstacle sensor. A translational potential of the mobile body and a rotational potential of the mobile body for avoiding interference with the obstacle are generated, based on the distance from the autonomous mobile body to the obstacle at each directional angle. An amount of control relating to a translational direction and a translational velocity of the mobile body and an amount of control relating to a rotational direction and an angular velocity of the mobile body are generated based on the generated potentials, and the movement mechanism is driven.
Owner:MURATA MASCH LTD
Image pickup apparatus
At the time of occurrence of camera shake, an angular velocity sensor detects an angular velocity. A rotation angle calculator integrates the angular velocity to calculate angle camera shake. A translational acceleration calculator subtracts an internal acceleration caused during operation of a lens unit from a first translational acceleration detected by an acceleration sensor, so as to calculate a second translational acceleration. A translational velocity calculator integrates the second translational acceleration to calculate a translational velocity. A rotation radius calculator calculates a rotation radius based on the angular velocity and the translational velocity. A shake amount calculator calculates a camera shake amount based on the angle camera shake and the rotation radius. An actuator drives a camera shake correction lens in a direction for canceling the camera shake amount.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
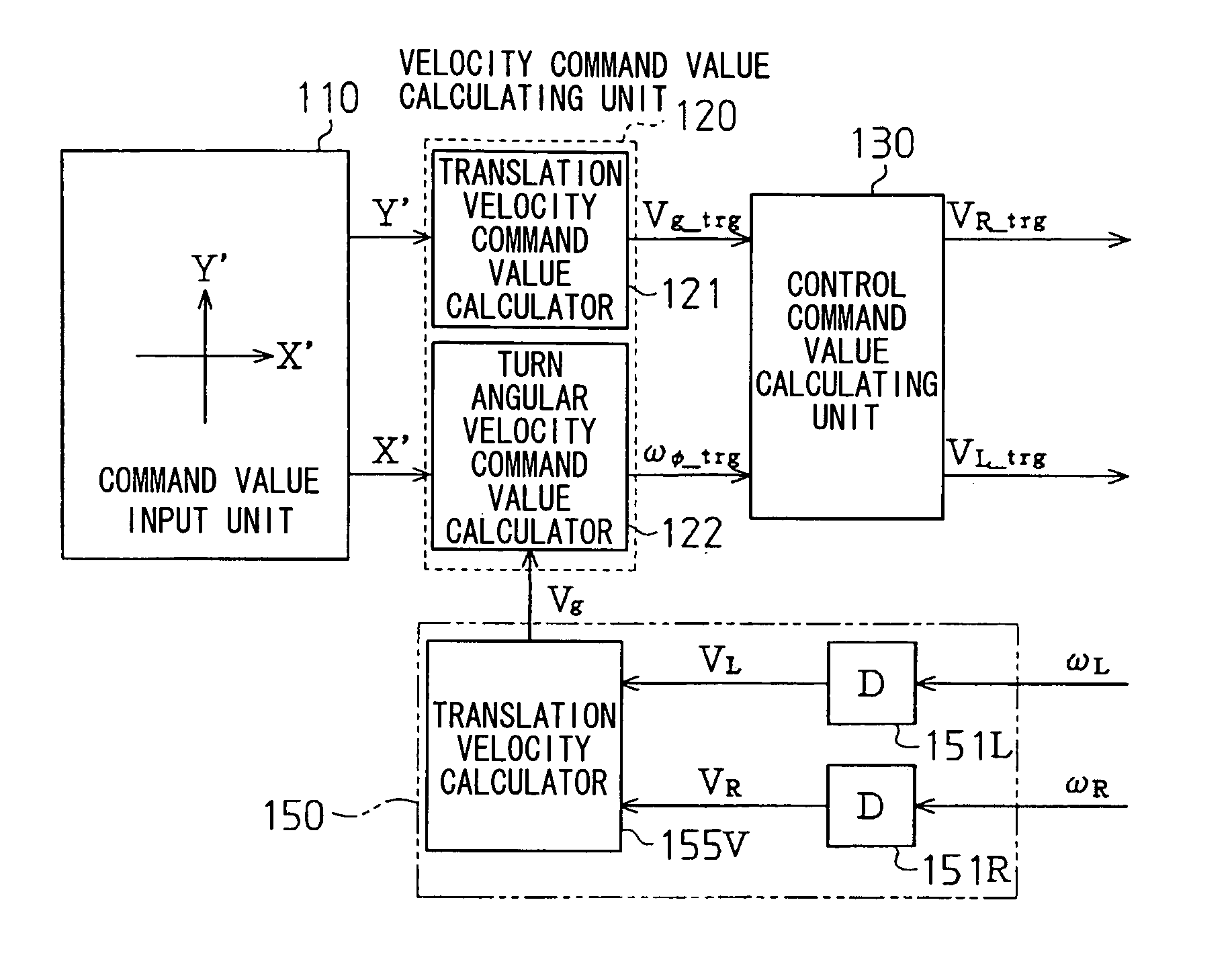
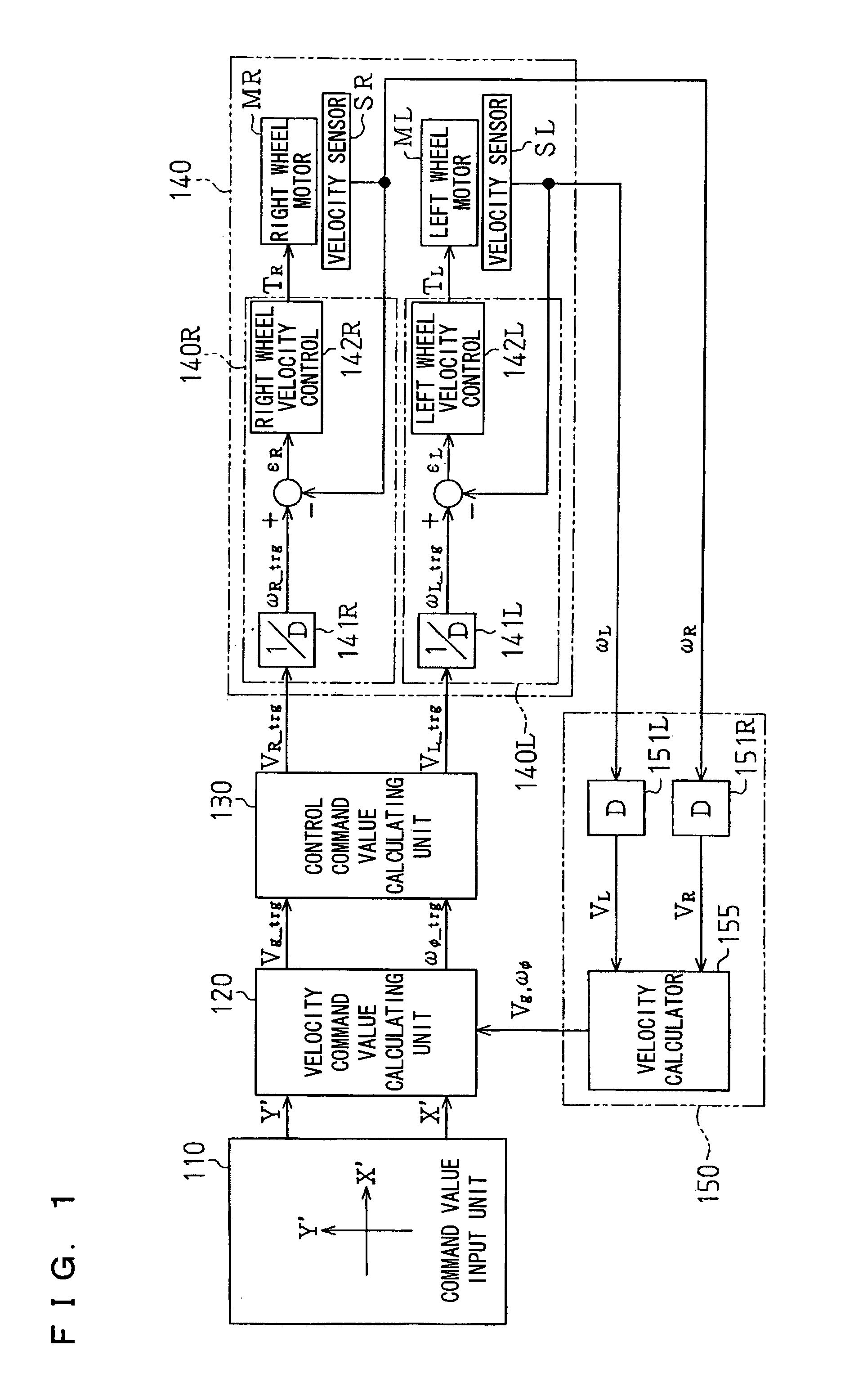
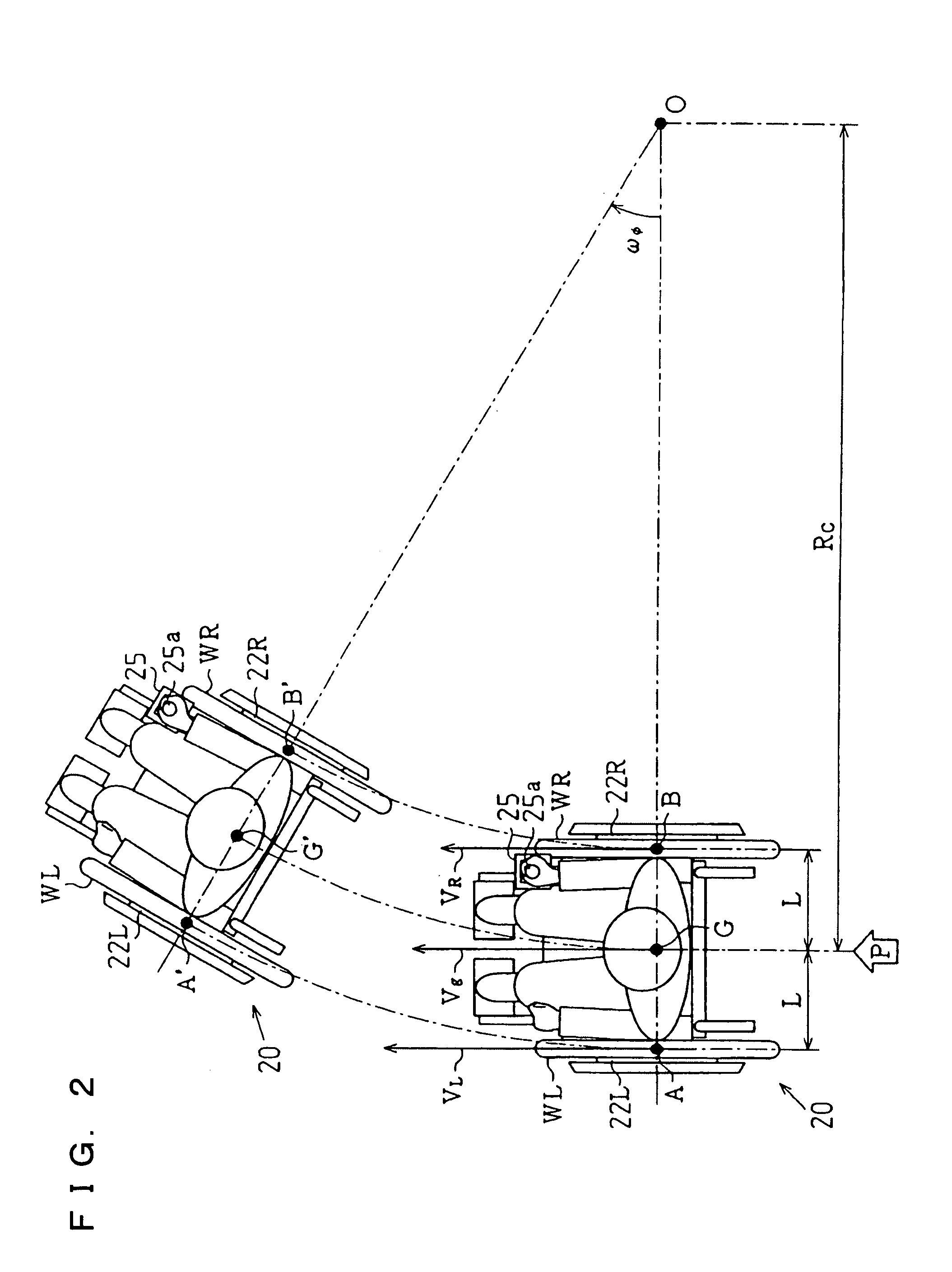
Electrically movable vehicle and control program for driving electrically movable vehicle
InactiveUS7138772B2Efficiently determinedImprove stabilitySingle-phase induction motor startersSynchronous motors startersDrive wheelAngular velocity
The invention provides an electrically movable vehicle drivable by a simplified mode of control and a control program for driving the vehicle. A normalized value Y′ representing translation motion and a normalized value X′ representing turning motion are fed from a command value input unit 110 to a velocity command value calculating unit 120. The calculating unit 120 determines a translation velocity command value Vg<sub2>—< / sub2>trg based on the normalized value Y′. The calculating unit 120 determines a turn angular velocity command value ωf<sub2>—< / sub2>trg that will always satisfy Expression (2–4) for preventing the vehicle from falling down. The translation velocity command value Vg<sub2>—< / sub2>trg and the turn angular velocity command value ωf<sub2>—< / sub2>trg determined by the unit 120 are fed to a control command value calculating unit 130, which calculates control command values for left and right drive wheels. The control command values are fed to a motor control unit 140 to control motors Mr, Ml and control the drive wheels.