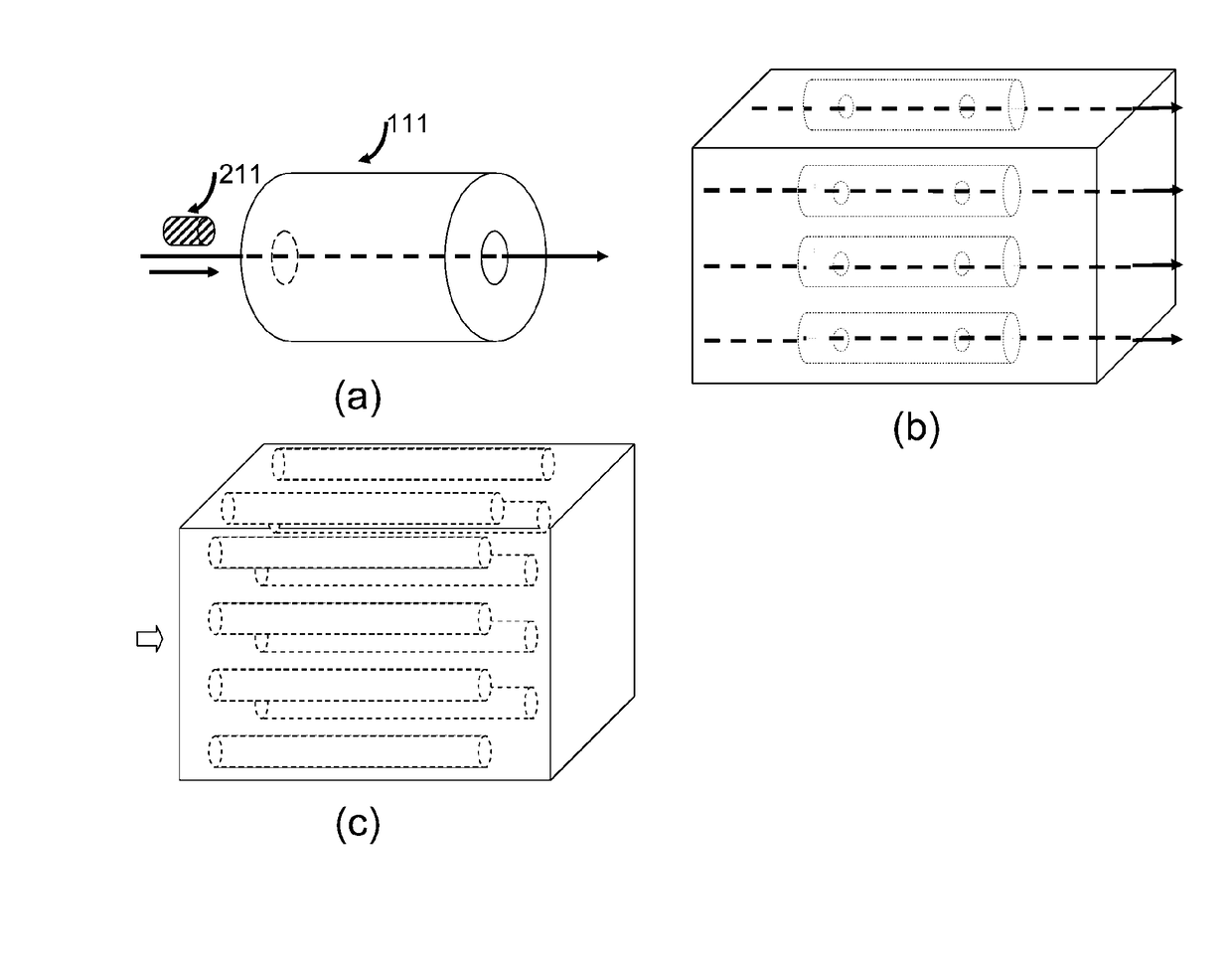
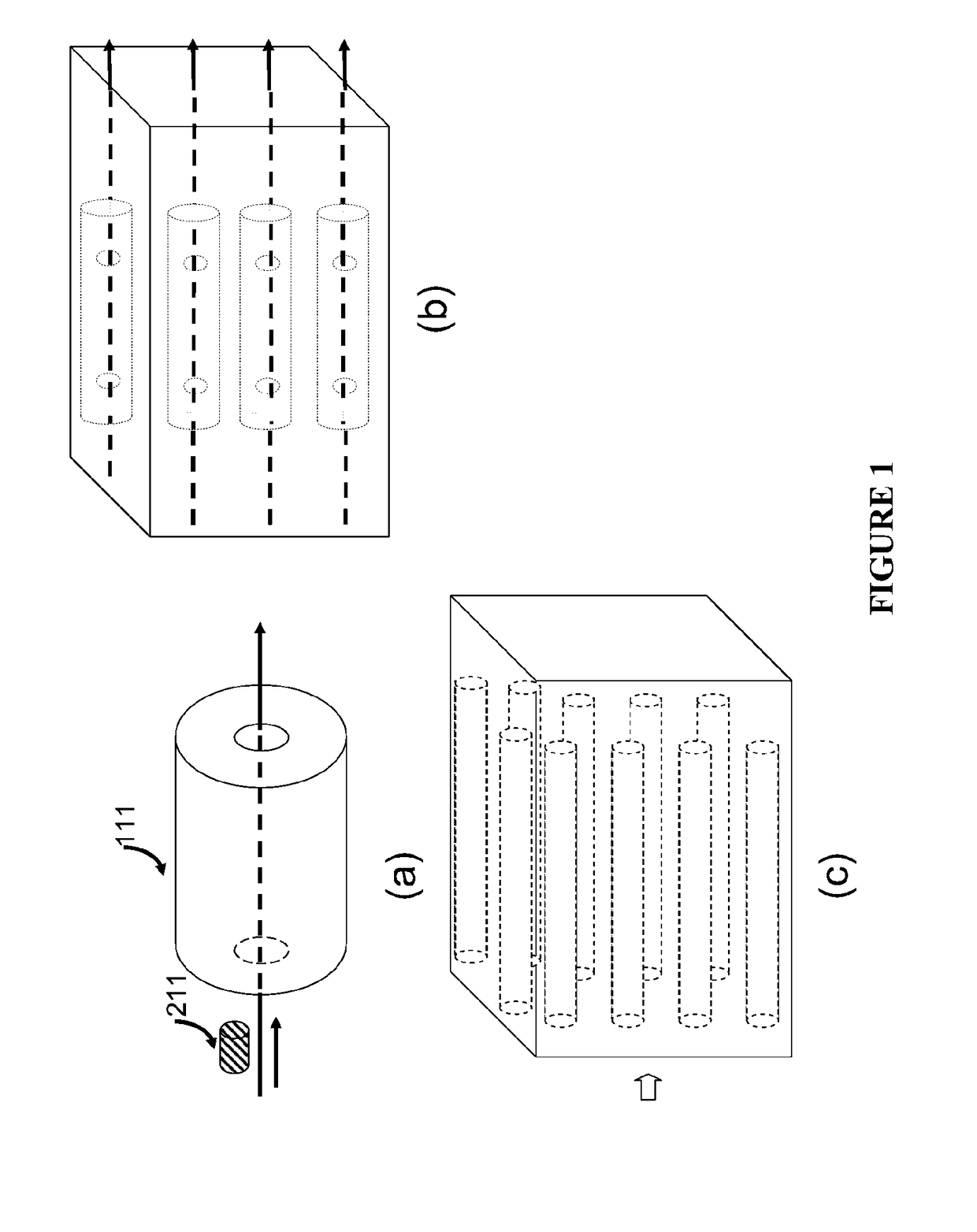
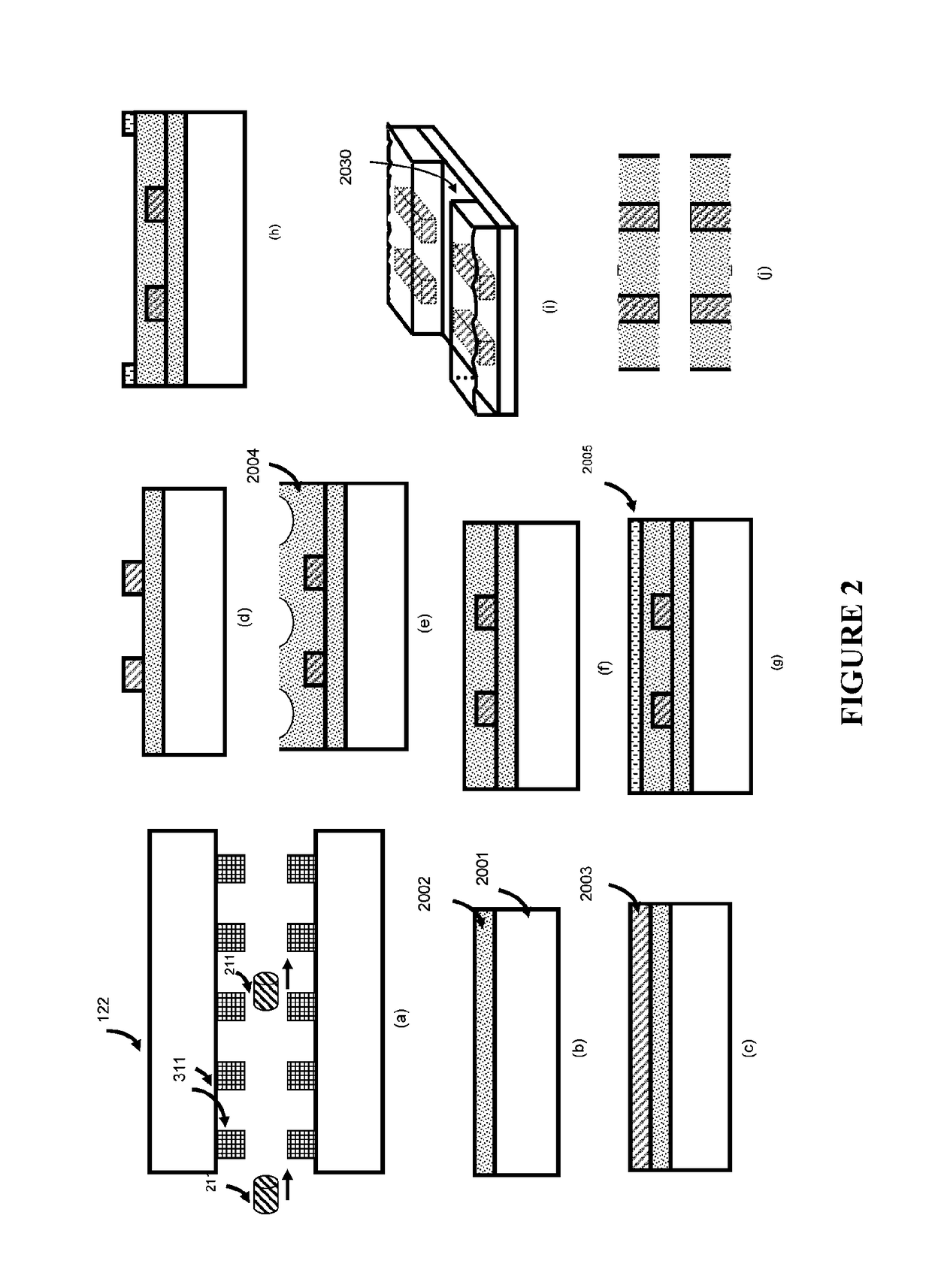
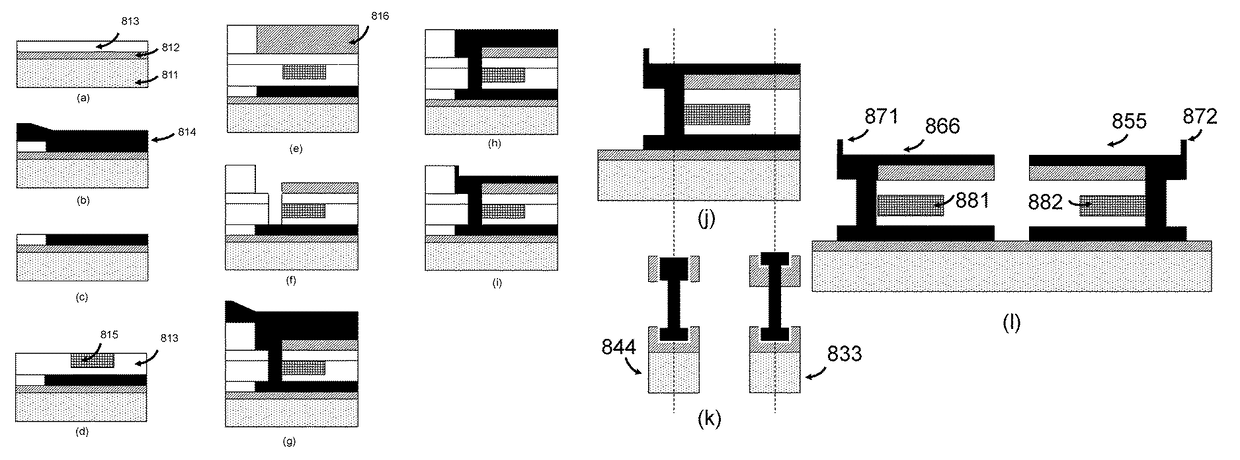
Patents
Literature
88 results about "Microscopic level" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Is an investigative method whereby every variable and condition is examined to the finest detail at the smallest recognizable unit of analysis. MICROSCOPIC LEVEL: "Examining data on a microscopic level will detail its molecular and anatomical makeup.".
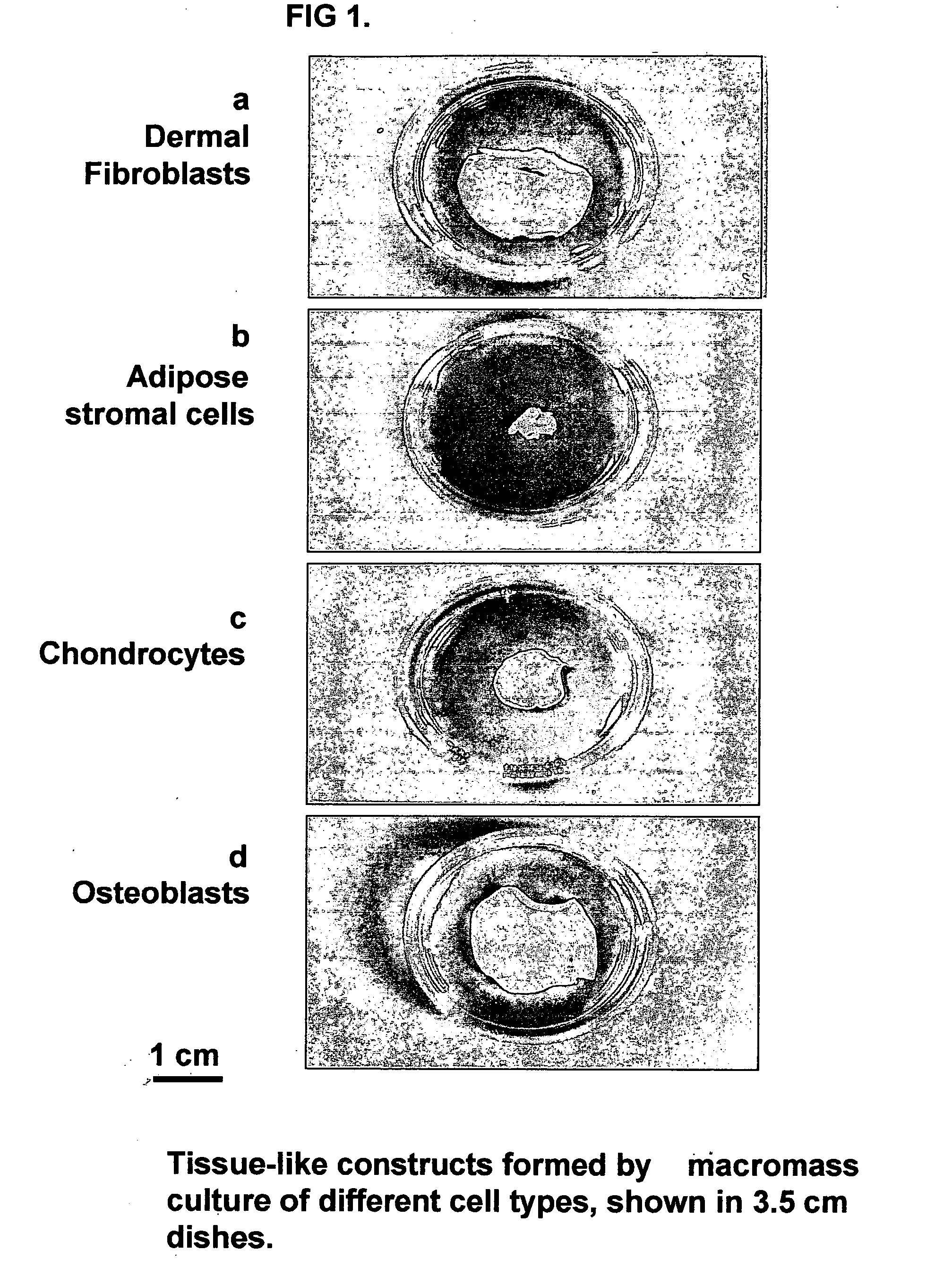
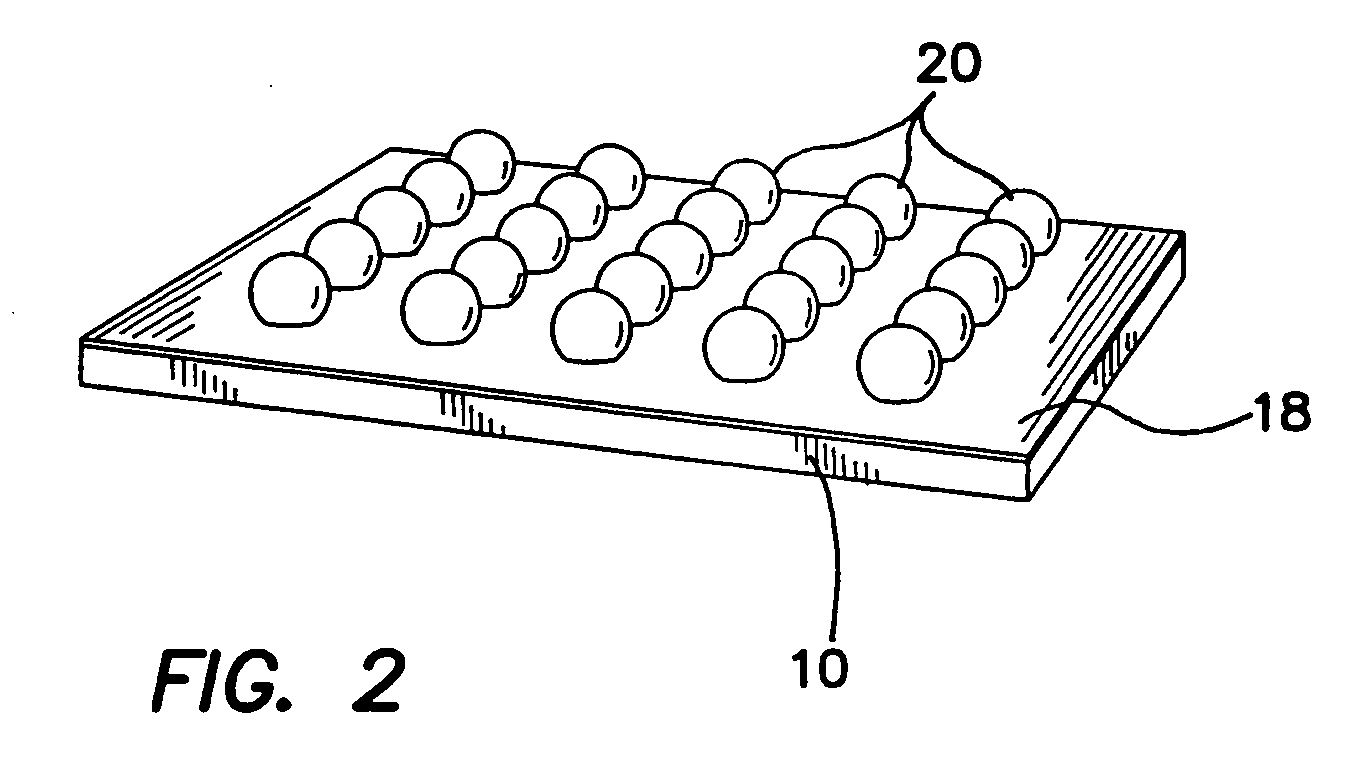
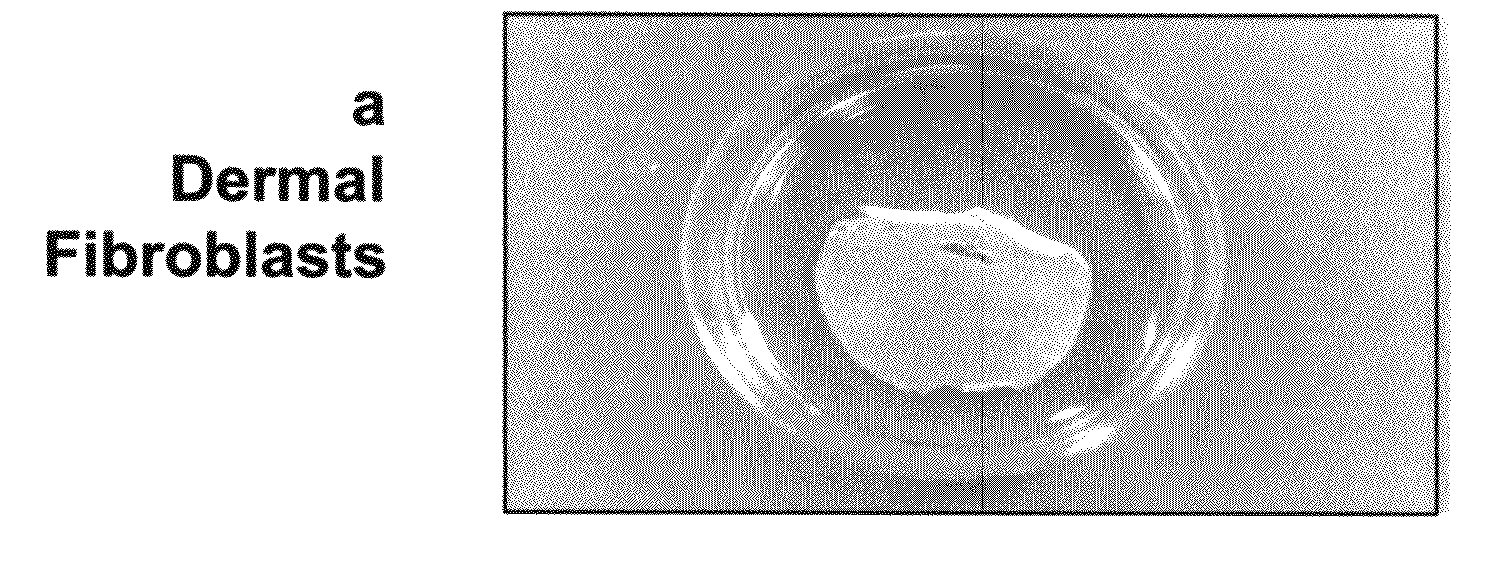
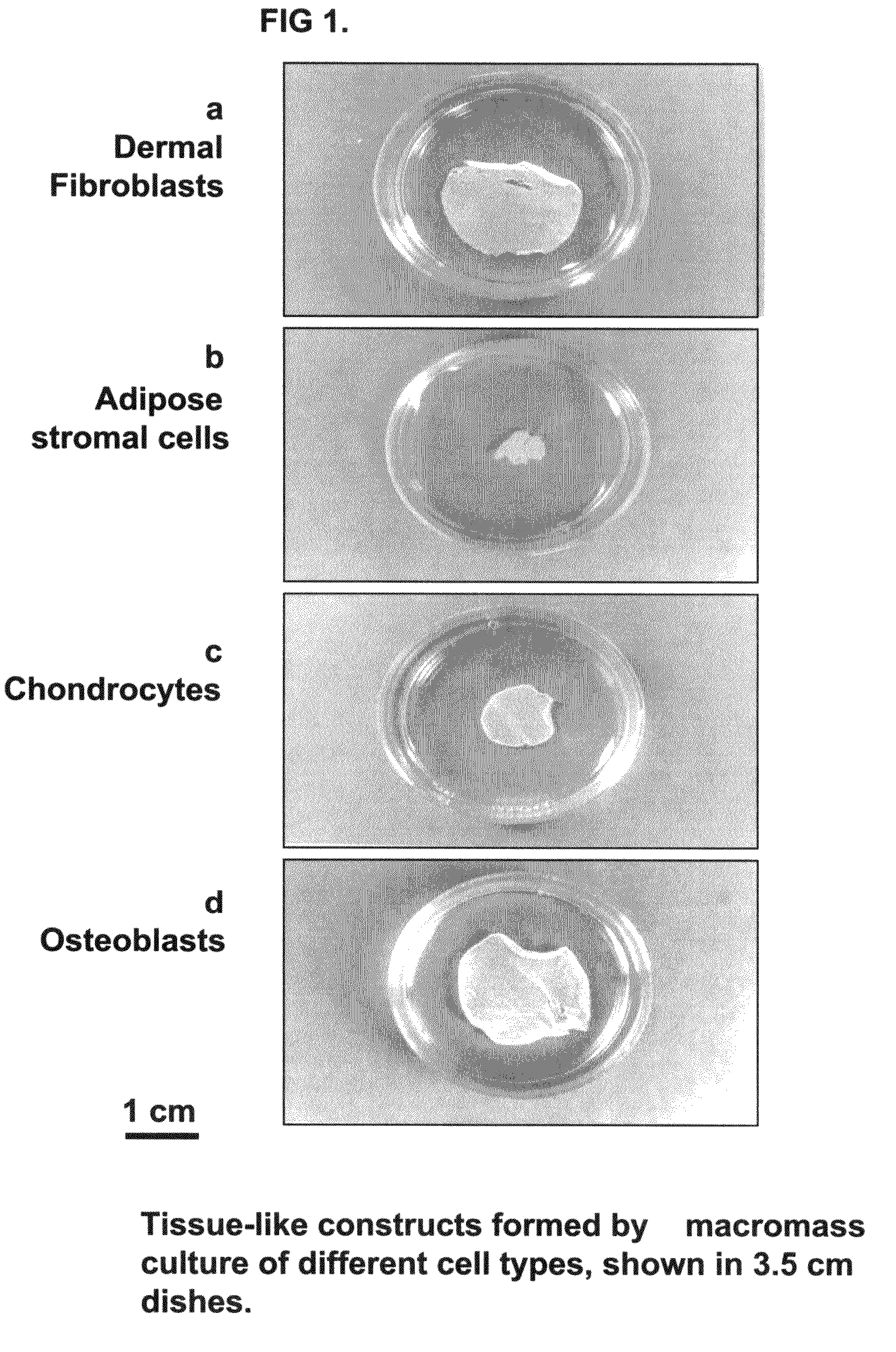
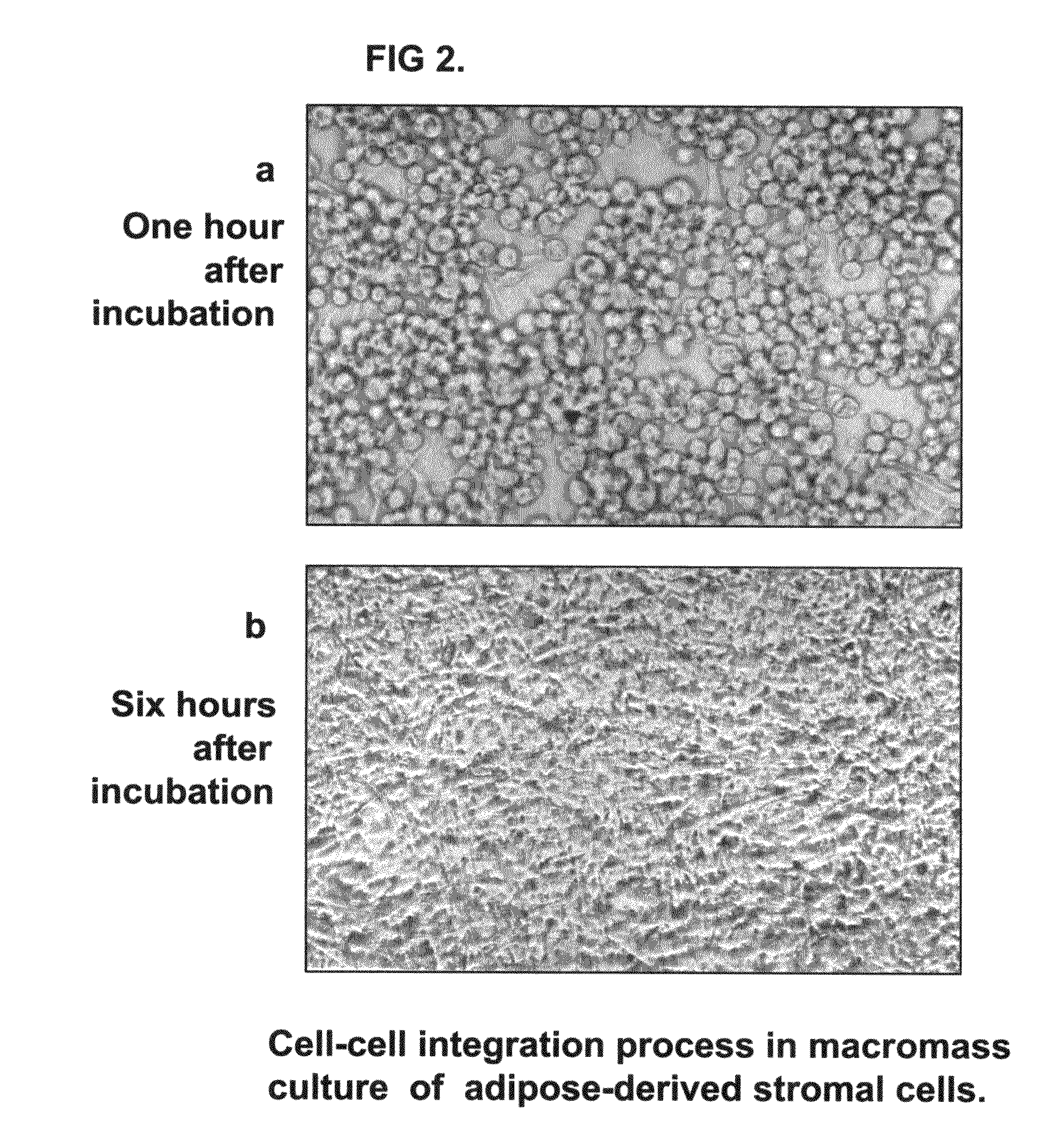
Tissue-like organization of cells and macroscopic tissue-like constructs, generated by macromass culture of cells, and the method of macromass culture
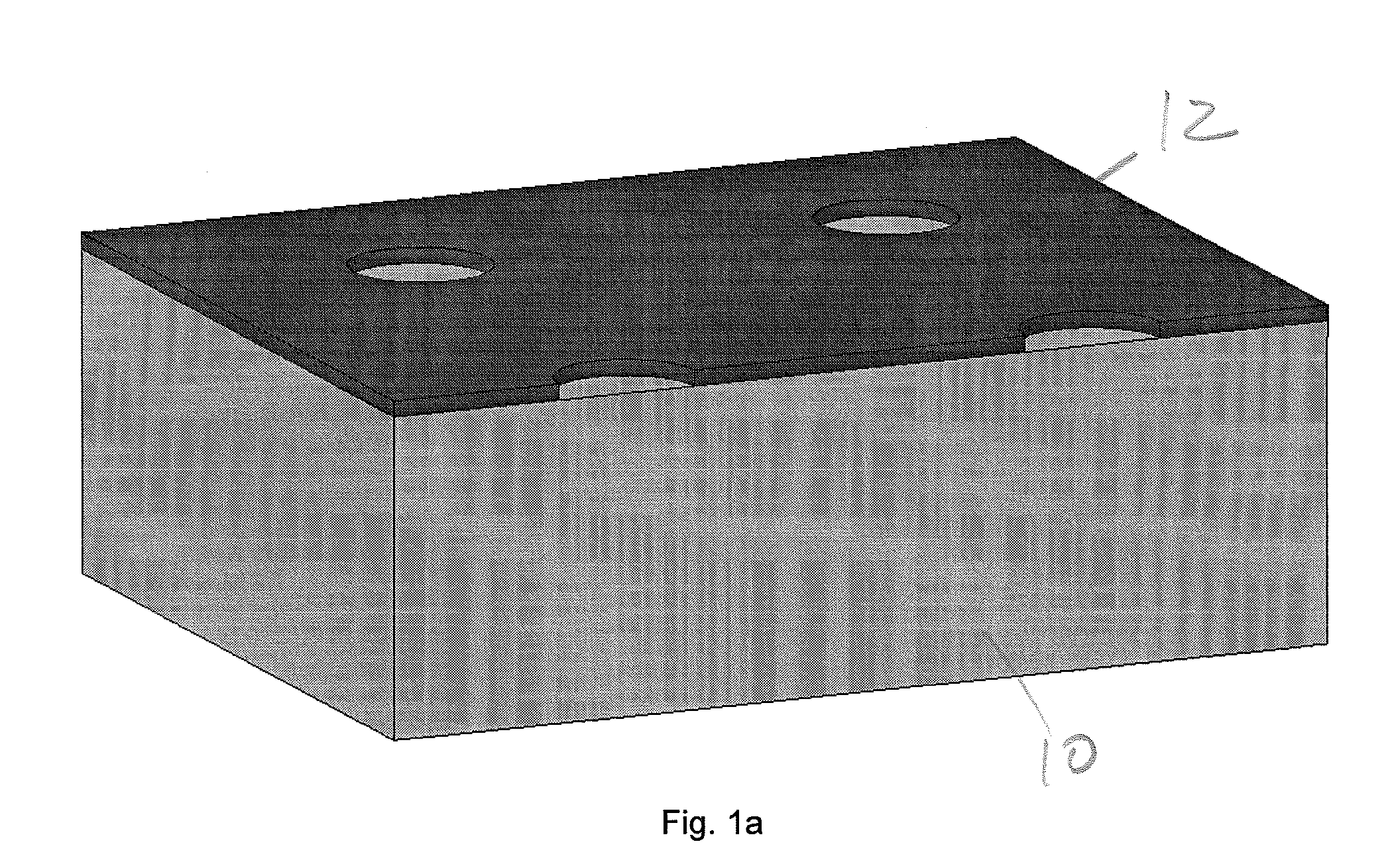
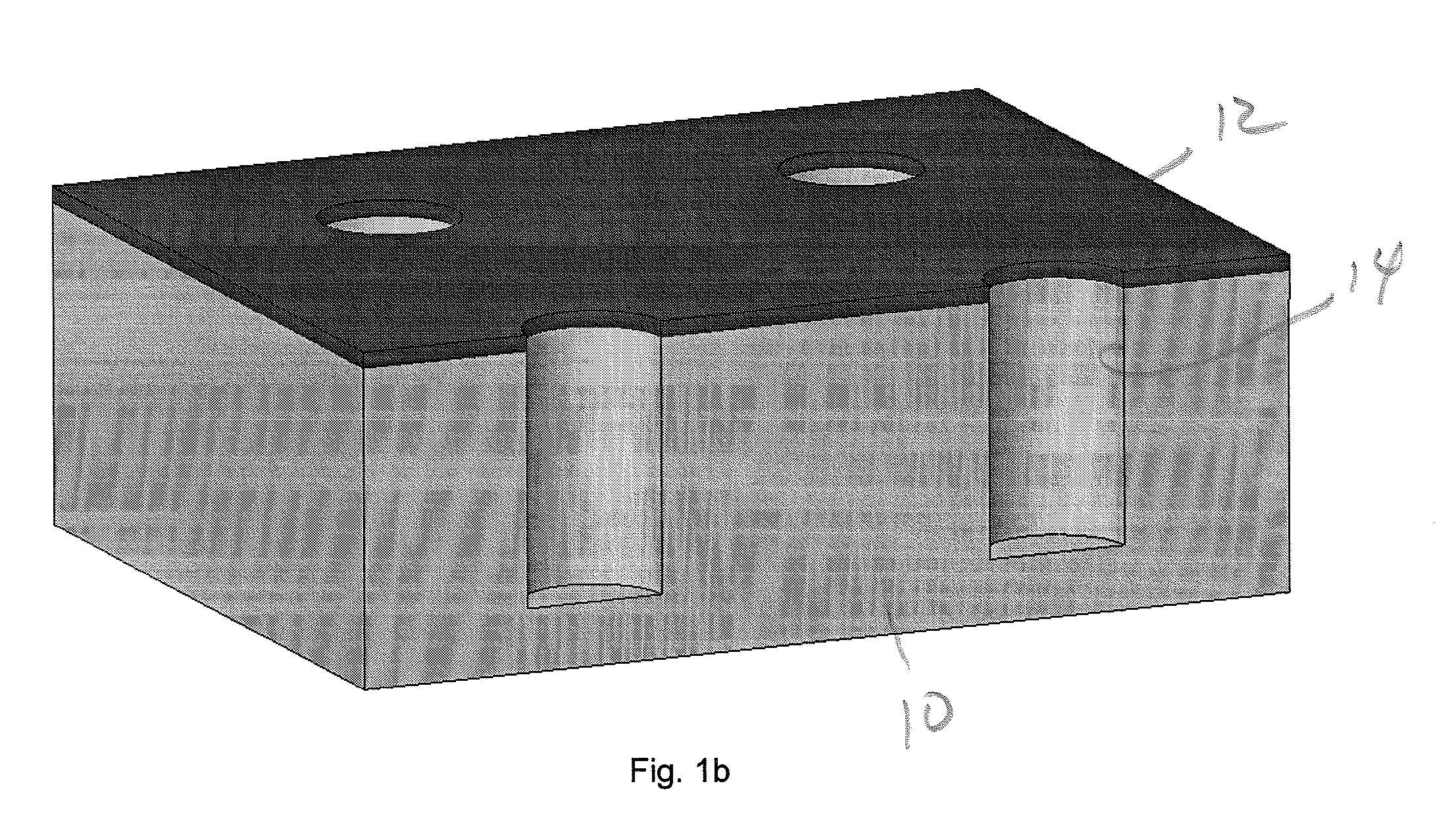
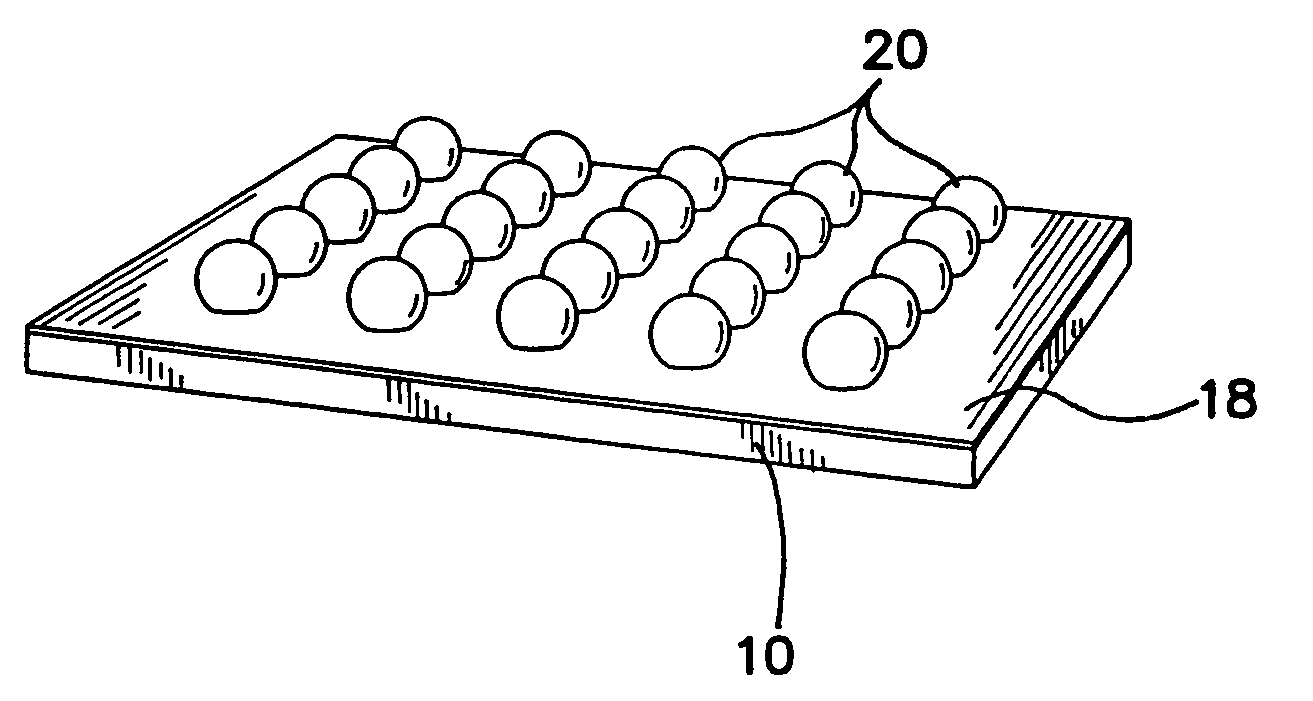
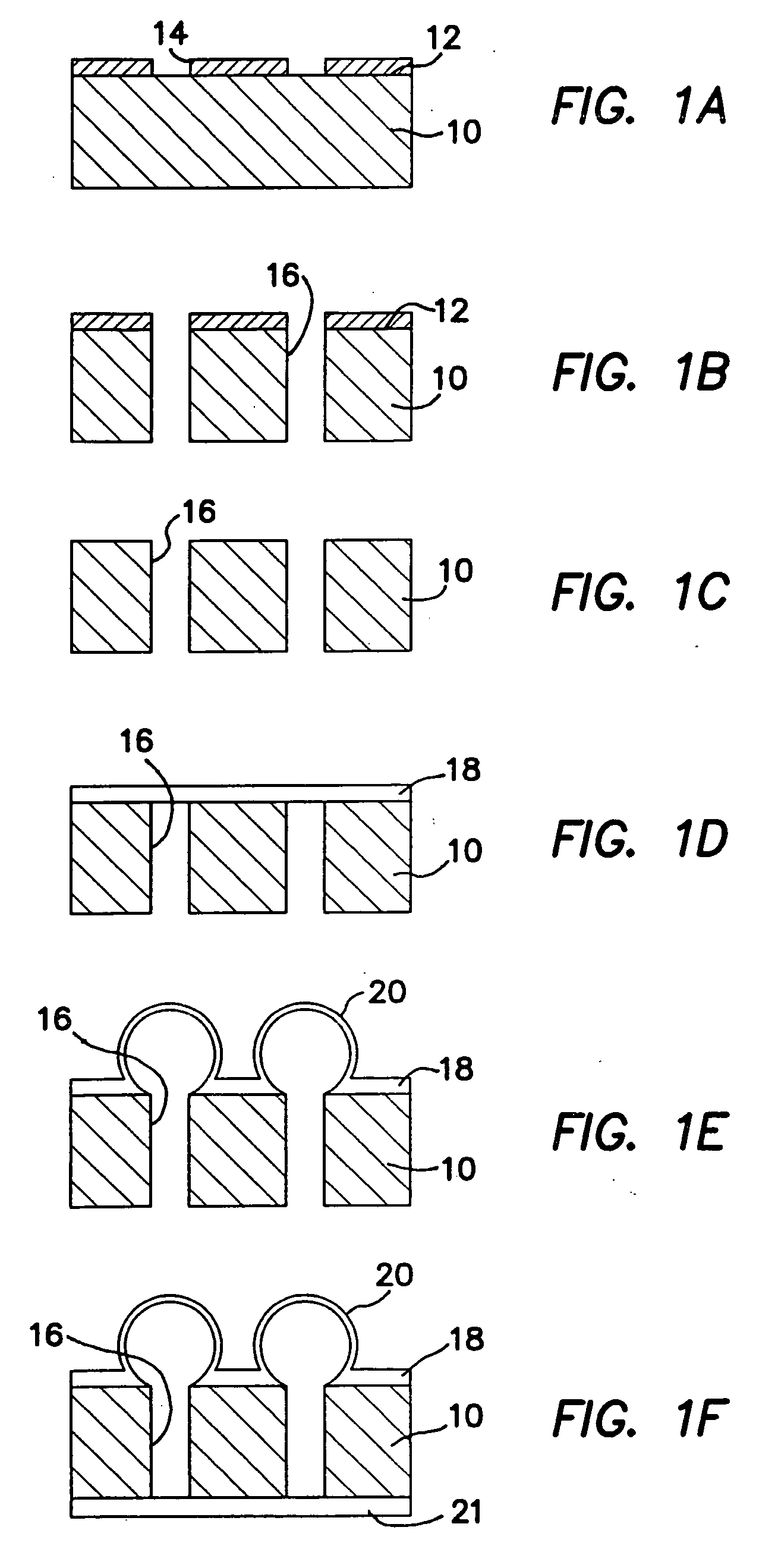
InactiveUS20040082063A1Sectioned easilySmall sizeEpidermal cells/skin cellsMammal material medical ingredientsHigh cellFiber
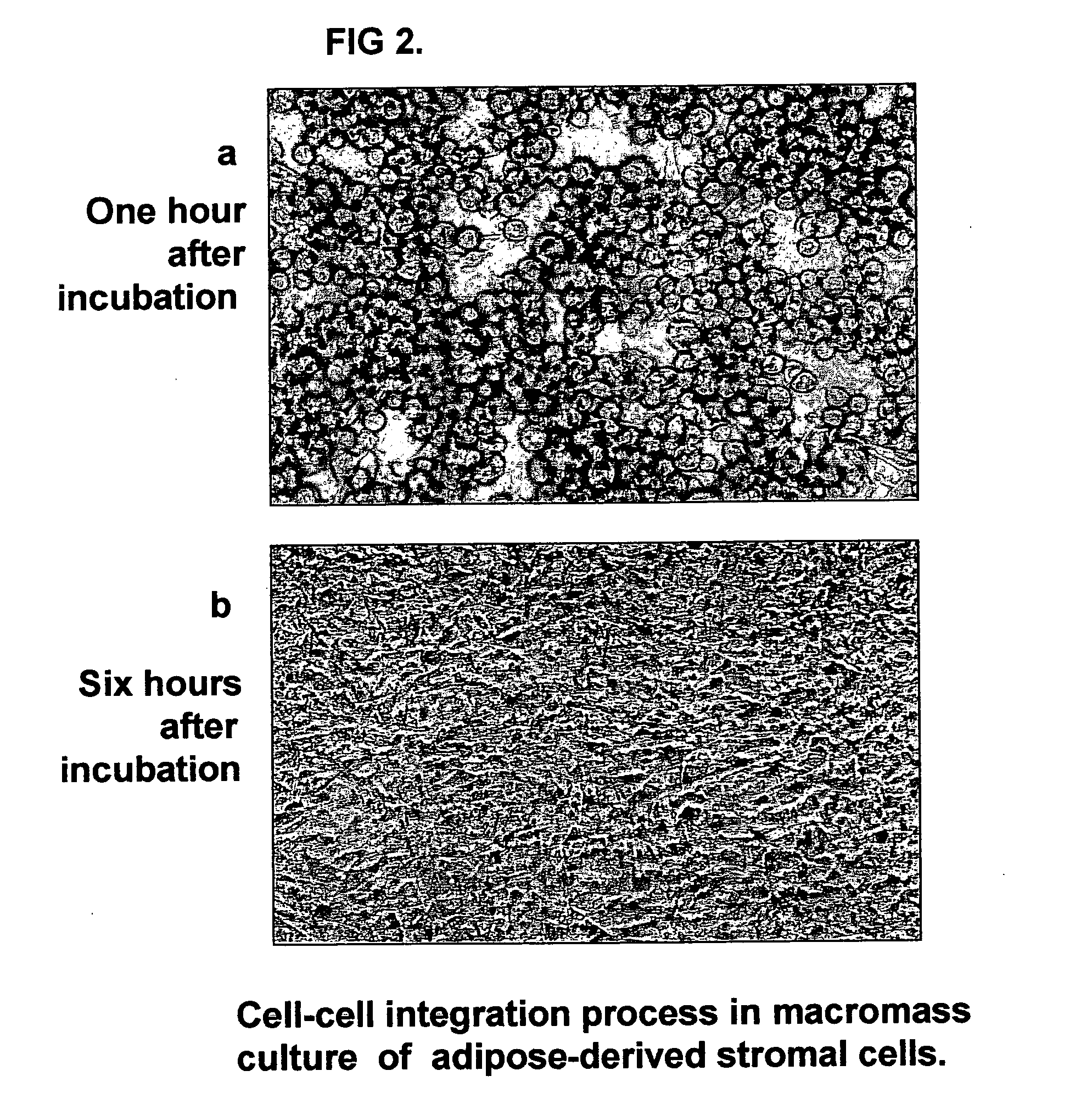
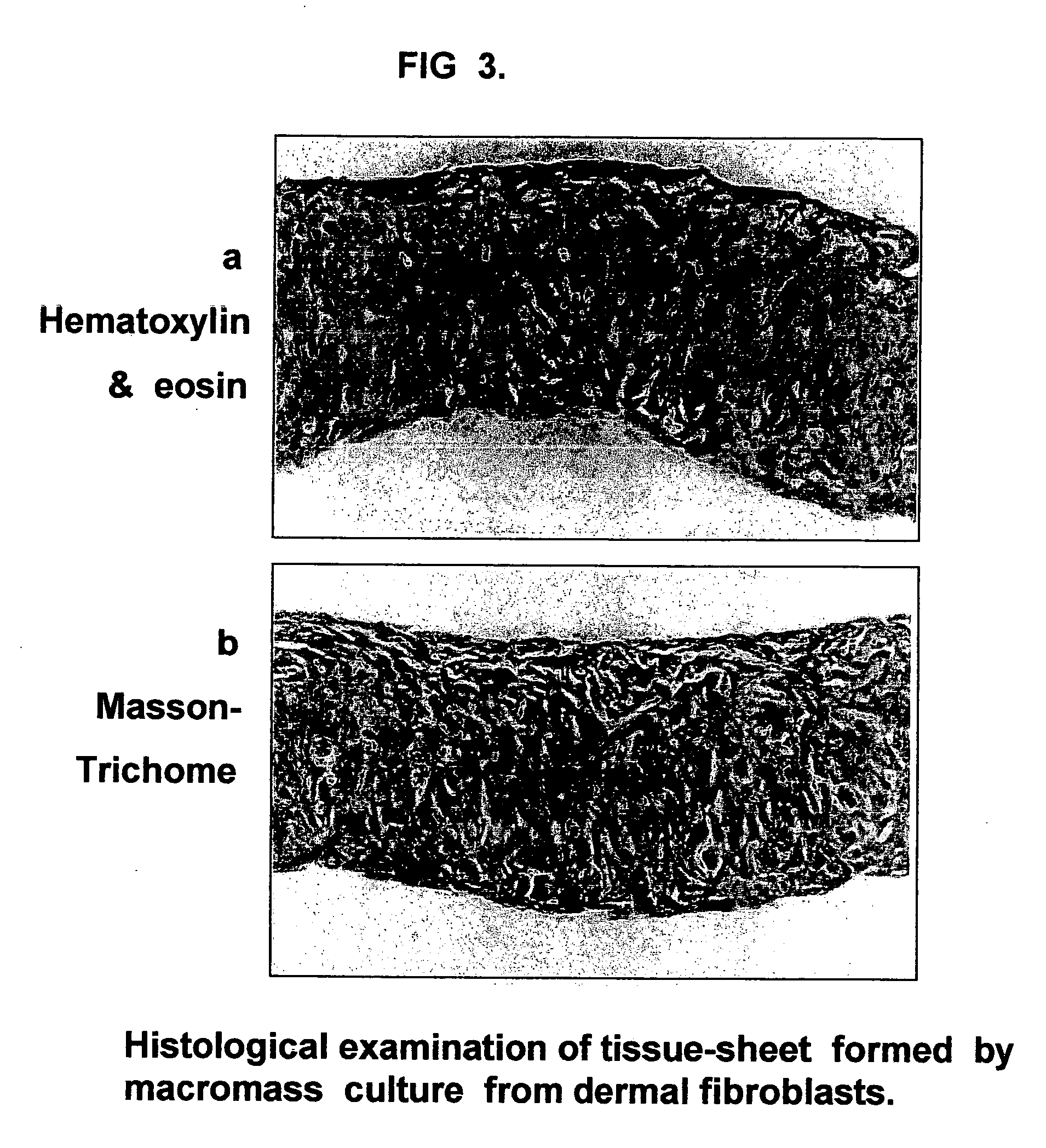
Three-dimensional tissue-like organization of cells by high cell-seeding-density culture termed as macromass culture is described. By macromass culture, cells can be made to organize themselves into a tissue-like form without the aid of a scaffold and three-dimensional macroscopic tissue-like constructs can be made wholly