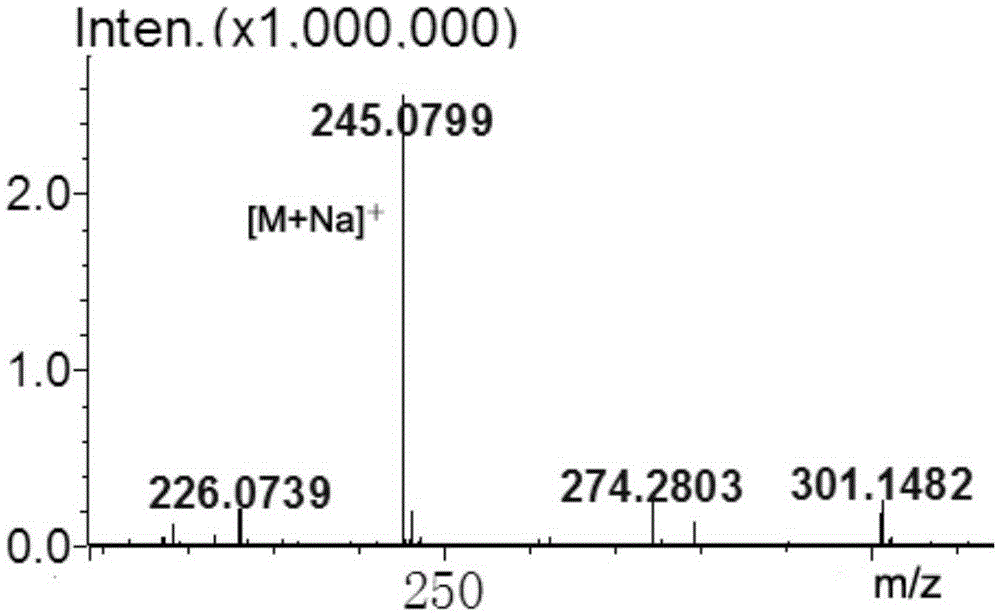
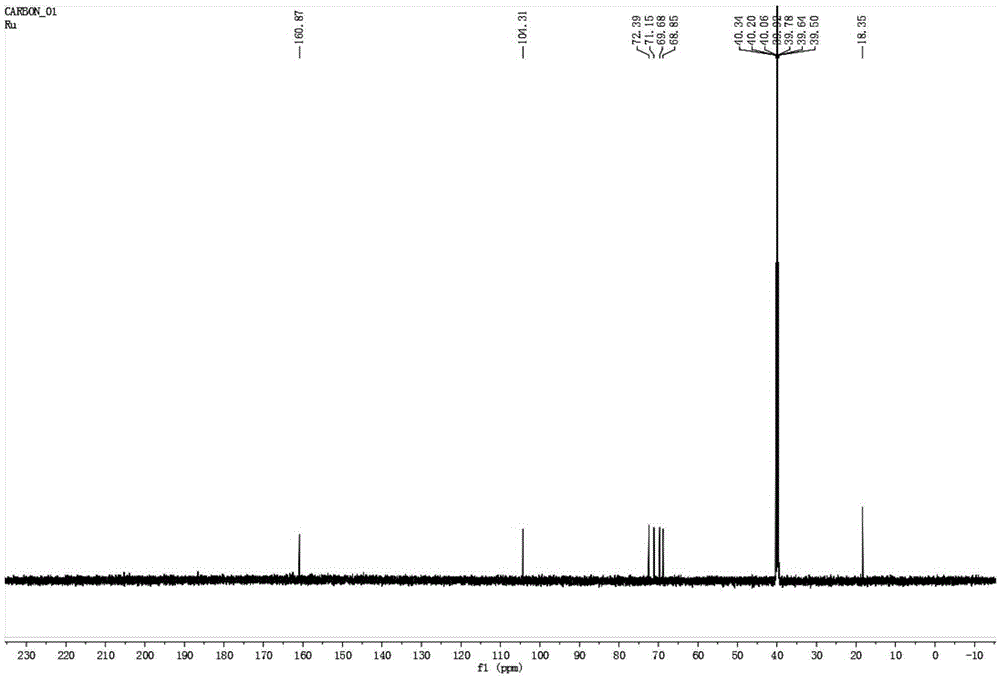
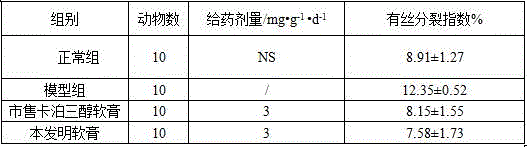
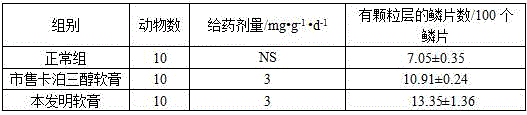
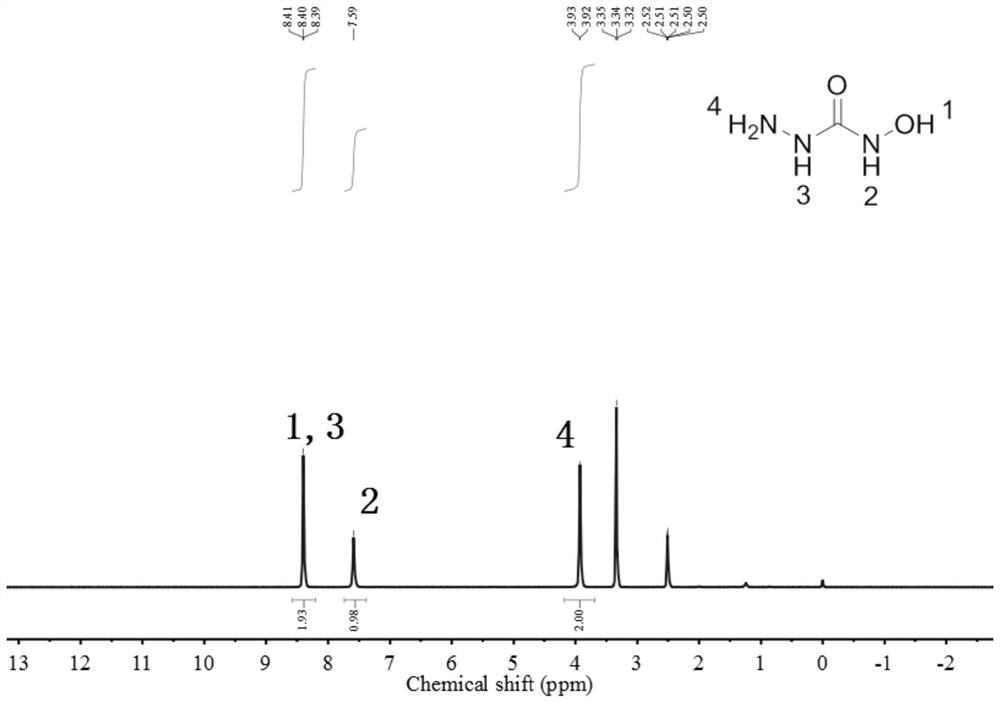
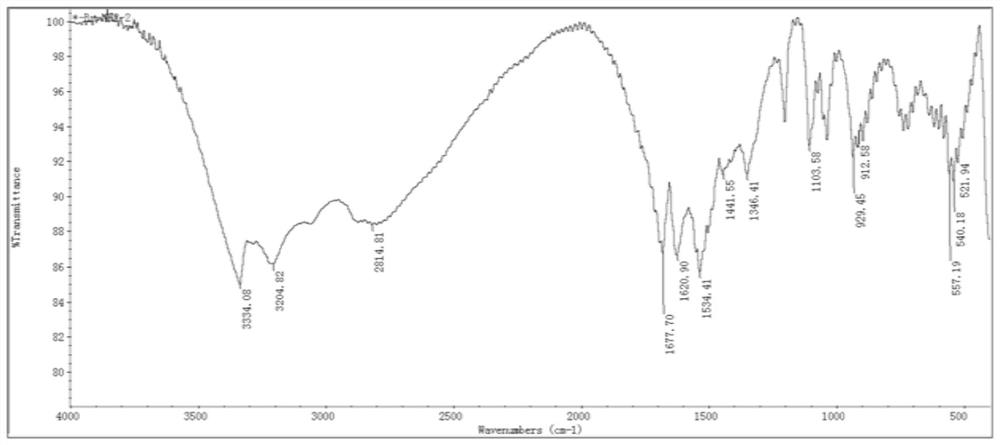
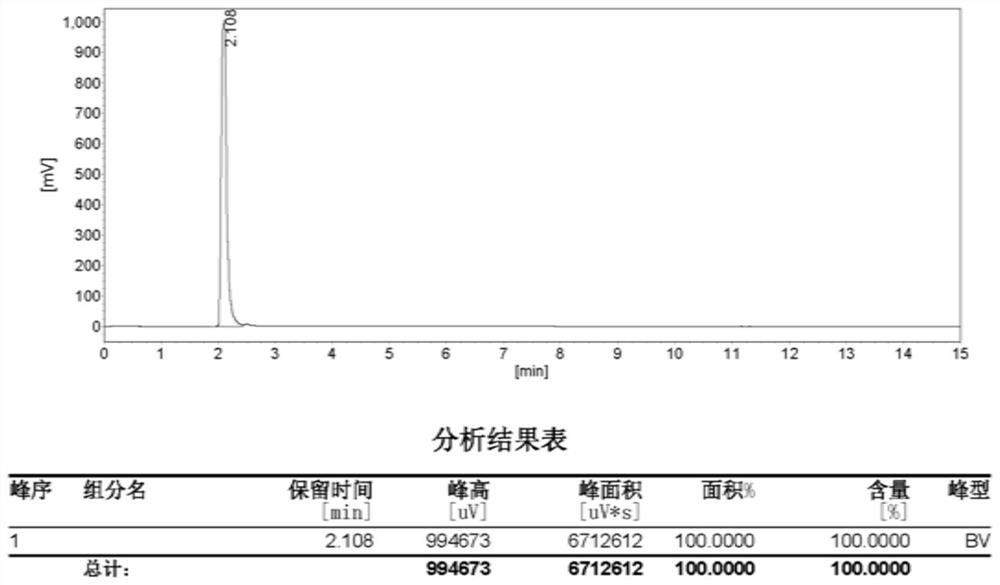
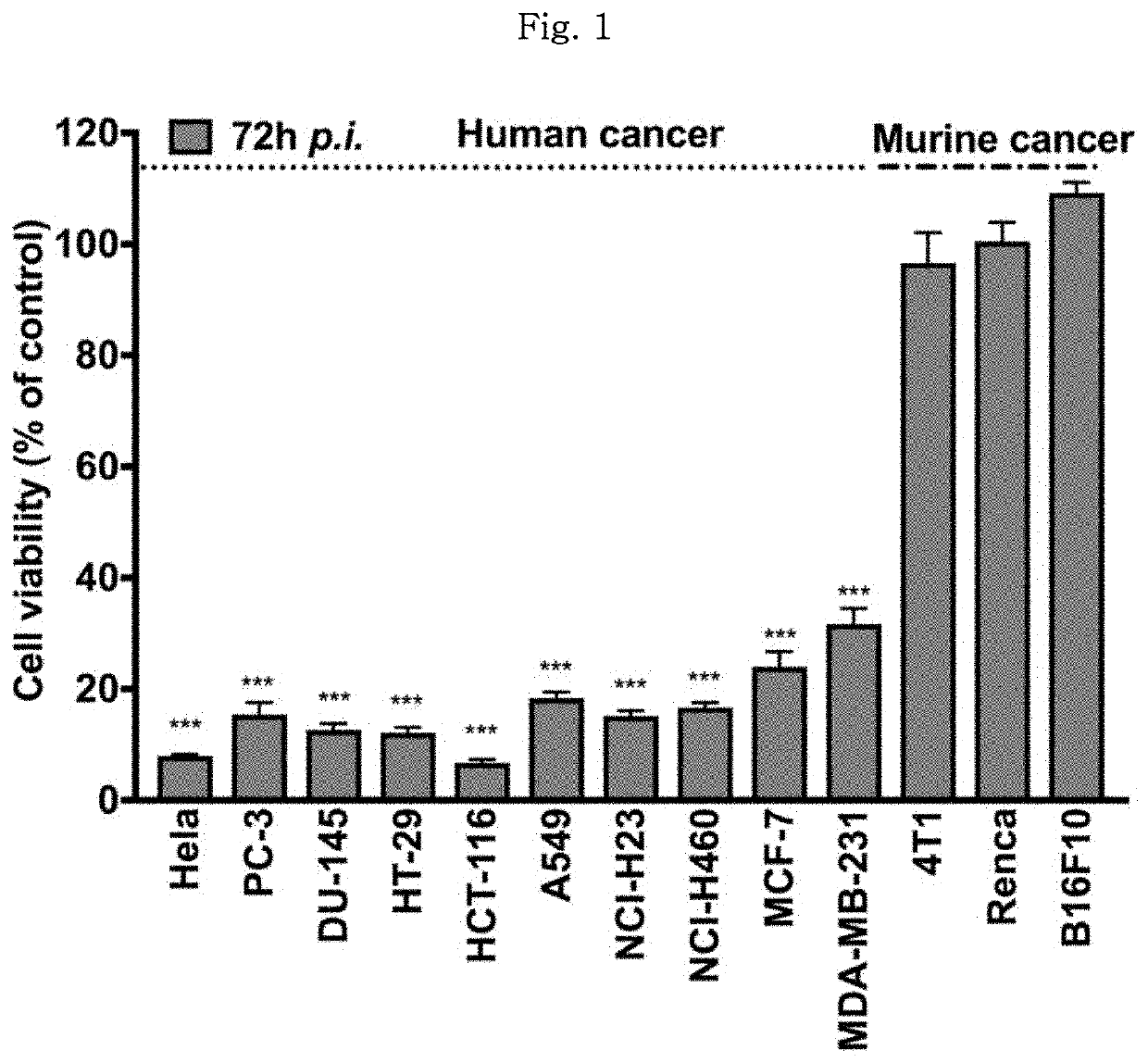
Patents
Literature
43 results about "Hydroxycarbamide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hydroxycarbamide, also known as hydroxyurea, is a medication used in sickle-cell disease, chronic myelogenous leukemia, cervical cancer, and polycythemia vera. In sickle-cell disease it increases hemoglobin and decreases the number of attacks. It is taken by mouth.
Compositions and methods for coating medical implants
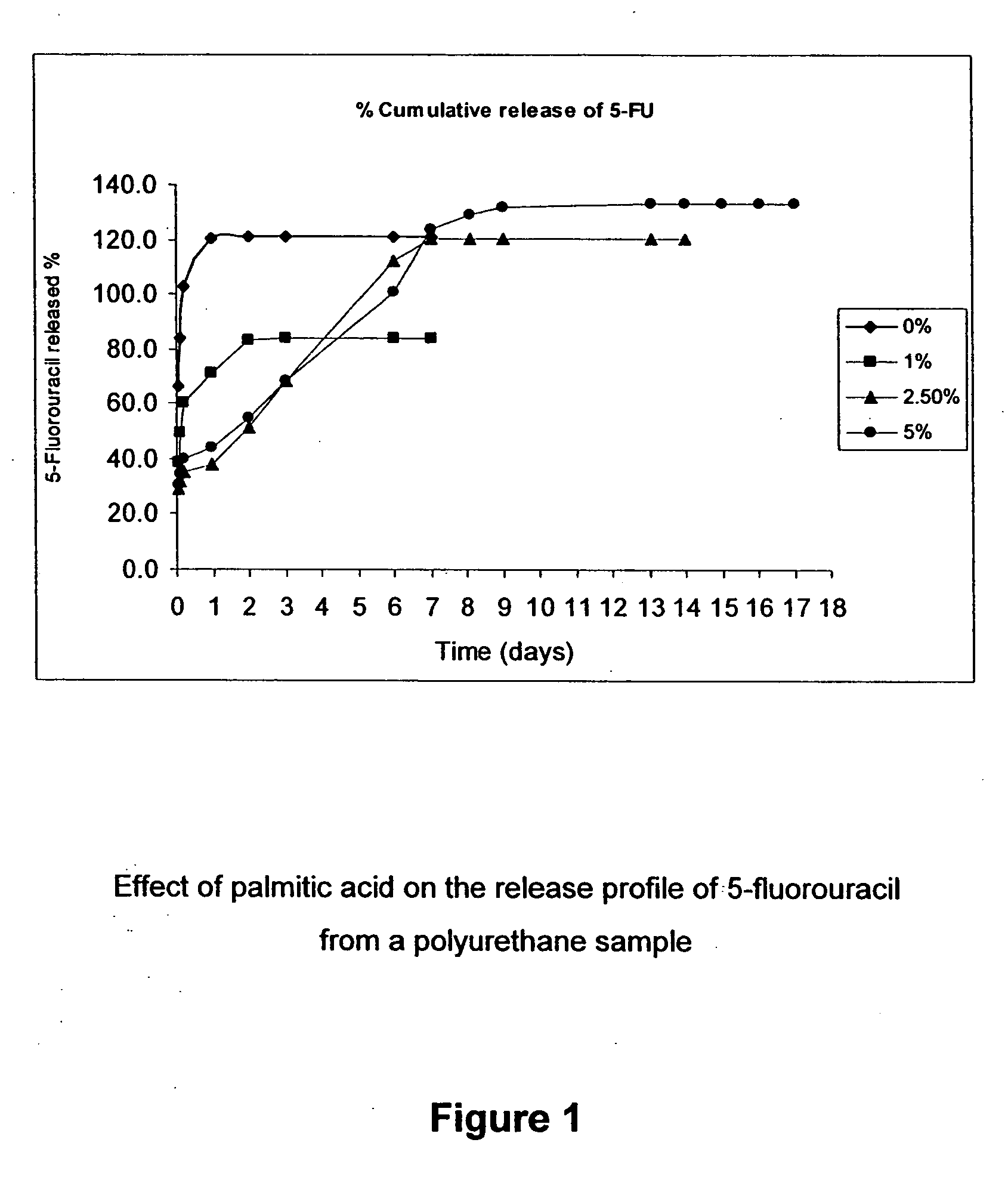
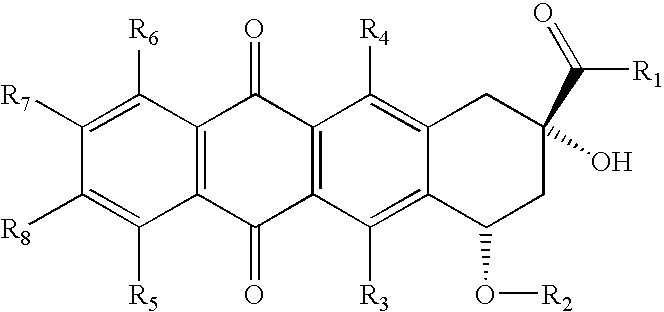
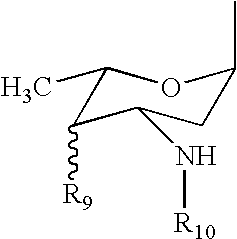
Medical implants are provided which release an anthracycline, fluoropyrimidine, folic acid antagonist, podophylotoxin, camptothecin, hydroxyurea, and / or platinum complex, thereby inhibiting or reducing the incidence of infection associated with the implant.