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Positioning device and method for enhancing vision and robot
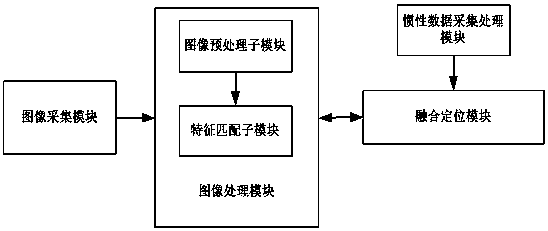
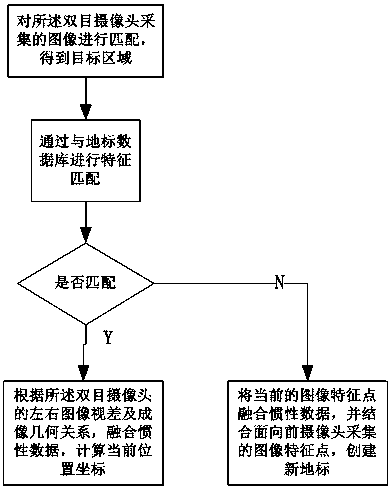
PendingCN108481327AAchieve integrationHigh precisionProgramme-controlled manipulatorImaging processingSelf positioning
The invention discloses a positioning device and method for enhancing vision and a robot. The positioning device is a movable vision positioning device and comprises an image collection module, an image processing module, an inertia data collection and processing module and a fusion positioning module. The image collection module comprises a forward inclined camera and a backward inclined two-lenscamera head which are positioned to different positions of the positioning device and used for enhancing the vision sensing effect of the positioning device. The image processing module comprises animage pretreatment submodule and a feature matching submodule and is used for processing collected image data. The inertia data collection and processing module is used for sensing rotary angle information, acceleration information and translational velocity of an inertia sensor in real time. The fusion positioning module is used for fusing environment information obtained by sensor modules to achieve reliable and robust self positioning. Compared with the prior art, the image data and the inertia data with matched features are fused, the landmark is updated through the relative position relation, accordingly, recognition feature matching is more accurate, and positioning algorithm robustness is enhanced.
Owner:AMICRO SEMICON CORP
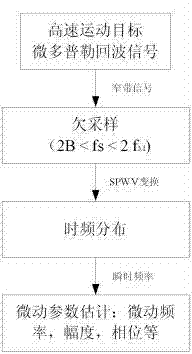
Undersampling based high-speed movement target micro-doppler parameter estimation method
InactiveCN104122539ALower requirementThe amount of sampled data is reducedRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEstimation methodsMicro doppler