from cells. Tissue-like organization and macroscopic tissue-like constructs can be generated from fibroblastic cells of mesenchymal origin (at least), which can be either differentiated cells or multipotent adult stem cells. In this work, tissue-like organization and macroscopic tissue-like constructs have been generated from dermal fibroblasts, adipose stromal cells-derived osteogenic cells, chondrocytes, and from osteoblasts. The factor causing macroscopic tissue formation is large scale culture at high cell seeding density per unit area or three-dimensional space, that is, macromass culture done on a large scale. No scaffold or extraneous matrix is used for tissue generation, the tissues are of completely cellular origin. No other agents (except high cell-seeding-density) that aid in tissue formation such as tissue-inducing chemicals, tissue-inducing growth factors, substratum with special properties, rotational culture, etc, are employed for tissue formation. These tissue-like masses have the potential for use as tissue replacements in the human body. Tissue-like organization by high cell-seeding-density macromass culture can also be generated at the microscopic level.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
Self-inflated micro-glass blowing
ActiveUS20080280124A1Easy to controlDecorative surface effectsConfectioneryMicroscopic scaleMicroscopic level
A method for glass-blowing on a microscopic level includes the steps of defining a plurality of microholes in a wafer, disposing a sheet of thermally formable material onto the wafer covering the microholes, heating the sheet of thermally formable material until a predetermined degree of plasticity is achieved, applying self-induced fluidic pressure by expansion of the heated trapped gas in the microholes to the sheet of thermally formable material, while the sheet is still plastic, and simultaneously forming a plurality of blown micro-objects in the sheet on the wafer by means of continued application of pressure for a predetermined time.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and apparatus for wafer-level micro-glass-blowing
A method for forming microspheres on a microscopic level comprises the steps of defining holes through a substrate, disposing a sheet of thermally formable material onto the substrate covering the holes, heating the sheet of thermally formable material until a predetermined degree of plasticity is achieved, applying fluidic pressure through the holes to the sheet of thermally formable material, while the sheet of glass is still plastic, and forming microspheres on the substrate in the sheet of thermally formable material by means of continued application of pressure for a predetermined time. The invention also includes a substrate having a plurality of holes defined therethrough, a layer of thermally formable material disposed onto the substrate covering the plurality of holes, and a plurality of microspheres thermally formed in the layer by means of applied pressure through the holes when it has been heated to a predetermined degree of plasticity.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for preparing multifunctional protective nano-coating through cyclic, periodical and alternate discharging
