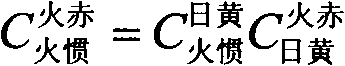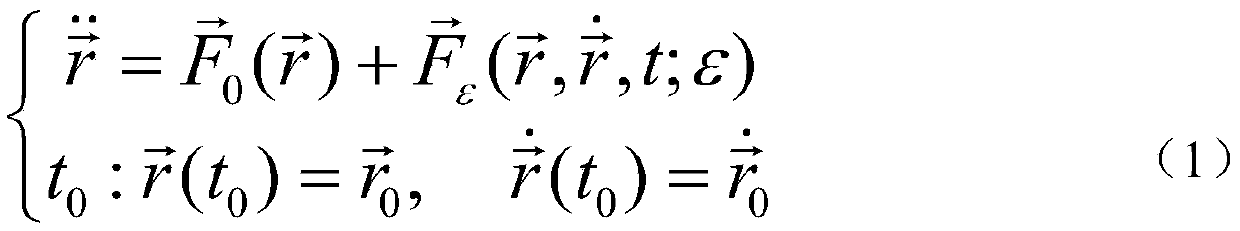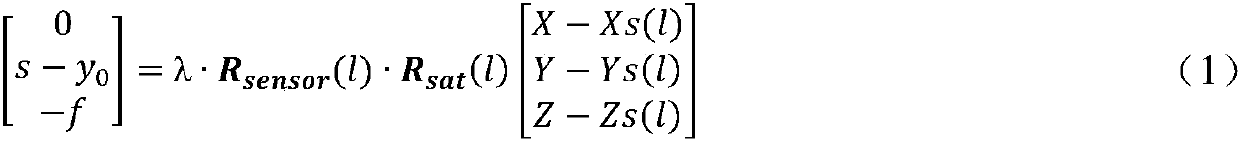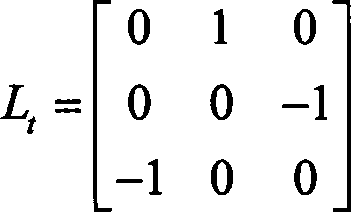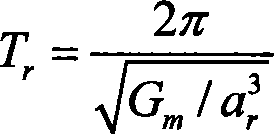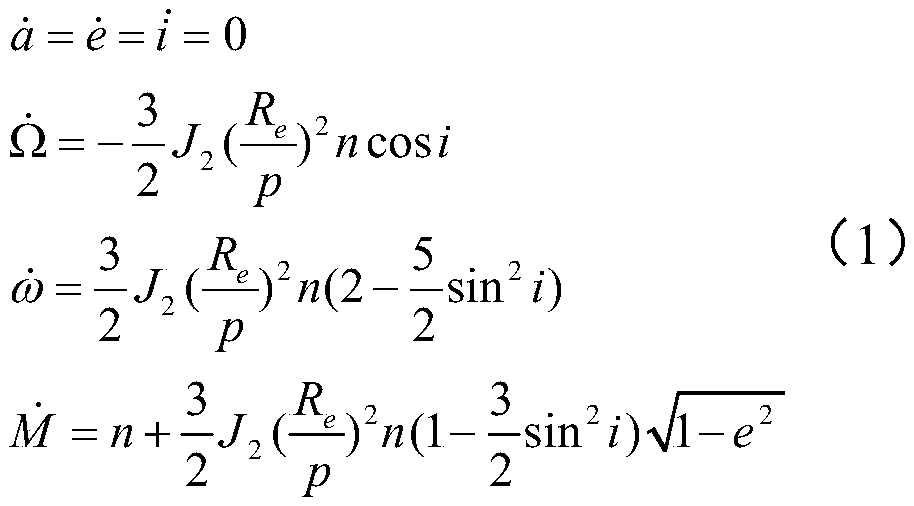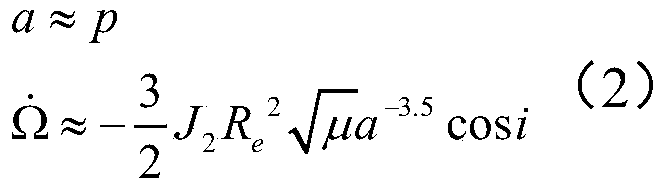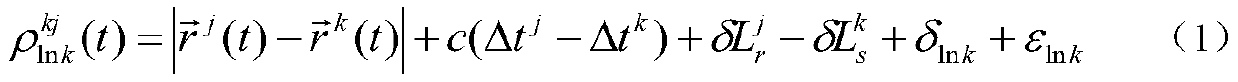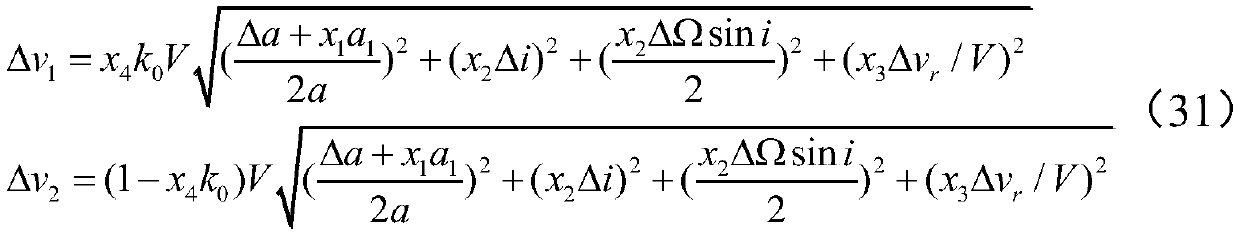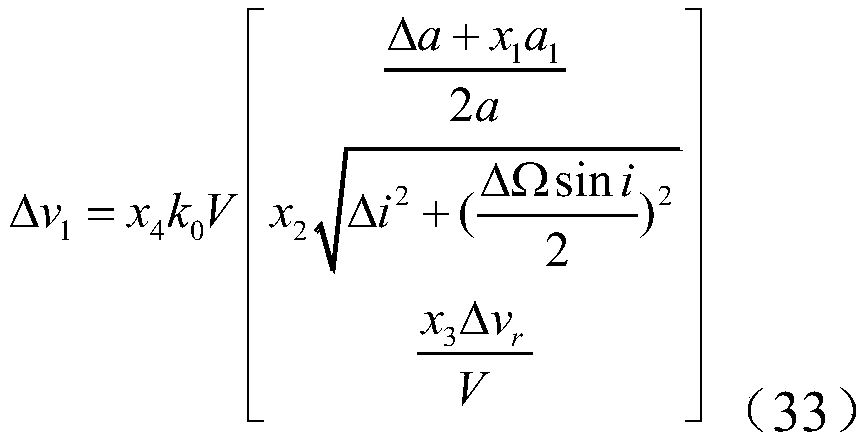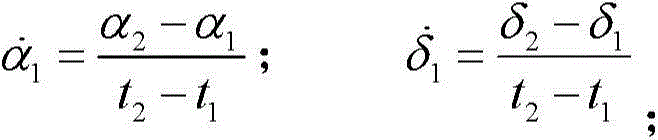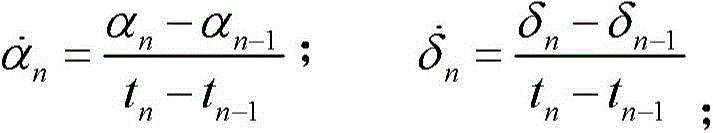Patents
Literature
163 results about "Orbital elements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
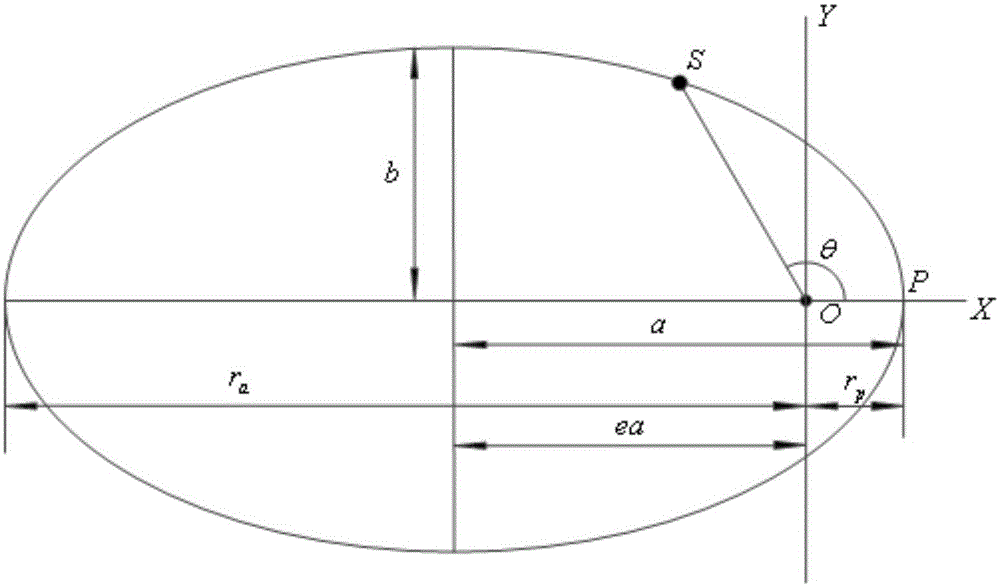
Orbital elements are the parameters required to uniquely identify a specific orbit. In celestial mechanics these elements are generally considered in classical two-body systems, where a Kepler orbit is used. There are many different ways to mathematically describe the same orbit, but certain schemes, each consisting of a set of six parameters, are commonly used in astronomy and orbital mechanics.
Satellite team configuring control method based on fuel consumption optimization
ActiveCN103257653AUniversal adaptabilityStar fuelPosition/course control in three dimensionsEngineeringOrbital elements
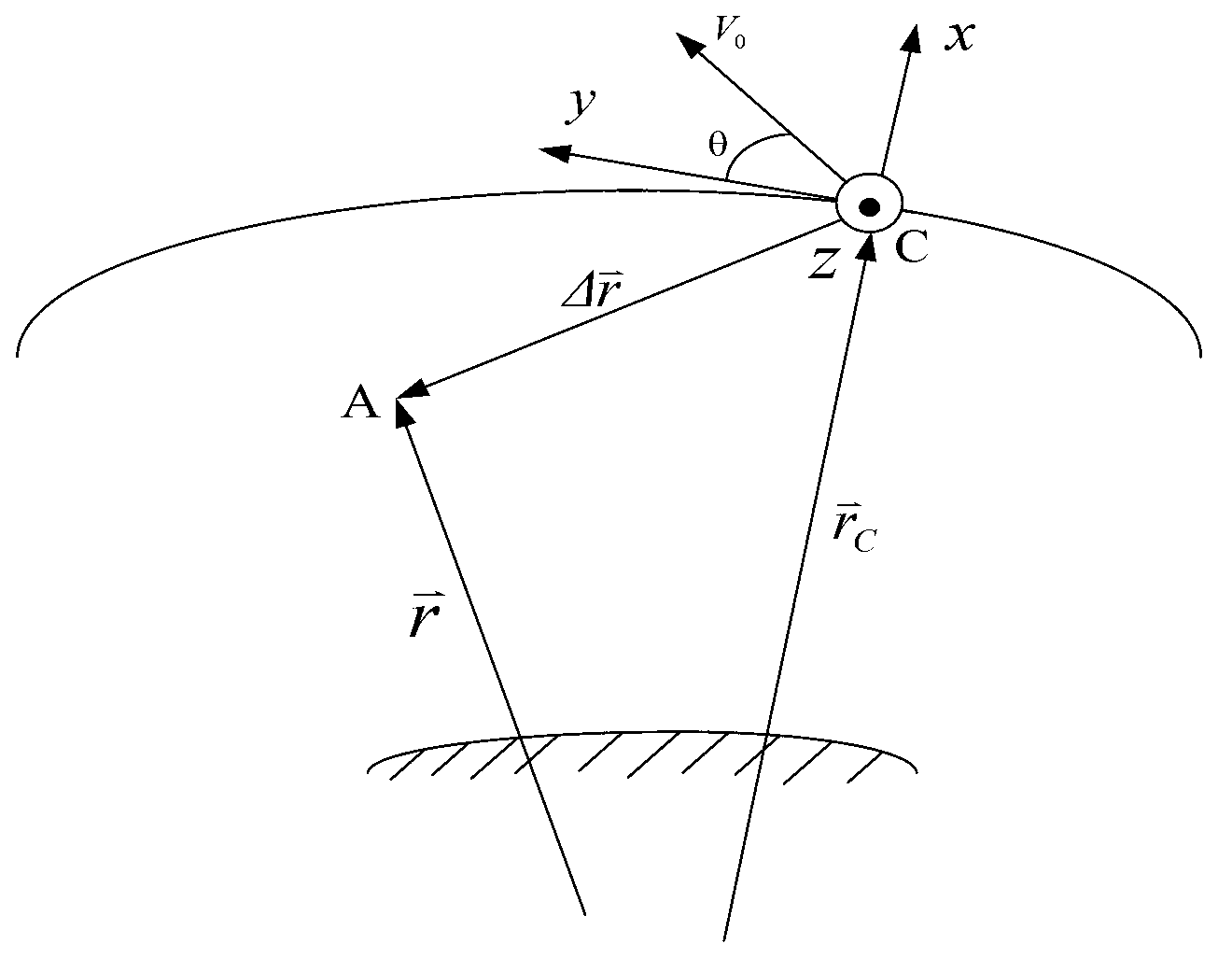
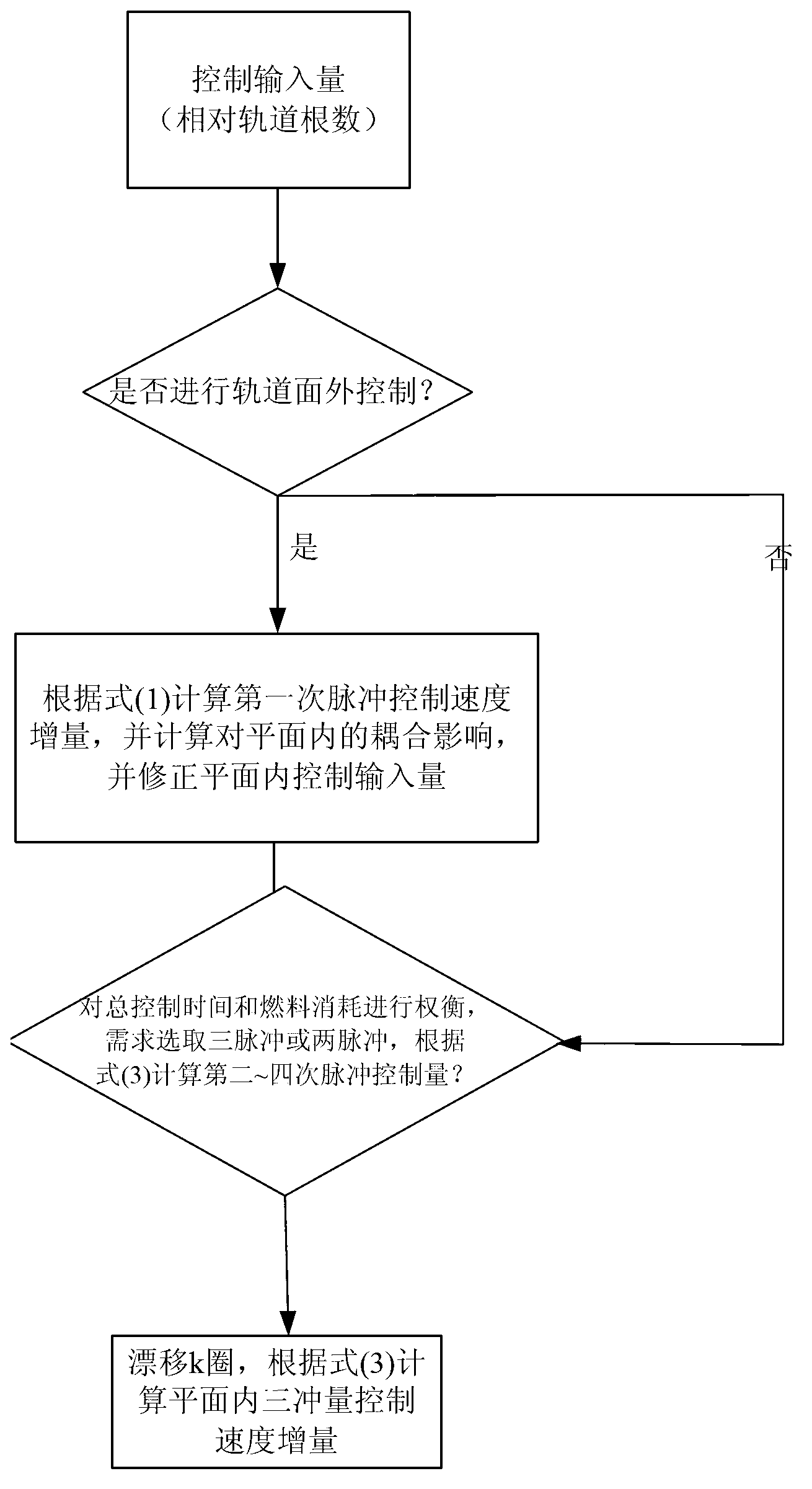
The invention provides a satellite team configuring control method based on fuel consumption optimization. The satellite team configuring control method based on the fuel consumption optimization comprises the following steps: team configuring control input is calculated, plane external orbit control is judged to be carried out or not according to the control input, if the plane external orbit control is needed, a corresponding speed increment and an orbit control time are worked out, coupling influences of the plane external orbit control on orbital elements in a plane are calculated, and the control input in the plane is corrected; then the orbital elements in the plane are jointly adjusted, the coupling influences among the adjustment of the orbital elements in the plane are taken into account, and effective compensation is carried out. An appropriate value k is determined according to whether drifting is needed to achieve passive control, and a three impulse speed increment and the orbit control time are obtained through calculation. The satellite team configuring control method based on the fuel consumption optimization achieves the team control based on fuel optimization, and can control configuring initialization, configuring maintenance and reconfiguration of the satellite team under the condition of a circle-similar non-equatorial orbit.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINYUE METER FACTORY
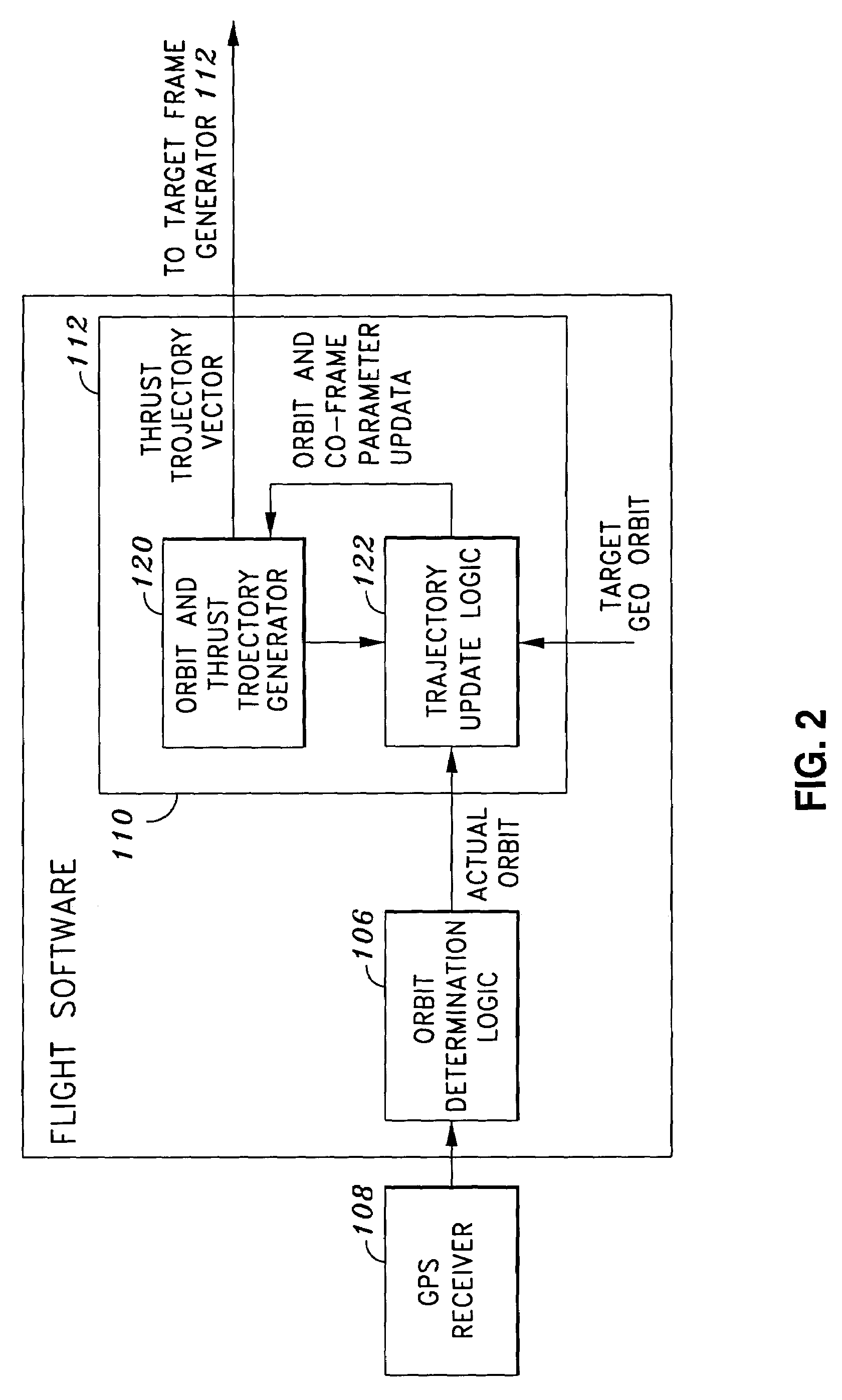
System and method of substantially autonomous geosynchronous time-optimal orbit transfer
InactiveUS7246775B1Reduce coverageImprove fuel efficiencyLaunch systemsVehicle position/course/altitude controlSynchronous orbitState parameter
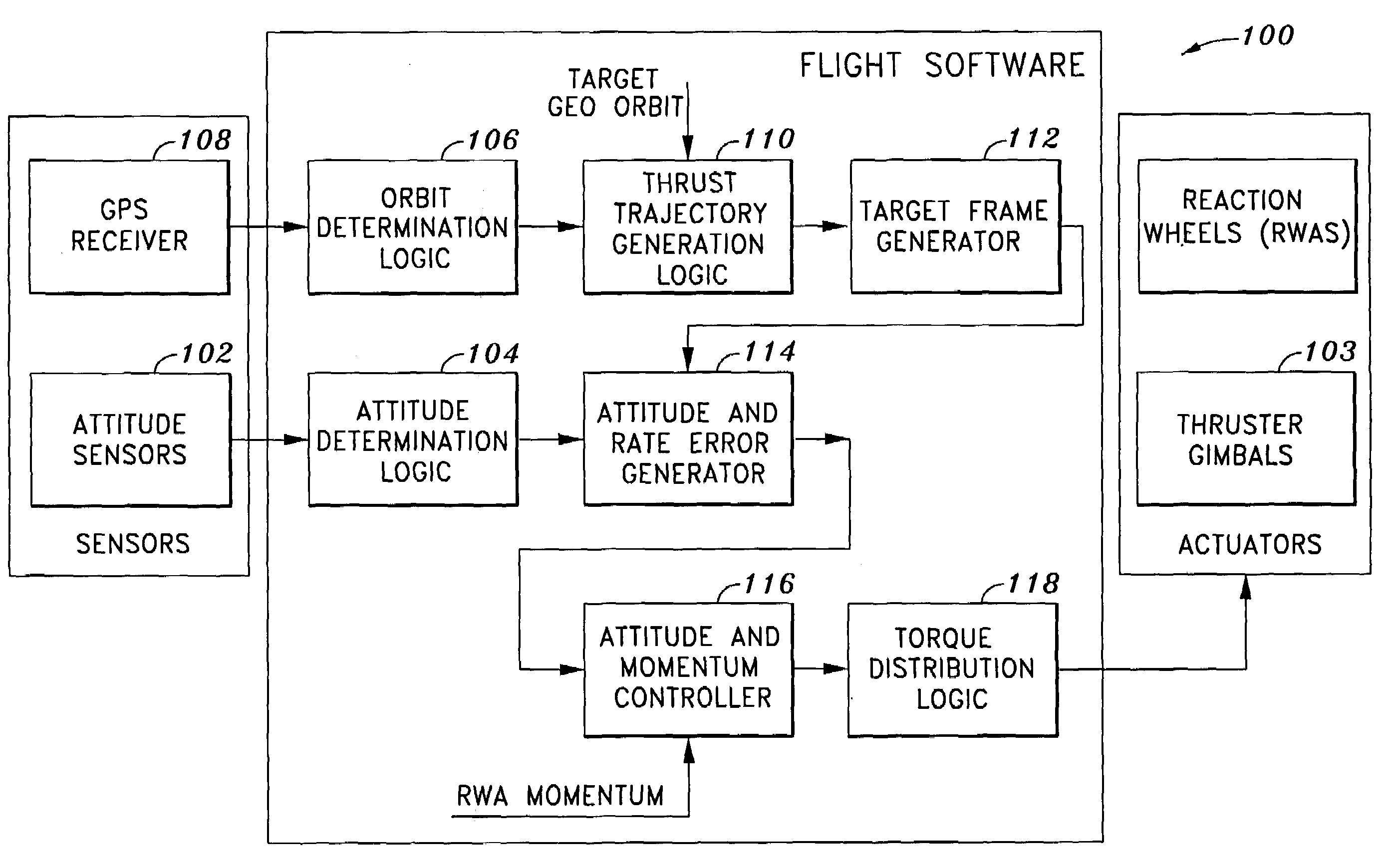
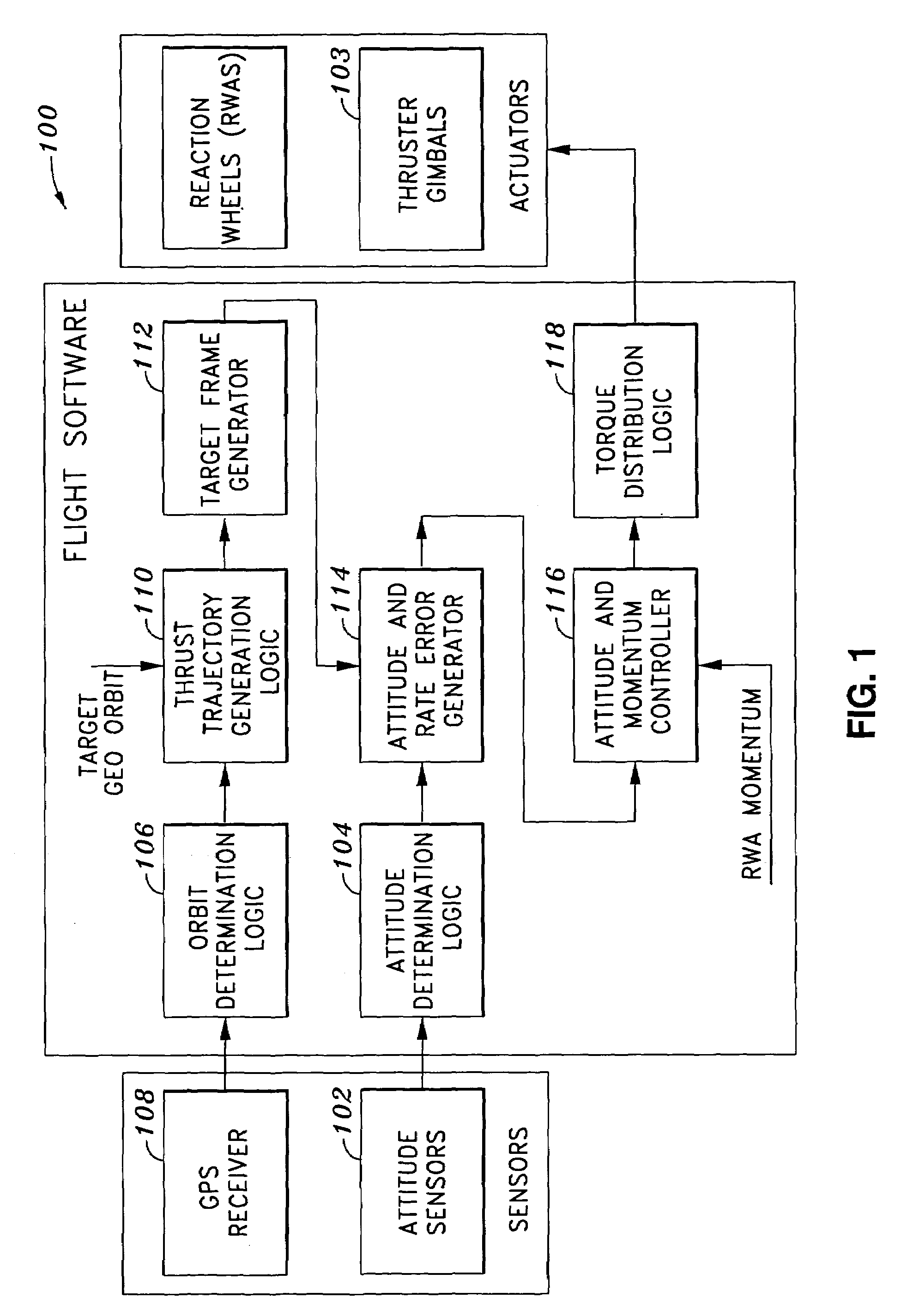
Method of and system for on-board substantially autonomous control for transferring a spacecraft from an initial orbit to a final geosynchronous orbit, by a trajectory that minimizes remaining transfer time and orbit transfer fuel. The spacecraft determines its orbit using a GPS-based system to determine the spacecraft orbital elements. Based on the measured orbit error, corrected co-state parameters are calculated and used to generate an updated thrust trajectory. The corrections are calculated using an innovative numerical procedure, carried out repetitively at a fixed interval until the target geosynchronous orbit is achieved.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Method for tracking ground station through low earth orbit space-borne antenna
ActiveCN104332707AImprove forecast accuracyImprove on-orbit pointing accuracyAntennasNatural satelliteLow earth orbit
