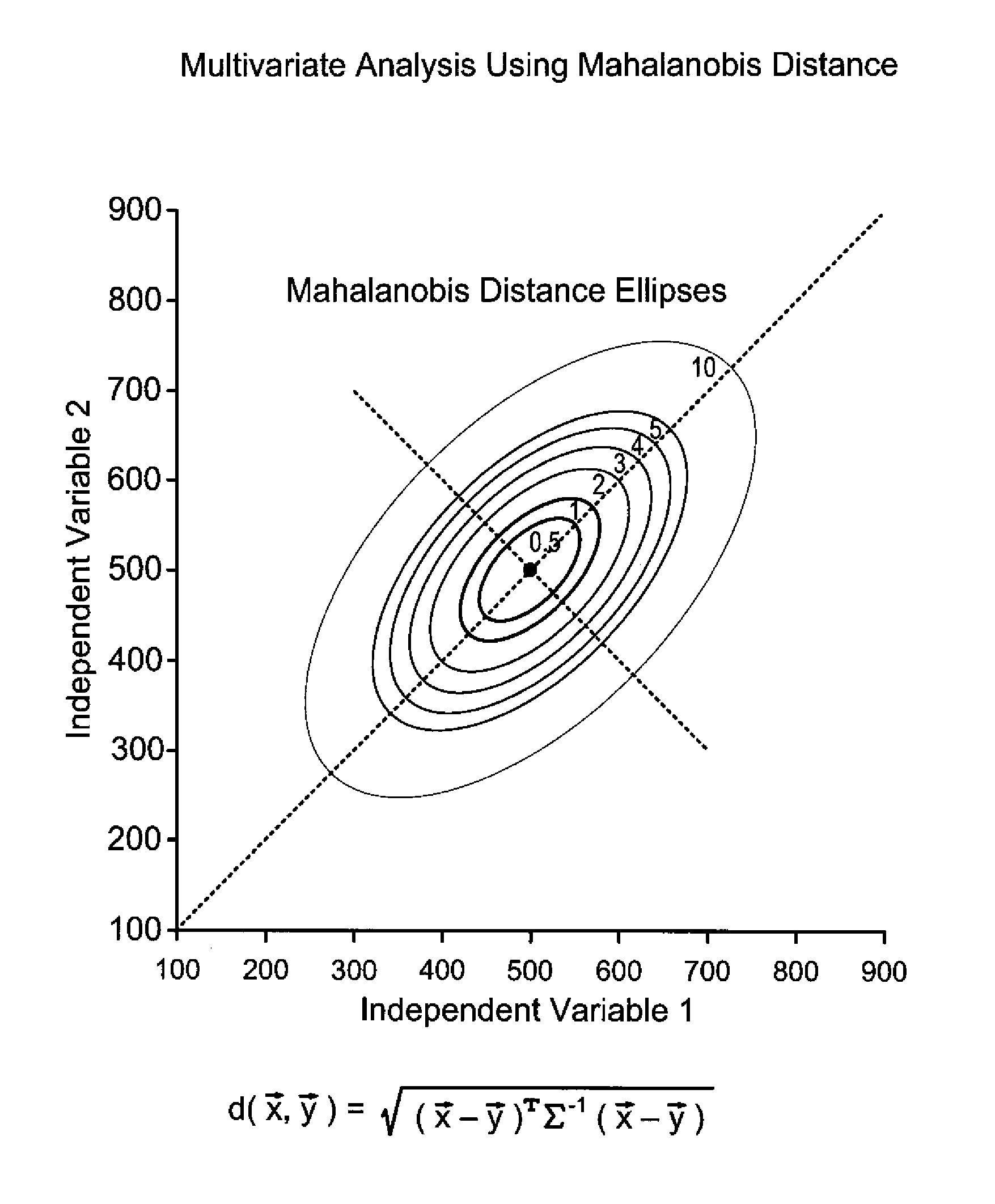
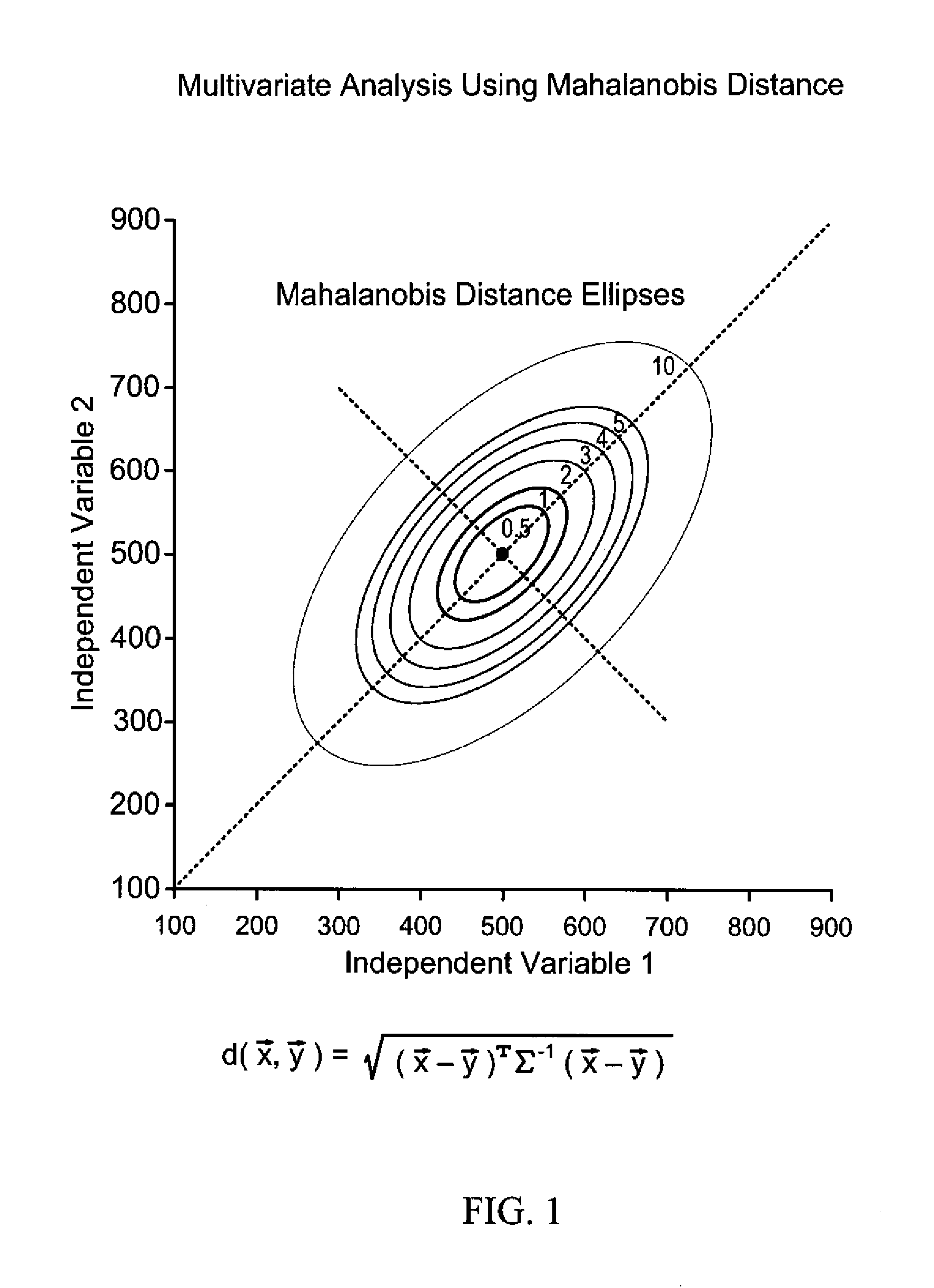
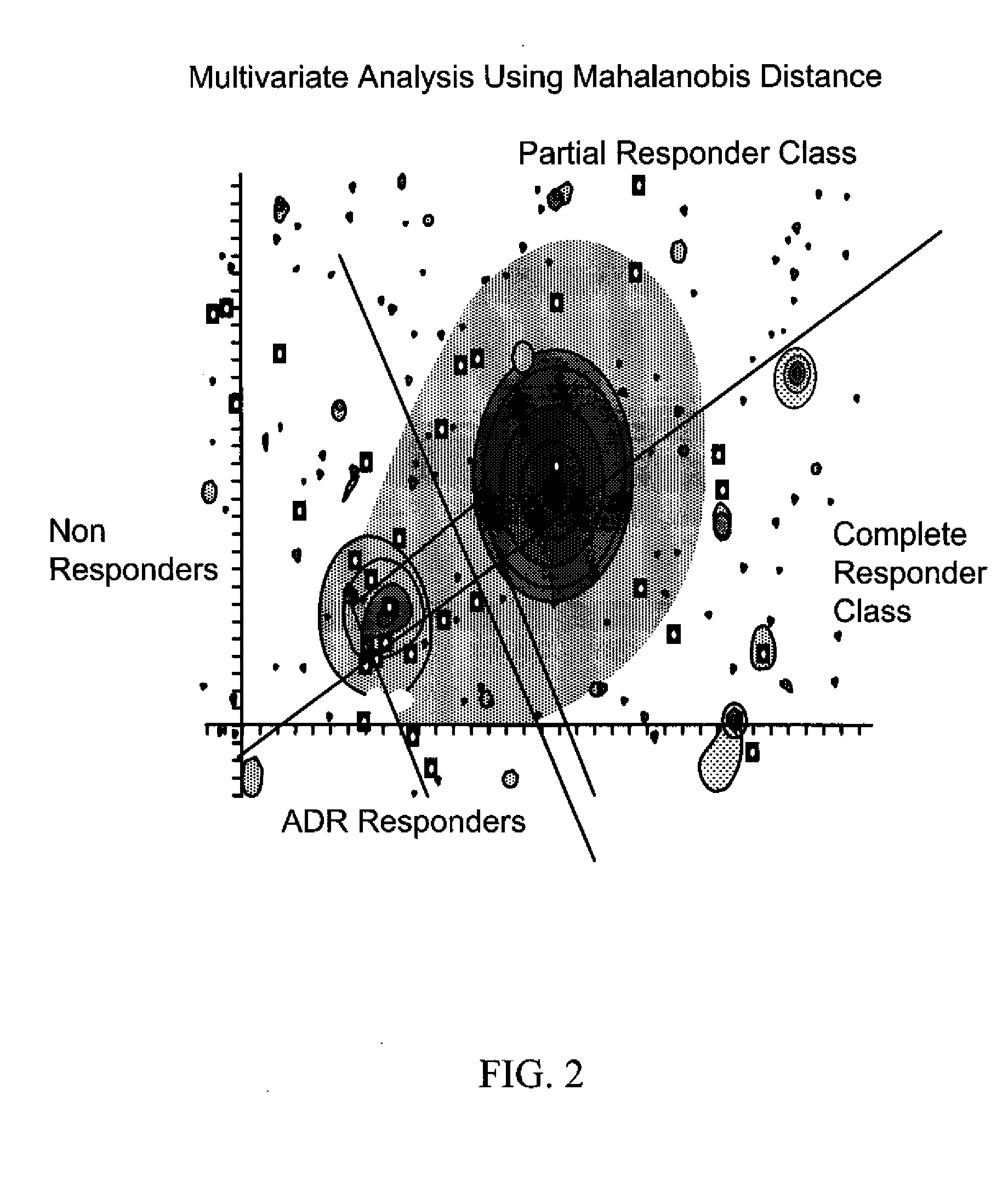
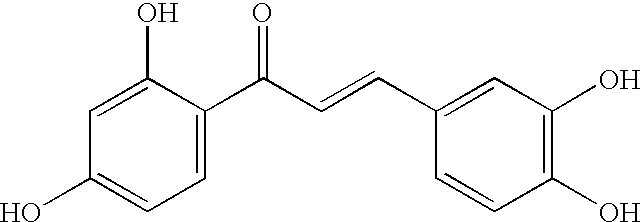
Patents
Literature
1826results about "Chemometrics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
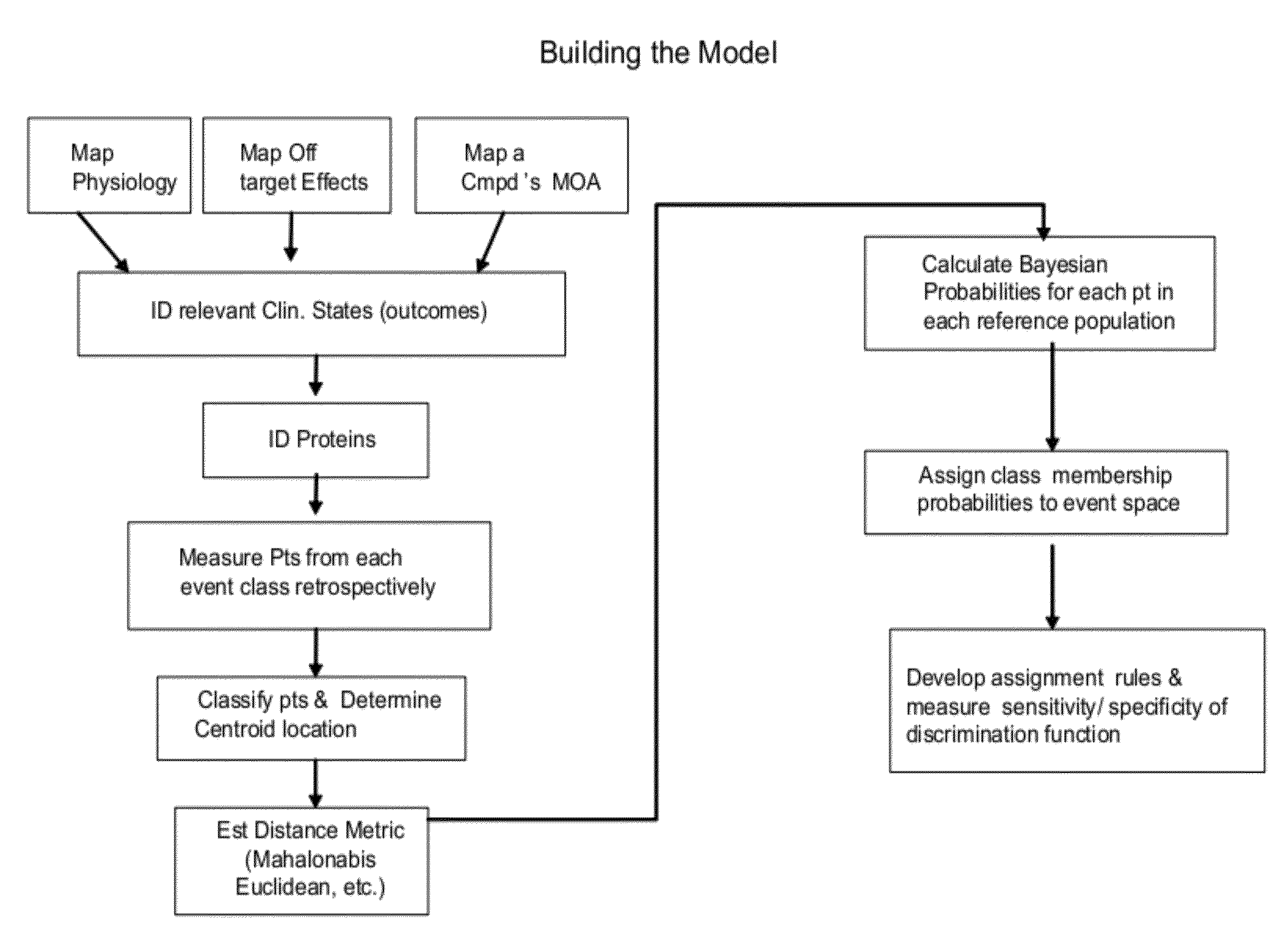
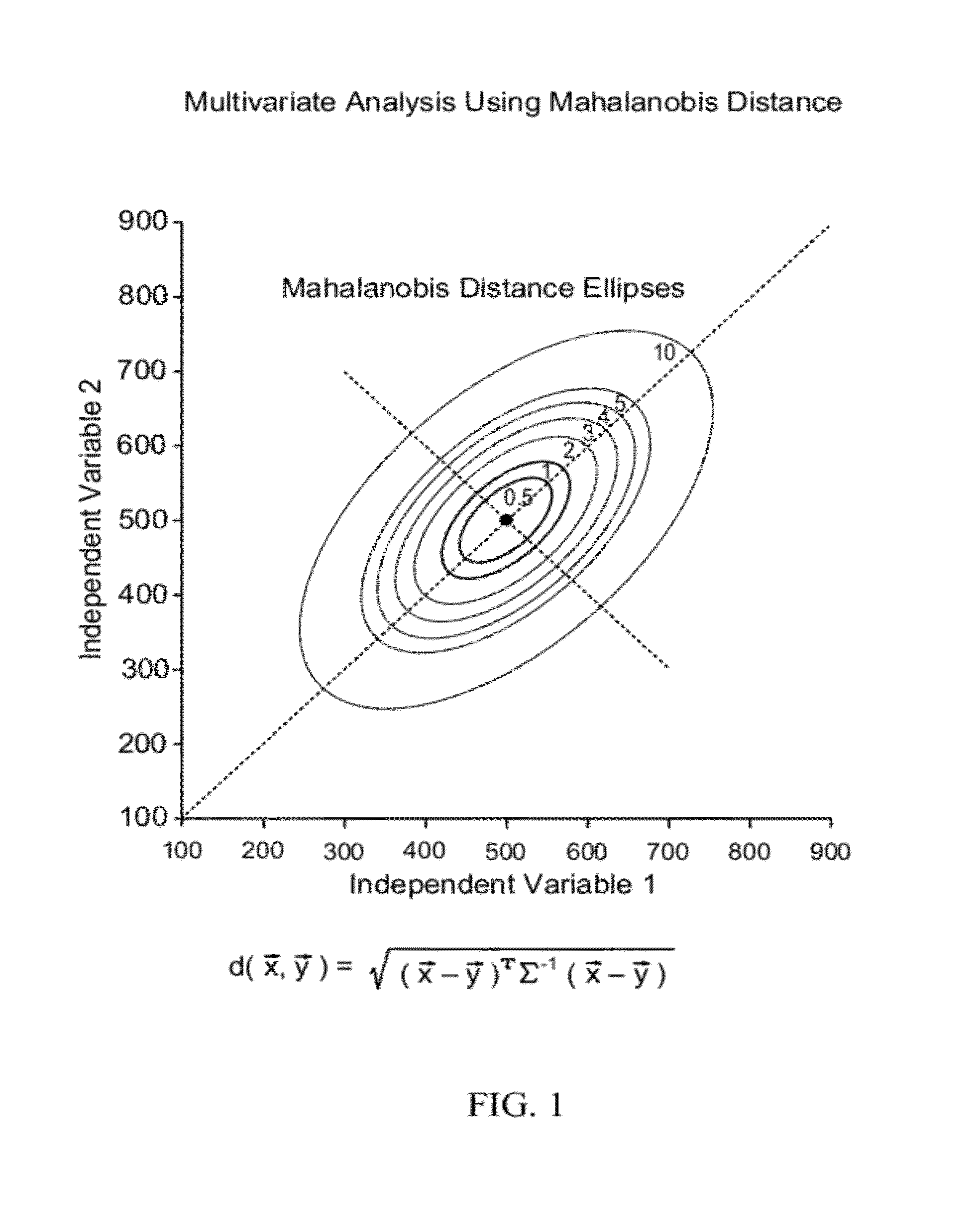
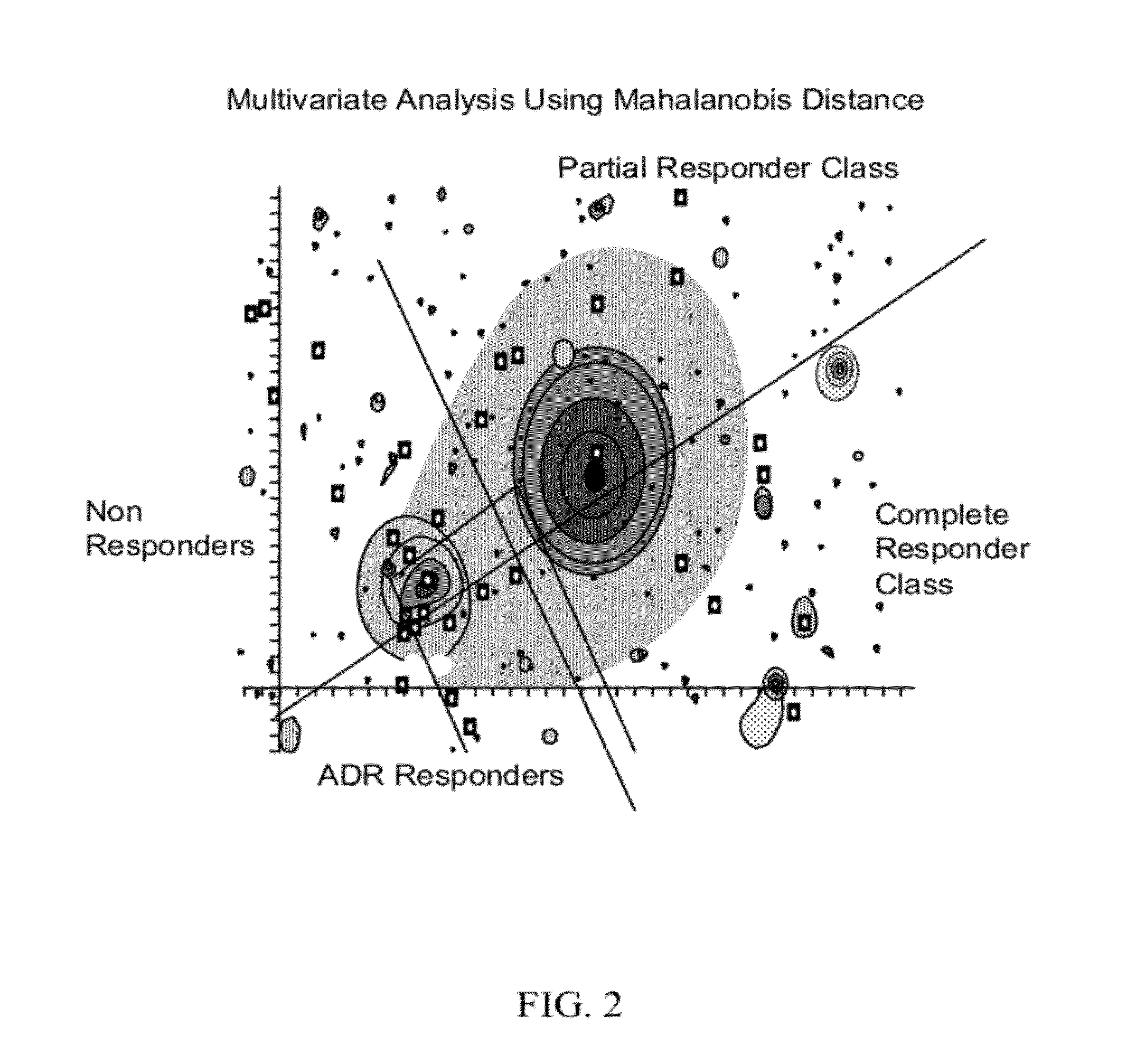
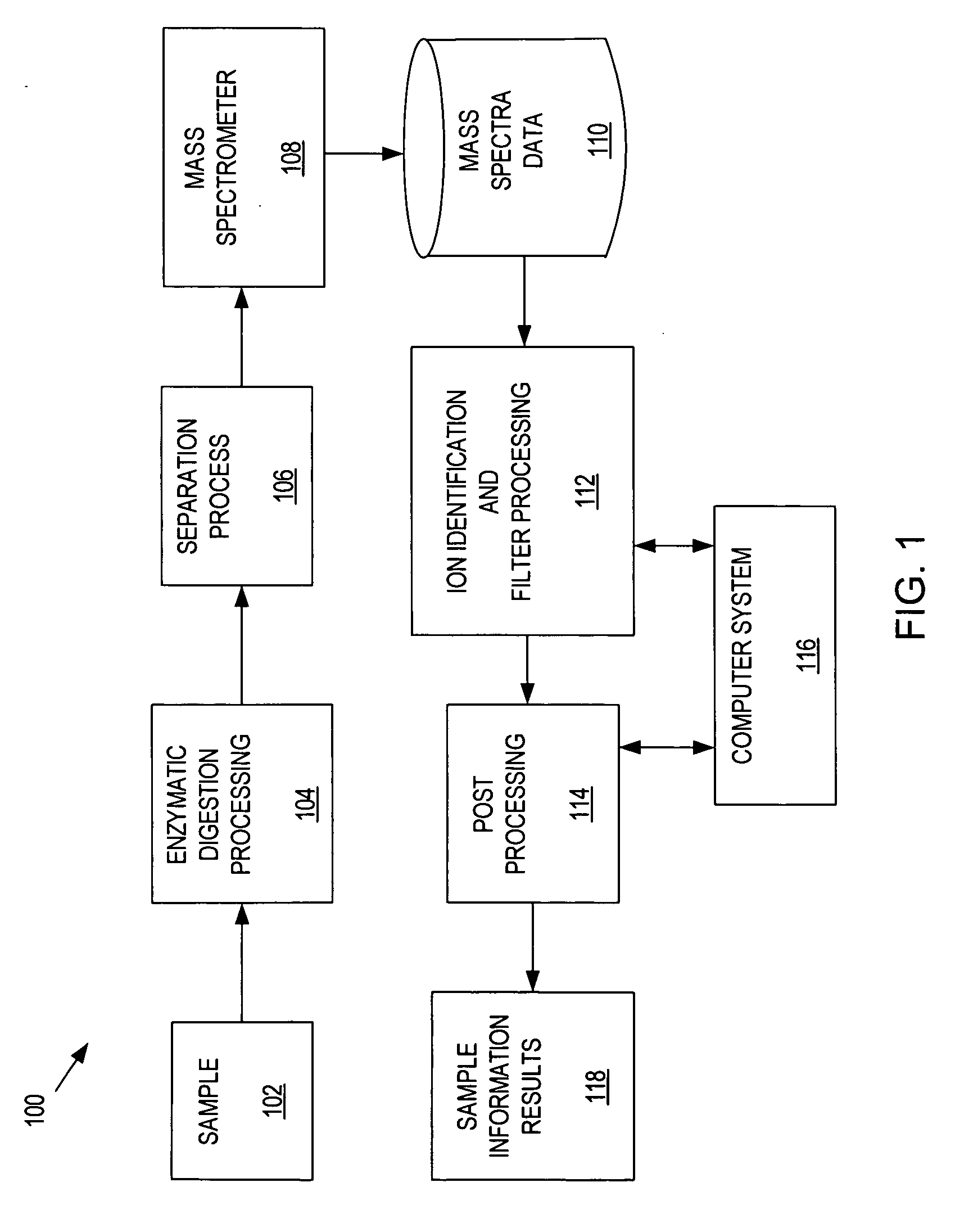
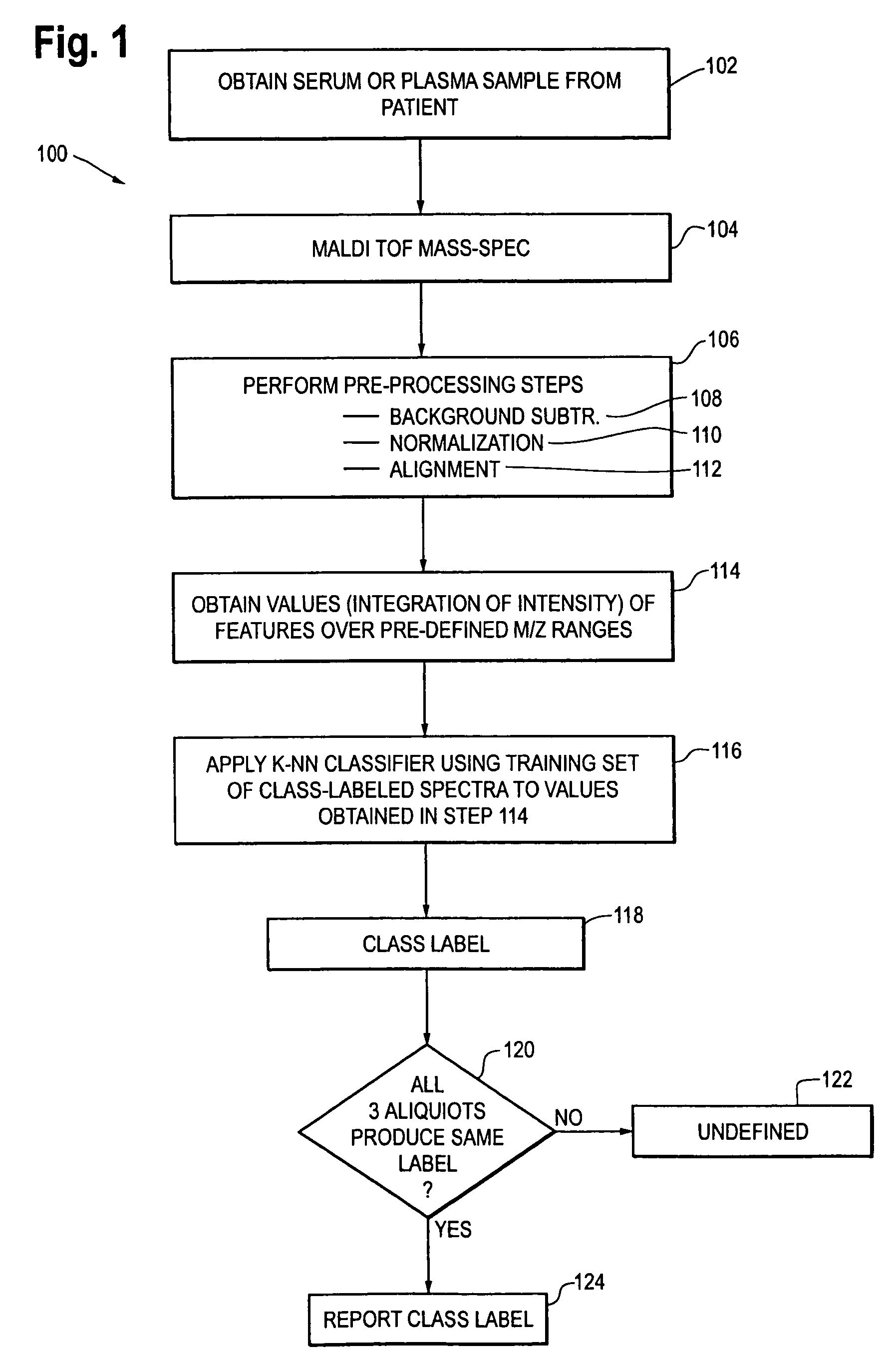
Methods and systems for assessing clinical outcomes
InactiveUS20090318775A1Increased futureImproved labelingBiostatisticsDiagnostic recording/measuringComputer terminalEnd user
Described herein are methods and systems useful for characterizing clinical outcomes of a subject. Provided herein includes computer-assessed methods, medical information systems, and computer-readable instructions that can aid an end-user in diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of a clinical outcome.