Owner:ANGIOTECH INT AG (CH)
Agents for intravitreal administration to treat or prevent disorders of the eye
Methods and preparations for treating disorders of the eye and / or causing posterior vitreous disconnection or disinsertion. Preparations containing (a) urea, (b) urea derivatives (e.g., hydroxyurea, thiourea), (c) a non-steroidal anti-inflamatory agent, (d) antimetabolites, (e) urea, urea derivatives, non-enzymatic proteins, nucleosides, nucleotides and their derivatives (e.g., adenine, adenosine, cytosine, cytadine, guanine, guanitadine, guanidinium, thymidine, thimitadine, uradine, uracil, cystine), uric acid, calcium acetal salicylate, ammonium sulfate or other compound capable of causing non-enzymatic dissolution of the hyaloid membrane or (e) any of the possible combinations thereof, are administered to the eye in therapeutically effective amounts.
Owner:透明视网膜技术公司
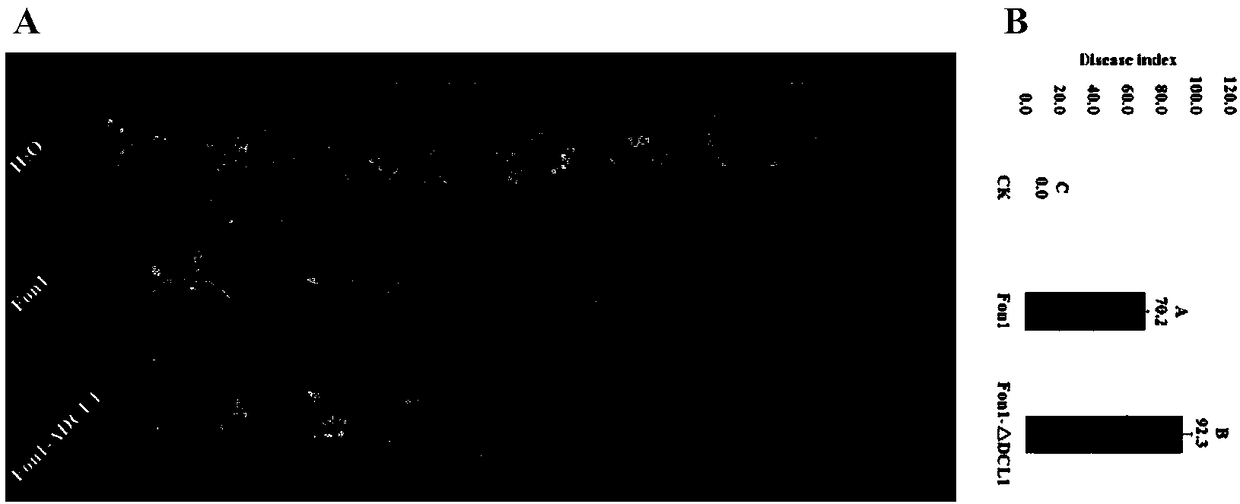
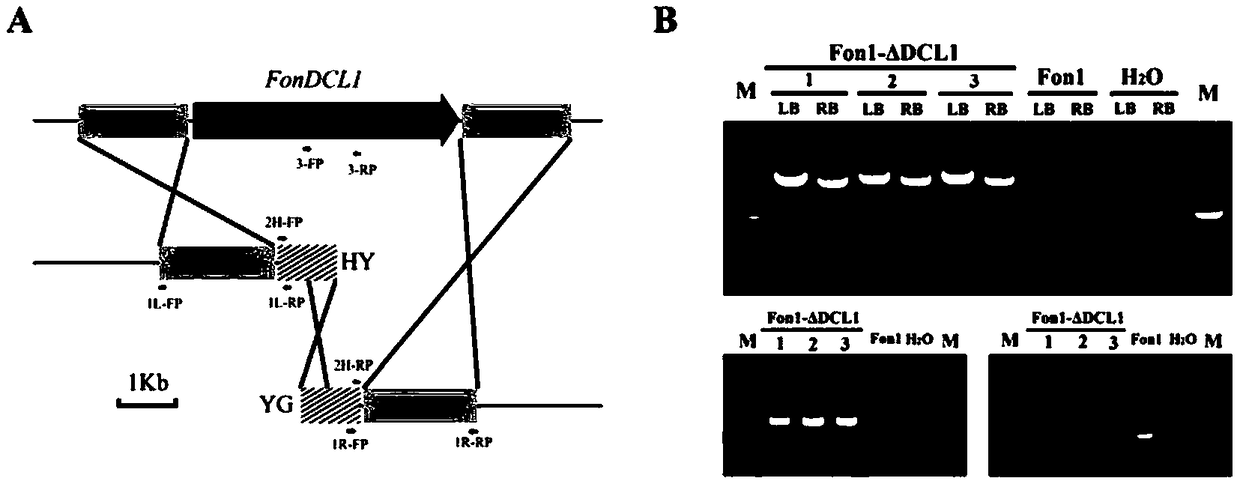
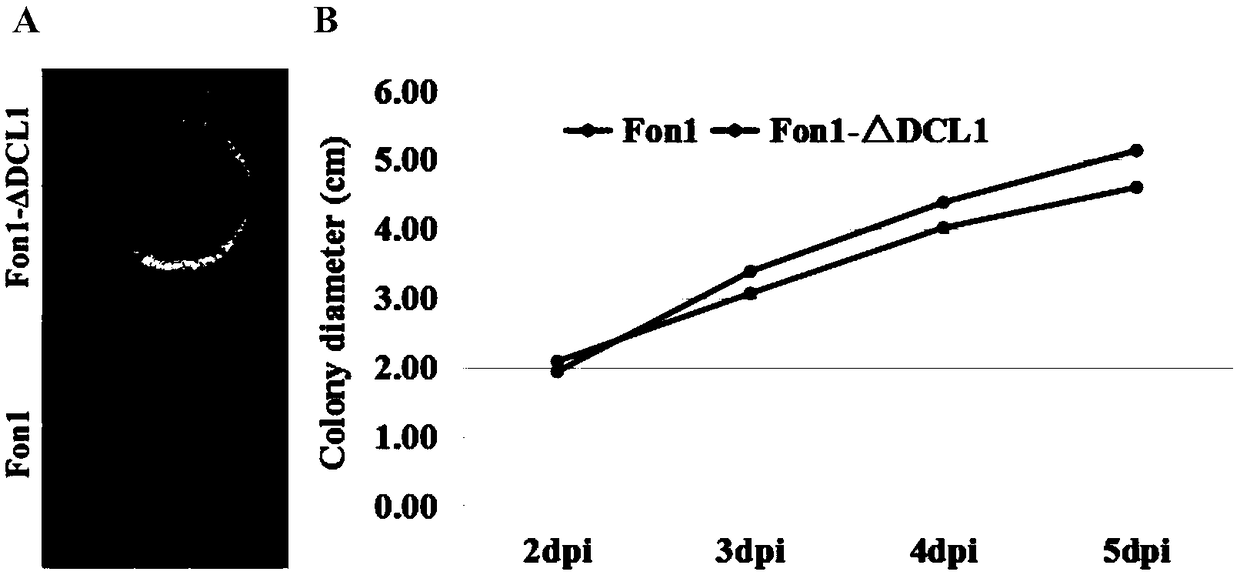
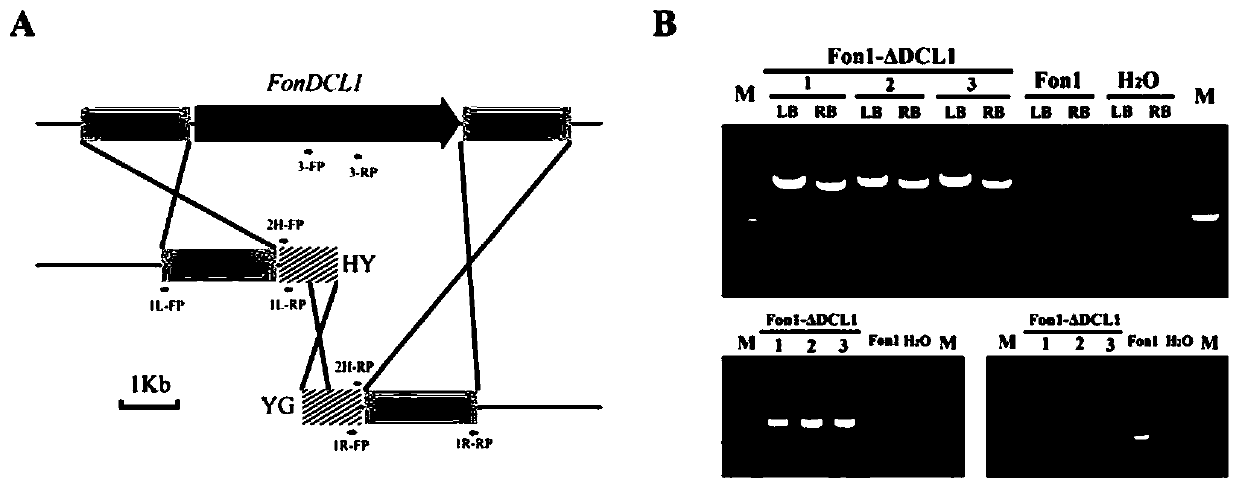
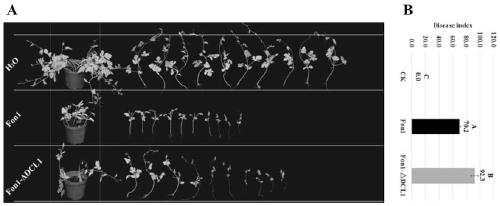
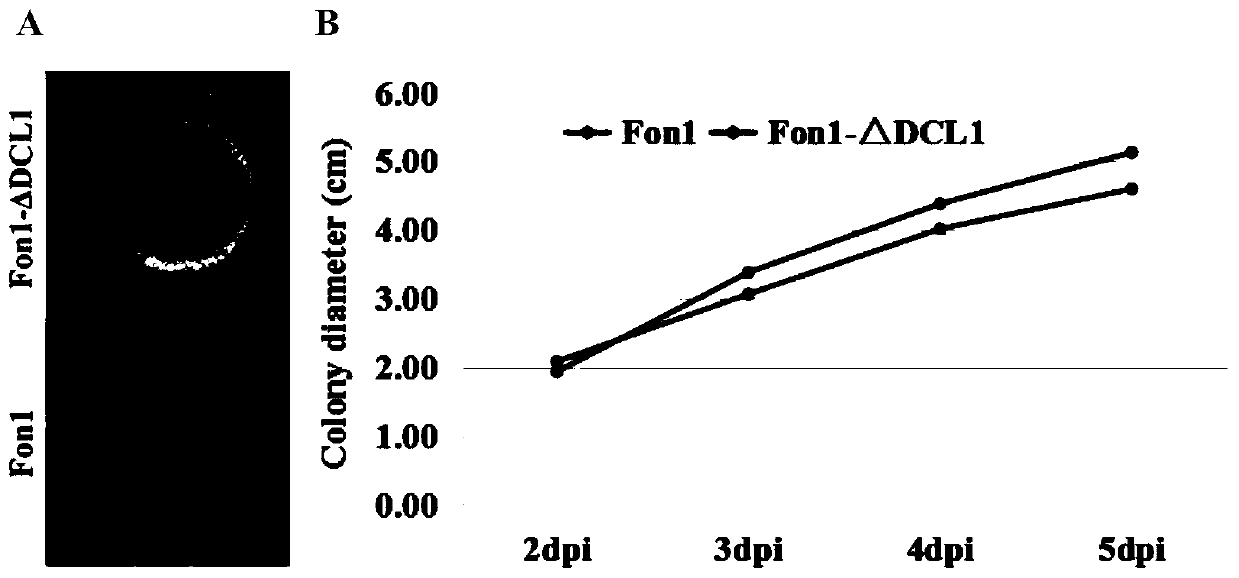
Fusarium oxysporum f.sp.niveum RNAi component FonDCL1 gene deletion mutant and construction method thereof
The invention discloses a fusarium oxysporum f.sp.niveum RNAi component FonDCL1 gene deletion mutant and a construction method thereof. According to the fusarium oxysporum f.sp.niveum RNAi component FonDCL1 gene deletion mutant and the construction method thereof, according to a reported Dicer like 1 protein sequence, homologous alignment is conducted on a Fon genomic sequence to obtain a fusariumoxysporum f.sp.niveum FonDCL1 gene, by adopting a homologous gene substitution principle, by means of a Split-marker strategy, the target gene FonDCL1 is substituted for a hygromycin B (HPH) gene DNAfragment, and by constructing a homologous gene recombinant fragment, through genetic transformation of a wild strain Fon1, the FonDCL1 gene deletion mutant is obtained. The FonDCL1 mutant has the advantages that the virulence to watermelon seedlings is enhanced, and the FonDCL1 mutant is more sensitive to abiotic stress factors of monensin sodium salt, hydroxycarbamide, a fluorescent whitening agent CFW, Congo red (CR), hydrogen peroxide and the like, so that a research foundation is provided for functional assignment of small RNA generated in processes of self growth and development and watermelon infection of the Fon1.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
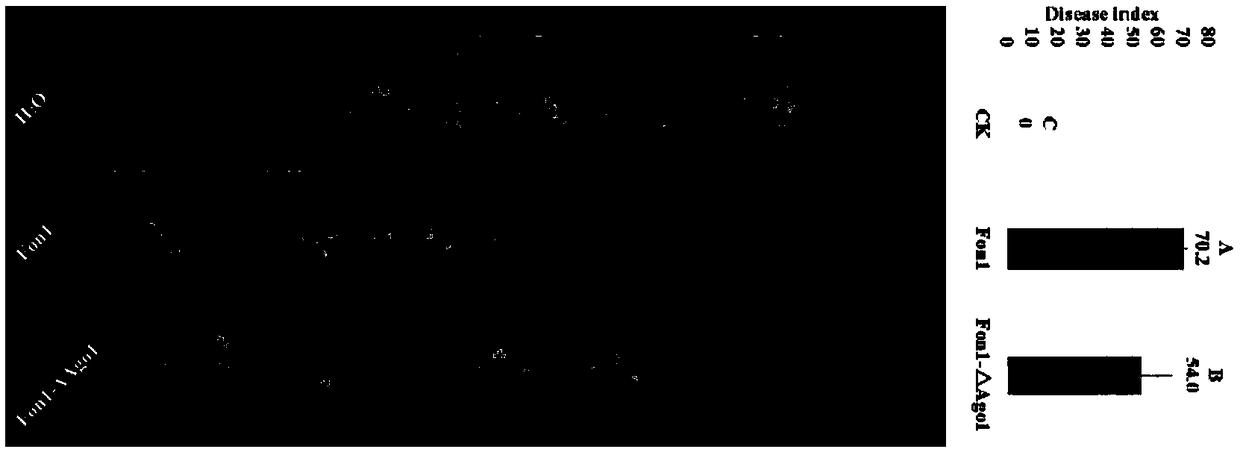
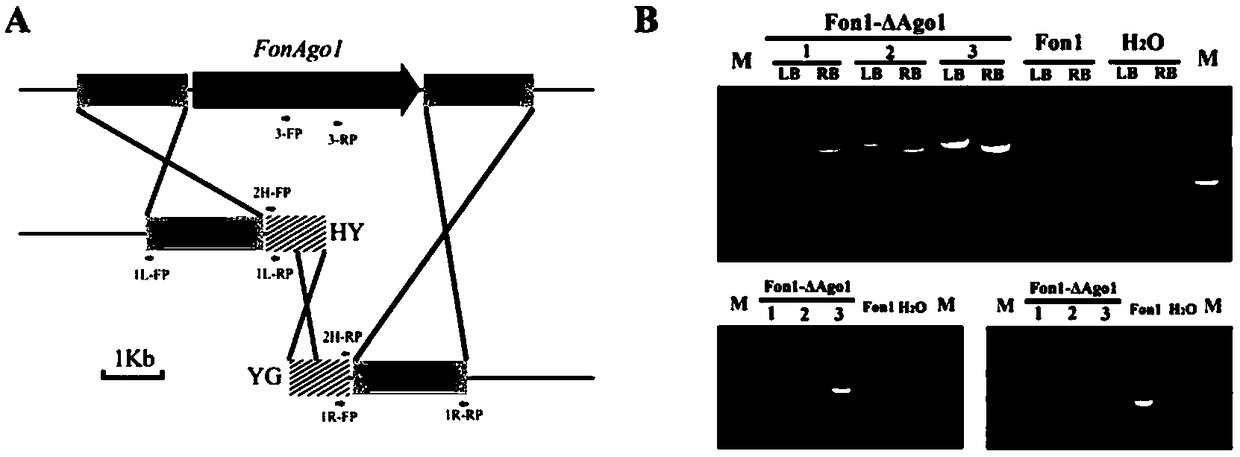
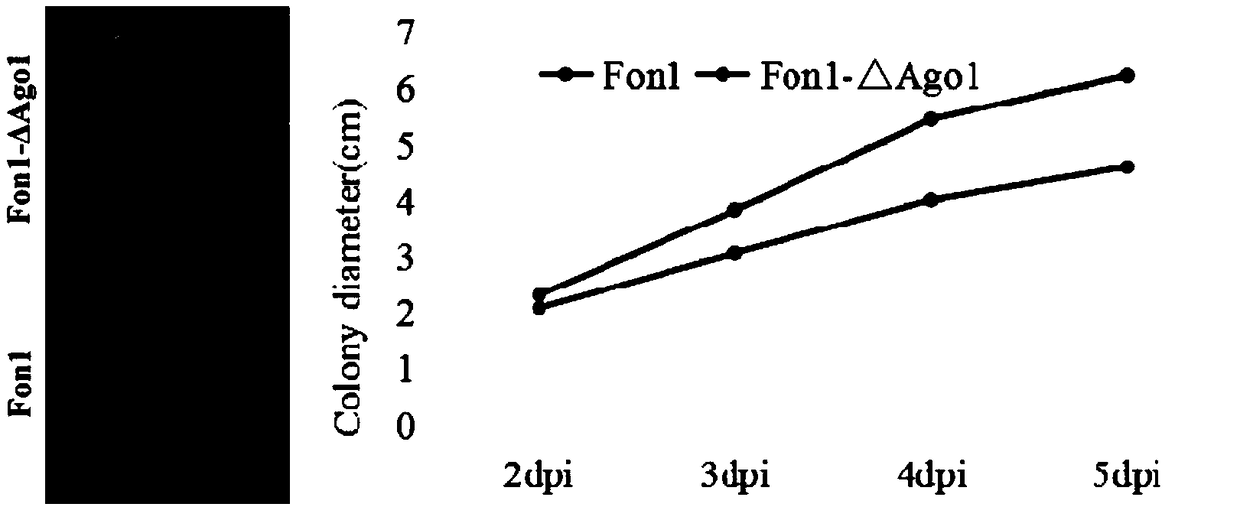
RNAi component FonAgol gene deletion mutant of fusarium oxyspirum f.sp.niveum and construction method of RNAi component FonAgol gene deletion mutant
The invention discloses an RNAi component FonAgol gene deletion mutant of fusarium oxyspirum f.sp.niveum and a construction method of the RNAi component FonAgol gene deletion mutant. The RNAi component FonAgol gene deletion mutant and the construction method thereof are characterized in that a reported Argonaute protein sequence is homologously compared with a Fon gemonic sequence to obtain a FonAgol gene of the fusarium oxyspirum f.sp.niveum; a target gene FonAgol is replaced with a DNA fragment of a hygromycin B (HPH) gene by adopting a homologous gene replacement principle and using a Split-marker strategy; a gene deletion mutant of the FonAgol is obtained by constructing a gene homologous recombination fragment and using genetic transformation of a wild strain Fon1. The FonAgol mutanthas the characteristics of higher sensitivity to pathogenicity weakening of watermelon seedlings, abiotic stress factors such as fluorescent brightener CFW, Congo red CR and hydroxycarbamide and the like, which provides a research foundation for growth and development of Fon1 and functional assignment of small RNA produced in the process of infection watermelons.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Preparation method of phenylurea herbicides
InactiveCN106831492ANot generatedImprove product qualityUrea derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationHydroxylamineBromine
The invention relates to a preparation method of phenylurea herbicides. The method comprises the following steps of (1) adding hydroxylamine salts into water; then, adding alkali so that the PH value of the reaction solution is 7 to 8; then, adding solvents; dripping 4-bromophenyl isocyanate at 5 to 20 DEG C; after the dripping is completed, performing heat insulation reaction; maintaining the weight content of the 4-bromophenyl isocyanate to be lower than 0.5 percent through HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography) central control; performing filtering to obtain solids; (2) adding the prepared solids into the water; adding alkali to regulate the pH value of the reaction solution to be 8 to 10; dripping dimethyl sulfate at 20 to 25 DEG C; meanwhile, adding alkali to control the pH value of the solution to be 8 to 10; after the dimethyl sulfate is completely dripped, performing heat insulation reaction; maintaining the weight content of 3-(4-bromophenyl)-1-hydroxycarbamide to be lower than 0.5 percent through HPLC central control to reach the reaction completion; performing filtering; obtaining a filter cake, wherein the filter cake is a finished product 3-(4-bromophenyl)-1-methoxyl-1-methylurea. The preparation method has the advantage that no 2-site bromization by-products are generated.
