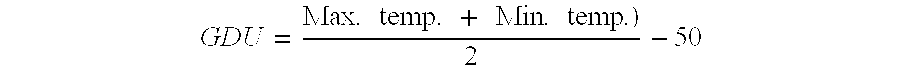Patents
Literature
684 results about "Genetically modified maize" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Genetically modified maize (corn) is a genetically modified crop. Specific maize strains have been genetically engineered to express agriculturally-desirable traits, including resistance to pests and to herbicides. Maize strains with both traits are now in use in multiple countries. GM maize has also caused controversy with respect to possible health effects, impact on other insects and impact on other plants via gene flow. One strain, called Starlink, was approved only for animal feed in the US, but was found in food, leading to a series of recalls starting in 2000.
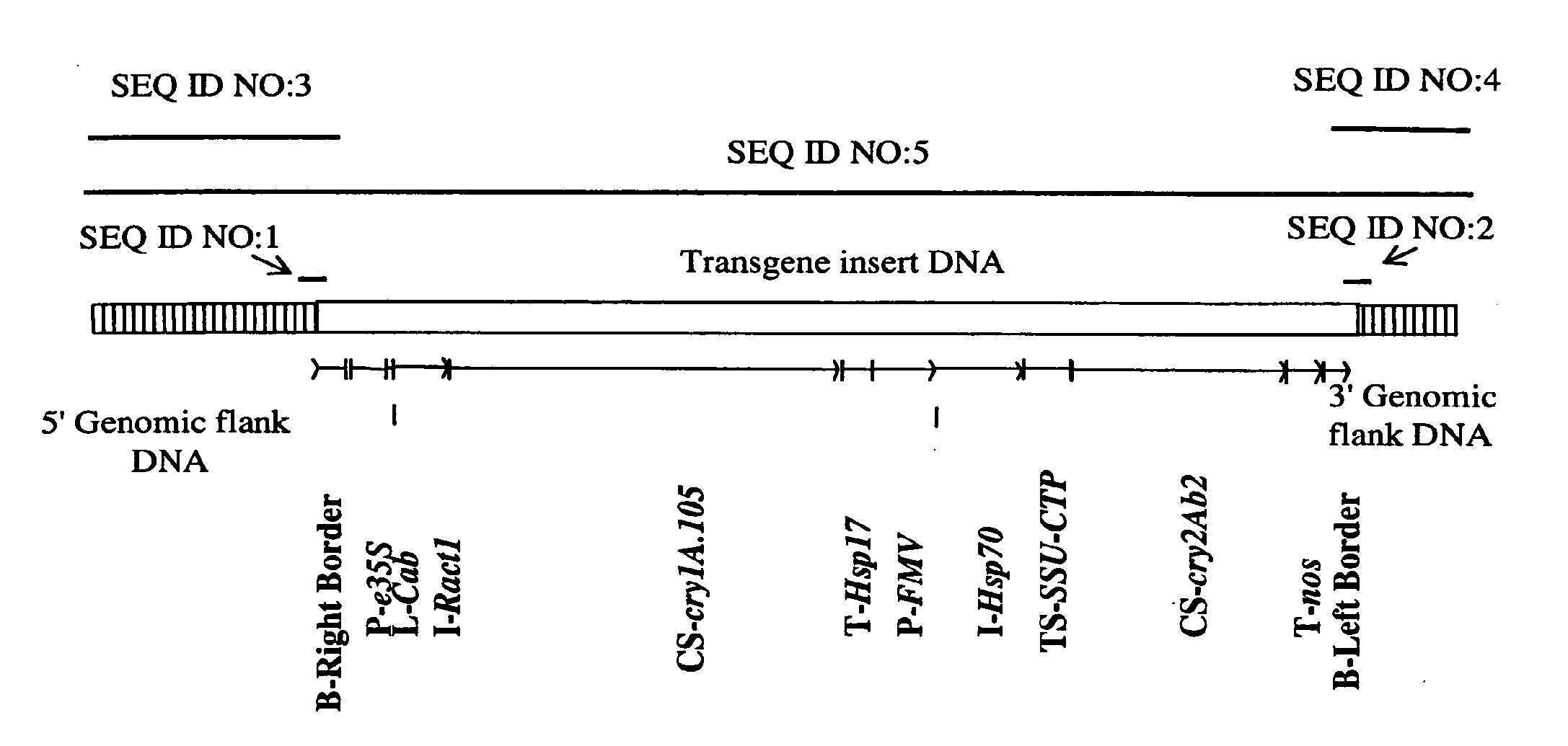
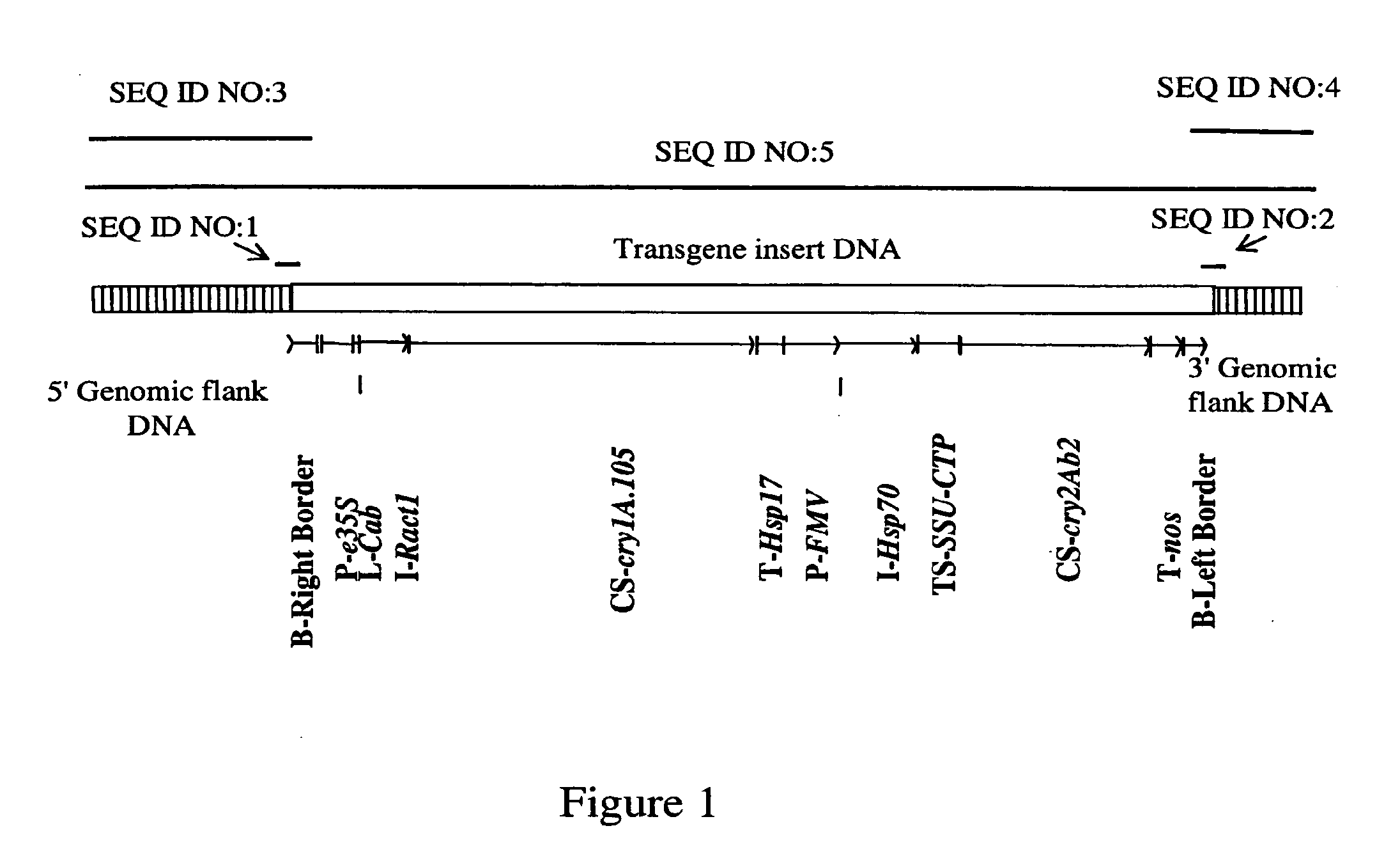
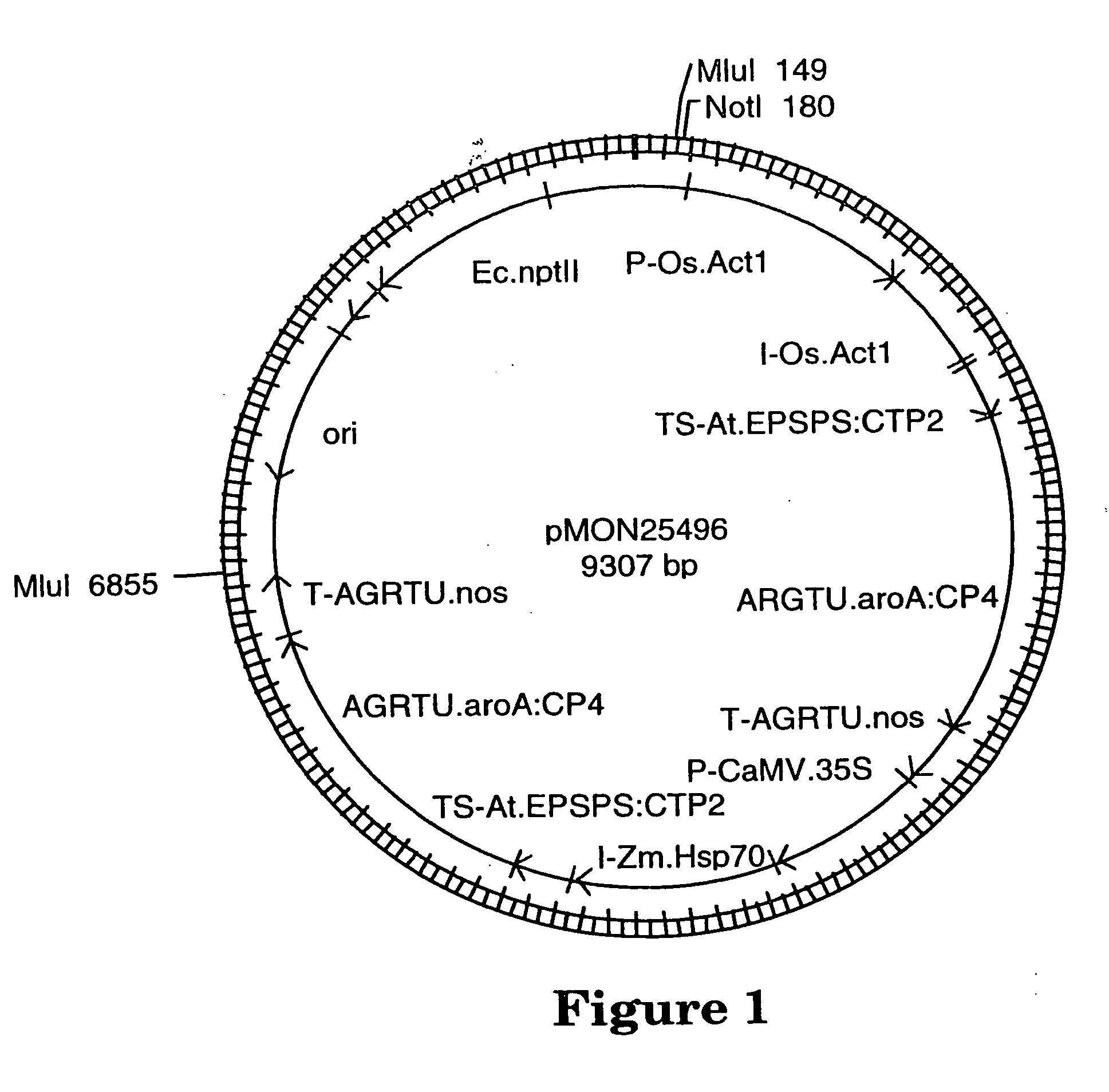
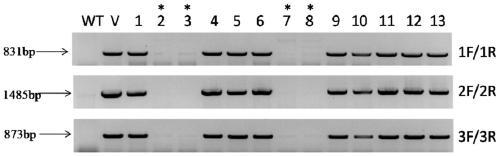
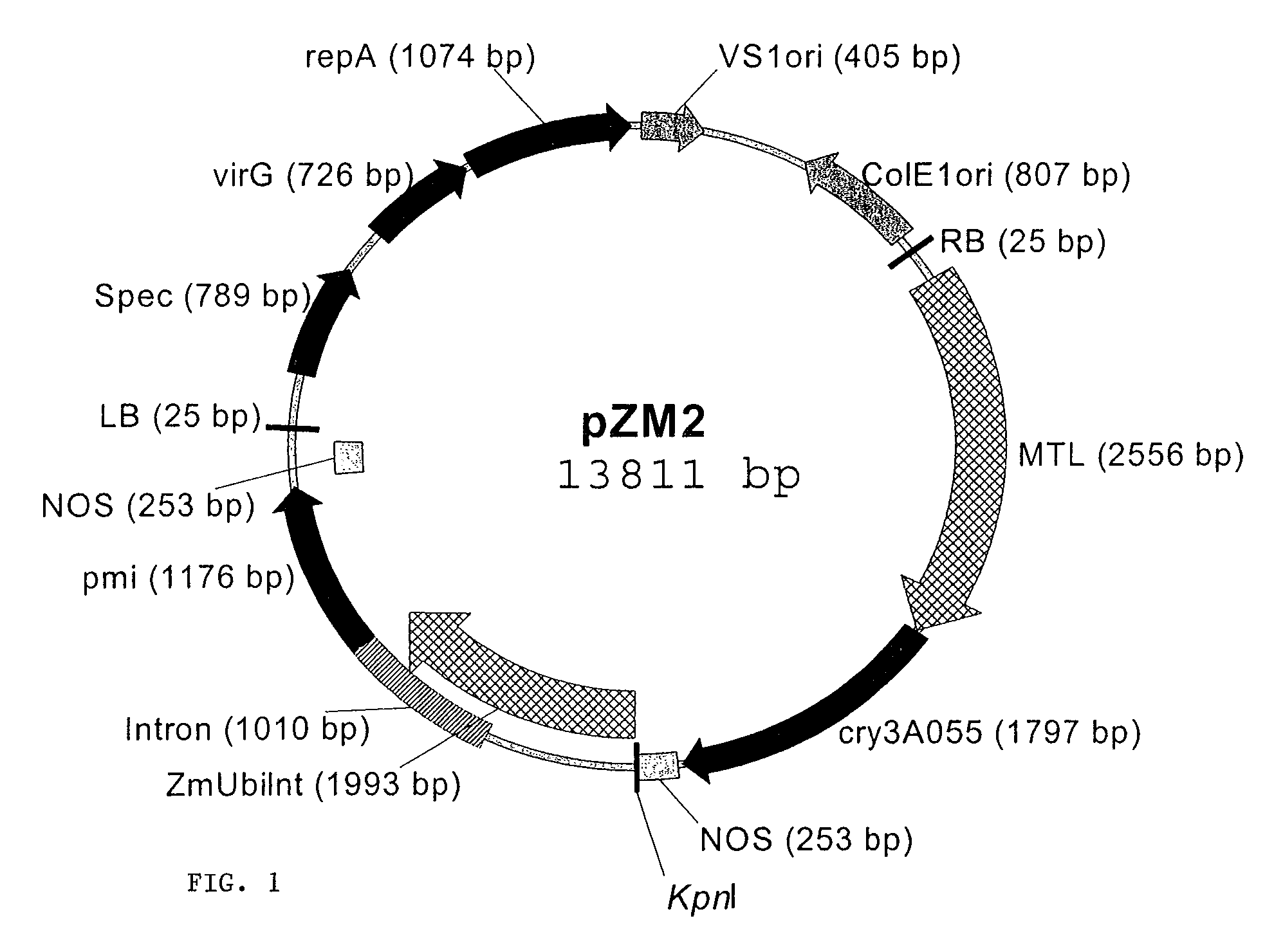
Corn Plant and Seed Corresponding to Transgenic Event MON89034 and Methods For Detection and Use Thereof
