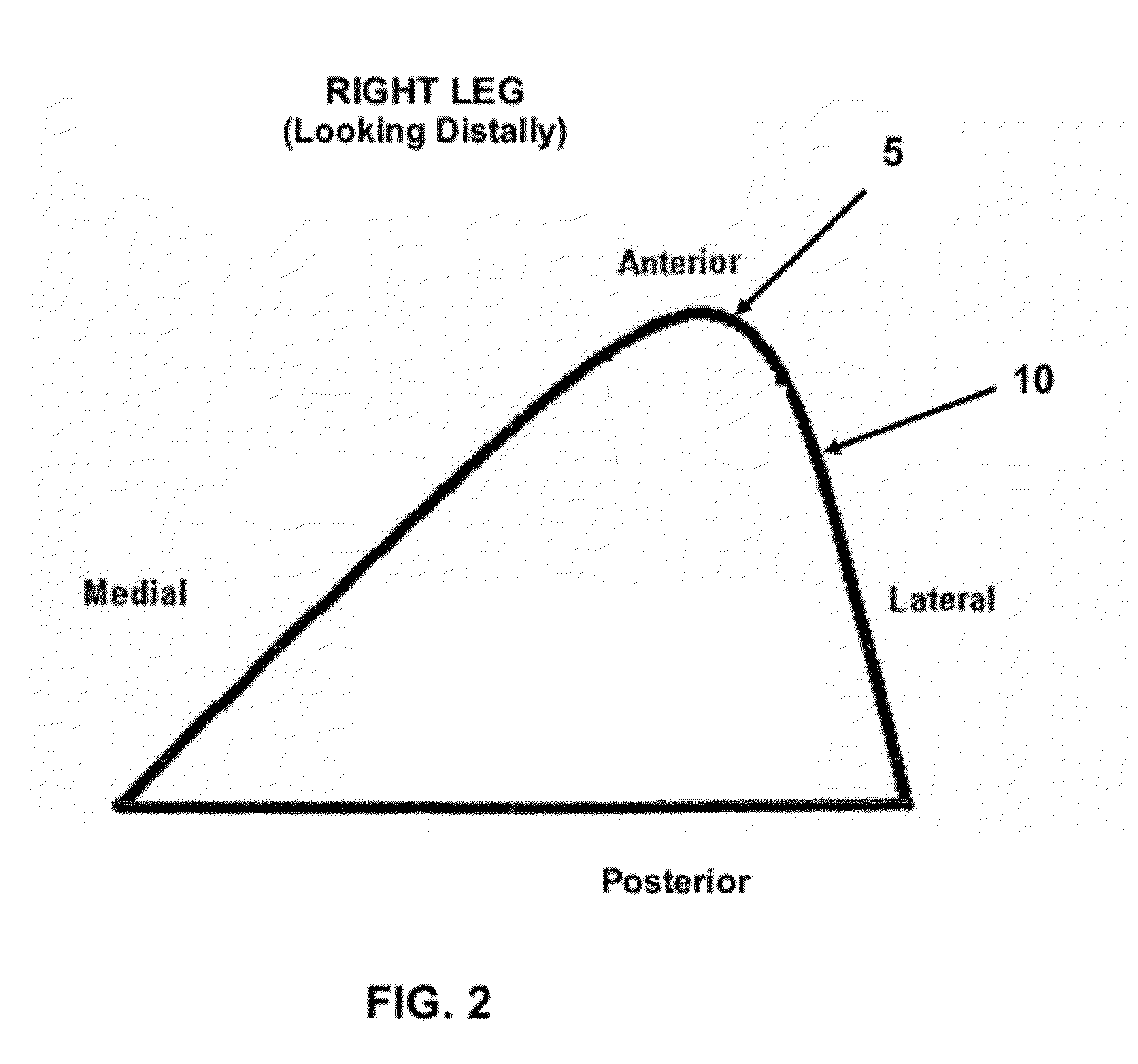
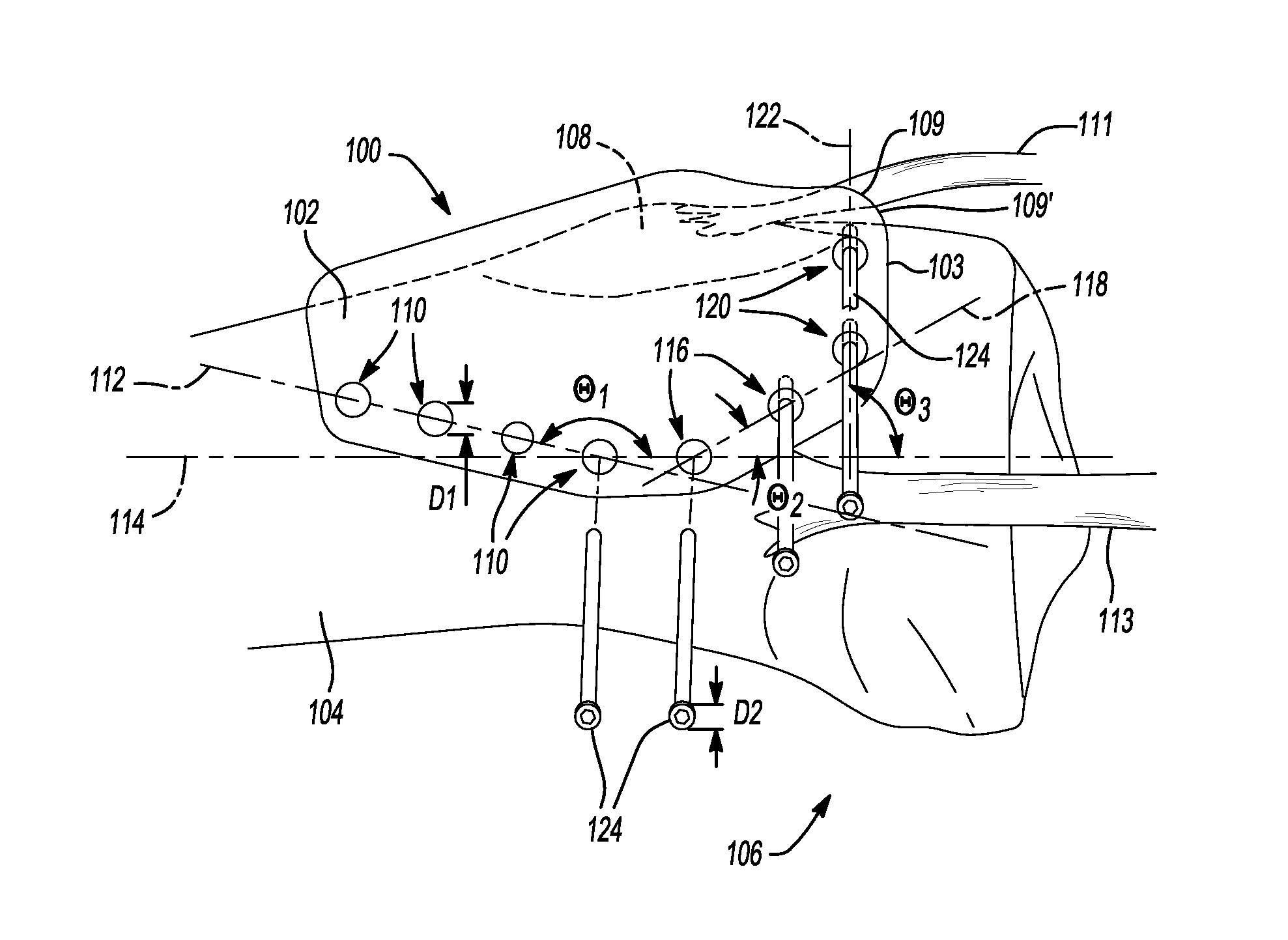
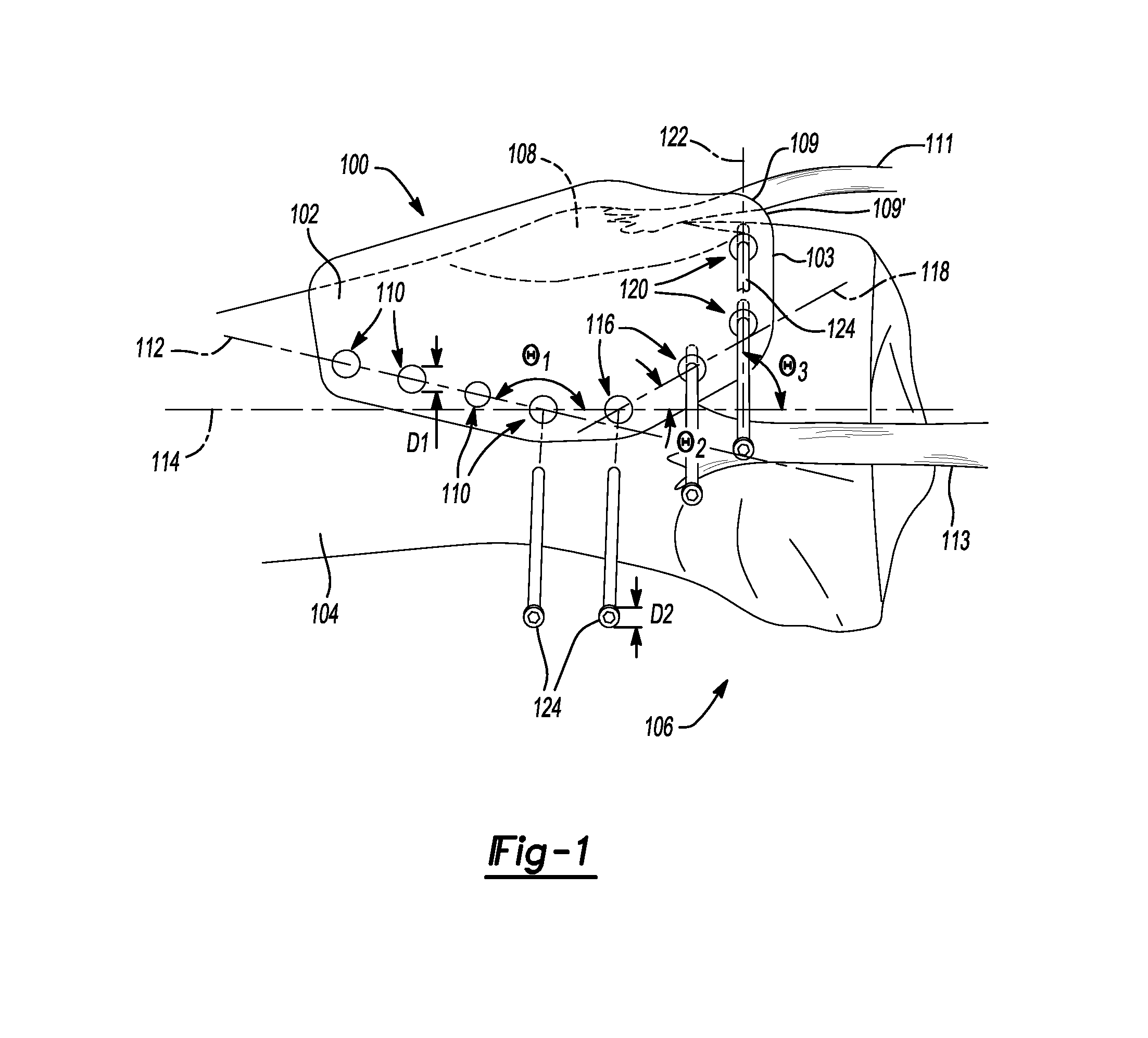
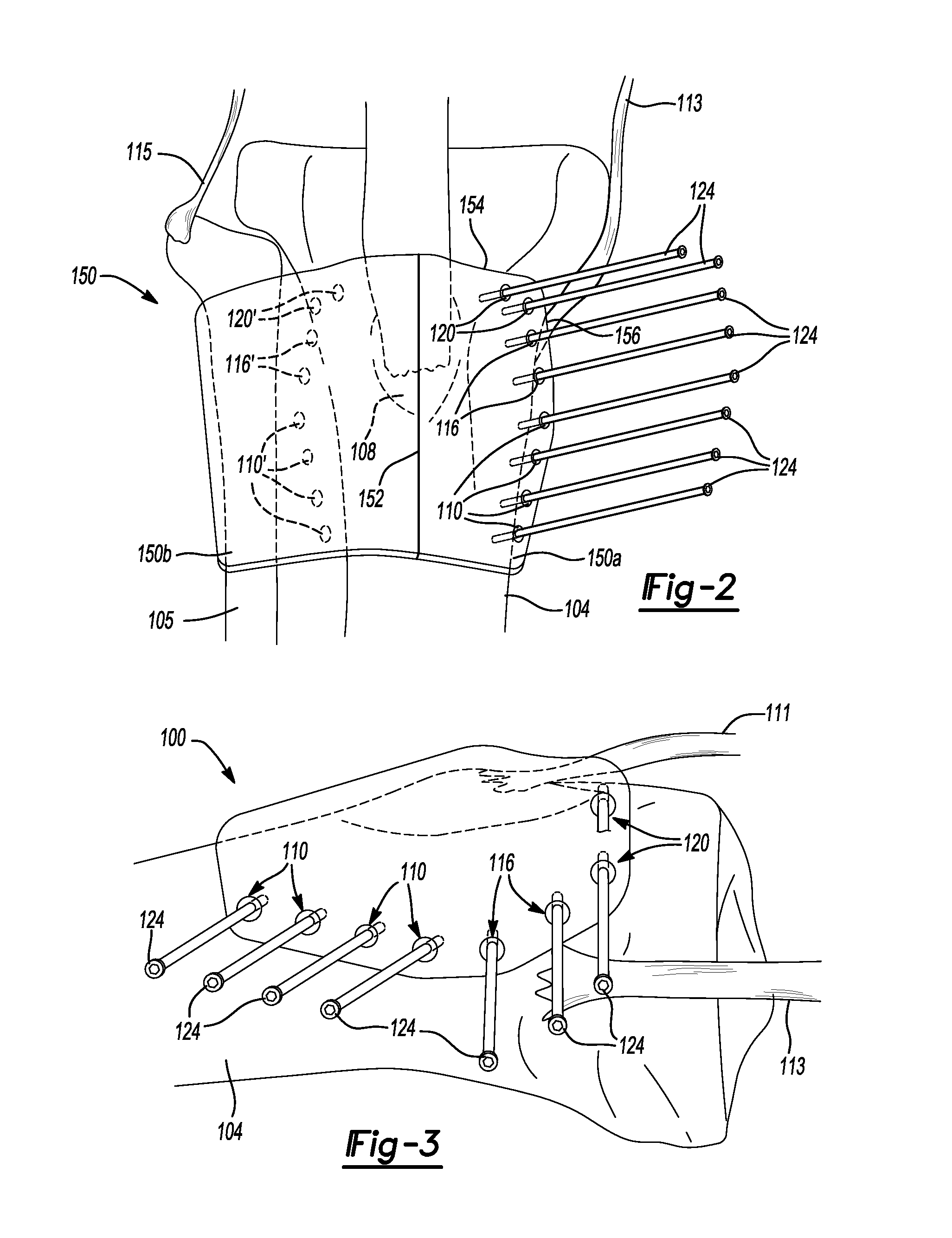
Patents
Literature
38 results about "Tibial tuberosity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
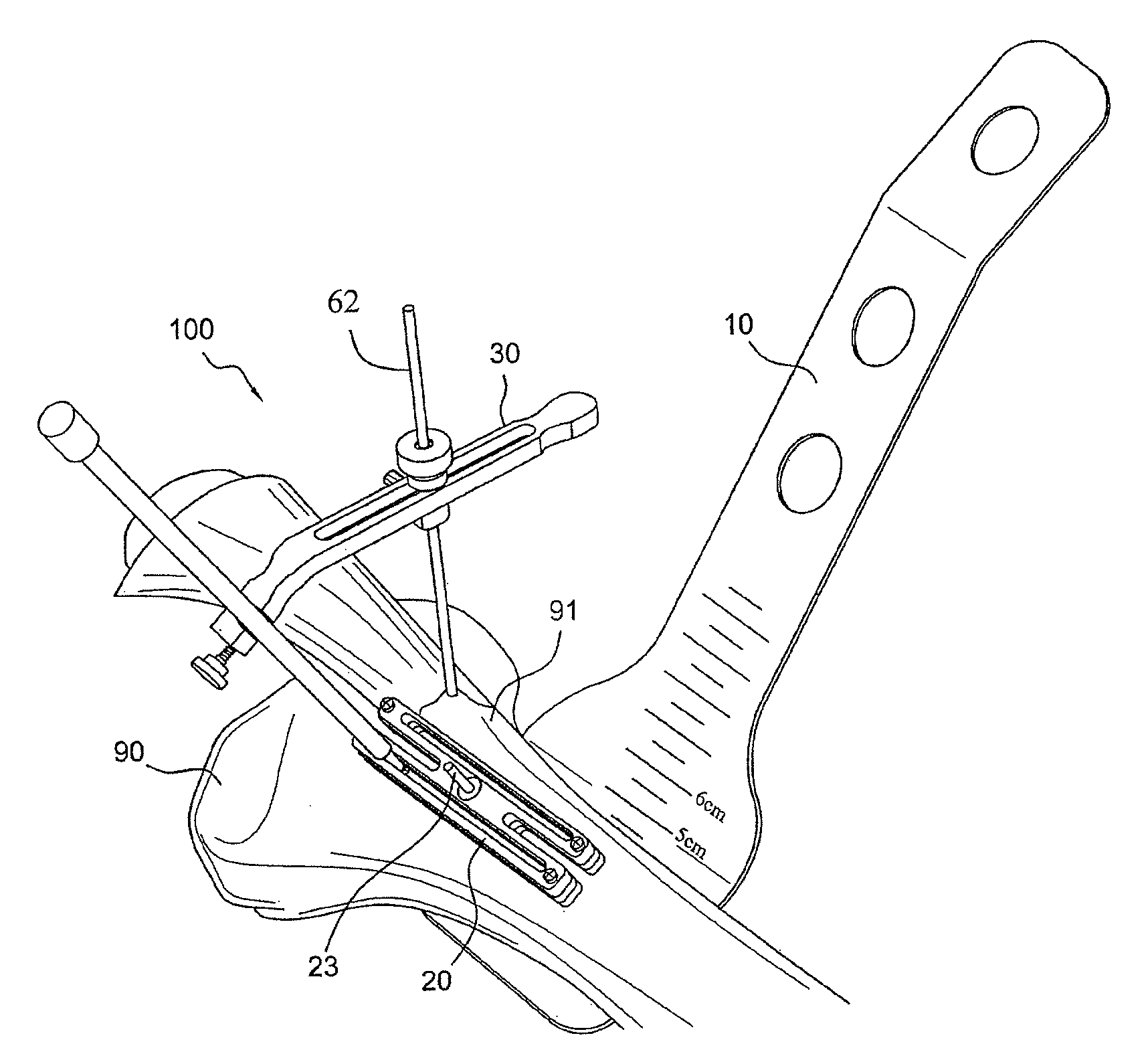
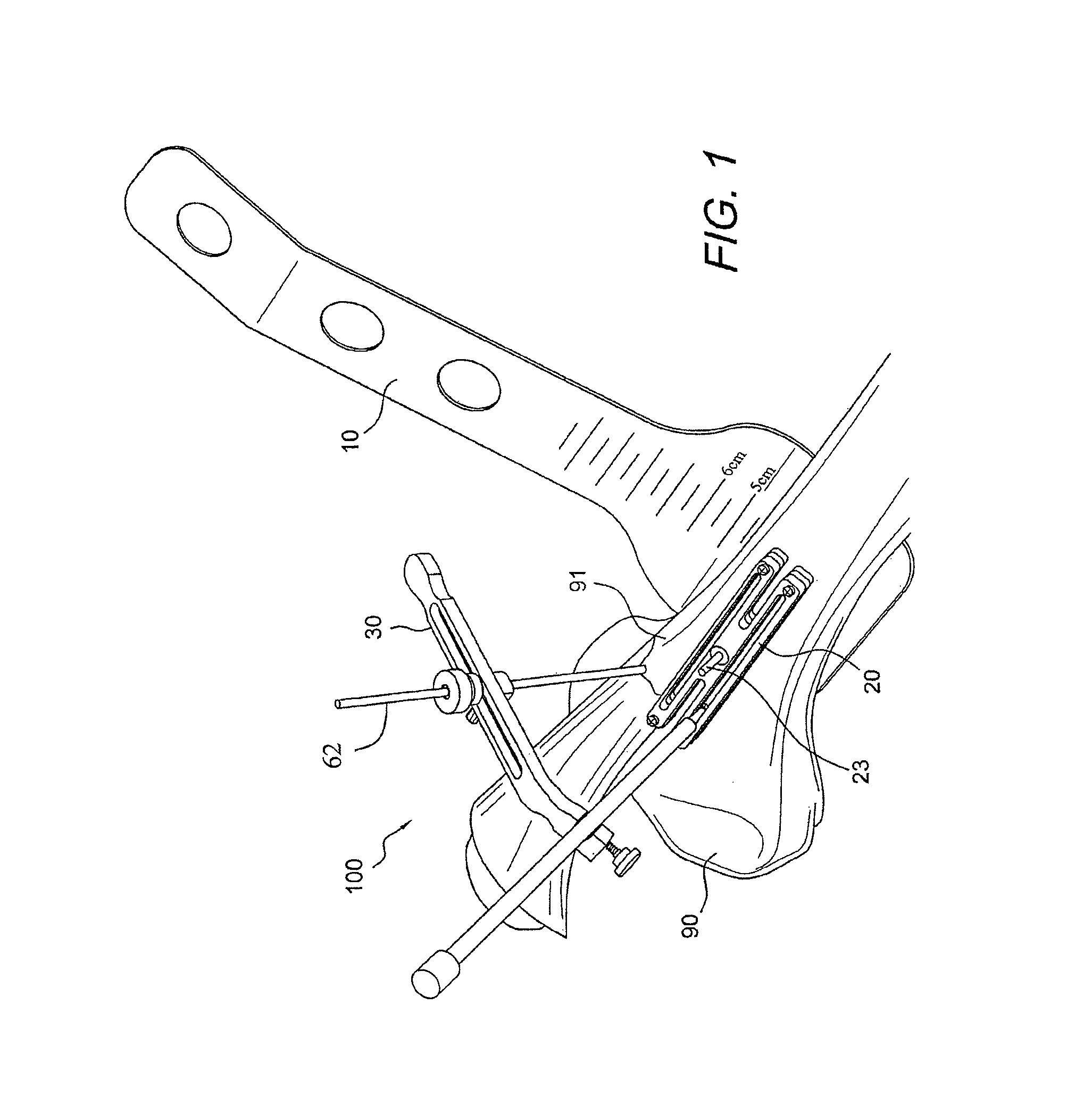
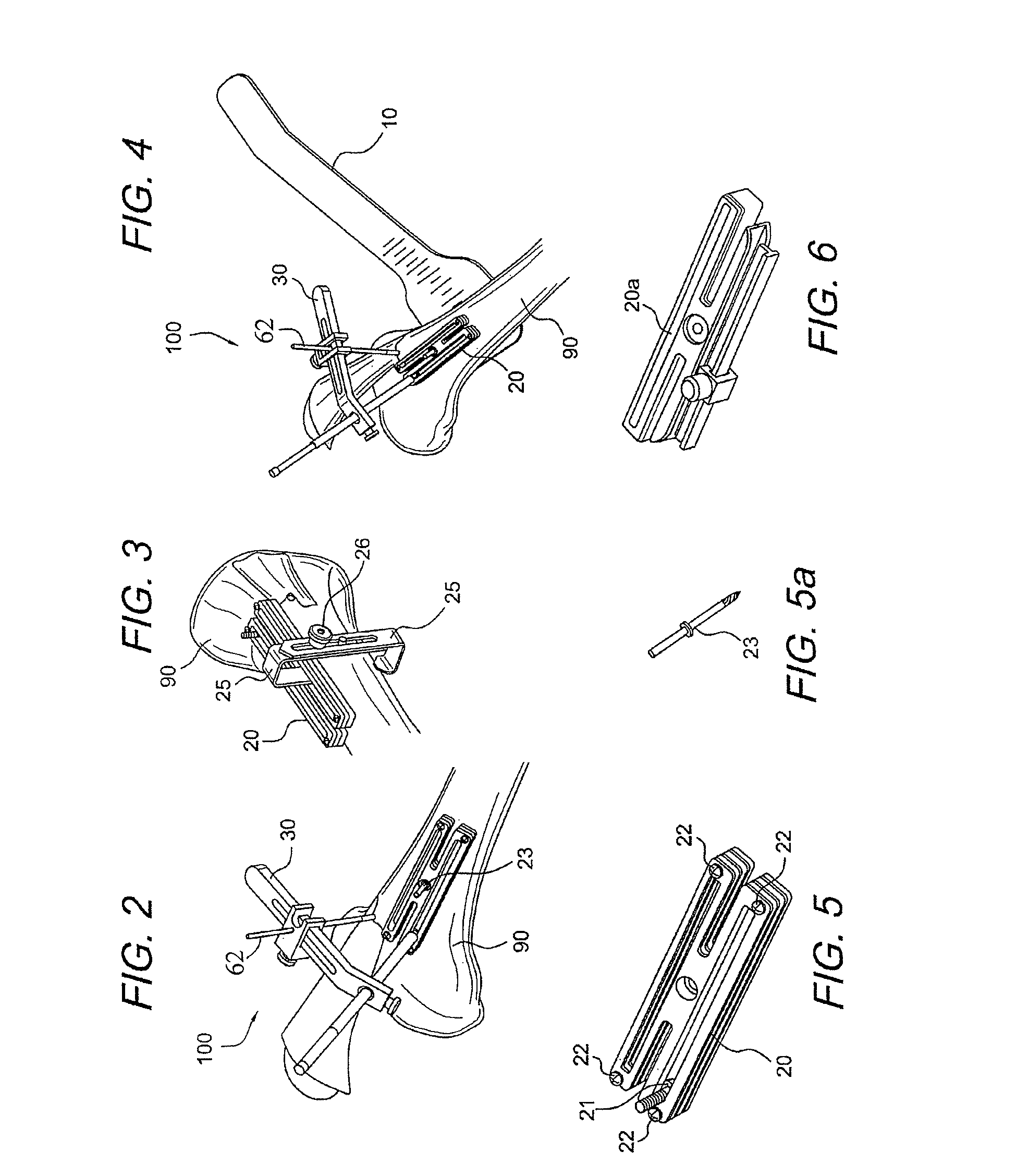
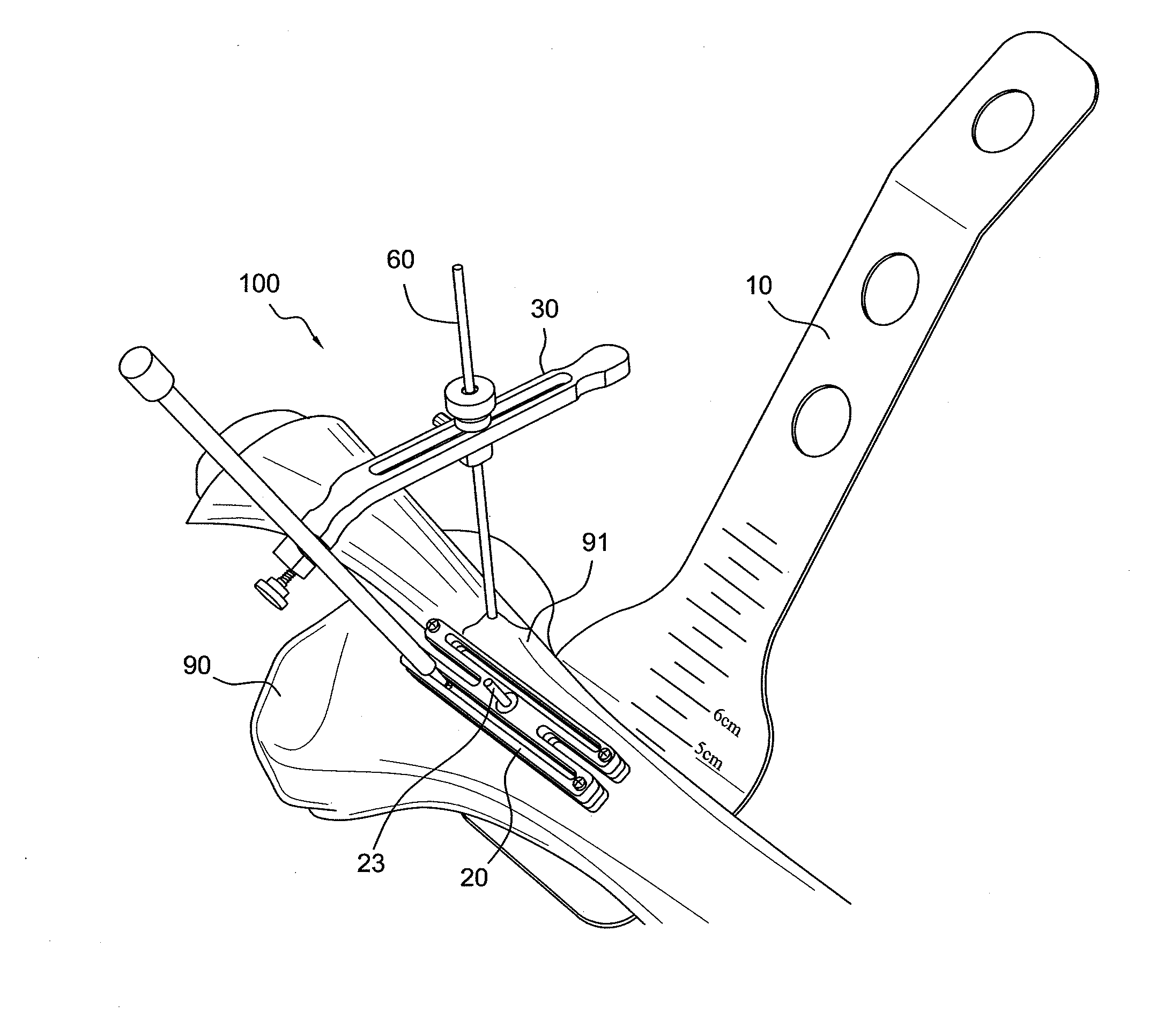
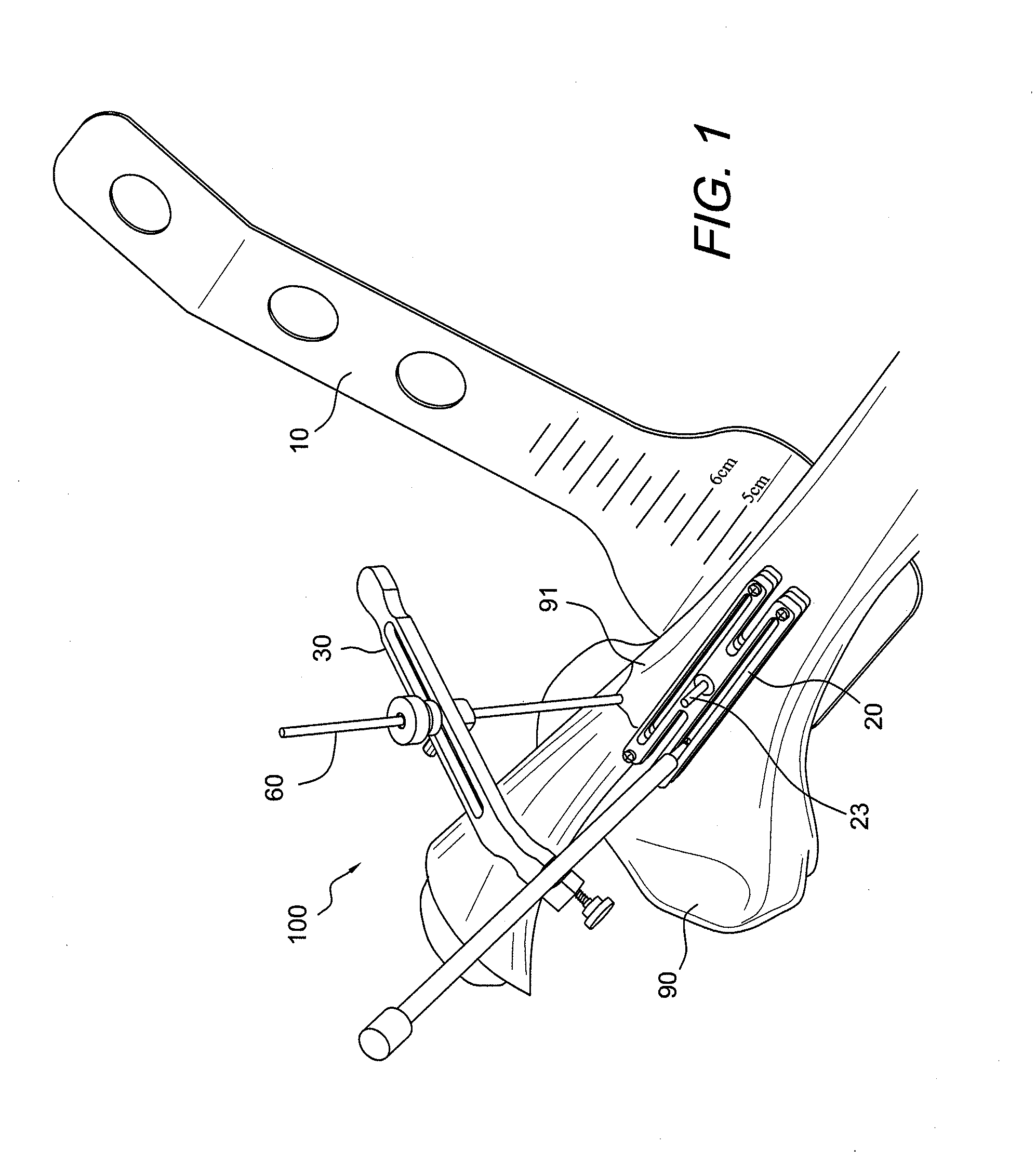
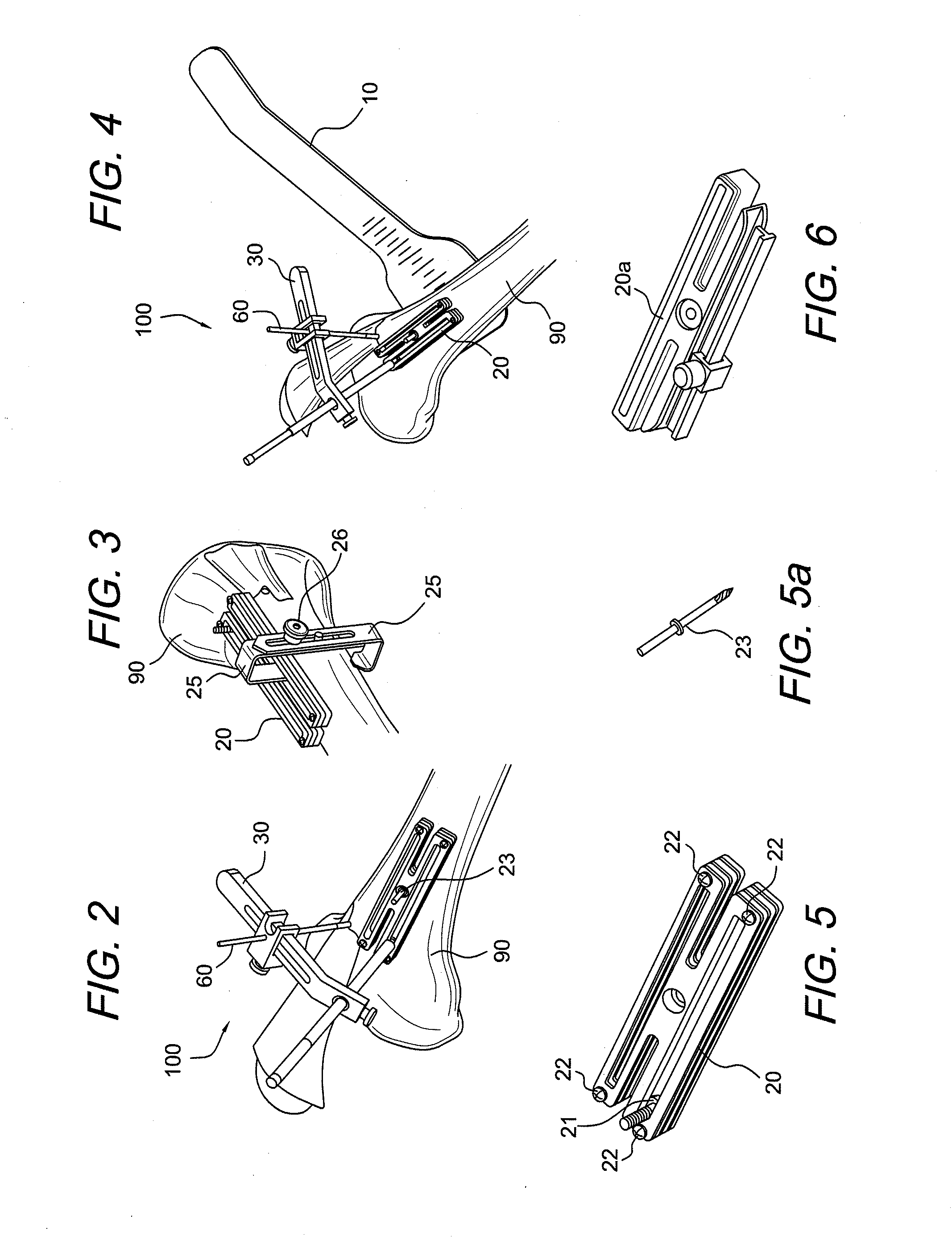
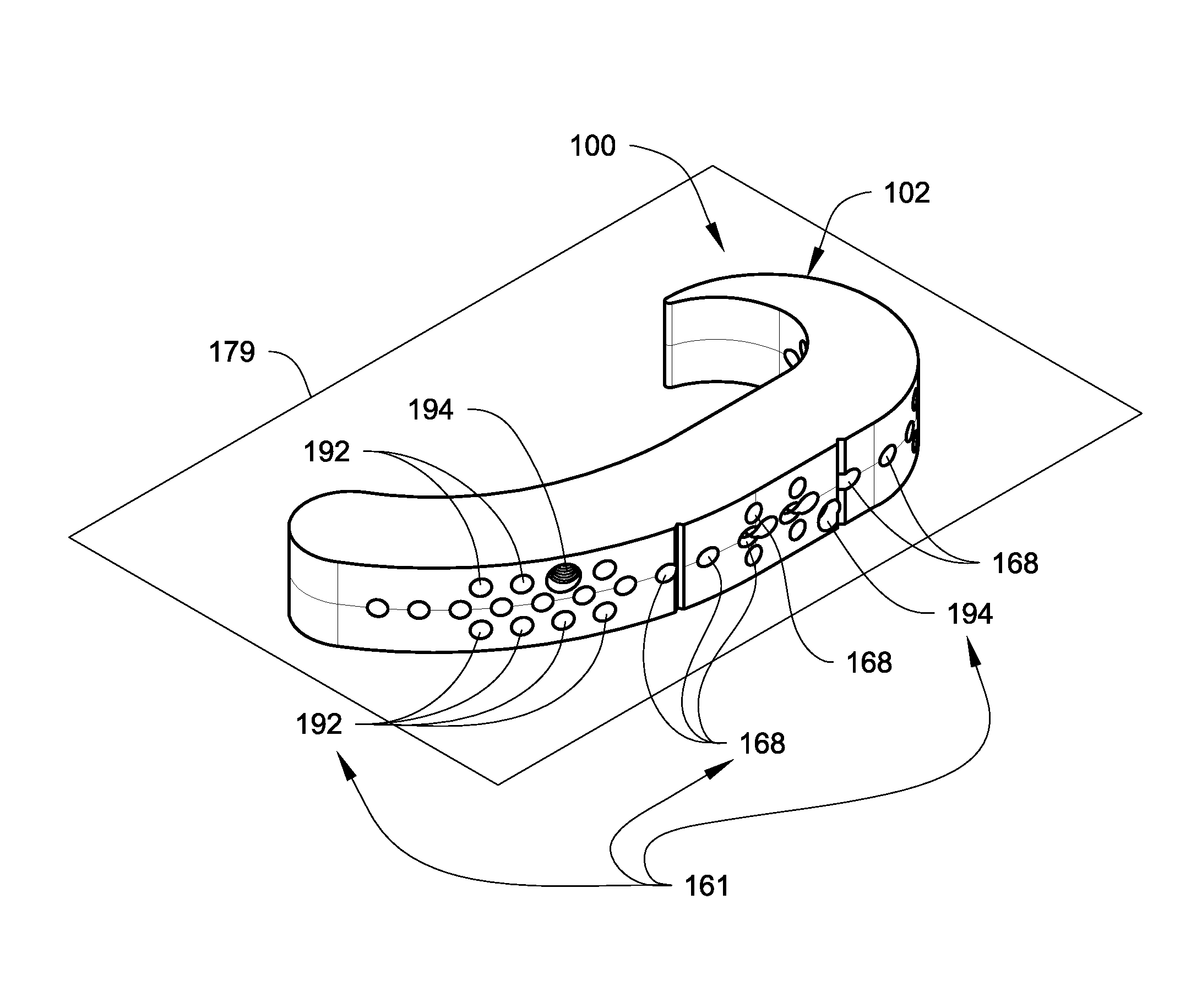
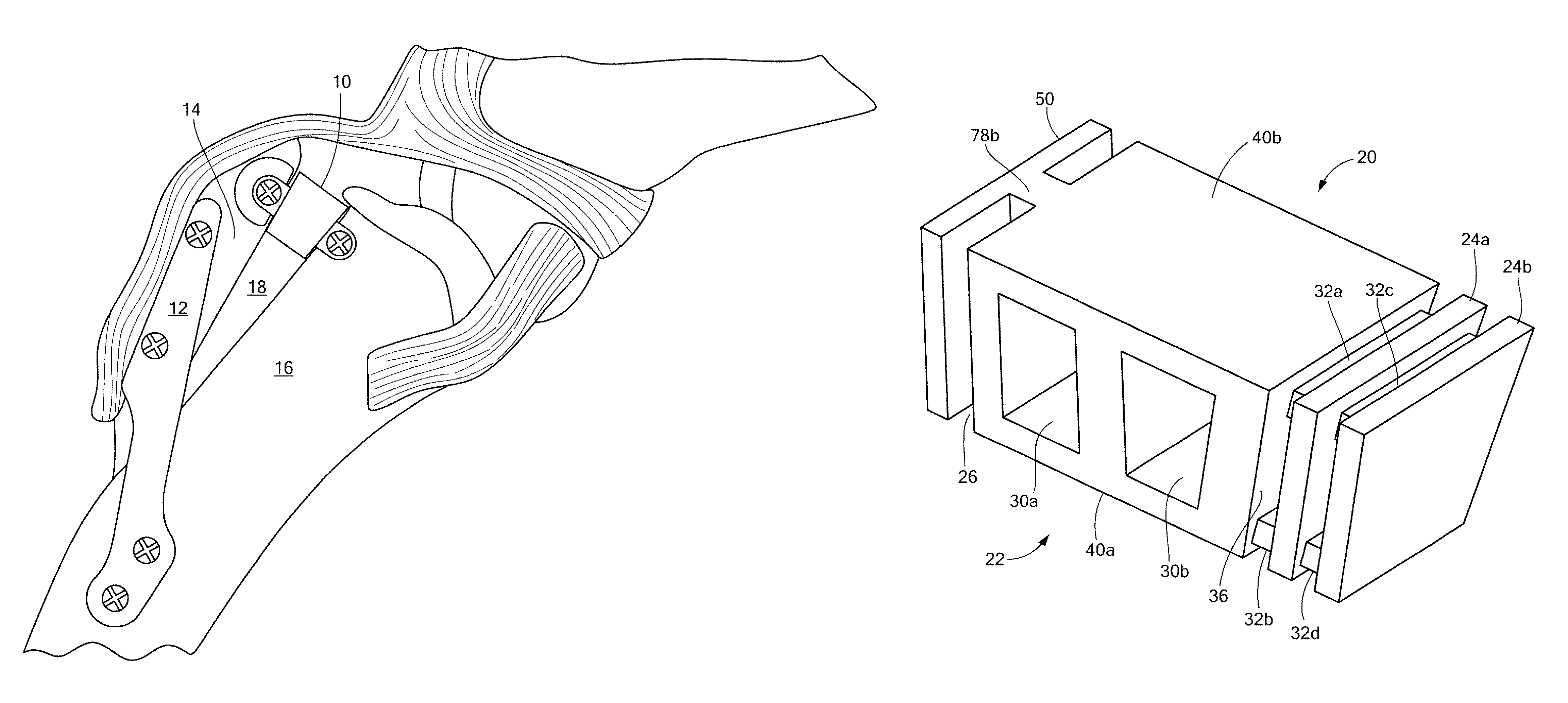
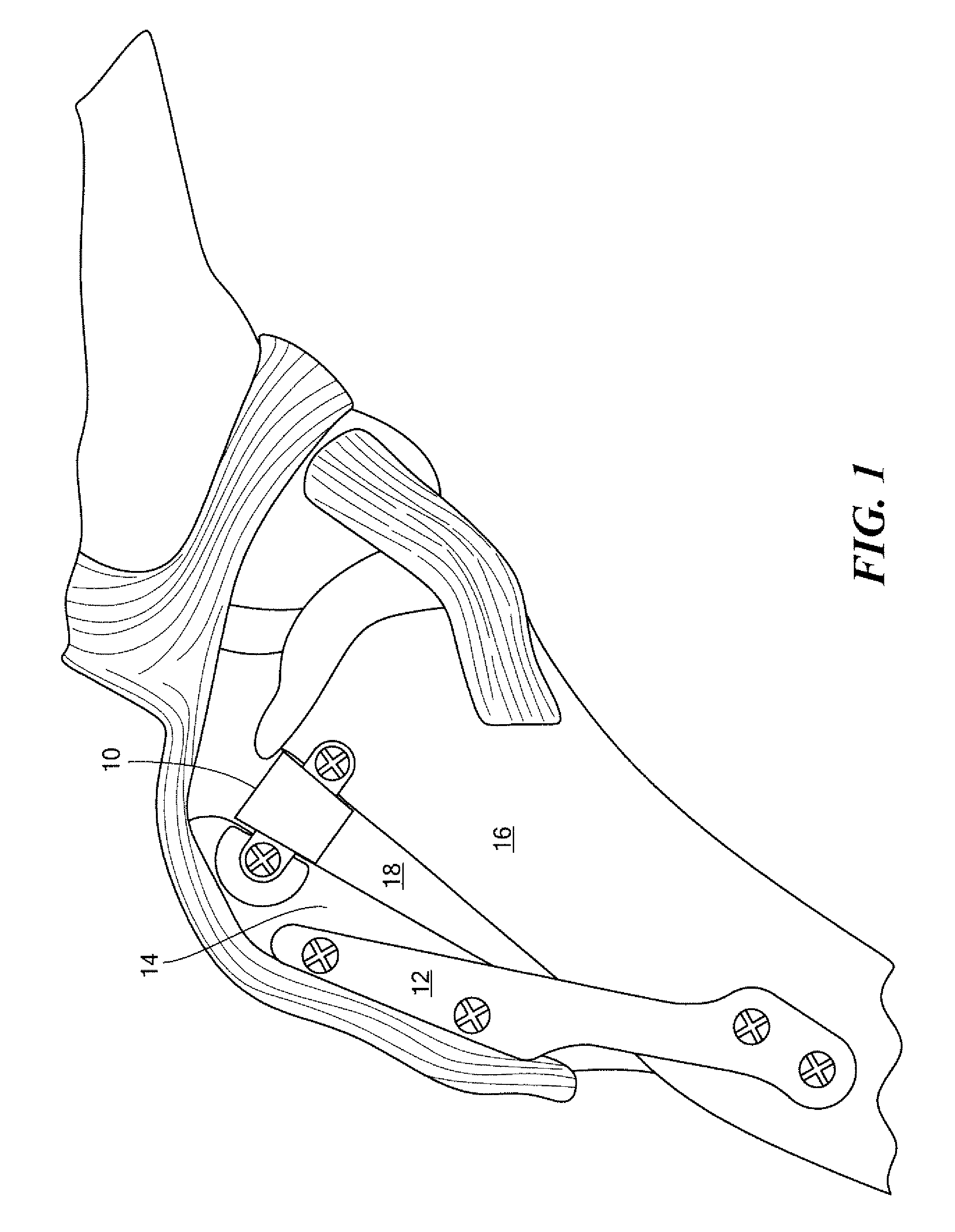
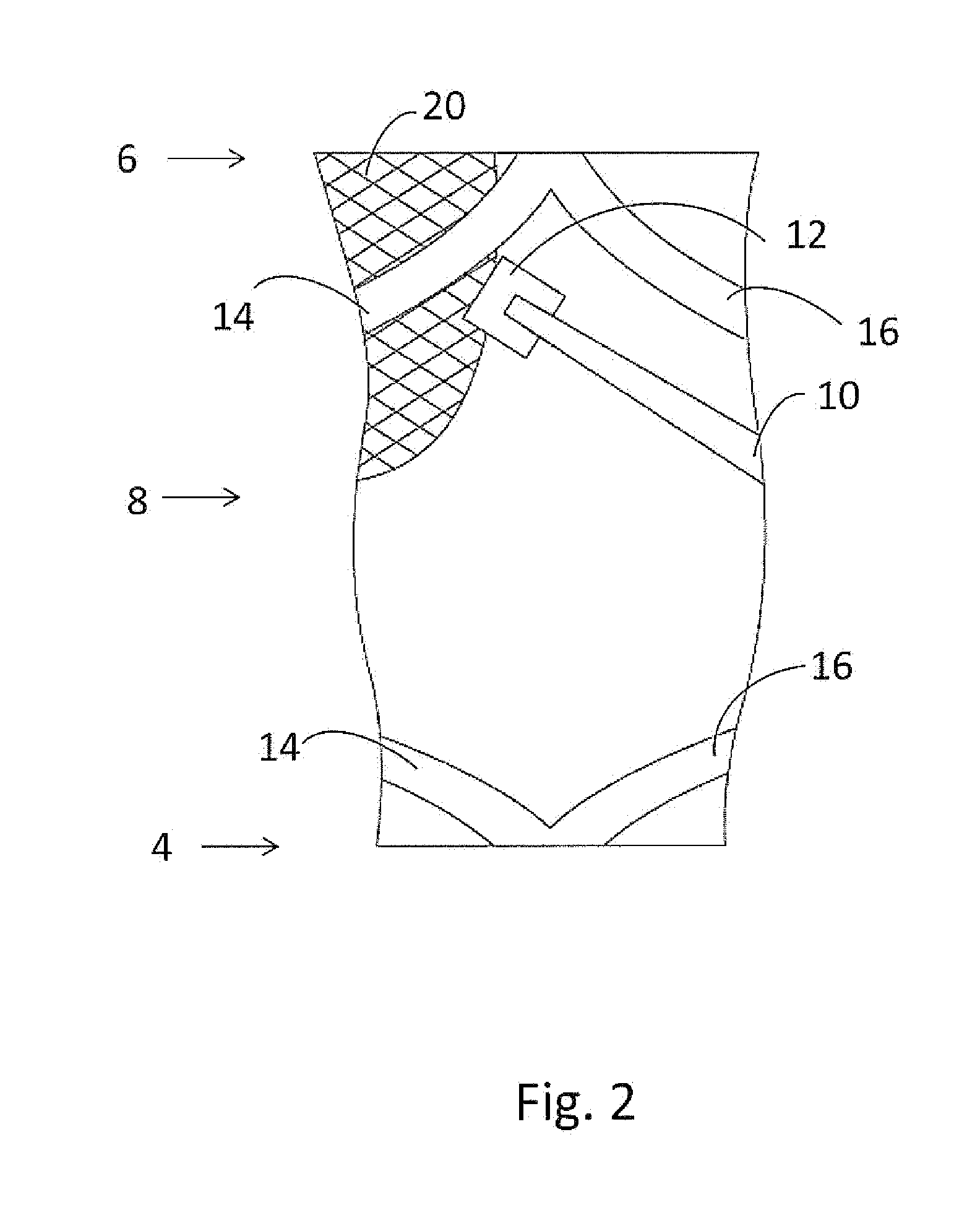
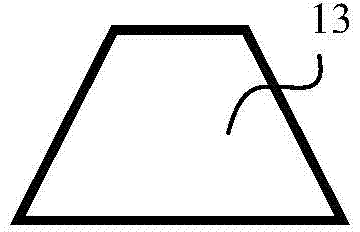
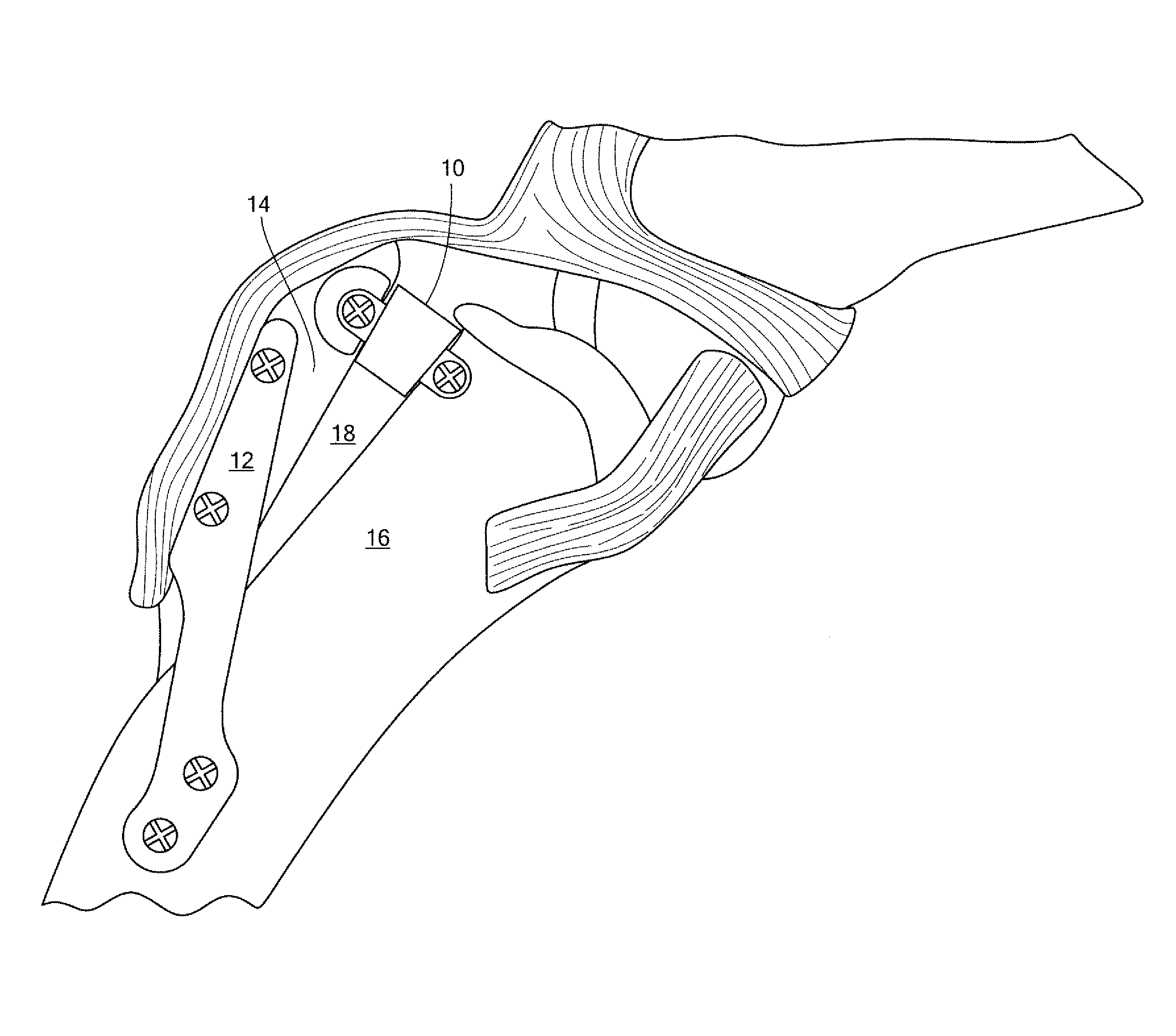
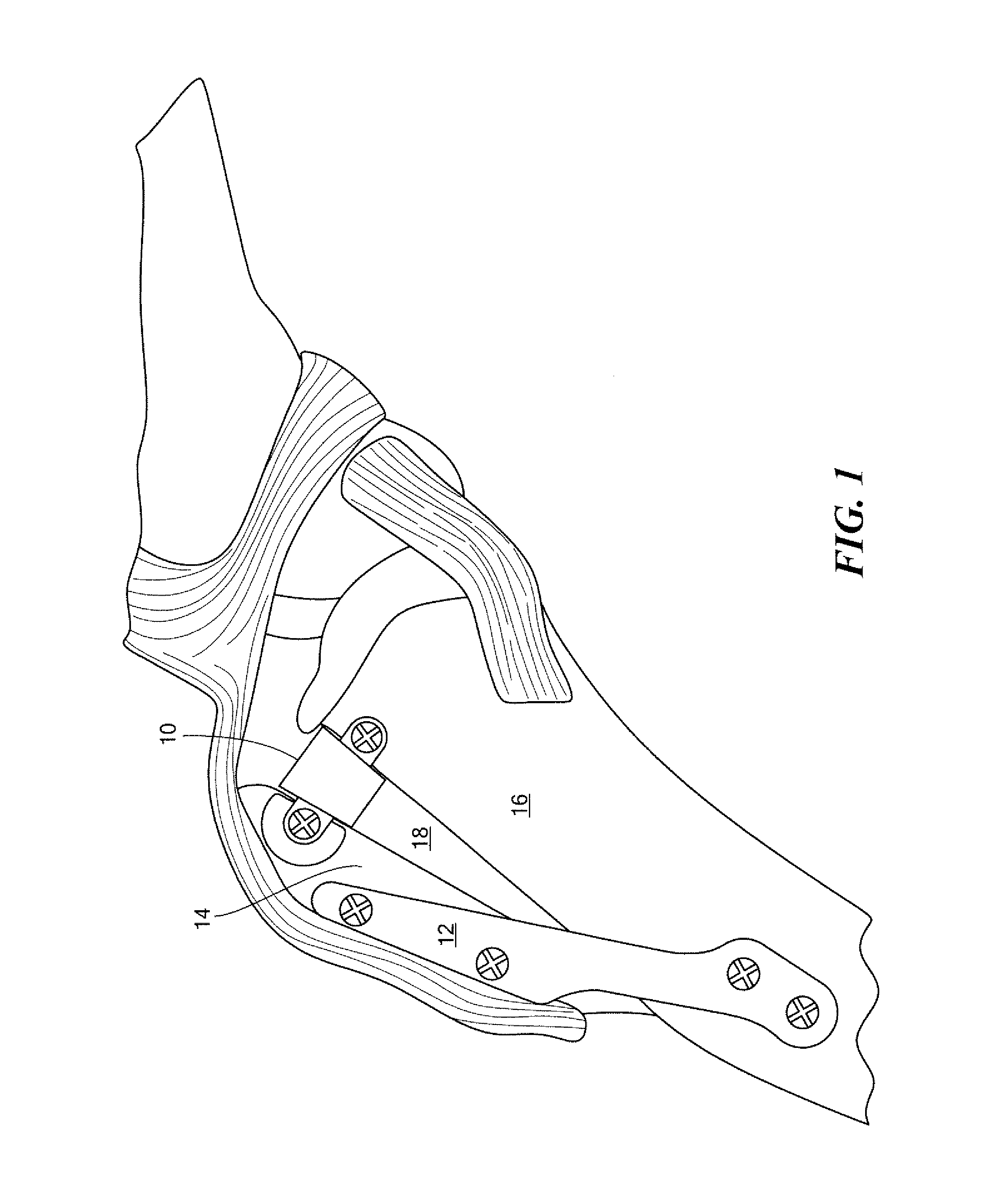
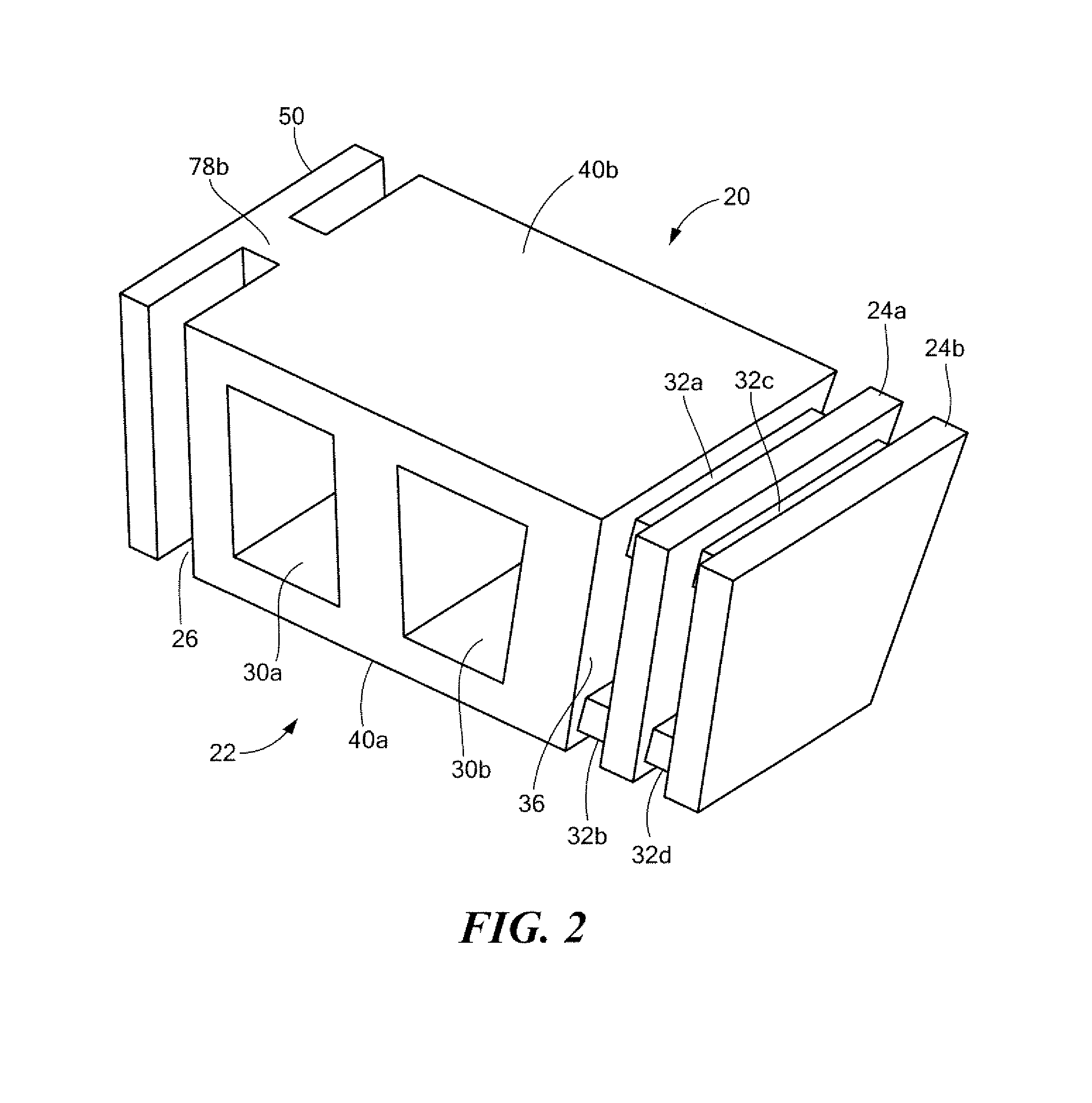
AMZ tibial tuberosity transfer system
ActiveUS8353915B2Large radiusSimple designNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSurgical sawsMedicineTransfer system
An AMZ tibial tuberosity transfer system and method of treatment of patellofemoral joints. The AMZ system includes 1) a retractor with a better conformation to anatomy and more curve (not just a bend), and also with a larger radius on the front of the retractor to allow for easier insertion; 2) a cutting block that can fully accept a collared pin; 3) a rod preferably formed of stainless steel; 4) a tuberosity pin guide; 5) an exit indicator that engages tightly the cutting block so there is no slope on exit indication; and 6) a horizontal bar provided with markings to measure the medial shift.
