Patents
Literature
203results about "Space shuttles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
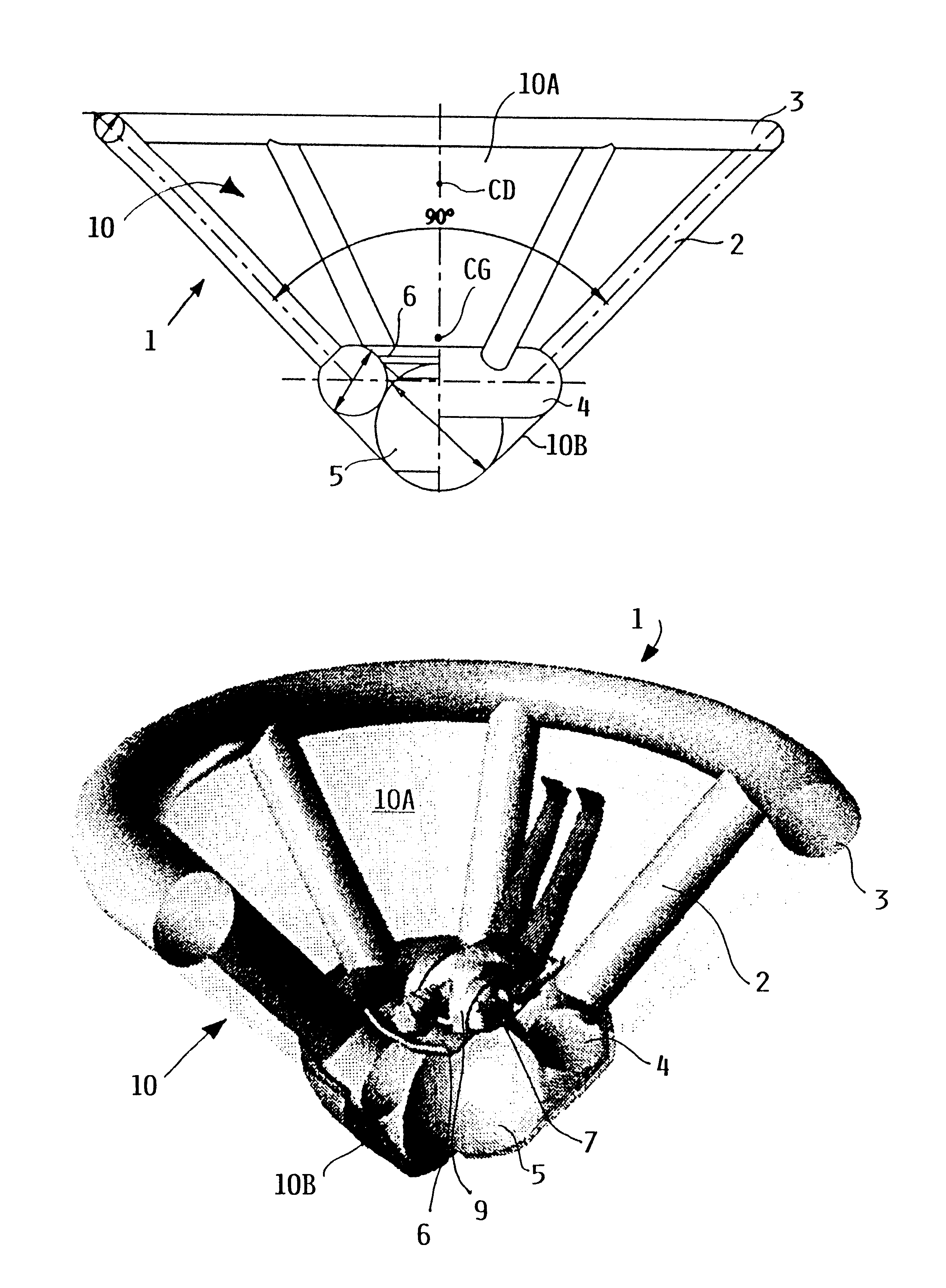
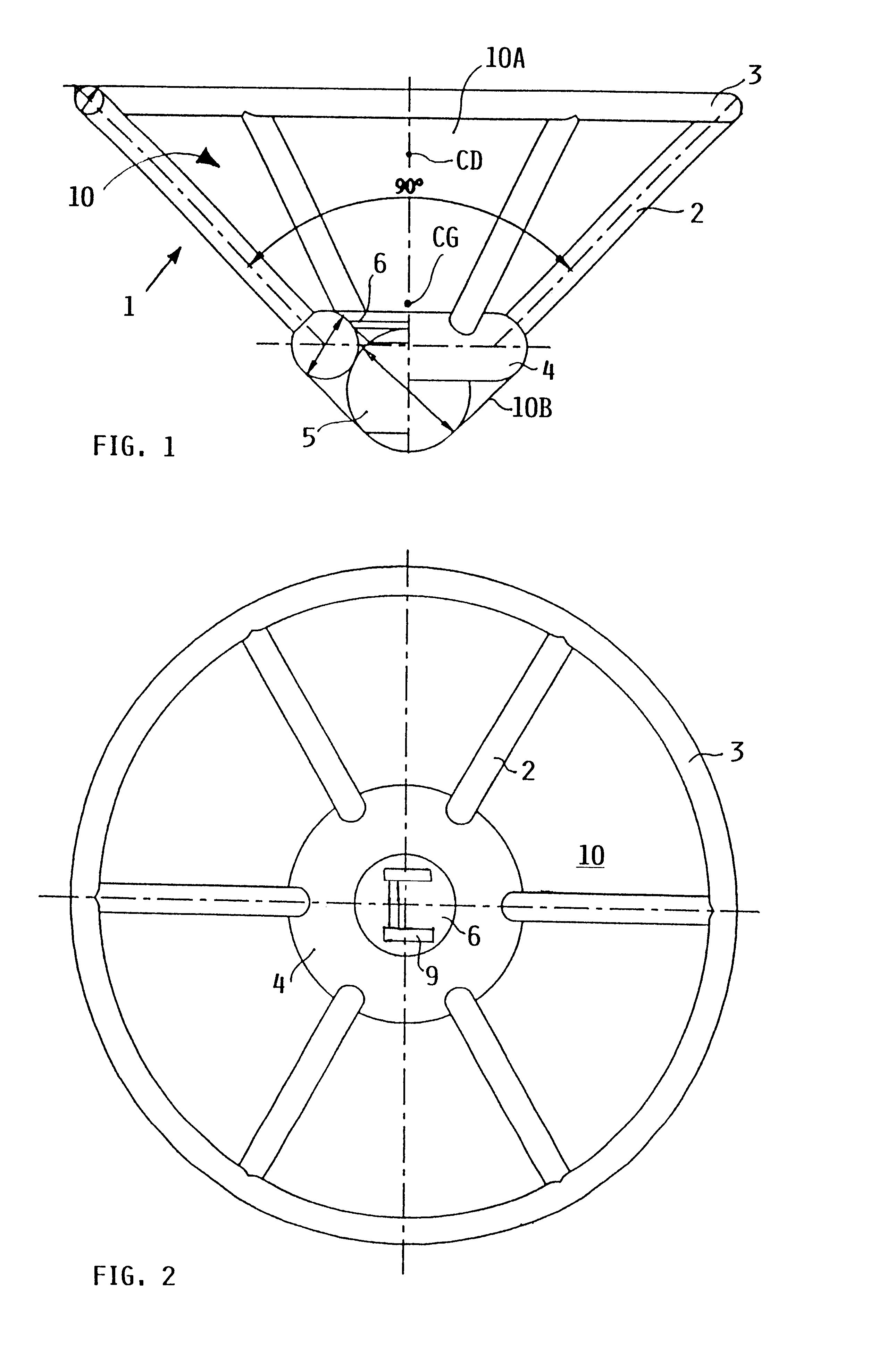
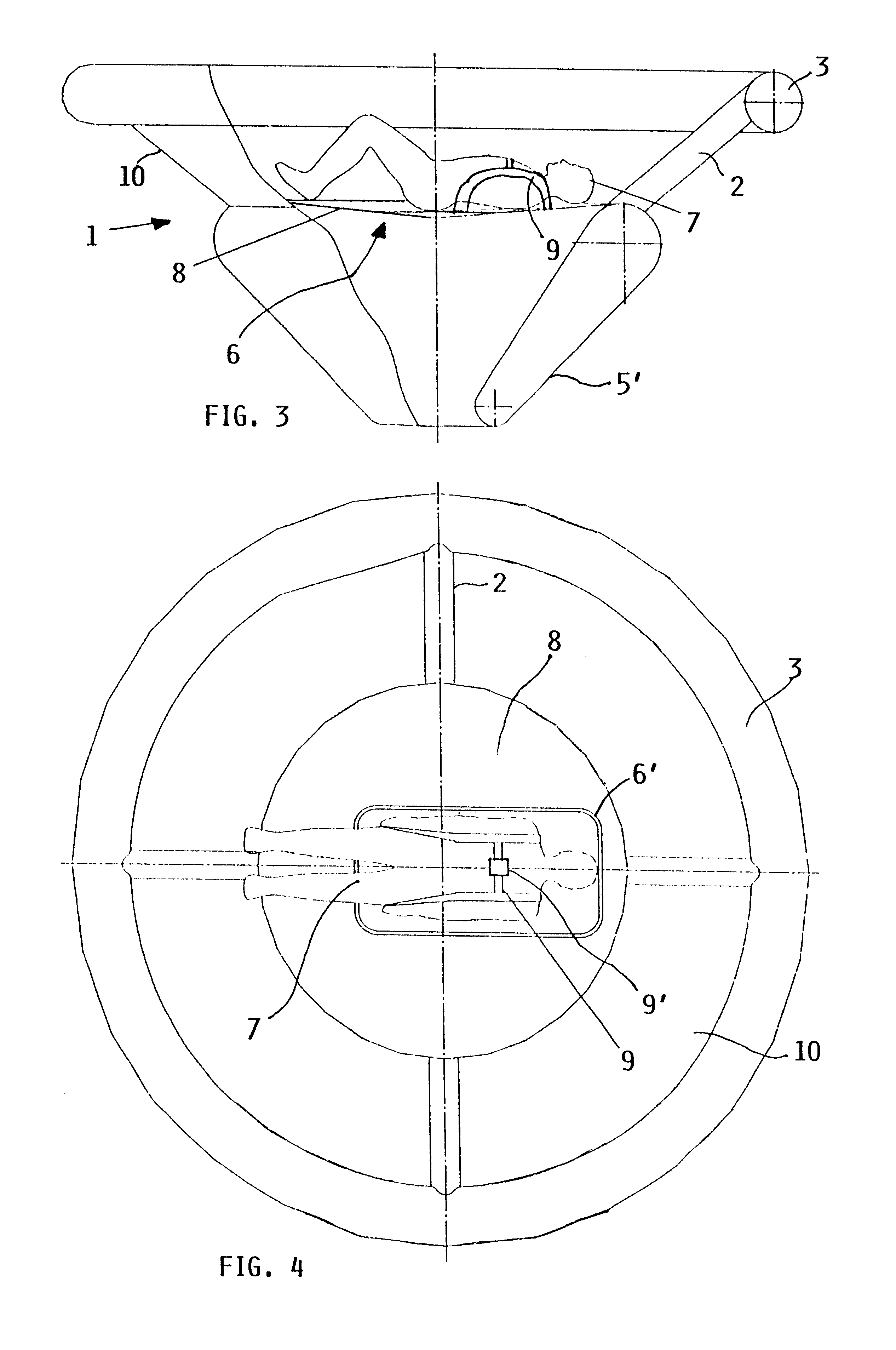
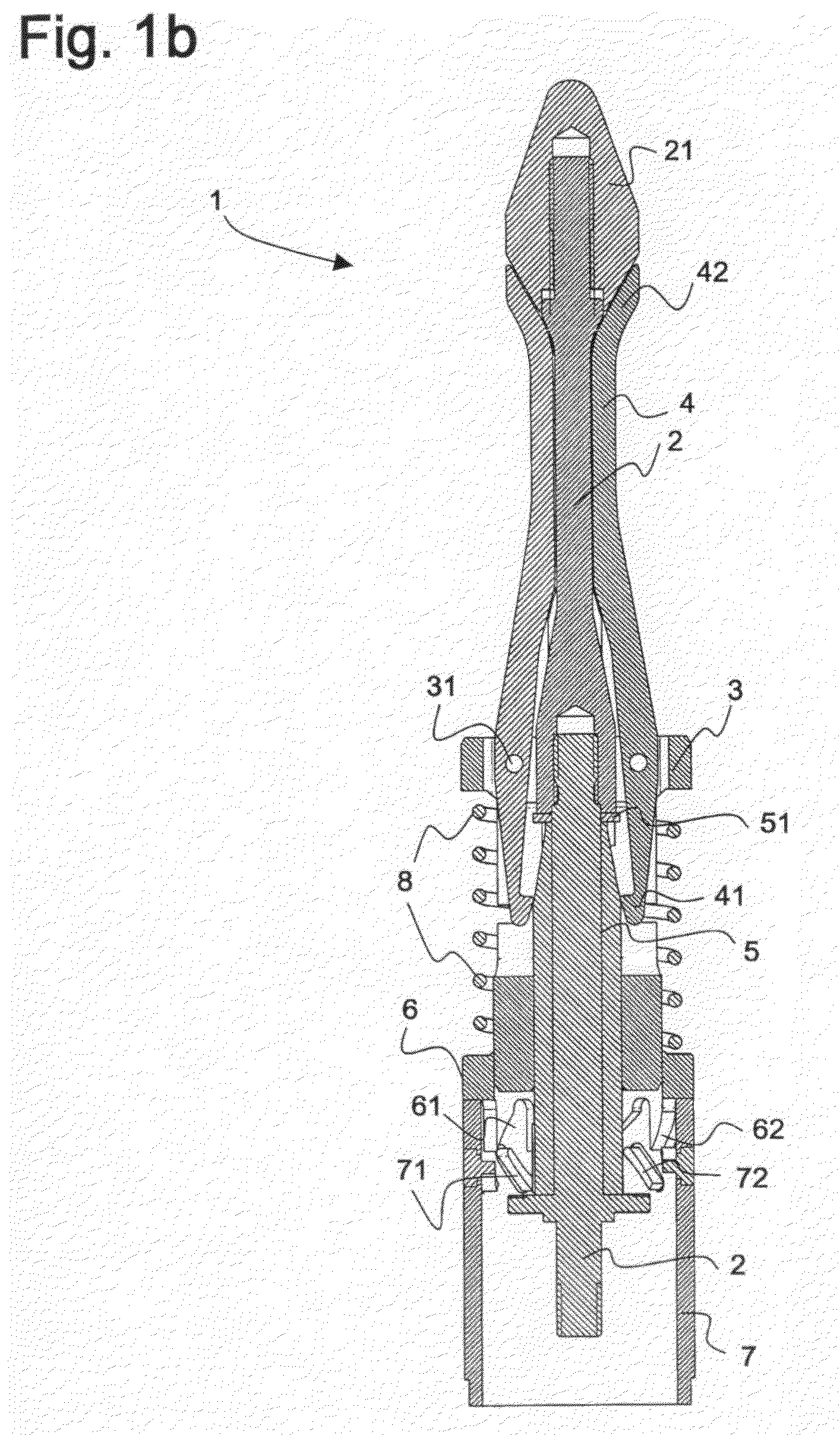
Inflatable flying body for the rescue descent of a person
InactiveUS6607166B1Slow its descentDistribute over timeAircraft ejection meansCosmonautic partsConical formsNose
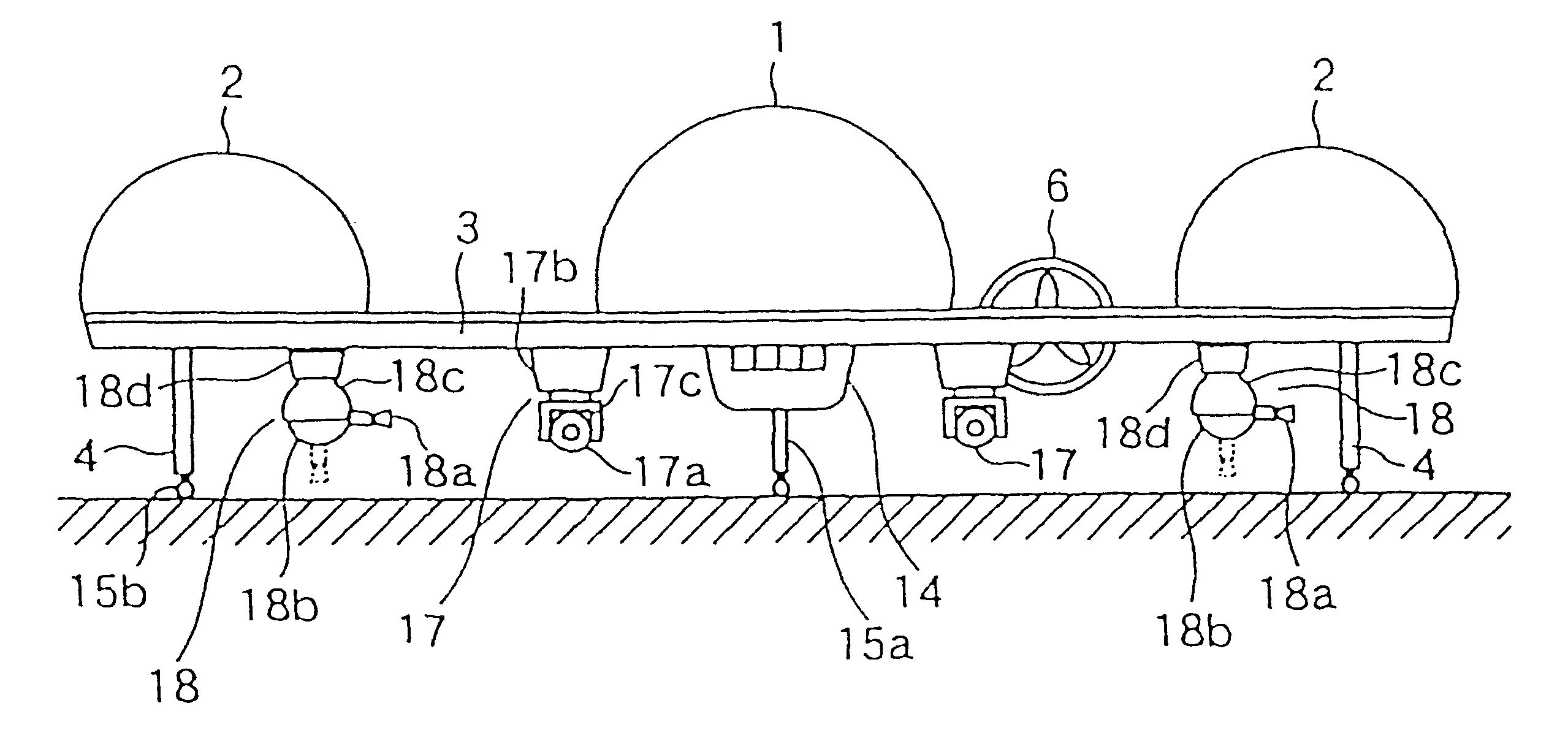
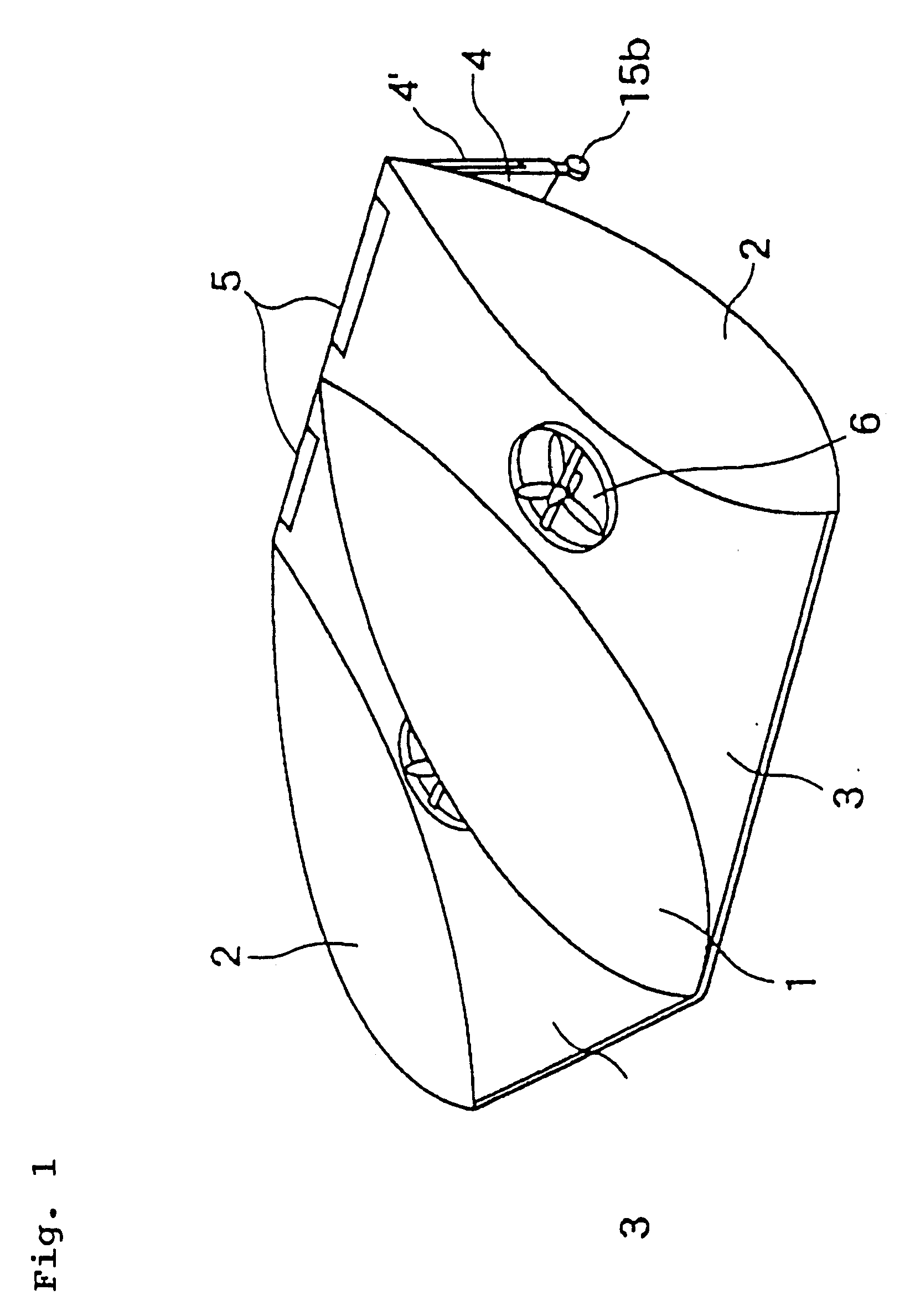
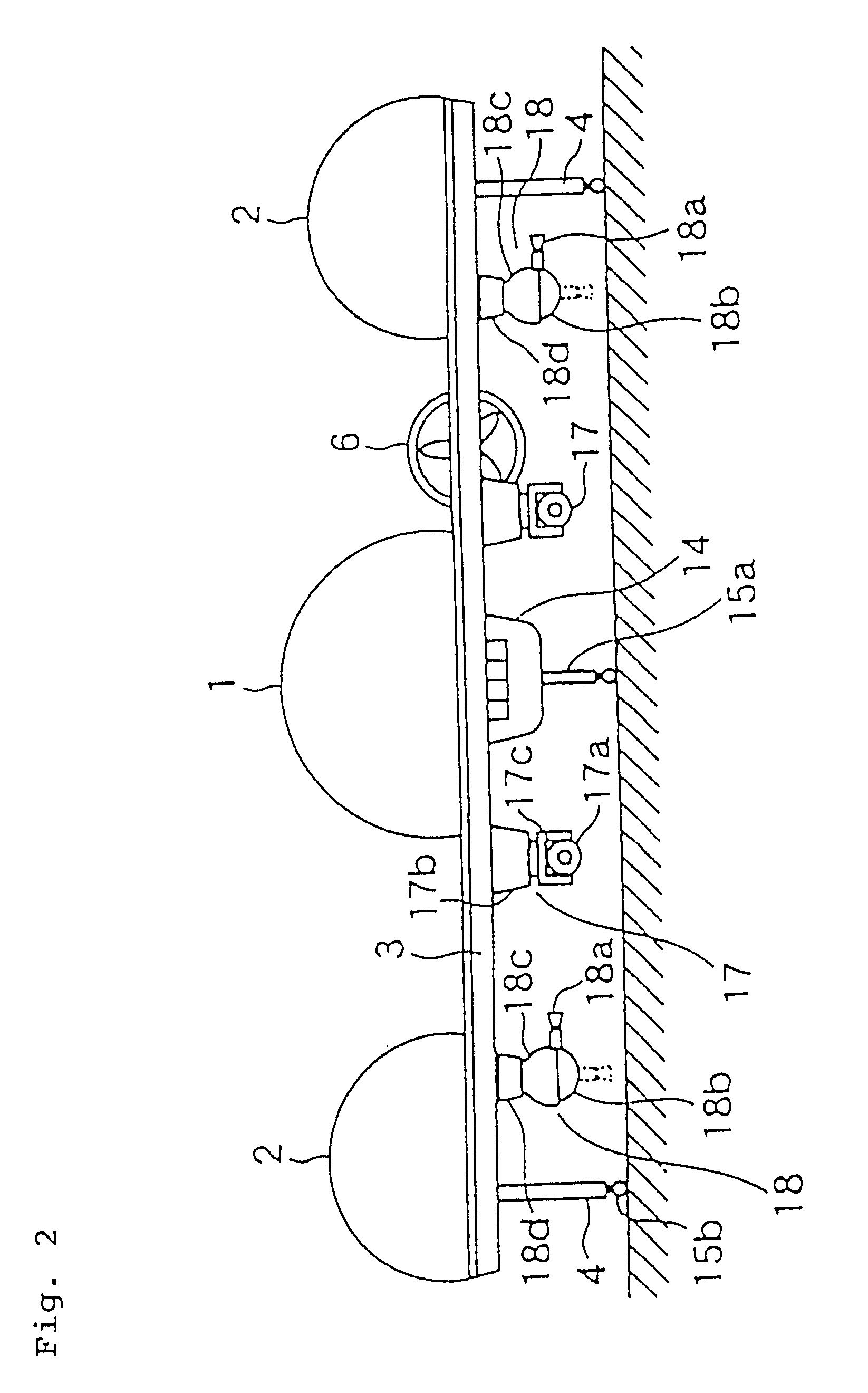
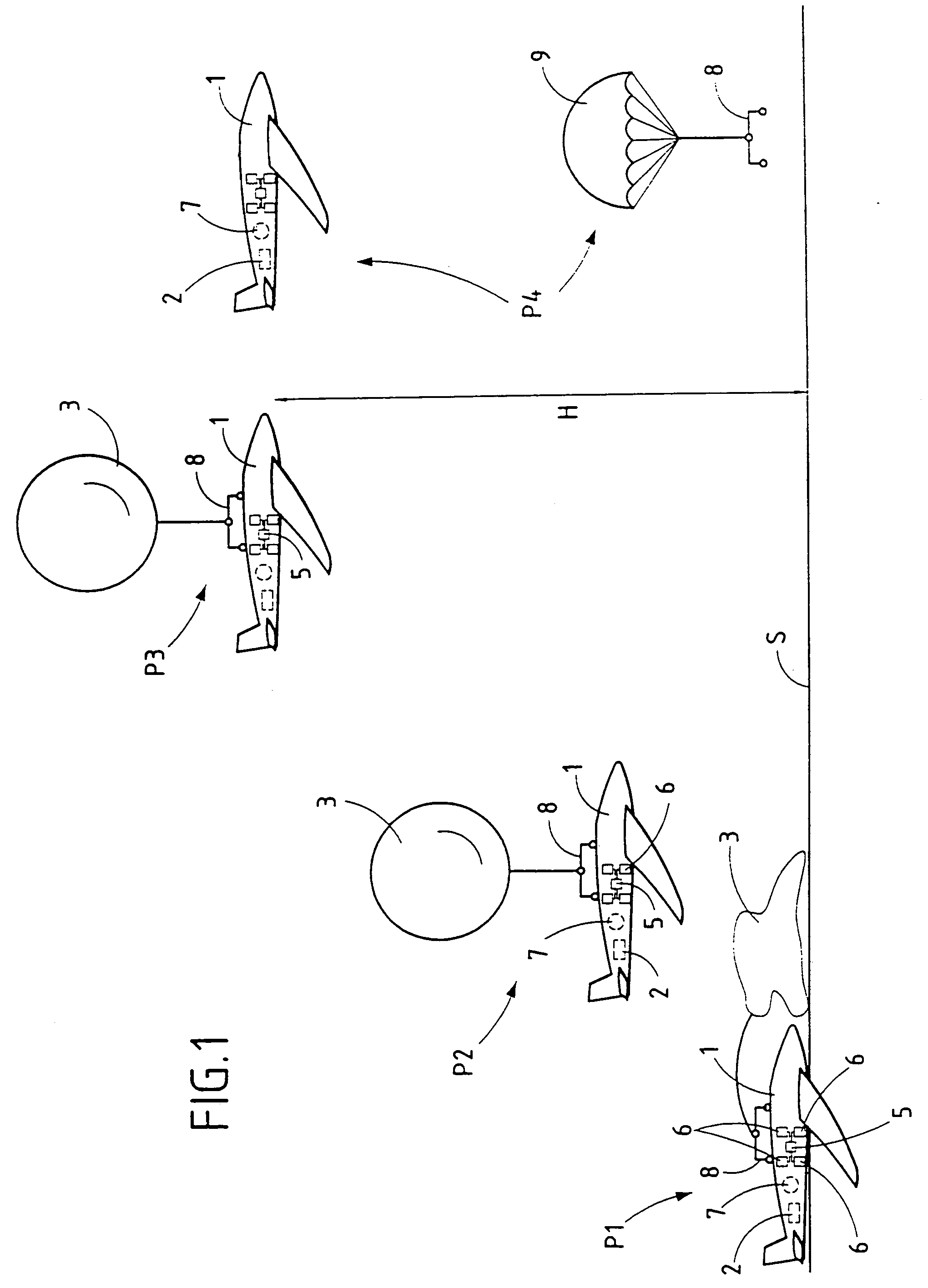
A person can safely descend from a burning high-rise building or the like using an inflatable flying body that has a hollow conical form in an inflated deployed condition, but is deflated and folded into a backpack form in a stowed condition. The flying body includes an upper stabilizing ring, a lower nose structure with a pneumatic damping body, spoke struts extending conically therebetween, a cover skin covering the abovementioned inflatable components to form the conical outer surface and provide aerodynamic braking drag, and gas generators to inflate the inflatable components. A person straps on the apparatus in the stowed backpack form and pulls a handle to actuate the gas generators for inflating the apparatus, whereby the expanding apparatus ejects the person from the building and then orients itself in a nose-down attitude during the descent. The pneumatic damping body damps and dissipates the landing impact energy.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
Satellite refuelling system and method
ActiveUS8074935B2Eliminating orReduce riskAircraft componentsCosmonautic ground equipmentsRobotic armActuator
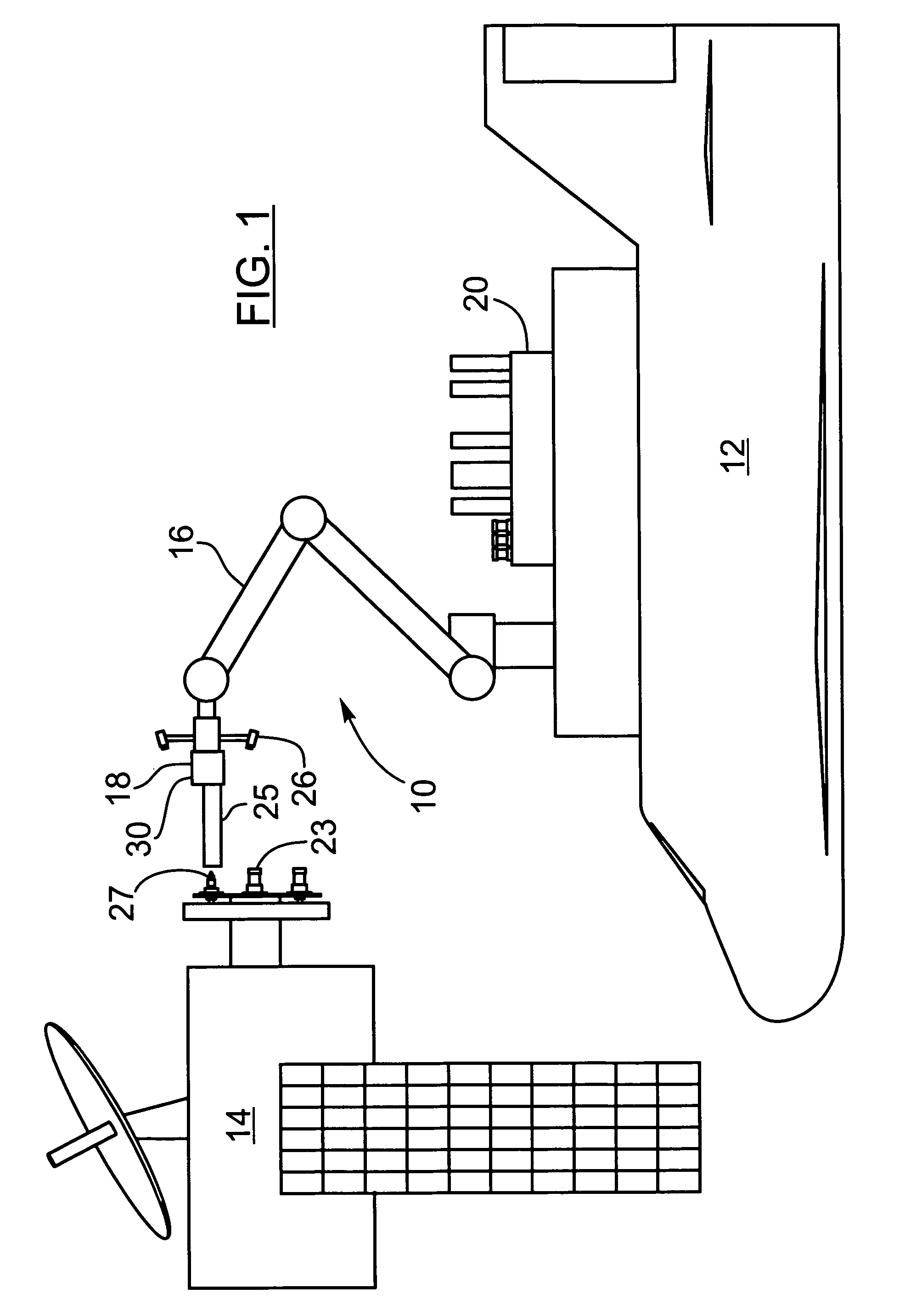
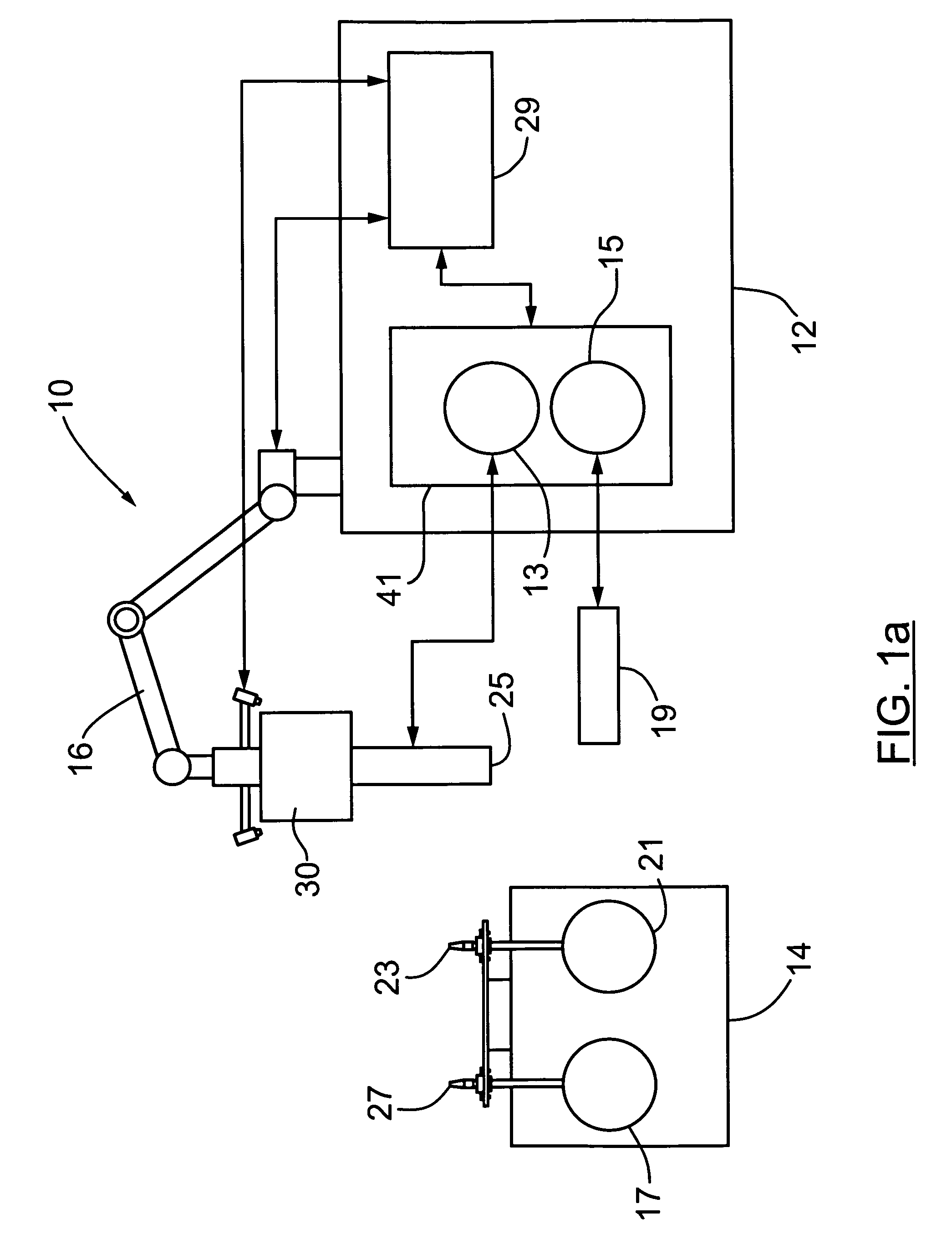
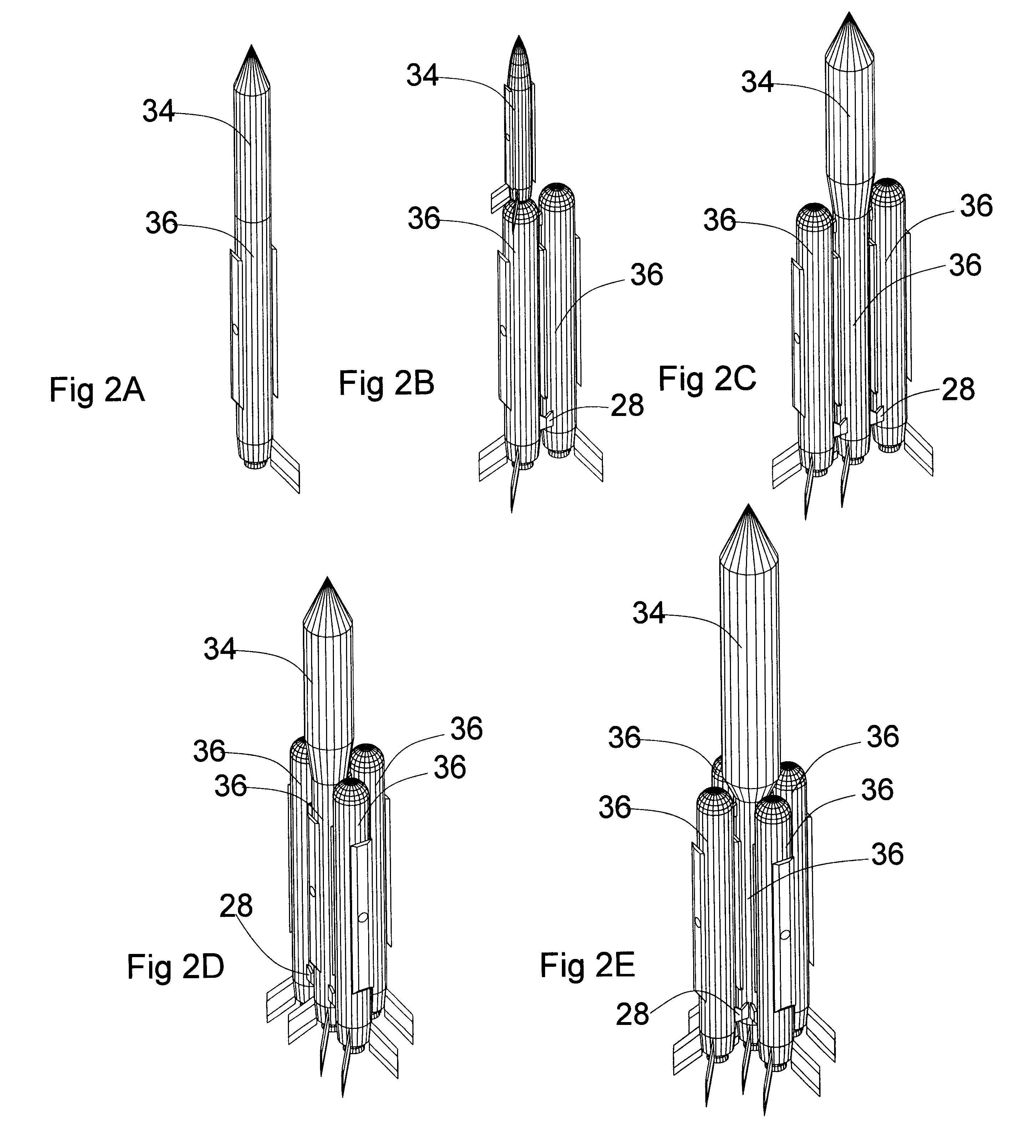
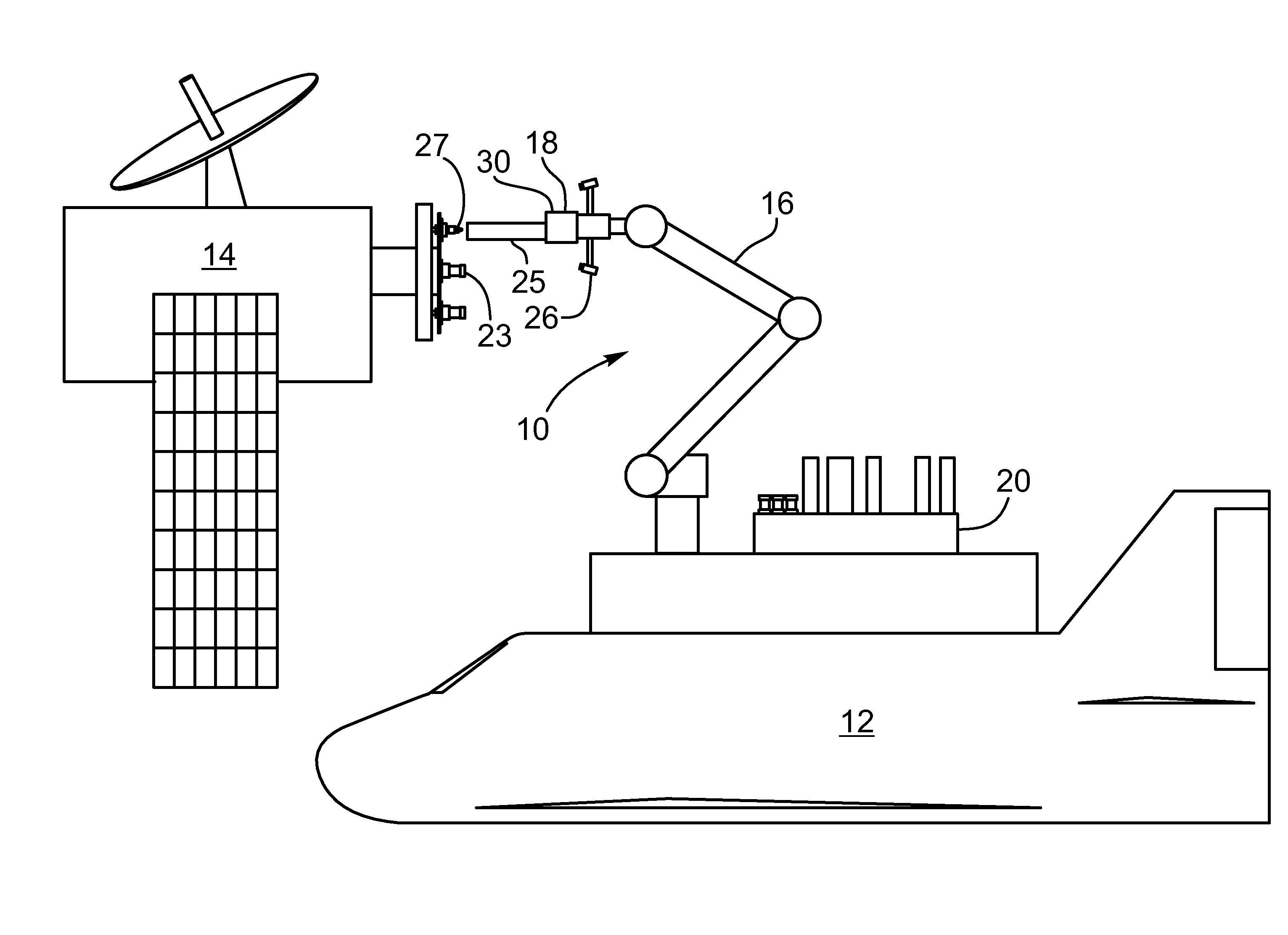
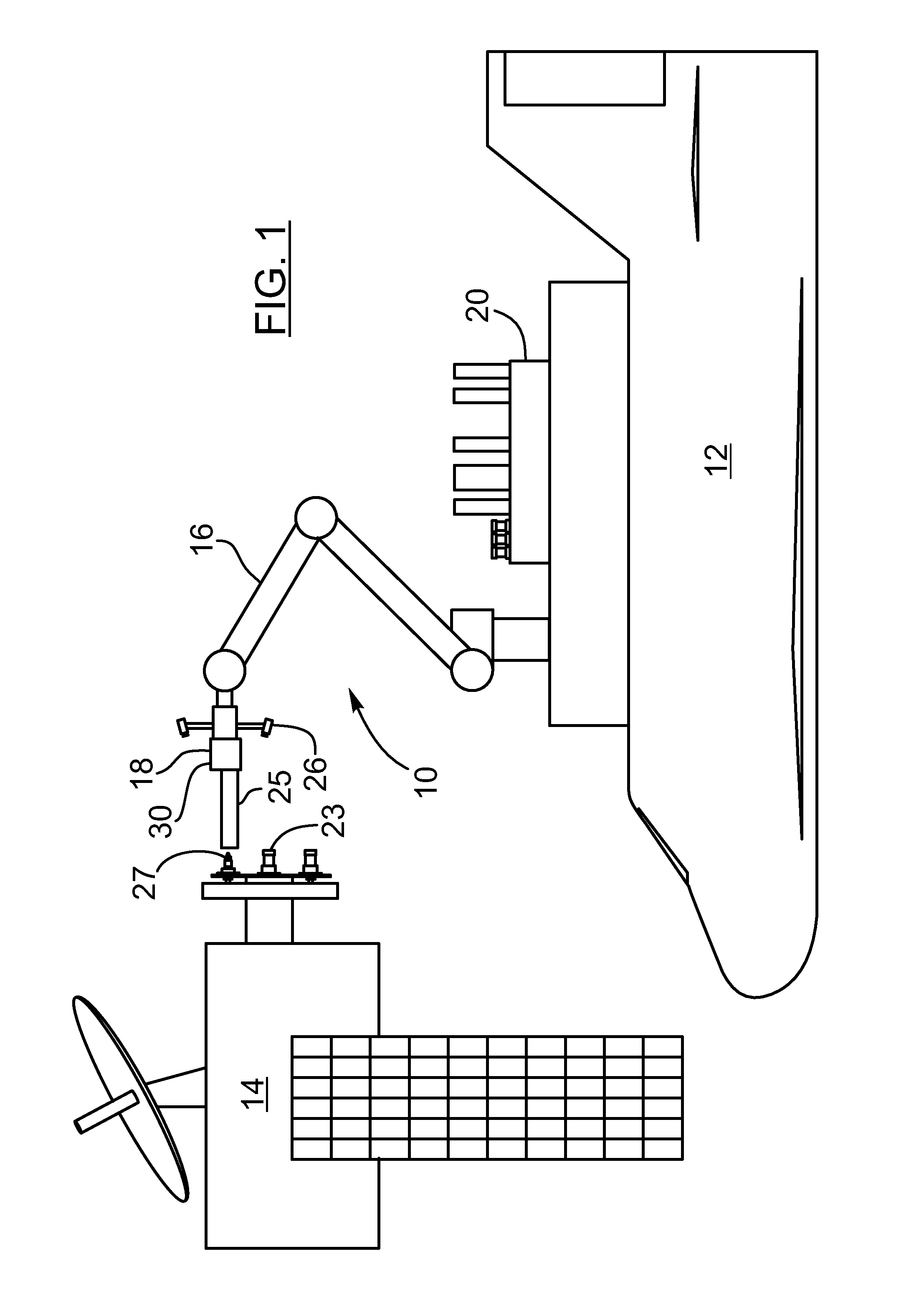
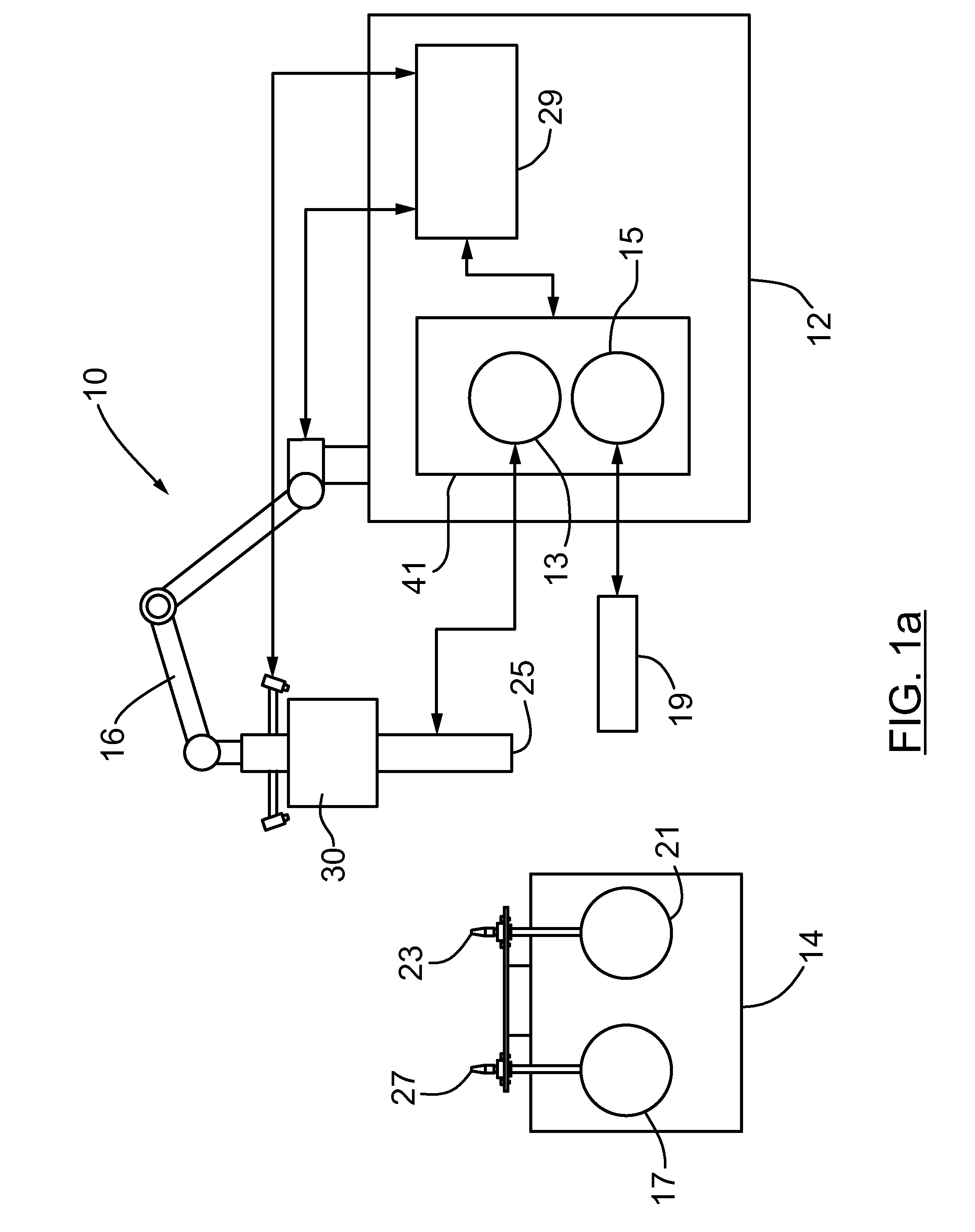
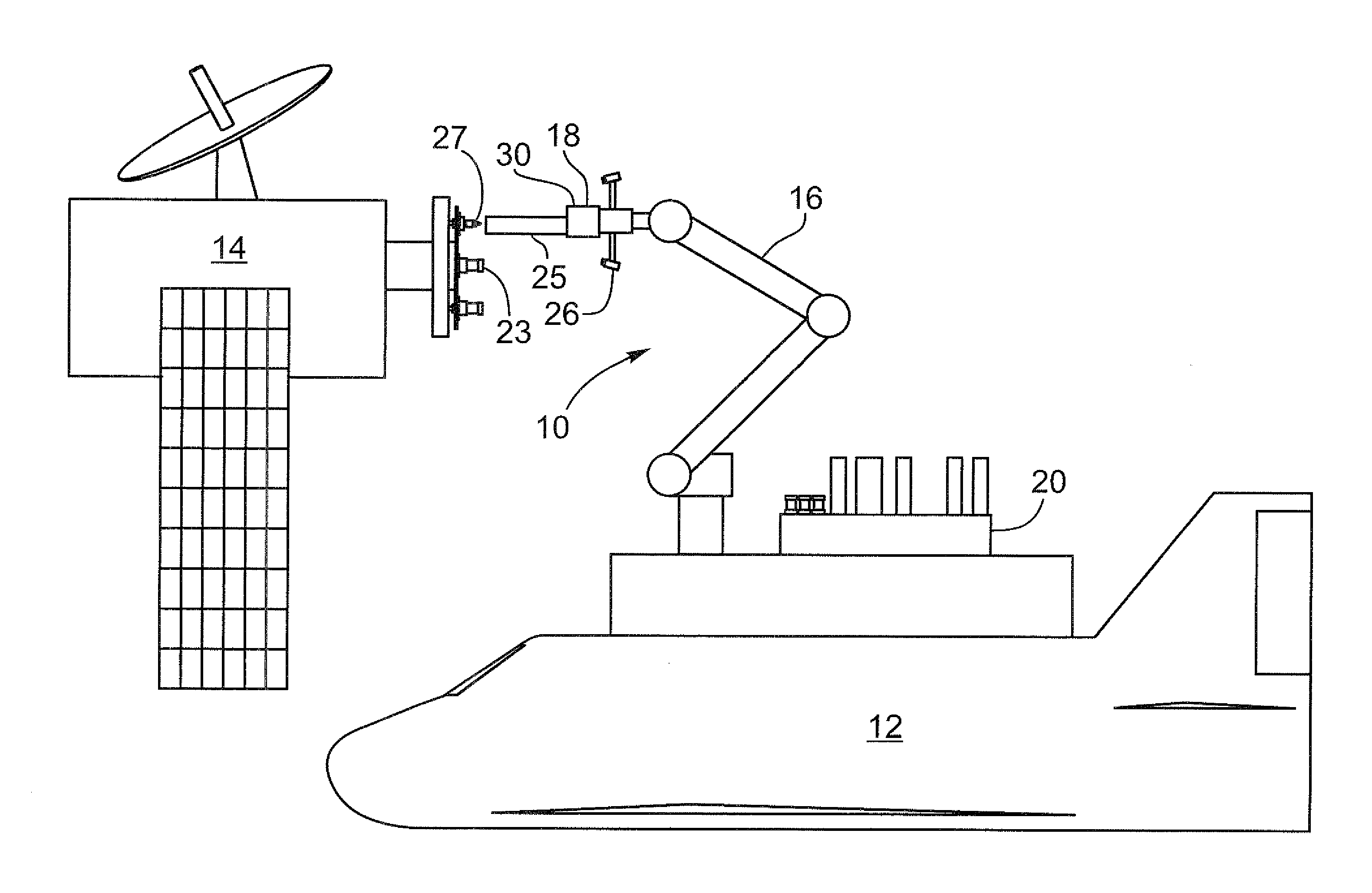
The present invention provides a method, system and apparatus for robotic refueling of satellites. The system may include a dedicated refueling satellite launched directly from either earth, or alternatively it could be launched from another larger mother spacecraft or space station in which the refueling satellite is ferried into space in the case of the larger space craft or it may be stored on the space station until needed from which it can be launched. The system includes a robotic arm, suitable tools which can be affixed to the end effector of the robotic arm required for accessing, opening and closing the fuel fill valve on the satellite being serviced, storage and retrieval stations on a tool caddy on which the tools and various fuel fill valve caps are stored. The system is under teleoperation by a remotely located operator, for example located on earth, in the mother station or in the space station. Cameras are included focussed on the robotic arm and end effector and images are transmitted to the operator to allow the operator to direct and control the refueling procedure. The system may also be configured to be operated autonomously under computer control.