ActiveUS20080260932A1Microbiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The present invention provides a transgenic corn event MON89034, and cells, seeds, and plants comprising DNA diagnostic for the corn event. The invention also provides compositions comprising nucleotide sequences that are diagnostic for said corn event in a sample, methods for detecting the presence of said corn event nucleotide sequences in a sample, probes and primers for use in detecting nucleotide sequences that are diagnostic for the presence of said corn event in a sample, growing the seeds of such corn event into corn plants, and breeding to produce corn plants comprising DNA diagnostic for the corn event.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Expression of Fatty Acid Desaturases in Corn
ActiveUS20080260929A1High nutritional valueIncrease SDA contentBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsStearidonic acidGenetically modified maize
The invention relates generally to the expression of desaturase enzymes in transgenic corn plants and compositions derived therefrom. In particular, the invention relates to the production of oils with improved omega-3 fatty acid profiles in corn plants and the seed oils produced thereby. Such oils may contain stearidonic acid, which is not naturally found in corn plants and has been shown to have beneficial effects on health.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
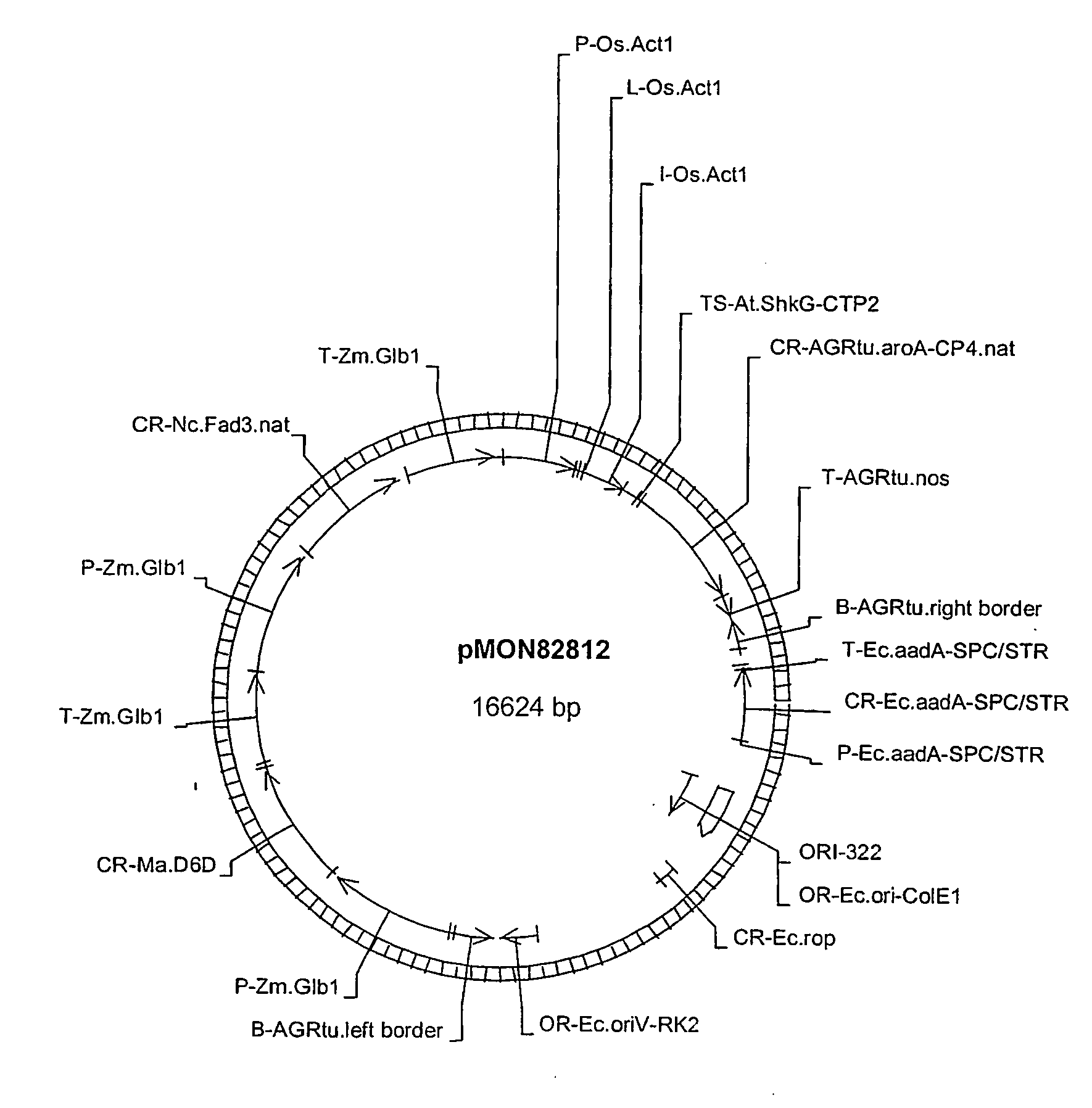
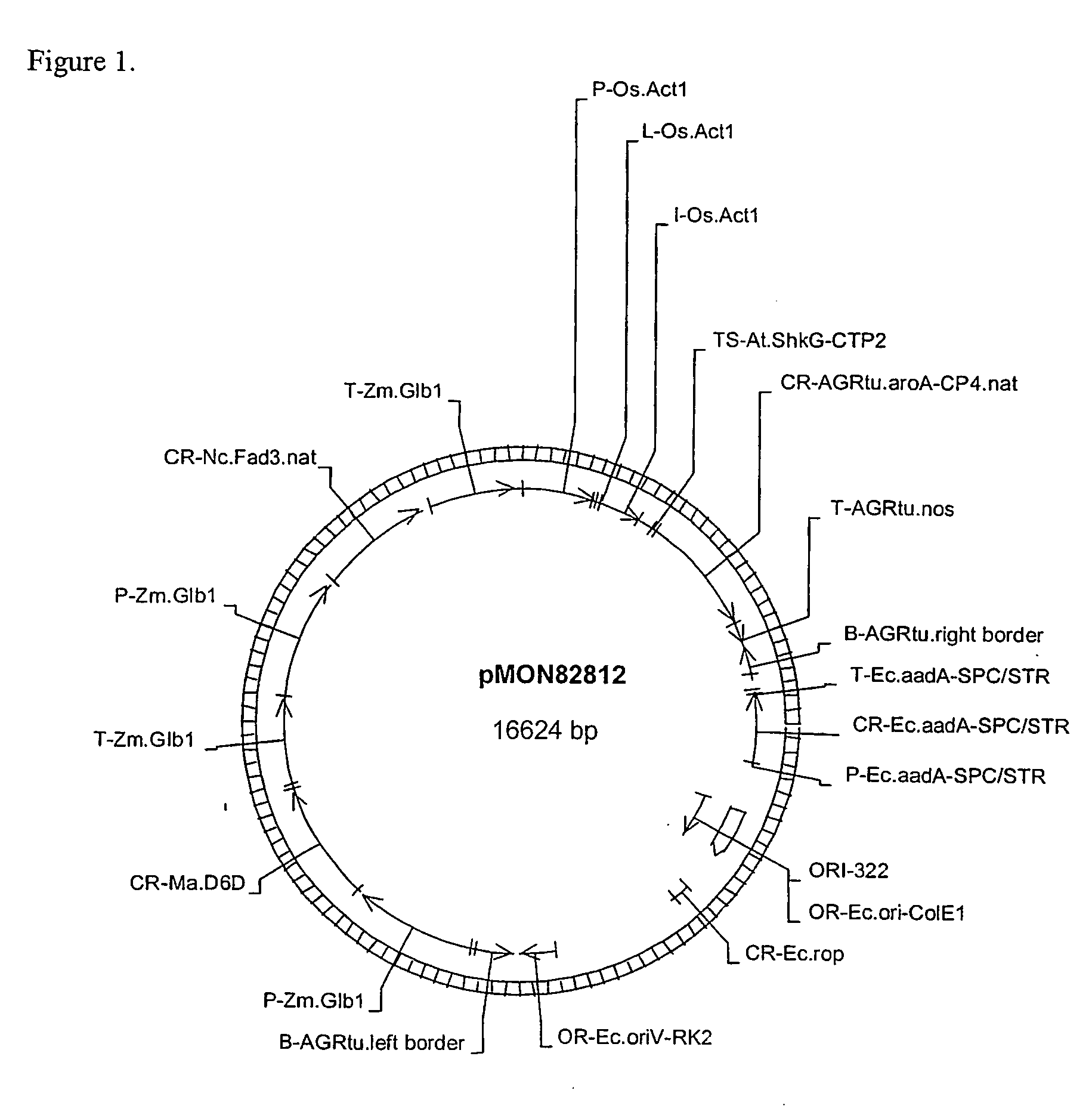
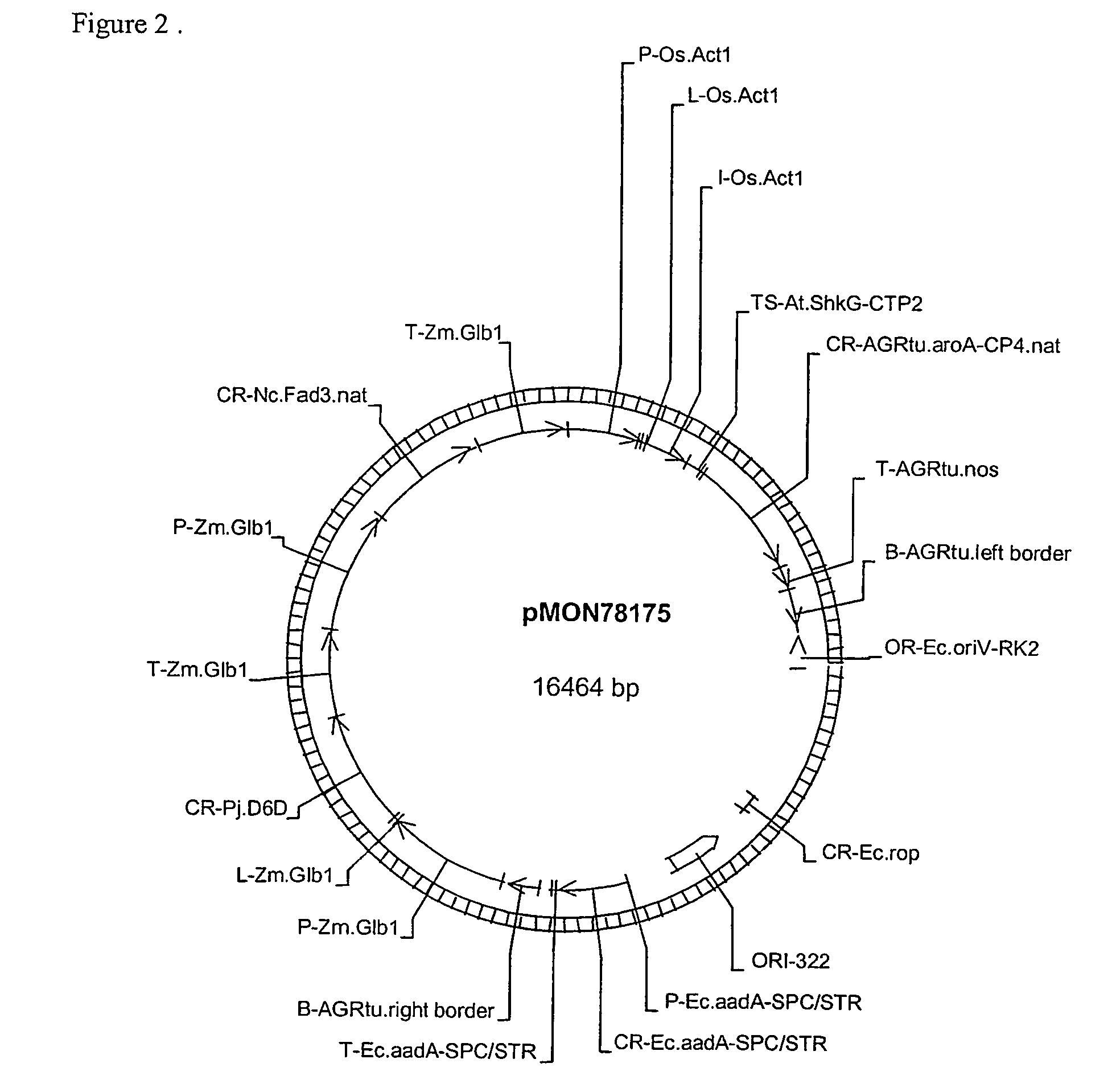
Corn event PV-ZMGT32(nk603) and compositions and methods for detection thereof
The present invention provides a DNA construct that confers tolerance to transgenic corn plant. Also provided are assays for detecting the presence of the PV-ZMGT32(nk603) corn event based on the DNA sequence of the recombinant construct inserted into the corn genome and of genomic sequences flanking the insertion site.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Inbred corn line BE9515
ActiveUS7411117B2BryophytesOther foreign material introduction processesGenetic MaterialsGenetically modified maize
An inbred corn line, designated BE9515, the plants and seeds of the inbred corn line BE9515, methods for producing a corn plant, either inbred or hybrid, produced by crossing the inbred corn line BE9515 with itself or with another corn plant, and hybrid corn seeds and plants produced by crossing the inbred line BE9515 with another corn line or plant and to methods for producing a corn plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic corn plants produced by that method. This invention also relates to inbred corn lines derived from inbred corn line BE9515, to methods for producing other inbred corn lines derived from inbred corn line BE9515 and to the inbred corn lines derived by the use of those methods.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
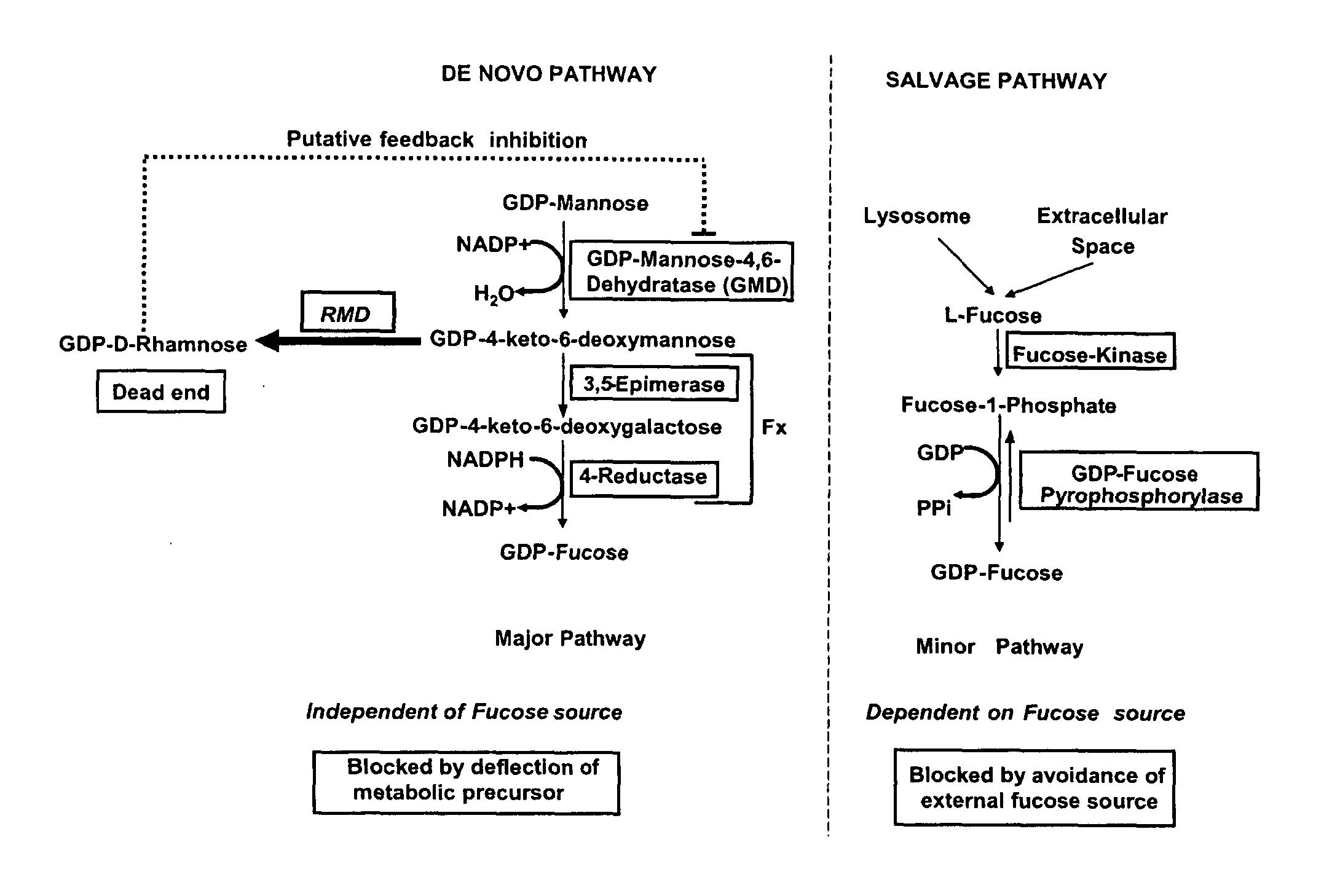
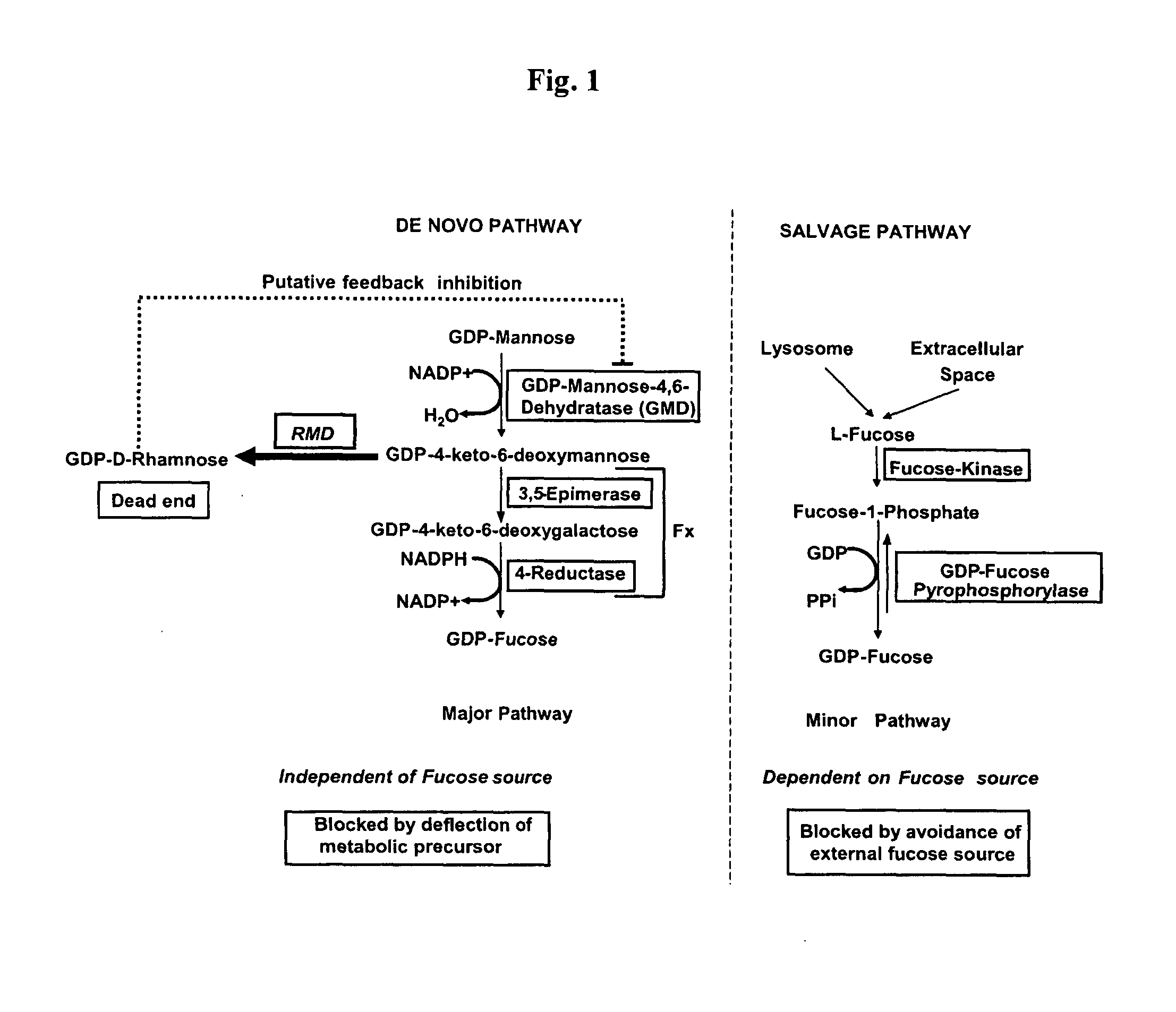
Aad-1 event das-40278-9, related transgenic corn lines, and event-specific identification thereof
ActiveUS20120214975A1Effectively block the fucose de novo pathwayReduce and eliminate allergic reactionImmunoglobulinsOxidoreductasesSugarGenetically modified maize
The present invention relates to cells for producing a molecule lacking fucose, having a reduced amount of fucose, or having other atypical sugars on its glycomoieties. It also relates to methods for producing a molecule lacking fucose, having a reduced amount of fucose, or having other atypical sugars on its glycomoieties using said cells and to molecules obtainable by said methods. The present invention further relates to molecules having an artificial glycosylation pattern.