Owner:ARTHREX
Amz tibial tuberosity transfer system
ActiveUS20090318924A1Good conformationLarge radiusNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSurgical sawsMedicineTransfer system
An AMZ tibial tuberosity transfer system and method of treatment of patellofemoral joints. The AMZ system includes 1) a retractor with a better conformation to anatomy and more curve (not just a bend), and also with a larger radius on the front of the retractor to allow for easier insertion; 2) a cutting block that can fully accept a collared pin; 3) a rod preferably formed of stainless steel; 4) a tuberosity pin guide; 5) an exit indicator that engages tightly the cutting block so there is no slope on exit indication; and 6) a horizontal bar provided with markings to measure the medial shift.
Owner:ARTHREX
Made-to-measure orthosis for compression/containment, for reinforcing the musculo-aponeurotic pump of the calf
InactiveUS20120116282A1Easy to installReduce rigidityFinger bandagesBreast bandagesYarnDistal portion
Owner:INNOTHERA TOPIC INT
Osteotomy below the tibial tuberosity by multiple drilling
ActiveUS9486228B2Regeneration of the bone in a relatively short time periodMinimize injuryMammal material medical ingredientsSurgical sawsSurgical procedure kitKnee Joint
Surgical devices, kits and methods of using thereof are described. Generally, the surgical kit includes an osteotomy guide device and / or a bone spacer guide device. The surgical kit can be used in a surgical method for correcting a malalignment of the knee joint