Owner:THERANOS
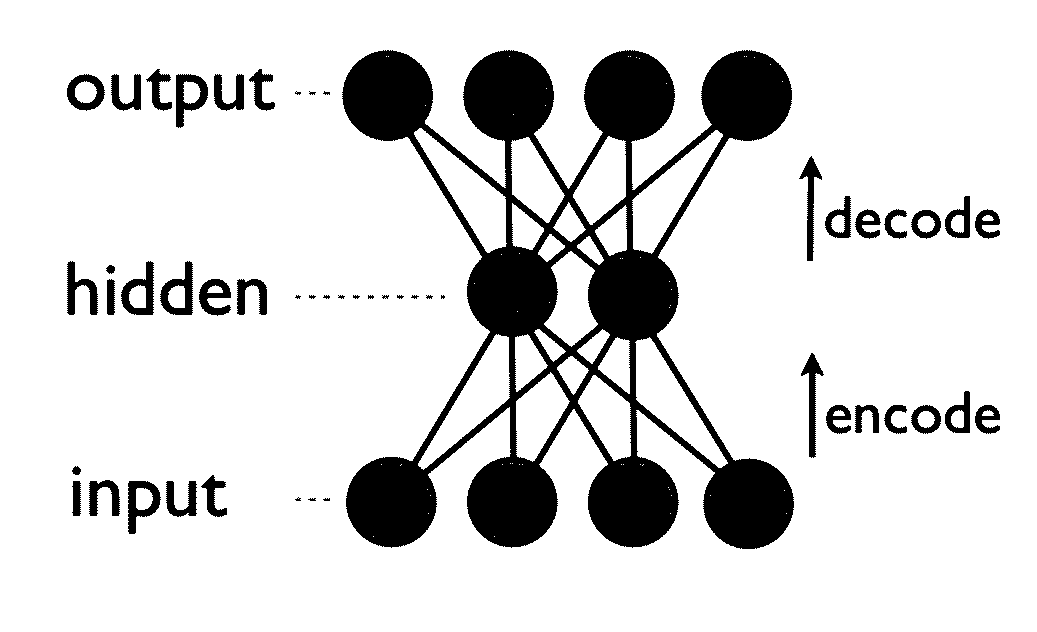
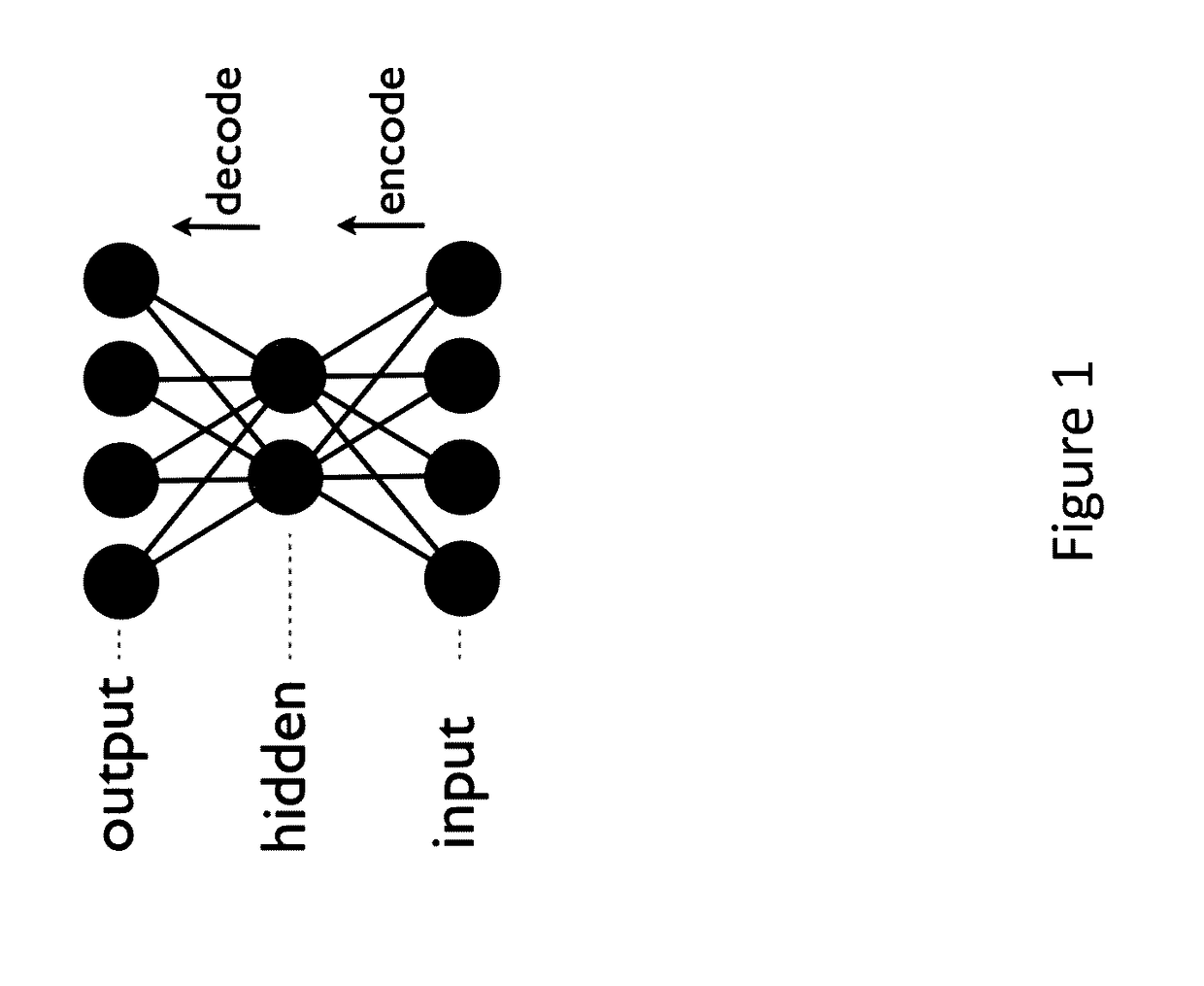
Text influenced molecular indexing system and computer-implemented and/or computer-assisted method for same
InactiveUS20020087508A1Chemical property predictionMathematical modelsSingular value decompositionAlgorithm
Owner:AXONTOLOGIC
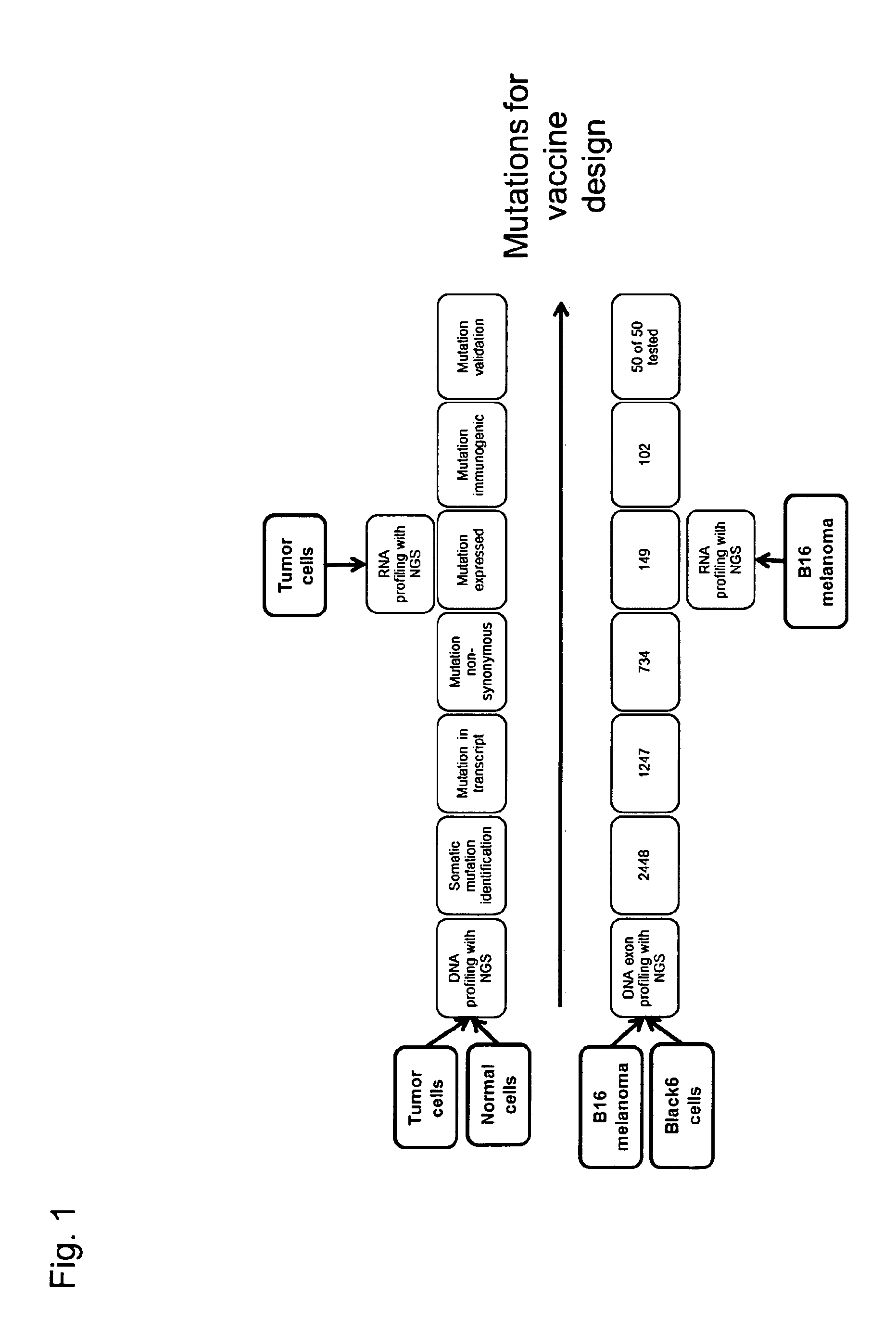
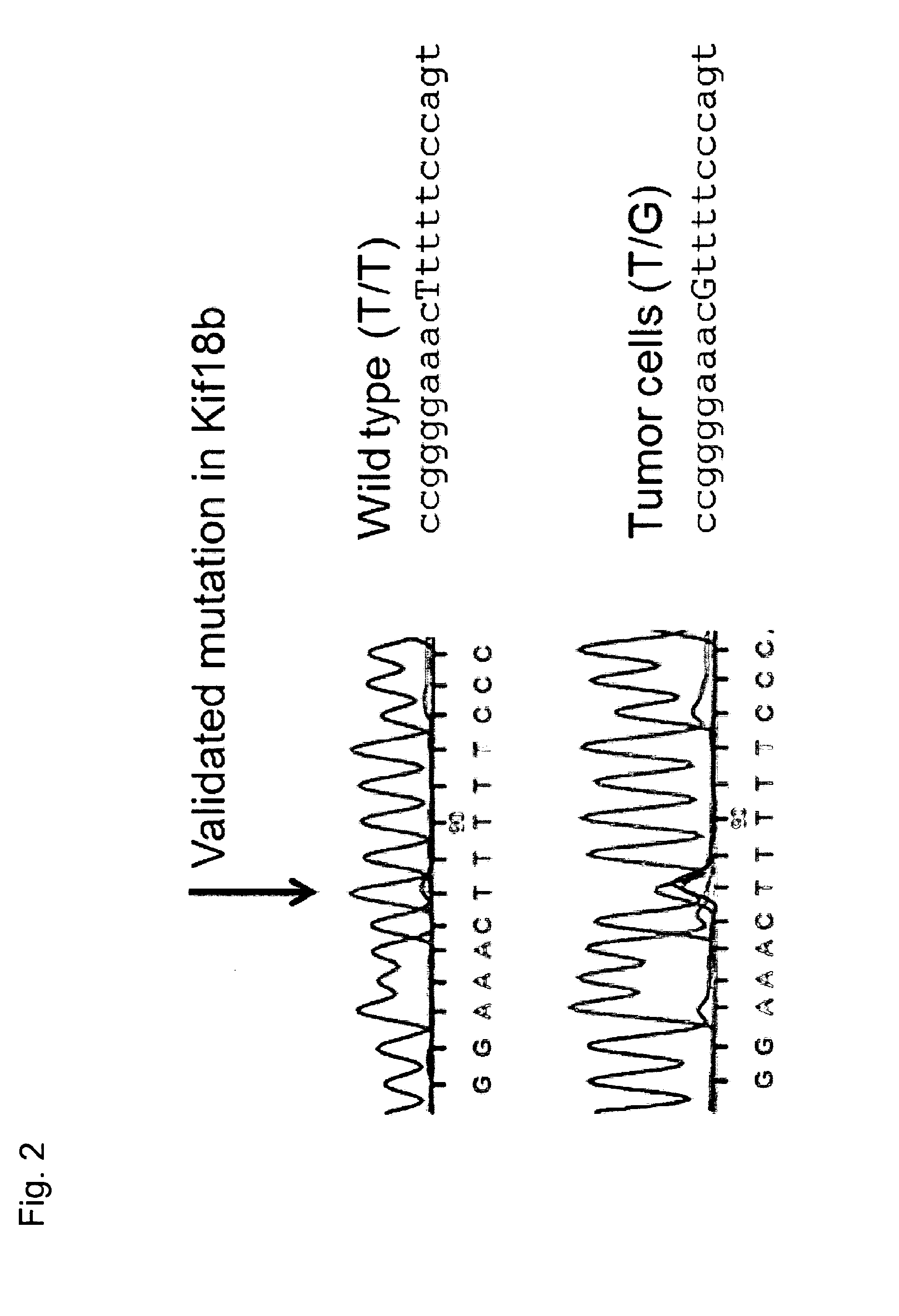
Individualized vaccines for cancer
ActiveUS20140178438A1Reduces steric hindranceImprove translationVaccinesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPrimary tumorTumour metastasis
The present invention relates to the provision of vaccines which are specific for a patient's tumor and are potentially useful for immunotherapy of the primary tumor as well as tumor metastases. In one aspect, the present invention relates to a method for providing an individualized cancer vaccine comprising the steps: (a) identifying cancer specific somatic mutations in a tumor specimen of a cancer patient to provide a cancer mutation signature of the patient; and (b) providing a vaccine featuring the cancer mutation signature obtained in step (a). In a further aspect, the present invention relates to vaccines which are obtainable by said method.
Owner:TRANSLATIONALE ONKOLOGIE AN DER UNIVSMEDIZIN DER JOHANNES GUTENBERG UNIV MAINZ GGMBH +1
Improvements in or Relating to Organic Compounds
ActiveUS20190145942A1High resolutionEasy to separateMolecular entity identificationComponent separationSimple Organic CompoundsFlavor
Owner:GIVAUDAN SA
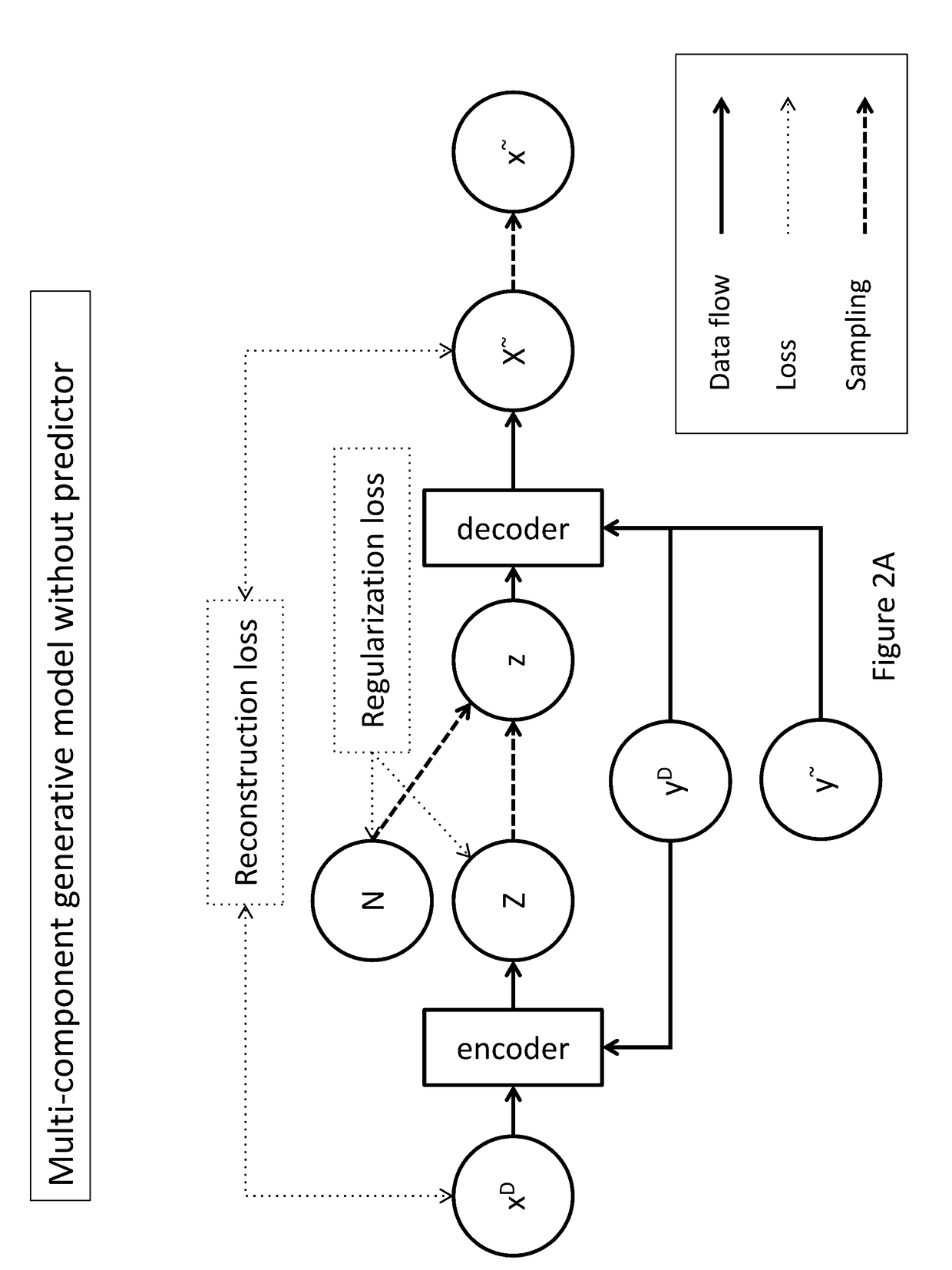
Generative machine learning systems for drug design
ActiveUS20170161635A1Minimizing reconstruction errorMinimize loss functionMolecular designProbabilistic networksChemical compoundStudy methods
In various embodiments, the systems and methods described herein relate to generative models. The generative models may be trained using machine learning approaches, with training sets comprising chemical compounds and biological or chemical information that relate to the chemical compounds. Deep learning architectures may be used. In various embodiments, the generative models are used to generate chemical compounds that have desired characteristics, e.g. activity against a selected target. The generative models may be used to generate chemical compounds that satisfy multiple requirements.
Owner:PREFERRED NETWORKS INC
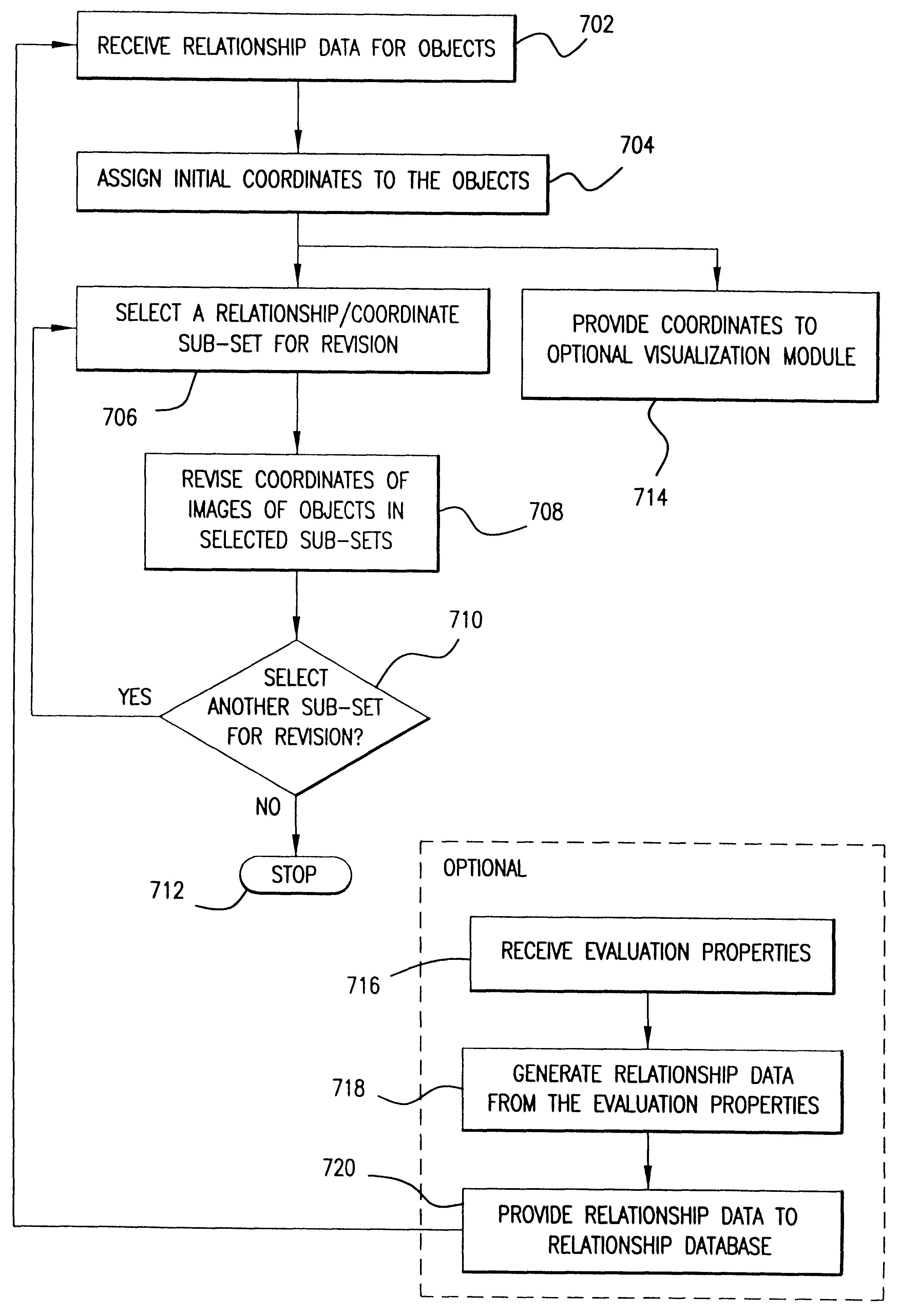
System, method, and computer program product for representing proximity data in a multi-dimensional space
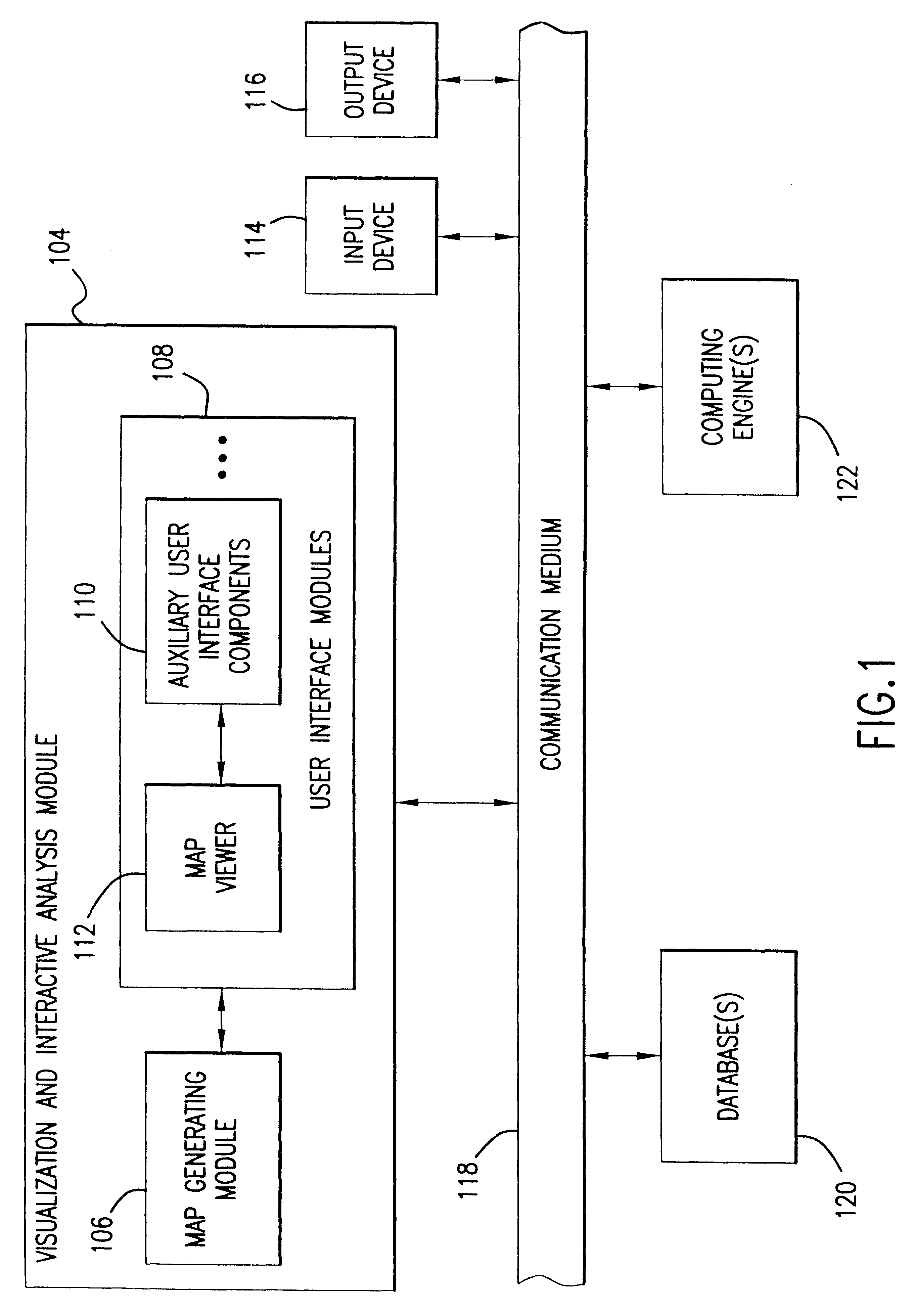
A system, method and computer program product for representing precise or imprecise measurements of similarity / dissimilarity (relationships) between objects as distances between points in a multi-dimensional space that represents the objects. Self-organizing principles are used to iteratively refine an initial (random or partially ordered) configuration of points using stochastic relationship / distance errors. The data can be complete or incomplete (i.e. some relationships between objects may not be known), exact or inexact (i.e. some or all of the relationships may be given in terms of allowed ranges or limits), symmetric or asymmetric (i.e. the relationship of object A to object B may not be the same as the relationship of B to A) and may contain systematic or stochastic errors. The relationships between objects may be derived directly from observation, measurement, a priori knowledge, or intuition, or may be determined indirectly using any suitable technique for deriving proximity (relationship) data.
