Time domain radio transmission system
a radio transmission system and time domain technology, applied in the field ofsignal transmission systems, can solve the problems of prolonging the length of a signal burst, adversely affecting the coupling of signals to the antenna, interfering with the signal radiated, etc., and achieve the effect of convenient frequency modulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
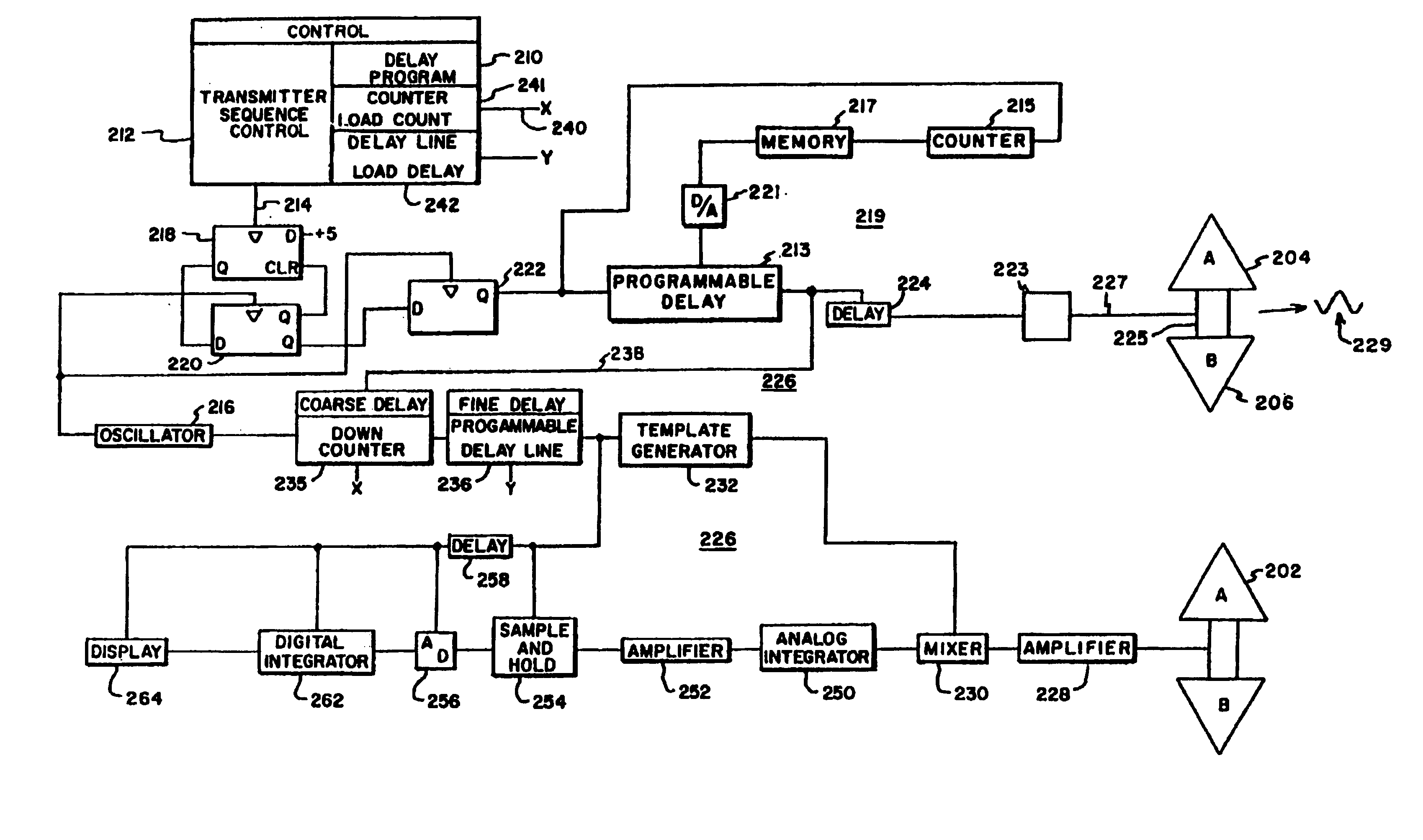
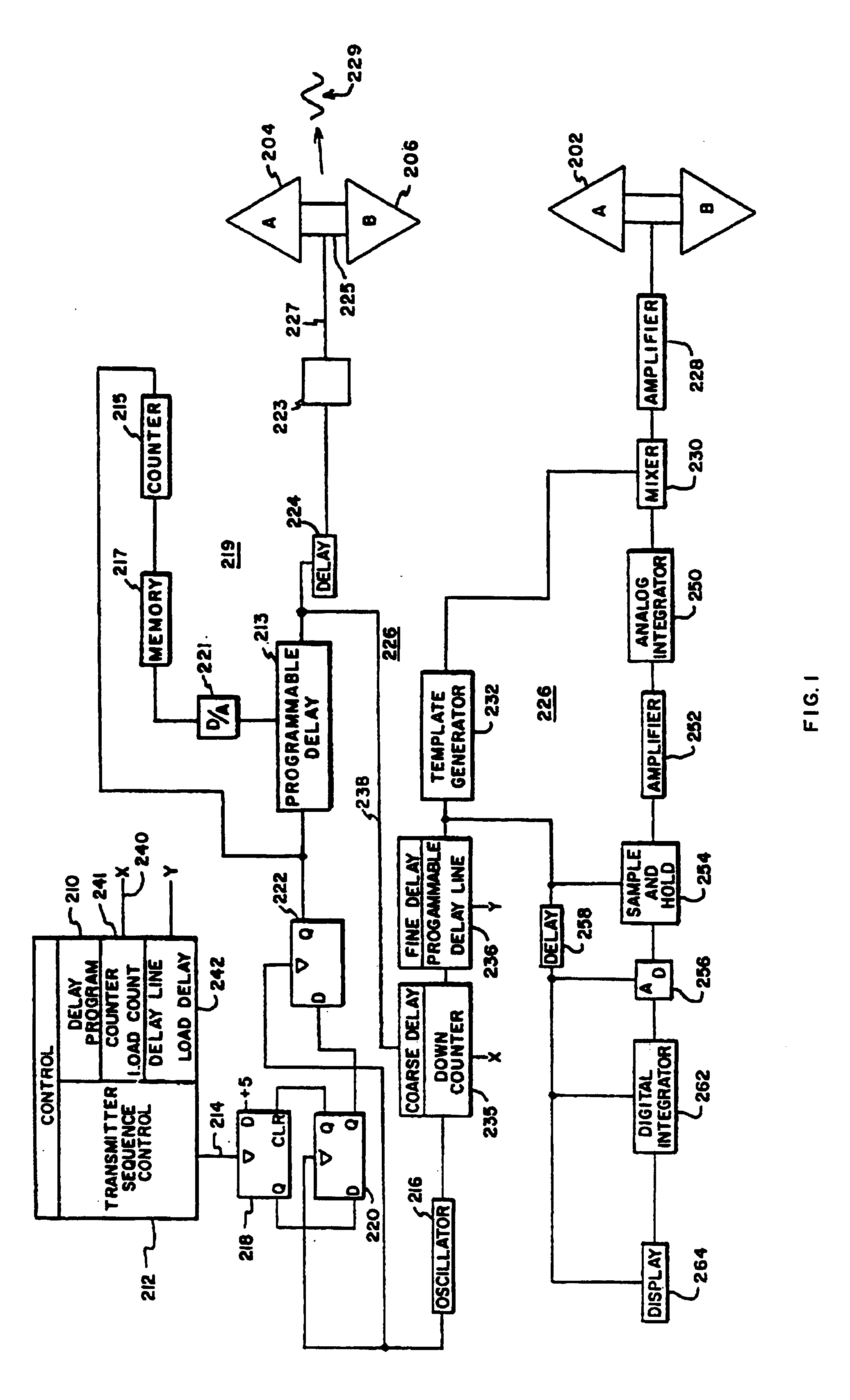
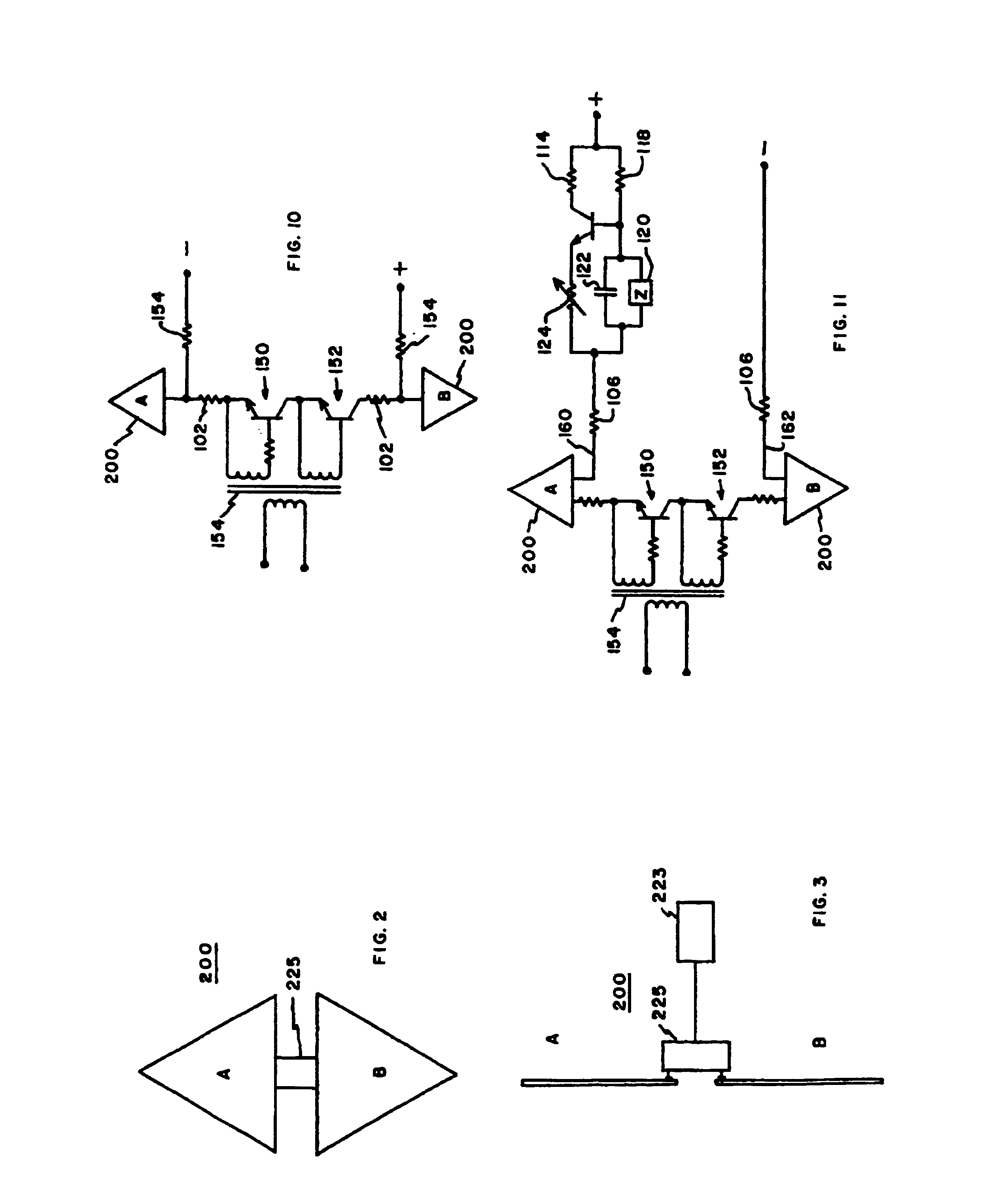
[0031]Referring to the drawings, FIG. 1 particularly illustrates a radar application of the present invention for determining range. Transmitting antenna 200 of transmitter 219 is a conformal reverse bicone, but flat, antenna having triangular elements A and B with closely spaced, 0,050 inches, bases. A dimension of an element normal to the base is approximately 4½ inches and is further discussed and illustrated in FIGS. 2 and 3. Typically, a reflector would be used as illustrated in FIG. 4.
[0032]The transmitter is basically controlled by control 210. It includes a transmit sequence control portion 212 which determines the timing of transmitted signal bursts, at, for example, 10,000 bursts per second, in which case transmit sequence control 212 generates an output at 10,000 Hz on lead 214. Oscillator 216 is operated at a higher rate, for example, 20 MHz.
[0033]The signal output of transmit sequence control 212 is employed to select particular pulse outputs of oscillator 216 to be the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com