Owner:MACDONALD DETTWILER & ASSOC INC
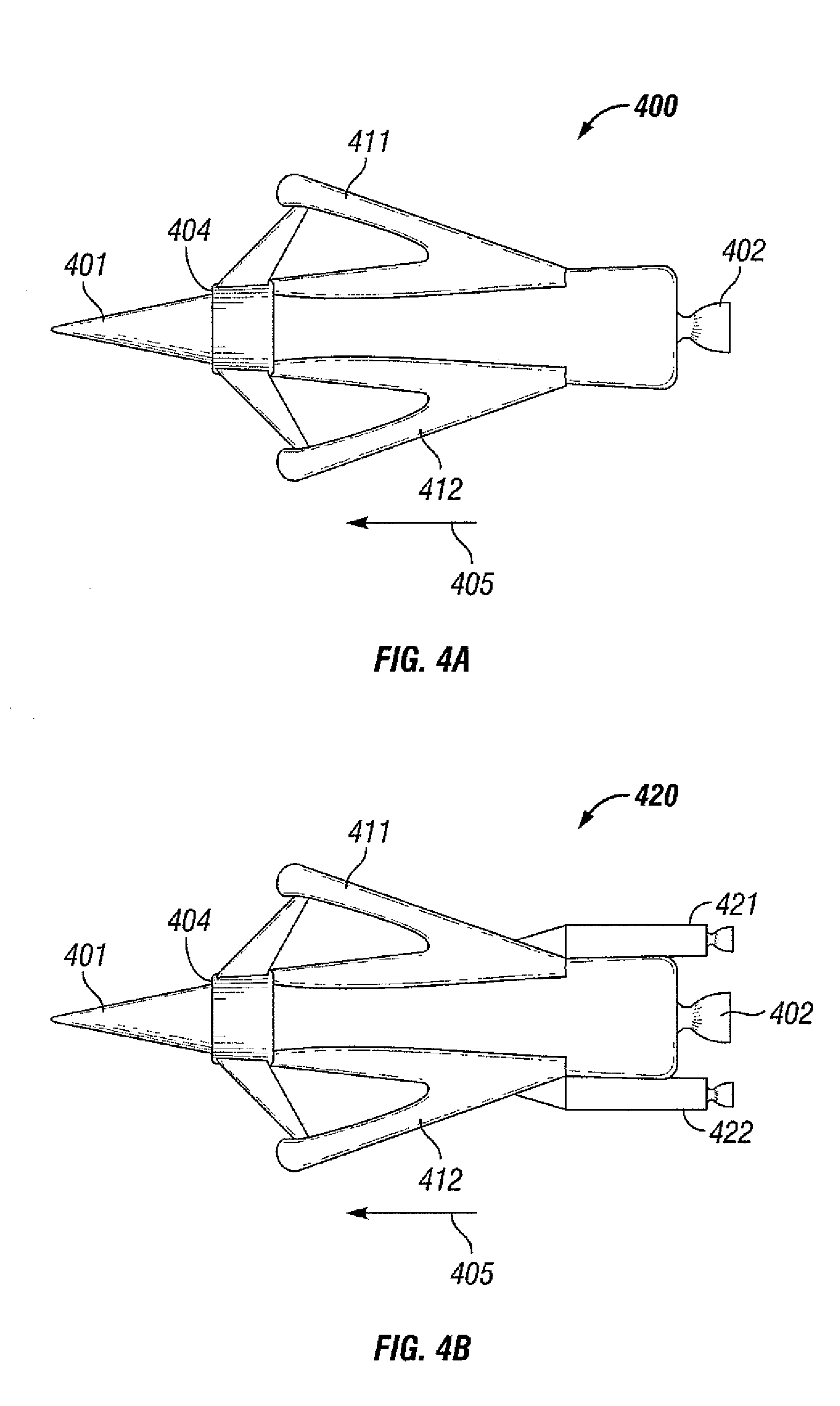
Spacecraft and aerospace plane having scissors wings
InactiveUS6745979B1Form differentAvoid connectionLaunch systemsCosmonautic partsJet aeroplaneAviation
A spacecraft such as a fly back booster or a reusable launch vehicle, or an aerospace plane has a fuselage and a set of scissors wings consisting of two main wings. Both of the main wings are rotatably mounted on the fuselage and can be yawed at opposite directions. If the spacecraft is launched vertically, both of its main wings can be yawed to be generally parallel with its fuselage so that it can connect with other vehicle or vehicles to form different launch configurations. When the spacecraft or aerospace plane is flying in the air, landing, or taking off horizontally, it can yaw both of its main wings in opposite directions to maximize its lift-to-drag ratio by optimizing the yaw angle of the main wings according to flying conditions. It can also produce desired aerodynamic characteristics such as forming a high drag configuration by adjusting the yaw angle of its main wings. The scissors wings can be used on a spacecraft that is launched vertically on the ground, or a spacecraft that is carried to the air and launched in the mid-air, or a spacecraft that takes off horizontally like an aircraft or glider. The scissors wings can also be used on an aerospace plane.
Owner:CHEN ZHUO
Satellite refuelling system and method
ActiveUS20120112009A1Eliminating orReduce riskCosmonautic ground equipmentsCosmonautic partsRobotic armActuator
Owner:MACDONALD DETTWILER & ASSOC INC
Propellant depot in space
InactiveUS7559508B1Improve efficiencyLow costLaunch systemsCosmonautic power supply systemsPropellant depotMature technology
A space transportation propellant depot has multiple locations, sources and capabilities. Maximizing known mature technologies coupled with realistic industrial techniques results in the incremental development of a propellant source on the moon. Propellant depots are economically driven locations with defined services, sources of propellant and innovation in the pursuit of transportation related commerce as mankind explores for resources beyond Earth.
Owner:TAYLOR THOMAS C +2
Reusable upper stage
InactiveUS20070012820A1Minimum amount of timeCompletely reusableCosmonautic partsSpace shuttlesControl systemPayload
This patent describes a reusable upper-stage, that utilizes a position-adjustable propulsion module and payload compartment, an aeroshell, a guidance and control system, and a deployable landing apparatus. The position-adjustable upper-stage propulsion module is shifted forward in the aeroshell prior to reentry into the atmosphere to allow the stage to reenter in a stable, nose-first orientation. It is shifted back to allow the stage to fall tail first and use its engine to do a final deceleration and a powered soft landing, supported by deployable landing apparatus.