The invention provides an undersampling based high-speed movement target micro-doppler parameter estimation method. The undersampling technology is introduced aiming at radar micro-doppler signals of high-speed movement targets. Radar micro-doppler echo signals are narrow-band signals with large center frequency values and a high sampling frequency is required when a traditional nyquist sampling frequency is used to sample the signals. But according to the undersampling theorem, the signals are sampled with the sampling frequency which is 2 times higher than that of a micro-doppler signal bandwidth and much smaller than the nyquist sampling frequency. According to the undersampling technology, target translational velocity information is saved, the signal sampling data size is greatly reduced, later computing costs and requirements for hardware equipment are lowered, meanwhile target tender moving information is remained, then time frequency distribution processing is performed on the sampling data, and time frequency characteristics of the echo signals can be obtained and tender moving parameter estimation of the targets can be performed.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Mobile circumferential scanning control device and control method, mobile circumferential scanning equipment, and unmanned vehicle
ActiveCN107765088ARun fastAvoid rescanningSpectral/fourier analysisOptical detectionAngular velocityComputer module
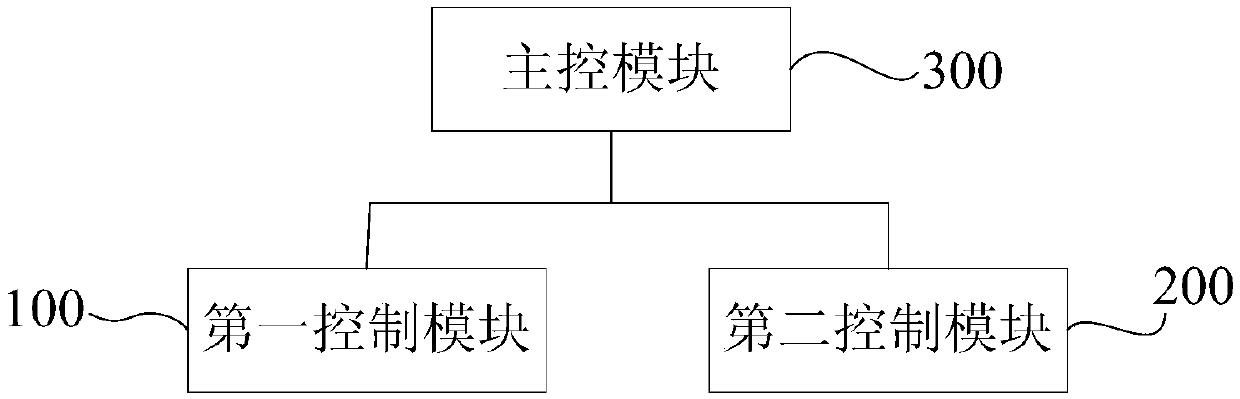
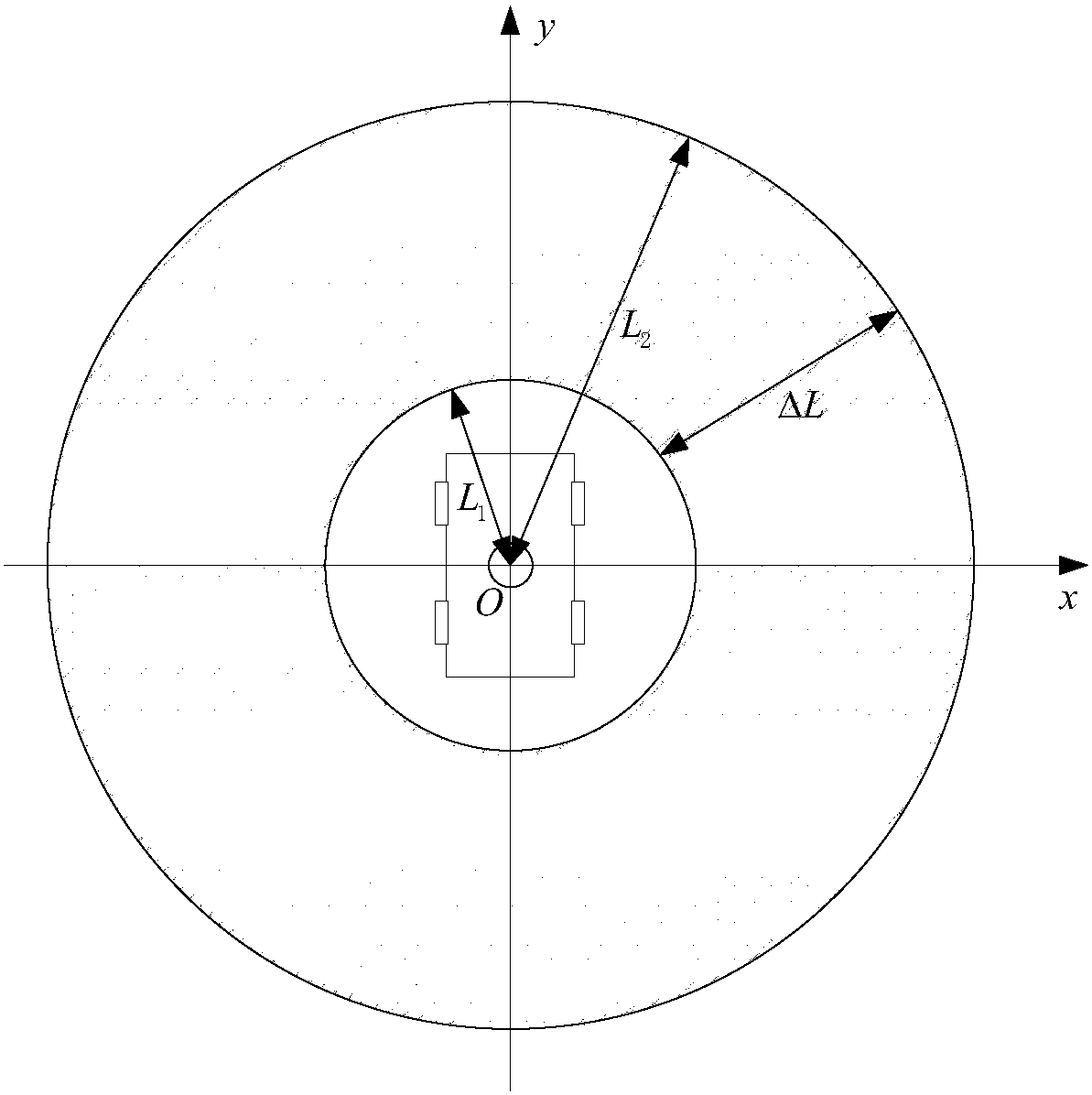
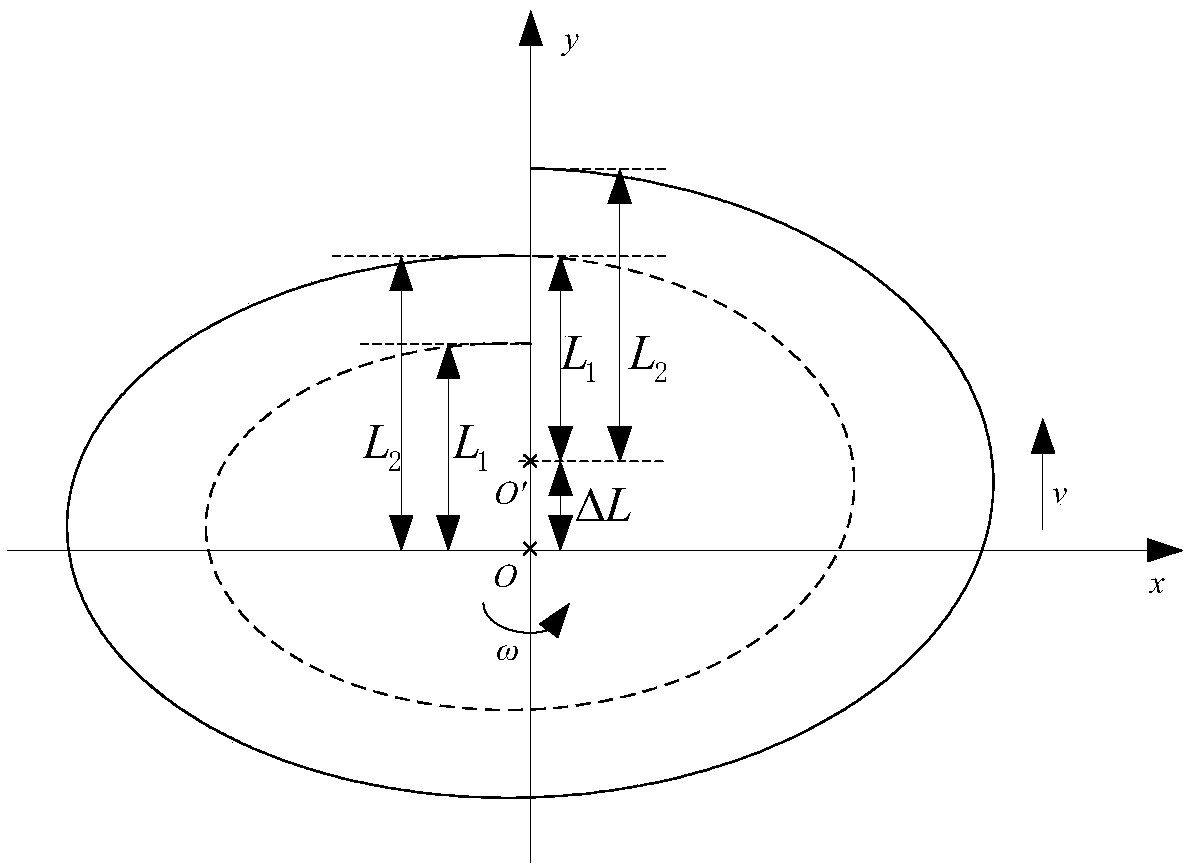
The invention discloses a mobile circumferential scanning control device and control method, mobile circumferential scanning equipment, and an unmanned vehicle. The mobile circumferential scanning control device is used in the mobile circumferential scanning equipment. The mobile circumferential scanning equipment includes a mobile platform and scanning equipment fixedly arranged on the mobile platform. The smallest scanning distance of the scanning equipment is L1, and the largest scanning distance is L2. The mobile circumferential scanning control device includes a first control module usedfor making the scanning equipment carry out circumferential scanning at a set circumferential scanning angular velocity omega relative to the mobile platform, a second control module used for making the mobile platform translate at a set translational velocity v so as to drive the scanning equipment to translate at the translational velocity v, and a main control module used for associating and restraining the translational velocity v and the circumferential scanning angular velocity omega in such a way that the translational distance of the mobile platform is Delta L when the scanning equipment completes 360-degree circumferential scanning, wherein Delta L=L2-L1. Repeated scanning can be avoided. The running speed of the platform and the overall working efficiency can be improved while the effect of circumferential scanning is ensured.