The invention provides a method for tracking a ground station through a low earth orbit space-borne antenna. The method comprises the following steps: 1) calculating UTC at the next pointing moment of the antenna; 2) calculating the number of transient satellite orbit at the next pointing moment of the antenna; 3) calculating the position of the satellite under a J2000 inertial coordinate system; 4) calculating the position of the ground station under the J2000 inertial coordinate system at the next pointing moment of the antenna; 5) calculating the opposite position vectors of the satellite and the ground station under the J2000 inertial coordinate system; 6) calculating the vector of the opposite position vectors of the satellite and the ground station under geo-center camber line; 7) calculating the vector of the opposite position vectors of the satellite and the ground station under the satellite orbit coordinate system; 8) calculating the vector of the opposite position vectors of the satellite and the ground station under a satellite body system; 9) calculating the vector of the opposite position vectors of the satellite and the ground station under an antenna coordinate system; 10) obtaining an antenna pointing angle, and driving the antenna to perform pointing tracking for the ground station.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Gravity-gradient-invariant-based method for estimating orbit element
ActiveCN107065025AStrong autonomyImprove anti-interference abilityGravitational wave measurementState parameterDecomposition
The invention provides a gravity-gradient-invariant-based method for estimating an orbit element. The method comprises: step one, carrying out preparation work; step two, carrying out decomposition of an ideal gravity gradient tensor under an east-noth-up (ENU) coordinate system and obtaining feature values; step three, solving decomposition of a measuring epoch J2 model gravity field tensor under the ENU coordinate system and obtaining feature values; step four, solving all measuring epochs r and phi by using feature values of a J2 gravity gradient matrix; step five, calculating an initial orbit element by using the r and phi; and step six, carrying out orbit element smoothing. Therefore, with utilization of the gravity gradient matrix invariant information measured during the satellite operating process, a geometrical distance between the satellite and the earth's core and the latitude of the earth's core are obtained by iterative solution; a measurement equation that uses a semi-major axis, an eccentricity ratio, an orbit inclination angle, a perigee depression angle, and a true anomaly in an orbital element as state parameters is provided by using an obtained data as an observed quantity; and a perturbation kinetic equation of the orbital element is introduced innovatively and five orbital elements are estimated by using a batching least square method. The gravity-gradient-invariant-based method has advantages of high autonomous degree, high anti-interference capability, and low building cost and the like and has advantages that the traditional method does not have in the deep space exploration field.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
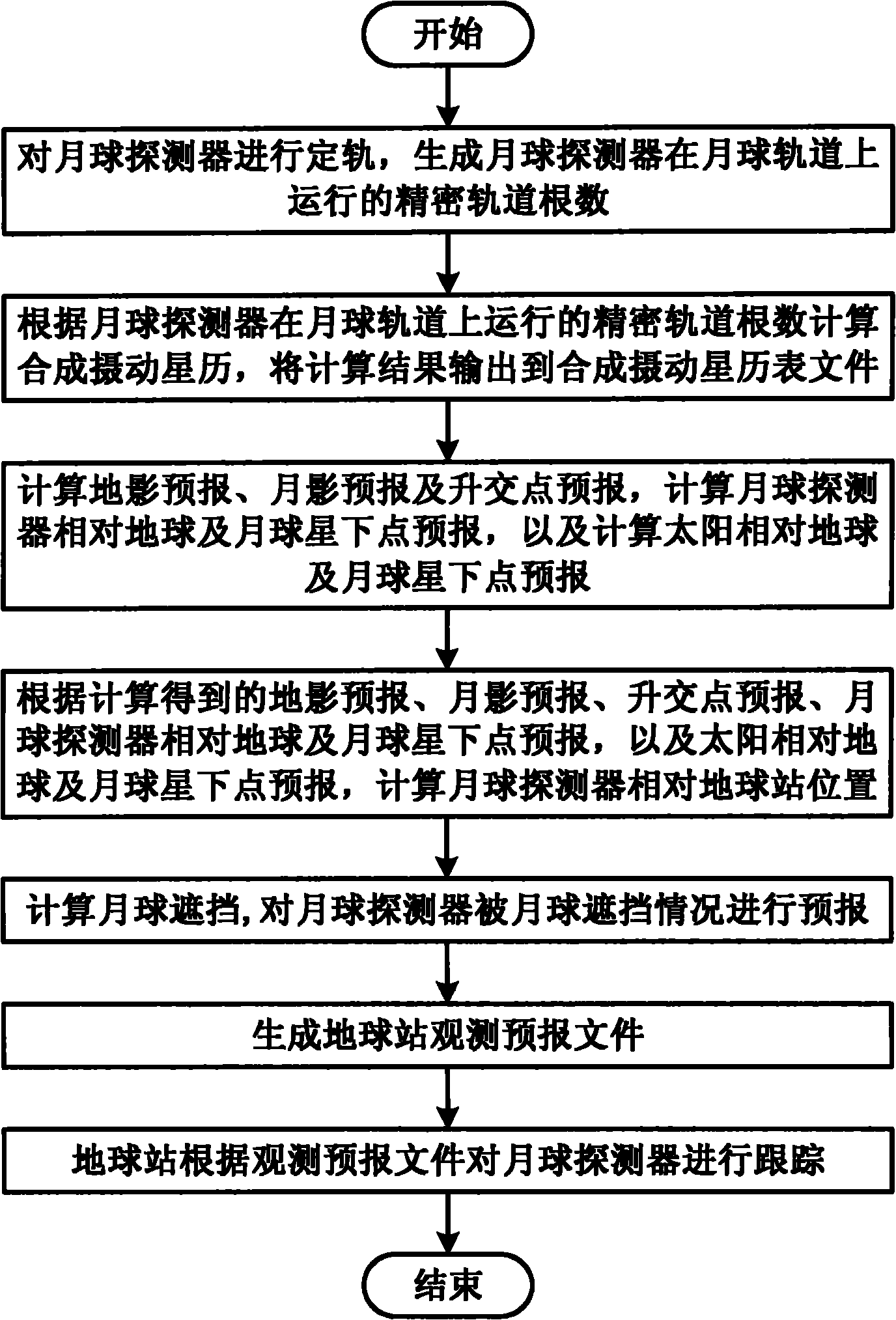
Method for tracking lunar probe by using earth station
ActiveCN101968542AImplement receipt trackingRealize precise orbit determinationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEphemerisLunar orbit
The invention discloses a method for tracking a lunar probe by using an earth station. The method comprises the following steps of: performing orbit determination on the lunar probe to generate a precise orbital element for the lunar probe to run on a lunar orbit; calculating a synthetic perturbation ephemeris according to the precise orbital element for the lunar probe to run on the lunar orbit and outputting a calculation result to a synthetic perturbation ephemeris file; calculating earth shadow forecast, moon shadow forecast and ascending node forecast, calculating substellar point forecast of the lunar probe relative to earth and moon and calculating the substellar point forecast of the sun relative to earth and moon; calculating the position of the lunar probe relative to the earth station; calculating shelter of the moon and forecasting the condition that the lunar probe is sheltered by the moon; generating an earth station observation forecast file; and tracking the lunar probe by the earth station according to the observation forecast file. By the method, the measurement and control of the lunar probe and the receiving of probe data are tracked by using the earth station.