that involves performing a fibular osteotomy and / or a tibial osteotomy, and / or administering stem cells. Generally, the osteotomy guide device is configured to allow drilling to occur around the tibia and across a horizontal cross-sectional plane of the tibia so that a direction of each of the drill holes that are formed in the tibia is substantially parallel to or on the same horizontal cross-sectional plane of the tibia. The osteotomy guide device allows drilling to be conducted efficiently and accurately.
Owner:JEE CAROLINE SIEW YOKE +2
Osteotomy below the tibial tuberosity by multiple drilling
ActiveUS20150071885A1Conducted efficiently and accuratelyRegeneration of the bone in a relatively short time periodBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsMedicineKnee Joint
Surgical devices, kits and methods of using thereof are described. Generally, the surgical kit includes an osteotomy guide device and / or a bone spacer guide device. The surgical kit can be used in a surgical method for correcting a malalignment of the knee joint that involves performing a fibular osteotomy and / or a tibial osteotomy, and / or administering stem cells. Generally, the osteotomy guide device is configured to allow drilling to occur around the tibia and across a horizontal cross-sectional plane of the tibia so that a direction of each of the drill holes that are formed in the tibia is substantially parallel to or on the same horizontal cross-sectional plane of the tibia. The osteotomy guide device allows drilling to be conducted efficiently and accurately.