Owner:长沙冰眼电子科技有限公司
Method and transducers for dynamic testing of structures and materials
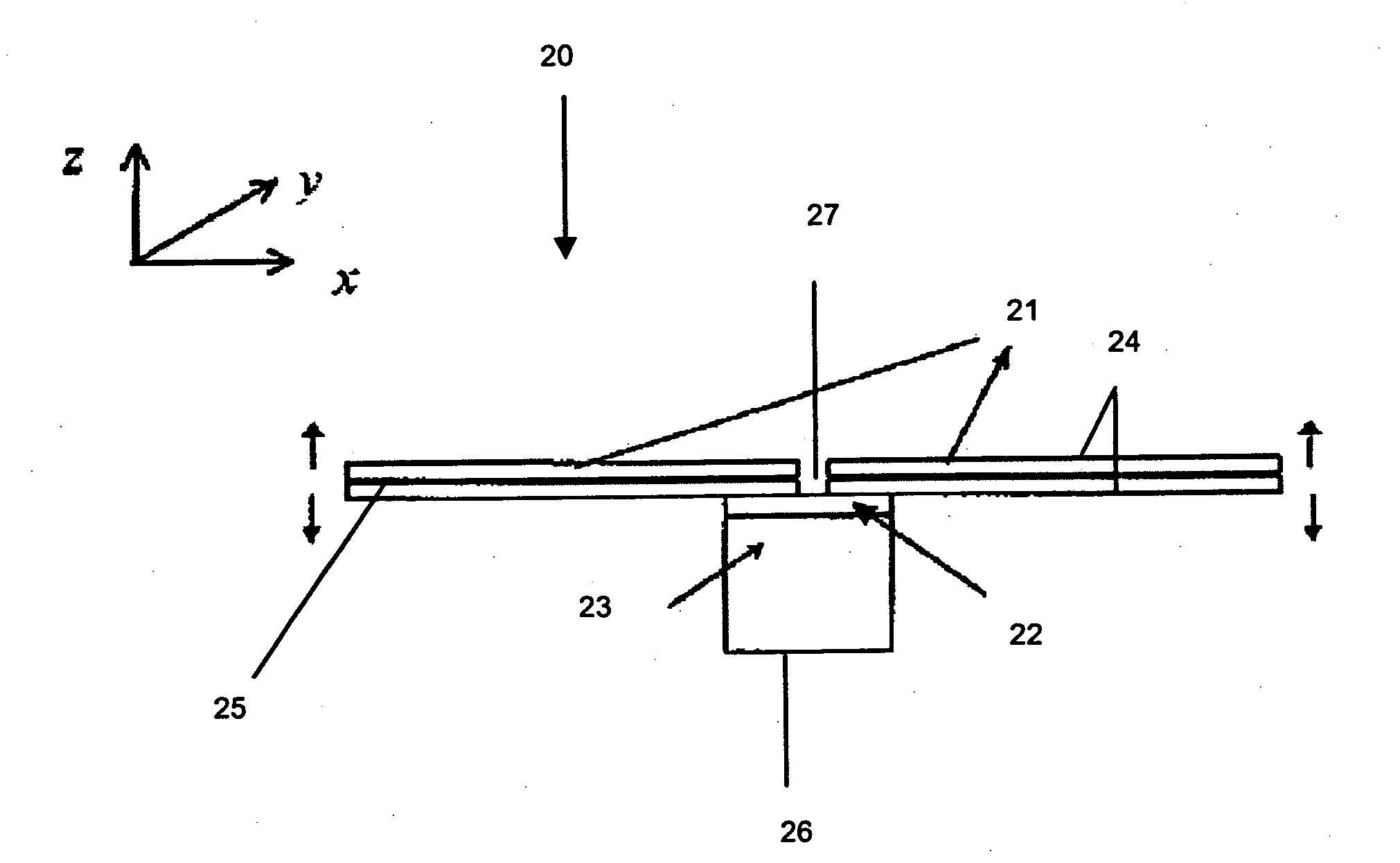
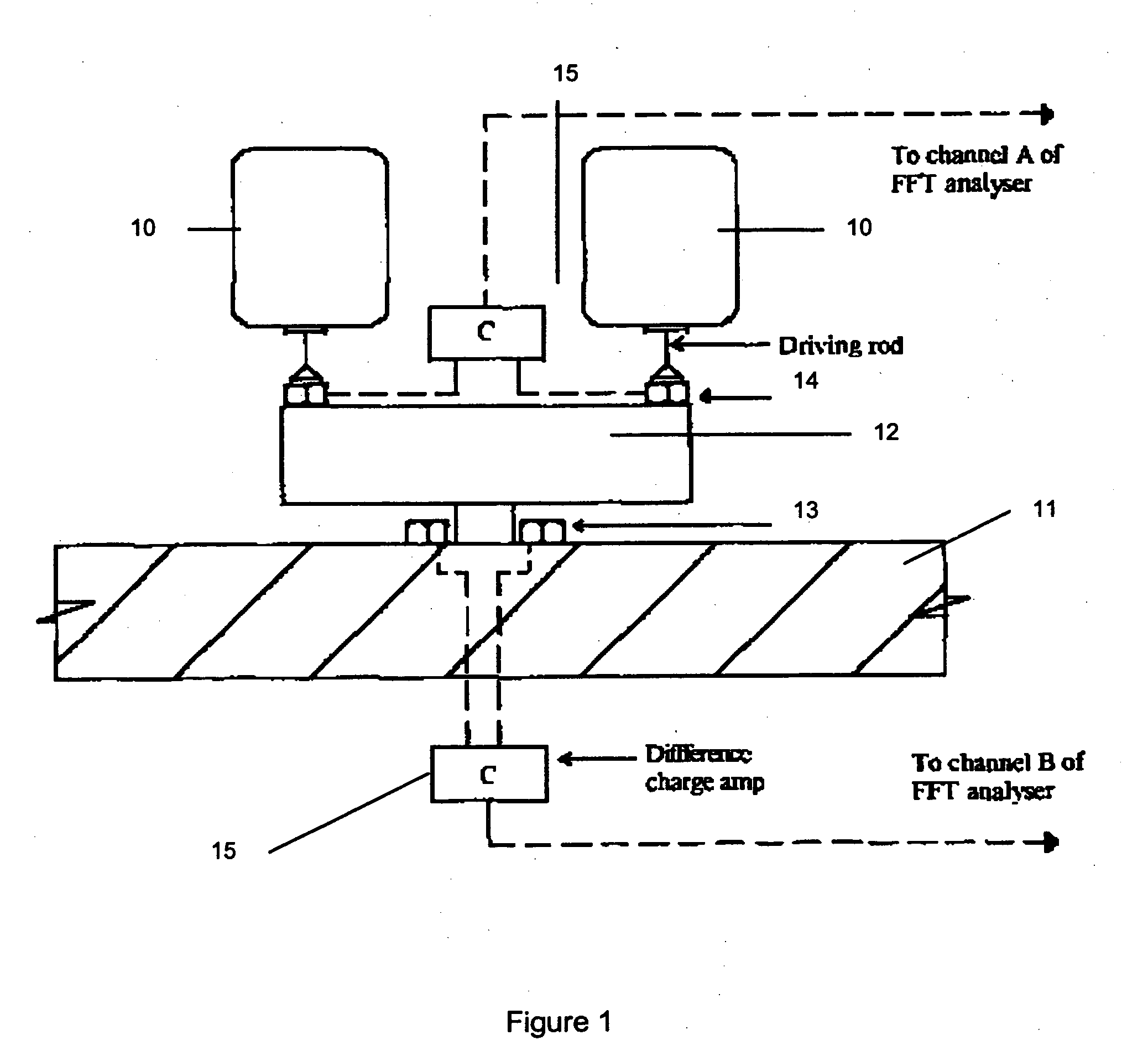
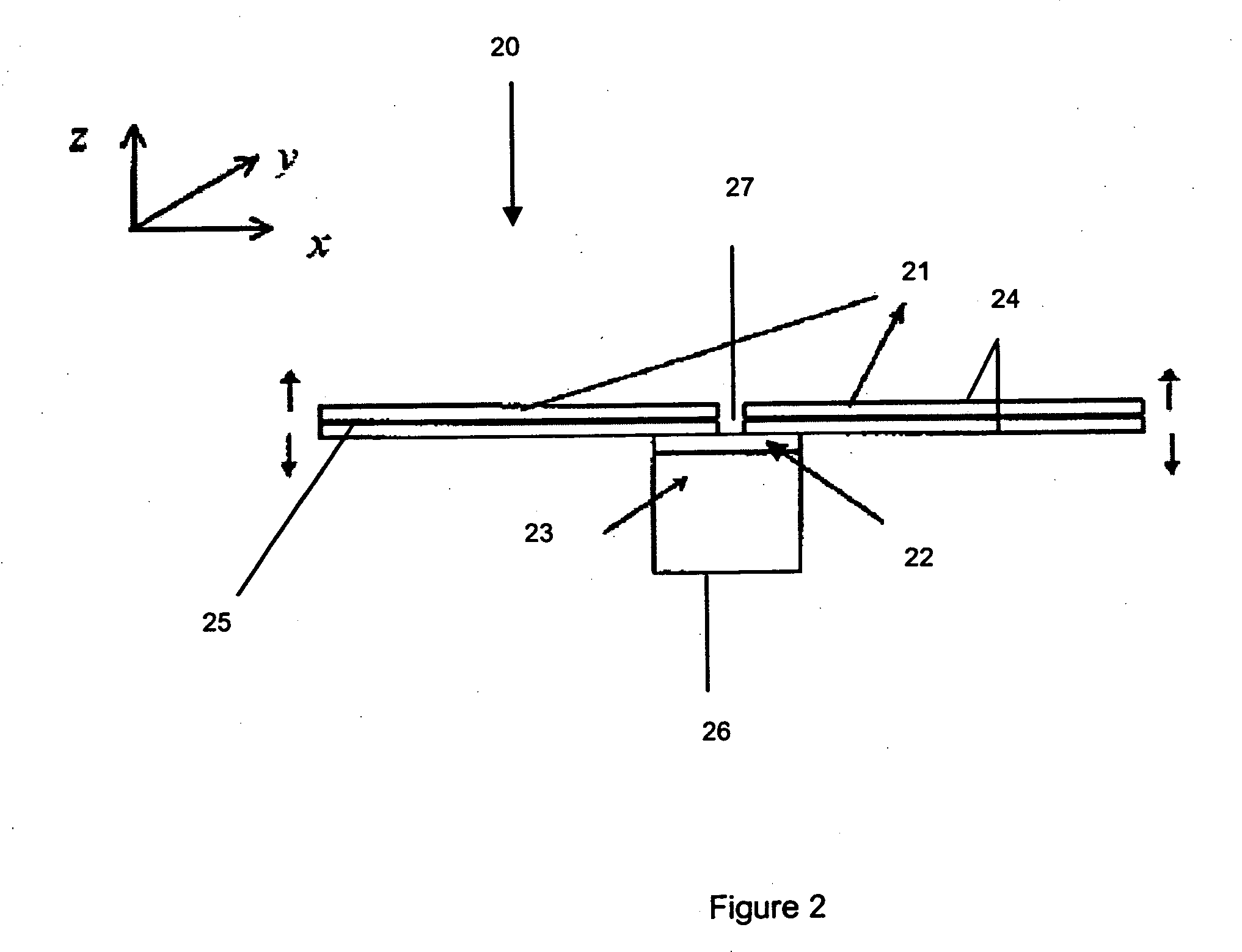
InactiveUS7332849B2Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTransducerRotation velocity
A transducer for dynamic testing of specimen is disclosed. The transducer comprises at least two equally-spaced actuators, and a supporting block for supporting the at least two equally-spaced actuators and for mounting the transducer to the specimen. Each of the at least two equally-spaced actuators is an electrically powerable for providing to the specimen: a force or a moment. The actuators may be bimorphs and the transducer may be able to operate as an actuator, a sensor, and simultaneously as an actuator and a sensor. This may be for the transducer being able to operate as a sensor, for measurement of at least one selected from the group consisting of: an excitation force exerted on the specimen, an excitation moment exerts on the specimen, a resultant translational velocity of the specimen at an excitation point, and a rotational velocity of the specimen at the excitation point. The at least two equally-spaced actuators are able to produce a force on the specimen when electricity supplied to the at least two equally-spaced actuators is in phase, and a moment on the specimen when the electricity supplied to the at least two equally-spaced actuators is out of phase.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
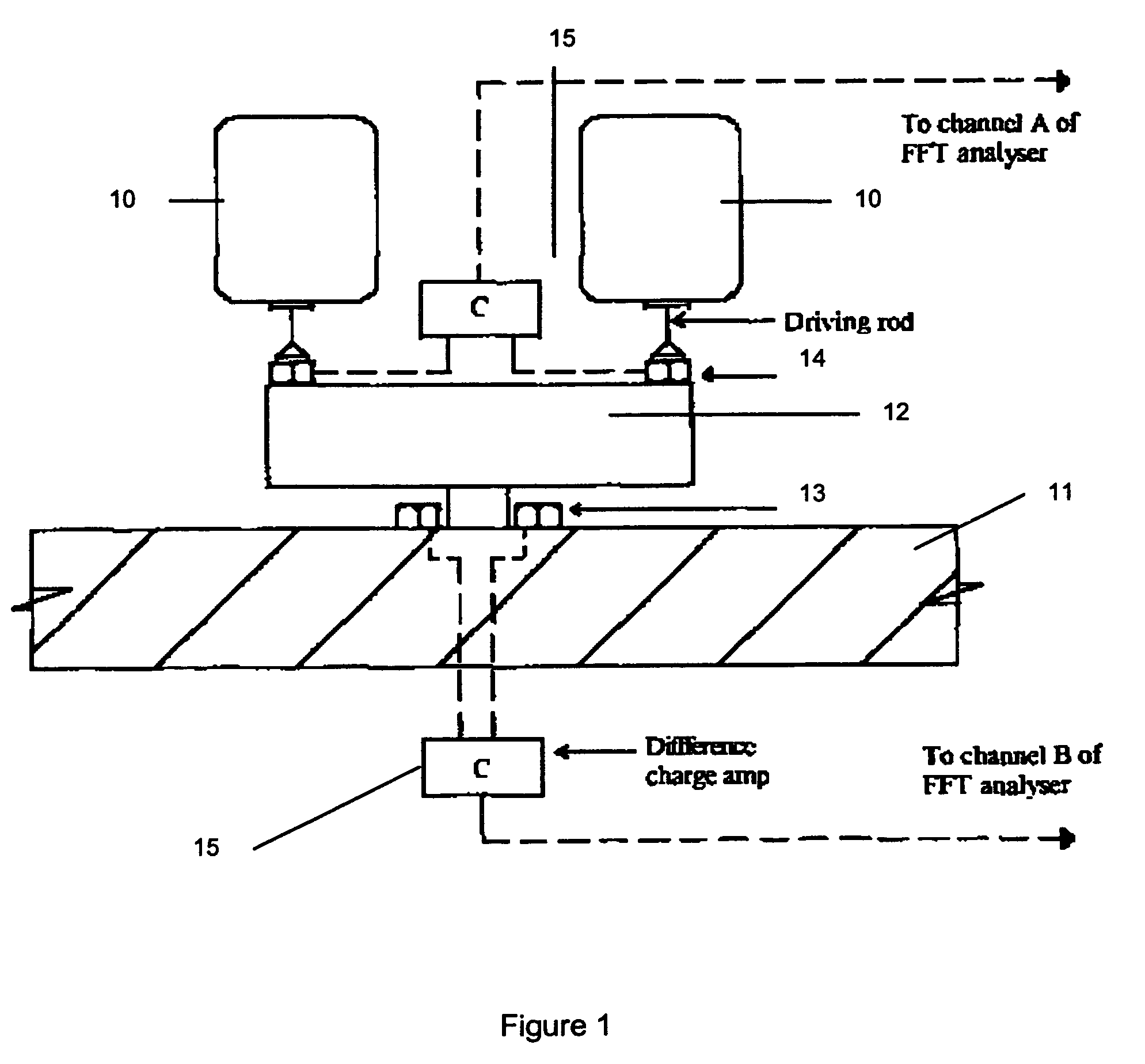
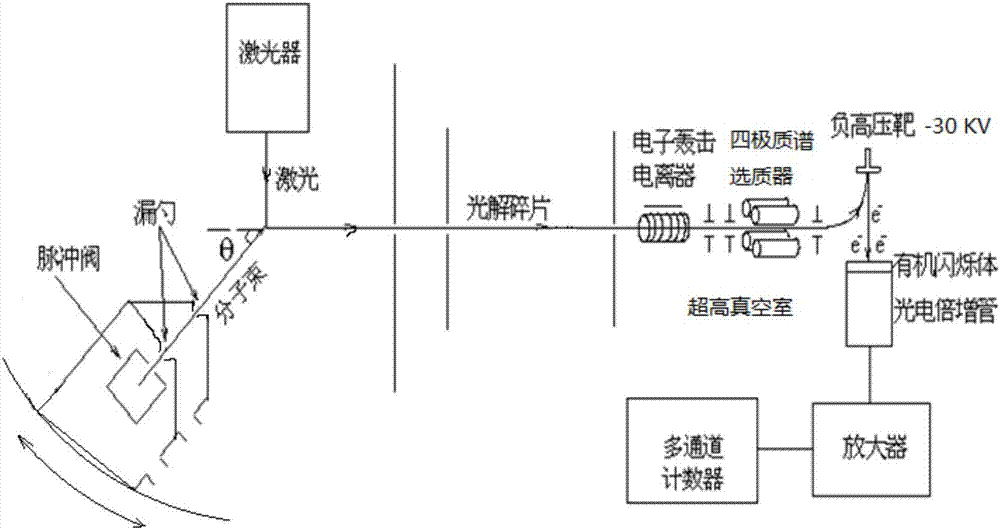
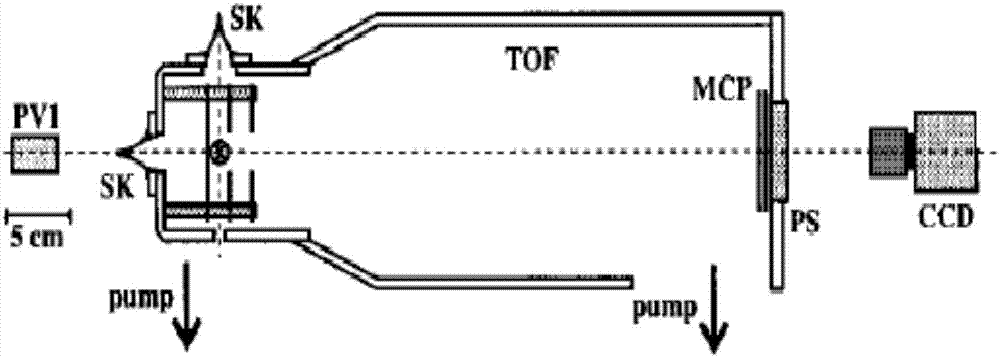
Low-voltage weak field accelerated ion imaging type miniature photodecomposition fragment translational velocity spectrometer
ActiveCN107144360AReduce distractionsImprove detection accuracyLight velocity measurementSpectrum investigationLow voltageData acquisition
The present invention relates to a low-voltage weak field accelerated ion imaging type miniature photodecomposition fragment translational velocity spectrometer. The low-voltage weak field accelerated ion imaging type miniature photodecomposition fragment translational velocity spectrometer comprises a source chamber, a reaction chamber, a vacuum pump, a pulse valve, a collimator, a photodecomposition laser, an ionization laser, a low-voltage weak field ion acceleration and focusing system, a microchannel board, a fluorescent screen, a data acquisition system, a sequential control system and a computer. The miniature photodecomposition fragment translational velocity spectrometer of the application innovatively uses a weak electric field (10-30 V / cm) to accelerate the ions and focuses the ions simultaneously, and an ion flight total distance is only about 12 cm. The miniature photodecomposition fragment translational velocity spectrometer of the