Owner:3 DIMENSIONAL PHARMA
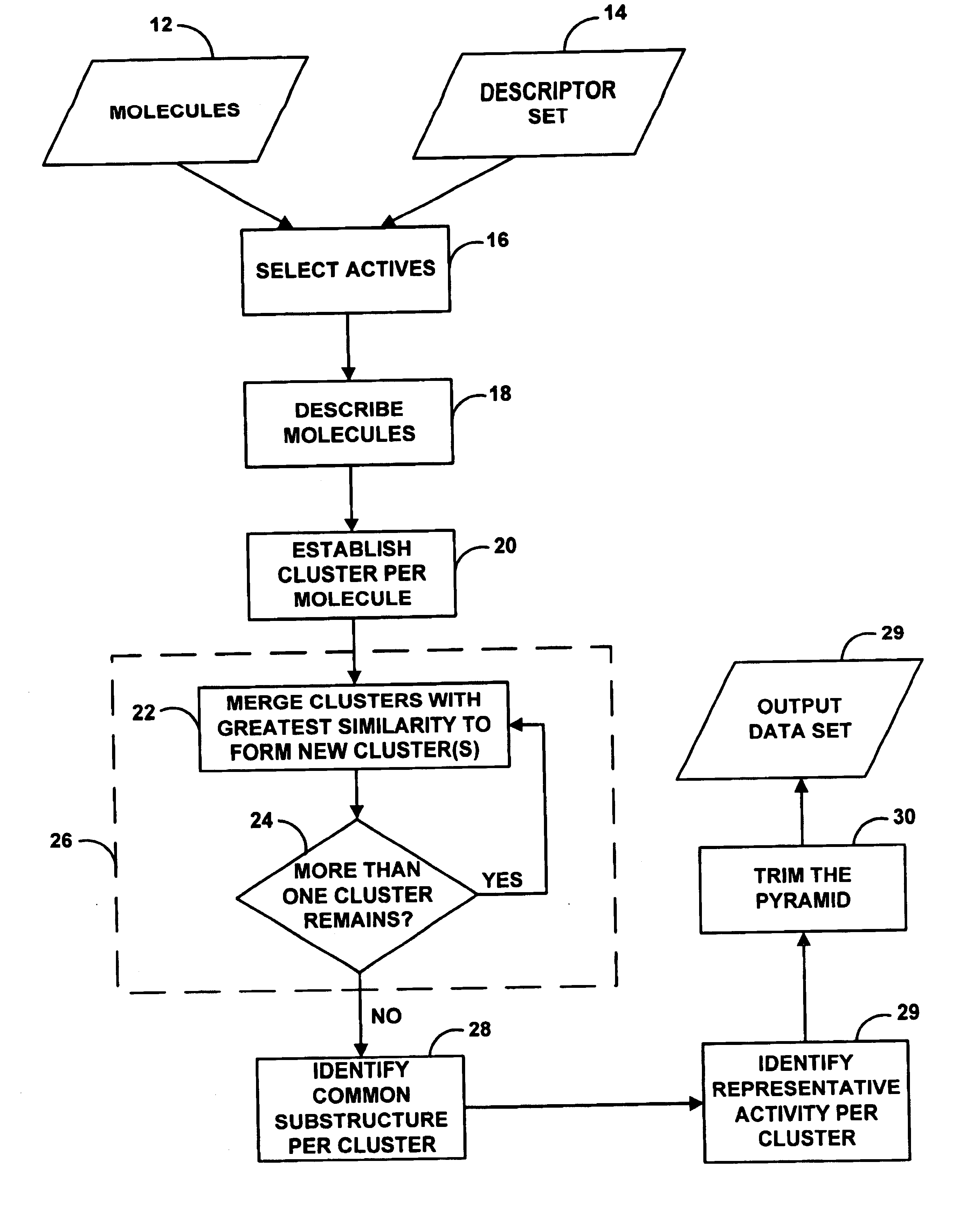
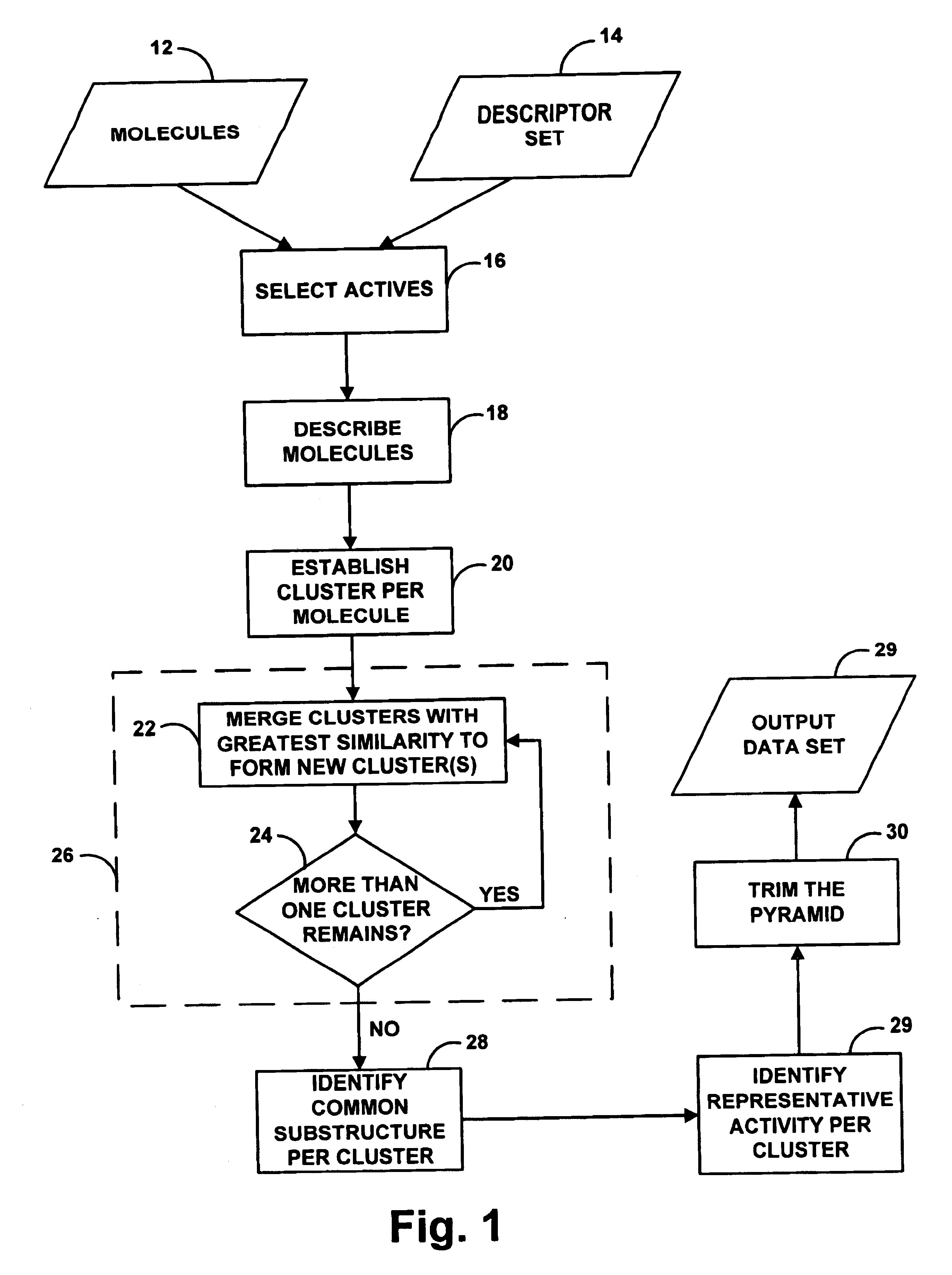
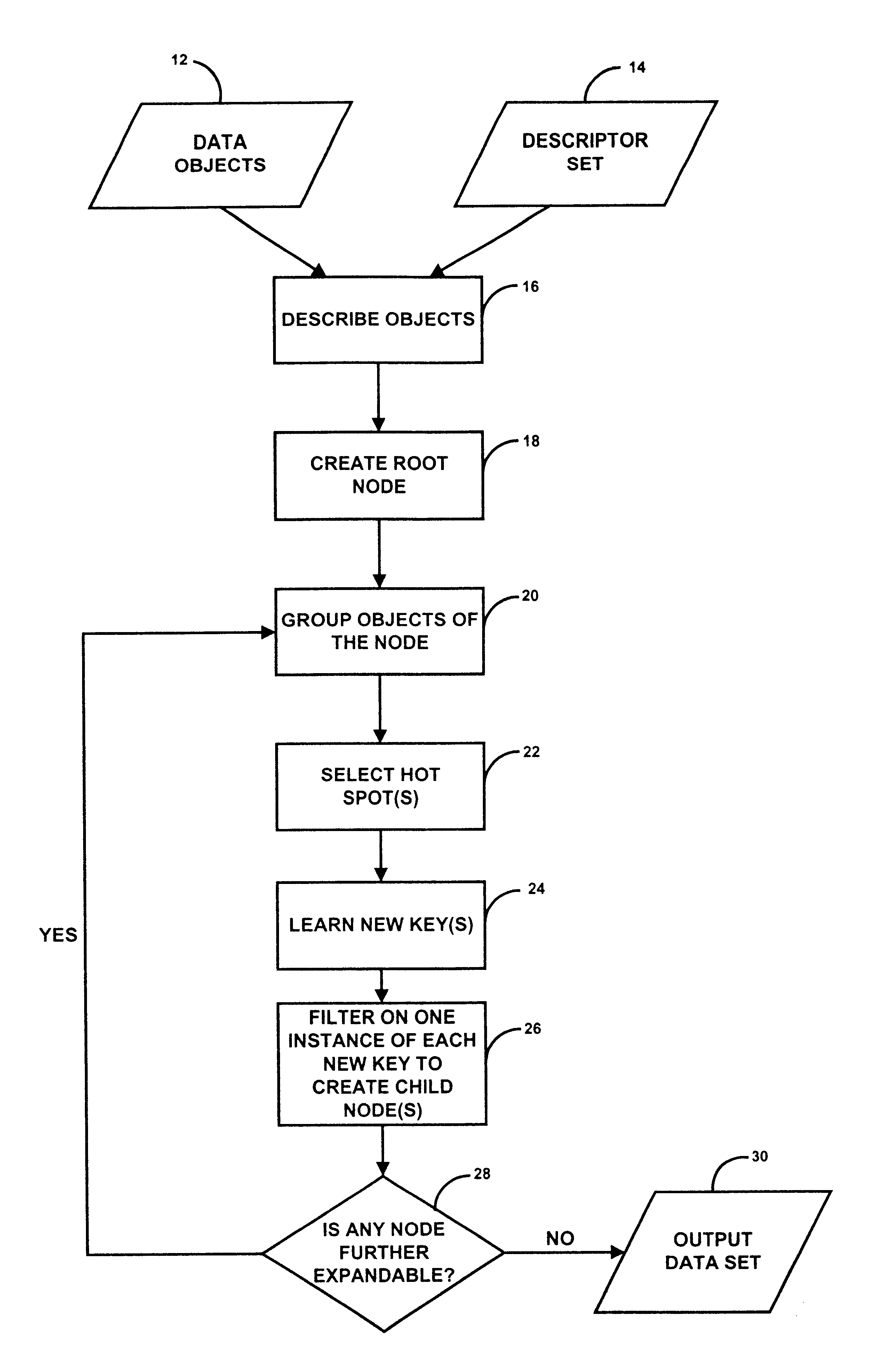
Method and system for artificial intelligence directed lead discovery though multi-domain agglomerative clustering
A system for helping a chemist to identify pharmacophoric mechanisms, based on a set of input data representing many chemical compounds. Given an input data set defining for each compound a feature characteristic and an activity characteristic, a computer agglomeratively clusters representations of the molecules based on their feature characteristics. The result of this process is a multi-domain pyramid structure, made up of a number of nodes each representing one or more molecules. For each node, the computer identifies a representative feature set (such as a largest substructure common among the molecules in the node) and a representative activity level (such as an average of the activity levels of the molecules in the node). The computer then provides as output to a chemist a description of all or part of the pyramid. This process thus converts a large set of raw data into an understandable and commercially useful form, which can assist the chemist in developing beneficial new pharmaceuticals.
Owner:SIMULATIONS PLUS +6
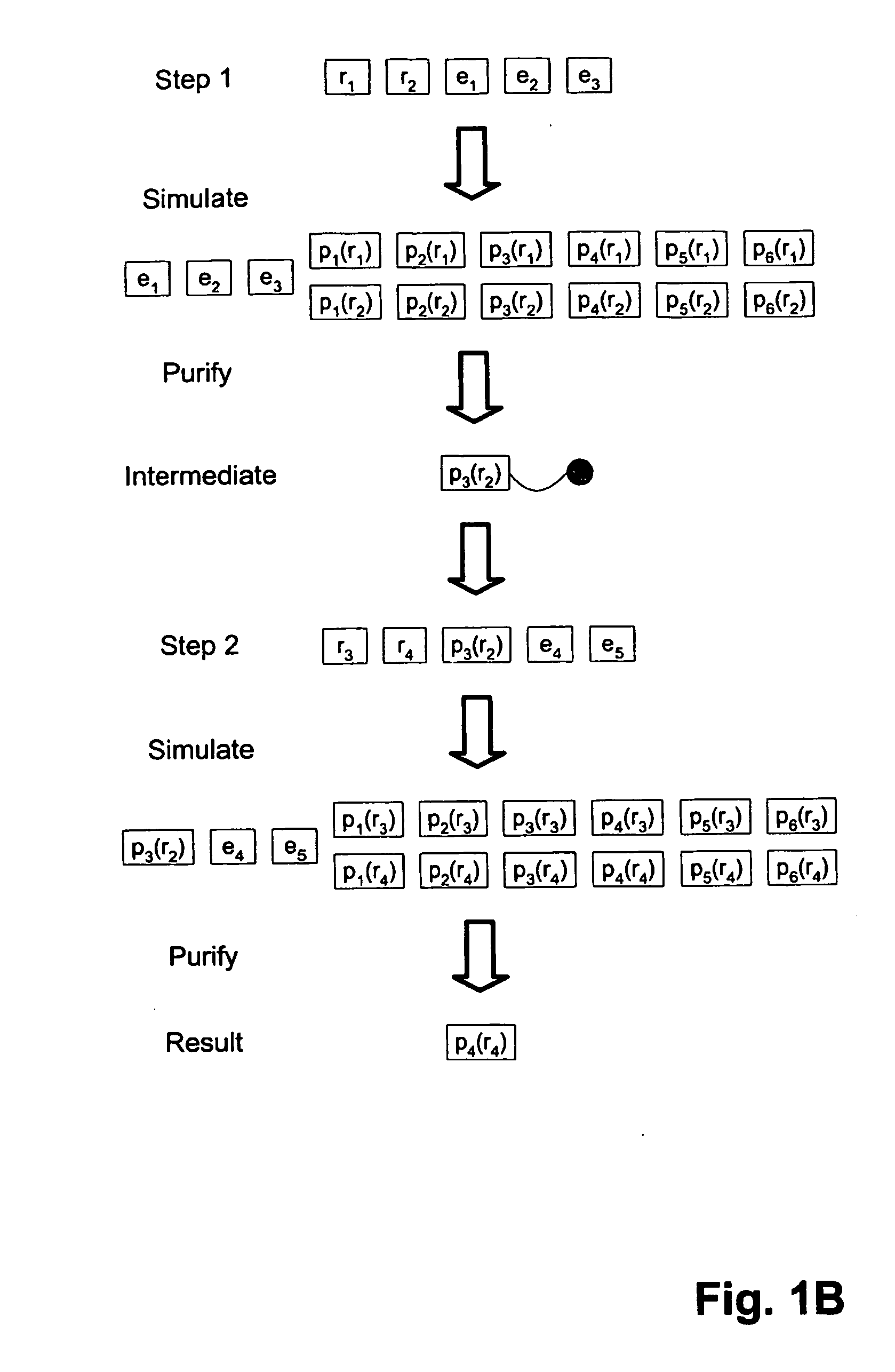
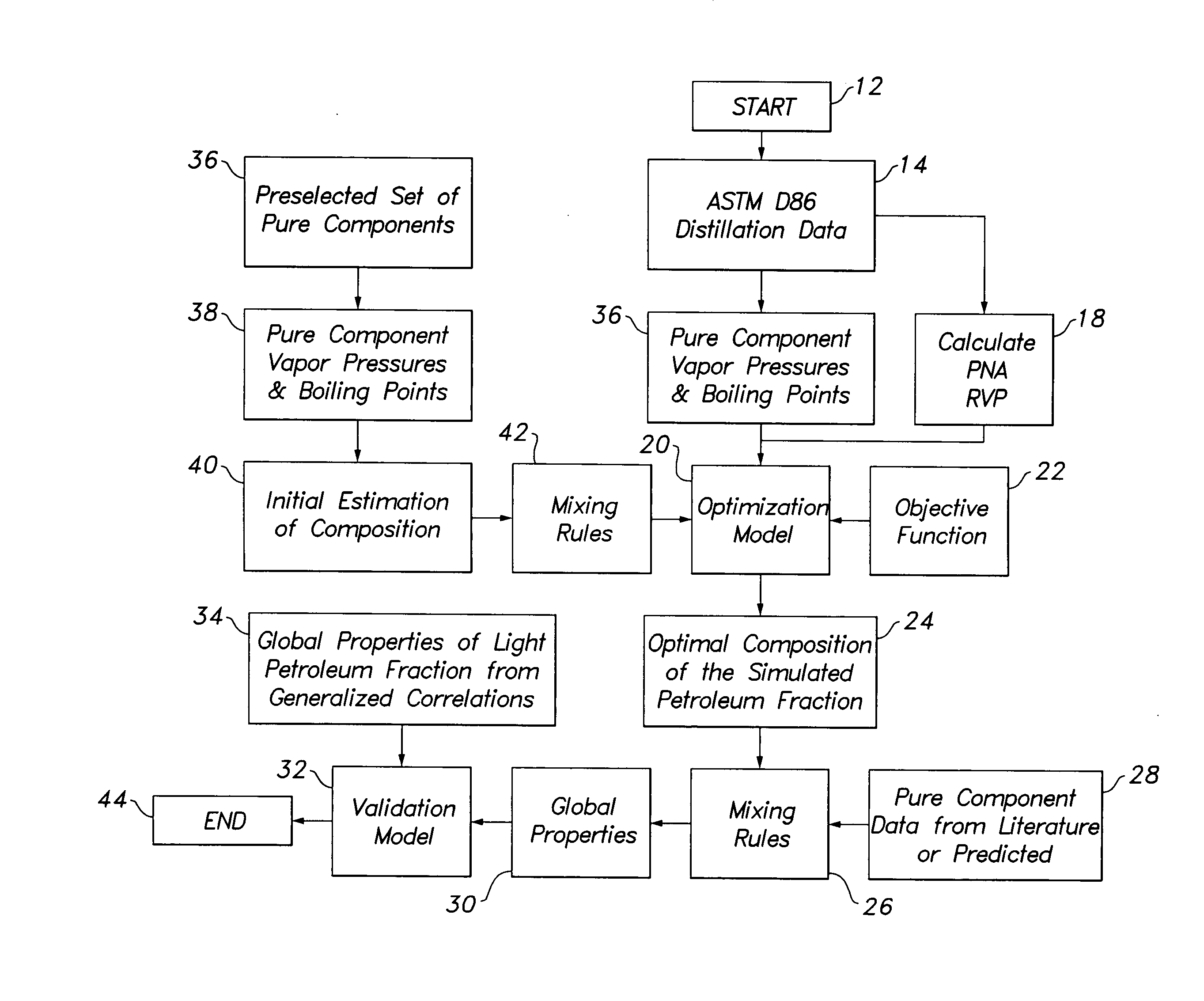
Method and apparatus for measuring the properties of petroleum fuels by distillation
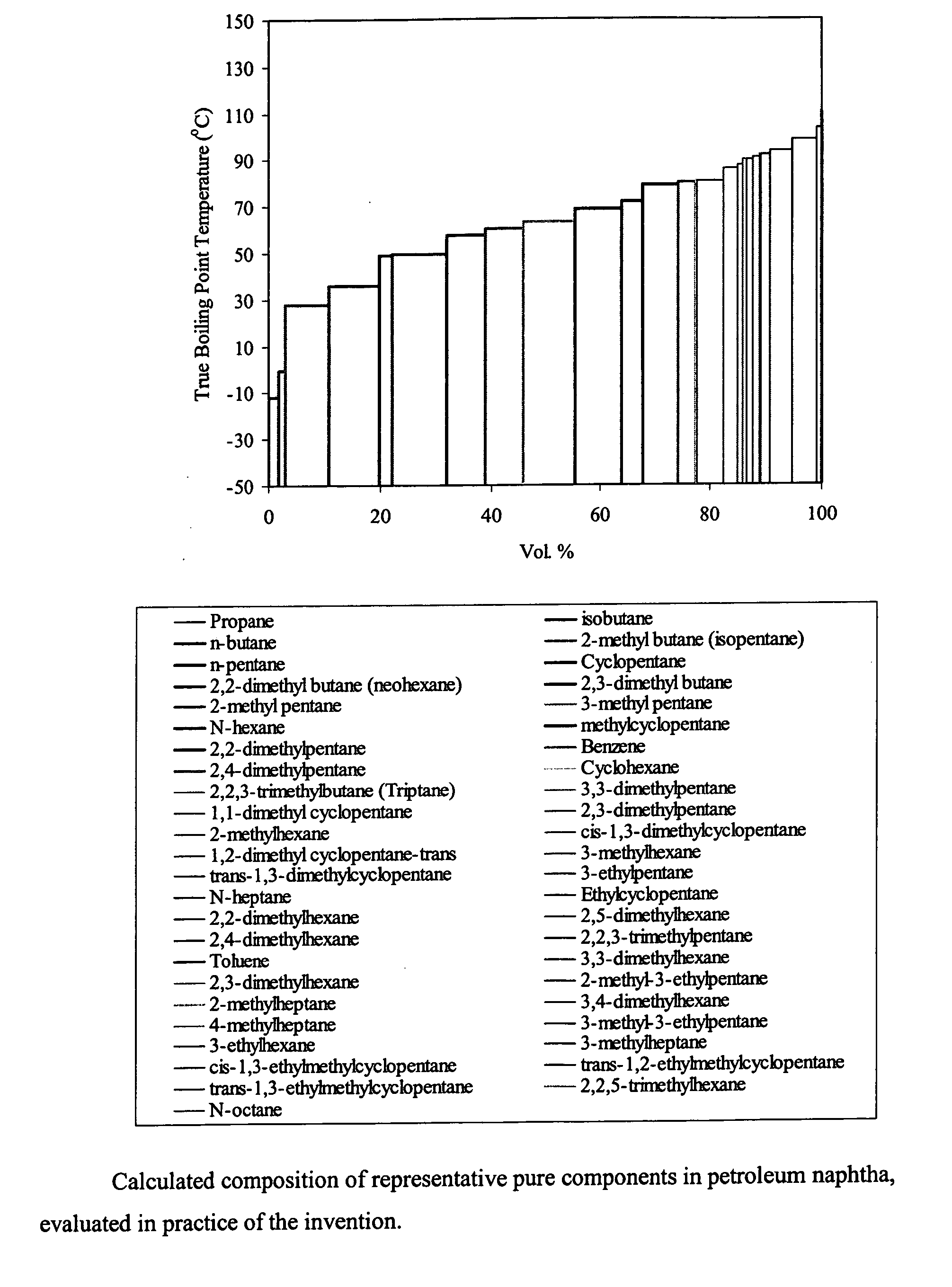
InactiveUS20070050154A1Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityChemical property predictionMaterial thermal analysisBoiling pointDistillation
It is a purpose of this invention to accurately measure the properties of petroleum and petroleum fractions from a small volume of sample oil in a short period of time with less cost and energy for the analysis by vaporizing and distilling the respective components contained in the sample to be measured by a distillation apparatus. The components in the sample oil are first separated and vaporized by the distillation apparatus and the boiling point distribution of the respective components is measured. The property estimation means is equipped with a property estimation model for evaluating the property estimate value outputted from the property estimation model. The method is incorporated into standard or otherwise any distillation test apparatus to provide accurate measure of the thermodynamic and transport properties of undefined multicomponent mixtures such as crude oil, petroleum fractions, gas condensates and the like.
Owner:KWAIT UNIV
Method and system for artificial intelligence directed lead discovery through multi-domain clustering
InactiveUS6904423B1Simple structureEasy to analyzeChemical property predictionMathematical modelsChemical structureComputer science
A system for analyzing a vast amount of data representative of chemical structure and activity information and concisely providing conclusions about structure-to-activity relationships. A computer may adaptively learn new substructure descriptors based on its analysis of the input data. The computer may then apply each substructure descriptor as a filter to establish new groups of molecules that match the descriptor. From each new group of molecules, the computer may in turn generate one or more additional new groups of molecules. A result of the analysis in an exemplary arrangement is a tree structure that reflects pharmacophoric information and efficiently establishes through lineage what effect on activity various chemical substructures are likely to have. The tree structure can then be applied as a multi-domain classifier, to help a chemist classify test compounds into structural subclasses.
