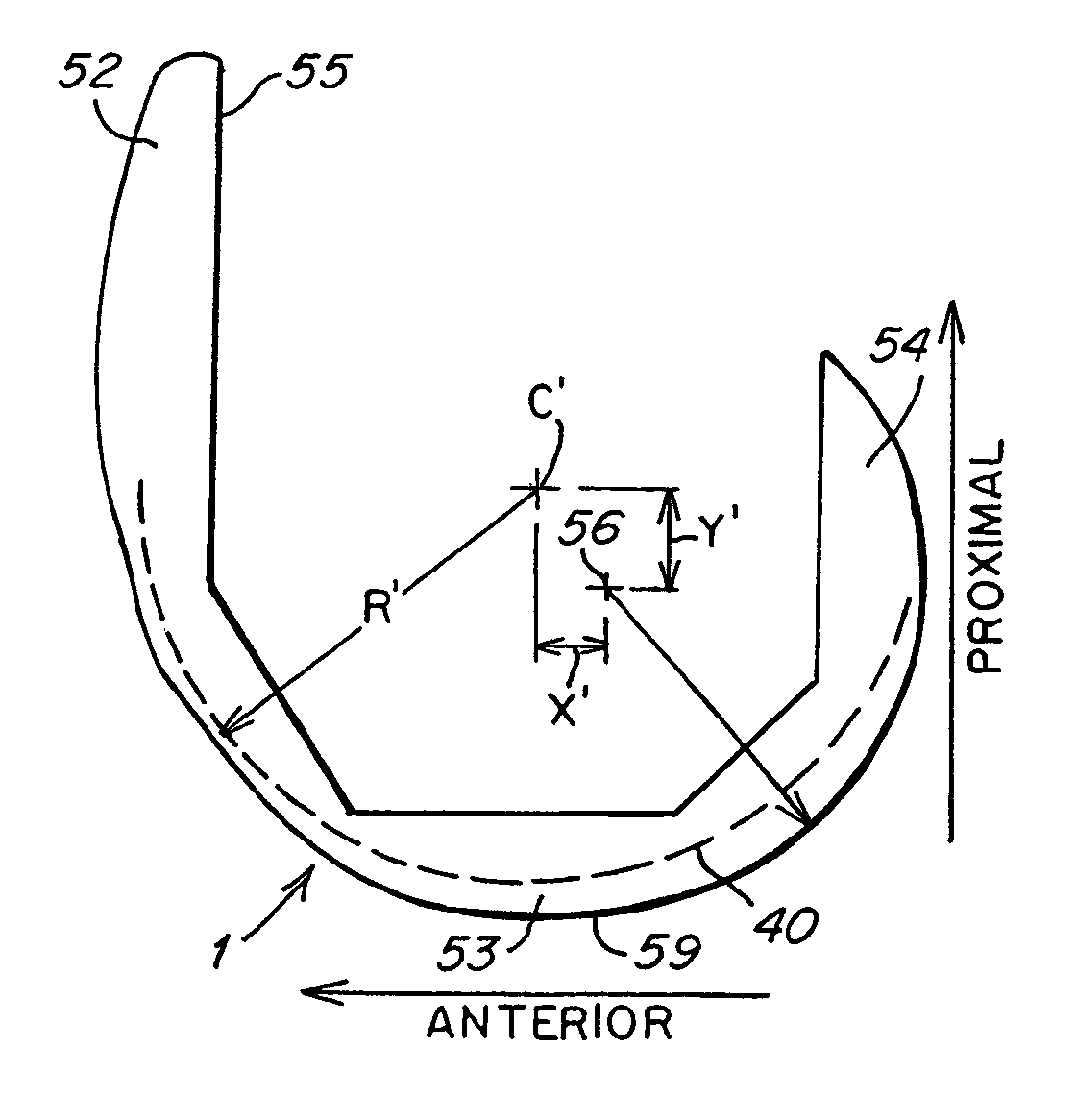
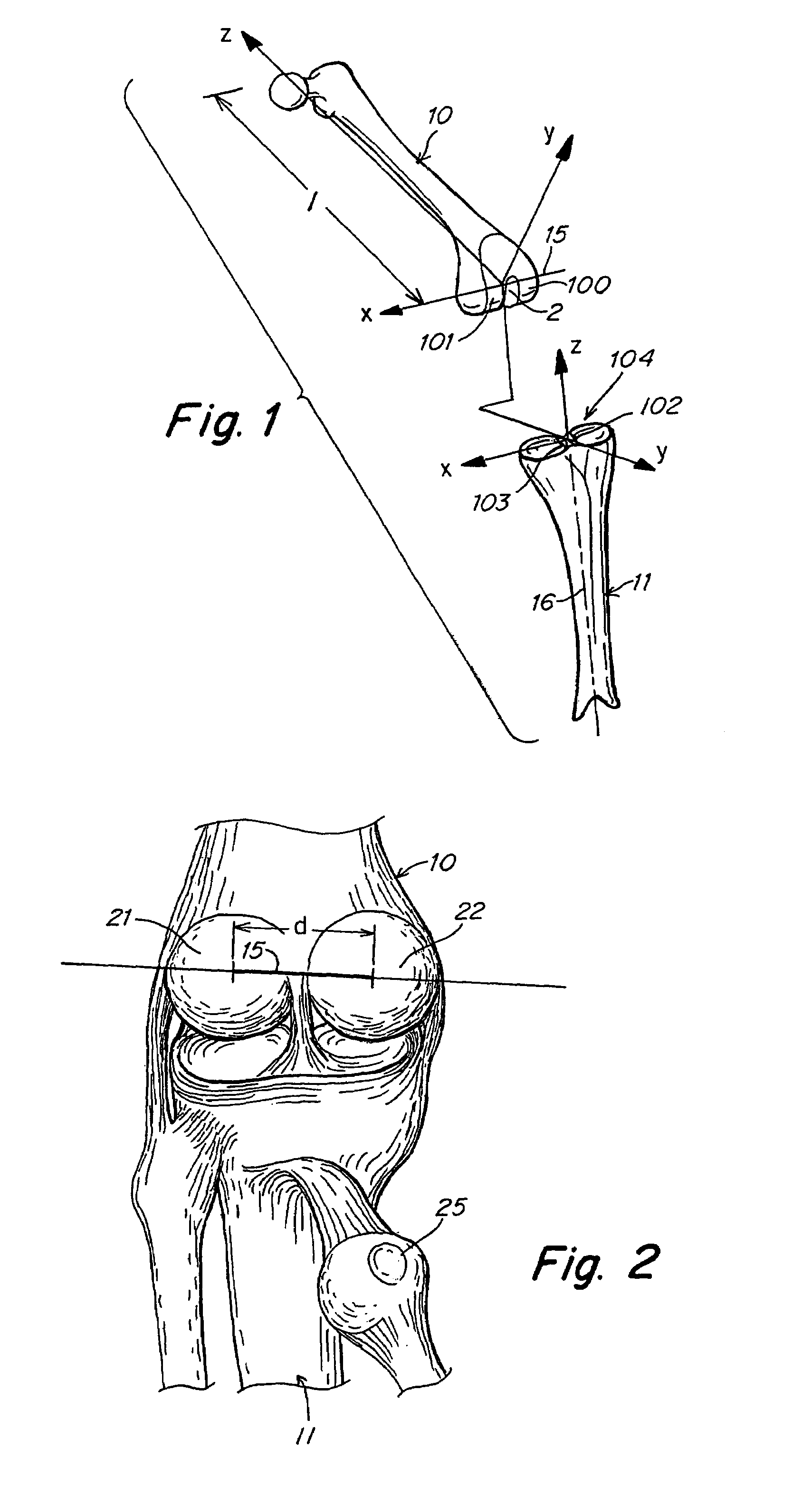
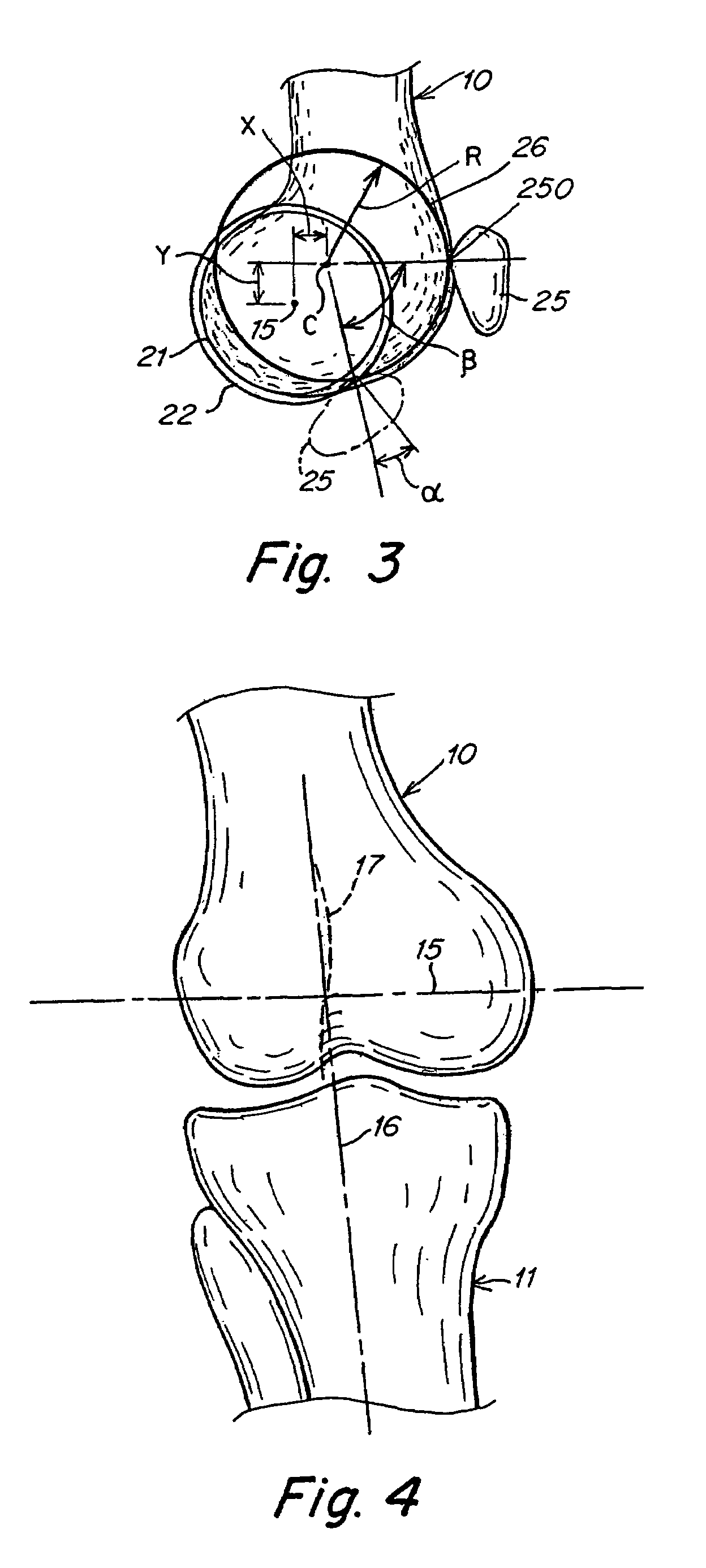
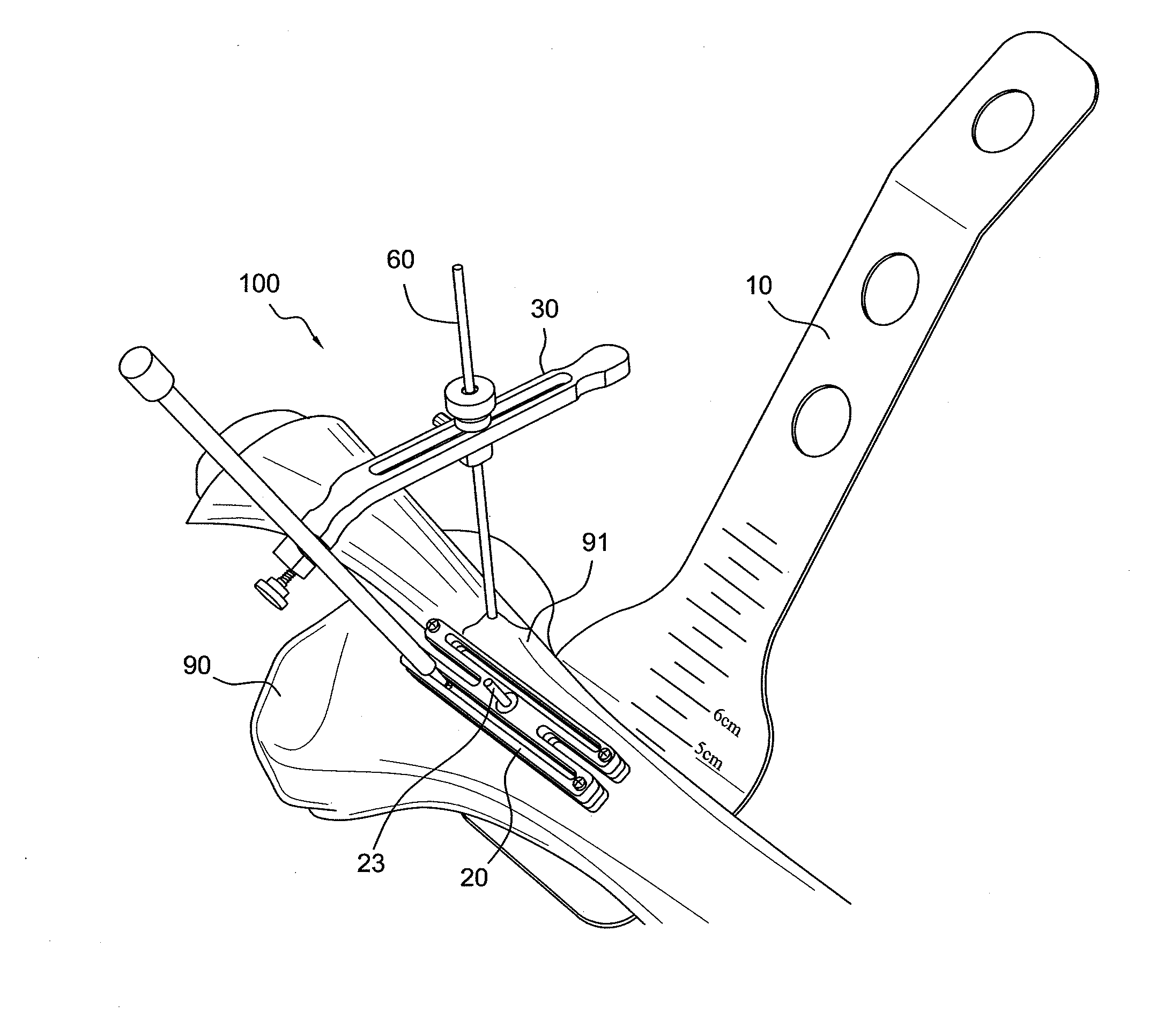
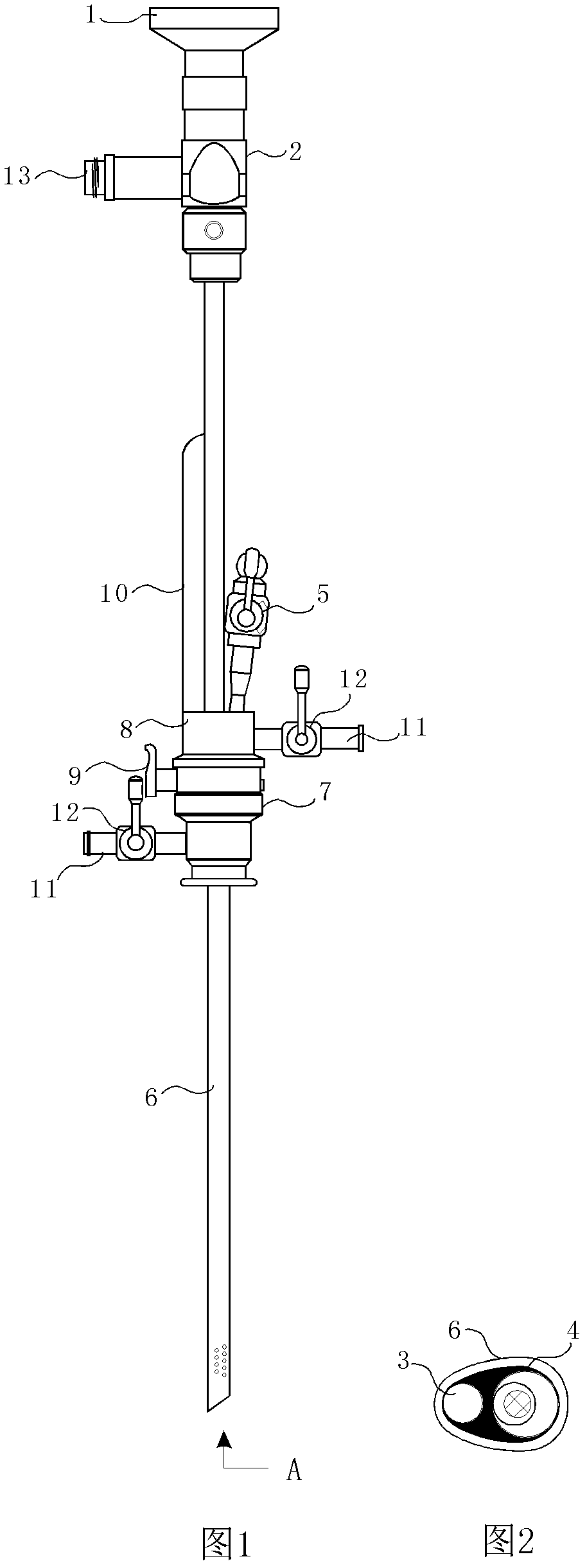
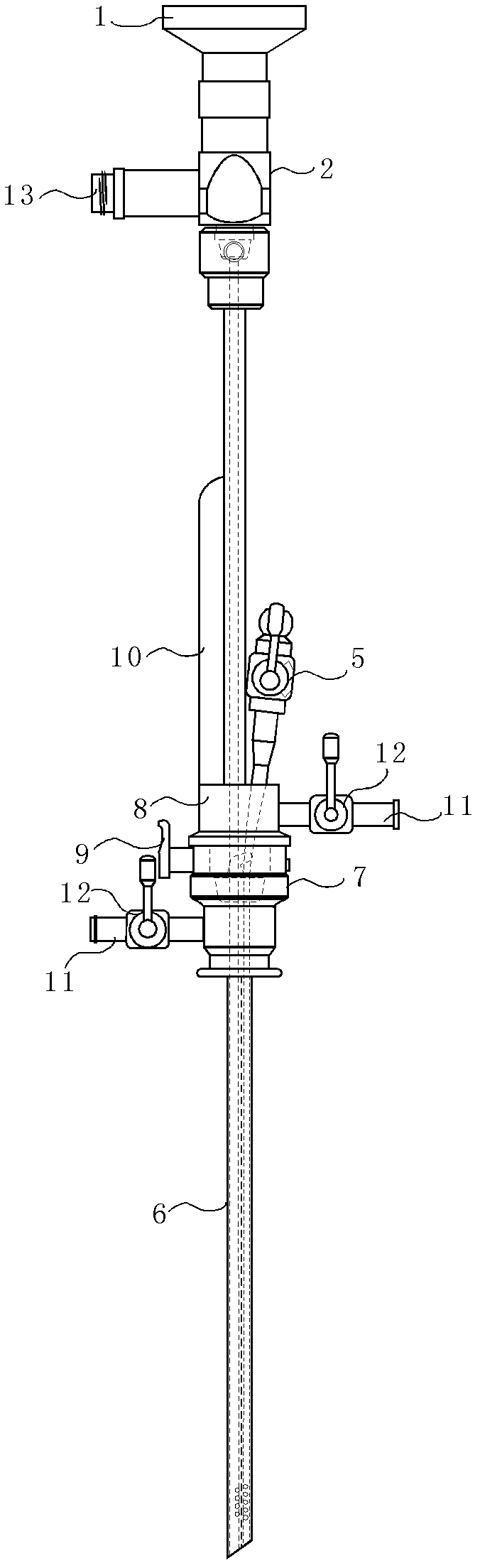
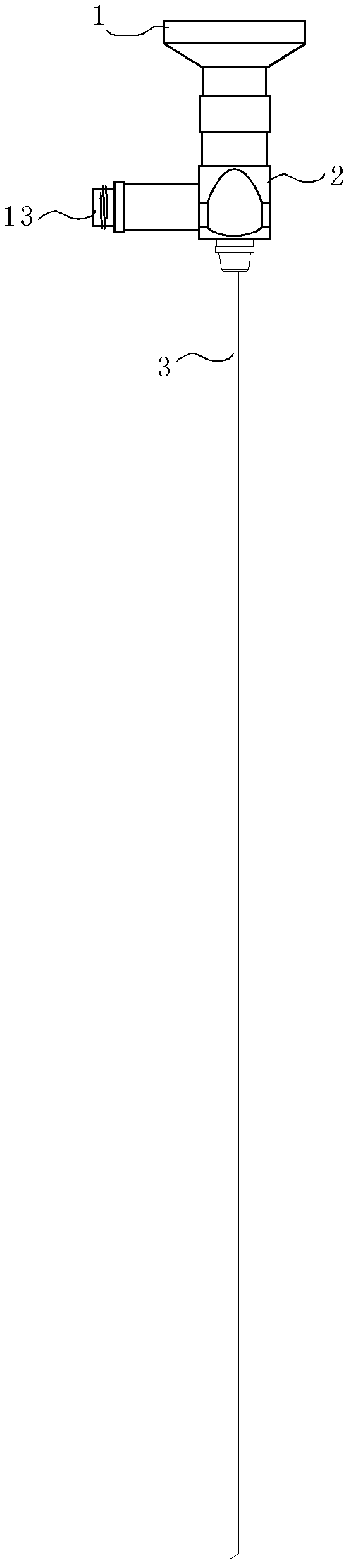
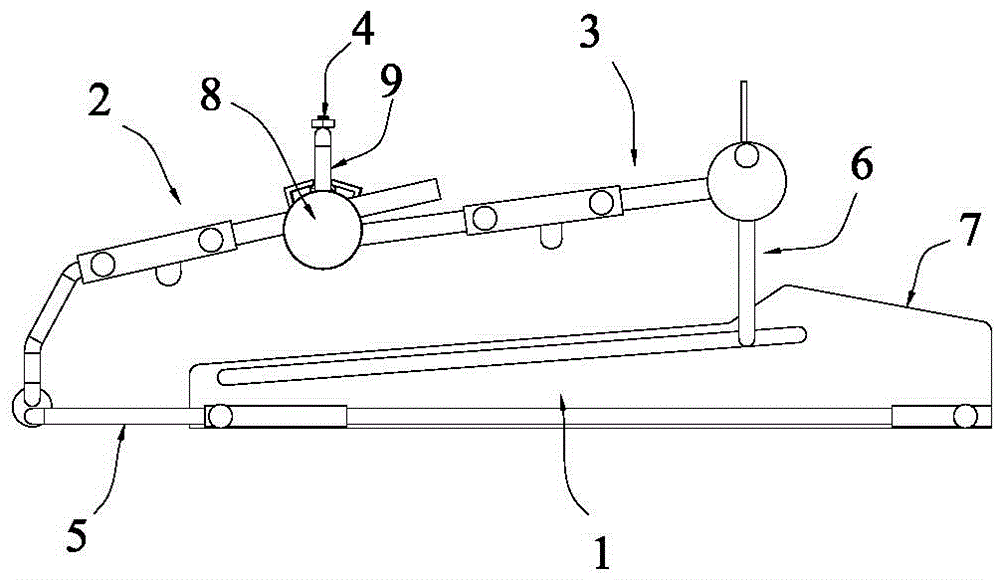
Patents
Literature
40 results about "Patellofemoral joint" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
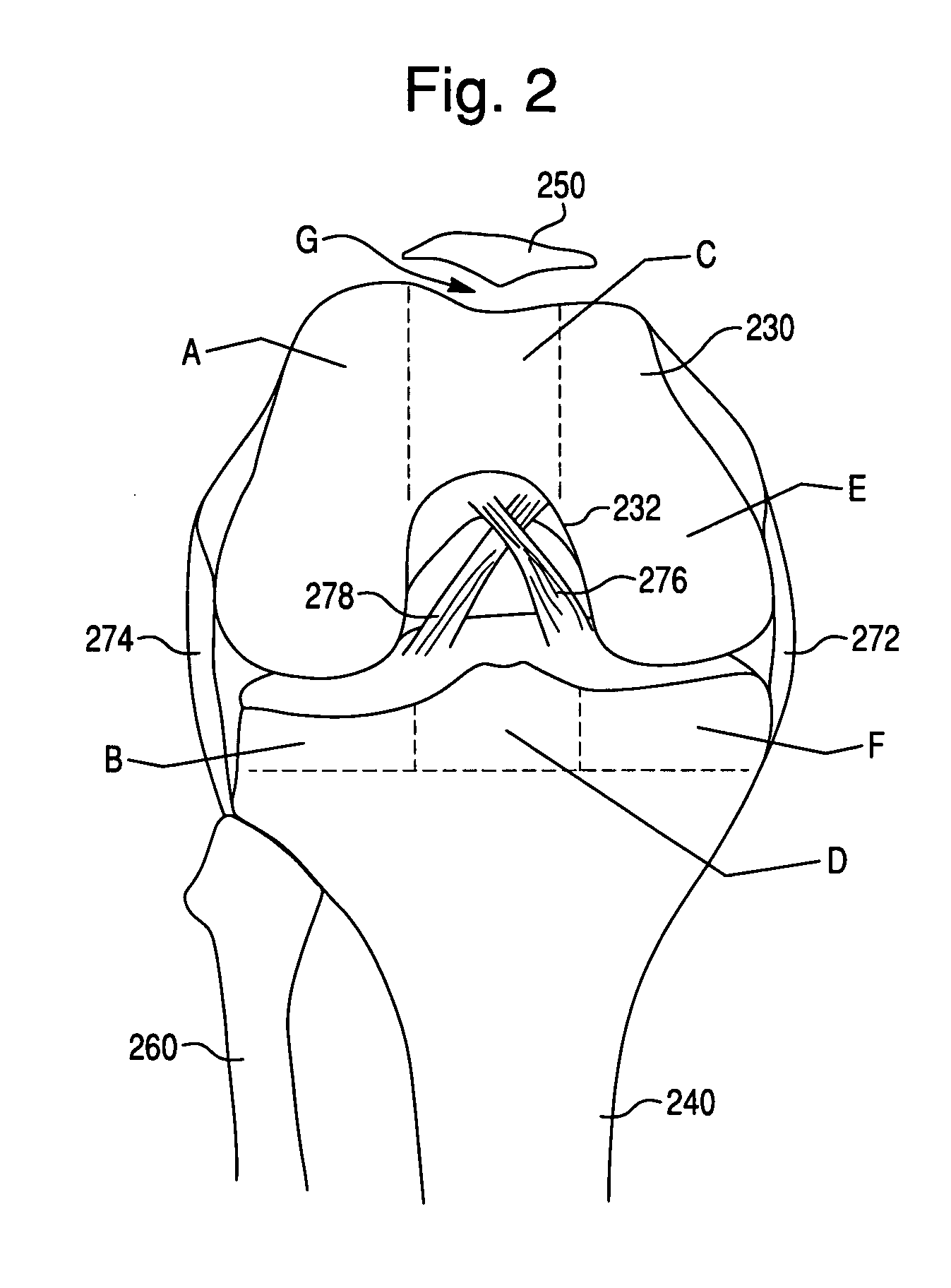
The patellofemoral joint is where your patella (kneecap) and femur (thigh bone) meet at the front of your knee. The underside of your kneecap sits in a groove within your thigh bone called the patellofemoral groove . Within this groove, the kneecap mostly moves lengthwise,...