Owner:NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORIES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
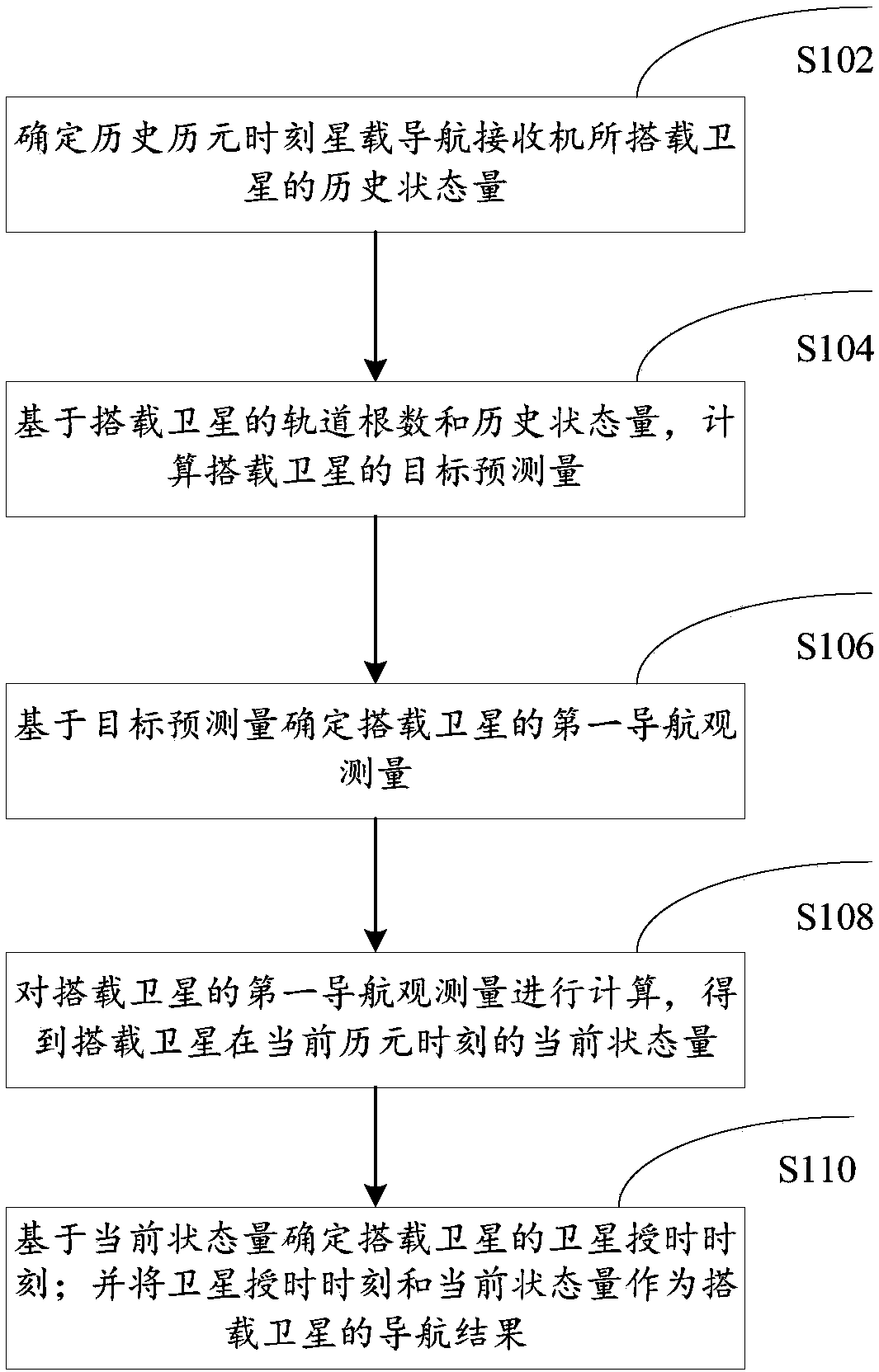
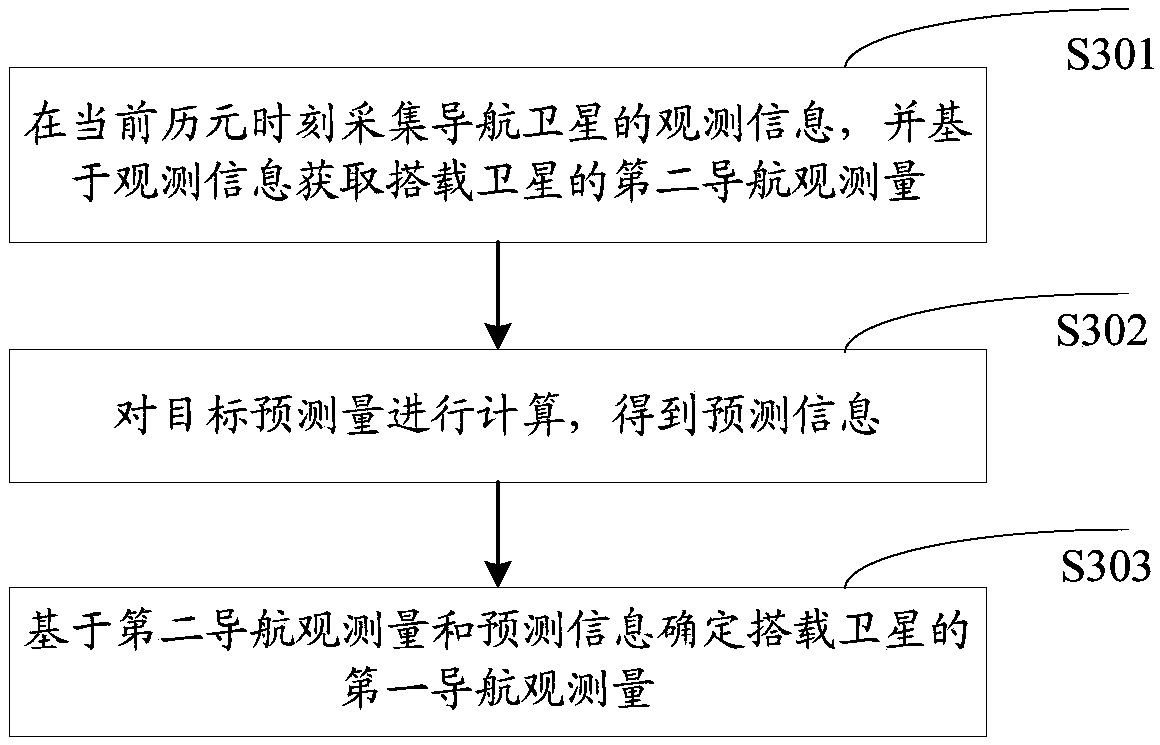
Positioning and time service method and device for spaceborne navigation receiver based on orbital element prediction
ActiveCN109521448AGuaranteed accuracyHigh precisionSatellite radio beaconingState variableOrbital elements
The invention provides a positioning and time service method and device for a spaceborne navigation receiver based on orbital element prediction. The positioning and time service method is applied tothe spaceborne navigation receiver and comprises the steps of determining historical state variables of a satellite carried by the spaceborne navigation receiver at a historical epoch moment; calculating a target prediction variables of the carried satellite based on the orbital elements and the historical state variables of the carried satellite; determining a first navigation observation variable of the carried satellite based on the target prediction variables; calculating the first navigation observation variable of the carried satellite to obtain the current state variable of the carriedsatellite at the current epoch moment; determining the satellite time service moment of the carried satellite based on the current state variable; and enabling the satellite time service moment and the current state variable to serve as a navigation result of the carried satellite. The positioning and time service method improves the accuracy of the navigation positioning and time service result,and better meets the requirements of the applications such as medium and high-orbit beam directional communication loads for the on-orbit positioning and time service accuracy.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Pulse and pneumatic assistance combination-based low-orbit orbit plane transfer method
InactiveCN106383994AGreat changeabilityIncrease flexibilitySpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsAviationDynamic equation
The invention discloses a pulse and pneumatic assistance combination-based low-orbit orbit plane transfer method, relates to a large-range orbit plane transfer method for an earth low-orbit spacecraft, and belongs to the field of aerospace. The method comprises the steps of firstly establishing the number of orbits and a dynamic equation of a flight process in atmosphere; changing an orbit of the spacecraft to a highly elliptic orbit in a maneuvering manner by applying a pulse, and enabling the spacecraft to enter the atmosphere by applying an de-orbit pulse at an apogee; selecting an optimization target as a maximum change amount of an orbit plane, giving constraints and obtaining an optimal control rate and a terminal state variable meeting aerodynamic requirements, thereby finishing pneumatic assisted orbit plane transfer; and enabling the spacecraft to fly out of the atmosphere and run to a target orbit height along a transfer orbit, and enabling the spacecraft to enter a target orbit by applying an orbit determination pulse. According to the method, the orbit plane transfer of the low-orbit spacecraft can be finished with relatively low fuel consumption; and the method is good in robustness, high in repeatability, small in influence of spacecraft orbit orientation, high in flexibility of a pneumatic assistance process, and wide in application range for the target orbit.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
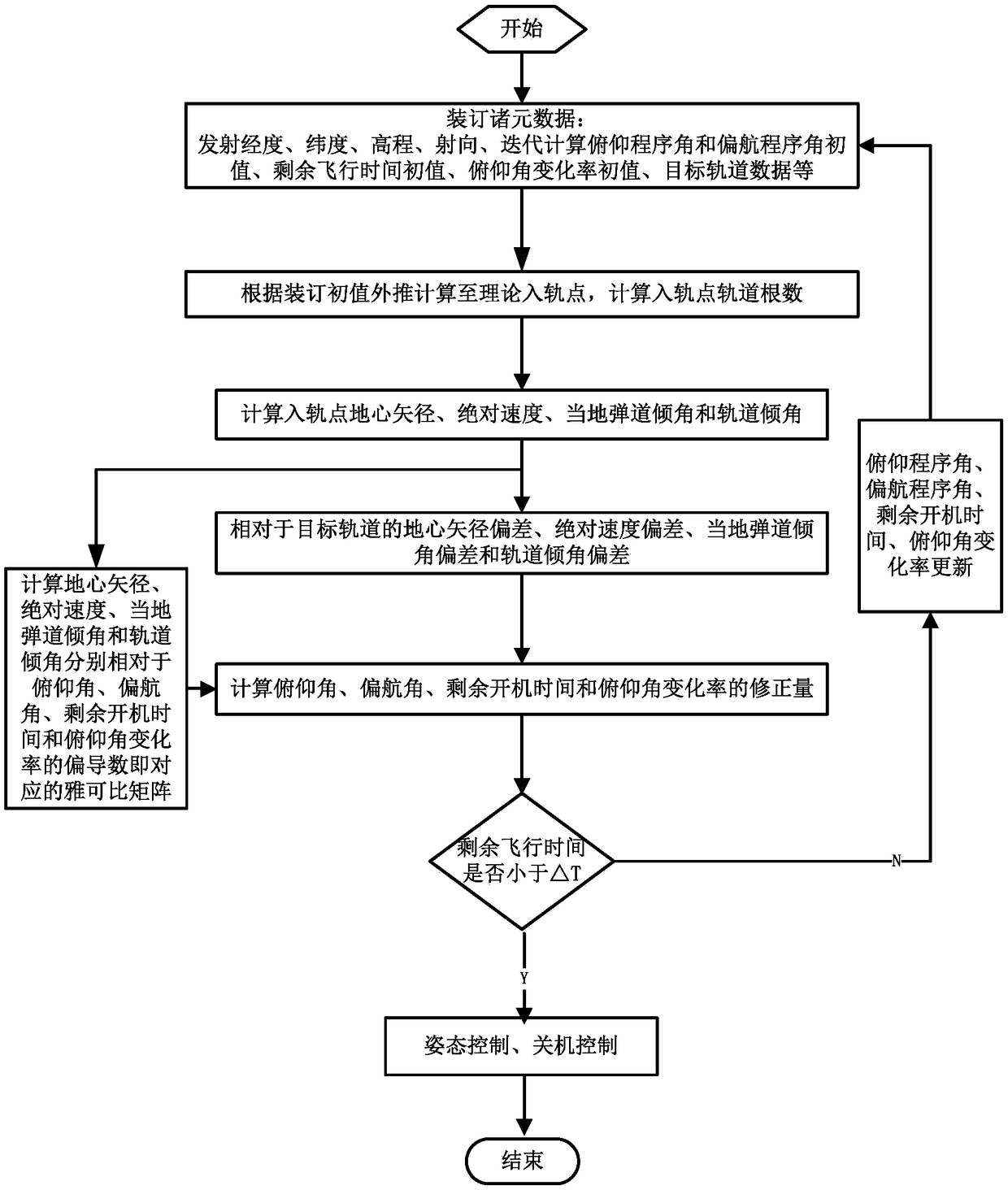
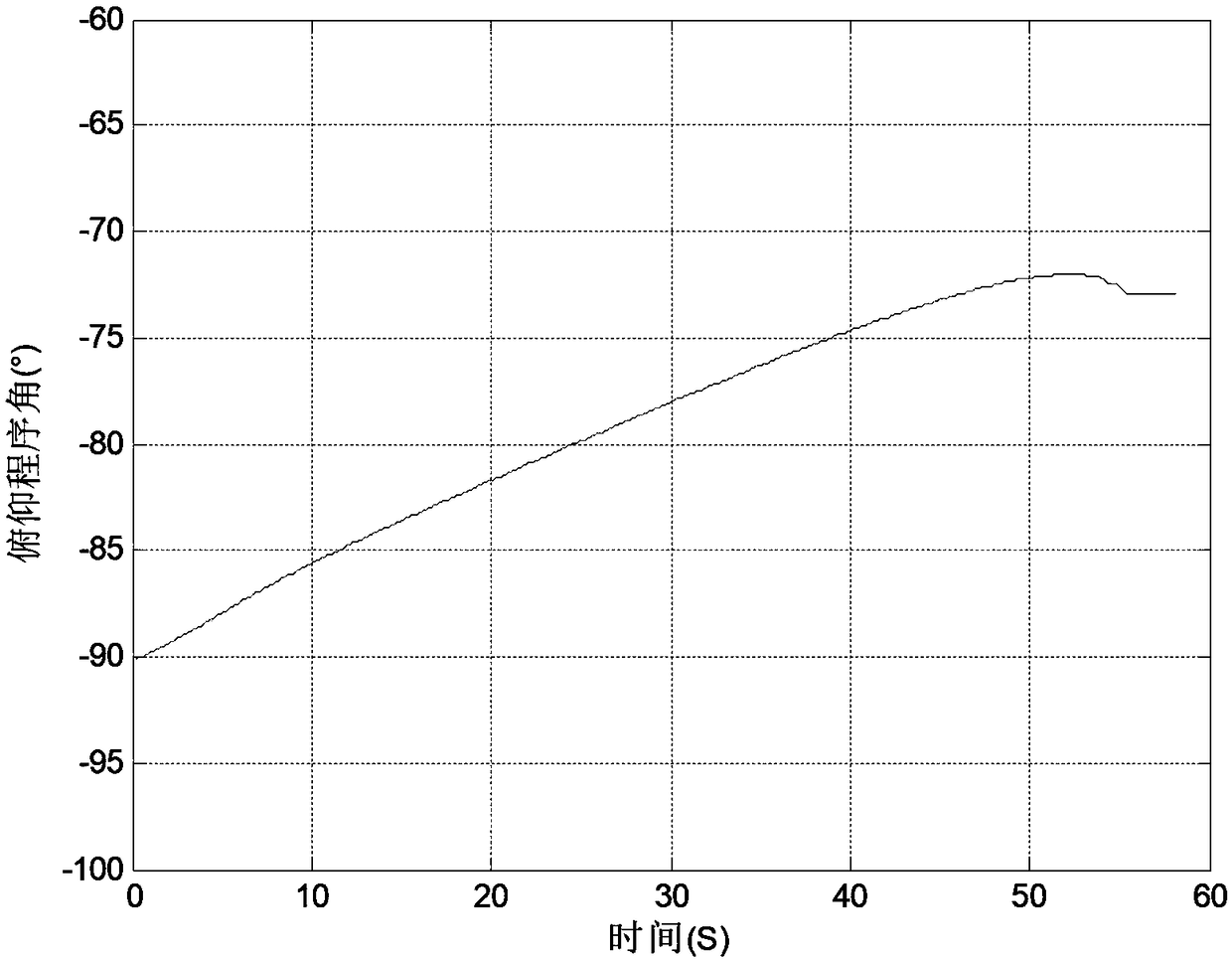
Real-time orbital maneuvering control method based on target orbital parameters
ActiveCN109484674AAchieve real-time calculationPreparing Computational Work Requirements LowCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusAttitude controlControl system
The invention discloses a real-time orbital maneuvering control method based on target orbital parameters, and relates to the technical field of control-and-guide controlling. The method comprises thesteps that target orbital elements are always taken as computation conditions in each iteration computation period, a theoretical shutdown point is deduced according to the initial values of launch data of a carrier, the distance from the Earth's center to a celestial body, absolute velocity, local ballistic pitch and an orbital pitch of the theoretical shutdown point are calculated, and the deflection amount relative to a target nominal value and a corresponding Jacobian matrix are resolved; the pitch program angle correction, yaw program angle correction, remaining flight time correction and pitch program angle variation rate correction in the current iteration computation period are resolved according to the Jacobian matrix, correction is conducted, and the correction results are takenas the initial values of the next iteration computation period; attitude control and shutdown control are conducted according to the computer flight program angle and the remaining flight time in thecurrent iteration computation period. The method has the advantages that real-time computation of a control-and-guide controlling system of the carrier is achieved, and the method has a higher engineering application value.
Owner:THE GENERAL DESIGNING INST OF HUBEI SPACE TECH ACAD
Bounded accompanying boundary control method of satellites under circular reference orbit
ActiveCN104076819ALarge design spaceIncrease flexibilityPosition/course control in three dimensionsCircular referenceBoundary knot method
The invention provides a bounded accompanying boundary control method of satellites under a circular reference orbit. The bounded accompanying boundary control method includes the steps of when a bounded accompanying model, between bounded boundaries, of the tracked satellite relative to the reference satellite needs to be achieved at the terminal moment, building a boundary quantitative analysis relation between the bounded accompanying boundary of the satellites under the circular reference orbit and satellite orbital element differences in advance, and carrying out solving to obtain the expected orbital element difference corresponding to a boundary-given accompanying task; carrying out calculation through a pre-given quantitative analysis control model to obtain pulse speed increments needing to be exerted on the tracked satellite at the initial moment and the terminal moment. The expected orbital element difference is solved through a boundary analysis model, design space of the accompanying model is expanded, and certain flexibility is brought to selecting formation or cluster flight mission models. The demands for the pulse speed increments with given boundaries are obtained through accurate calculation of the quantitative analysis control model, and the bounded accompanying boundary control method has the advantages of being high in control accuracy and simple in control process.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Mars self-orientating method of large elliptical orbit Mars probe
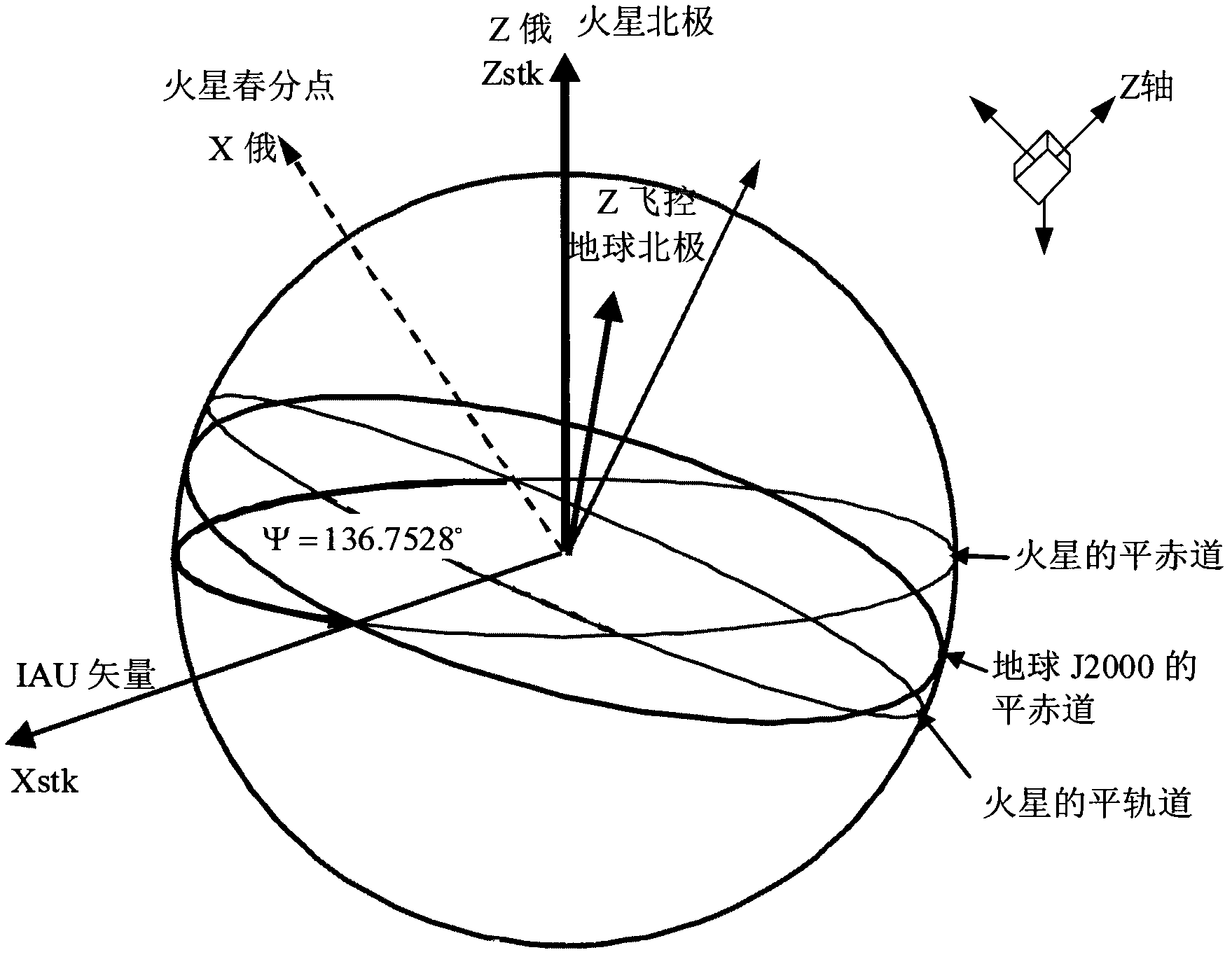
ActiveCN103017760ARealize autonomous fire directional controlNavigation by astronomical meansAttitude controlShort termsOrbital elements
The invention discloses a Mars self-orientating method of a large elliptical orbit Mars probe, to enable a Mars probe to accomplish three-axis stable control to Mars orientation under the condition that the Mars probe does not completely depend on ground monitoring and control and self-orientation sensors are not available. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out corresponding short-term orbit recursion calculation according to the number of initial orbits and a reference coordinate system for describing the number of the orbits; adopting a simplified analysis method for Mars self-recursion, and adopting a high precision numerical method for orbit recursion on the ground; establishing a Mars orientation reference coordinate system by taking a Mars center-probe position vector as the Z-axis direction; and turning to a posture working mode for Mars-orientation after the Mars receives remote control instructions. Compared with the prior art, the Mars self-orientating method has the beneficial effects that under the condition that the ground communication has time delay and the self-orientation sensors cannot achieve engineering application, the Mars self-orientation control of the Mars probe is reliably realized through the orbit recursion and the establishment of the orientation reference coordinate system.
