Molecular dynamics-based asphaltene and silicon dioxide interface energy evaluating method
A technology of molecular dynamics and silicon dioxide, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of inaccurate adhesion between asphalt and aggregates, large influence of human factors, etc., and achieve high accuracy High reliability, reliable results, and the effect of reducing road rutting
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
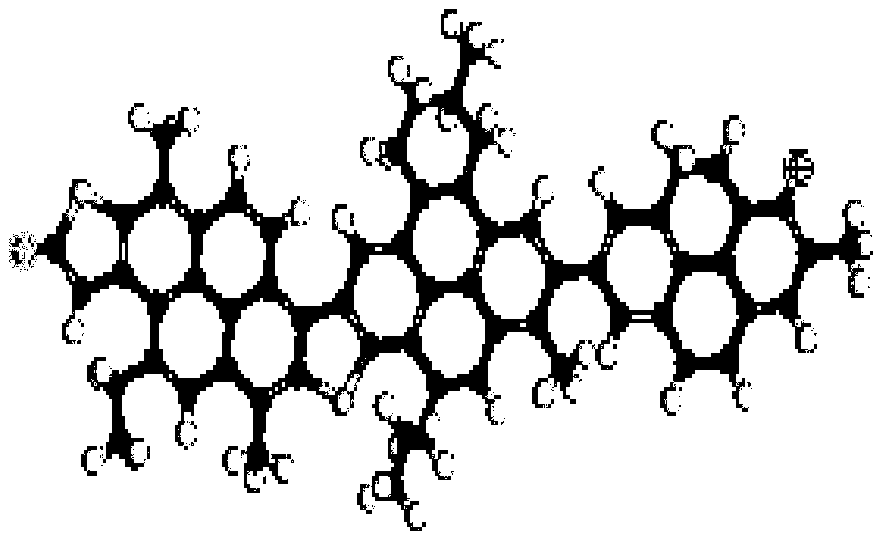
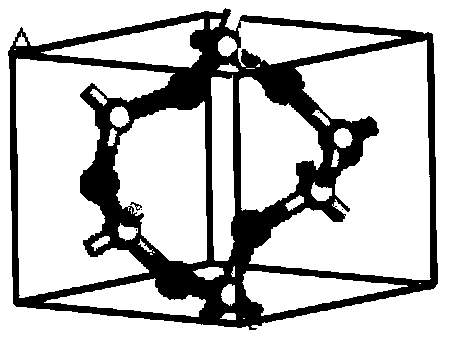
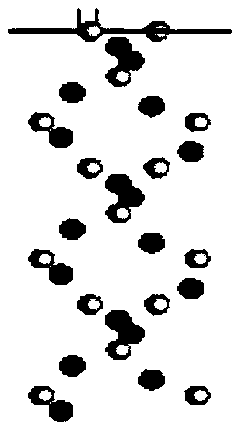
[0049] In the present embodiment, draw C by MaterialStudio software in step (2) 64 h 52 S 2 The molecular structure is used as a repeating unit, and two repeating units are selected to sort out the geometry of the structure by consulting the standard bond length and bond angle. The set temperature is 271.15K, and the target density is 0.772g / cm 3 , and change the molecular size to be the same as the size of the silica supercell recorded in step (1), use the AmorphousCell module to build an asphaltene polymer model and use the Discover module to perform energy minimization. Step (4) sets the ensemble temperature to be the same as step (2), so that the asphaltene polymer / silicon dioxide interface model built in step (3) is in a regular ensemble, and the time for running molecular dynamics is set to 90 ps and The corresponding step size is 0.3fs. After the asphaltene polymer / silica interface model reaches equilibrium, the force field model is determined to be the molecular opti...
Embodiment 3
[0053] In the present embodiment, draw C by MaterialStudio software in step (2) 64 h 52 S 2 The molecular structure is taken as the repeating unit, and 4 repeating units are selected to sort out the geometry of the structure by consulting the standard bond length and bond angle. The set temperature is 275.15K, and the target density is 0.842g / cm 3 , and change the molecular size to be the same as the size of the silica supercell recorded in step (1), use the AmorphousCell module to build an asphaltene polymer model and use the Discover module to perform energy minimization. Step (4) sets the ensemble temperature to be the same as step (2), so that the asphaltene polymer / silicon dioxide interface model constructed in step (3) is in a regular ensemble, and the time for running molecular dynamics is set to 100 ps and The corresponding step size is 0.5fs. After the asphaltene polymer / silica interface model reaches equilibrium, the force field model is determined to be the molecu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com