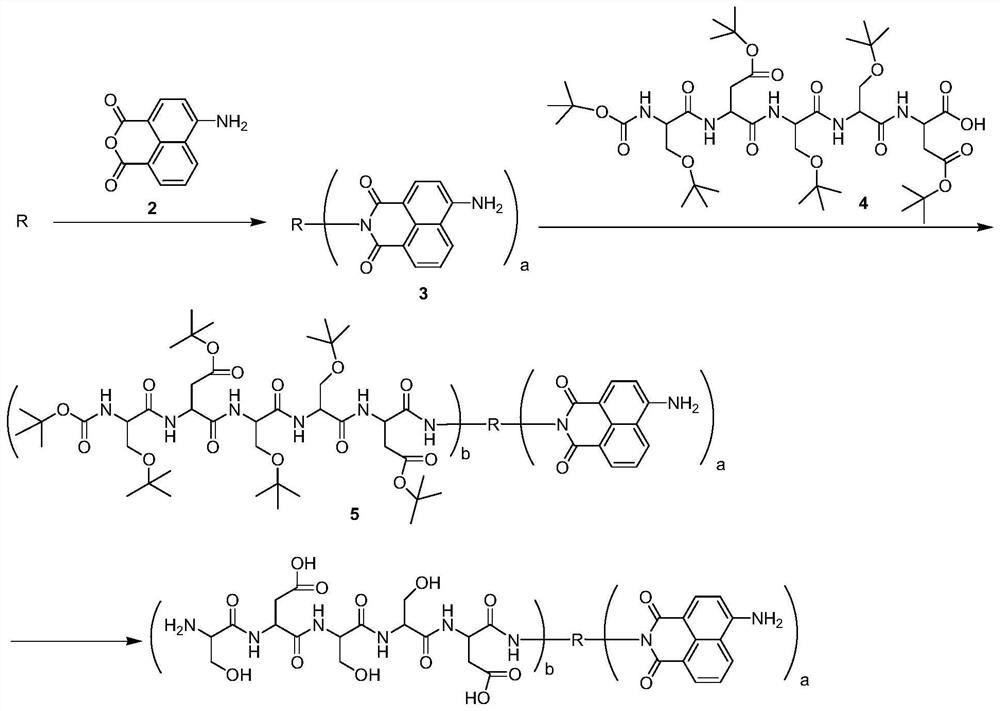
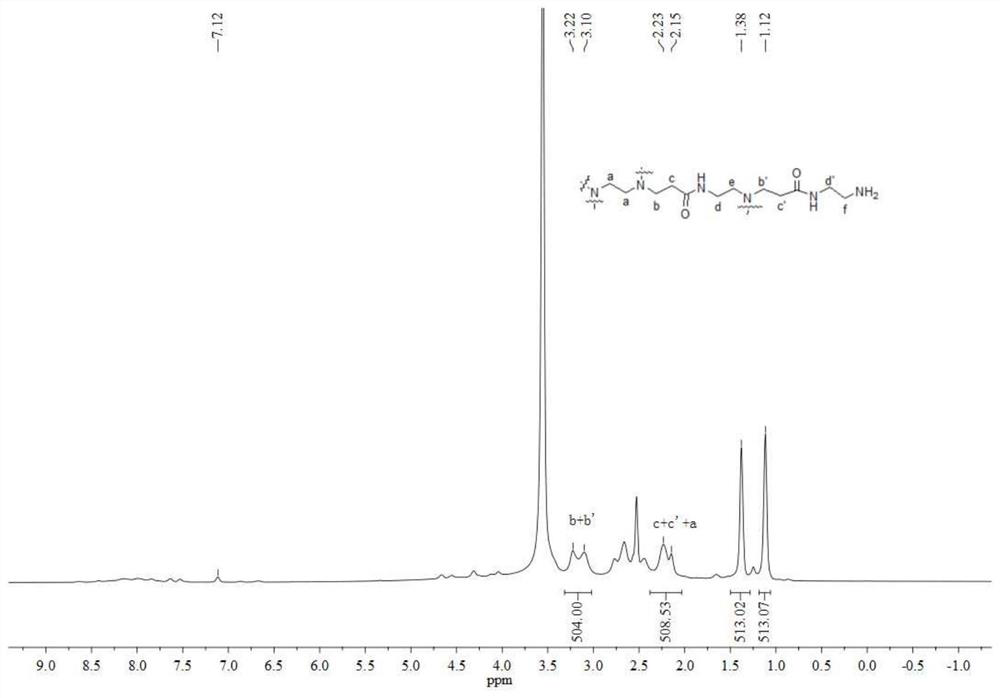
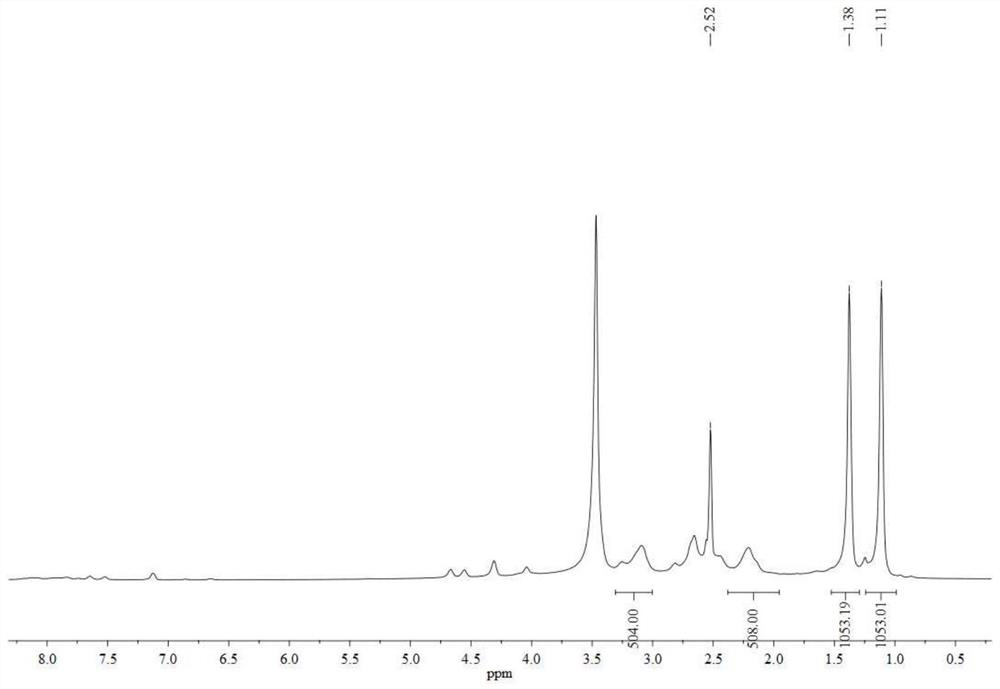
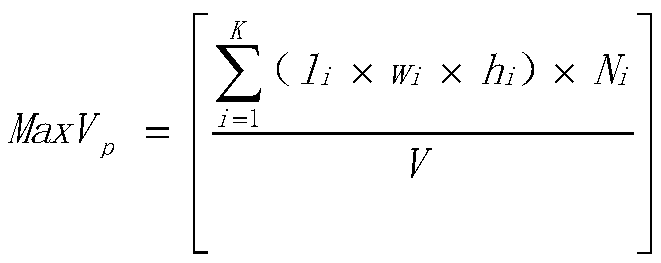Patents
Literature
46 results about "Molecular Response" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
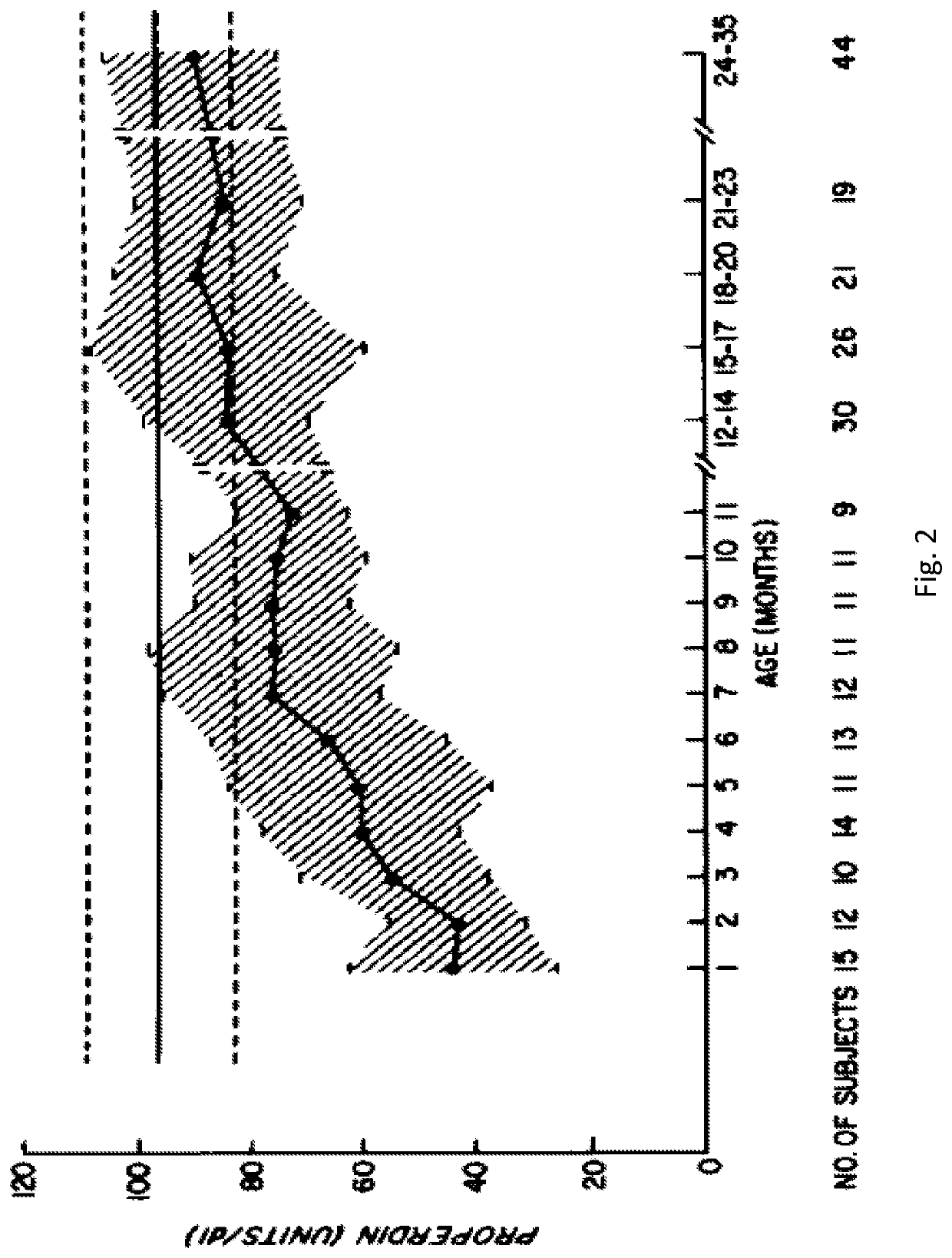
An assessment of the molecular response of the disease to the therapy.
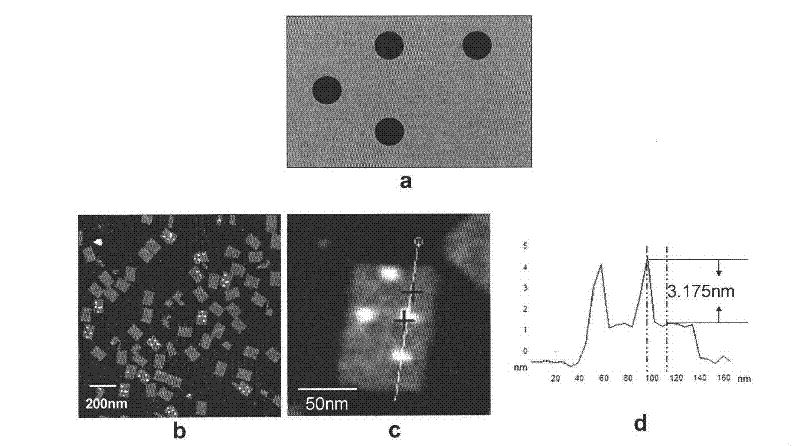
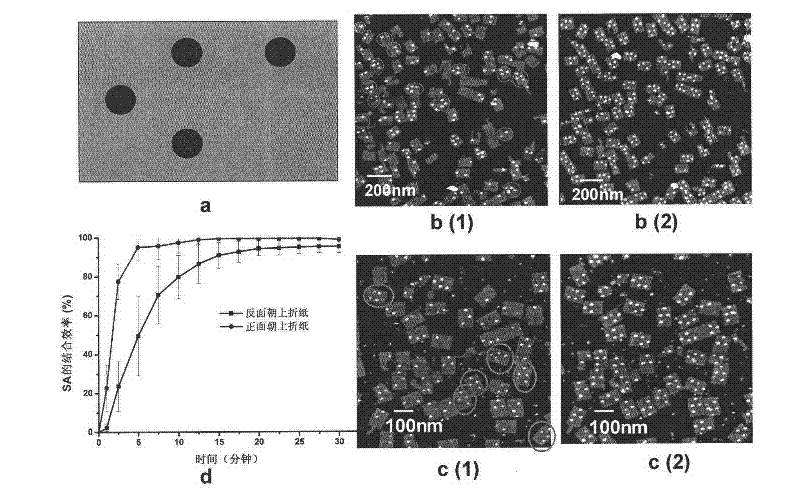
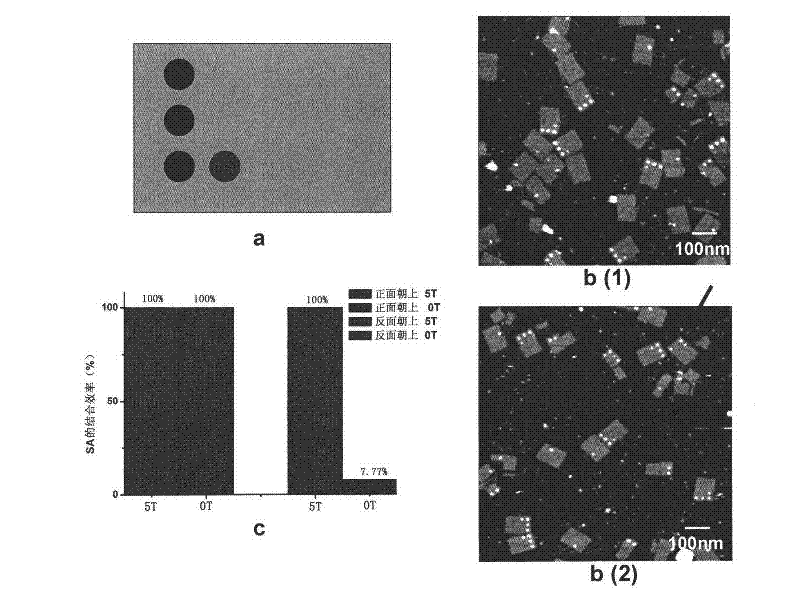
Method related to DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) folded paper and structure and application thereof
InactiveCN102559891ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringA-DNA
The invention discloses a method related to DNA folded paper and a structure and an application thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing a DNA folded paper staple chain of a tail end modification reactant I, and arranging a connector between the tail end of the staple chain and the reactant I; (2) performing self-assembly on the staple chain obtained in the step (1) and a scaffold chain; (3) adding a reactant II which is specifically combined with the reactant I; and (4) detecting information on the combination of the reactant I and the reactant II. The connector is arranged between the reactant I and a staple short chain, so that the reaction locus of the reactant I which is effective to the reactant II on the DNA folded paper can be accurately controlled in particular to the DNA folded paper absorbed on a solid-liquid interface. The method can be taken as a detection method for a gene chip, and be used for specifically distributing reactants. The method can be used for detecting monomolecular reactions, and has extremely high sensitivity and specificity.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
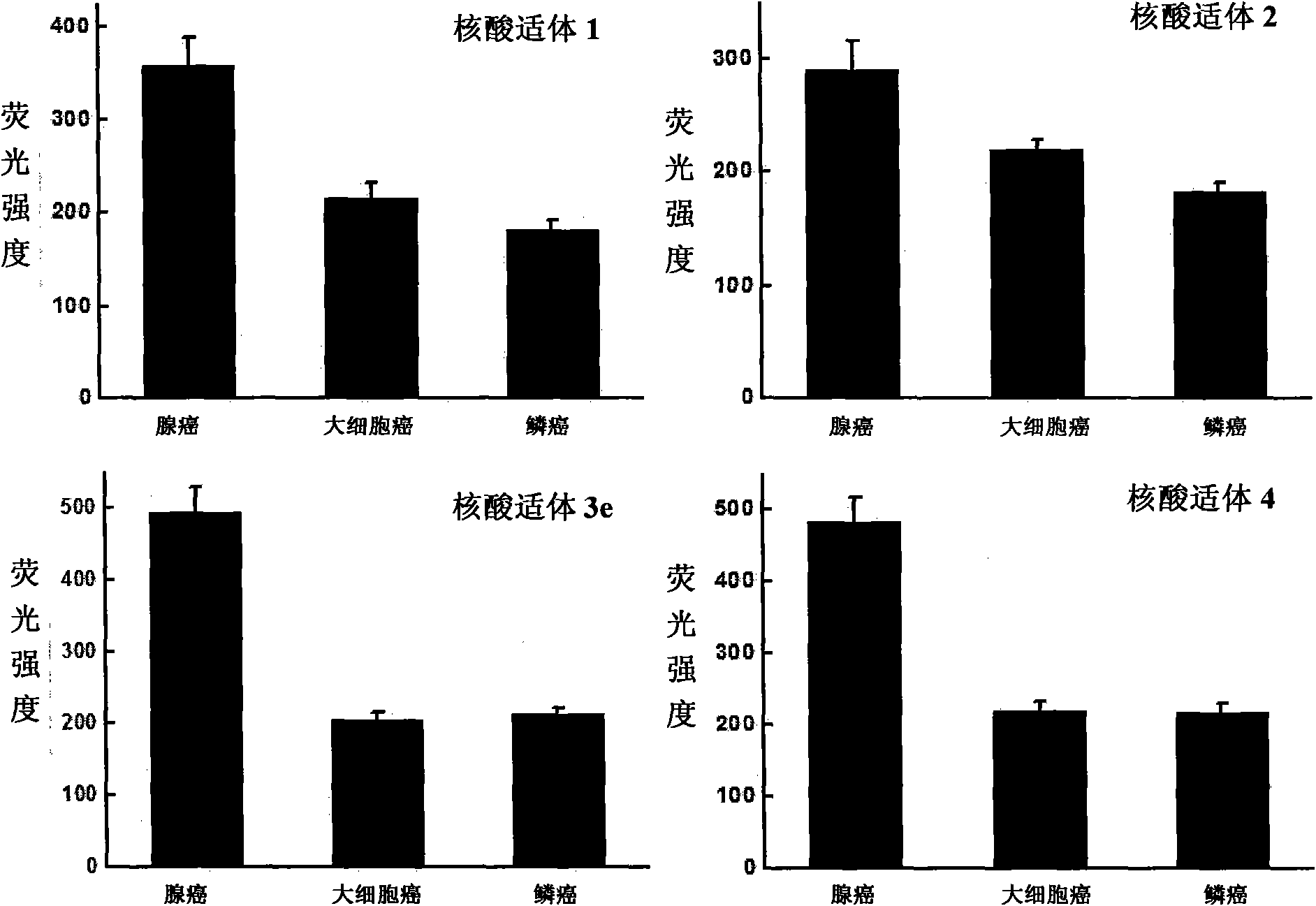
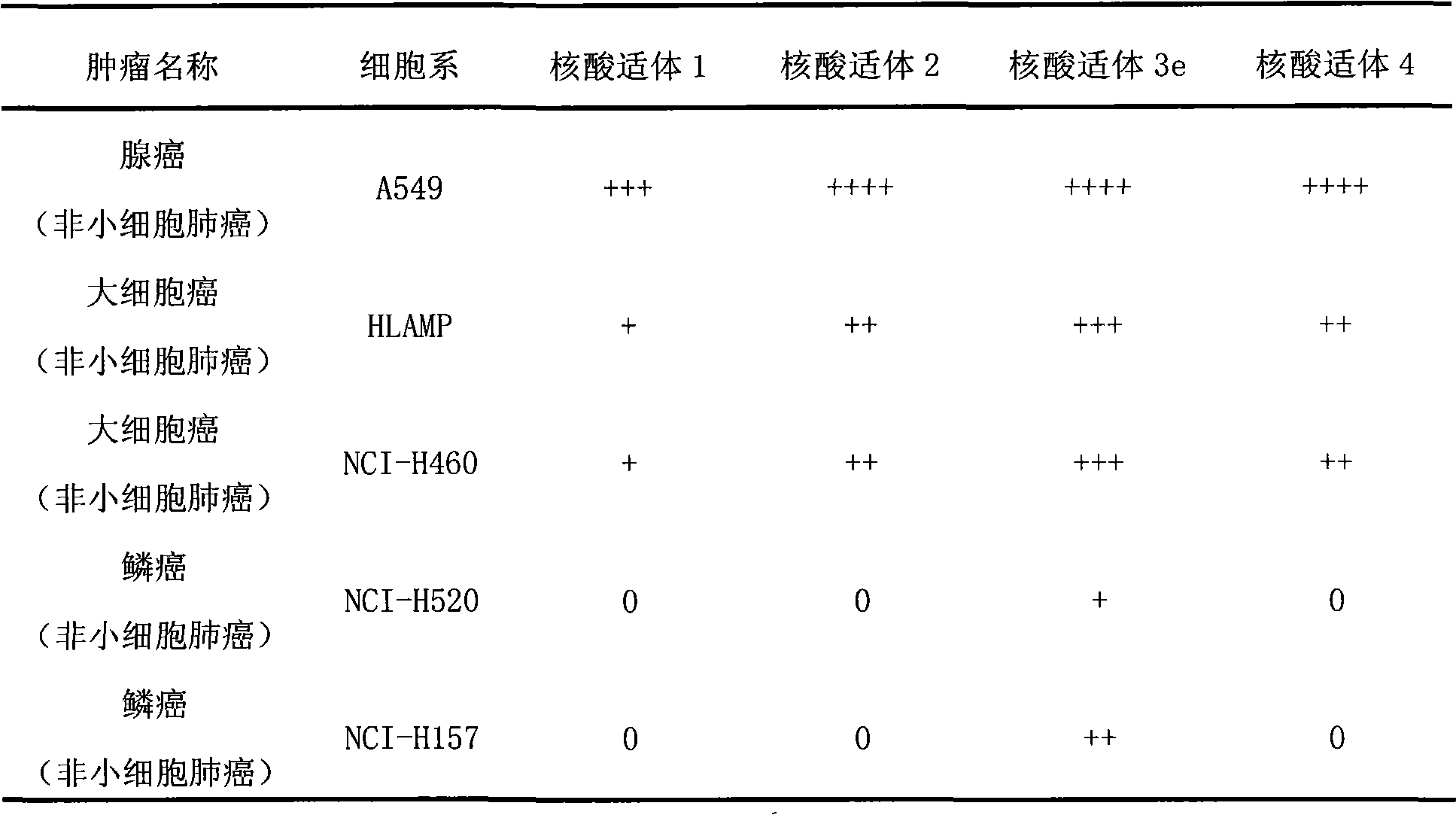
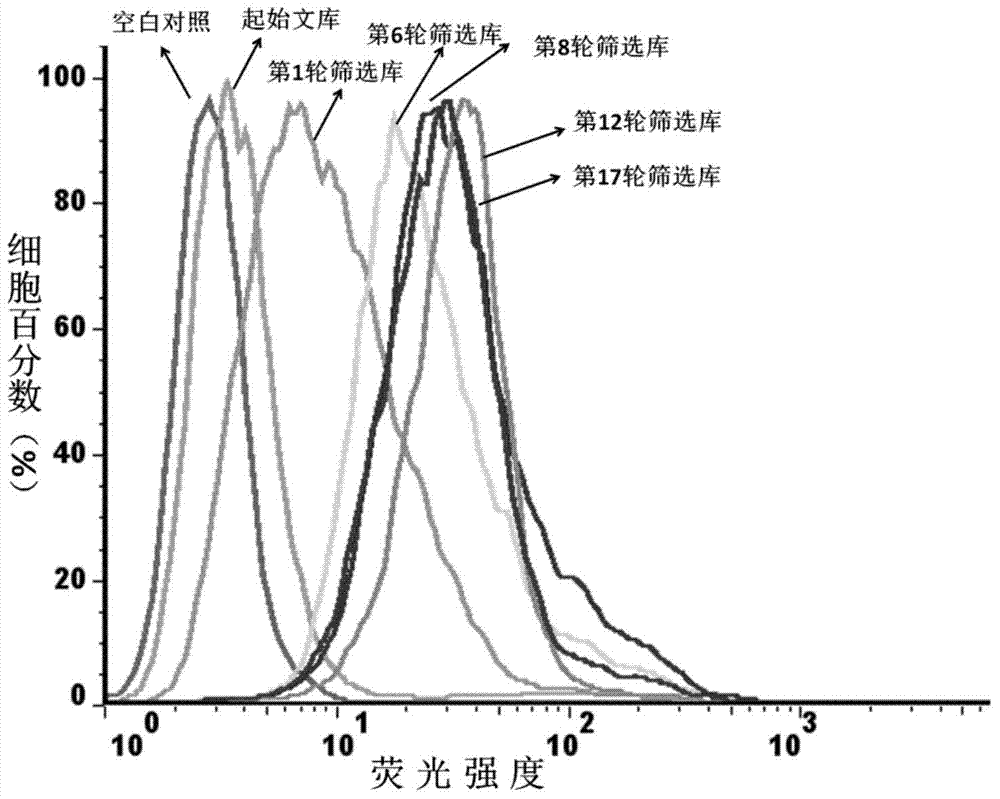
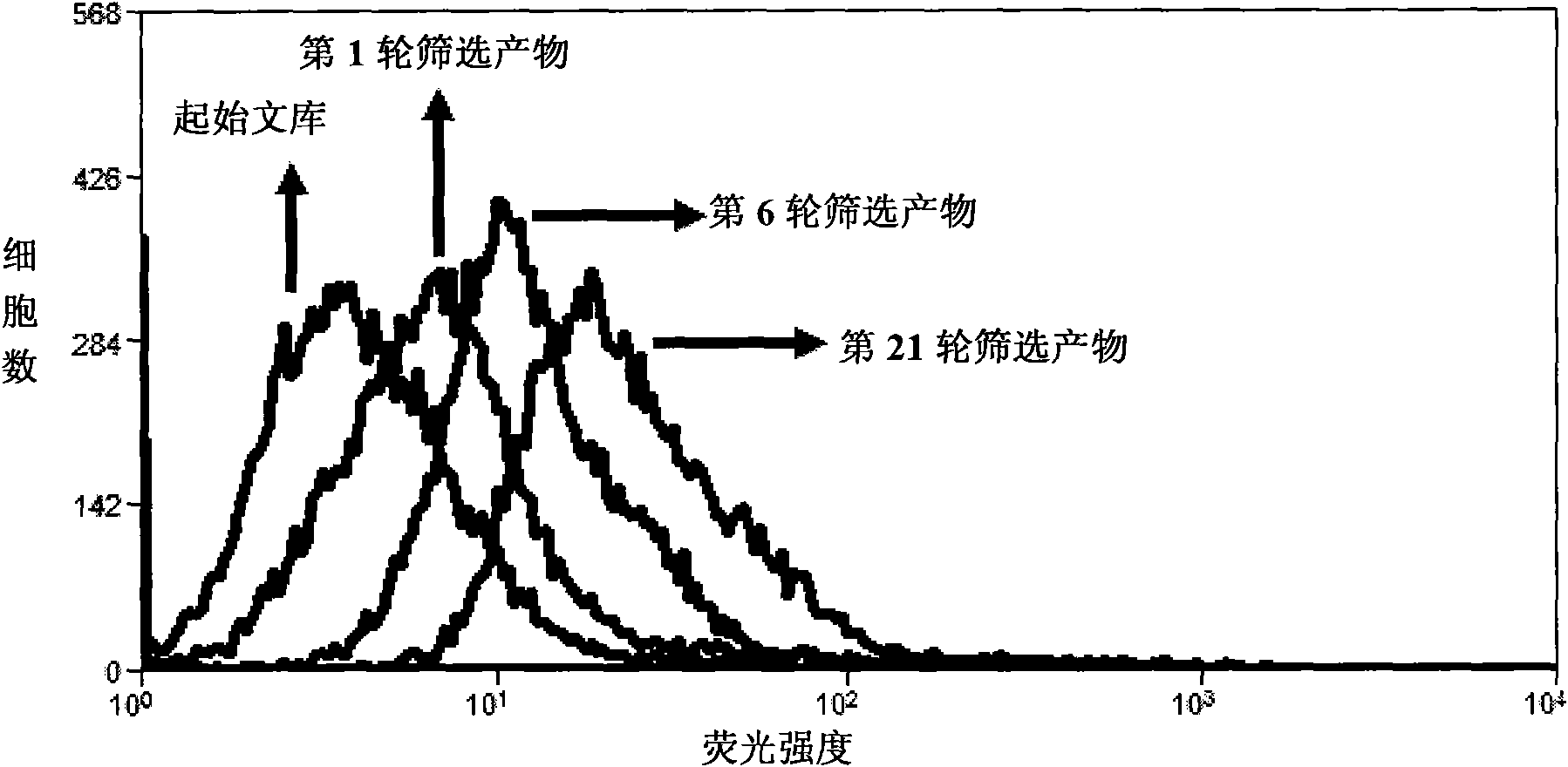
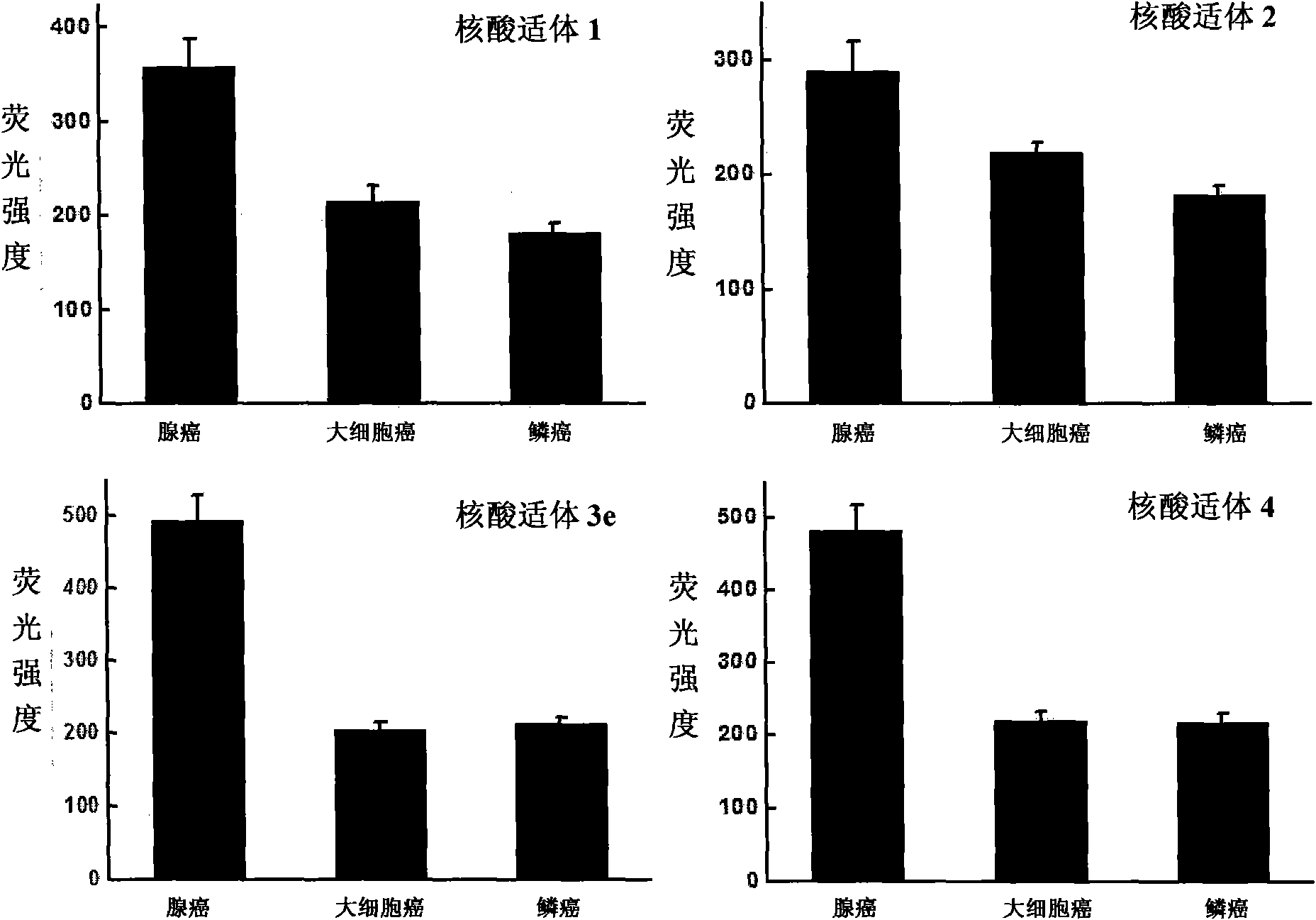
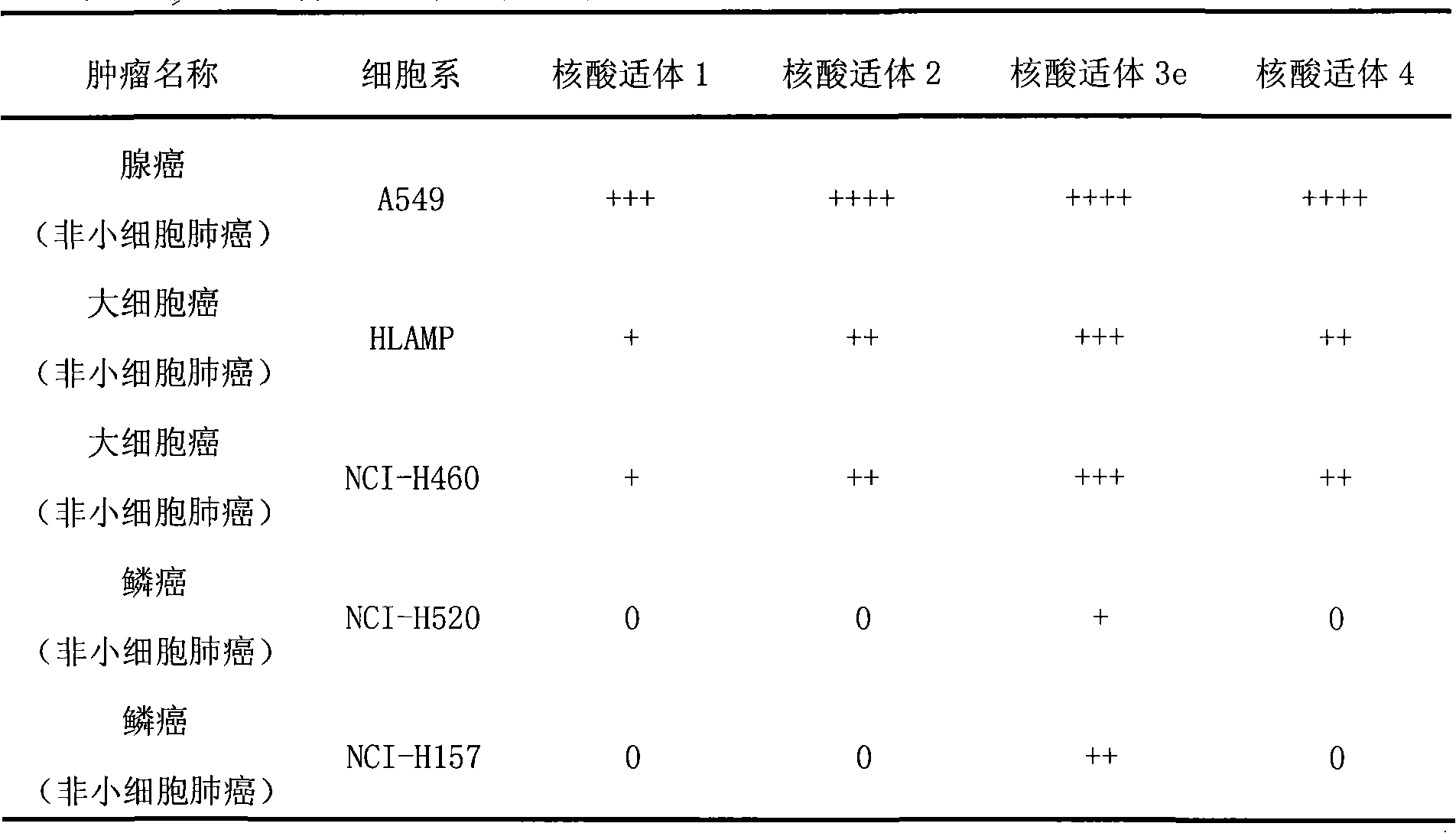
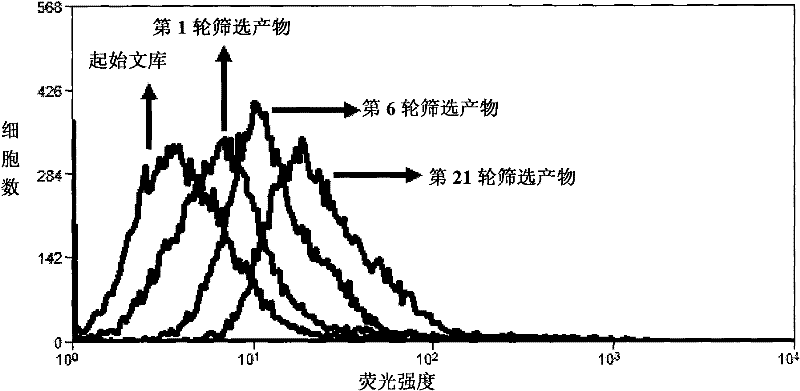
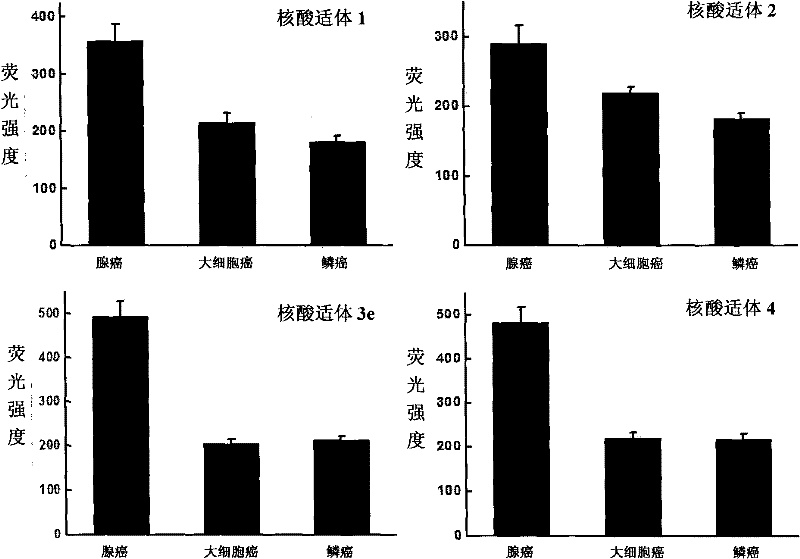
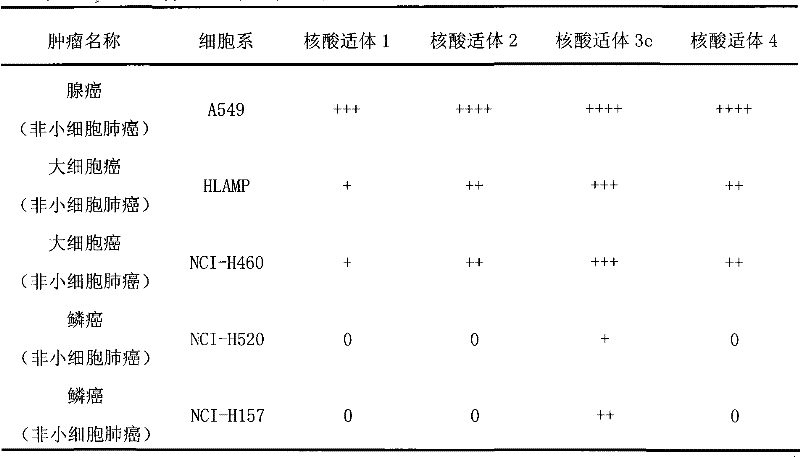
Aptamer for grouping different subtype non-small cell lung cancers and screening method thereof
InactiveCN101955939AMicrobiological testing/measurementIndividual particle analysisAptamerScreening method
The invention discloses an aptamer for grouping different subtype non-small cell lung cancers and a screening method thereof. The aptamer provided by the invention is a DNA fragment having a nucleotide sequence represented by sequences from No.1 to No.2 in a sequence table. The aptamer can be applied to grouping of different subtype non-small cell lung cancers. The aptamer of the invention can group different subtypes of the non-small cell lung cancers according to a molecular response signal under the situation that a tumor marker of non-small cell lung cancer is unknown. The identification of a combination target of the aptamer by using the aptamer is favorable for finding the tumor marker of non-small cell lung cancer, for earlier diagnosis and more accurate grouping of the non-small cell lung cancers, and for finding a new medicinal function target of oncotherapy.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
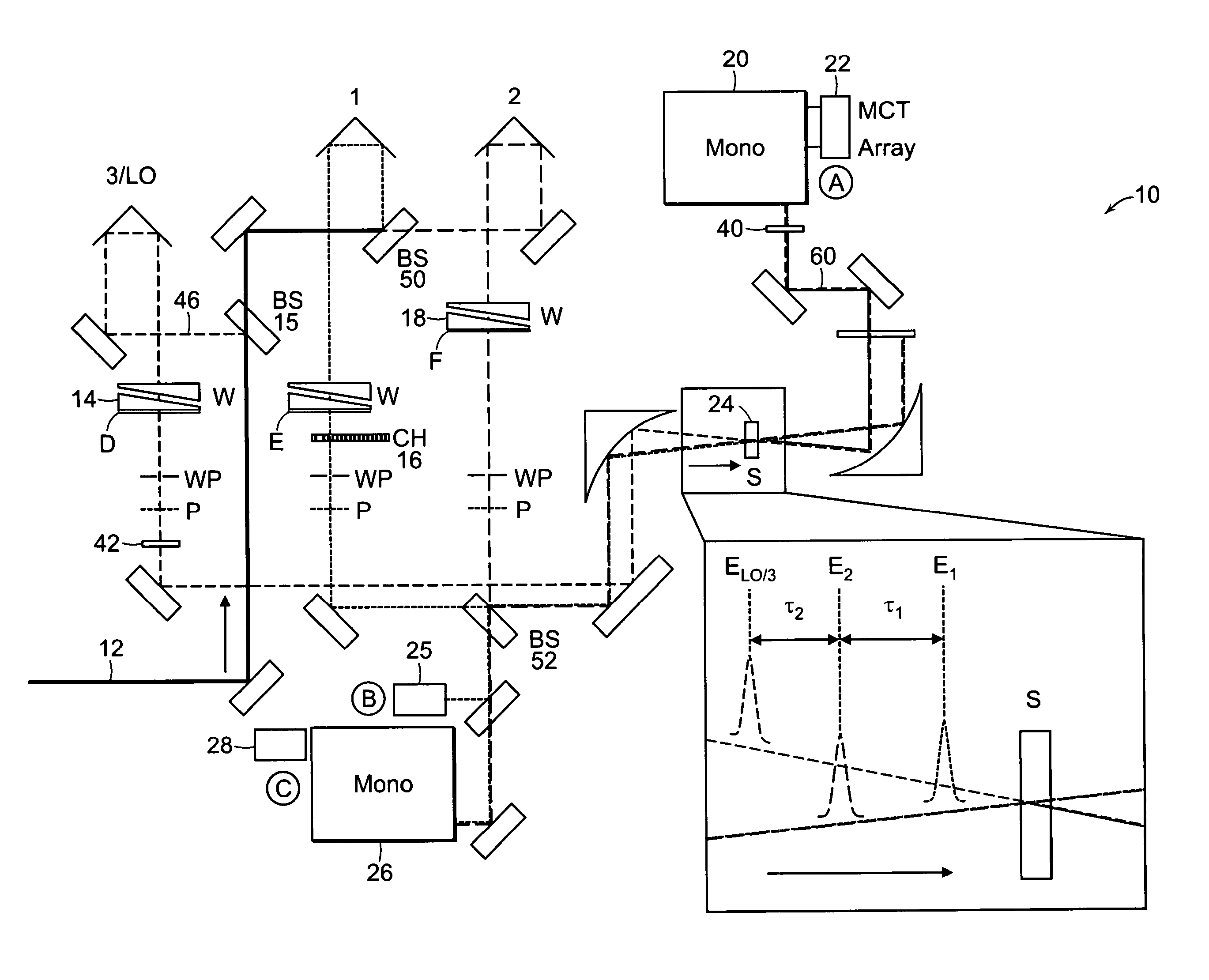
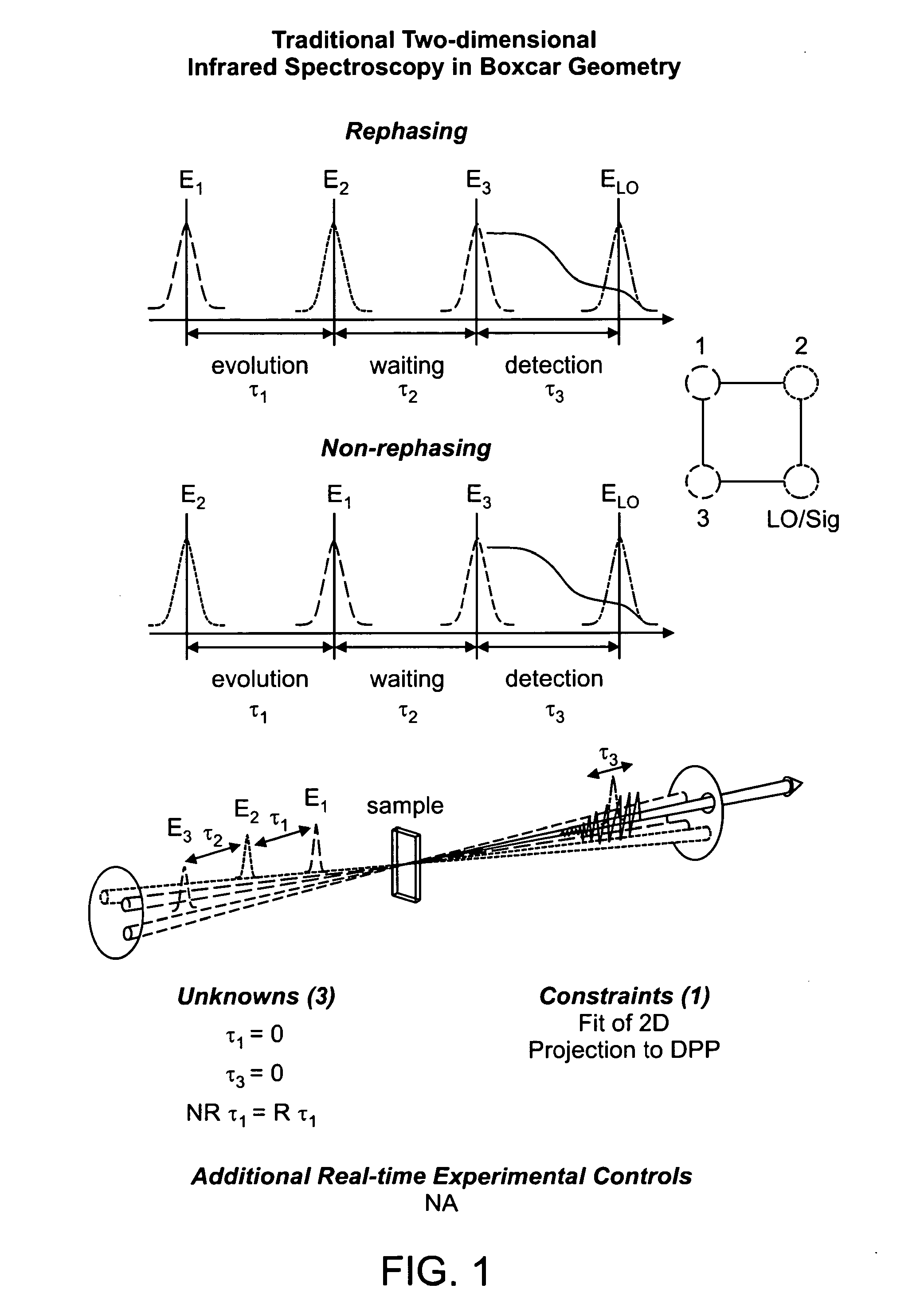
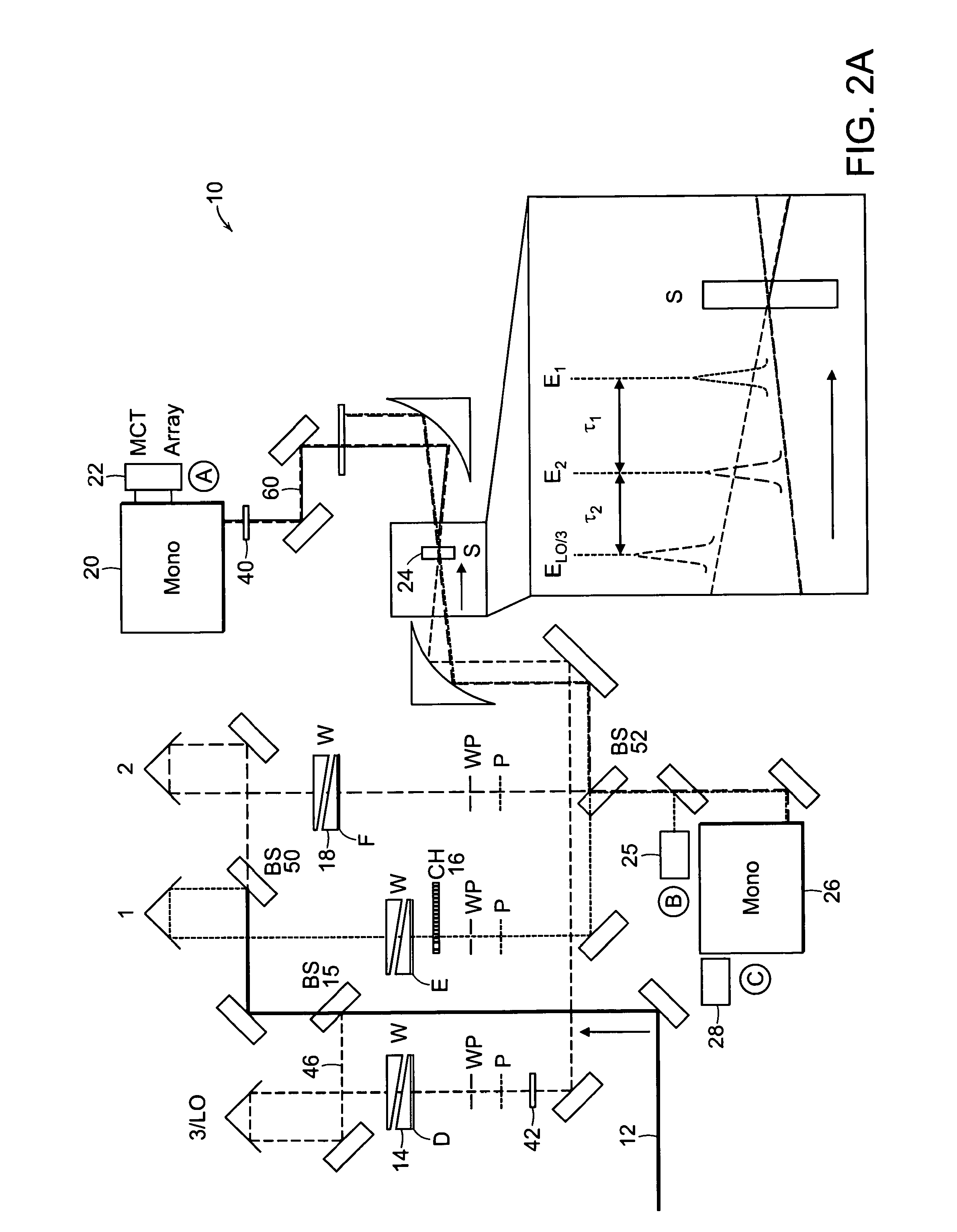
Two-dimensional fourier transform spectrometer
InactiveUS20100171952A1Reduce ambiguityReduce subjectivityRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryFrequency spectrumFourier transform on finite groups