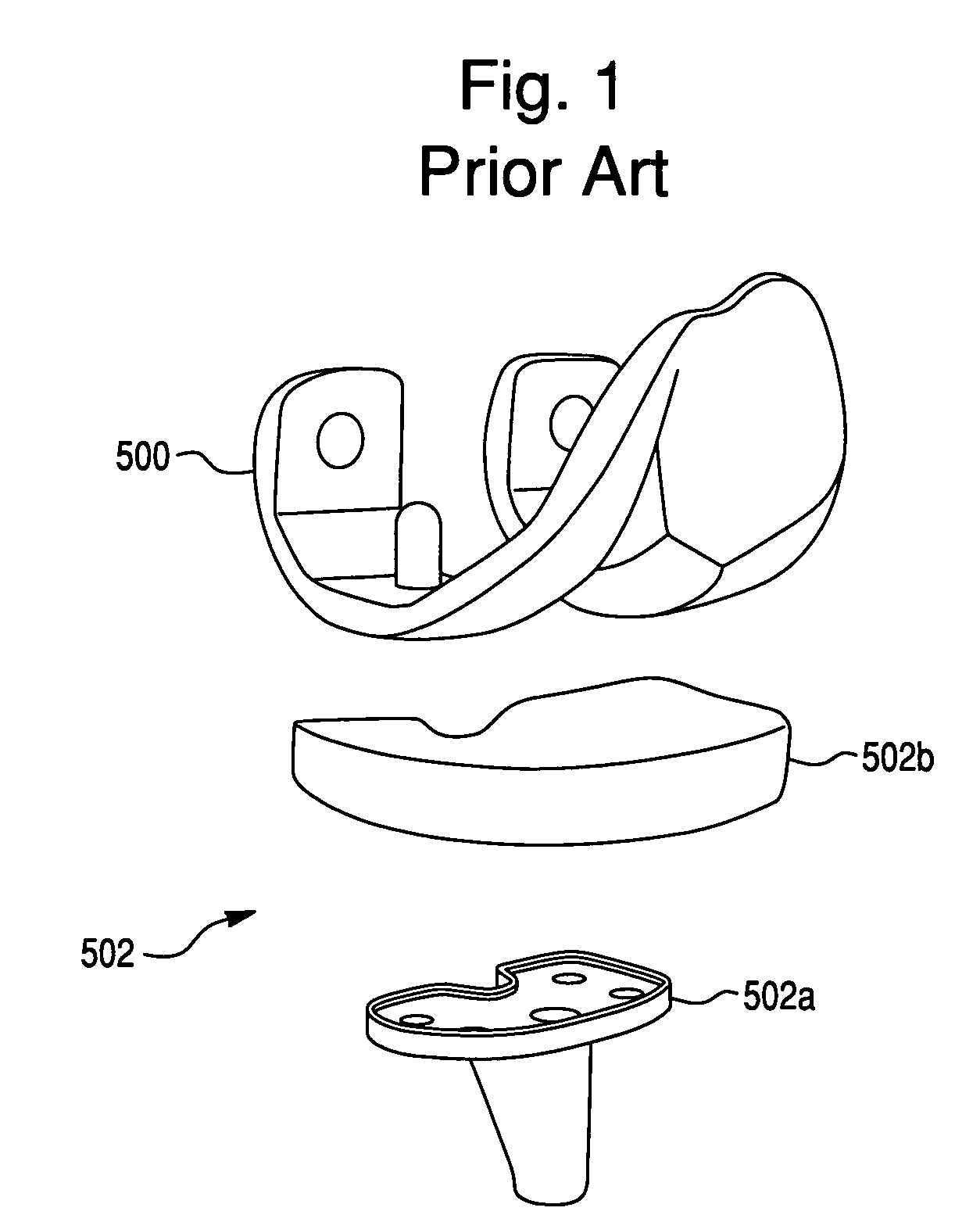
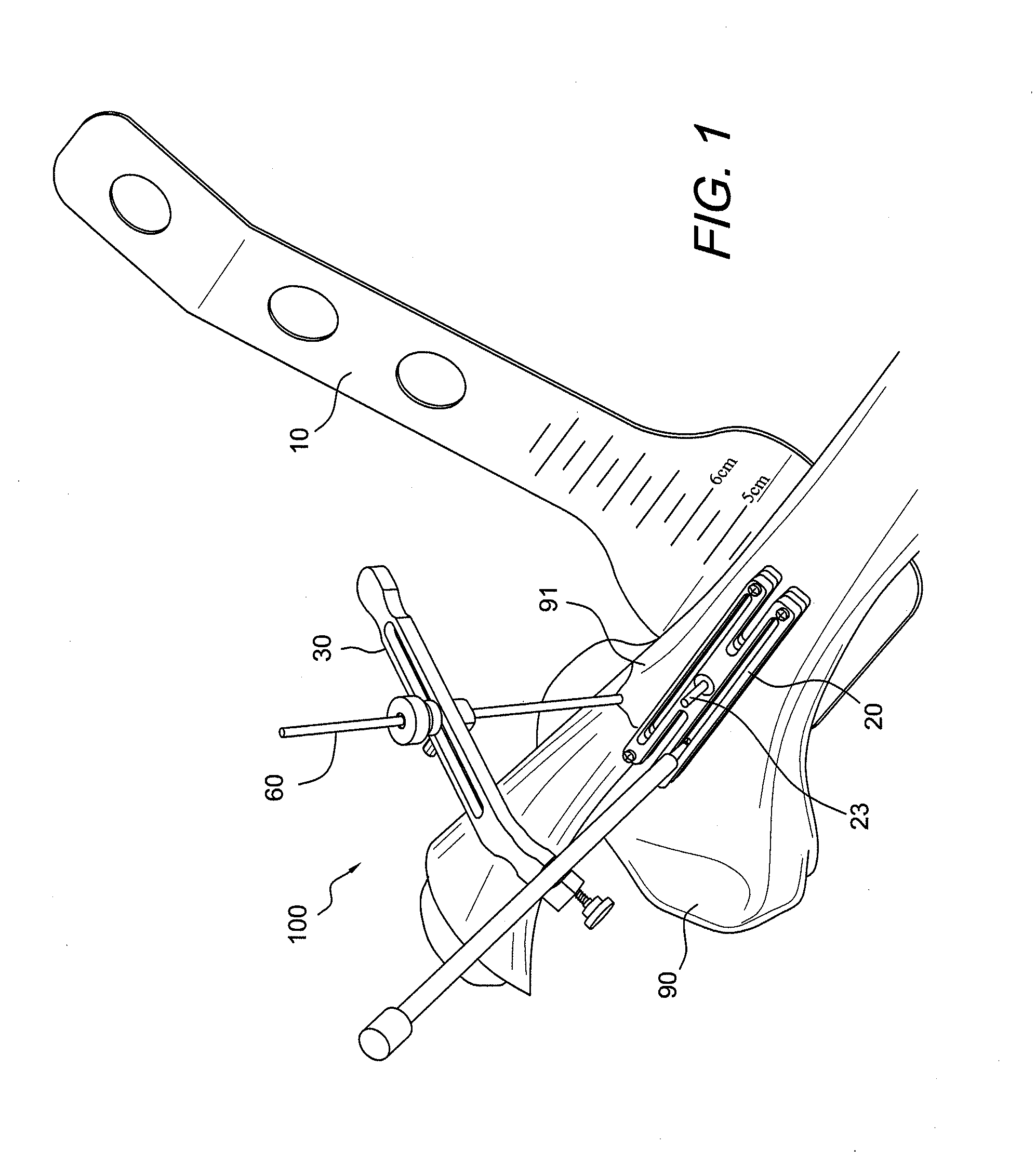
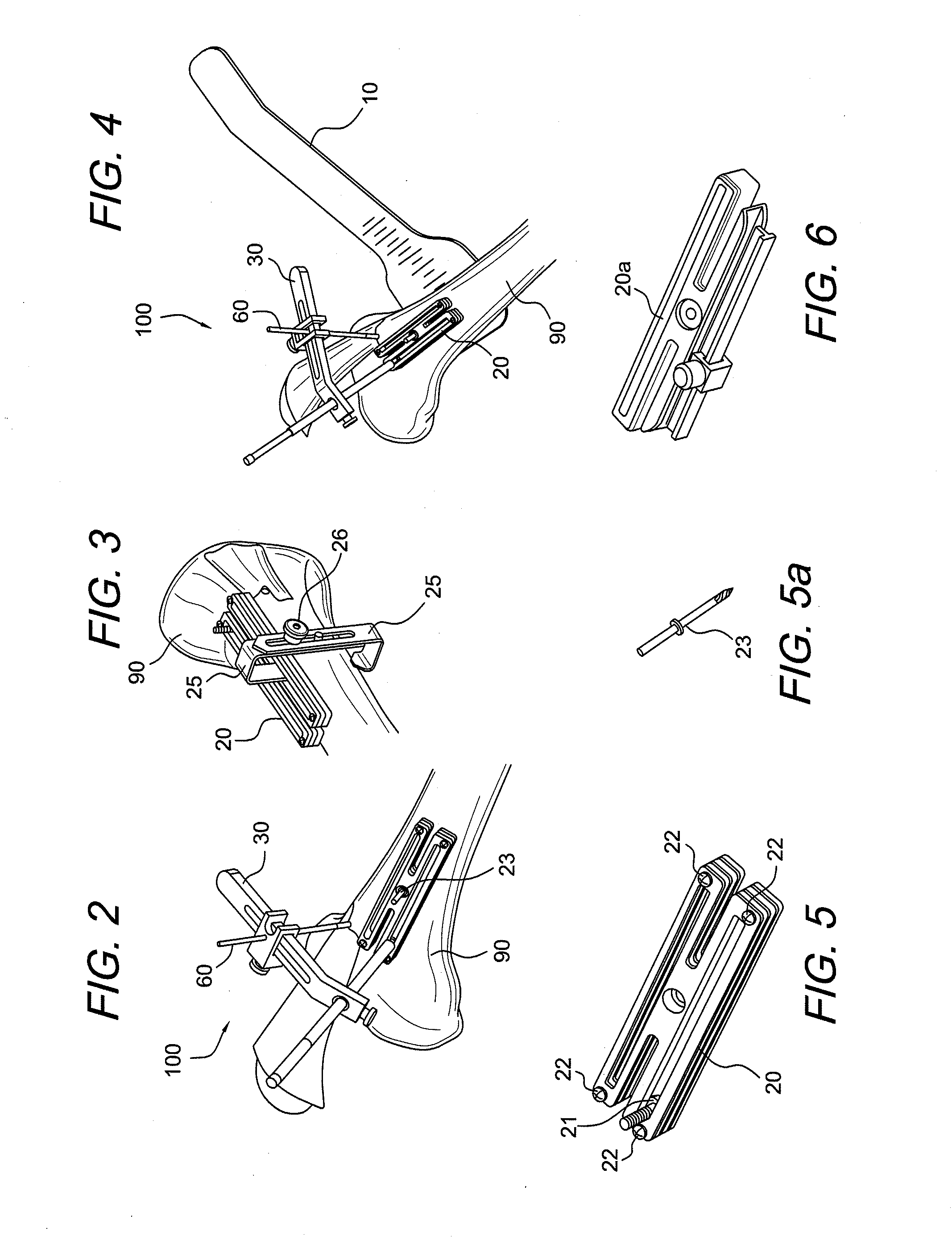
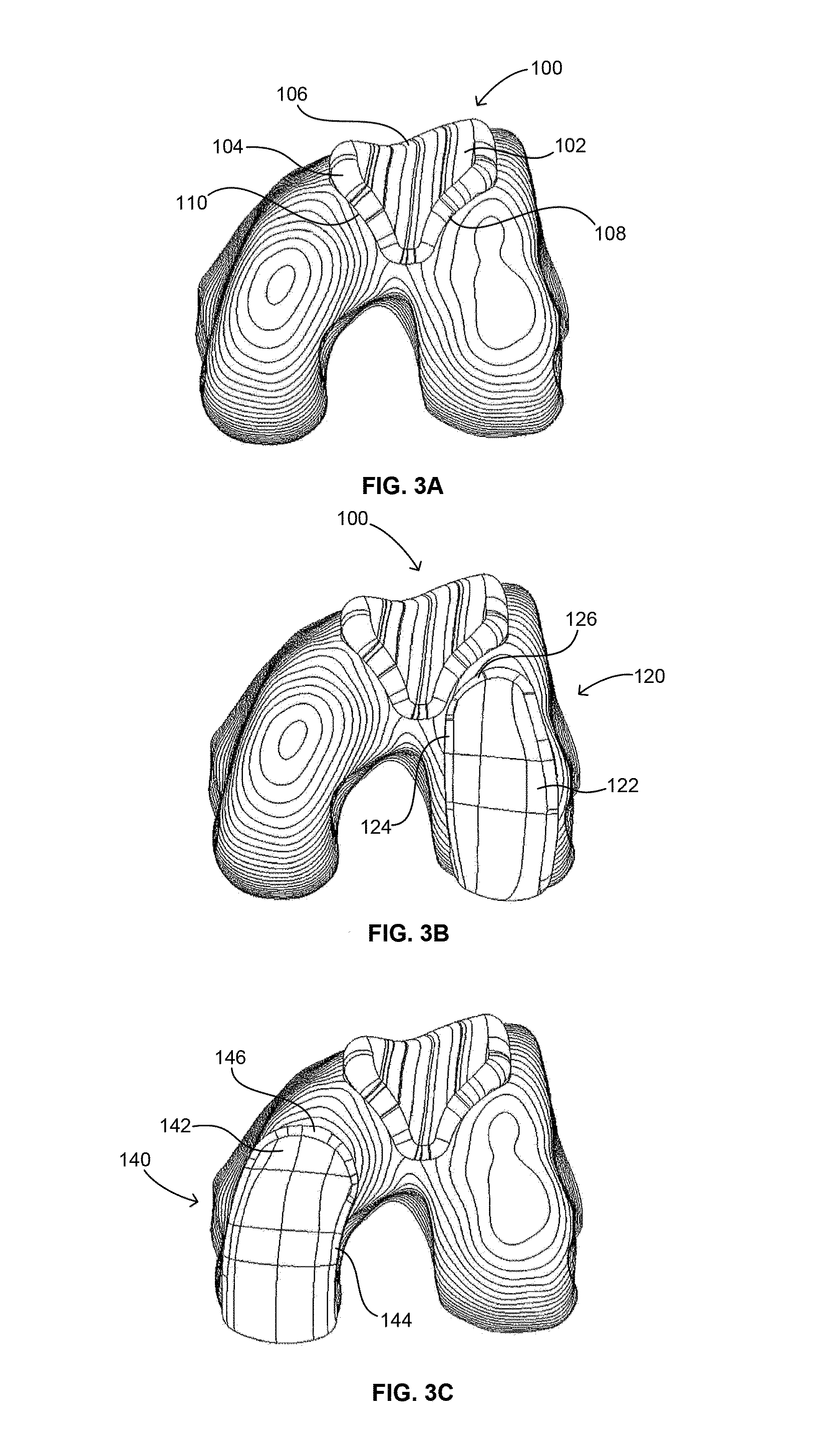
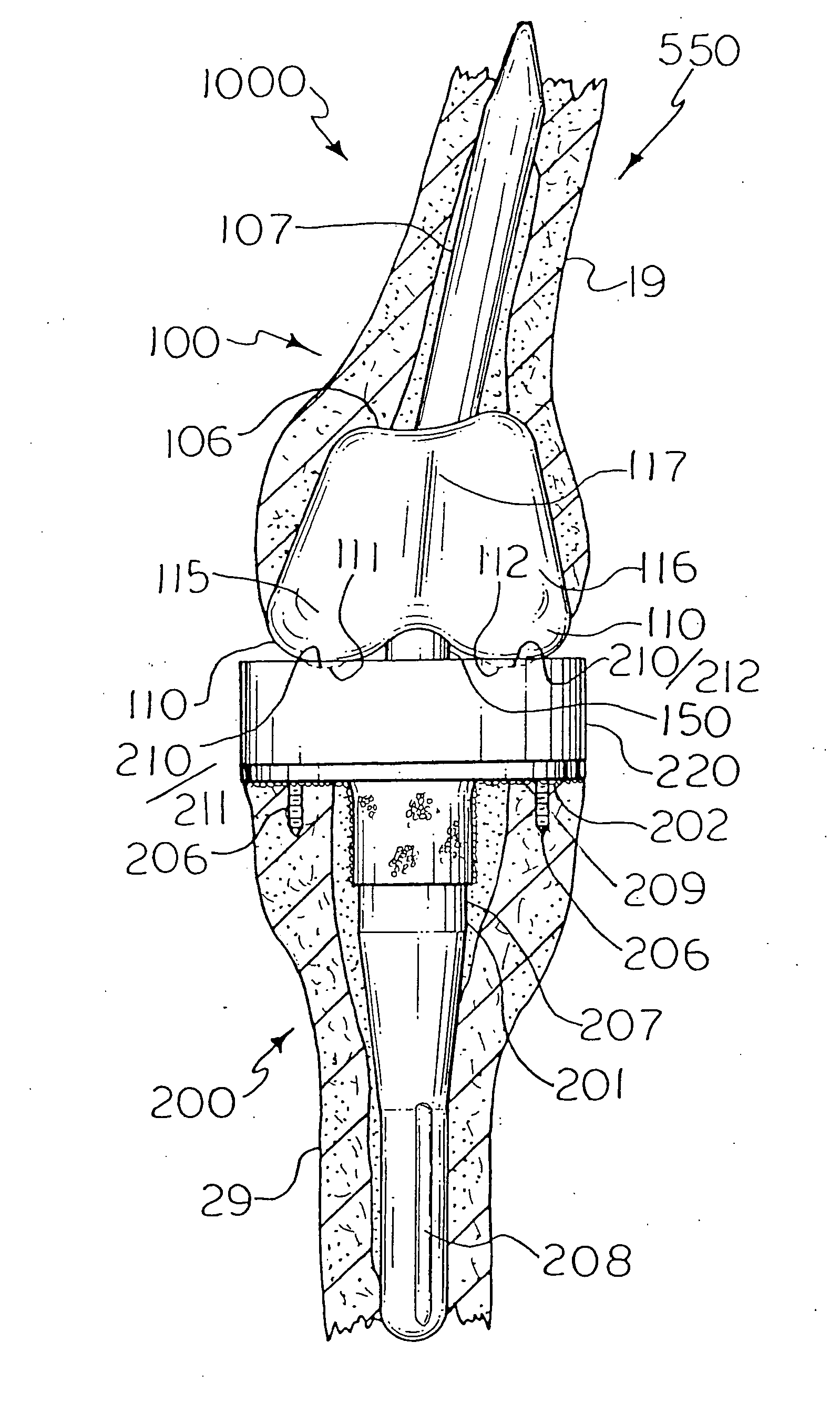
Systems and methods for compartmental replacement in a knee
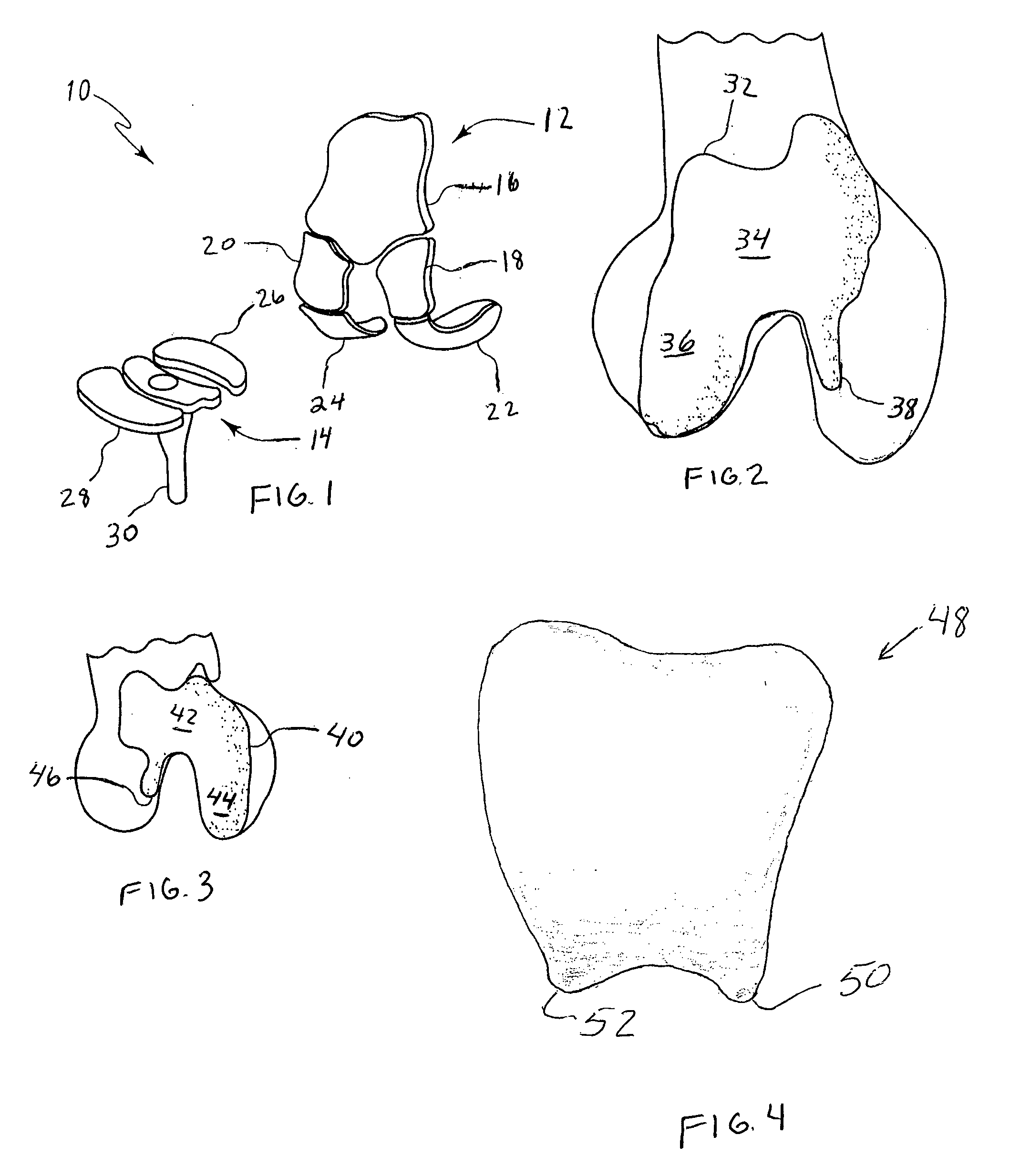
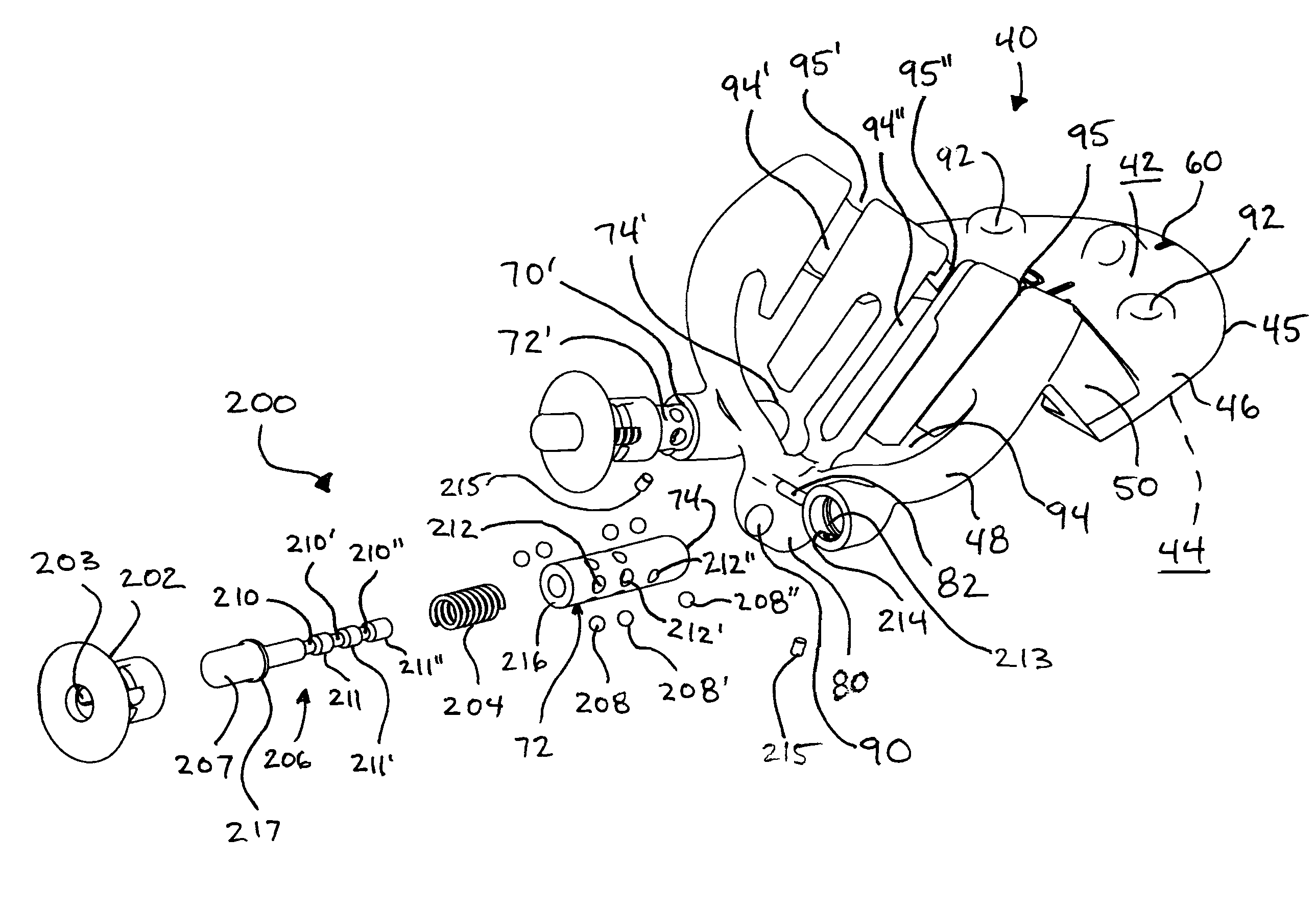
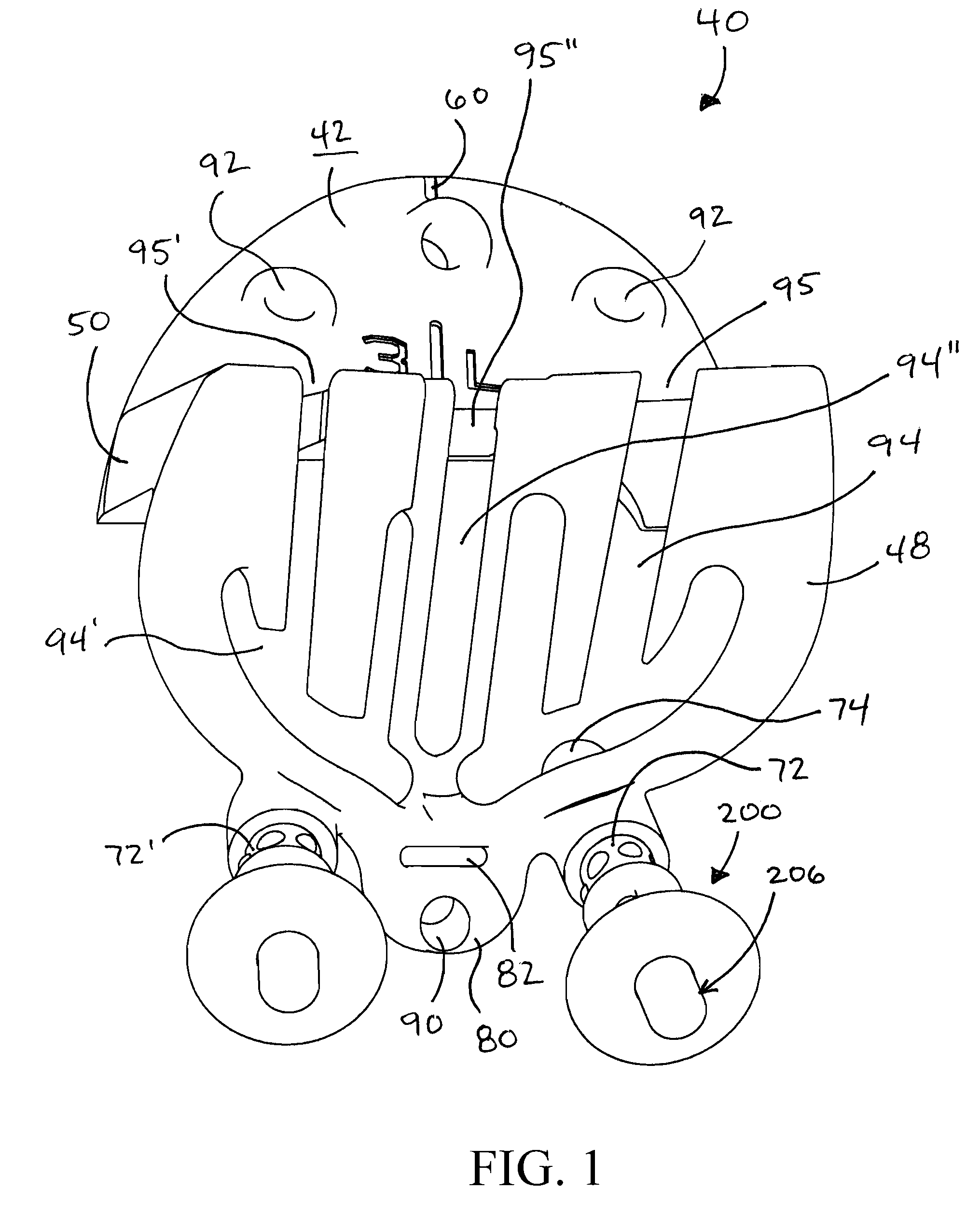
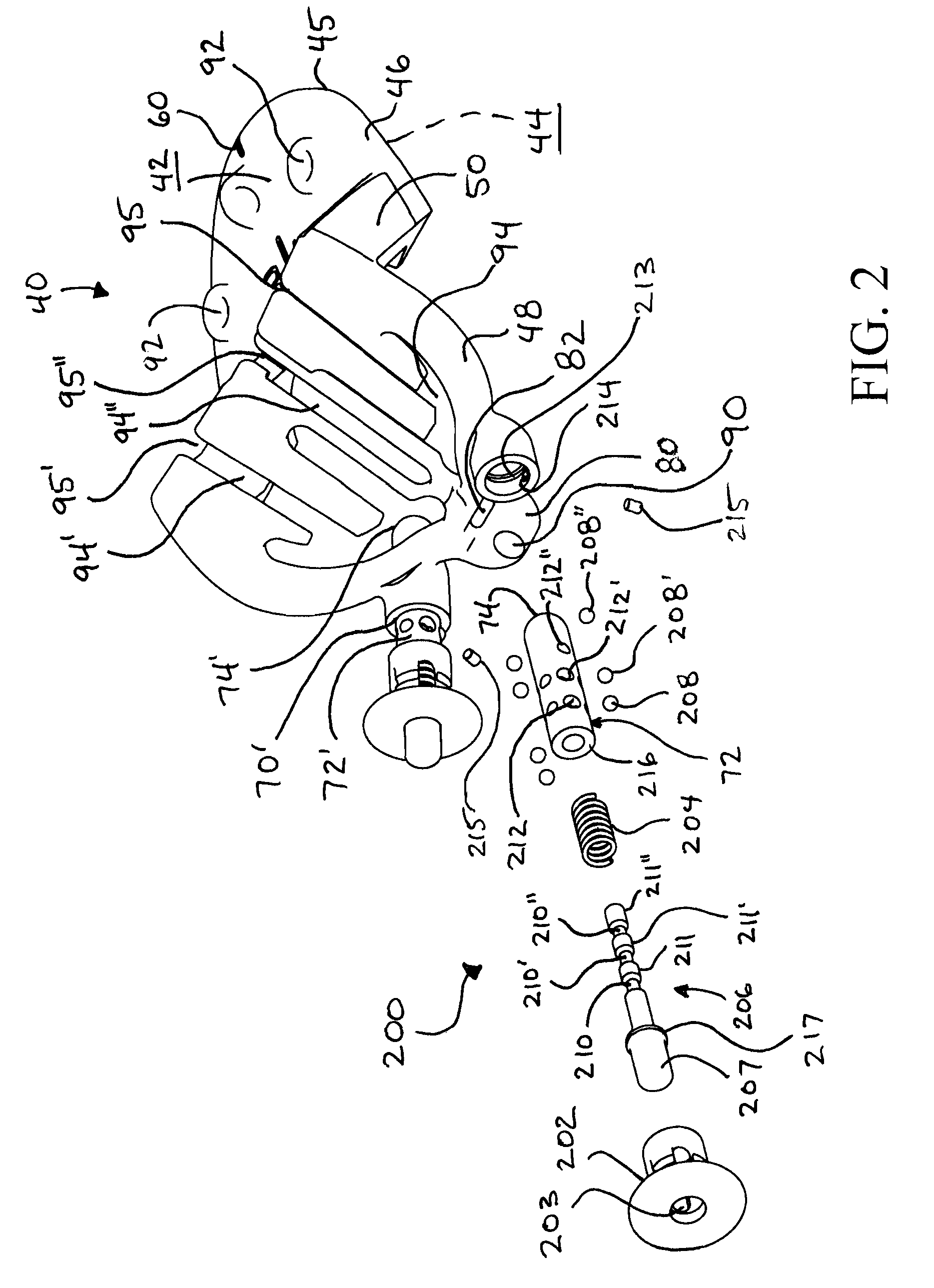
A knee replacement system provides a knee implant that may be used to more accurately replicate the diameter of a natural knee. In one embodiment, a patellofemoral component is connected to the posterior portion of a condylar component by screws that pass through the femur allowing the patellofemoral component and the condylar component to be torqued against opposing sides of the femur. Two additional screws are used to connect the patellofemoral component to an anterior portion of the condylar component. A gap may be left between the patellofemoral component and the anterior portion of the condylar component if needed to provide precise replication of the diameter of the natural knee from the patellofemoral component to the condylar component.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
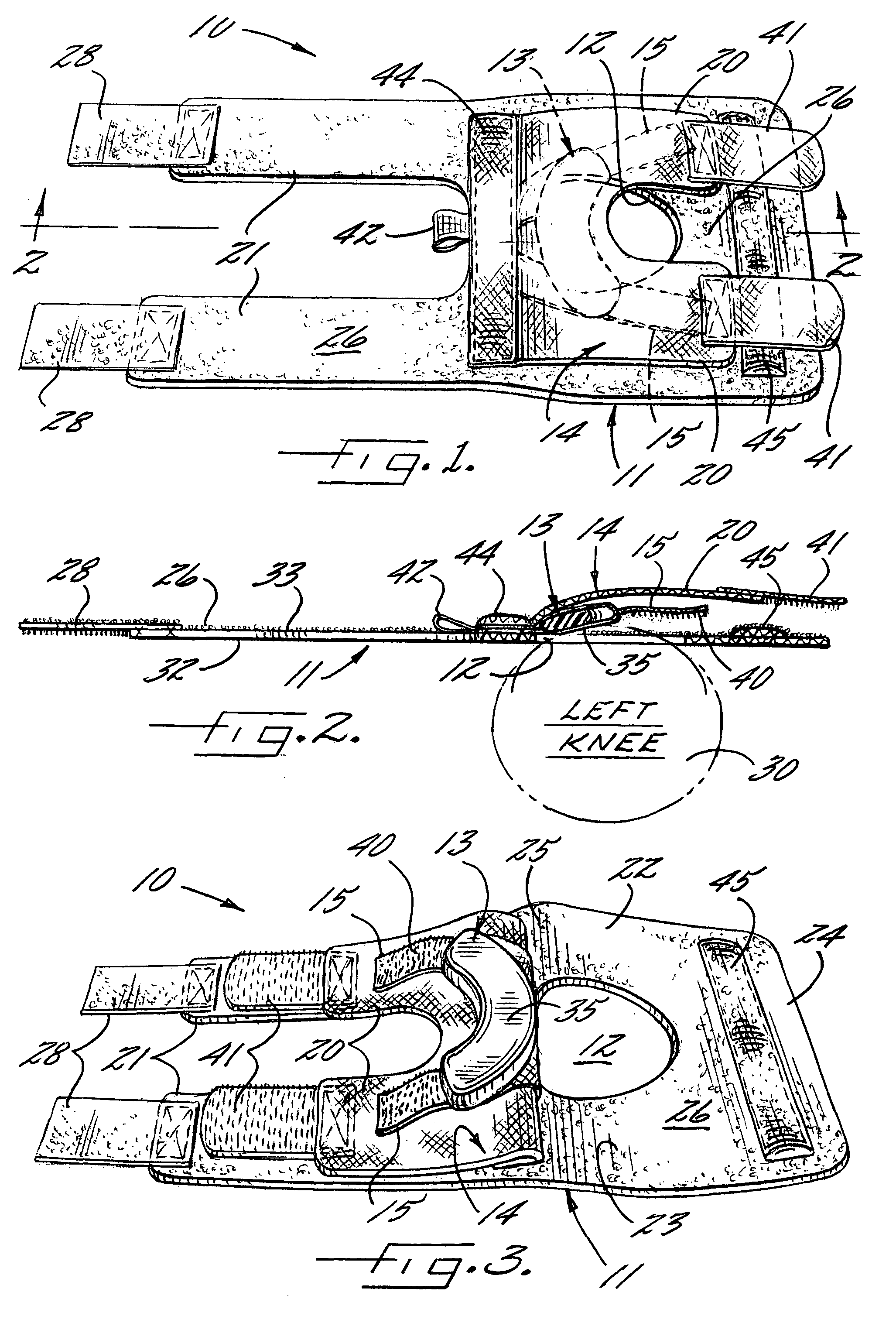
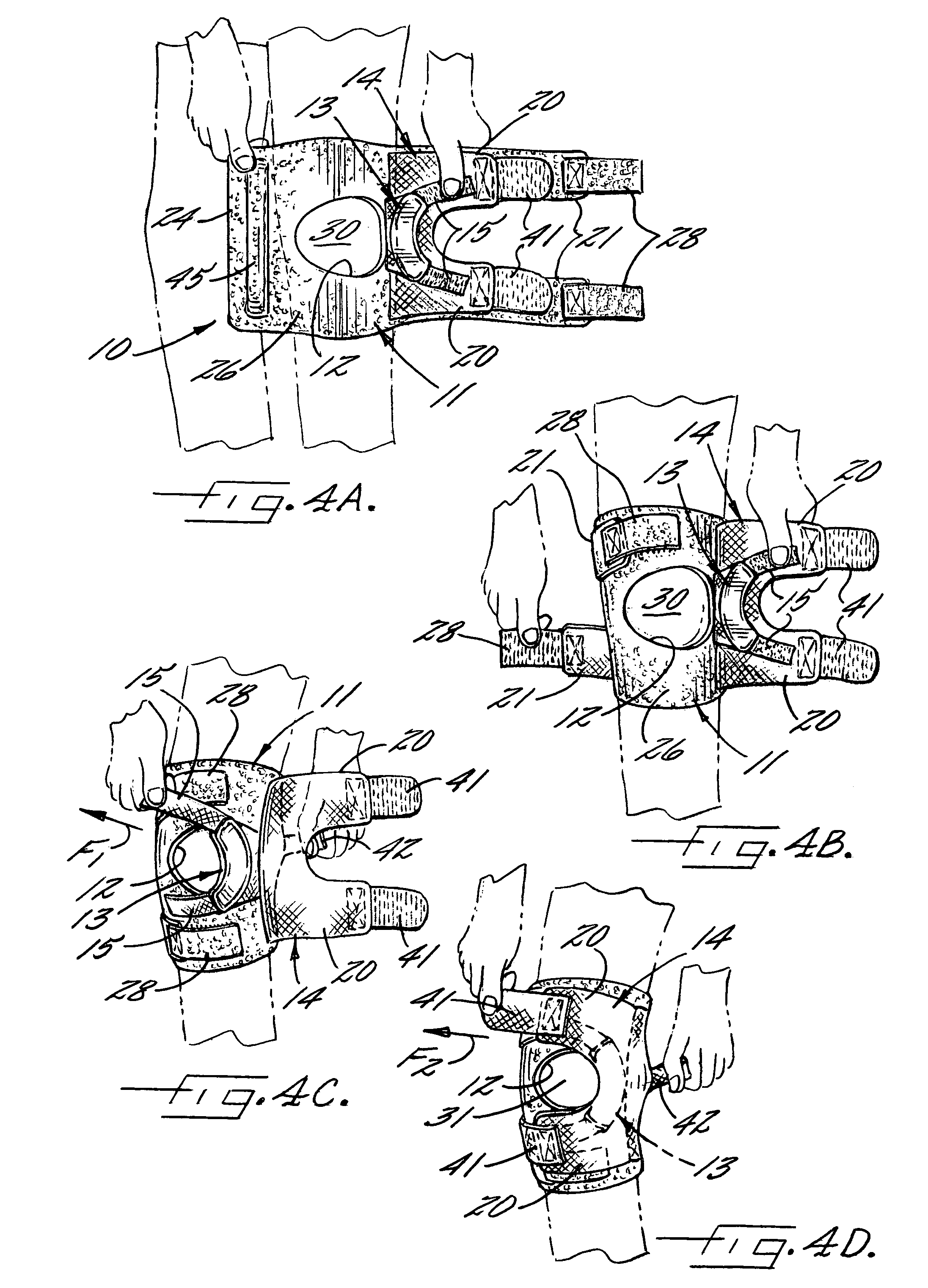
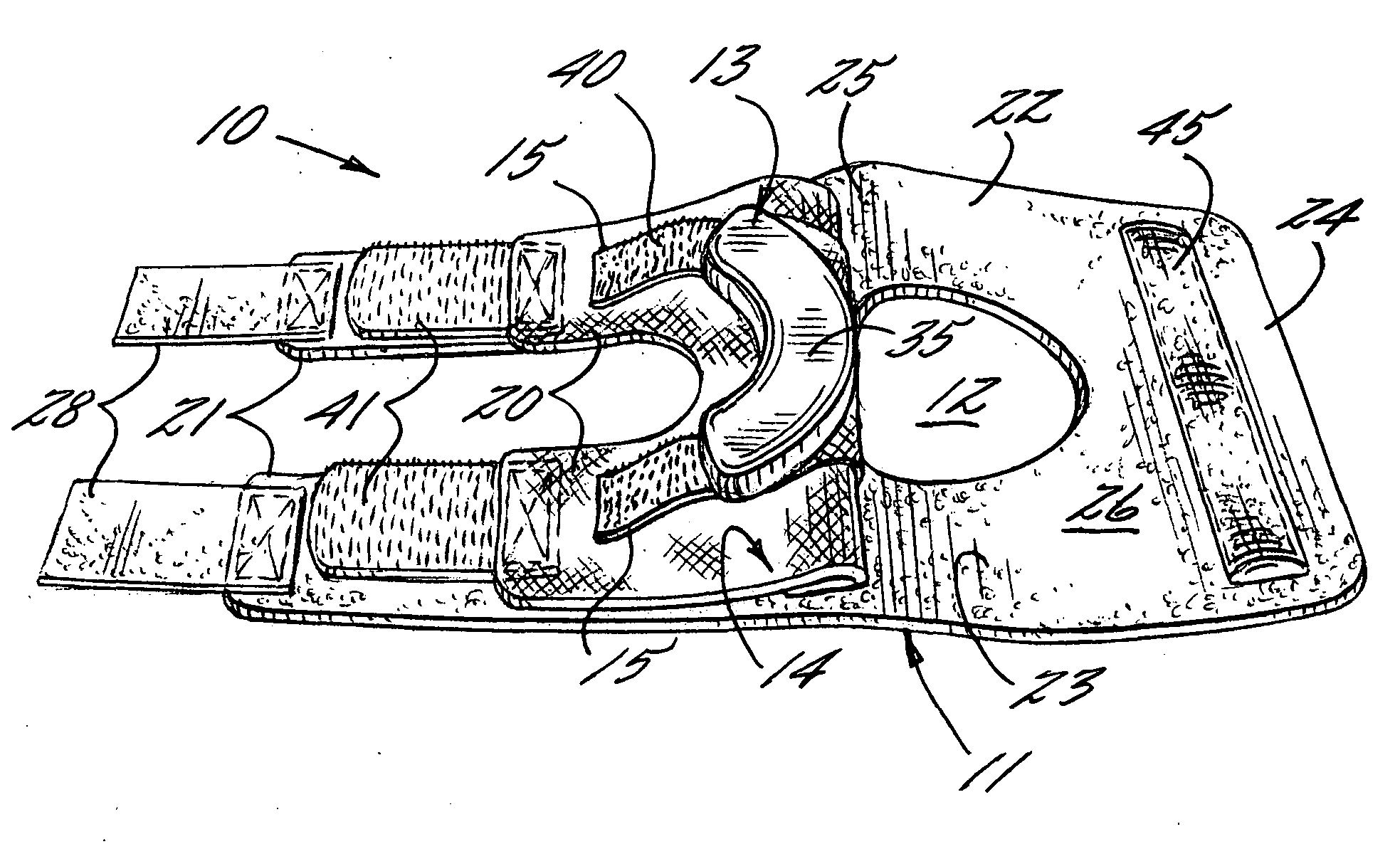
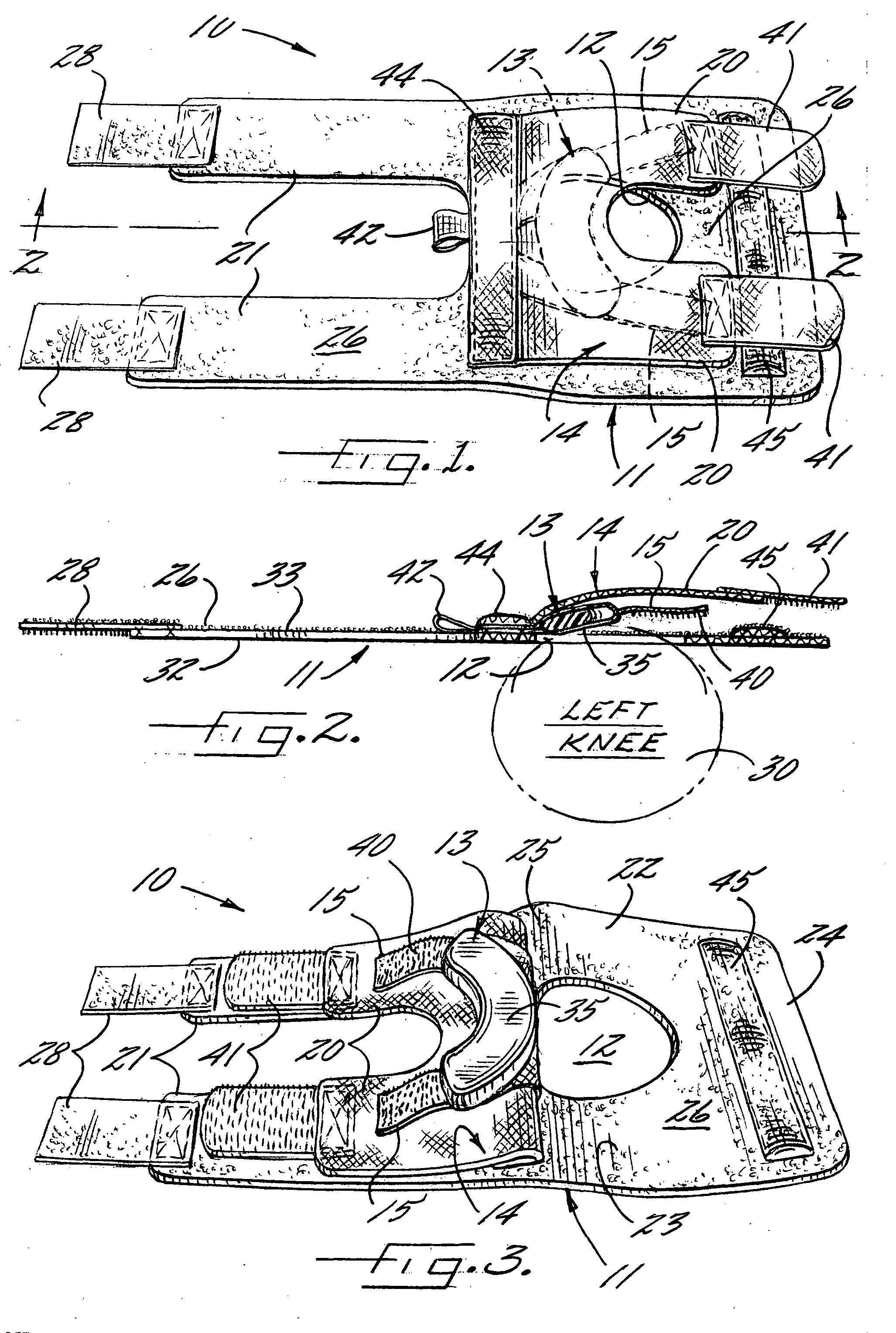
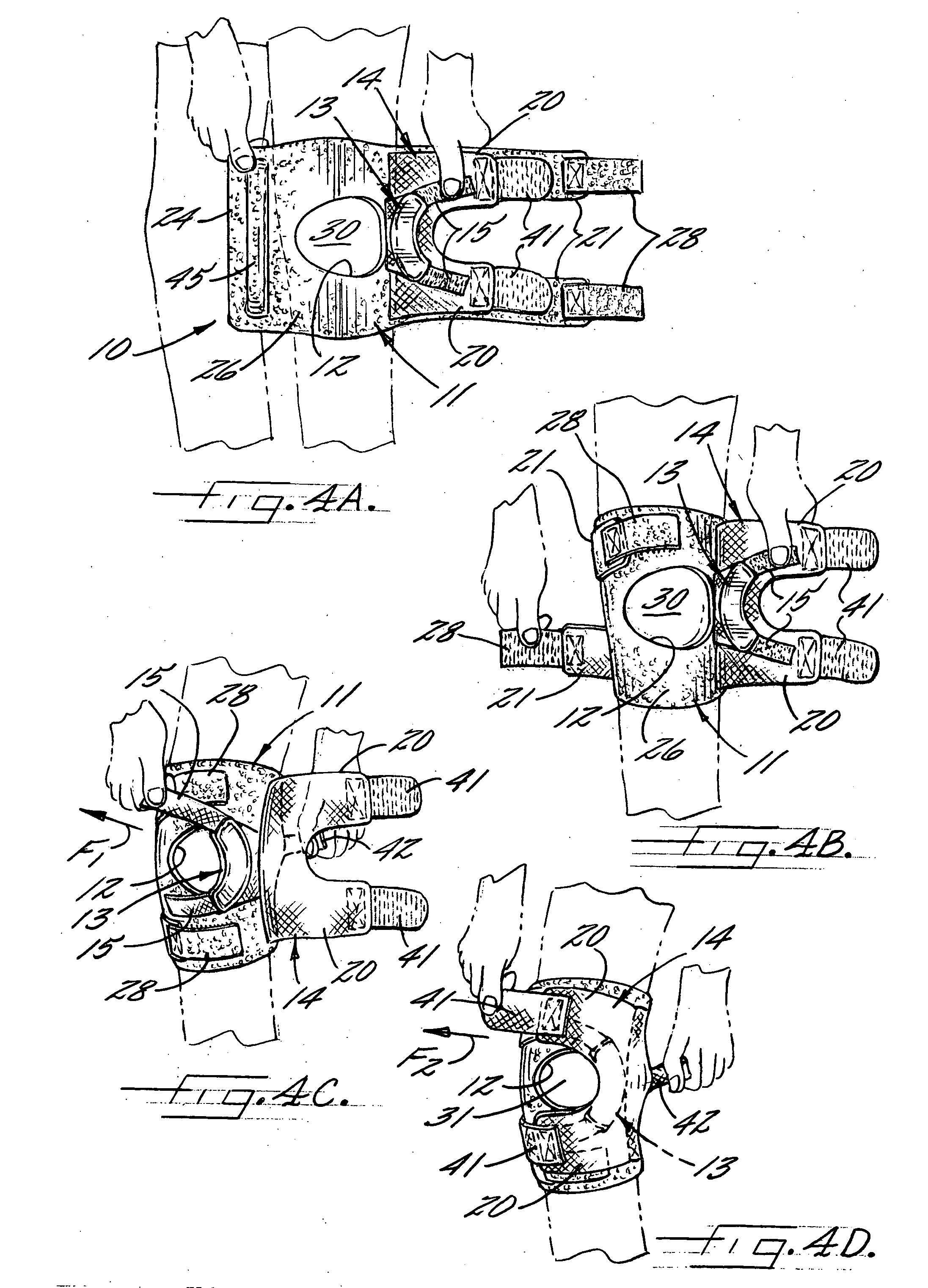
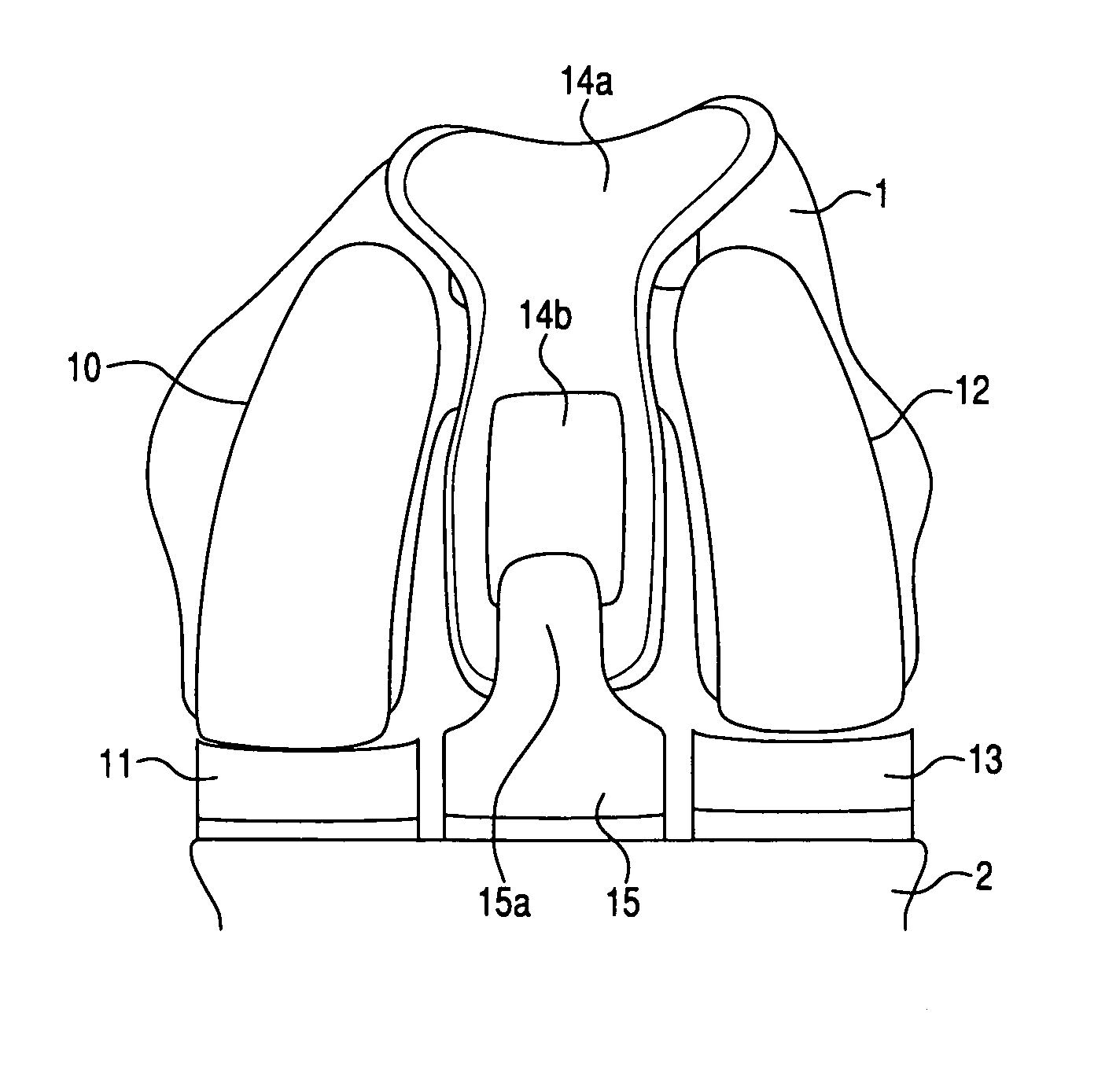
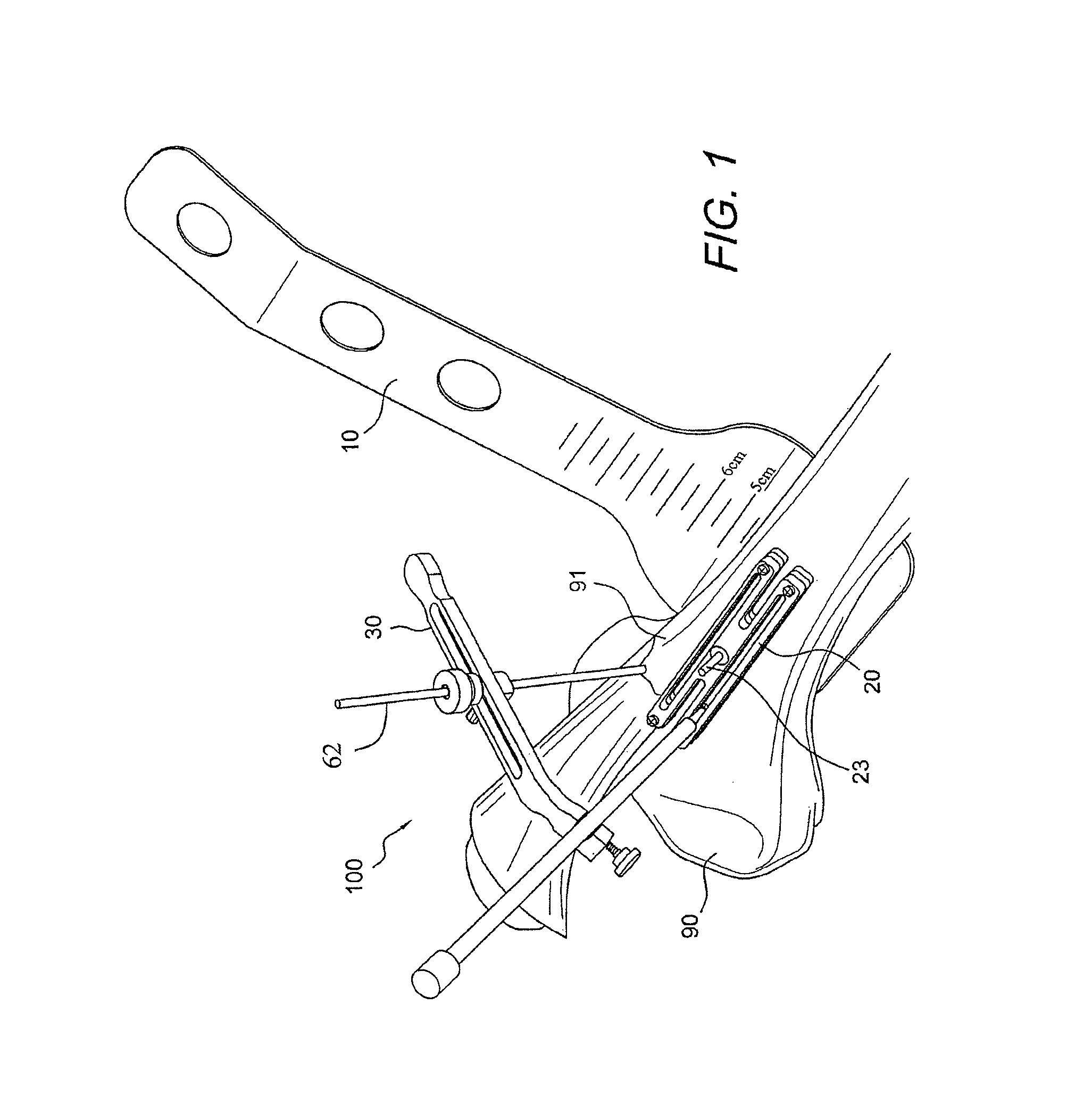
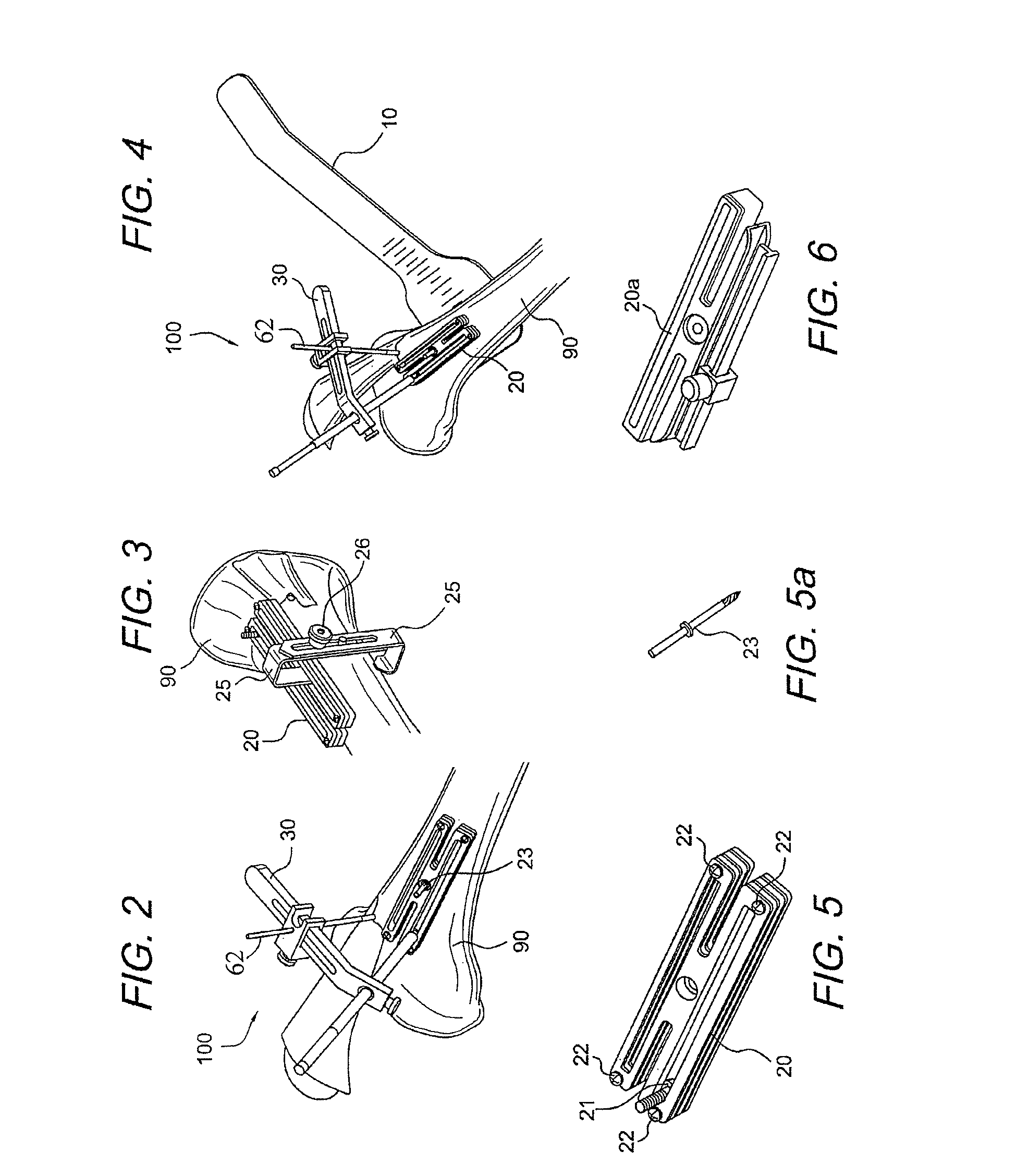
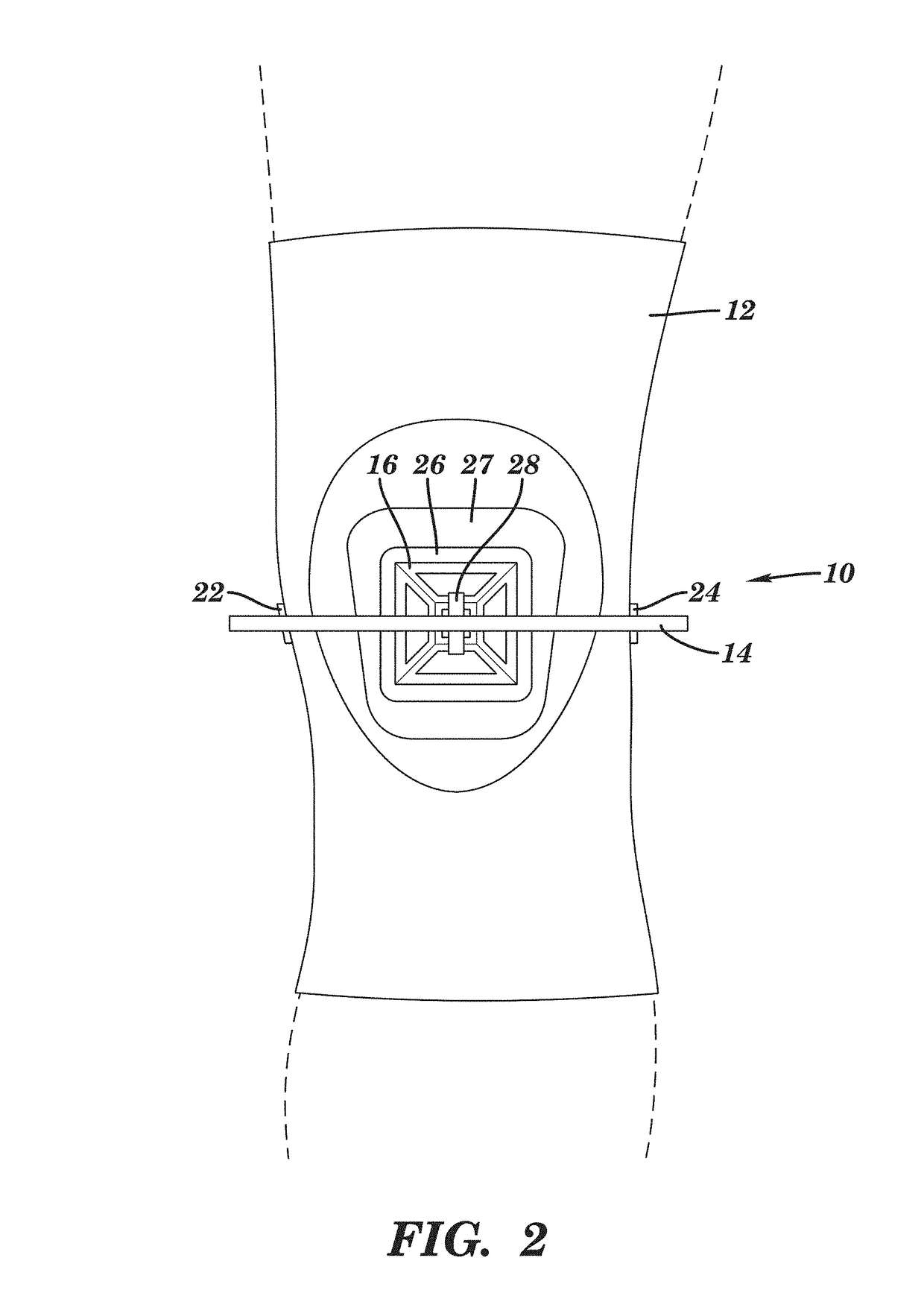
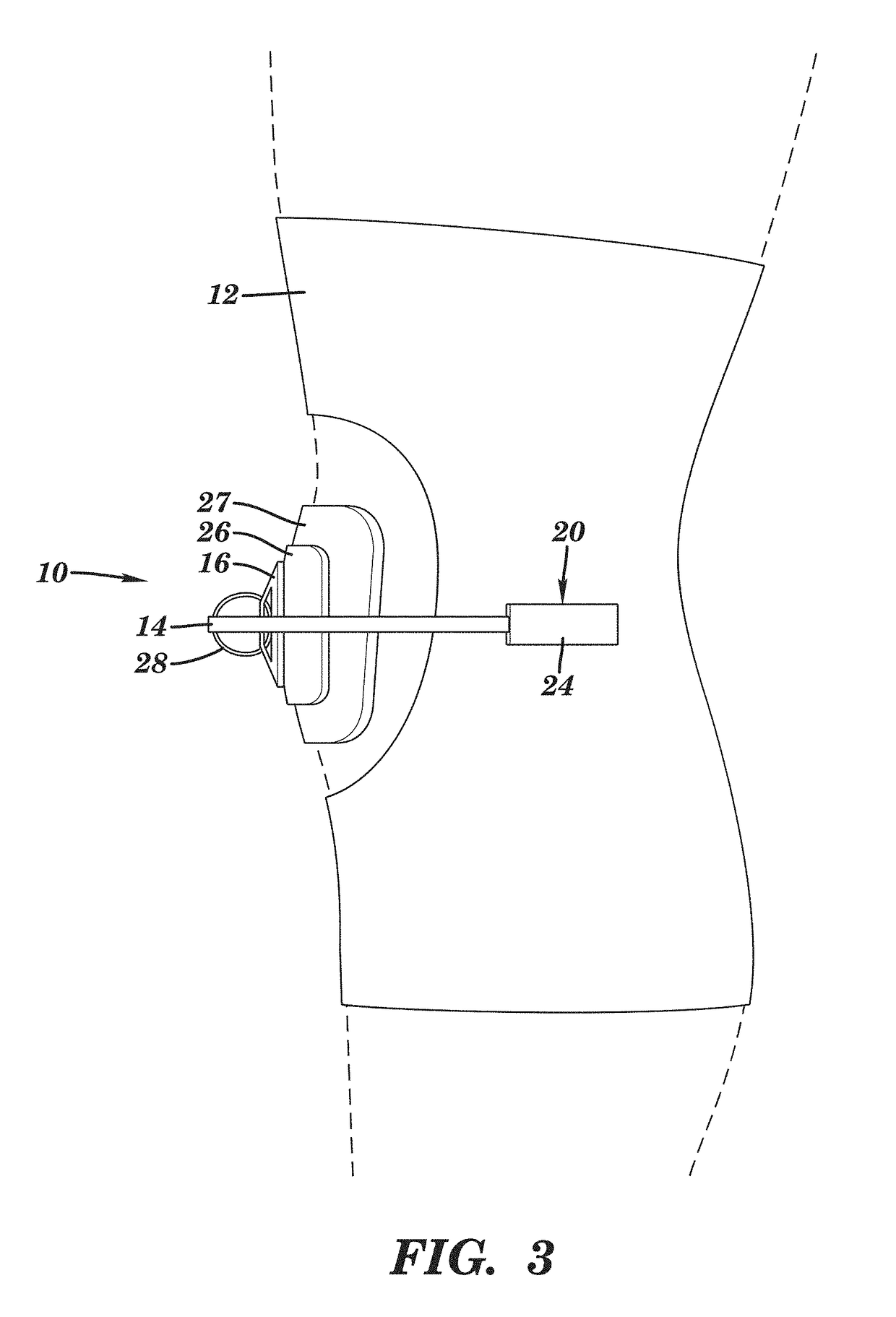
Patella stabilizing knee brace
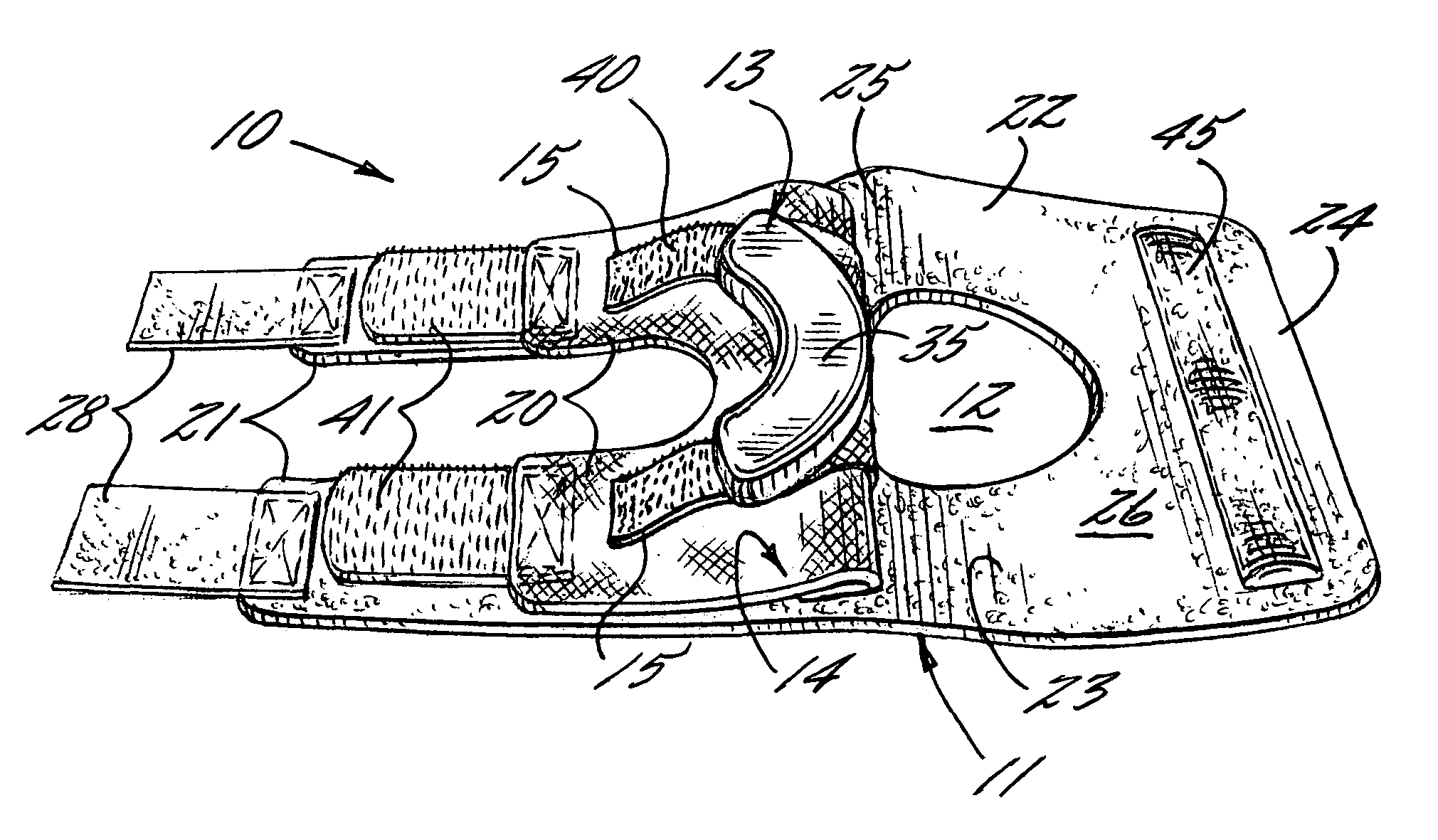