present invention adopts the low-voltage weak field, so that a short shaft of an ion swing ball of a stationary state can reach the larger time difference, thereby being very conducive to a subsequent time slice operation. The miniature photodecomposition fragment translational velocity spectrometer of the application has the better performances, such as the resolution, etc., than the currently universal majority of ion imaging type photodecomposition fragment translational energy spectrometers of strong electric field (100-350 V / cm) acceleration and long-distance (38-105 cm) flight, and can provide the more accurate, simpler, more convenient and efficient experiment means for the photodecomposition dynamics research.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Mechanical oscillator for wafer scan with spot beam
InactiveUS20050247891A1Overcome limitationsElectric discharge tubesThermometers using material expansion/contactionEngineeringActuator
The present invention is directed to a scanning apparatus and method for processing a substrate, wherein the scanning apparatus comprises a first link and a second link rigidly coupled to one another at a first joint, wherein the first link and second link are rotatably coupled to a base portion by the first joint, therein defining a first axis. An end effector, whereon the substrate resides, is coupled to the first link. The second link is coupled to a first actuator via at least second joint. The first actuator is operable to translate the second joint with respect to the base portion, therein rotating the first and second links about the first axis and translating the substrate along a first scan path in an oscillatory manner. A controller is further operable to maintain a generally constant translational velocity of the end effector within a predetermined scanning range.
Owner:AXCELIS TECHNOLOGIES
Wafer scanning system with reciprocating rotary motion utilizing springs and counterweights
The present invention is directed to a scanning apparatus and method for processing a workpiece, wherein the scanning apparatus comprises a wafer arm and moving arm fixedly coupled to one another, wherein the wafer arm and moving arm are operable to rotate about a first axis. An end effector, whereon the workpiece resides, is coupled to the wafer arm. A rotational shaft couples the wafer arm and moving arm to a first actuator, wherein the first actuator provides a rotational force to the shaft. A momentum balance mechanism is coupled to the shaft and is operable to generally reverse the rotational direction of the shaft. The momentum balance mechanism comprises one or more fixed spring elements operable to provide a force to a moving spring element coupled to the moving arm. A controller is further operable to maintain a generally constant translational velocity of the end effector within a predetermined scanning range.
