Empirical mode decomposition based moving vehicle target classification method
A technology of empirical mode decomposition and target classification, which is applied in the field of target classification and classification of moving vehicle targets, and can solve problems such as difference in entropy value and unsatisfactory classification results.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
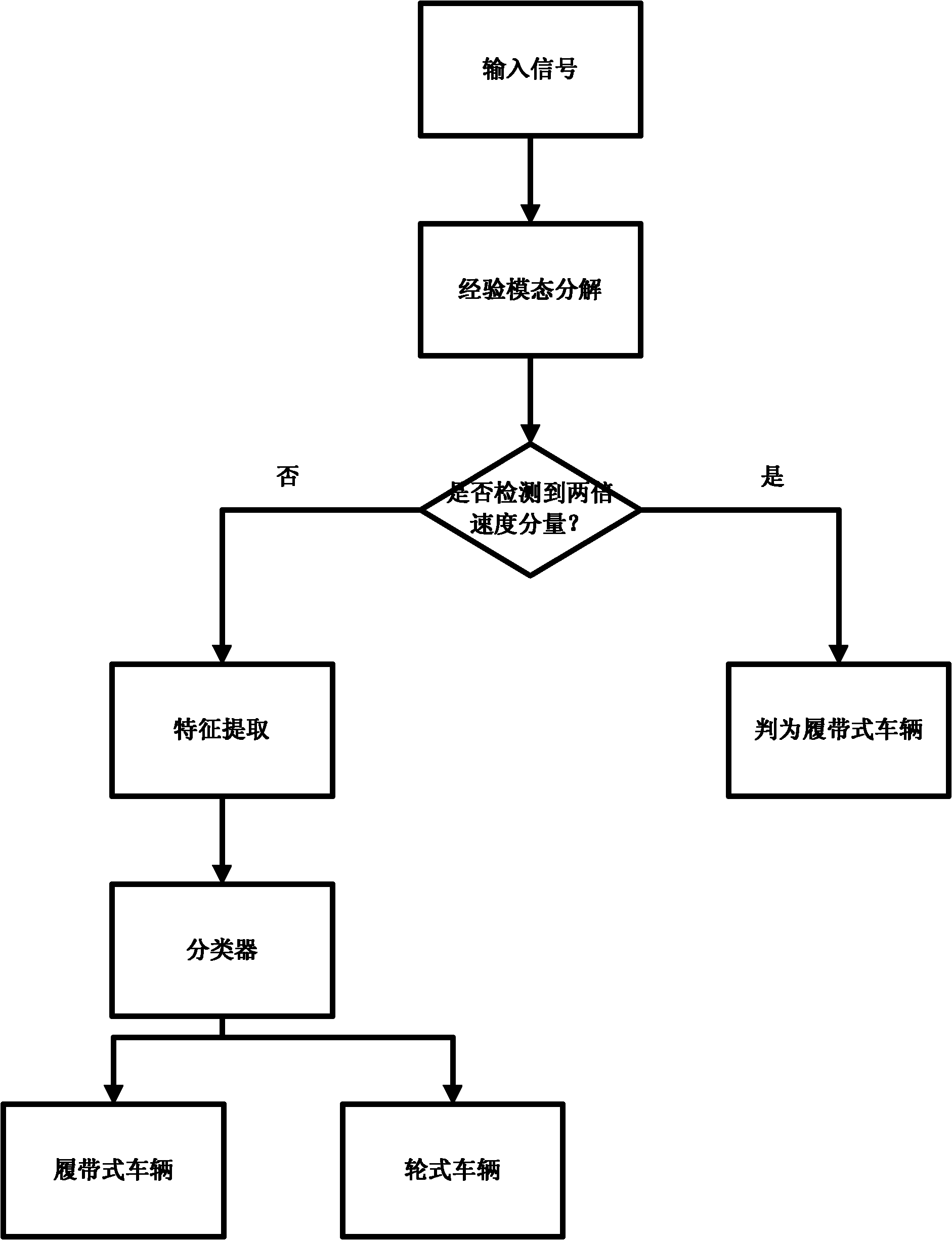
[0024] refer to figure 1 , the specific implementation steps of this embodiment are as follows:
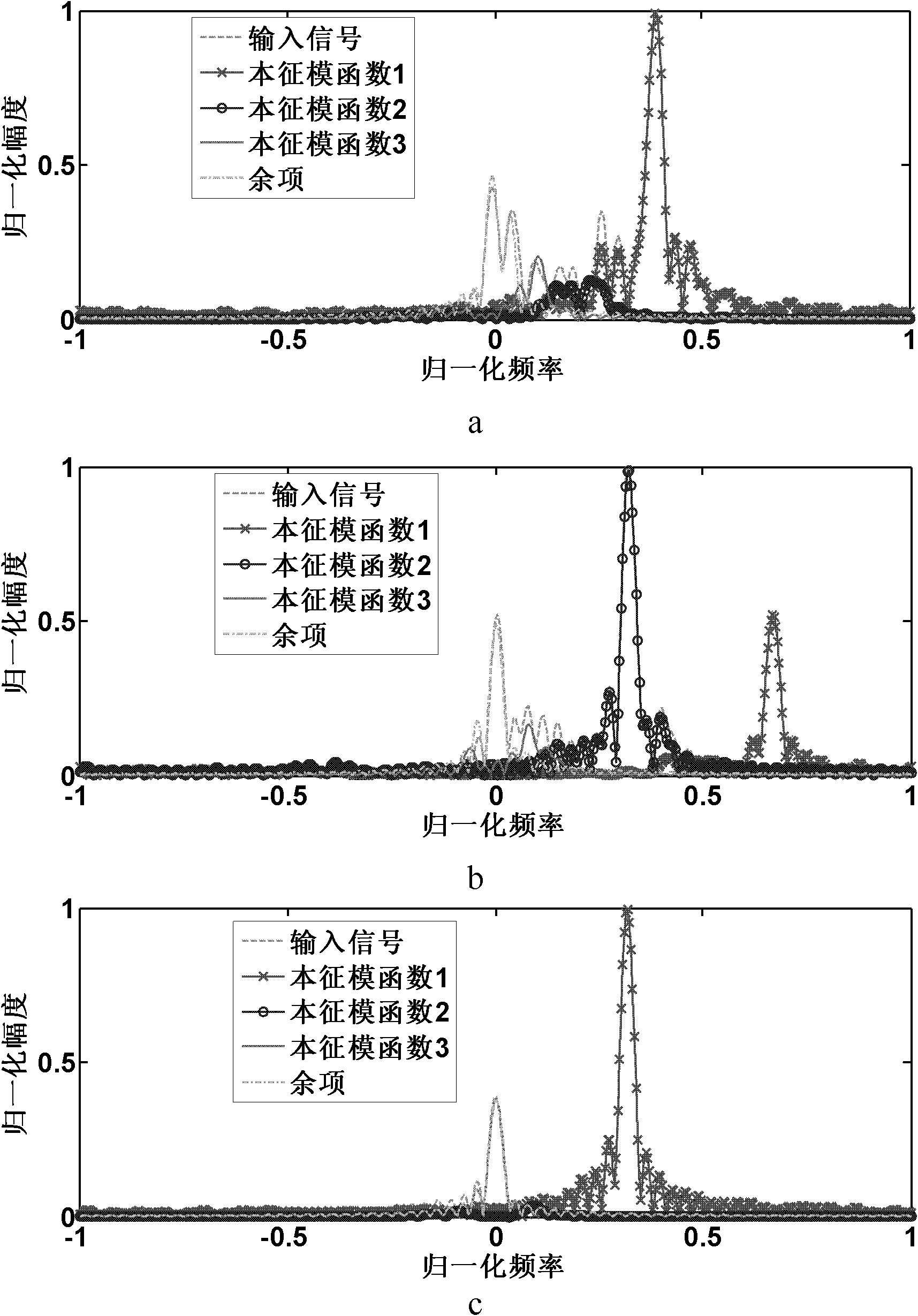
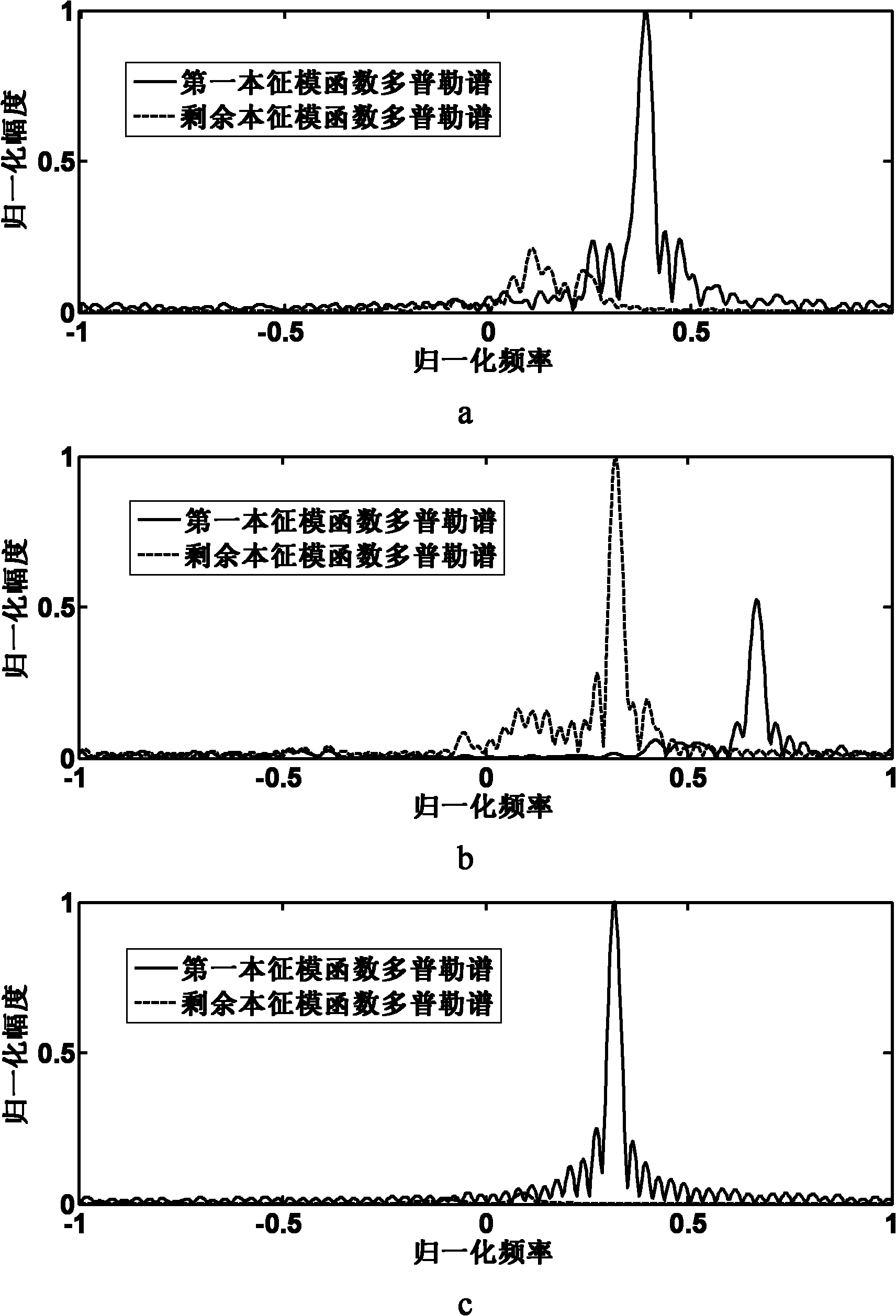
[0025] Step 1, perform empirical mode decomposition on the input Doppler echo signal.
[0026] The Doppler echo signal received by the radar is: s={s 1 ,s 2 ,...,s N}, where s i is the value of the i-th point of the Doppler echo signal s, i=1, 2,..., N, N is the number of accumulated pulses, and the Doppler echo signal s is subjected to empirical mode decomposition according to the following steps :
[0027] 1a) Define a temporary signal x=s;
[0028] 1b) Search the temporary signal x point by point, and record all extreme points of the temporary signal x;
[0029] 1c) Interpolate the minimum and maximum points of the temporary signal x to obtain the lower envelope e of the temporary signal x min and upper envelope e max ;
[0030] 1d) Compute the envelope mean of the temporary signal x:
[0031] 1e) Subtract the envelope mean from the temporary signal x to get a new ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com