Owner:上海航天控制工程研究所
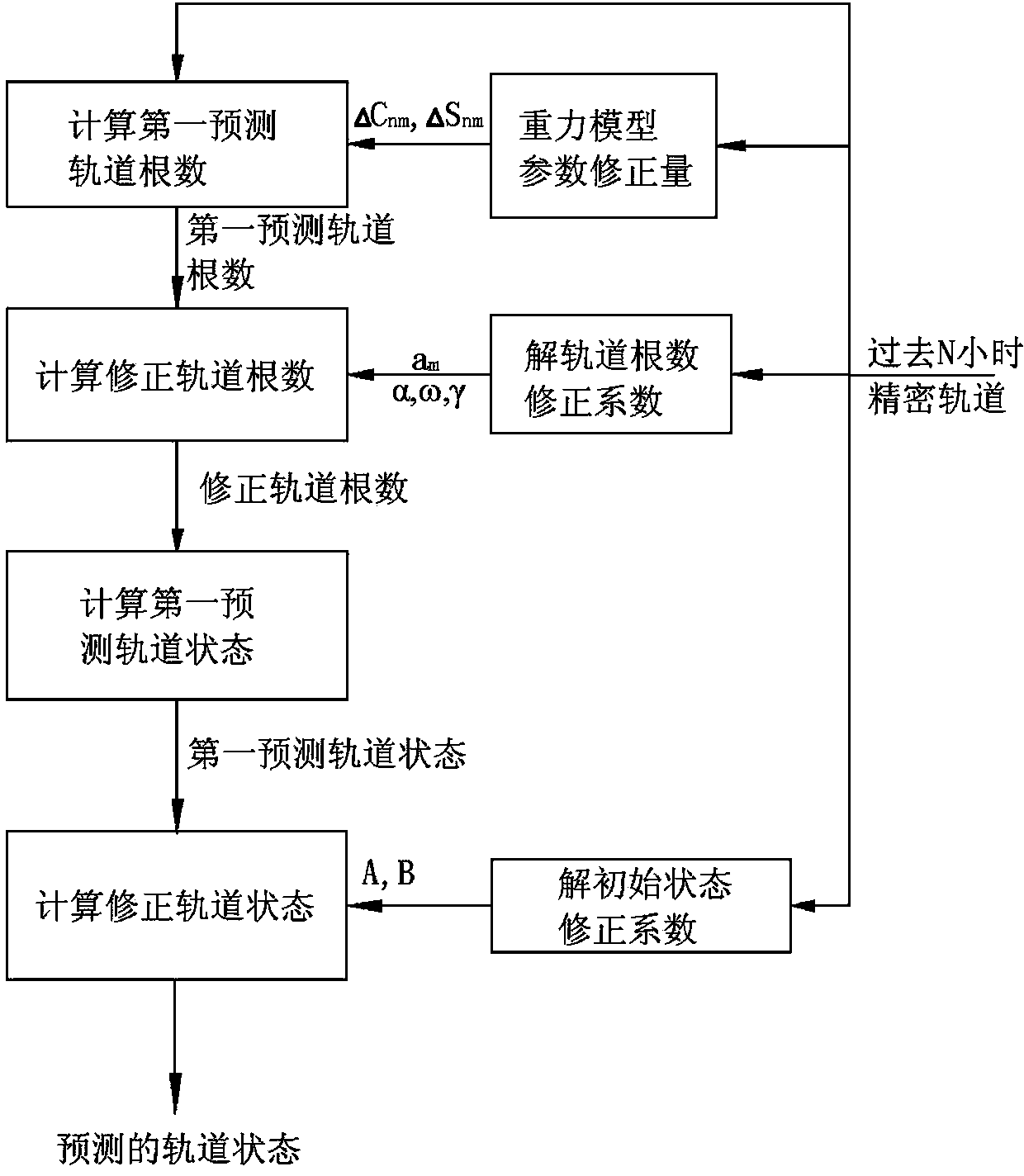
Prediction method for satellite orbit
The invention provides a prediction method for a satellite orbit. The prediction method comprises the following steps: obtaining a precise satellite post orbit in N hours in the past, obtaining an initial state of the satellite; calculating a satellite stress parameter; calculating the first prediction orbit quantity of the satellite in M hours in the future according to the satellite stress parameter; calculating an orbit quantity correction coefficient according to the precise satellite post orbit in N hours in the past; correcting the first prediction orbit quantity according to the orbit quantity correction coefficient, and obtaining the correction orbit quantity; calculating the orbit state by using the correction orbit quantity to obtain a first prediction orbit state; calculating an initial state correction coefficient of the satellite according to the precise satellite post orbit in N hours in the past; correcting the first prediction orbit state according to the initial state correction coefficient, and obtaining the predicted satellite orbit state. The technique disclosed by the invention can be applied to prediction of the satellite orbit; the requirement of real-time orbit determination of navigating and positioning satellites based on the prediction method can be met.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
High-precision satellite-borne orbit prediction method based on numerical fitting
ActiveCN110132261AImprove forecast accuracyNavigation by terrestrial meansNavigation by astronomical meansSpace environmentNumerical fitting
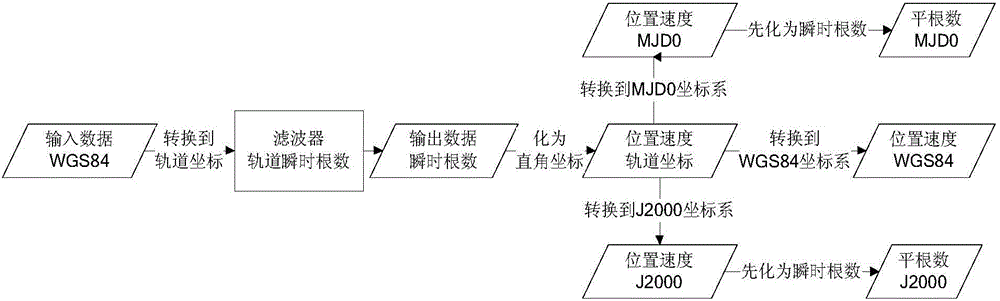
The invention discloses a high-precision satellite-borne orbit prediction method based on numerical fitting. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, obtaining atmospheric environment parameters including the latest solar radiation flow and a geomagnetic index, satellite star parameters and the latest precise orbital elements of the satellite, combining the star and space environment parameters, carrying out orbit prediction by utilizing a ground high-precision numerical method so as to obtain a set of satellite instantaneous orbital elements in a prediction arc section, then, converting into an average element to perform numerical fitting so as to obtain a change item coefficient of each orbital element, arranging multiple sets of primary orbits to carry out segmented extrapolation according to an satellite-borne predication requirement, carrying out orbit prediction according to the arranged initial orbital element and the change item coefficient to obtain the average element of the satellite at the prediction moment, if the prediction precision requirement is high, arranging a plurality of sets of initial values for staged prediction, converting the average element ofthe satellite at the prediction moment into the instantaneous element, so that the instantaneous position of the satellite is obtained. According to the method in the invention, the problem that the precision of satellite-borne orbit prediction is poor in the prior art is solved.
Owner:CHINA XIAN SATELLITE CONTROL CENT
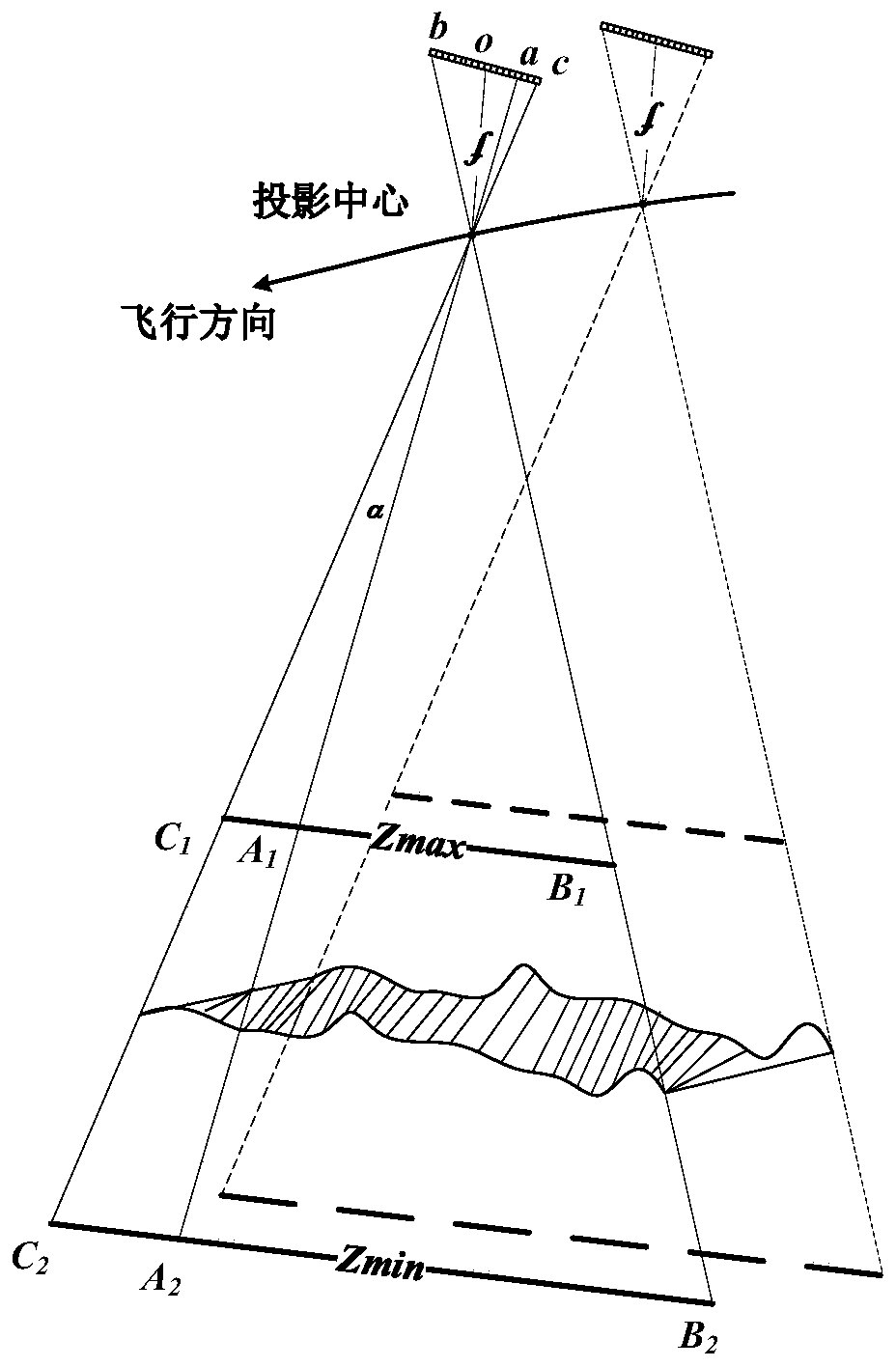
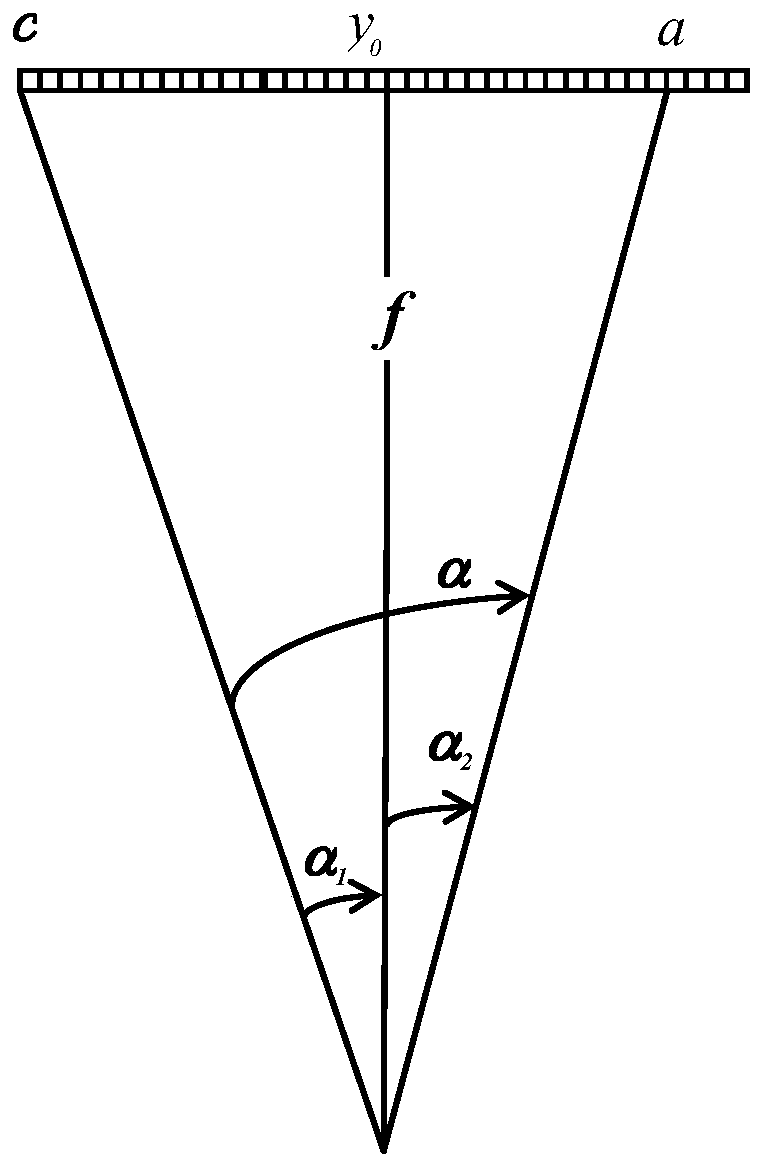
Method for establishing equivalent geometric imaging model of high-resolution satellite image by using RPC parameters
ActiveCN110500995AHigh positioning accuracyMutual conversion solutionImage enhancementImage analysisSatellite imageModelling analysis
The invention relates to a method for establishing an equivalent geometric imaging model of a high-resolution satellite image by using RPC parameters. The method comprises: selecting a random scanningline of a high-resolution satellite image and listing a collinear condition equation of a projection center, an image point and a corresponding object square point; on the basis of operating characteristics and geometric characteristics of the high-resolution satellite, abstracting three rotation angles and six orbital numbers in an equivalent principal distance, a principal point coordinate, andan offset matrix and forming 11 independent parameters of an equivalent geometric imaging model; and with RPC parameters, calculating parameters of the equivalent geometric imaging model directly. Therefore, inherent problems of the over-parameterization of the RPC, strong correlation between parameters, and residual error existence of the fitting tight imaging model are solved; the parameters have the obvious geometric and physical meanings; and modeling analysis can be carried out on various imaging error sources conveniently. The mutual conversion of RPC parameters is realized; and the positioning accuracy of high-resolution satellite image is improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for calculating lunar orbit real-time in star
ActiveCN101226062AReduce positioning errorsInstruments for comonautical navigationOn boardRelative motion
The invention provides a method of on-board real-time calculation on circumlunar orbit, belonging to the technical field of real-time calculation on circumlunar orbit for spaceflights, comprising a plurality of steps: (1) take the orbit determination as the initial value and use numerical method to calculate the actual orbit; (2) select a two-body orbit as a reference orbit; (3) calculate the actual orbit in relation to the reference orbit trajectory; (4) according to the general law of relative movement between two two-body orbits, calculate a two-body orbit in relation to the reference orbit trajectory similar to the actual orbit in relation to the reference orbit trajectory; step (1) to step (4) are finished on Earth and then send the result on board; (5) the satellite, adopting the calculation method of two-body orbit, calculates real-time the orbit number of the satellite according to the two-body orbit calculated from the step (4). The method of on-board real-time calculation on circumlunar orbit has an advantage that the satellite orbit can be worked out on board in small calculation amount and also does not need to keep real-time connections with ground.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Initial orbit determination method for deep space target celestial body based on space-based autonomous optical observation