Owner:JEE CAROLINE SIEW YOKE +2
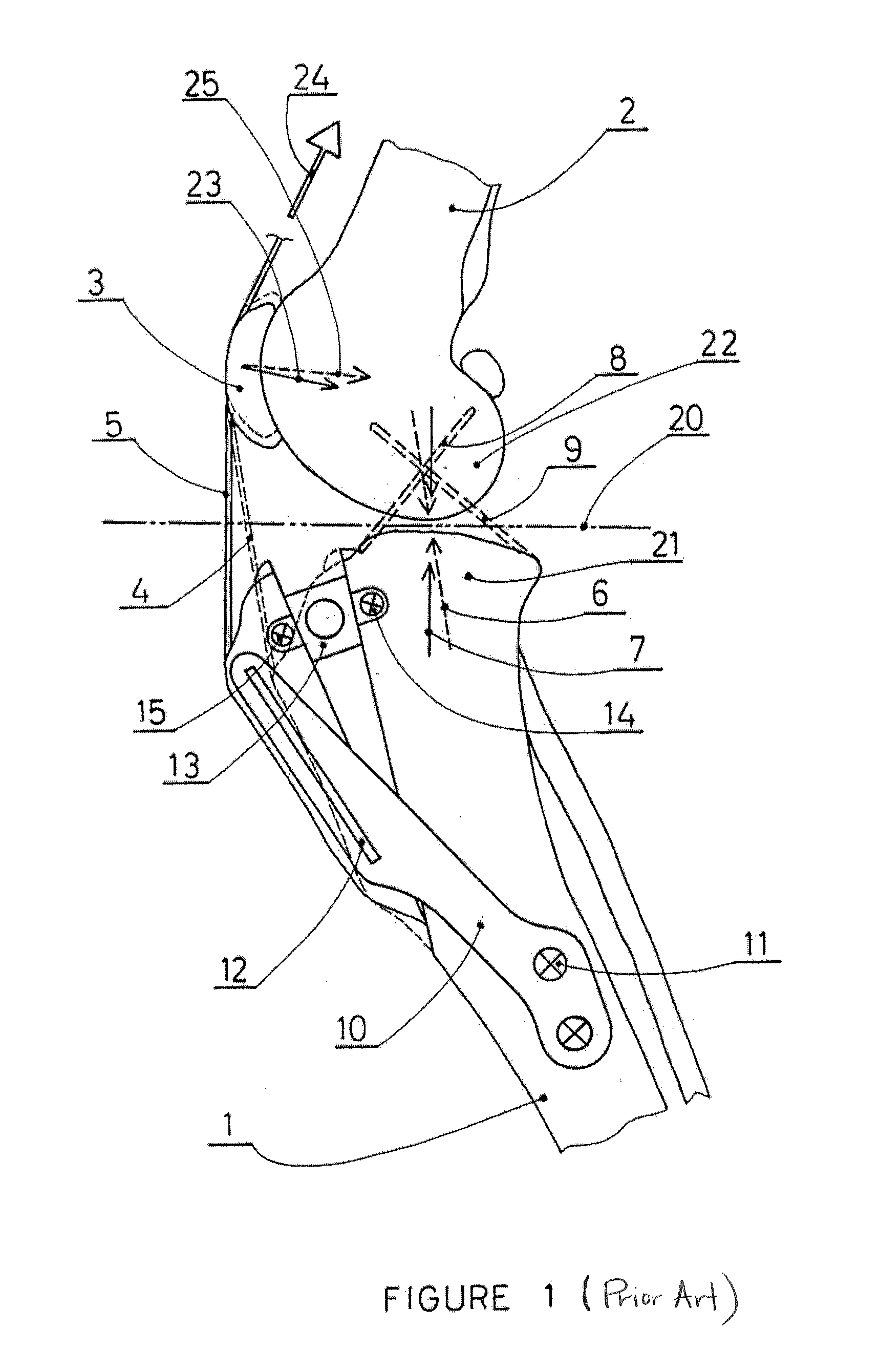
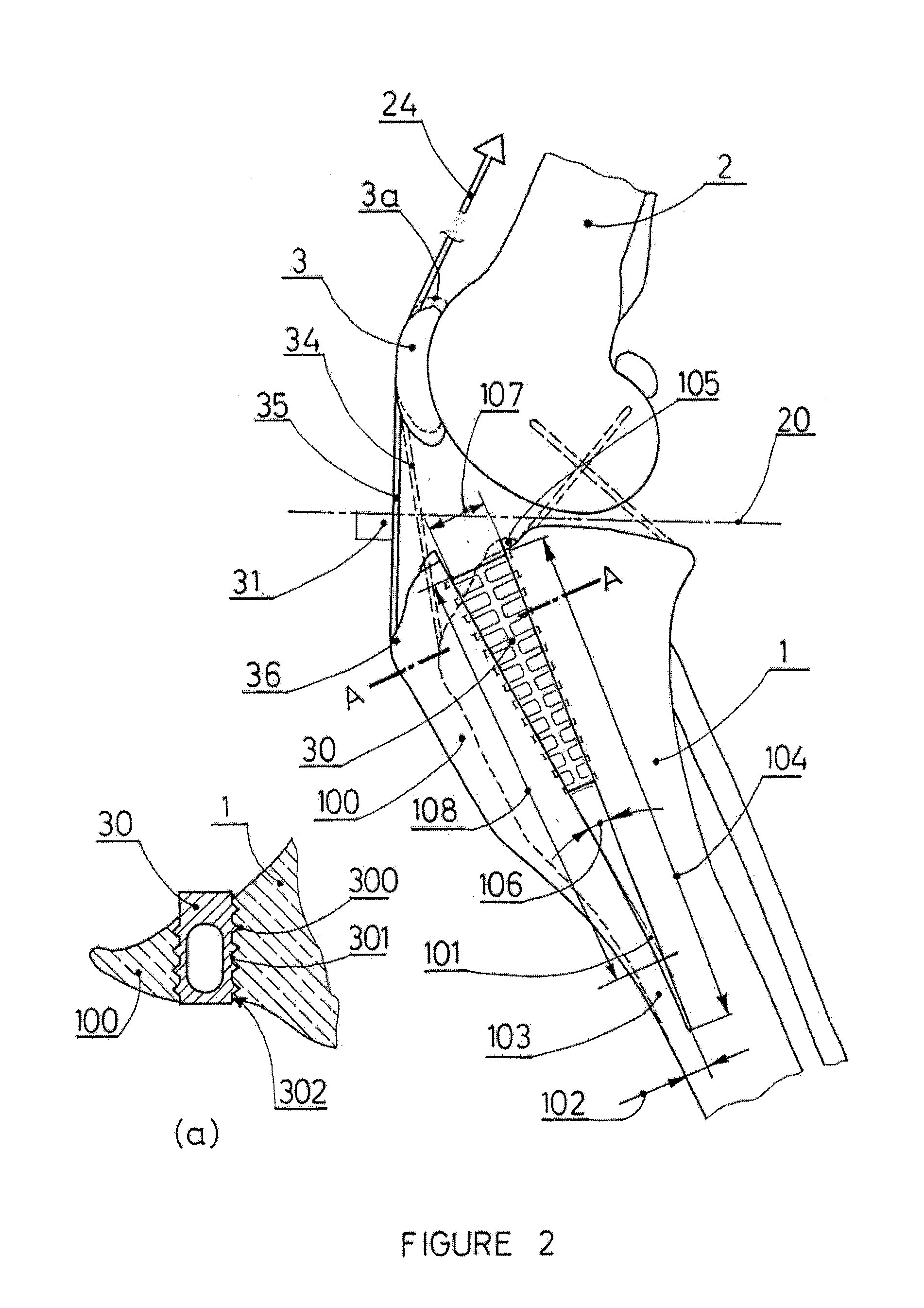
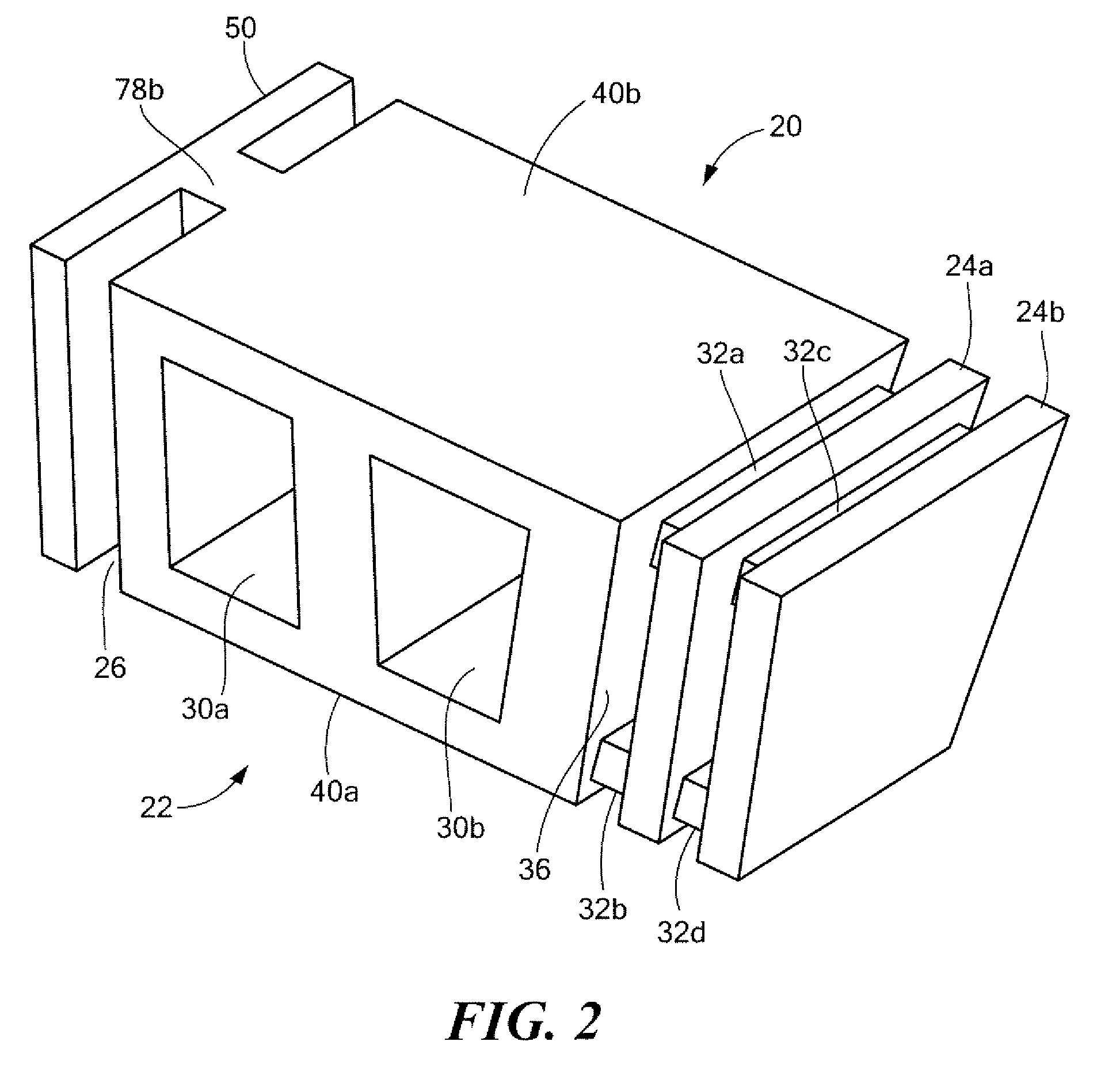
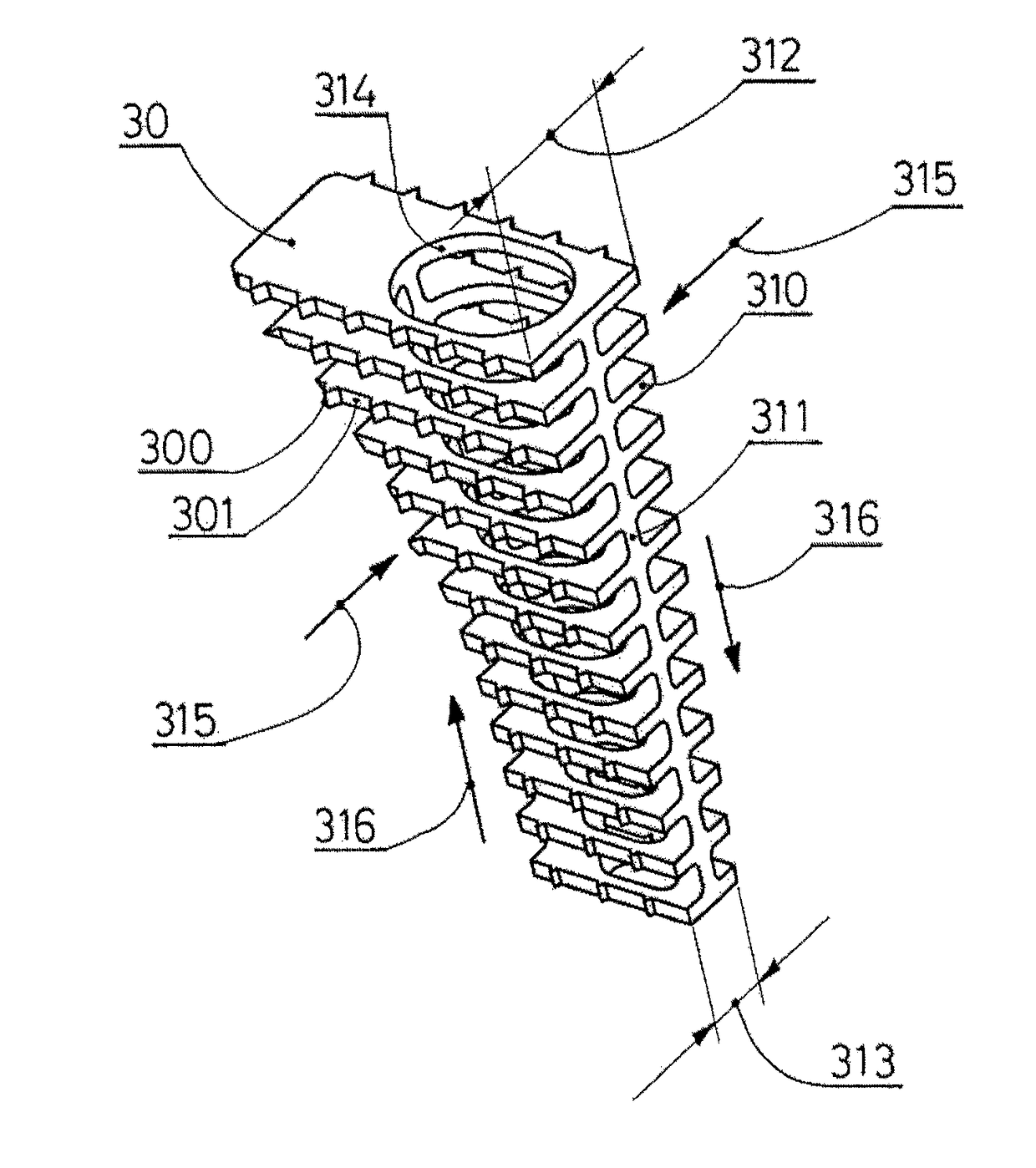
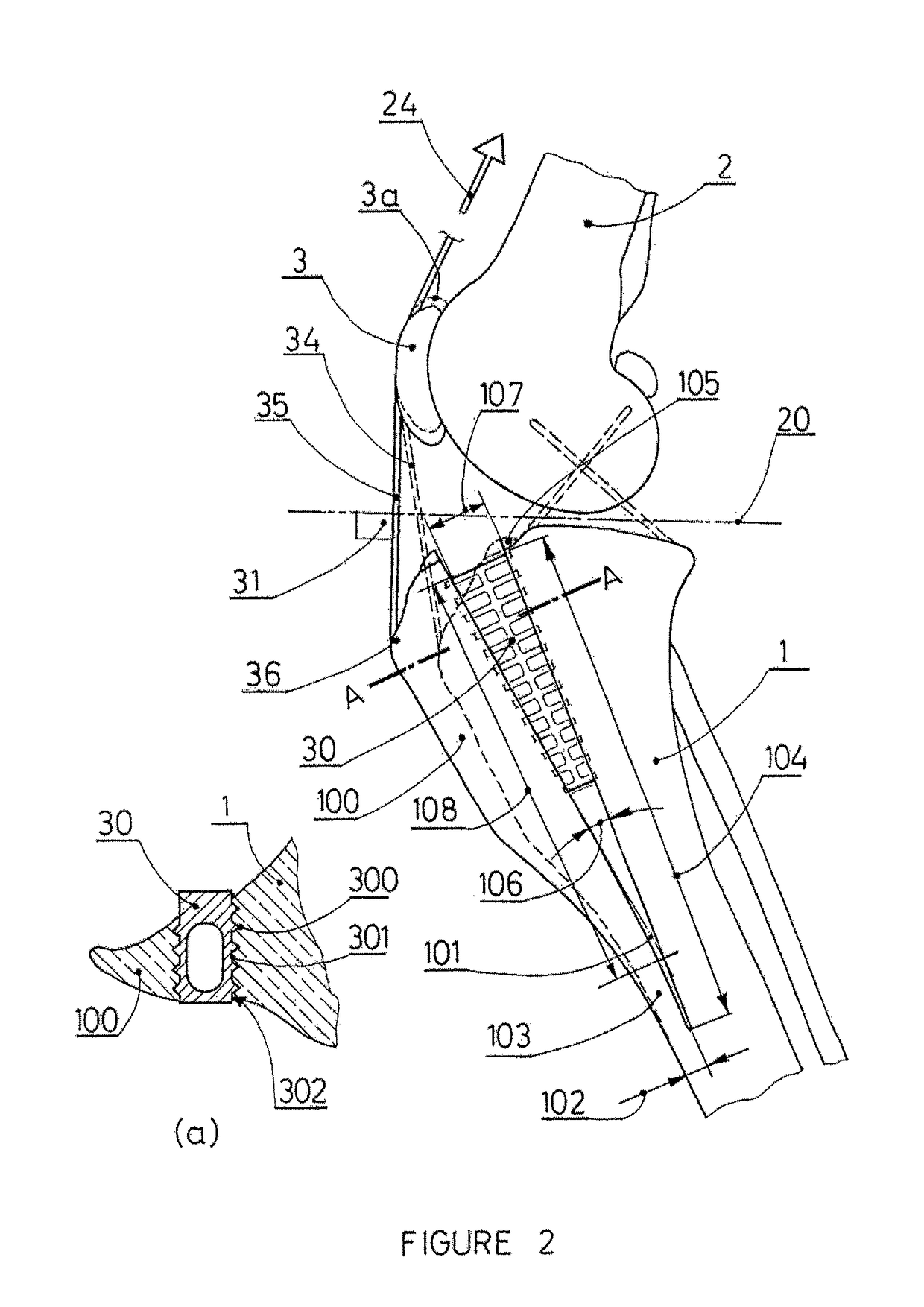
Tibial tuberosity advancement cage for ACL injuries
Methods and implants to treat anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries are disclosed. The methods involve advancing the insertion of the patellar tendon to the proximal tibia by means of a partial osteotomy and a wedge-shaped cage (30). The wedge-shaped cage is specifically designed to facilitate transfer of not only compressive loads, but also of shear loads due to pull by the patellar tendon at its insertion to the tibial tuberosity. The cage decreases the angle between the patellar tendon and the common tangent plane formed by the condyles of the femur and the condyles of the tibia (sometimes called tibial plateau) and consequently modifies the internal joint force, restoring stability to the joint even if the ACL is ruptured. The methods and implants are applicable to both human and canine patients.
Owner:KYON
Method and apparatus for performing multidirectional tibial tubercle transfers
Apparatus for performing a multidirectional tibial tubercle transfer, comprising a jig for positioning against the anterior portion of the tibia, the jig comprising first and second guide surfaces which simultaneously converge towards one another as they extend distally down, and posteriorly towards, the tibia; a medial extender for attaching to the jig, wherein the medial extender comprises a third guide surface which is directed towards a point distal to the point of convergence of the first and second guide surfaces as the third guide surface extends distally down, and posteriorly towards, the tibia; and a lateral extender for attaching to the jig, wherein the lateral extender comprises a fourth guide surface which is directed towards a point distal to the point of convergence of the first and second guide surfaces as the fourth guide surface extends distally down, and posteriorly towards, the tibia.
Owner:KINAMED
Tibial Tubercule Osteotomy
ActiveUS20160089166A1RemissionPromotes bone in-growthSkullSurgical sawsTibial tuberosityPre operative
Patient-specific guides for a tibial tubercle osteotomy are provided. The guides include a guide body defining a portion with a bone-engaging surface that conforms as a negative surface to a corresponding surface of a specific patient's tibia, and a guide portion that guides a surgical instrument to a specific location on the specific patient's tibia, wherein the bone-engaging surface and guide portion are configured during a pre-operative planning stage. Methods for performing a tibial tubercle osteotomy with the patient-specific guides are also provided.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Tibial tuberosity advancement implant
A tibial tuberosity advancement implant and method includes a spacer body made of biocompatible, biodegradable material and having a main section with at least one bony growth orifice therethrough and a proximal slot and at least one fin extending from the main section by at least one connector. A metal clip is slideable into the proximal slot of the spacer body main section and includes spaced screw holes for securing the spacer body to the advanced tibial tuberosity and the tibia when the implant is placed in the space between the advanced tibial tuberosity and the tibia.