Owner:AXCELIS TECHNOLOGIES
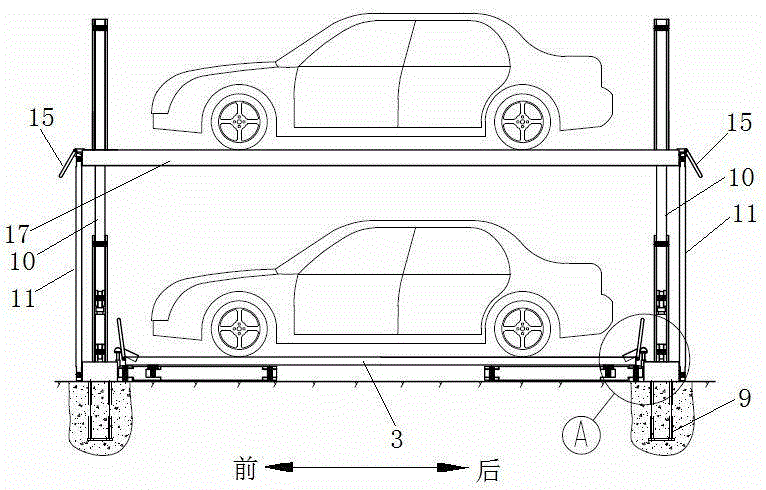
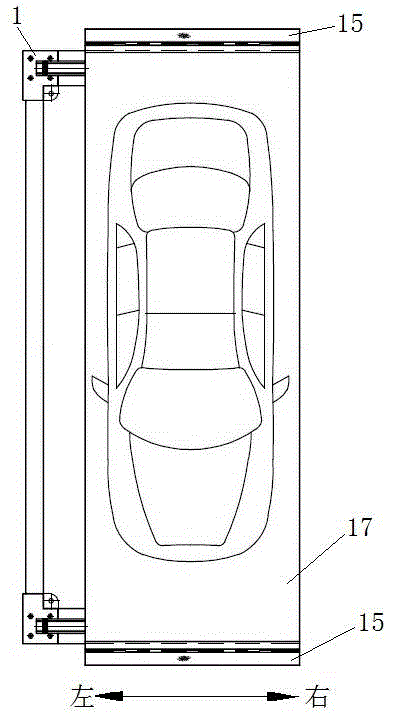
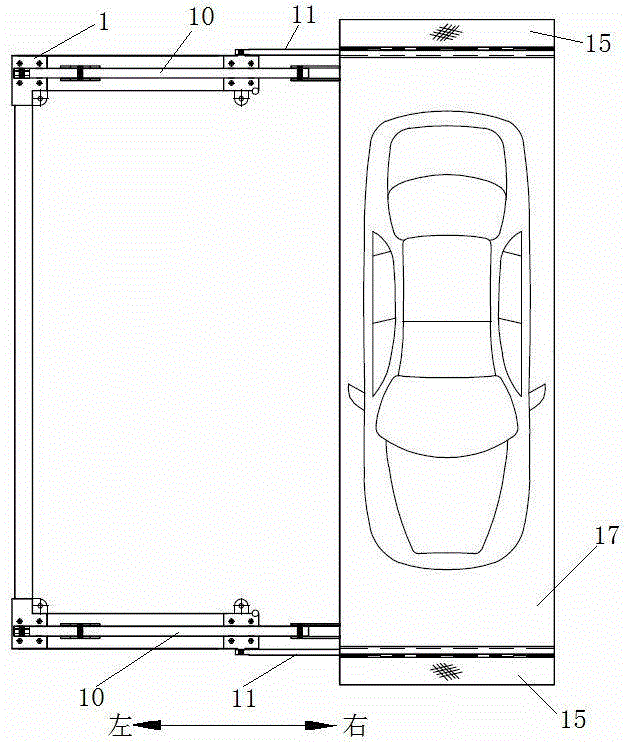
Double-layer solid parking equipment
The invention discloses double-layer solid parking equipment which comprises an upper parking mechanism and a lower parking mechanism, wherein the upper parking mechanism is capable of rotating around the lower parking mechanism; the upper parking mechanism comprises an upper vehicle bearing frame, a driving arm, a driven arm and a rotating drive; the upper end of the driven arm is hinged to the upper vehicle bearing frame and the lower end of the driven arm is hinged to a rack; one end of the rotating drive is hinged to the rack; a hinged support is arranged on the left side of the rack; the left side of the front and rear ends of the upper vehicle bearing frame is connected with a driving arm connection frame; the highest point of the driving arm connection frame is hinged to the upper end of the driving arm; the lower end of the driving arm is hinged to the free end of the rotating drive; the lower-middle part of the driving arm is connected with the hinged support and is capable of rotating around a hinged fulcrum A; the distance between the hinged fulcrum A and the hinge joint of the driving arm connection frame is equal to the distance between the hinge joints at two ends of the driven arm. According to the equipment, the rotating fulcrums of the driving arm and the driven arm are designed on different planes, so that the interference problem caused by out-put and in-put of warehouse of the upper vehicles is solved. The lower parking mechanism adopts a rotating pair and is provided with a stroke increasing mechanism, so that the translational velocity is greatly improved.
Owner:湖南有位智能科技有限公司
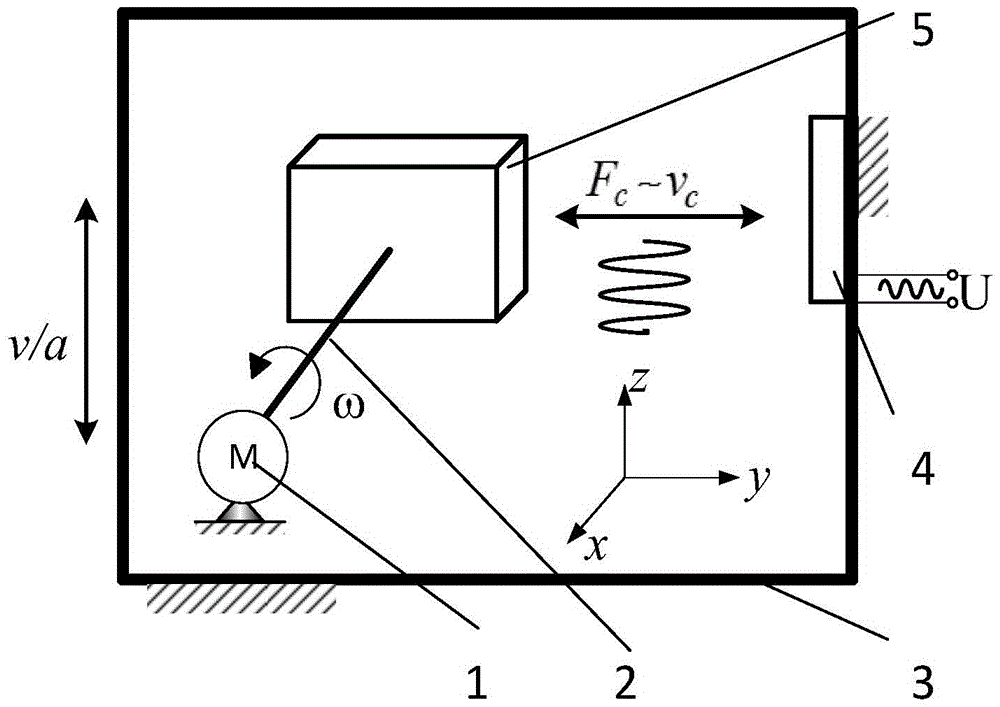
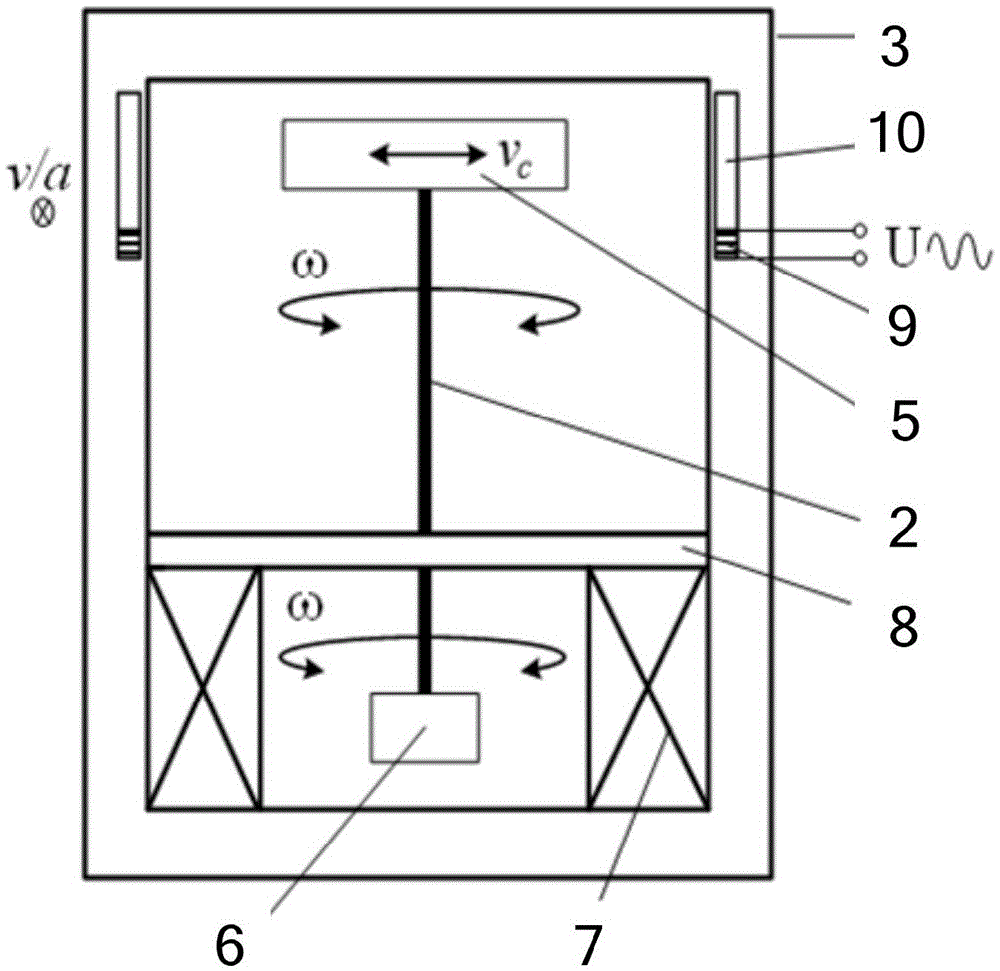
Geostrophic force effect based translational velocity or acceleration sensing device and structure
InactiveCN105526927AApplicable to different signal feature detection requirementsImprove anti-interference abilityTurn-sensitive devicesAcceleration measurement using gyroscopesEngineeringCoriolis effect (perception)
The invention provides a geostrophic force effect based translational velocity or acceleration sensing device and structure, wherein a drive structure and an electromagnetic coil interact to drive a sensitive magnetic structure to rotate, when the sensing device has translational velocity meeting a condition of generating a geostrophic force effect, the sensitive magnetic structure generates deflection; a sensing mechanism converts the deflection displacement into an output electric signal. The invention innovatively applies a function sensitive material and a geostrophic effect to the translational velocity or acceleration detection, realizes a novel translation detection mechanism and method, and can be used for realizing a reciprocating translation detection means without detection stroke limitation.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method and transducers for dynamic testing of structures and materials
