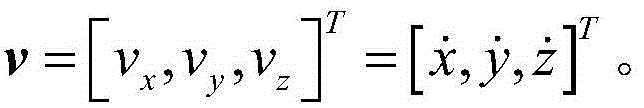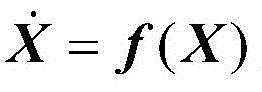Initial orbit determination method for deep space target celestial body based on space-based autonomous optical observation
A target celestial and optical technology, applied in the field of deep space exploration, can solve the problems of measurement delay, observation geometry difference, measurement discontinuity, and inability to accurately determine the orbit information of deep space targets in real time, achieving easy implementation and simple measurement scheme. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0038] In order to better illustrate the purpose and advantages of the present invention, the content of the invention will be further described below with reference to the accompanying drawings and examples.
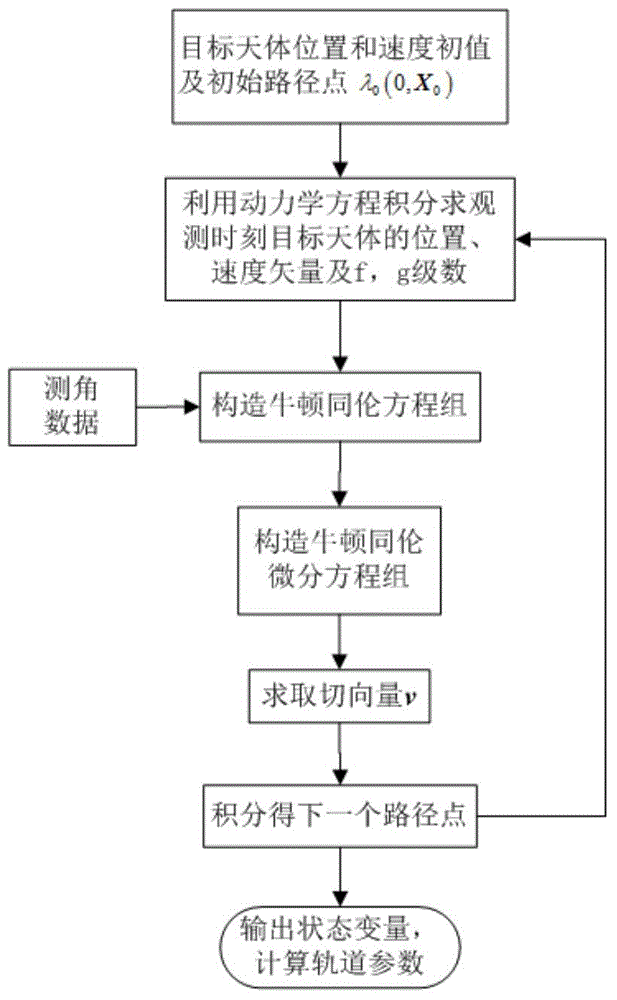
[0039] In this example, for the monitoring task of deep sky objects, an optical initial orbit determination scheme based on Newton homotopy is given. Combined with the angle measurement information of the optical navigation camera, the Newton homotopy path tracking algorithm is used to calculate the orbit information of the target celestial body, and realize High-precision initial orbit determination of deep-sky objects. The specific implementation method of this example is as follows:
[0040]Step 1: Connect the optical navigation camera to the detector. The detector is in orbit around the sun. The target celestial body is captured by the optical navigation camera, and the angle measurement information (right ascension β, Declination ε) is used to solve the position a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com