Owner:BUEHLER DAVID
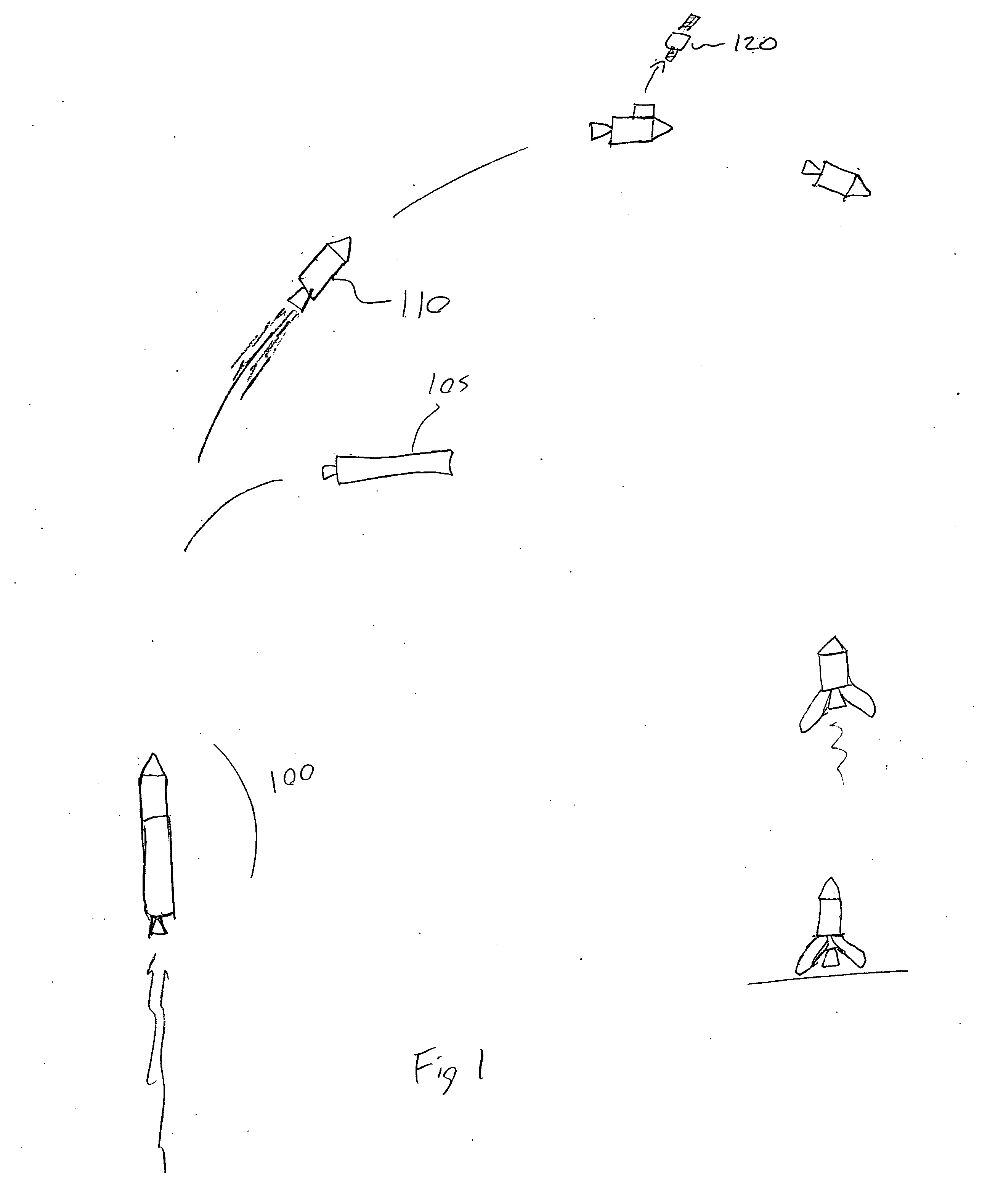
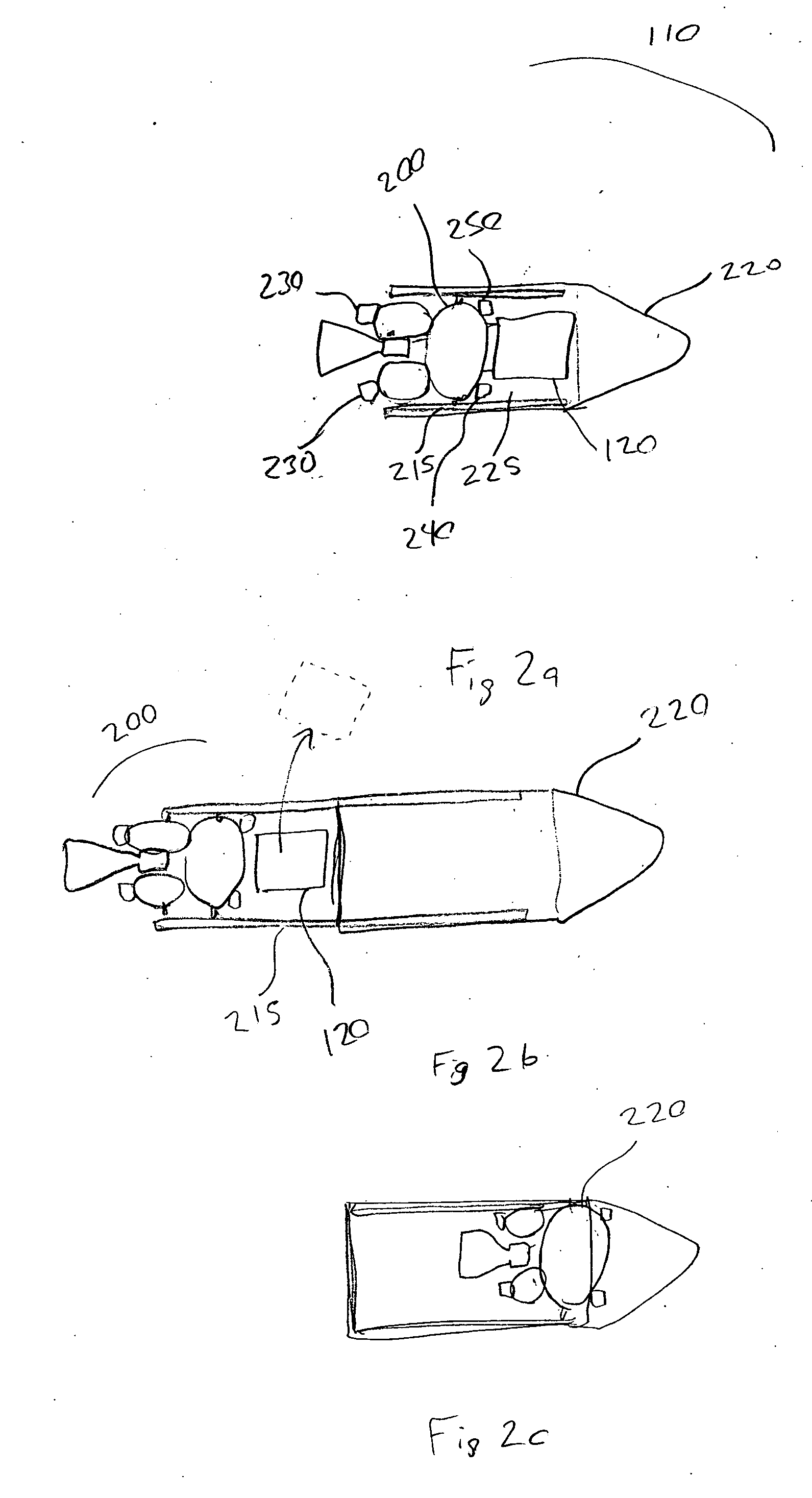
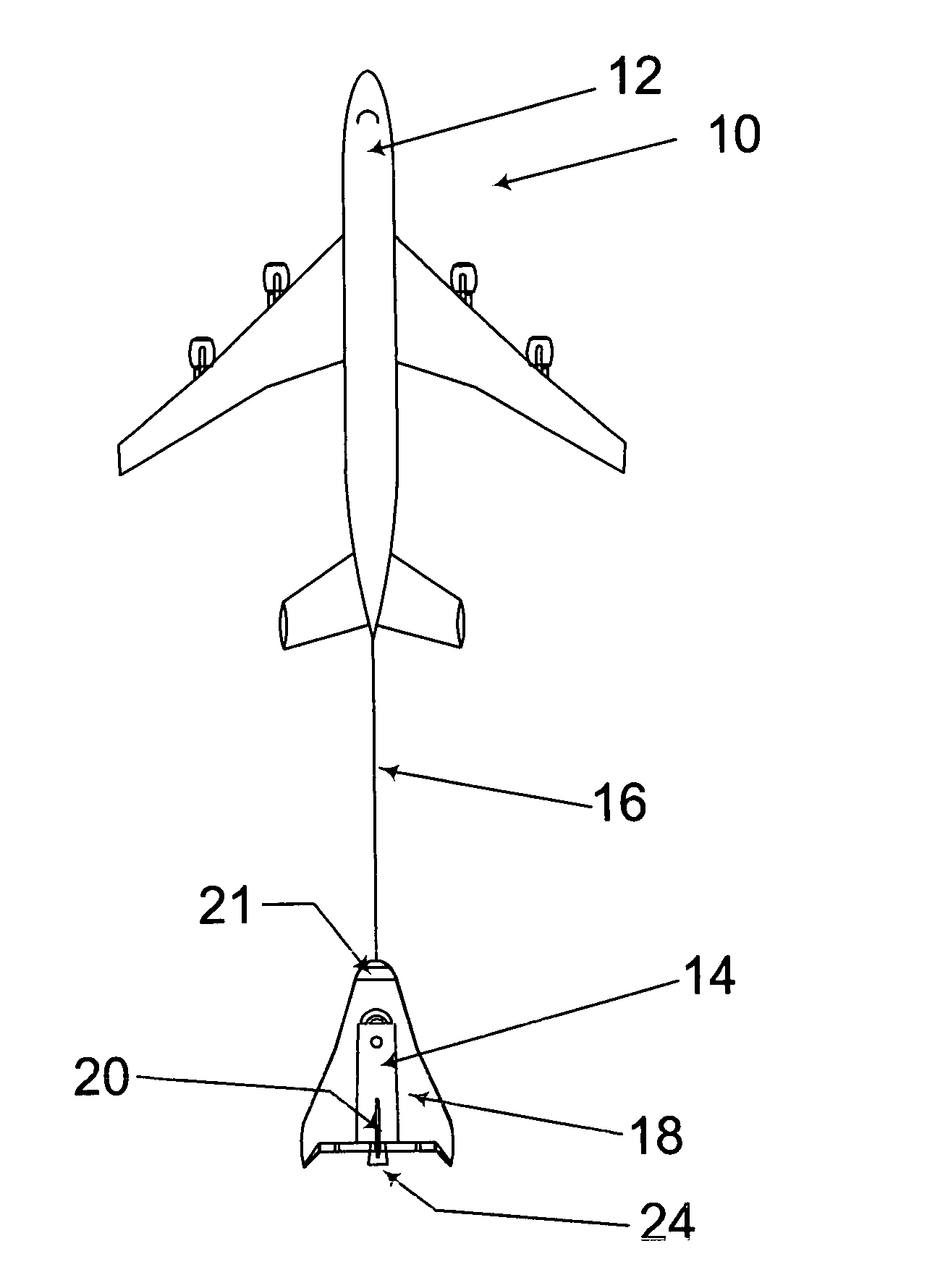
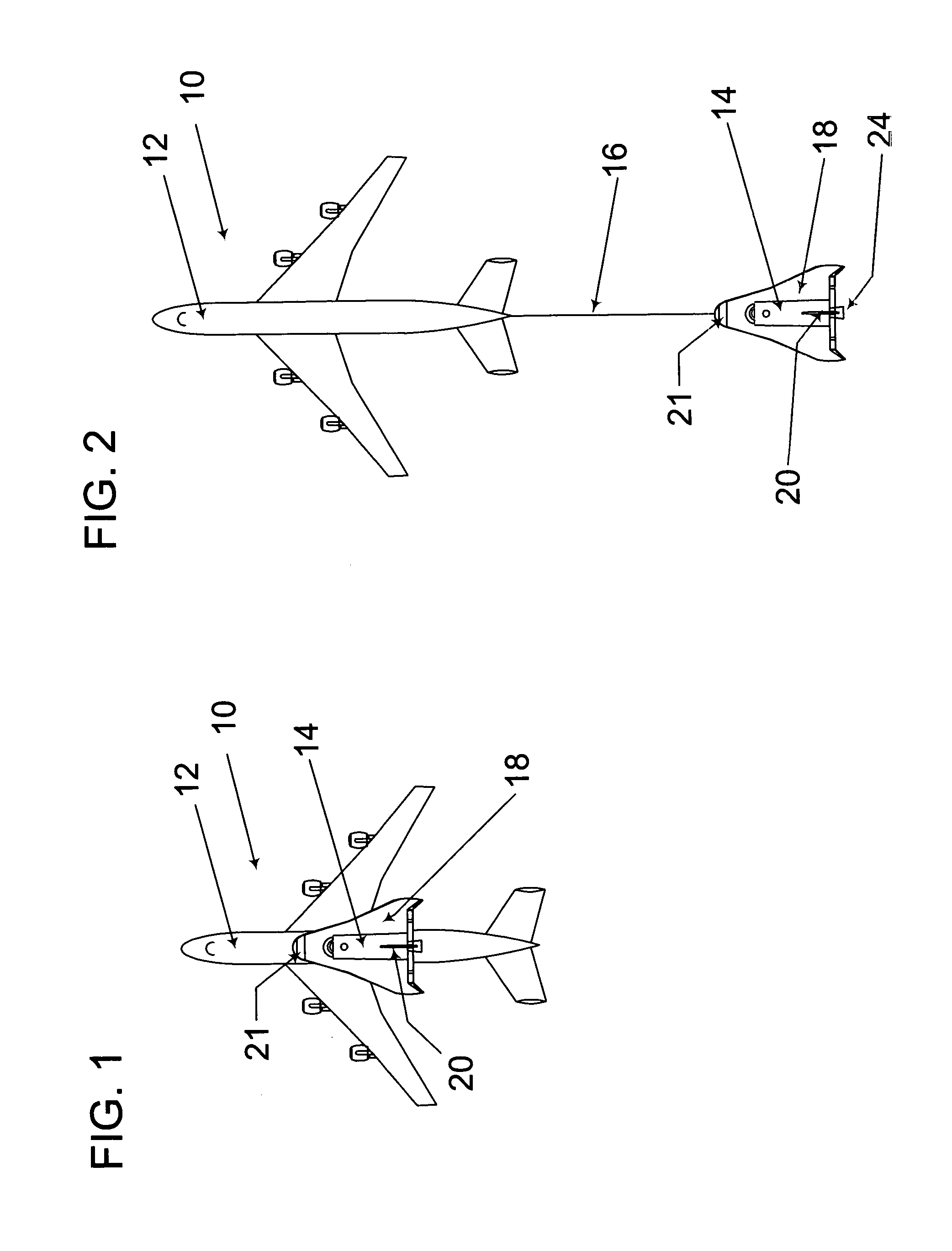
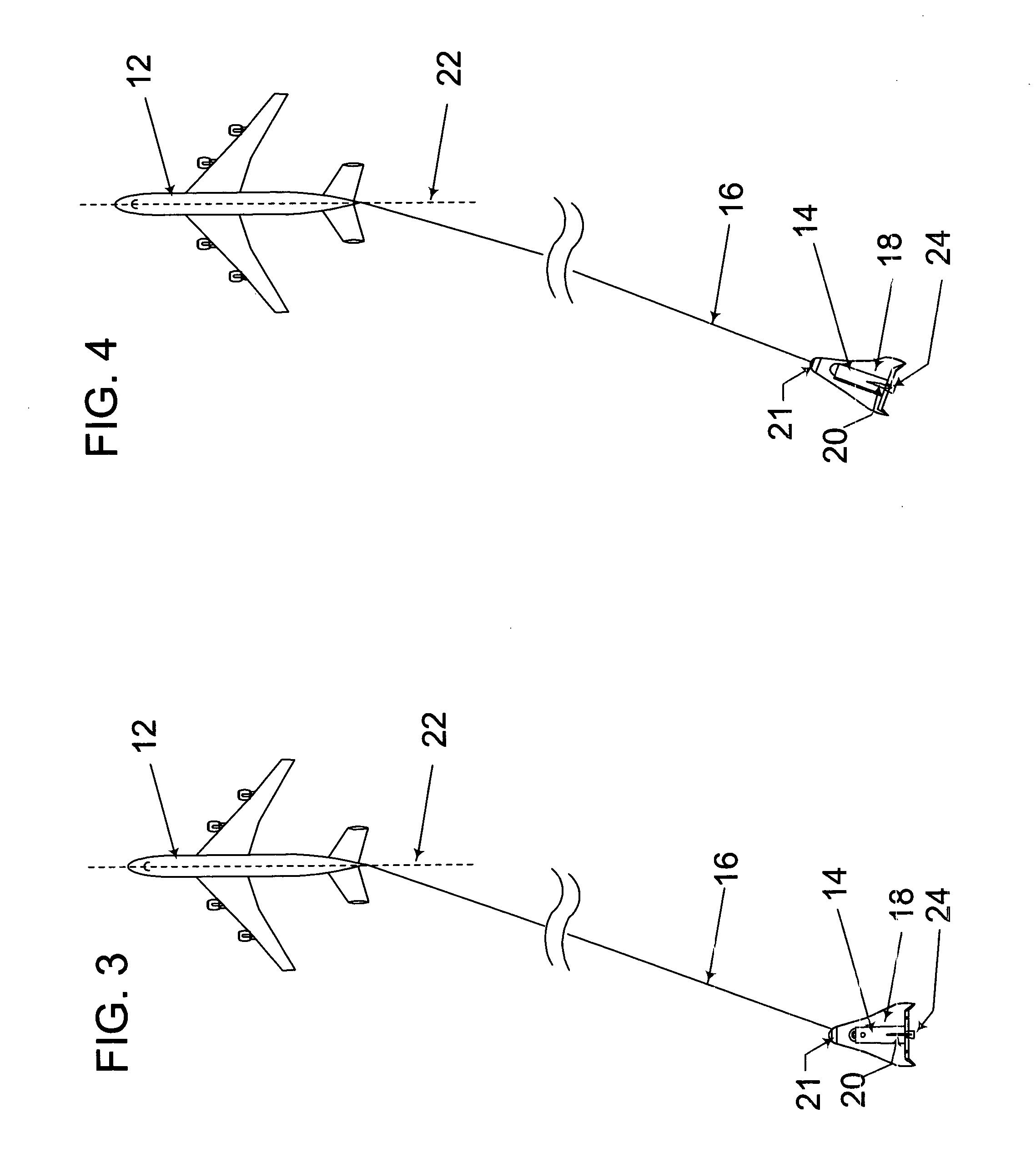
Space shuttle with a device for docking to a satellite
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV
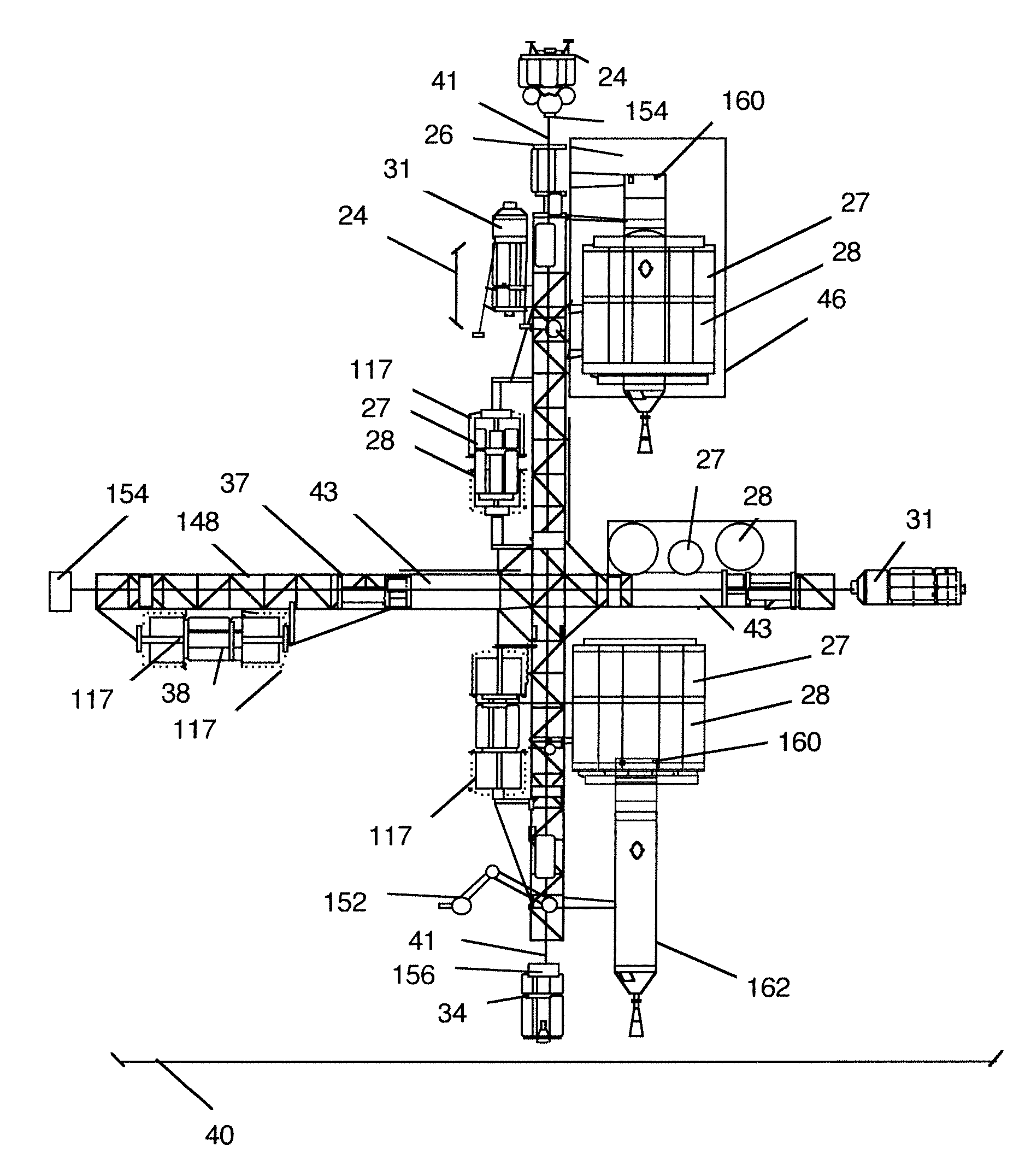
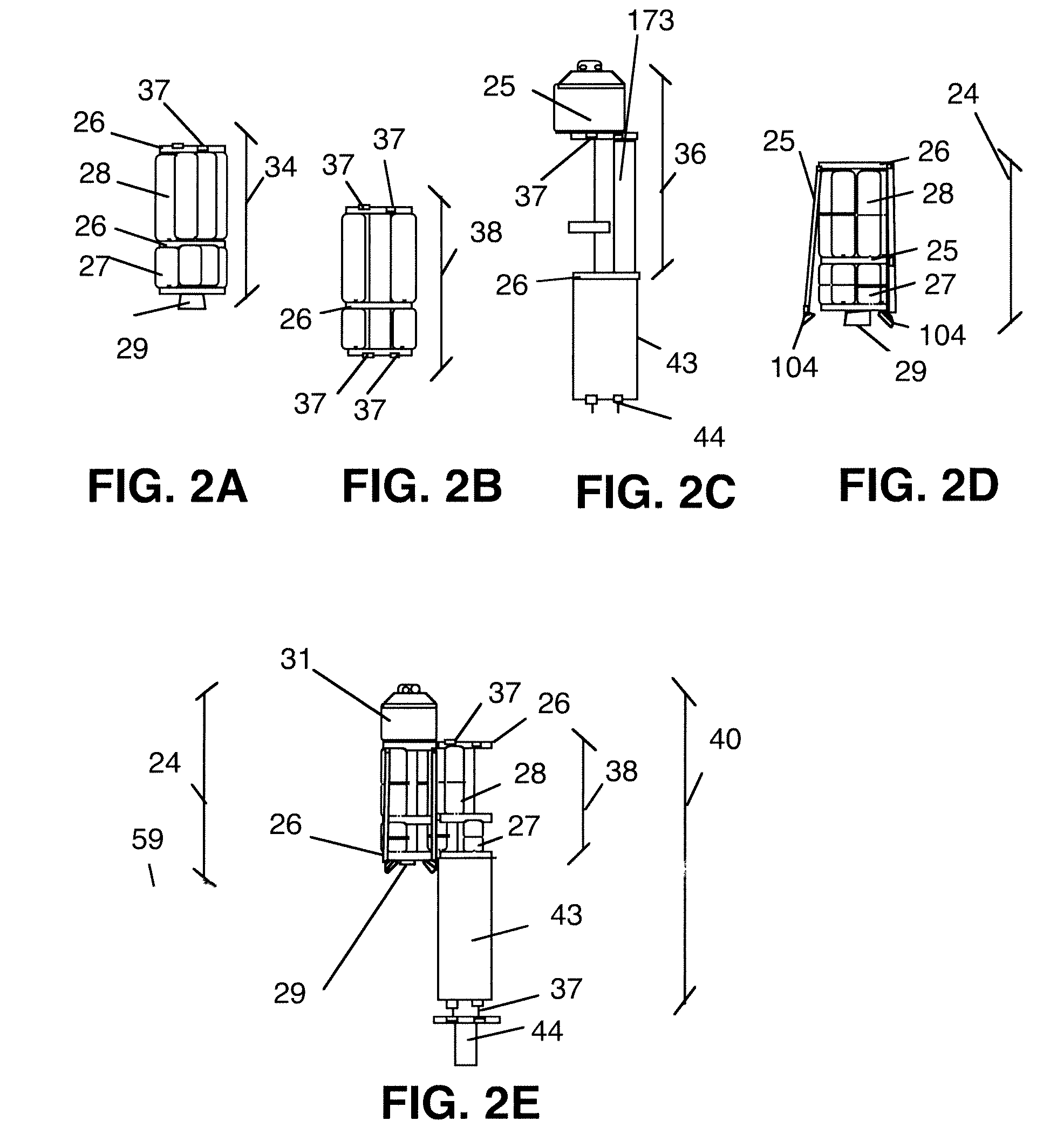
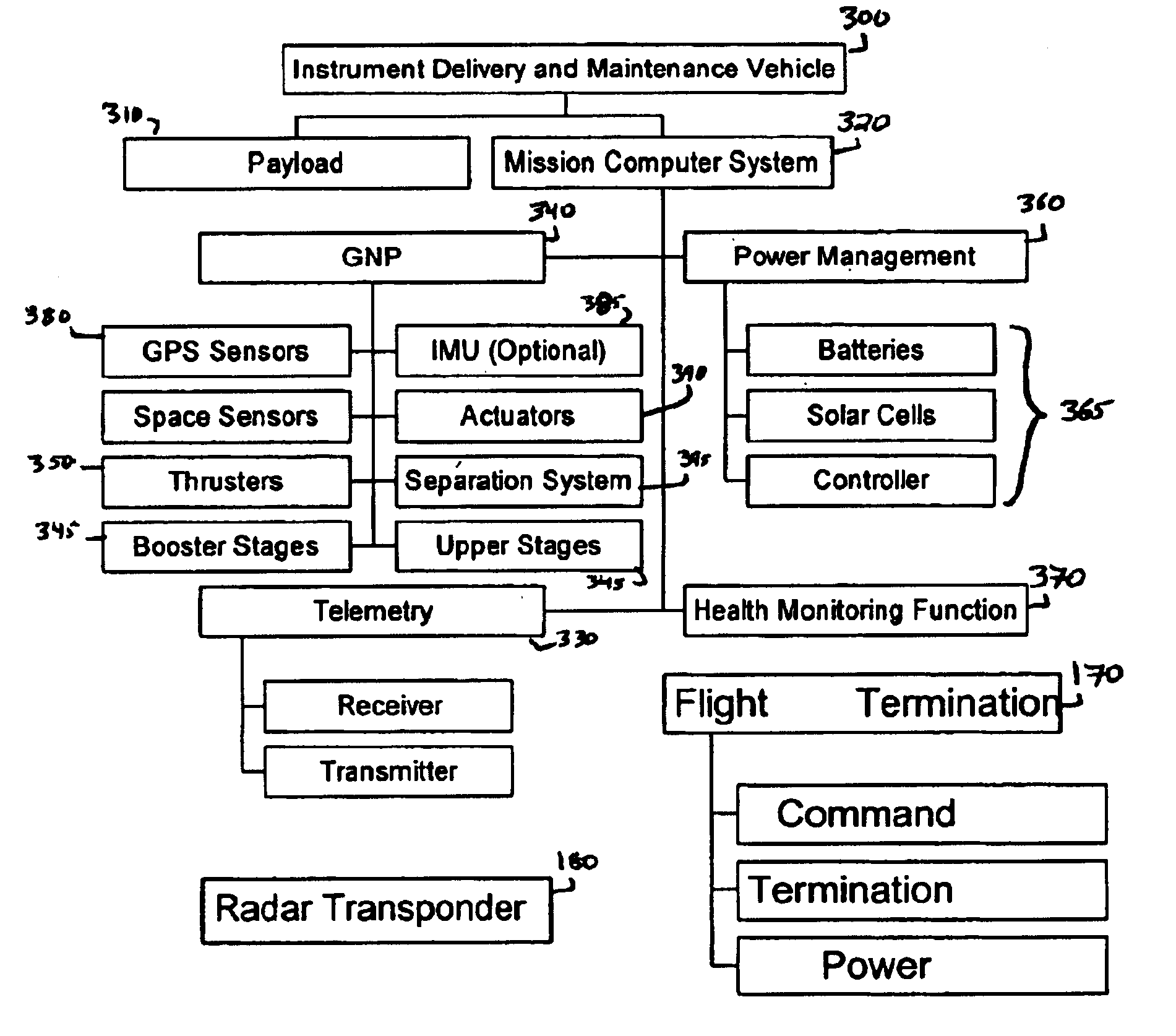
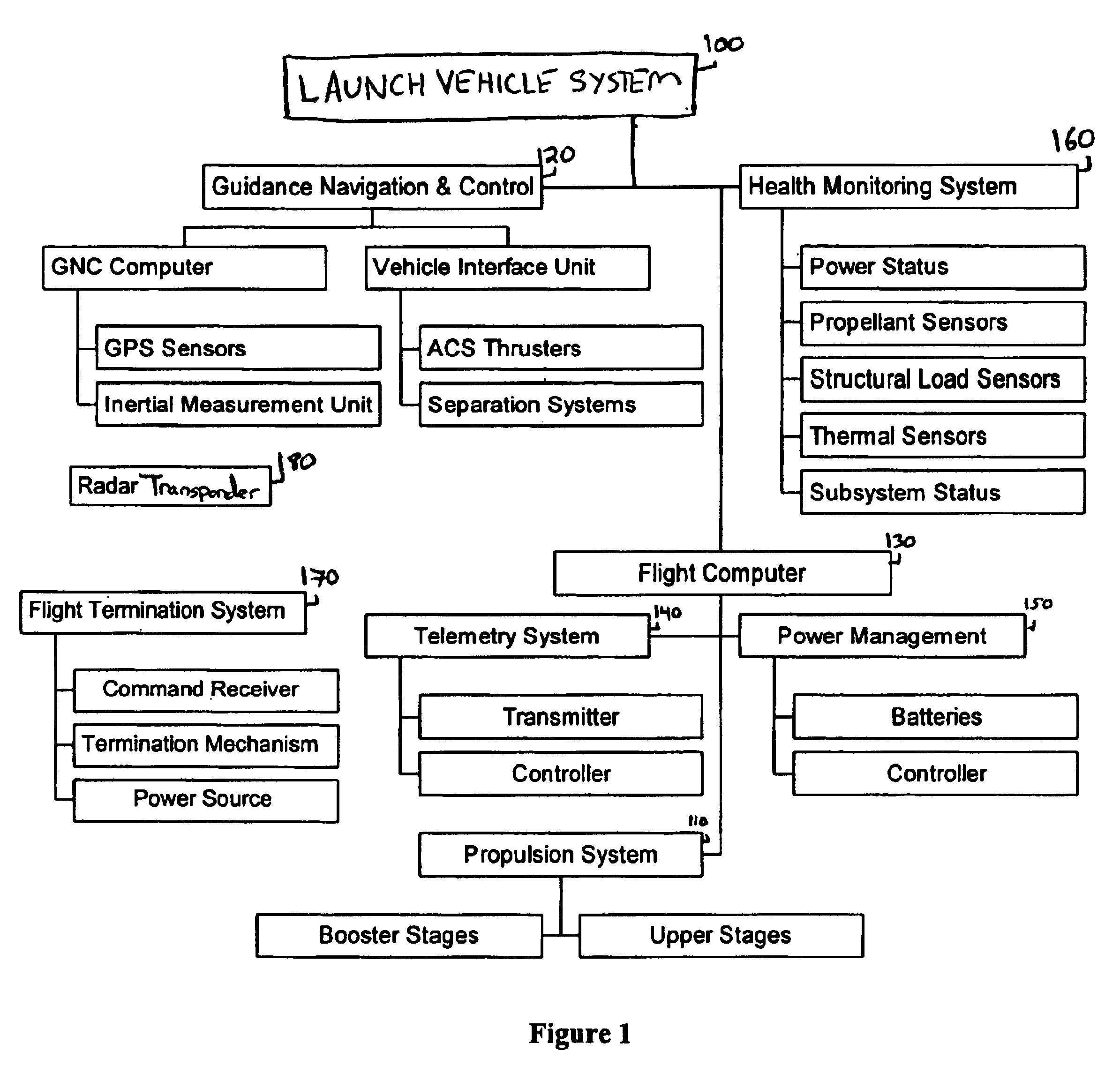
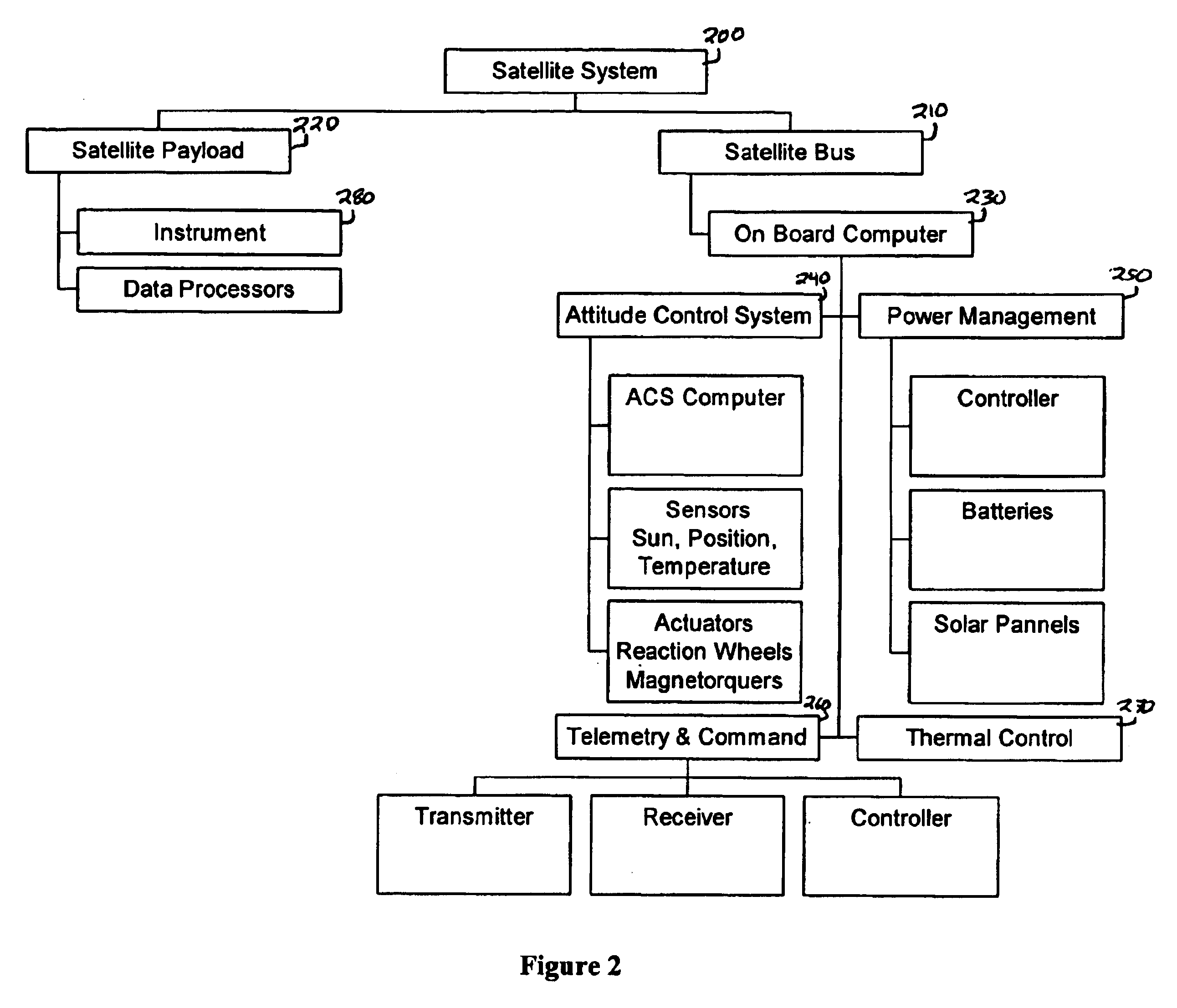
System for the delivery and orbital maintenance of micro satellites and small space-based instruments
InactiveUS6921051B2Low costLaunch systemsCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusAviationSpace launch
A low cost, on demand, dedicated launch system is provided for placing micro satellites or space-based instruments at orbital and sub-orbital altitudes and velocities. The invention describes a space launch vehicle (SLV) that incorporates a single, integrated guidance, navigation, and control unit (GNCU) that performs all guidance and control for the SLV from main stage ignition to orbital insertion. The GNCU can remain with the payload after orbital insertion to provide satellite station keeping and orbital maneuvering capability. The use of a single integrated avionics unit for all guidance, navigation, and control simplifies the SLV, reducing weight and significantly reducing cost. In addition, this architecture allows for a combined launch and satellite bus system as the GNCU can also be used as a satellite bus. This further reduces cost and increases the payload capacity to orbit by optimizing the use of launch vehicle and satellite bus subsystems and reducing non-instrument mass delivered to orbit. All support functions are provided by the IDMV. This approach represents a significant improvement over conventional systems, especially with respect to the orbital launch of payloads less than about 100 kg.