Owner:常州沃腾化工科技有限公司
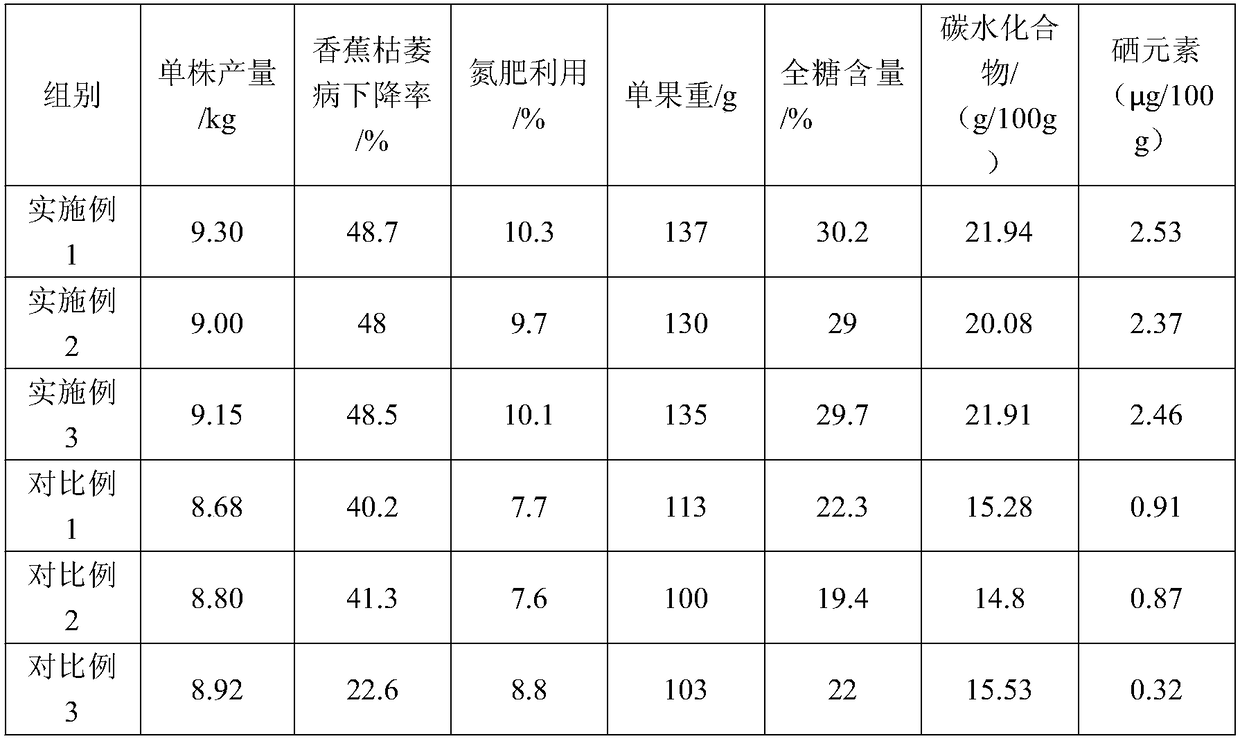
Method for planting selenium-rich Gaozhou bananas
InactiveCN108094078AIncrease acidityPromote absorptionSuperphosphatesCalcareous fertilisersGrowth plantFarmyard manure
The invention discloses a method for planting selenium-rich Gaozhou bananas. The method includes stirring thoroughly decomposed farmyard manure, lime and calcium superphosphate; covering fertilizer-free surface soil to obtain planting substrates; planting banana seedlings in the substrates. The method has the advantages that fertilizers such as alkaline compound fertilizers and banana cauloid biochar are applied to Gaozhou bananas in growth periods, accordingly, growth of plants can be promoted, nutrient substances required by growth of the plants can be provided, and the high-yield healthfulselenium-rich Gaozhou bananas can be obtained. The alkaline compound fertilizers comprise hydroxycarbamide, calcium superphosphate and potassium chloride.
Owner:广东日可威富硒食品有限公司
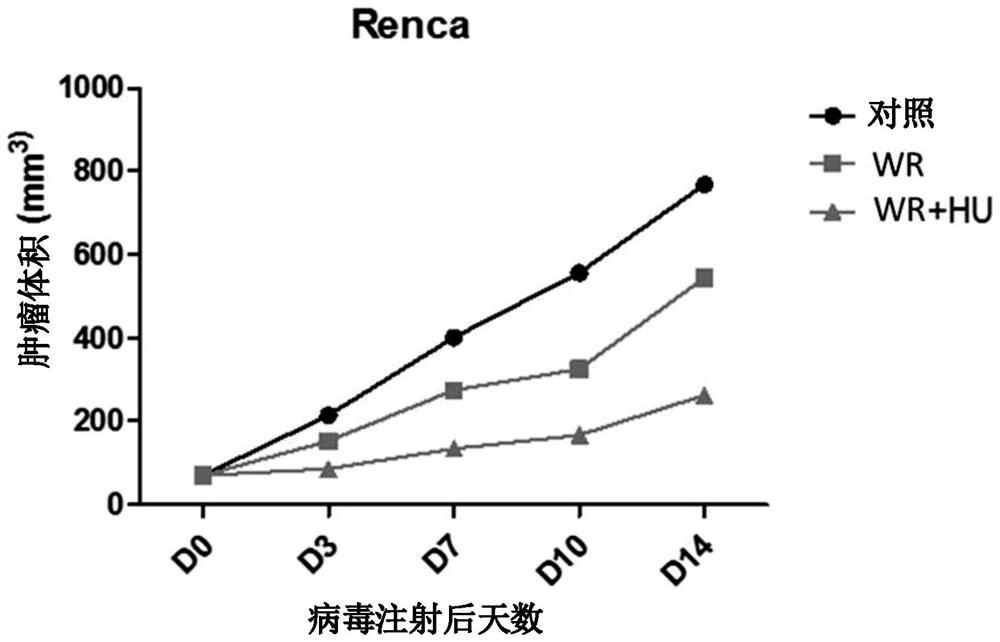
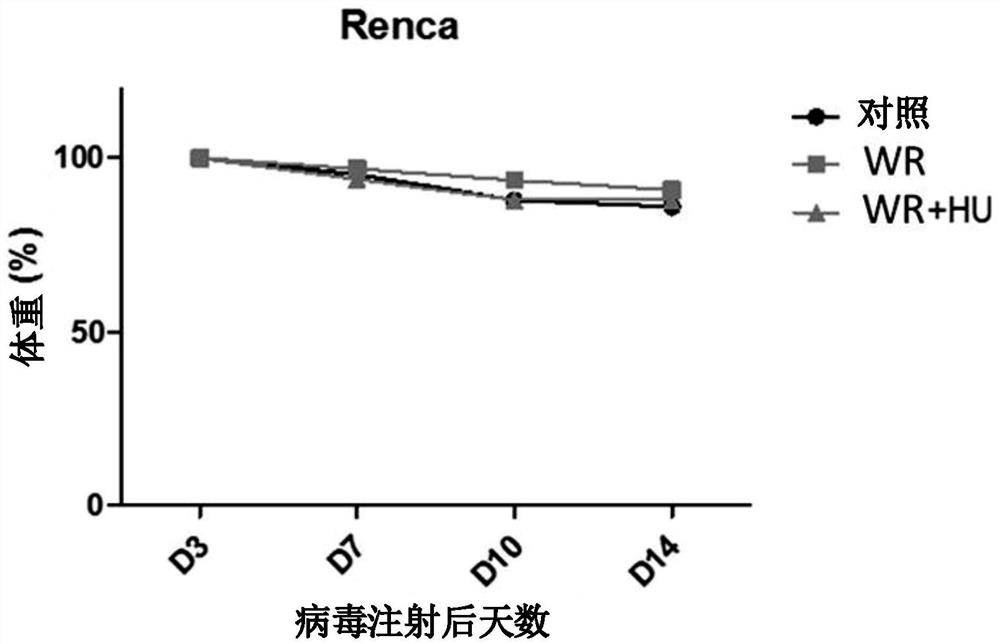
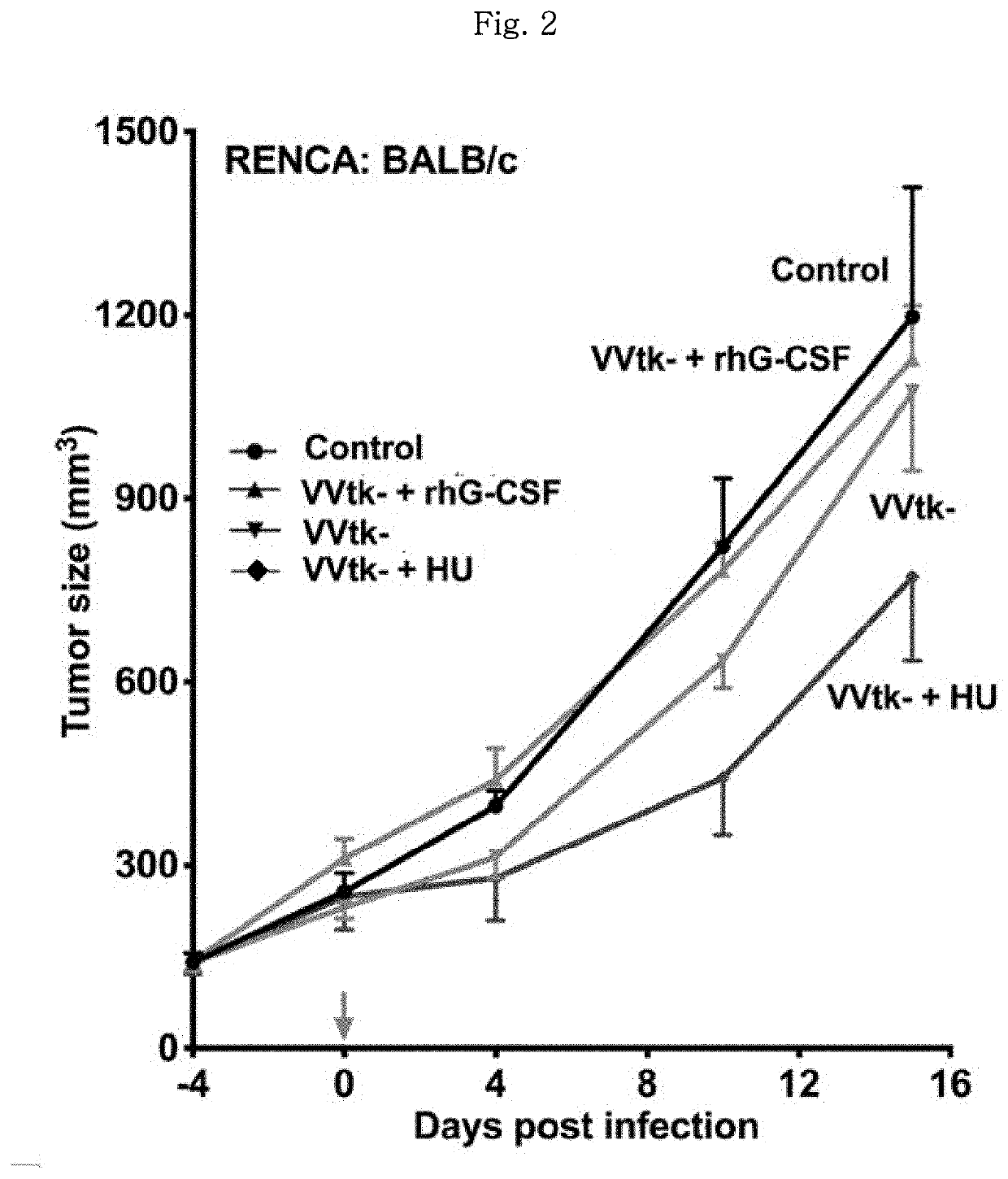
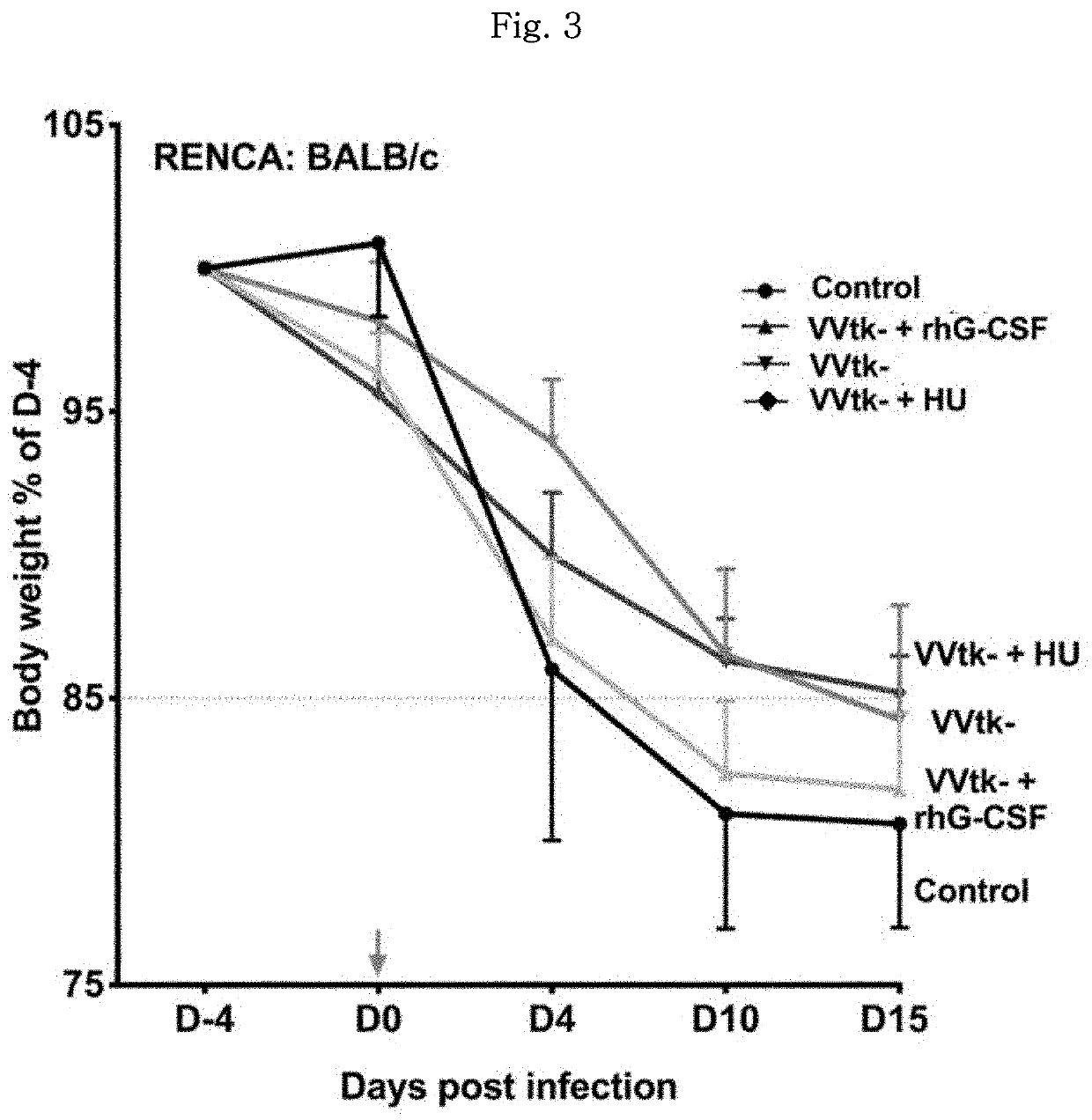
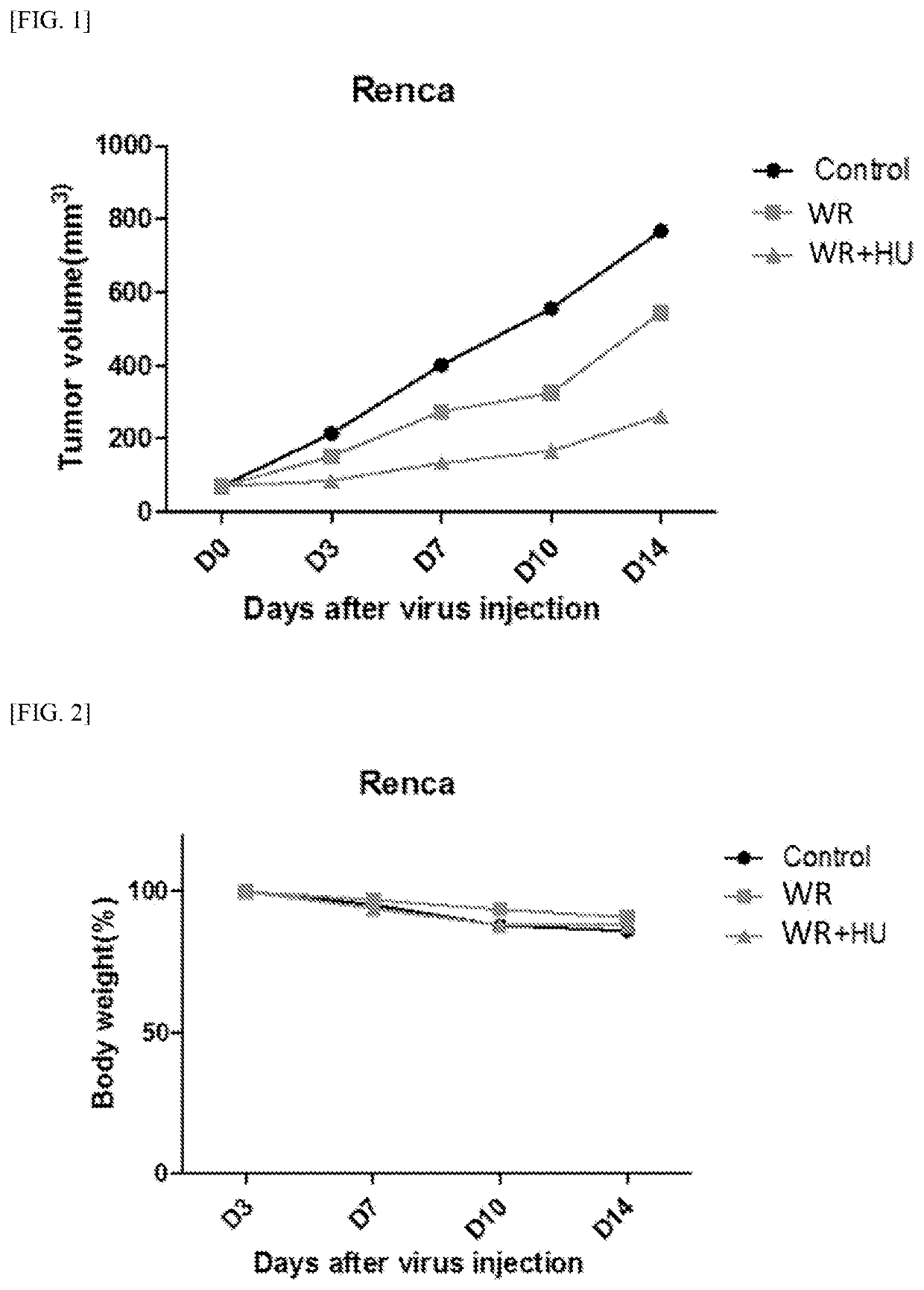
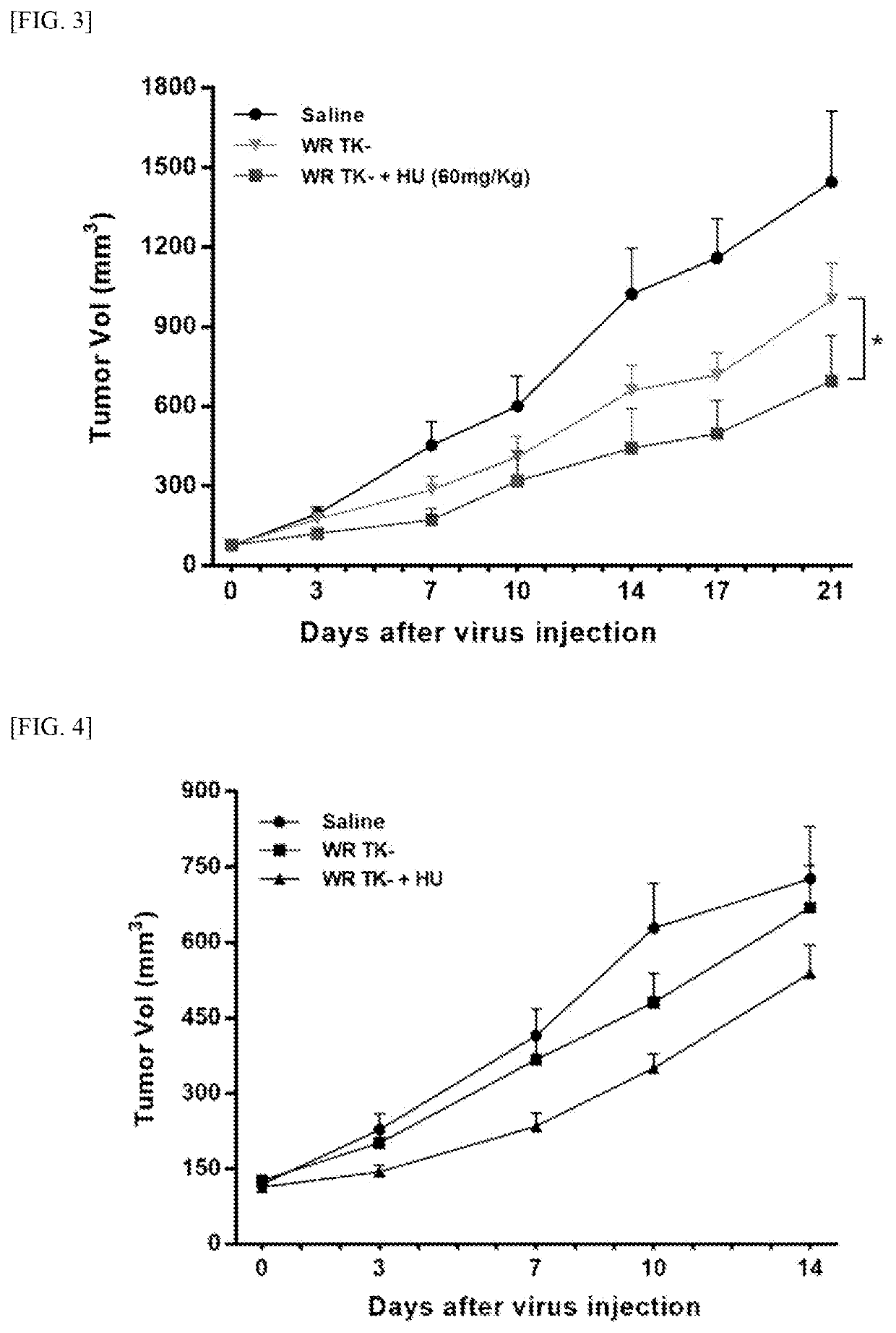
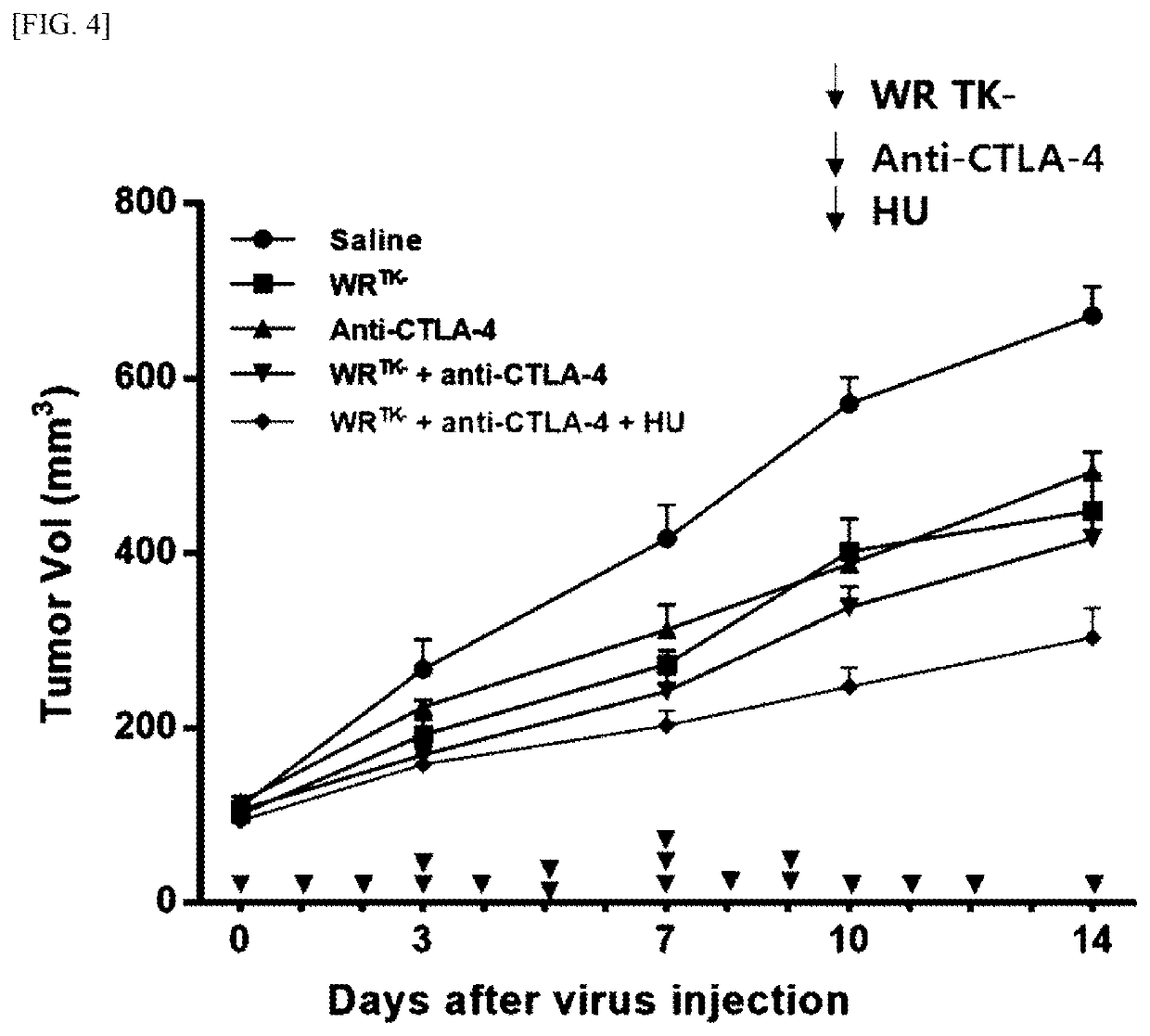
Pharmaceutical composition for treating cancer comprising vaccinia virus and hydroxyurea as active ingredients
PendingCN114340649AEffective treatmentGood anticancer effectPeptide/protein ingredientsTransferasesAnticarcinogenic EffectPharmaceutical drug
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating cancer, comprising vaccinia virus and hydroxyurea as active ingredients. The pharmaceutical composition for treating cancer, comprising vaccinia virus and hydroxyurea as active ingredients according to the present invention, exhibits a higher anti-cancer effect and safety than conventional vaccinia virus alone administration. Therefore, the pharmaceutical composition comprising vaccinia virus and hydroxyurea as active ingredients according to the present invention can be advantageously used for treating cancer.
Owner:拜耳诺克斯有限公司