Owner:MWI VETERINARY SUPPLY
Marrow cavity puncture bag with guide positioning mark
ActiveCN106618746AImprove the odds of successShorten the timeSurgical furnitureSurgical drapesEmergency treatmentLower border
The invention provides a marrow cavity puncture bag with a guide positioning mark. The bag comprises an aseptic packing bag, an aseptic hole towel and pre-operation aseptic gloves. A round hole is formed in the aseptic hole towel. The periphery of the round hole is provided with circular ring sheet. A sterilized cotton layer is arranged in the ring sheet. The lower surface of the aseptic hole towel is a waterproof layer. The upper portion of the ring sheet is provided with a waterproof layer. A horizontal marking line and a vertical marking line are arranged on the aseptic hole towel. The horizontal marking line is used for aligning with the lower border of patella of the human body. The vertical marking line is used for aligning with the tibial tuberosity of the human body. The marrow cavity puncture bag combines the positioning and sterilization of the puncture part. After the aseptic packing bag is opened, the bag can be used, and the success rate of puncturing the marrow cavity is hugely increased, the time used for puncturing the marrow cavity is also shortened, thus precious rescue time is saved for the patients of patients of critical emergency conditions suffering from the clinical acute diseases such as cardiopulmonary resuscitation, shock, massive hemorrhage and the like. The marrow cavity puncture bag with guide positioning mark is a light, convenient and practical technique, and can provide safe and convenient operation for the rescue in the battlefield and areas inflicted by disaster, pre-hospital emergency rescue and hospital emergency treatment. The 'life road' is founded.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV QILU HOSPITAL
Garment for Promoting Dynamic Alignment of a Knee
InactiveUS20140378883A1Improve stabilityReduce the risk of injuryNon-surgical orthopedic devicesThighPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
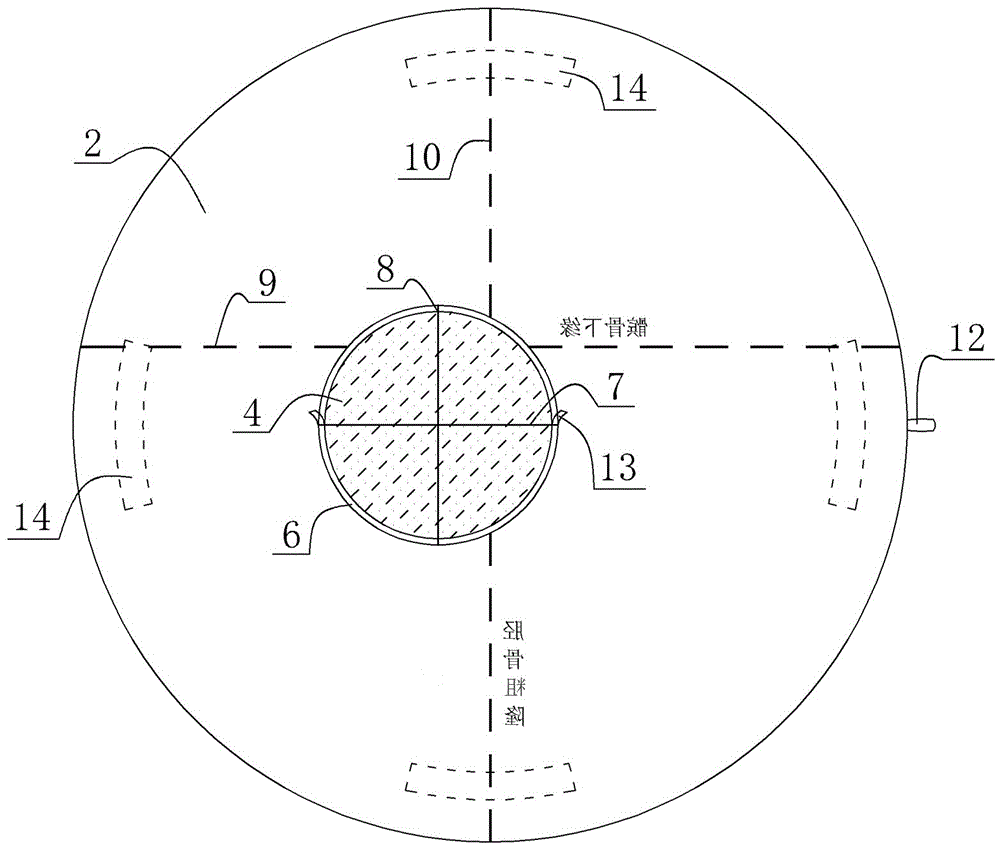
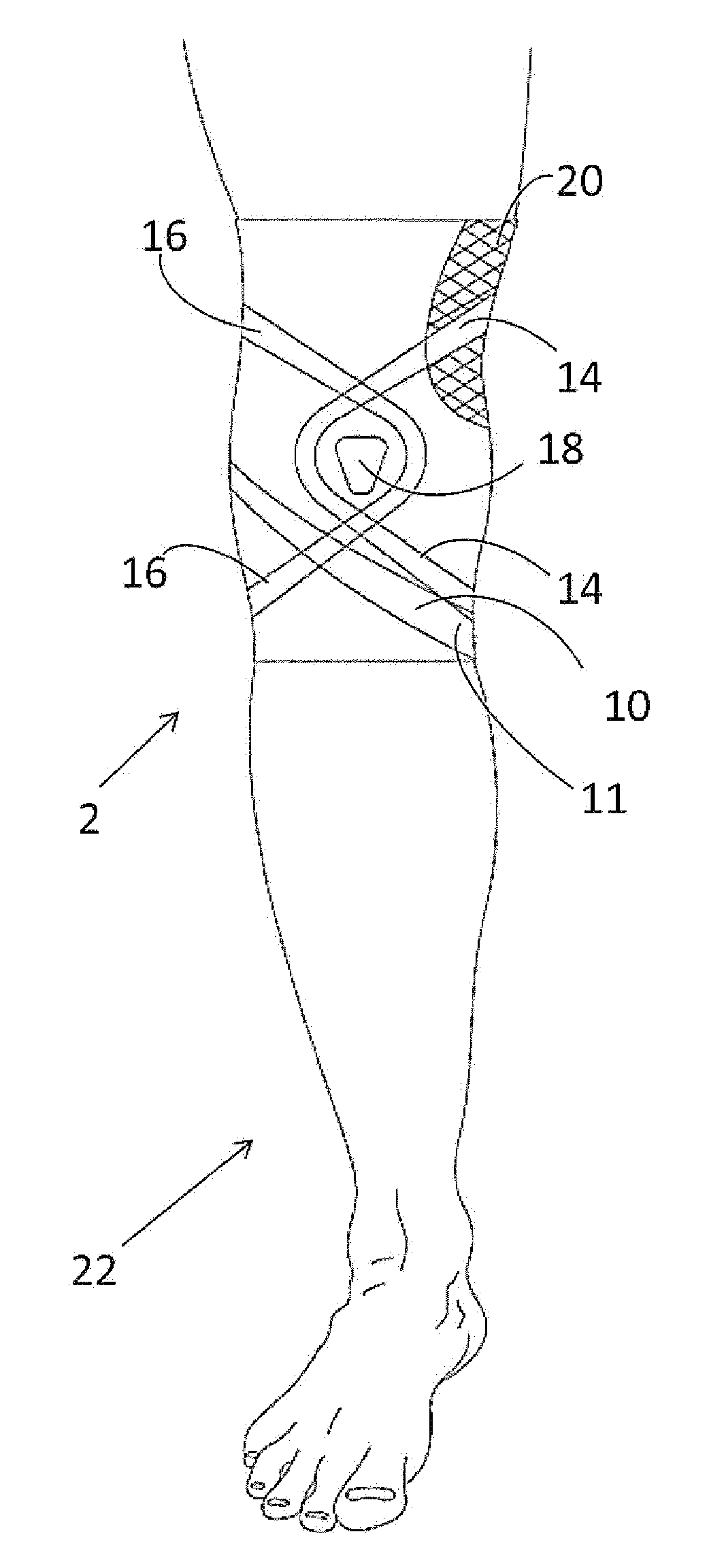
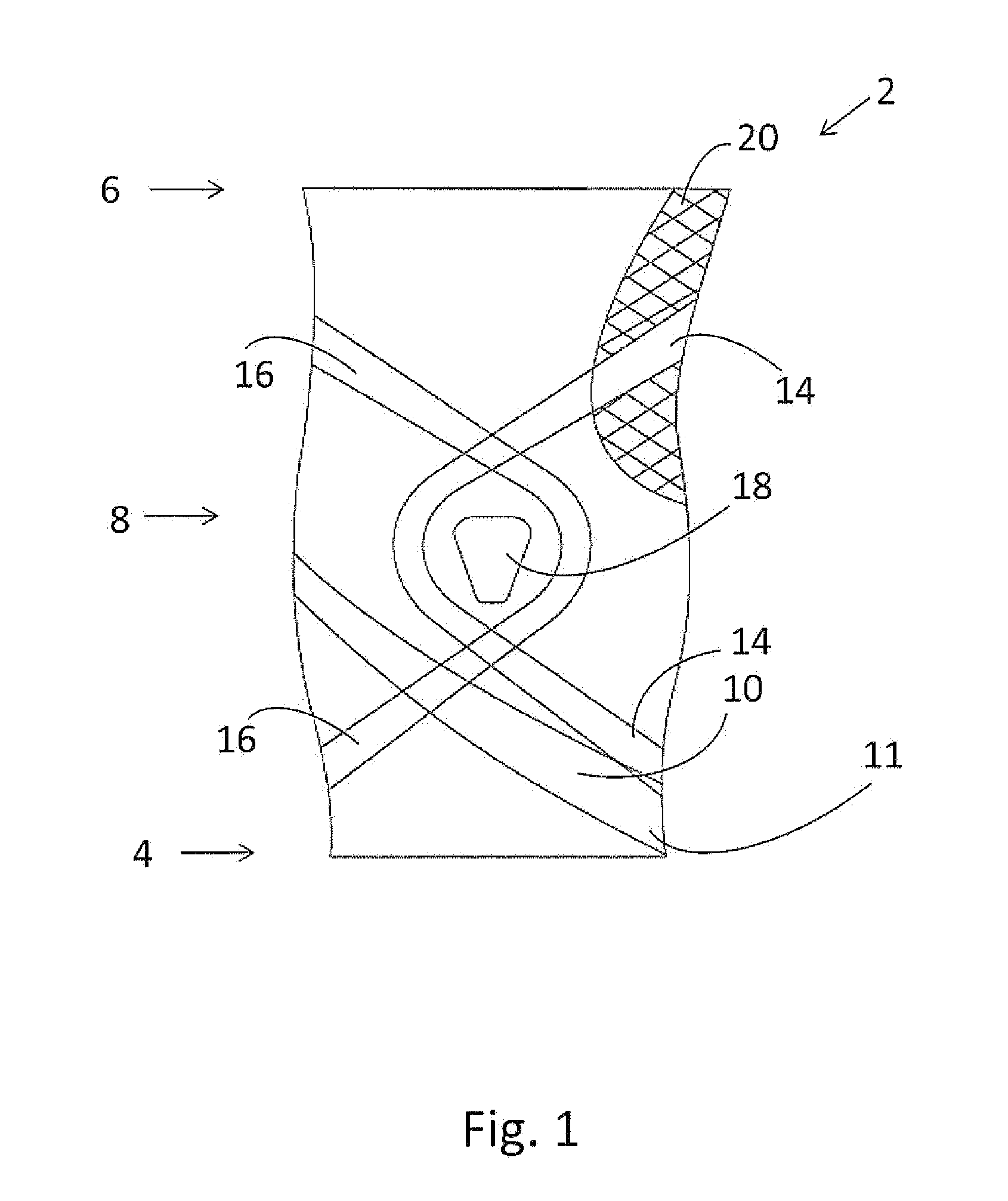
A garment for promoting dynamic alignment of a knee of a wearer, comprising a sleeve configured to substantially conform to the knee, upper calf and lower thigh of the wearer, a strap positioned on the sleeve so as to provide a tension to promote an outward turning of the knee during flexion and extension of the knee, and wherein when the sleeve and strap are in its operative positions, a first end of the strap is attachable at a first position of the sleeve and a second end of the strap is attachable to a second position of the sleeve where the first position is medial and inferior to the patella and the second position is superior of the popliteal area behind the knee, and wherein the strap extends from the first position to the second position across the patella or tibial tuberosity and lateral aspect of the knee.
Owner:COOPER RANDALL
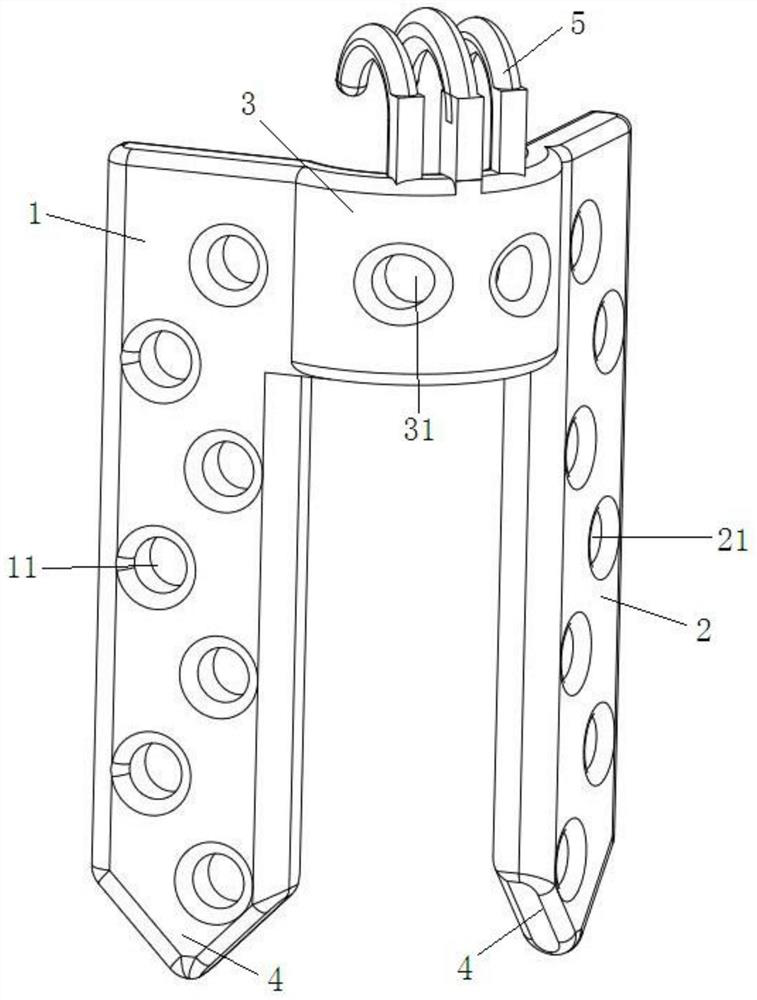
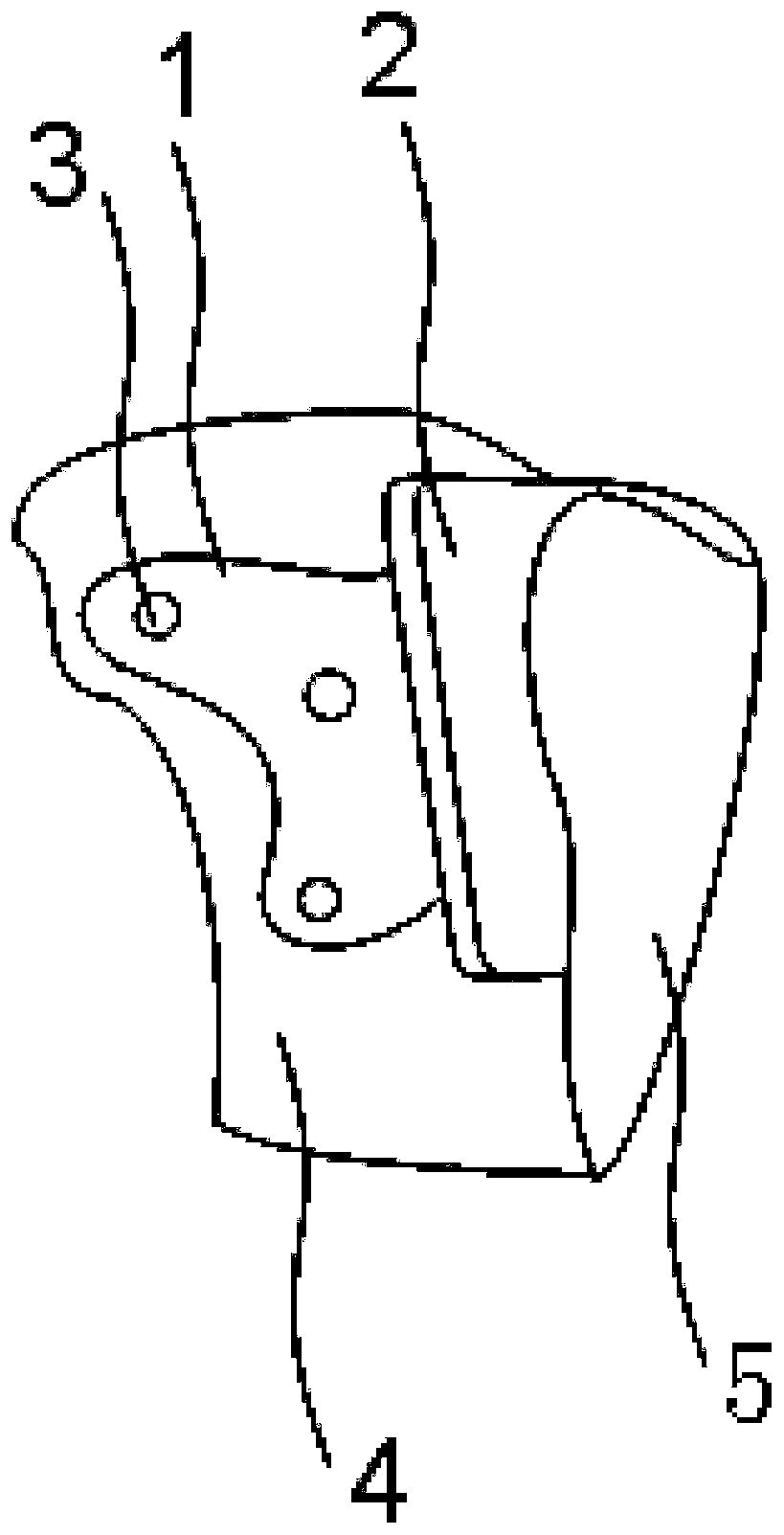
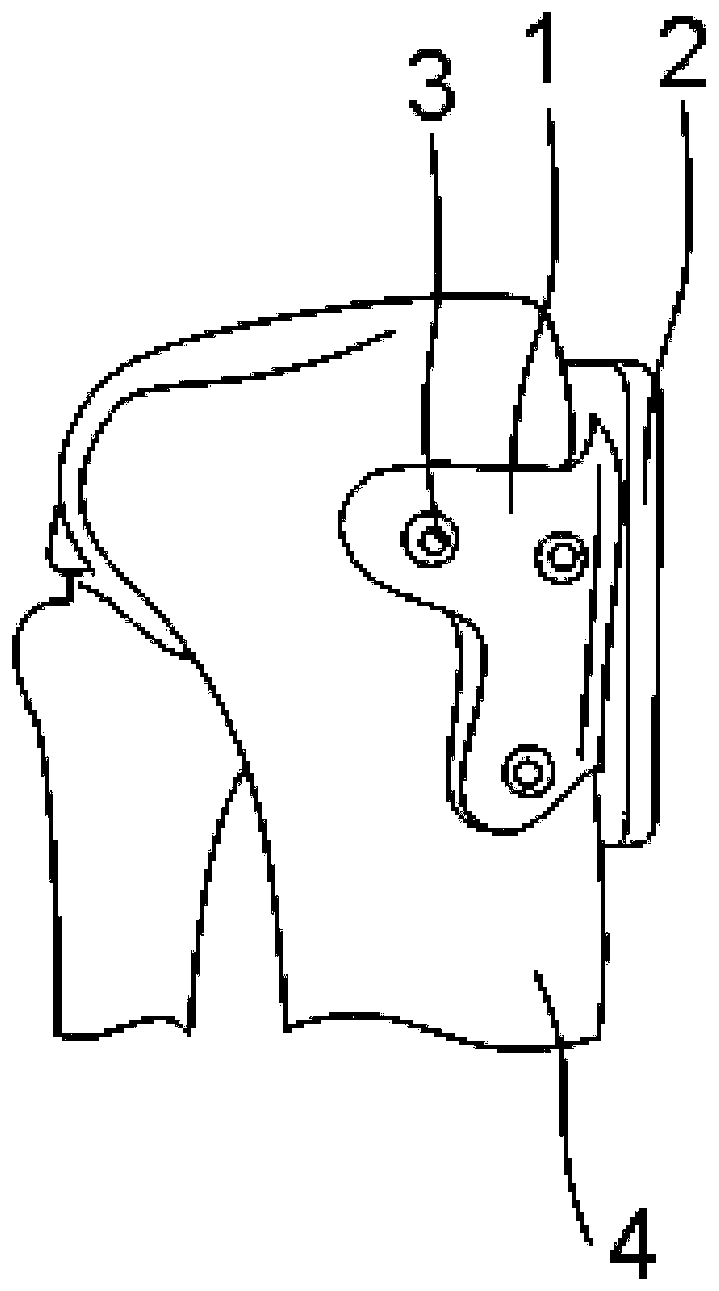
Fixing structure for tibial tuberosity fracture
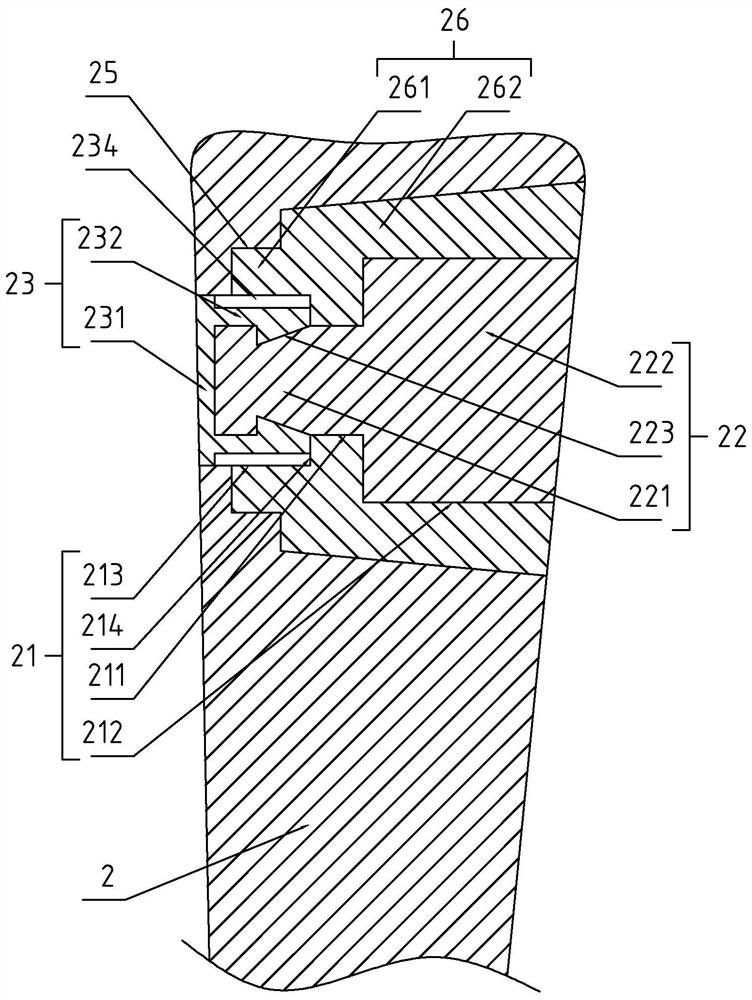
ActiveCN111904570AInhibition biasReduced bone hardness requirementsInternal osteosythesisFastenersTibial boneBone tissue
The invention provides a fixing structure for tibial tuberosity fracture. The fixing structure comprises a wrapping structure and a hooking structure, the wrapping structure is suitable for wrapping atibial tuberosity fracture block and bone tissues around the tibial tuberosity fracture block and is fixed by screws, and the hooking structure is fixedly arranged on the wrapping structure and is suitable for being hooked at the joint of the patellar ligament and the fracture block. According to the fixing structure, a wrapping method is adopted, the fracture block and bone tissues located around the fracture block are tightly wrapped after being reset and squeezed, and fixing is achieved through the multiple screws; after the hooking structure is arranged, the hooking structure is hooked atthe joint of the patellar ligament and the fracture block, the fracture block is prevented from being pulled to be deviated by the patellar ligament, and the force for resisting the patellar ligamentto pull the fracture block to be deviated comes from the whole wrapping structure instead of a single screw; and through the arrangement, excessive force is prevented from being applied to a single position of a bone, and the problem of comminuted fracture caused by fixing the fracture block can be avoided as much as possible. For patients with osteoporosis, the fixing structure can also be adopted according to conditions.
Owner:青岛山大齐鲁医院(山东大学齐鲁医院(青岛))
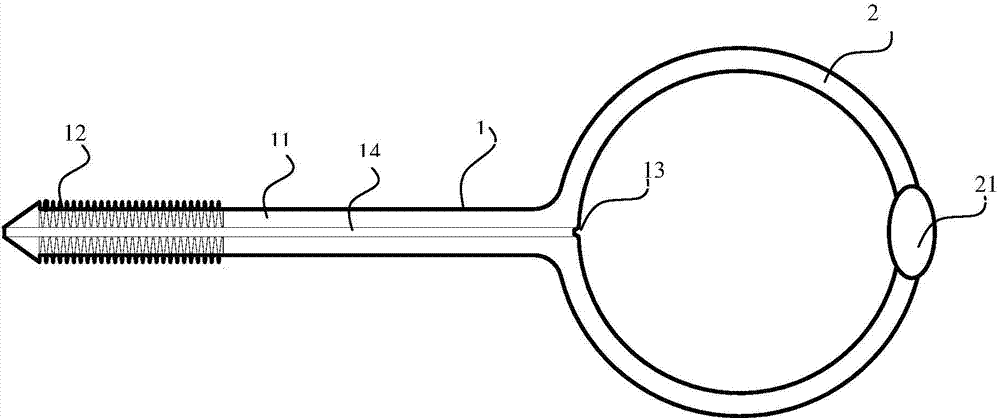
Tractor for greater trochanter of femur
InactiveCN104771215AEasy to useSimple structureExternal osteosynthesisSoft tissue infectionKnee Joint
The invention discloses a tractor for the greater trochanter of the femur, which comprises a pulling screw and a traction ring, the pulling screw is provided with a transverse passage through which a guide needle can pass, the traction ring is connected with the end of the pulling screw, and the longitudinal height of the traction ring is greater than the diameter of the pulling screw. The tractor for the greater trochanter of the femur provided by the invention has a simple and ingenious structure, is convenient to use, is applicable to cases such as the displaced pelvic ring fracture, the central dislocation of the hip joint and old posterior hip joint dislocation accompanied by fractures around the knee joint or skin and soft tissue infection around the knee joint, and also is suitable for continued traction when the traction of the tubercle of the tibia is too long, traction screws are loose or screw holes are infected and the traction screws have to be replaced.