Owner:PROBIOGEN AG
Inbred maize line PH4GP
InactiveUS6720487B1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationGenetic MaterialsGenetically modified maize
An inbred maize line, designated PH4GP, the plants and seeds of inbred maize line PH4GP, methods for producing a maize plant, either inbred or hybrid, produced by crossing the inbred maize line PH4GP with itself or with another maize plant, and hybrid maize seeds and plants produced by crossing the inbred line PH4GP with another maize line or plant and to methods for producing a maize plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic maize plants produced by that method. This invention also relates to inbred maize lines derived from inbred maize line PH4GP, to methods for producing other inbred maize lines derived from inbred maize line PH4GP and to the inbred maize lines derived by the use of those methods.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Hybrid maize 36K67
According to the invention, there is provided a hybrid maize plant, designated as 36K67, produced by crossing two Pioneer Hi-Bred International, Inc. proprietary inbred maize lines. This invention relates to the hybrid seed 36K67, the hybrid plant produced from the seed, and variants, mutants, and trivial modifications of hybrid 36K67. This invention also relates to methods for producing a maize plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic maize plants produced by those methods. This invention further relates to methods for producing maize lines derived from hybrid maize line 36K67 and to the maize lines derived by the use of those methods.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Transgenic corn plants having seeds with modified cornstarch characteristics and method of making the transgenic corn plants
InactiveUS7009092B1Pollution problemEasy to modifyOther foreign material introduction processesEnzymesAmyrisRetrogradation
Cornstarch characteristics can be changed by expressing a non-corn plant starch branching enzyme in a corn plant. In a preferred embodiment, transgenic corn plants containing the barley starch branching enzyme IIa transgene was generated. Some transgenic corn plants produced seeds containing cornstarch with lowered gelatinization temperature and retrogradation rate while others produced seeds containing cornstarch with higher retrogradation rate when compared to non-transgenic corn plants.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Inbred maize line PH705
InactiveUS7326833B1Vector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationGenetic MaterialsTransgene
An inbred maize line, designated PH705, the plants and seeds of inbred maize line PH705, methods for producing a maize plant, either inbred or hybrid, produced by crossing the inbred maize line PH705 with another maize plant, and hybrid maize seeds and plants produced by crossing the inbred line PH705 with another maize line or plant and to methods for producing a maize plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic maize plants produced by that method. This invention also relates to inbred maize lines derived from inbred maize line PH705, to methods for producing other inbred maize lines derived from inbred maize line PH705 and to the inbred maize lines derived by the use of those methods.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Corn plant and seed corresponding to transgenic event MON89034 and methods for detection and use thereof
The present invention provides a transgenic corn event MON89034, and cells, seeds, and plants comprising DNA diagnostic for the corn event. The invention also provides compositions comprising nucleotide sequences that are diagnostic for said corn event in a sample, methods for detecting the presence of said corn event nucleotide sequences in a sample, probes and primers for use in detecting nucleotide sequences that are diagnostic for the presence of said corn event in a sample, growing the seeds of such corn event into corn plants, and breeding to produce corn plants comprising DNA diagnostic for the corn event.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Hybrid maize plant and seed 32B33
According to the invention, there is provided a hybrid maize plant, designated as 32B33, produced by crossing two Pioneer Hi-Bred International, Inc. proprietary inbred maize lines. This invention relates to the hybrid seed 32B33, the hybrid plant produced from the seed, and variants, mutants, and trivial modifications of hybrid 32B33. This invention also relates to methods for producing a maize plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic maize plants produced by those methods. This invention further relates to methods for producing maize lines derived from hybrid maize line 32B33 and to the maize lines derived by the use of those methods.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Inbred corn line LLD19BM
ActiveUS7820889B1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationGenetic MaterialsGenetically modified maize
An inbred corn line, designated LLD19BM, the plants and seeds of the inbred corn line LLD19BM, methods for producing a corn plant, either inbred or hybrid, produced by crossing the inbred corn line LLD19BM with itself or with another corn plant, and hybrid corn seeds and plants produced by crossing the inbred line LLD19BM with another corn line or plant and to methods for producing a corn plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic corn plants produced by that method. This invention also relates to inbred corn lines derived from inbred corn line LLD19BM, to methods for producing other inbred corn lines derived from inbred corn line LLD19BM and to the inbred corn lines derived by the use of those methods.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
Methods for transforming immature maize embryos
InactiveUS7057089B2Promote embryogenic-tissue formationSmall sizeStable introduction of DNAFermentationEmbryogenesisGenetically modified maize
Methods are provided for transforming freshly isolated, immature maize embryos and for producing transgenic maize plants. The methods comprise obtaining immature embryos from a maize plant, contacting the embryos with an auxin-depleted or phytohormone-depleted transformation support medium and introducing a nucleotide construct into cells from the embryos prior to subjecting the embryos to conditions which promote embryogenic-tissue formation. The methods additionally comprise identifying or selecting transformed cells and regenerating such cells into transformed maize plants.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