Owner:SPACE LAUNCH CORP
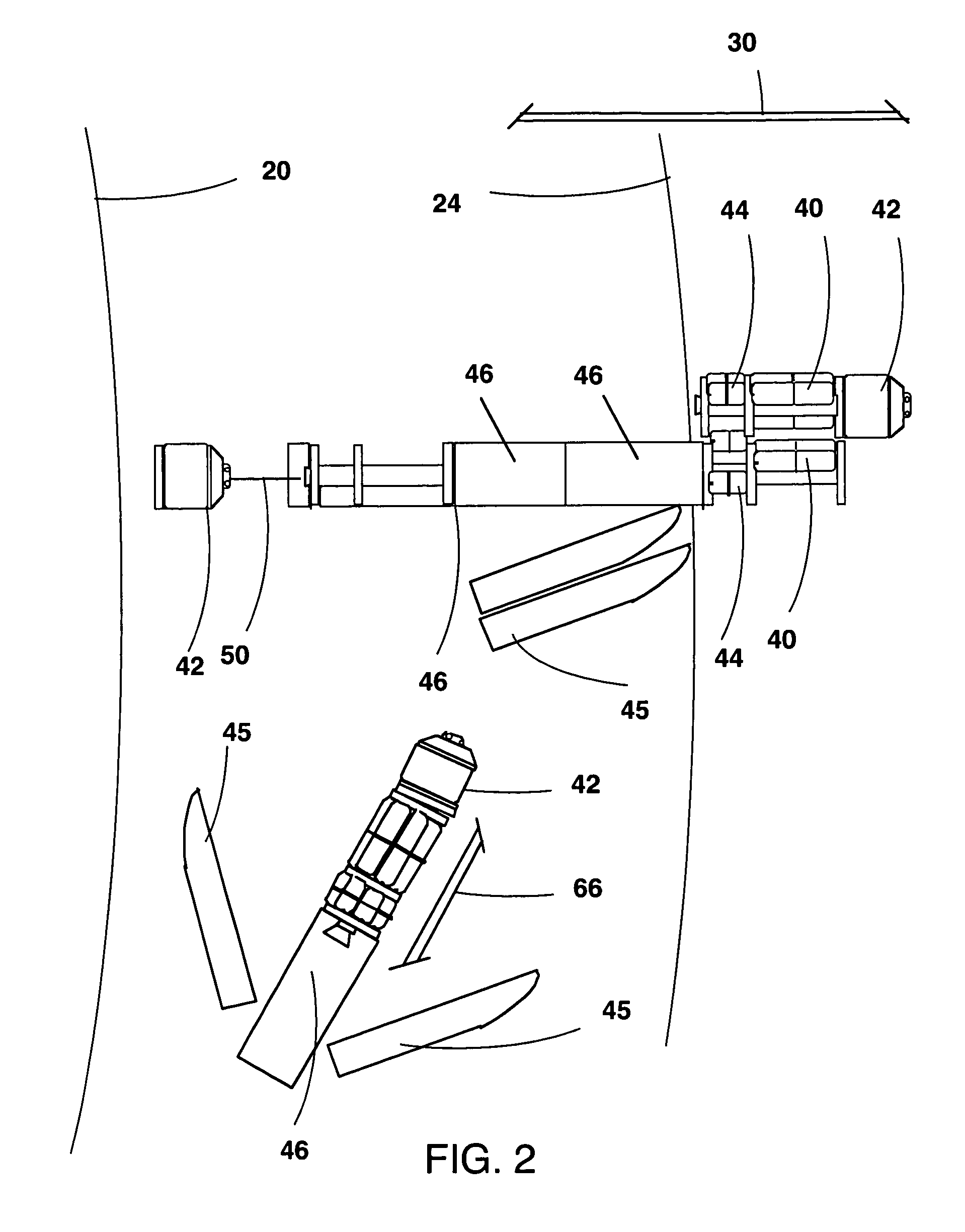
Airship shaped space craft
InactiveUS6471159B1Launch safetyReduce the average velocitySpace shuttlesSystems for re-entry to earthReverse orderJet engine
The present airship-shaped space craft has a middle fuselage extending in a fore-and-aft direction, and a pair of two outer fuselages extending in the fore-and-aft direction located symmetrically on both sides of the middle fuselage. In the above fuselages, gas of a specific gravity of which is smaller than that of air is filled, and the middle fuselage is connected with the outer fuselages by a horizontal wing. The horizontal wing is provided with propelling devices supported in a gimbal fashion for generating thrust in any optional direction, jet engines with backwards directed nozzles to be controlled within a range from a slantwise upward direction to a slantwise downward direction, and rocket engines with ejection nozzles to be controlled in right-and-left and up-and-down directions. During ascent of the space craft, at first the propelling devices, then the jet engines and at last the rocket engines are actuated so as to make the space craft reach and fly along a satellite orbit. Upon return of the space craft, the rocket engines, the jet engines and the propelling devices are actuated in reverse order, and aerodynamic heating at reentry into the atmospheric space can be reduced by making the space craft descend slowly. Also, control of the flight in the atmospheric space becomes easy, so that the space craft can safely and easily land on a predetermined narrow area of the ground.
Owner:BUNDO MUTSURO
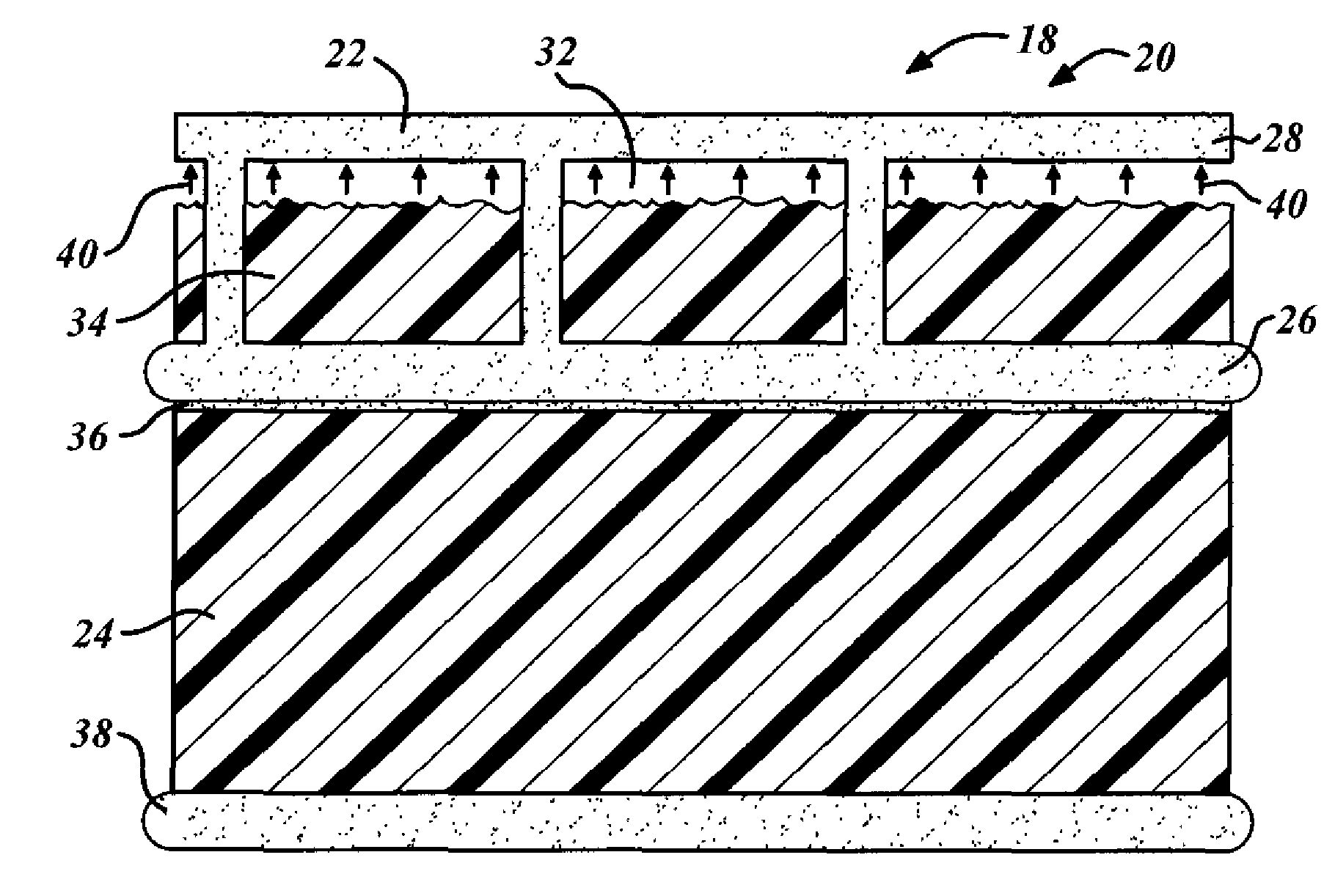
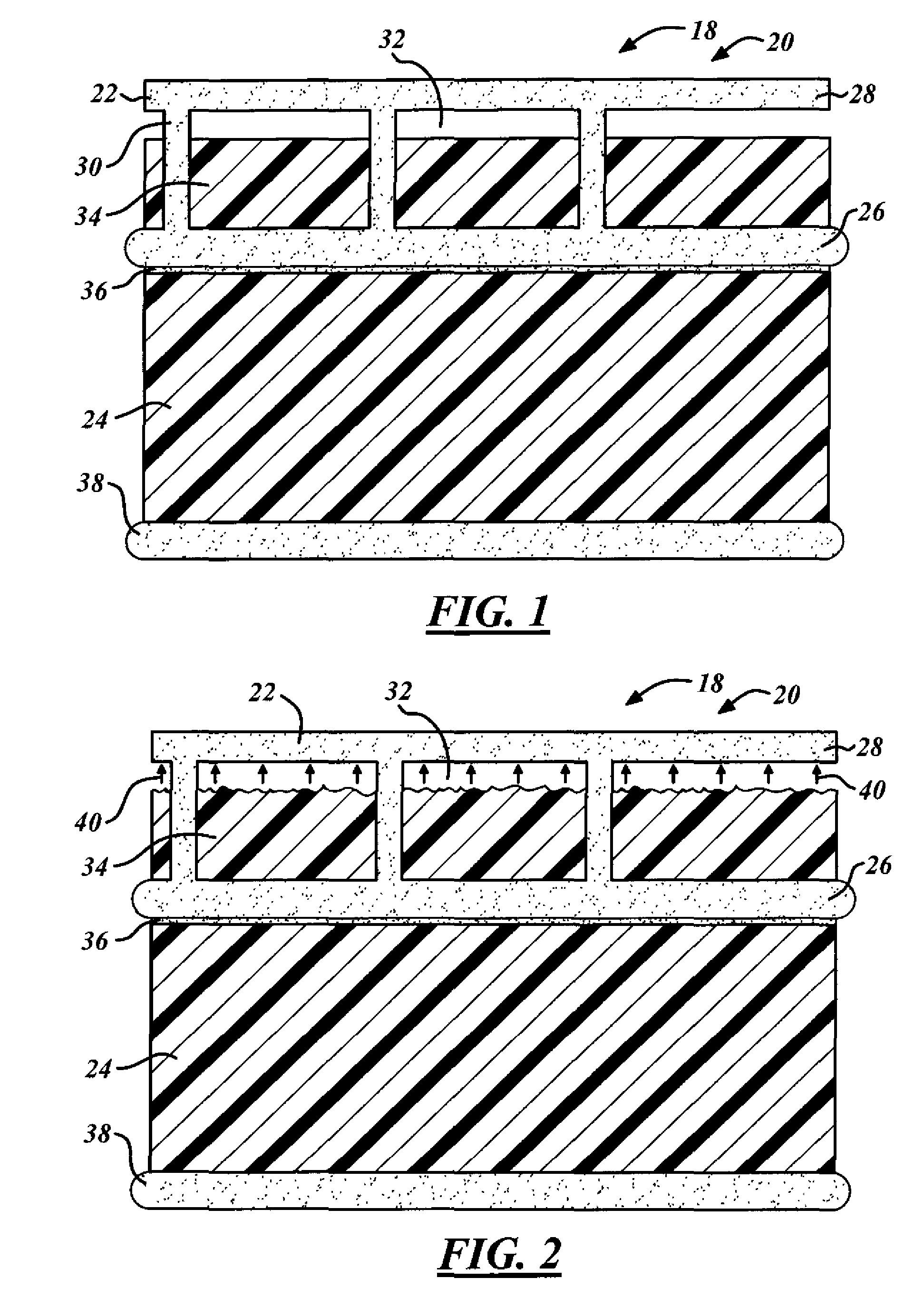
Cryogenic fuel tank insulation assembly
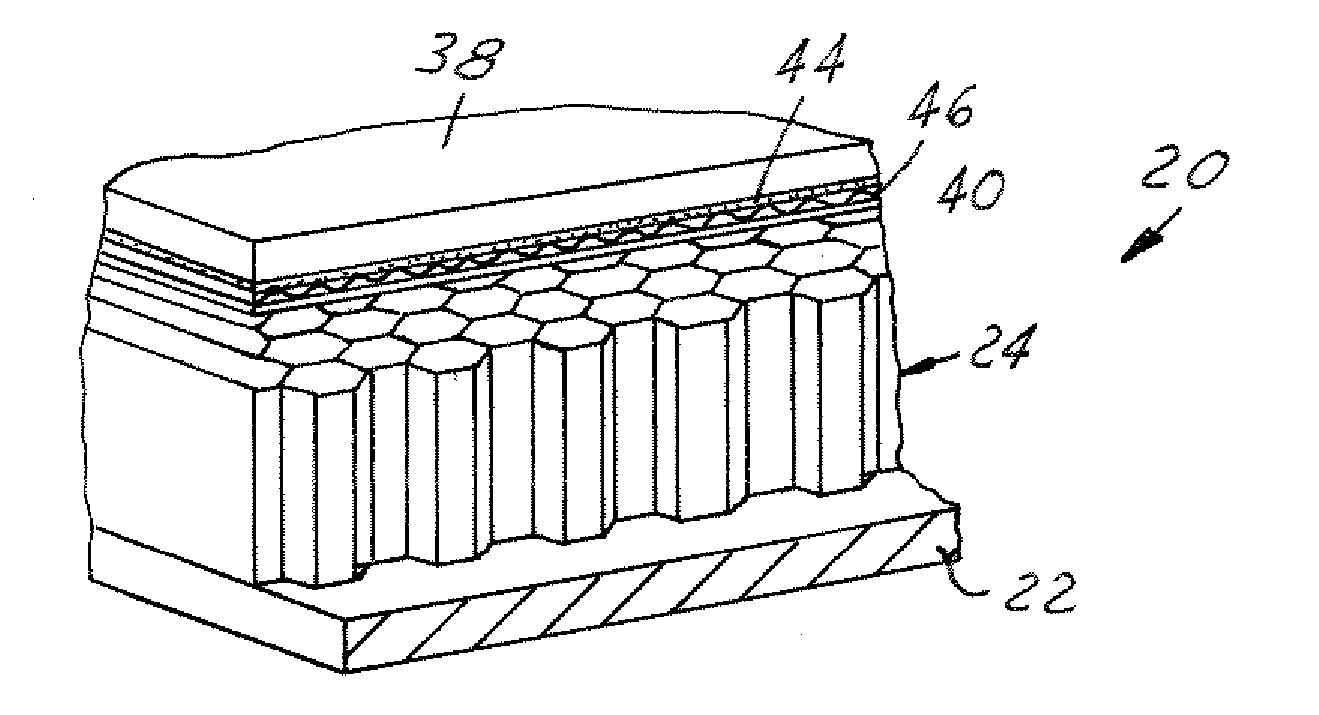
ActiveUS20050089661A1Excellent Adhesive PropertiesImprove the immunityCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic safety/emergency devicesFuel tankProcess engineering
A cryogenic fuel tank assembly 10 is provided comprising a cryogenic fuel tank wall 22. A foam assembly 24 is affixed to the cryogenic fuel tank wall 22, the foam assembly 24 having an inner surface 30 and an outer surface 32. A first solid film 40 bonded to the outer surface 32 to provide a uniform outer bonding surface 42. A thermal protection system assembly 38 is bonded to the uniform outer bonding surface 42.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Geopositionable expendable sensors and the use therefor for monitoring surface conditions
InactiveUS6885299B2Narrow downFinish quicklyCosmonautic environmental control arrangementElectric signal transmission systemsTerrainRadioactive agent
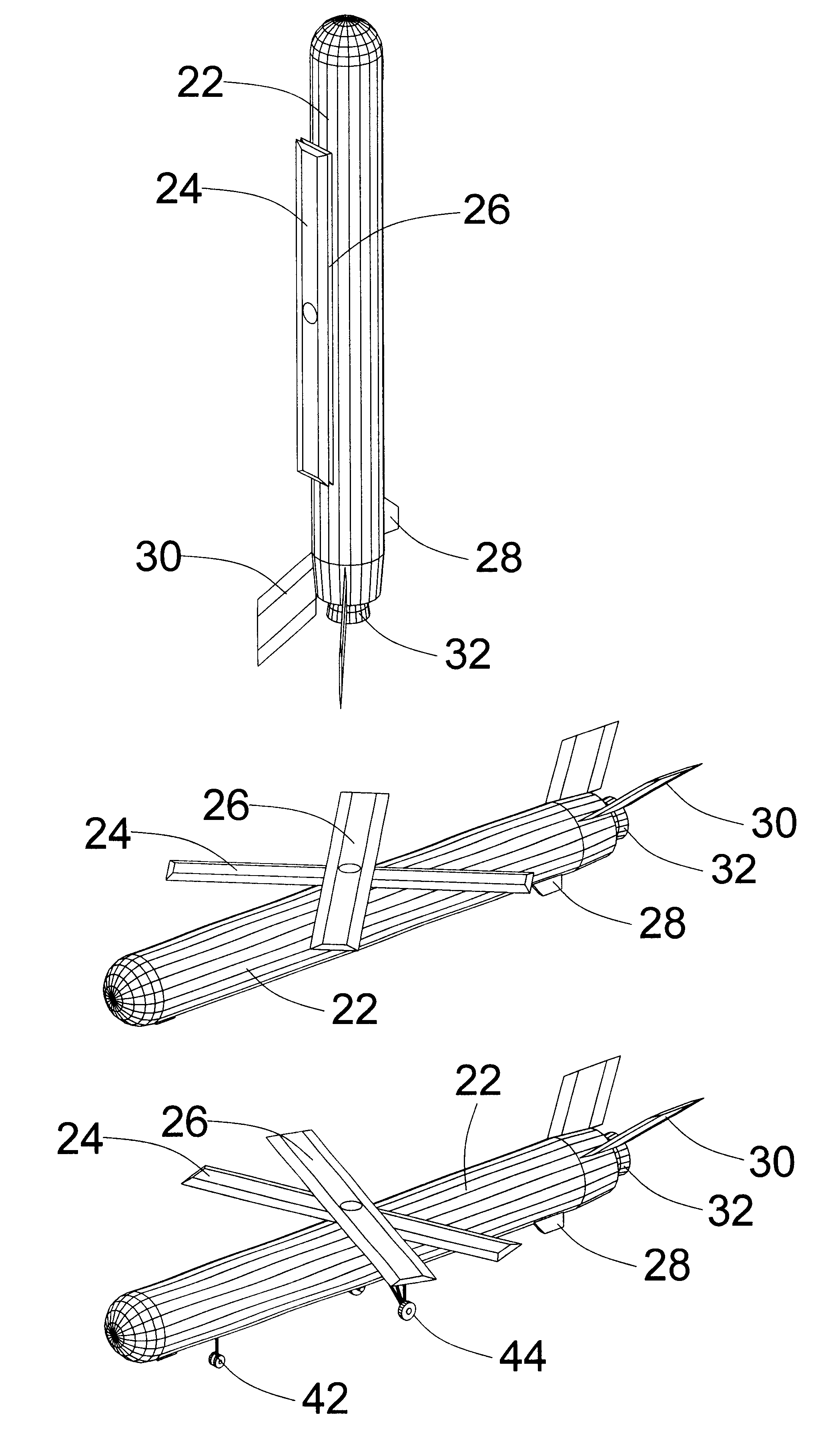
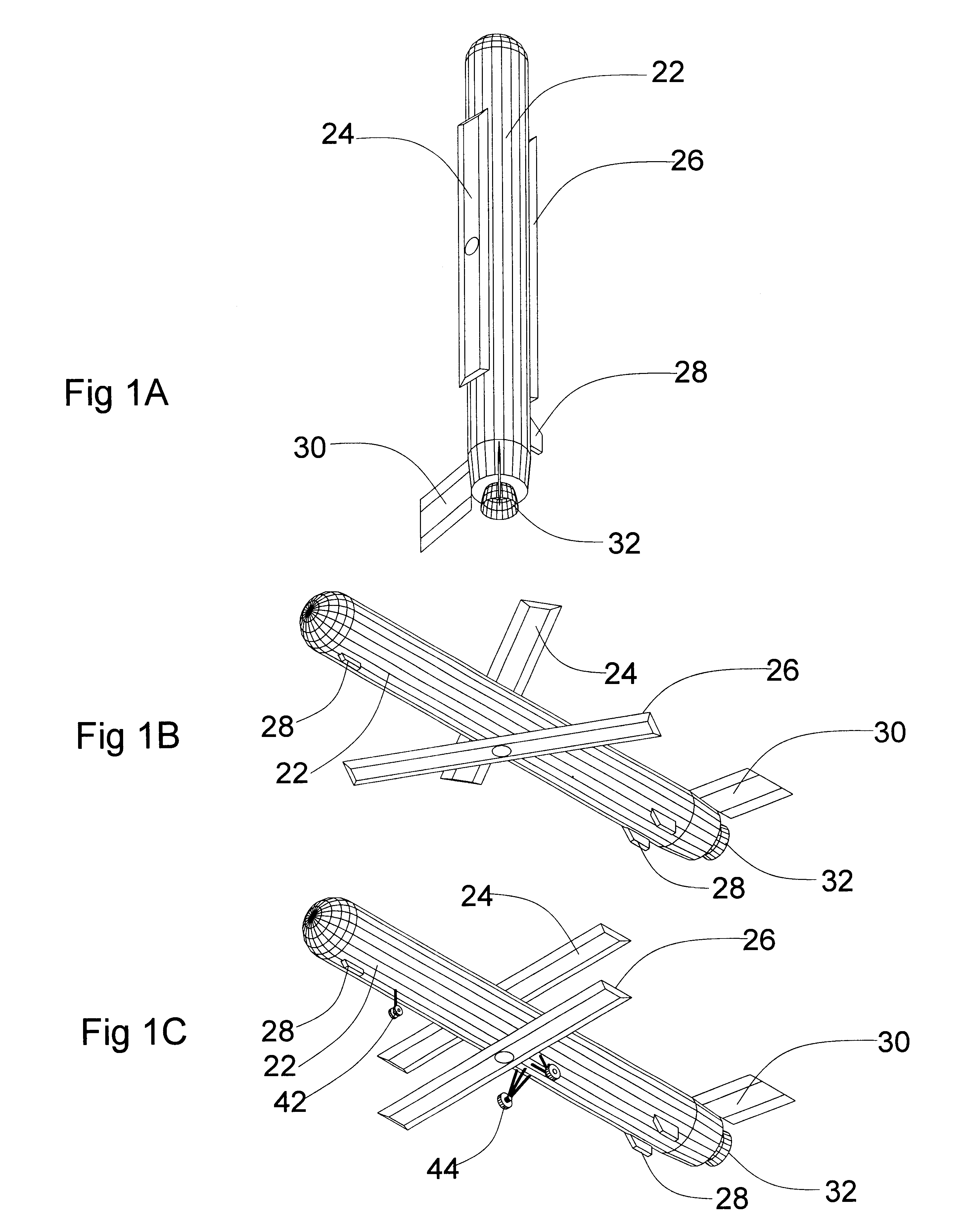
A sensor system for monitoring for the presence of contamination with one or more contaminating biological, chemical and / or radioactive agents on a terrain surface, and creating a contamination map thereof. The sensor system includes a plurality of sensor pods, a ground station, an airborne dispensing portion, and an airborne monitoring portion. The sensor pods include a pod housing, a descent slowing airfoil, a detector unit for detection of the contaminating agent and outputting contaminating agent data, a processor for processing the contaminating agent data, a GPS unit for determining the position of the sensor, and a transmitter for transmitting contamination agent data and position data to the airborne monitoring portion. The airborne monitoring portion receives the transmitted data from the sensor pods, and relays the data to the ground station, where the contamination map is made available.