Owner:JINSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
Tibial tuberosity advancement implant
A tibial tuberosity advancement implant and method includes a spacer body made of biocompatible, biodegradable material and having a main section with at least one bony growth orifice therethrough and a proximal slot and at least one fin extending from the main section by at least one connector. A metal clip is slideable into the proximal slot of the spacer body main section and includes spaced screw holes for securing the spacer body to the advanced tibial tuberosity and the tibia when the implant is placed in the space between the advanced tibial tuberosity and the tibia.
Owner:MWI VETERINARY SUPPLY
Adapted compression/splint orthosis for reinforcement of the calf musculoaponeurotic pump
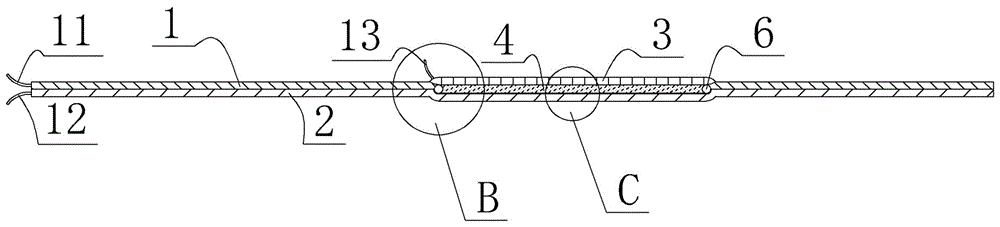
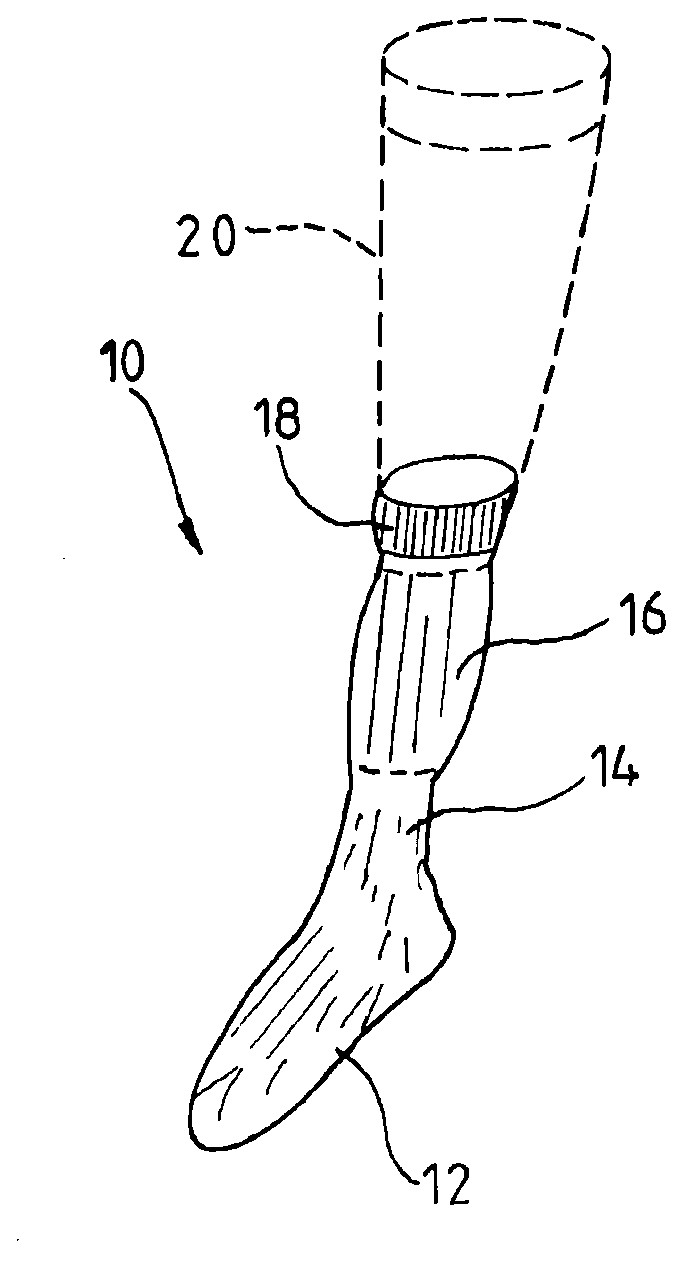
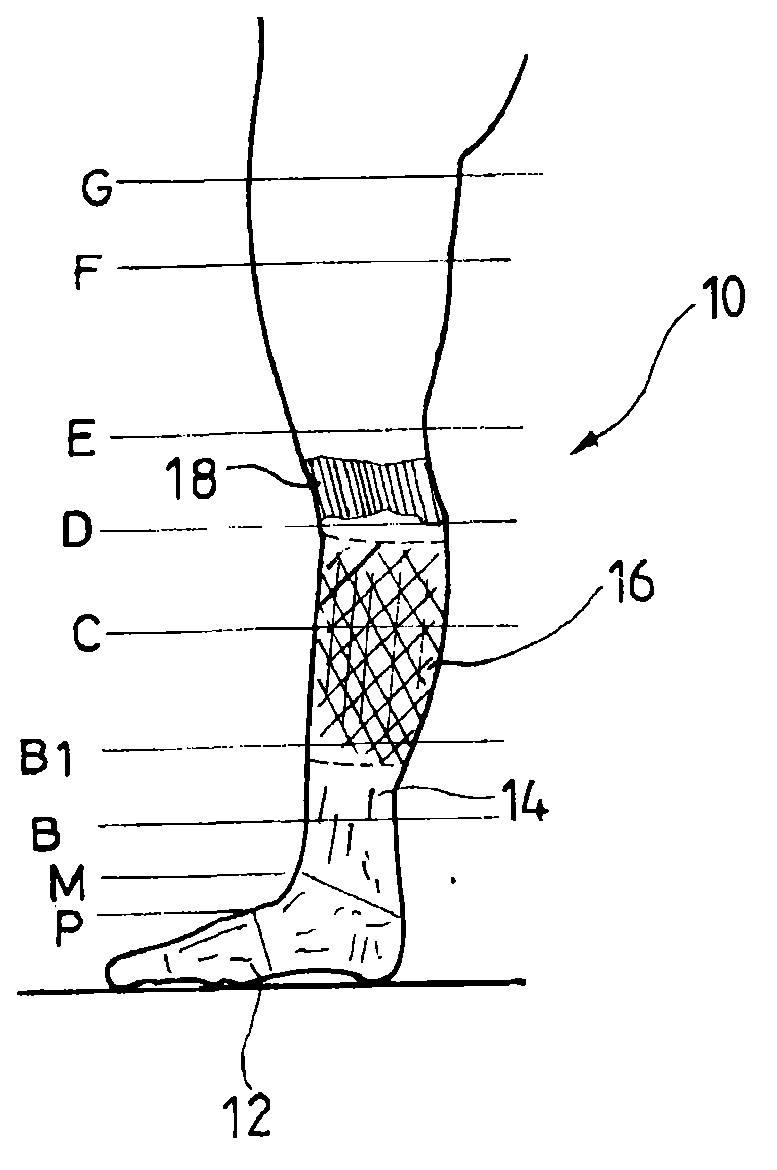
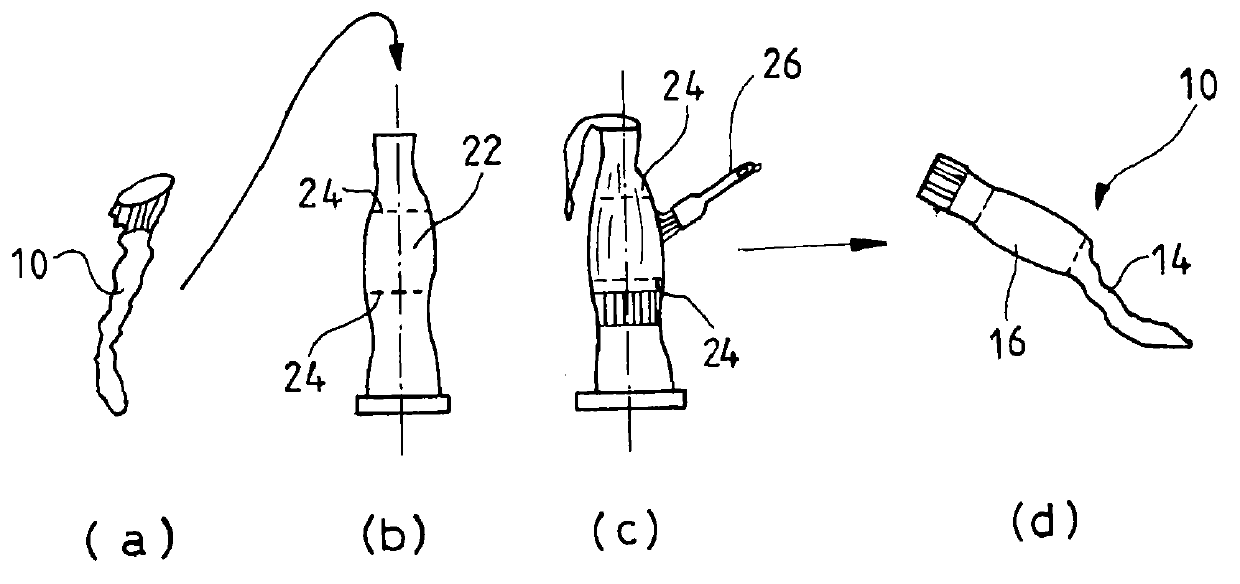
The orthosis (10) is related herein and comprises an elastic compressive distal portion (14), extending upwards from the ankle, associated with an adjacent rigid splint proximal portion (16), enveloping the region of the calf comprised between the level of the point where the Achilles tendon joins the calf muscles and the level located below the tibial tuberosity. This rigid splint proximal portion (16) is an essentially non-elastic, deformable tubular portion, made by: placing the orthosis onto a template representative of the morphology of the patient's calf; applying in situ on the orthosis, in the region of the splint proximal portion, a hardenable biocompatible resin; hardening the resin with the orthosis maintained on the template; and removing the orthosis in its finished state.
Owner:INNOTHERA TOPIC INT
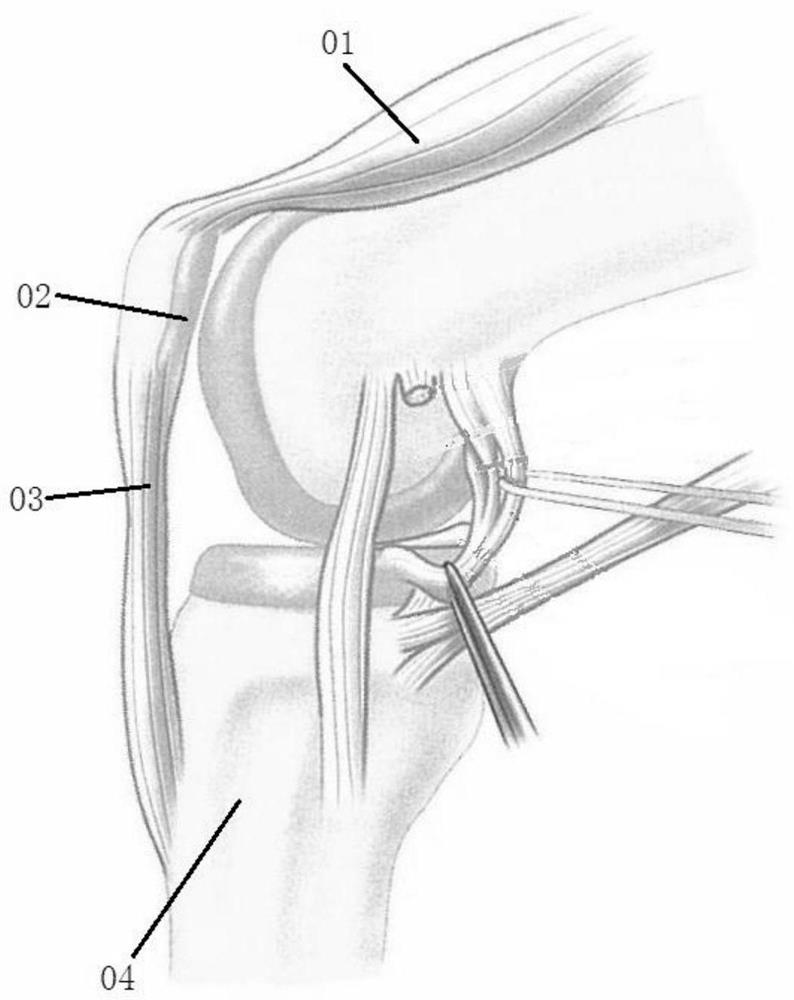
3D printing personalized anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction tibial tunnel positioner and preparation method thereof
PendingCN110192916AHigh precisionImprove surgical efficiencySurgerySurgical incisionTibial tuberosity
The invention relates to a 3D printing personalized anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction tibial tunnel positioner and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the technical field of an arthroscopic surgery. The positioner is personalized according to the preoperative CT and MRI data of a patient, and printing and molding can be quickly performed by a 3D printer, and the anterior cruciateligament tunnel can be accurately positioned through a minimally invasive surgical incision of an arthroscope. The positioner includes a bone fitting portion, a slotted positioning tube and a slot cover: the bone fitting portion adopts contact fit positioning design of a tibial tuberosity and a tibia inner side, and a positioning point of the positioning tube is personalized according to the patient's preoperative three-dimensional reconstruction data, the side of the positioning tube has a notch to facilitate the removal of the positioner after a Kuntscher needle is inserted, and a baffle plate fits with the notch of the positioner to reduce the Kirkner needle insertion error. The personalized anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction tibial tunnel positioner structure is simple and novel, and is suitable for personalized anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction and anterior cruciate ligament revision.
Owner:FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF KUNMING MEDICAL UNIV
Tibial tuberosity advancement cage for ACL injuries
Methods and implants to treat anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries are disclosed. The methods involve advancing the insertion of the patellar tendon to the proximal tibia by means of a partial osteotomy and a wedge-shaped cage (30). The wedge-shaped cage is specifically designed to facilitate transfer of not only compressive loads, but also of shear loads due to pull by the patellar tendon at its insertion to the tibial tuberosity. The cage decreases the angle between the patellar tendon and the common tangent plane formed by the condyles of the femur and the condyles of the tibia (sometimes called tibial plateau) and consequently modifies the internal joint force, restoring stability to the joint even if the ACL is ruptured. The methods and implants are applicable to both human and canine patients.
Owner:KYON
Knee joint tibial plateau prosthesis
ActiveCN111374804AGuaranteed ImplantationAvoid stress spreadLigamentsJoint implantsKnee JointPatellar ligament
The invention provides a knee joint tibial plateau prosthesis. The prosthesis comprises a tibial plateau prosthesis and a tibial tubercle prosthesis, wherein the tibial tubercle prosthesis is arrangedat tibial tubercle of the tibial plateau prosthesis, the part, bulging out of tibial plateau prosthesis, of the tibial tubercle prosthesis is of a bone trabecula structure, a placement groove which is arranged in a concave manner and used for connecting the tibial tubercle to a patellar tendon free lower bone block at a patellar tendon stop point is formed in the bone trabecula structure, a solidcross beam with a smooth surface is arranged at a groove opening of the placement groove in a spanning manner, the cross beam and the bone trabecula are integrally arranged, and patellar ligament suture holes are symmetrically formed in the prosthesis on two sides of the cross beam, wherein the placement groove can provide a back implantation space for the patellar tendon free lower bone block toensure that the patellar ligament is completely implanted in the tibial plateau prosthesis, the patellar ligament can be integrally wound and fixed through the cross beam, stress dispersion of the patellar ligament can be avoided, the cross beam and the bone trabecula structure are integrally arranged, and looseness of the cross beam under long-term telescoping drive of the patellar ligament is further avoided.
Owner:BEIJING CHUNLIZHENGDA MEDICAL INSTR
Tibia node traction device with rotation massage function
PendingCN106963536AAvoid pressure soresPromote circulationRoller massageFractureHuman bodyPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention discloses a tibia node traction device with a rotation massage function. The device comprises a fixing frame (18) which is used for placing patient legs (5); a track box (19) is arranged on the lower portion of the fixing frame (18), an elongated slot which is located on the lower portion of the axis of the fixing frame (18) is formed in bottom of the track box (19), tracks are arranged on two sides of the elongated slot, a walking car (16) is arranged on each track, a motor (17) is arranged on the walking car (16), a motor shaft (20) extends upwards, over the fixing frame (18), and is connected to a massage cushion (14), the motor drives the massage cushion (14) to rotate, and massage contacts which are contact with human body are densely arranged on the top of the massage cushion (14). According to the tibia node traction device, pressure sores in a patient crus heelpiece can be avoided, the continuous massage for patients can be achieved through the massage cushion, and the patient recovery is improved.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZUNYI MEDICAL COLLEGE
Oral traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating epiphysitis of tibial tuberosity
InactiveCN103990070AMedicinal and calmGood curative effectAnthropod material medical ingredientsSkeletal disorderSide effectRHODIOLA ROSEA ROOT
The invention discloses an oral traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating epiphysitis of tibial tuberosity. The oral traditional Chinese medicine composition is prepared from the following medicinal raw materials: radix pseudostellariae, rhodiola rosea, radix dipsaci, semen cuscutae, radix achyranthis bidentatae, hypericum sampsonii hance, corydalis tuber, radix curcumae, coix seed, selfheal and bombyx batryticatus. The oral traditional Chinese medicine composition provided by the invention is used for treating the epiphysitis of tibial tuberosity and in line with the physiological characteristics of immature yin and yang of children and has a good curative effect, a small side effect and high compliance of sick children.
Owner:褚立旺
Osteotomy guide plate in operation of precisely treating tibial tuberosity introversion and application of osteotomy guide plate
The invention discloses an osteotomy guide plate in an operation of precisely treating tibial tuberosity introversion, includin a fixing part and an osteotomy plane. The fixing part and the osteotomyplane are fixed at a certain angle; the fixing part is provided with a curved surface matched with the outer contour of the tibia; at least three pre-drilled holes which are not located on the same straight line are formed in the fixing part and are fixed to the tibia through hollow rivets. And the osteotomy plane is arranged between the tibia and the osteotomy block to form an osteotomy operationarea. By means of a 3D printing osteotomy guide plate technology, the artificial error caused by an operation is reduced, the osteotomy position and the osteotomy depth are more accurate, and the osteotomy inward movement distance is more accurate; the 3D printing osteotomy guide plate helps simplify the operation process, improve the operation efficiency, shorten the operation time and reduce the trauma to a patient, and is beneficial to postoperative recovery; and generally speaking, the 3D printing osteotomy guide plate is more accurate, individualized and safer for use.
Owner:蔡秋晨
External fixing frame
The invention discloses an external fixing frame. The external fixing frame comprises a traction plate and a traction needle fixedly connected with the traction plate, and further comprises a thread transmission mechanism which is fixedly connected with the traction needle and drives the traction needle to move in the axial direction. When the external fixing frame is used, a periosteum is stripped under a tibia tuberosity of a patient, a small bone block is cut out, the periosteum on the surface of a tibia is protected, firstly, the traction plate is arranged between the cut tibia bone block and the periosteum on the surface of the tibia, then, the traction needle is connected with the traction plate and the bone block, finally, the thread transmission mechanism drives the traction needle to move in the axial direction of the traction needle. Therefore, by driving the traction needle and the traction plate to move, the periosteum is pulled while the bone block is pulled, so that vasculature neogenesis at a shank part can be promoted, neovasculature can be established, nutrient blood at the shank part can be increased, and then natural healing of a diabetic foot wound surface is promoted.