Owner:SIMULATIONS PLUS +6
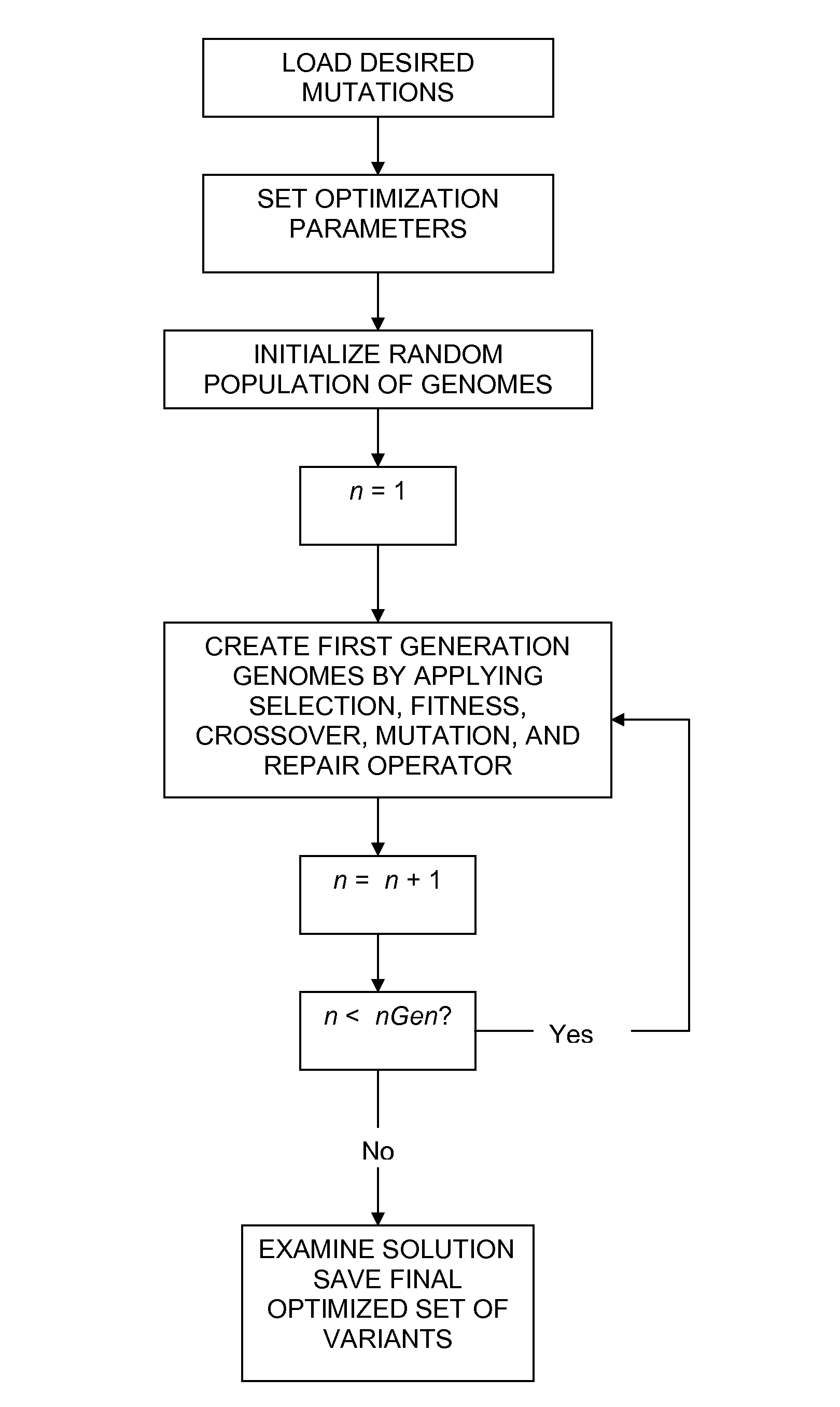
Method of generating an optimized, diverse population of variants
The disclosure relates to a method of generating a diverse set of variants to screen improved and novel properties within the variant population, a system for creating the diverse set of variants, and the variant peptides.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
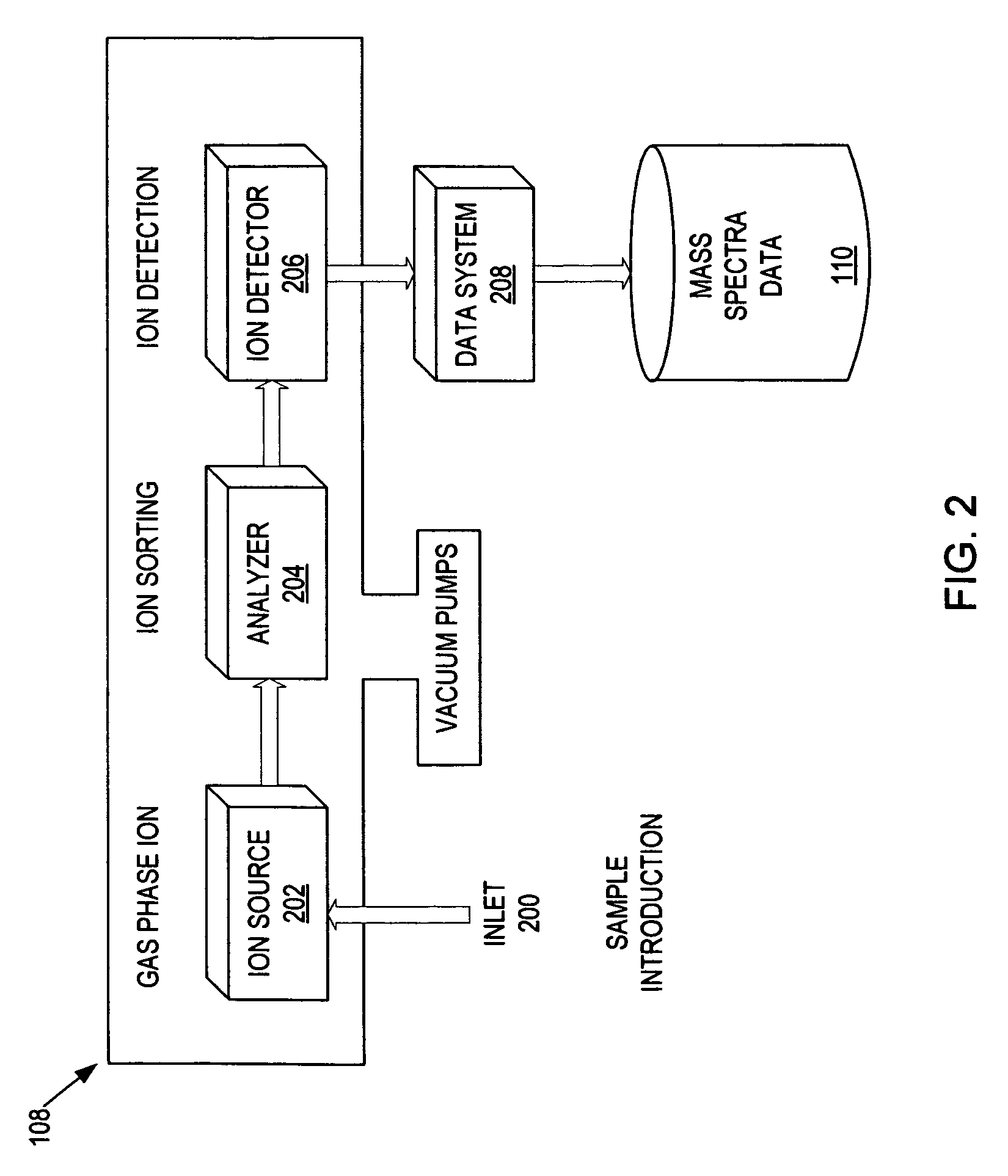
Ion detection and parameter estimation for n-dimensional data
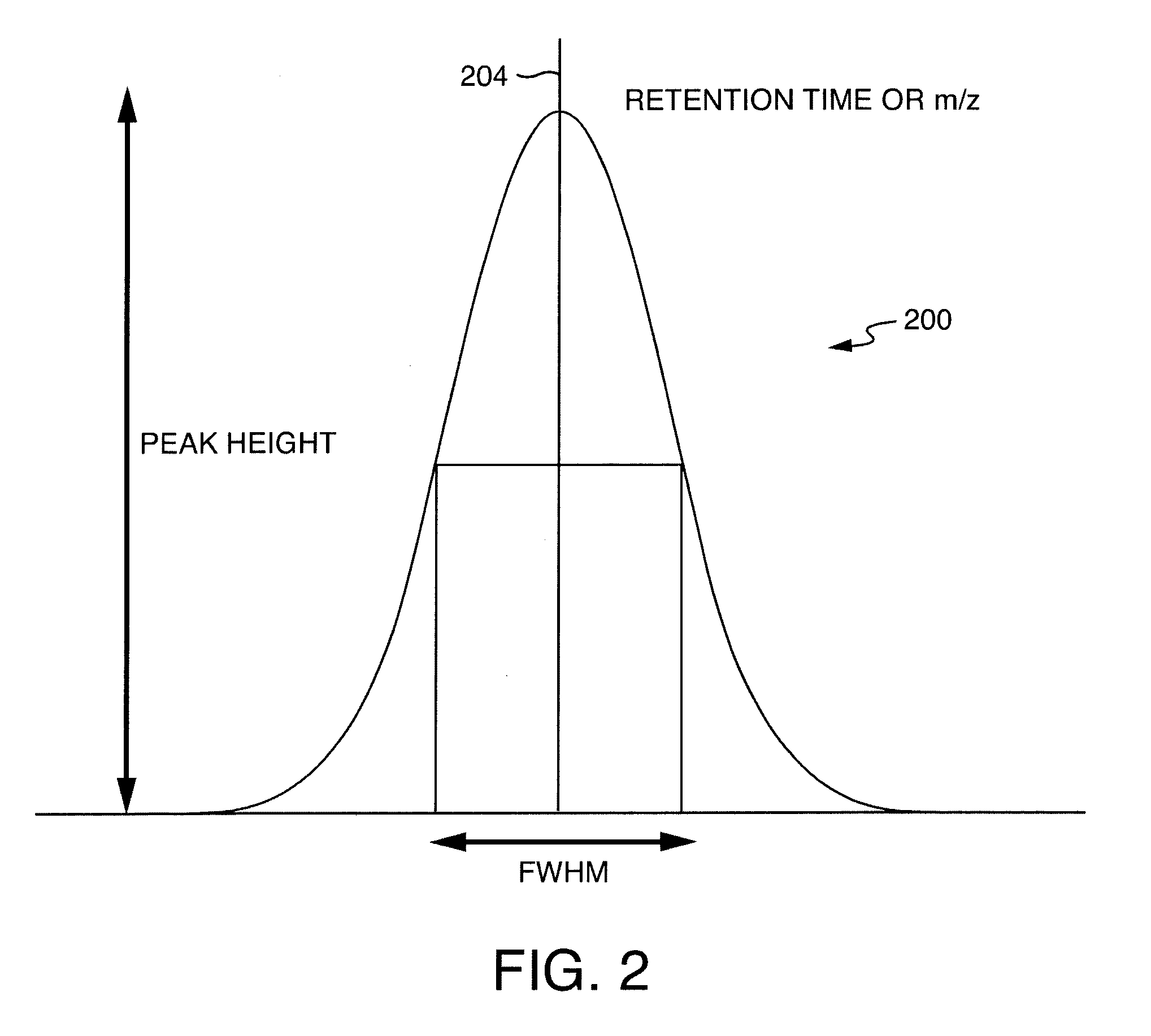
ActiveUS20090294645A1Reduce artifactsFaster and efficient characterizationMolecular entity identificationIsotope separationRetention timeMass-to-charge ratio
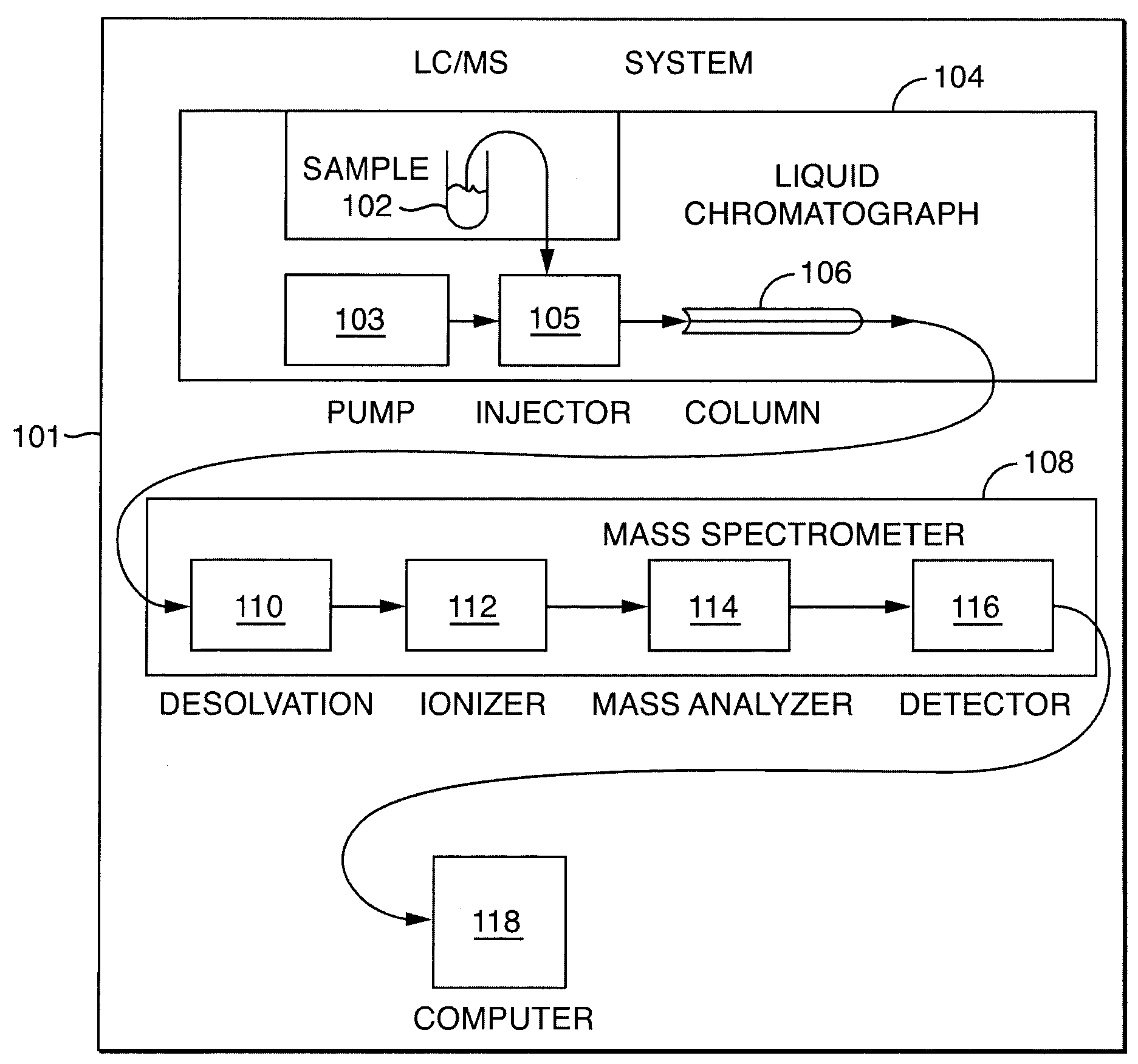
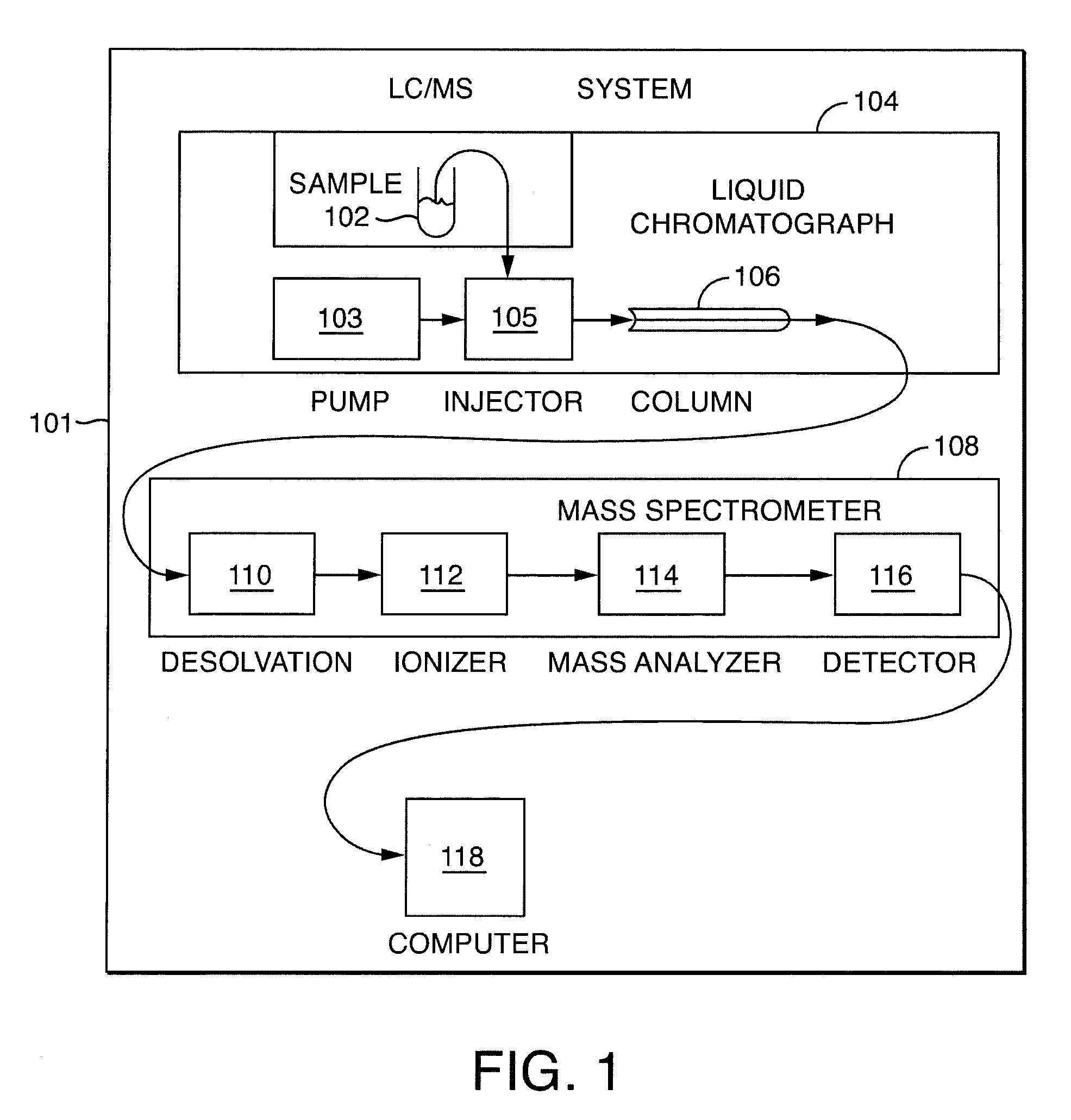
Methods and apparatus for LC / IMS / MS analysis involve obtaining noisy raw data from a sample, convolving the data with an artifact-reducing filter, and locating, in retention-time, ion mobility, and mass-to-charge-ratio dimensions, one or more ion peaks of the convolved data.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
Methods and Systems for Assessing Clinical Outcomes
InactiveUS20120053425A1Increased futureImproved labelingBiostatisticsDiagnostic recording/measuringData miningData science
Owner:THERANOS IP CO LLC
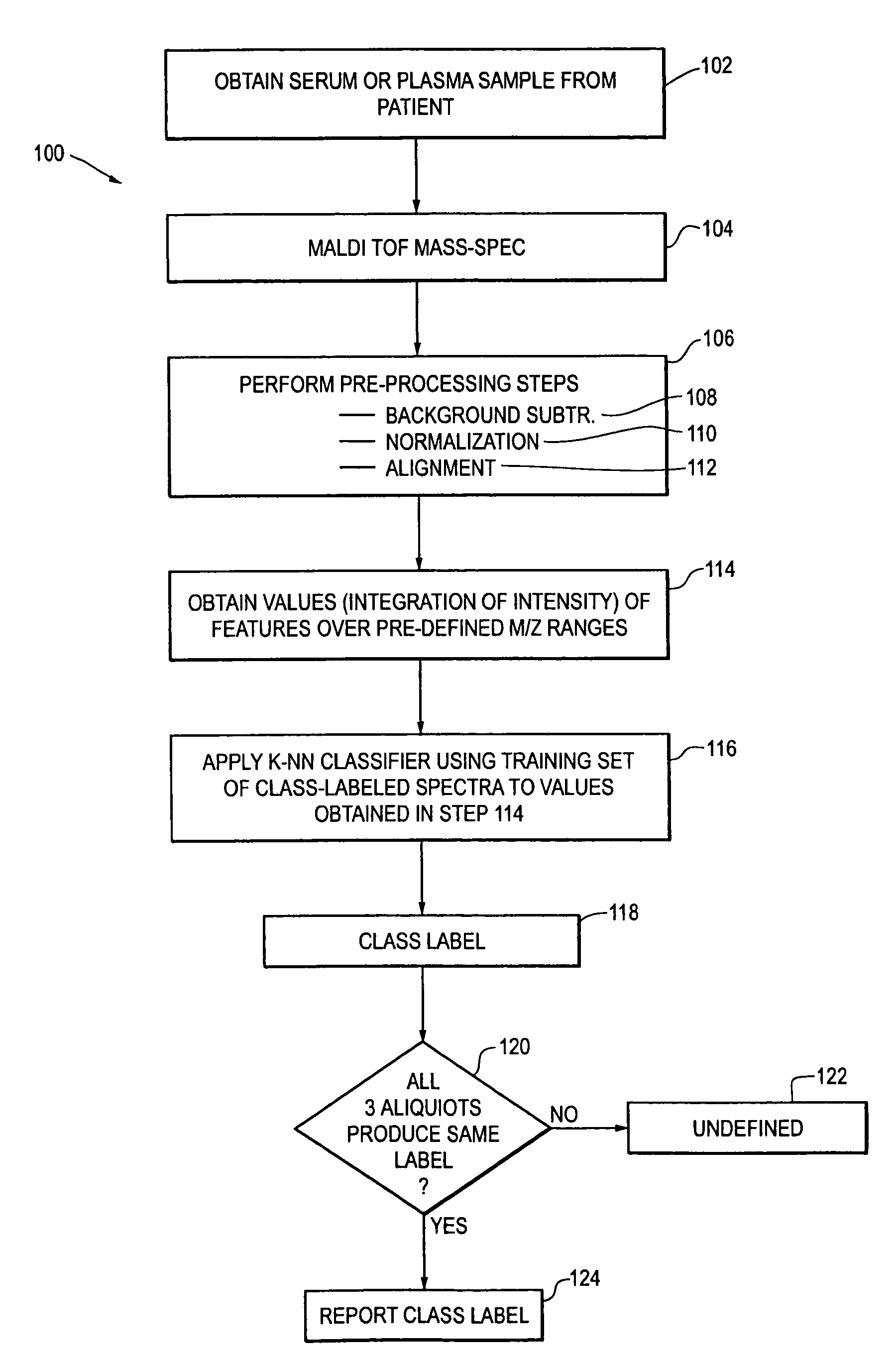
Method for the identification of molecules and biomarkers using chemical, biochemical and biological data
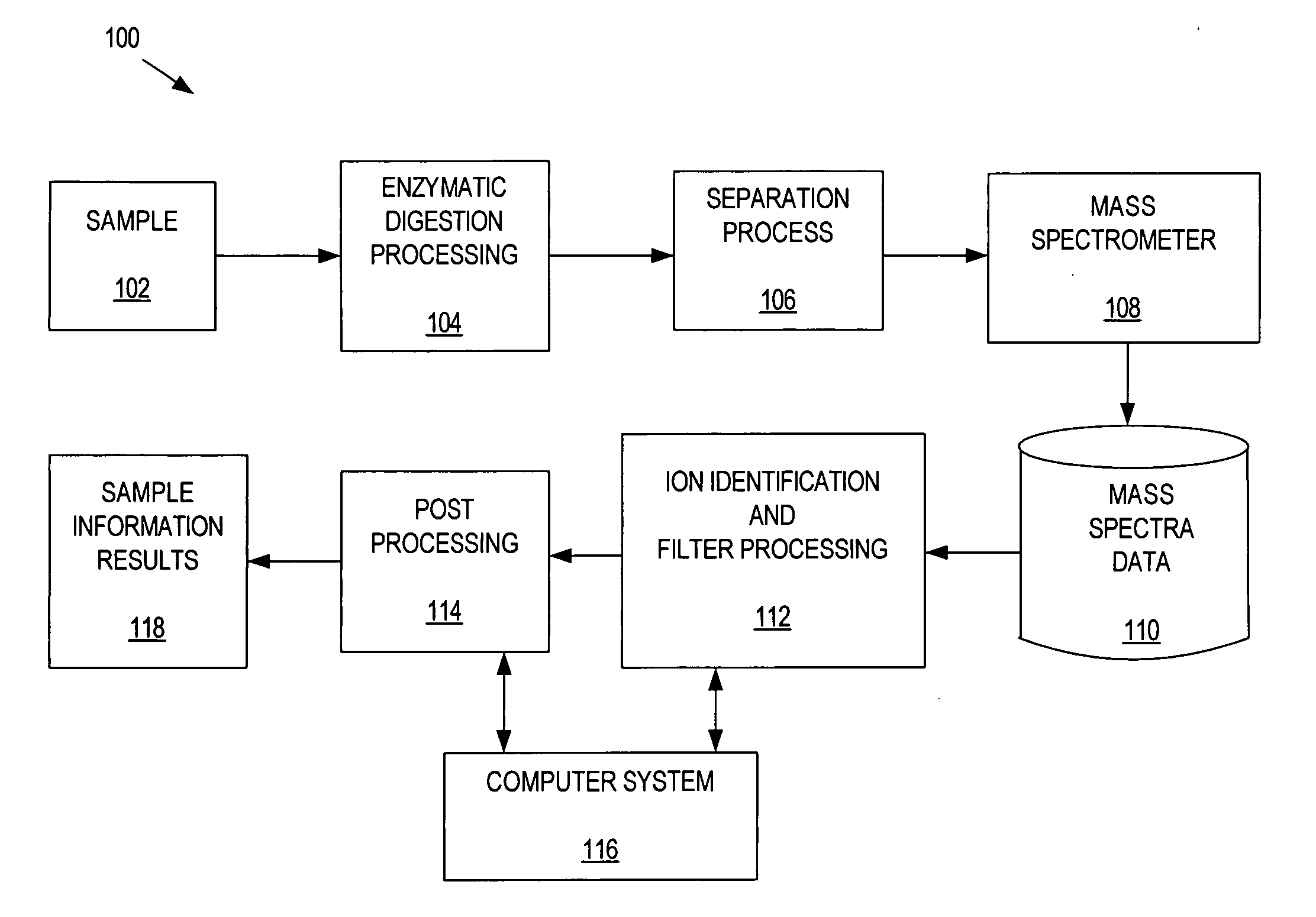
ActiveUS20070043518A1Molecular entity identificationProteomicsGenomicsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
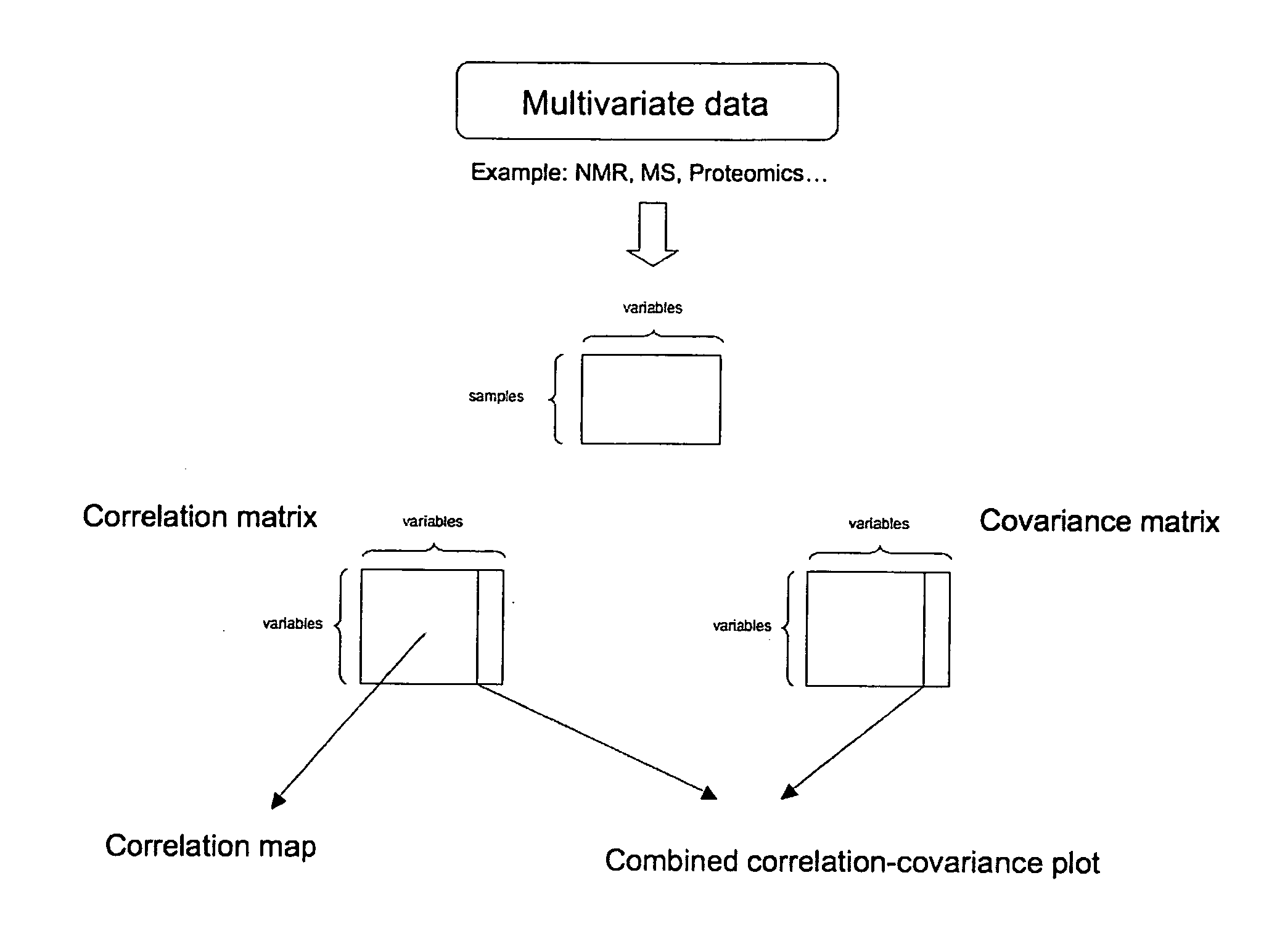
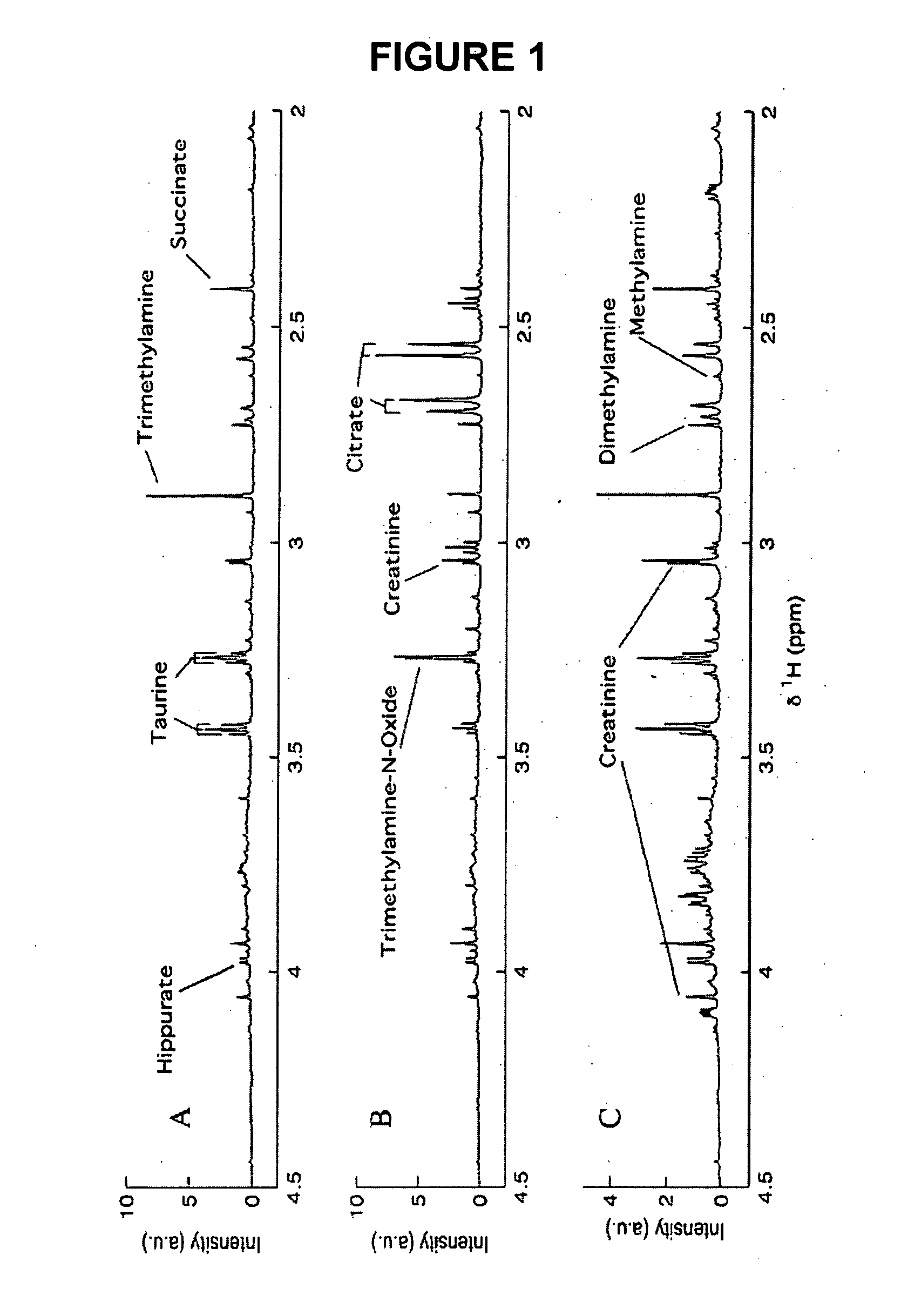
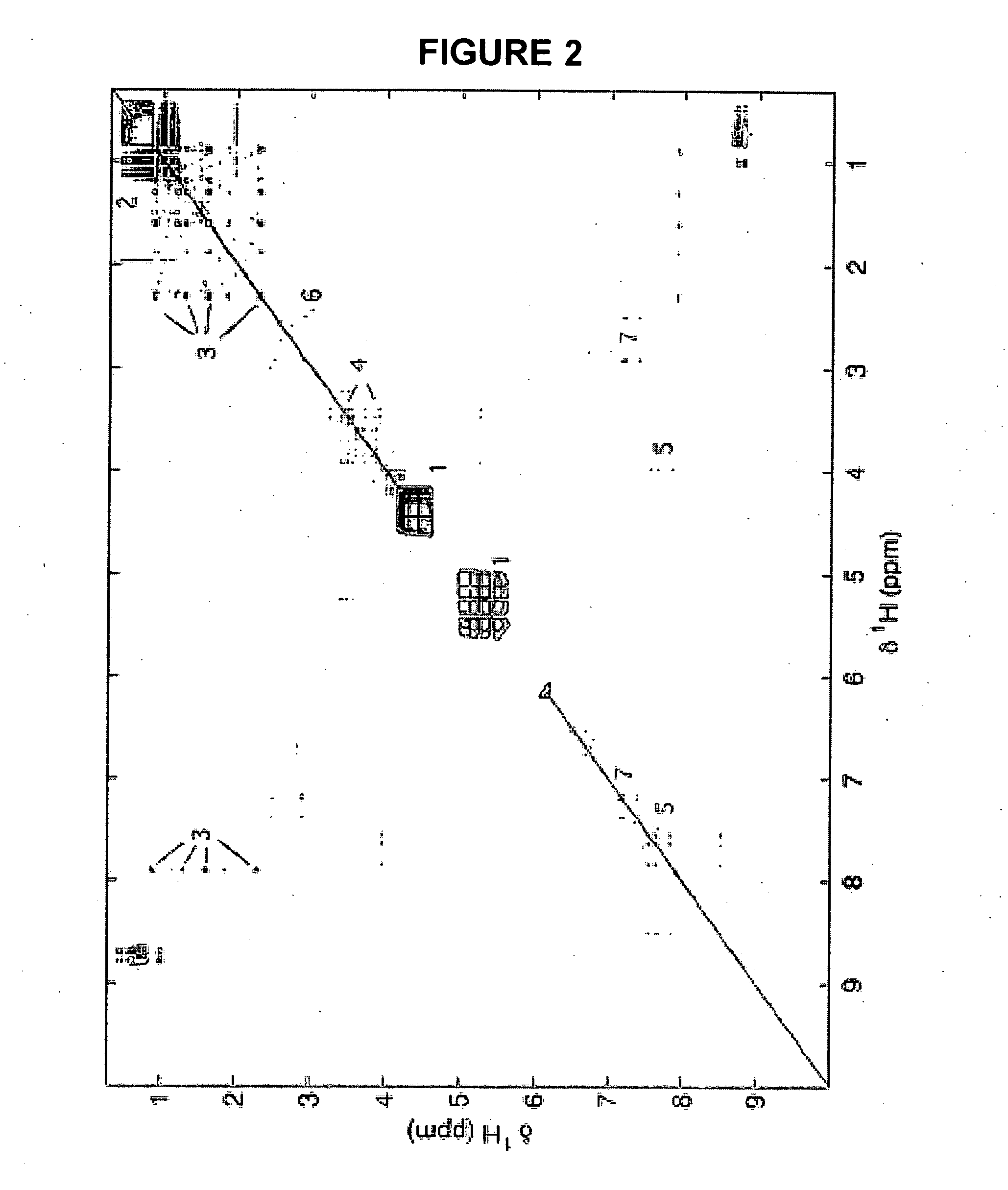
This invention pertains generally to the field of multivariate statistics, and in particular to new methods for the analysis (e.g., chemometrics) of chemical, biochemical, and biological data, including, for example, spectral data, including but not limited to nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectral data. These methods are useful, for example, in metabonomics, proteomics, transcriptomics, genomics, etc., and form a part of other methods, for example, methods for the identification of chemical species, methods for the identification of biomarkers that are useful in methods of classification, diagnosis, prognosis, etc.