An apparatus for stabilizing movement of the patella in the patellofemoral joint comprises in one embodiment a base having an opening, a buttress secured to the base sheet member, a tensioning member secured to the base sheet member, a pair of tensioning arms secured to the buttress, a pair of tensioning arms secured to the tensioning member, a pair of compression members formed from the base, and a stabilizing member secured to an edge of the base. A method of stabilizing movement of the patella in the patellofemoral joint during physical activities comprises in one embodiment the steps of positioning a support brace having an opening against the knee, extending a portion of the brace against the knee to apply a first force against portions of the knee in the opening, and extending another portion of the brace against the knee to apply a second force against the knee.
Owner:MEDICAL SPECIALTIES
Patella stabilizing knee brace
ActiveUS20050020951A1Restrict movementSmooth motionRestraining devicesFeet bandagesButtressKnee Joint
An apparatus for stabilizing movement of the patella in the patellofemoral joint comprises in one embodiment a base having an opening, a buttress secured to the base sheet member, a tensioning member secured to the base sheet member, a pair of tensioning arms secured to the buttress, a pair of tensioning arms secured to the tensioning member, a pair of compression members formed from the base, and a stabilizing member secured to an edge of the base. A method of stabilizing movement of the patella in the patellofemoral joint during physical activities comprises in one embodiment the steps of positioning a support brace having an opening against the knee, extending a portion of the brace against the knee to apply a first force against portions of the knee in the opening, and extending another portion of the brace against the knee to apply a second force against the knee.
Owner:MEDICAL SPECIALTIES
Prosthetic knee
A hinged knee prosthesis includes a femoral component with a tibiofemoral articular surface that is distinct from the patellofemoral articulating surface. Fully congruent tibiofemoral articulation is provided for virtually all flexion angles. Additionally, the bearing is capable of at least limited axial rotation relative to the tibial component but is restrained against dislocation. Accordingly, dislocation is much less likely even n those situations where collateral ligaments are insufficient.