InactiveCN104457705ASimple measurement schemeEasy to implementInstruments for comonautical navigationPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryMeasurement deviceTrack algorithm
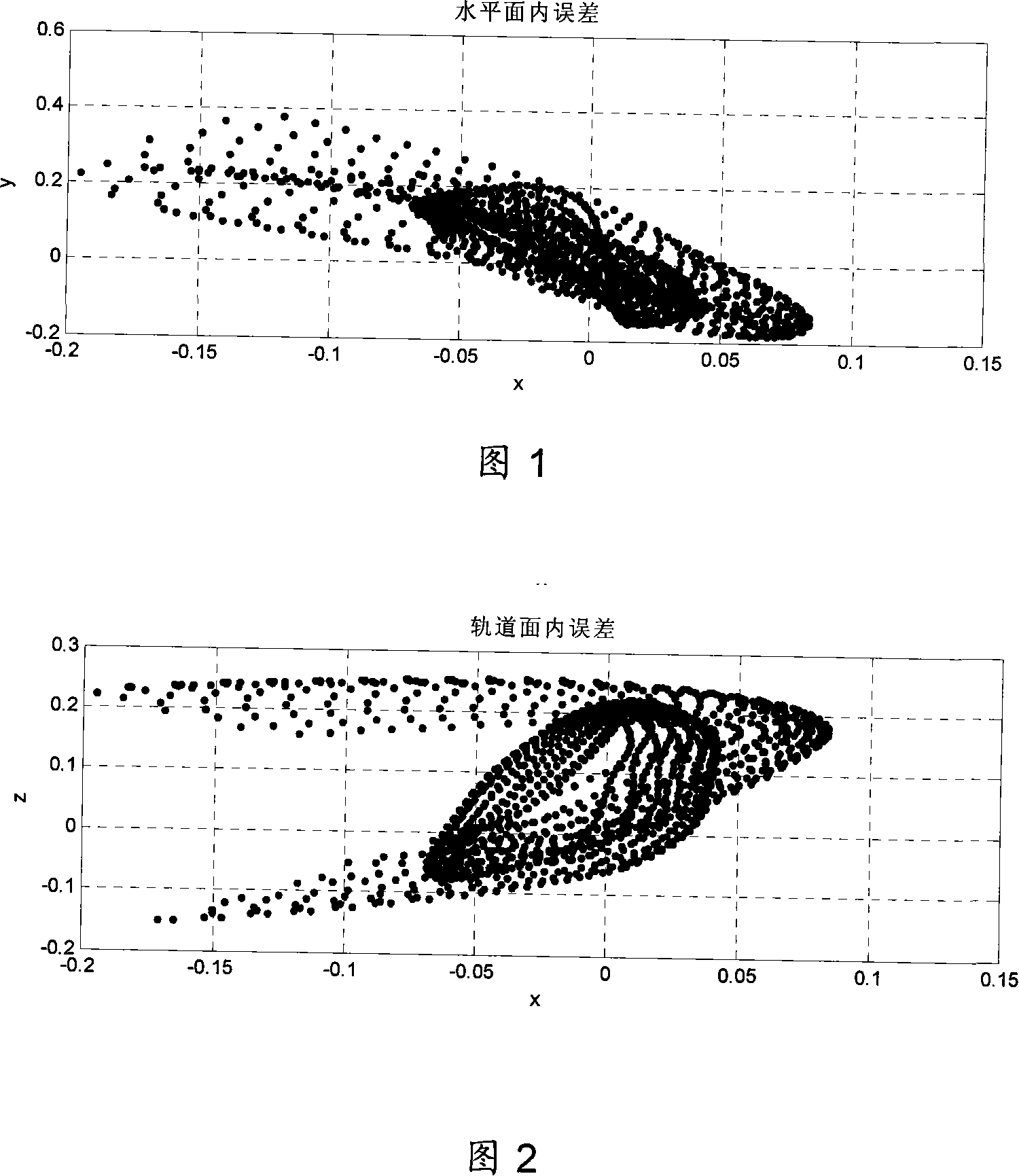
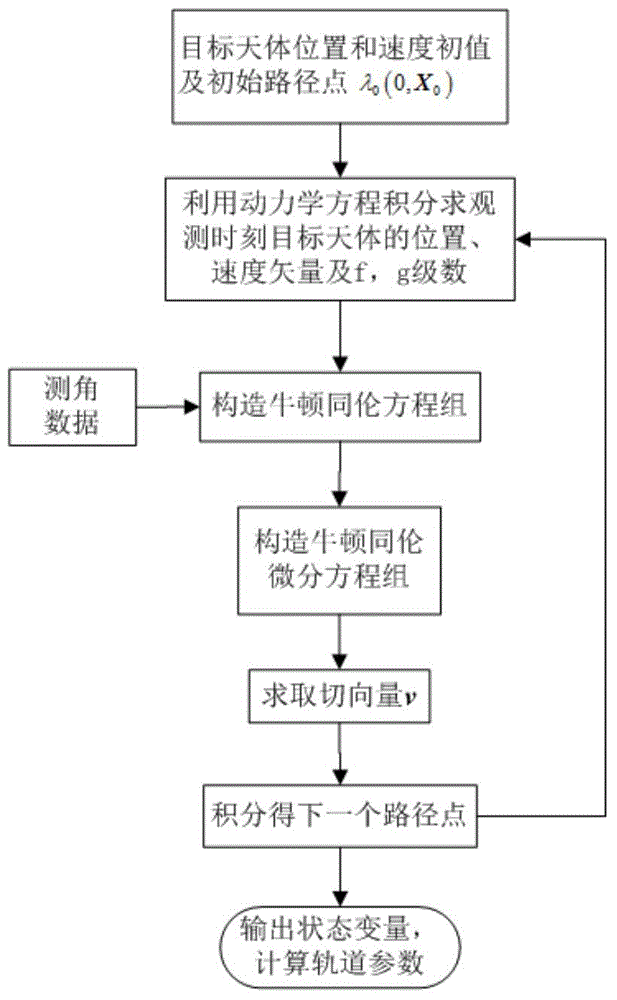
The invention discloses an initial orbit determination method for a deep space target celestial body based on space-based autonomous optical observation, relates to an optical autonomous initial orbit determination method for a deep space celestial body, and belongs to the technical field of deep space detection. The method comprises the following implementation steps: 1, acquiring angle measurement information (right ascension beta and declination epsilon) of the target celestial body from a detector; 2, establishing an orbital kinetic equation of the target celestial body under a heliocentric inertia coordinate system; 3, establishing an observation condition equation set of the autonomous initial orbit determination of the detector by utilizing the angular position information of the target celestial body solved in the step 1 and known detector orbit parameter information; and 4, solving the orbital element information of the target celestial body by utilizing a Newton homotopy path following algorithm, thereby realizing initial orbit determination. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the position and speed information of the target celestial body can be accurately acquired in real time in the field of deep space probe navigation, the initial value sensitivity is reduced, the convergence rate, solving success rate and calculation efficiency are improved, and the positioning efficiency is further improved. Moreover, the method is simple in measurement device and easy to implement.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
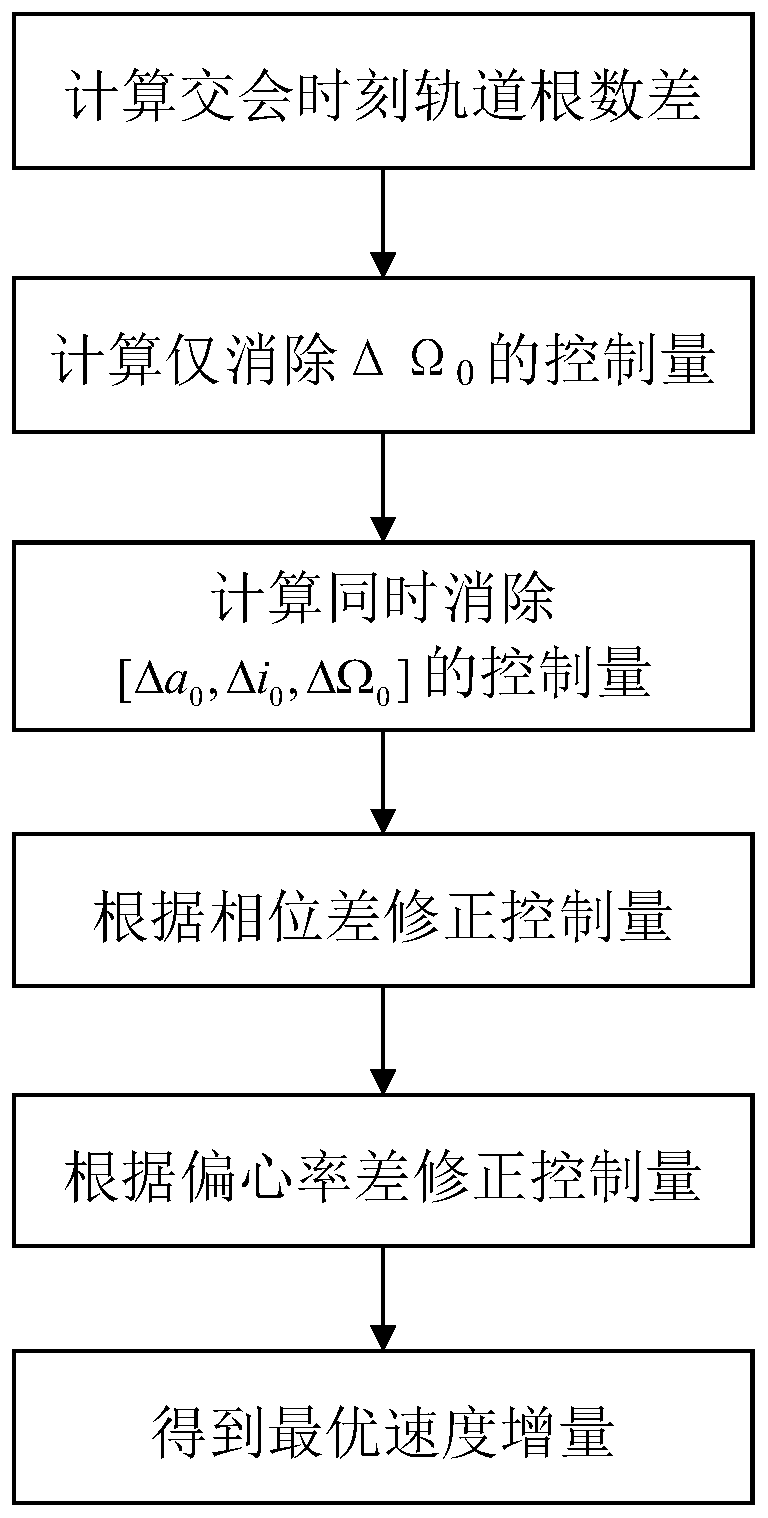
Method for rapidly estimating long-term orbital rendezvous optimal speed increment under J2 perturbation
ActiveCN110789739ADecrease speed incrementImprove optimization efficiencyCosmonautic vehiclesLinear/angular speed measurementOrbital planeSimulation
The invention discloses a method for rapidly estimating a long-term orbital rendezvous optimal speed increment under J2 perturbation. The method includes the steps of calculating the orbital element difference of a non-maneuvering spacecraft and a target at the rendezvous moment, calculating an optimal control amount when only the ascending node ascensional difference is eliminated, substituting the optimal control amount as the initial value into a control amount optimizing model for eliminating the semi-major axis, dip angle and ascending node ascensional difference at the same time to obtain a new optimal control amount, modifying the control amount according to the phase difference in an orbital plane, modifying the control amount according to the eccentricity ratio vector difference,and finally obtaining the estimated optimal rendezvous speed increment. The method realizes the purpose of rapidly estimating the optimal rendezvous speed increment when precise solution is not neededand is high in estimating precision and suitable for the situations with large initial ascending node ascensional difference from a target orbit and small element differences from other orbits.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
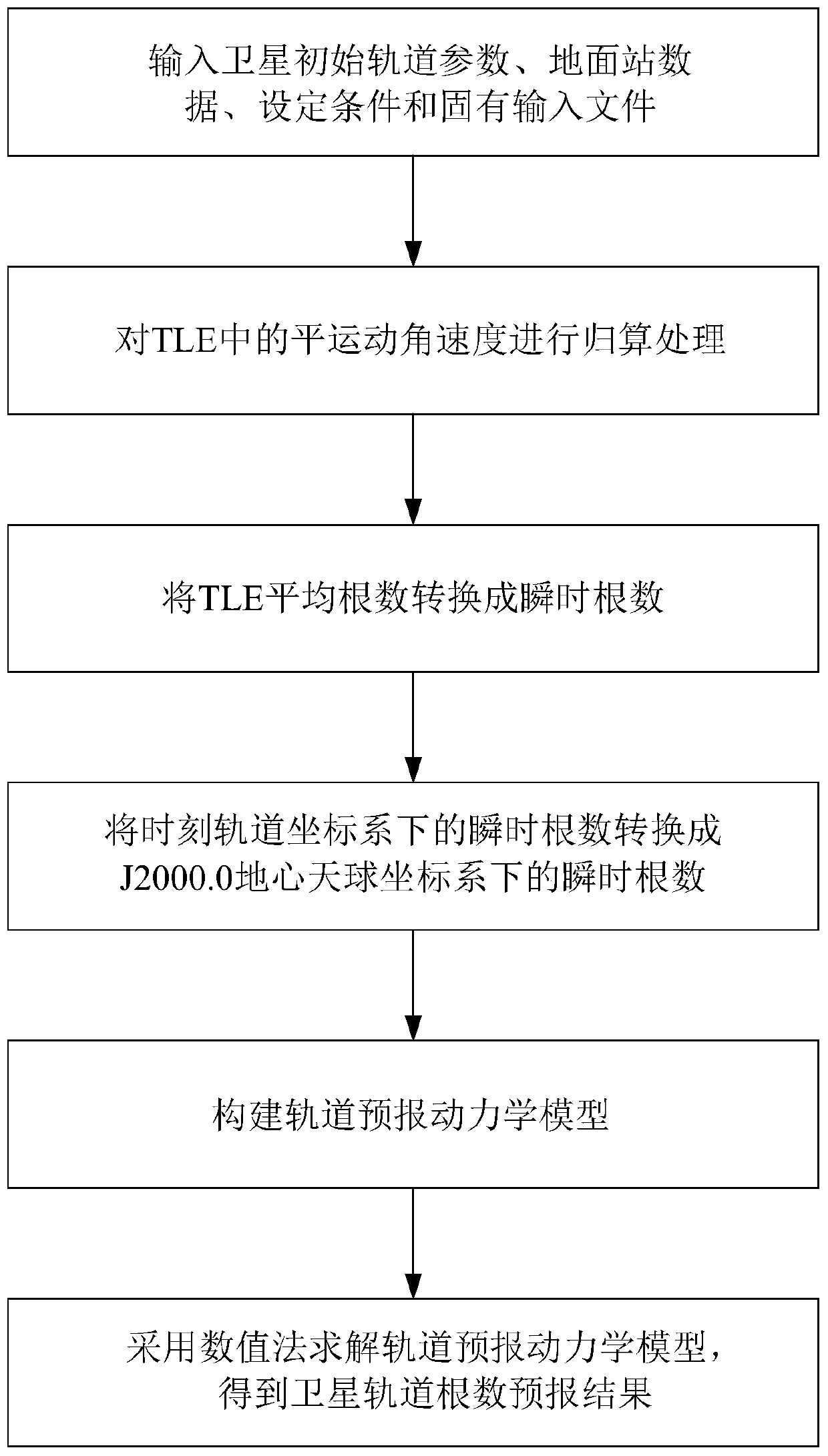
Low-earth-orbit satellite long-term orbit prediction method based on two line element
PendingCN110595485AHigh solution accuracyReduce computationInstruments for comonautical navigationSustainable transportationAngular velocityOrbit prediction
The invention relates to a low-earth-orbit satellite long-term orbit prediction method based on a two line element. The method comprises the following steps: performing related processing on a two line element in an orbital coordiante system at a moment t, thus obtaining a satellite orbital element initial value applicable to an orbit prediction dynamical model in a J2000.0 geocentric celestial coordinate system; and solving the orbit prediction dynamical model by adopting a numerical method, thus obtaining a satellite orbital element prediction result, wherein the related processing comprisesreduction processing performed on angular velocity of peace movement in the two line element, conversion of a mean element into an instant element in the orbital coordinate system at the moment t andconversion of the instant element in the orbital coordinate system at the moment t into an instant element in the J2000.0 geocentric celestial coordinate system. The low-earth-orbit satellite long-term orbit prediction method based on the two line element is high in prediction precision.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
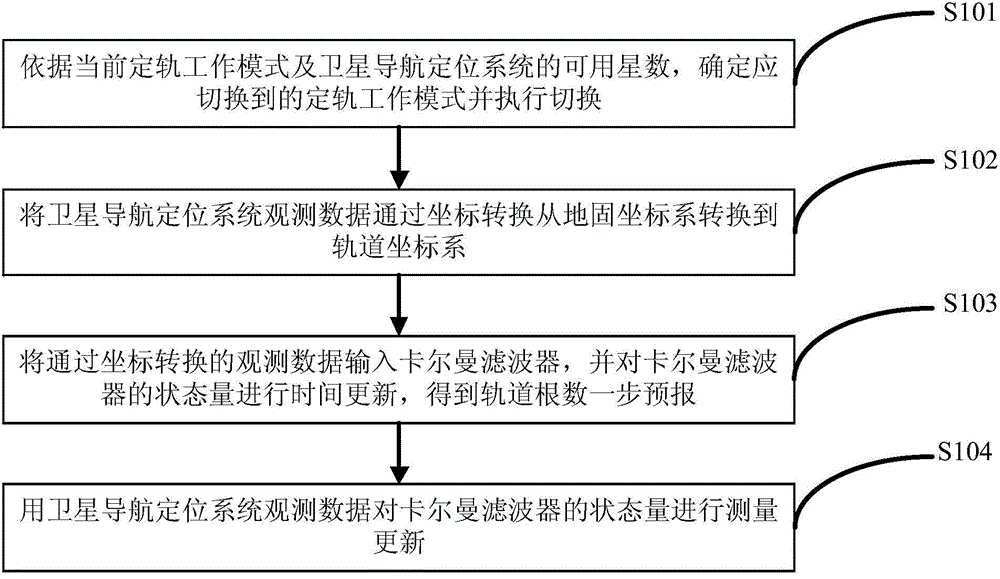
Method and system for realizing real-time orbit determination for single satellite navigation positioning system
InactiveCN105652297AHigh precisionHigh positioning accuracySatellite radio beaconingKaiman filterObservation data
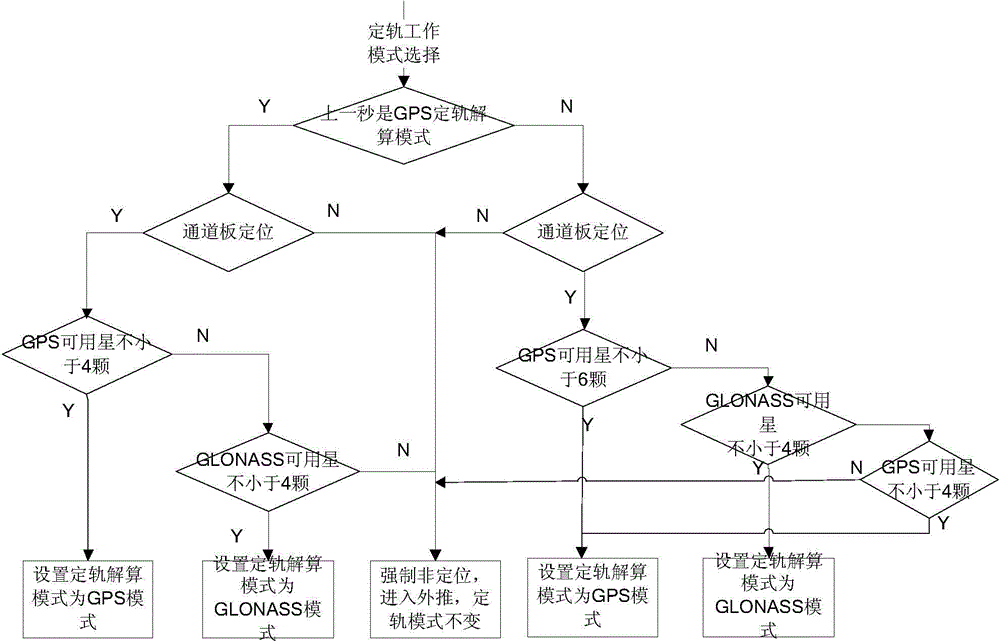
The invention provides a method and a system for realizing real-time orbit determination for a single satellite navigation positioning system. The method comprises steps that a should-be-switched-to orbit determination work mode is determined according to a present orbit determination work mode and the available star number of the satellite navigation positioning system, and switching operation is carried out; the observation data of the satellite navigation positioning system is transferred from an earth-fixed coordinate system to an orbit coordinate system through coordinate transformation; the observation data after coordinate transformation is inputted to a Kalman filter, time update for the state quantity of the Kalman filter is carried out, and orbital element one-step forecast is acquired; measurement update for the state quantity of the Kalman filter is carried out by utilizing the observation data of the satellite navigation positioning system. The Kalman filtering method on the basis of a dynamic orbit model and the system are employed, being closer to practical modeling, switching among different orbit determination modes can be realized, demands of high precision real-time orbit determination and autonomous satellite navigation can be satisfied, and the method and the system can be applied to multiple types of satellite navigation positioning systems such as GPS, GLONASS, second-generation Beidou and GALILEO.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
