Inertial system spacecraft attitude control/angular momentum management method
A technology for angular momentum management and attitude control, which is applied in the field of attitude control of aerospace satellites and can solve problems such as high dimension of state space equations and workload of controller design.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
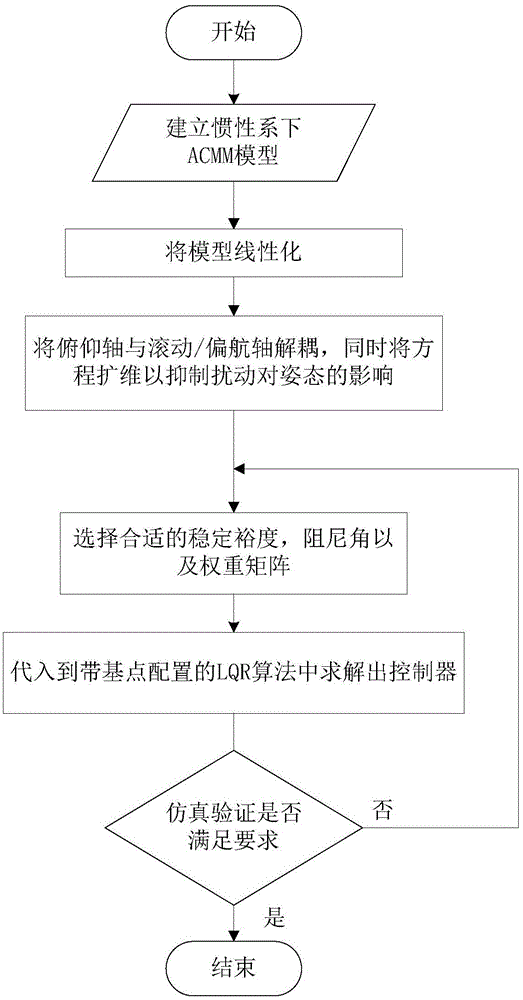
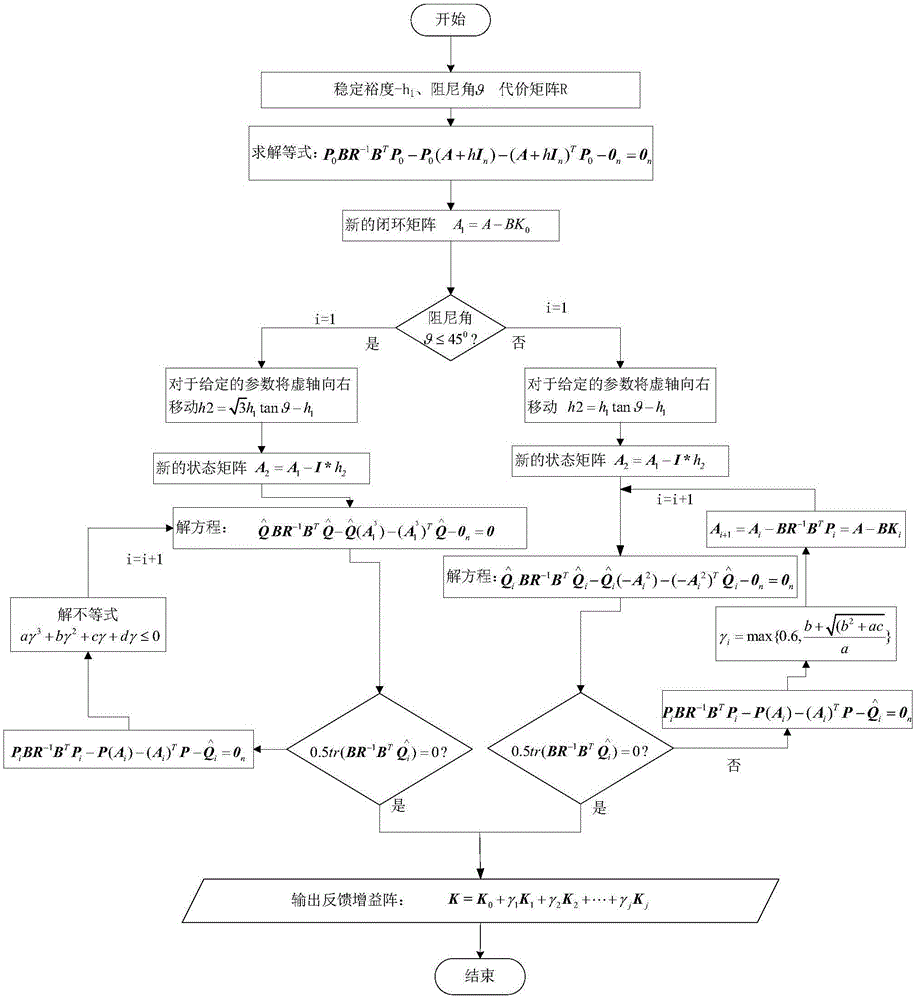
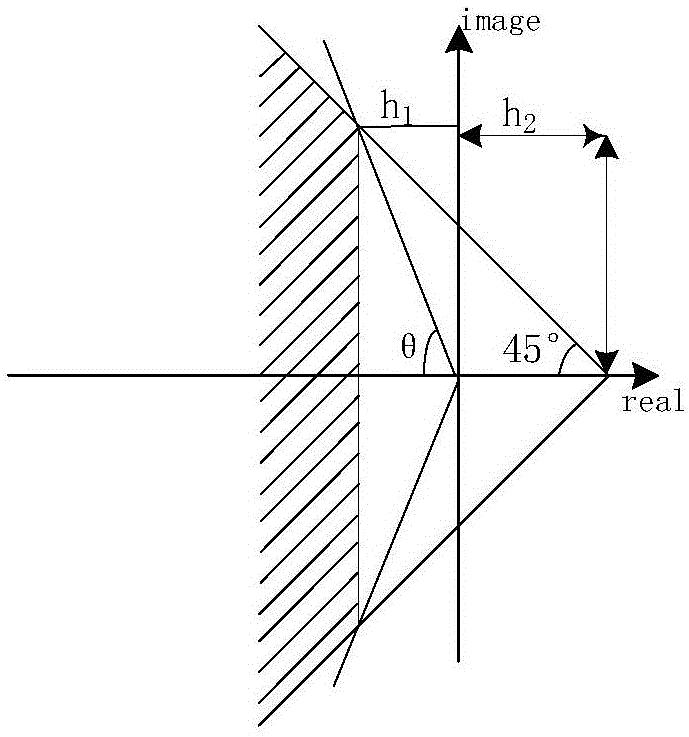
[0132] see figure 1 —— Figure 7 In this paper, the simulation verification of the space station with "T" configuration is carried out. In the simulation, the dynamic model adopts the central rigid body model with flexible attachment, and the actuator only adopts CMG. Since the balance attitude does not coincide with the body and the inertial system, without loss of generality, the initial attitude angle and attitude angular velocity are taken as zero, and the system interference moment is shown in Table 1. The moment of inertia in this system is:
[0133] I b = 5.1 - 0.2 0.1 - 0.2 8.3 - 0.08 0.1 - 0.08 4.8 X 10 6 k g · m 2
[0134] Table 1 Other disturbance moments
[0135]
[0136] The orbit of the space station is a near-circular orbit of 400km, so the orbital angular velocity is approximately taken as ω 0 =0.0011rad / s. From the state equations (15) and (17), it can be seen that the cons...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com