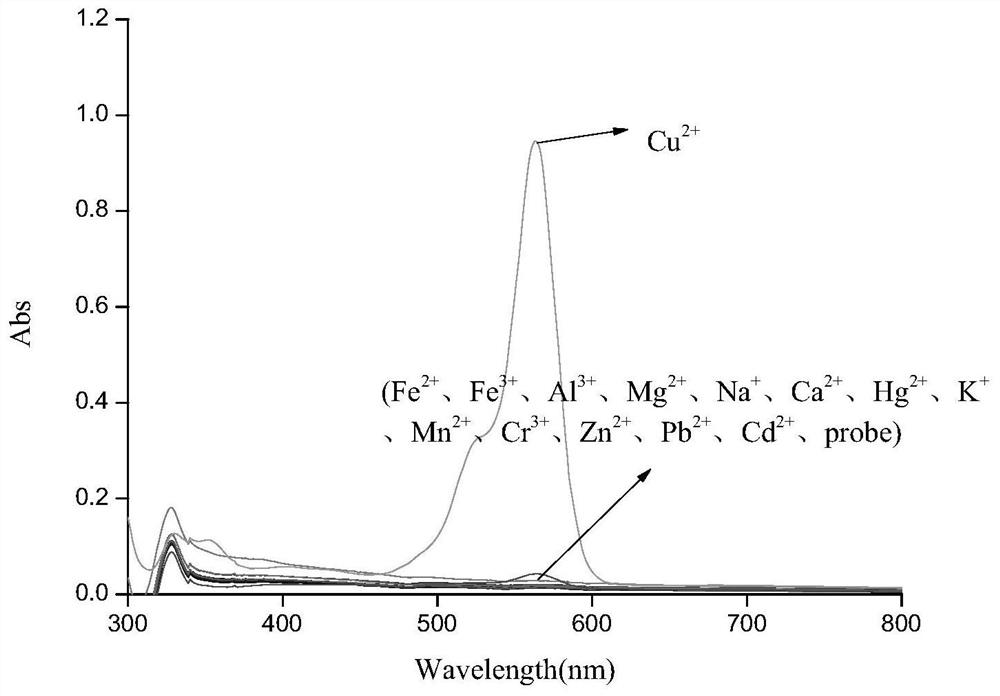
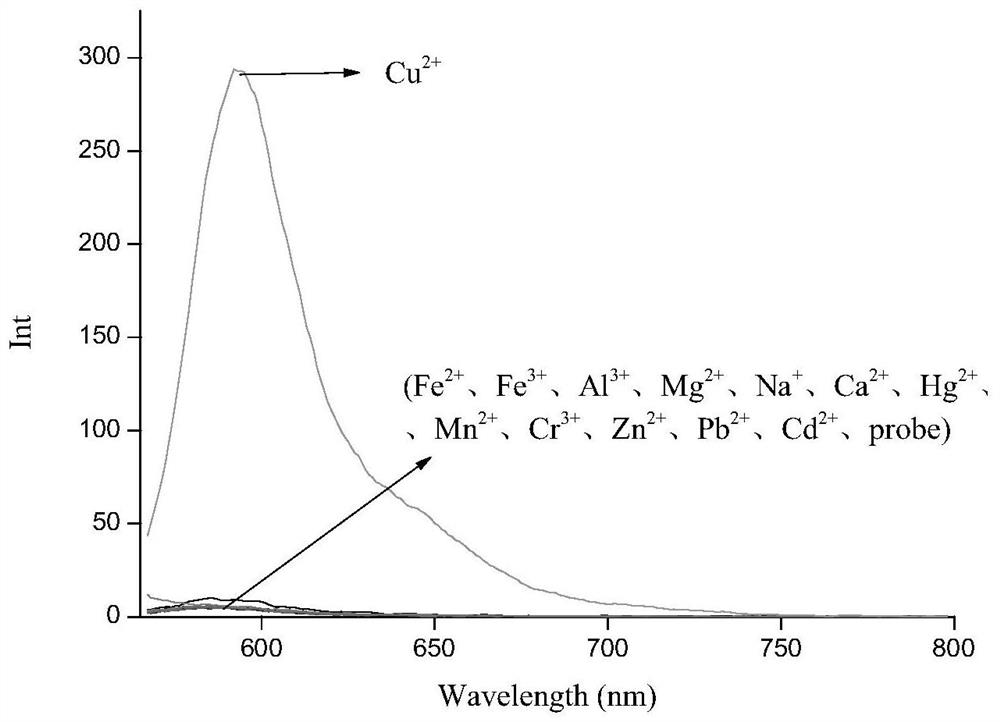
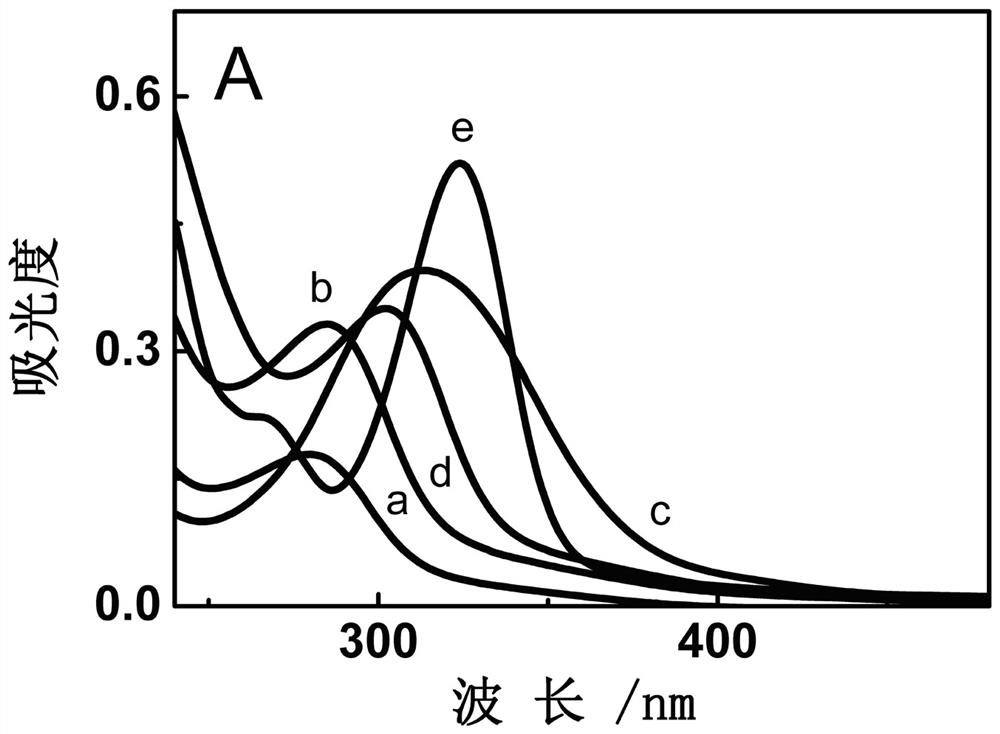
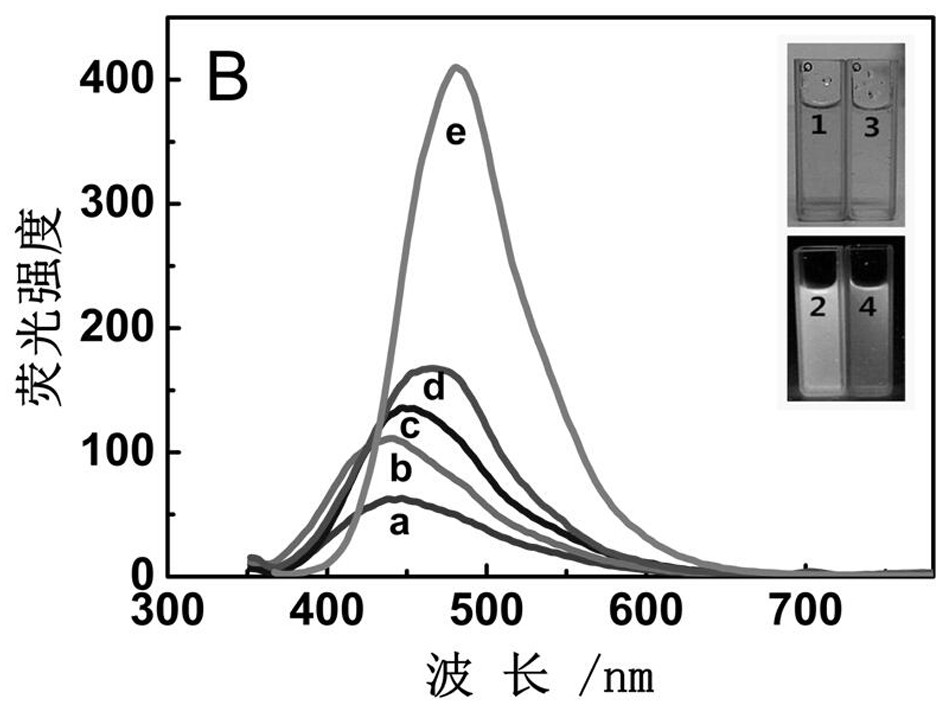
Six-membered spiro rhodamine copper ion fluorescent probe containing hydroxyurea structure as well as preparation method and application of six-membered spiro rhodamine copper ion fluorescent probe
ActiveCN113061140AEnabling UV-Vis SpectrophotometryEasy to detectOrganic chemistryColor/spectral properties measurementsFluoProbesHydroxylamine
The invention discloses a six-membered spiro rhodamine copper ion fluorescent probe containing a hydroxyurea structure as well as a preparation method and application of the six-membered spiro rhodamine copper ion fluorescent probe. The six-membered spiro rhodamine copper ion fluorescent probe containing the hydroxyurea structure has a structural general formula as shown in (I). The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking a rhodamine compound, phosphorus oxychloride and dry 1, 2-dichloroethane, reacting at 90 DEG C for 4 hours, cooling to room temperature, carrying out reduced pressure distillation to remove a solvent, dissolving the obtained solid in dry acetonitrile, adding sodium azide, stirring overnight at room temperature, adding a drying agent for drying, filtering, reacting the obtained filtrate at 82 DEG C for 40 minutes, and cooling to room temperature, and adding a mixed solution of hydroxylamine hydrochloride and triethylamine, and reacting to obtain a target product. The fluorescent probe provided by the invention has good sensitivity to copper ions, and can qualitatively and quantitatively detect the copper ions in a solution.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
Phenylalkyl n-hydroxyureas for treating leukotriene related pathologies
InactiveUS20120029048A1Preventing or treating atherosclerotic plaqueBiocideSenses disorderN-HydroxyureaLeukotriene
The method of treating patients by administering N-[3-[5-[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-2-thienyl]-1-methyl-2-propynyl]-N-hydroxyurea for treatment of leukotriene related pathologies and compositions for this use.
