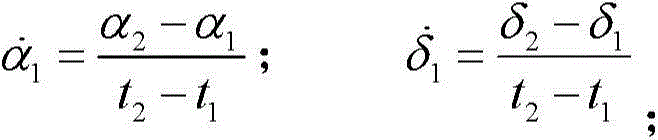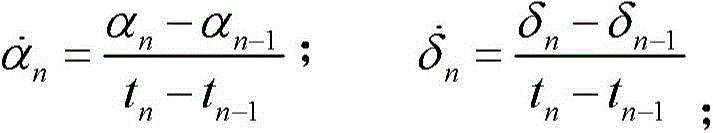Asteroid orbit identifying method based on observation angle data
A method of identification, a technology for asteroids, applied in directions such as measuring angles, measuring devices, mapping and navigation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] Select the observation data of asteroid numbered 53917 published on the website of the Small Planet Center (MPC) on February 20, 2014 (see Table 1), and take it as an example to identify, the steps are as follows.
[0075] In the following, YJD represents the number of days from January 1, 2000 in the observation epoch, lon represents right ascension, lat represents declination, and deg represents the unit of angle.
[0076] Table 1 Observation data of asteroid 53917
[0077] YJD
lon(deg)
lat(deg)
5163.74042
118.3713
32.24538
5163.74108
118.3711
32.24535
5163.75165
118.3695
32.24482
5163.75232
118.3694
32.2448
5163.7634
118.3677
32.24426
5163.76407
118.3676
32.24421
5163.77615
118.3657
32.24364
5163.77681
118.3656
32.24361
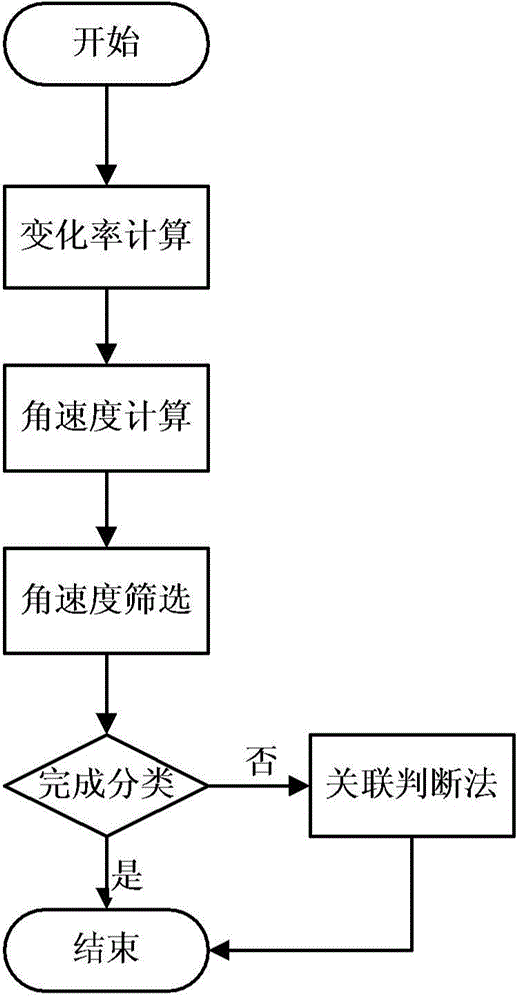
[0078] Step 1, calculate the rate of change of the observed quantity
[0079] The results are shown in T...
Embodiment 2
[0090] Select the asteroid numbered K06D14P published on the website of the Small Planet Center (MPC), and use the simulation software to simulate a period of observation data of the asteroid observed by an observatory in Beijing on February 9, 2014 (see Table 4). It is identified as an example, and the steps are as follows.
[0091] Table 4 Observation data of asteroid K06D14P
[0092] YJD
lon(deg)
lat(deg)
5155.15451
97.5240
-34.6077
5155.15799
97.5997
-34.5125
5155.16146
97.6751
-34.4175
5155.16493
97.7501
-34.3228
5155.16840
97.8247
-34.2283
5155.17188
97.8989
-34.1341
5155.17535
97.9727
-34.0402
5155.17882
98.0462
-33.9465
[0093] Step 1, calculate the rate of change of the observed quantity
[0094] The results are shown in Table 5. In the text, dlon represents the rate of change of right ascension, dlat represents the rate of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com