Interstellar transfer finite thrust injection iterative guidance method of low thrust-weight ratio aircraft
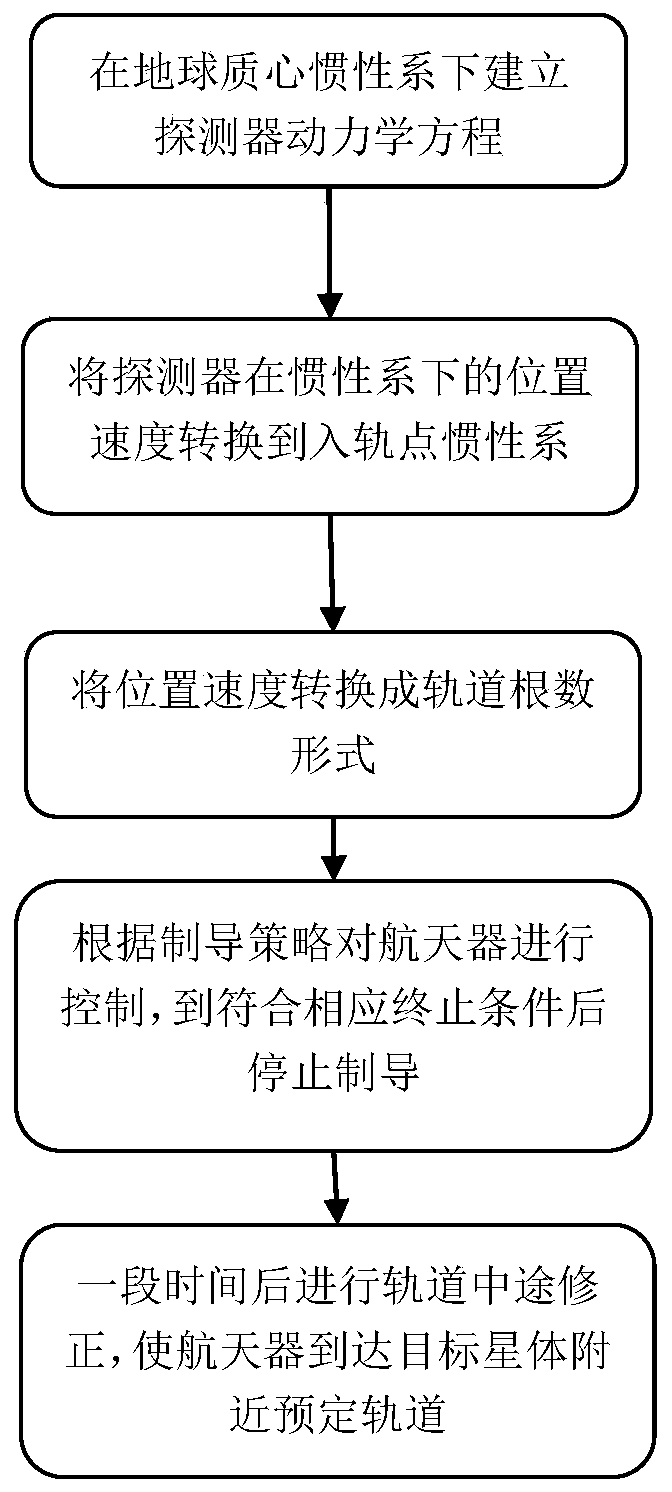
ActiveCN109911249ADirect transferLarge convergence rangeSpacecraft guiding apparatusAviationInjection point
The invention discloses an interstellar transfer finite thrust injection iterative guidance method of a low thrust-weight ratio aircraft, and belongs to the field of aerospace. The method comprises the steps of establishing a detector kinetic equation under an inertial system of center of mass of the earth; converting the location speed of a detector under the inertial system into an injection point inertial system, and expressing in an orbital element form. Simplifying the detector kinetic equation, controlling the detector according to a guidance strategy, and stopping the guidance when theguidance meets a corresponding terminal condition, then the detector enters an interstellar transfer orbit, and direct transfer of the detector from a near-earth orbit to the interstellar transfer orbit is realized, wherein the corresponding terminal condition is that an engine of the detector meets a power-off condition to establish the detector kinetic equation, solving midcourse correction pulse according to a shooting equation, and performing orbit midcourse correction, so as to enable the detector to reach a target orbit near a target star, so that accurate interstellar transfer with thelow thrust-weight ratio is realized. The interstellar transfer finite thrust injection iterative guidance method of the low thrust-weight ratio aircraft has the advantages of fast calculation speed, good convergence and high applicability.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
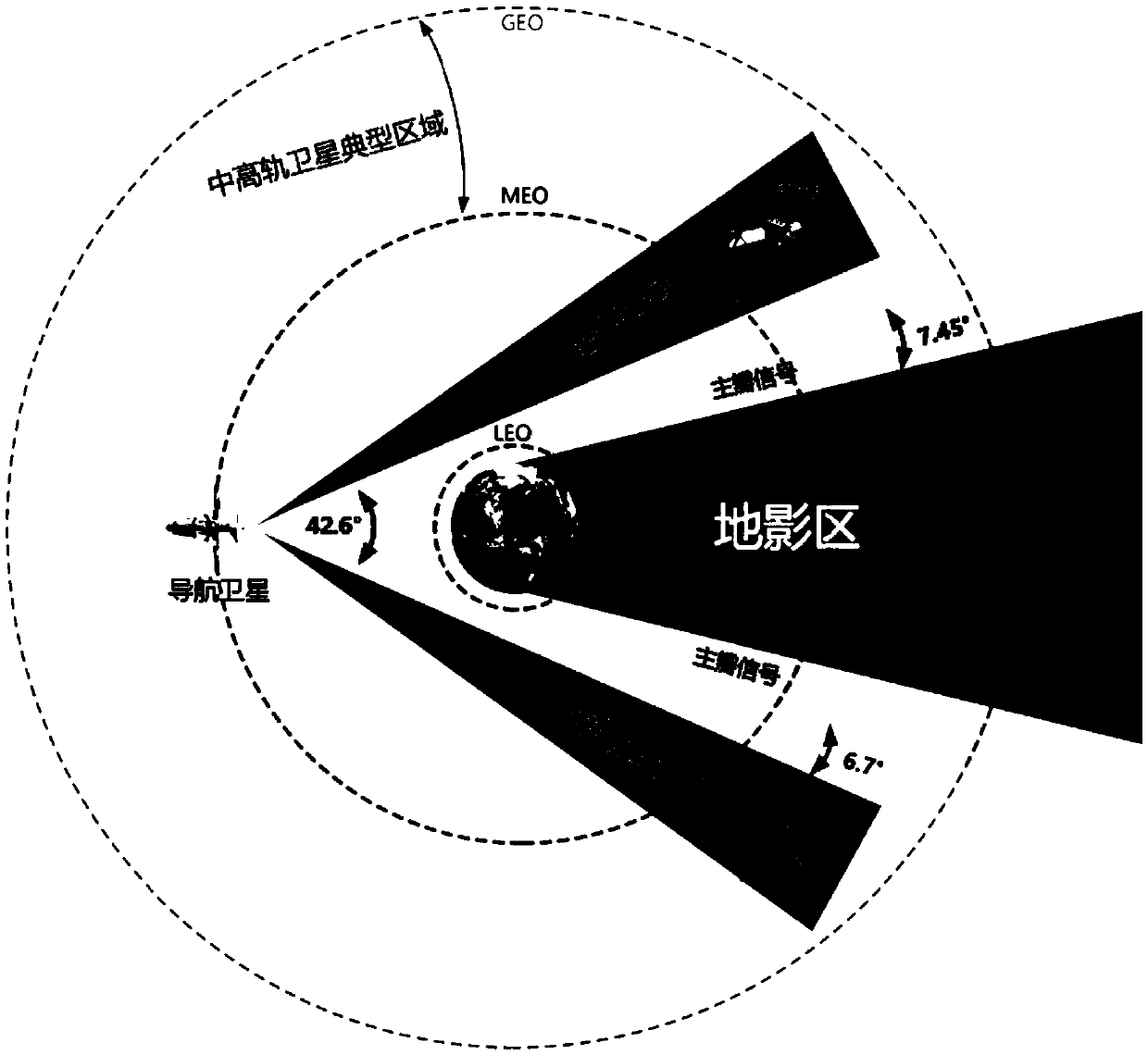
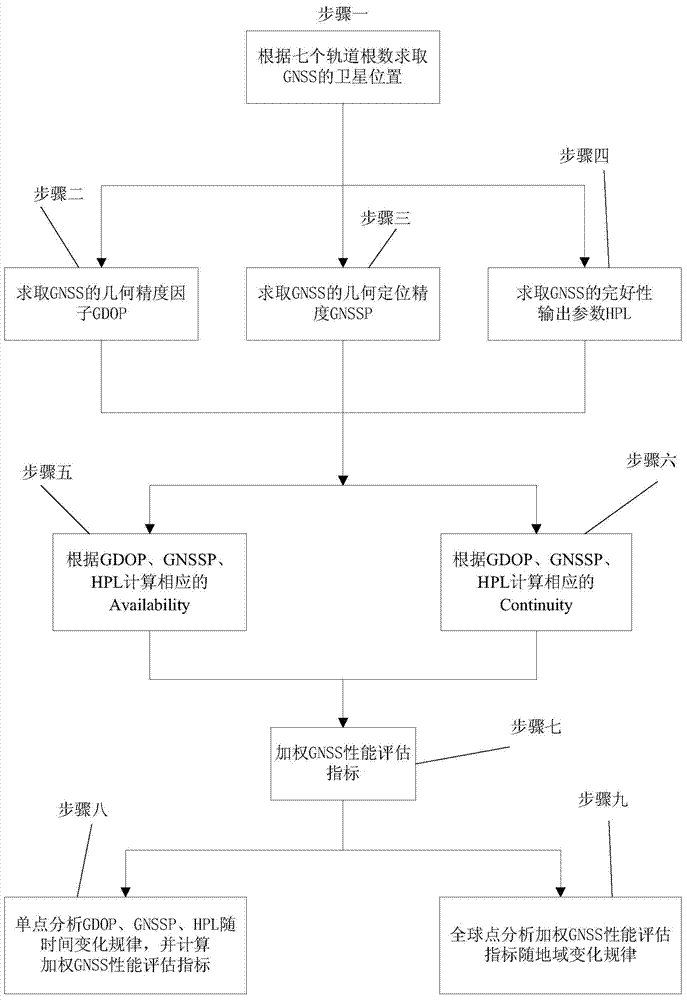
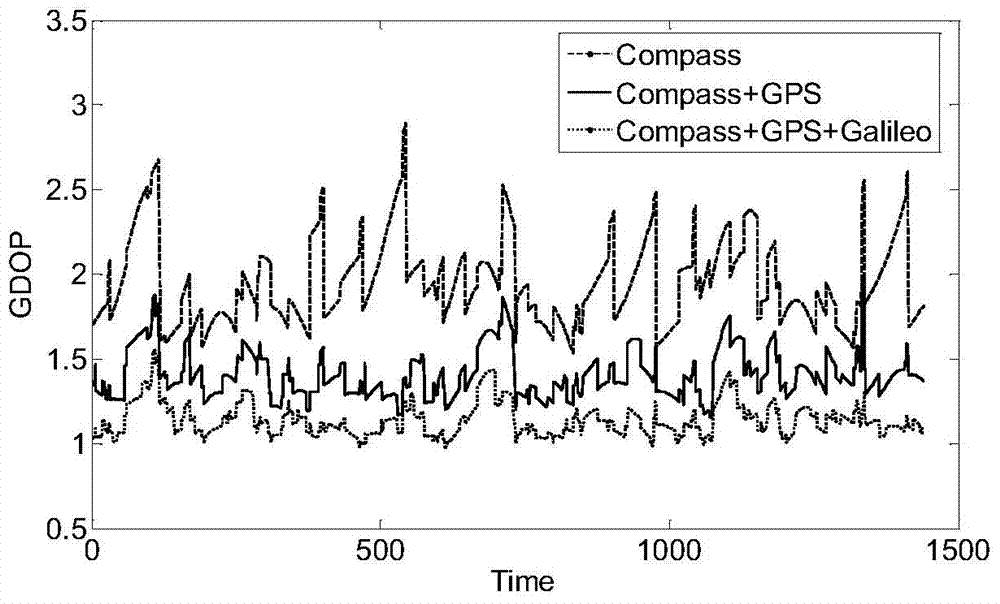
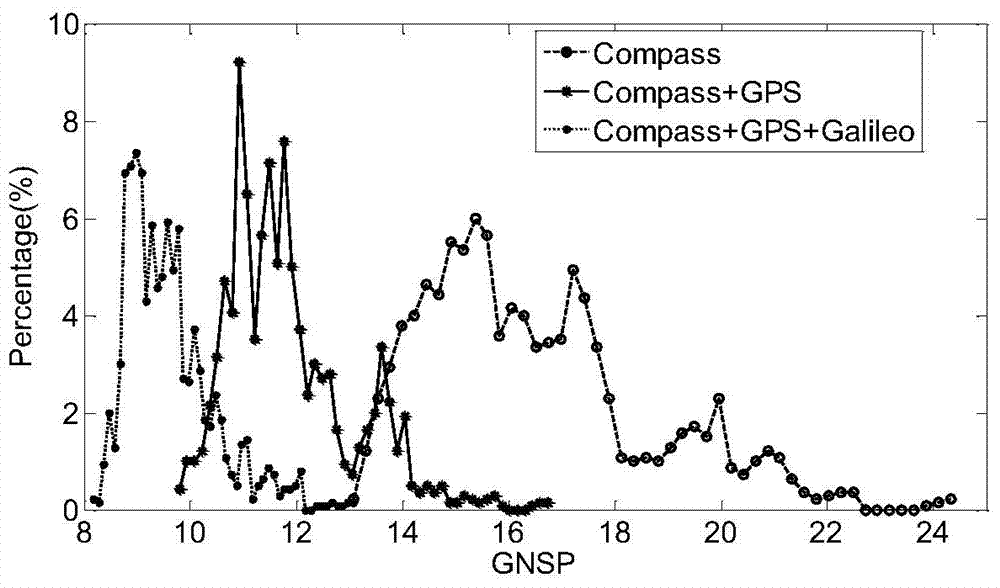
Assessment method for GNSS interoperability
InactiveCN103901443AFlat curveSmall range of variationSatellite radio beaconingEnvironmental resource managementUsability
The invention relates to an assessment method for GNSS interoperability, and belongs to the field of satellite navigation systems. The assessment method includes the steps that the position of a GNSS satellite is calculated according to an orbital element, the geometric dilution of precision (GDOP) of the GNSS satellite is calculated, geometric positioning of precision (GNSSP) of a GNSS is calculated, the integrity output parameter horizontal protection level (HPL) is calculated, usability of GNSS performance assessment parameters and continuity of the GNSS performance assessment parameters are calculated, weighted GNSS performance assessment indexes are calculated, single-point assessment interoperability is selected, and global-point assessment interoperability is selected. Along with the increase of the number of systems, the value of GNSSP probability density distribution central point is smaller, and distribution is more centralized.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
GEO target multipoint preferred short arc orbit determination method based on space-based optical observation data
ActiveCN111551183AHigh precisionImprove stabilityInstruments for comonautical navigationObservation dataRadar
The invention discloses a GEO target multi-point preferred short arc orbit determination method based on space-based optical observation data. The GEO target multi-point preferred short arc orbit determination method is an orbit determination scheme with high robustness and high precision for GEO target short arcs of the space-based optical observation data. The specific technical scheme is as follows, the method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out short-arc orbit determination on angle measurement numbers of any two points based on GEO target orbit near-circle hypothesis; andthen carrying out orbit selection by utilizing the residual first-order variation of the observation data sequence, finally converting a plurality of groups of optimized orbit elements into a position vector and a speed vector, and carrying out merging processing to obtain a high-precision and steady GEO target short arc orbit determination result. The scheme is a GEO target high-stability and high-precision short-arc orbit determination method suitable for space-based optical observation data, and can be expanded and applied to the field of short-arc orbit determination of global high-orbitand low-orbit targets by space-based foundation optics and radars.
Owner:NO 63921 UNIT OF PLA
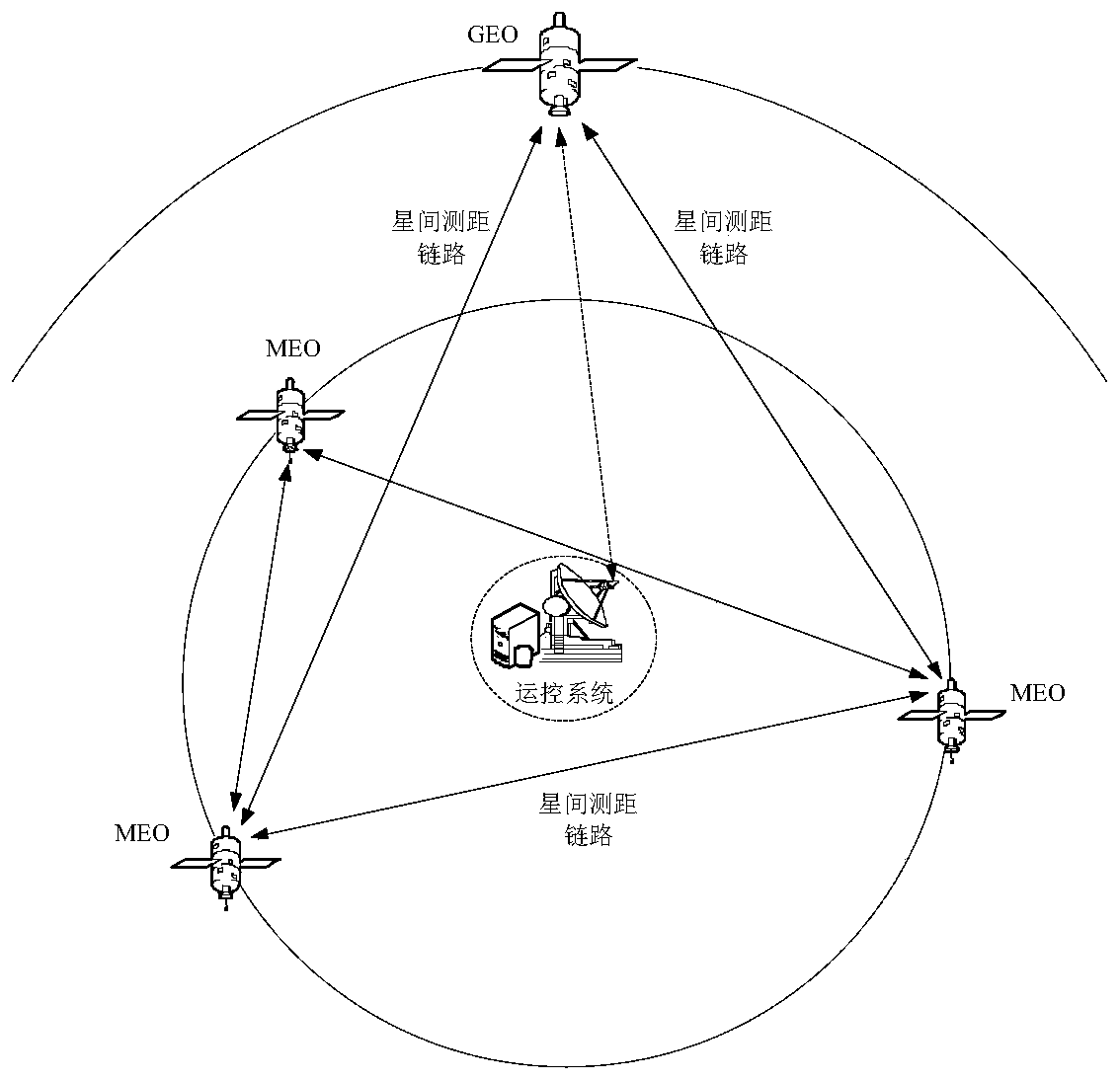
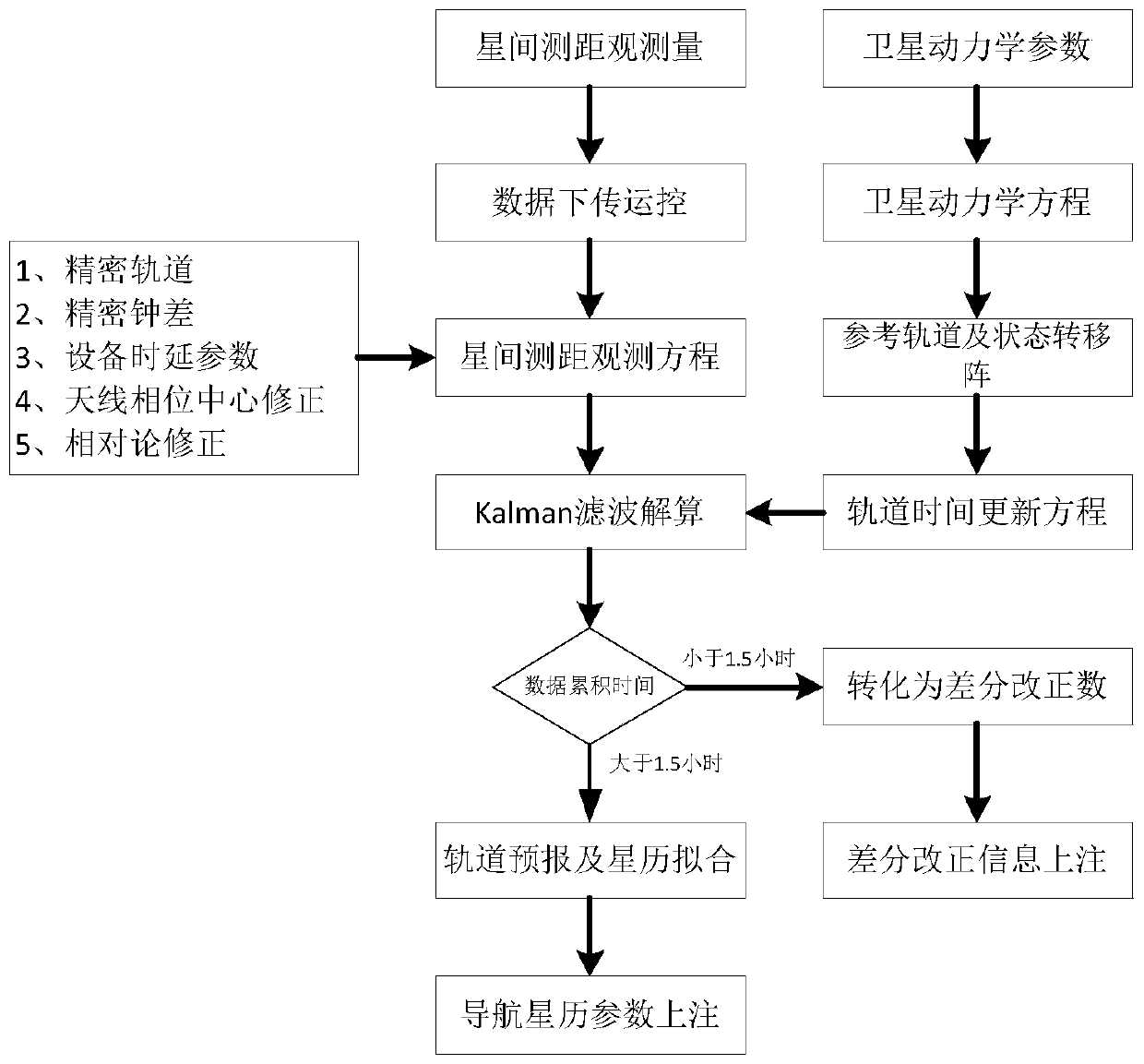
Method for realizing rapid recovery of GEO satellite after maneuvering through inter-satellite measurement
ActiveCN110426720AObservation accuracy is excellentImprove orbit accuracySatellite radio beaconingHigh level techniquesDynamic modelsObservation data
The invention provides a method for realizing rapid recovery of a GEO satellite after maneuvering through inter-satellite measurement. Inter-satellite bidirectional ranging observation data between the GEO satellite and a configurable chain Beidou satellite can be obtained by utilizing an inter-satellite link load; a non-maneuverable Beidou satellite orbit serves as a reference, an orbit determination observation equation is established by utilizing the inter-satellite ranging observation amount between the non-maneuverable Beidou satellite orbit and the GEO satellite, and a satellite state time updating equation can be built by utilizing an orbit dynamics model of the GEO satellite after maneuvering; the observation equation and the satellite state time updating equation are used, the sixnonsingular orbital elements serve as to-be-estimated parameters, a precise orbit of the GEO satellite after maneuvering is obtained, and by using the improved orbit, satellite position information of the GEO satellite after maneuvering is obtained through an upper injection differential correction mode or an orbit forecast and navigation ephemeris parameter fitting mode. The method effectively shortens the time of Beidou GEO satellite navigation positioning service interruption caused by orbital maneuvering, and improves the continuity and availability of services of a satellite navigation system.