Owner:IMPERIAL INNOVATIONS LTD
Methods and systems for peak detection and quantitation
InactiveUS20050288872A1Reduce the amount requiredParticle separator tubesMolecular entity identificationPattern recognitionData set
Methods, systems and computer readable media for identifying peaks in a three-dimensional mass spectrometry / elution time dataset. The dataset is represented as a matrix of intensity values with column and row positions corresponding to specific elution time and m / z value, respectively. Peaks may be detected using a watershed image segmentation technique. Further provided are methods, systems and recordable media for creating a mask matrix to be overlaid on a large three-dimensional dataset represented as an image matrix, to identify a much smaller portion of the three dimensional dataset of interest, and to greatly reduce the amount of subsequent processing required for processing data of interest. The mask matrix has the same dimension as the image matrix and includes areas corresponding to one or more peaks identified by the watershed segmentation technique.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
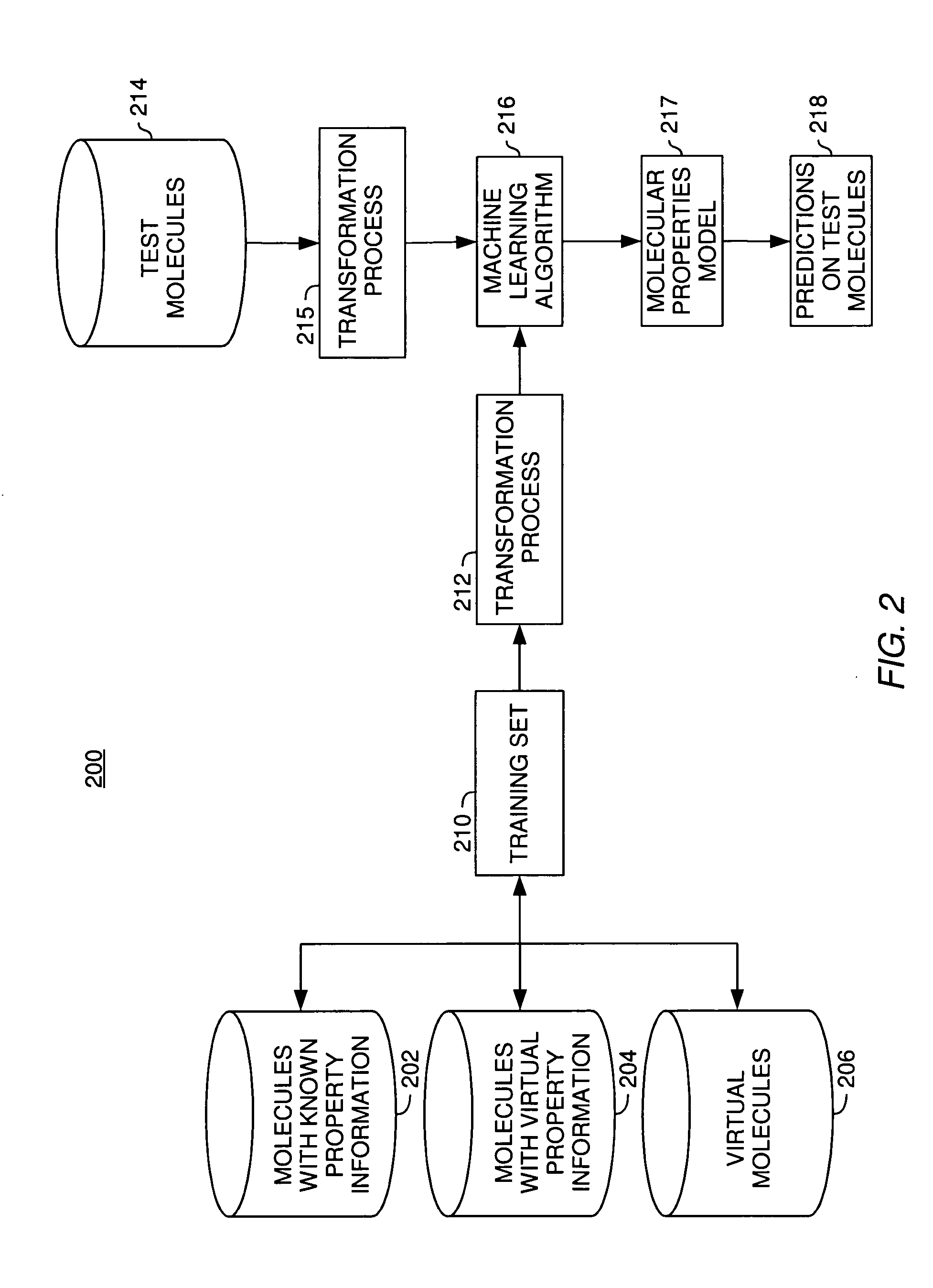
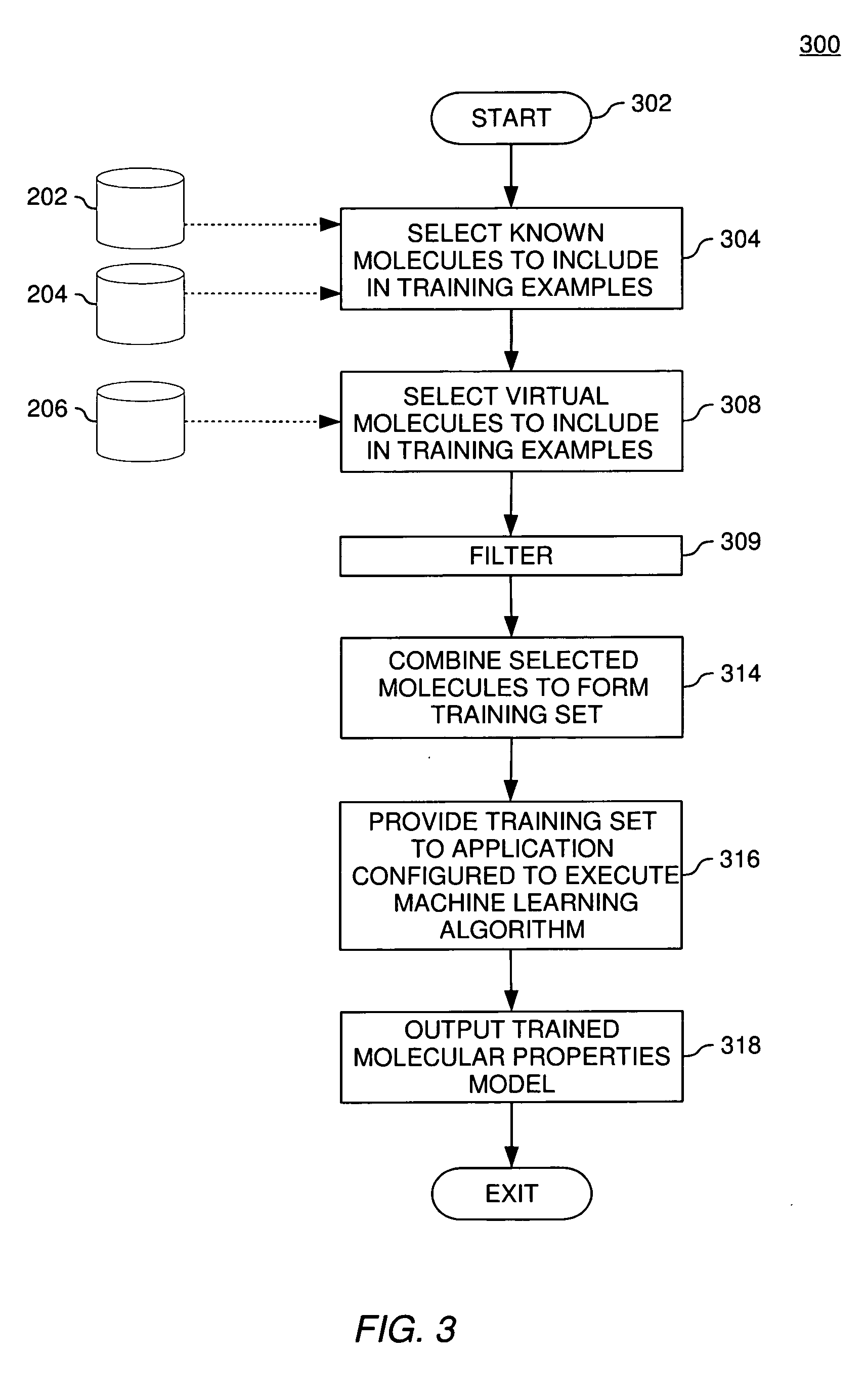
Methods for molecular property modeling using virtual data
InactiveUS20050278124A1Chemical property predictionBiological testingComputer scienceMolecular property
Embodiments of the invention provide methods, systems, and articles of manufacture for modeling molecular properties based on information obtained from sources other than direct empirical measurements of the properties. Embodiments of the invention use “virtual data” related to molecular properties to train a molecular properties model. Virtual data about a molecule may include real-valued data (e.g. measurement values falling along a continuous range) or a positive or negative assertion about whether a molecule exhibits a property of interest. Virtual data may be generated using a variety of techniques and may be further characterized by confidence in the accuracy of the virtual data. In addition to virtual data, embodiments of the invention may use “virtual molecules” paired with “virtual data” to train a molecular properties model. The virtual molecules may themselves be generated in a variety of ways.
Owner:NUMERATE
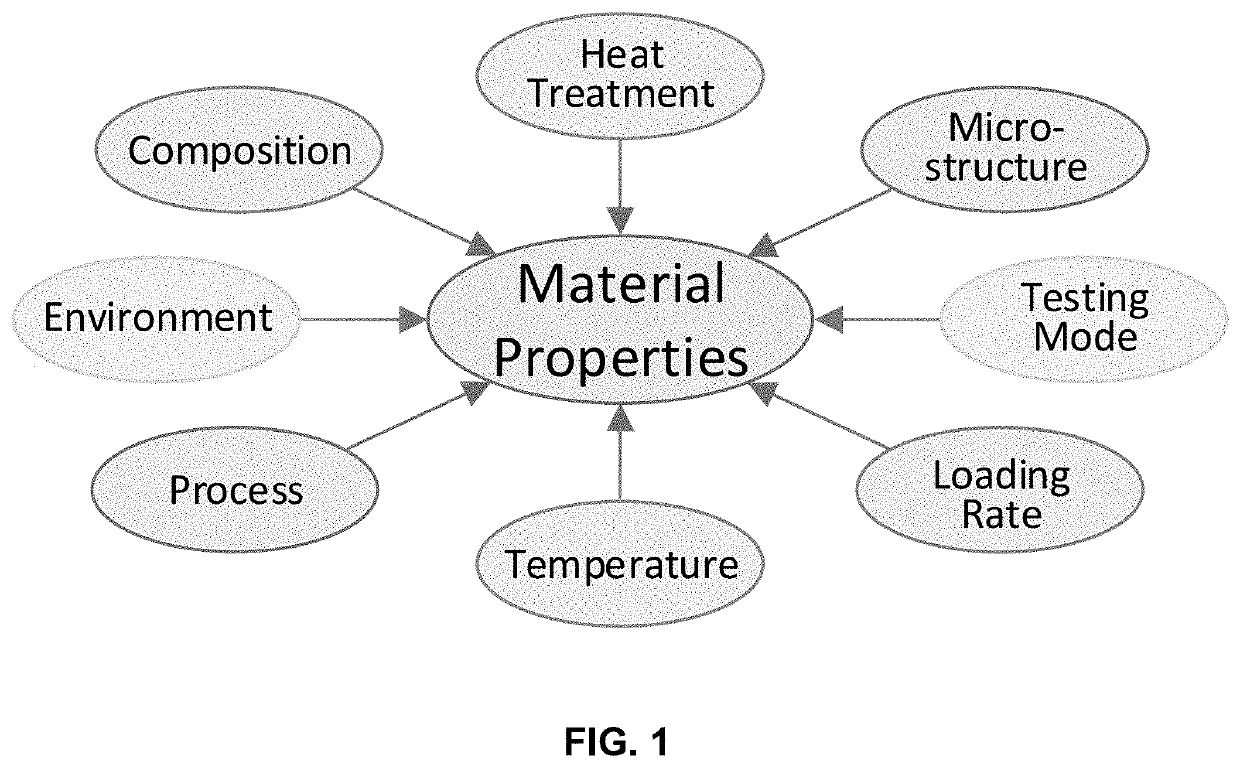
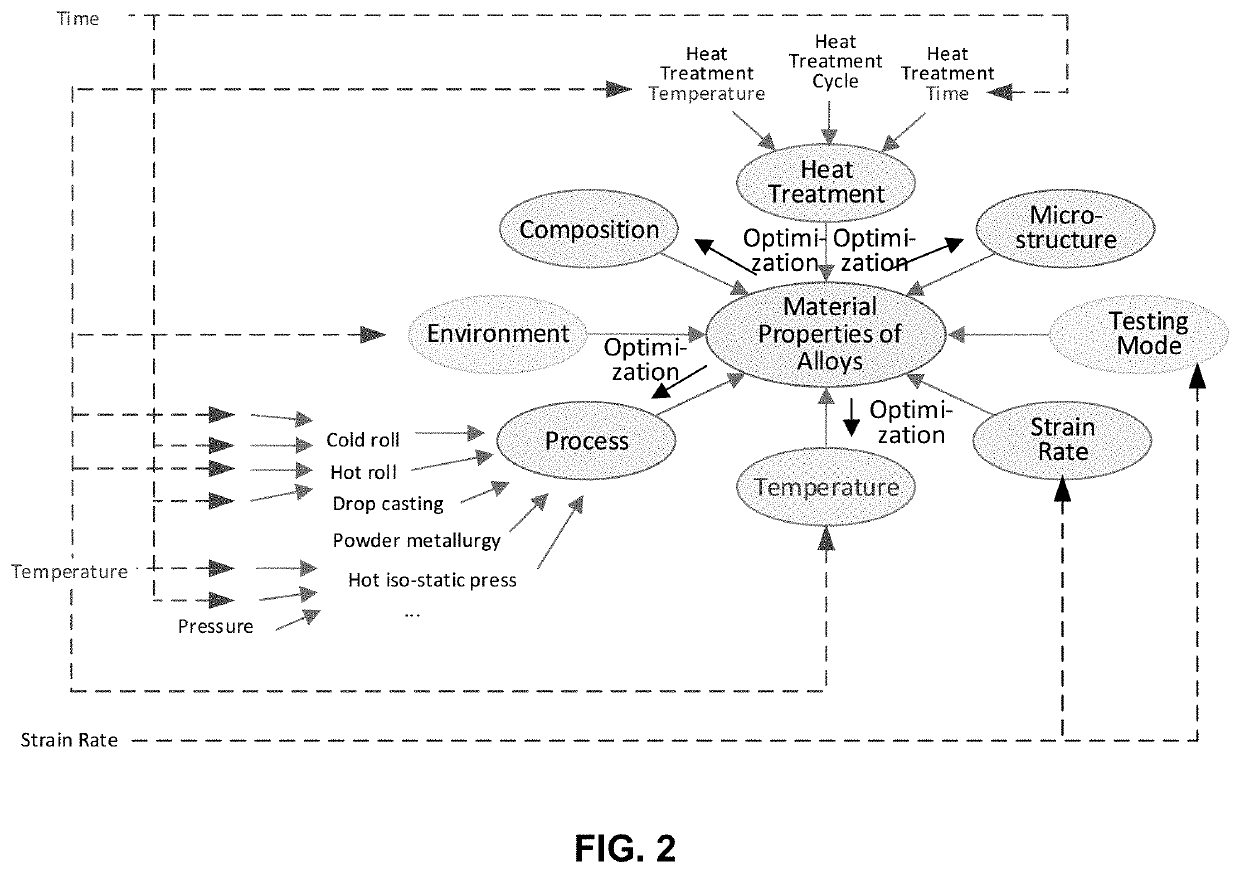
Machine Learning to Accelerate Alloy Design
PendingUS20200257933A1Tightly coupledEasy to predictChemical property predictionTurbinesPrior informationRegression analysis
This invention presents an innovative framework for the application of machine learning for identification of alloys or composites with desired properties of interest. For each output property of interest, we identify the corresponding driving (input) factors. These input factors may include the material composition, heat treatment, process, microstructure, temperature, strain rate, environment or testing mode. Our framework assumes selection of optimization technique suitable for the application at hand and data available, starting with simple linear, or quadratic, regression analysis. We present a physics-based model for predicting the ultimate tensile strength, a model that accounts for physical dependencies, and factors in the underlying physics as a priori information. In case an artificial neural network is deemed suitable, we suggest employing custom kernel functions consistent with the underlying physics, for the purpose of attaining tighter coupling, better prediction, and extracting the most out of the—usually limited—input data available.