The present invention relates to a system and methods for acquiring two-dimensional Fourier transform (2D FT) spectra. Overlap of a collinear pulse pair and probe induce a molecular response which is collected by spectral dispersion of the signal modulated probe beam. Simultaneous collection of the molecular response, pulse timing and characteristics permit real time phasing and rapid acquisition of spectra. Full spectra are acquired as a function of pulse pair timings and numerically transformed to achieve the full frequency-frequency spectrum. This method demonstrates the ability to acquire information on molecular dynamics, couplings and structure in a simple apparatus. Multi-dimensional methods can be used for diagnostic and analytical measurements in the biological, biomedical, and chemical fields.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
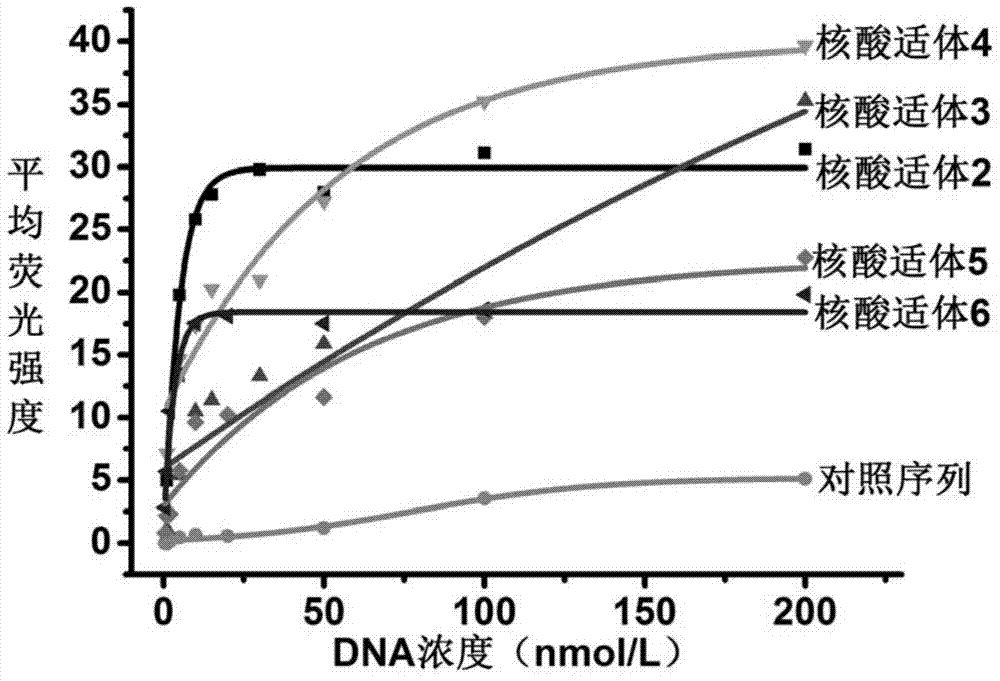
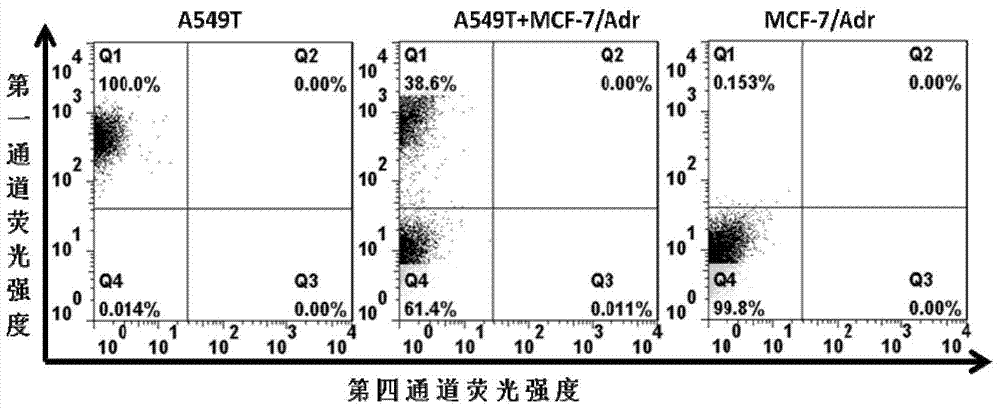
Aptamer for recognizing adriamycin-resistant breast cancer cells as well as screening method and application of aptamer
ActiveCN104498500AHigh affinityIncreased drug resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAptamerNucleotide
The invention discloses an aptamer for recognizing adriamycin-resistant breast cancer cells. The aptamer can be a single-stranded DNA molecule. Particularly, the aptamer can be an aptamer (1) formed by nucleotide molecules as shown in SEQ ID No. 1, an aptamer (2) formed by nucleotide molecules as shown in SEQ ID No. 2, an aptamer (3) formed by nucleotide molecules as shown in SEQ ID No. 3, an aptamer (4) formed by nucleotide molecules as shown in SEQ ID No. 4, an aptamer (5) formed by nucleotide molecules as shown in SEQ ID No. 5 and an aptamer (6) formed by nucleotide molecules as shown in SEQ ID No. 6. By adopting the aptamer disclosed by the invention, the resistance to medicines of tumors can be monitored in real time according to molecular response signals under the condition that the medicine resistance mechanism is unknown so that the treatment scheme can be changed timely and the success rate of chemotherapy can be increased.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and apparatus for discovery, development and clinical application of multiplex assays based on patterns of cellular response
InactiveUS20150025812A1Improve diagnostic capabilitiesHealth-index calculationBiostatisticsVaccine efficacyCell type
A method for the discovery, development and clinical application of multidimensional multiplex synthetic biomarker assays based on patterns of cellular response.After stimulation or inhibition, a selected multiplicity of cell types are assayed for a multiplicity of cellular or molecular responses, and known machine learning techniques are used to synthesize the cellular responses into an optimized clinical biomarker. The computationally derived algorithm includes the relationships within and between the component steps so as to produce an optimized synthetic clinical biomarker. During discover of the assay one or more of the component steps are repeated iteratively until a final clinically optimized algorithm is produced.Such a multidimensional multiplex cell response assay may provide improved diagnostic performance with respect to entities such as immune status, infection, and antibiotic and vaccine efficacy, among others.
Owner:PARADIS NORMAN A
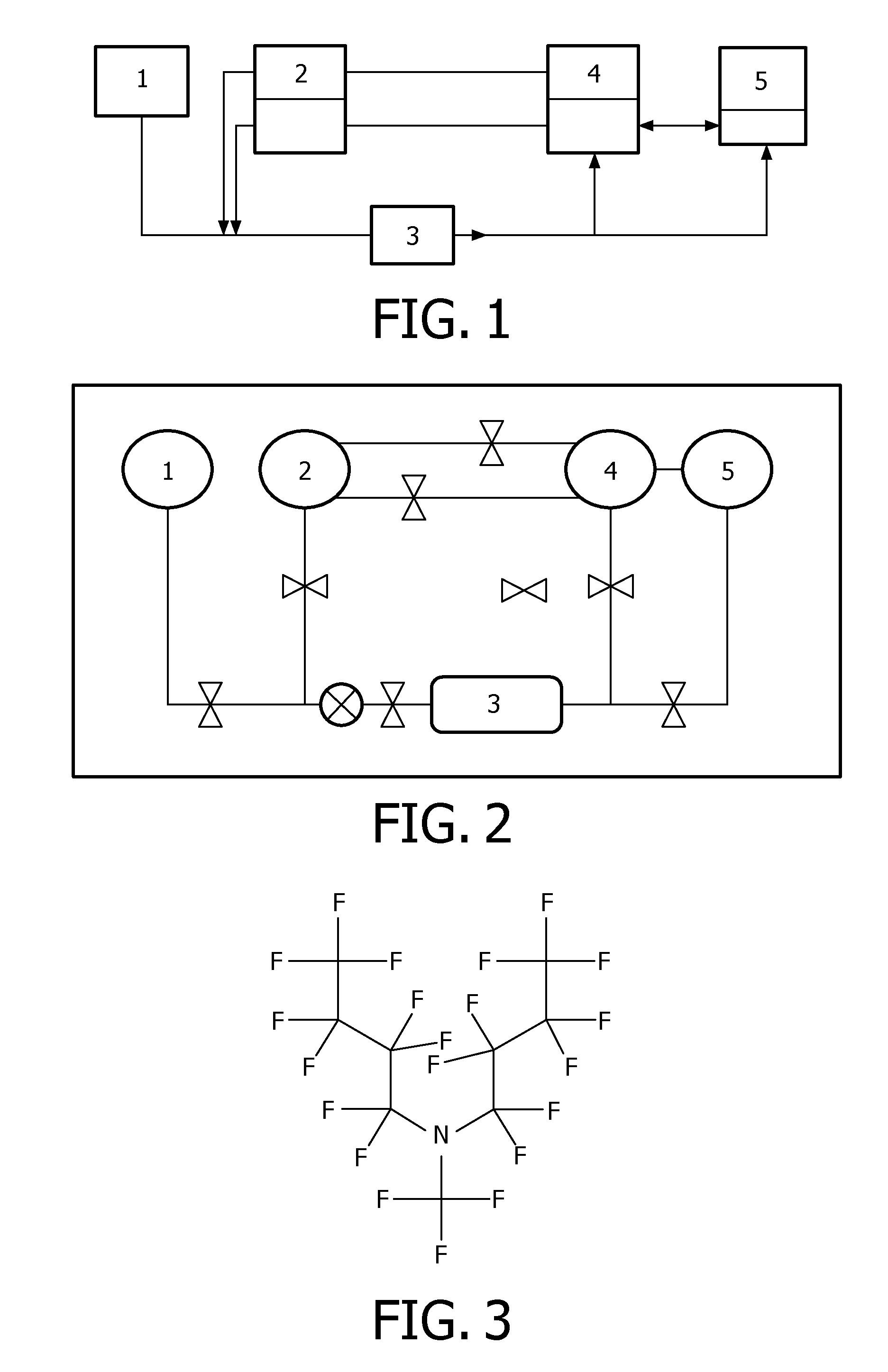
Method for performing molecular reactions by using immiscible intermediate fluids
InactiveUS20140017687A1Low costIncrease speedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusReaction zoneGravity separation
The present invention relates to a method for performing molecular reactions in a device comprising the steps of (a) introducing one or more reagent solution(s) and an immiscible intermediate fluid into the device, wherein the device comprises a substrate, on which chemically or biochemically recognizable entities are immobilized; (b) performing molecular reactions between the immobilized chemically or biochemically recognizable entities and the reagent solution(s); or on the immobilized chemically or biochemically recognizable entities in the presence of the reagent solution(s); (c) displacing the reagent solution(s) present on the substrate by the immiscible intermediate fluid; (d) separating