Non-linear ultrasonic diagnostic imaging using intermodulation component signals
A technology for ultrasonic diagnosis and intermodulation components, which is applied in the field of medical diagnostic imaging systems and can solve problems such as attenuation, reduction of image diagnosis quality, and reduction of echo signal-to-noise ratio characteristics.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
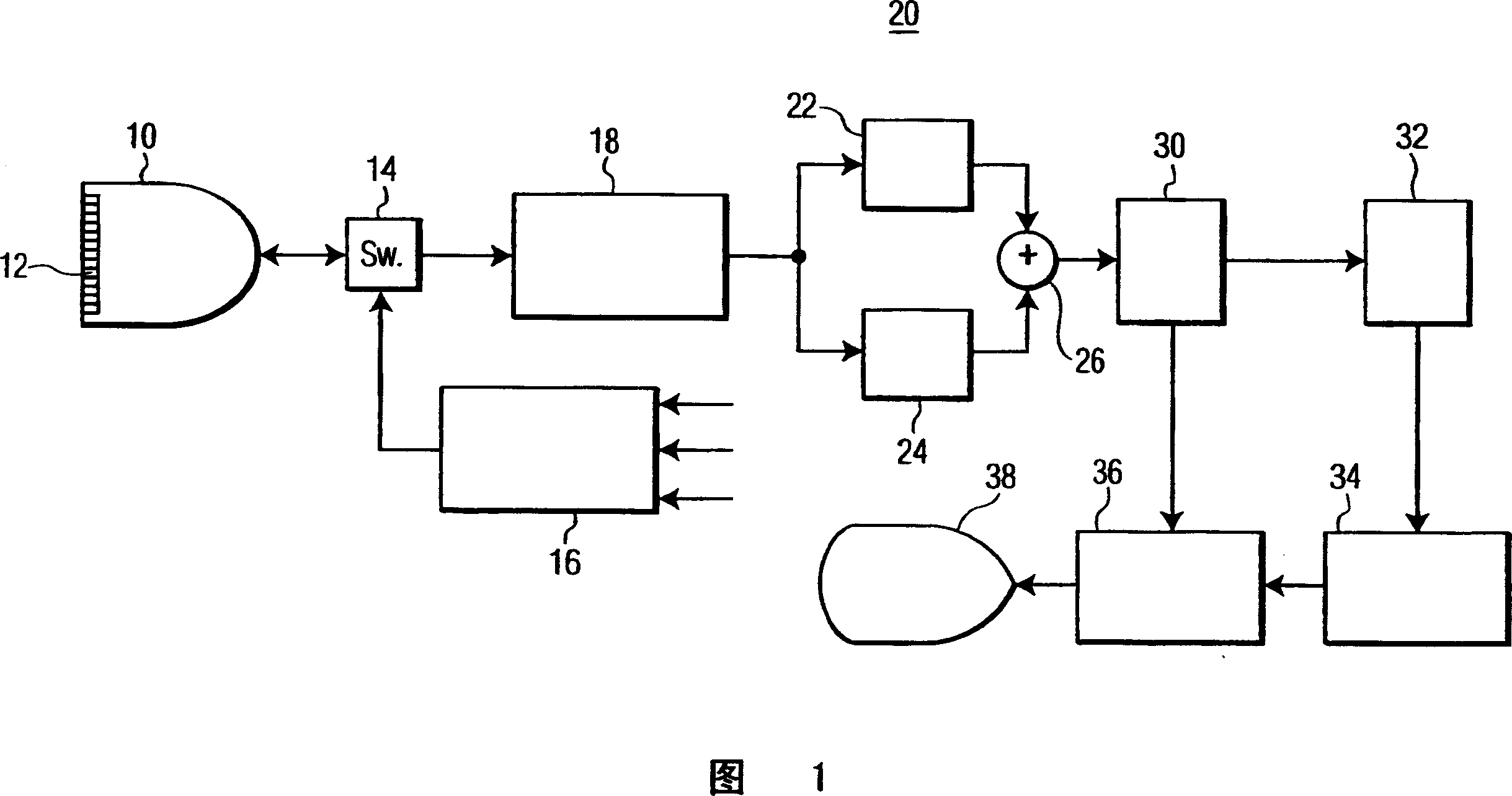
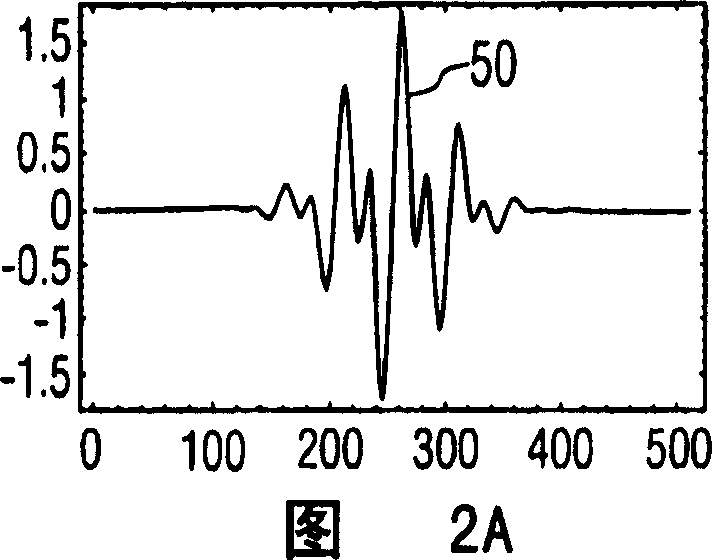
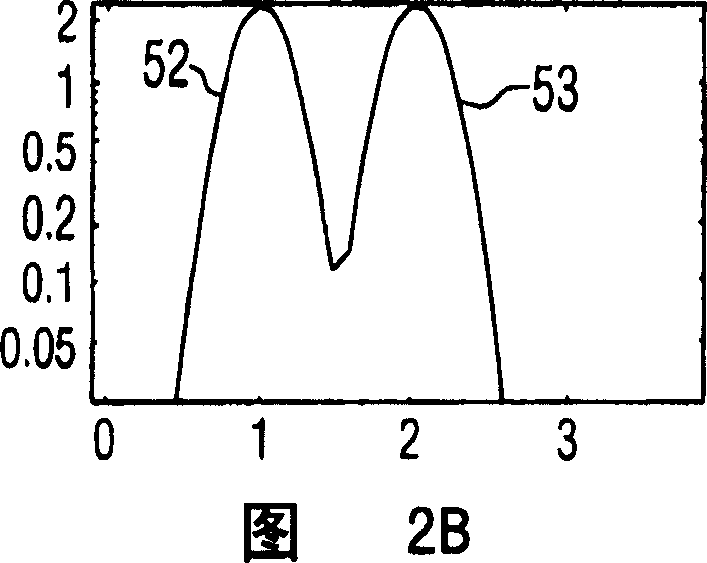
[0013] Referring first to Figure 1, there is shown an ultrasonic diagnostic imaging system constructed in accordance with the principles of the present invention. The ultrasound system of FIG. 1 utilizes a transmitter 16 that transmits a multi-frequency beam to non-linearly generate a difference frequency signal within the subject to be imaged. The transmitter is coupled to elements of the array transducer 12 of the scan head 10 via a transmit / receive switch 14 . As shown, the transmitter responds to a number of control parameters that determine the characteristics of the transmitted beam. Two main frequencies f of the multi-frequency beam 1 and f 2 controlled, the two frequencies determine the difference (f 1 -f 2 ) The frequency at which the frequency component is located. The amplitudes and intensities a and b of these two transmitted frequency components are also controlled such that the transmitted beamforming (bsin(2πf 1 t)+asin(2πf 2 t)) form. The received diffe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com