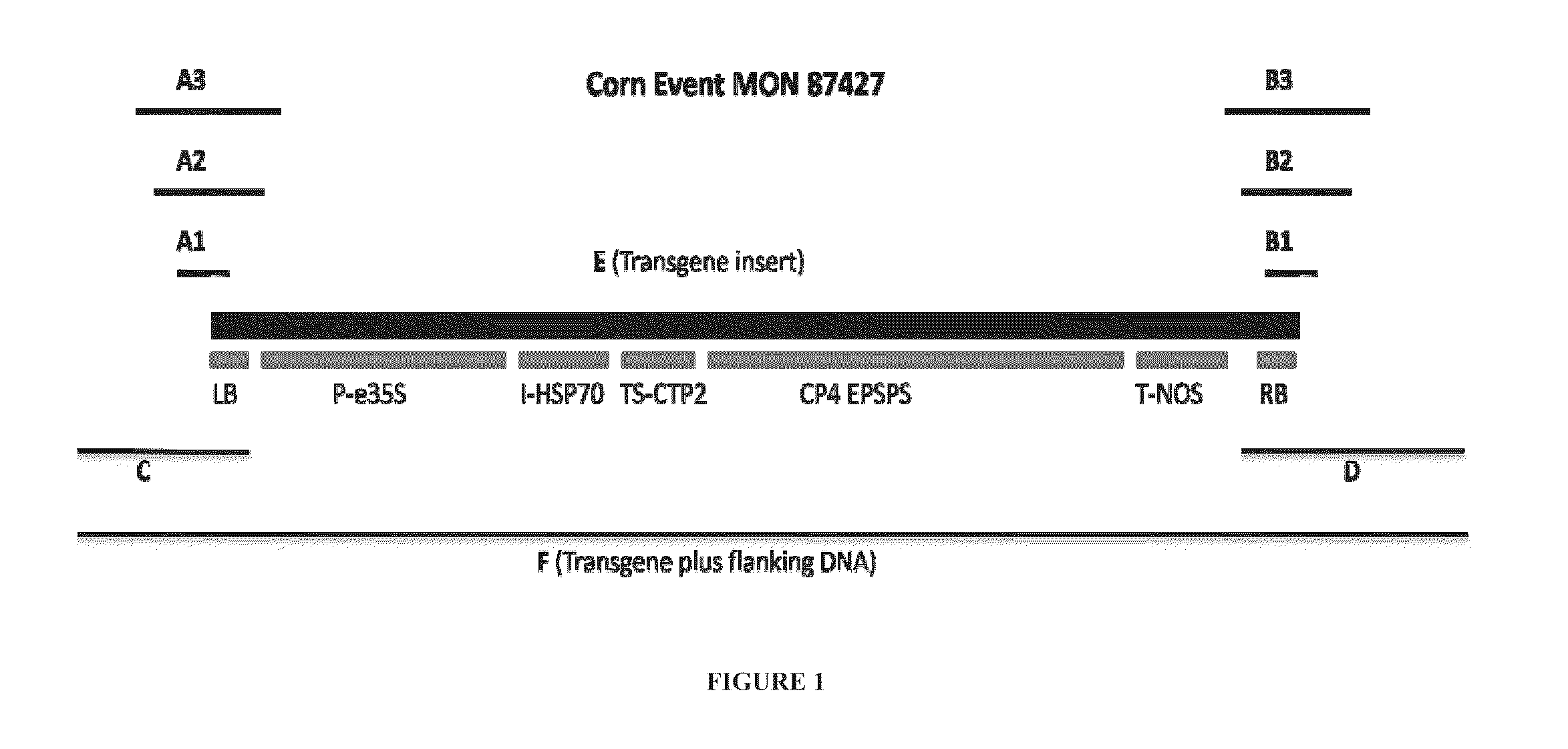
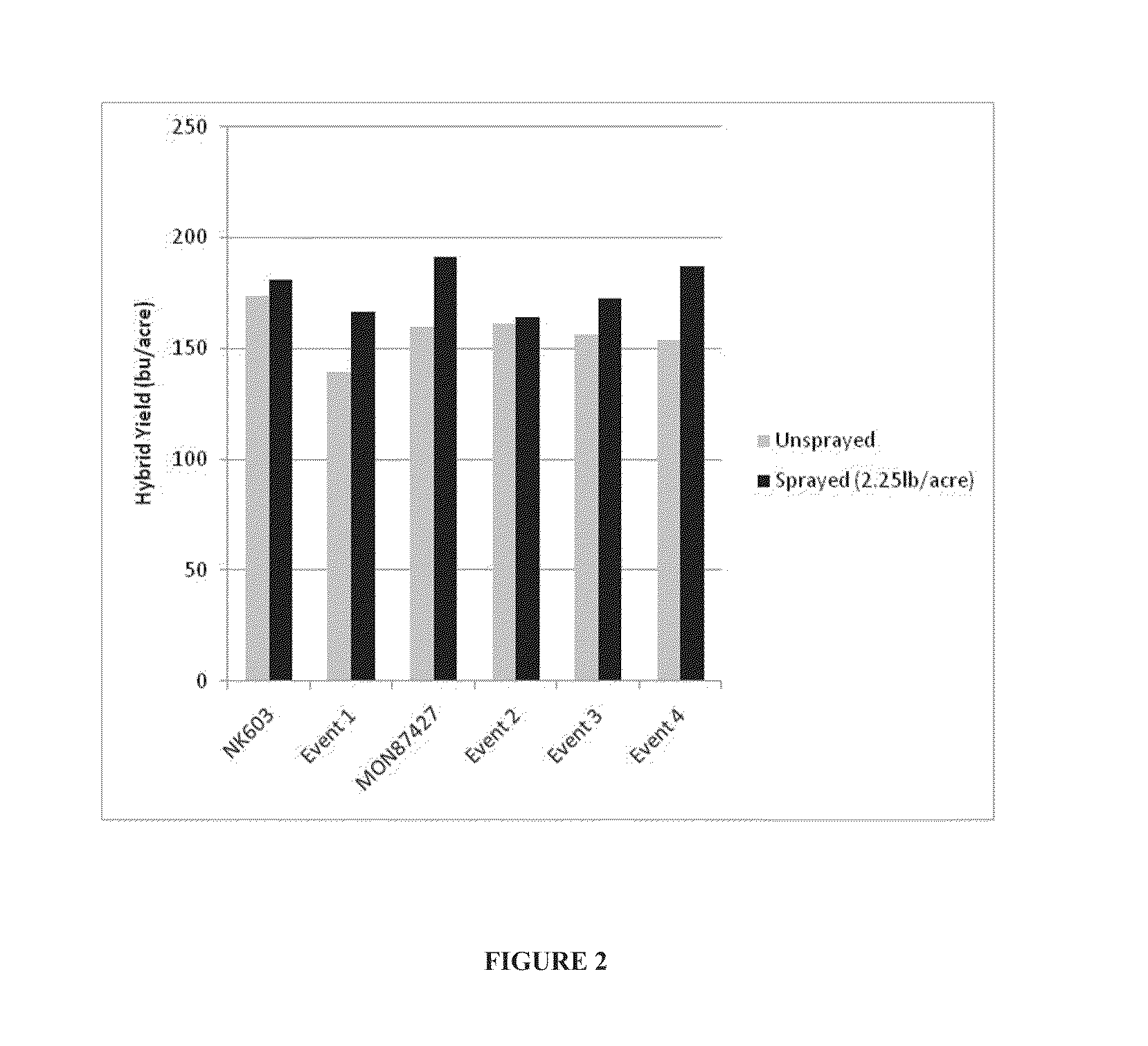
Transgenic maize event MON 87427 and the relative development scale
The invention provides transgenic maize event MON 87427 and plants, plant cells, seeds, plant parts, and commodity products derived from event MON 87427. The invention also provides nucleotides specific for transgenic maize event MON 87427 and plants, plant cells, seeds, plant parts, and commodity products comprising nucleotides specific for transgenic maize event MON 87427. The invention also provides methods related to transgenic maize event MON 87427 and to the Roundup® Hybridization System (RHS). The invention also provides a Relative Development Scale useful for monitoring and determining reproductive development in maize that reconciles developmental differences across various maize varieties. This is useful for determining the optimal timing of a treatment regimen in which tassel development stage is an important factor, including various methods in making hybrid seed.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Inbred maize line PH4GP
InactiveUS7169984B1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationGenetic MaterialsTransgene
An inbred maize line, designated PH4GP, the plants and seeds of inbred maize line PH4GP, methods for producing a maize plant, either inbred or hybrid, produced by crossing the inbred maize line PH4GP with itself or with another maize plant, and hybrid maize seeds and plants produced by crossing the inbred line PH4GP with another maize line or plant and to methods for producing a maize plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic maize plants produced by that method. This invention also relates to inbred maize lines derived from inbred maize line PH4GP, to methods for producing other inbred maize lines derived from inbred maize line PH4GP and to the inbred maize lines derived by the use of those methods.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Inbred maize line PH705
ActiveUS6903254B1Excellent plant healthOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationGenetic MaterialsTransgene
An inbred maize line, designated PH705, the plants and seeds of inbred maize line PH705, methods for producing a maize plant, either inbred or hybrid, produced by crossing the inbred maize line PH705 with another maize plant, and hybrid maize seeds and plants produced by crossing the inbred line PH705 with another maize line or plant and to methods for producing a maize plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic maize plants produced by that method. This invention also relates to inbred maize lines derived from inbred maize line PH705, to methods for producing other inbred maize lines derived from inbred maize line PH705 and to the inbred maize lines derived by the use of those methods.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Hybrid maize plant and seed 38H67
According to the invention, there is provided a hybrid maize plant, designated as 38H67, produced by crossing two Pioneer Hi-Bred International, Inc. proprietary inbred maize lines. This invention relates to the hybrid seed 38H67, the hybrid plant produced from the seed, and variants, mutants, and trivial modifications of hybrid 38H67. This invention also relates to methods for producing a maize plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic maize plants produced by those methods. This invention further relates to methods for producing maize lines derived from hybrid maize line 38H67 and to the maize lines derived by the use of those methods.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
A Novel Culture Method for Corn Transformation
InactiveUS20040210958A1Stable and efficient transformationOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationPlant hormoneGenetically modified maize
The present invention relates to a novel culture system for generating transformed corn plants from mature seeds. In particular, the invention relates to the use of plant hormones during germination to affect the culture response. Transgenic corn plants can then be easily produced.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Method of developing corn dwarfing material via gene editing
PendingCN110128518AImportant breeding valuePlant peptidesFermentationGenome editingDNA fragmentation
The invention provides a method of developing a corn dwarfing material via gene editing. The method comprises designing, for target gene ZmGA20ox3 / ZmGA20ox5 of corn, a sgRNA based on CRISPR / Cas9, connecting a fragment having sgRNA-coding DNA to a Cas-carrying carrier, and converting the corn with the constructed carrier to achieve site-directed mutagenesis of the gene ZmGA20ox3 / ZmGA20ox5 so as toobtain a transgenic corn plant with corresponding gene function deficiency. The biological functionality of the corn gene ZmGA20ox3 / ZmGA20ox5 is disclosed herein for the first time; the corn gene ZmGA20ox3 / ZmGA20ox5 is edited through CRISPR / Cas9 technology; a mutant material with no transgenic gene insert fragment is acquired through further screening; the corn dwarfing material has important breeding value.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Zea mays (L.) with capability of long term, highly efficient plant regeneration including fertile transgenic maize plants having a heterologous gene, and their preparation
InactiveUS6284945B1Careful shakingPromote shakingTransferasesPlant tissue cultureHeterologousCallithamnion granulatum
Protoplasts which regenerate reproducibly in a short time to normal, fertile plants can be regenerated from an auxin-autotrophic genotype of Zea mays (L.). Starting from immature embryos on hormone-free media, an auxin-autotrophic, embryogenic callus is formed on the shoot basis of the seedlings, which callus retains its embryogenic potential over a substantial period of time when subcultured on hormone-free medium. In addition to fully-developed embryos, adventitious embryos are also formed under suitable culture conditions (6-9% of sucrose in the medium). When the sucrose content is reduced to 2-3% and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid is added, soft, granular calli are formed which consist of embryogenic cell aggregates (type II callus). After subculturing the type II callus in the form of a cell suspension culture, totipotent protoplasts can be isolated. From these protoplasts, the maize plants according to the invention are regenerated.