the immiscible intermediate fluid and the reagent solution(s); and reusing the reagent solution(s) and / or immiscible intermediate fluid for one or more repetitions of steps (a) to (e). The invention further relates to a device for performing a molecular reaction, comprising a reaction zone, reservoirs and liquid connections and a col lection and regeneration zone wherein the immiscible intermediate fluid and the reagent solution(s) are separable by gravitational separation; or a redirection and distribution module, wherein the immiscible intermediate fluid and reagent solution(s) are separated. The invention also relates to the use of an immiscible intermediate fluid for displacing a reagent solution present in a reaction zone in a microfluidic device, as well as the use of a corresponding device for performing a sequencing reaction or a nucleic acid synthesis reaction.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
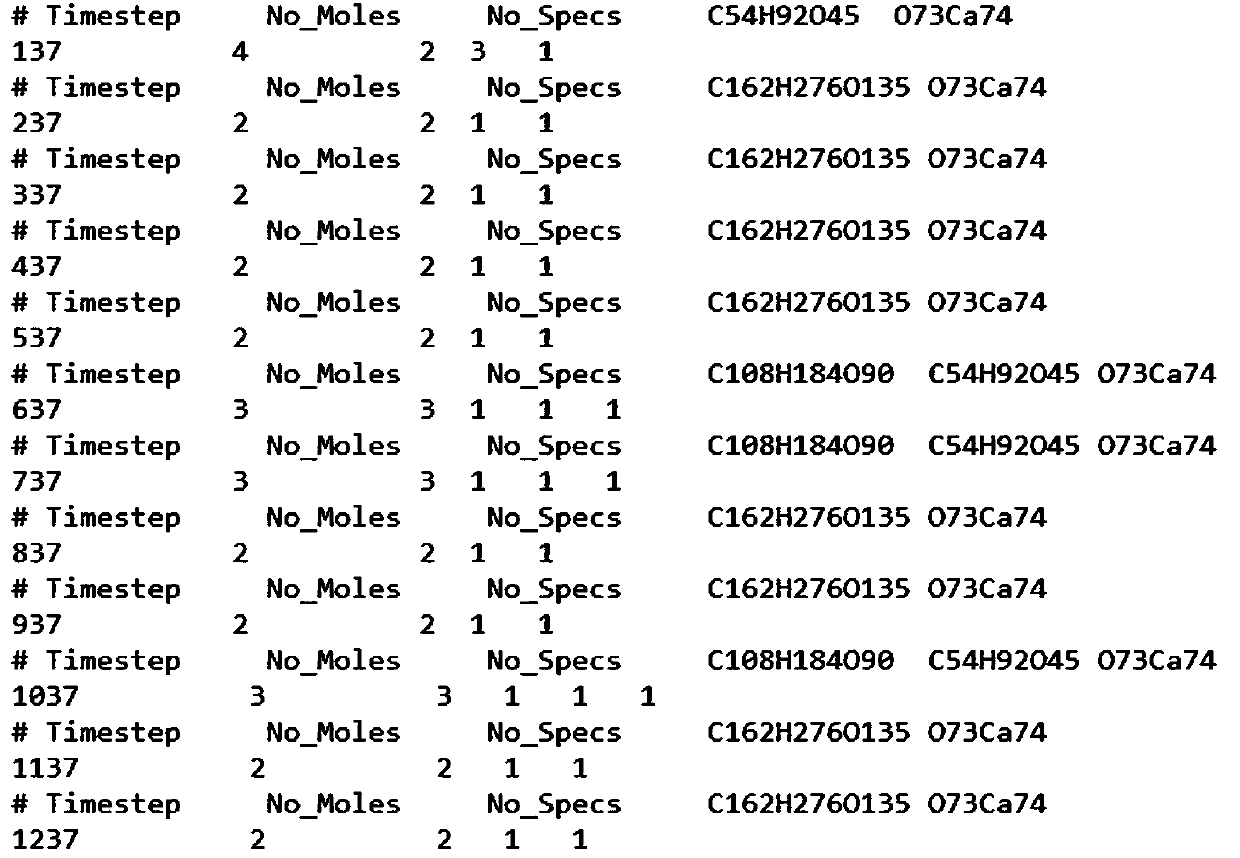
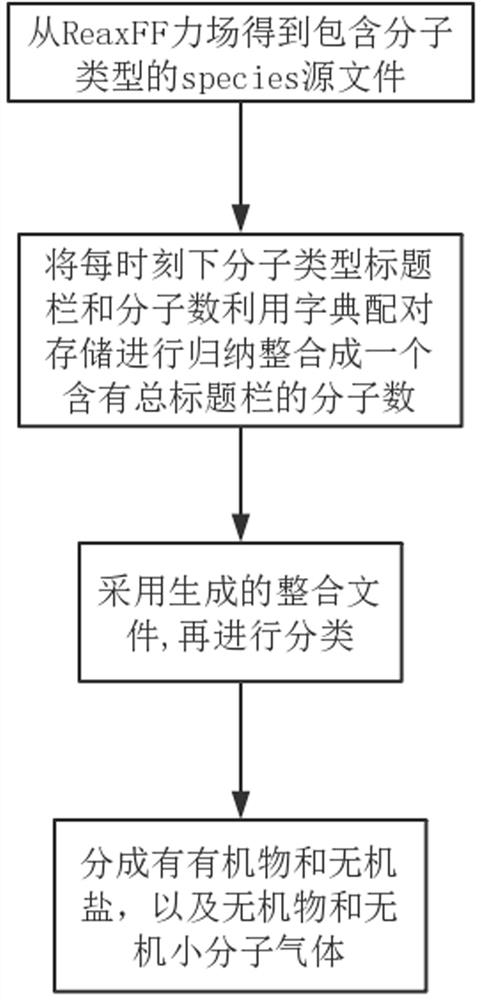
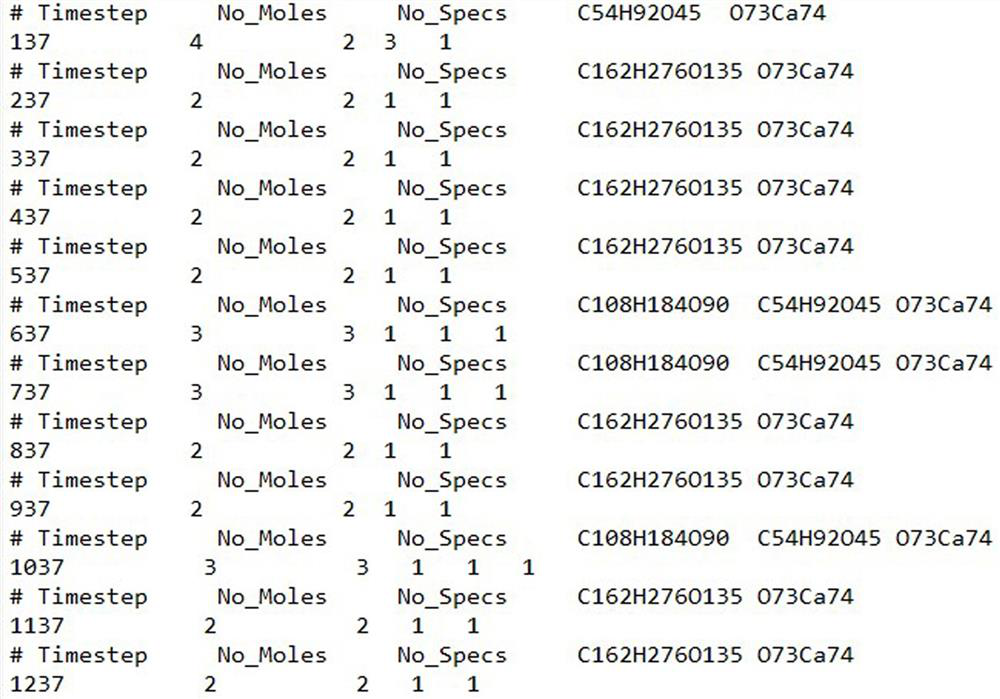
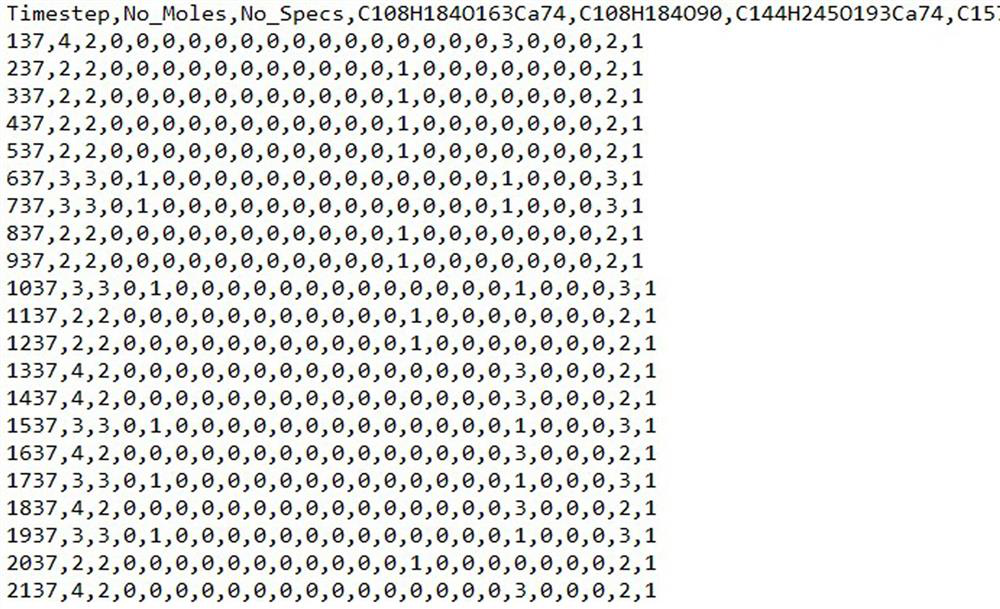
Python-based ReaxFF force field calculation result data processing method
ActiveCN110767267AEfficient and convenient readingShorten the timeComputational theoretical chemistryInstrumentsMolecular classificationData file
The invention relates to a Python-based ReaxFF force field calculation result data processing method and belongs to the technical field of chemical molecular reaction kinetics. The method comprises steps of step 1, reading and integrating data of a molecular type information specis file; step 2, performing molecular classification of the integrated molecular information output.txt file; and 3, calculating the molecular weight of each product to obtain the molecular mass percentage of each product. The processing method is advantaged in that various data file types generated by simulation can be efficiently and conveniently read, and the time and steps consumed by the data file in format transfer are reduced; the method can conclude molecular types of diversified simulation products, can obtain change of various products along with the time, and provides convenience for the reaction molecular dynamics simulation to explore the pyrolysis combustion micromechanisms under various working conditions and clarify the change rule of products.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
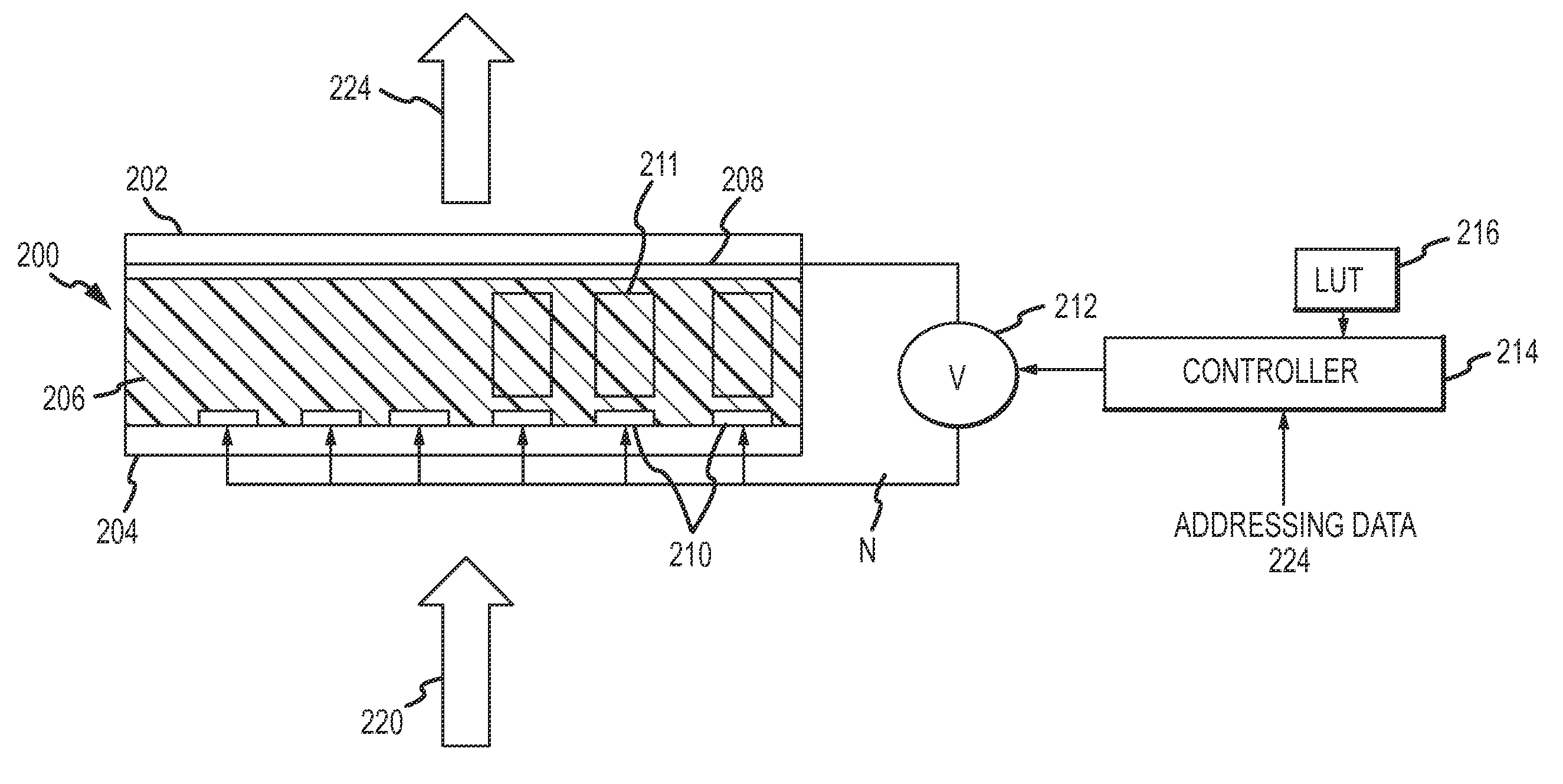
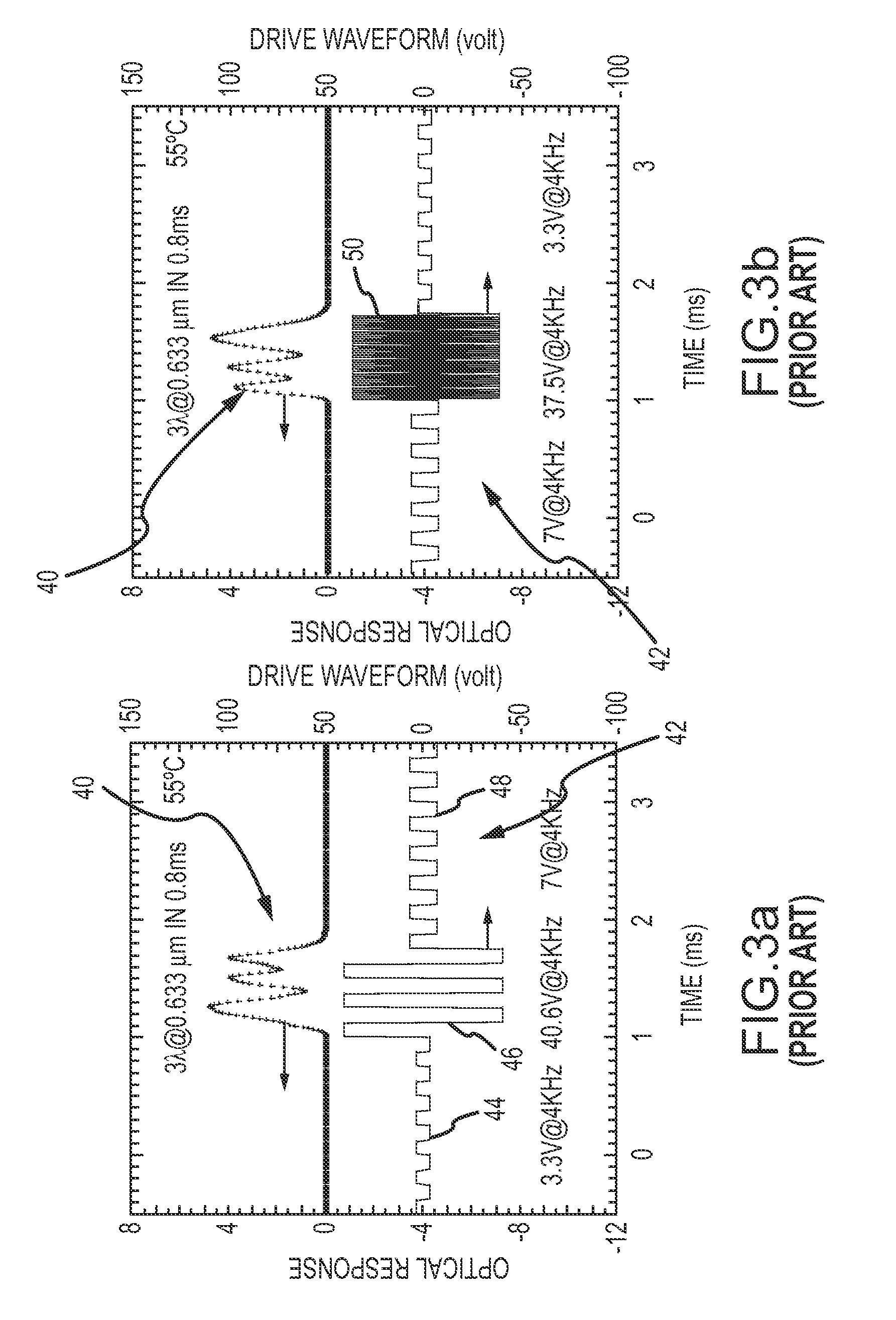
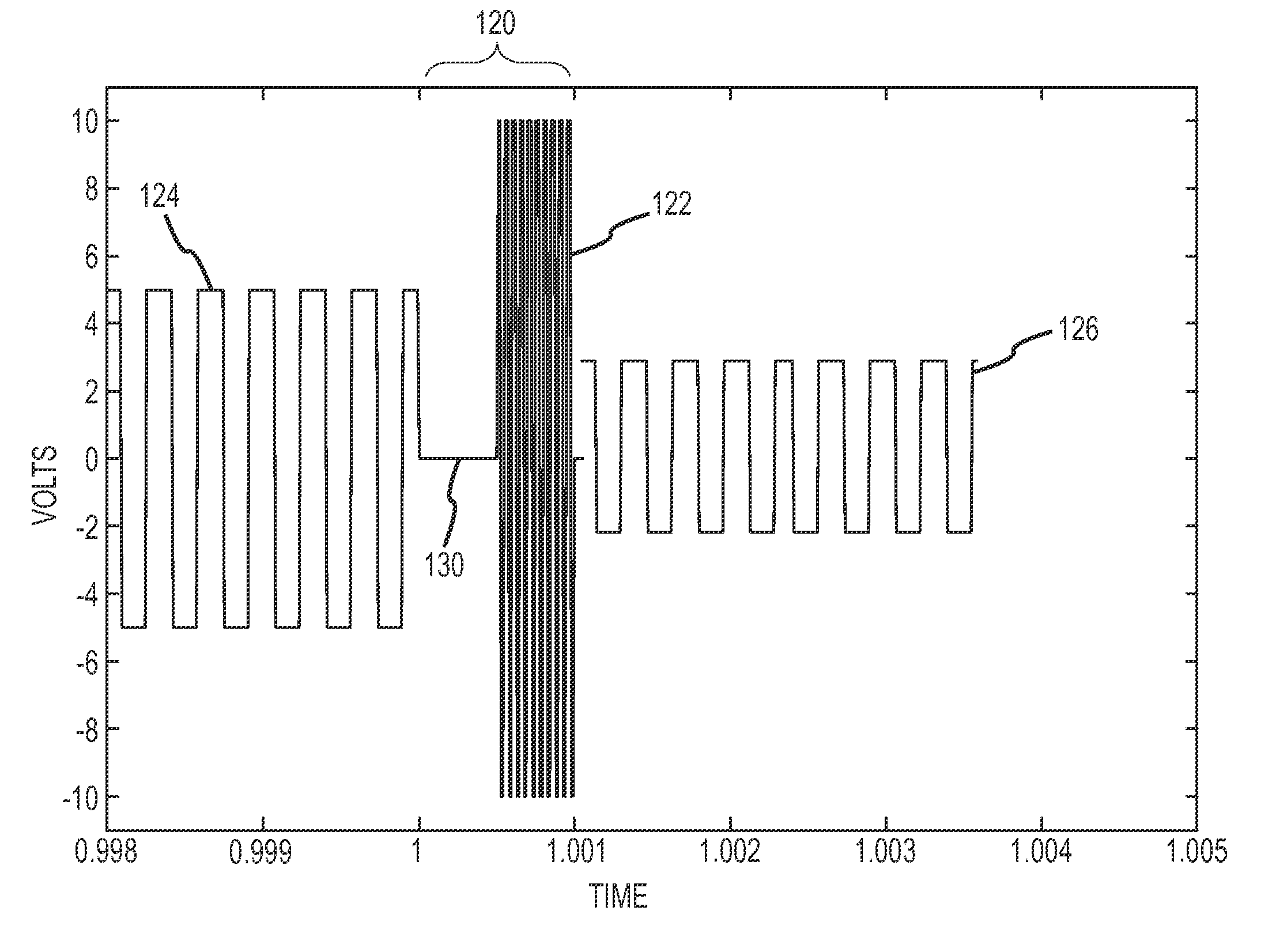
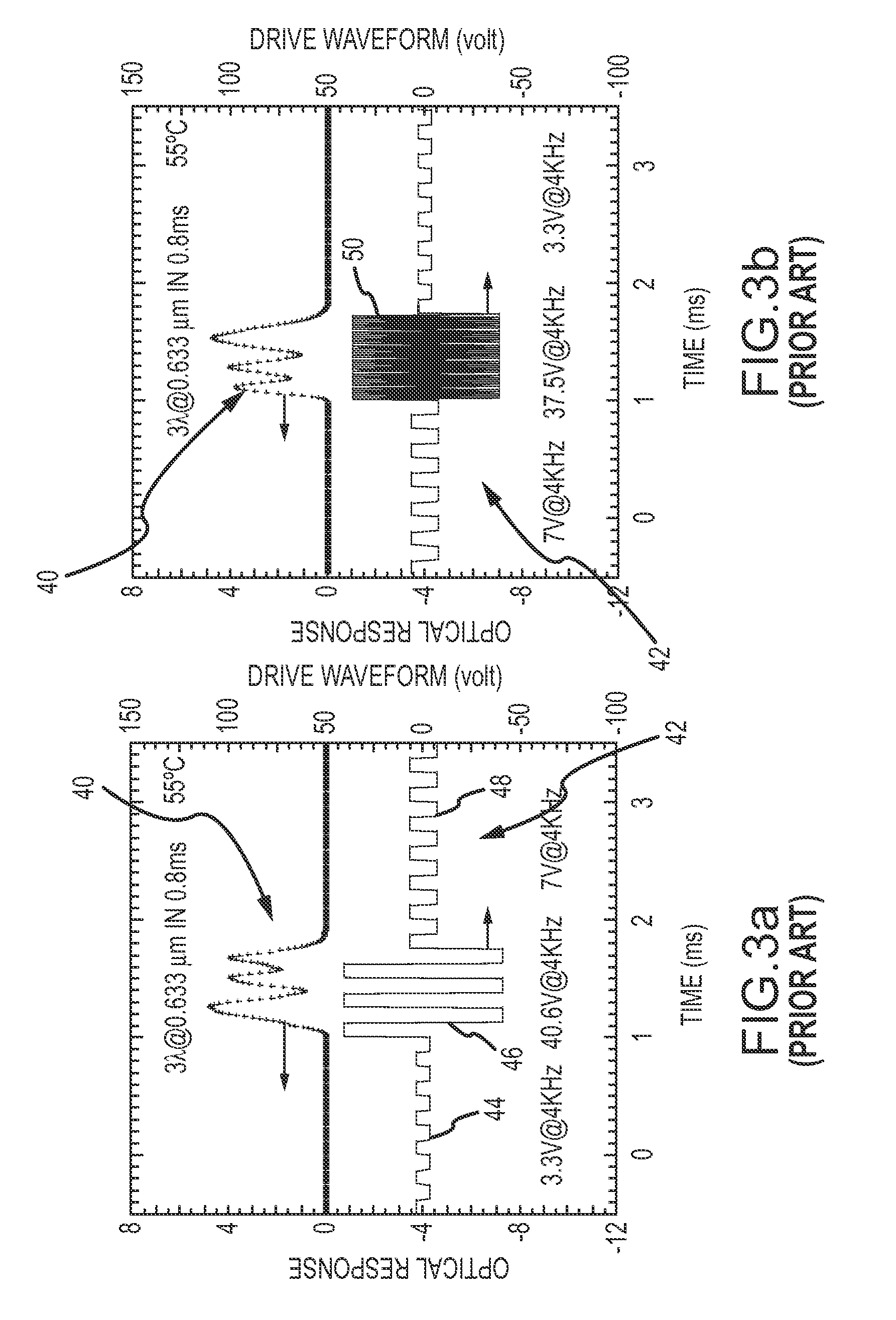
Two-stage drive waveform for switching a dual frequency liquid crystal (DFLC) at large tilt angles
InactiveUS20110001896A1Easy to operateOptimal switching timeStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsEngineeringLinearity
A two-stage drive waveform switches a DFLC from a high tilt state such as above the LC's linear region or near the ‘saturated’ or ‘field-driven homeotropic’ state of the LC to a low tilt state quickly and without scattering. A relaxation voltage is applied to delay the onset of the high amplitude high frequency kick voltage when switching from a high tilt state to a low tilt state. The relaxation voltage allows the molecules to ‘relax’ in accordance with their own elasticity towards their low tilt state in the direction of the average azimuth angle of the low tilt state. Once the tilt angle has relaxed sufficiently, the kick voltage is applied to drive the molecules quickly to the low tilt state. Most unexpectedly, optimal switching time and the desired molecular response is achieved by delaying the onset of the large kick voltage via application of the relaxation voltage. The relaxation voltage may constitute a lower amplitude holding voltage, a small or zero DC voltage or a smooth windowing of the kick voltage. Whether to apply the relaxation voltage at all and how to apply the relaxation voltage for optimal switching are suitably controlled as a function of the high tilt state. The DFLC is suitably switched from the low-to-high tilt state in the conventional manner without application of a relaxation voltage.