InactiveUS20070267944A1Avoid supportPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesVibration testingTransducerRotation velocity
A transducer for dynamic testing of specimen is disclosed. The transducer comprises at least two equally-spaced actuators, and a supporting block for supporting the at least two equally-spaced actuators and for mounting the transducer to the specimen. Each of the at least two equally-spaced actuators is an electrically powerable for providing to the specimen: a force or a moment. The actuators may be bimorphs and the transducer may be able to operate as an actuator, a sensor, and simultaneously as an actuator and a sensor. This may be for the transducer being able to operate as a sensor, for measurement of at least one selected from the group consisting of: an excitation force exerted on the specimen, an excitation moment exerts on the specimen, a resultant translational velocity of the specimen at an excitation point, and a rotational velocity of the specimen at the excitation point. The at least two equally-spaced actuators are able to produce a force on the specimen when electricity supplied to the at least two equally-spaced actuators is in phase, and a moment on the specimen when the electricity supplied to the at least two equally-spaced actuators is out of phase.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
Movable trolley for light ship welding
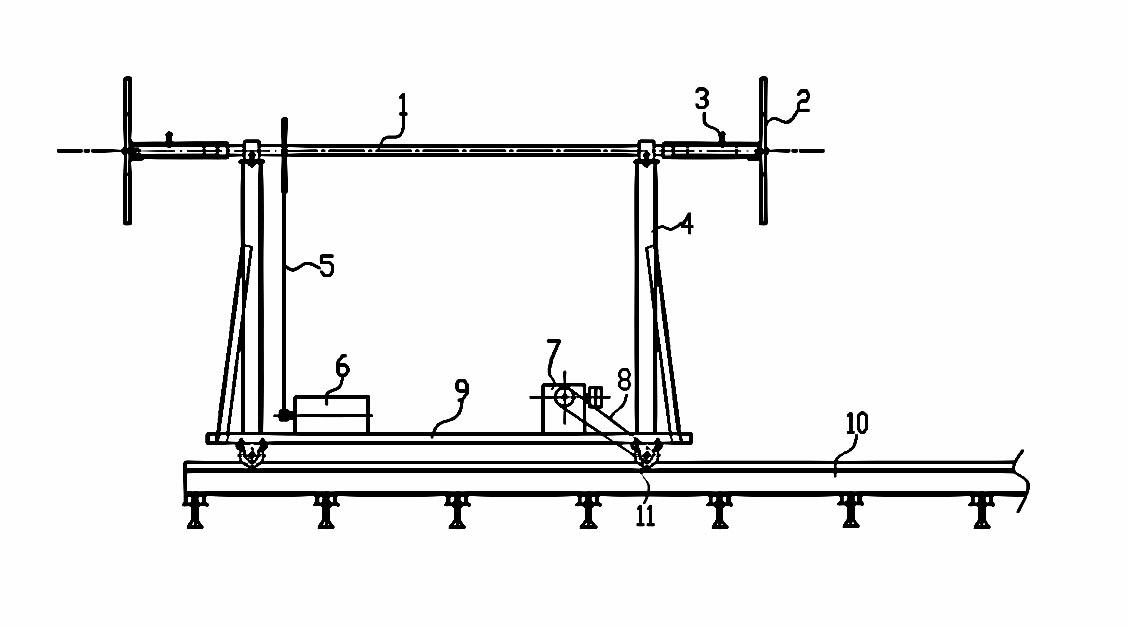
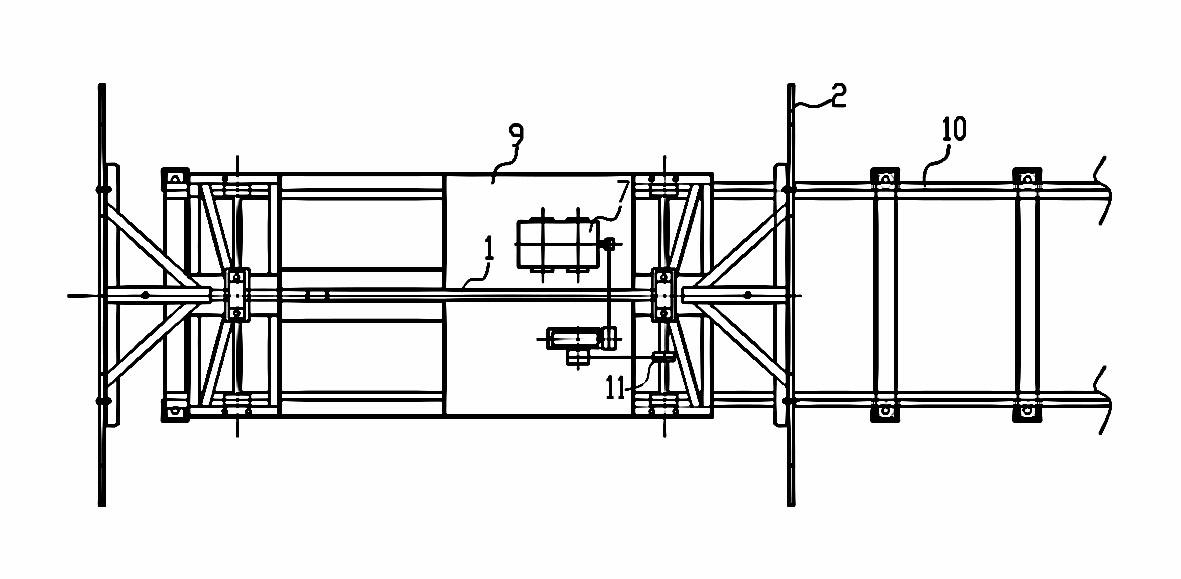
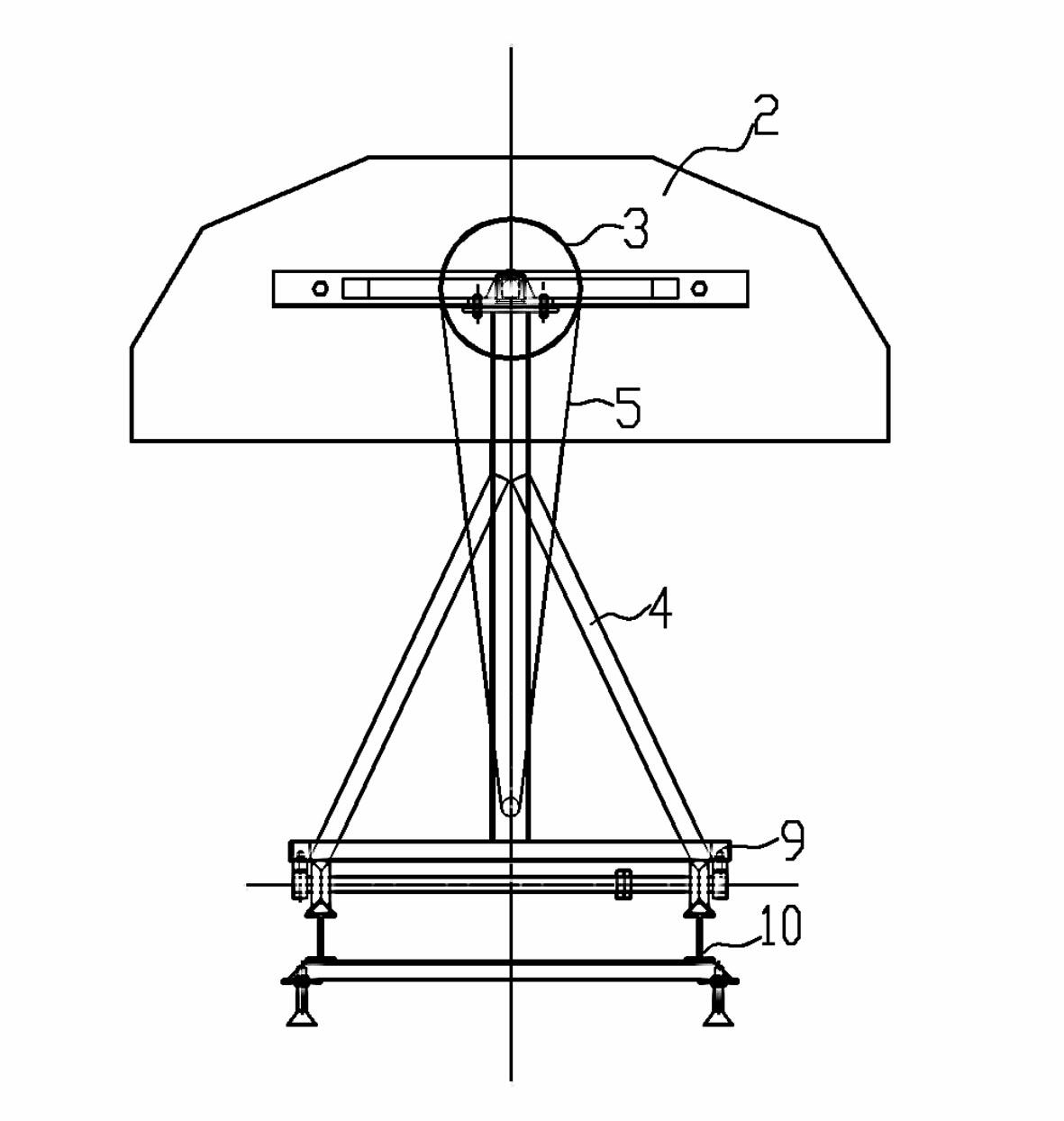
ActiveCN102229032AControl welding deformationImprove ergonomicsWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesMarine engineeringTranslational velocity
The invention relates to a movable trolley for light ship welding, which is characterized by comprising a section of walking rail (10) laid on the ground, wherein a movable trolley is arranged on the rail (10); a driving device (7) is arranged on a trolley chassis (9) and is connected with one of wheel axles (11) through a transmission device; a pair of supporting frames (7) which is longitudinally arranged is arranged on the trolley chassis (9); a transversely arranged supporting shaft (1) is arranged on the supporting frames (7); a longitudinally arranged supporting plate (2) is arranged at two ends of the supporting shaft (1) respectively; and an upper outline of the supporting plate (2) has an arc-shaped structure connected by a plurality of lines, and can adapt to a ship body. The invention has the advantages that: a positive building method and a vertical welding process for the traditional ship body are changed, and due to the adoption of a reverse building method and a flat welding process, the reverse building method adapts to the flat welding process by adjusting the translational velocity (namely the moving speed of the ship body) of the movable trolley and welding process parameters (mainly a wire feed speed).