ActiveCN107201511AOvercome the fatal flawAccelerate the speed of chemical depositionChemical vapor deposition coatingChemical vapor depositionMoisture
The invention provides a method for preparing a multifunctional protective nano-coating through cyclic, periodical and alternate discharging, and belongs to the technical field of plasma. According to the method, a reaction chamber is vacuumized, and inert gas is introduced into the reaction chamber; a base material is made to move in the reaction chamber; monomer steam is introduced into the reaction chamber for chemical vapor deposition, and the deposition process includes a pretreatment stage and a film plating stage; in the pretreatment stage, plasma discharges continuously at the high power; in the film plating stage, the plasma discharges periodically and alternately; and the pretreatment stage and the film plating stage repeated cyclically at least once. In the technological process of film plating, more active sites are introduced onto the surface of the base material cyclically, effective film plating is improved, the film structure is more compact, the nano-coating of the multi-layer composite structure is obtained, and multiple protection is provided for a product; and on the microscopic level, the coating structure is more compact, and on the macroscopic level, the coating has excellent hydrophobicity, adhesive force, acid and alkali resistance, mechanical performance, and moisture and heat resistance.
Owner:JIANGSU FAVORED NANOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Apparatus for Disease Detection
ActiveUS20130183660A1Low costHigh degree of sensitivityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological bodyDisease
Among others, the present invention provides apparatus for detecting a disease, comprising a system delivery biological subject and a probing and detecting device, wherein the probing and detecting device includes a first micro-device and a first substrate supporting the first micro-device, the first micro-device contacts a biologic material to be detected and is capable of measuring at the microscopic level an electric, magnetic, electromagnetic, thermal, optical, acoustical, biological, chemical, physical, or mechanical property of the biologic material.
Owner:CHANGWEI SYST TECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Method for transferring graphene
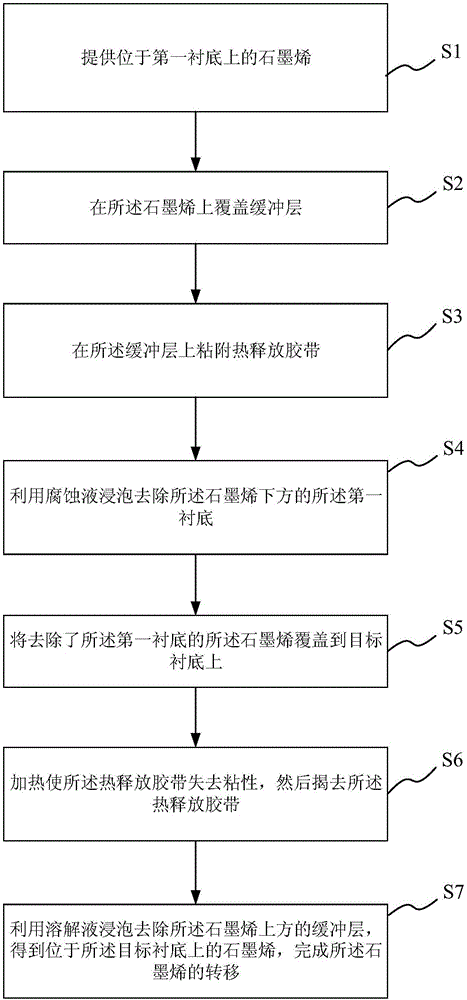
The invention provides a method for transferring graphene. The method comprises the following steps: providing graphene on a first substrate; covering a buffer layer on the graphene; adhering a heat release adhesive tape on the buffer layer; soaking the first substrate in a corrosive solution to remove the first substrate under the graphene; covering the graphene without the first substrate on a target substrate; heating to make the heat release adhesive belt become non-sticky, removing the heat release adhesive belt; and soaking the buffer layer in a dissolving solution to remove