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
Nucleic acid aptamer for classification of different-subtype non-small cell lung cancers and screening method thereof
InactiveCN101914543AMicrobiological testing/measurementIndividual particle analysisScreening methodTumor therapy
The invention discloses a nucleic acid aptamer for classification of different-subtype non-small cell lung cancers and a screening method thereof. The nucleic acid aptamer provided by the invention is a DNA segment which comprises nucleotide shown as any one of sequences 1 to 9 in a sequence table. The nucleic acid aptamer can be applied to the classification of the different-subtype non-small cell lung cancers. By using the nucleic acid aptamer of the invention, the differentiation of the different-subtype non-small cell lung cancers can be realized on a molecular response signal under the condition that tumor markers of the non-small cell lung cancers are unknown. When used for identifying a target combined with the nucleic acid aptamer, the nucleic acid aptamer is favorable for finding out the tumor markers of the different-subtype non-small cell lung cancers, performing earlier diagnosis and more accurate classification of the non-small cell lung cancers and finding out new medicament acting target points for tumor therapy.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
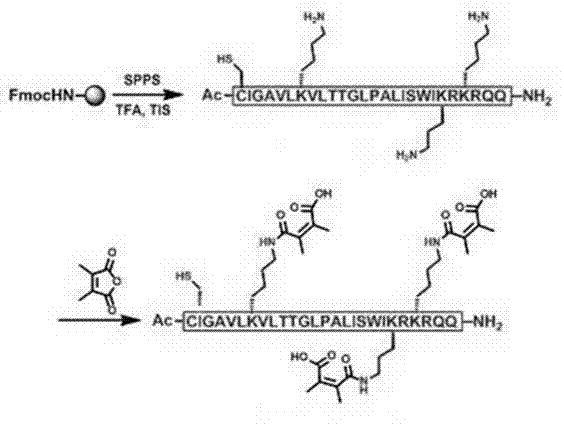
Acid-activated CSP targeted antimicrobial peptide and preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN102827288AHigh selectivityPromote aggregationAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntimicrobial peptidesStreptococcus mutans
The invention provides an acid-activated CSP targeted antimicrobial peptide, which is prepared by reacting 2,3-dimethylmaleic anhydride (DMMAn), an antimicrobial peptide melittin and a CSP targeted molecule. Moreover, the invention provides a preparation method and two applications of the acid-activated CSP targeted antimicrobial peptide. According to the acid-activated CSP targeted antimicrobial peptide, the selectivity of the antibacterial peptide and the aggregation degree of the antibacterial peptide on the surface of SM (Streptococcus Mutans) bacteria can be improved through the CSP targeted molecule, and the toxicity of the antibacterial peptide melittin is lowered through the protection of the DMMAn on amidogens; and after entering a decayed tooth, the CSP targeted antibacterial peptide can be activated by the acid condition of a microenvironment, so that the CSP targeted antibacterial peptide has sterilizing activity.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
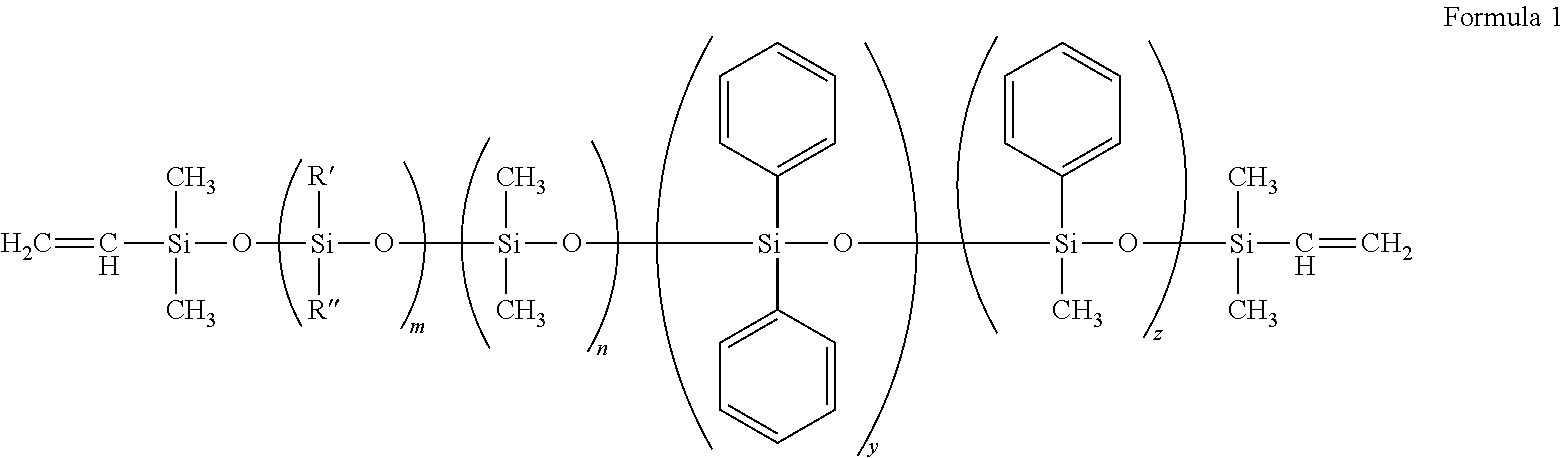
Polymer compositions suitable for intraocular lenses and related methods
ActiveUS8216310B2Reduce the ratioPrevent curingTissue regenerationAdhesivesCross-linkPolymer science
A polymeric material with a molecular response time that makes it suitable for use near fragile body tissues. The polymeric material is useful for both low modulus and high modulus applications thereby simplifying the multi-part polymeric article manufacturing process and creating better integrated multi-part polymeric articles. Cross-linked polymers with different moduli may be obtained utilizing the same or similar starting materials but modifying the amount of catalyst, the amount of cross-linking agent, and / or the amount of methyl vinyl cyclics.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
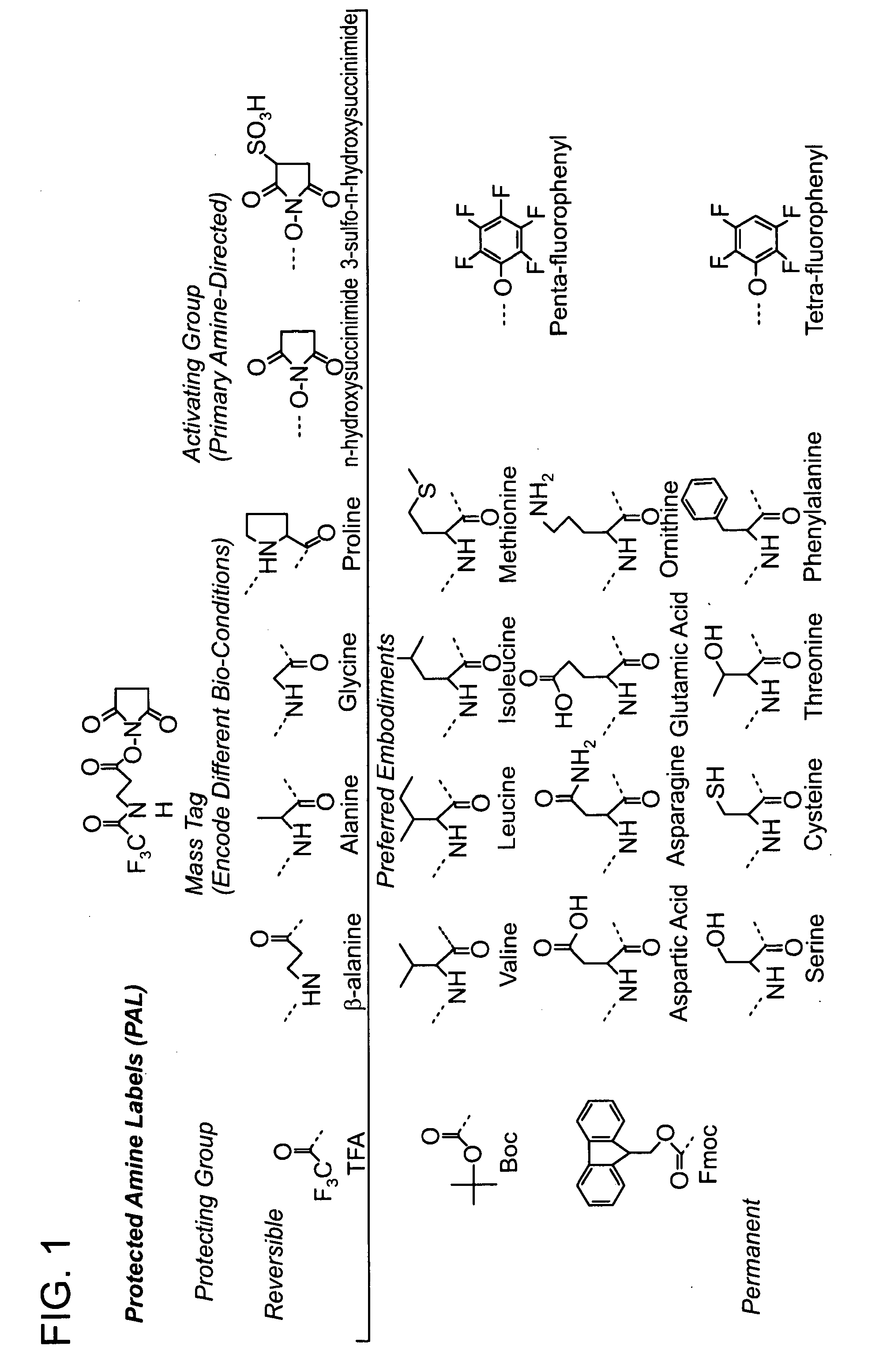
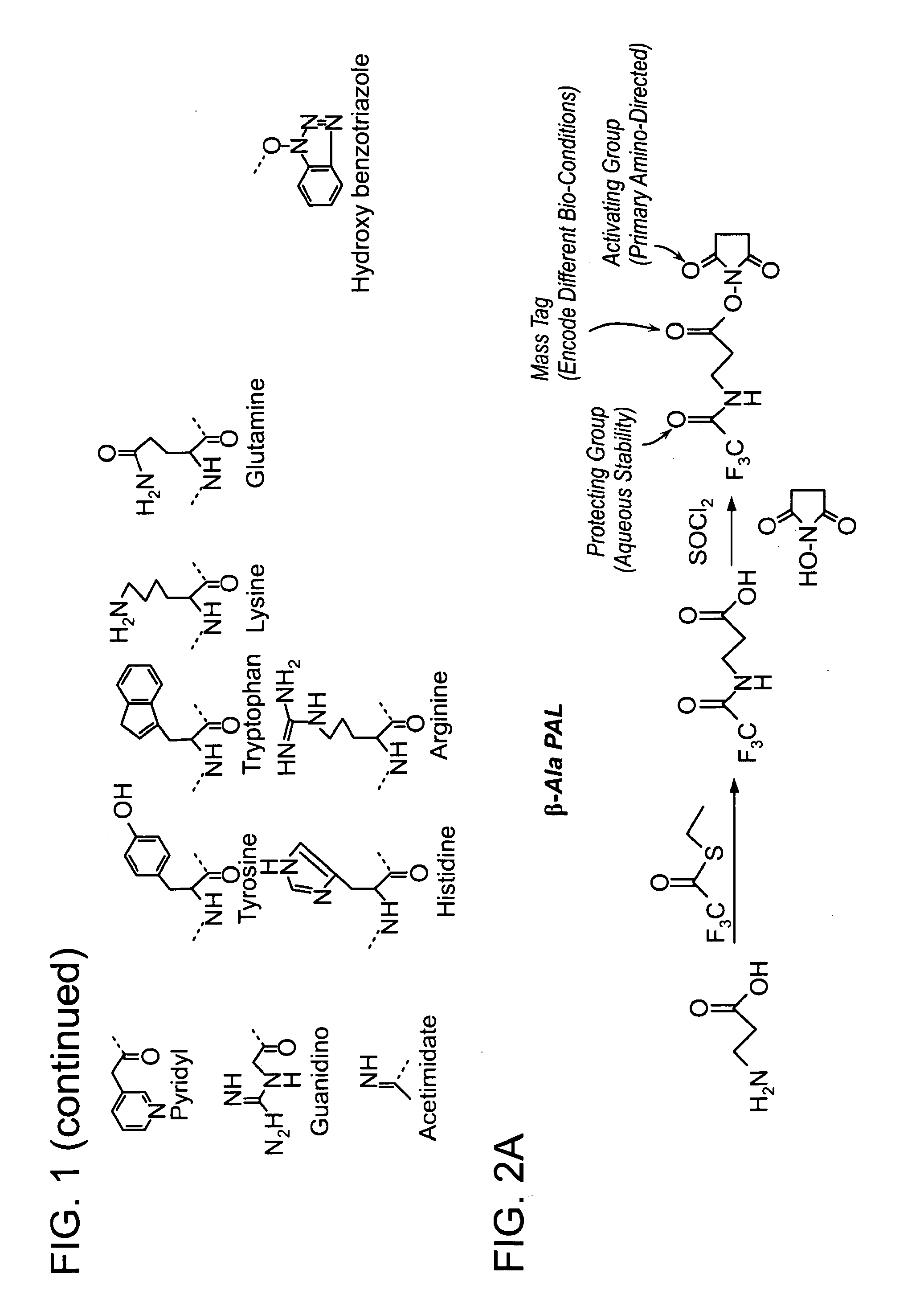
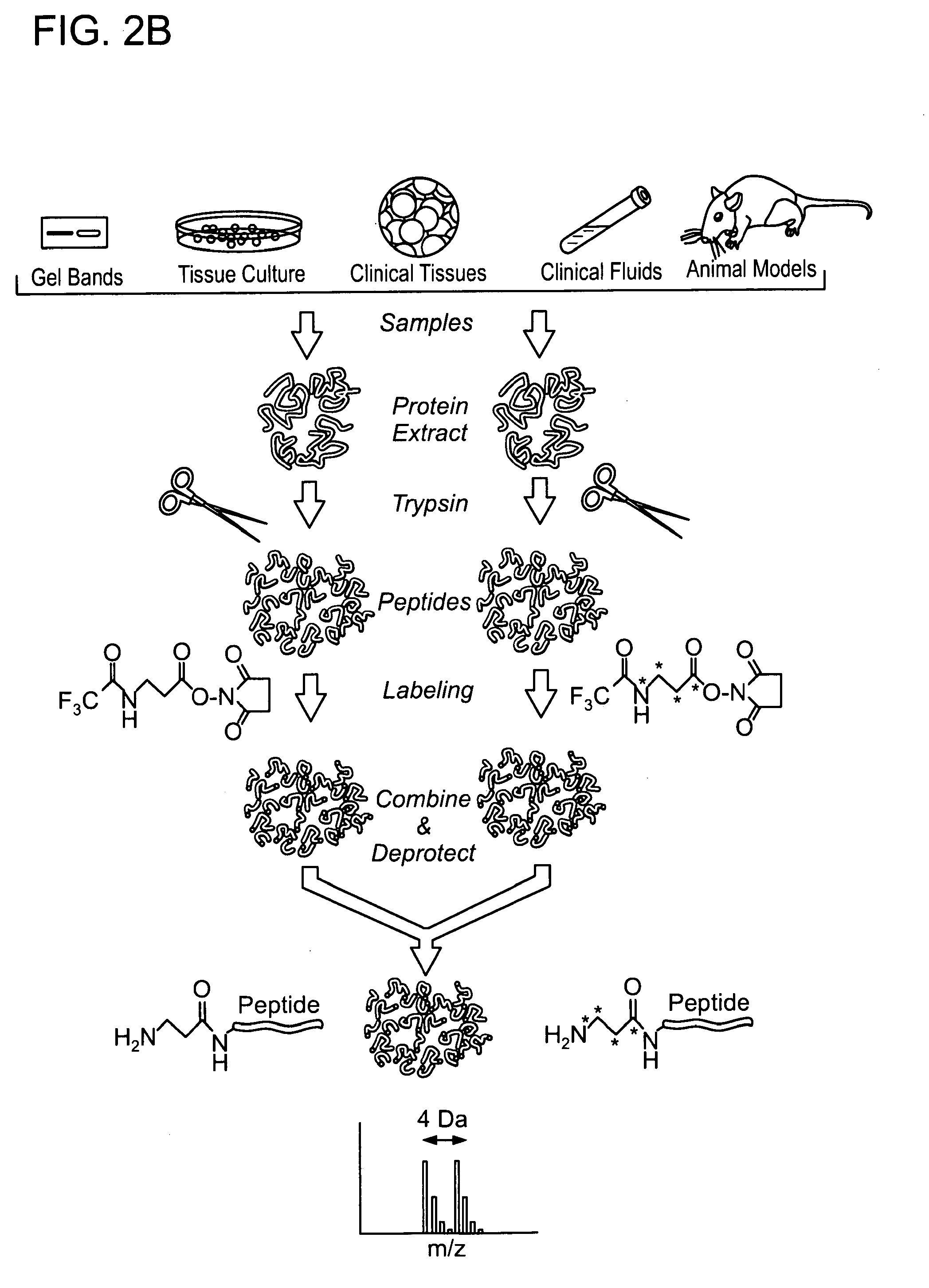
Protected amine labels and use in detecting analytes