Owner:COOPER GUY F +4
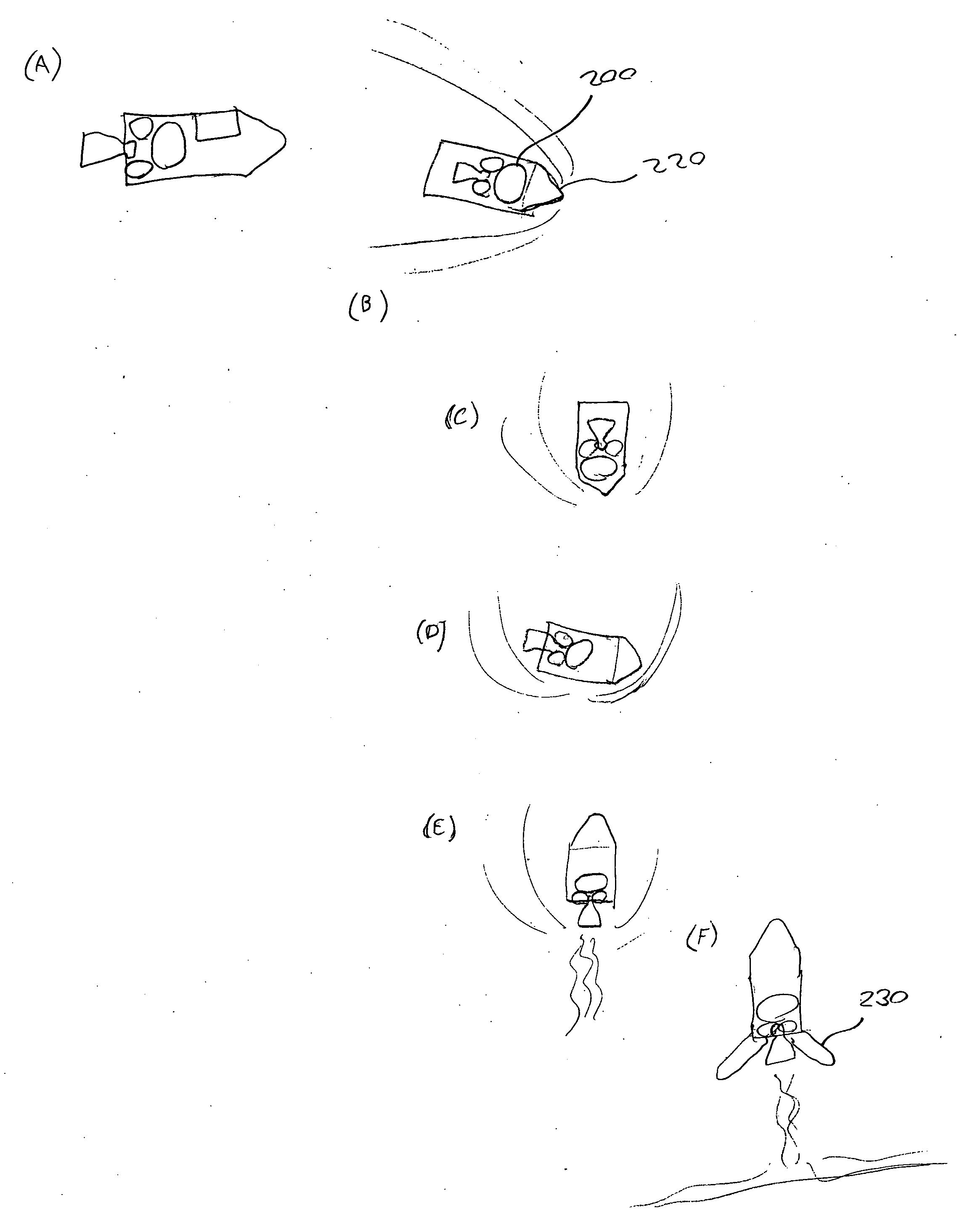
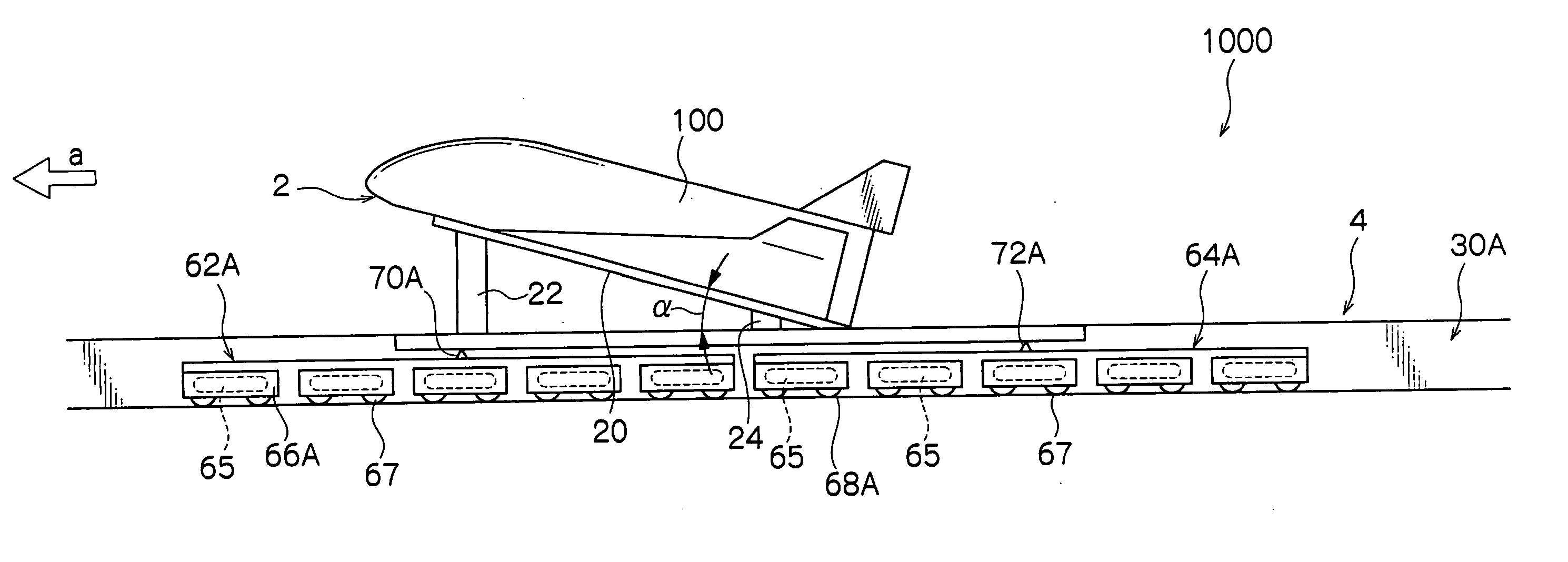
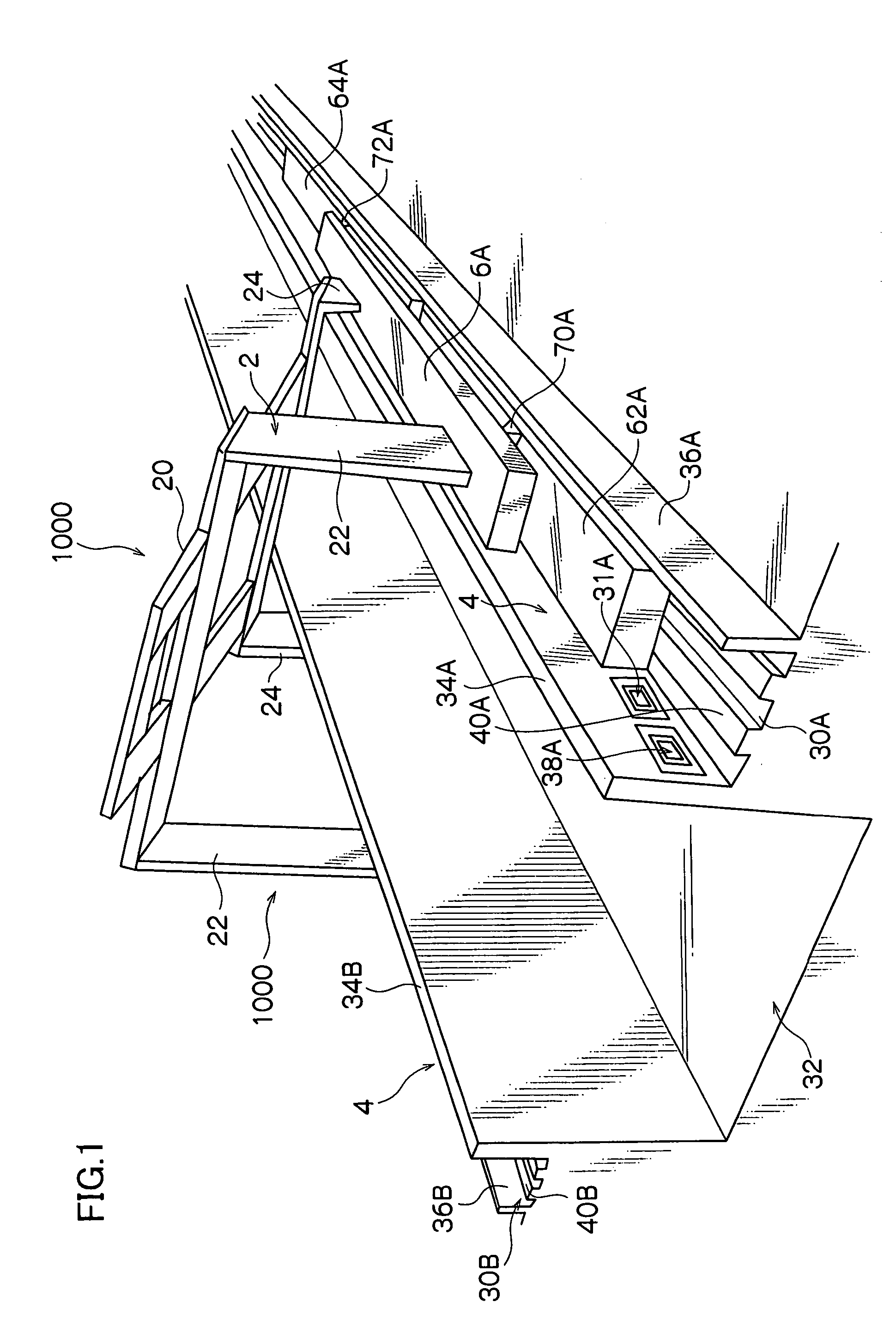
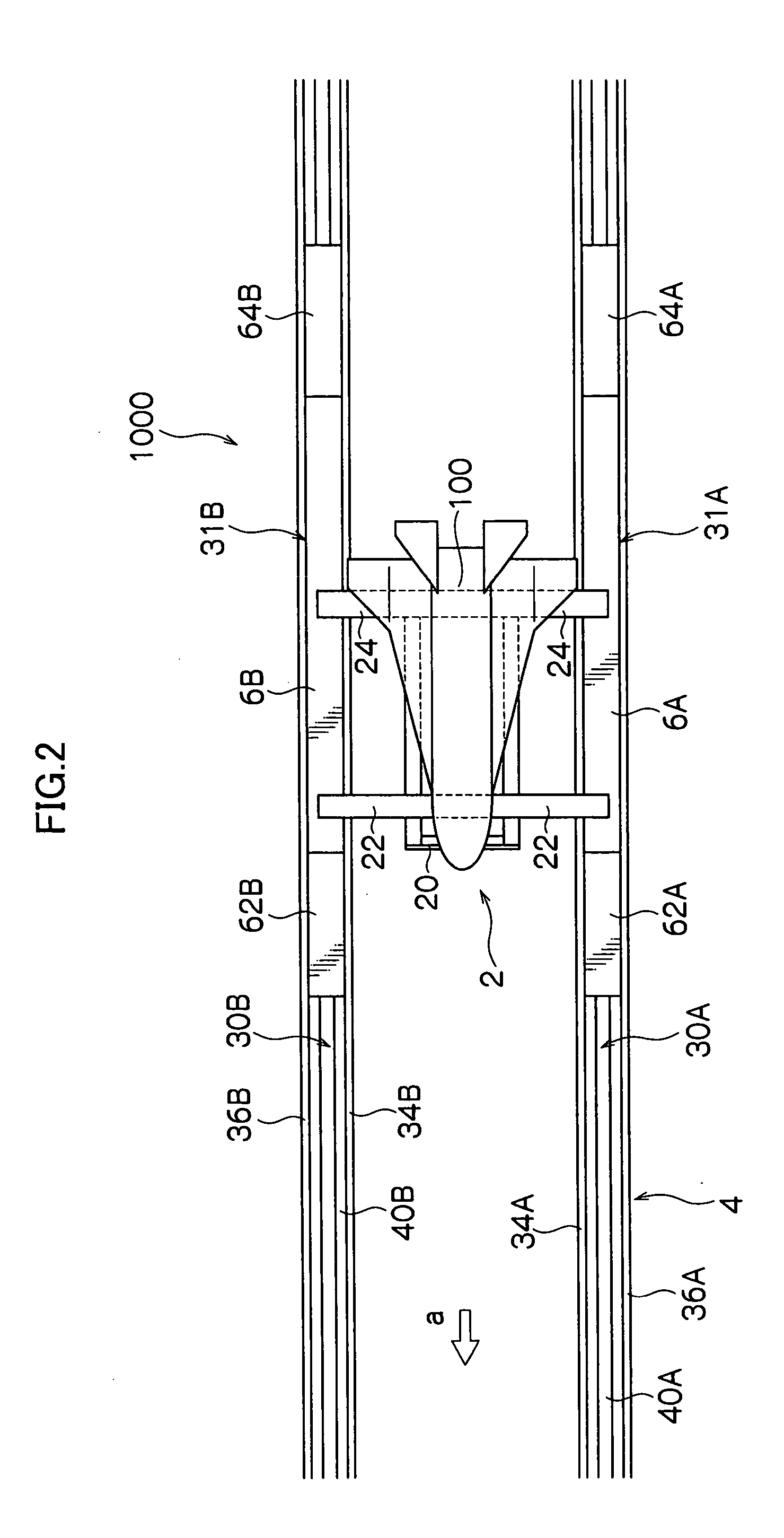
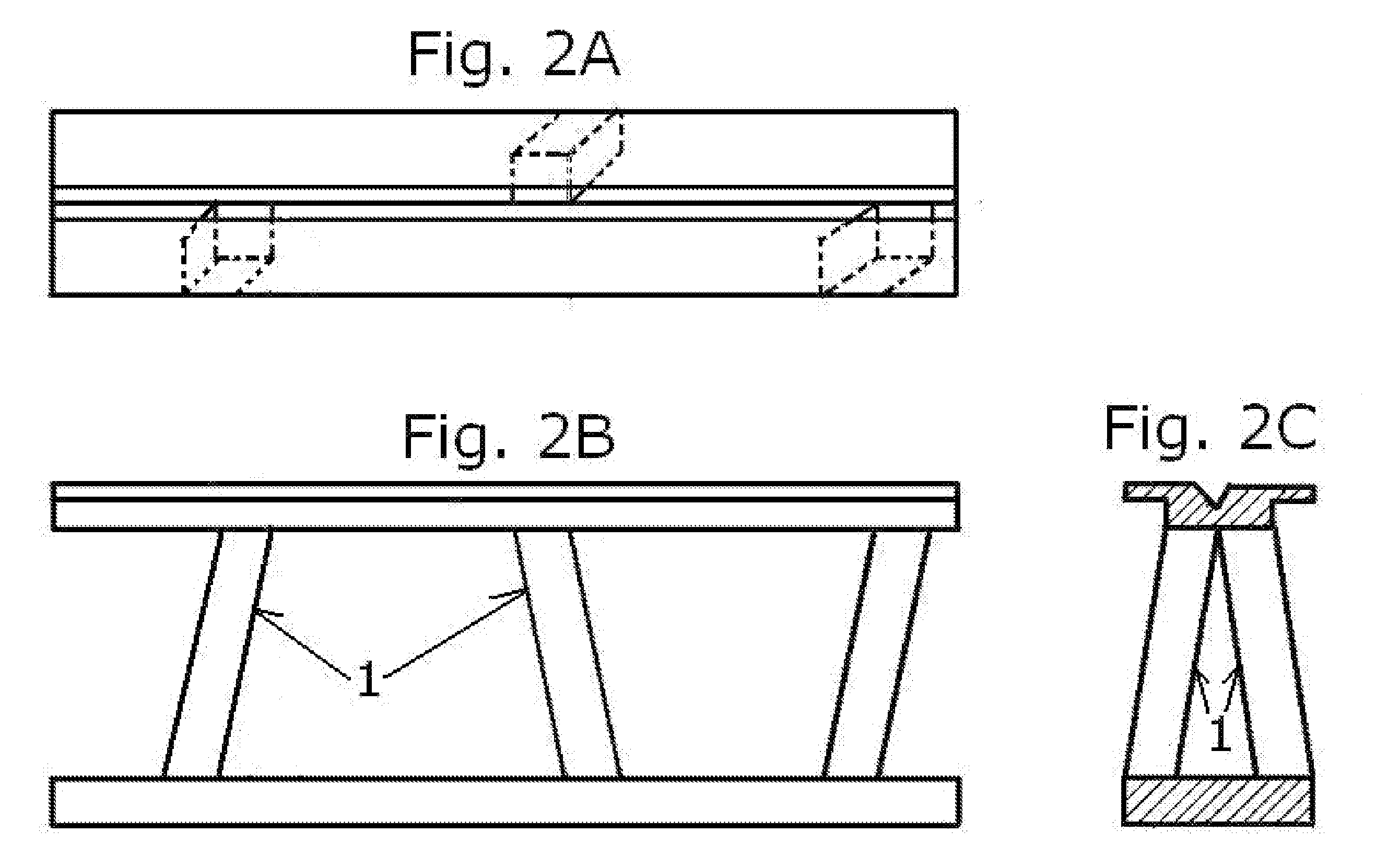
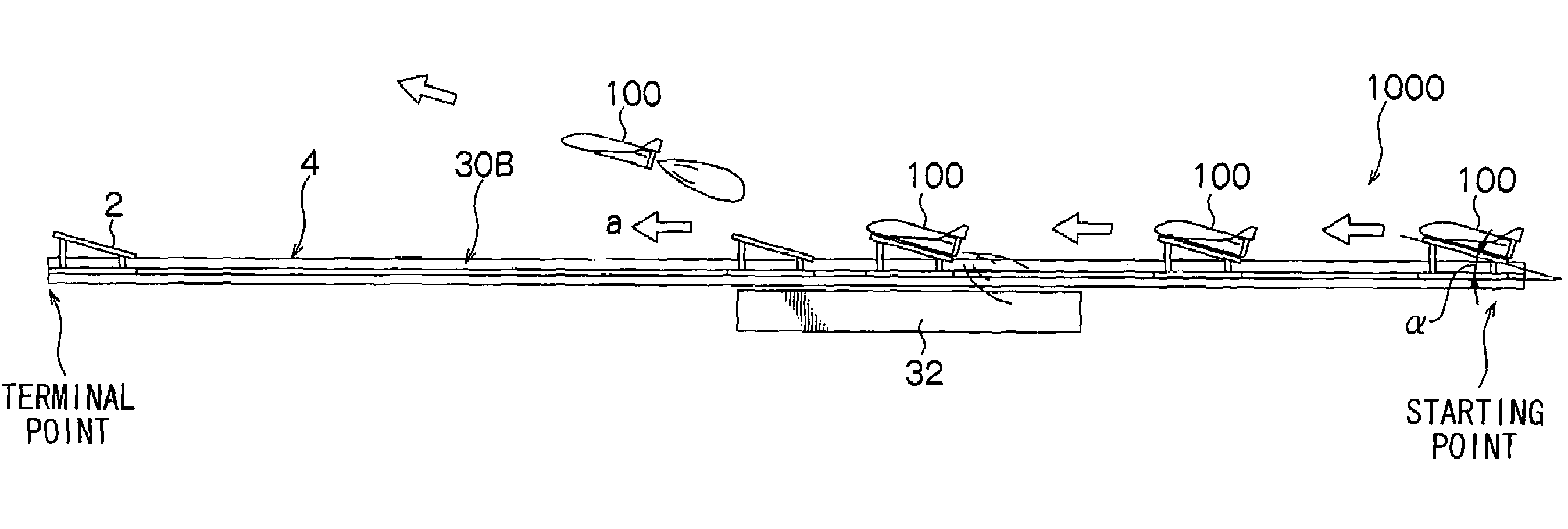
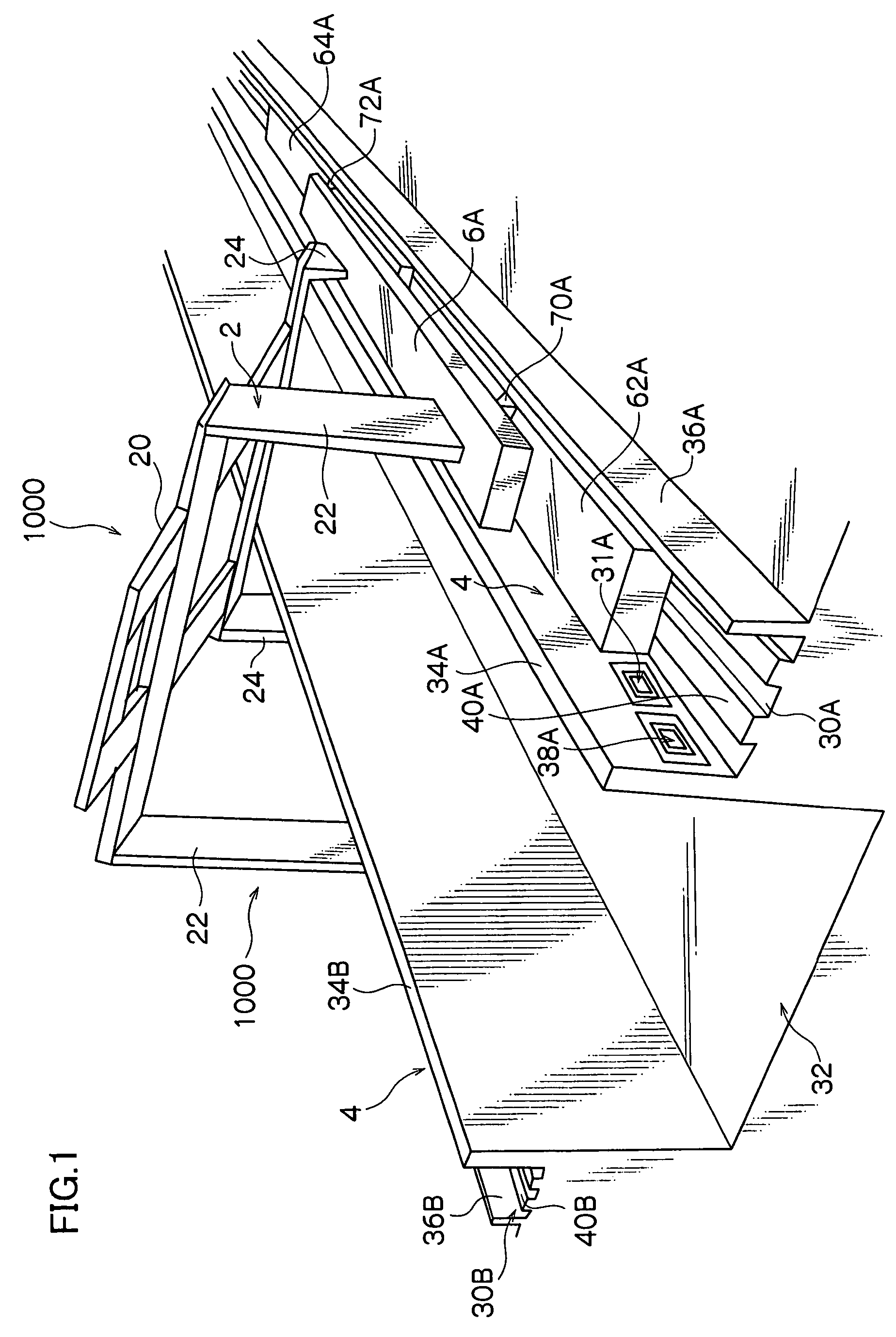
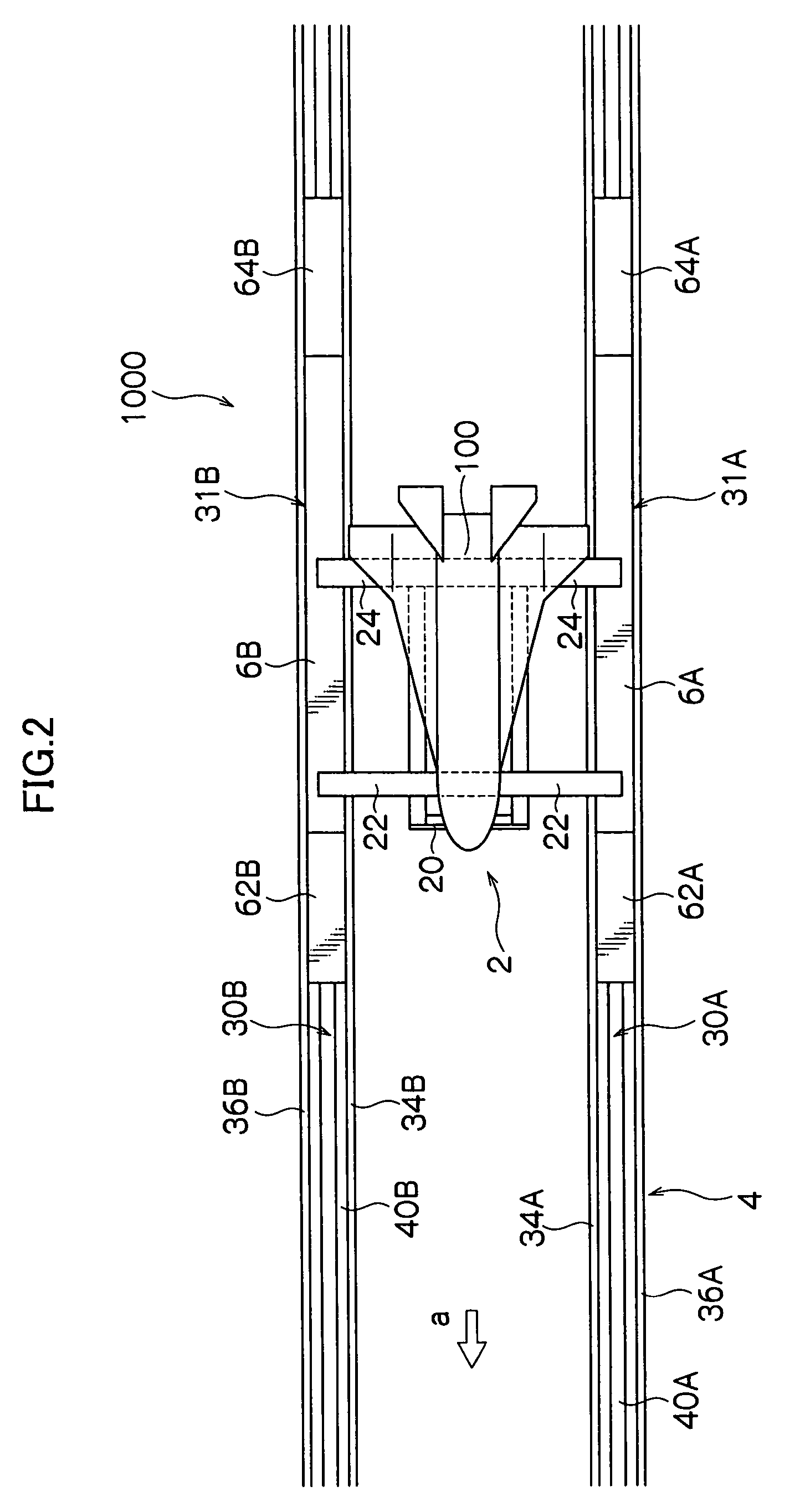
Flying vehicle-launching apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050082424A1Accelerated safely and efficientlyCosmonautic ground equipmentsLaunch systemsFlight vehicleAngle of attack
A flying vehicle-launching apparatus and method for launching a winged flying vehicle by accelerating the vehicle in a predetermined direction includes a flying vehicle-supporting platform, a guide device, and a driving device. The flying vehicle-supporting platform supports the winged flying vehicle so that it can lift off therefrom. The guide device supports the flying vehicle-supporting platform across two or more separated and parallel guide ways and guides the flying vehicle-supporting platform along the guide ways. In the flying vehicle-launching method, a propulsive engine of the winged flying vehicle is started after initiating acceleration with a flying vehicle-accelerating device. The winged flying vehicle is released from the flying vehicle-accelerating device in a predetermined angle of attack that is positive to a direction of acceleration after reaching a predetermined velocity.
Owner:CENTRAL JAPAN RAILWAY COMPANY
High altitude airborne craft used as radio relay and method for placing said airborne craft on station
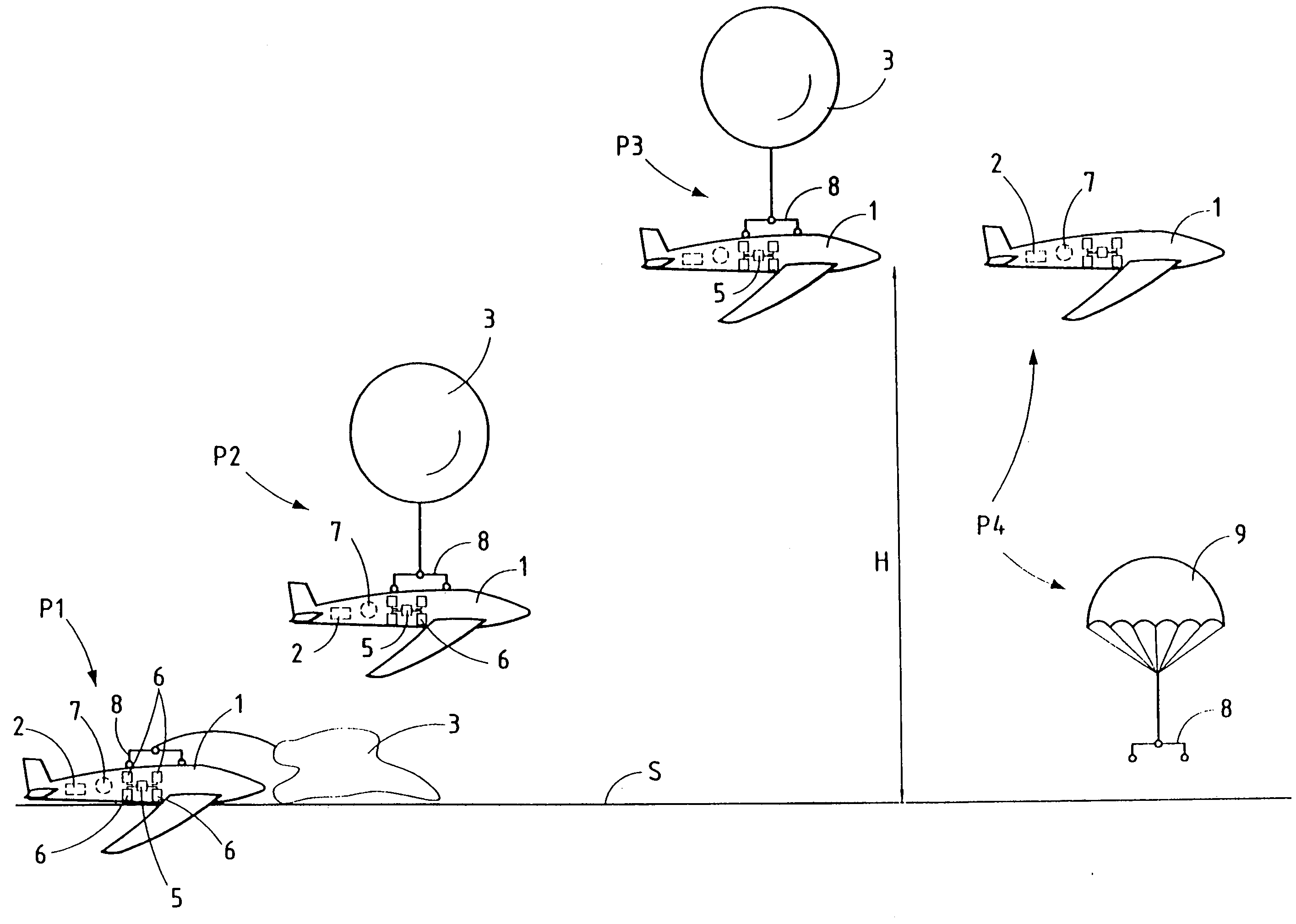
InactiveUS7313362B1Low costAircraft componentsCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusFlight vehicleStratosphere
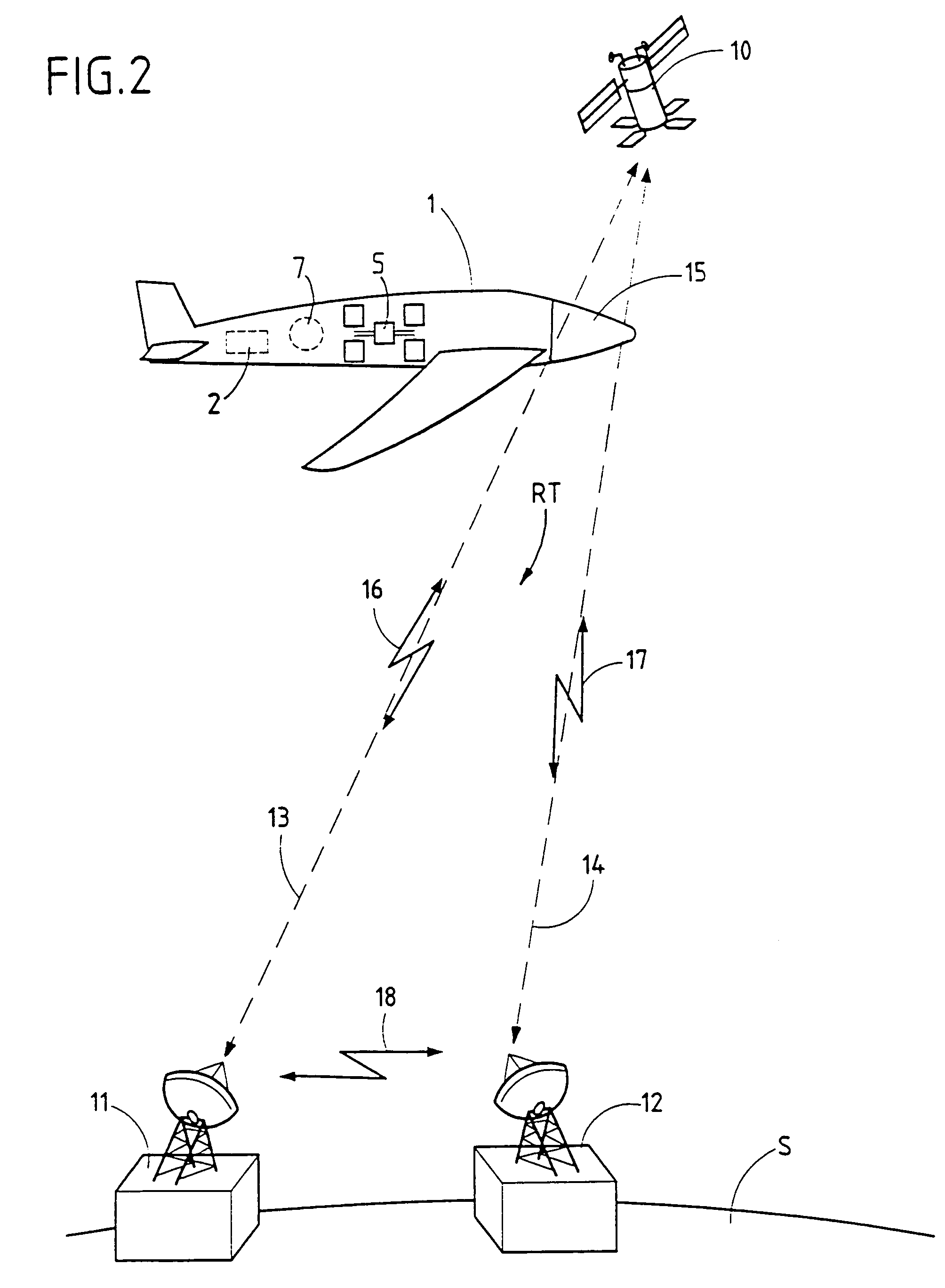
The present invention relates to an aircraft and to a method of getting the aircraft onto station. According to the invention, said aircraft (1) includes propulsion means (2) capable only of enabling said aircraft (1) to move and to orient itself at high altitude, and said aircraft (1) is taken to its station in the high atmosphere, in particular in the stratosphere, by means of an independent transporter (3).
