Near-real time earthquake source position positioning method
A positioning method and near-real-time technology, applied in seismology, seismic signal processing, measuring devices, etc., can solve problems such as low information utilization, poor timeliness, and single method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
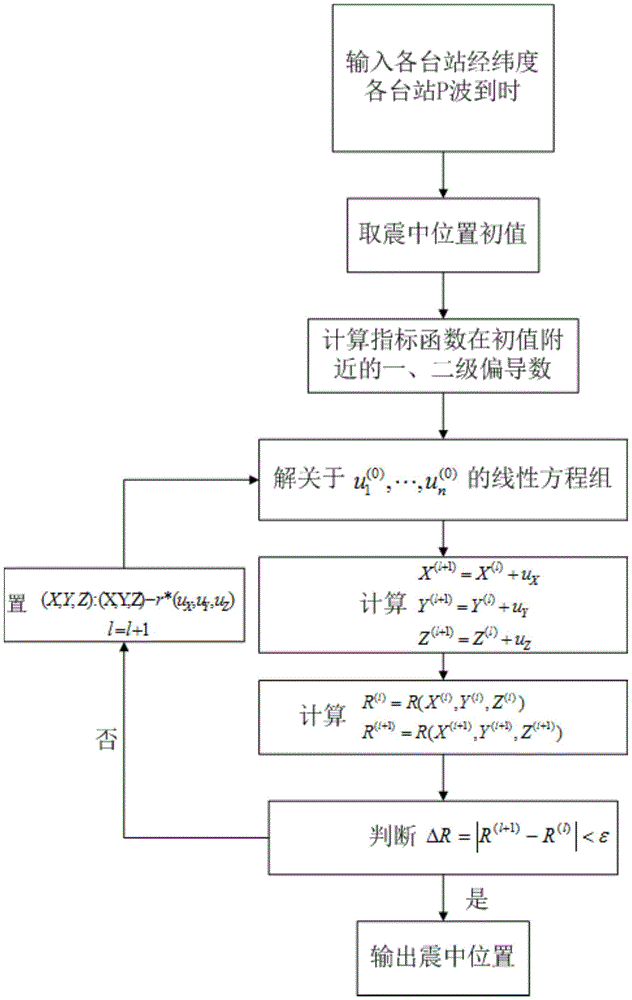
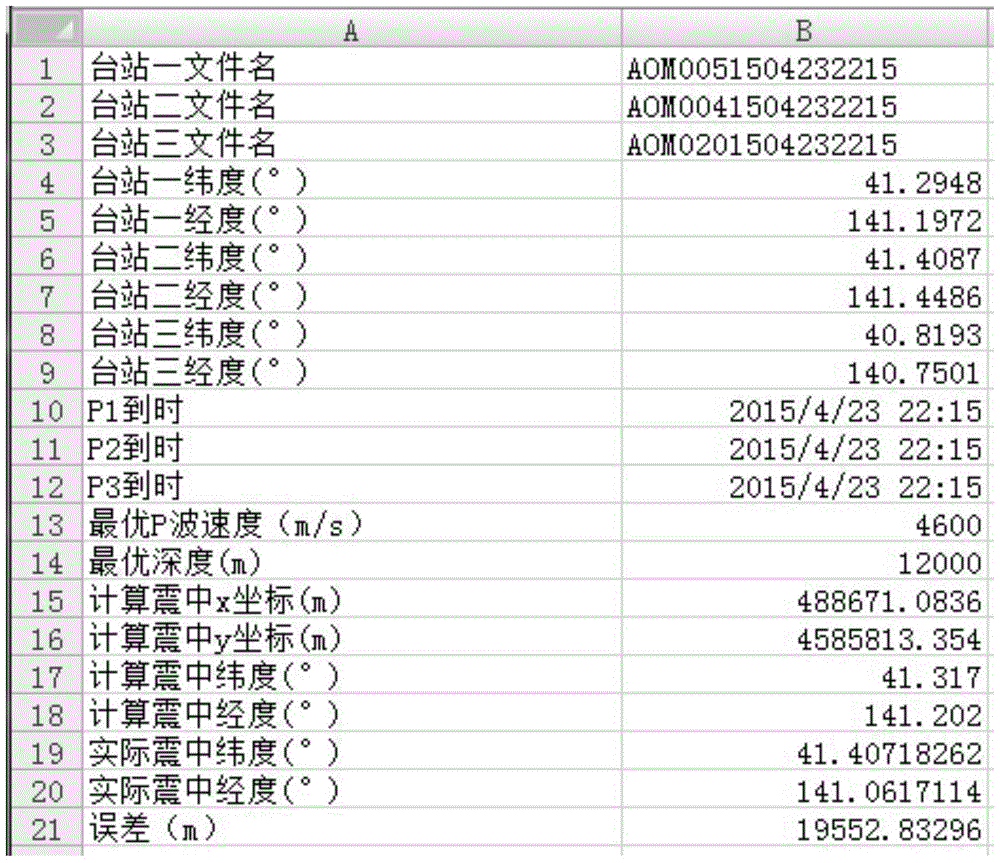
[0046] Example: Taking a 3.8-magnitude earthquake in Japan on April 23, 2015 as an example, according to the P wave information of three stations, the location of the earthquake source is located and compared with the actual information. Such as figure 2 As shown, the specific operation steps are as follows:
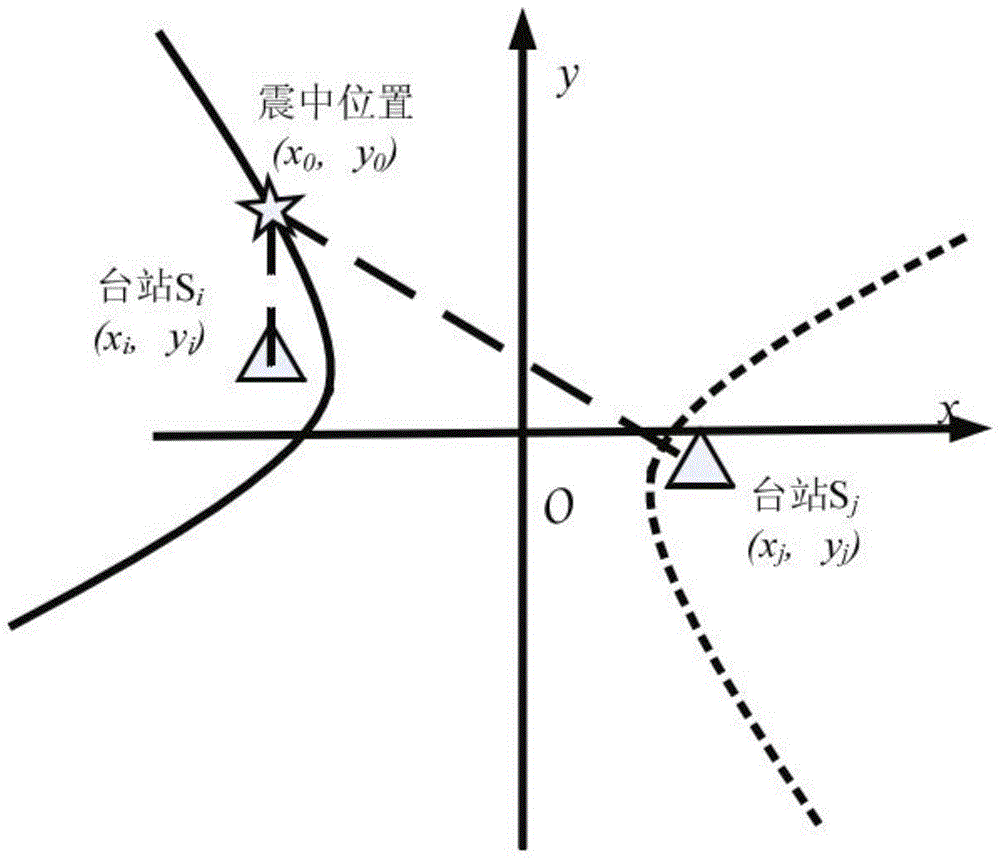
[0047] Step 1: After the earthquake, open the seismic acceleration records of the first three seismic stations that first obtained the P wave arrival time, and read the station numbers AOM0051504232215, AOM0041504232215, AOM0201504232215, and geographical coordinates (Lat1, Long1), (Lat2, Long2), (Lat3, Long3)), identify the arrival time of P wave (Time1, Time2), calculate the arrival time difference in pairs, and convert the latitude and longitude coordinate data of the seismic station into plane Cartesian coordinates (x11, x12), (x21, x22), (x31, x32);
[0048] Step 2: For any two stations, assuming that the S1 coordinates of one station are (x11, y12), the arrival ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com