Owner:IMAGARS
Method For Predicting Composition of Petroleum
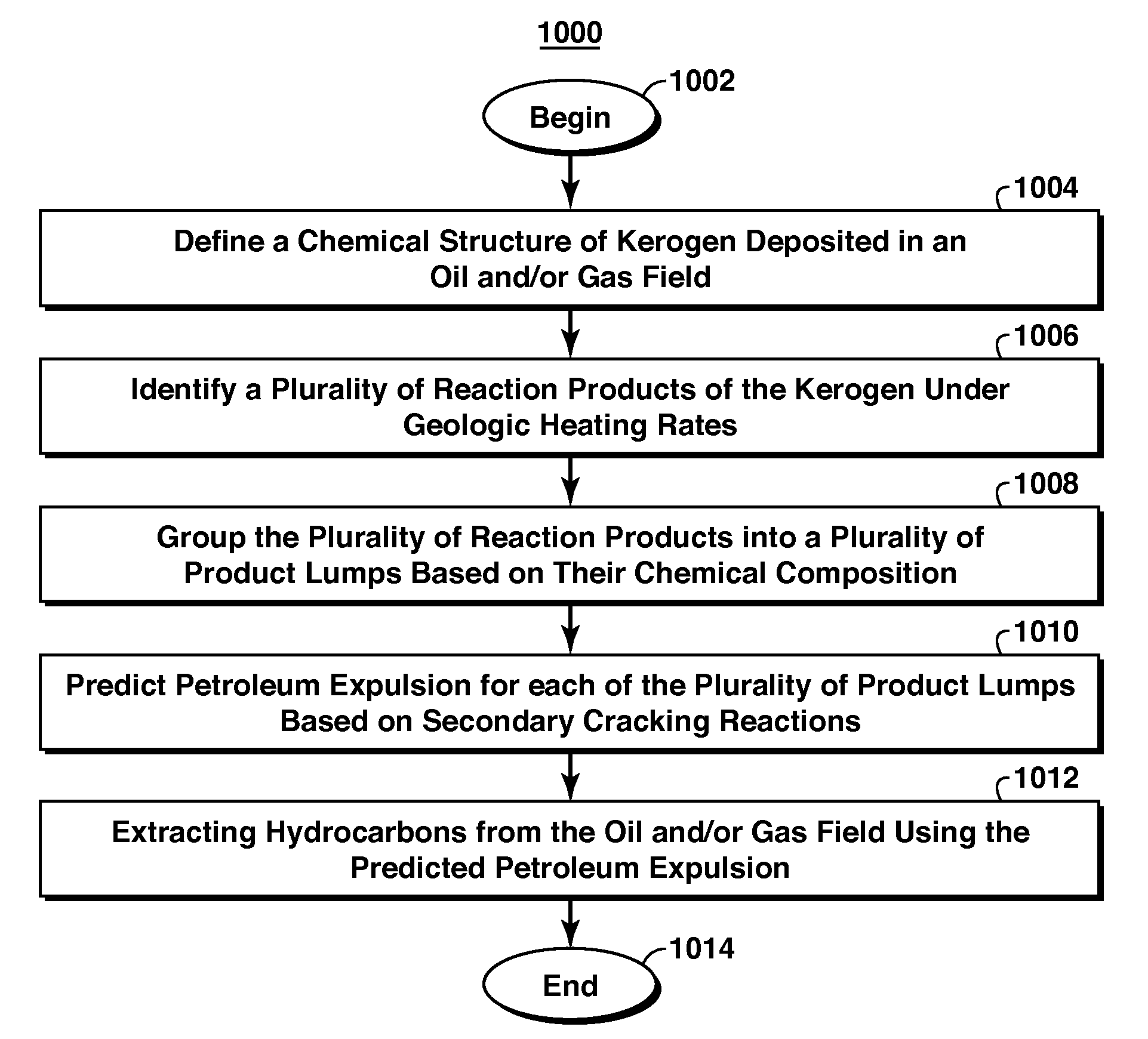
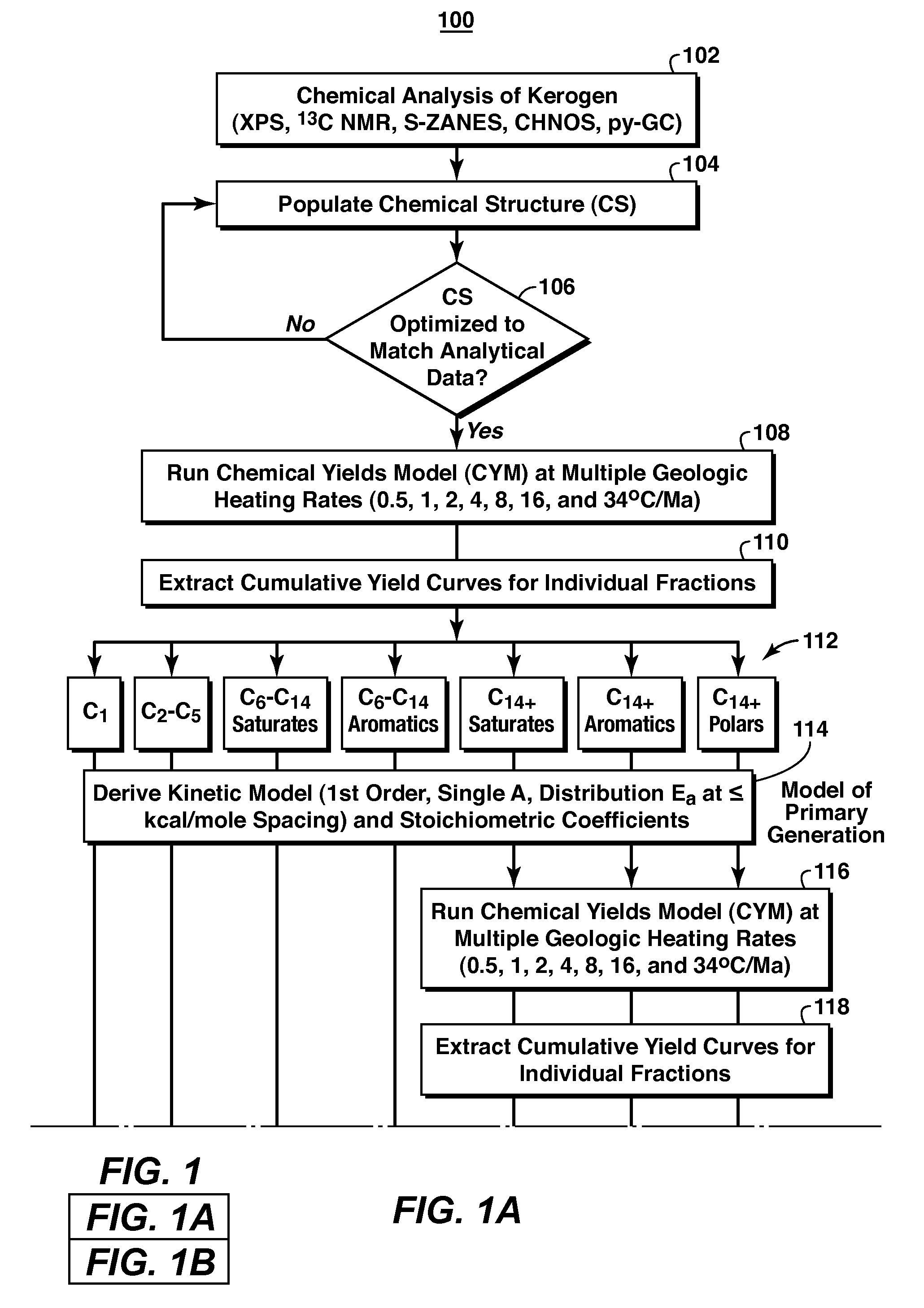
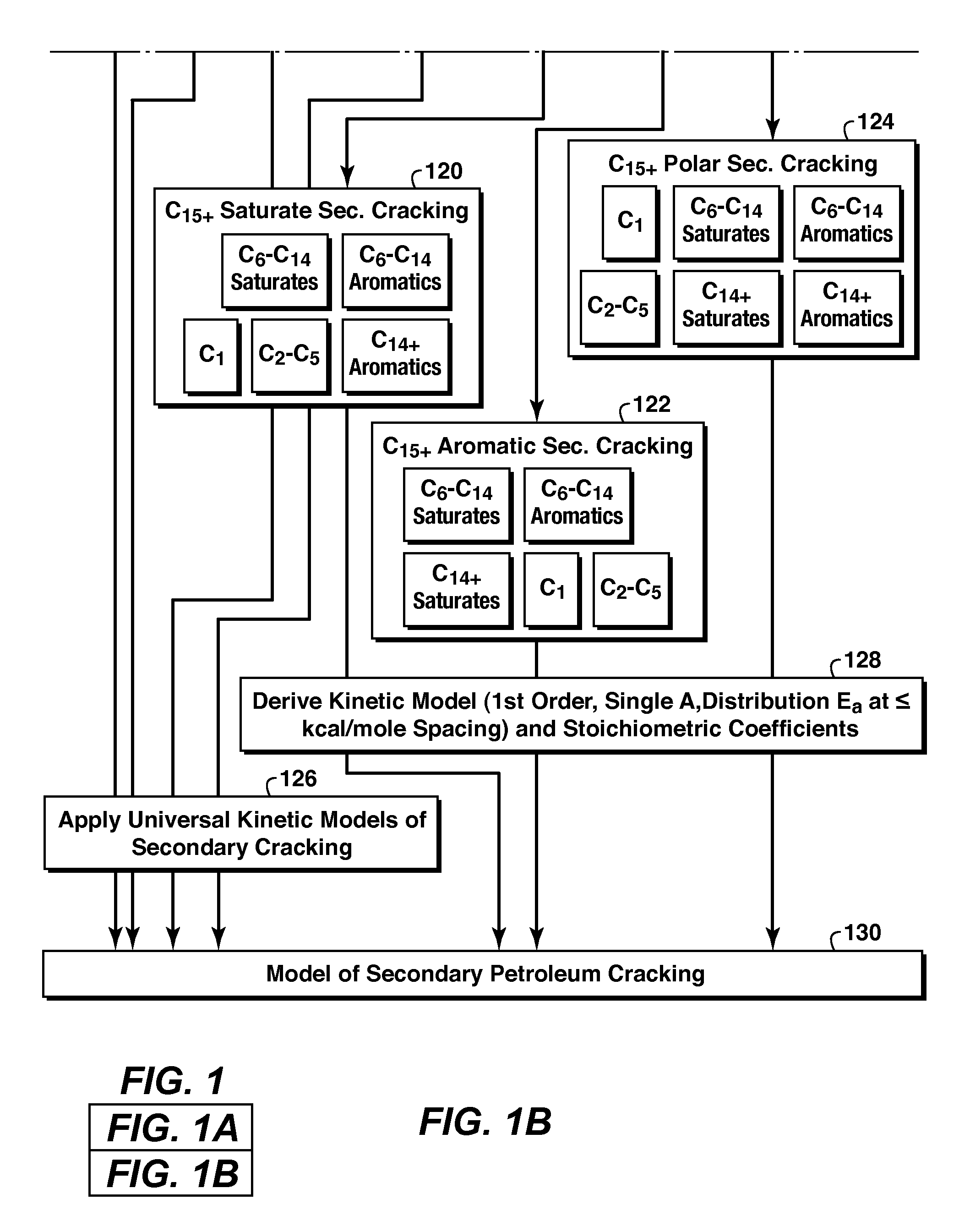
A method for predicting petroleum expulsion is provided. An exemplary embodiment of the method comprises defining a chemical structure of a kerogen and identifying a plurality of reaction products of the kerogen under geologic heating rates. The exemplary method also comprises grouping the plurality of reaction products into a plurality of product lumps based on their chemical composition and predicting petroleum expulsion for each of the plurality of product lumps based on secondary cracking reactions.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Methods and systems for discovery of chemical compounds and their syntheses
InactiveUS20050177280A1Overcome deficienciesChemical property predictionSampled-variable control systemsCADA compoundChemical compound
Owner:ORIGENIS
Method for measuring the properties of petroleum fuels by distillation
ActiveUS20100204925A1Readily apparentChemical property predictionAnalysing gaseous mixturesBoiling pointDistillation
Owner:KUWAIT UNIV OF
Method for evolving molecules and computer program for implementing the same
InactiveUS20100010946A1Process can be speededEasy to implementMolecular designGenetic modelsComputer scienceGoal attainment
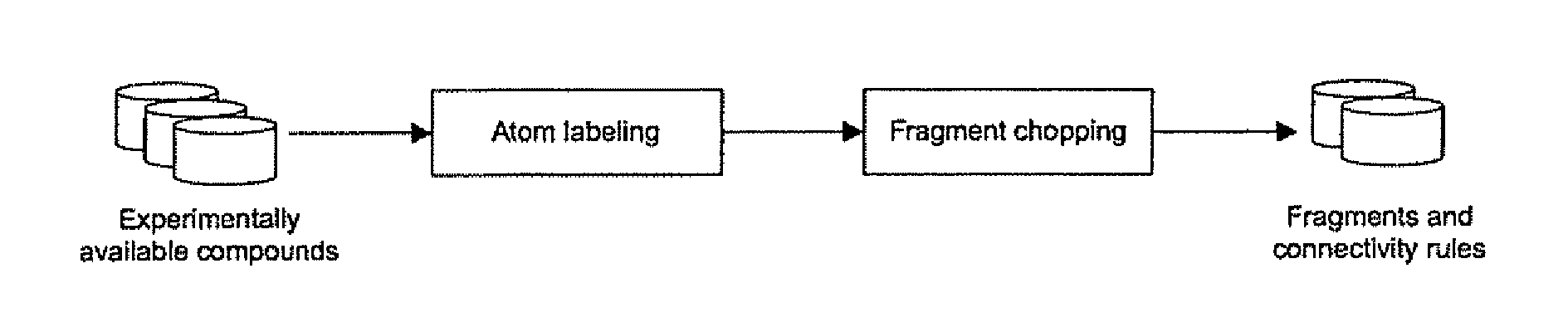
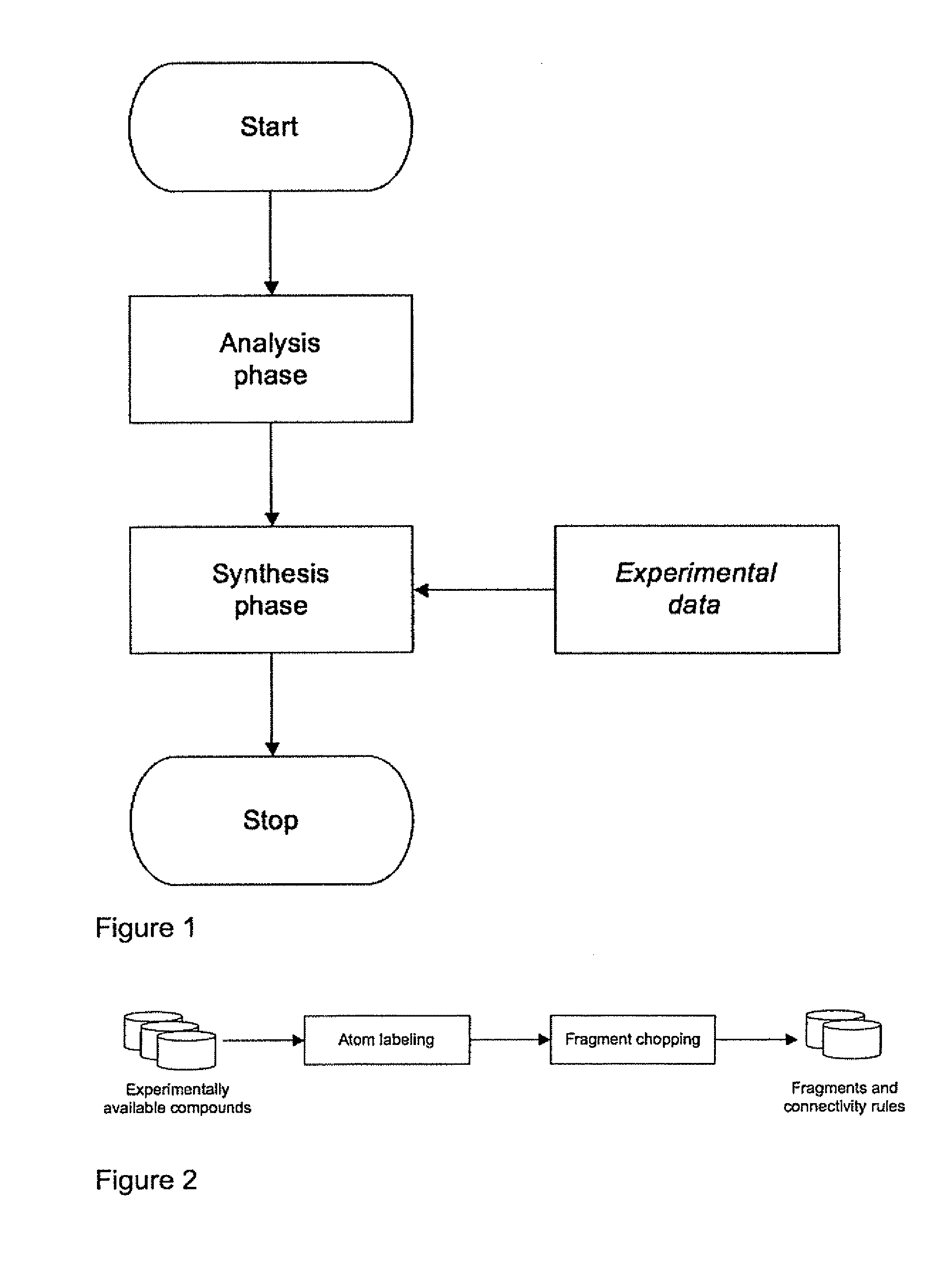
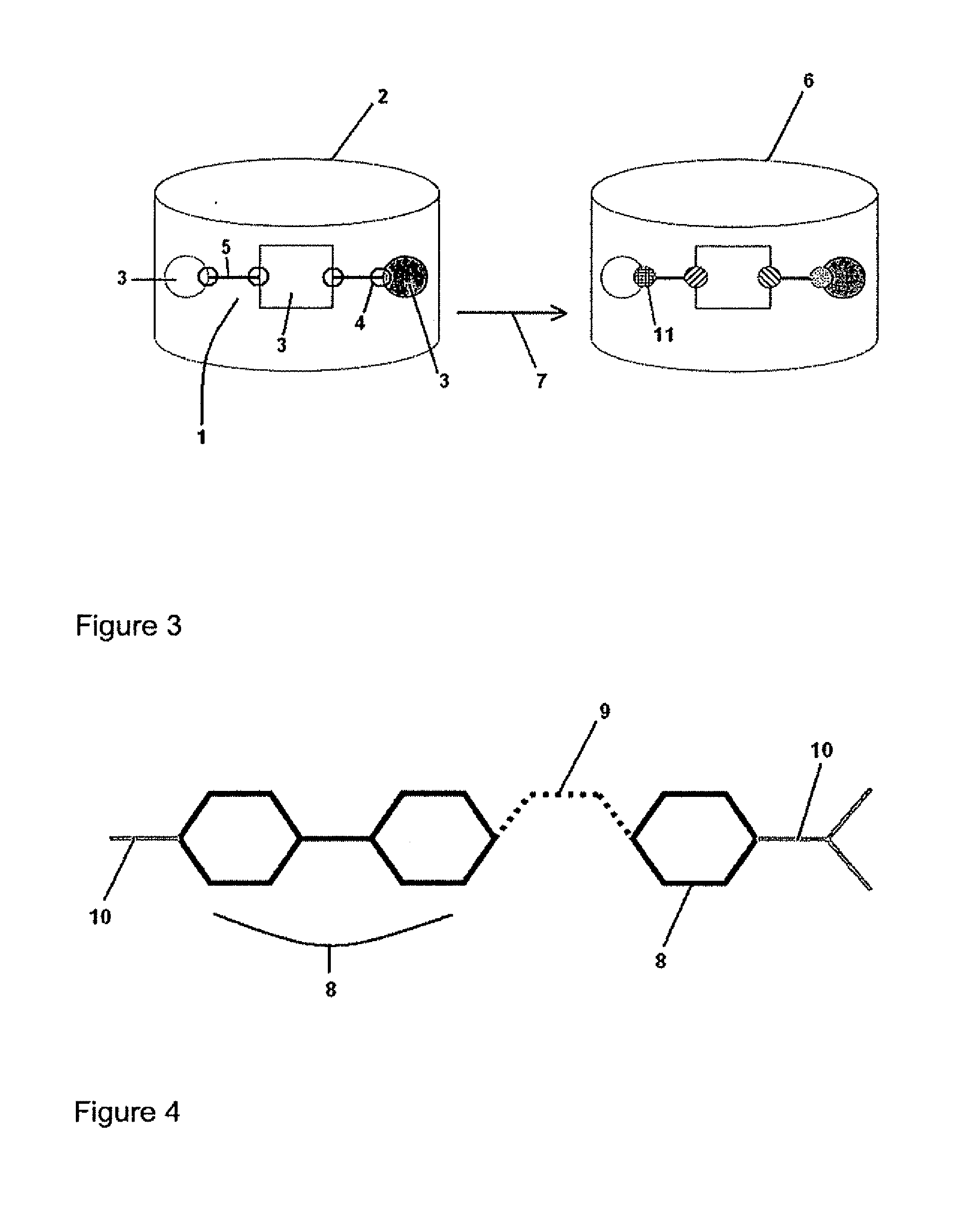
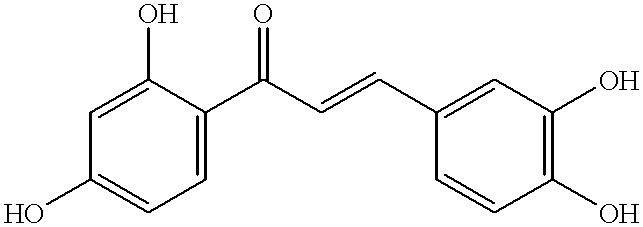
A computer-based method and system of evolving a virtual molecule with a set of desired properties is described that begins with extracting fragments from existing molecules and labeling those fragments. Connectivity rules existing between the fragments in the existing molecules are determined followed by combining these fragments according to the connectivity rules. The molecules generated by the combination are evaluated and some are selected for modification. The evaluation and modification steps are repeated for the selected molecules until either 1) a target evaluation value is achieved or 2) the evaluation step has been performed a predefined number of times.
Owner:SILICOS
Text influenced molecular indexing system and computer-implemented and/or computer-assisted method for same
InactiveUS6332138B1Chemical property predictionMathematical modelsSingular value decompositionComputer-aided
An extension of the vector space model for computing chemical similarity using textual and chemical descriptors is described. The method uses a chemical and / or textual description of a molecule / chemical and a decomposes a molecule / chemical descriptor matrix by a suitable technique such as singular value decomposition to create a low dimensional representation of the original descriptor space. Similarities between a user probe and the textual and / or chemical descriptors are then computed and ranked.
Owner:AXONTOLOGIC
Computational method for determining oral bioavailability
InactiveUS20030069721A1Chemical property predictionAnalogue computers for chemical processesSoft independent modelling of class analogiesLinear regression
A method for determining oral bioavailibility based on the linear regression computer program, SIMCA (Soft Independent Modelling of Class Analogy) is described.
Owner:PARATEK PHARM INC
Method and system for designing a material
InactiveUS20140236548A1More predictableIncrease uncertaintyChemical property predictionMolecular designEngineeringOptimal design
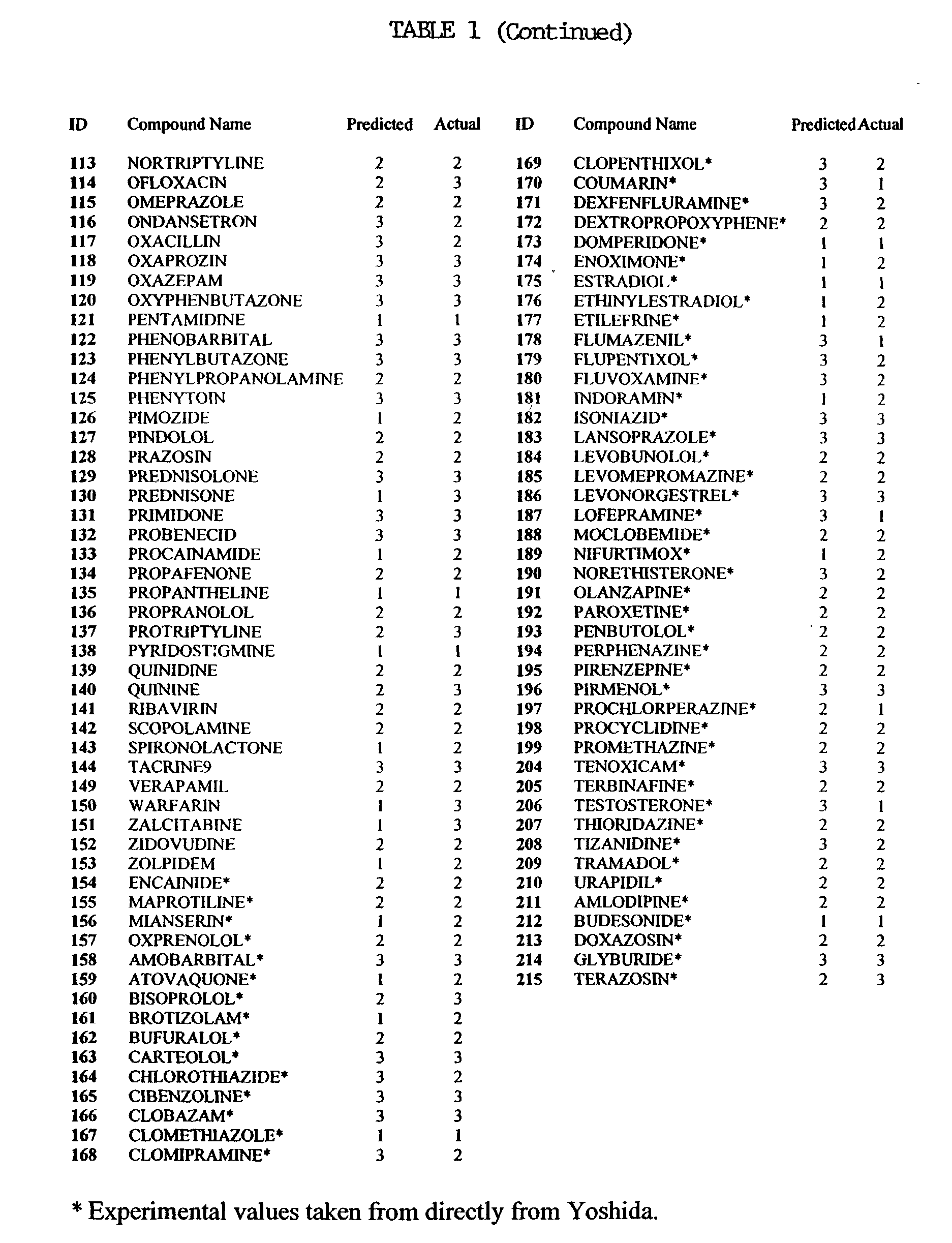
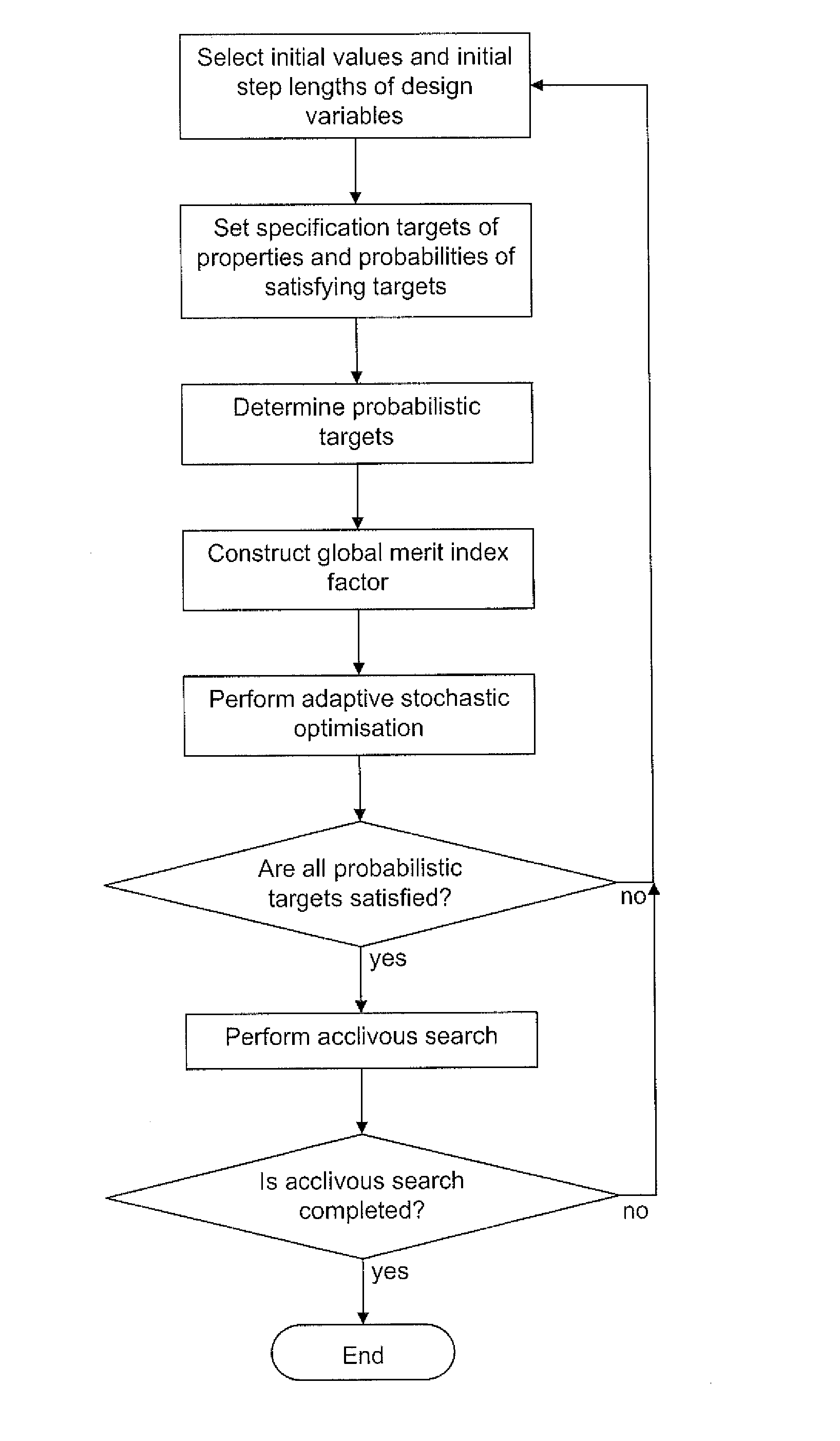
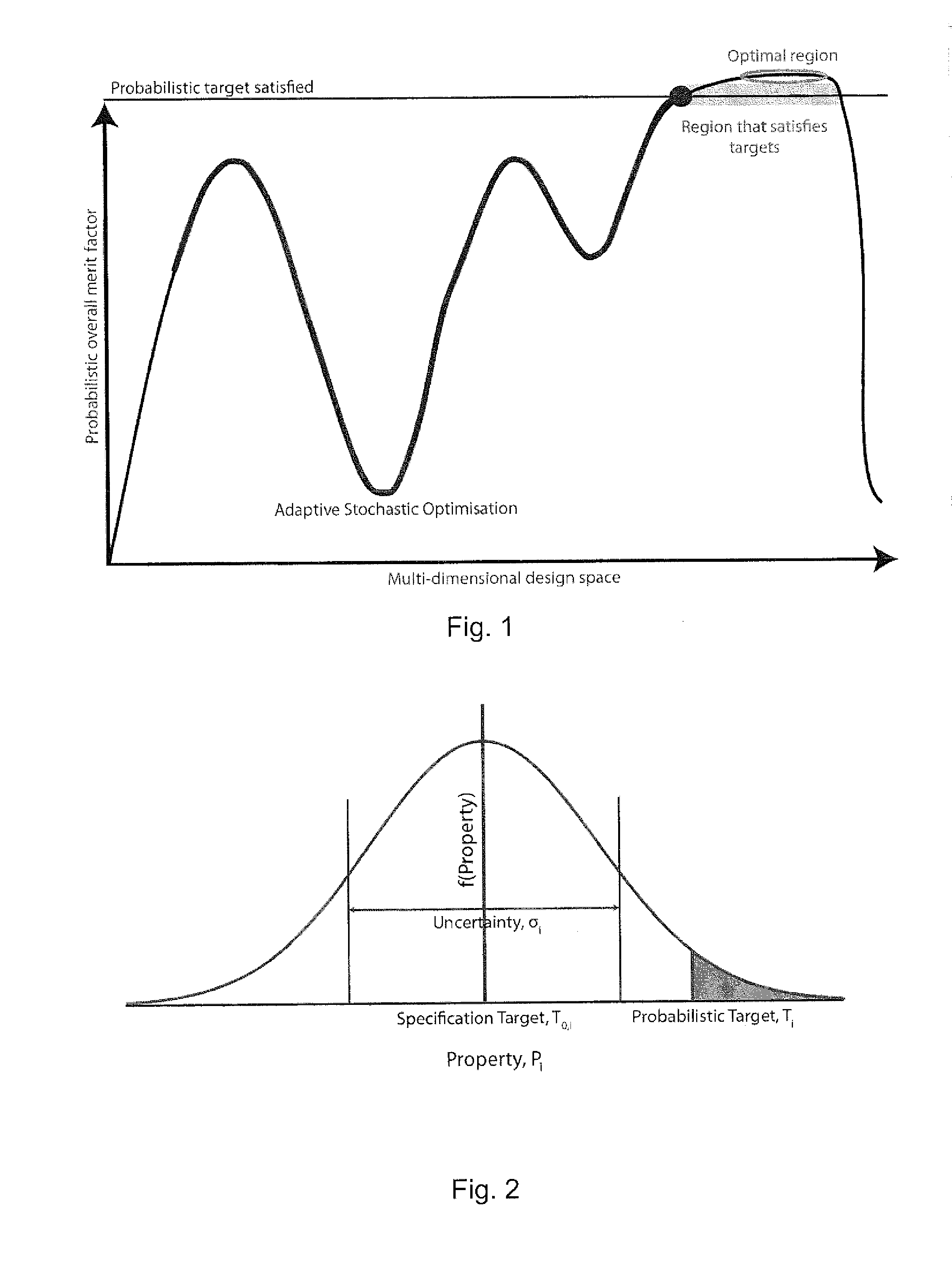