Owner:BUECHEL PAPPAS TRUST
Multi-compartmental prosthetic device with patellar component transition
A prosthetic device for forming at least a portion of a joint may have a plurality of segmented components fixed relative to a femur of a body including: a patellofemoral component and a condyle component. Each segmented component may be configured such that a placement at which the segmented component will be fixed relative to the femur is not constrained by a connection to another of the segmented components that is fixed relative to the femur. In an installed configuration, the patellofemoral and condyle components may be fixed relative to the femur such that: a gap is provided between an edge of the patellofemoral component and an opposing edge of the condyle component, and a transition region is provided that extends from a first femoral coronal plane that intersects the patellofemoral component to a second femoral coronal plane that intersects the condyle component.
Owner:MAKO SURGICAL CORP
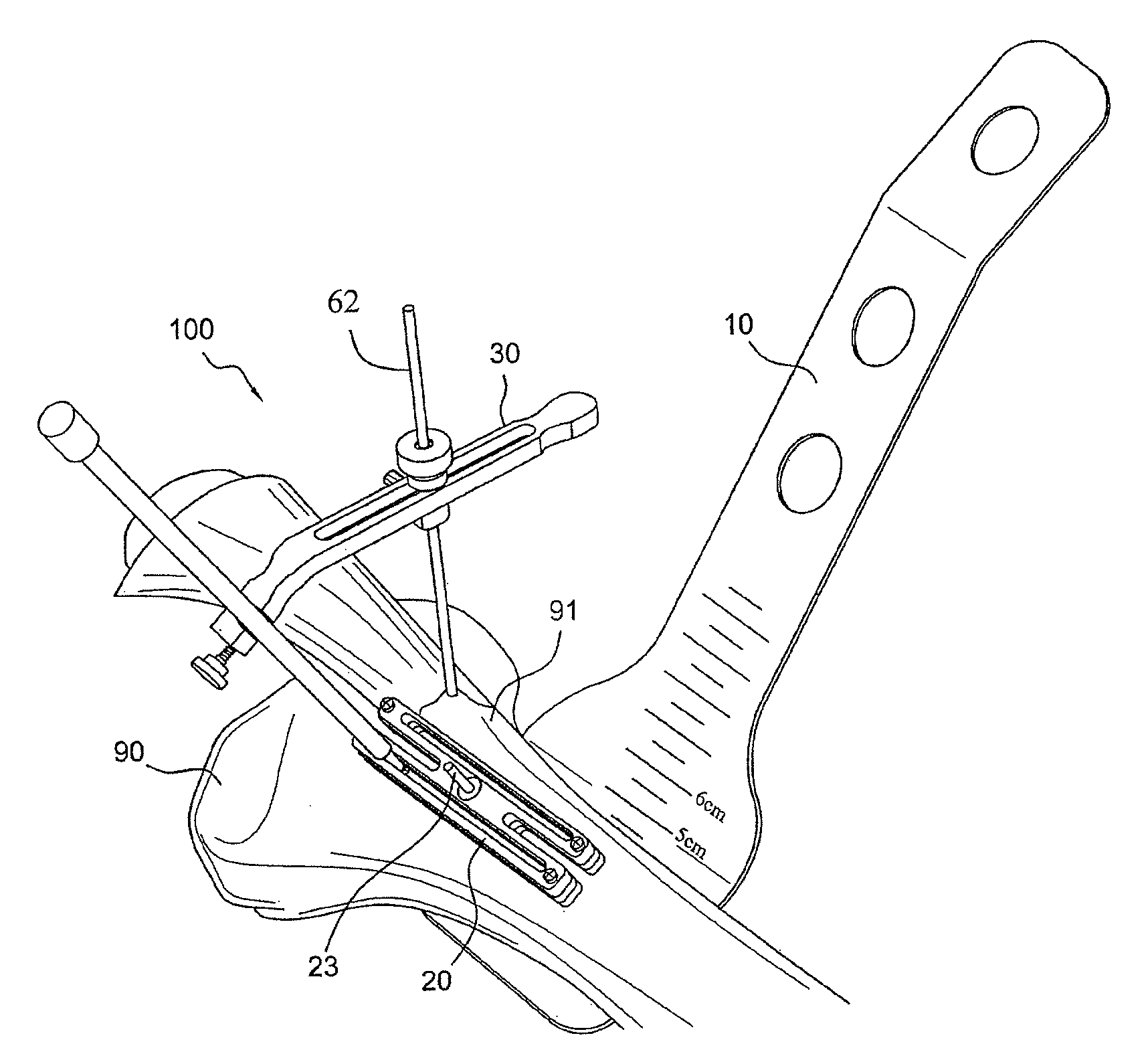
AMZ tibial tuberosity transfer system
ActiveUS8353915B2Large radiusSimple designNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSurgical sawsMedicineTransfer system
An AMZ tibial tuberosity transfer system and method of treatment of patellofemoral joints. The AMZ system includes 1) a retractor with a better conformation to anatomy and more curve (not just a bend), and also with a larger radius on the front of the retractor to allow for easier insertion; 2) a cutting block that can fully accept a collared pin; 3) a rod preferably formed of stainless steel; 4) a tuberosity pin guide; 5) an exit indicator that engages tightly the cutting block so there is no slope on exit indication; and 6) a horizontal bar provided with markings to measure the medial shift.