the buffer layer on the graphene to obtain graphene on a target substrate to finish the transferring of graphene. According to the method, a buffer layer is used to assist the transferring of graphene, the required steps are few, the process is fast and convenient, the upper and lower surfaces of graphene are clean, no substance is adhered on the upper and lower surfaces of the graphene, the wrinkles in the microscopic level are reduced, thus the effective usable area of graphene is enlarged, and the graphene can be more suitable for being used to prepare electronic devices.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Self-inflated micro-glass blowing
ActiveUS8151600B2Easy to controlTurning machine accessoriesOptical articlesMicroscopic levelBiomedical engineering
A method for glass-blowing on a microscopic level includes the steps of defining a plurality of microholes in a wafer, disposing a sheet of thermally formable material onto the wafer covering the microholes, heating the sheet of thermally formable material until a predetermined degree of plasticity is achieved, applying self-induced fluidic pressure by expansion of the heated trapped gas in the microholes to the sheet of thermally formable material, while the sheet is still plastic, and simultaneously forming a plurality of blown micro-objects in the sheet on the wafer by means of continued application of pressure for a predetermined time.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
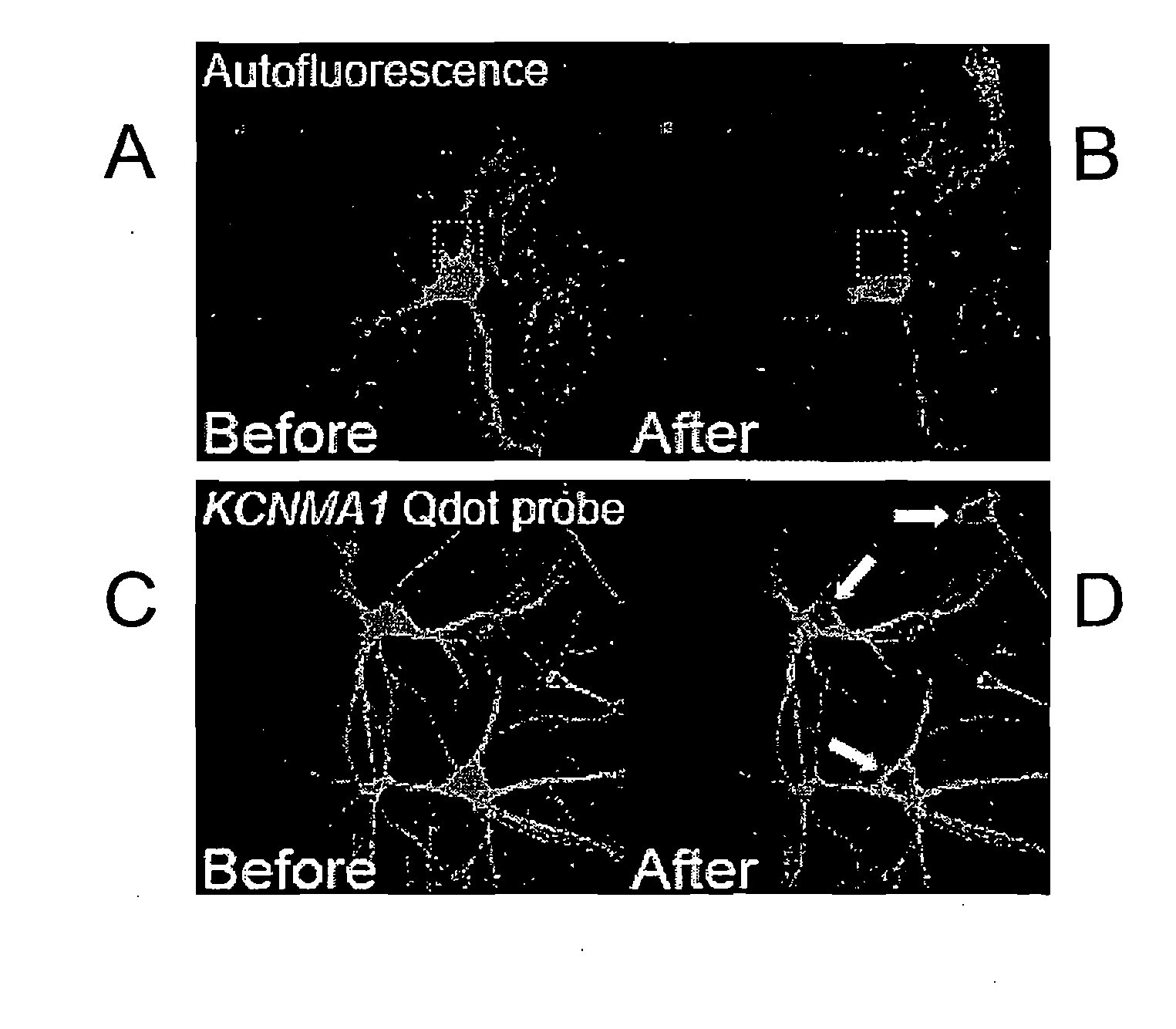
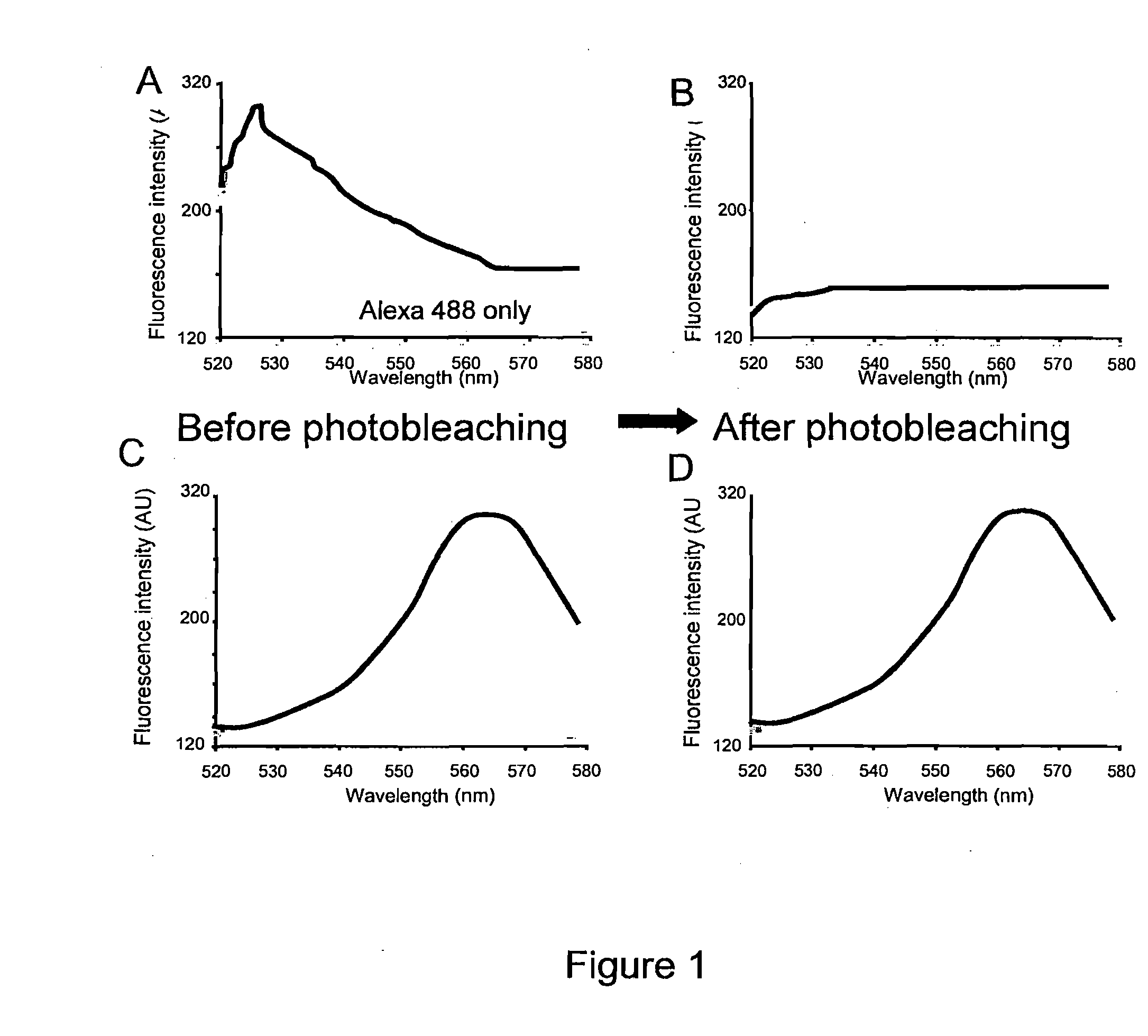