The invention is directed towards novel amino acid based compounds, which may be isotopically enriched, and methods of use of such compounds for characterising one or more molecules of a sample by mass spectrometry, the method comprising: (a) reacting the one or more molecules with the compound; and (b) characterising the one or more molecules by mass spectrometry.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
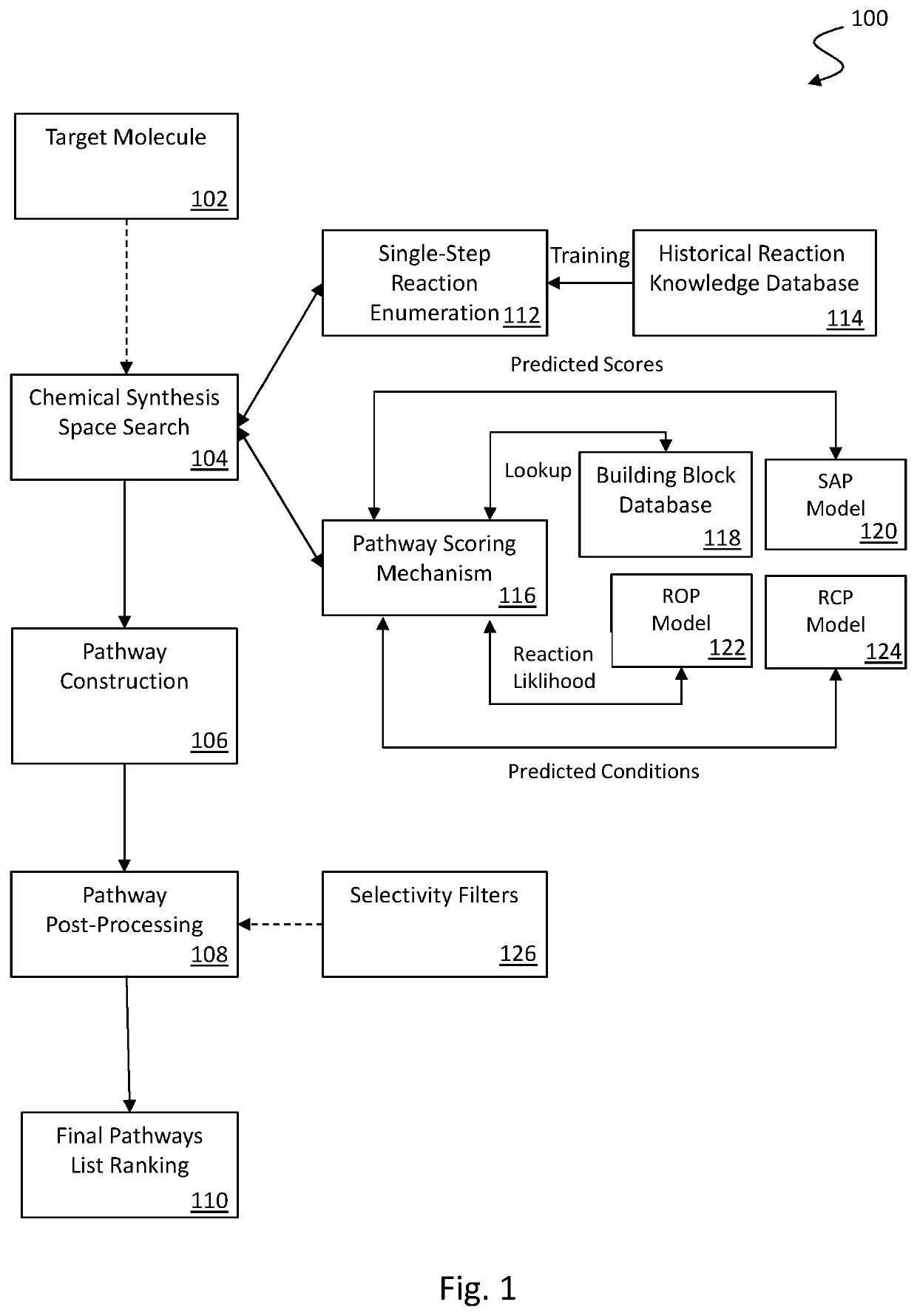
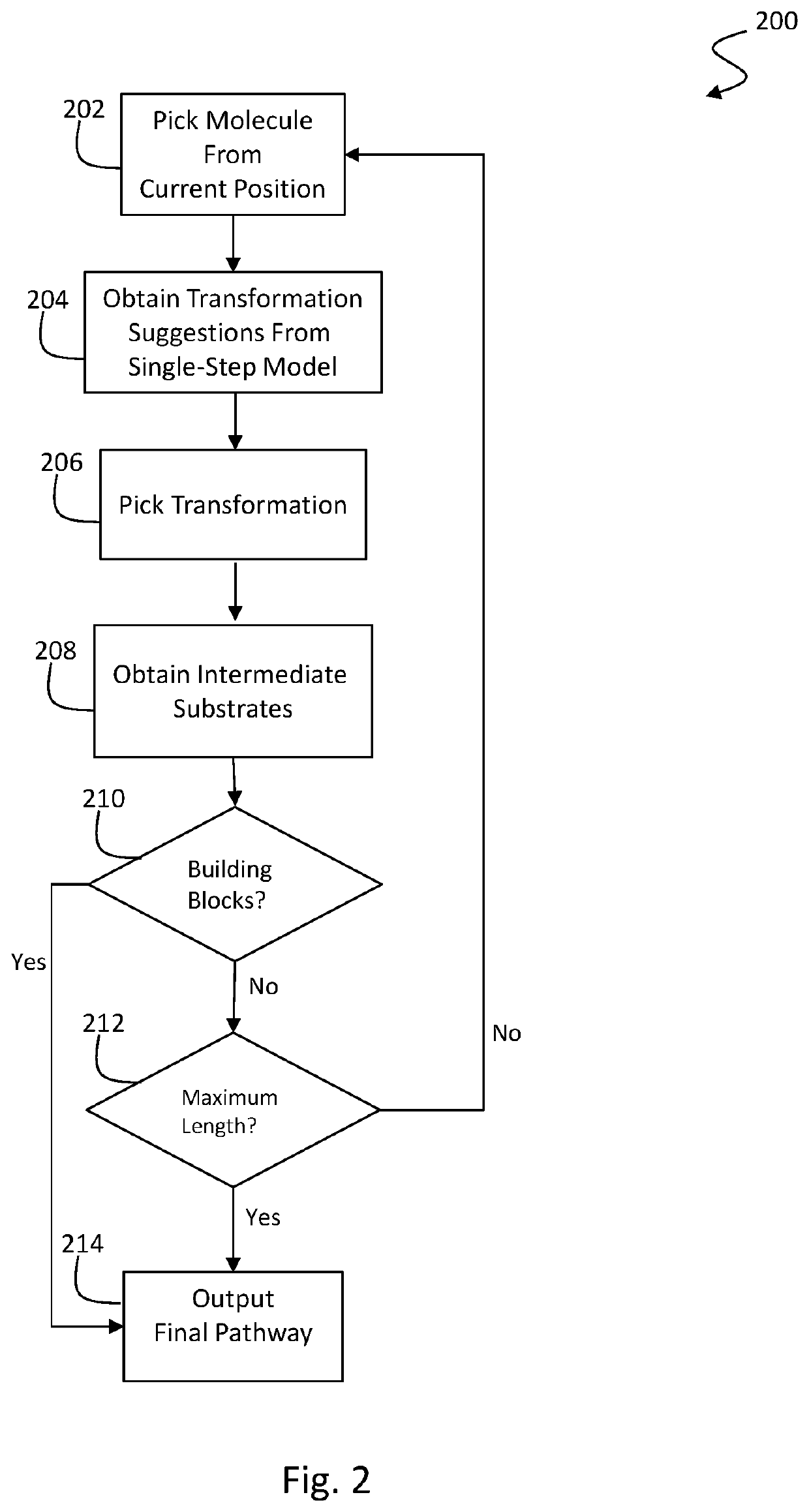
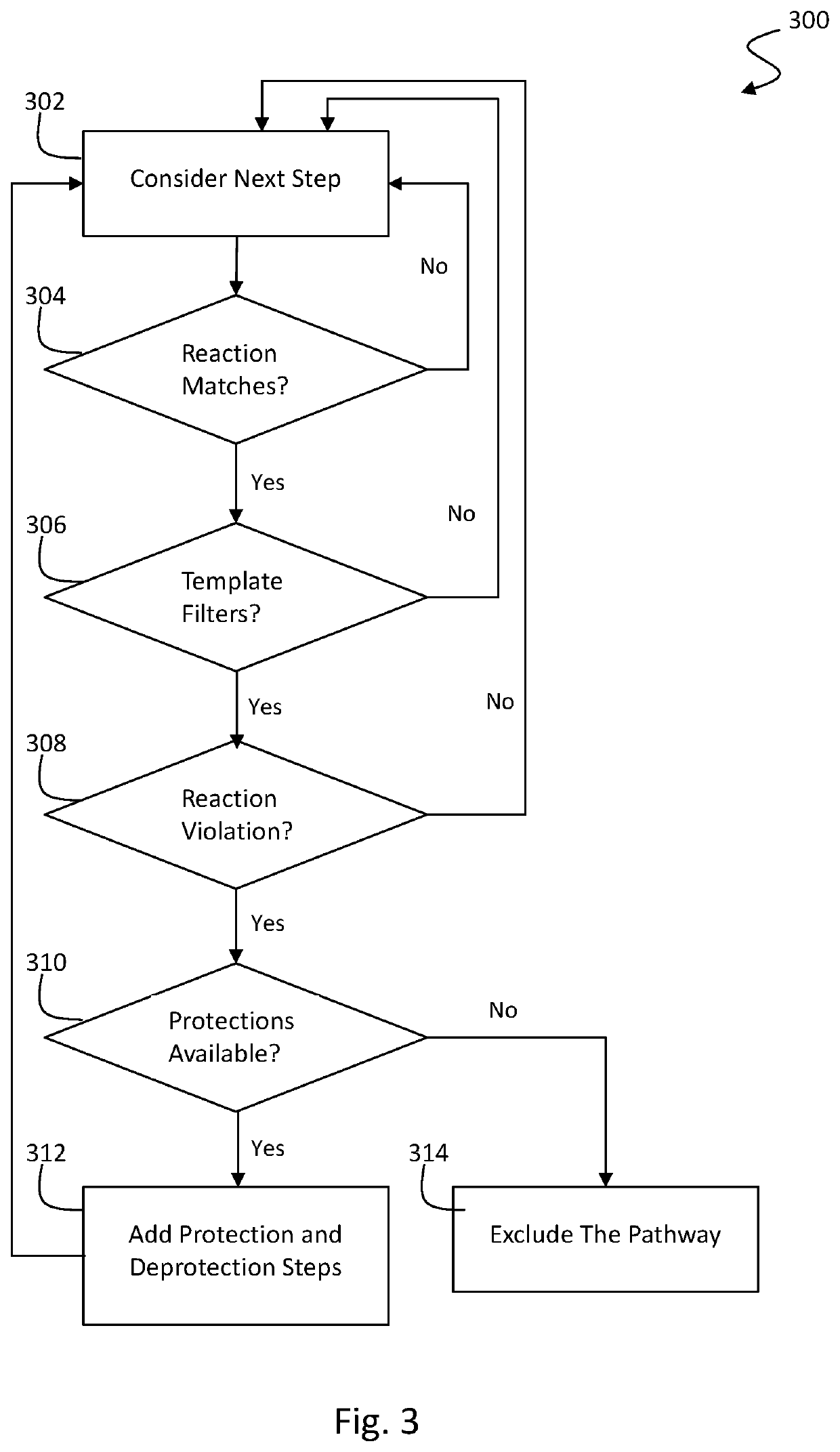
Retrosynthesis systems and methods
PendingUS20220172802A1SaveSave reactionChemical processes analysis/designChemical machine learningChemical synthesisChemical compound
A synthesis protocol for a reaction pathway of a target molecule can be determined by: providing target compound data; performing a chemical synthesis search for at least one reaction pathway for the target compound; processing the target compound data through a single-step reaction enumeration algorithm to obtain at least one reaction step of the least one reaction pathway; processing at least one reaction step with the at least one reaction pathway scoring mechanism model to obtain a reaction step score; constructing reaction pathways based on at least one reaction step and at least one reaction step score; providing a selectivity filter having a selectivity criteria; filtering the reaction pathways so that reactions violating the selectivity criteria is filtered out; ranking the reaction pathways; and providing the reaction pathway ranking.
Owner:INSILICO MEDICINE IP LTD
Irregular goods package three-dimensional material loading method based on chemical reaction optimization algorithm
The invention discloses an irregular goods package three-dimensional material loading method based on a chemical reaction optimization algorithm. The method comprises the steps that molecules and a molecular group are constructed; calculating initial potential energy PEk and initial kinetic energy KEk; if a single molecule is subjected to a bimolecular meta-reaction, randomly selecting a collisionreaction mode of two molecules with another randomly selected molecule, recording the lowest potential energy in the molecules and the molecule with the lowest potential energy, and judging whether the lowest potential energy meets the requirements or not; if the single molecule generates the meta-reaction of the single molecule, randomly selecting a single molecule reaction mode, recording the lowest potential energy in the molecule and the molecule with the lowest potential energy, judging whether the lowest potential energy meets the requirements or not, If not, returning to calculate theinitial kinetic energy and potential energy; otherwise, optimizing the material loading scheme. Compared with a traditional manual loading mode, the optimization effect of the loading layout scheme isgreatly improved, compared with an original genetic algorithm mode, the optimization effect is slightly improved, but the algorithm execution speed is much higher.
Owner:SICHUAN AEROSPACE SYST ENG INST
Two-stage drive waveform for switching a dual frequency liquid crystal (DFLC) at large tilt angles
InactiveUS8330693B2Easy to operateReduces the push on the moleculesStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsDual frequencyEngineering
A two-stage drive waveform switches a DFLC from a high tilt state to a low tilt state quickly and without scattering. A relaxation voltage is applied to delay the onset of the high amplitude high frequency kick voltage when switching from a high tilt state to a low tilt state. The relaxation voltage allows the molecules to ‘relax’ in accordance with their own elasticity towards their low tilt state in the direction of the average azimuth angle of the low tilt state. The kick voltage is then applied to drive the molecules quickly to the low tilt state. Optimal switching time and the desired molecular response is achieved by delaying the onset of the large kick voltage via application of the relaxation voltage. The relaxation voltage may constitute a lower amplitude holding voltage, a small or zero DC voltage or a smooth windowing of the kick voltage.