Owner:ARTHREX
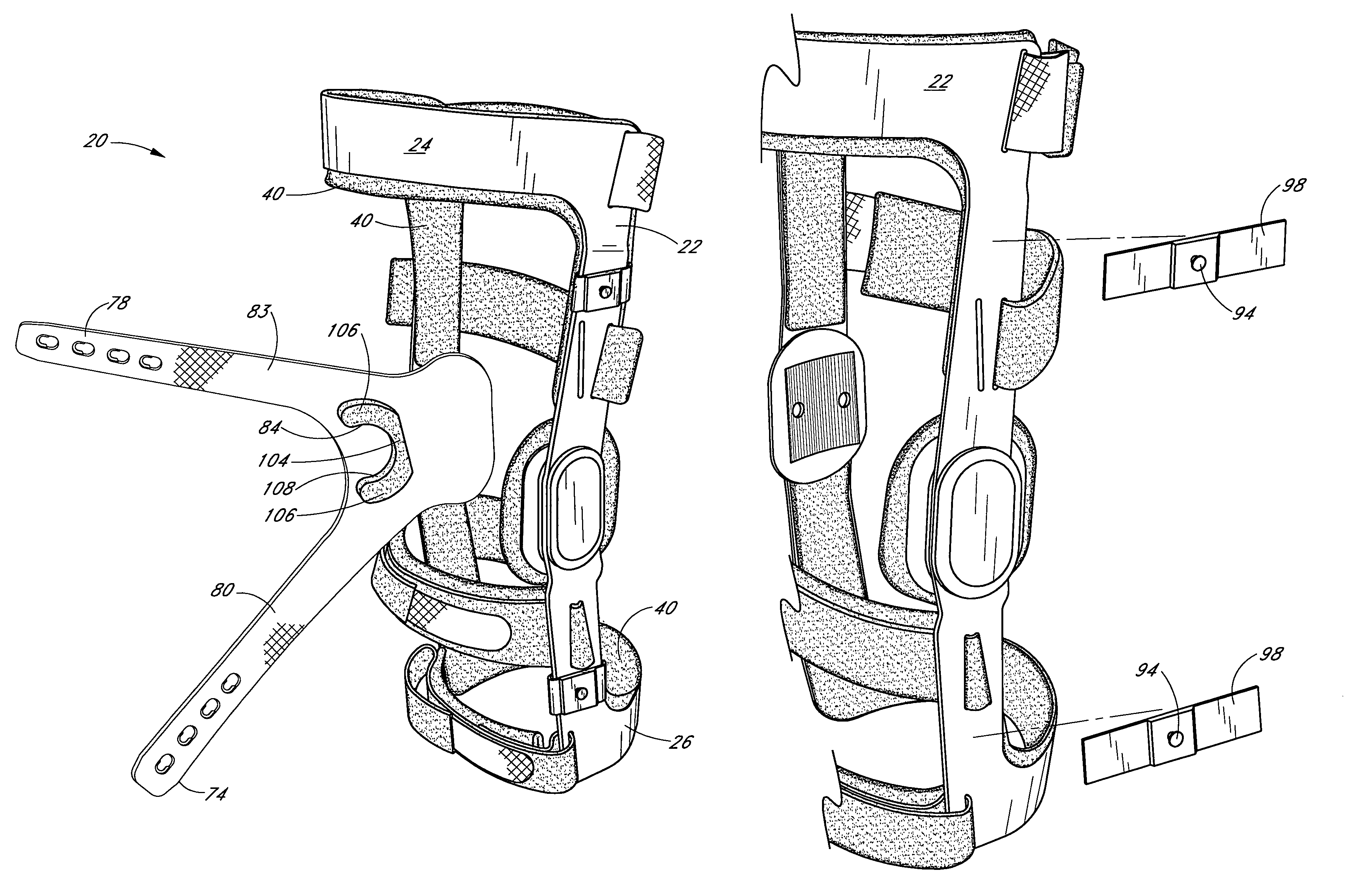
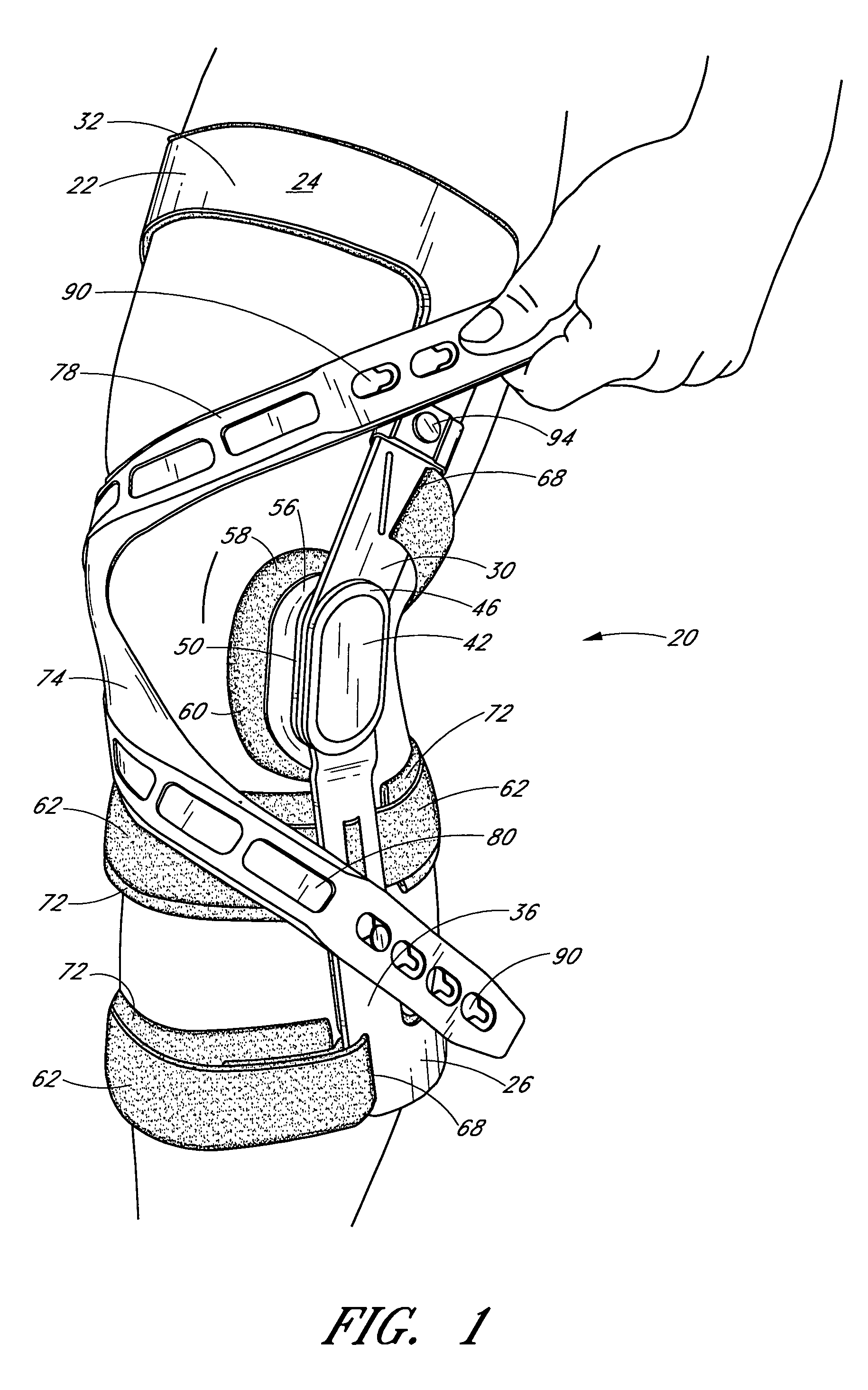
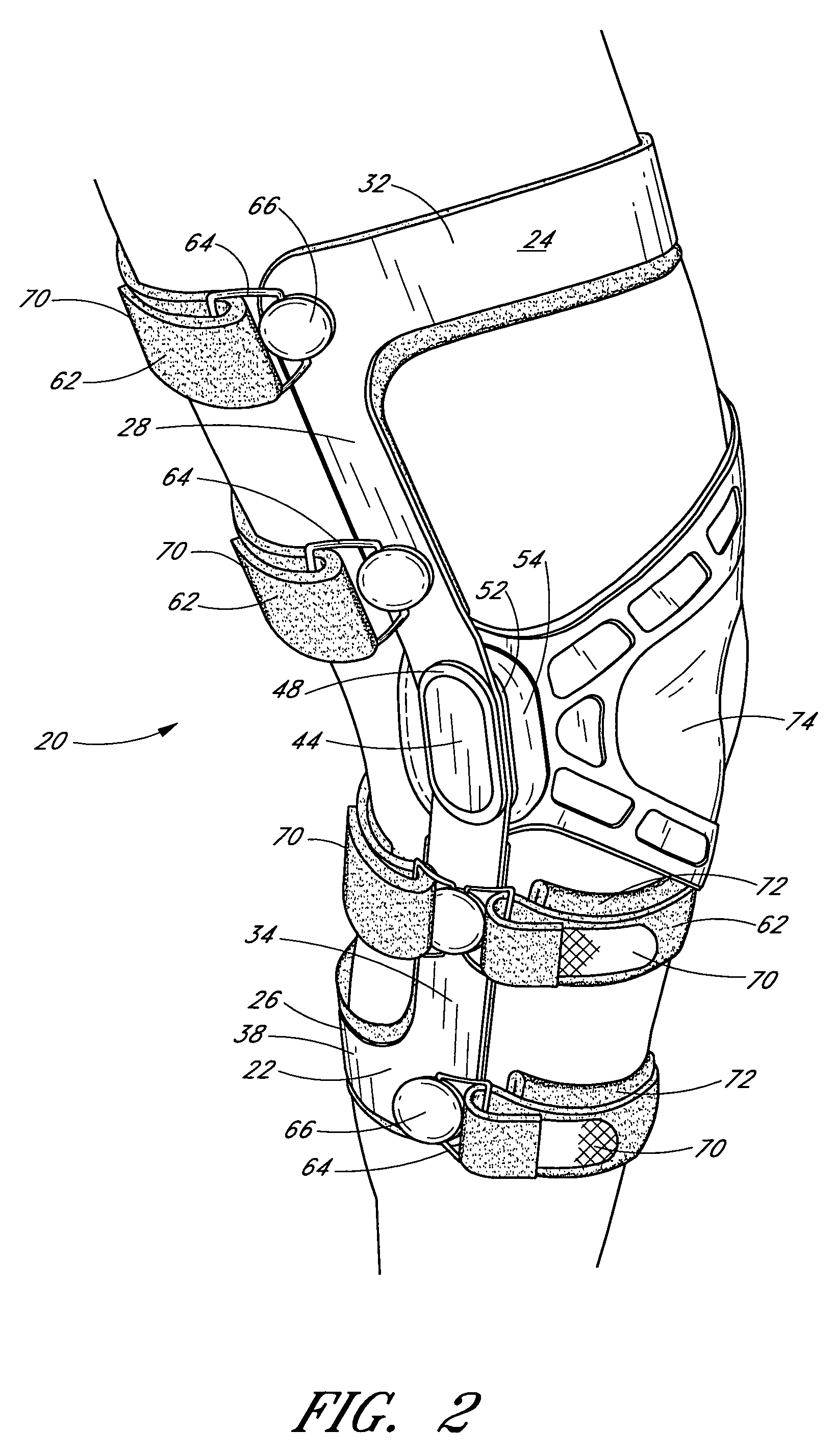
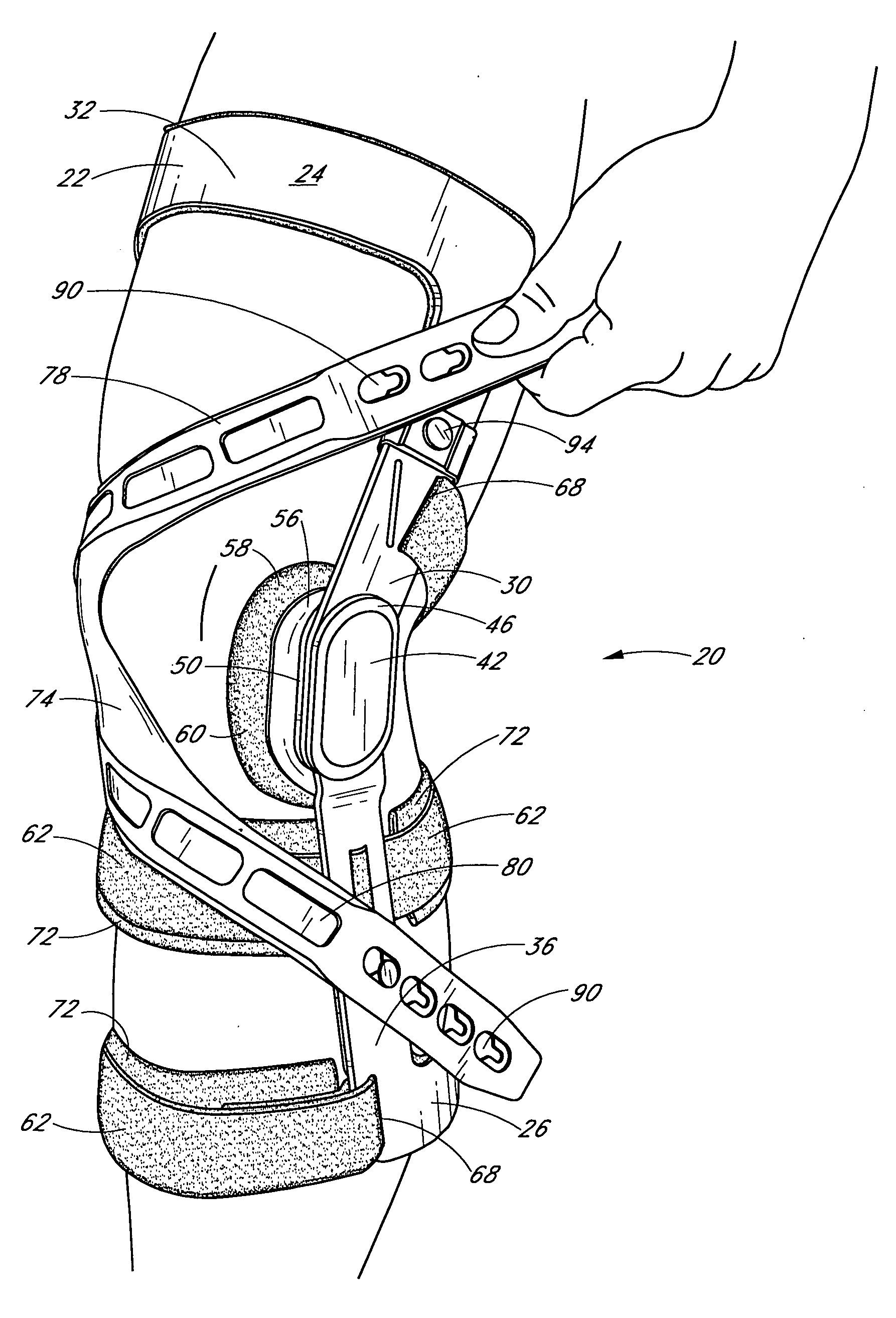
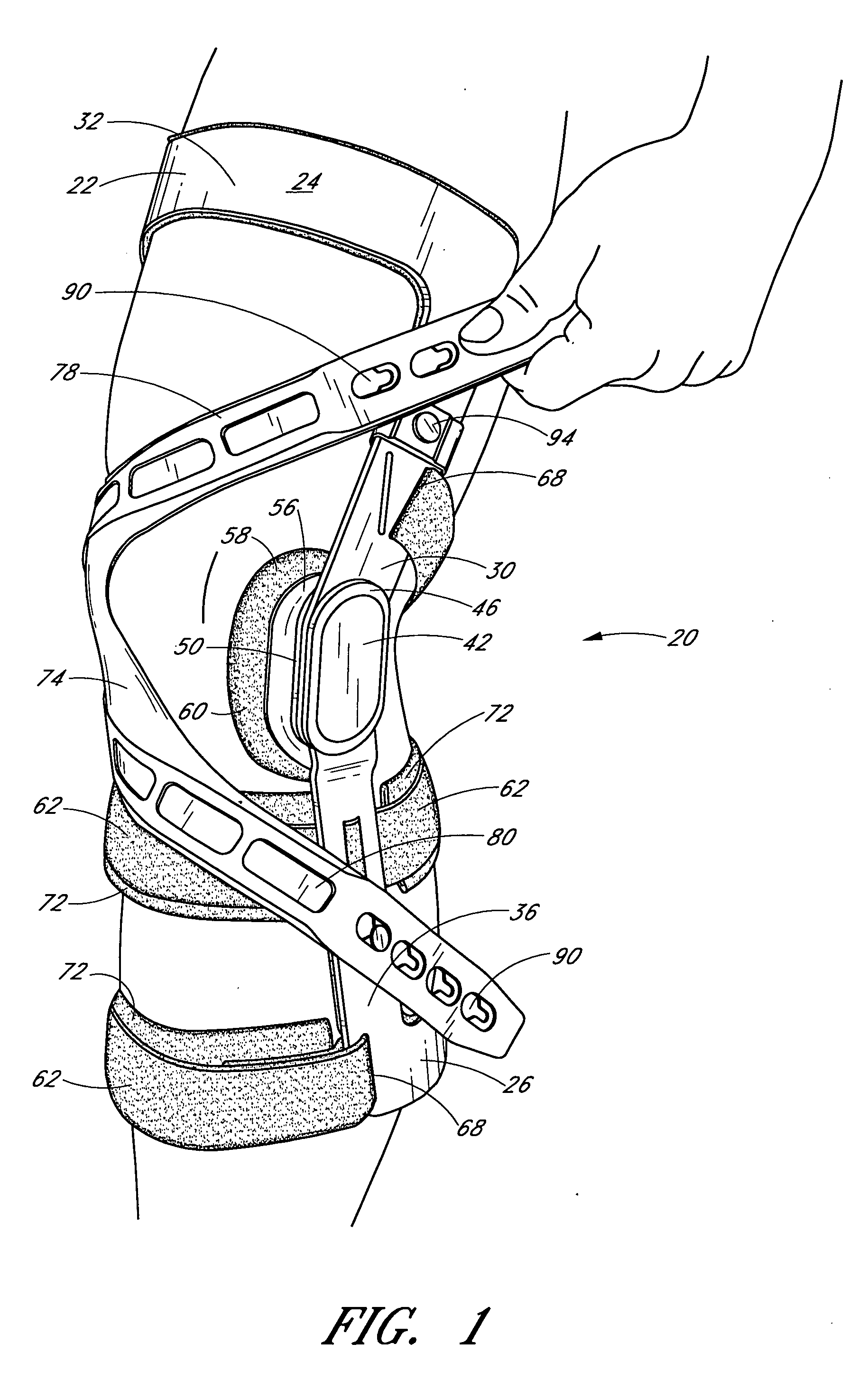
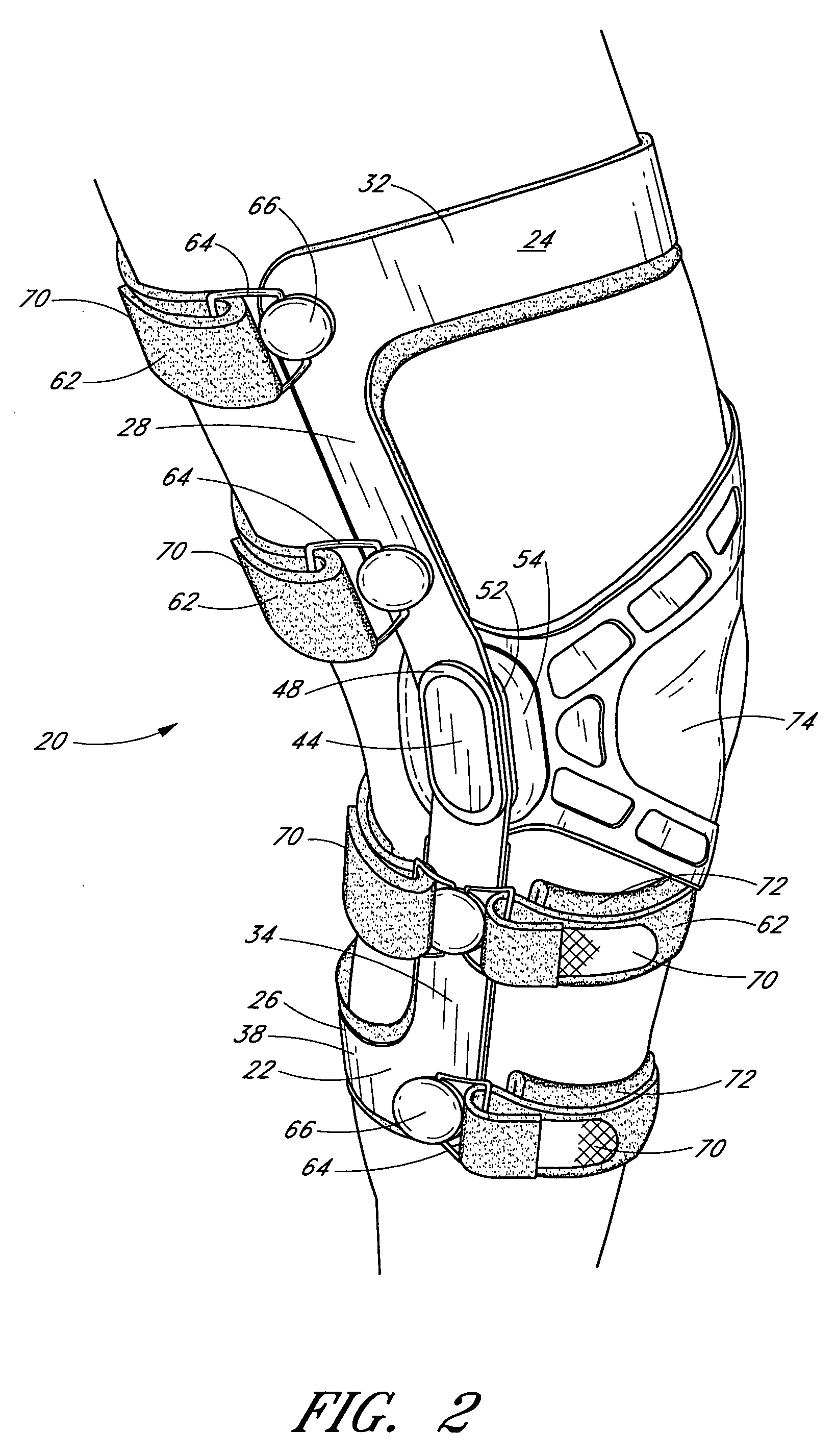
Knee brace having a rigid frame and patellofemoral support
Embodiments of the knee brace disclosed herein provide a combination of external ligament support and / or relief from pain caused by osteoarthritis with patellofemoral support. The brace includes a rigid frame and a flexible strap configured to extend across the wearer's patella to provide anterior loading thereto. The strap is operatively secured at either end to components of the rigid frame, thereby providing maximum leverage for applying force to the wearer's patella. In some embodiments, the strap includes a removable and adjustable buttress for directly contacting the wearer's patella. The patellar strap provides dynamic loading to the patella through the wearer's range of motion for relief of patellofemoral dysfunction, such as patellar shift, subluxation and dislocation, and malalignments such as patella alta, patella baja, tilt and glide. In some embodiments, a conversion kit is provided for converting a rigid brace frame into a knee brace capable of providing patellofemoral support to a wearer's knee. The kit includes at least a patellar strap and at least one tab for securing the strap to the rigid frame.
Owner:DJ ORTHOPEDICS
Knee brace having a rigid frame and patellofemoral support
Embodiments of the knee brace disclosed herein provide a combination of external ligament support and / or relief from pain caused by osteoarthritis with patellofemoral support. The brace includes a rigid frame and a flexible strap configured to extend across the wearer's patella to provide anterior loading thereto. The strap is operatively secured at either end to components of the rigid frame, thereby providing maximum leverage for applying force to the wearer's patella. In some embodiments, the strap includes a removable and adjustable buttress for directly contacting the wearer's patella. The patellar strap provides dynamic loading to the patella through the wearer's range of motion for relief of patellofemoral dysfunction, such as patellar shift, subluxation and dislocation, and malalignments such as patella alta, patella baja, tilt and glide. In some embodiments, a conversion kit is provided for converting a rigid brace frame into a knee brace capable of providing patellofemoral support to a wearer's knee. The kit includes at least a patellar strap and at least one tab for securing the strap to the rigid frame.
Owner:DJ ORTHOPEDICS
Knee joint prosthesis with a femoral component which links the tibiofemoral axis of rotation with the patellofemoral axis of rotation
A femoral component is provided for use in a knee joint prosthesis. The femoral component may be configured to provide one or more desirable kinematic relationships with a tibial component and / or patella so as to mimic the flexion and extension motion of a natural knee joint. The femoral component may be configured so that the patella follows a substantially circular pathway during knee flexion and extension. The femoral component may be configured so that the patella follows a curved patellar path during flexion and extension, and the curved patellar path has an origin located anterior and proximal to the geometrical center axis of the knee. The femoral component may be configured so that the patella follows a curved patellar path that lies in a plane which is parallel to and offset from a plane that extends through the center of the femoral head of a femur and is perpendicular to the geometric center axis of the knee. The femoral component may be configured so that at least a portion of the patella substantially follows a patellar path in a plane perpendicular to the geometrical center axis of a knee throughout knee flexion.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF VERMONT
Amz tibial tuberosity transfer system
ActiveUS20090318924A1Good conformationLarge radiusNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSurgical sawsMedicineTransfer system
An AMZ tibial tuberosity transfer system and method of treatment of patellofemoral joints. The AMZ system includes 1) a retractor with a better conformation to anatomy and more curve (not just a bend), and also with a larger radius on the front of the retractor to allow for easier insertion; 2) a cutting block that can fully accept a collared pin; 3) a rod preferably formed of stainless steel; 4) a tuberosity pin guide; 5) an exit indicator that engages tightly the cutting block so there is no slope on exit indication; and 6) a horizontal bar provided with markings to measure the medial shift.
Owner:ARTHREX
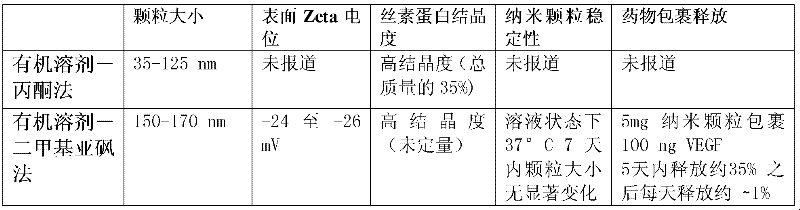
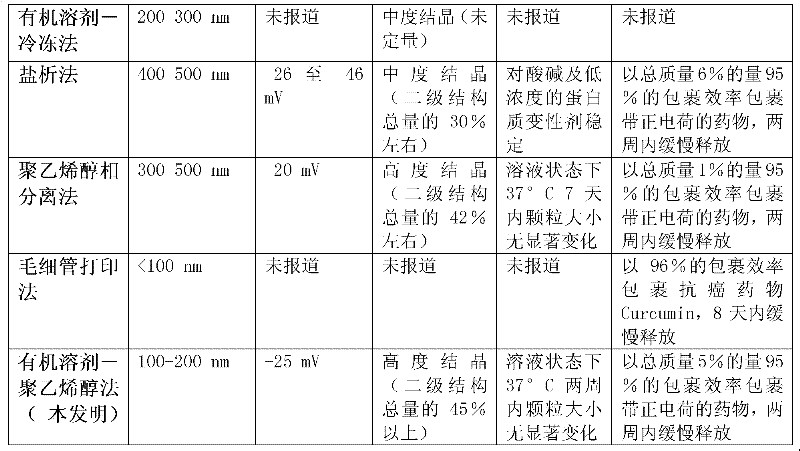
Method for preparing fibroin nanoparticles taking polyvinyl alcohol as stabilizer
InactiveCN102344686AAchieve mass productionEliminate the ultracentrifugation stepCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsTissue repairOrganic solvent
The invention relates to a method for preparing fibroin nanoparticles taking polyvinyl alcohol as a stabilizer. The method comprises the following process steps of: (1) preparing fibroin extracted from silk into 5-8 percent by weight in volume of fibroin solution; (2) adding a polyvinyl alcohol solution into the fibroin solution to obtain a blended solution; (3) dropwise adding the blended solution into a water-soluble organic solvent which can be used for inducing beta-folding of the fibroin, and stirring continually for 1-6 hours to obtain a fibroin nanoparticle solution; (4) further purifying and enriching the fibroin nanoparticle solution to obtain uniform fibroin nanoparticles; and (5) storing the obtained fibroin nanoparticles. According to the preparation method, fibroin nanoparticles with uniform and stable particle sizes and high yield can be prepared; and the fibroin nanoparticles are suitable for large-scale production and are widely applied in a plurality of fields such as medicament release, patellofemoral joint biological lubricants, face-lifting, beauty treatment, tissue repair and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU SIMEITE BIOTECH CO LTD
Minimally invasive collective integral acupotomy scope and operation method thereof
ActiveCN102429632ATraumaGood treatment effectSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisTibiaInlet channel
The invention discloses a minimally invasive collective integral acupotomy scope, which comprises a light microscope assembly of a scope-acupotomy integral body, a tube core assembly of the scope-acupotomy integral body and a hard sleeve assembly of the scope-acupotomy integral body. The light microscope assembly of the scope-acupotomy integral body comprises a lens, a lens base and a light guide tube. The tube core assembly of the scope-acupotomy integral body comprises a knife tube core. The hard sleeve assembly of the scope-acupotomy integral body comprises a knife tube. The light guide tube is inserted in the knife tube core. The knife tube core is inserted in the knife tube. An operation method of the minimally invasive collective integral acupotomy scope disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: (1) holding the acupotomy scope, and inserting the acupotomy scope into a knee joint through front external approach; (2) opening a water inlet channel to full a joint cavity; and (3) sequentially searching suprapatellar bursa, patellofemoral joint, internal tibia clearance, fossa intercondyloidea, external tibia clearance, knee lateralis sulci, rear internal clearance and rear external clearance, wherein the scope surface angle of the whole acupotomy scope is correspondingly adjusted according to searched specific parts in the searching process.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INFUMEDI MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Intelligent knee joint training instrument
InactiveCN105796284AIncrease painStimulate natural resilienceChiropractic devicesReciprocating motionKnee Joint
The invention discloses an intelligent knee joint training instrument. The intelligent knee joint training instrument comprises a base, a leg bracket mechanism, a shank bracket mechanism, an adjustable grasping body, a horizontal adjusting support, a push frame, a reciprocating traction driving device and a traction controller; the horizontal adjusting support is arranged at the tail portion of the base, the side wall of the base is provided with a sliding groove, the leg bracket mechanism is connected with the push frame through the shank bracket mechanism, and the traction controller which extends into the base through the sliding groove and is connected with the reciprocating traction driving device is arranged at the lower end of the push frame. The intelligent knee joint training instrument is exquisite and reasonable in structural design, the leg is straightened by simulating natural motion of a human body, the knee patella is grasped through the grasping body to conduct up-and-down and right-and-left reciprocating motion to achieve massage recovery treatment on the knee patella, therefore, natural resilience of the human body is stimulated, patella extroversion is corrected, the mechanical environment of the patellofemoral joint is improved, quadriceps are strengthened, and the recovery effect is good.