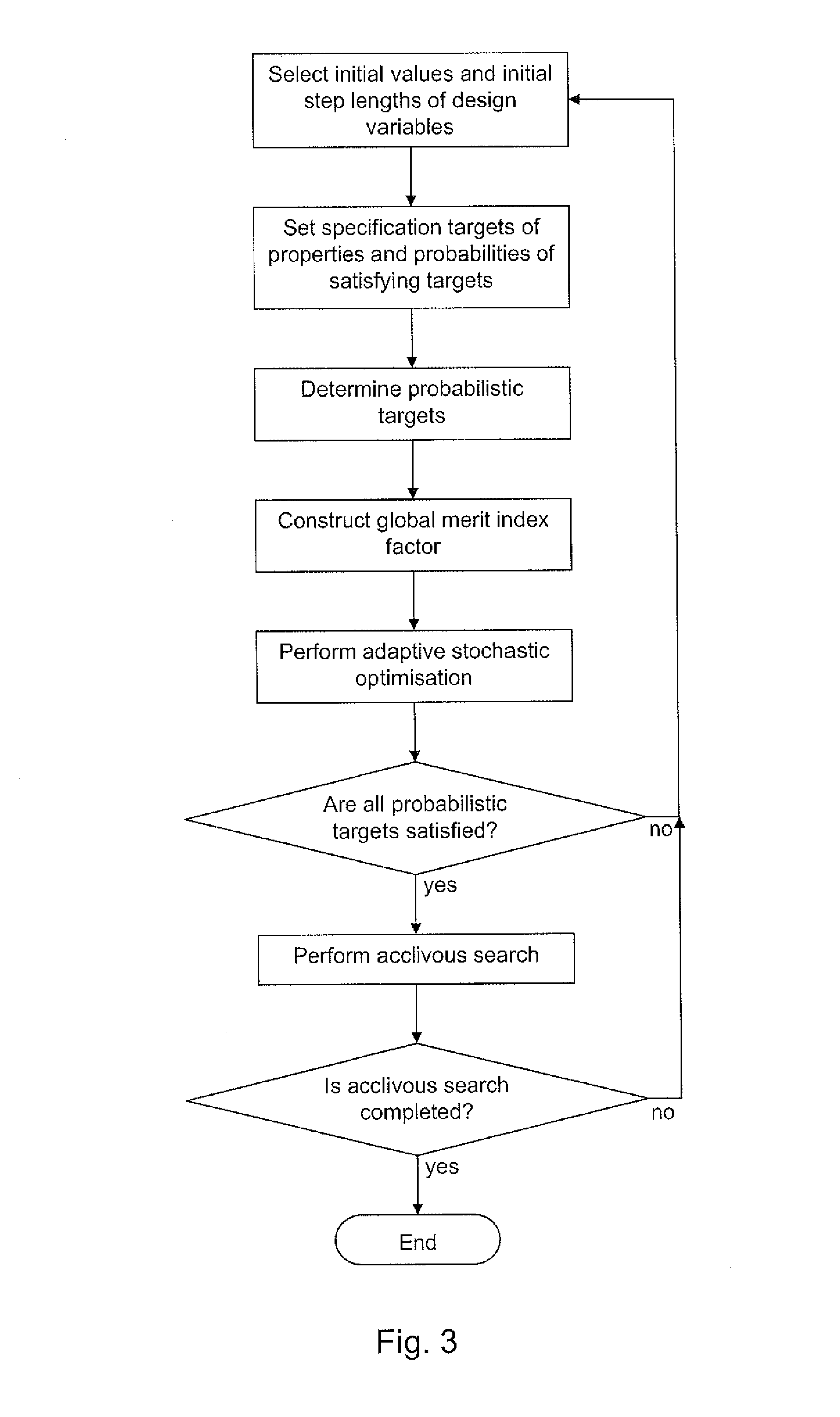
A method of designing a material by optimising values for design variables includes the steps of: (i) providing one or more property models that produce a prediction for a value of a respective property of the material as a function of the design variables and produce a value for the uncertainty in the prediction, (ii) setting a specification target for a desired value for each property and a probability for that specification target to be met or exceeded, (iii) determining a probabilistic target for a value for each property, the probabilistic target being based on the specification target and the probability, and defining a merit index factor based on the degree to which a given prediction satisfies the probabilistic target, (iv) constructing an overall merit factor from the individual merit index factors of the properties, and (v) determining a set of optimal design variables that optimise the overall merit factor.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
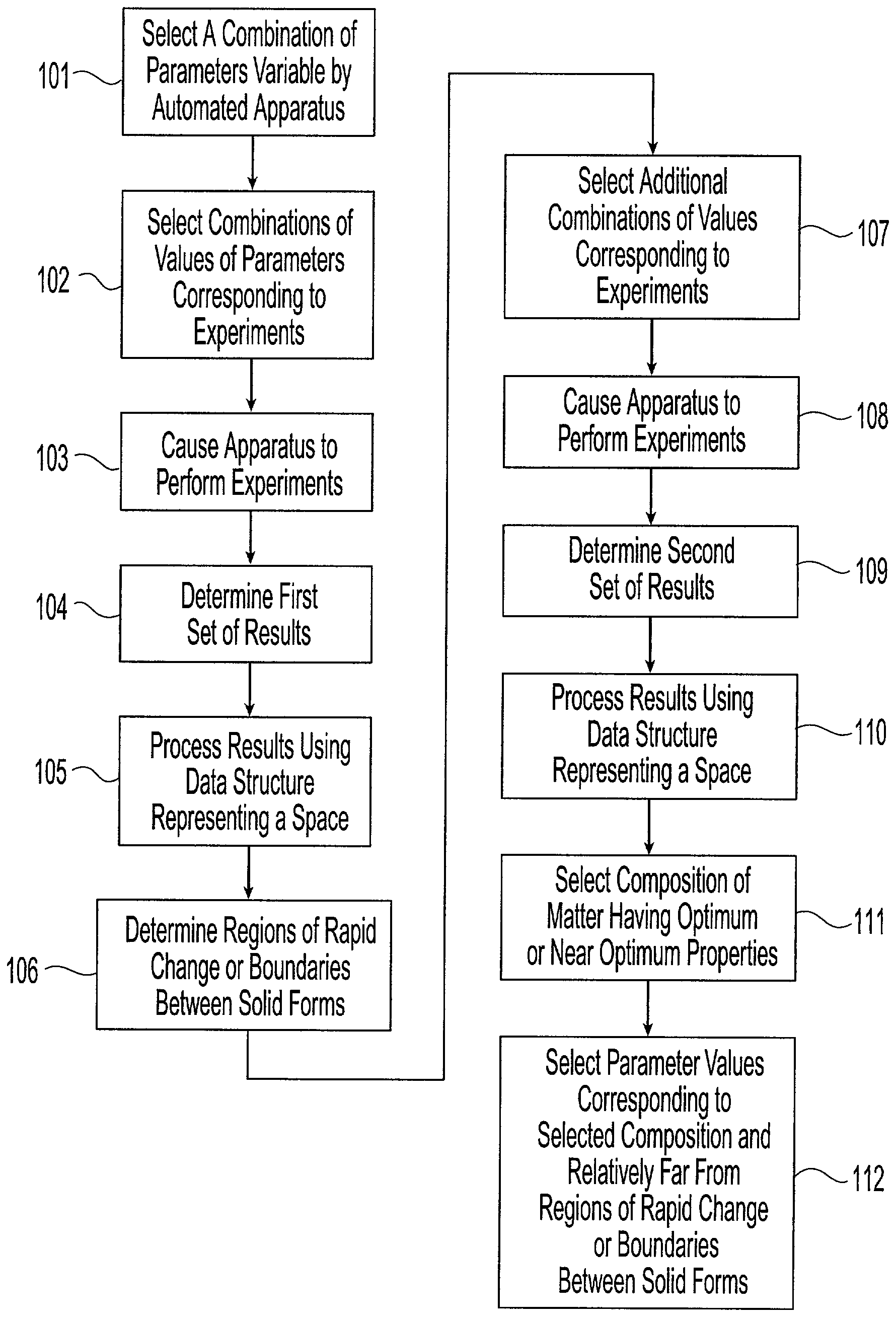
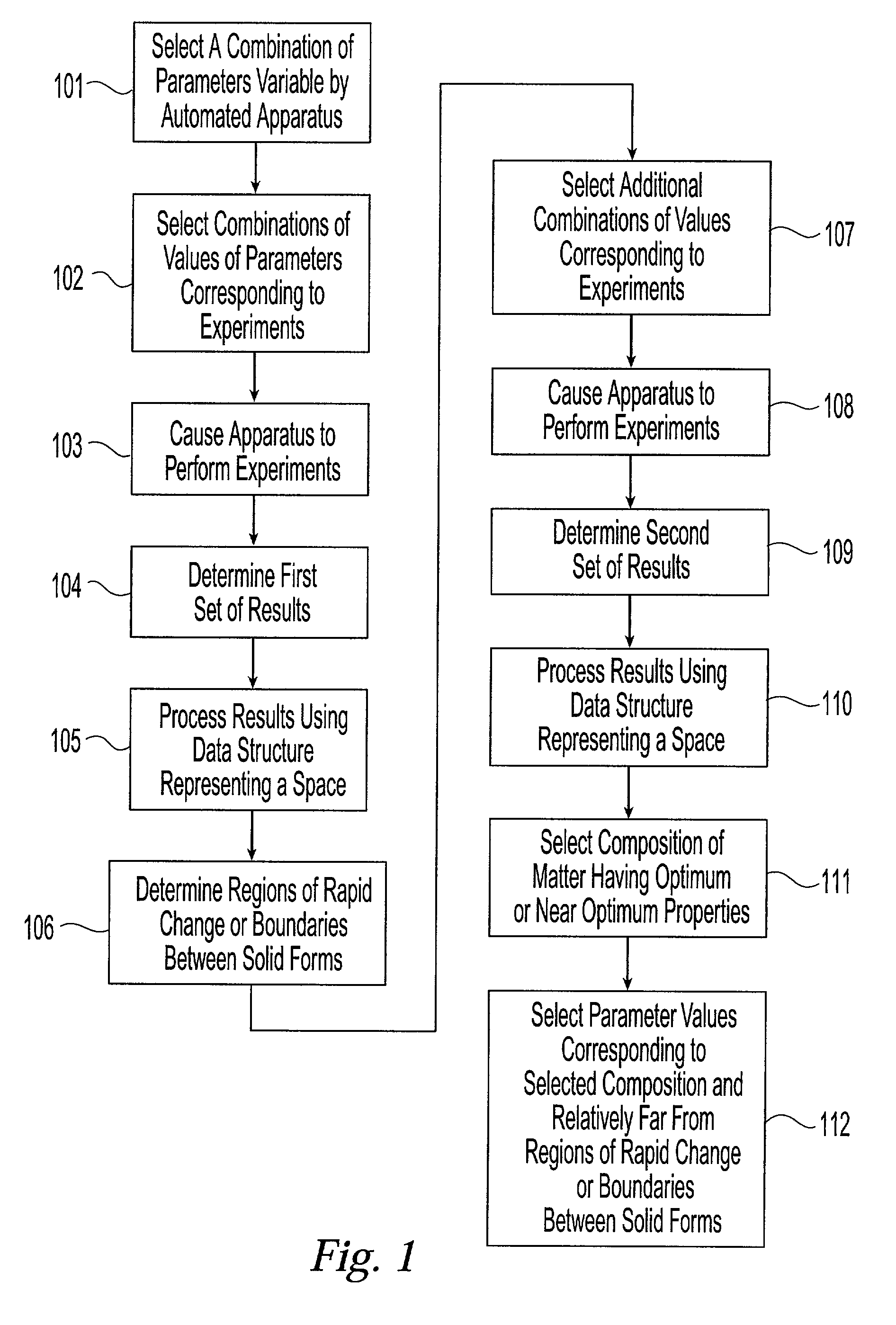
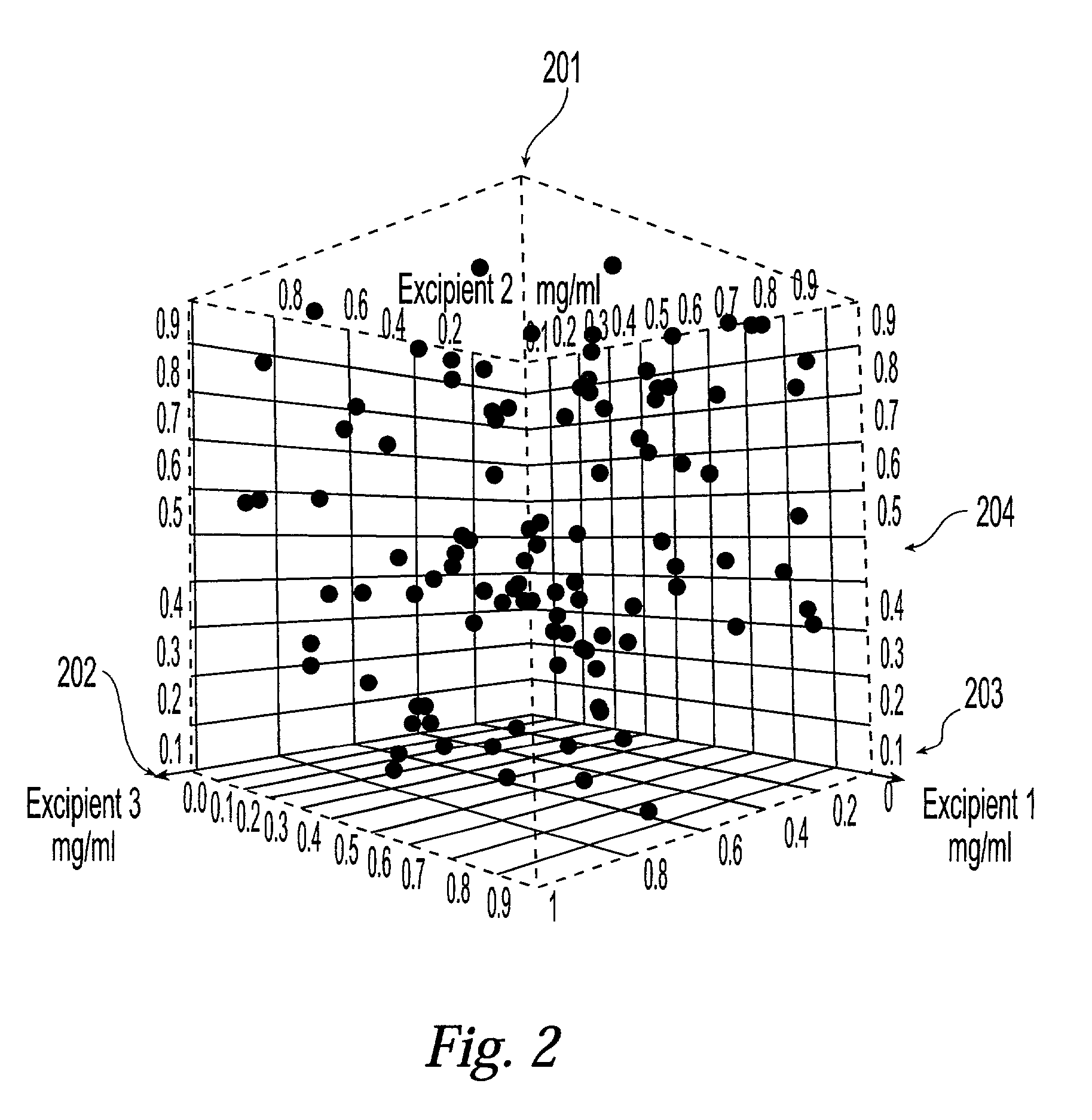
Method and system for planning, performing, and assessing high-throughput screening of multicomponent chemical compositions and solid forms of compounds
InactiveUS20050089923A9Chemical property predictionComponent separationCompound aChemical composition
A method and system for planning and assessing the results of high-throughput solid form screening and high-throughput formulation screening are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods and systems for using high-throughput solid form screening and high-throughput formulation screening to select compounds and formulations for further testing, or to prioritize testing.
Owner:TRANSFORM PHARMACEUTICALS INC
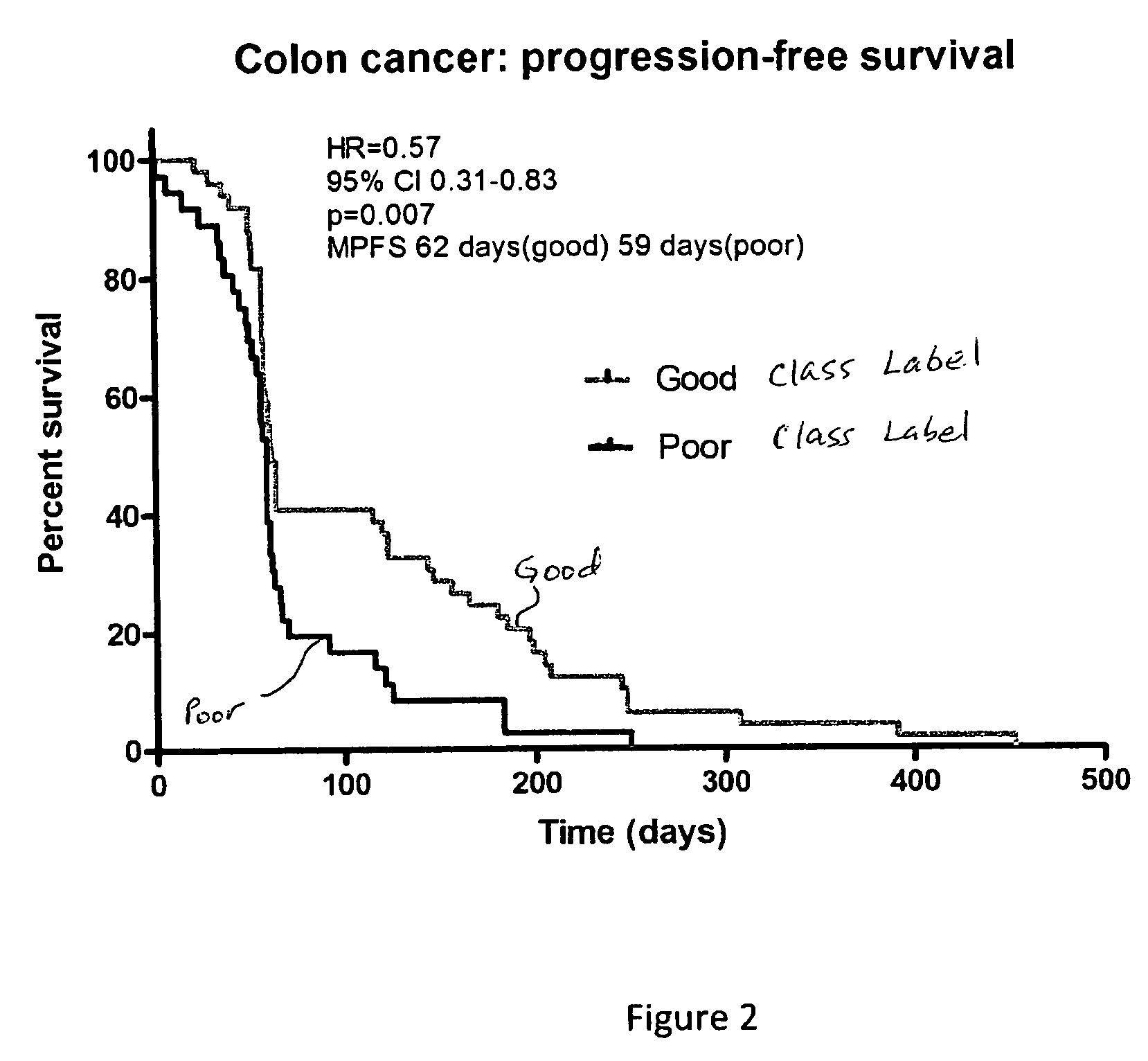
Selection of colorectal cancer patients for treatment with drugs targeting EGFR pathway
Owner:BIODESIX
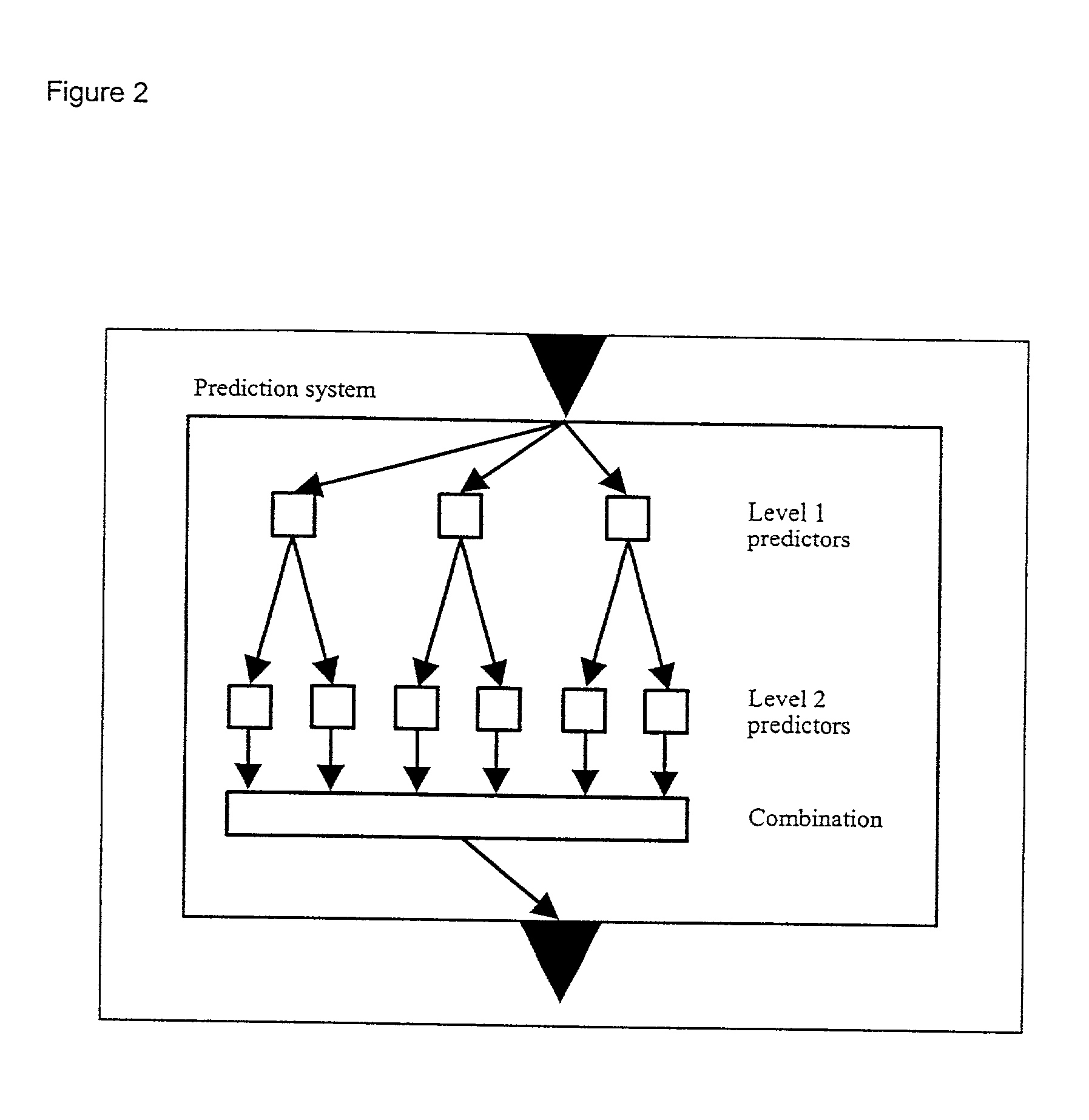
Computer predictions of molecules
InactiveUS20010049585A1Enhance homology based modellingImprove accuracyChemical property predictionOrganic chemistry methodsComputer scienceTest set
A method for predicting a set of chemical, physical or biological features related to chemical substances or related to interactions of chemical substances including using at least 16 different individual prediction means, thereby providing an individual prediction of the set of features for each of the individual prediction means and predicting the set of features on the basis of combining the individual predictions, the combining being performed in such a manner that the combined prediction is more accurate on a test set than substantially any of the predictions of the individual prediction means.
Owner:STRUCTURAL BIOINFORMATICS ADVANCED TECH
Method and device for partitioning a molecule
ActiveUS20050228592A1Efficient and fast transmissionWide range of usesMolecular designDigital data processing detailsComputer scienceDrug discovery
A method for partitioning a molecular subset is described. The partitioning method takes into account molecular structure and its manner of storage and transmission, transformations to be applied to the molecular subset and their implementation, and constraints imposed by the implementation of the partitioning method. Using this method, a molecular subset can be stored, transmitted, and processed more efficiently. The resulting efficiency makes it possible to design and run applications which require complex molecular processing, such as rational drug discovery, virtual library design, etc.