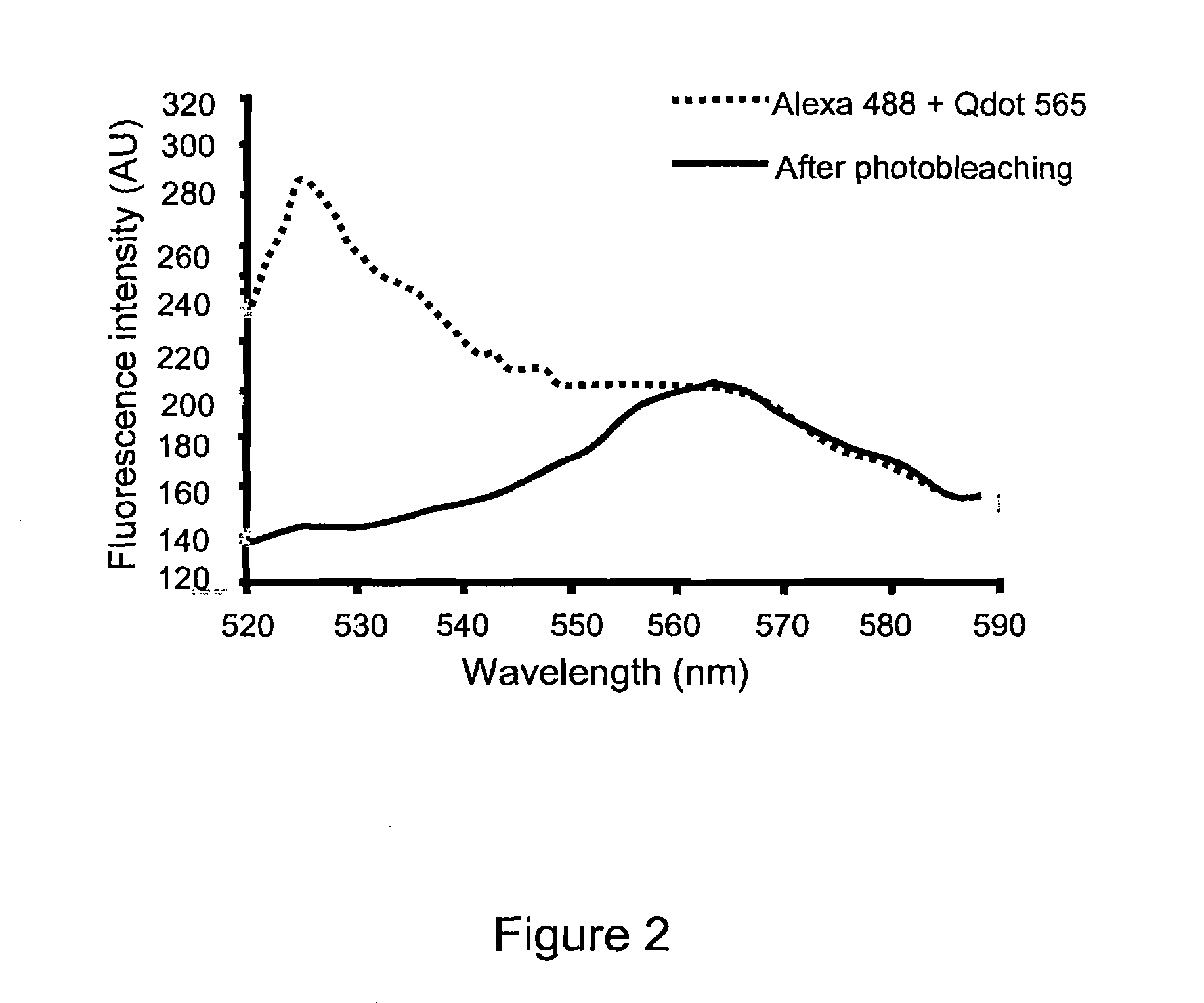
Low Level Fluorescence Detection at the Light Microscopic Level
InactiveUS20100216652A1Microbiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMicroscopic levelPolynucleotide
The present invention discloses methods of removing unwanted fluorescence from a sample by photobleaching said sample to enhance detection of proteins and fragments thereof, polynucleotides and fragments thereof, and biomolecules and fragments thereof in a sample by contacting said proteins, polynucleotides and biomolecules with a fluorescent reporter, wherein said fluorescent reported comprises a fluorescent semiconductor crystal or SCN, wherein said SCN further comprises a targeting moiety.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Micro-Devices for Improved Disease Detection
ActiveUS20130236882A1Low costHigh and much improved degreeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyMicro devices
Among others, the present invention provides micro-devices for detecting or treating a disease, each comprising a first sorting unit capable of detecting a property of the biological subject at the microscopic level and sorting the biological subject by the detected property; a first detection unit capable of detecting the same or different property of the sorted biological subject at the microscopic level; and a first layer of material having an exterior surface and an interior surface, wherein the interior surface defines a first channel in which the biological subject flows from the first sorting unit to the first detection unit.