Owner:中国人民解放军61540部队
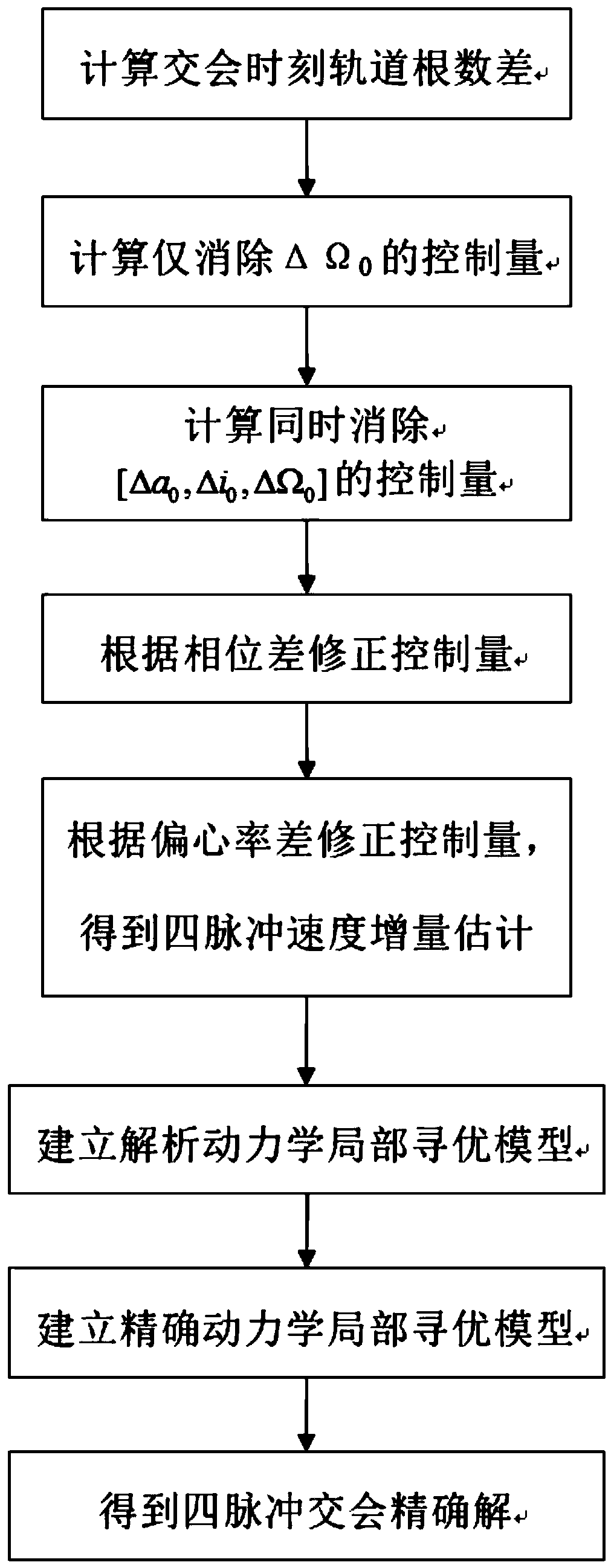
Perturbation orbit four-pulse intersection rapid optimization method
The invention discloses a perturbation orbit four-pulse rendezvous rapid optimization method, which comprises: according to known conditions of a spacecraft and a target, obtaining a control quantityand a minimum speed increment through a control model taking elimination of an orbit element difference at a rendezvous moment as an optimization result; establishing a four-pulse rendezvous optimization model according to the control quantity and the speed increment, taking the values of the moments and the sizes of the first two pulses in the neighborhood according to the estimated values in theabove steps, and recalculating the last two pulses according to the actual orbit recursion result; and replacing the analytic perturbation kinetic model with a full-perturbation accurate kinetic model, taking the optimal solution of the analytic kinetic model as an initial value, and solving again to obtain a four-pulse intersection optimal solution under the accurate kinetic model. The problemsof low calculation speed and the like in the prior art are solved, and calculation efficiency is improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
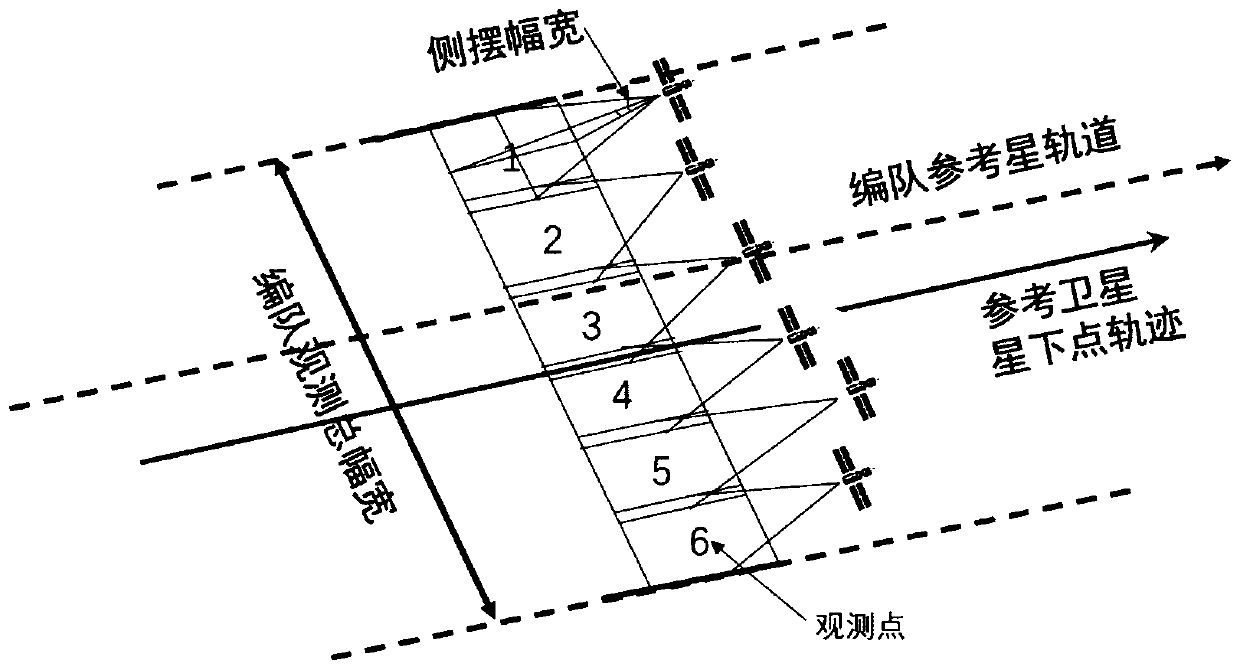
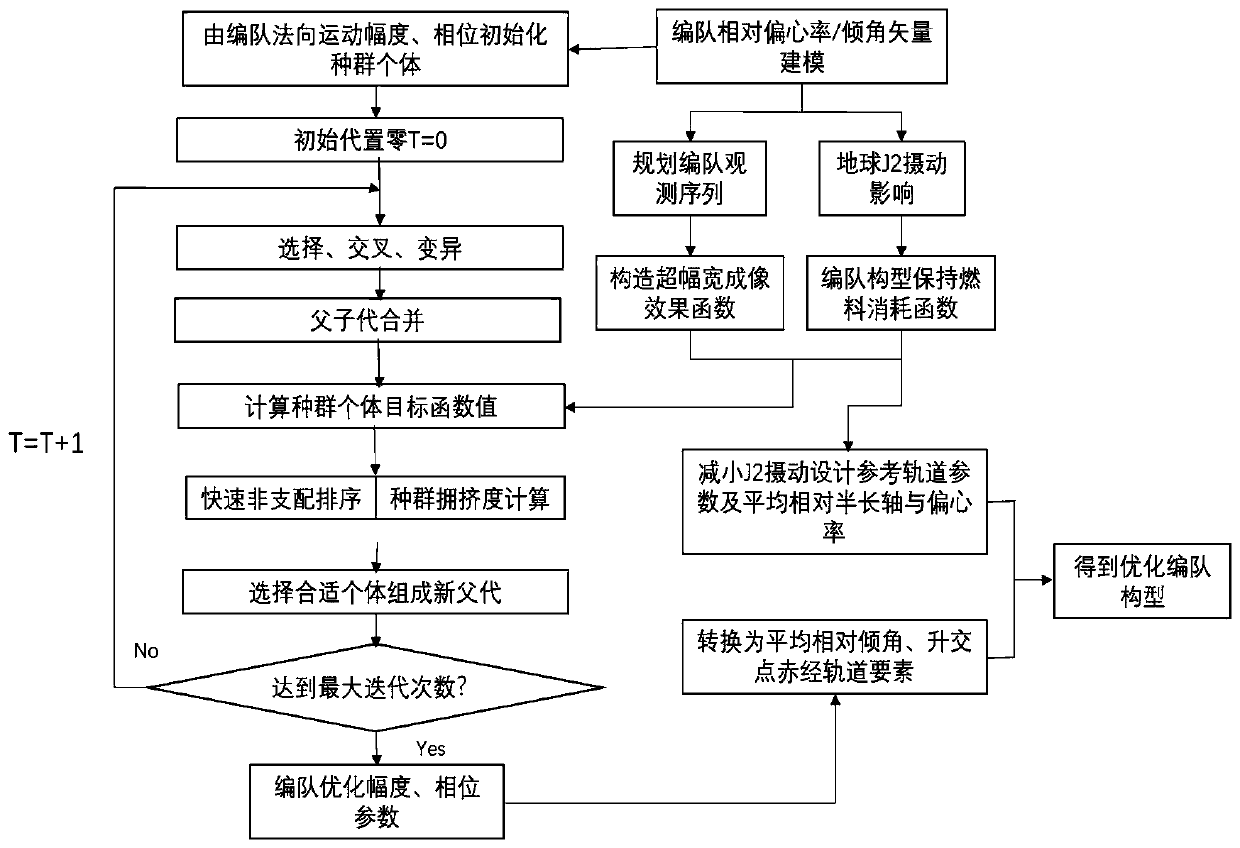
NSGAII-based optimization method for super-width imaging satellite formation configuration
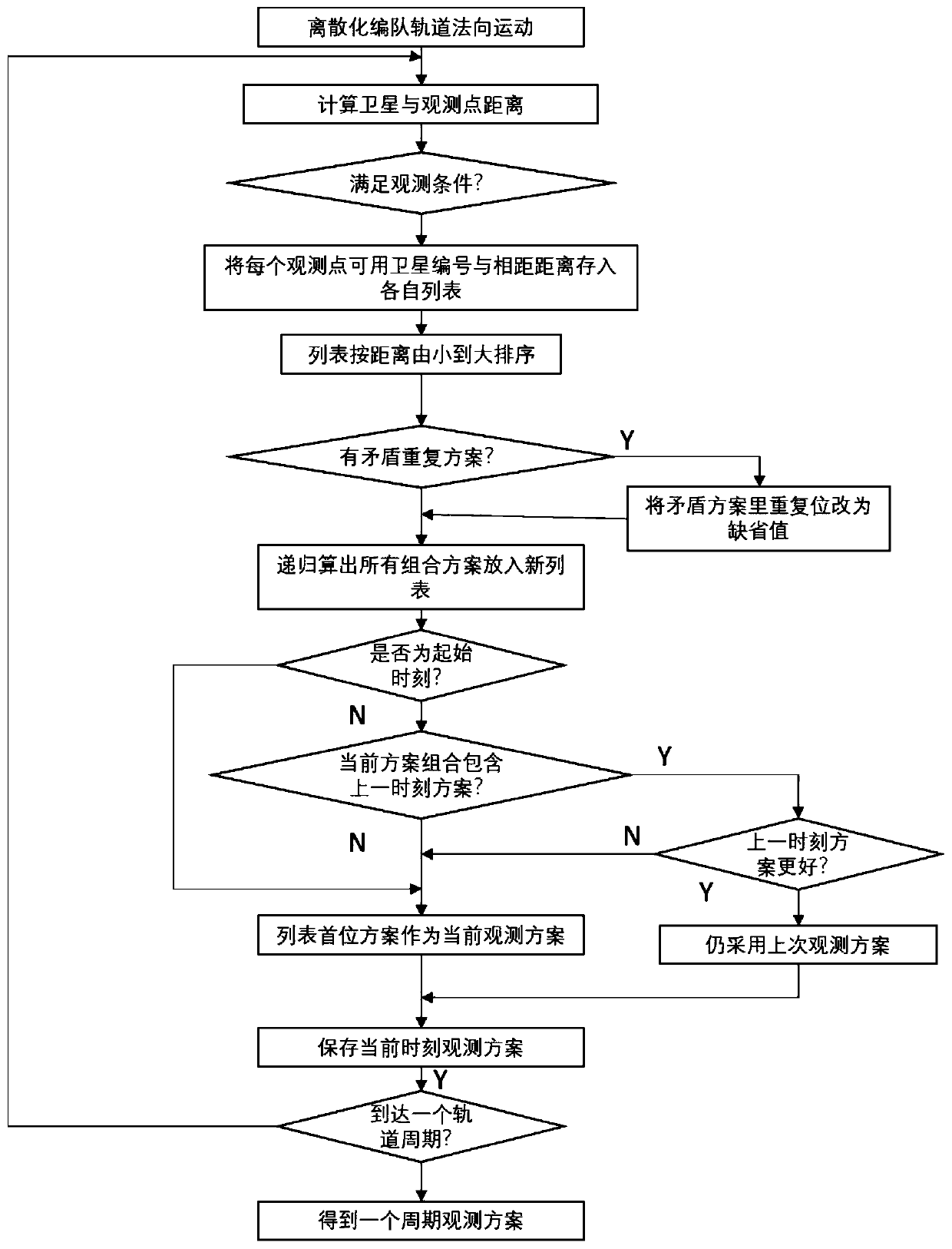
ActiveCN110096069AStable Observation Width EffectPosition/course control in three dimensionsSatellite observationRelative motion
The invention discloses an NSGAII-based optimization method for super-width imaging satellite formation configuration, which relates to super-width imaging satellite formation design, and belongs to the technical field of control and regulation. The NSGAII-based optimization method comprises the steps of: firstly, utilizing a relative eccentricity / inclination vector method for modeling relative motions of formation spacecrafts; secondly, considering an influence of the Earth J2 perturbation on relative orbital elements of formation, and deducing fuel consumption required to compensate for theperturbation influence; thirdly, planning a formation satellite observation task sequence through carrying out discretization on the formation satellite observation process, and further constructing an objective function for evaluating the super-width imaging effect; and finally, acquiring the satellite formation configuration considering fuel consumption and the super-width imaging effect by adopting an NSGAII algorithm. The NSGAII-based optimization method has effective algorithm, aims at the multi-objective optimization problem of reducing the fuel consumption required for maintaining the formation pattern and improving the super-width imaging observation effect, and realizes the optimal design of the satellite formation configuration.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Classical orbit three-dimensional spatial relationship construction method based on OSG three-dimensional engine
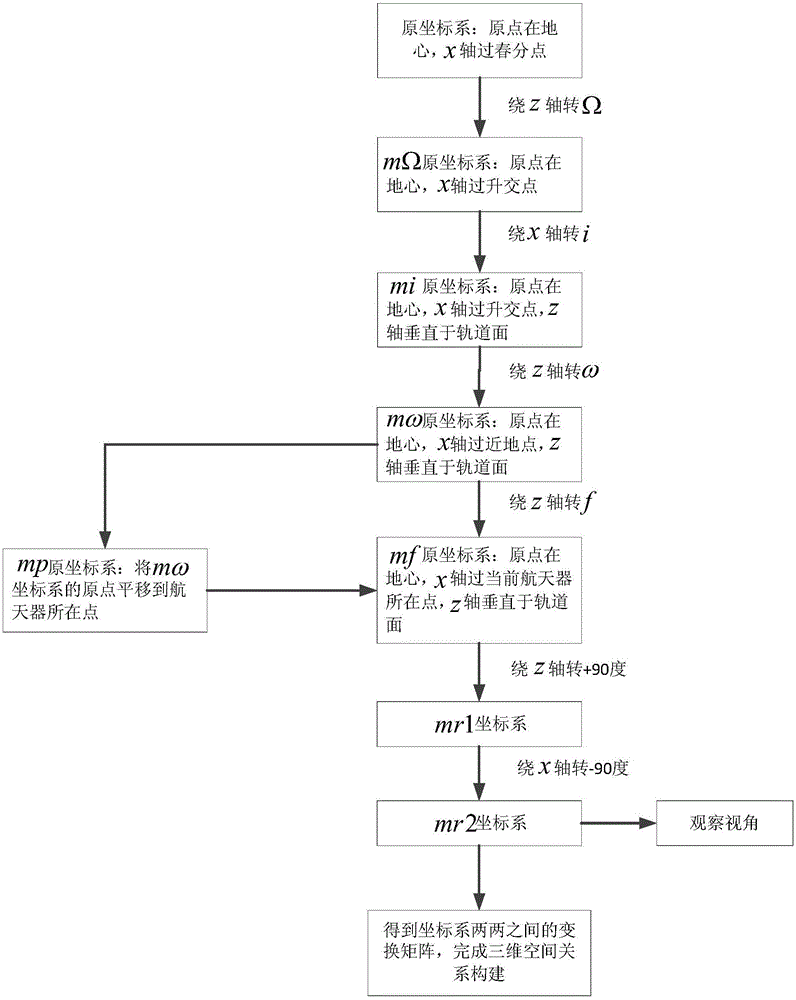
ActiveCN105035371ASolve the display effectResolving orbital radicals requires a secondary transformationCosmonautic condition simulationsSpecial data processing applicationsAxis–angle representationAngular degrees
The invention discloses a classical orbit three-dimensional spatial relationship construction method based on an OSG three-dimensional engine. Spatial relationships are directly established based on six elements of an orbital system, and geometrical angle changing processes of the right ascension of an ascending node, the orbit inclination, the perigee argument and the true anomaly can be dynamically displayed. An orbital element parameter representation process is based on the space geometry relationships, and satellite visual angle tracking and position calculation are not subjected to secondary coordinate transformation. The orbital elements can be visually displayed, and an orbital system (VVLH) visual angle positioning problem under a traditional model is solved by the introduction of two layers of new coordinate systems. Four attitude input interfaces of matrixes, Euler angles, Euler axial angles and the quaternion of a relative orbital system are provided by a spacecraft, and the spacecraft body axis and the orbit axis are displayed and customized through the spacecraft, the analysis of the correctness of the in-orbit attitude of the spacecraft is facilitated, and problems that the orbital elements cannot be visually displayed, the orbital elements need the secondary transformation, the attitude adjustment and visual angle adjustment of the orbital system require additional data, and the position and orientation of the spacecraft cannot be accurately displayed are solved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Stationary satellite imaging yaw guidance angle calculating method
ActiveCN108710379AImproving Imaging AccuracyImprove stabilityCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsNatural satelliteInertial coordinate system
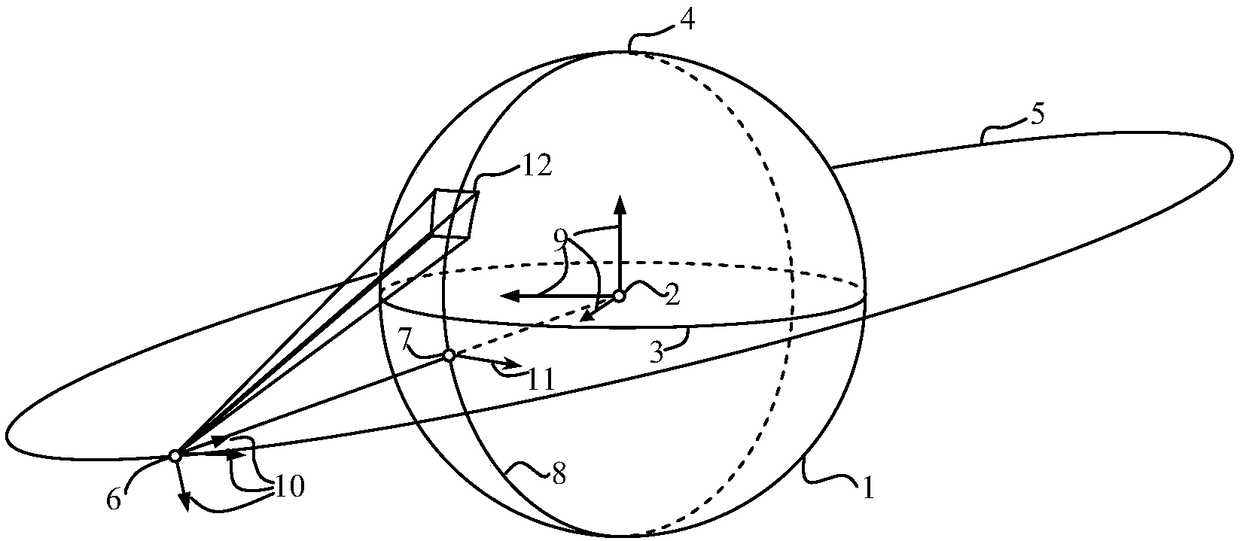
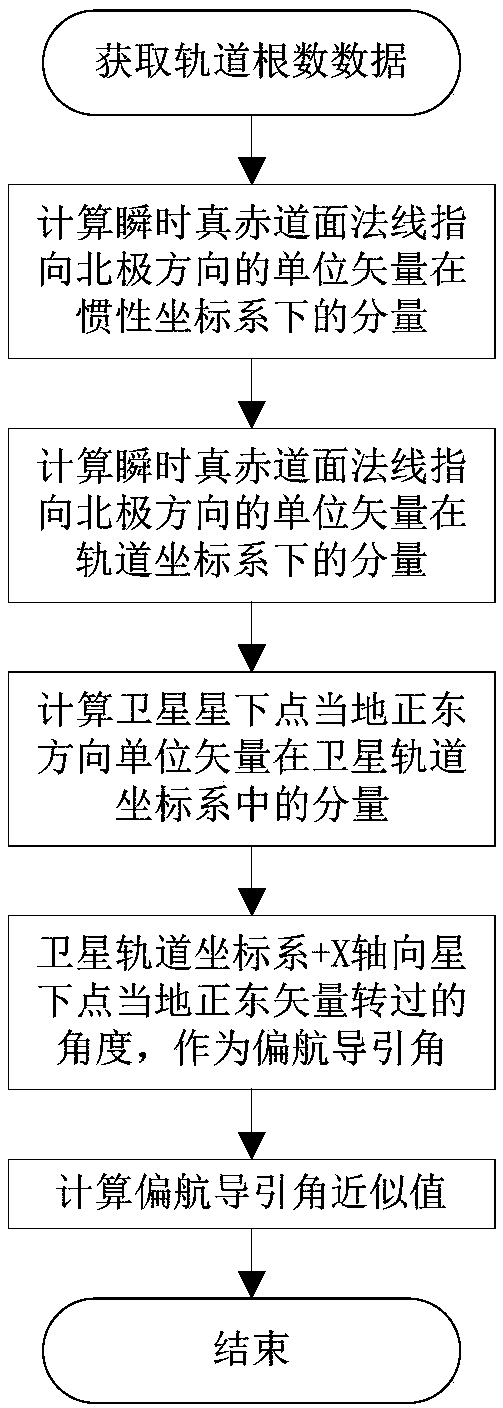
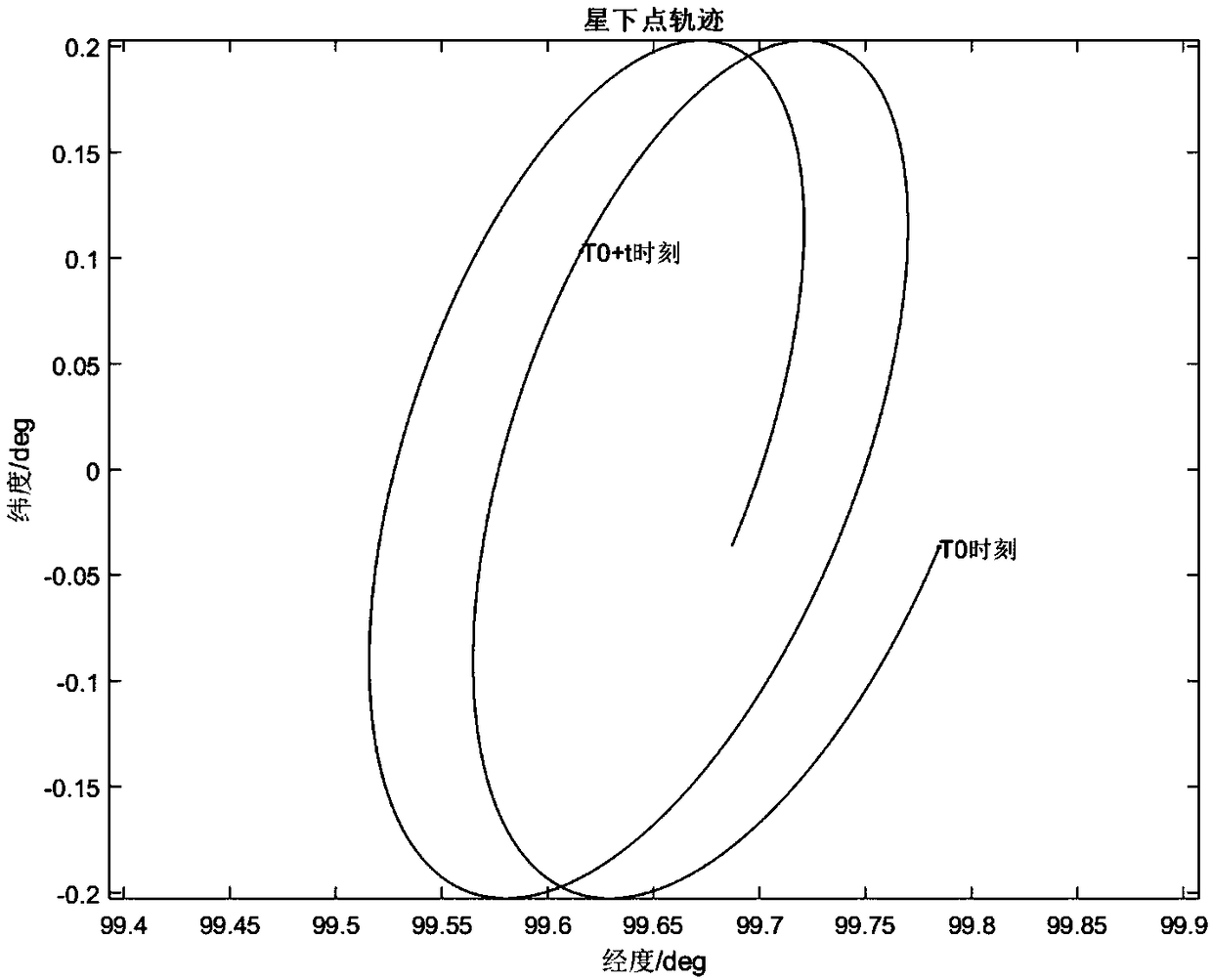
The invention discloses a stationary satellite imaging yaw guidance angle calculating method. The stationary satellite imaging yaw guidance angle calculating method comprises the following steps: calculating a component of a unit vector pointing to a north pole direction, of an instant true equatorial plane normal in an inertial coordinate system according to an earth reference system transformation relationship; calculating a component of the unit vector pointing to the north pole direction, of the instant true equatorial plane normal in an orbital coordinate system according to the satelliteinstantaneous orbit elements; calculating a component of a unit vector in the local due east direction, of a sub-satellite point of the satellite in a satellite orbital coordinate system; calculatingan angle at which the satellite orbital coordinate system + X-axis vector rotate to the local due east vector of the sub-satellite point as a yaw guide angle; and ignoring a second-order small amountwhen the dip angle is small, and calculating a yaw guidance angle approximate value. The invention can eliminate the imaging rotation caused by the orbital deviation and the earth motion through theyaw attitude guiding control, and ensure that the reference of a remote sensing instrument is parallel to the local geographic orientation of the sub-satellite point, thereby improving the imaging precision and stability of the stationary remote sensing satellite.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST +1