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
Single-molecule mechanical method for measuring inhibition of small-molecule drug on protein and nucleic acid interaction
PendingCN112255396AImprove versatilityGain reliabilityMaterial magnetic variablesMagnetic beadPharmacometrics
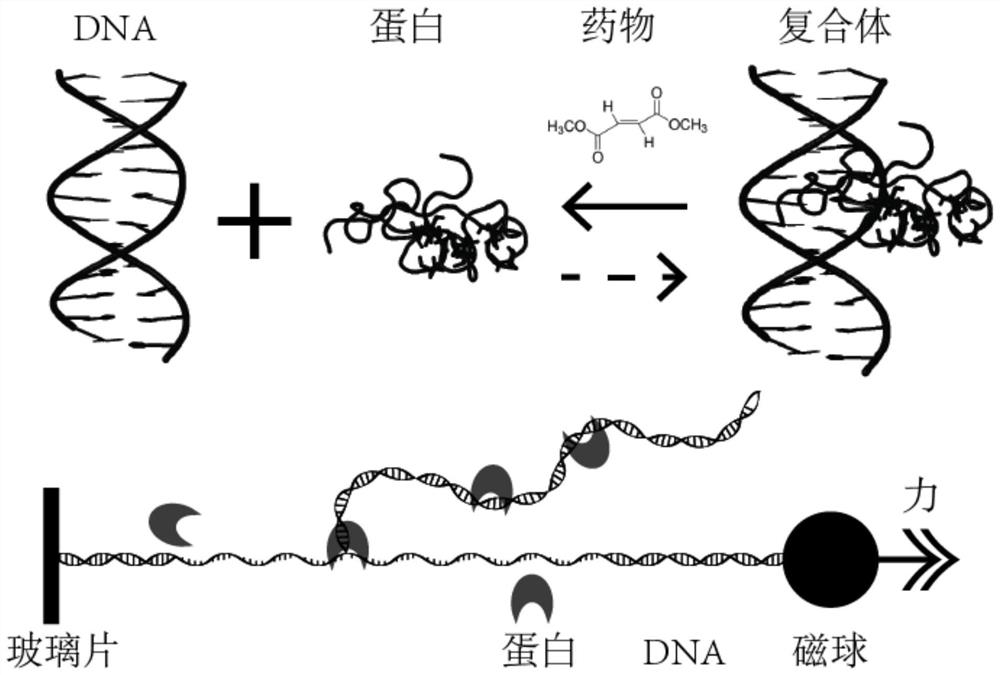
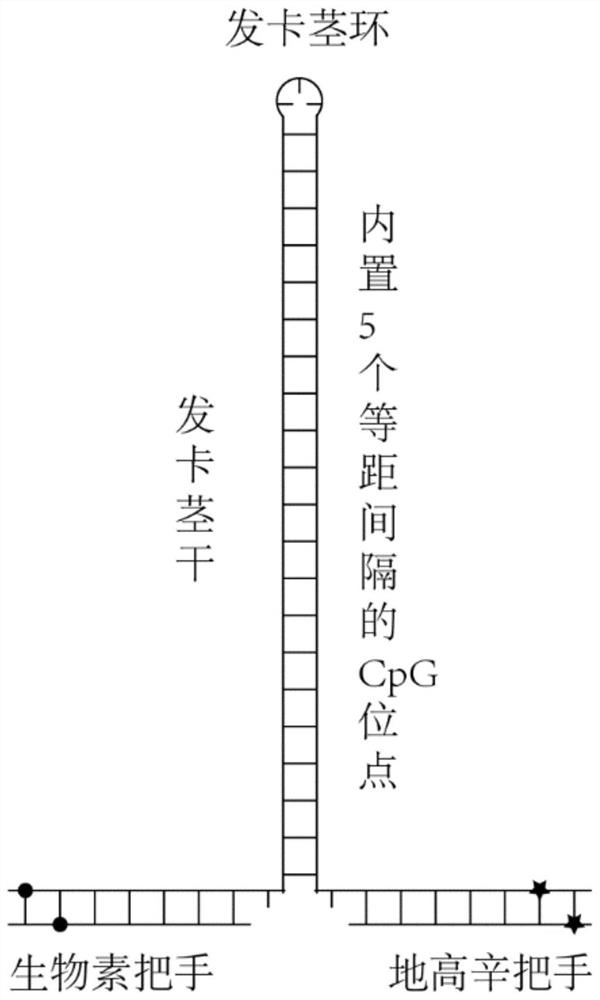
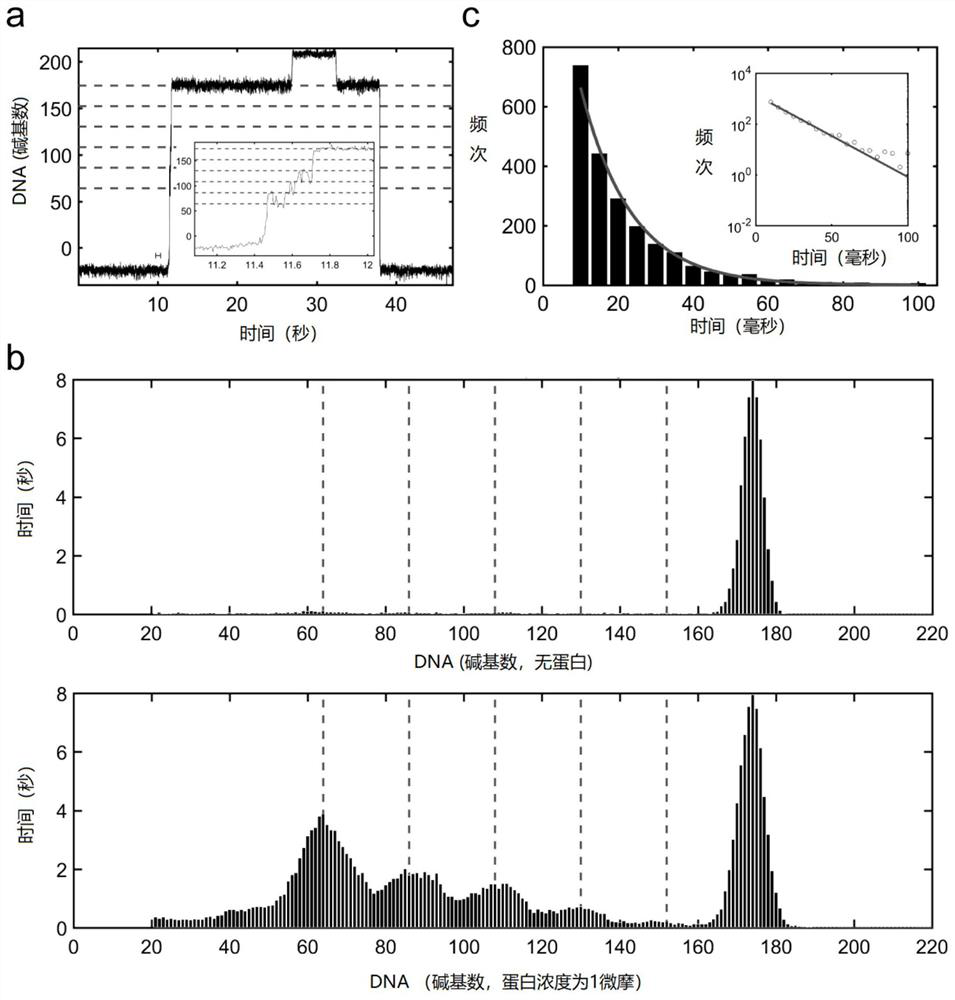
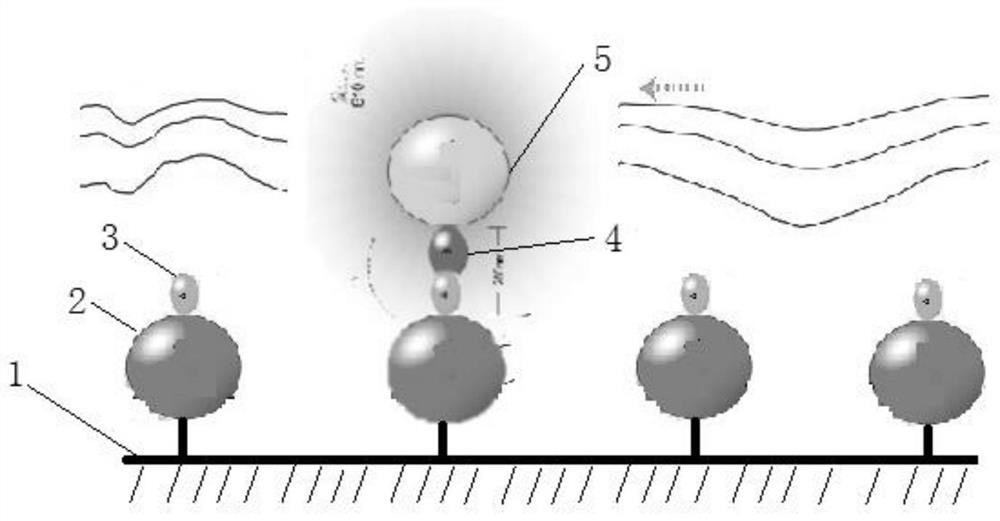
The invention relates to a single-molecule mechanical method for measuring inhibition of a small-molecule drug on protein and nucleic acid interaction. The method includes: first, designing and constructing a monomolecular reactor based on a DNA hairpin structure, the stem portion of which comprises a motif interacting with protein, and the handle portion of which is labeled with digoxin and biotin by polymerase chain reaction; secondly, preparing protein interacting with the DNA; thirdly, fixing the DNA hairpin structure between a magnetic bead and a glass sheet, and carrying out a DNA melting experiment in a microfluidic reaction tank through a monomolecular mechanics method; and finally, systematically testing the influence of the concentration of the small-molecule drug on the meltingreaction of the DNA combined with the protein, drawing a drug dose-response curve, calculating a half inhibition concentration, and evaluating the drug effect of the small-molecule drug on the proteinand nucleic acid interaction. The invention belongs to the field of biomacromolecule interaction and monomolecular pharmacology, and develops a new method for directly measuring small-molecule drug inhibition on protein nucleic acid interaction for molecular biology research, drug development and pharmacological evaluation.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Homogeneous chemiluminiscence detection method and application thereof
PendingCN111665237AReduce matrix effectHigh sensitivityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceLaboratory glasswaresMicrosphereImmuno detection
The invention relates to a homogeneous chemiluminiscence detection method and application thereof in the field of chemiluminiscence analysis. The method comprises the following steps: S1, enabling a liquid-phase reactant containing a first microsphere in chemiluminescence pairing microspheres and a to-be-detected object suspected to contain a to-be-detected target molecule to be in contact reaction with the surface of a solid-phase support, wherein the surface of the solid-phase support is provided with a corresponding second microsphere in the chemiluminescence pairing microspheres; S2, exciting one microsphere in the chemiluminescence pairing microspheres to generate active oxygen by utilizing energy or an active compound, and reacting the other microsphere in the chemiluminescence pairing microspheres with the active oxygen contacted with the microsphere to generate a chemiluminescence signal; and S3, detecting the intensity of the chemiluminescence signal in the step S2, and analyzing whether a to-be-detected target molecule and / or the concentration of the to-be-detected target molecule exist / exists in the to-be-detected object. The method can simultaneously detect a pluralityof to-be-detected molecules, is high in reaction speed, and effectively eliminates the matrix effect in homogeneous immunoassay.
Owner:上海索昕生物科技有限公司
Method for investigating molecules such as nucleic acids
InactiveCN110785236AMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresMolecular biologyMolecular Response
A method for manipulating a microdroplet of a reaction medium in an immiscible carrier medium with a target molecule bound to a solid support for the purposes of effecting a chemical transformation isprovided. It is characterised by the steps of (a) bringing the microdroplet into contact with the solid support under conditions where the microdroplet and solid support are caused to combine, (b) allowing the reaction medium to react with the target molecule and (c) thereafter exerting a force to induce the reaction medium to become detached from the solid support and reform a microdroplet in the carrier fluid. In one embodiment the solid support is a particle, bead or the like.
Owner:BASE4 INNOVATION LTD
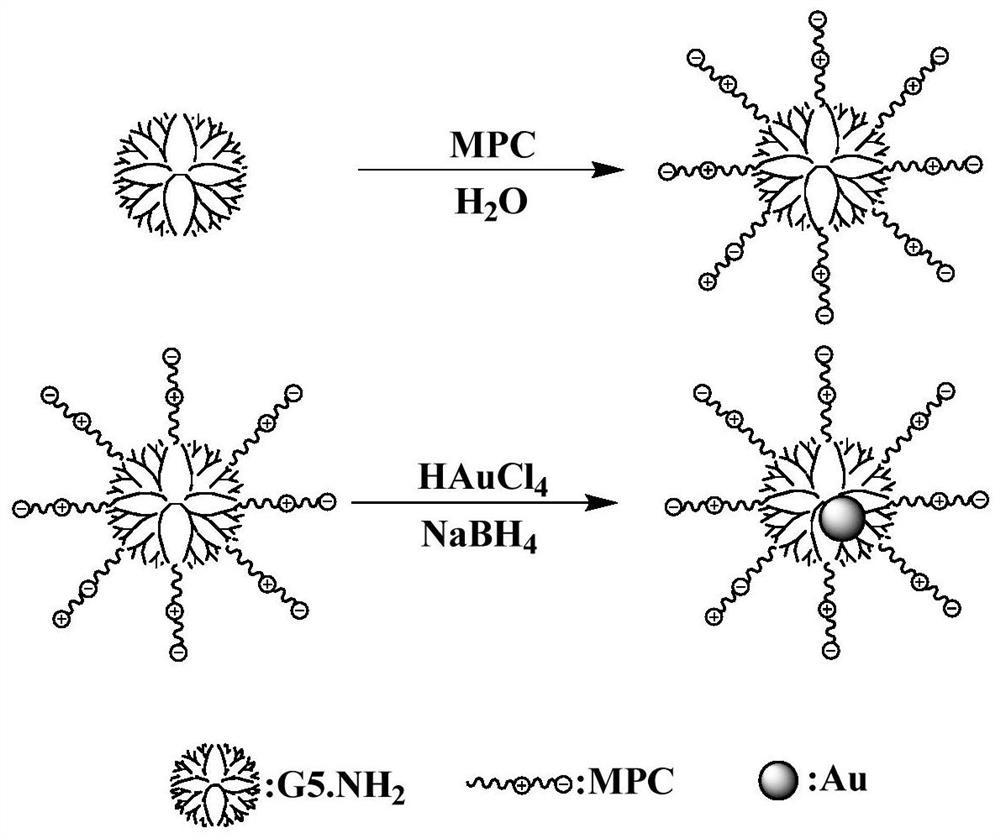
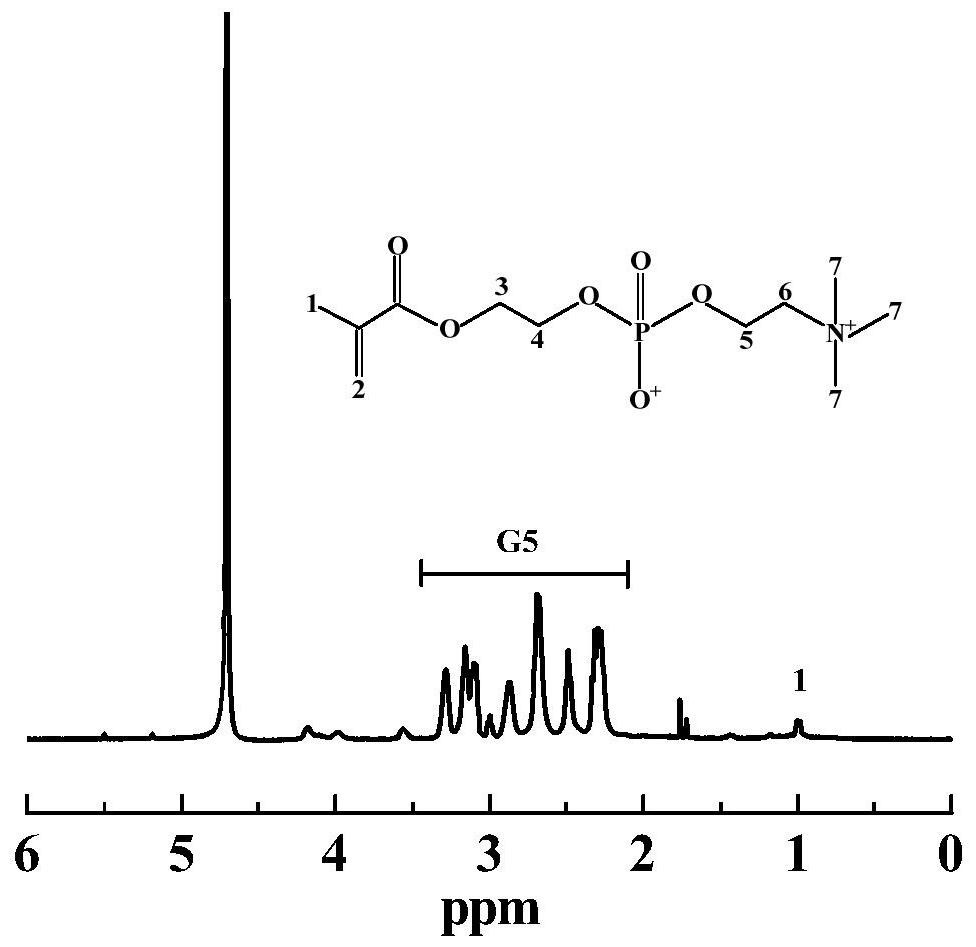
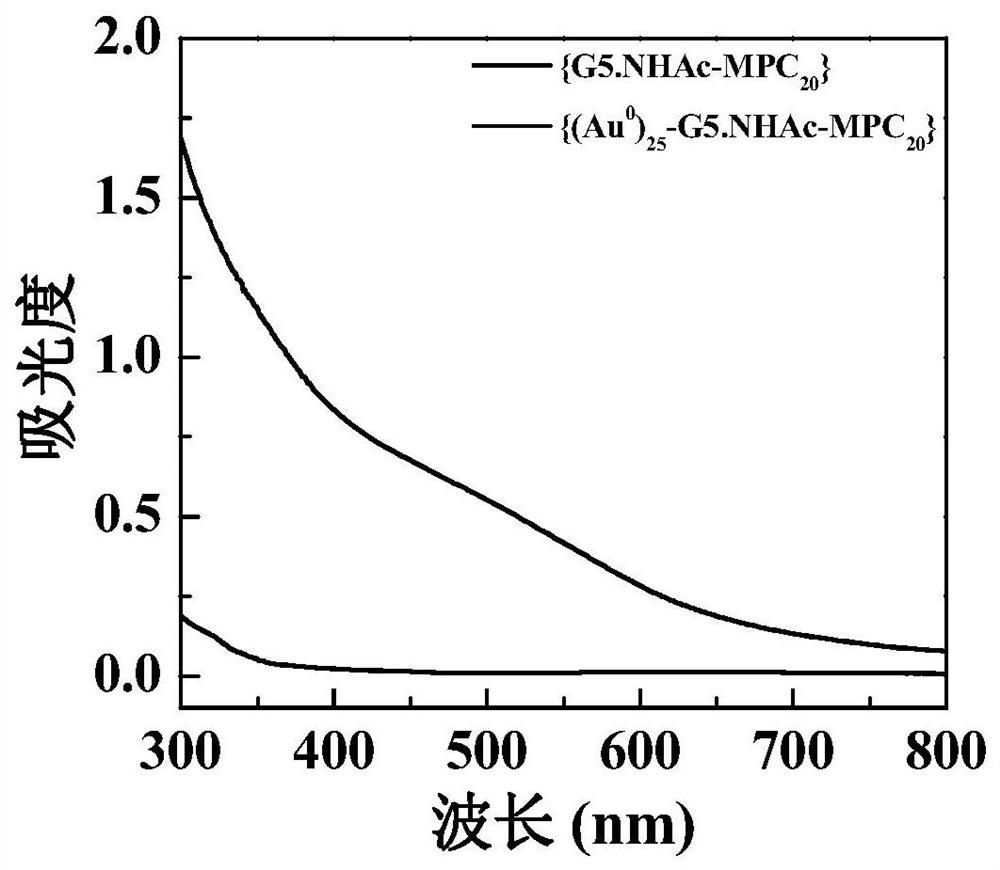
A kind of MPC-modified dendrimer-wrapped gold nanoparticles and its preparation and application
ActiveCN110623938BEasy to manufactureEasy to operateOrganic active ingredientsInorganic non-active ingredientsDendrimerGold particles
The present invention relates to a kind of MPC-modified dendrimer wrapped nano-gold particles and its preparation and application, comprising dissolving MPC in a solvent, adding polyamide-amine dendrimers dissolved in the solvent to react, and then adding chlorine Auric acid solution and sodium borohydride solution, after dialysis, freeze-drying, that is. The preparation process of the present invention is short and easy to operate; and the material has low toxicity at the dosage, good biocompatibility, can compress the CpG gene, and the compound loaded with the CpG gene can effectively stimulate immune cells and then kill tumor cells, which is very important. The application of viral vectors in tumor immunotherapy provides a reference.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Dendrimer transgene carrier modified with bone-targeting peptide and naphthalimide, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108753829BEasy to purifyLow toxicityOther foreign material introduction processesDendrimerTarget peptide
The present invention provides a dendrimer transgene carrier modified with bone-targeting peptide and naphthalimide, which includes a dendrimer skeleton, a bone-targeting peptide group, and a functional group containing naphthalimide. The targeting peptide group and the naphthalimide functional group are covalently bonded on the surface of the dendrimer; the dendrimer is a polyamide-amine dendrimer. The invention also provides the preparation method of the gene transfection carrier and the application of the dendrimer transgene carrier as a nucleic acid molecule delivery carrier. The invention adopts a brand-new modification method and a functional group to modify the dendrimer, the reaction is simple and efficient, the yield is high, the efficient transfection effect is achieved in the cell transfection process, and the bone targeting performance is better. The production of materials is simple and low in cost, the cytotoxicity of the transfection process is low, and gene molecules can be effectively and safely transported into cells. The dendrimer transgene carrier of the present invention has the advantages of high efficiency, low toxicity, low price, and simple synthesis .