Owner:BAYER CROPSCIENCE AG
Inbred maize line PH6WA
InactiveUS6846976B1Excellent plant healthOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationGenetic MaterialsGenetically modified maize
An inbred maize line, designated PH6WA, the plants and seeds of inbred maize line PH6WA, methods for producing a maize plant, either inbred or hybrid, produced by crossing the inbred maize line PH6WA with another maize plant, and hybrid maize seeds and plants produced by crossing the inbred line PH6WA with another maize line or plant and to methods for producing a maize plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic maize plants produced by that method. This invention also relates to inbred maize lines derived from inbred maize line PH6WA, to methods for producing other inbred maize lines derived from inbred maize line PH6WA and to the inbred maize lines derived by the use of those methods.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Inbred corn line BS112
ActiveUS7790967B2Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationGenetic MaterialsGenetically modified maize
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Hybrid maize 33F36
ActiveUS7041886B2Good for healthPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsHybrid seedGenetic Materials
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Inbred maize line PH51H
InactiveUS7259302B1Excellent plant healthVector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationGenetic MaterialsTransgene
An inbred maize line, designated PH51H, the plants and seeds of inbred maize line PH51H, methods for producing a maize plant, either inbred or hybrid, produced by crossing the inbred maize line PH51H with itself or with another maize plant, and hybrid maize seeds and plants produced by crossing the inbred line PH51H with another maize line or plant and to methods for producing a maize plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic maize plants produced by that method. This invention also relates to inbred maize lines derived from inbred maize line PH51H, to methods for producing other inbred maize lines derived from inbred maize line PH51H and to the inbred maize lines derived by the use of those methods.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Hybrid maize 38W21
ActiveUS7112729B2High yieldWeight optimizationPlant genotype modificationPlant cellsHybrid seedGenetic Materials
According to the invention, there is provided a hybrid maize plant, designated as 38W21, produced by crossing two Pioneer Hi-Bred International, Inc. proprietary inbred maize lines. This invention relates to the hybrid seed 38W21, the hybrid plant produced from the seed, and variants, mutants, and trivial modifications of hybrid 38W21. This invention also relates to methods for producing a maize plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic maize plants produced by those methods. This invention further relates to methods for producing maize lines derived from hybrid maize line 38W21 and to the maize lines derived by the use of those methods.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Method of reducing insect resistant pests in transgenic crops
The present invention discloses Resistance Management (RM) practices that are critical to safeguard Bacillus thuringiensis as a natural resource and sustain genetically modified corn expressing Bt toxins as a suitable method for ECB and WCRW management. A useful tool in developing RM strategies is to develop laboratory selected colonies that exhibit high levels of resistance to a particular toxin. The availability of selected strains allows determination of the genetic expression of resistance (i.e., dominant vs. recessive, autosomal vs. sex-linked) and whether or not the resistance mechanism is specific for a given toxin. In addition, the availability of resistant strains will allow estimation of the particular resistance allele frequency in the field, and provides a tool to identify the biochemical and physiological basis of resistance and a means to develop molecular probes to monitor the evolution of resistance in the field.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Corn event MIR604
