A Design Method for Realizing Markov Chains Using Reversible Unimolecular Reactions
A Markov chain and design method technology, applied in the field of chemical reaction network calculation, can solve the problem of not realizing Markov chain calculation, and achieve the effect of reducing the types and the number of reactions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
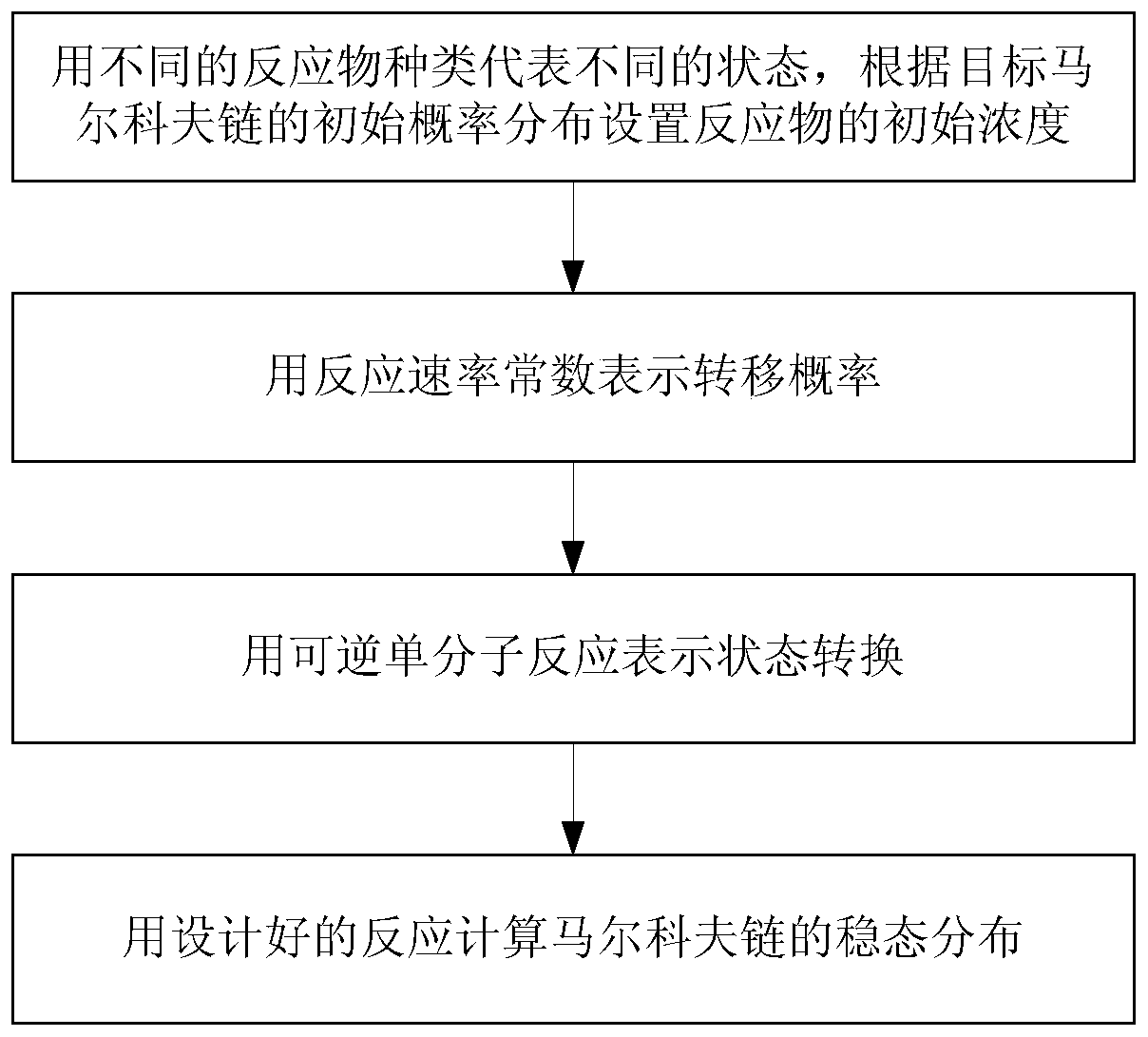
[0021] Such as figure 1 Shown, realize the design method of Markov chain with unimolecular