Owner:DONGGUAN XUTE ROBOT CO LTD
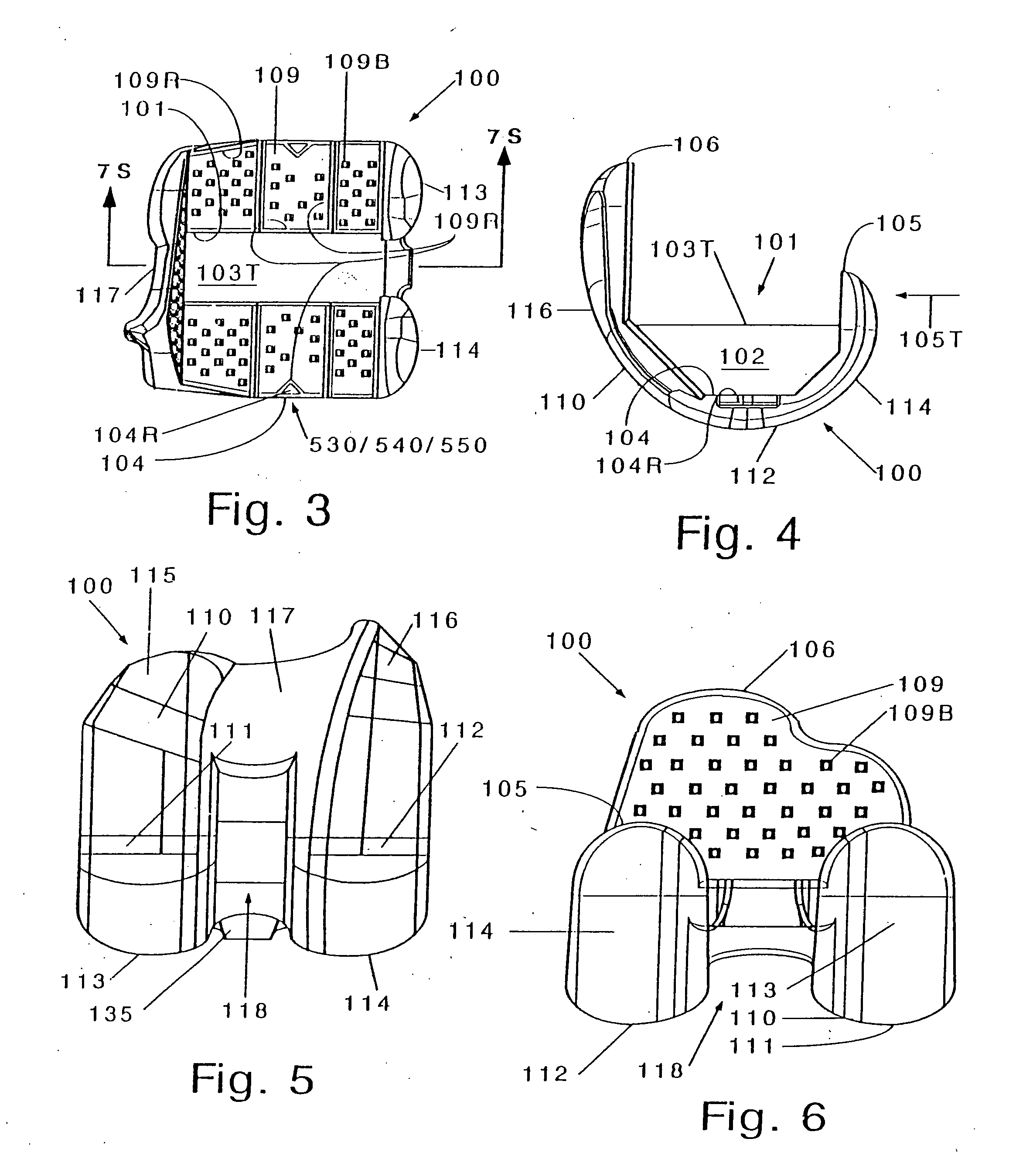
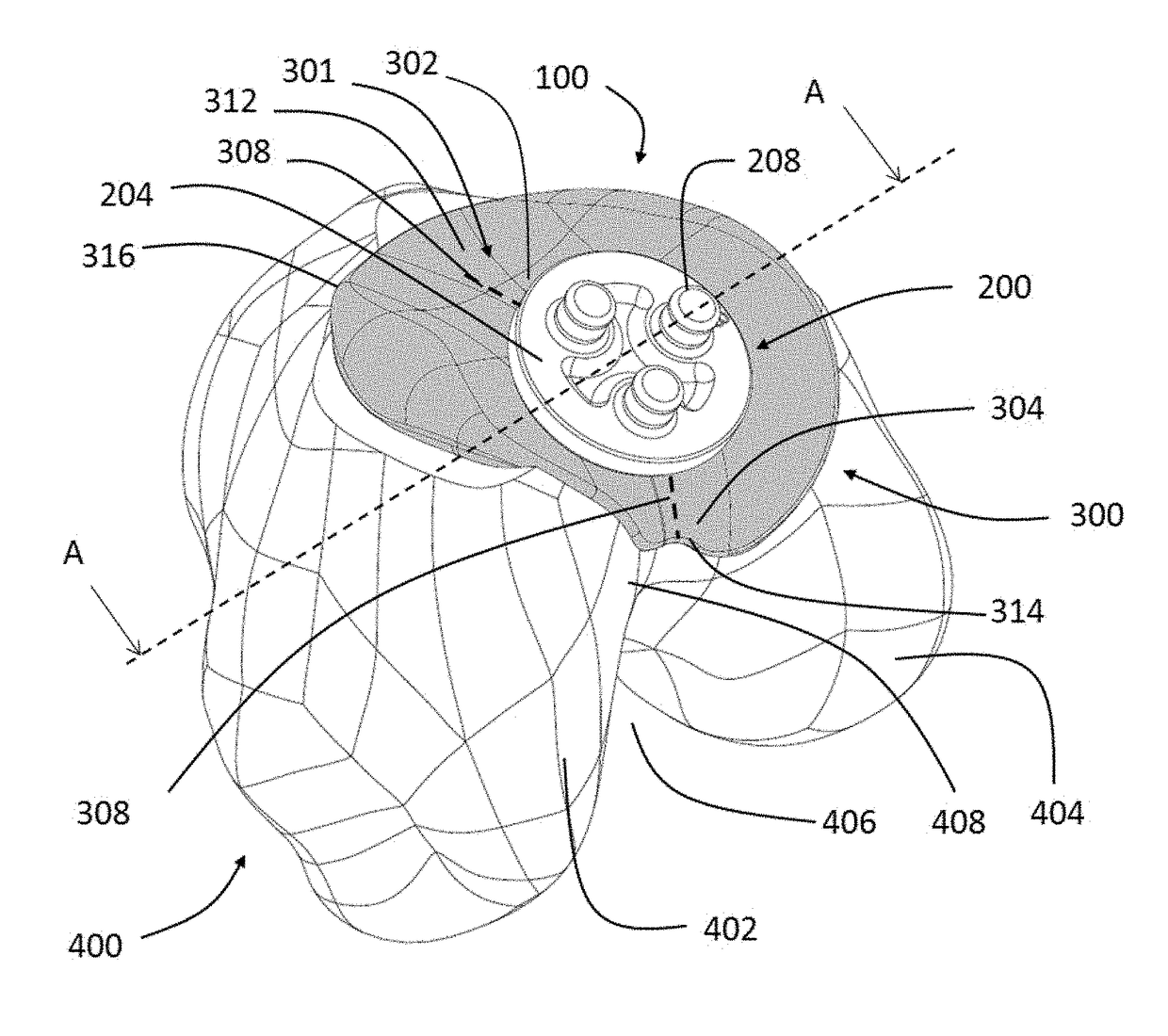
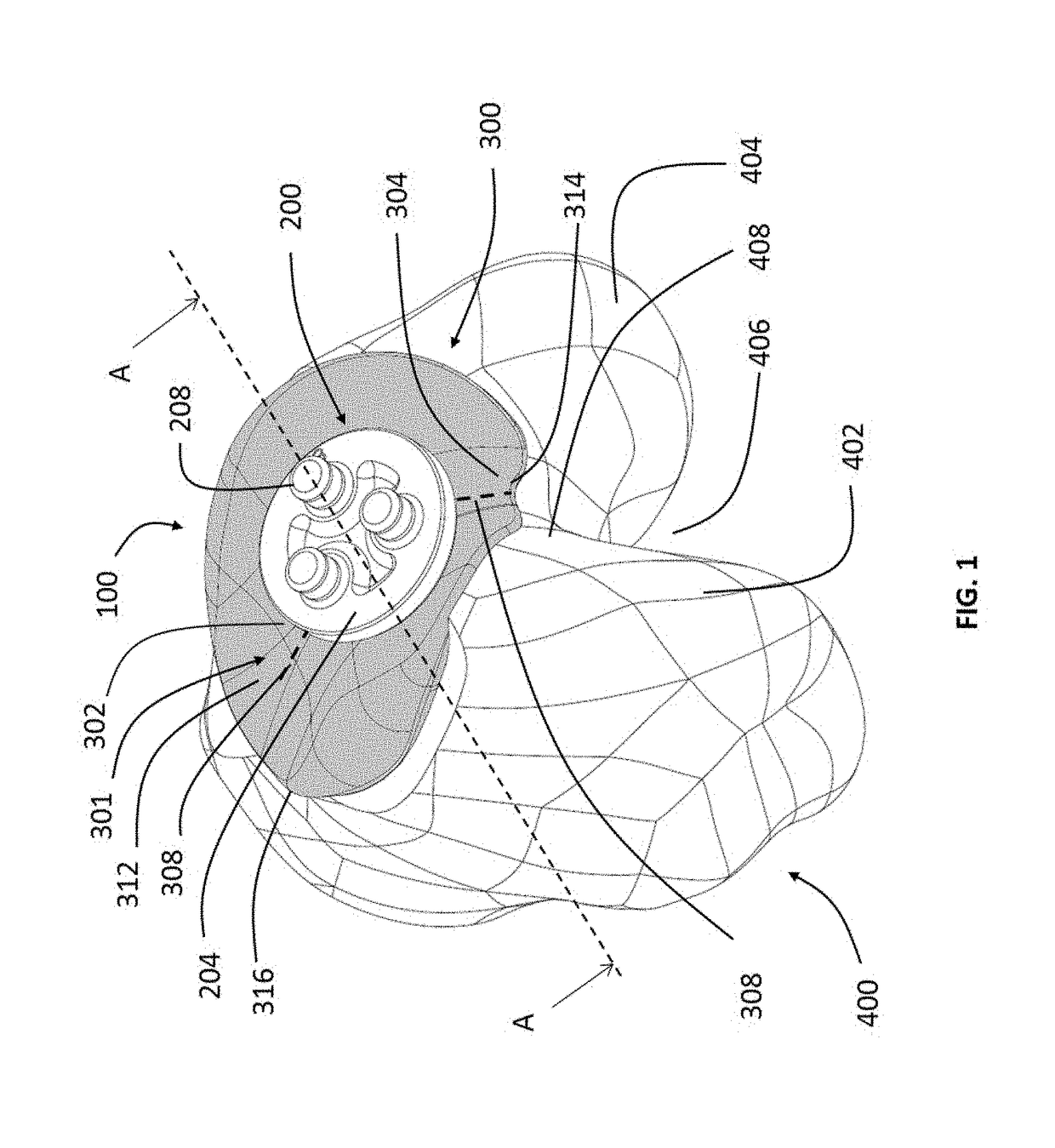
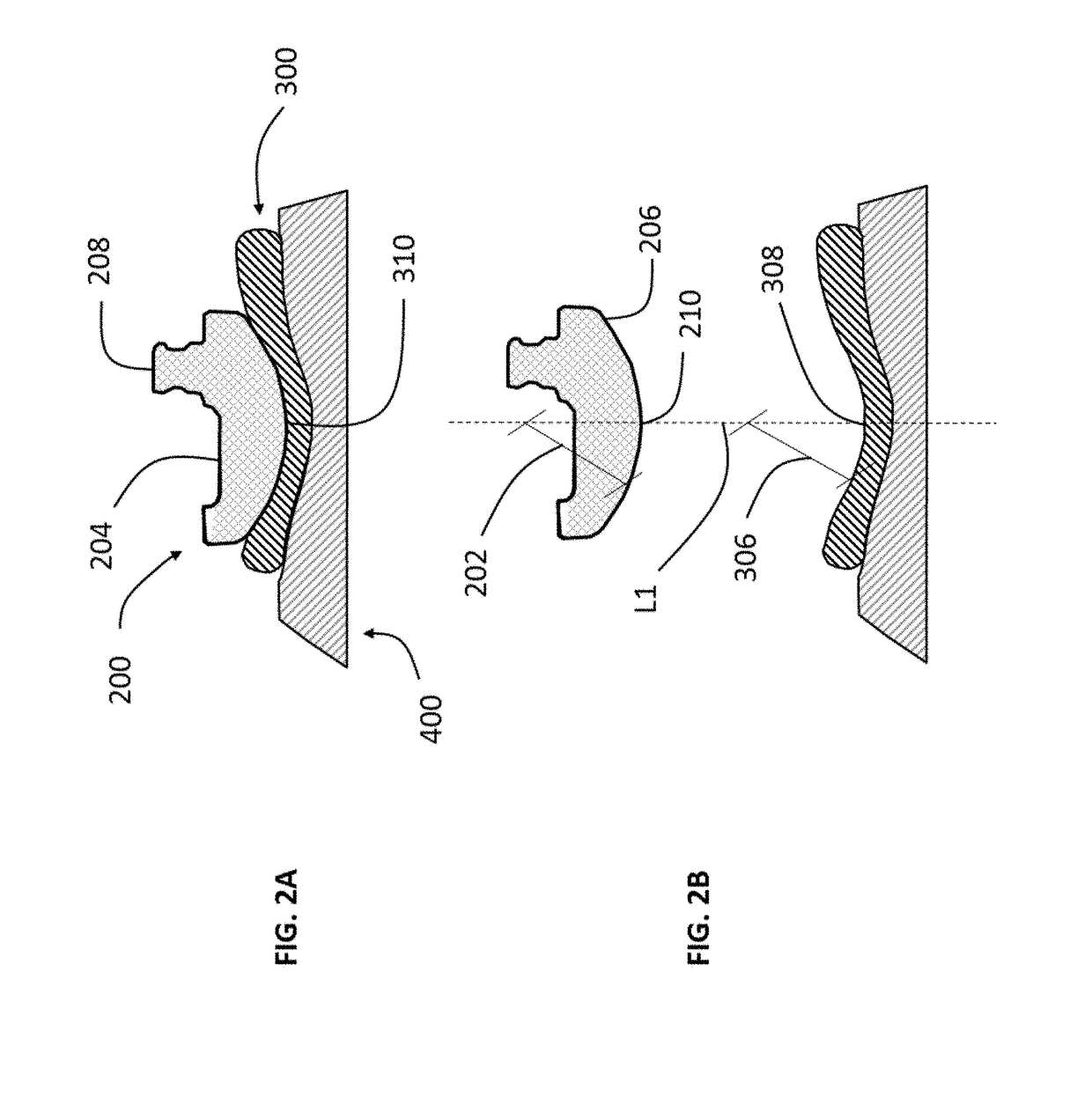
Extended patellofemoral
ActiveUS9655727B2Expand coverageLow variabilityJoint implantsKnee jointsArticular surfacesArticular surface
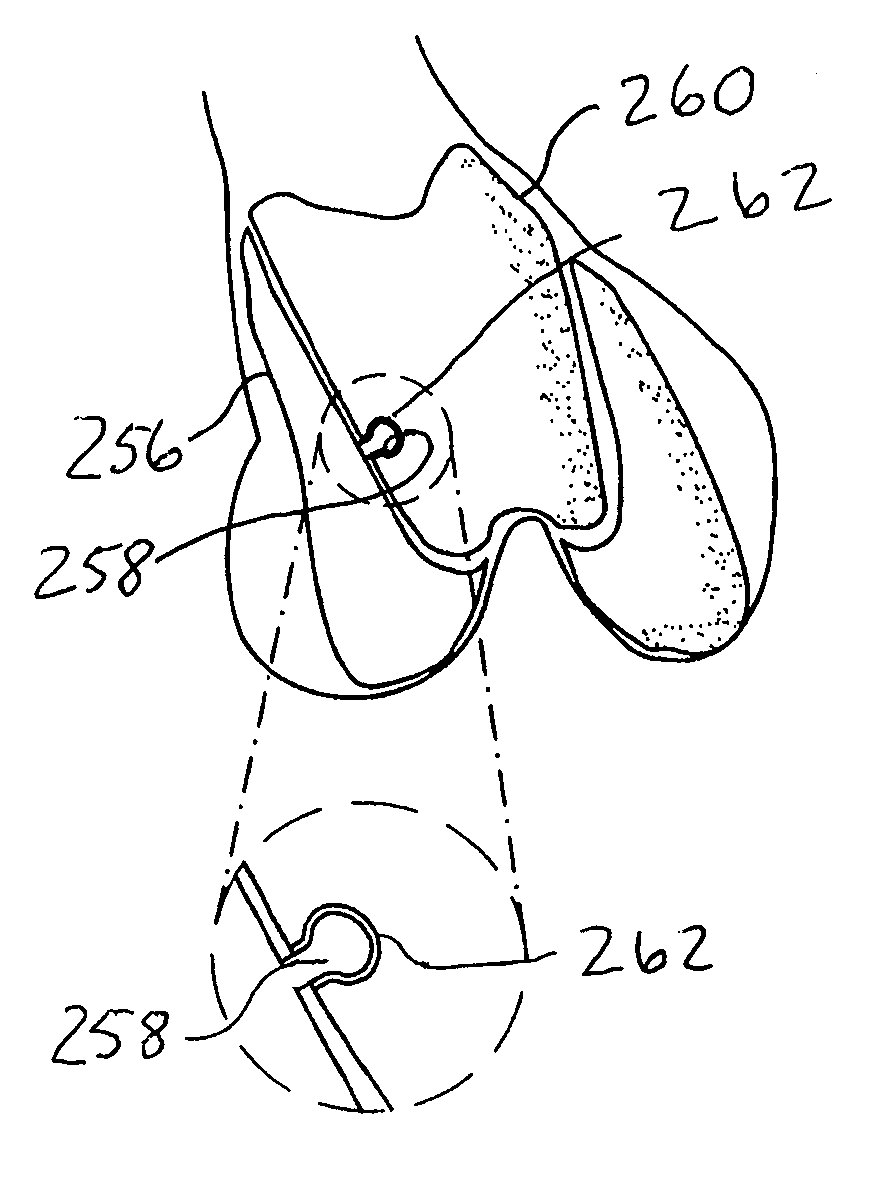
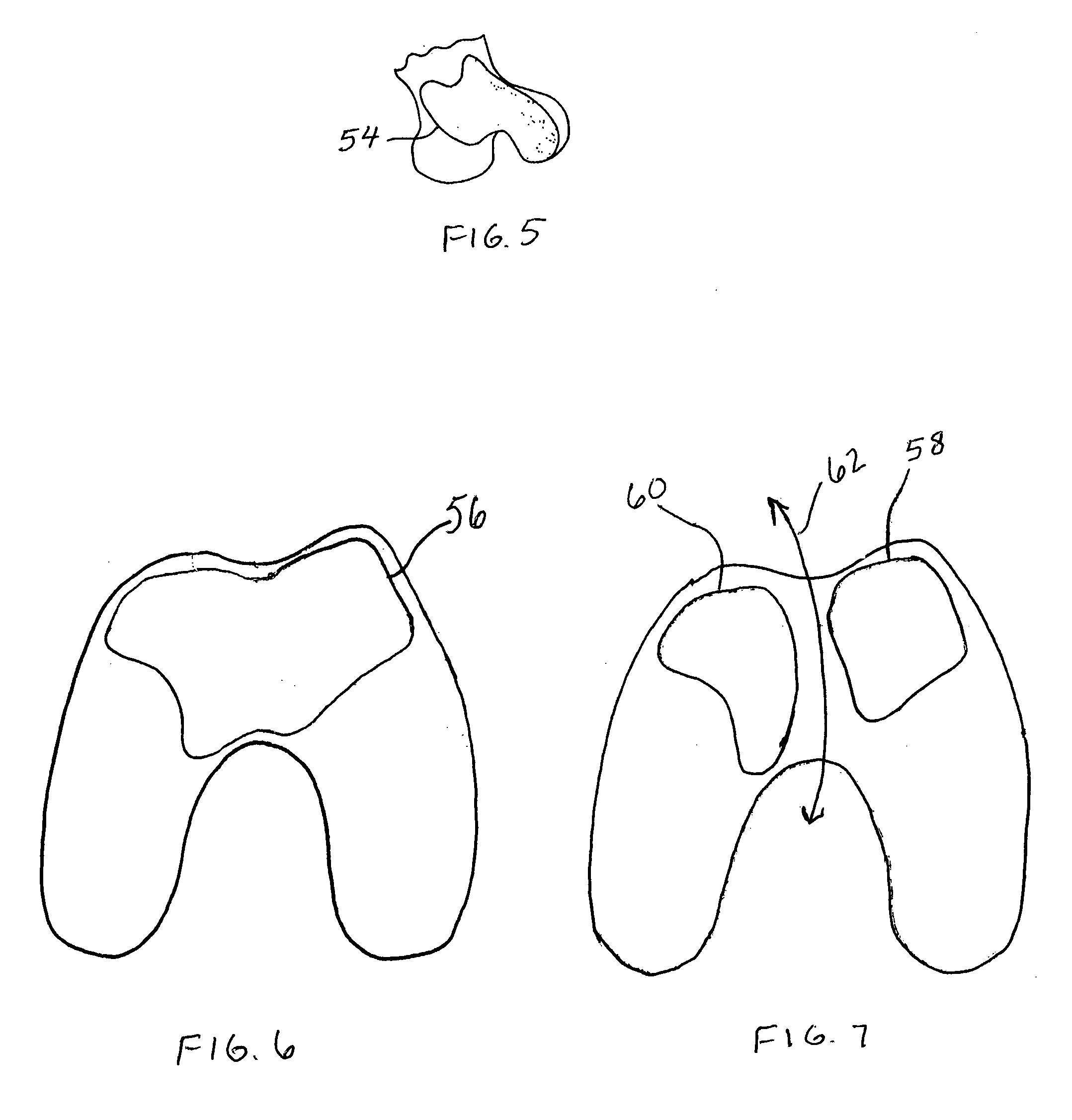
Disclosed herein are knee replacement systems for replacing the articular surface of a distal femur. The systems include one or more unicompartmental components, namely patellofemoral, lateral condylar and medial condylar components. The components are configured such that when engaged to the femur the peripheries thereof do not cross specific locations and / or regions of the femur, namely the intercondylar notch and condylopatellar notch. The patellofemoral components described herein preferably have an extension portion extending posteriorly from a posterior periphery thereof towards an intercondylar notch or the femur without contacting the intercondylar notch of the femur when the patellofemoral component is engaged to the femur. The extension portion preferably extends posteriorly from a posterior periphery of the patellofemoral component towards the condylopatellar notch of the femur without contacting the notch.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Patello-femoral milling system
An orthopedic system prepares a surface of an anatomical structure to receive an orthopedic prosthesis. A method for using the same is also disclosed. The orthopedic system includes a surgical instrument and a guide. The guide includes an anterior portion and a distal portion that is at least partially elevated relative to the anterior portion. The distal portion includes at least one track that is sized to receive the surgical instrument while preparing the surface of the anatomical structure.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Optimizing patellar femoral mechanics through alternative depth referencing
In knee-replacement surgery, restoration is achieved with respect to the patellar femoral joint in the distal plane is, thereby optimizing patellar femoral mechanics. The depth of the trochlea is increased with increasing implant size. In the preferred embodiment, this is achieved by referencing the extent of the lateral femoral condyle or trochlear region, and resecting the distal femur in accordance with the extent of the lateral femoral condyle or trochlear region. As an alternative, the invention provides for distal femoral and proximal tibial components having bone-contacting and articulating surfaces which account for the measured extent of the lateral femoral condyle or trochlear region. A method of preparing a distal femur according to the invention includes the steps of installing a rod or stem within the intramedullary canal, and attaching a referencing fixture thereto. The extent of the lateral femoral condyle or trochlear region is measured using the referencing fixture, and the distal femur is resected in accordance with the extent of the lateral femoral condyle or trochlear region. The method typically further includes the step of placing a spacer between the referencing fixture and the lateral femoral condyle or trochlear region. The preferred alternative embodiment of the invention involving the use of modified components proceeds similarly, except that after measuring the extent of the lateral femoral condyle or trochlear region using the referencing fixture, distal femoral and proximal tibial components are implanted having bone-contacting and articulating surfaces which take the measurement into account.
Owner:MASINI MICHAEL A
Extended patellofemoral
ActiveUS20150164647A1Expand coverageLess implant sizeJoint implantsKnee jointsArticular surfacesArticular surface
Disclosed herein are knee replacement systems for replacing the articular surface of a distal femur. The systems include one or more unicompartmental components, namely patellofemoral, lateral condylar and medial condylar components. The components are configured such that when engaged to the femur the peripheries thereof do not cross specific locations and / or regions of the femur, namely the intercondylar notch and condylopatellar notch. The patellofemoral components described herein preferably have an extension portion extending posteriorly from a posterior periphery thereof towards an intercondylar notch or the femur without contacting the intercondylar notch of the femur when the patellofemoral component is engaged to the femur. The extension portion preferably extends posteriorly from posterior periphery of the patellofemoral component towards the condylopatellar notch of the femur without contacting the notch.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
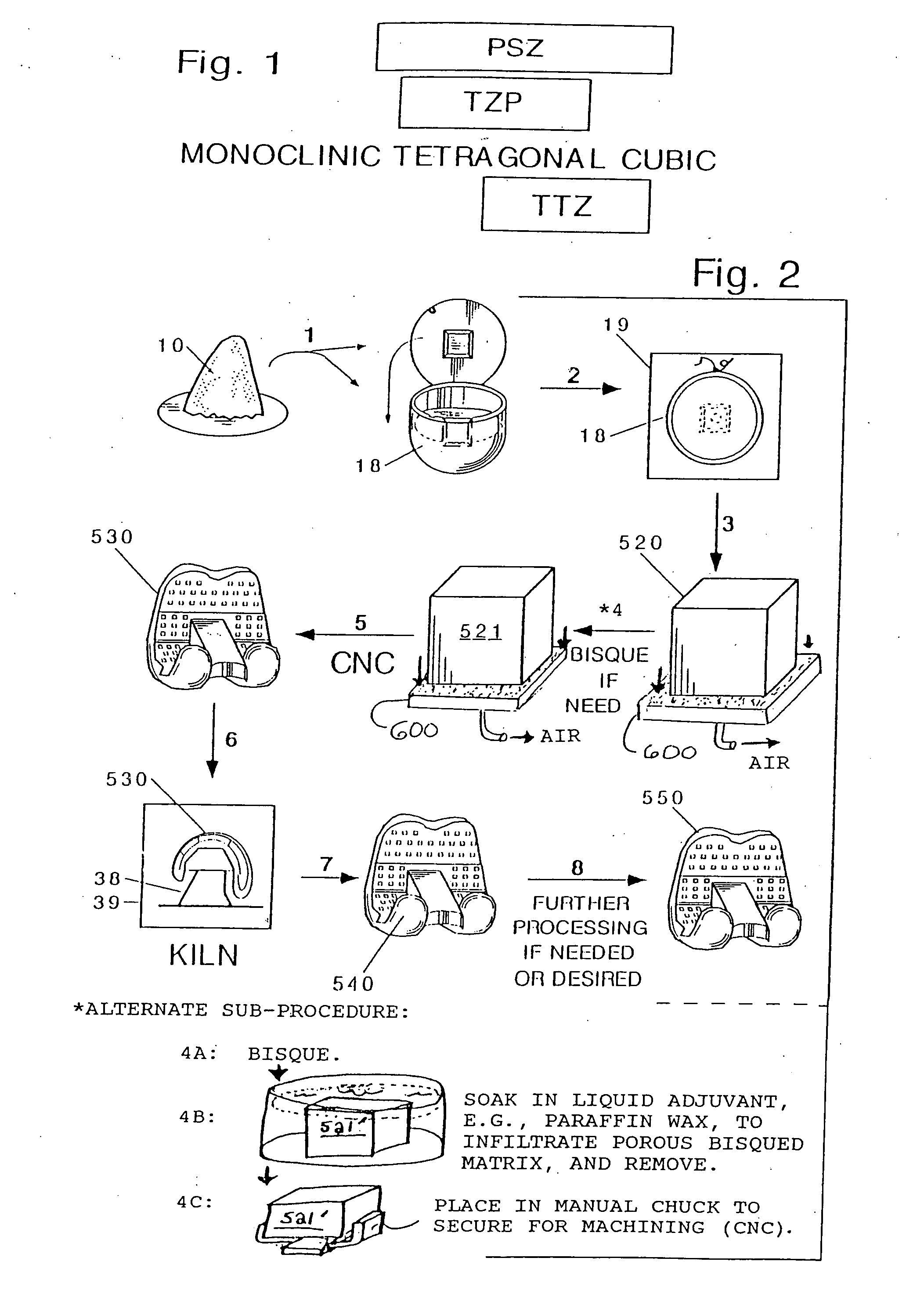
Ceramic manufactures
ActiveUS20120271429A1Avoid disadvantagesHigh strengthAnkle jointsJoint implantsTibiaUnicompartmental knee
Fired magnesium oxide stabilized transformation toughened zirconia ceramic can be for or of an implant or implant component of a one-piece unicompartmental knee spacer device; a multi-piece unicompartmental joint aligning device; a temporal mandibular joint cap implant; a vertebra cap; an ankle joint ensemble or component; a bridge, a tooth or teeth; a patellofemoral joint implant; a tibial tray for a knee joint replacement implant; an intermediary articulation plate for a tibial tray and liner for a knee joint replacement implant; or the intermediary articulation plate assembled in combination with the tibial tray.