Owner:TALLIKUT PHARMA
Multiple target point type Tamibarotene derivative as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105175285AAchieve synergyEnhanced inhibitory effectUrea derivatives preparationOrganic active ingredientsLeukemiaHydroxycarbamide
The invention provides a multiple target point type Tamibarotene derivative as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. Particularly, RAR (retinoic acid receptor) agonist Tamibarotene is connected with antineoplastic drug hydroxycarbamide, fluorouracil and lenalidomide on sales through ester bonds or amido bonds respectively to obtain three multiple target point mutual prodrugs. The invention provides a method for preparing the compound and the application of the compound in preparing antineoplastic drugs, particularly drugs for curing various leukemias. The invention further relates to a drug combination of the compound.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Application of 5-LO (lipoxygenase) inhibitor for treatment of malignant tumor in blood system
The present invention relates to an application of a 5-LO (lipoxygenase) inhibitor for treatment of malignant tumor in a blood system. The hematological malignancy is confirmed to be leukemia relating to ALOX5 (Arachidonate) gene through test, and the hematologic tumor cancer gene ALOX5 directly causes the occurrence and development of the leukemia. The 5-LO inhibitor is also called zileuton with the formula of 1-[1-(1-Benzothiophen-2-yl)ethyl]-1-Hydroxyurea. The 5-LO inhibitor includes but not limited to N-hydroxyurea derivatives, comprising 1-[(2R-level)-4-[5-[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]thiophene-2-yl]-N-2-yl]-1-hydroxyurea, also called ABT-761 and 1-[(5)-4-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)phenyl]-N-2-yl]-1-hydroxyurea, also called BW-B 70C.. The 5-LO inhibitor can be used for inhibiting the stem cells of leukemia so as to treat the hematological malignancies, and the inhibiting of the stem cells of leukemia can be used for inhibiting one or more hematological malignancy as well as symptoms at the phase of crisis.
Owner:JIAXING XIUGUANG BIOTECH CONSULTING CO LTD
Application of alpha-L-rhamnosidase to preparing hydroxycarbamide and glycoside derivatives
InactiveCN105418711ASignificant transglycosylation activityImprove targetingSugar derivativesFermentationTumor targetMicroorganism
The invention relates to application of alpha-L-rhamnosidase to preparing hydroxycarbamide and glycoside derivatives. The hydroxycarbamide and glycoside derivatives are hydroxyurea and rhamnoside, and a molecular formula of the hydroxycarbamide and glycoside derivatives is C7H14N2O6. Amino acid sequences of the alpha-L-rhamnosidase are shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The application has the advantages that hydroxycarbamide is used as a raw material, rhamnose is used as a glycosyl donor, and the hydroxycarbamide and rhamnoside can be synthesized from the alpha-L-rhamnosidase of a microbial source by means of one-step transglycosylation reaction; a method has simple steps, is low in cost and mild in condition and is environmental friendly, and the alpha-L-rhamnosidase has a potential application prospect; products of the alpha-L-rhamnosidase contain rhamanopyranosyl as compared with the hydroxycarbamide which is the raw material, accordingly, the stability and the targeting can be improved, and the products have broad application prospects for being used as tumor targeted medicines.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Medicine composition for treating psoriasis
ActiveCN105534996AOintment deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCurative effectMedical prescription
The invention discloses a medicine composition for treating psoriasis. The medicine composition is characterized by being prepared from, by weight, 1-10 parts of calcipotriol, 1-10 parts of hydroxyurea, 1-20 parts of glycerol monostearate, 1-20 parts of fat-soluble matrix, 1-20 parts of an emulsifier, 5-20 parts of a moisturizing agent, 1-8 parts of a transdermal absorbent and 20-70 parts of purified water. The medicine composition is scientific in formula and simple in preparation technology and has the remarkable treatment curative effect on psoriasis vulgaris and psoriasis inveterate.
Owner:CHANGSHA BAISHUN BIOTECH
Novel method for preparing dihydroxyurea
InactiveCN102659637AEasy to purifyShorten the timeUrea derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationHydroxylamineEmulsion
The invention relates to a novel method for preparing dihydroxyurea and belongs to the field of organic synthesis. The dihydroxyurea belongs to a novel salt-free reducing agent which is used for spent fuel post treatment and has good application prospects. The novel method is mainly characterized in that under the anhydrous conditions, solid phosgene and hydroxylamine are used for synthesizing the dihydroxyurea. Concretely, hydroxylamine and potassium acetate are firstly placed into a three-opening flask, are placed into an ice salt bath and are stirred into emulsion. In addition, the solid phosgene is dissolved into 1, 4-dioxane, the mixed liquid is placed into a constant-pressure liquid dripping funnel, when the temperature is below 0 DEG C, the solid phosgene mixing liquid is dripped into the emulsion at the controlled speed, and the temperature is maintained at 0 to 5 DEG C. The reaction is continuously carried out for 2 hours after the dripping completion, and then, the pH of the solution is regulated to 2 to 3 through concentrated hydrochloric acid. Solid materials are removed through filtering, solvents are removed through rotary evaporation on filter liquid, and solid is obtained. A proper amount of tetrahydrofuran is used for extracting the dihydroxyurea in the solid, the solvents are removed through the rotary evaporation, coarse dihydroxyurea is obtained, ethanol is used for recrystallization, and the pure dihydroxyurea is obtained. Through the detection and characterization on products by various methods, the product purity is 95 percent, and the yield is 57 percent.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
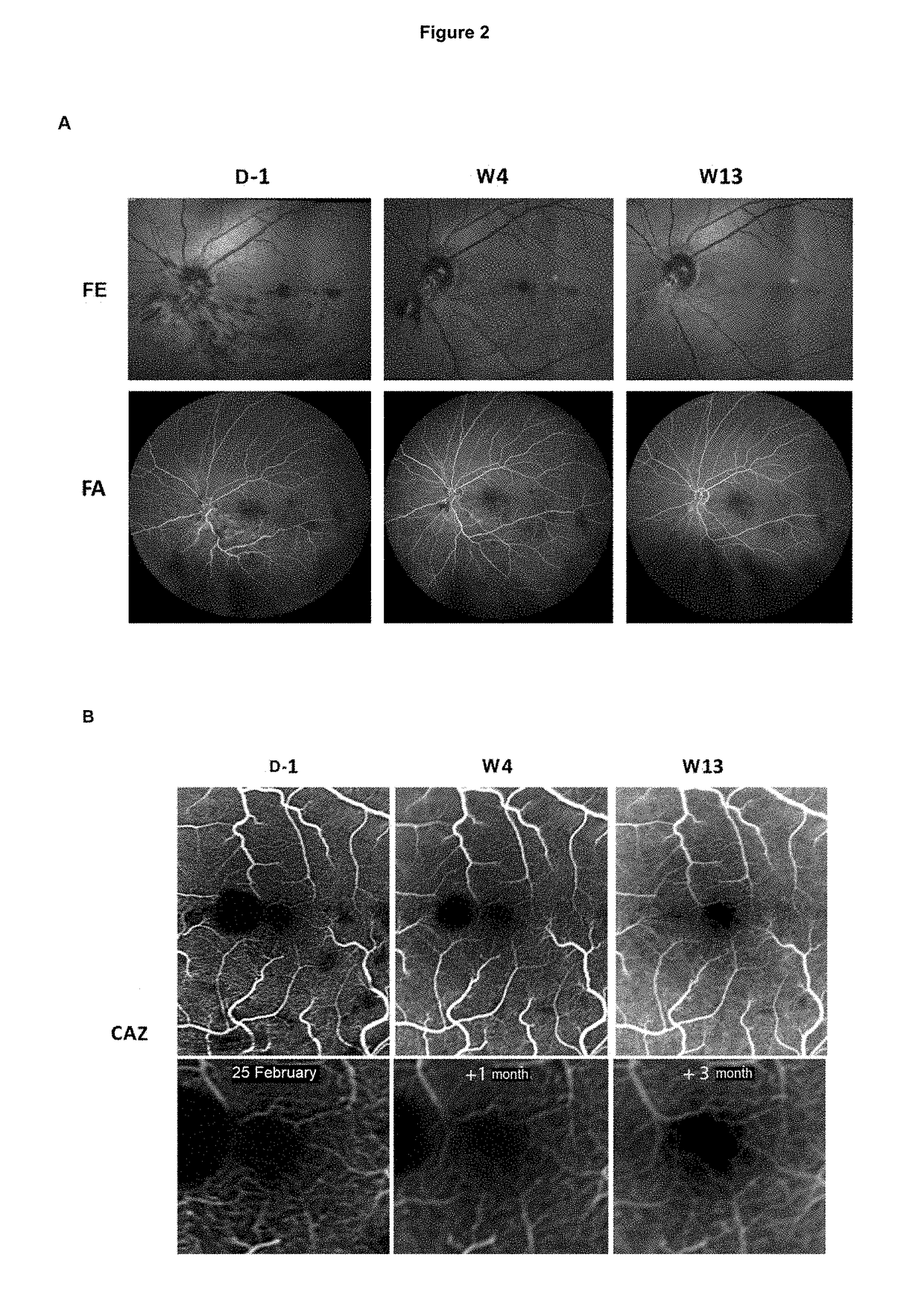
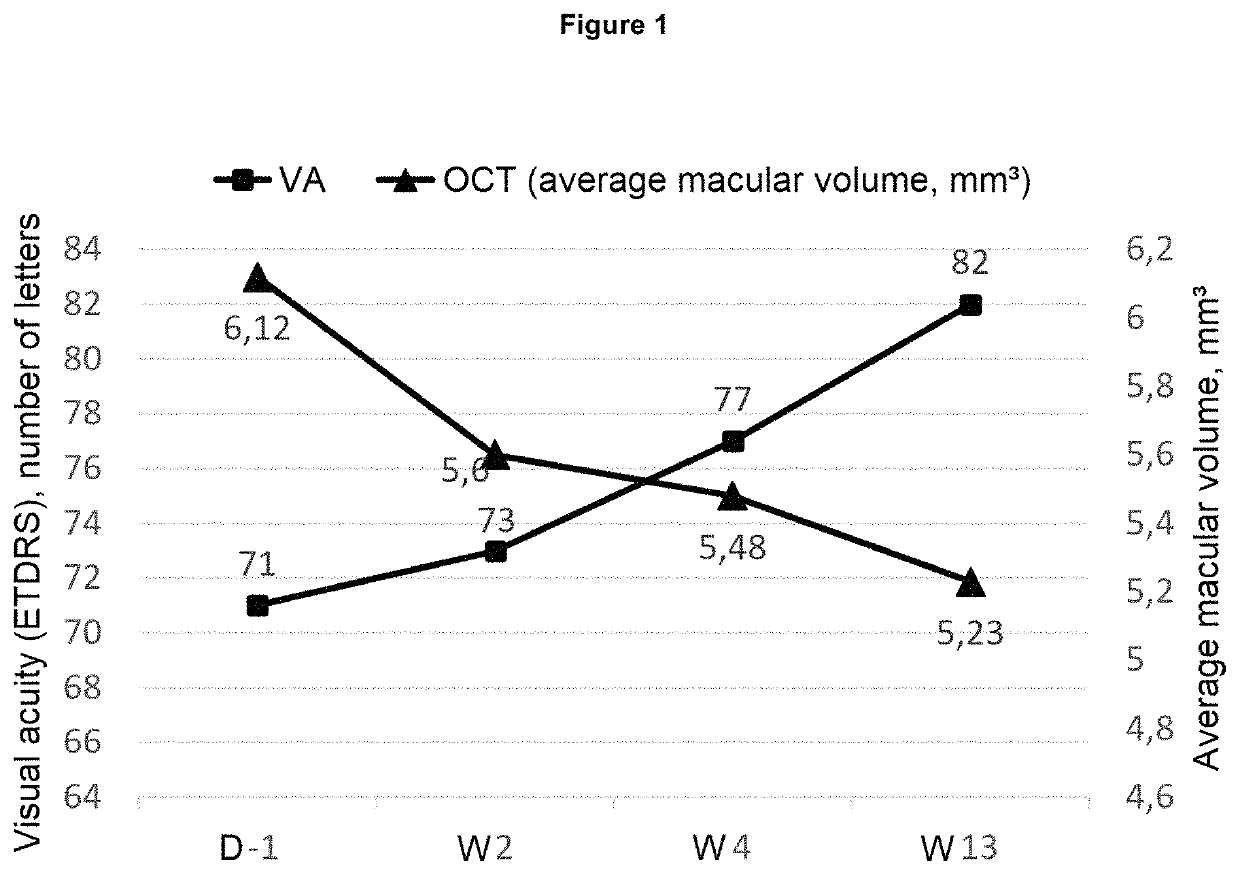
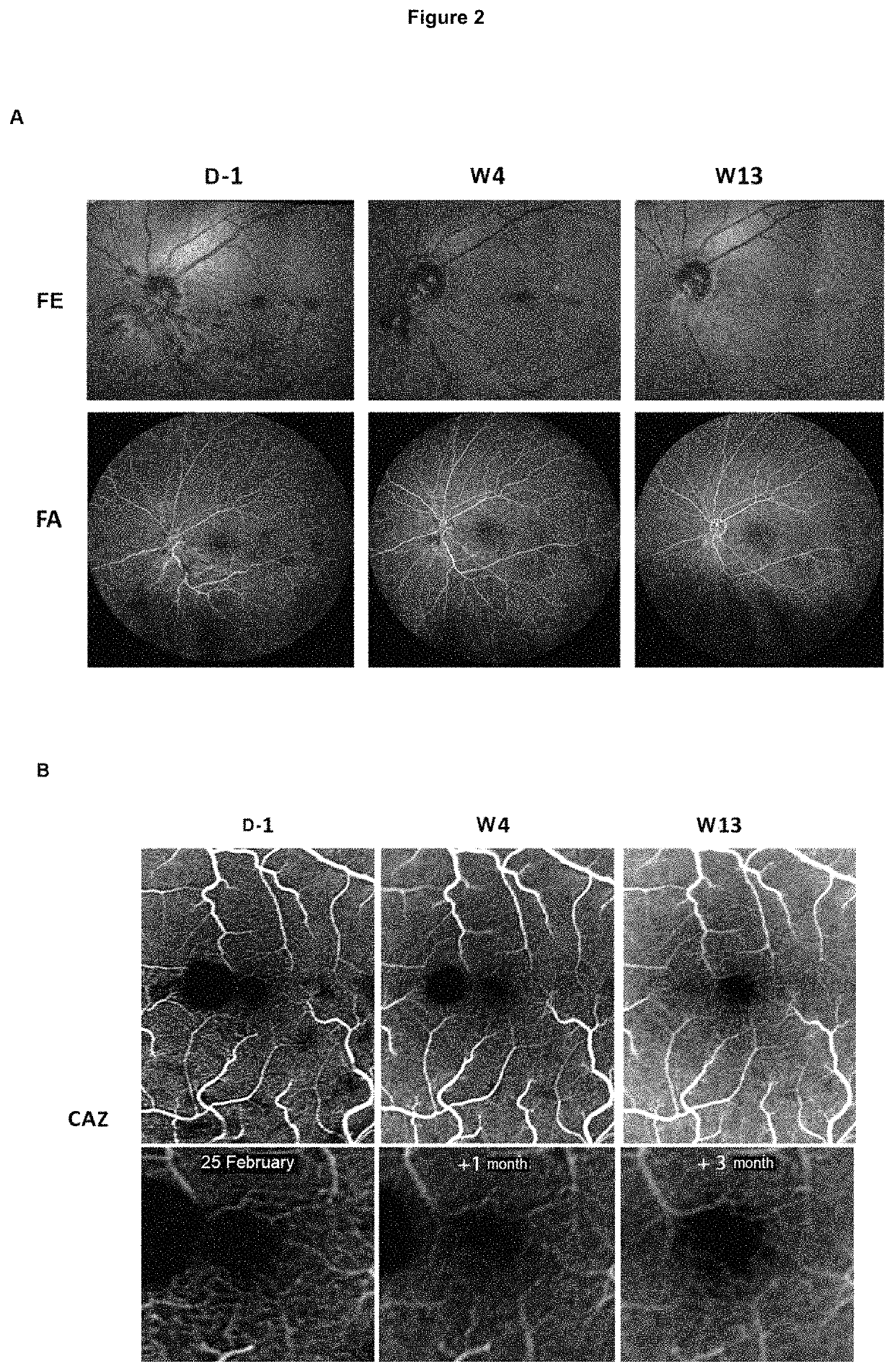
Use of hydroxycarbamide for preventing retinal nonperfusion
ActiveUS20180221313A1Reducing and delaying extensionReduce complicationsSenses disorderAmide active ingredientsVisual acuityHydroxycarbamide
The present invention relates to the use of hydroxycarbamide (HC) for reducing and / or delaying the extension of capillary nonperfusion, a cause of irreparable visual impairment in patients suffering from central retinal vein occlusion (CRVO). This is the first systemic treatment which makes it possible to reduce retinal ischemic complications in patients in whom (CRVO) has been recently diagnosed and is consequently in a rapidly progressive phase. Given the low toxicity of HC evaluated on a large scale in children and adults in the context of other diseases for decades, the results of the present study open up a new therapeutic approach in the treatment of CRVO.