Owner:RPX CORP
Spacecraft Launch and Exploration System
InactiveUS20110042521A1Maximum flexibilityMaximum safetyCosmonautic ground equipmentsLaunch systemsSingle stageOn board
This invention is a launch-to-space, refuel and return system which comprises: a unique circular and straight maglev track and maglev sled spacecraft launcher; a single stage-to-LEO spacecraft (Mother Spacecraft); an orbiting space platform (OSP); a currently utilized Space Shuttle is altered to improve its safety, range, longevity and versatility which serves as a prototype for the Mother Spacecraft design. The Mother Spacecraft is releasably attached to the maglev sled and propulsion for the maglev sled is supplied by magnetic propulsion and on-board rocket propulsion. The collapsible OSP can fit into the Space Shuttle storage bay and is remotely deployed. The OSP is a refueling depot for the Mother Spacecraft, the Space Shuttle, as well as a rendezvous point for various space missions. A single, liquid, non-cryogenic rocket fuel is standardized throughout the entire system which eliminates: all vertical launches; all expendables; all solid rocket propellants.
Owner:SAMPLE DANIEL S
Flying vehicle-launching apparatus and method
InactiveUS7232092B2Accelerated safely and efficientlyCosmonautic ground equipmentsLaunch systemsFlight vehicleAngle of attack
A flying vehicle-launching apparatus and method for launching a winged flying vehicle by accelerating the vehicle in a predetermined direction includes a flying vehicle-supporting platform, a guide device, and a driving device. The flying vehicle-supporting platform supports the winged flying vehicle so that it can lift off therefrom. The guide device supports the flying vehicle-supporting platform across two or more separated and parallel guide ways and guides the flying vehicle-supporting platform along the guide ways.In the flying vehicle-launching method, a propulsive engine of the winged flying vehicle is started after initiating acceleration with a flying vehicle-accelerating device. The winged flying vehicle is released from the flying vehicle-accelerating device in a predetermined angle of attack that is positive to a direction of acceleration after reaching a predetermined velocity.
Owner:CENTRAL JAPAN RAILWAY COMPANY
Passenger transport module system for supersonic aircraft
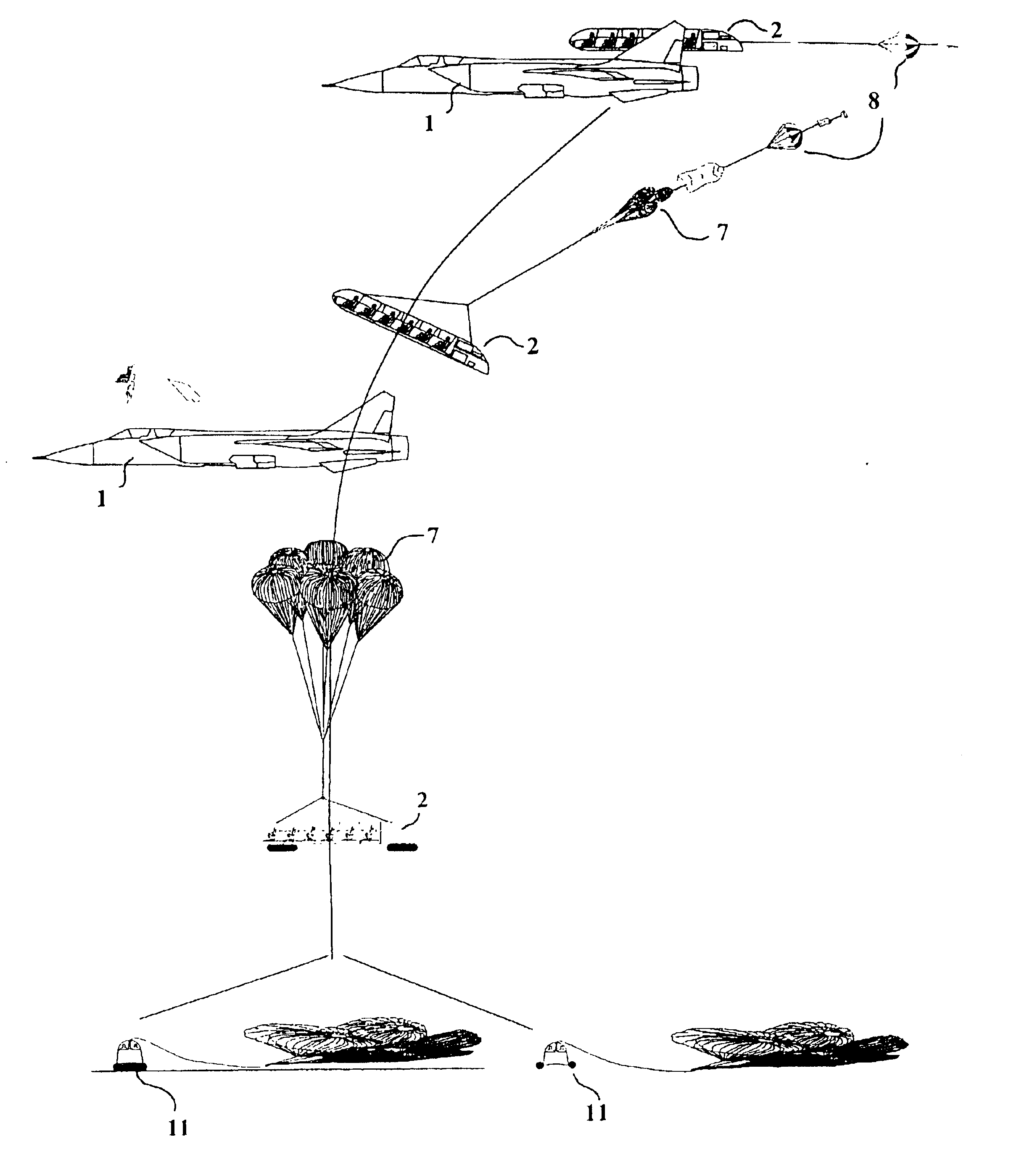
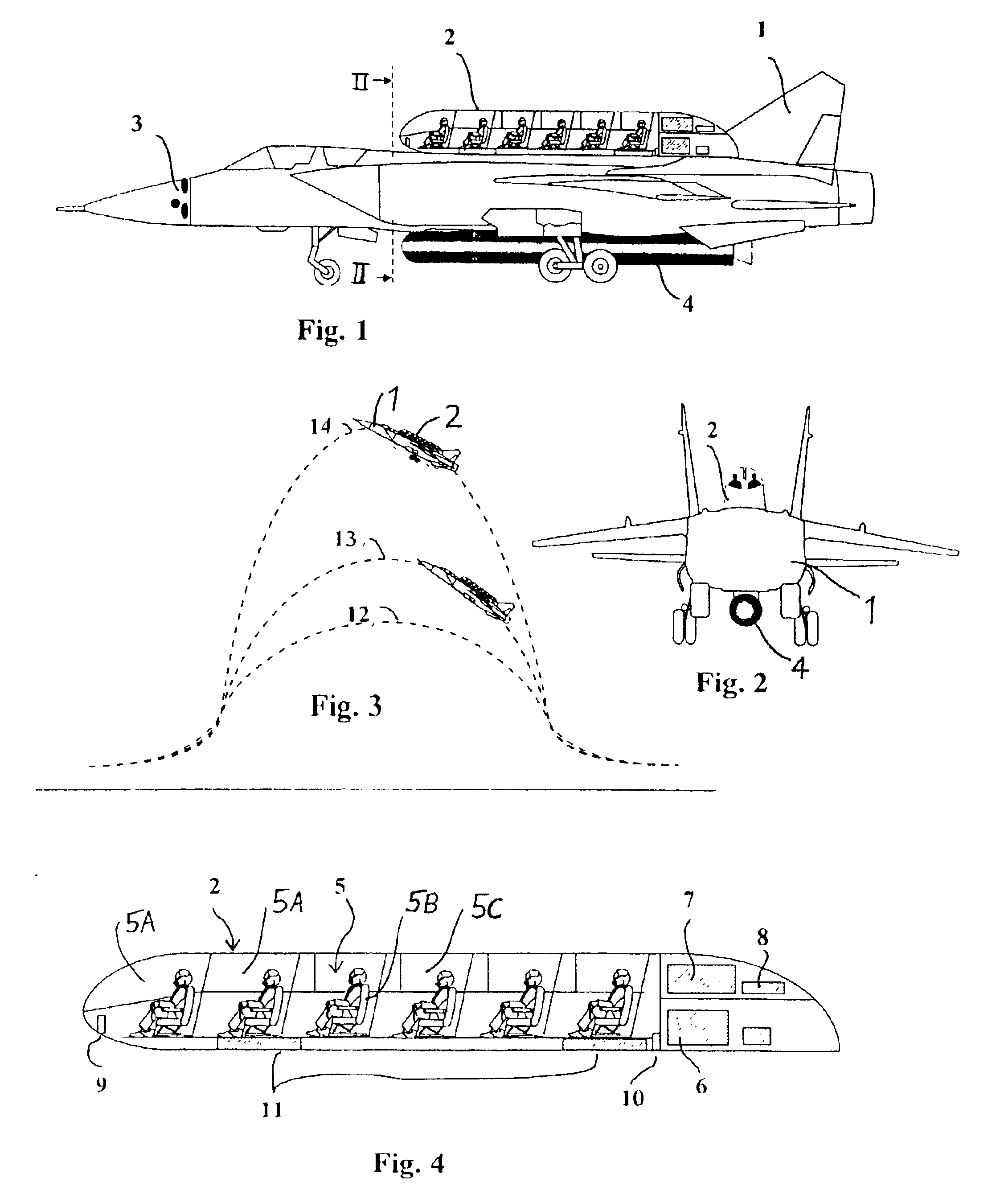
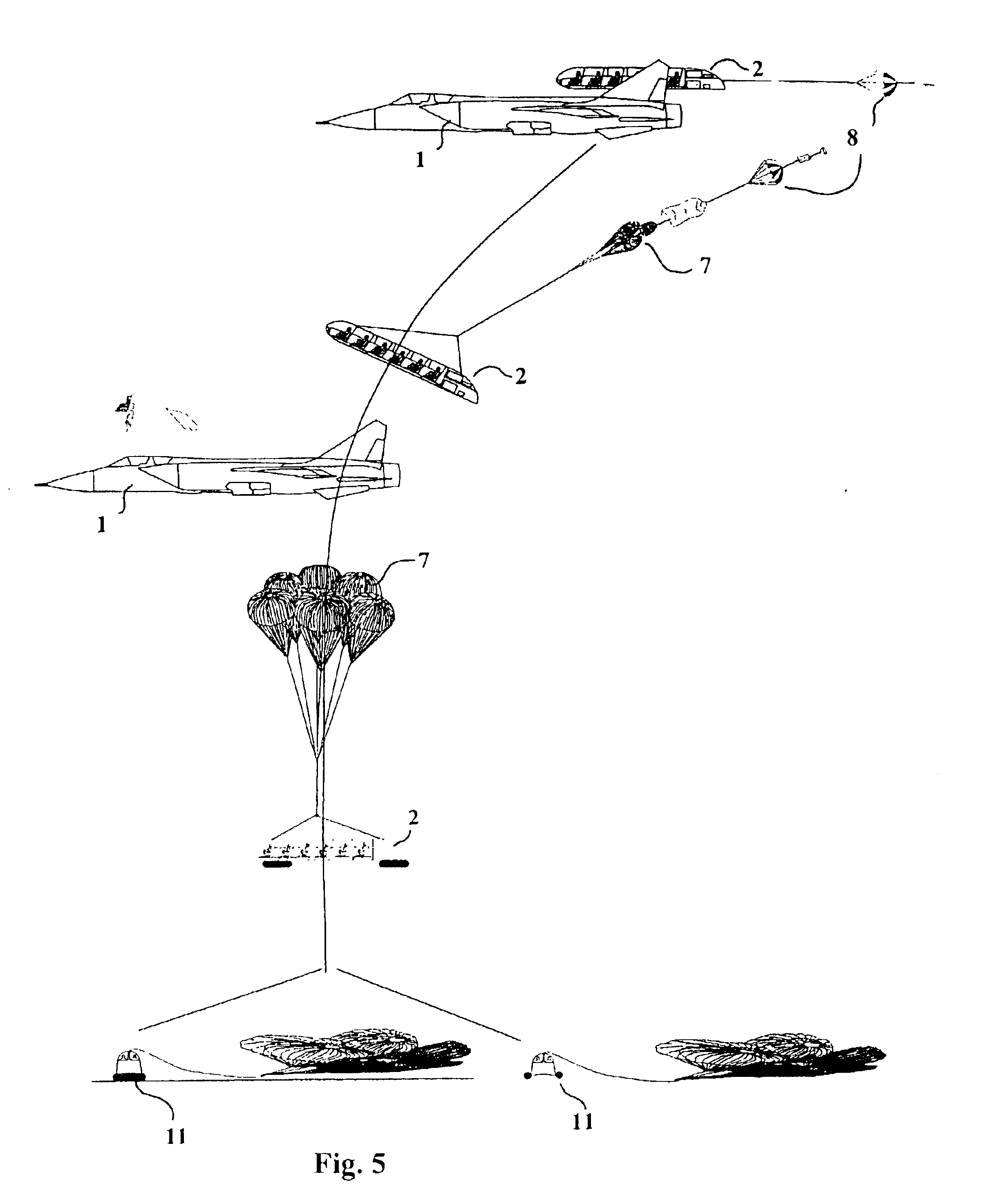
InactiveUS6817579B2Solve insufficient capacityLittle complicationAircraft ejection meansConvertible aircraftsLife supportSTI Outpatient
An autonomous passenger module is releasably carried on a super-sonic aircraft, such as a military fighter jet, for carrying plural passengers on supersonic and near space flights. The passenger module is equipped with passenger service and life support systems to provide oxygen and the like, a parachute system, and a landing airbag or flotation aid system. The module remains mounted on the aircraft throughout a normal flight. In an emergency situation, the module separates from the aircraft by means of releasable connector elements and descends using parachutes. The module provides high passenger capacity at a low cost in a simple manner for commercial supersonic flights using an existing supersonic aircraft as a carrier platform.
Owner:INDEN WERNER
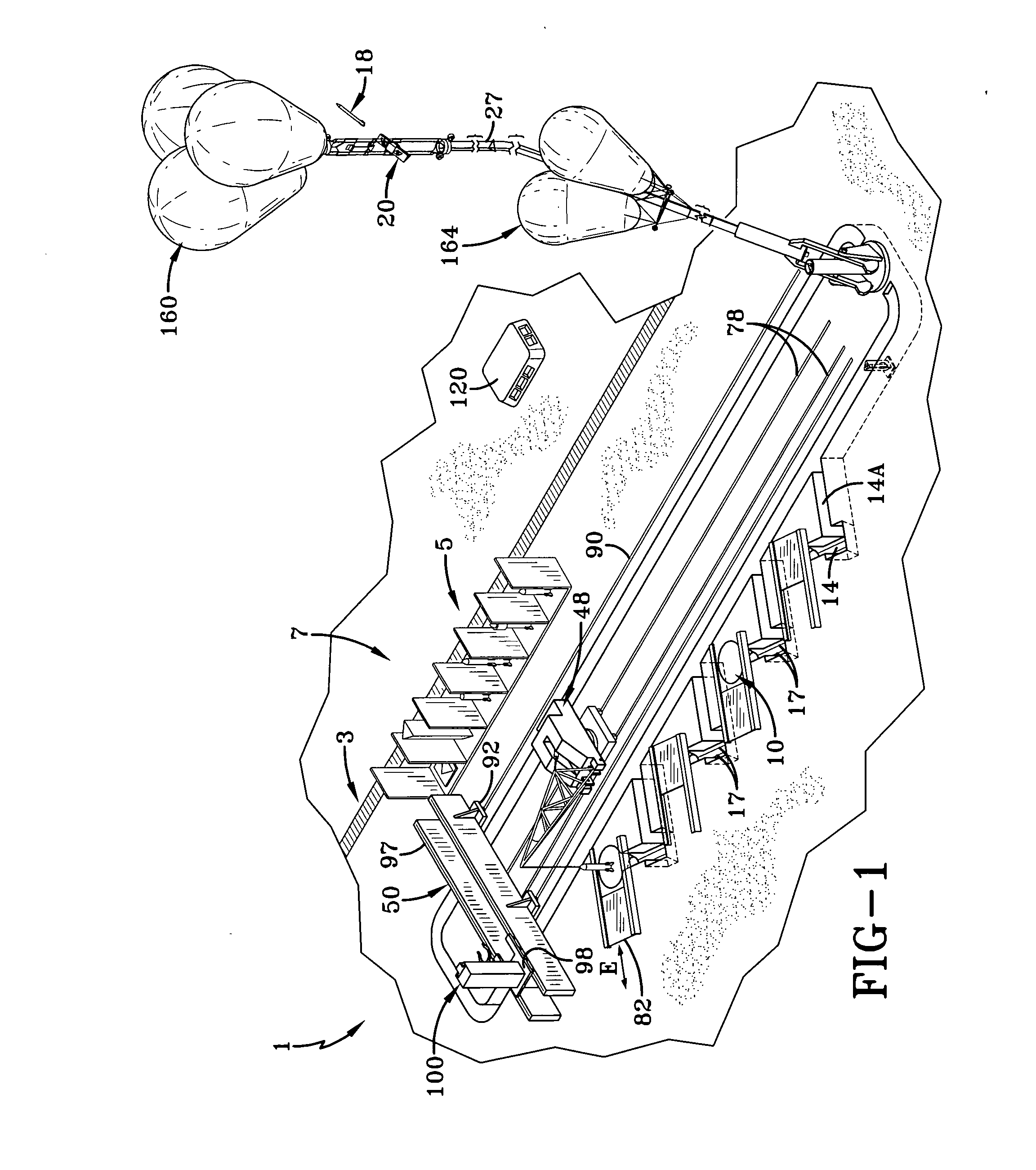
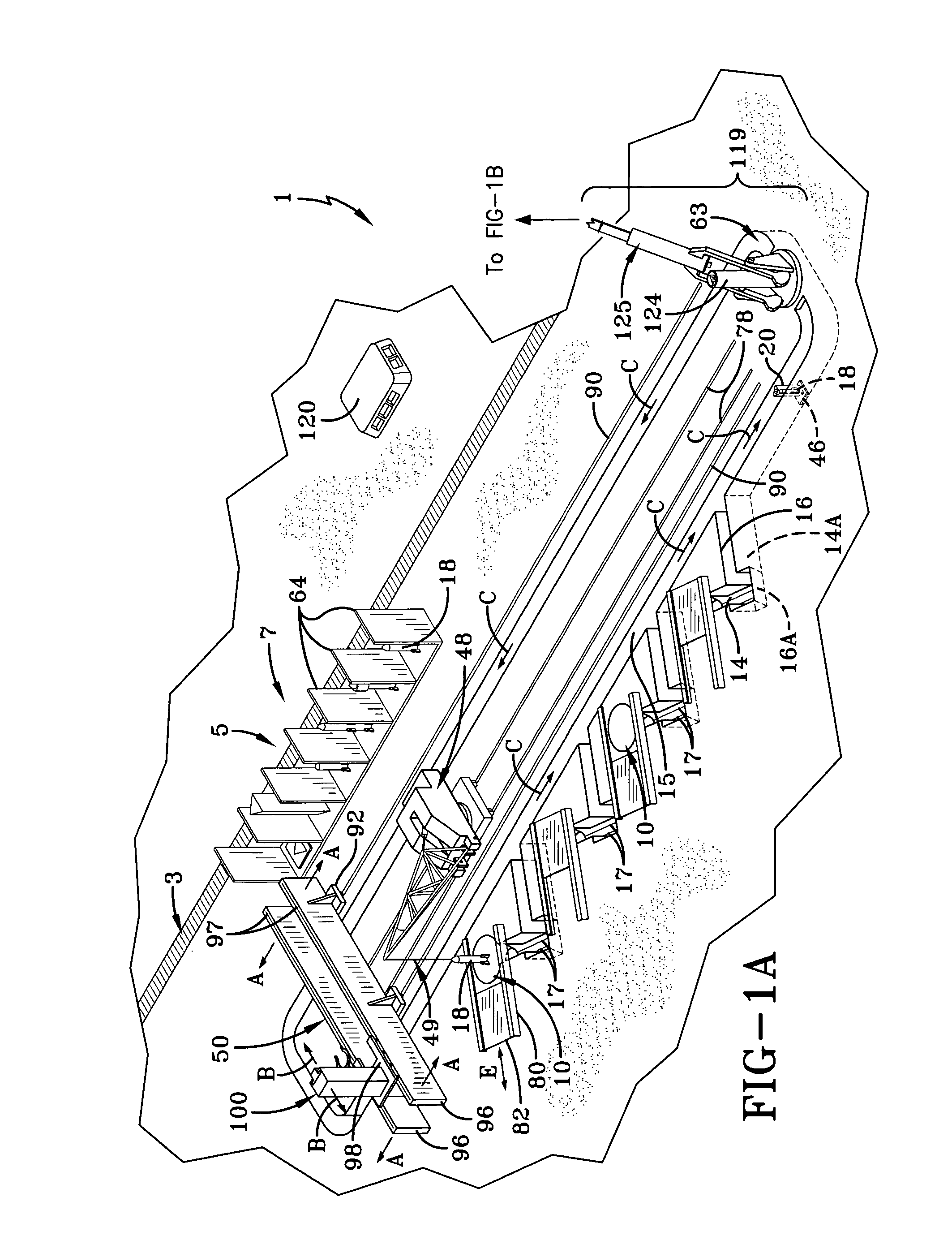
Rocket Launch System and Supporting Apparatus
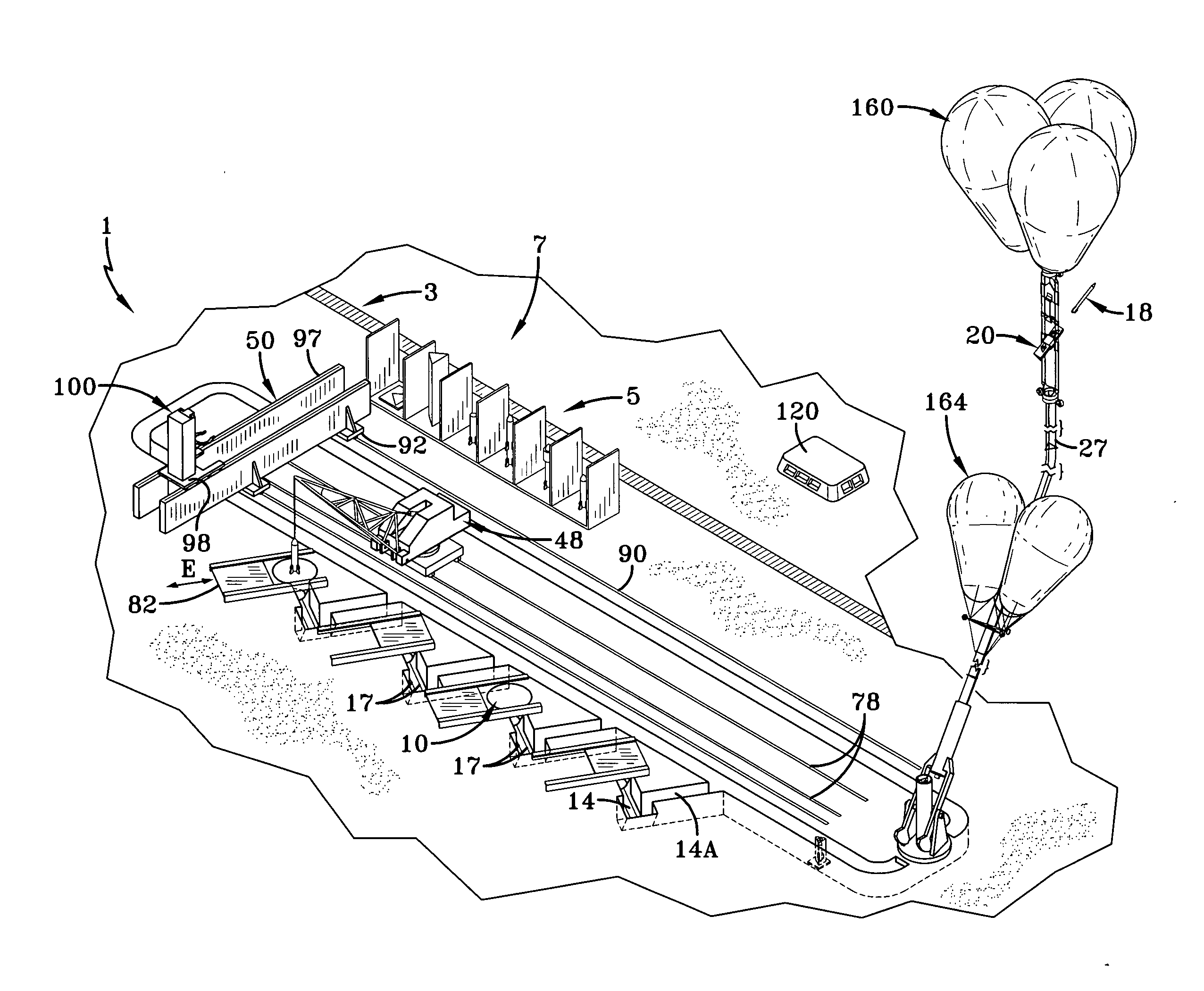
ActiveUS20130007935A1Overall light weightRocket launchersCosmonautic ground equipmentsDocking stationRocket launch
A rocket launch system (1) includes a tubular rocket launcher carriage (2) with electromotive cableway traction drives (26) conveyed beneath a two axis pivot (63) anchored to the earth, elevated into a co-axial transfer tube (124, 143) leading to three primary tether cables (27) whose weight is offset by balloons (164). The carriage is conveyed to a docking station (166) supported into the stratosphere by a pair of secondary cables (184) suspended under an attachment frame (162) for tensioning balloons. The carriage is engaged by a carriage end gripper (196) guided by two secondary and two tertiary cables (186) and lifted by a lower hoist (198) guided by the secondary cables. This lower hoist is supported by an upper hoist (168) suspended from the tensioning balloons attachment frame. The carriage, which engages a lift ring (183) guided by two secondary cables, is elevated further, rotated as desired, with rocket release and nearly recoilless ejection during freefall of the carriage, with engine ignition occurring at a safe distance.
Owner:CHIN +1
Reversible space plane
A reversible aerospace plane includes an air intake at a first end of the aerospace plane, at least one heat exchanger disposed in the aerospace plane, an engine at a second end of the aerospace plane, wherein the aerospace plane is configured to accelerate in a first direction and configured to glide and land in a second direction, wherein the second direction is substantially in a reverse direction from the first direction.
Owner:JANEKE CHARL E
Centripetal aerodynamic platform spacecraft
ActiveUS20170190446A1Reducing required liquid oxygenReducing booster tank capacity weightCosmonautic environmental control arrangementLaunch systemsGravitationSpacecraft
An aerodynamic platform or spacecraft including a habitable 1G centripetal force rotating gravity producing interior corridor within an aerodynamic shell and an aerodynamic drone booster launch system with reentry and reuse capability.