Owner:CERAMIC MEDICAL PROD LLC +1
Patellofemoral implant
A femoral implant for articulation with a patella or a patellar implant includes a body having an articular surface defining a trochlear groove. The trochlear groove is defined by a first trochlear radius at a first location along the trochlear groove and by a second trochlear radius at a second location along the trochlear groove, the first radius being different than the second radius. The configuration of the trochlear groove is such that it narrows as a patella or patellar implant moves from an extension configuration to a flexion configuration. A kit includes the femoral implant along with a patellar implant. A method of trialing involves use of the femoral implant or kit to ensure a smooth transition of the patella or the patellar implant from the femoral component to the adjacent bone.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
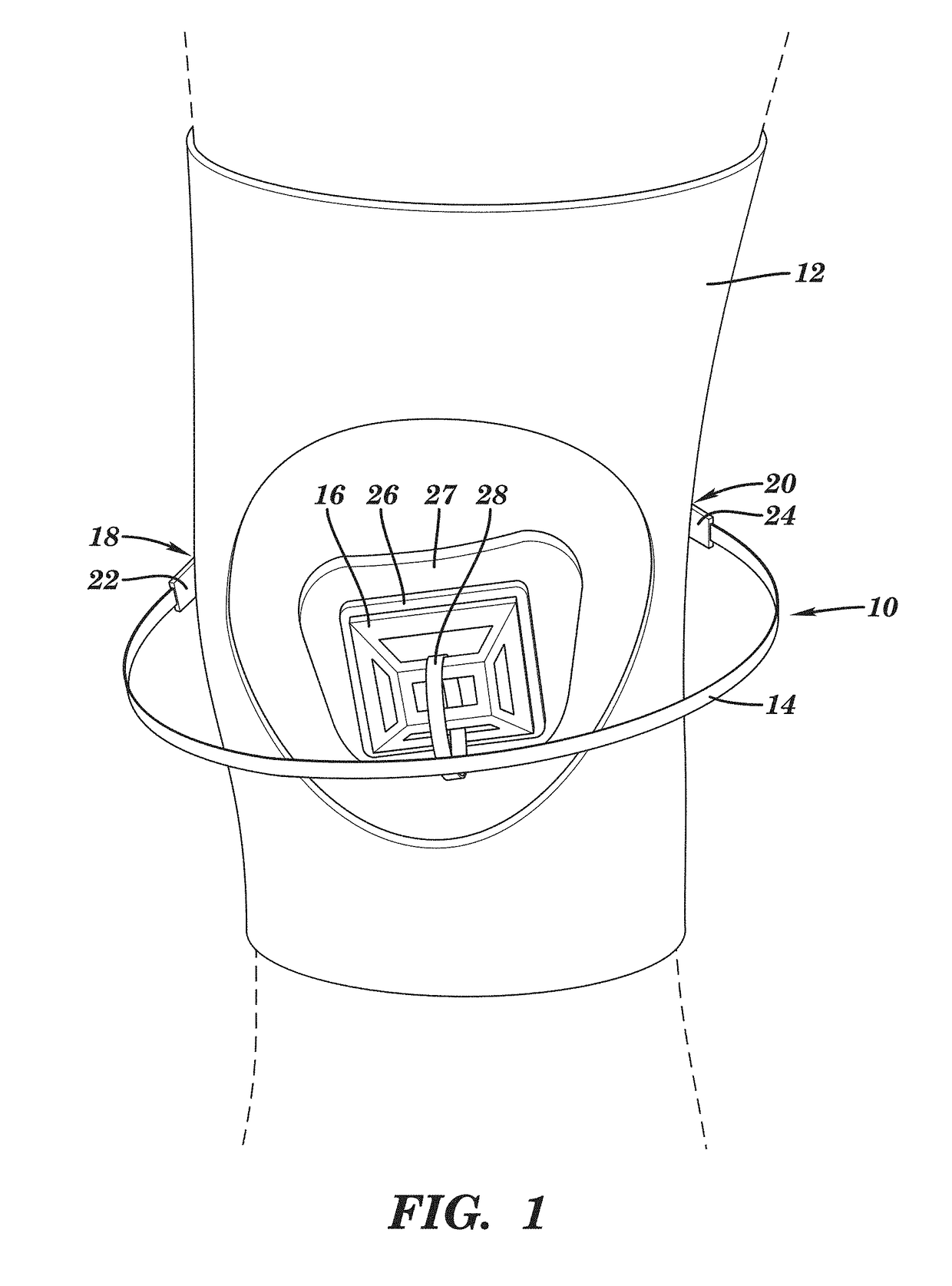
Device for managing patellofemoral pain and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20190000660A1Relieve painLoss can be compensatedNon-surgical orthopedic devicesPatellofemoral painKnee Joint
A device for managing patellofemoral pain includes a wearable anchor structure configured to be positioned adjacent to the knee joint of a user. A spring mechanism is attachable, during use, to the anchor structure at first and second attachment positions located laterally and medially of the knee joint, respectively. An attachment component is coupled to the spring mechanism and has an attachment surface configured to be removably attached, during use, to the skin over the patella of the user such that the spring mechanism applies a tension force on the attachment component in an anterior direction. Methods for managing patellofemoral pain and realigning the patella and a patellofemoral pain management kit are also disclosed.
Owner:K NEESIO LLC
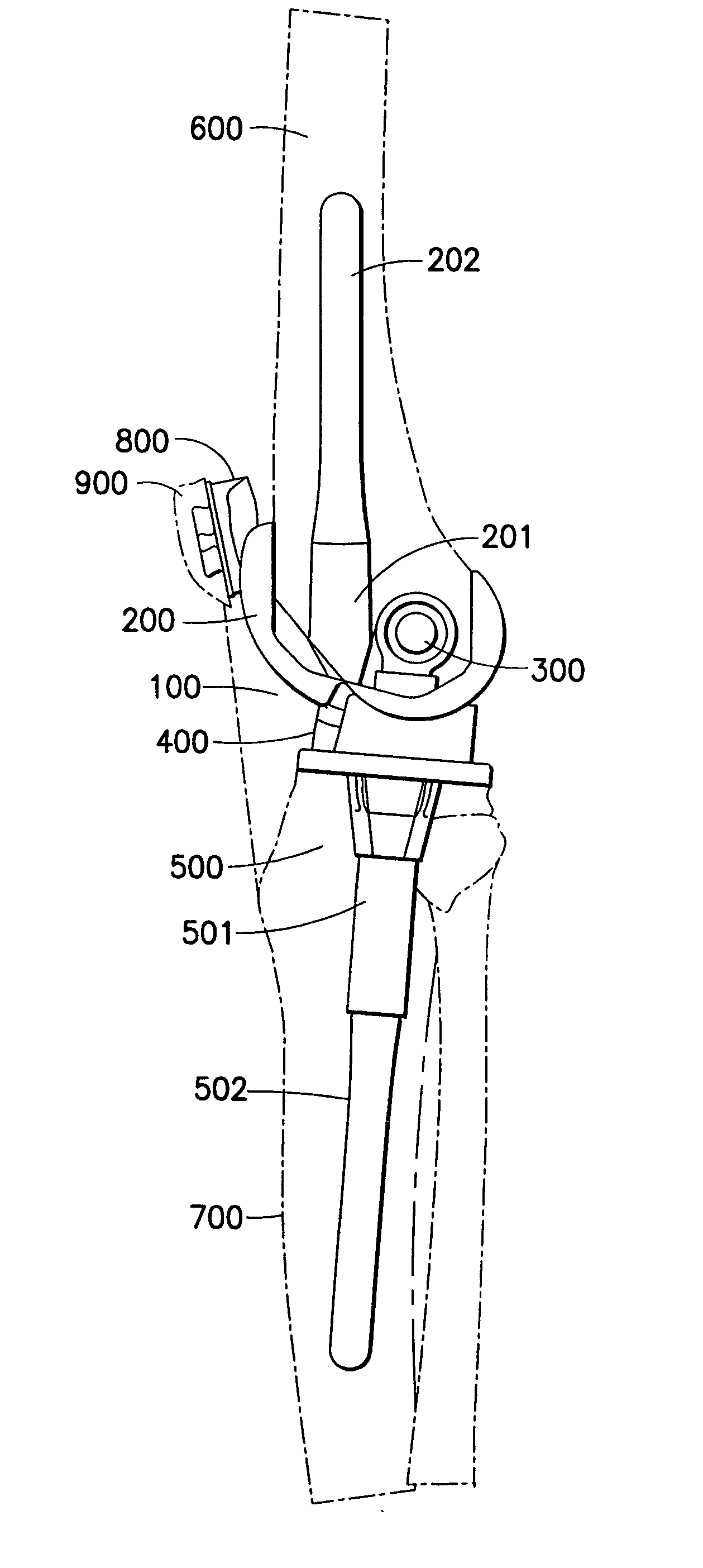
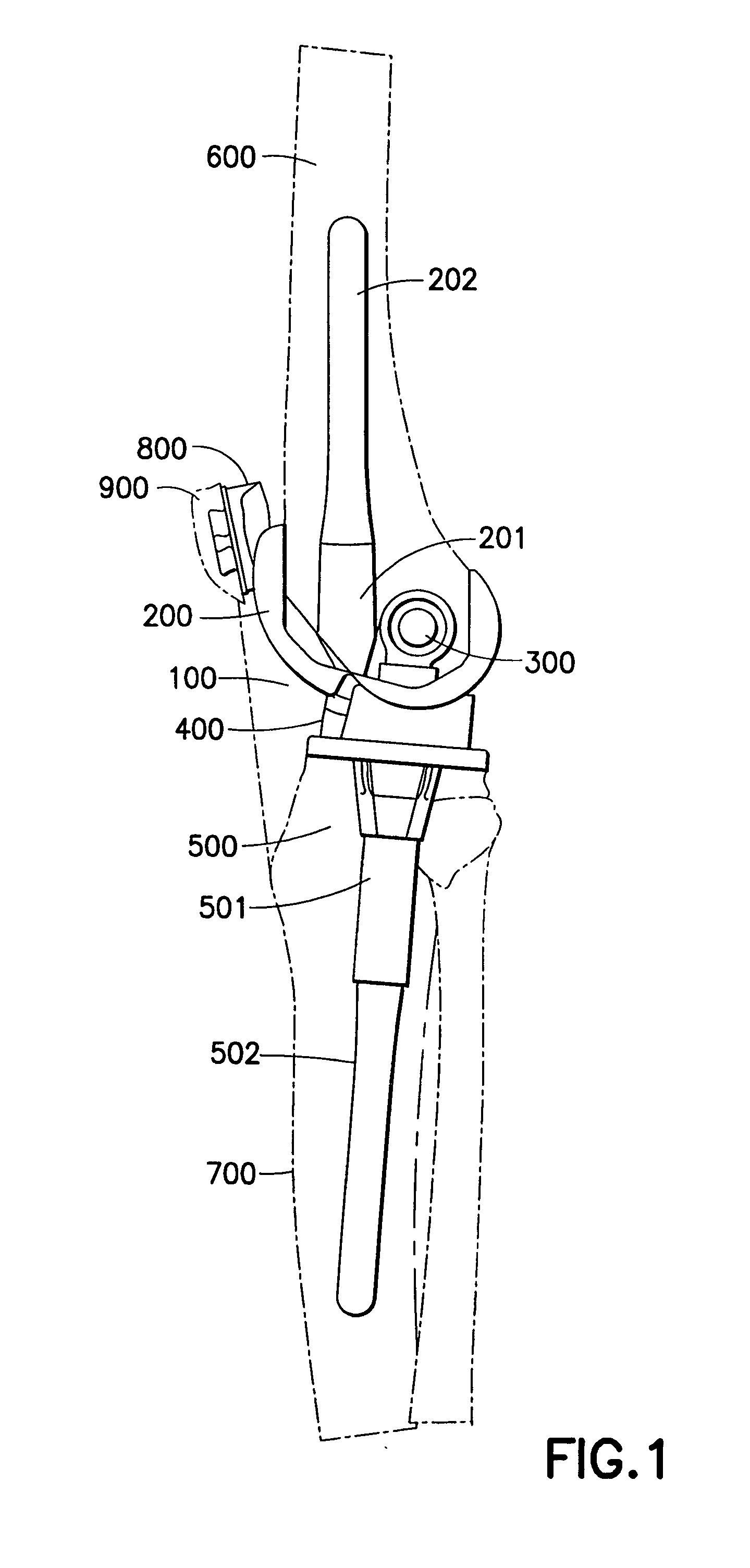
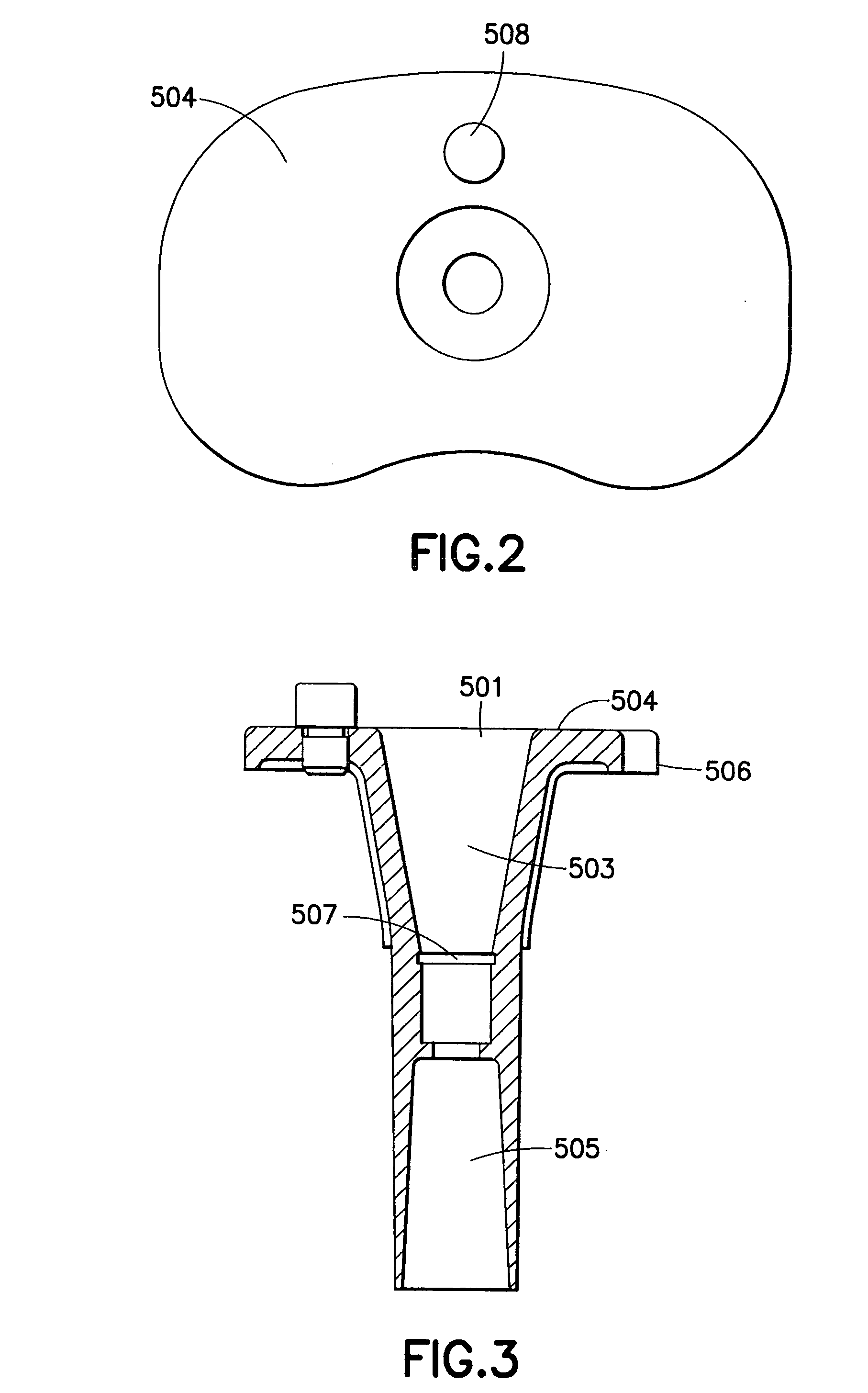
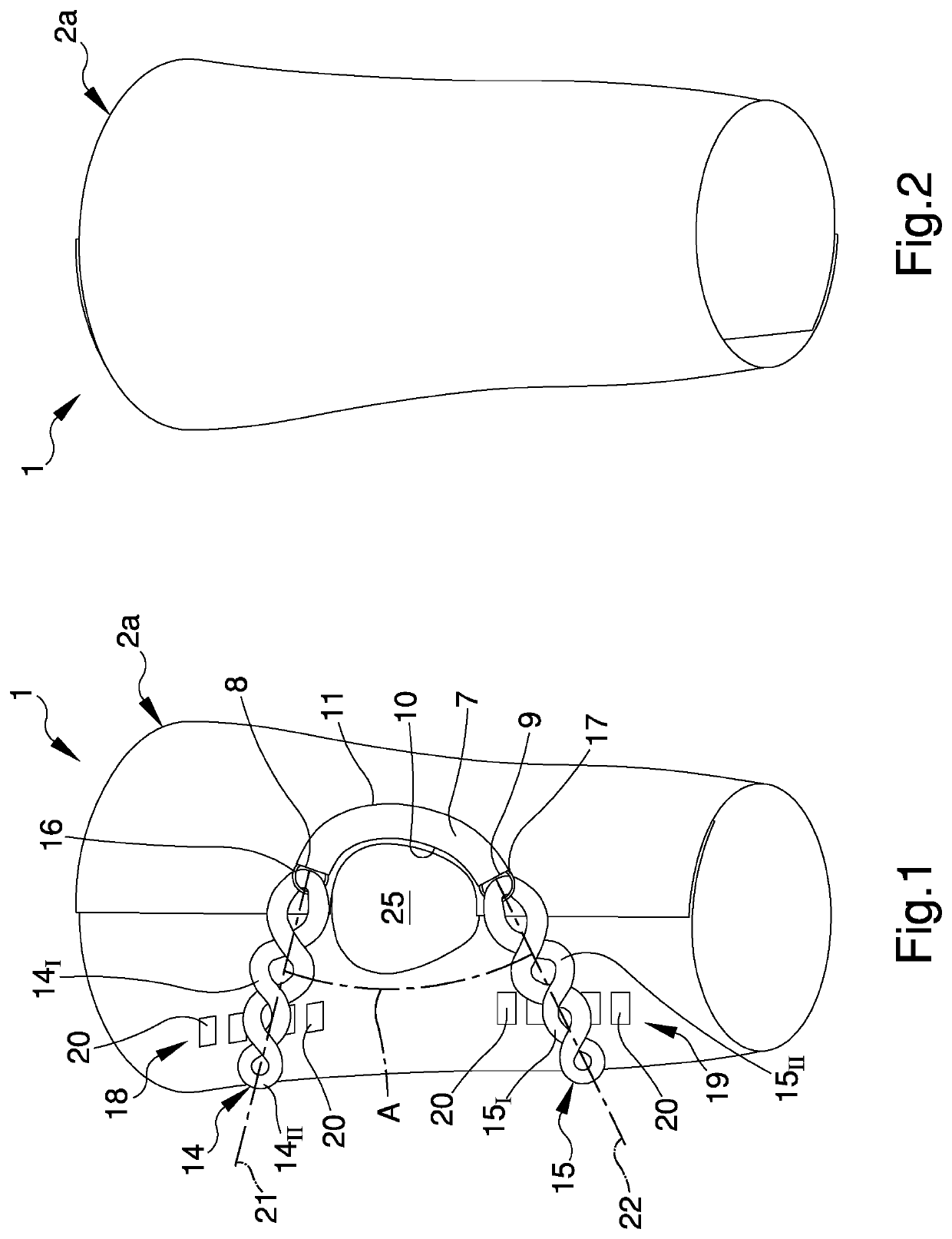
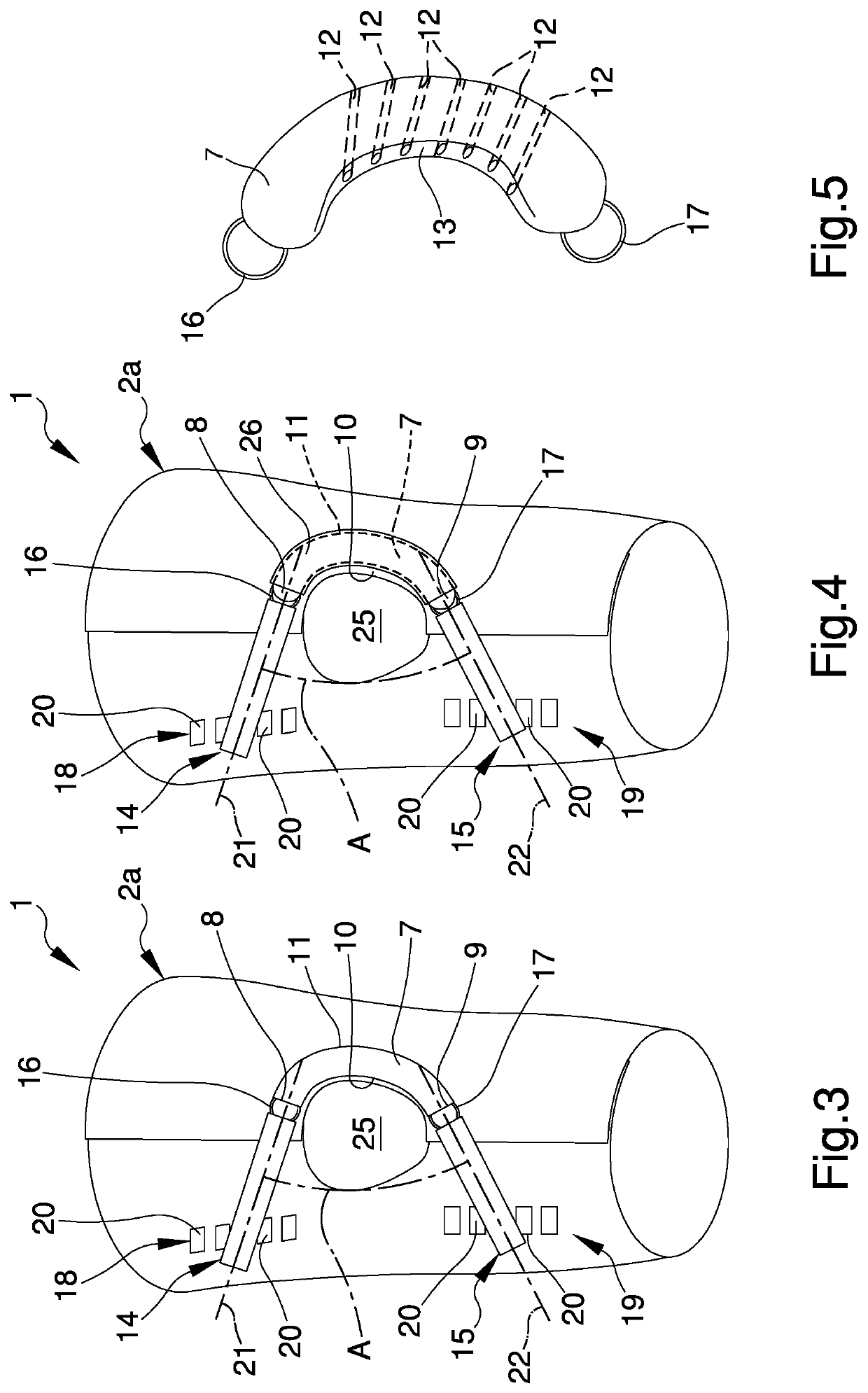
Joint stabilization device, particularly for the patellofemoral joint
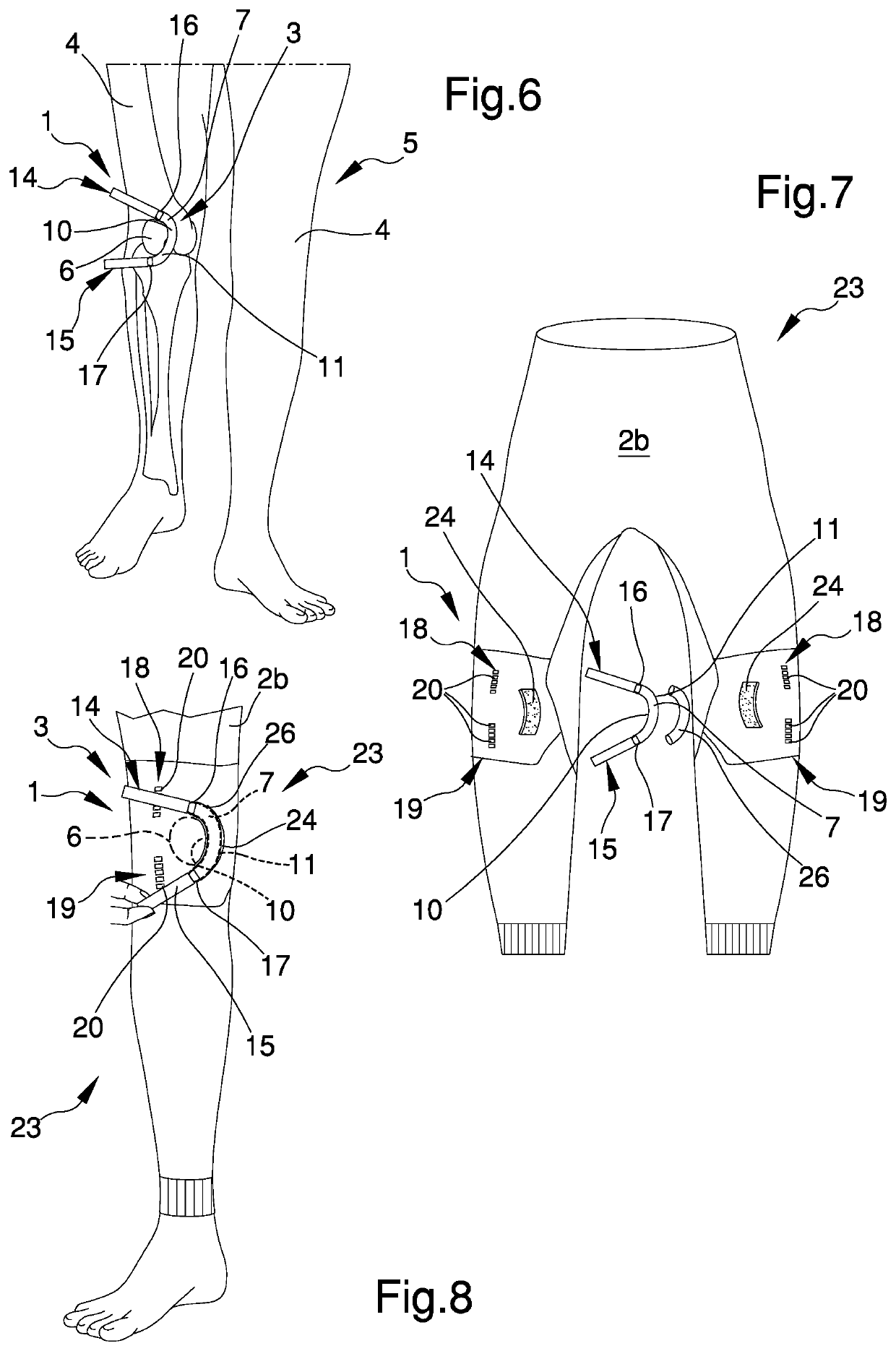
PendingUS20210128337A1Reduce recoveryShorten the timeGarment special featuresTrousersPhysical medicine and rehabilitationEngineering
Owner:OSTI LEONARDO +1
Knee joint correction auxiliary device
The invention discloses a knee joint correction auxiliary device which comprises a bandage capable of covering the knee joint and a pressurizing bag for providing pressure for the knee joint. A positioning hole capable of exposing the patella of the knee joint is formed in the center of the bandage, and connecting bands used for fixing the bandage are connected to the two sides of the bandage; thepressurizing bag is connected to the outer surface of the bandage and filled with a filler. The knee joint flexion rehabilitation device has a good effect in rehabilitation treatment of knee joint flexion deformity; by using the device provided by the invention, the patellar femoral joint pressure in the treatment process can be effectively reduced; the pressing pain of the anterior knee area ofthe patient during pressurization is reduced; a patient can adjust the pressurization pressure by increasing or decreasing the number of the pressurization bags, the treatment effect and use comfort of the patient are guaranteed, additional injuries caused by too large pressure are avoided, the patient can recover as soon as possible, meanwhile, the device can guarantee the continuous pressurization correction effect, and secondary injuries such as pressure sores can be effectively avoided.