Owner:UNIVERSITÉ PARIS CITÉ +5
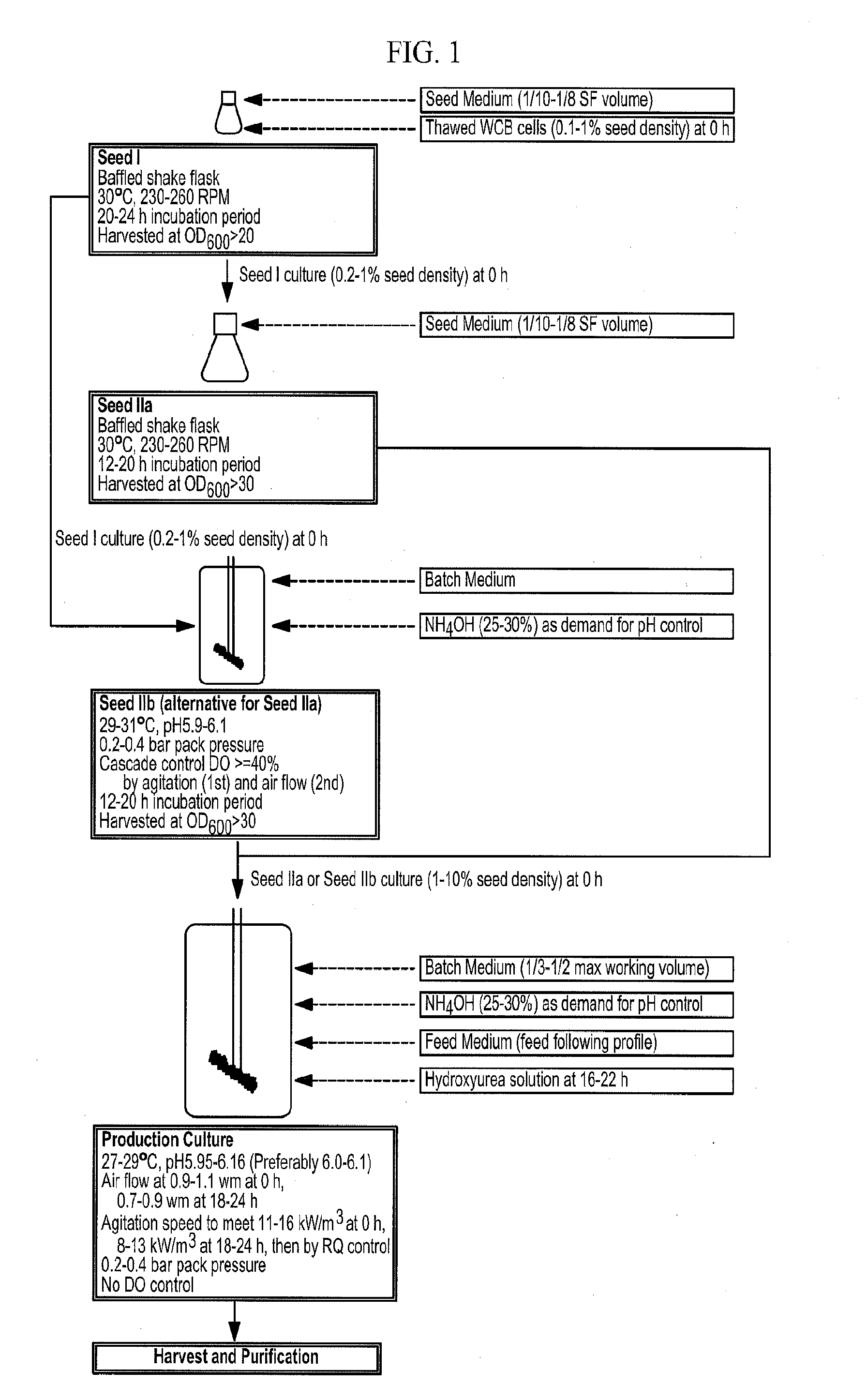
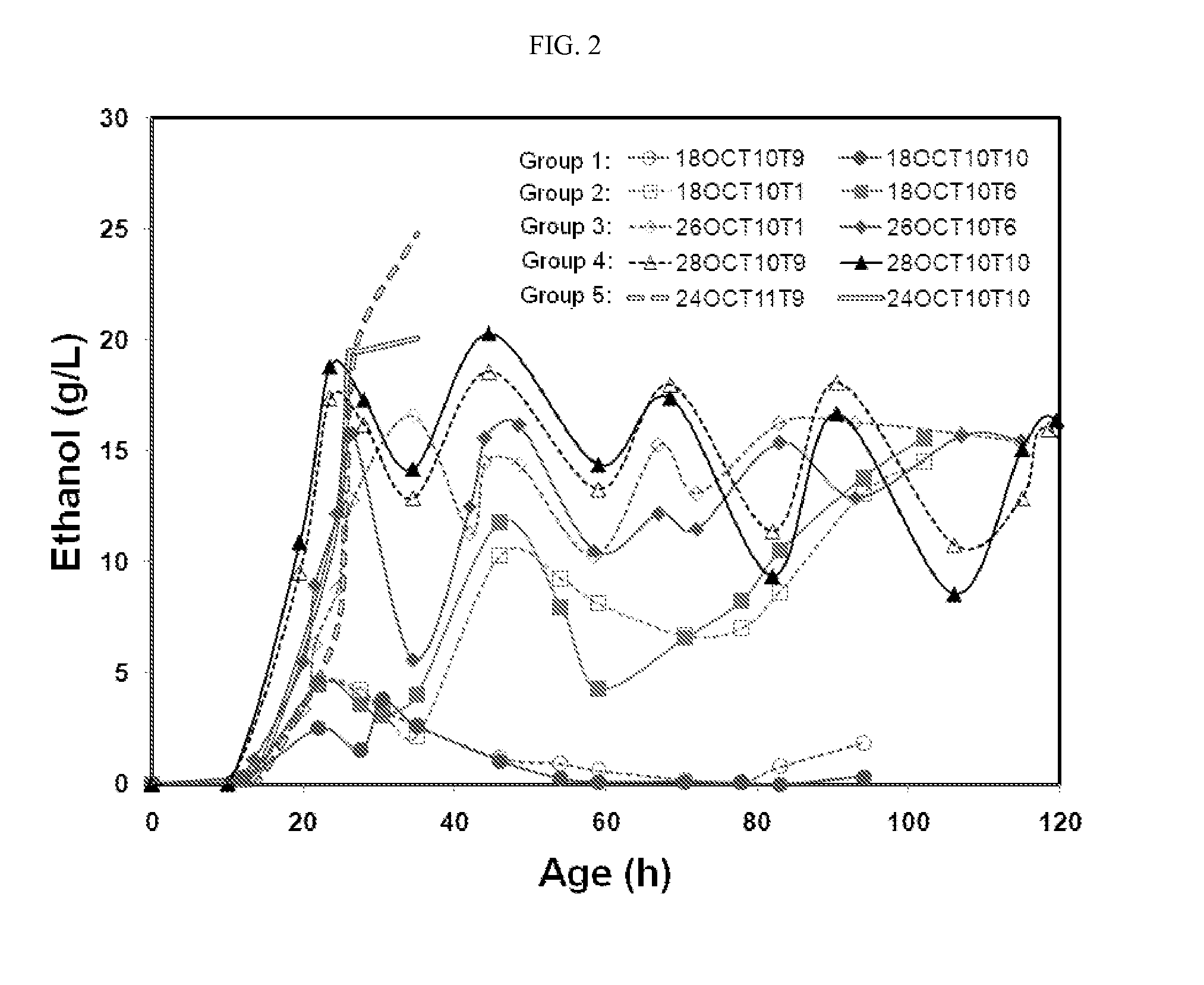
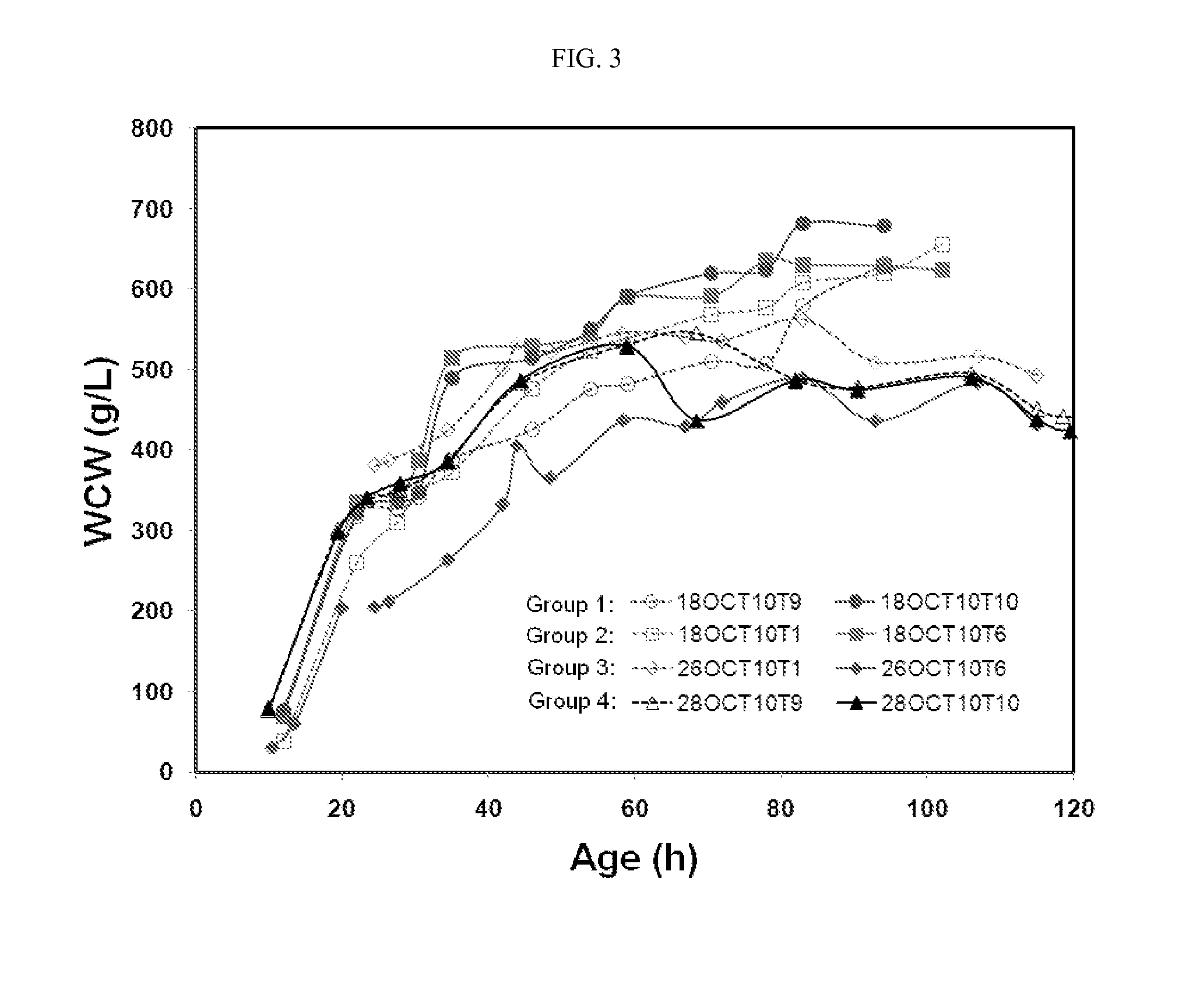
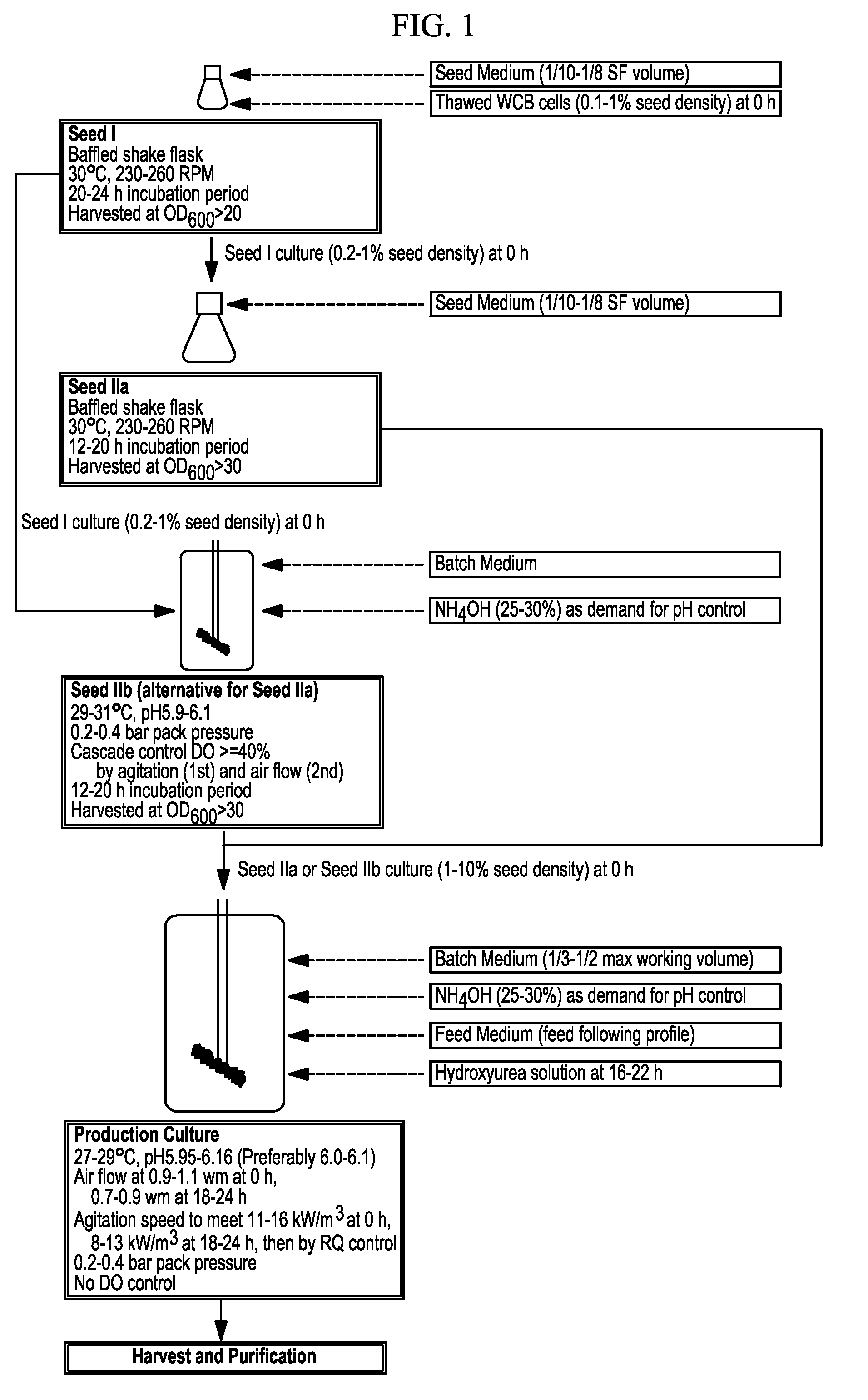
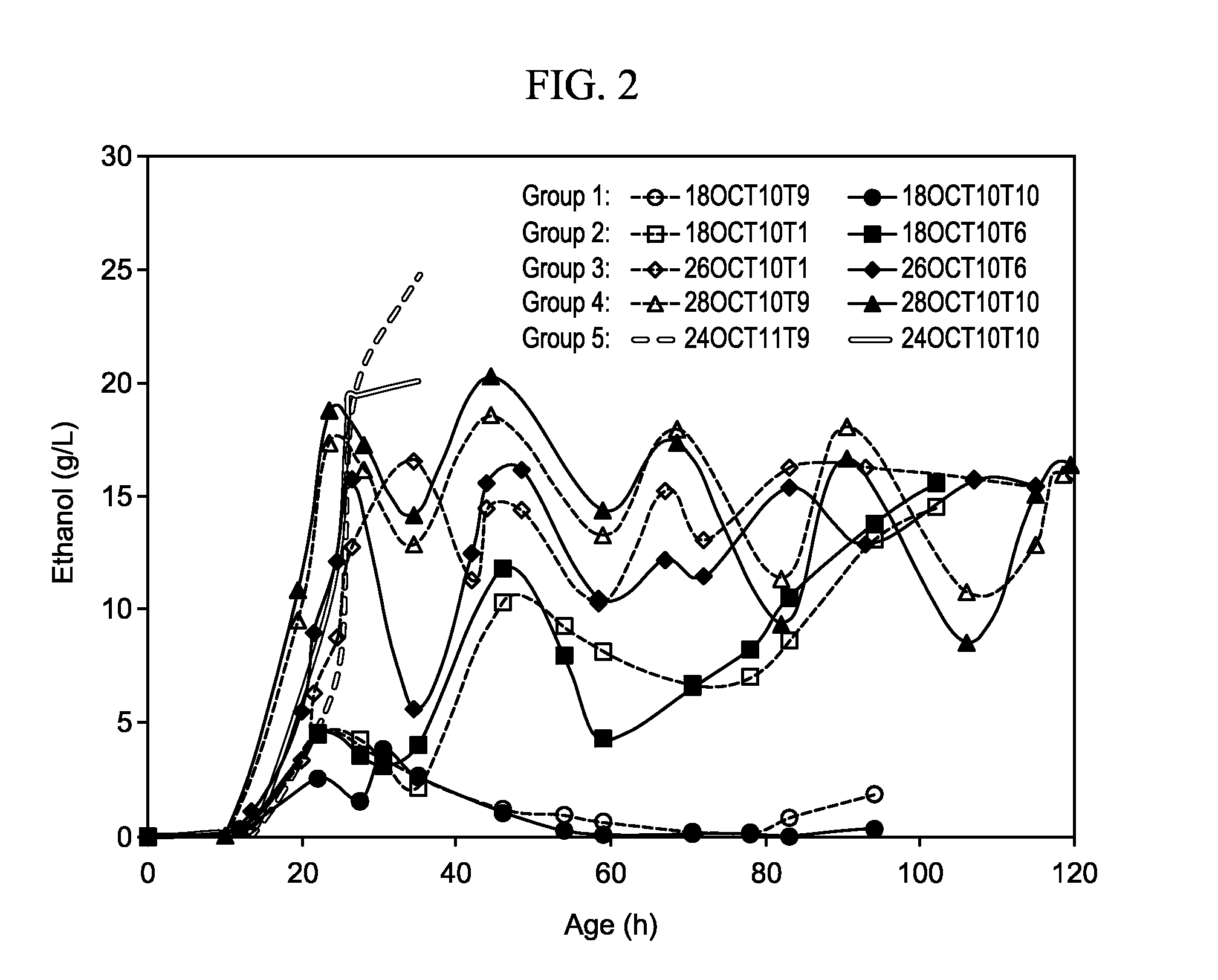
Methods of producing antibodies in yeast
InactiveUS20160024203A1Immunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsFermentationPichia pastorisYeast
The present invention describes a method for producing an antibody in Pichia pastoris, such as by fed-batch fermentation. The method includes the addition of about 2.0-5.0 g / L of hydroxyurea during the fermentation process to sustain a constant cell density and enhance the whole broth titer of the antibody. The method may also include a strategy of increasing the ethanol concentration to about 18-22 g / L and then maintaining the ethanol level at about 5-17 g / L to stabilize the cell mass and enhance the production rate of the antibody. The method may further include a respiratory quotient control for monitoring the ethanol profile and to improve the quality of the antibody by, for example, eliminating clipping of the heavy chain.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Preparation method of amino hydroxyurea
ActiveCN114436901AShort synthetic routeRaw materials are cheap and easy to getOrganic chemistryAgainst vector-borne diseasesTrans esterificationEngineering
The invention relates to a preparation method of amino hydroxyurea, which comprises the following steps: under the condition of ammonia ester exchange and in the presence of an acid-binding agent, contacting a substance shown in a formula A with a substance shown in a formula B in a solvent to obtain a contacted material, carrying out reduced pressure rotary evaporation and first drying on the contacted material to obtain a crude product; mixing the crude product with ethanol and water, re-dissolving, recrystallizing, filtering and secondarily drying; and carrying out second drying to obtain the target product amino hydroxyurea. The method for one-step preparation of amino hydroxyurea through ammonia-ester exchange provided by the invention has the advantages of short synthetic route, cheap and easily available raw materials, high process safety, simple operation, low production cost and high reaction yield, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
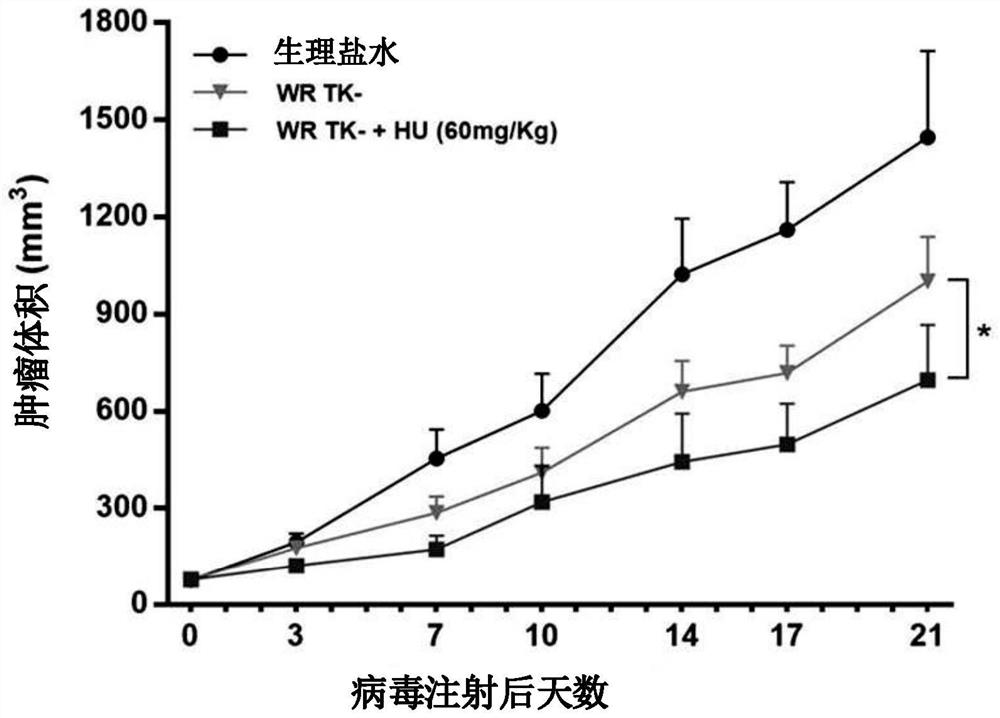
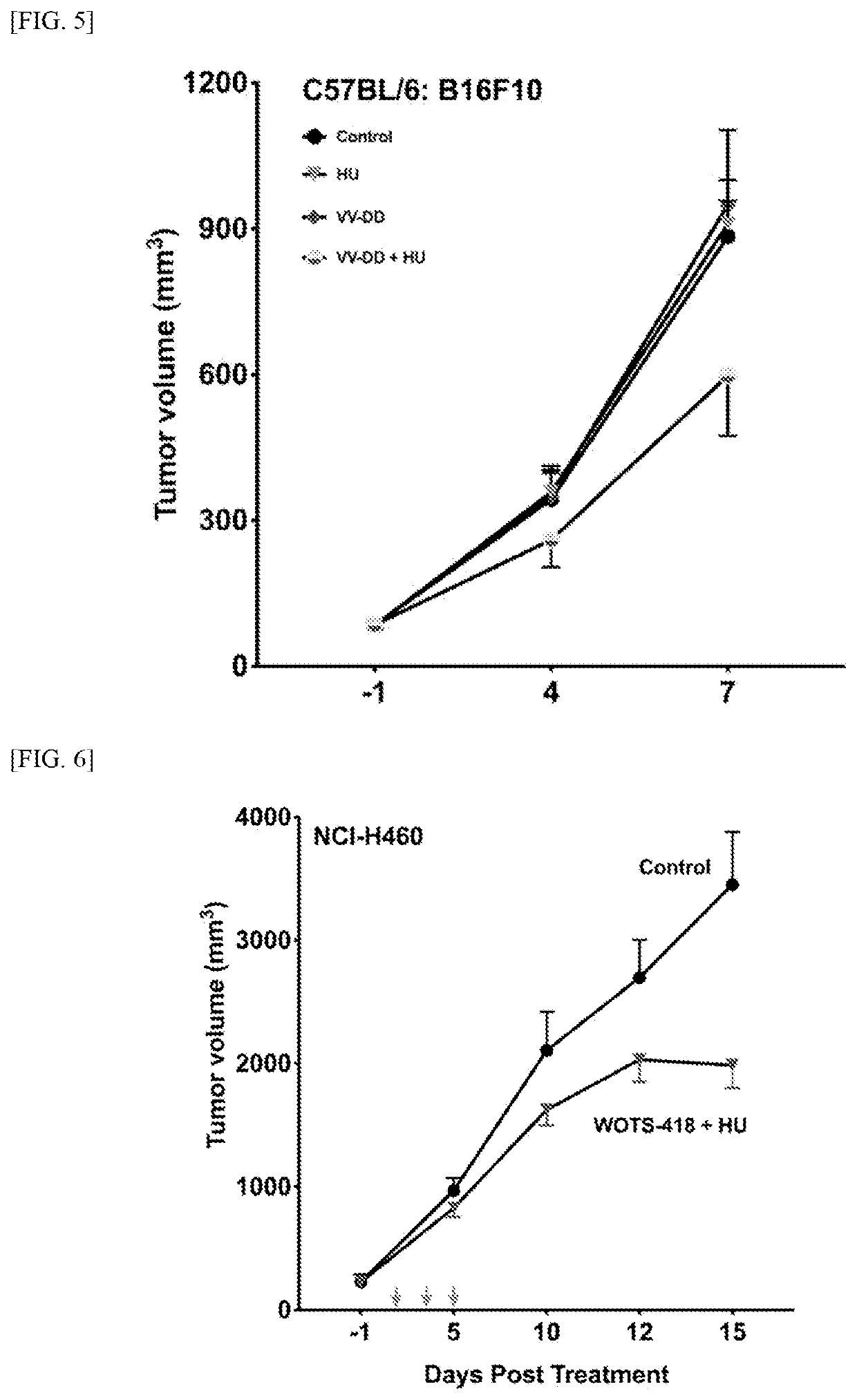
Pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating cancer comprising anticancer virus and hydroxyurea as effective components
PendingUS20200405794A1Good anticancer effectImprove securityViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCancer cellPharmaceutical drug
Owner:BIONOXX INC
Use of hydroxycarbamide for preventing retinal nonperfusion
The present invention relates to the use of hydroxycarbamide (HC) for reducing and / or delaying the extension of capillary nonperfusion, a cause of irreparable visual impairment in patients suffering from central retinal vein occlusion (CRVO). This is the first systemic treatment which makes it possible to reduce retinal ischemic complications in patients in whom (CRVO) has been recently diagnosed and is consequently in a rapidly progressive phase. Given the low toxicity of HC evaluated on a large scale in children and adults in the context of other diseases for decades, the results of the present study open up a new therapeutic approach in the treatment of CRVO.