Owner:西安九清医疗科技有限公司
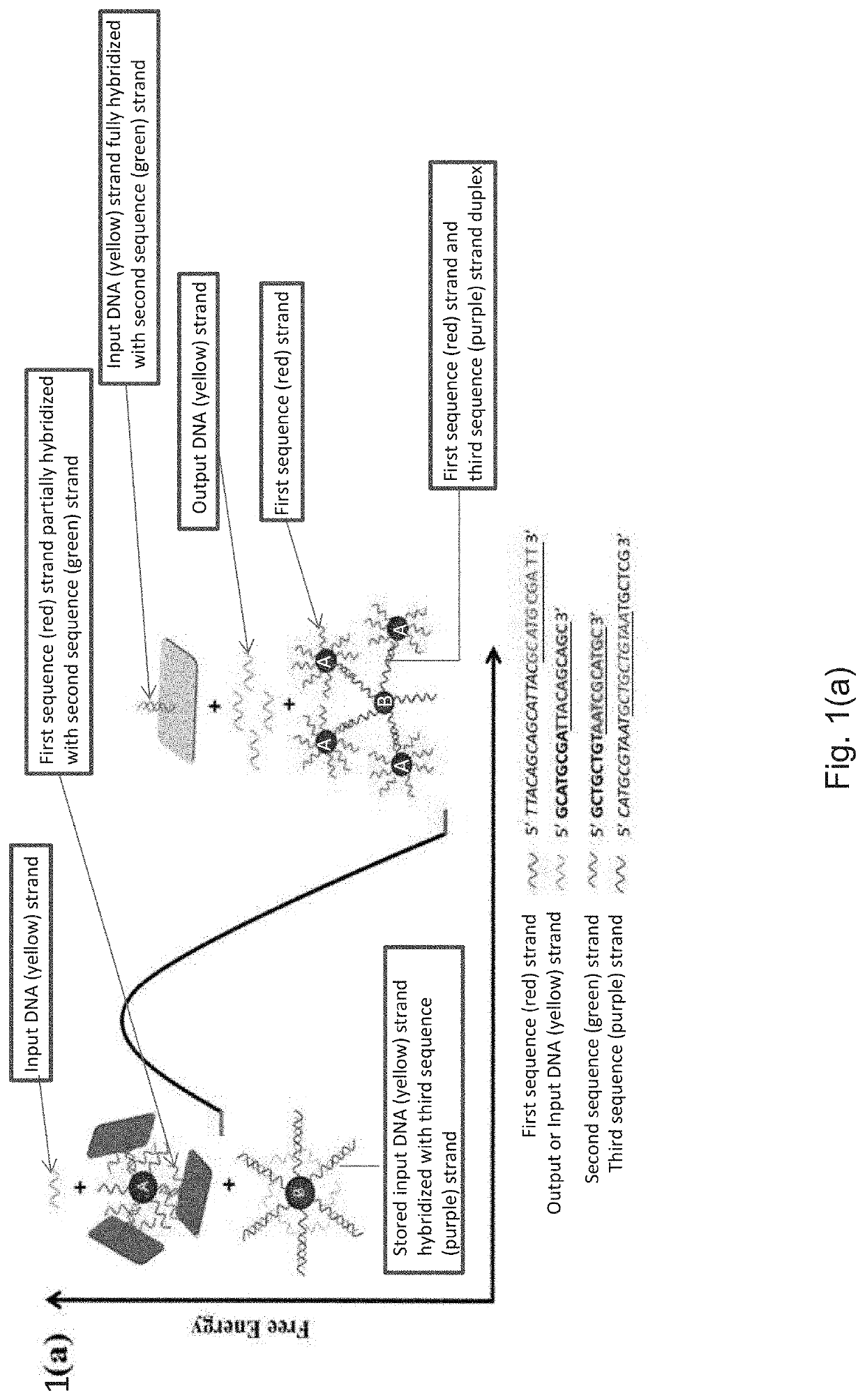
Methods for Isothermal Molecular Amplification with Nanoparticle-Based Reactions
PendingUS20210024990A1High sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementNanomedicineAnalyte moleculeNanoparti cles
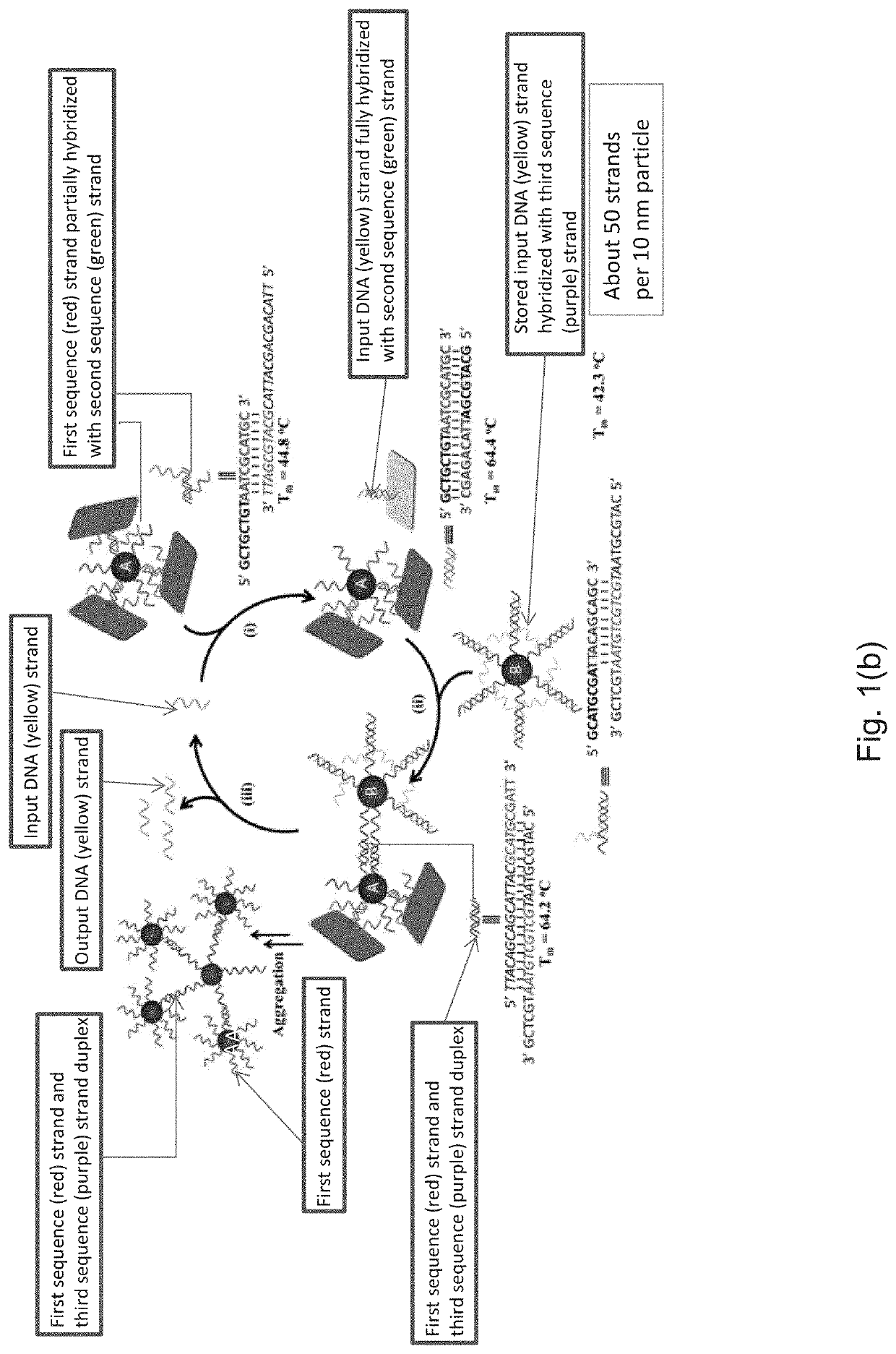
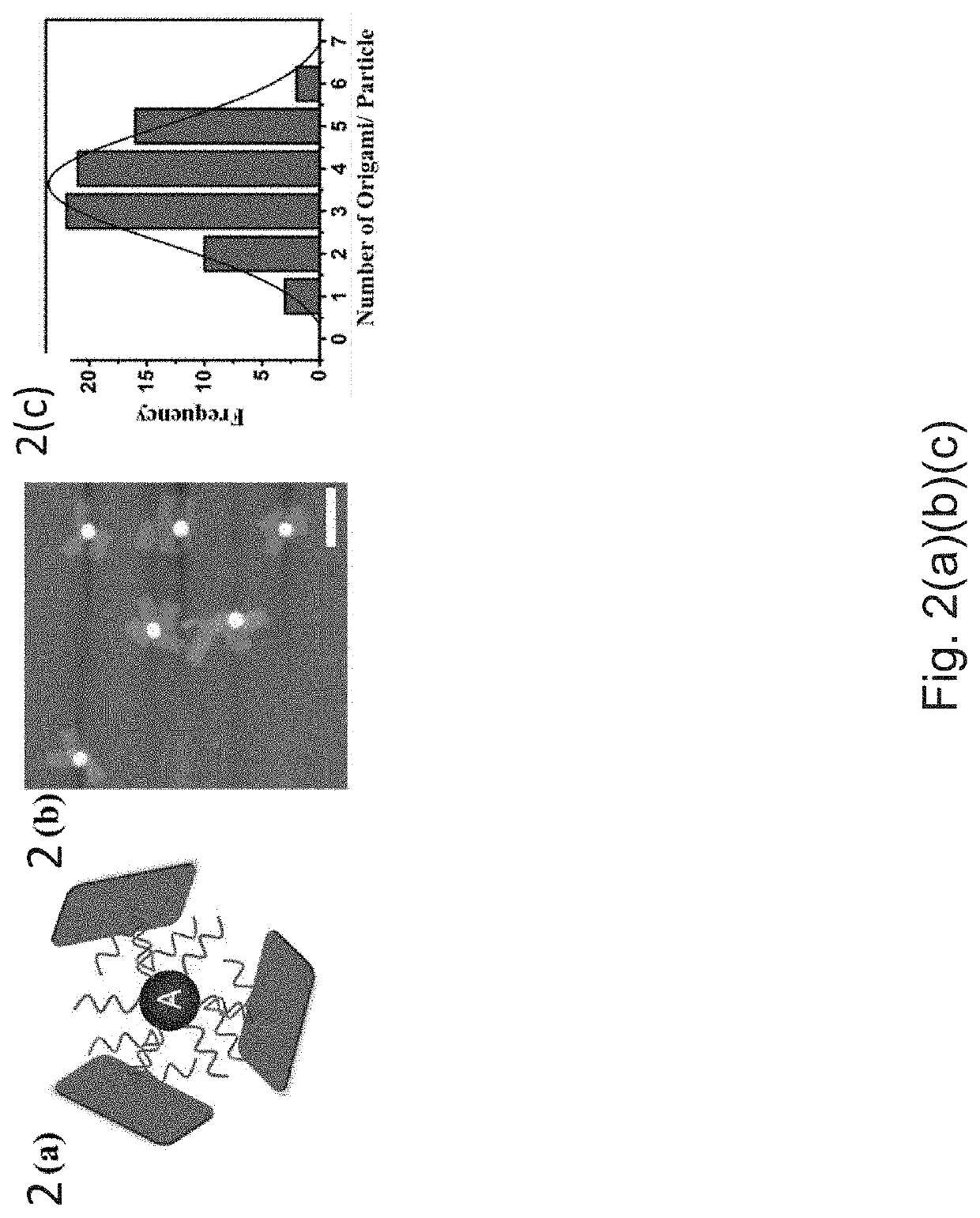
The present method of detection involves increasing an amount of analyte molecules by an isothermal molecular amplification approach. In the present approach a starting molecule of interest may be amplified through a reaction it induces with specifically engineered and functionalized particles, namely protected particles A and storage particles B. This reaction may result in a set of output DNA molecules that is larger in number than the input DNA molecules. Thus the reaction between nanoparticles for amplification of a certain DNA sequence (input DNA molecules) may occur when there is a match with a targeted molecule (stored molecules on storage particles B) and if the DNA sequence of the input DNA molecules does not match (partially or completely) the targeted molecule the reaction may not occur. Without a certain molecular input of the input DNA molecule the reaction may not occur.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
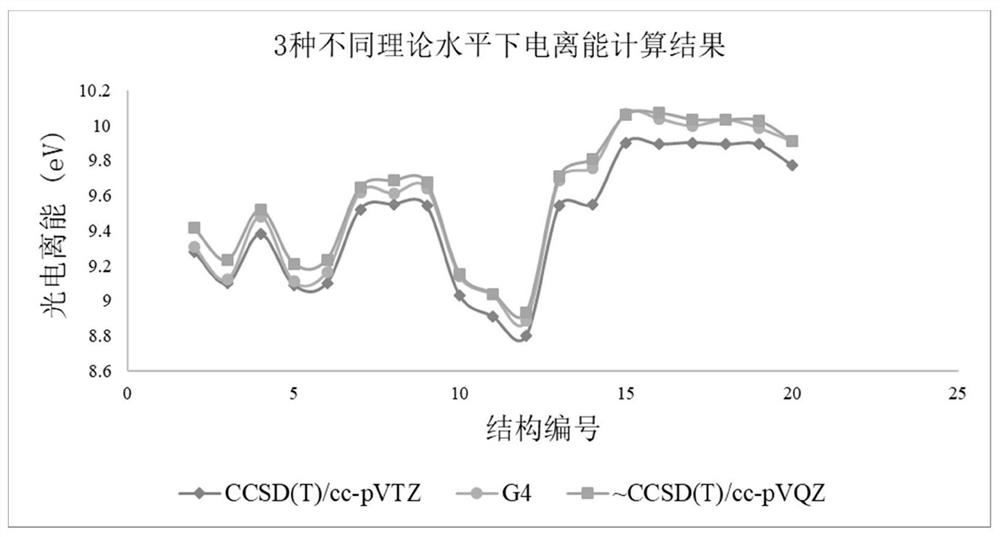
Method for determining vinyl ether ozonization single-molecule reaction product based on high-level quantum chemistry calculation method and experiment
PendingCN114724637AAvoid wastingLow costChemical property predictionChemical processes analysis/designVinyl etherQuantum chemical
The invention discloses a method for determining a vinyl ethyl ether ozonization single-molecule reaction product based on a high-level quantum chemical calculation method in combination with an experiment. According to the method, the first principle density functional theory is combined with the de novo calculation theory, reaction kinetics simulation is adopted, existence of specific products is proved theoretically, and experiment condition setting is guided through simulation results; and determining ionization energy by comparing theoretical ionization energy and experimental signals under three different high-level quantum chemical calculation methods so as to determine the existence of the product, thereby perfecting the product identification method of the substance ozonization reaction. According to the invention, high-level quantum chemical calculation and dynamic simulation are used to verify the reaction feasibility, and a simulation result is used to guide the setting of an important experimental condition-reaction time, so that the cost is saved, the waste of drugs and instrument energy is avoided, and the method accords with the green chemistry concept.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Nucleic acid aptamer for classification of different-subtype non-small cell lung cancers and screening method thereof
InactiveCN101914543BMicrobiological testing/measurementIndividual particle analysisAptamerNucleotide
The invention discloses a nucleic acid aptamer for classification of different-subtype non-small cell lung cancers and a screening method thereof. The nucleic acid aptamer provided by the invention is a DNA segment which comprises nucleotide shown as any one of sequences 1 to 9 in a sequence table. The nucleic acid aptamer can be applied to the classification of the different-subtype non-small cell lung cancers. By using the nucleic acid aptamer of the invention, the differentiation of the different-subtype non-small cell lung cancers can be realized on a molecular response signal under the condition that tumor markers of the non-small cell lung cancers are unknown. When used for identifying a target combined with the nucleic acid aptamer, the nucleic acid aptamer is favorable for findingout the tumor markers of the different-subtype non-small cell lung cancers, performing earlier diagnosis and more accurate classification of the non-small cell lung cancers and finding out new medicament acting target points for tumor therapy.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
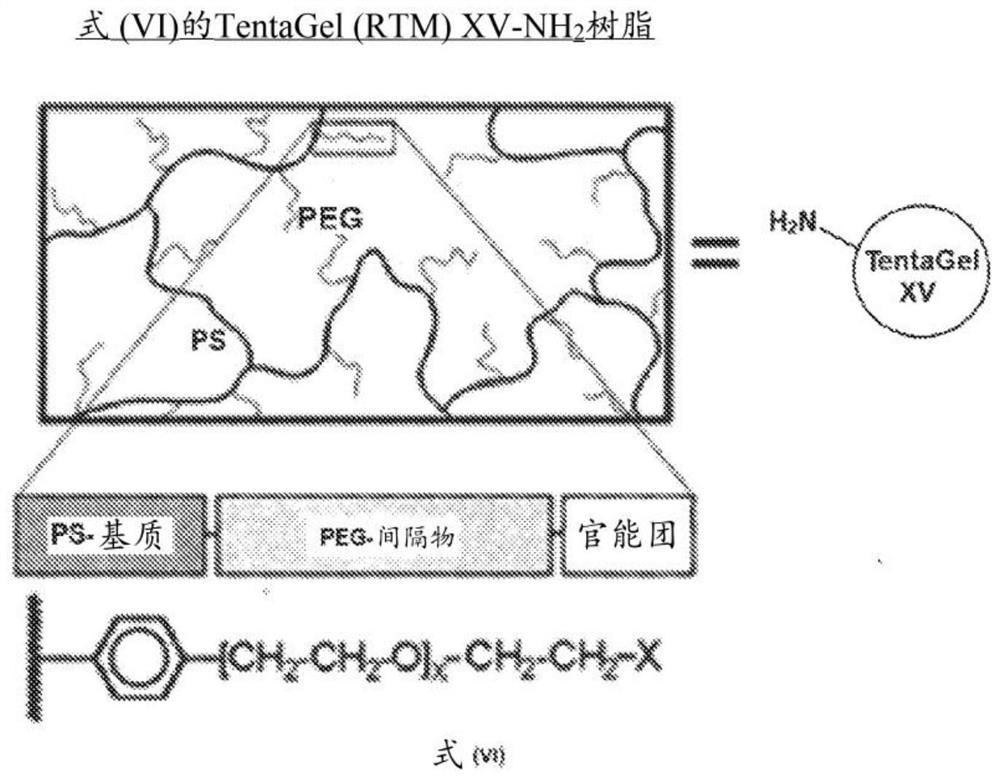
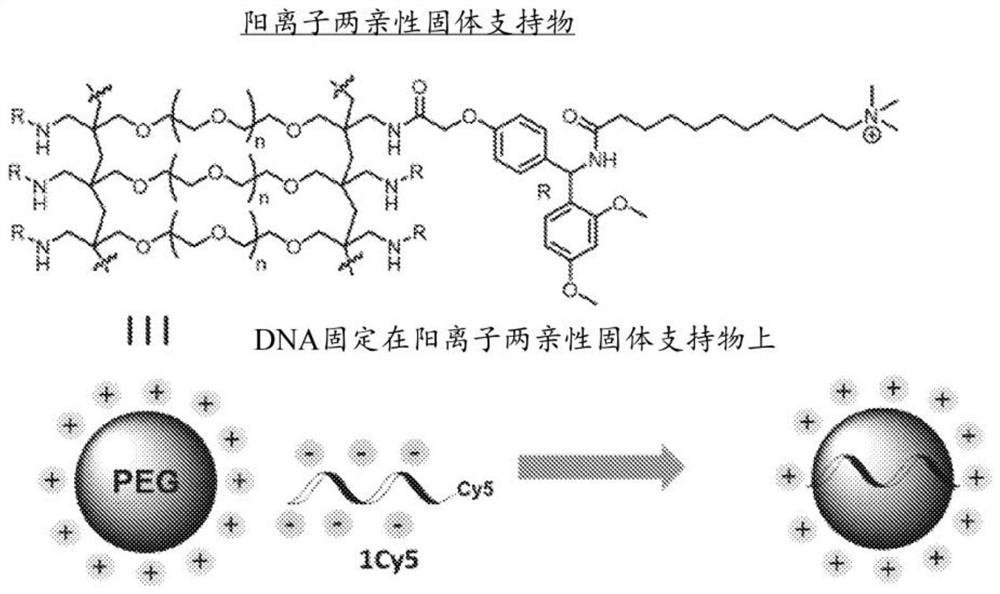
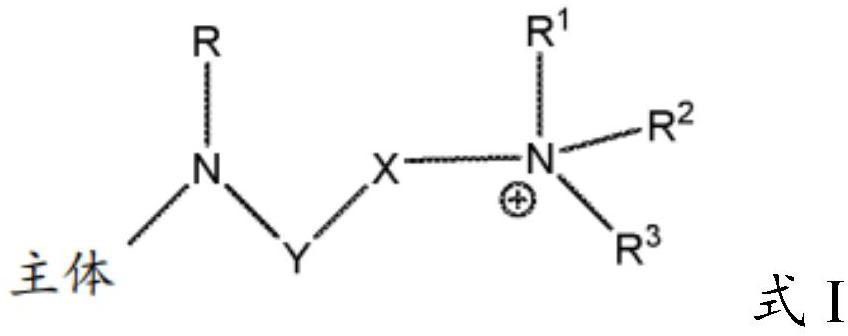
Solid support
ActiveCN112119056AMicrobiological testing/measurementOrganic chemistry methodsPolymer sciencePolyethylene glycol
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
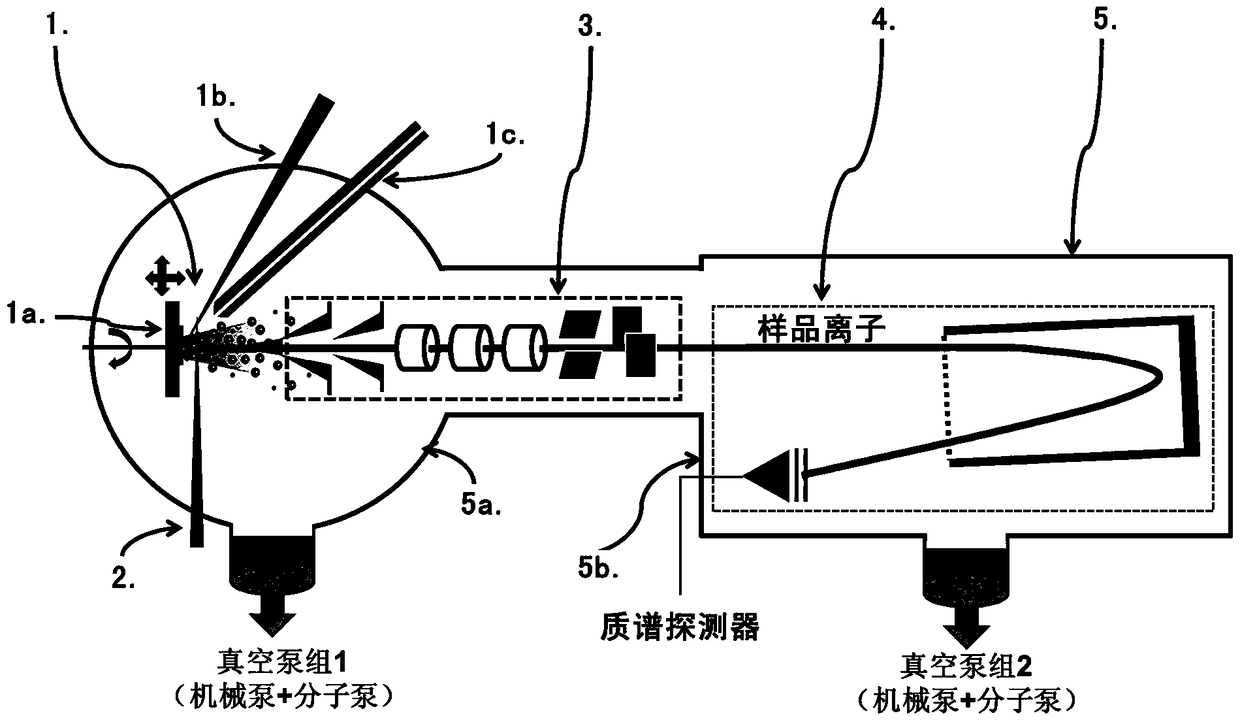
A Mass Spectrometry Device for Studying Plasma-Small Molecule System Reaction
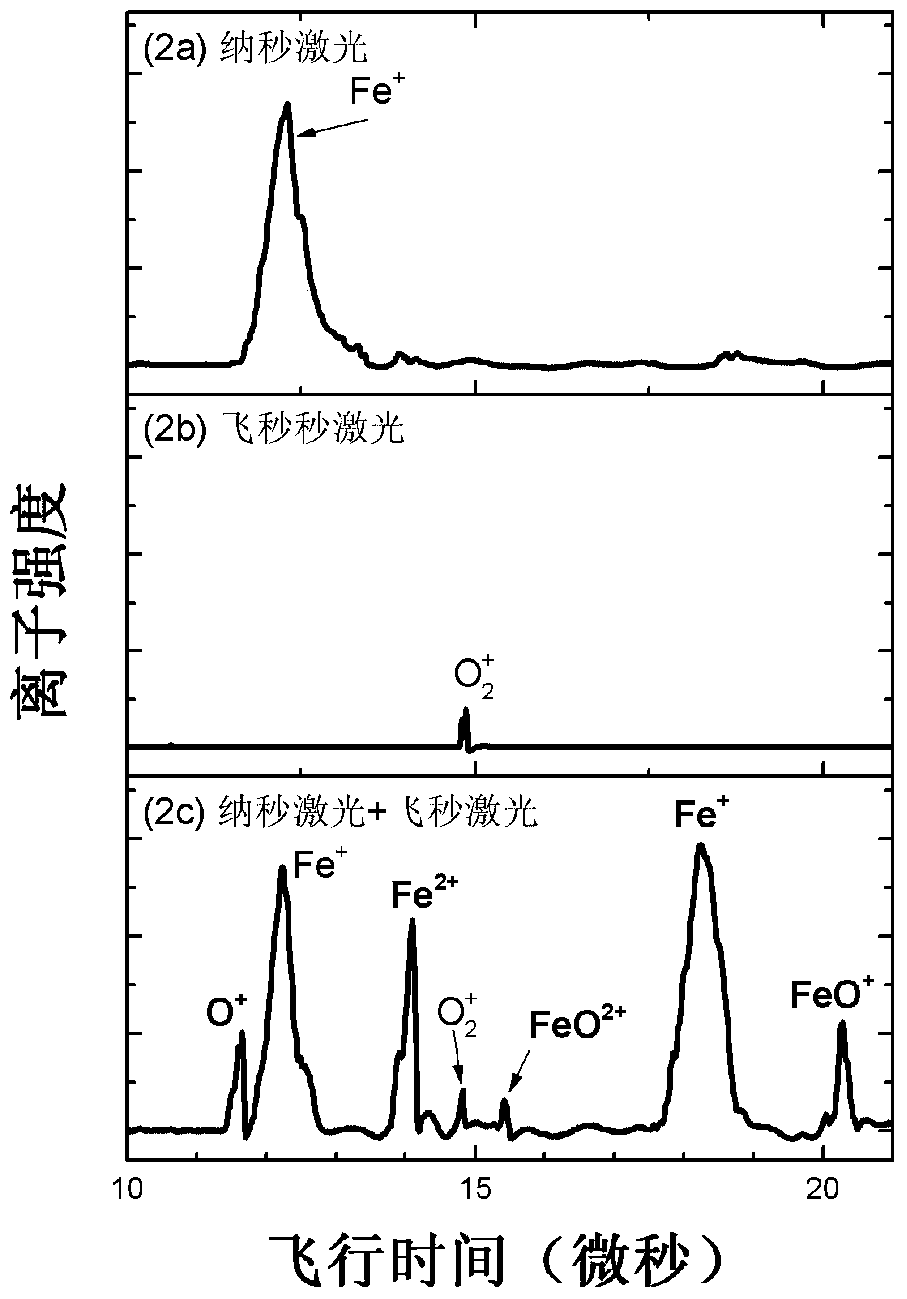
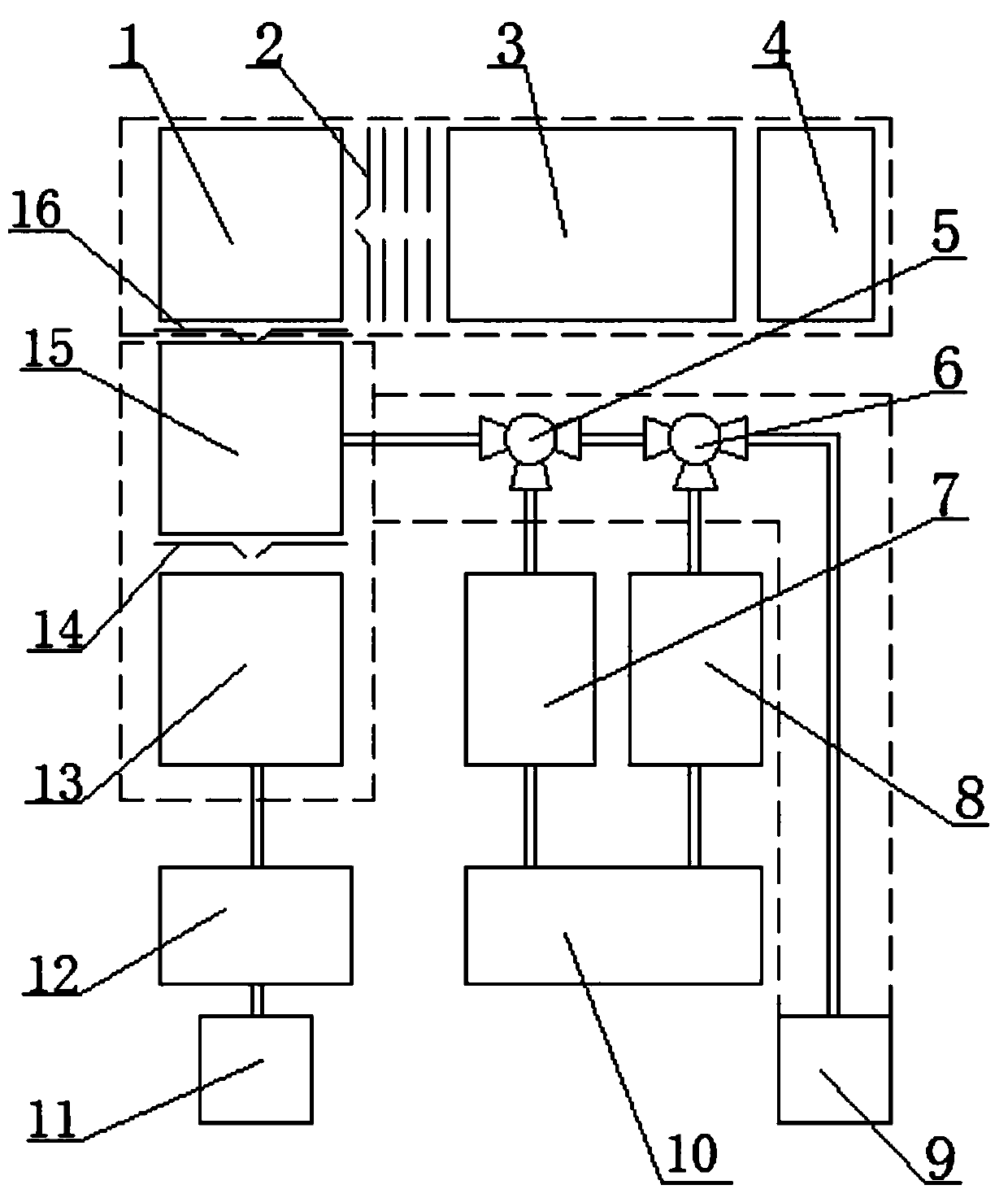
InactiveCN105762055BAchieve high-efficiency ionizationAccurate analysisMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMass spectrometersFemto second laserGas phase
The invention relates to a mass spectrometry device for studying plasma-small molecule system reactions. The mass spectrometer for researching plasma-small molecule system reaction comprises plasma-small molecule reaction unit (1), femtosecond laser ionization system (2), ion extraction system (3), mass analyzer (4), Vacuum chamber (5). Among them, the nanosecond laser sputtering solid target is used to generate plasma, and the gas phase small molecules enter the plasma generation area through the capillary, and react with the plasma near the surface of the target. Femtosecond laser ionization technology was used to ionize the reaction products, and finally, combined with time-of-flight mass spectrometry, the reaction products were analyzed and confirmed. The device can accurately, efficiently and real-time characterize the product composition of the reaction between plasma and gas phase molecules, and provide model support for the accurate cognition of the actual plasma and gas reaction in the production process.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
An Ion Molecular Reaction Mass Spectrometry System
ActiveCN107887251BAvoid lostExtended detection typesStability-of-path spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMass analyzer
The invention provides an ion molecular reaction mass spectrum system including a hollow cathode discharge power source which is connected with a reagent gas source at the front end and which is connected with an ion molecular reaction system at the rear end; a mass analyzer located behind the ion molecular reaction system, wherein ion paths inside the mass analyzer and the ion molecular reactionsystem are angled; a deflection system disposed between and communicating with the mass analyzer and the ion molecular reaction system; and a to-be-measured gas source communicating with the ion molecular reaction system through a pipeline. By using the deflection system to screen sample ions, the ion molecular reaction mass spectrum system is compact in overall structure, avoids sample ion loss caused by long-distance transmission, greatly expands the types of instrument detection, improves the instrument's comprehensive analysis capabilities, and is especially suitable for the detection of volatile organic compounds.