Owner:XIANGYA HOSPITAL CENT SOUTH UNIV
Minimally invasive collective integral acupotomy scope and operation method thereof
ActiveCN102429632BTraumaGood treatment effectSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisTibiaInlet channel
The invention discloses a minimally invasive collective integral acupotomy scope, which comprises a light microscope assembly of a scope-acupotomy integral body, a tube core assembly of the scope-acupotomy integral body and a hard sleeve assembly of the scope-acupotomy integral body. The light microscope assembly of the scope-acupotomy integral body comprises a lens, a lens base and a light guide tube. The tube core assembly of the scope-acupotomy integral body comprises a knife tube core. The hard sleeve assembly of the scope-acupotomy integral body comprises a knife tube. The light guide tube is inserted in the knife tube core. The knife tube core is inserted in the knife tube. An operation method of the minimally invasive collective integral acupotomy scope disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: (1) holding the acupotomy scope, and inserting the acupotomy scope into a knee joint through front external approach; (2) opening a water inlet channel to full a joint cavity; and (3) sequentially searching suprapatellar bursa, patellofemoral joint, internal tibia clearance, fossa intercondyloidea, external tibia clearance, knee lateralis sulci, rear internal clearance and rear external clearance, wherein the scope surface angle of the whole acupotomy scope is correspondingly adjusted according to searched specific parts in the searching process.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INFUMEDI MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Guide tool for resection of patellofemoral joint
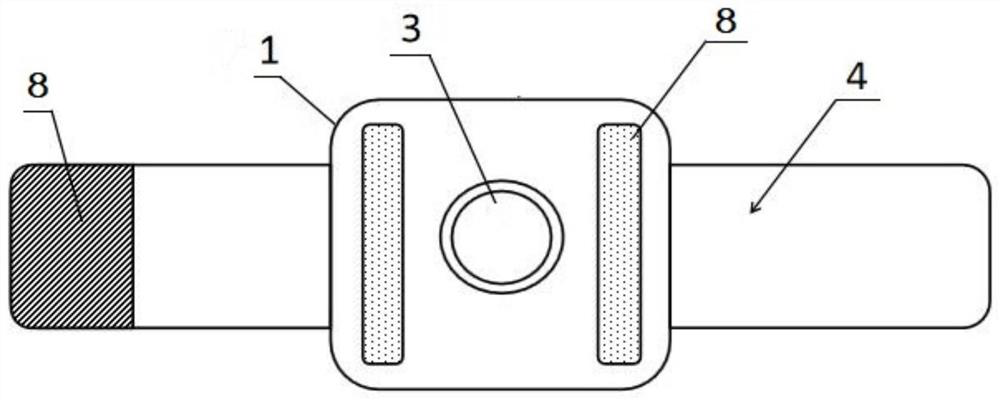
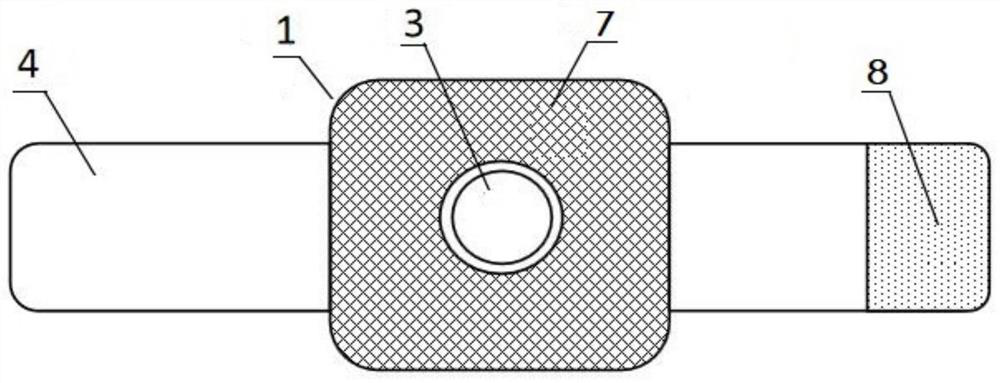
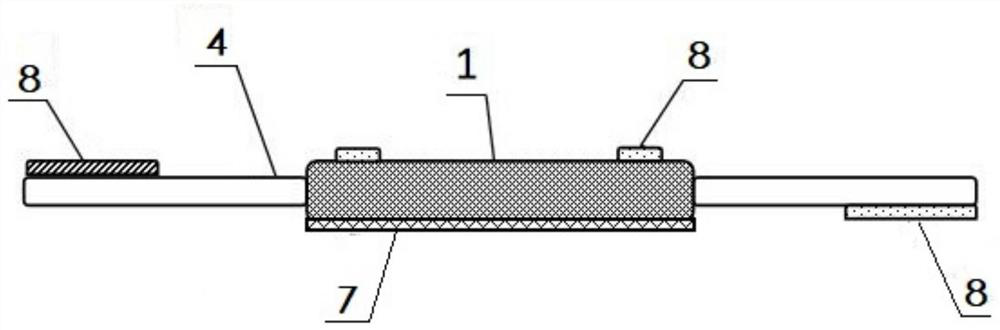
Owner:BIOMET UK HEALTHCARE
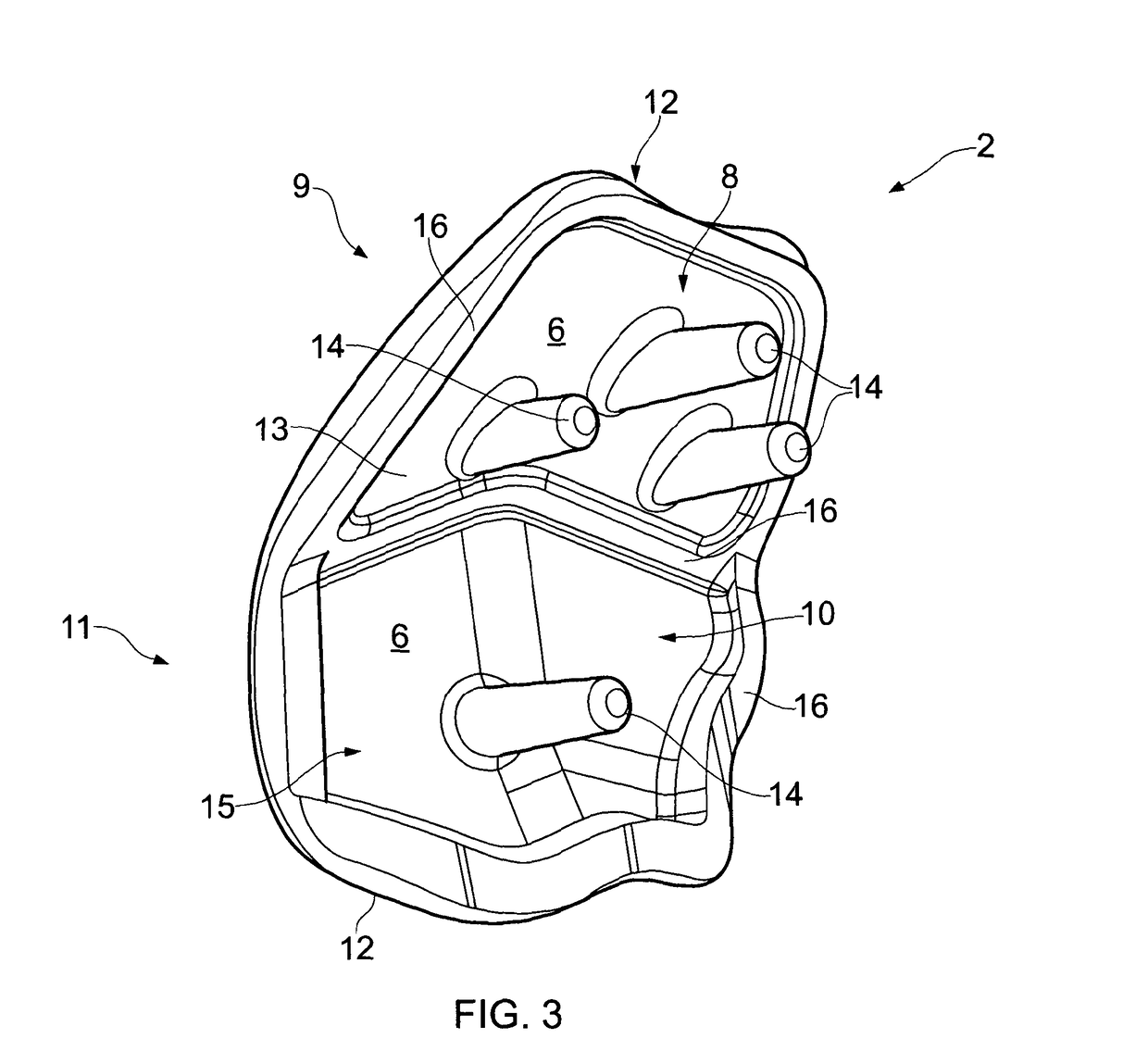
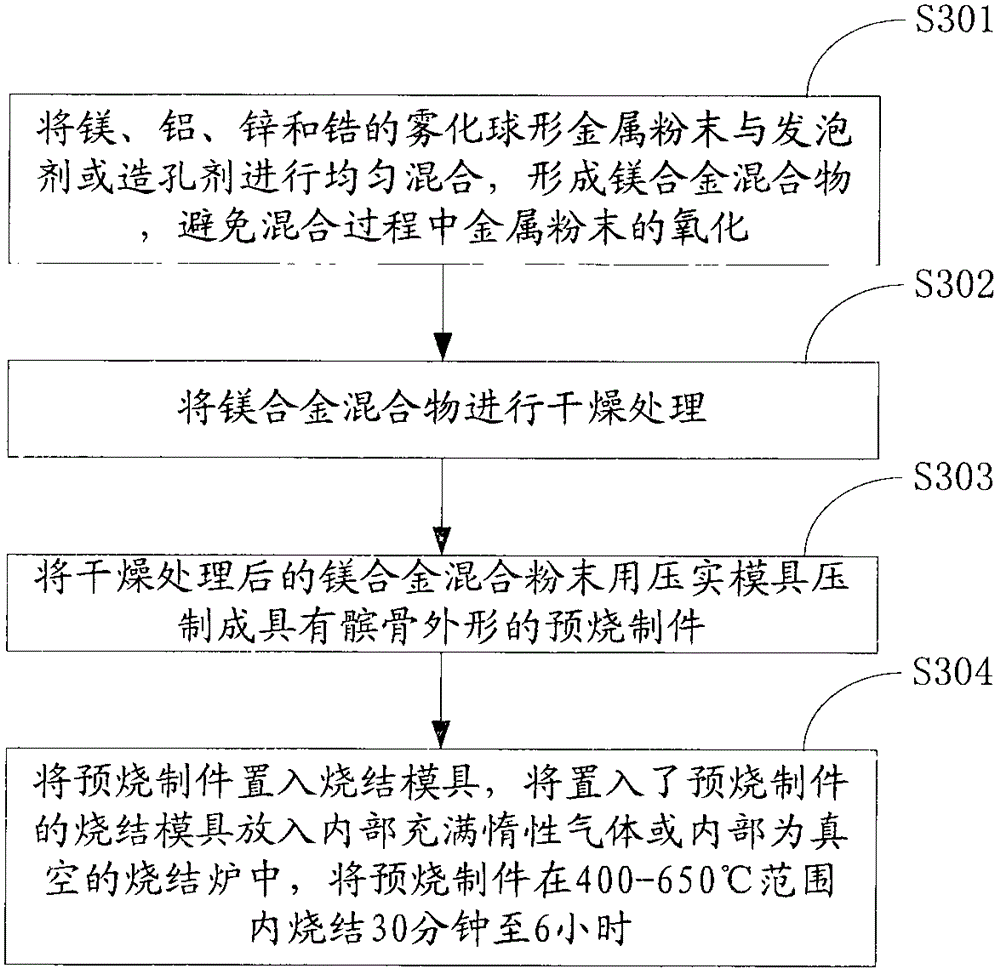
Patella tissue engineering scaffold and its manufacturing material and preparation method
A scaffold for patellar tissue engineering, wherein the scaffold is formed of magnesium, aluminum, zinc and zirconium, wherein the mass ratio of magnesium, aluminum, zinc and zirconium is: 85-95:0-6:0-4:0-4; The shape of the stent is consistent with that of the human patella, and the stent is formed by interweaving trabeculae, and a plurality of holes are formed between the trabeculae. The diameter of the holes is 0.1-0.8 mm, and the porosity of the holes is 30. ~80%. The above-mentioned support has the same shape as the human patella, and can be well matched with the patellofemoral articular surface of the human body or the artificial knee joint, which can reduce the wear of the patella tissue engineering support, thereby reducing the generation of wear debris, and the above-mentioned support The above-mentioned material is used, so the above-mentioned bracket can be degraded in the human body, and metal ions beneficial to the human body, such as magnesium ions, are produced after degradation. Therefore, the above-mentioned bracket does not produce wear debris that is harmful to the human body. In addition, a material for manufacturing the above bracket and a preparation method of the above bracket are also provided.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Method for predicting onset risk of patellar-femoral joint pain syndrome
The invention discloses a method for predicting the onset risk of patellar-femoral joint pain syndrome, and belongs to the technical field of disease prevention. The prediction is completed through acase control test. The method comprises the following steps: S1, incorporating 120 patients with patellar-femoral joint pain syndrome; S2, matching 120 healthy sports enthusiasts according to a ratioof 1: 1; S3, performing an isokinetic muscle strength test technology; S4, using a statistical method of conditional logistic regression to determine a strength index influencing the patellar-femoraljoint pain syndrome, and constructing a correlation equation; and S5, measuring knee extension, hip extension, hip flexion and hip adduction strength of susceptible people, substituting the strength into the correlation equation obtained in step S5, and calculating the onset risk of the patellar-femoral joint pain syndrome. According to the method for predicting the onset risk of the patellar-femoral joint pain syndrome, logistic regression capable of predicting the onset risk condition is used as the statistical method, the related equation is constructed, knee extension, hip extension, hip flexion and hip adduction force of susceptible people are measured and substituted into the equation, and the onset risk of the people can be calculated.
Owner:四川省骨科医院
Patella axis position movement track photographing device
The present invention relates to the technical field of medical equipment, in particular to a patella axial motion locus photographing device, comprising a photographing table, characterized in that a photographing device is provided at the front end of the photographing table, which includes a driving cylinder, a hinge shaft, a bearing , bearing seat, turn frame, elastic clamping plate and X-ray box fixing device, said X-ray box fixing device is made up of front splint, rear splint, extension spring, tension spring and elastic clamping plate, and said turn frame is composed of The front strut, the rear strut, the left side plate and the right side plate are connected and fixed to form a square cylinder. The invention makes the arrangement of the patella dynamic on the static X-ray film, and displays the patellofemoral joint under different flexion angles of the knee joint. Joint correspondence relationship undoubtedly provides a sensitive and accurate examination method for patellofemoral instability diagnosis. The differential aspect plays a unique role and helps plan the selection of appropriate reconstructive surgery.
Owner:侯红军
An energy-saving bionic tension-compression body patellofemoral joint for bipedal walking robot
ActiveCN113021405BImprove stabilityIncrease the leverage armJointsVehiclesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationKnee Joint
An energy-saving bionic tension-compression patellofemoral joint for a bipedal walking robot belongs to the technical field of mechanical bionic engineering. The invention consists of a bionic double ball component of a compression body, a bionic sliding lever component and a ligament assembly of a tension body. The invented energy-saving bionic tension-compression body knee joint utilizes a special joint geometry structure, introduces bionic slider components to reduce energy consumption, and is guided and restricted by bionic ligaments. Excessive joint movement; the invention is suitable for biped walking robots and can achieve low energy consumption , high stability, high flexibility and natural anthropomorphic gait.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
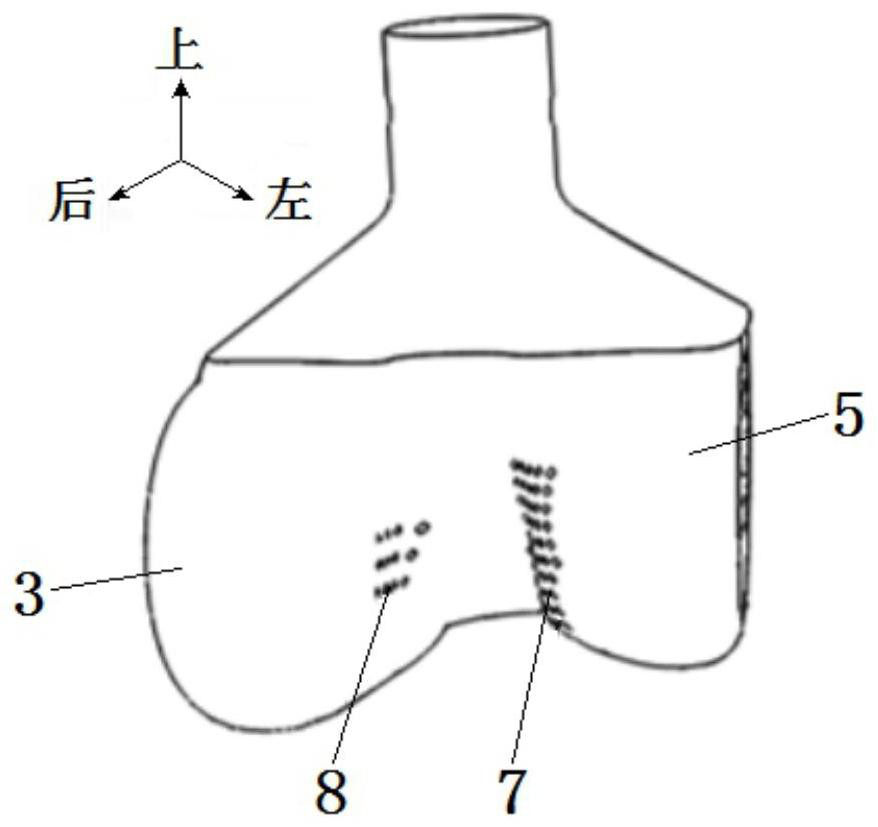
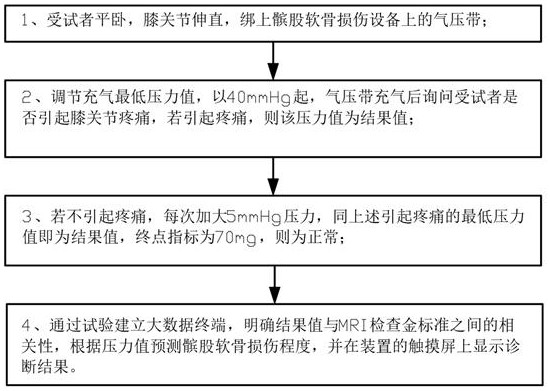
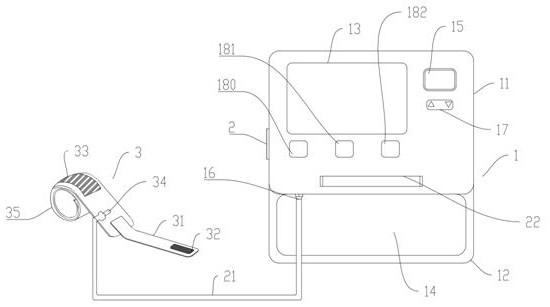
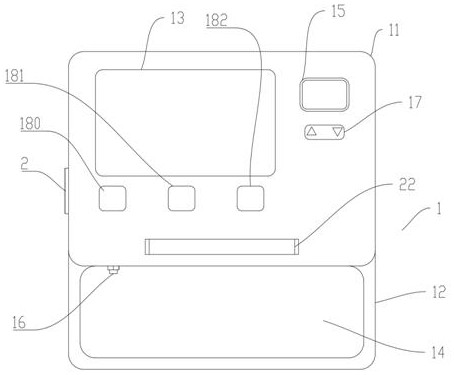
Pressure device for detecting patellofemoral cartilage injury and quantitative evaluation method
PendingCN113143219ALow costAccurate assessmentDiagnostics using pressureSensorsMedical equipmentCartilage lesion
The invention relates to the technical field of medical equipment, in particular to a pressure device for detecting patellofemoral cartilage injury and a quantitative evaluation method. The device comprises a case part and a pressure belt, the case part is composed of a lower case box and an upper sliding cover display interface, and a touch screen is arranged on the sliding cover display interface; a display screen is arranged on the right side of the touch screen, a pressure adjusting button is arranged below the display screen, three buttons are arranged below the touch screen and are an equipment starting button, an inflation starting button and a deflation button in sequence from left to right, a handle is arranged at the sideline of a display interface of the sliding cover, an air pressure belt storage groove is formed in the case box, an air pressure outlet is formed in the inner wall of the air pressure belt containing groove and connected with a pressure belt through a guide pipe. The patellofemoral articular cartilage injury is quantitatively evaluated through the minimum pressure value of patellofemoral joint pain, and the non-invasive, convenient and accurate patellofemoral articular cartilage injury evaluation method is constructed.
Owner:昆山市第一人民医院
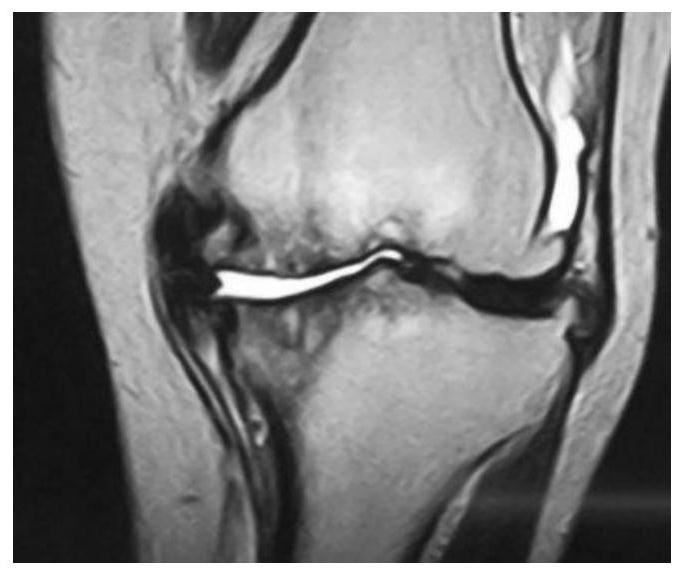
MRI classification image processing system and method for knee osteoarthritis, and terminal
PendingCN112635027ASatisfactory clinical effectImage enhancementImage analysisSubchondral boneCartilage injury
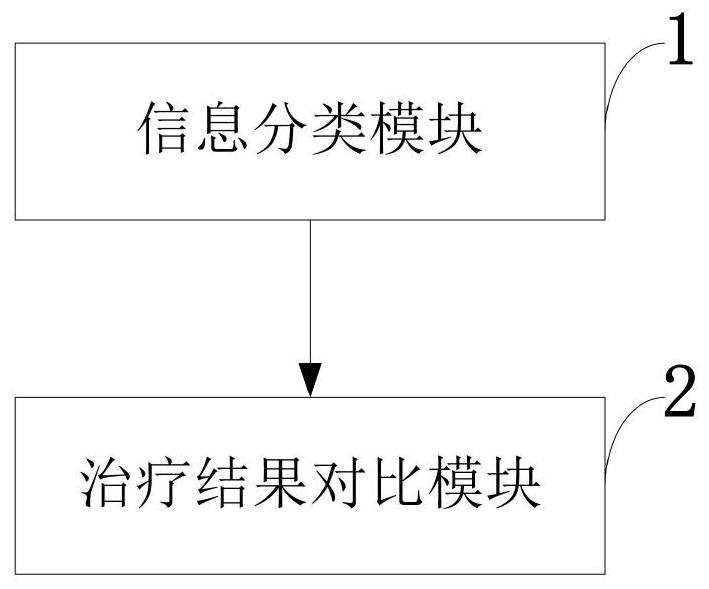
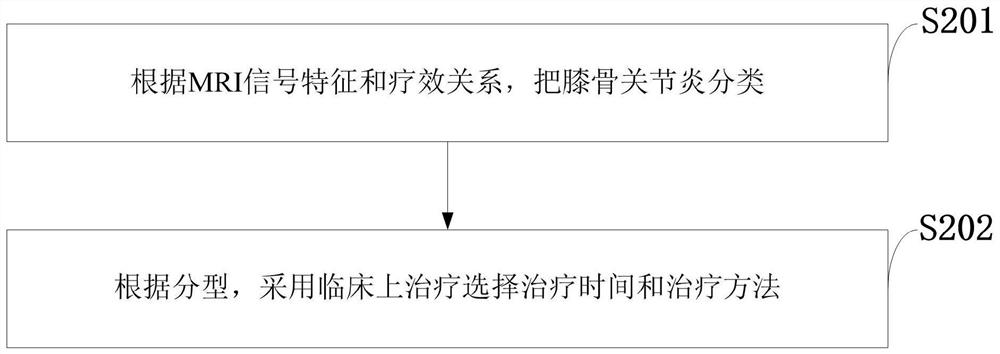
The invention belongs to the technical field of image processing, and discloses an MRI classification image processing system and method for knee osteoarthritis, and a terminal. The method comprises the following steps: classifying knee osteoarthritis according to the relation between MRI signal features and a treatment method; according to typing, clinically selecting the treatment time and treatment method, wherein the knee osteoarthritis is classified into a compartment cartilage injury type, a wide cartilage injury type, a subchondral bone type, a dislocation type, an osteoarthritis acute attack type, a patellar-femoral joint type, an inflammation type and a mixed type. The system comprises an information classification module used for classifying knee osteoarthritis according to MRI signal characteristics and a curative effect relationship; and a treatment result comparison module, which is used for selecting treatment time and a treatment method by adopting clinical treatment according to the typing, classifying the gonitis into eight types according to the MRI image characteristics and the clinical treatment effect, and obtaining a satisfactory clinical effect for the patient according to the classification.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com