Owner:UNIVERSITÉ PARIS CITÉ +5
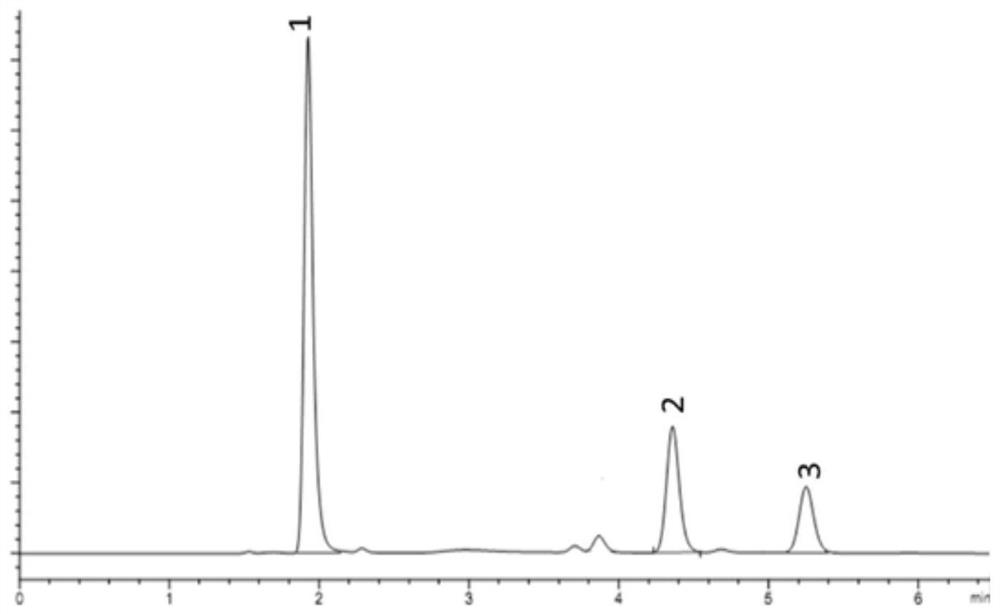
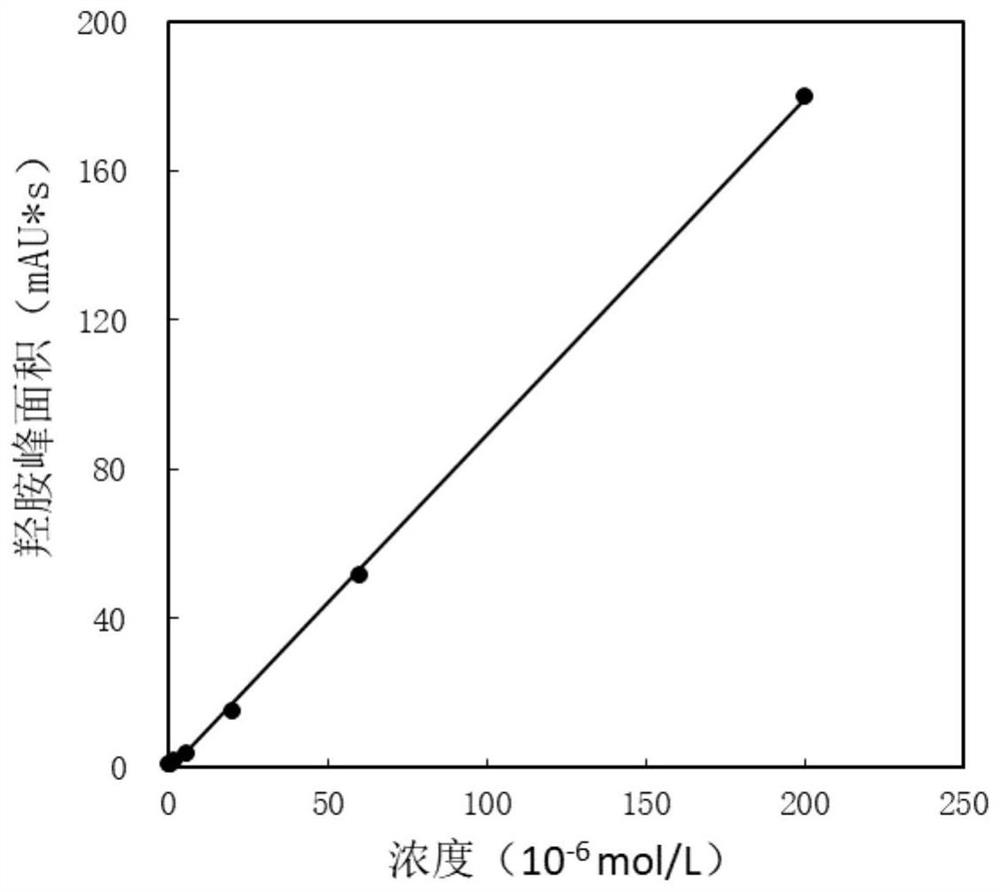
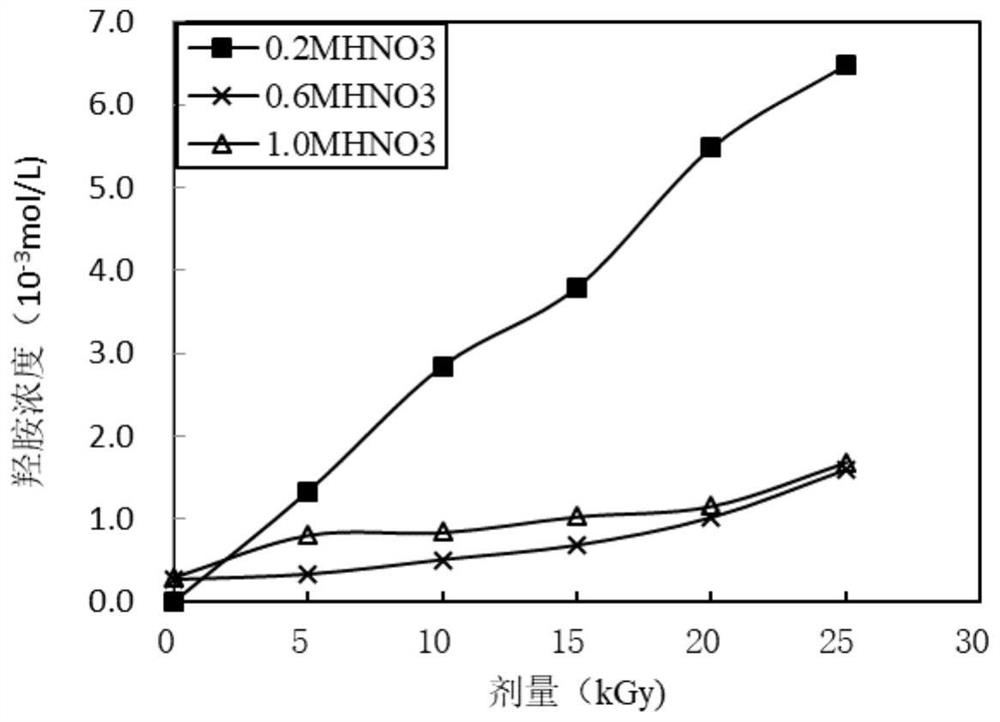
Analytical method of hydroxylamine when hydroxysemicarbazide coexists
ActiveCN109632979BAnalysis does not affectEasy to operateComponent separationHydroxylamineRelative standard deviation
The invention discloses a hydroxylamine analysis method in a coexistence of amino hydroxyl urea. The method comprises the following steps of neutralizing and diluting a to-be-detected amino hydroxyl urea coexisting sample, then putting into a volumetric flask, adding a nitrobenzaldehyde solution, then carrying out constant volume and evenly shaking by using an acetic acid solution, and standing atroom temperature; then, analyzing the to-be-detected sample by using a method for combining a high performance liquid chromatography column and an ultraviolet detector so as to obtain the peak area of hydroxylamine, and calculating to obtain the concentration of hydroxylamine in the to-be-detected sample by using a standard working curve of hydroxylamine. The lowest detecting concentration of hydroxylamine can reach 2 * 10 <-7> mol / L, and the relative standard deviation of the analysis method of the embodiment is 0.8%. According to the method, chemical derivatization - liquid chromatography method is established to analyze hydroxylamine, and analysis of hydroxylamine is not influenced by liquid chromatography method, the method is simple to operate, high in sensitivity and good in repeatability.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
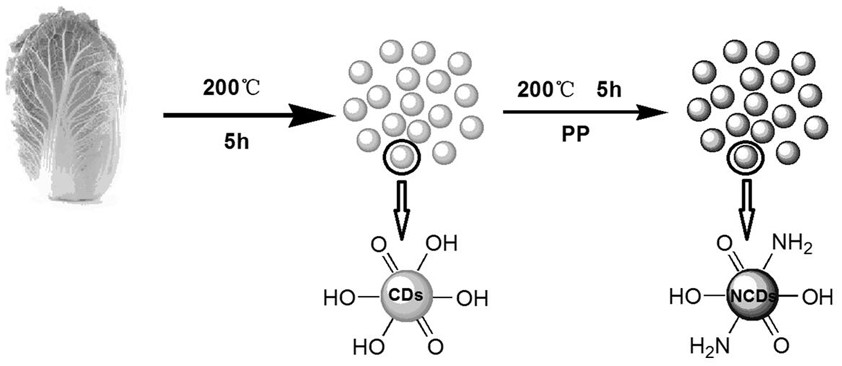
Functionalized inorganic fluorescent microsphere based on nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN114854404AGood monodispersityRich in functional groupsNanoopticsNano-carbonFluoProbesDiethylenetriamine
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Methods for producing antibodies
InactiveUS20160024204A1Immunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsFermentationPichia pastorisAntiendomysial antibodies
The present invention describes a method for producing an antibody in Pichia pastoris, such as by fed-batch fermentation. The method includes a respiratory quotient control for monitoring the ethanol profile and to improve the quality of the antibody by, for example, eliminating clipping of the heavy chain. The method may also include a strategy of increasing the ethanol concentration to about 18-22 g / L and then maintaining the ethanol level at about 5-17 g / L to stabilize the cell mass and enhance the production rate of the antibody. The method may also include the addition of about 2.0-5.0 g / L of hydroxyurea during the fermentation process to sustain a constant cell density and enhance the whole broth titer of the antibody.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Pharmaceutical composition comprising vaccinia virus and hydroxyurea as active ingredient for treatment of cancer
PendingUS20220304960A1Good effectImprove securityPeptide/protein ingredientsTransferasesCowpox virusPharmaceutical drug
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising Vaccinia virus and hydroxyurea as active ingredients for prevention or treatment of cancer. The pharmaceutical composition comprising Vaccinia virus and hydroxyurea as active ingredients for treatment of cancer according to the present invention exhibits higher anticancer effects and safety than the conventional administration of Vaccinia virus alone. Therefore, the pharmaceutical composition comprising Vaccinia virus and hydroxyurea as active ingredients according to the present invention may be advantageously used for treating cancer.
Owner:BIONOXX INC
A kind of aqueous UV polyurethane acrylate dispersion with self-initiating function and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107254251BImprove mechanical propertiesGood storage stabilityAnti-corrosive paintsPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPolyesterCarboxylic acid
The invention discloses an aqueous UV urethane acrylate dispersion with a self-initiation function and a preparation method of the dispersion. The aqueous UV urethane acrylate dispersion comprises the following constitution raw materials in parts by weight: 10-20 parts of polyester polyol or polyether polyol, 10-30 parts of diisocyanate, 2-10 parts of hydroxy carboxylic acid, 0.04-0.2 part of a catalyst, 5-15 parts of an organic solvent, 1-5 parts of hydroxycarbamide, 0.1-0.6 part of a polymerization inhibitor, 10-30 parts of a monohydroxy acrylate monomer, 15-35 parts of oligomer with a photo-initiation group and a terminal hydroxyl group, 1-5 parts of organic amine and 140-180 parts of deionized water. The aqueous UV urethane acrylate dispersion has functions of self initiation or co-initiation under the action of a trace amount of an initiator, is high in resin curing efficiency and can be deeply cured, and a dispersion film is good in surface scratching resistance, high in hardness, good in weather resistance and excellent in chemical resistance.