A novel transgenic corn event designated MIR604, is disclosed. The invention relates to DNA sequences of the recombinant constructs inserted into the corn genome and of genomic sequences flanking the insertion site that resulted in the MIR604 event. The invention further relates to assays for detecting the presence of the DNA sequences of MIR604, to corn plants and corn seeds comprising the genotype of MIR604 and to methods for producing a corn plant by crossing a corn plant comprising the MIR604 genotype with itself or another corn variety.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Corn with transgenic insect protection traits utilized in combination with drought tolerance and/or reduced inputs particularly fertilizer
InactiveUS20090300980A1Effective absorptionClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsGenetically modified insectPotassium
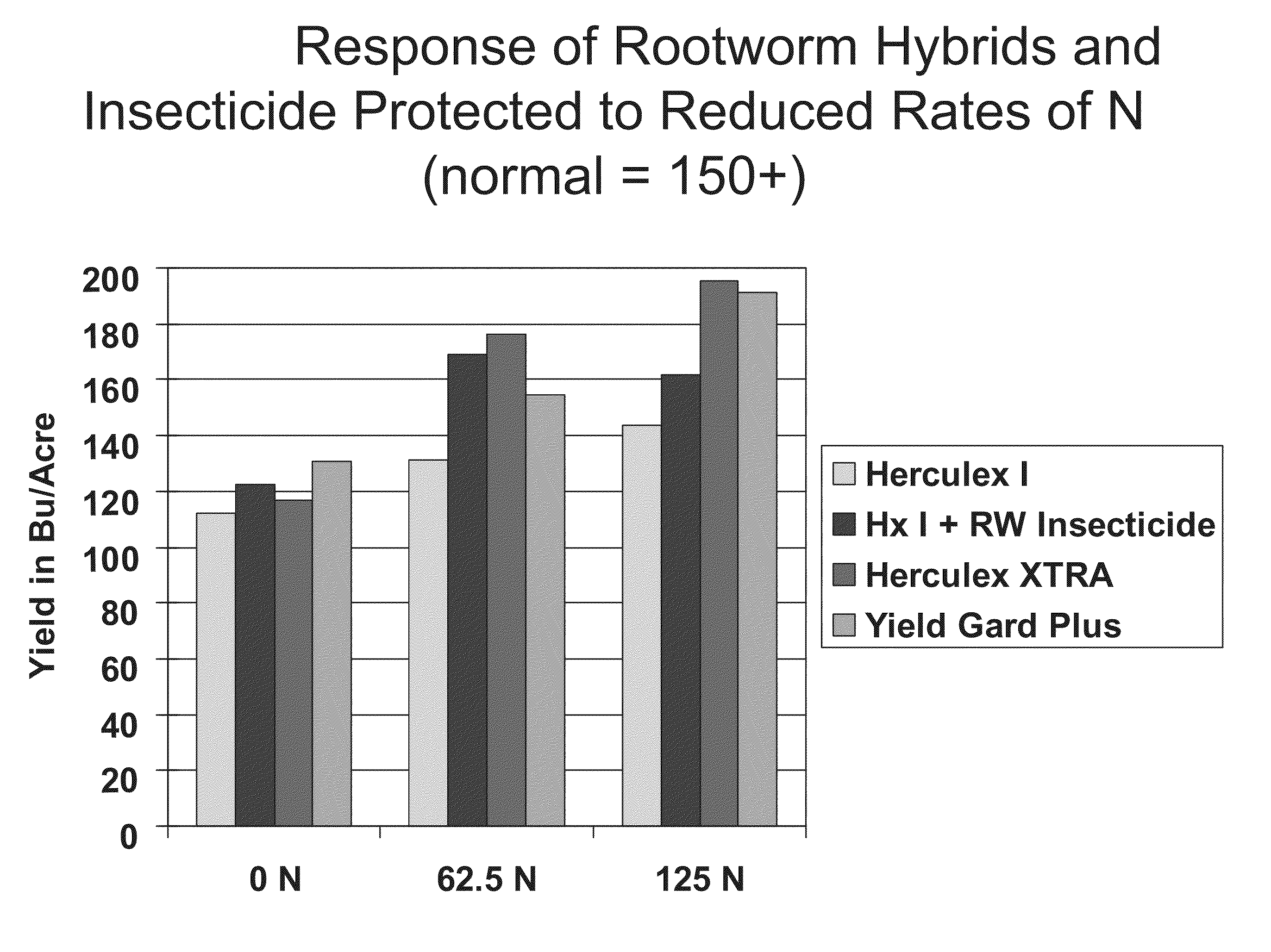
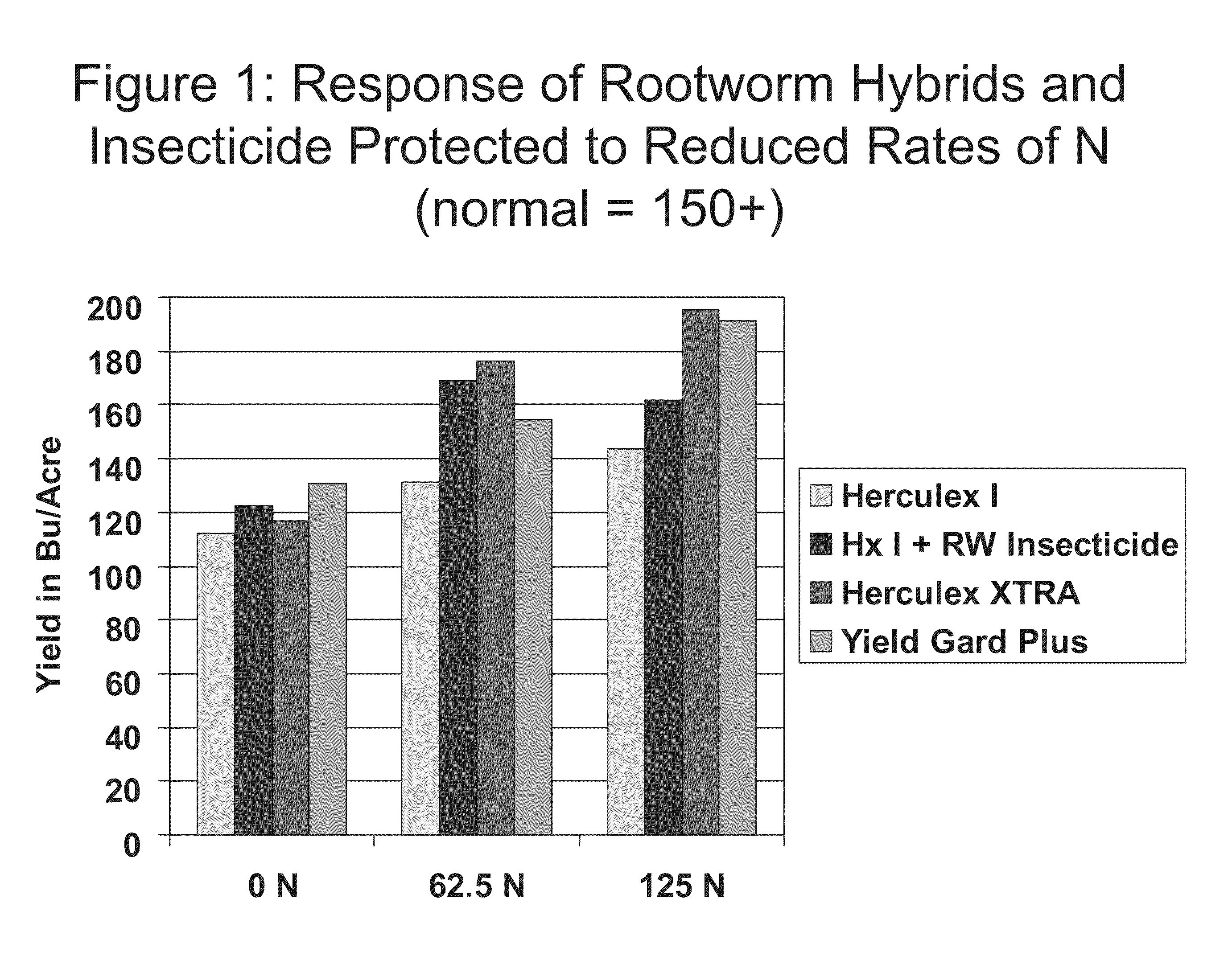
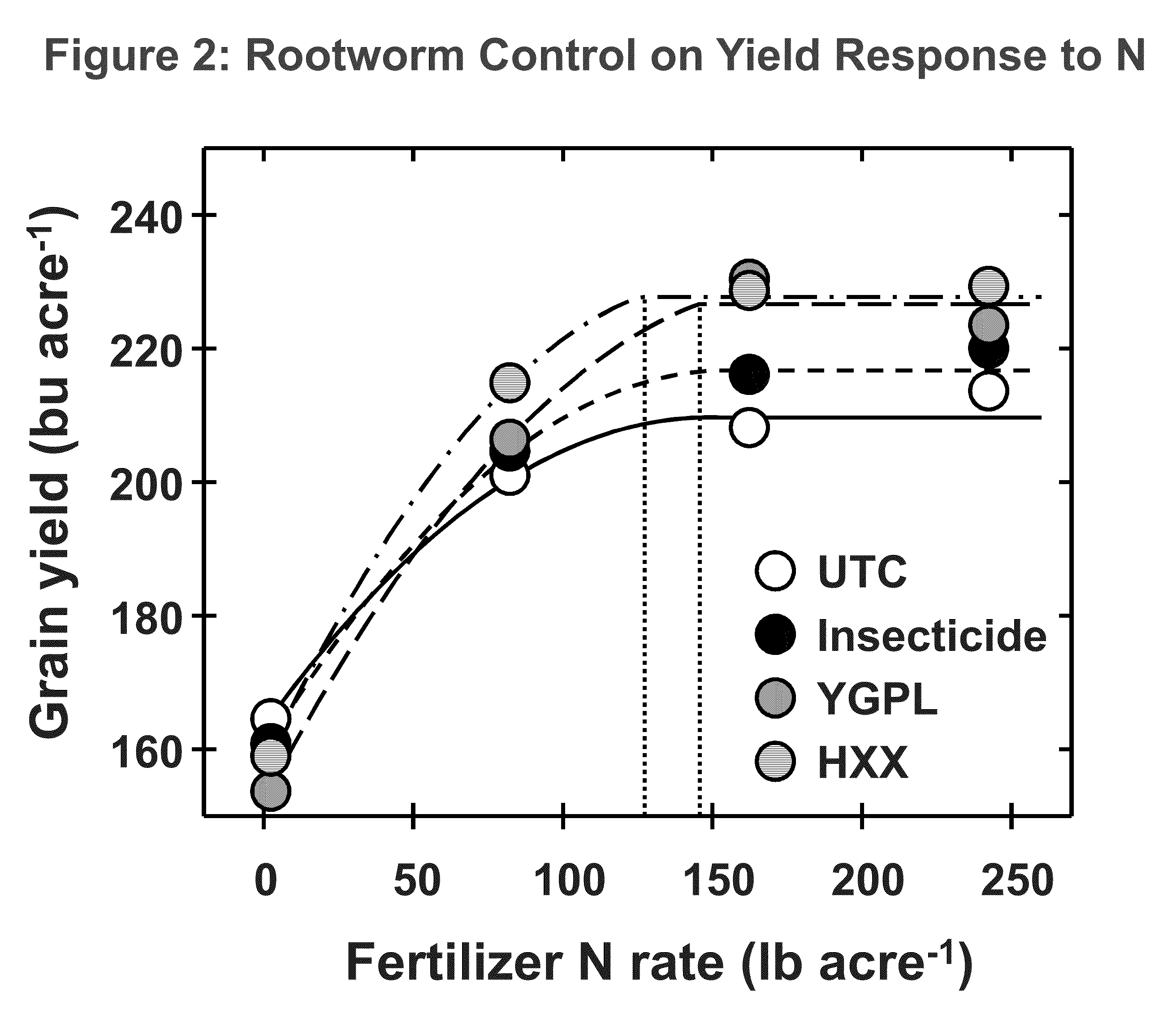
The subject invention relates in part to the use of insect-protected corn to modify fertility recommendations for given yield targets on any transgenic corn type. The insect-protected plants are unexpectedly more effective at assimilating not only nitrogen but also less valuable nutrients such as phosphorous, potassium and micronutrients such as zinc. The subject invention also relates to the discovery that transgenic corn plants with insect protection traits exhibit drought tolerance. For example, the protected plants are also much more effective at extracting moisture and are therefore more drought resistant and require less supplemental irrigation to produce the same yields as unprotected plants.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
Inbred maize line PH5WB
InactiveUS7173174B1Excellent plant healthOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationGenetic MaterialsTransgene
An inbred maize line, designated PH5WB, the plants and seeds of inbred maize line PH5WB, methods for producing a maize plant, either inbred or hybrid, produced by crossing the inbred maize line PH5WB with itself or with another maize plant, and hybrid maize seeds and plants produced by crossing the inbred line PH5WB with another maize line or plant and to methods for producing a maize plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic maize plants produced by that method. This invention also relates to inbred maize lines derived from inbred maize line PH5WB, to methods for producing other inbred maize lines derived from inbred maize line PH5WB and to the inbred maize lines derived by the use of those methods.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Hybrid maize plant and seed 34H31
InactiveUS6897360B1Improve performanceImprove drought toleranceOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationHybrid seedGenetic Materials
According to the invention, there is provided a hybrid maize plant, designated as 34H31, produced by crossing two Pioneer Hi-Bred International, Inc. proprietary inbred maize lines. This invention relates to the hybrid seed 34H31, the hybrid plant produced from the seed, and variants, mutants, and trivial modifications of hybrid 34H31. This invention also relates to methods for producing a maize plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic maize plants produced by that method. This invention further relates to methods for producing maize lines derived from hybrid maize line 34H31 and to the maize lines derived by the use of those methods.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com