Owner:BENGBU SHENZHOU MACHINERY
Particle size grading method of micro-nano-scale emulsion droplets and solid particles
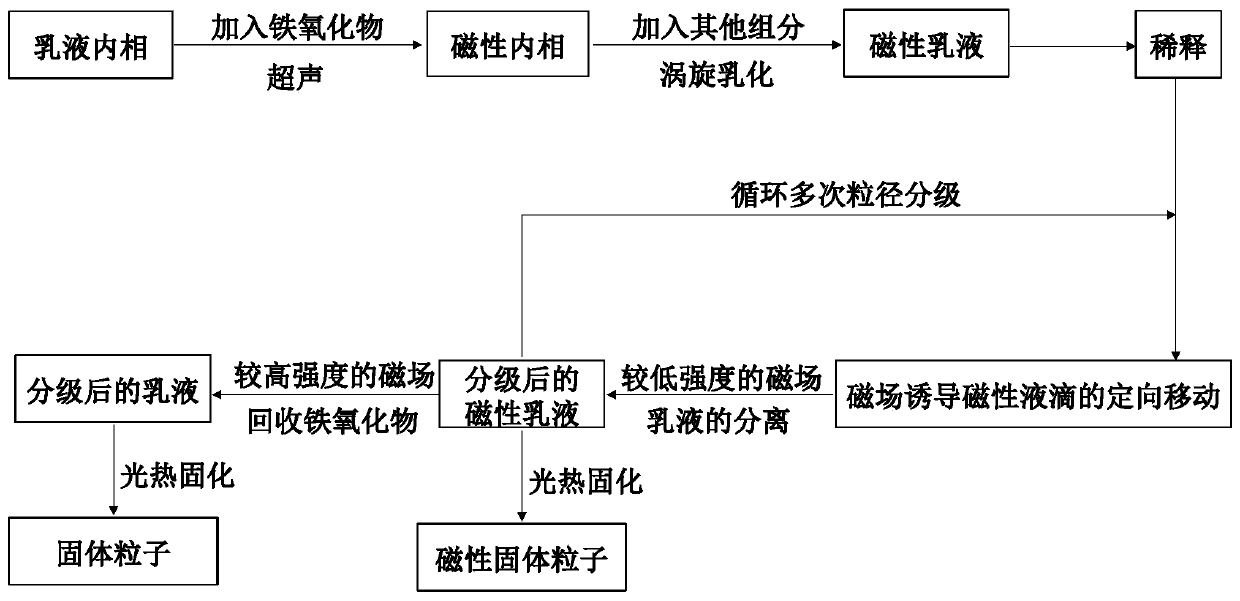
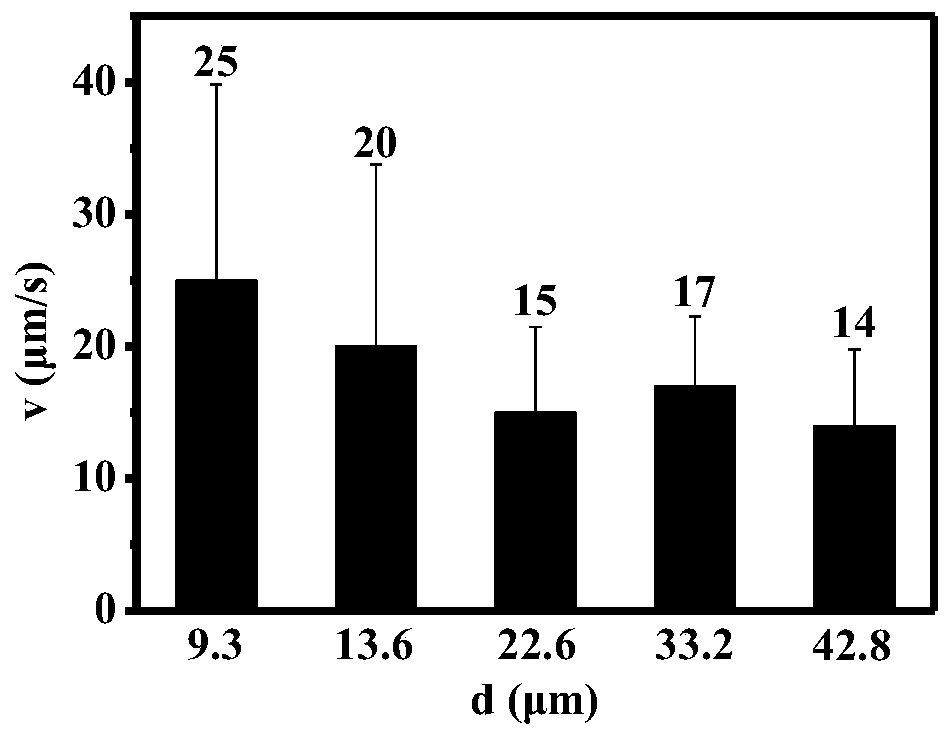
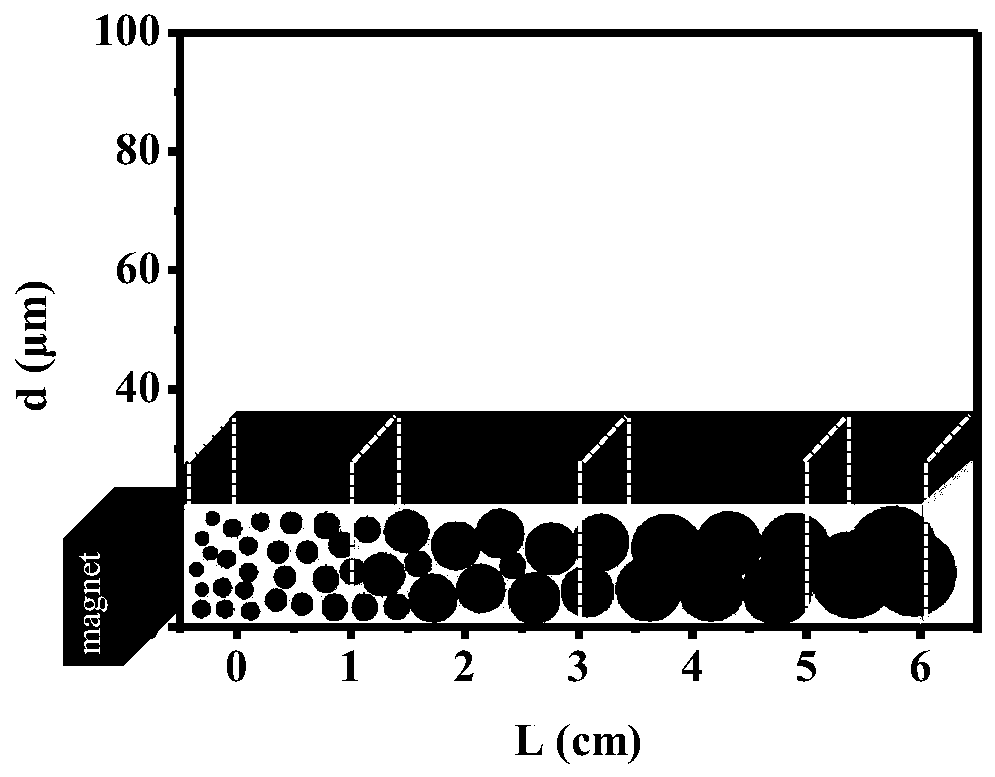
PendingCN110346251AAvoid interferenceAchieve recyclingParticle size analysisBrown iron oxideTranslational velocity
The invention provides a particle size grading method of micro-nano-scale emulsion droplets and solid particles. According to the method, the quantitative relation between the particle size of the droplets and the translational velocity is utilized to induce variable-velocity translation of the emulsion droplets containing magnetic particles through an external magnetic field, and therefore the emulsion droplets with the particle size within a micron-submicron-nano range are graded. Besides, by controlling magnetic field intensity, polymerization and sedimentation of the magnetic particles canbe induced, so that the magnetic particles in the droplets obtained after grading are removed, interference of the additional magnetic particles on emulsion properties and functions is avoided, and meanwhile cyclic utilization of iron oxide is realized. For an emulsion containing polymerizable monomers composed of internal-phase droplets, the solid particles with a uniform particle size can be obtained through ultraviolet light initiated polymerization or thermally initiated polymerization. In addition, multiple times of particle size grading treatment can be adopted to meet the application demand for high particle size uniformity. The method can provide technical support for application of the emulsion to food, medicine, biochemical separation, nanomaterials and other fields.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com