Owner:HUNAN BANFERT NEW MATERIALS TECH
Transgenic cell selection
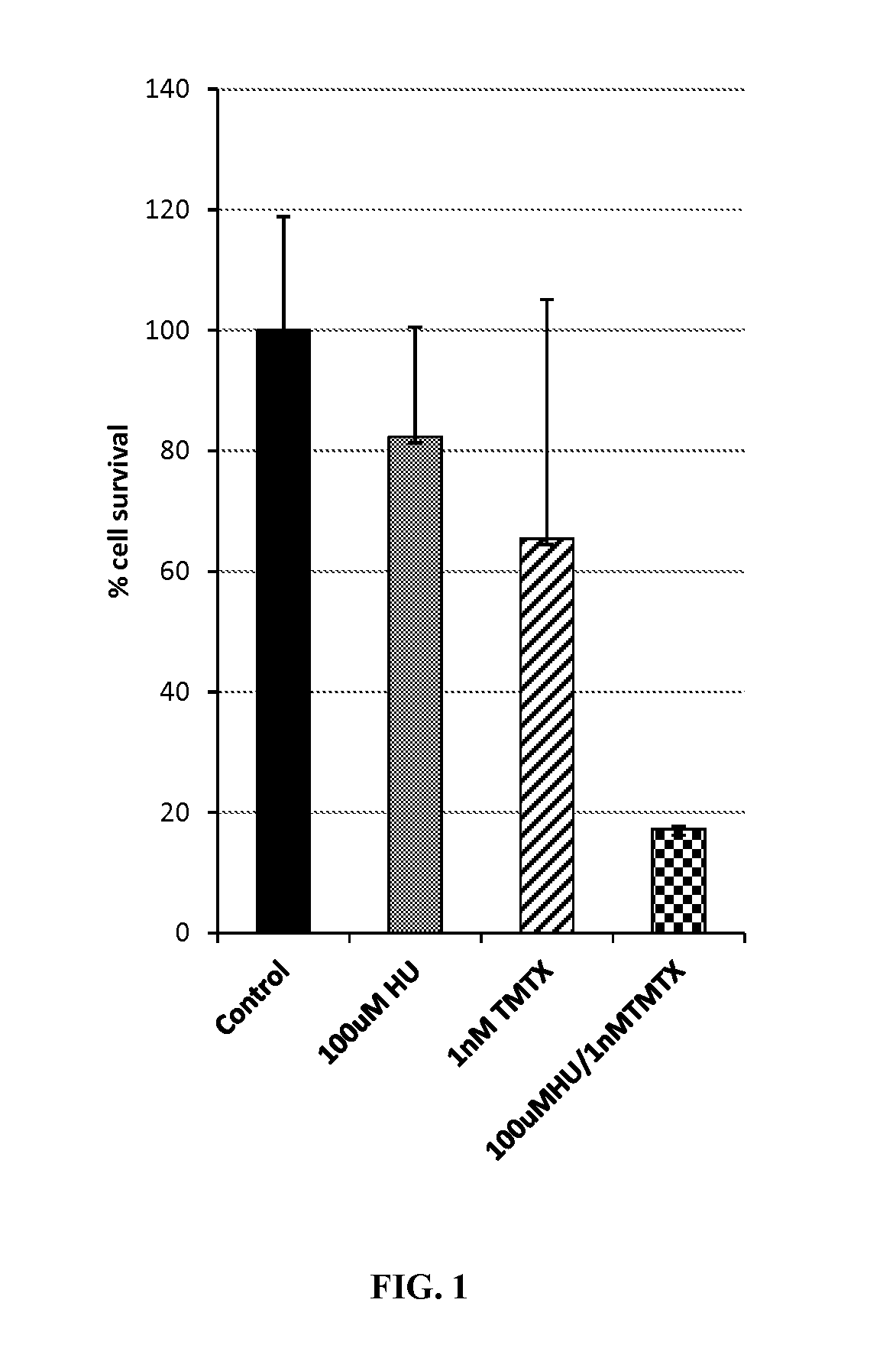
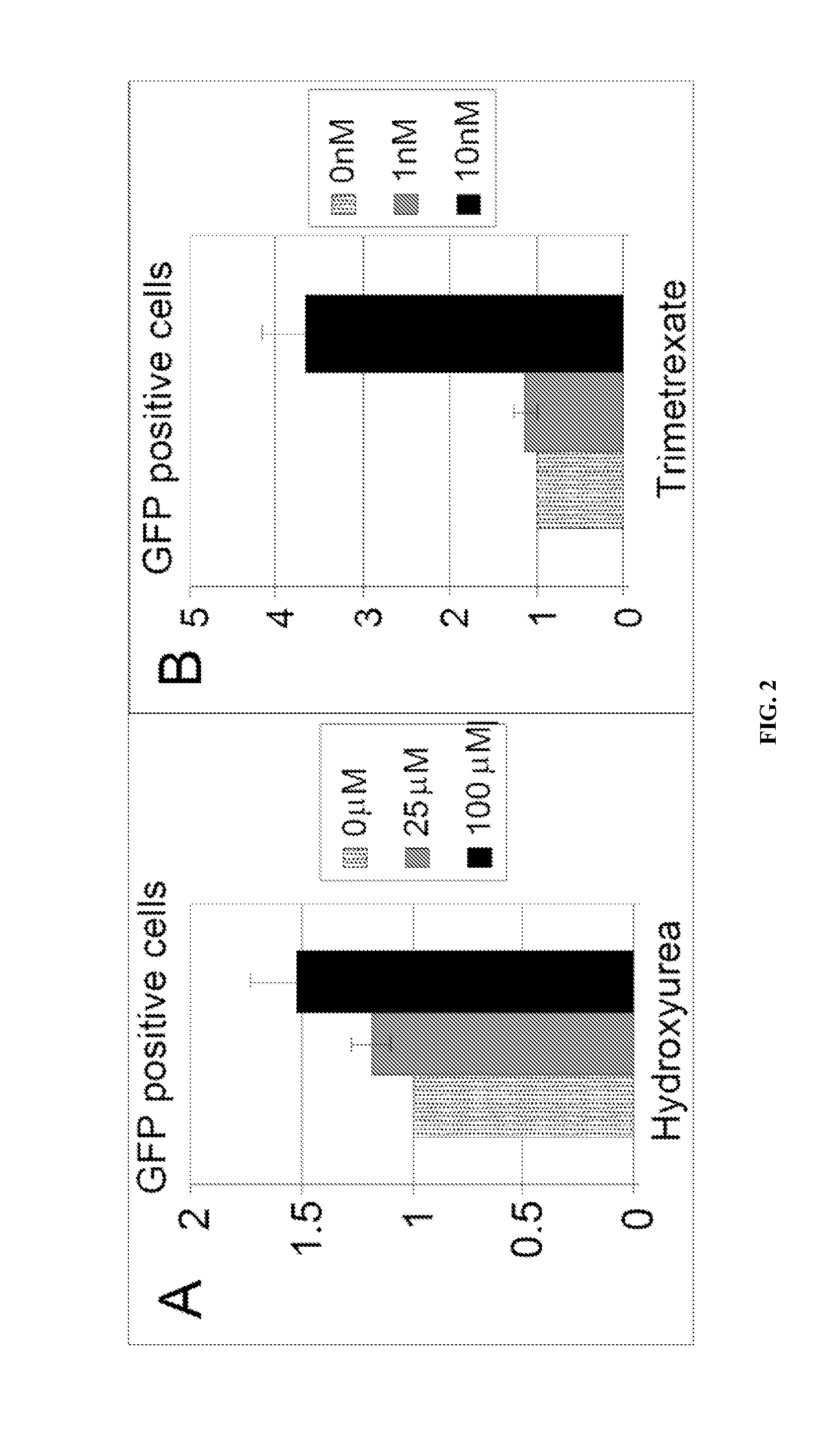
InactiveUS20160010094A1Imparting resistanceBiocideGenetic material ingredientsResistant genesCytotoxic drug
Methods for selecting transgenic cells comprising two or more drug resistance genes with a combination of cytotoxic drugs (e.g., trimetrexate (TMTX) and hydroxyurea (HU)). Such selection can be completed in vitro or in vivo. Transgenic cells and vectors comprising combinations of resistance genes are also provided. Transgenic cells of the embodiments can be used as cell based therapeutics, such as for treatment of HIV infection.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA +1
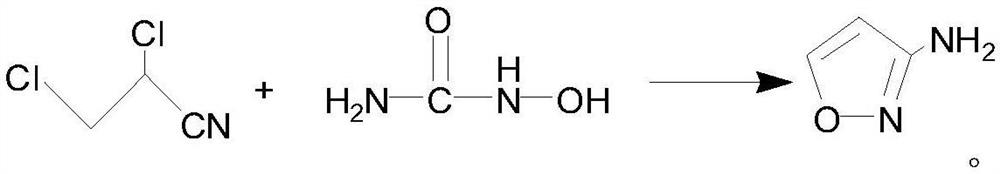
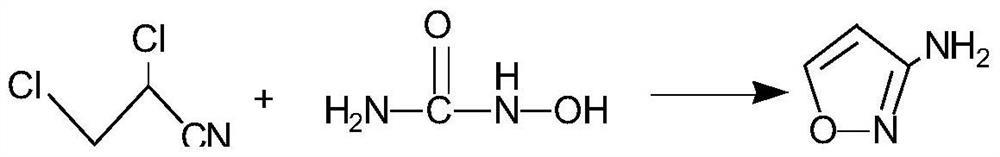
Preparation method of 3-aminoisoxazole
InactiveCN112047897AAggregation does not occurAvoid rapid exothermOrganic chemistryPtru catalystAcrylonitrile
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines, and particularly relates to a preparation method of 3aminoisoxazole, which comprises the following steps: (1) preparing 2, 3dichloropropionitrile: adding acrylonitrile, N, Ndimethylformamide and pyridine into a reaction vessel, cooling to 5-15 DEG C, introducing chlorine into the reaction vessel, and keeping the reaction temperature at 1020 DEG C; controlling the temperature to be 15-25 DEG C and stirring for 5 hours after the chlorine gas is introduced; blowing excessive chlorine until the reaction liquid is yellowish or colorless andtransparent to obtain 2, 3dichloropropionitrile; and (2) preparation of 3amino isoxazole: under an alkaline condition, synthesizing 3amino isoxazole by taking hydroxyurea and 2, 3dichloropropionitrile as raw materials and N, Ndimethylformamide as a catalyst. The preparation method is used for solving the technical problems of extremely easy material punching and high process risk caused by the adoption of a 2, 3dibromopropionitrile intermediate in the existing 3amino isoxazole preparation.
Owner:YANGZHOU TIANHE PHARM CO LTD
Multi-target tamibarotene derivative and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN105175285BAchieve synergyEnhanced inhibitory effectUrea derivatives preparationOrganic active ingredientsLeukemiaHydroxycarbamide
The invention provides a multiple target point type Tamibarotene derivative as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. Particularly, RAR (retinoic acid receptor) agonist Tamibarotene is connected with antineoplastic drug hydroxycarbamide, fluorouracil and lenalidomide on sales through ester bonds or amido bonds respectively to obtain three multiple target point mutual prodrugs. The invention provides a method for preparing the compound and the application of the compound in preparing antineoplastic drugs, particularly drugs for curing various leukemias. The invention further relates to a drug combination of the compound.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Pharmaceutical composition for treating cancer comprising anticancer virus, immune checkpoint inhibitor and hydroxyurea as active ingredients
PendingUS20220362316A1Good anticancer effectImprove securityViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsAntibody ingredientsPharmaceutical drugBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
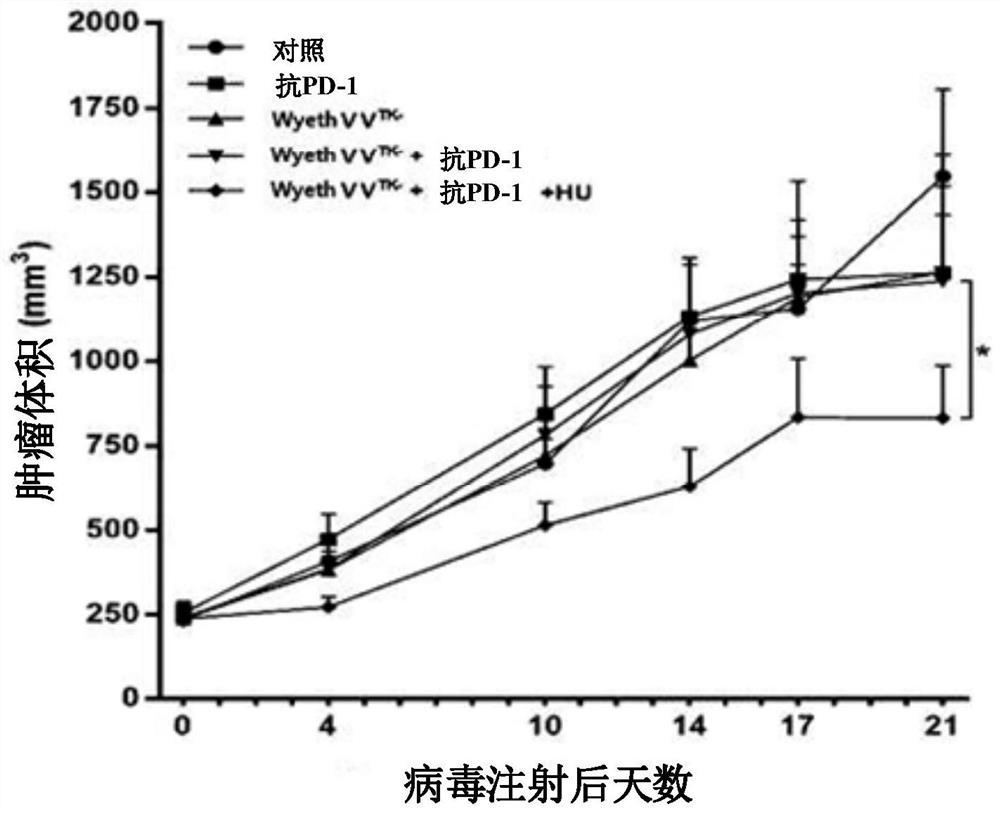
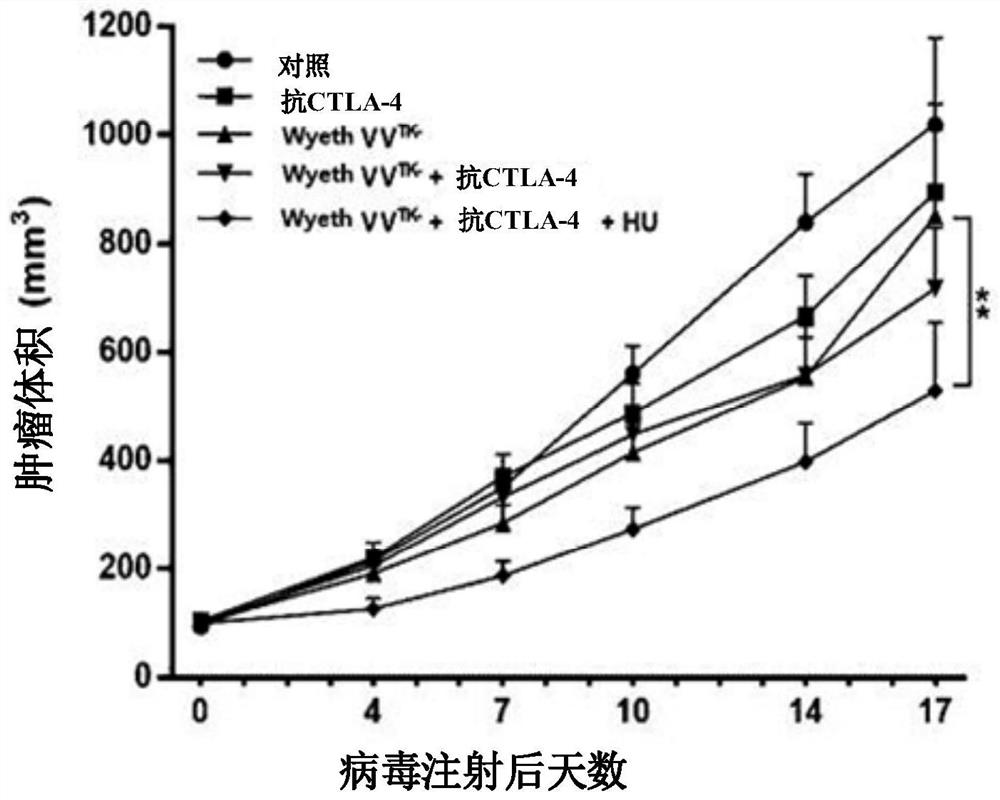
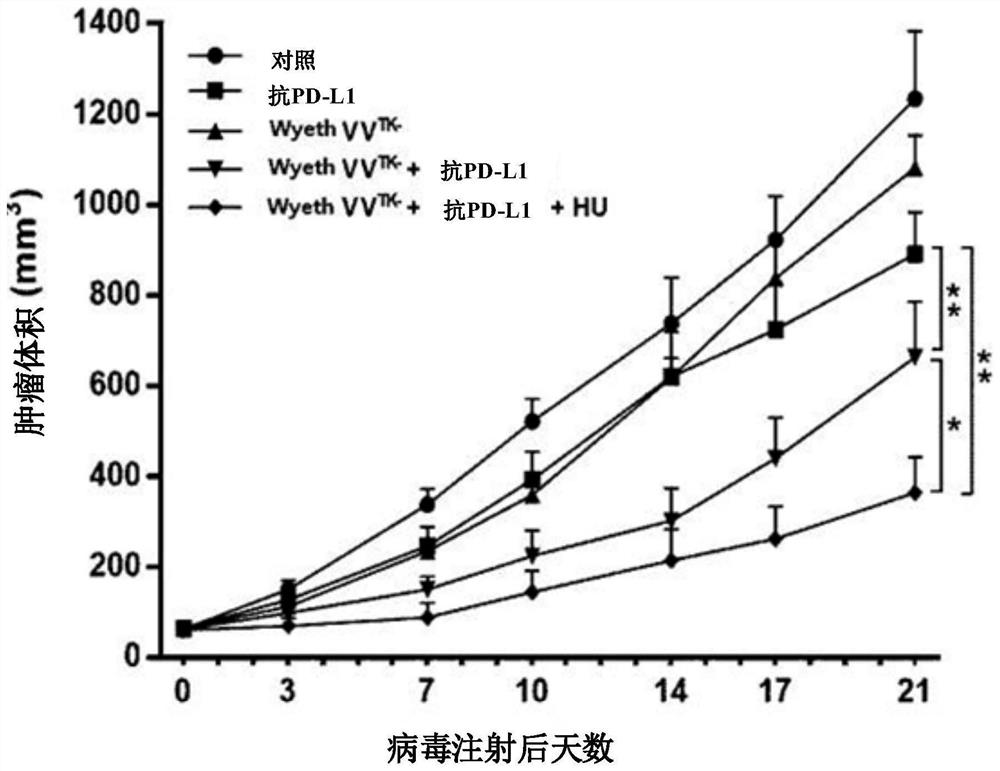
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for treating cancer comprising an anticancer virus, an immune checkpoint inhibitor and hydroxyurea as active ingredients. The pharmaceutical composition for treating cancer of the present invention, comprising an anticancer virus, an immune checkpoint inhibitor and hydroxyurea as active ingredients, has an excellent anticancer effect and safety as compared to a conventional case of single administration of an anticancer virus or combined administration of an anticancer virus and an immune checkpoint inhibitor. Accordingly, the pharmaceutical composition for treating cancer of the present invention, comprising an anticancer virus, an immune checkpoint inhibitor and hydroxyurea as active ingredients, may be effectively used in treating cancer.
Owner:BIONOXX INC
Fondcl1 gene deletion mutant of watermelon Fusarium wilt RNAi component and its construction method
The invention discloses a fusarium oxysporum f.sp.niveum RNAi component FonDCL1 gene deletion mutant and a construction method thereof. According to the fusarium oxysporum f.sp.niveum RNAi component FonDCL1 gene deletion mutant and the construction method thereof, according to a reported Dicer like 1 protein sequence, homologous alignment is conducted on a Fon genomic sequence to obtain a fusariumoxysporum f.sp.niveum FonDCL1 gene, by adopting a homologous gene substitution principle, by means of a Split-marker strategy, the target gene FonDCL1 is substituted for a hygromycin B (HPH) gene DNAfragment, and by constructing a homologous gene recombinant fragment, through genetic transformation of a wild strain Fon1, the FonDCL1 gene deletion mutant is obtained. The FonDCL1 mutant has the advantages that the virulence to watermelon seedlings is enhanced, and the FonDCL1 mutant is more sensitive to abiotic stress factors of monensin sodium salt, hydroxycarbamide, a fluorescent whitening agent CFW, Congo red (CR), hydrogen peroxide and the like, so that a research foundation is provided for functional assignment of small RNA generated in processes of self growth and development and watermelon infection of the Fon1.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Pharmaceutical composition for treating cancer comprising anti-cancer virus, immune checkpoint inhibitor and hydroxyurea as active ingredients
PendingCN114364390AEffective treatmentGood anticancer effectViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsAntibody ingredientsAnticarcinogenic EffectPharmaceutical drug
Owner:拜耳诺克斯有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com