Owner:THE FIRST HOSPITAL OF HUNAN UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE (CLINICAL RES INST OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE)
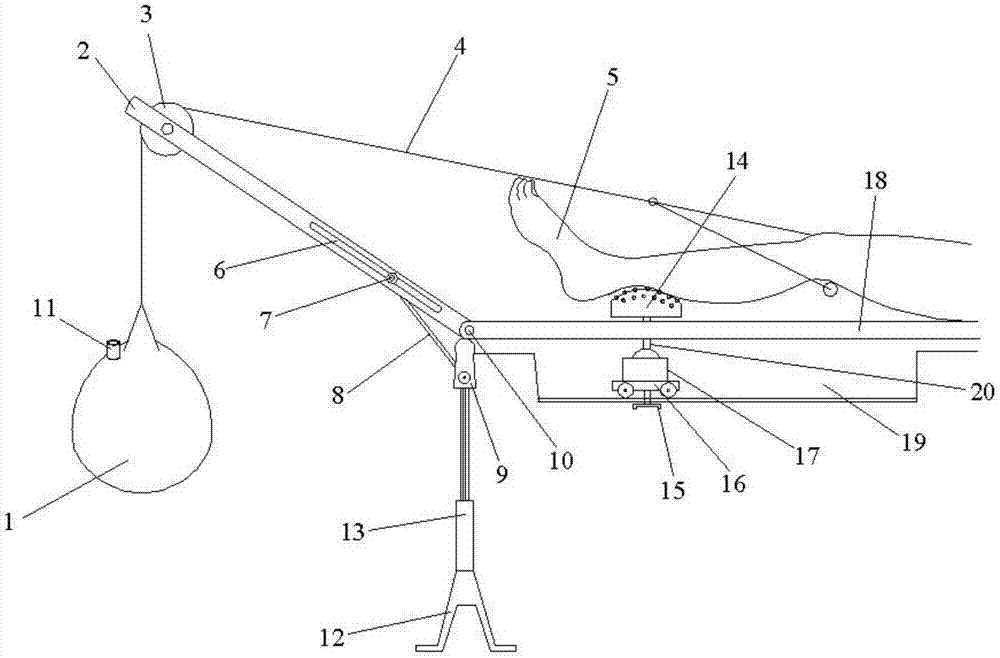
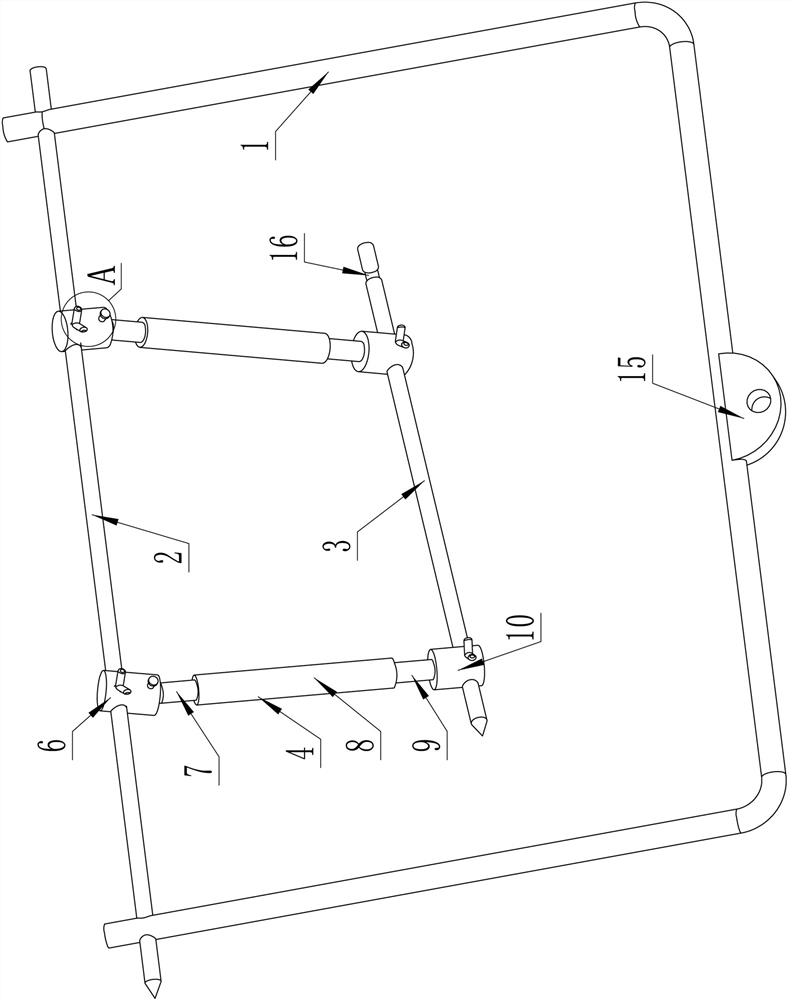
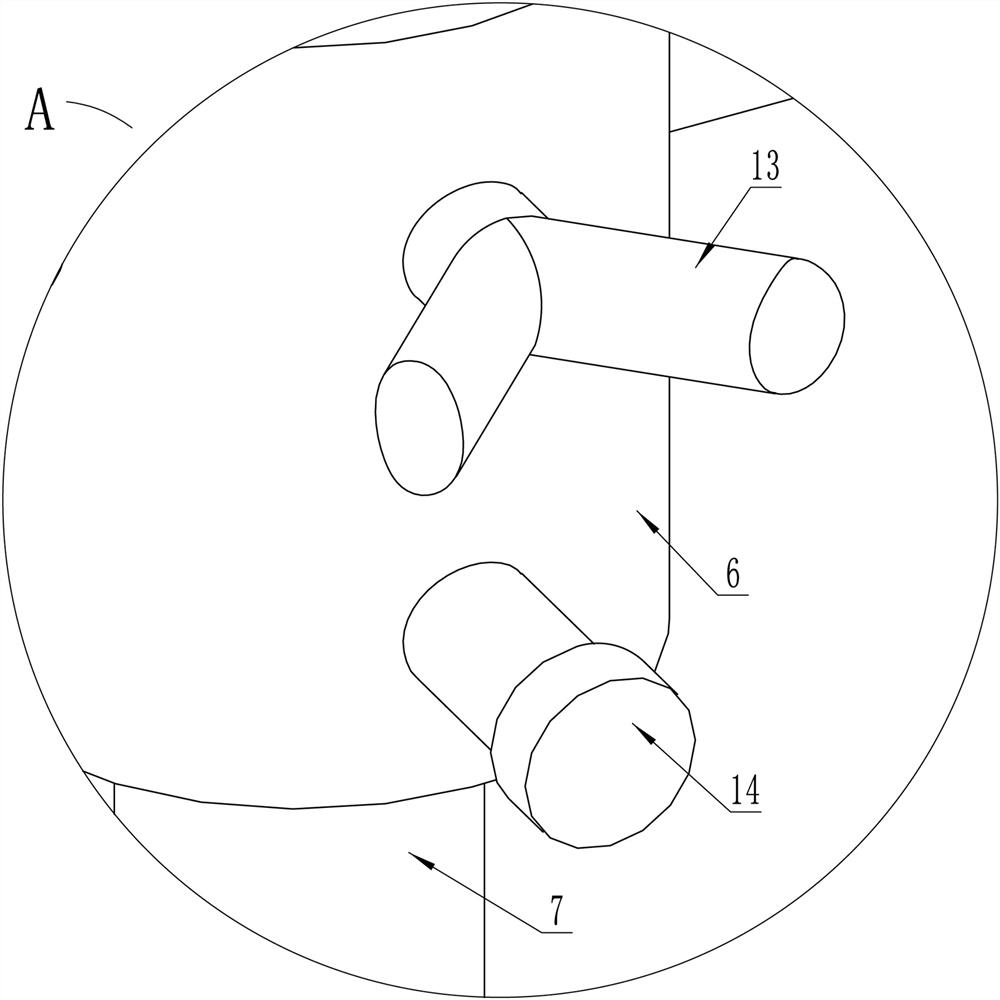
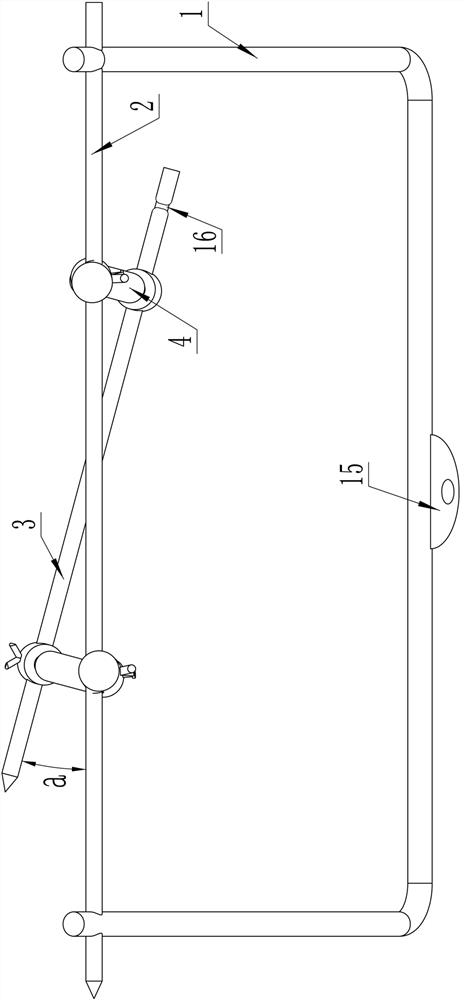
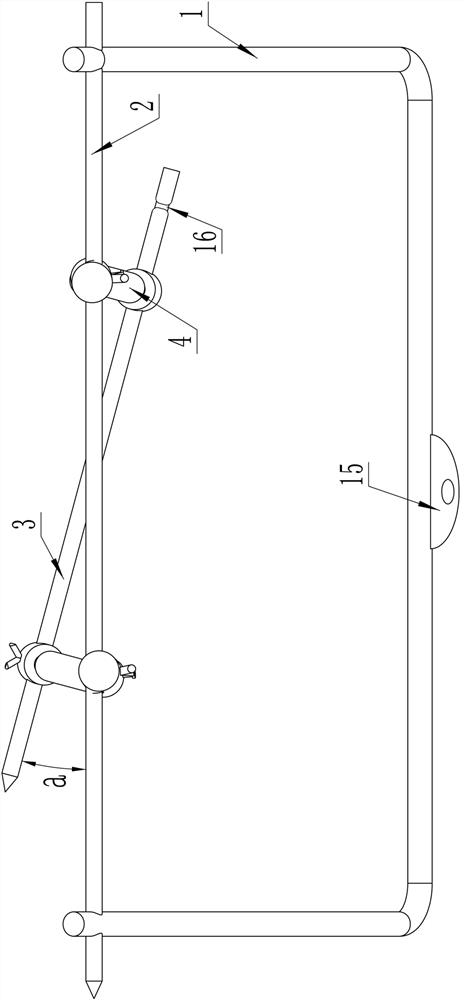
A tibial tubercle traction device for patients with osteoporosis
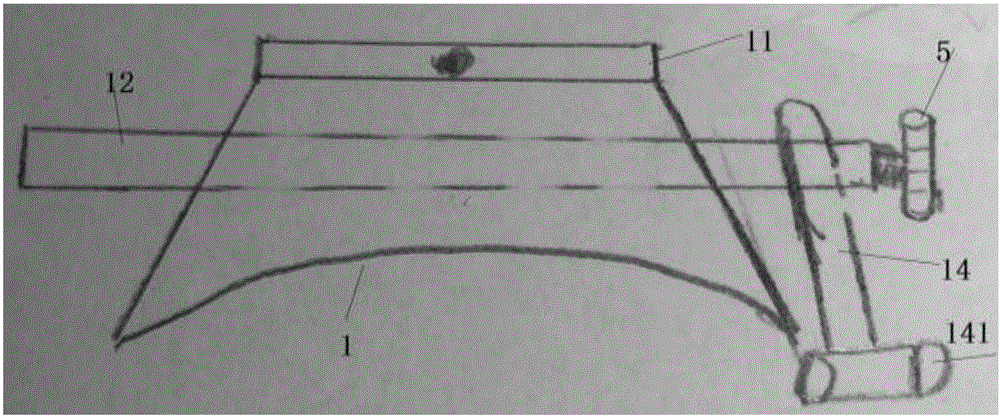
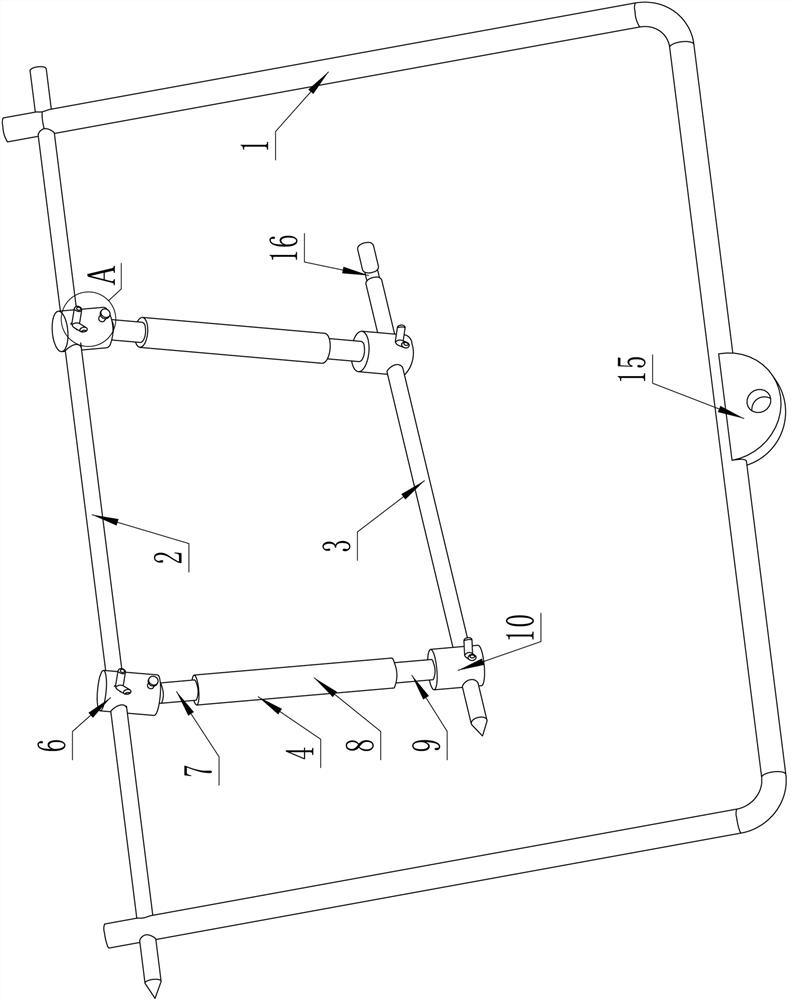
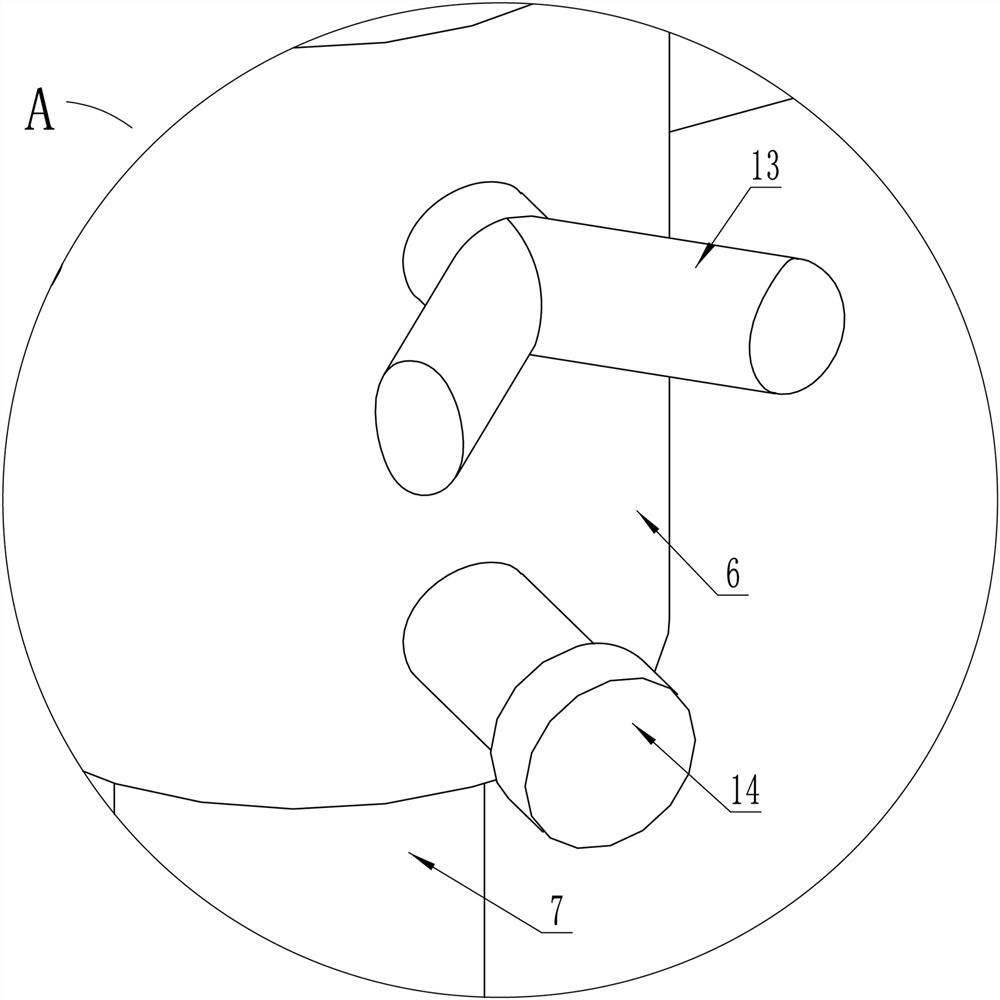
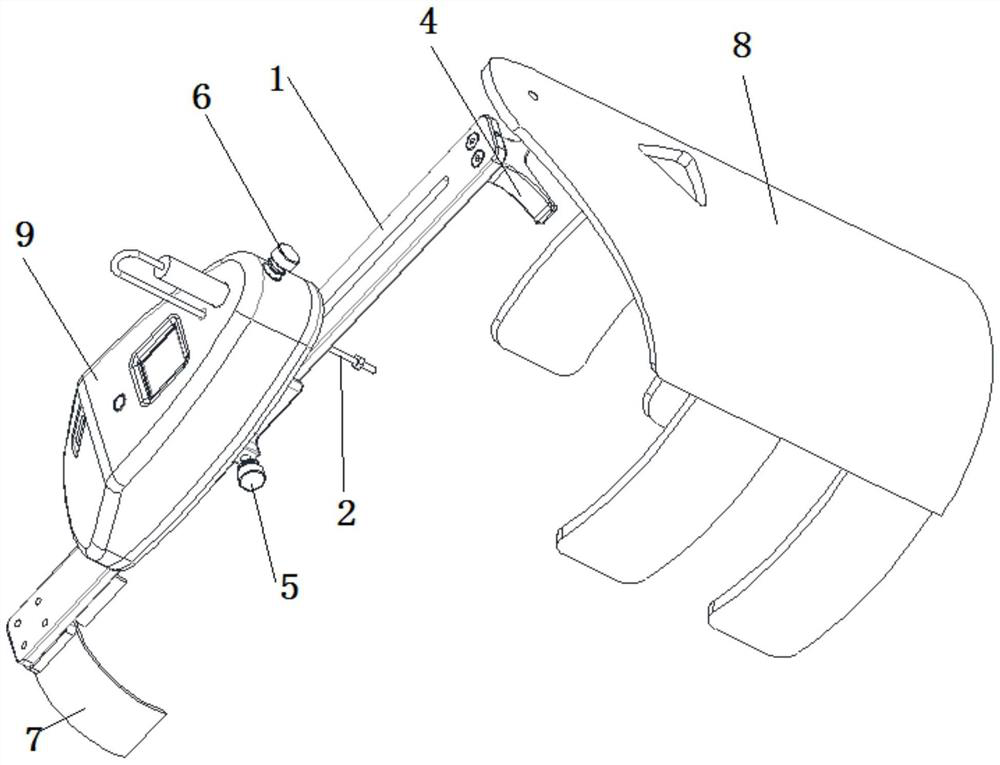
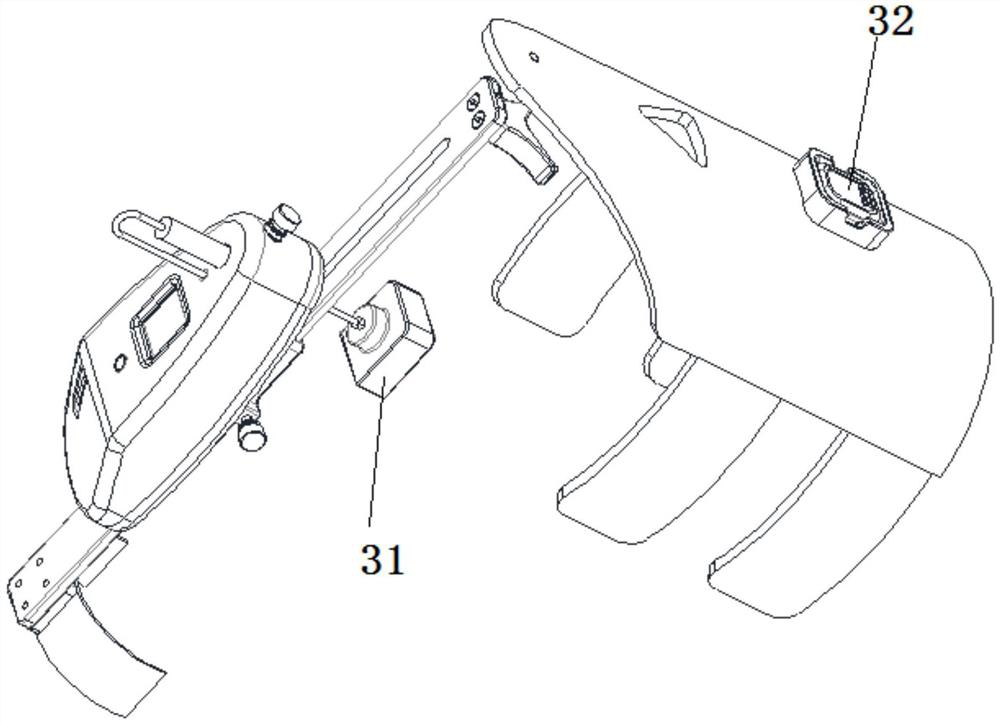
ActiveCN112137704BAdjustable lengthSolve the problem of difficult installationExternal osteosynthesisEngineeringTibial tuberosity
The present invention relates to a tibial tuberosity traction device for patients with osteoporosis, which comprises a traction arch, a first traction pin and a second traction pin; the second traction pin is arranged below the first traction pin, and A traction needle is arranged crosswise in the horizontal direction to form a preset horizontal angle a; the traction bow is connected to the first traction needle, and an adjustable length is provided between the first traction needle and the second traction needle. There are two adjustment rods; the adjustment rod is provided with a universal ball, and the adjustment rod is rotatably connected with the first traction needle and / or the second traction needle through the universal ball. The invention has the advantages of simple structure, reasonable design and convenient use, is suitable for patients with osteoporosis, can prevent the loosening of traction needles, relieve pain of patients, and enhance the traction effect.