Owner:VERSEON INT CORP
Method of diagnosing, prognosing and monitoring alzheimer's disease
ActiveUS20120245854A1Enhanced sensitivity and selectivityFast and reliable diagnosisNanomedicineNanosensorsMedicineCyclodextrin
The present invention provides a system and method for diagnosing, monitoring or prognosing Alzheimer's disease using at least one sensor comprising carbon nanotubes coated with cyclodextrin or derivatives thereof and / or at least one sensor comprising metal nanoparticles coated with various organic coatings in conjunction with a learning and pattern recognition algorithm.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Method of predicting toxicity for chemical compounds
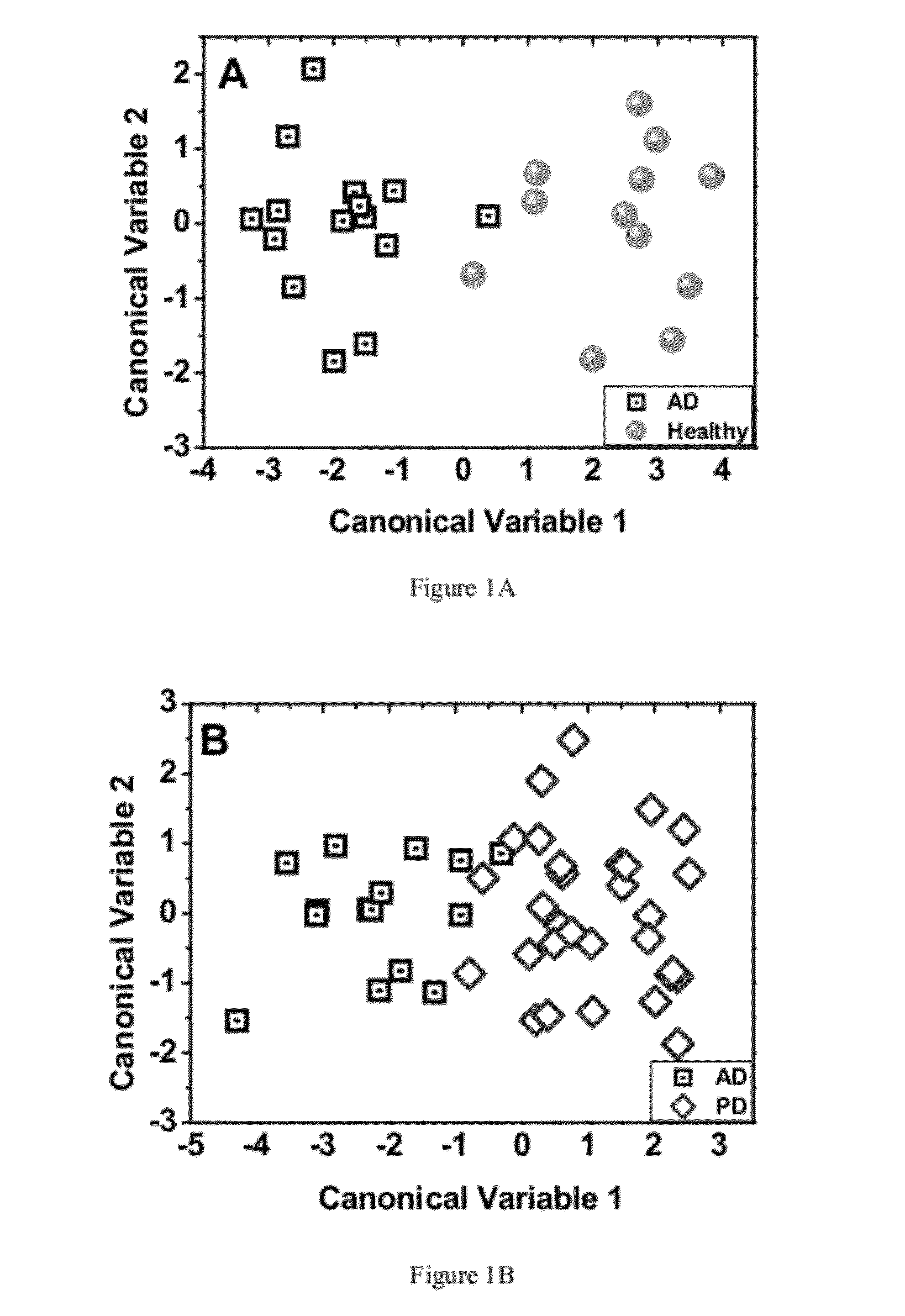
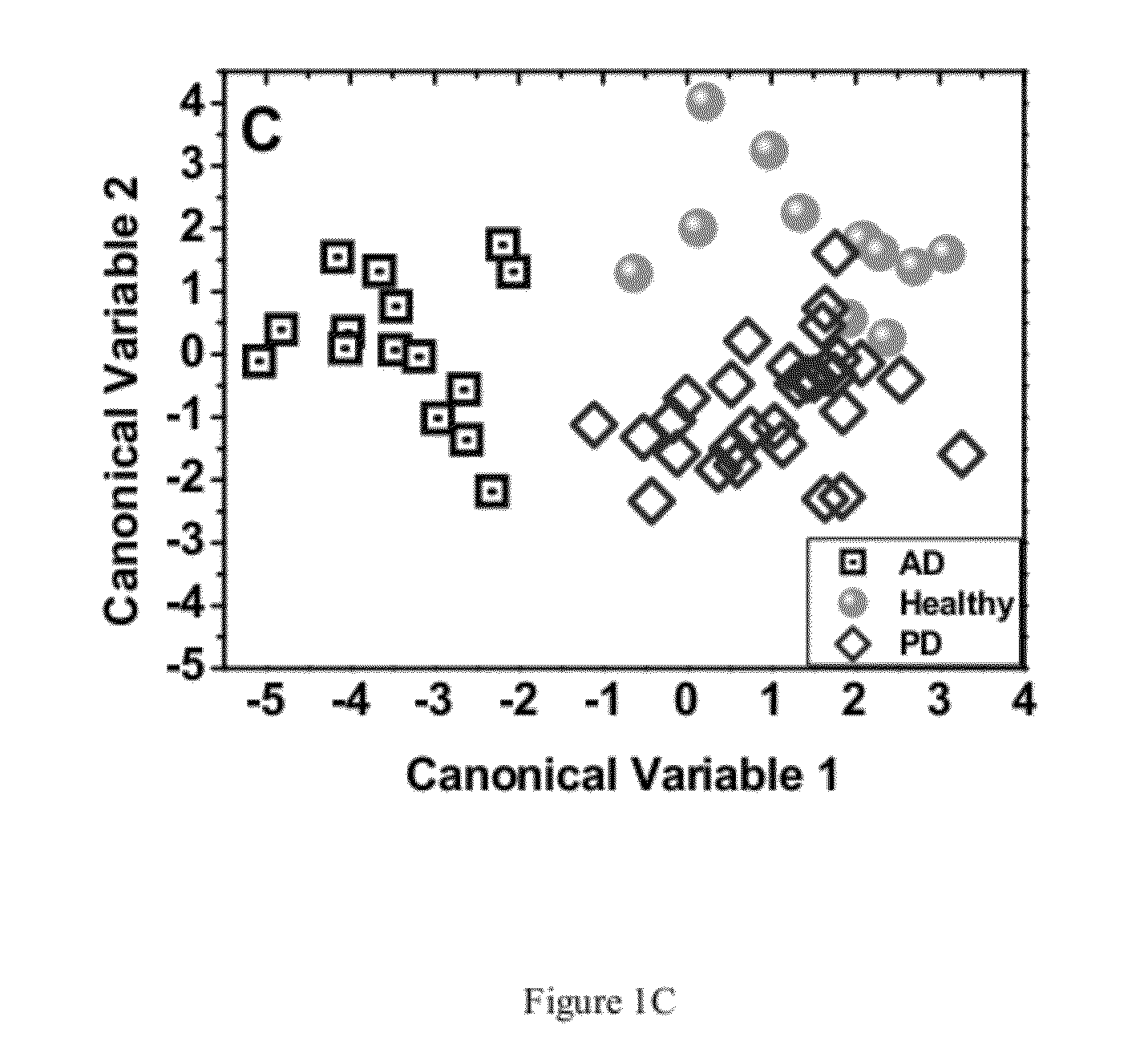
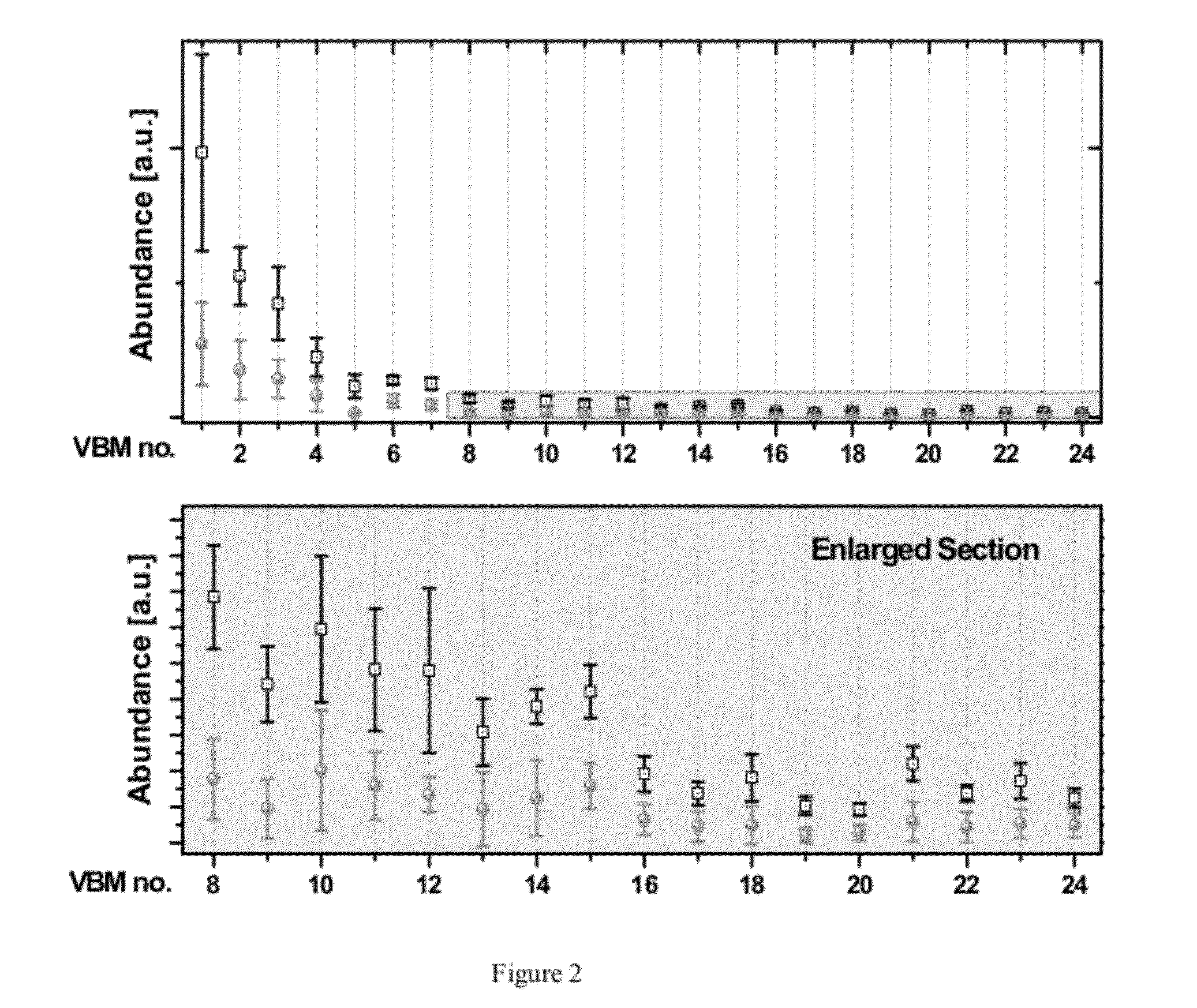
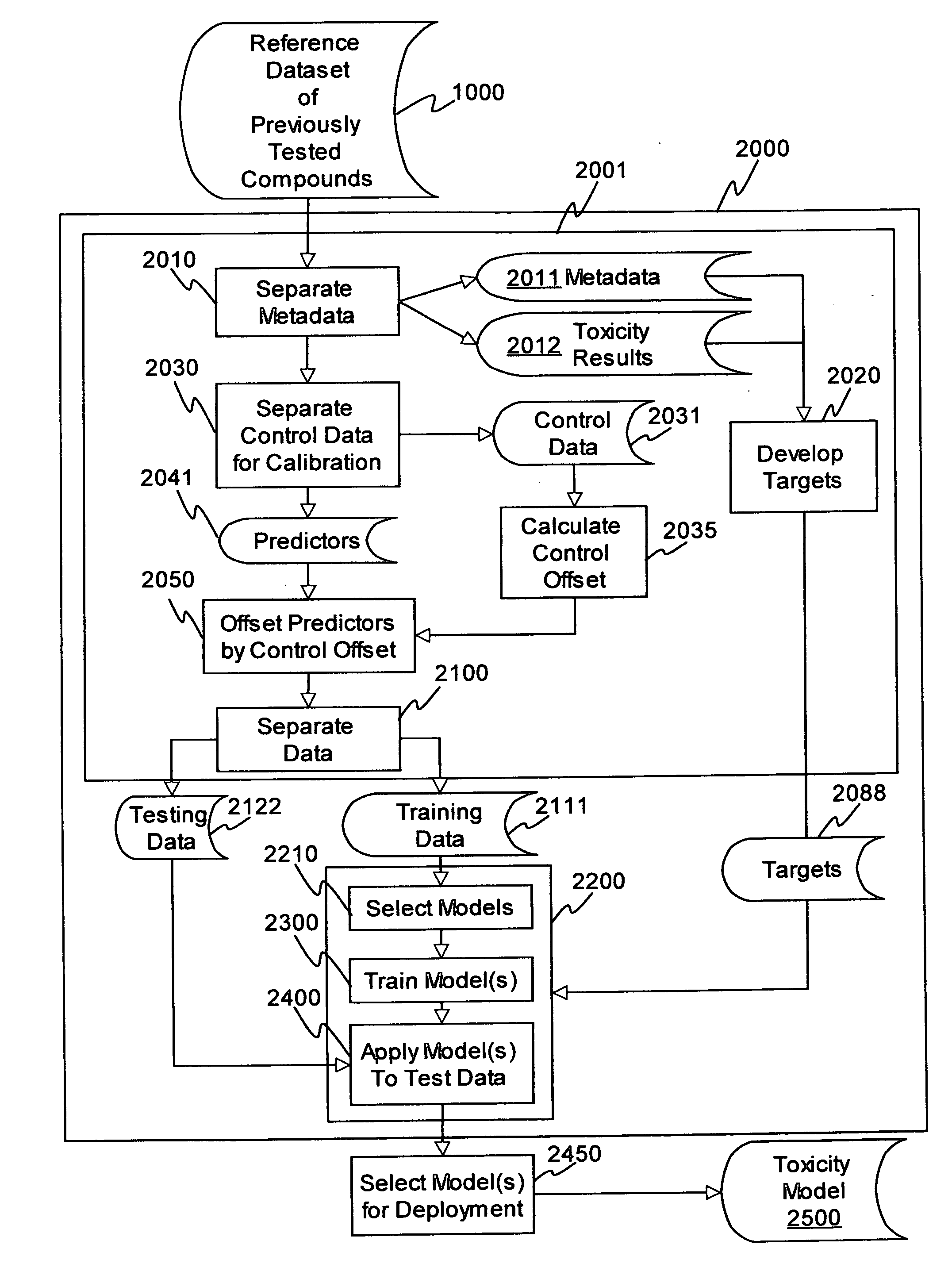
InactiveUS20140278130A1Chemical property predictionBiological testingClinical valueChemical compound
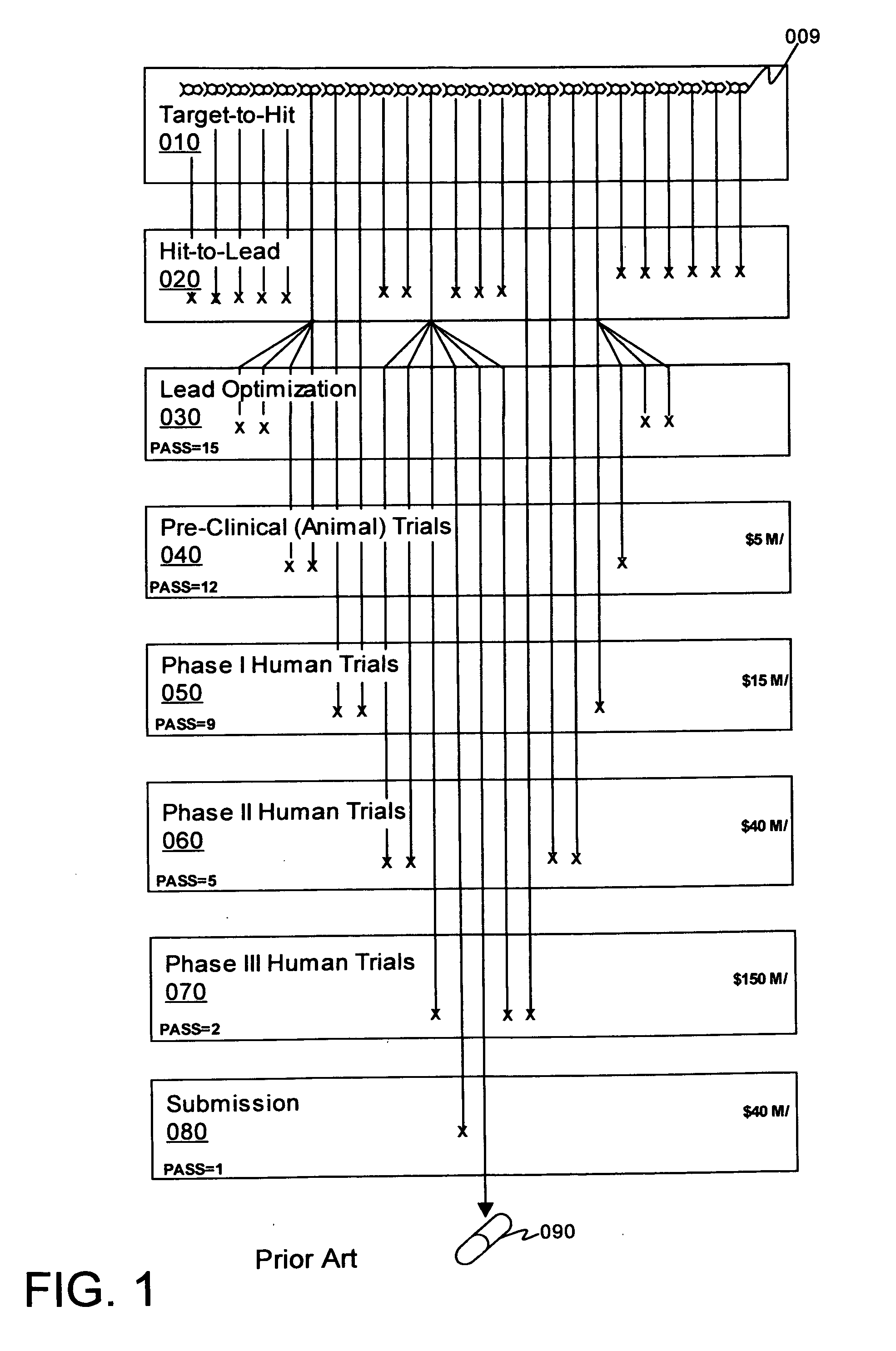
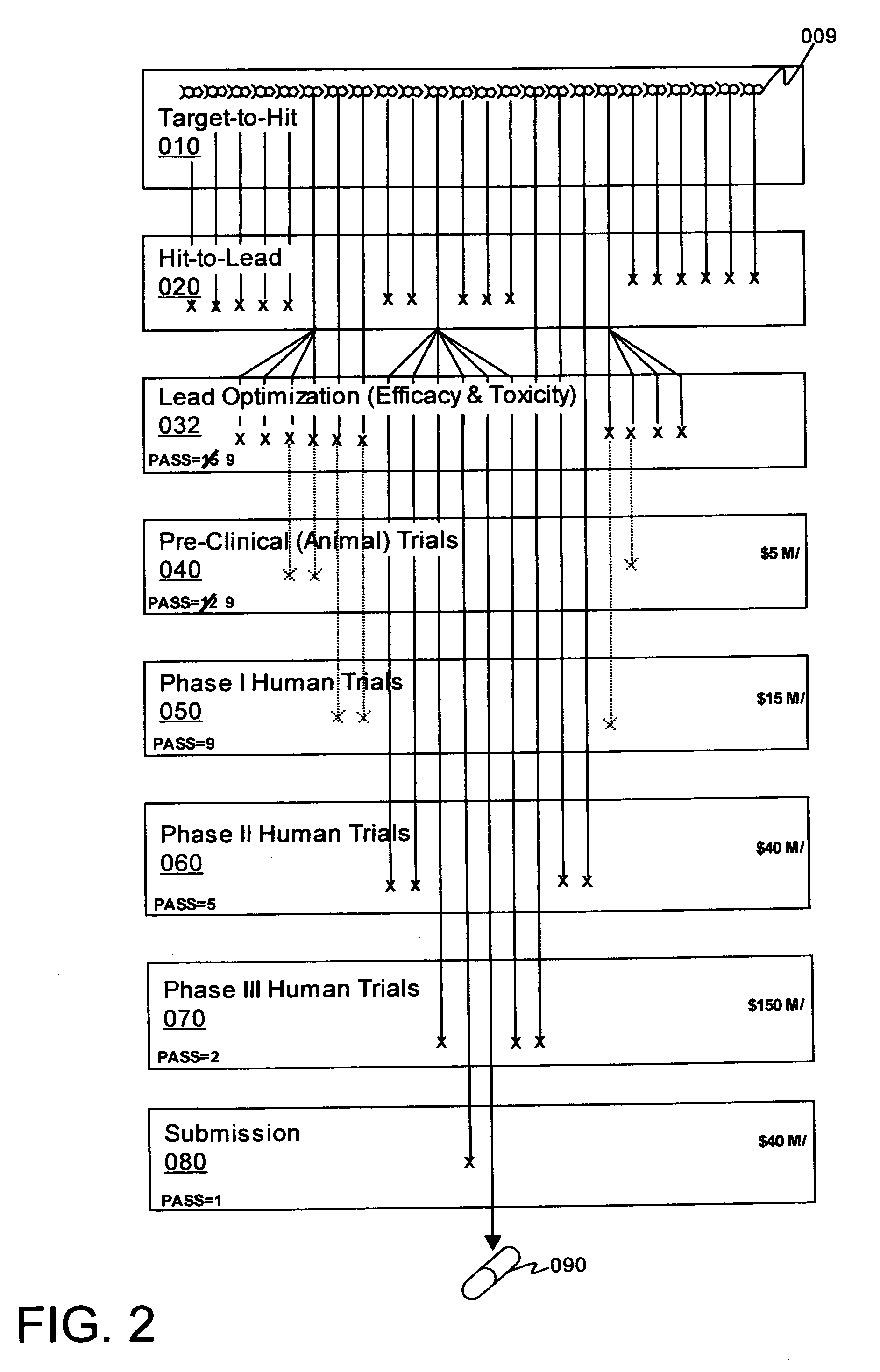
The invention disclosed herewith is a computer-implemented method for evaluating the toxicity of chemical compounds. In particular, some embodiments of the invention comprise importing microarray data representing measurements of the RNA transcription from hepatocytes, and running at least one algorithm (such as a coefficient penalized linear regression algorithm) on the imported data to assess potential adverse drug effects. After the evaluation has been carried out, the results are exported to reports or databases.In some embodiments of the invention, the algorithm has been trained on reference data using machine learning techniques.In some embodiments of the invention, the evaluation of toxicity is carried out concurrently with the evaluation of efficacy, where it can be used to assess the clinical value of the compounds evaluated.In some embodiments of the invention, the evaluation of toxicity is inserted into a pharmaceutical evaluation process prior to expensive testing of toxicity in animals.
Owner:BOWLES WILLIAM MICHAEL +1
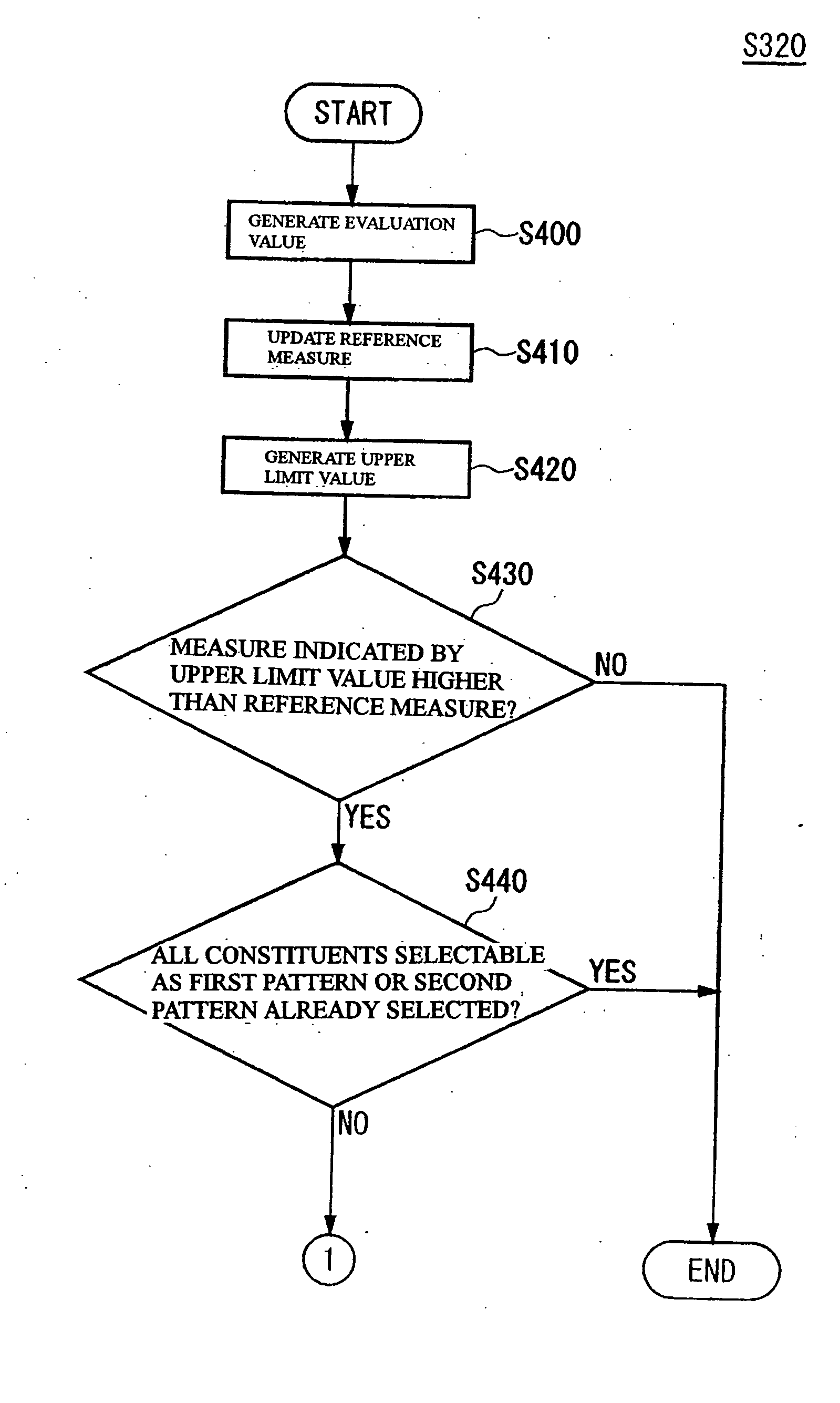
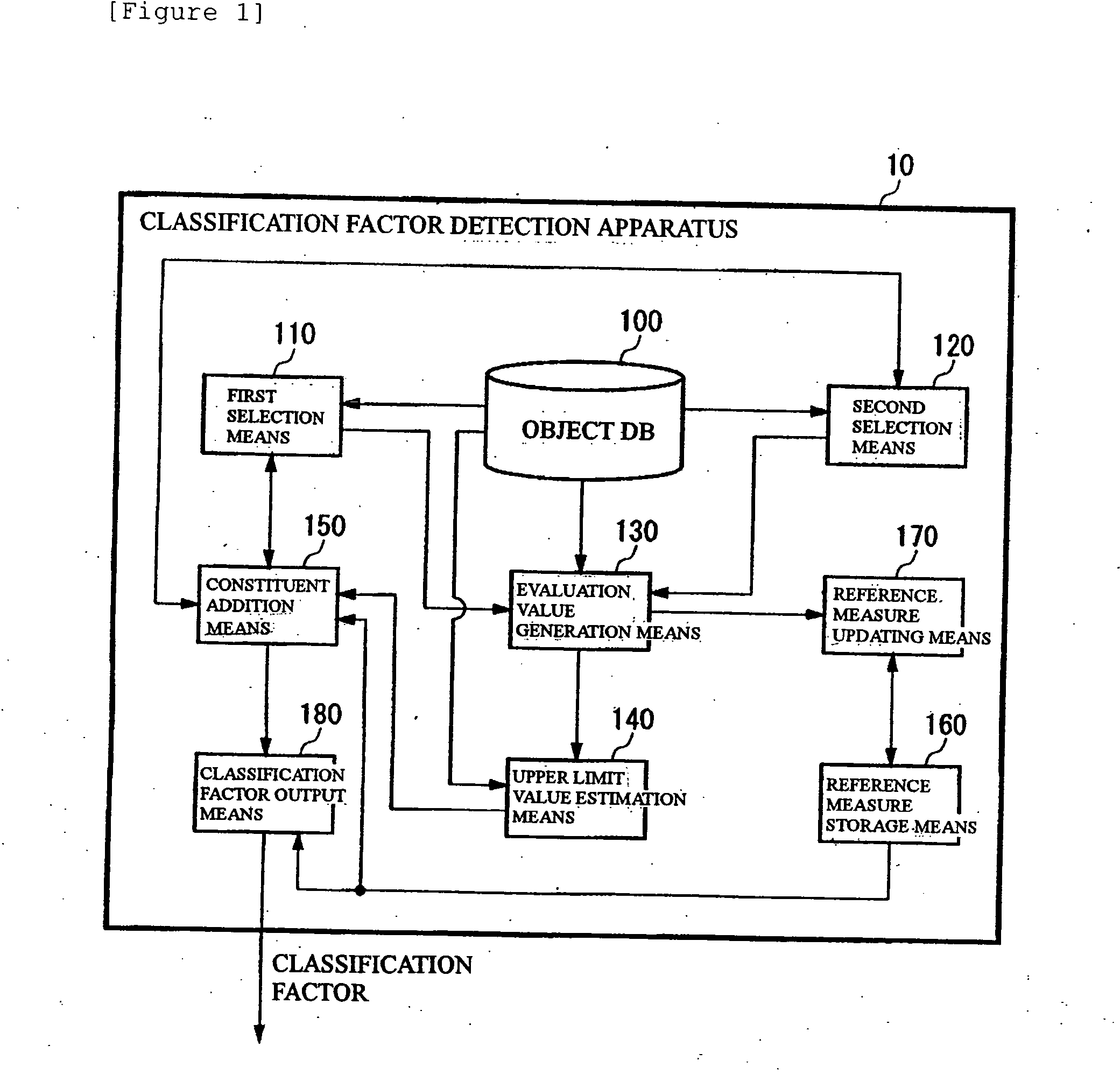
Classification factor detection
InactiveUS20050021554A1Data processing applicationsLibrary screeningArtificial intelligenceDevice Sensor
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com