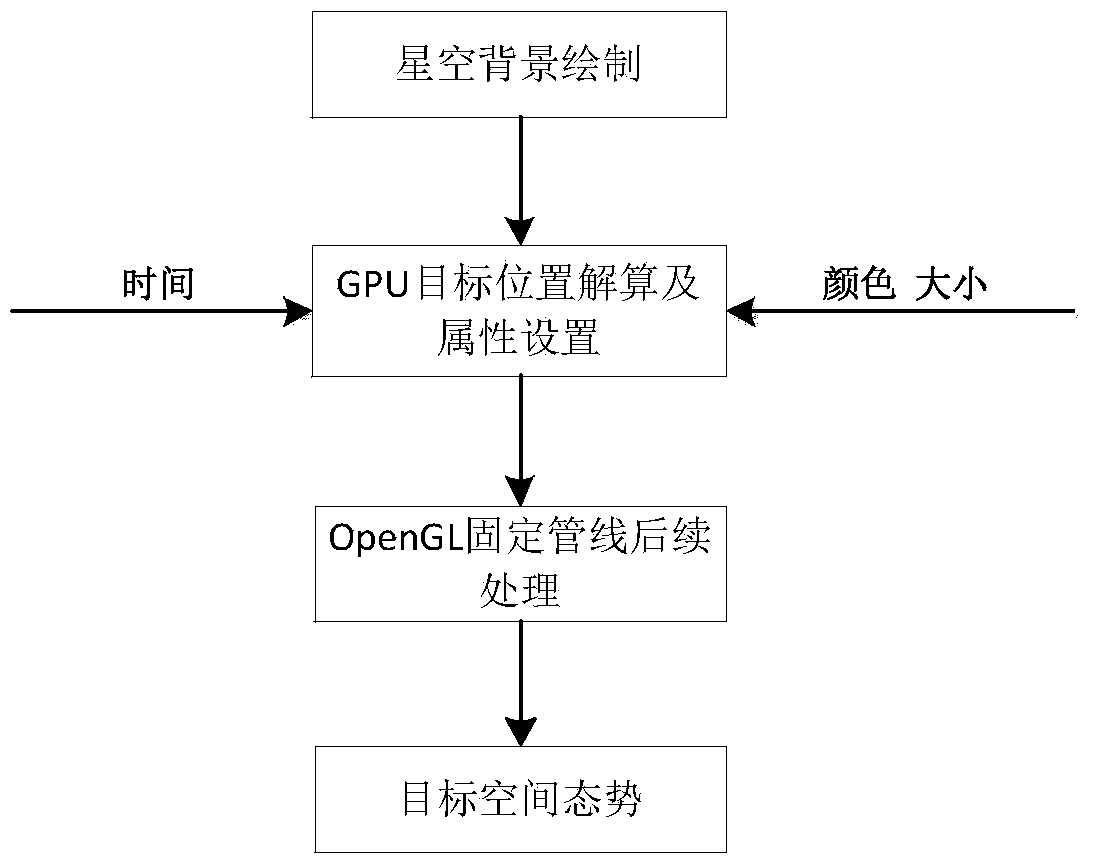
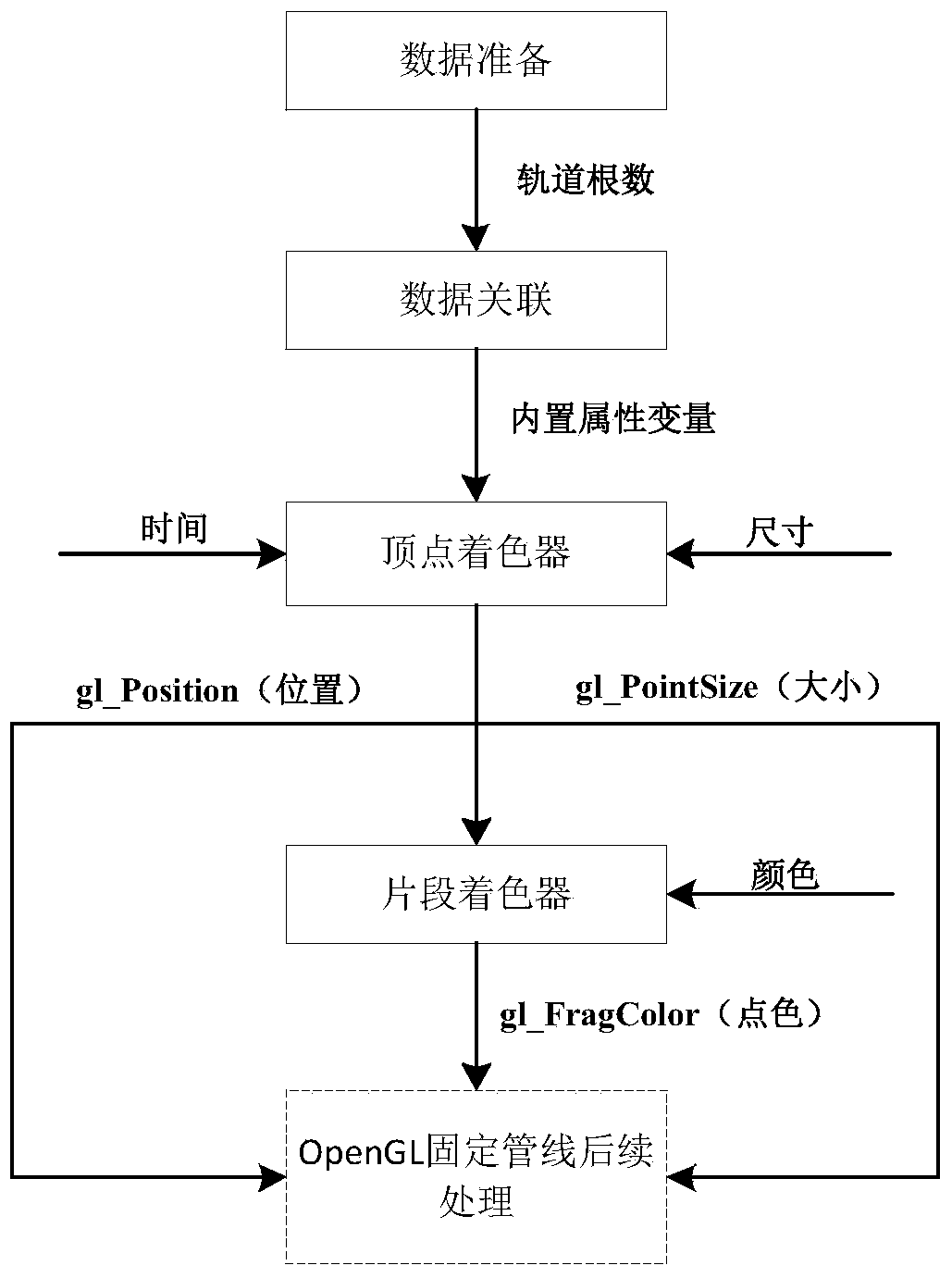
A space target real time simulation method
ActiveCN103679780AThe acceleration effect is obviousImprove real-time performanceAnimationReal-time simulationSky
The invention relates to a space target real time simulation method, and belongs to the technical field of spaceflight simulation. According to the method, firstly, a visualized star sky background is constructed; then through the combination with orbital elements of space targets, and via a programmable processor, high speed resolving and drawing of positions, sizes and colors are completed; and finally, through the combination with viewpoint positions and user clipping information, generation of a space situation in a target direction is completed. According to the invention, characteristics of parallel processing and high precision floating point computing of a GPU is fully utilized; the acceleration effect is obvious; the real-time performance is good; and a reliable means is provided for real time simulation of the targets in space situation expression.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
Free trajectory construction method for specifying launching elevation angle
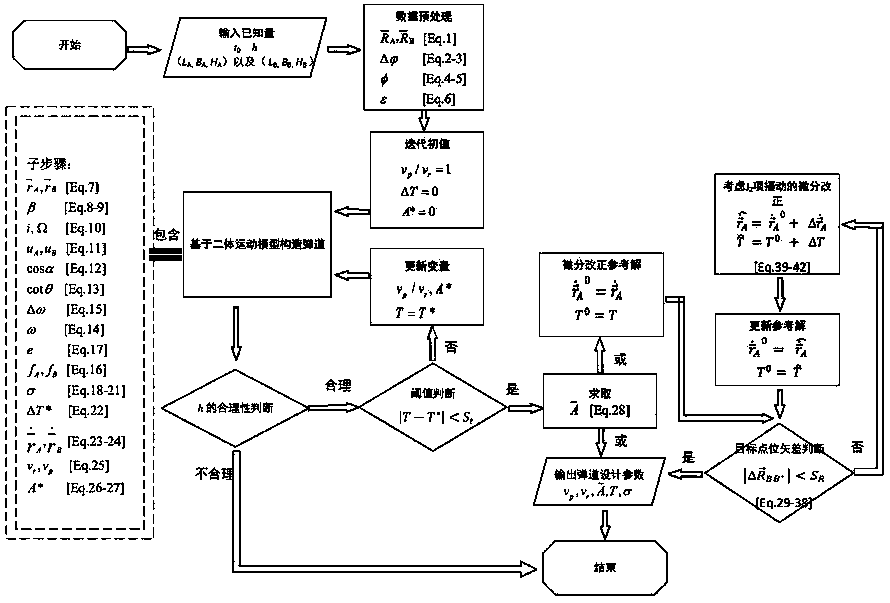
ActiveCN110609972AEnsure reliabilityEnsuring Computational EfficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingElevation angleRectangular coordinates
The invention discloses a free trajectory construction method with a specified launching elevation angle. The method comprises the steps of firstly, orderly calculating the earth-fixed rectangular coordinate vectors of a launching point and a target point, the difference between the earth latitude and the geocentric latitude, a horizontal included angle and the difference between the ratio of geocentric radial modes of the point A and the point B and 1; solving the variables, such as the launching speed of a forward trajectory or a reverse trajectory in an orbit coordinate system, the launching speed of the forward trajectory or the reverse trajectory in an earth-fixed coordinate system, the number sigma of trajectories / orbits, flight time and the like in the iterative initial state and the two-body motion model, wherein the newly solved flight time is T *; enabling T to be equal to T *, repeatedly iteratively calculating the launching speed of the missile and the like, ending iteration until the absolute value of (T-T *) is smaller than a set threshold St, finally obtaining the launching speed and flight time T of the missile under the two-body motion model, and outputting the design parameters vp, vr, T and sigma. According to the present invention, the forward trajectory and the reverse trajectory can be constructed at the specified launching elevation angles under a two-body motion model and a kinetic model considering the J2 perturbation of an earth gravitational field respectively, and then all trajectories from the launching points to the target points are obtained by traversing the launching elevation angles.
Owner:ZIJINSHAN ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Apogee ignition high-precision analytical orbit autonomous prediction method
ActiveCN105334731AAccurate calculationReduce calculation errorsAdaptive controlSynchronous orbitEngineering
The invention relates to an apogee ignition high-precision analytical orbit autonomous prediction method. Orbit information of each phase of a transfer orbit including apogee ignition can be accurately calculated. The second type of nonsingular orbital elements are selected for recurrence so as to be suitable for the situations of small orbit inclination angles and low eccentricity. Therefore, the apogee ignition high-precision analytical orbit autonomous prediction method is also suitable for orbit calculation of each phase of a synchronous orbit and has great significance.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Asteroid orbit identifying method based on observation angle data
ActiveCN104792299AEliminate distractionsSimple methodAngle measurementLinear/angular speed measurementEarth satelliteNatural satellite
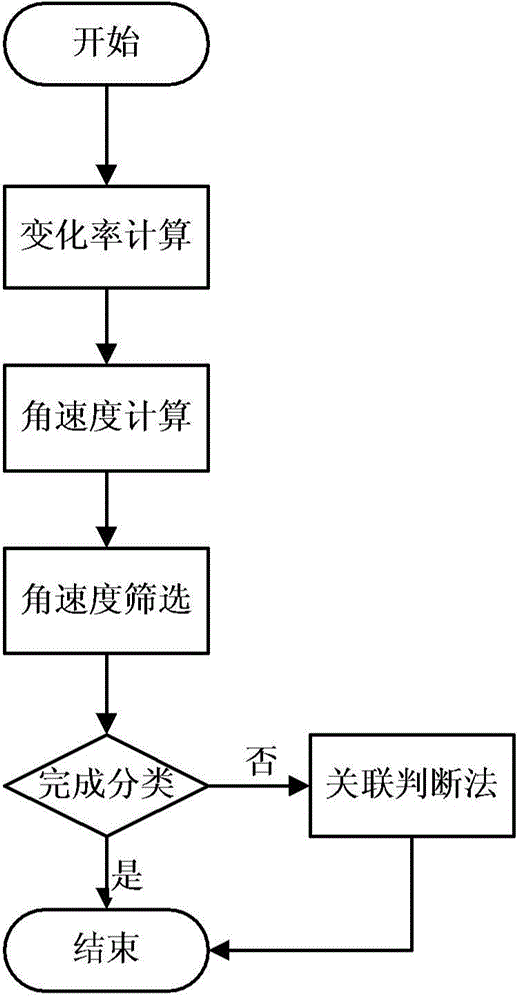
The invention discloses an asteroid orbit identifying method based on observation angle data. The method comprises steps as follows: calculation of the change rate, that is, calculation of the observation angle data along with the time change rate; calculation of the angular velocity; screening of the angular velocity: the angular velocity of a current observation arc section is compared with a given threshold, and whether data of the section belong to an asteroid or a man-made earth satellite or are undetermined is judged preliminarily; correlation judgment: observation forecast is performed by using orbit elements of the catalogued man-made earth satellite, theoretically calculated values and measured values of all observation epochs are compared, if the error is small enough, the arc section is judged to belong to the man-made earth satellite, and otherwise, the arc section belongs to the asteroid. The method is convenient and easy to implement, can be applied to multiple research fields related to astronomical observation as well as quick recognition of near-earth asteroids, and wins precious early warning and emergency time for follow-up work.
Owner:NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORIES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com