Owner:WILLIAMS SR LAWRENCE ELLIS
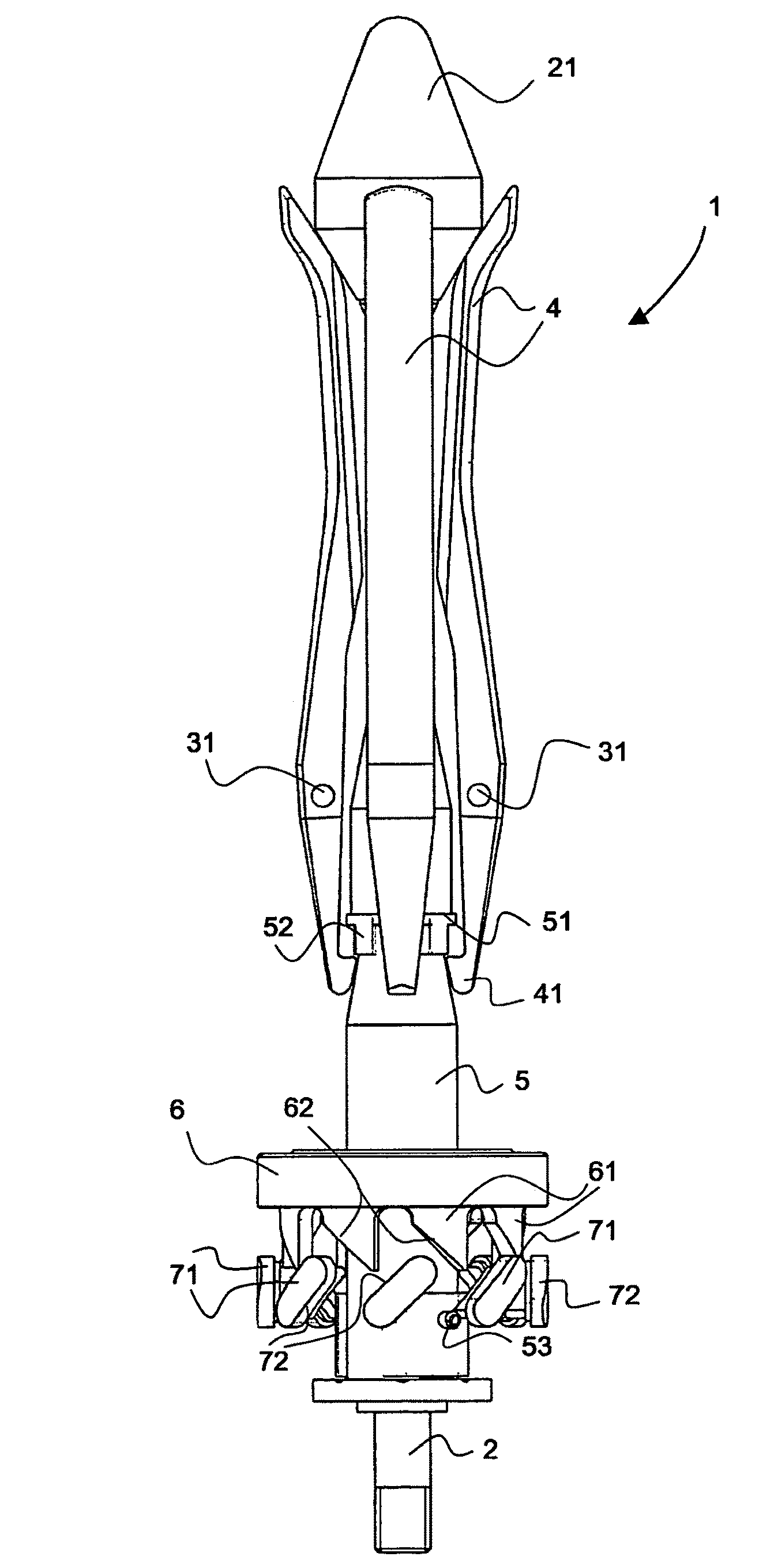
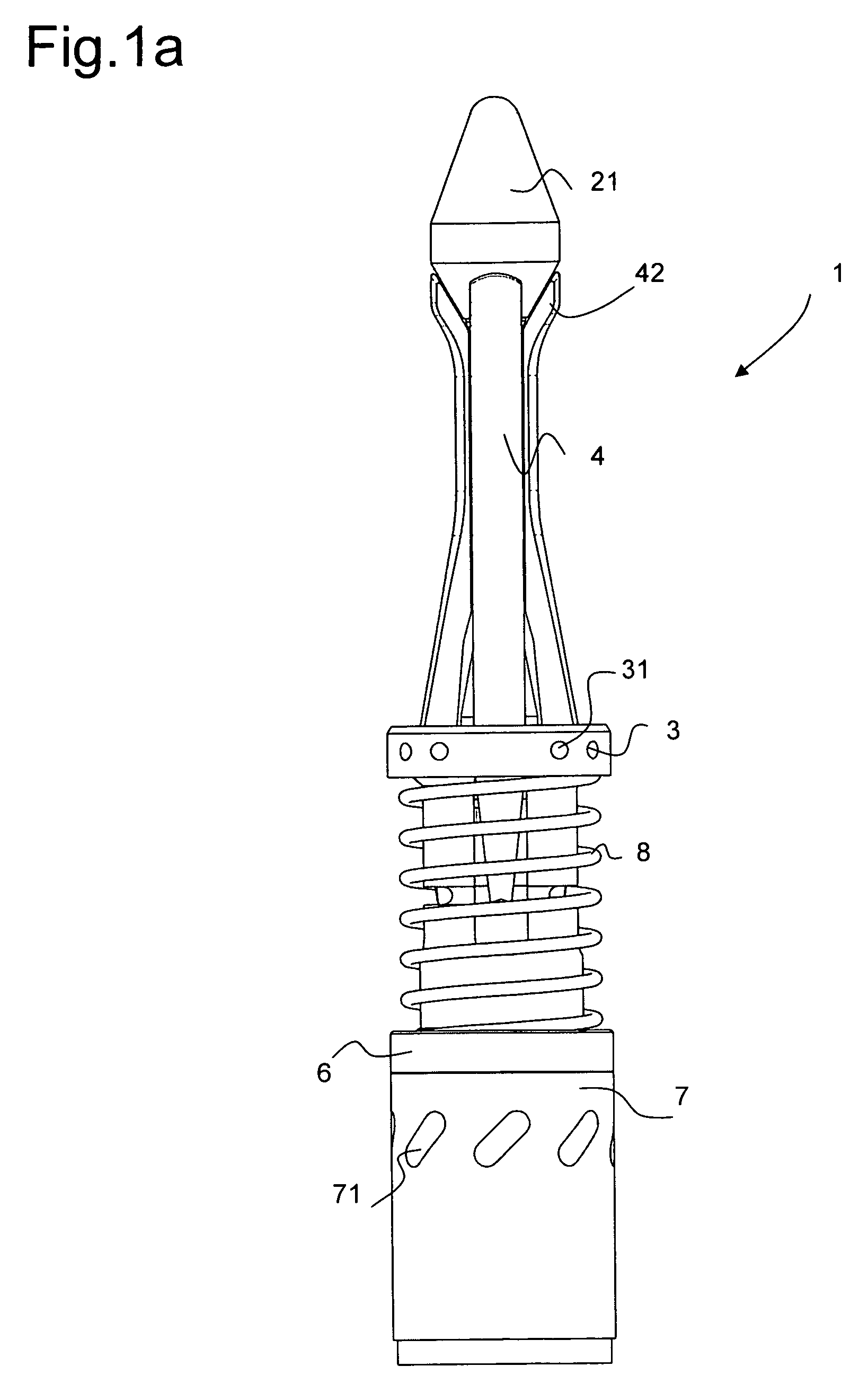
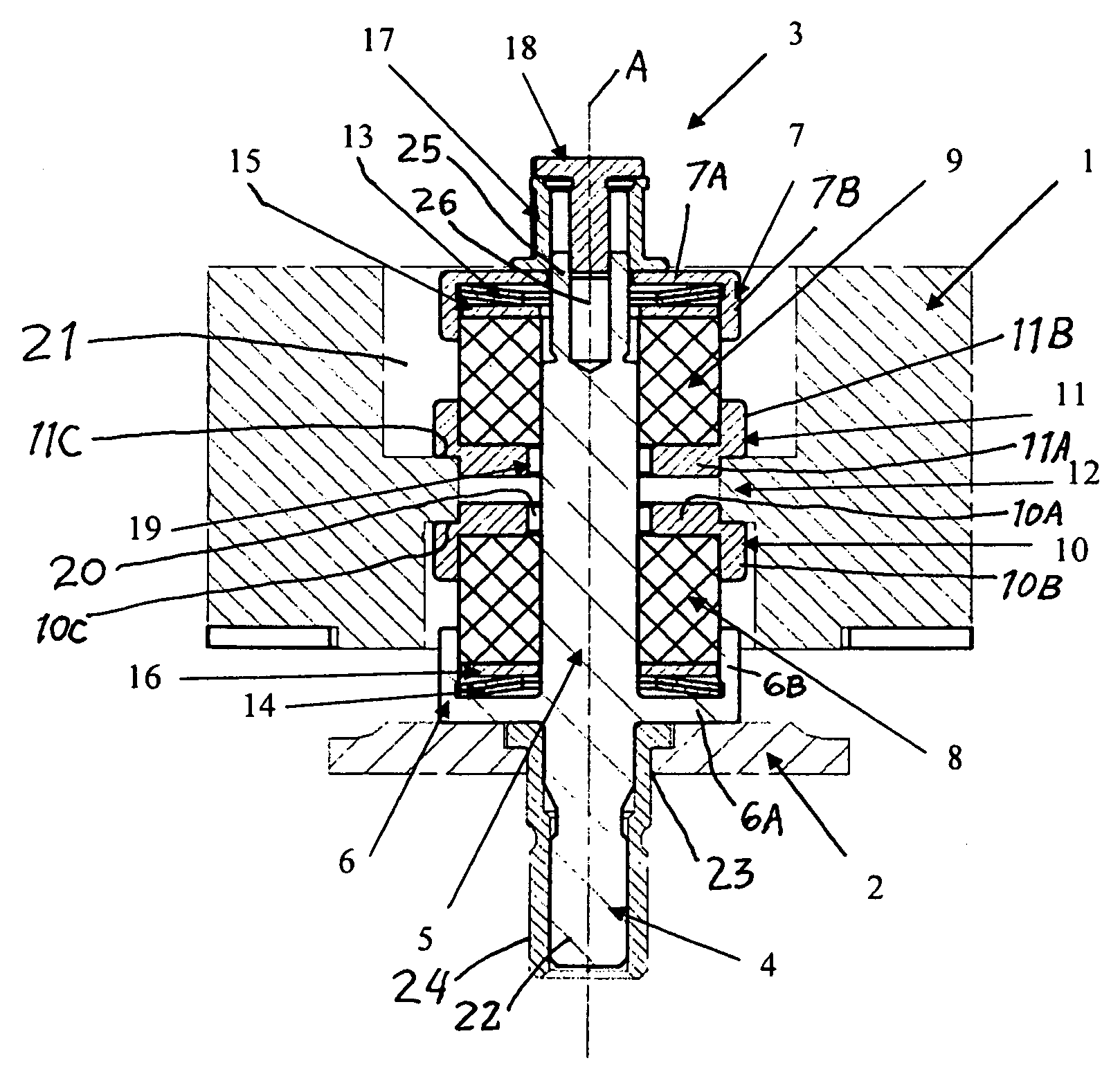
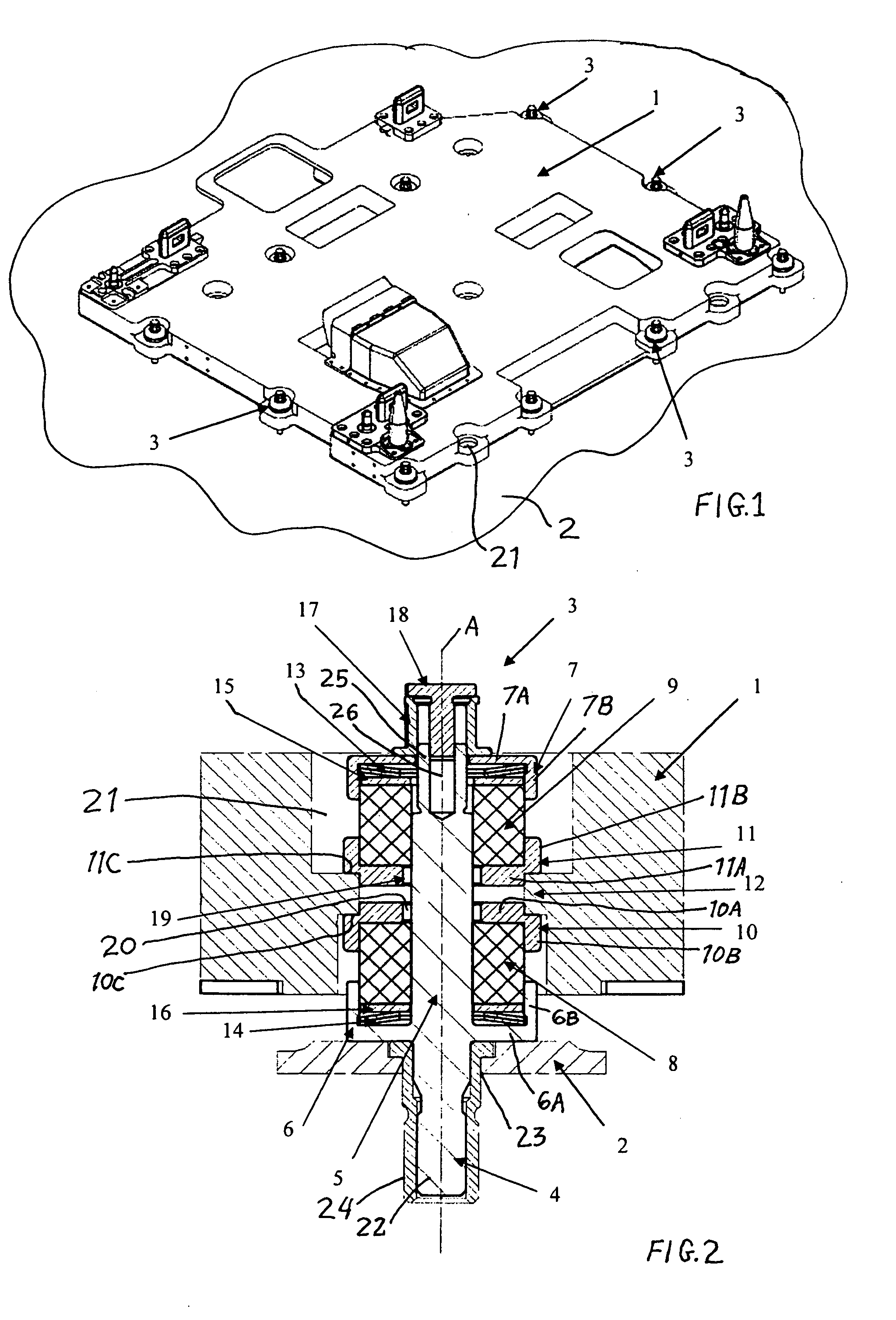
Multi-axis spring damping system for a payload in a spacecraft
InactiveUS20090278292A1Simple structural arrangementEasy to implementPortable framesSpringsMulti axisControl theory
A multi-axis spring damping element includes two spring damping cushion members received between caps on a bolt shaft, and an axial adjustment mechanism at a free end of the bolt shaft. The other end of the bolt shaft is connected to a support structure, and a load to be supported in a vibration-damped manner is carried by intermediate caps between the two spring damping cushion members. A plurality of such spring damping elements forms a spring damping system, for example for supporting a payload-carrying pallet on a load platform of a spacecraft.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
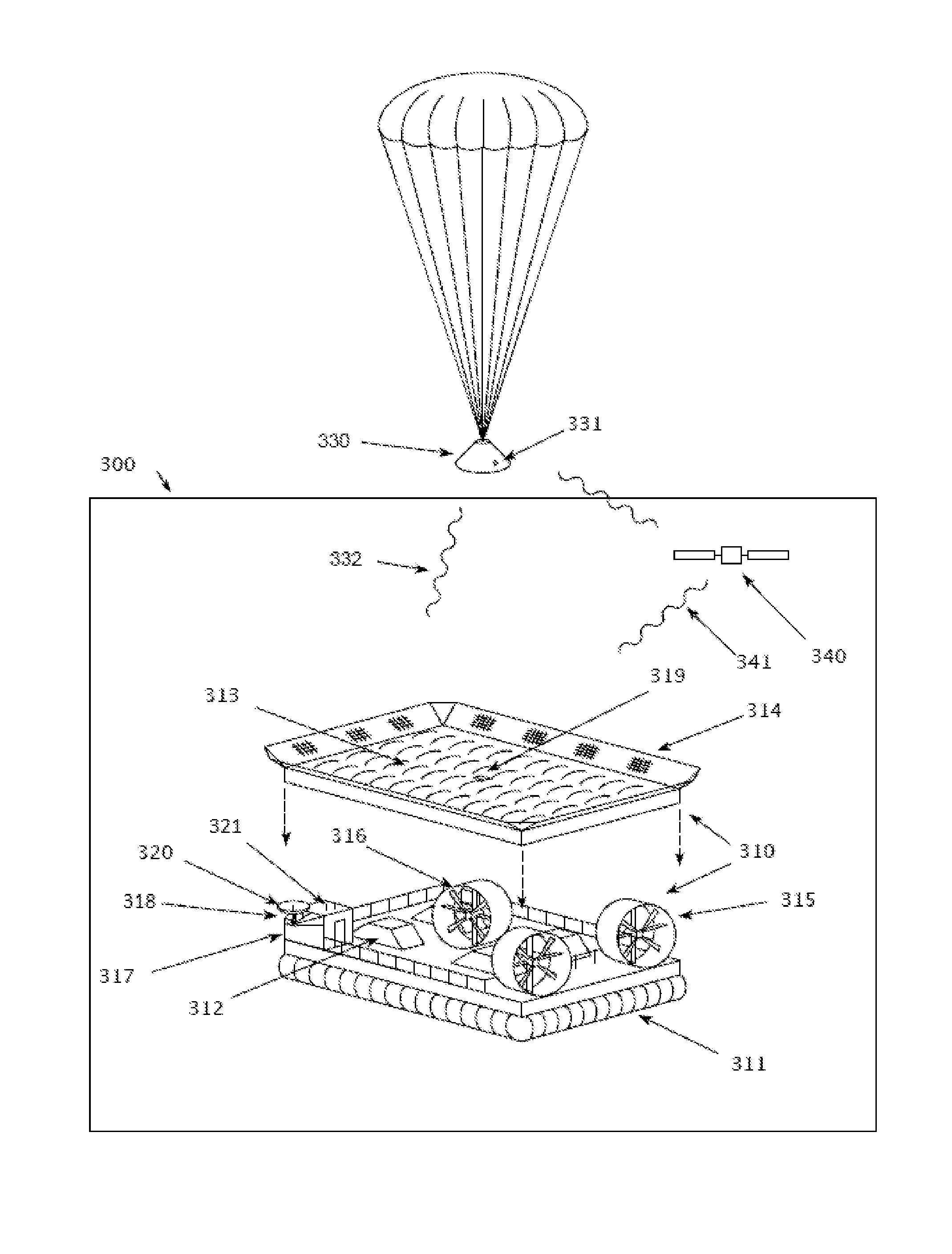
Movable ground based recovery system for reuseable space flight hardware
A reusable space flight launch system is configured to eliminate complex descent and landing systems from the space flight hardware and move them to maneuverable ground based systems. Precision landing of the reusable space flight hardware is enabled using a simple, light weight aerodynamic device on board the flight hardware such as a parachute, and one or more translating ground based vehicles such as a hovercraft that include active speed, orientation and directional control. The ground based vehicle maneuvers itself into position beneath the descending flight hardware, matching its speed and direction and captures the flight hardware. The ground based vehicle will contain propulsion, command and GN&C functionality as well as space flight hardware landing cushioning and retaining hardware. The ground based vehicle propulsion system enables longitudinal and transverse maneuverability independent of its physical heading.
Owner:NASA
Materials for self-transpiring hot skins for hypersonic vehicles or reusable space vehicles
InactiveUS7281688B1Provide protectionSpace shuttlesCosmonautic thermal protectionFlight vehicleSpace vehicle
A self-transpiring hot skin for a hypersonic or reusable space vehicle that can provide protection to the vehicle during short periods of abnormally high heat flux (either planned in the flight profile or an off-nominal event). The hot skin includes a ceramic composite structure having an internal cavity that is coupled either to the insulating layer or directly to the support structure of the hypersonic vehicle. The internal cavity includes a material system that vaporizes, sublimes or decomposes into a gas when the temperature exceeds the upper temperature capability of the composite material. The gas transpires through the outer layer of the composite material to provide cooling to the outer layer below the upper temperature capability. Cooling may occur both by conduction of heat from the composite material to the transpiring gas and by the interaction of the transpiring gas with the boundary layer of hypersonic flow over the outer surface, leading to a reduction of the heat flux entering the surface.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Space transportation node including tether system
InactiveUS7503526B1Simple processFacilitating commerceCosmonautic environmental control arrangementLaunch systemsCelestial bodyElectric cables
A transportation node system orbits a celestial body. The node system includes a truss having two ends, the truss rotating around its center of mass while orbiting the celestial body. The truss stores payloads. The node system also includes tether tips, each attached to one end of the truss via a tether so that each tether tip can extend from the truss and retract to the truss for transfer of payloads. The tether runs through the length of the truss and connects to each tether tip, each tether tip being capable of engaging payloads. The node further includes at least one tether cable reel that reels in and reels out the tether so the tether tips can extend from and retract to the truss.
Owner:TAYLOR THOMAS C +2
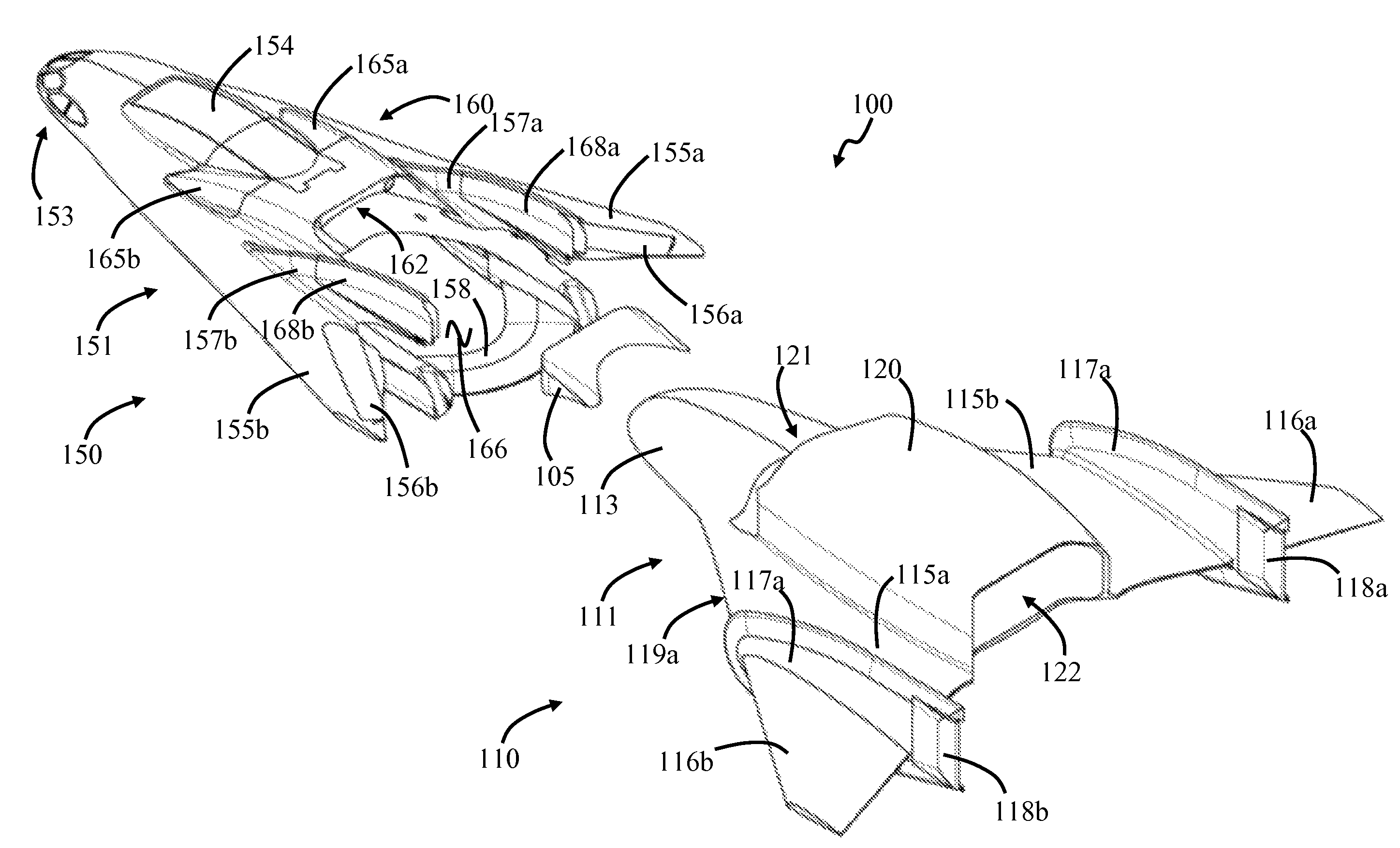
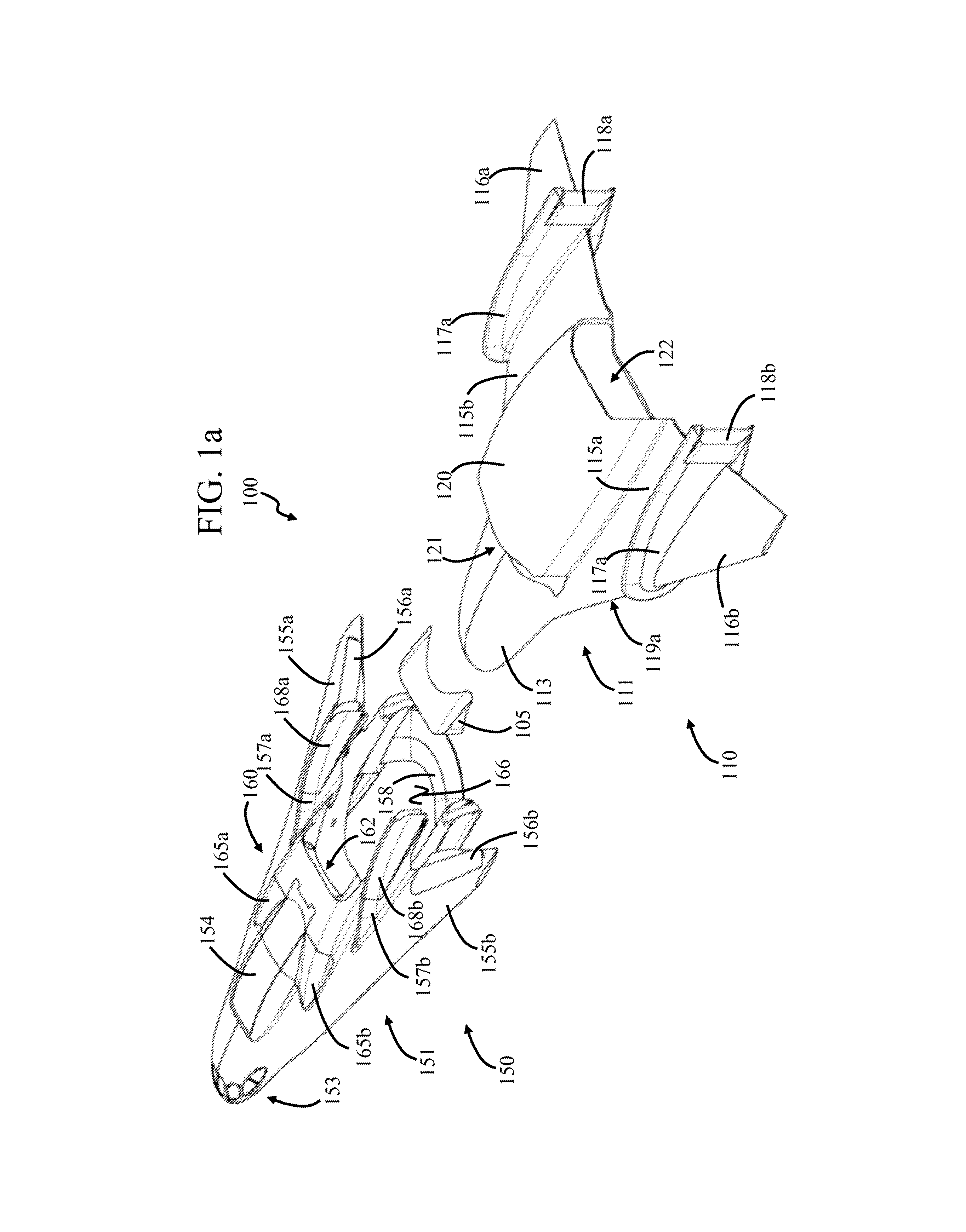
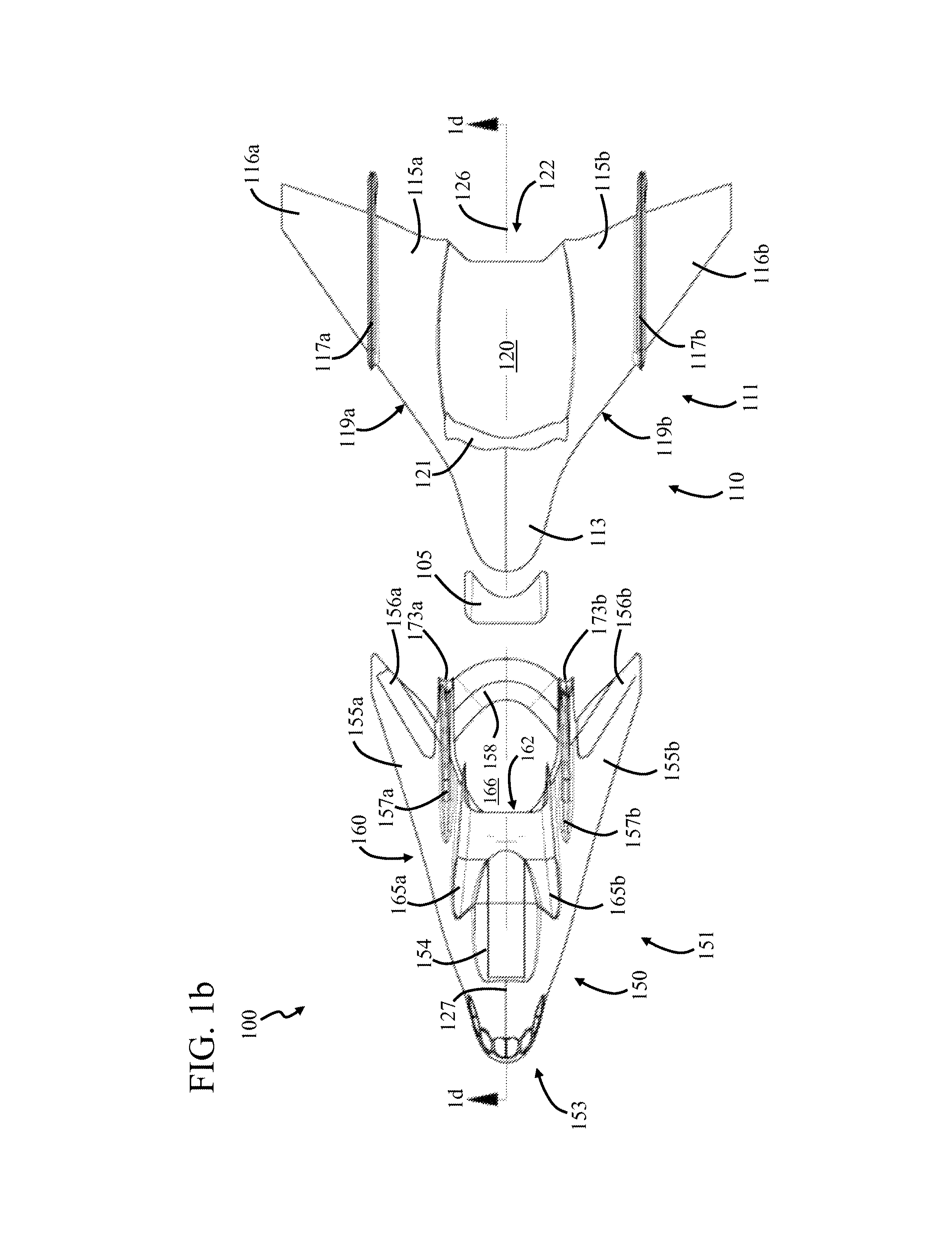
In-line staged horizontal takeoff and landing space plane
A vehicle includes a first sub-vehicle, and a second sub-vehicle which is repeatably moveable between coupled and uncoupled conditions with the first sub-vehicle. The first and second sub-vehicles each include a landing system and propulsion system. The first and second sub-vehicles are in the coupled condition during take-off. The first and second sub-vehicles are separately flyable in the uncoupled condition. Both vehicles are launched horizontally, by a ramp, or vertically, using atmospheric lift to achieve atmospheric flight, orbital, or sub-orbital launch.