reversible reaction among the present invention, comprise the following steps:
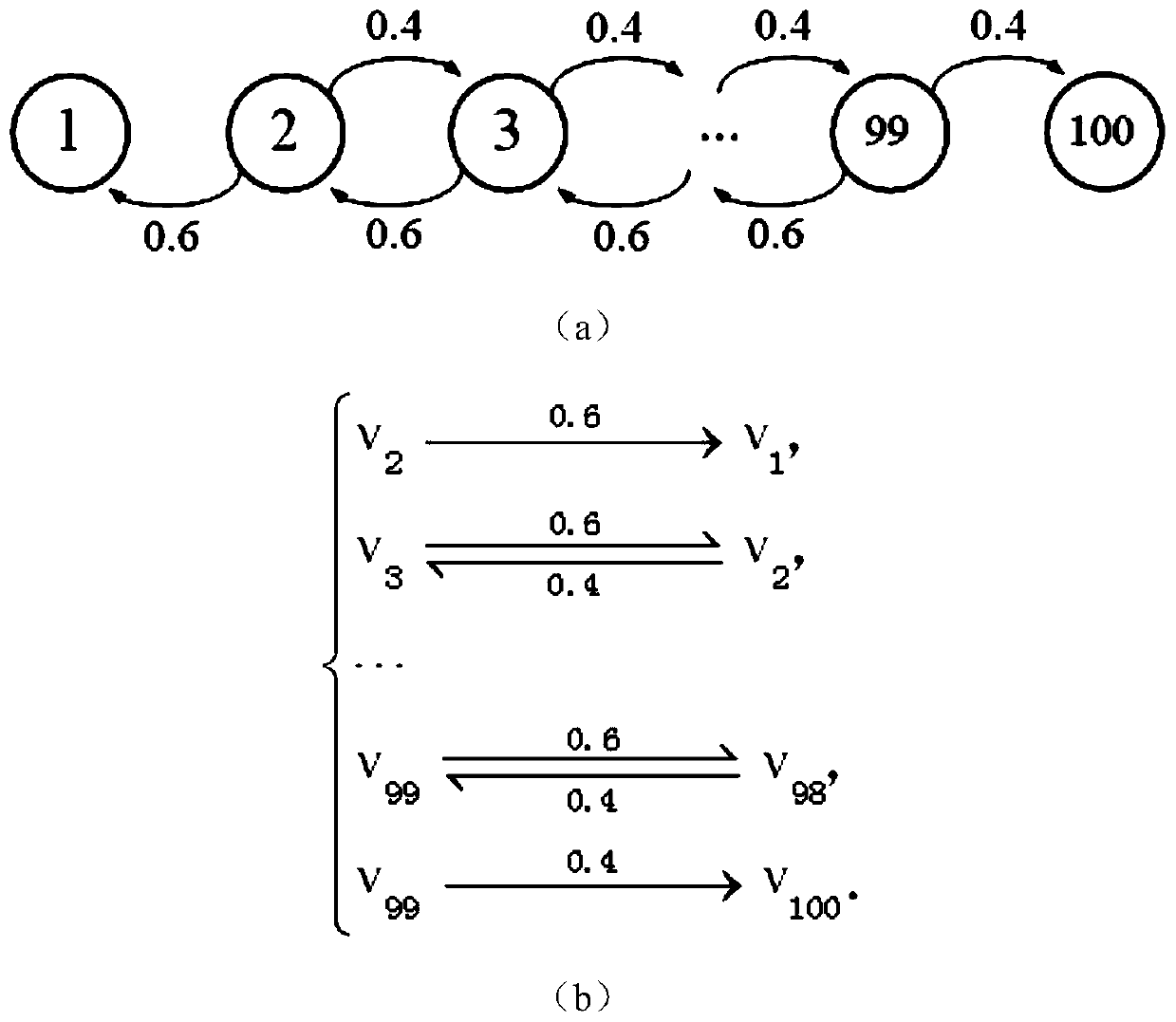
[0022] (1) Using different reactant species ν i (i=1,2,...,k)ν i , i=1,2,...k represent different states, and set the initial concentration of the reactant according to the initial probability distribution of the target Markov chain (the Markov chain of the steady-state distribution to be solved); that is, the initial concentration of all reactants must be equal to or proportional to the initial state distribution of the target Markov chain;