Owner:山西白求恩医院
Novel tibial tuberosity traction model
PendingCN111951653AEasy to useUnderstanding Traction EffectsCosmonautic condition simulationsEducational modelsHuman anatomyHuman body
Owner:王俊杰
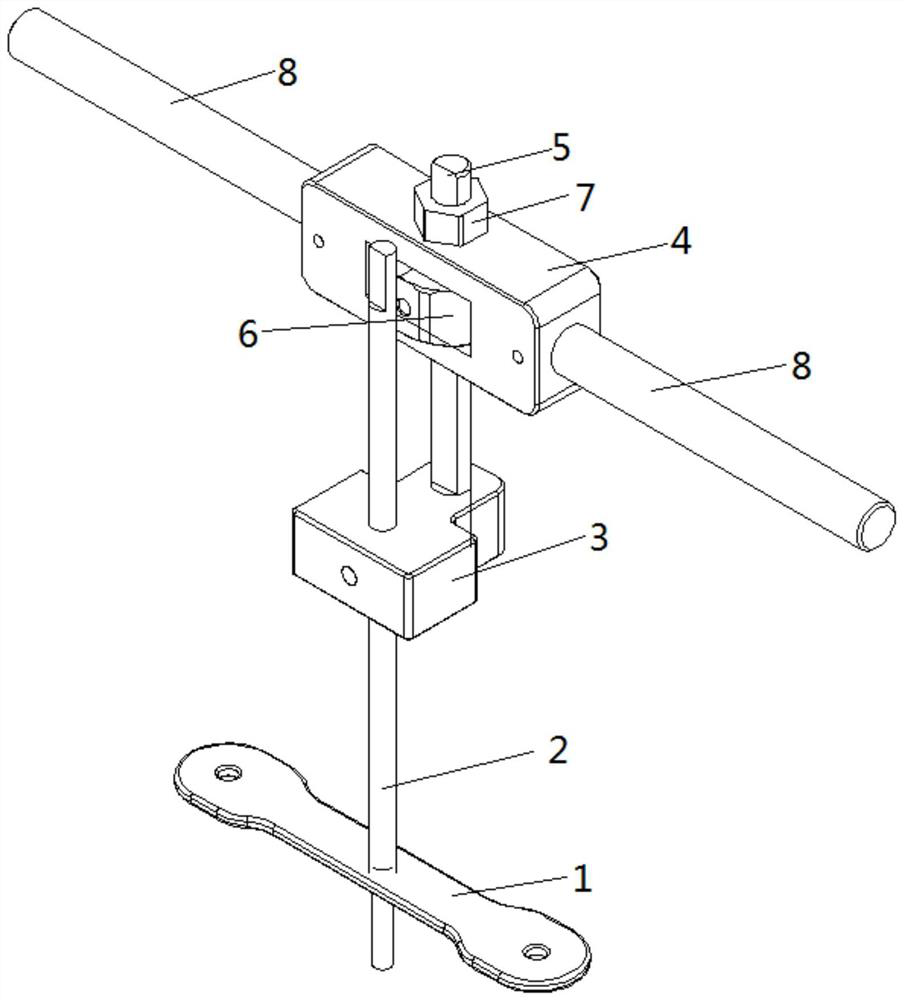
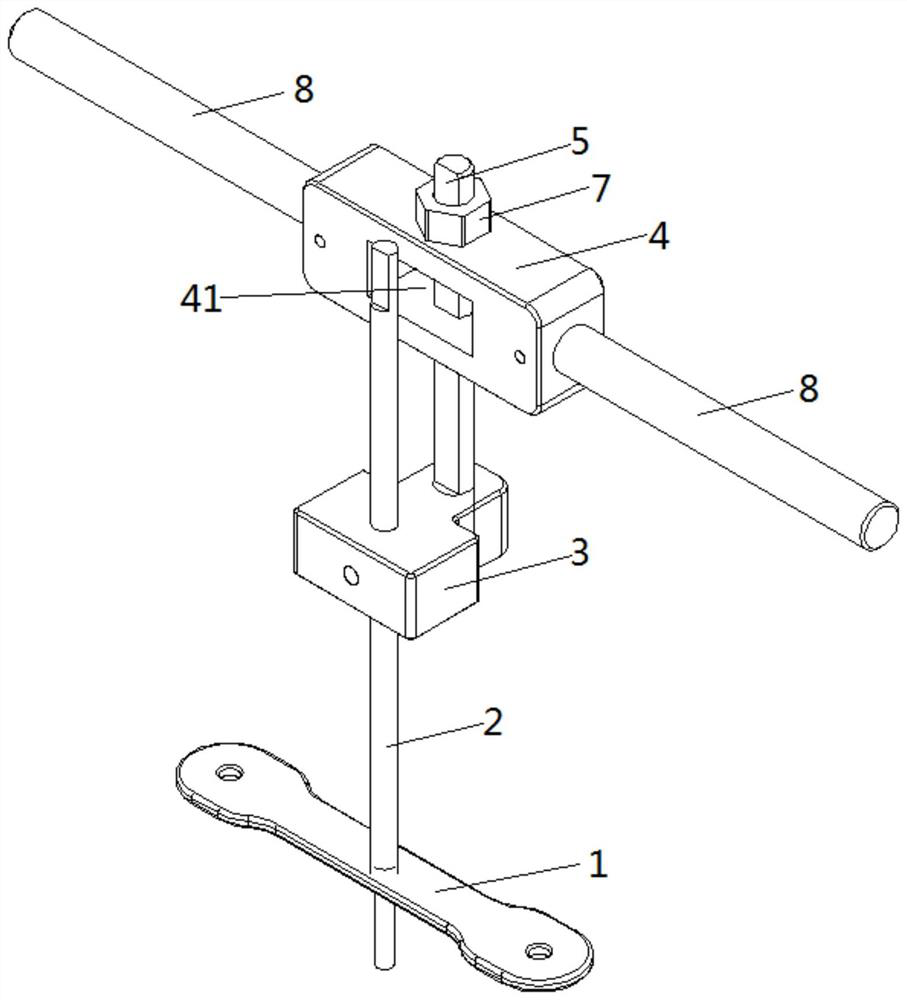
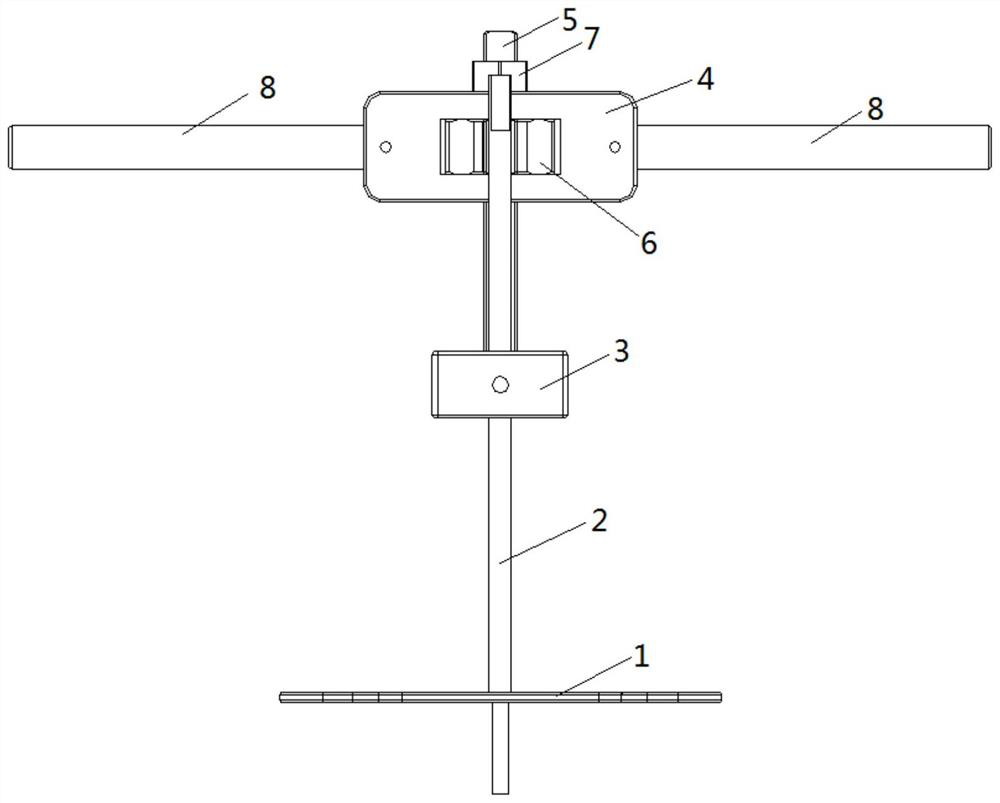
Tibial tuberosity traction nail embedding guider
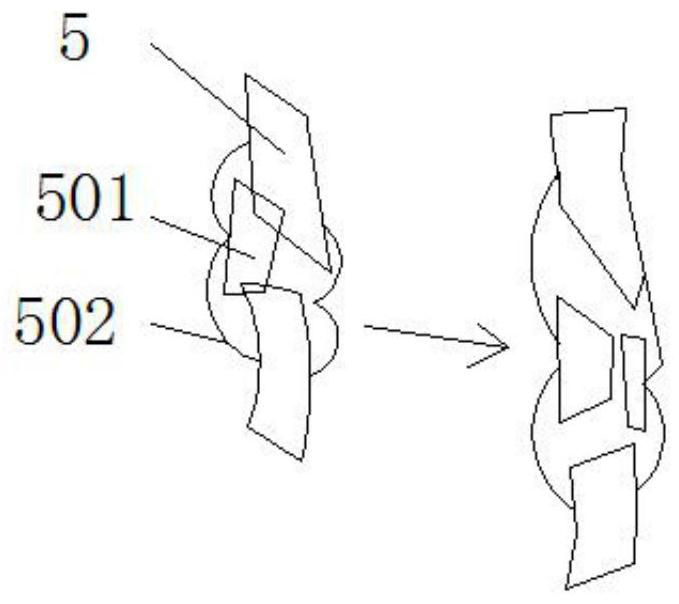
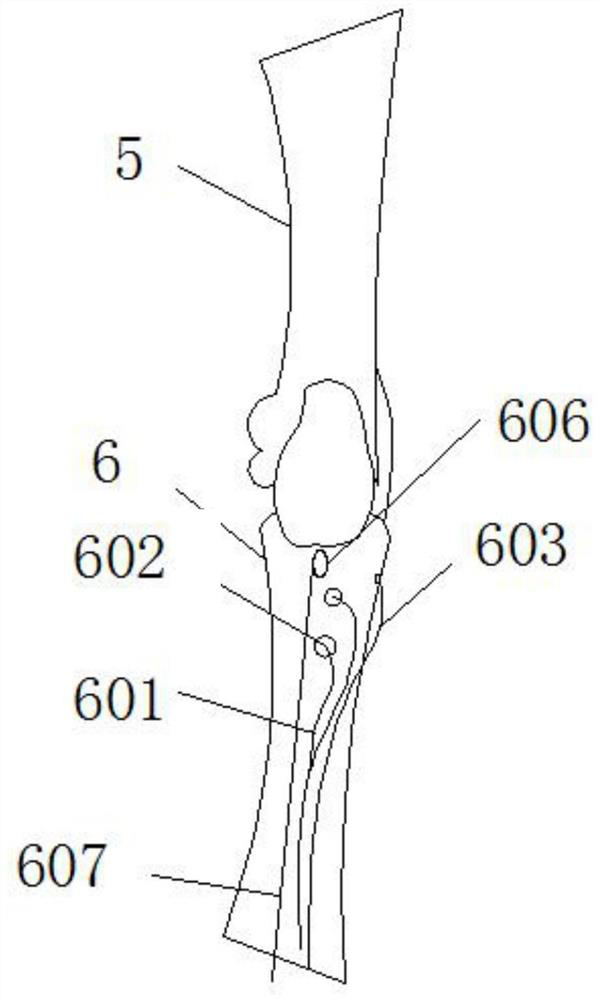
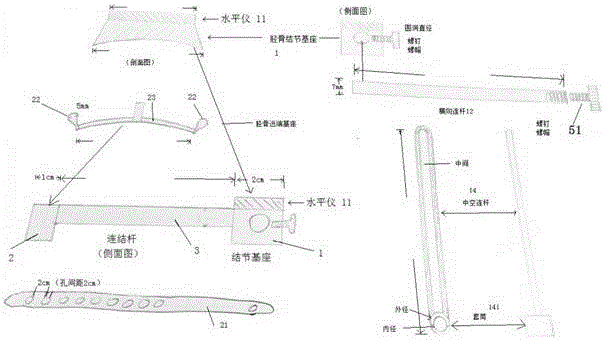
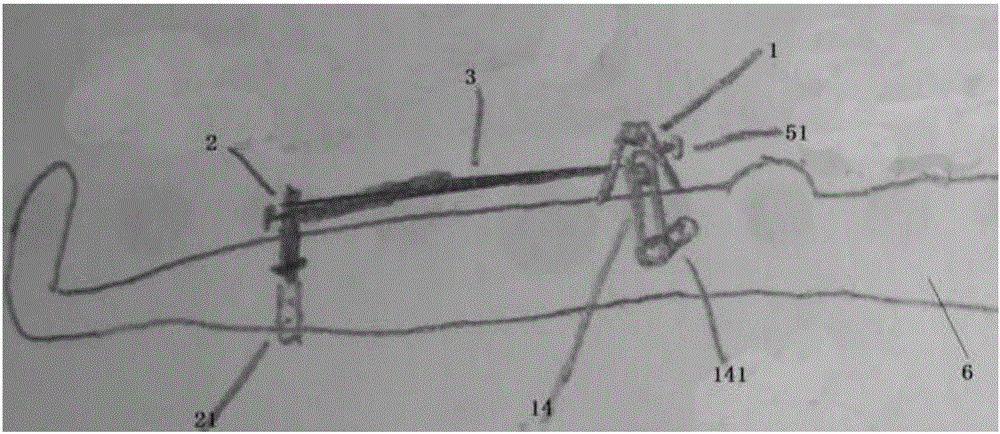
ActiveCN106037924AGuaranteed to be verticalInstruments for stereotaxic surgeryOsteosynthesis devicesForce linesPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention discloses a tibial tuberosity traction nail embedding guider, comprising a tibial tuberosity base, a tibial distal base and a connecting rod, wherein the tibial tuberosity base and the tibial distal base are fixed on the tibial crest separately, and form a force line support by the connecting rod. The force line support is parallel to the tibial crest; the tibial distal base is a fixing device; the tibial tuberosity base comprises a visual level, a horizontal hole, a horizontal connecting rod and a hollow connecting rod; the visual level is installed on the top of the tibial tuberosity base and used for checking the precise position of a nail during nail embedding; the horizontal hole is a horizontal through hole of the tibial tuberosity base; the horizontal connecting rod can freely slide in the horizontal hole and keeps perpendicular to the force line support; and when fixation is needed, the horizontal connecting rod is fixed at the horizontal position of the tibial tuberosity base by a fixing bolt in the horizontal hole. Finally, an optimal and perfect nail path that the traction nail is perpendicular to the tibia in the longitudinal direction and parallel to the tibia in the horizontal direction can be obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI YANGPU CENT HOSPITAL
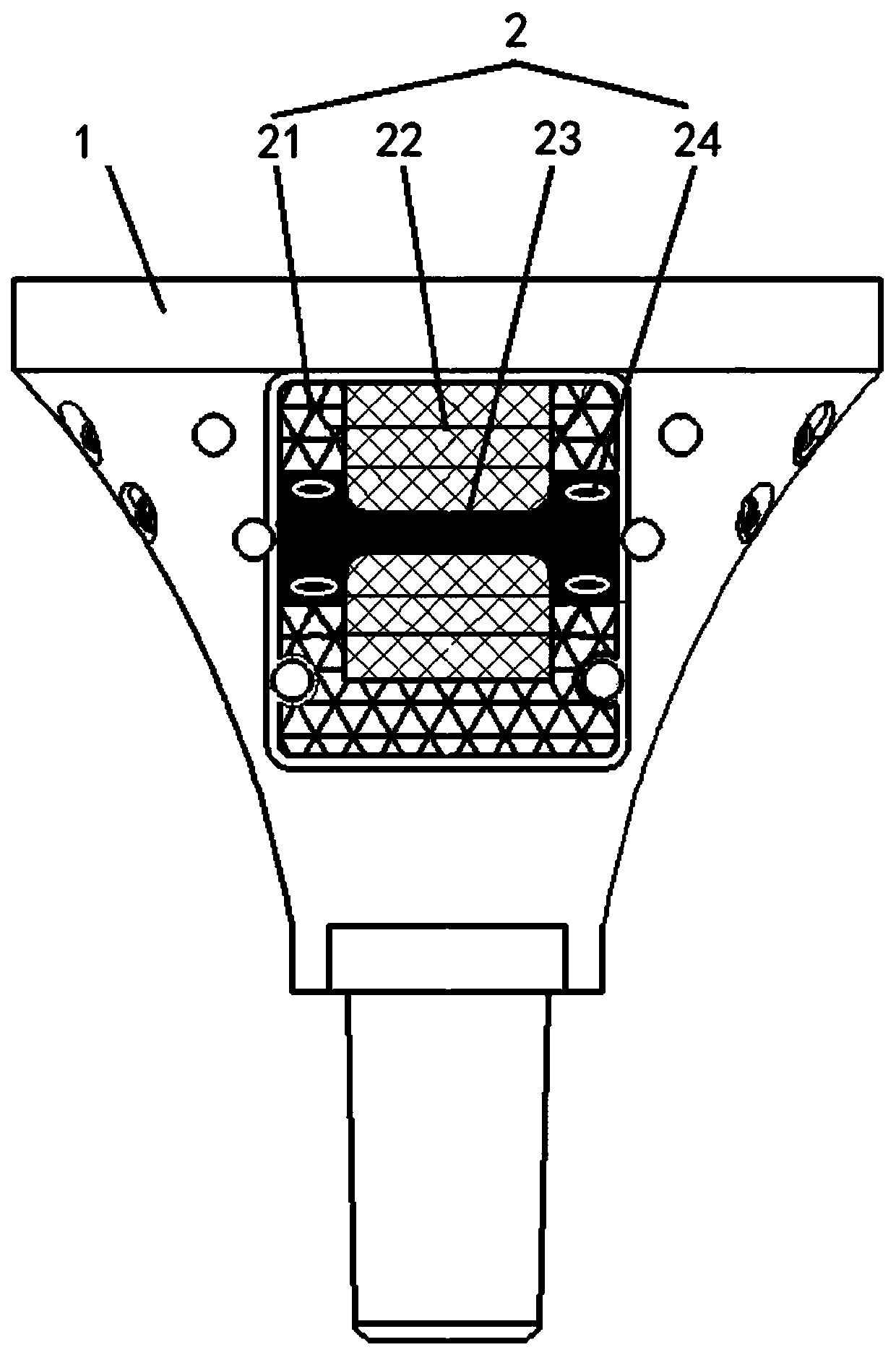
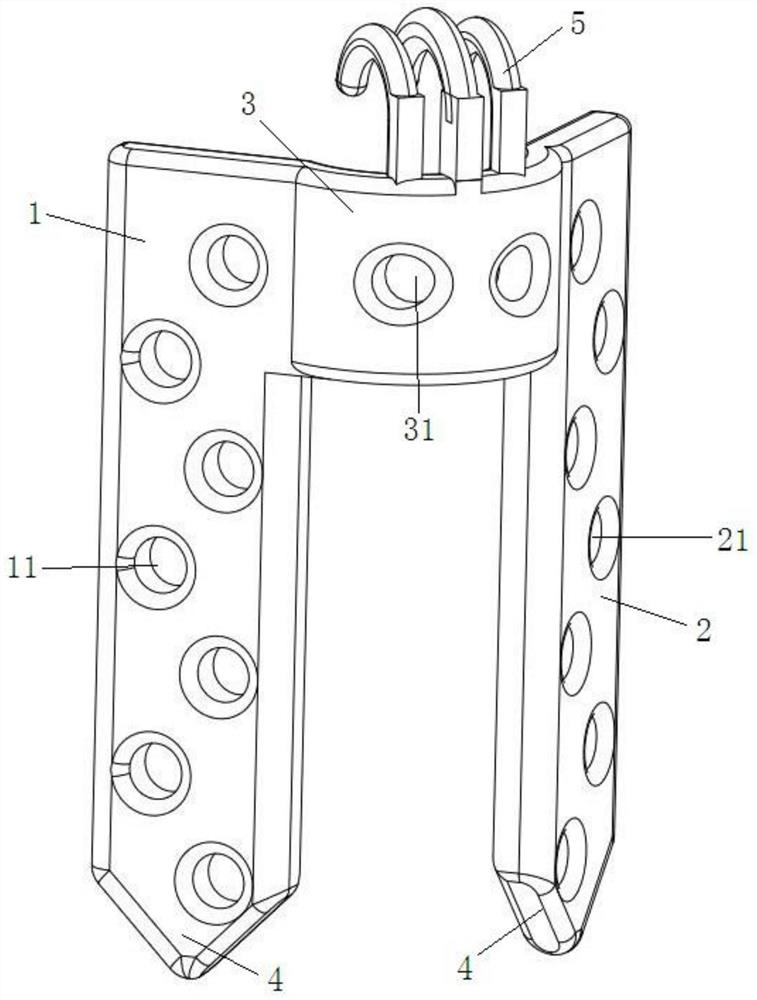
Tibial tubercle bone fracture plate and use method thereof
A tibial tubercle internal fixation bone fracture plate comprises a central part (1), a head part (2), side parts (3) and a tail part (4), and is characterized in that the central part (1) is matchedwith the front part of a tibial tubercle and is provided with 2.4 mm or 2.7 mm locking holes or pressurizing holes, screw holes are uniformly distributed, and locking screws or cortical bone screws can be placed in the screw holes; the upper part of the central part (1) is connected with two thin plates of the head part (2), the thin plates are parallel left and right and are respectively providedwith 2.4 mm or 2.7 mm locking holes or pressurizing holes, and locking screws or cortical bone screws can be placed in the locking holes or the pressurizing holes; the two sides of the center part (1) are each provided with two side part (3) thin plates, the thin plates on the two sides are parallel to each other up and down and are provided with 2.0 mm locking holes or 2.0 mm pressurizing holes,and locking screws or cortical bone screws can be placed in the locking holes or the pressurizing holes; and the tail end of the central part (1) is provided with three thin plates of the tail part (4), which are mutually dispersed towards the far end and are respectively provided with 2.4 mm or 2.7 mm locking holes or pressurizing holes, and locking screws or cortical bone screws can be placed in the locking holes or the pressurizing holes.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Tibial tuberosity traction device for osteoporosis patient
ActiveCN112137704AAdjustable lengthSolve the problem of difficult installationExternal osteosynthesisEngineeringTibial tuberosity
The invention relates to a tibial tuberosity traction device for an osteoporosis patient. The tibial tuberosity traction device comprises a traction bow, a first traction needle and a second tractionneedle. The second traction needle is arranged below the first traction needle and is crossed with the first traction needle in the horizontal direction to form a preset horizontal included angle a. The traction bow is connected with the first traction needle, and two adjusting rods with the adjustable length are arranged between the first traction needle and the second traction needle. Universalballs are arranged on the adjusting rods, and the adjusting rods are rotatably connected with the first traction needle and / or the second traction needle through the universal balls. The tibial tuberosity traction device is simple in structure, reasonable in design, convenient to use, suitable for osteoporosis patients and capable of preventing the traction needle from loosening, relieving pain ofthe patients and enhancing the traction effect.
Owner:山西白求恩医院
A fixation structure for tibial tuberosity fracture
ActiveCN111904570BInhibition biasReduced bone hardness requirementsInternal osteosythesisFastenersTibial boneBone tissue
The present invention provides a fixation structure for tibial tubercle fractures, comprising: a wrapping structure, suitable for wrapping tibial tubercle fracture fragments and surrounding bone tissue, and fixed by screws; a hook structure, fixedly arranged on the wrapping structure, suitable for The hook hangs at the junction of the patellar ligament and the fracture fragment. The fixation structure of the present invention adopts a wrapping method to reset and squeeze the bone tissue around the fracture block and wrap it tightly, and fix it by using several screws; after the hook structure is set, the hook The structure is hooked at the junction of the patellar ligament and the fracture fragment, preventing the patellar ligament from pulling the fracture fragment away. The strength against the patellar tendon pulling the fragment is from the whole wrapping structure instead of a single screw; through the above settings, the single position of the bone is avoided Excessive force can avoid comminuted fractures caused by fixing the fracture block; for osteoporosis patients, it can also be used according to the situation.
Owner:青岛山大齐鲁医院(山东大学齐鲁医院(青岛))
Axial displacement measuring equipment for knee joint cruciate ligament injury
PendingCN112826506AJudging the degree of damageAccurate operationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAxial displacementKnee Joint
The invention relates to the technical field of axial displacement measurement, and discloses an axial displacement measurement device for knee joint cruciate ligament injury, which comprises a guide plate and a displacement sensor, the lower end of the guide plate is fixed to the shank and tightly attached to the shank. The upper end of the guide plate is fixed on a femoral condyle, and the upper end of the guide plate deviates from a patella and a tibia by a certain distance through a supporting device arranged at the upper end of the guide plate, so that a movable space is reserved for the tibia during axial displacement measurement; the displacement sensor is arranged on the guide plate, and the front end of the displacement sensor abuts against the tibial tuberosity during measurement. The anterior and dislocation reduction speed and amplitude data of the tibia under different flexion and extension and inward and outward turning conditions can be measured, quantitative measurement is carried out on cruciate ligament injuries, and doctors are assisted in diagnosing patients.
Owner:SHANGHAI INNOMOTION
Teaching model for tibial tuberosity bone traction operation
InactiveCN114283663AAvoid destructionIncrease profitCosmonautic condition simulationsEducational modelsTibial boneHuman body
According to the technical scheme, the teaching model is characterized in that the teaching model comprises a simulated femur, a simulated tibia and simulated skin and flesh wrapping the outer side of the simulated femur and the outer side of the simulated tibia, and through holes penetrating through the two sides are formed in the tuberosity bone position of the simulated tibia; an embedded part for a bone nail to penetrate through is arranged in the through hole, is used for simulating a human skeleton and is made of a material with the hardness similar to that of the skeleton, and the outer diameter of the embedded part is larger than that of the bone nail; the simulated skin and flesh comprises thighbone skin and flesh fixed on the simulated thighbone, tibia skin and flesh fixed on the simulated tibia, and detachable skin and flesh detachably and fixedly connected between the thighbone skin and flesh and tibia skin and flesh, and the detachable skin and flesh are correspondingly arranged at the tuberosity of the simulated tibia and can completely cover the embedded part. The whole treatment process can be continuously familiar through continuous practice and simulation operation on the human body model during learning, and a real patient can conveniently master a correct operation process.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO WENZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com