Owner:EXODUS SPACE CORP INC
Method and system for accelerating an object
A system for accelerating an object that includes a towing vehicle, a tether connected to the towing vehicle, an object having at least one airfoil connected to the tether and a controller for controlling movement of the object, wherein, the towing vehicle moves in a first direction at a first speed pulling the object in the first direction and the controller controls movement of the object to move the object at an angle to the first direction and accelerate the object to a speed substantially greater than the first speed.
Owner:JOHANSEN DANA R
Hiigh wing monoplane aerospace plane based fighter.
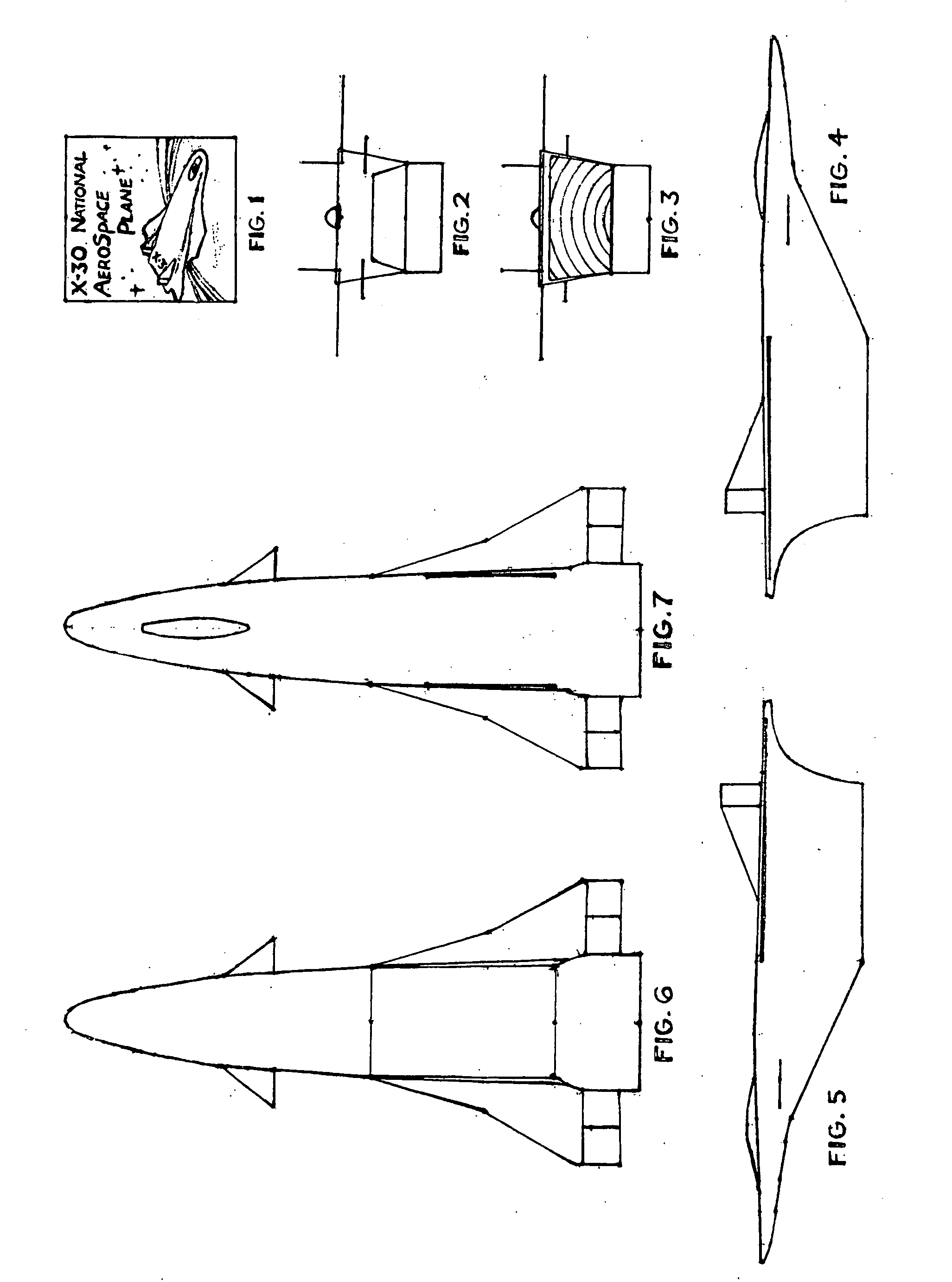
The Hypersonic Orbital Fighter and the methods of flying it are disclosed. The Hypersonic Orbital Fighter is characterized by a winged, modified lifting body shape with the forward ventral section comprising an X-30 type compressive air inlet, throttleable supersonic combustion ramjet array under the center of gravity and half-cone exhaust outlet at the back, fore mounted canards, cockpit / payload area top front and mid section and one or more tailplanes at the top back. Flight profile comprising runway takeoff, high subsonic climb up to 65,000 feet, alternatively full power climb from zero to 65,000 feet, with progressive acceleration from there up to Mach 24 @ required orbital altitude. Able to intercept missiles from early through post-boost phase from chosen orbit or suborbital arc, to intercept aircraft and to interdict surface targets. Winged dynamic soaring capability in reentry followed by powered runway landing.
Owner:TOWNE ANDREW JAMES
In-line staged horizontal takeoff and landing space plane
A vehicle includes a first sub-vehicle, and a second sub-vehicle which is repeatably moveable between coupled and uncoupled conditions with the first sub-vehicle. The first and second sub-vehicles each include a landing system and propulsion system. The first and second sub-vehicles are in the coupled condition during take-off. The first and second sub-vehicles are separately flyable in the uncoupled condition. Both vehicles are launched horizontally, by a ramp, or vertically, using atmospheric lift to achieve atmospheric flight, orbital, or sub-orbital launch.
Owner:EXODUS SPACE CORP INC
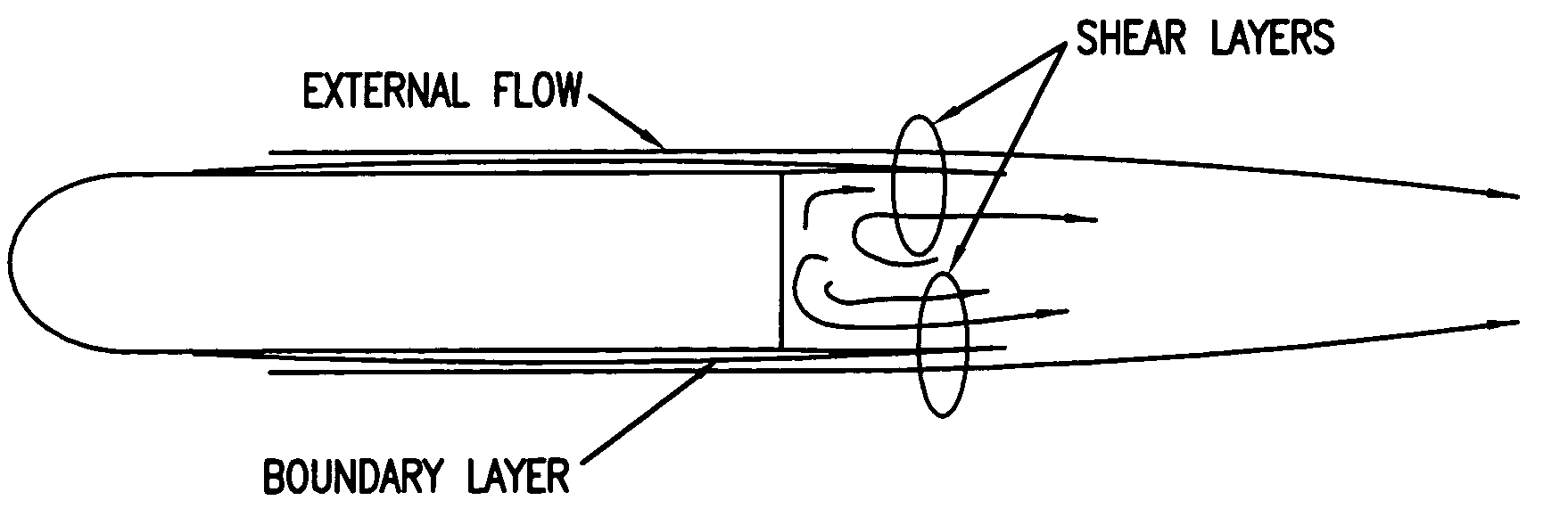
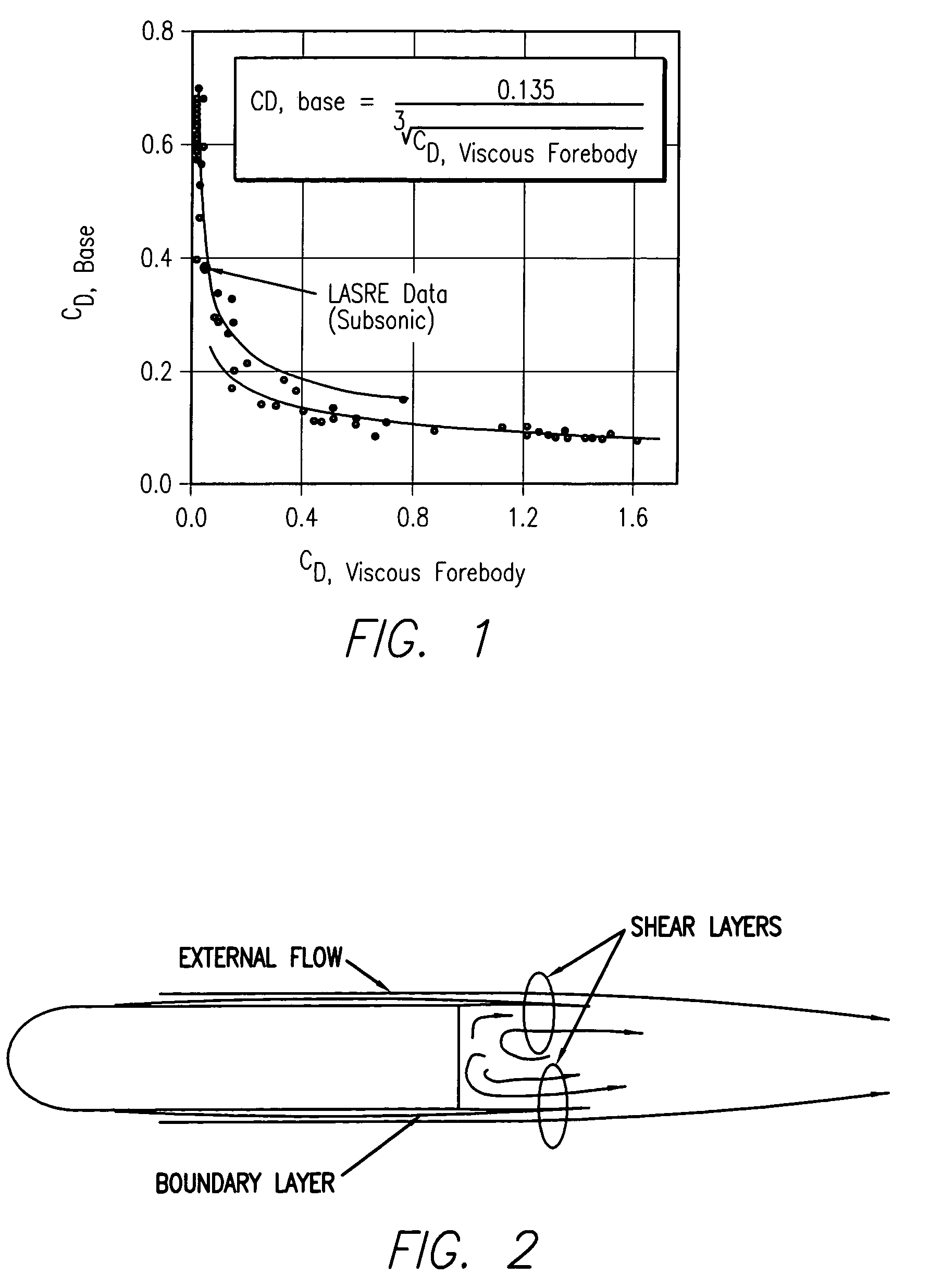
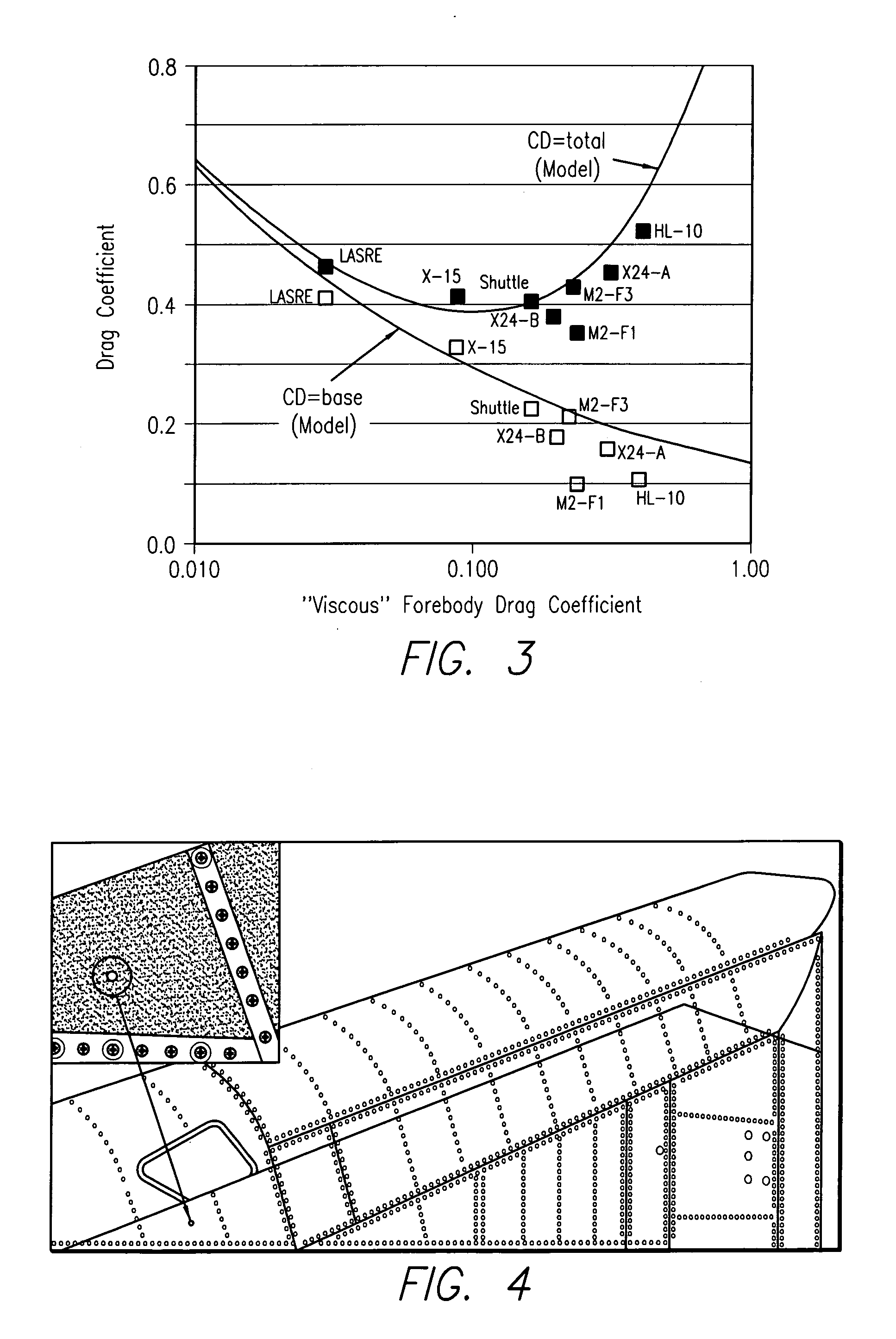
Method for reducing the drag of blunt-based vehicles by adaptively increasing forebody roughness
InactiveUS6892989B1Reduce resistanceIncreased dragActuated automaticallyCosmonautic partsAutomotive engineering
Owner:NASA
Cooled insulation surface temperature control system
InactiveUS7055781B2Avoid erosionCosmonautic thermal protectionSpace shuttlesTemperature controlPorous layer
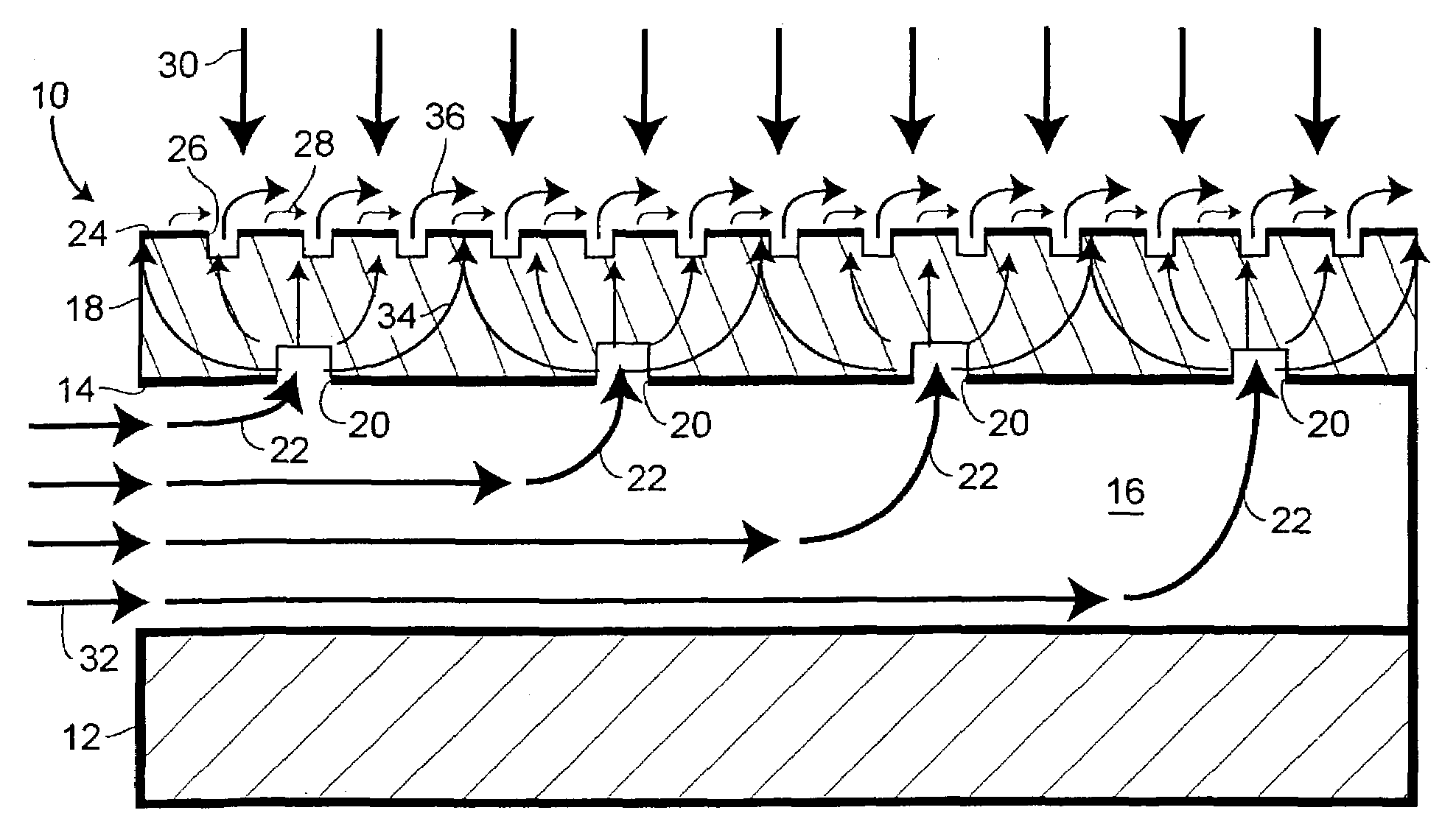
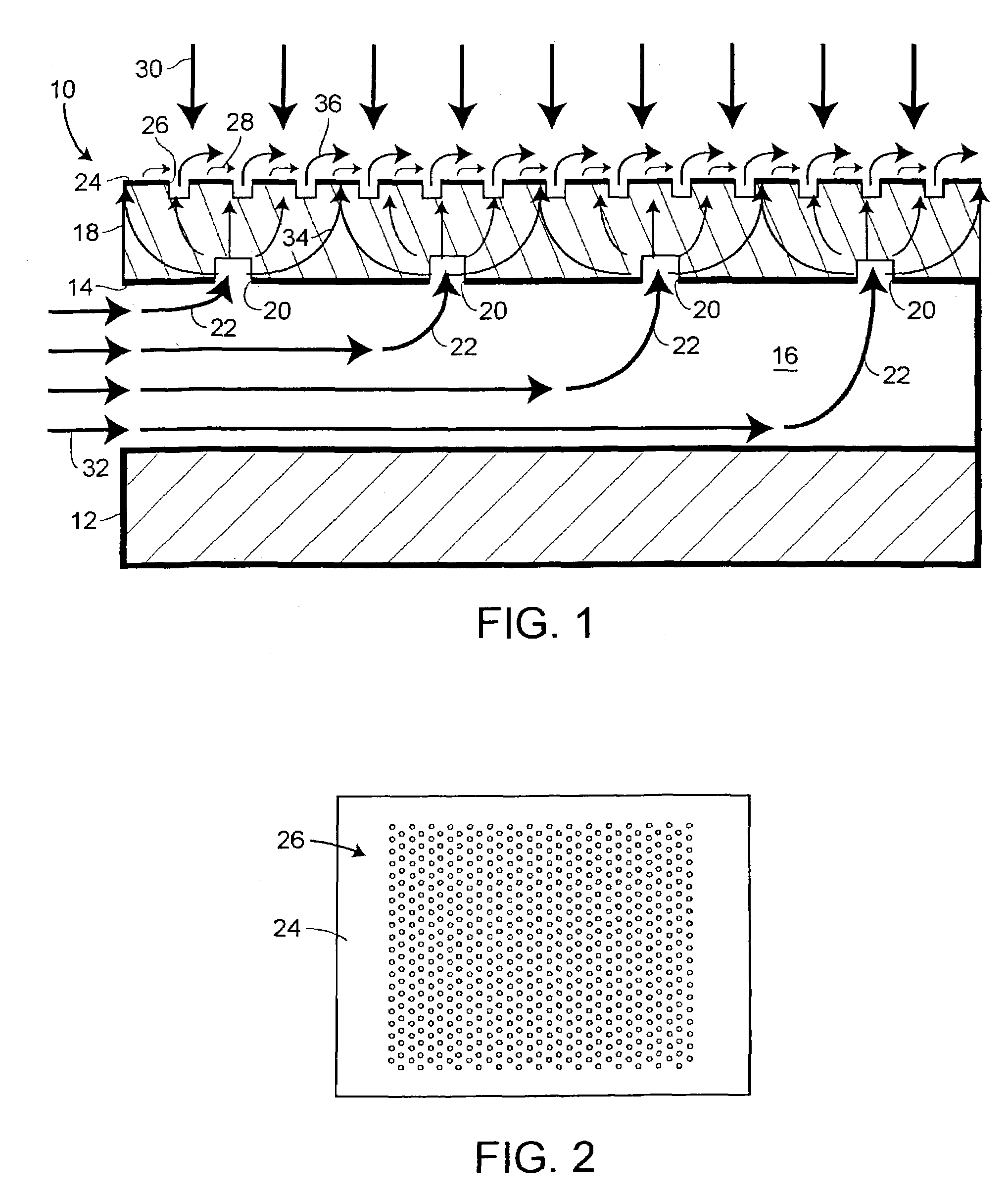
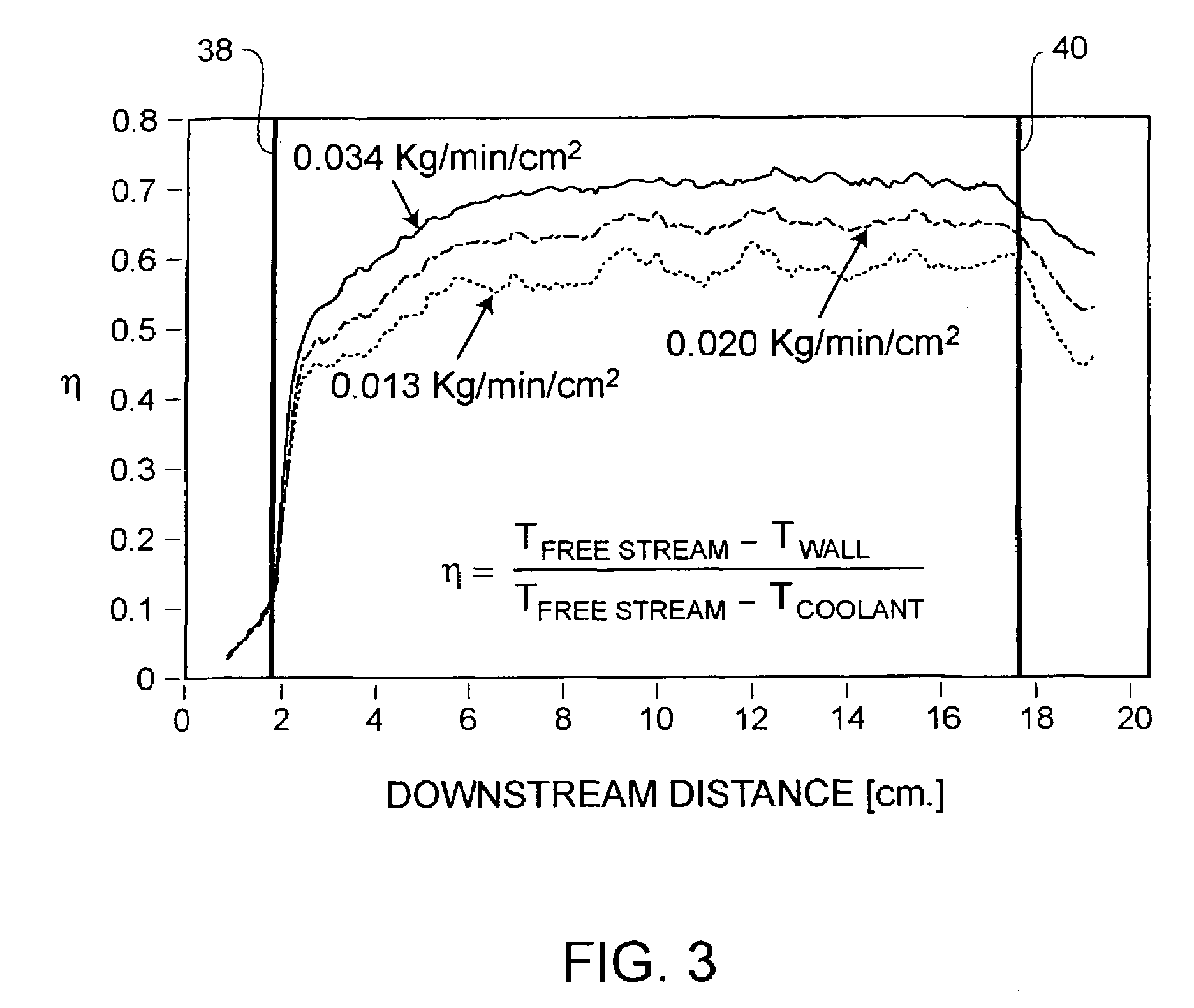
An apparatus and method for surface temperature control is provided. Surface temperature control is achieved by flowing coolant in and then out of a low strength porous layer attached to a structural plenum. A semi-permeable layer may be attached to the outer surface of the porous layer to prevent erosion of the porous layer and to facilitate surface film cooling.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
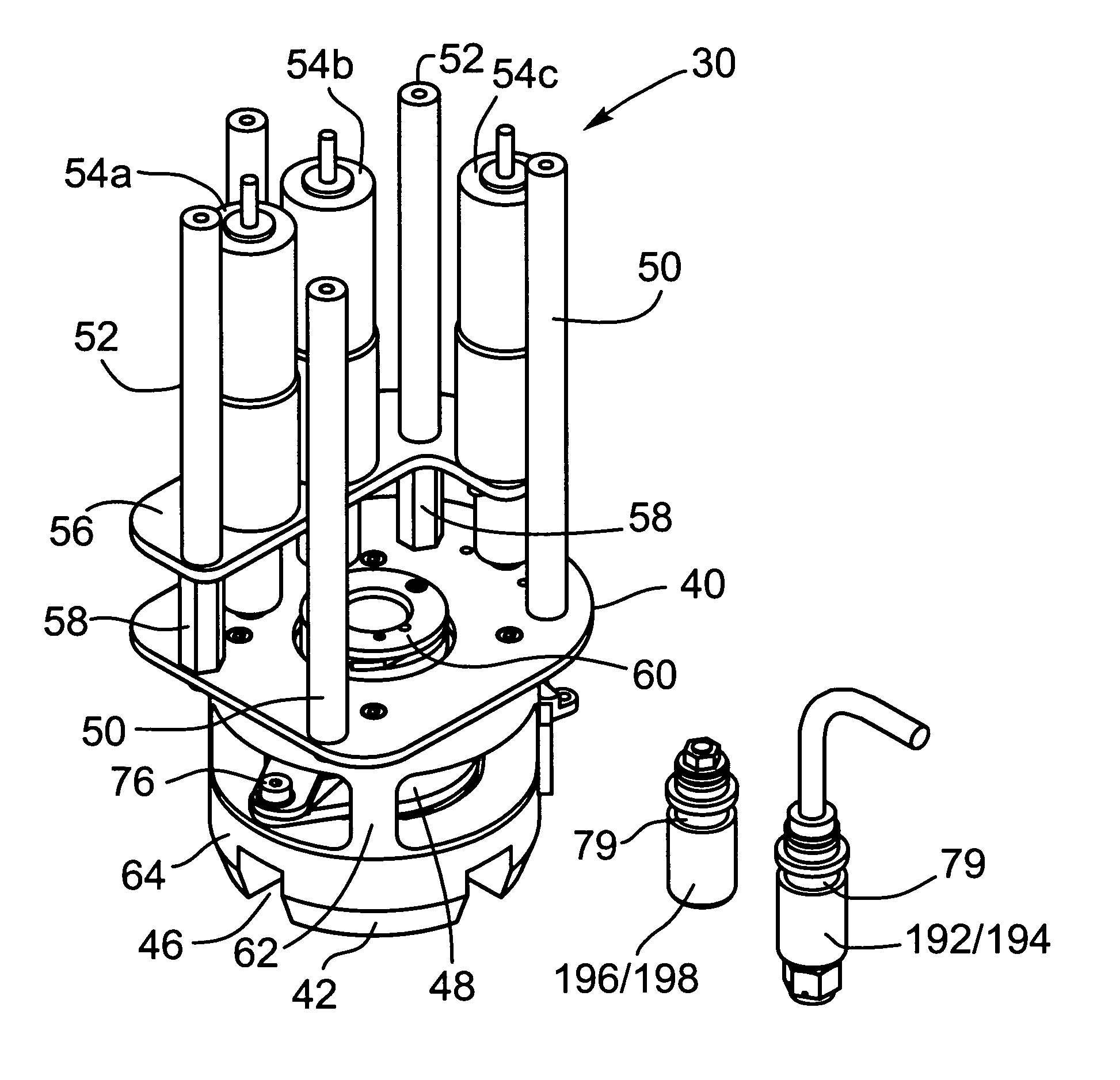
Robotic satellite refueling tool
A tool for fuelling an unprepared or partially prepared client satellite required for accessing, opening and closing a fuel fill valve on the satellite being serviced, storage and retrieval stations on a tool caddy on which the tools and various fuel fill valve caps are stored. The tool includes interchangeable socket modules, a support frame, a socket module holder mechanism, a socket drive mechanism, a clamping mechanism to secure the tool to a reaction area on the fuel fill valve and oxidizer fill valve, and a valve actuation mechanism. The interchangeable socket modules include a first module for removing and replacing the access valve cap, a second module for coupling the fuel fill line to the fuel tank, a third module for engaging the access valve cap on the oxidizer fill valve, and a fourth module for coupling the oxidizer fill line to the oxidizer tank.
Owner:MACDONALD DETTWILER & ASSOC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com