[0023] (2) Use the reaction rate constant to express the transition probability k ij (i=1,2,...,k j=1,2,...,k), set the value of the reaction rate constant according to the transition probability;
[0024] (3) Reversible unimolecular reaction Indicates a state transition;
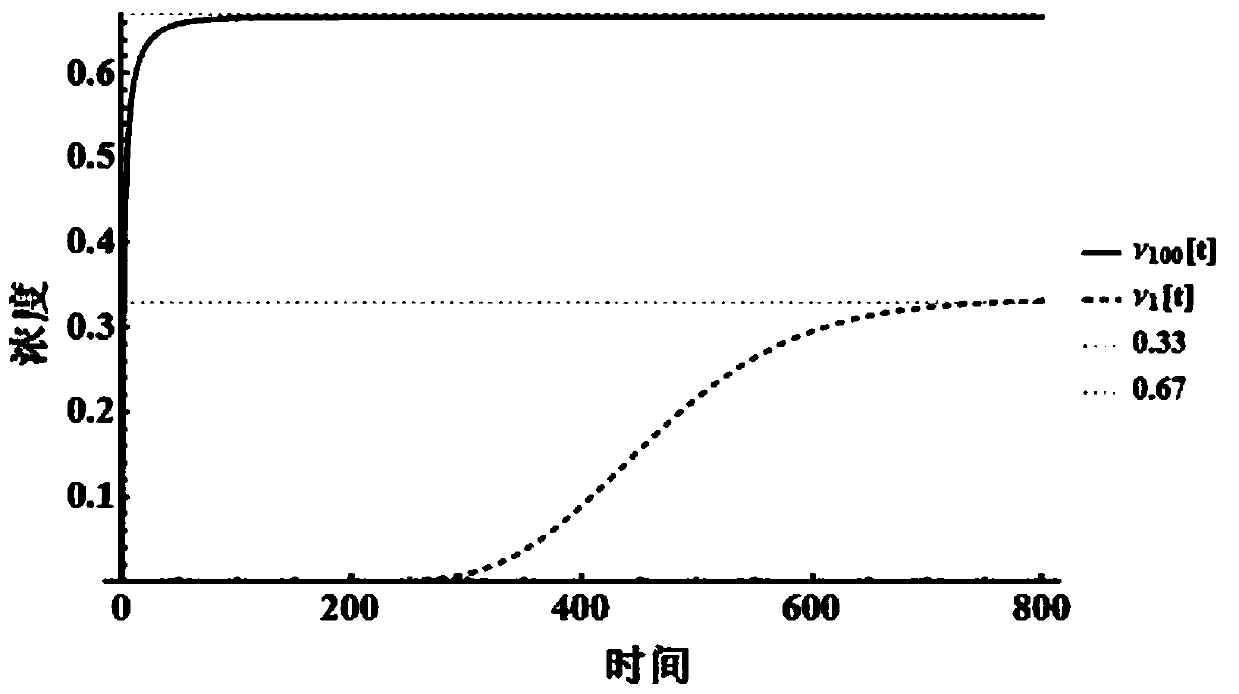
[0025] (4) Use the designed reaction to calculate the steady-state distribution of the Ma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com