Owner:天津智谱仪器有限公司
A Design Method for Realizing Markov Chains Using Reversible Unimolecular Reactions
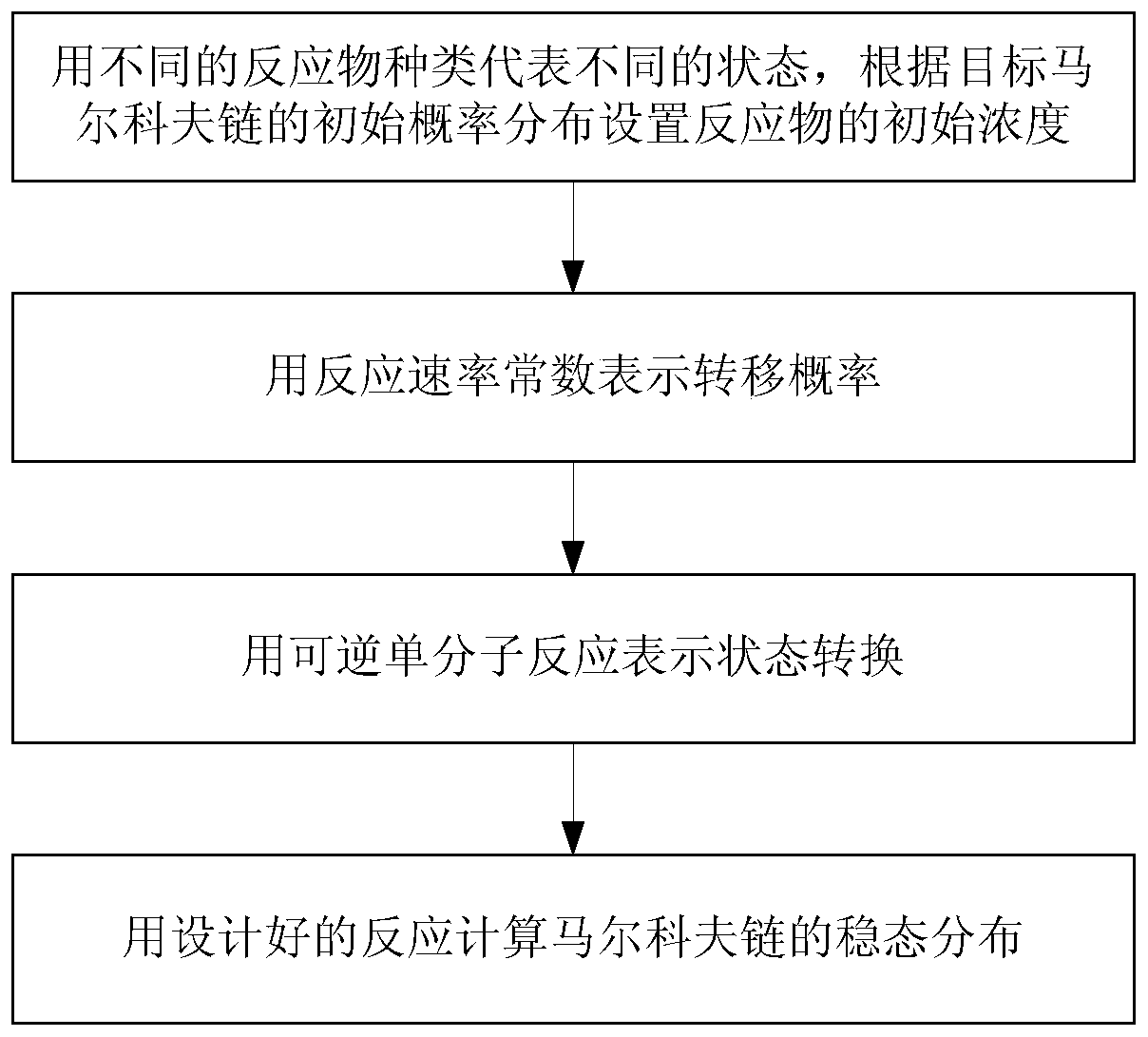
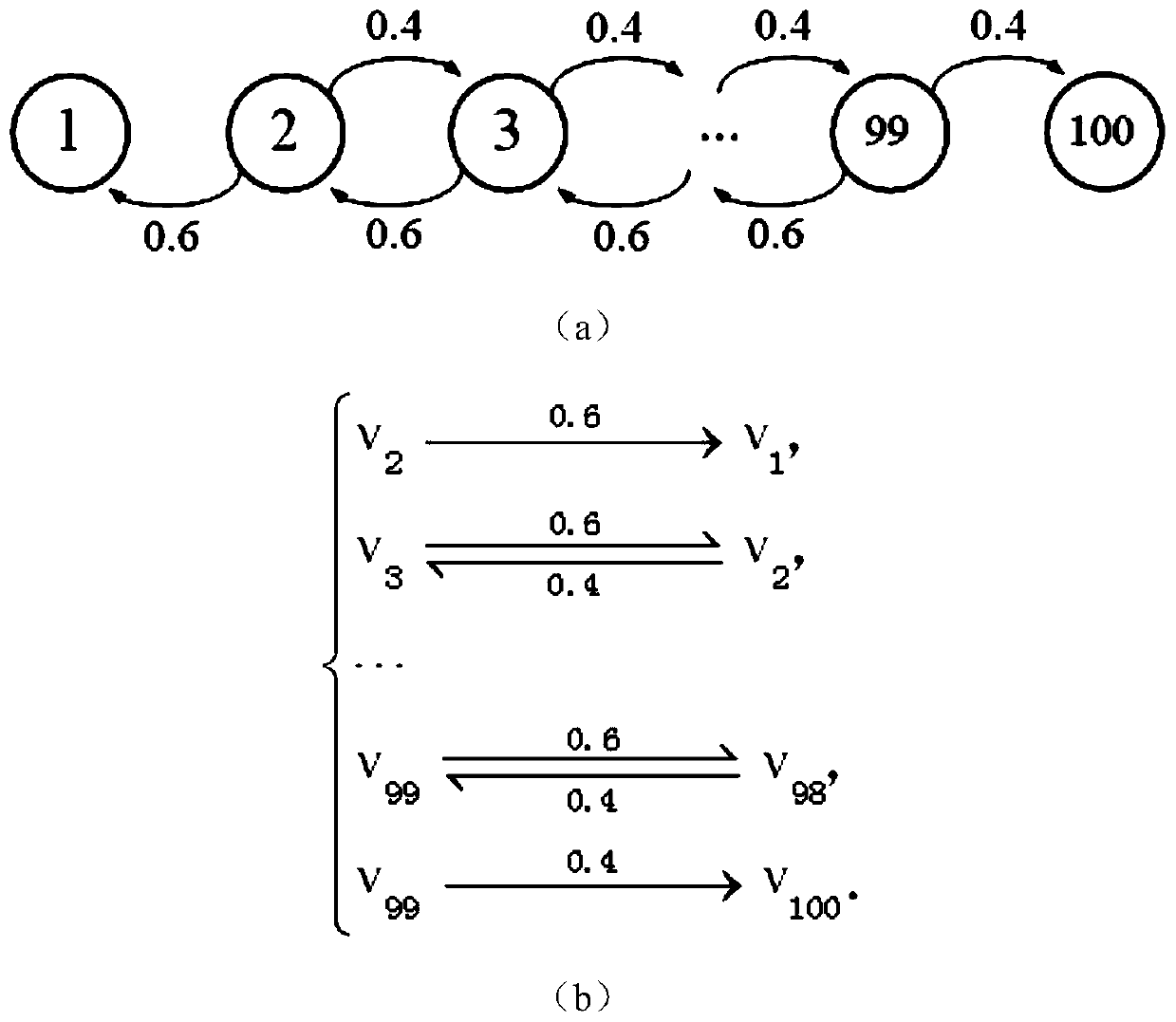
ActiveCN107423554BReduce typesReduced responseCharacter and pattern recognitionChemical processes analysis/designContinuous-time Markov chainAlgorithm
The invention discloses a design method for realizing a Markov chain by using a reversible unimolecular reaction. The final concentration of the reactant is used to characterize the steady-state probability distribution of the Markov chain, which is suitable for discrete-time Markov chains and continuous-time Markov chains. Markov chain. The method of the invention solves the problem that the method for estimating the steady-state distribution of the Markov chain by DNA reaction in the prior art cannot realize the calculation of the continuous time Markov chain, and simultaneously effectively reduces the types of reactants and the number of reactions required.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
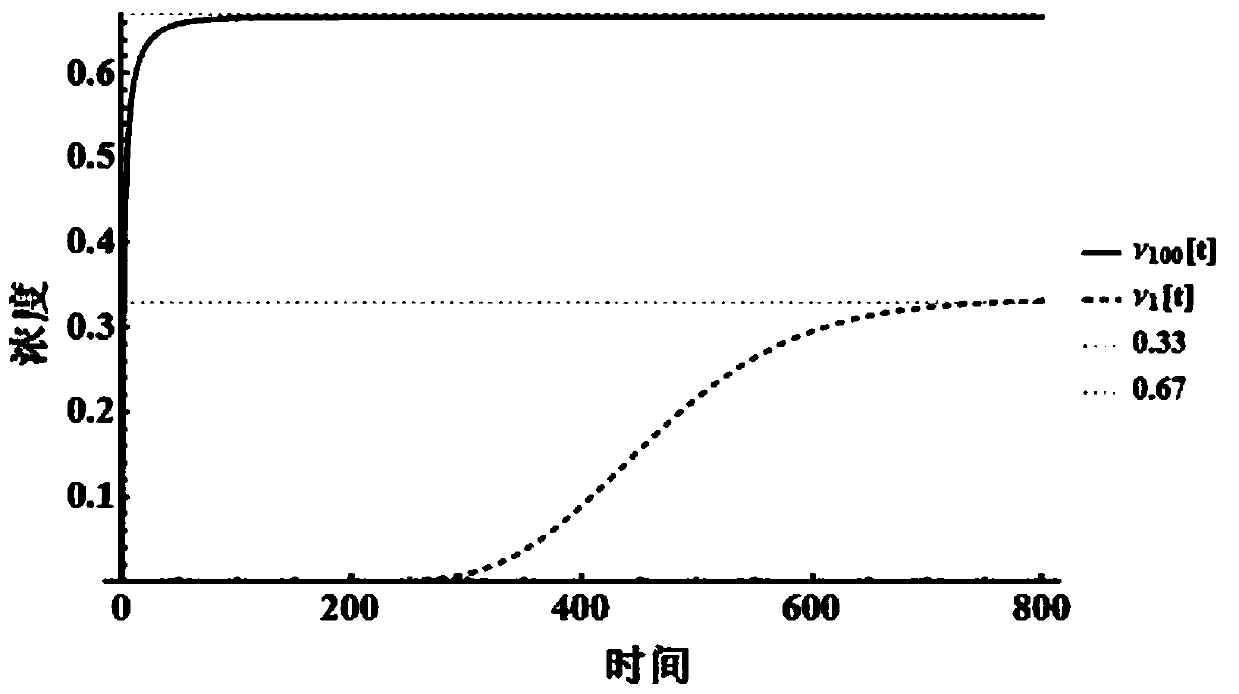
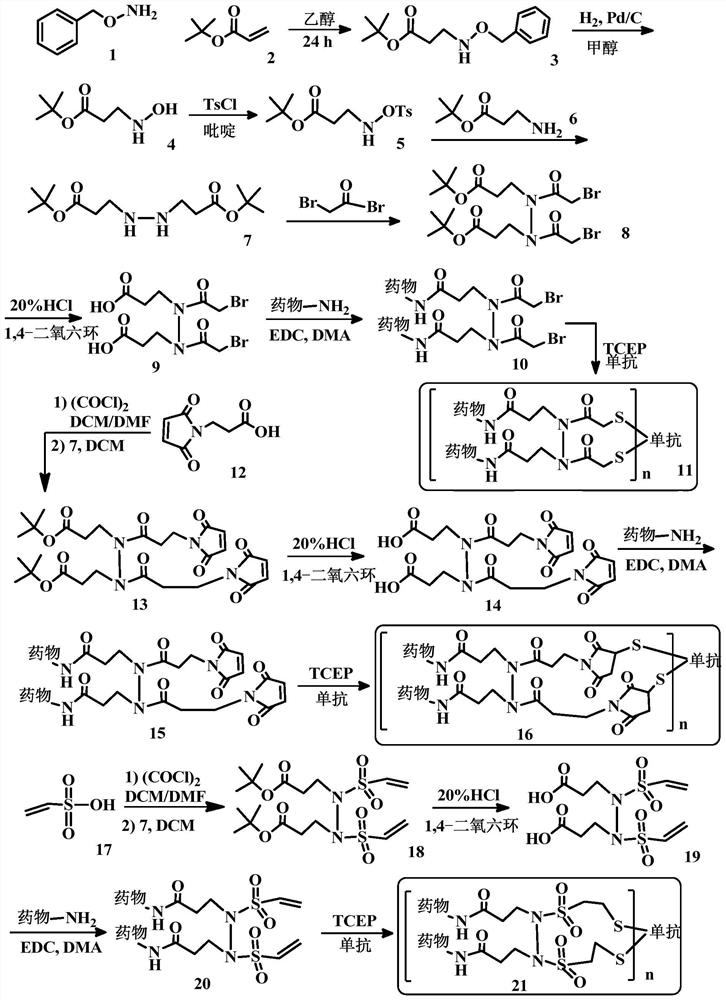
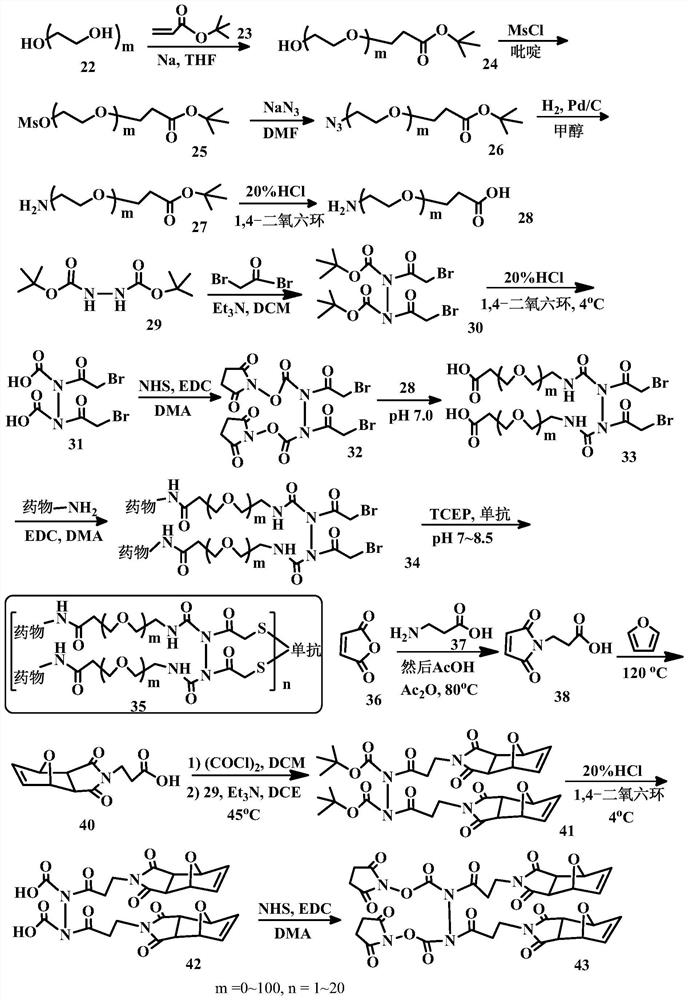
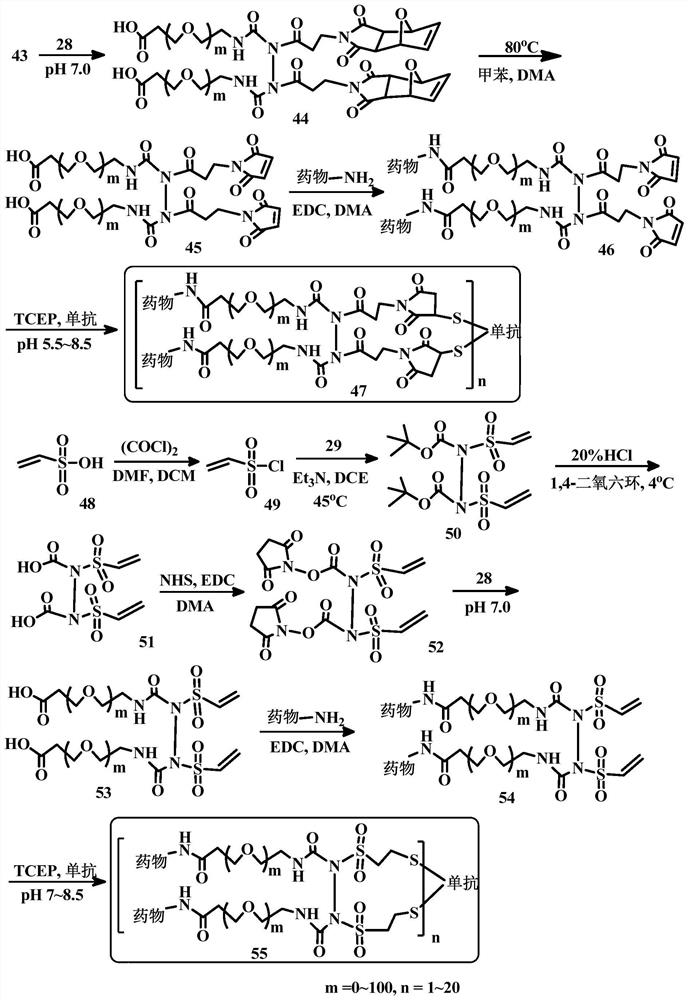
Bridge linkers for conjugate coupling of cell-binding molecules
PendingCN113350518AAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
The present invention relates to bridge linkers for conjugate coupling of cell-binding molecules. More specifically, the present invention relates to the preparation of a novel class of bridge linkers that specifically conjugates cell-binding molecules with small molecule drugs, in particular cytotoxic agents, by reacting with sulfydryl pairs on the cell-binding molecules. The invention also relates to a method for preparing the cell-binding agent-drug (cytotoxic agent) conjugate, which comprises the steps of: one is to modify a small drug molecule by using the bridge linker and then react with a cell-binding agent; and the other is to modify a cell-binding agent by using the bridge linker and then react with the small drug molecule. The invention also relates to the use of the conjugates in the treatment of cancer, infections and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:HANGZHOU DAC BIOTECH
System, Device, and Method for Identifying and Monitoring Breast Milk Composition
PendingUS20200393376A1Shoot accuratelyIncrease contrastMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological material analysisBreast feedNutrition
Owner:MAO FOODTECH LTD
A method for data processing of reaxff force field calculation results based on python
ActiveCN110767267BEfficient and convenient readingShorten the timeComputational theoretical chemistryInstrumentsMolecular classificationData file
A method for data processing of ReaxFF force field calculation results based on Python, belonging to the technical field of chemical molecular reaction dynamics, the method includes the following steps: Step 1, read and integrate the data of the species file of molecular type information; Step 2, integrate The molecular information output.txt file is used for molecular classification; step 3, the molecular weight of each product is calculated to obtain the molecular mass percentage of each product. The processing method provided by the present invention can efficiently and conveniently read the various data file types generated by the simulation, and reduce the time and steps spent on data files in the transfer format; and the method can summarize the molecular types of the simulation products with diversity, and can The change of various products over time is obtained, which provides convenience for the reaction molecular dynamics simulation to explore the microcosmic mechanism of pyrolysis combustion under various working conditions and to clarify the product change rule.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com