Owner:CHANGWEI SYST TECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Apparatus for detecting tumor cells
ActiveUS20140030799A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioCancel noiseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyCirculating cancer cell
Among others, the present invention provides apparatus for detecting circulating tumor cells, comprising a system delivery biological subject and a probing and detecting device, wherein the probing and detecting device includes a first micro-device and a first substrate supporting the first micro-device, the first micro-device contacts a biologic material to be detected and is capable of measuring at the microscopic level an electrical, magnetic, electromagnetic, thermal, optical, acoustical, biological, chemical, electro-mechanical, electro-chemical, electro-optical, electro-thermal, electro-chemical-mechanical, bio-chemical, bio-mechanical, bio-optical, bio-thermal, bio-physical, bio-electro-mechanical, bio-electro-chemical, bio-electro-optical, bio-electro-thermal, bio-mechanical-optical, bio-mechanical thermal, bio-thermal-optical, bio-electro-chemical-optical, bio-electro-mechanical-optical, bio-electro-thermal-optical, bio-electro-chemical-mechanical, physical or mechanical property, or a combination thereof, of the biologic subject.
Owner:CHANGWEI SYST TECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Micro-devices for disease detection
ActiveUS20140017670A1High degree of sensitivityImprove convenienceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDiseaseMicro devices
Among others, the present invention provides micro-devices for detecting or treating a disease, each comprising a first micro sensor for detecting a property of the biological sample at the microscopic level, and an interior wall defining a channel, wherein the micro sensor is located in the interior wall of the micro-device and detects the property of the biological sample in the microscopic level, and the biological sample is transported within the channel.
Owner:NINGKASAI TECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
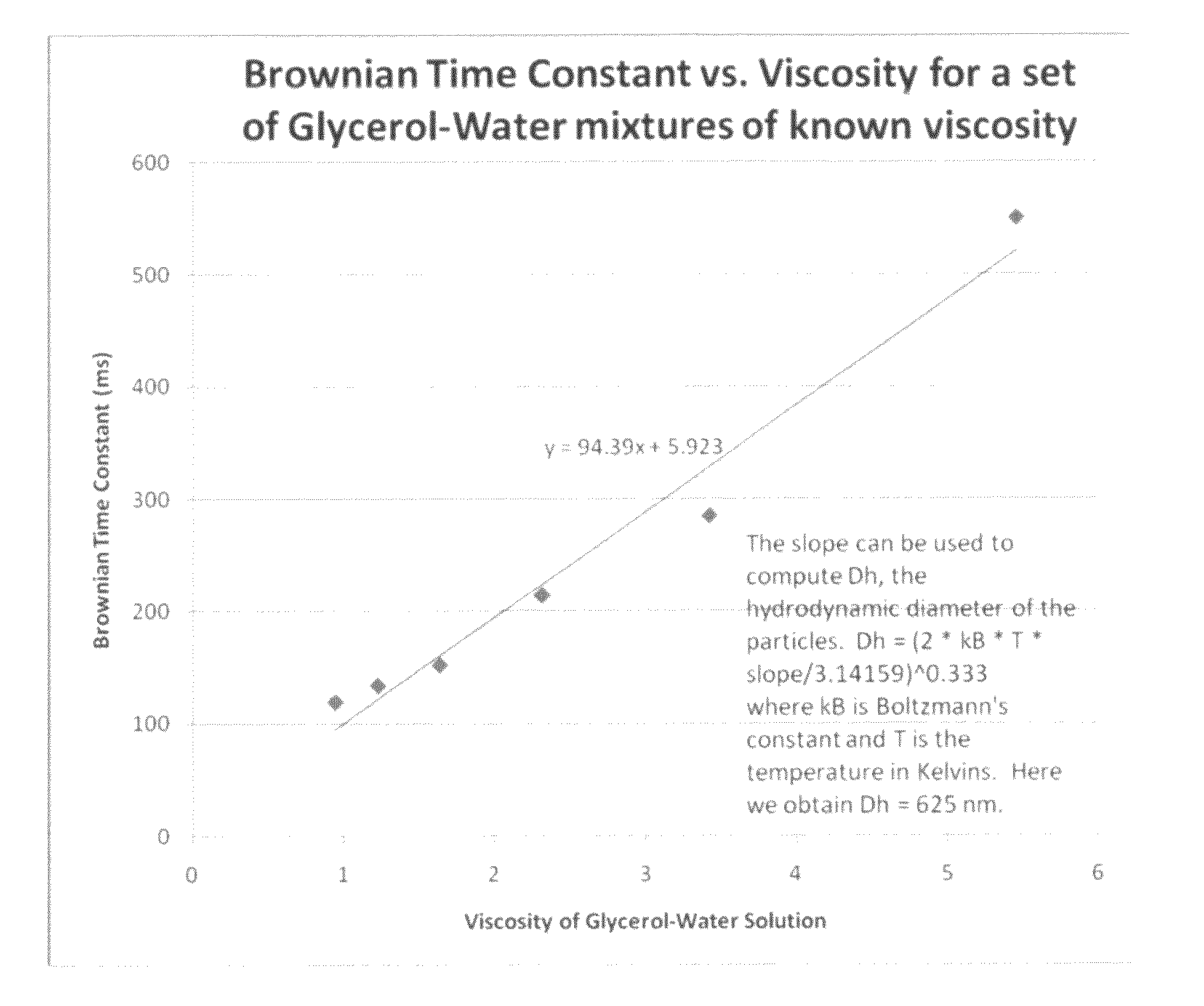
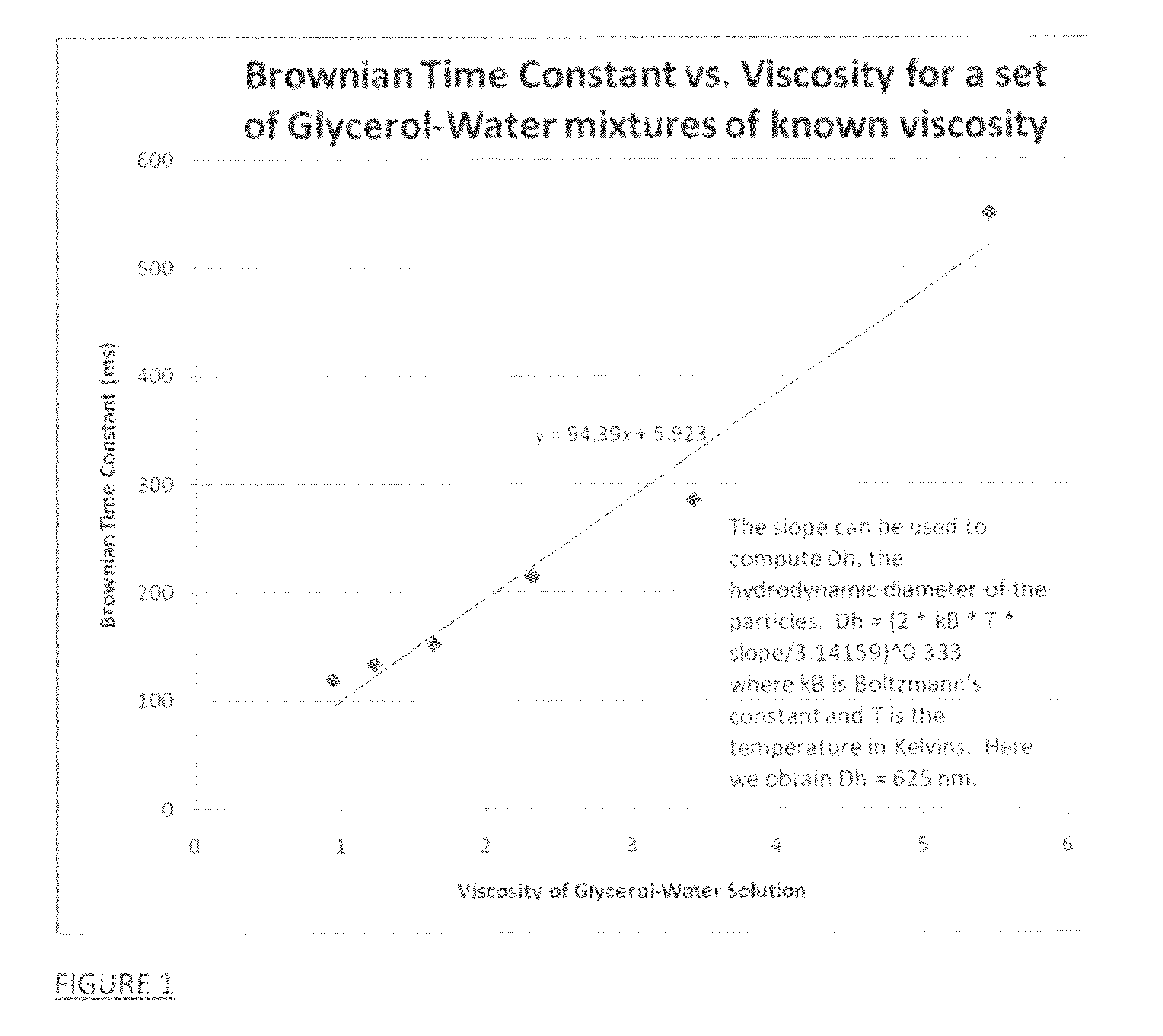
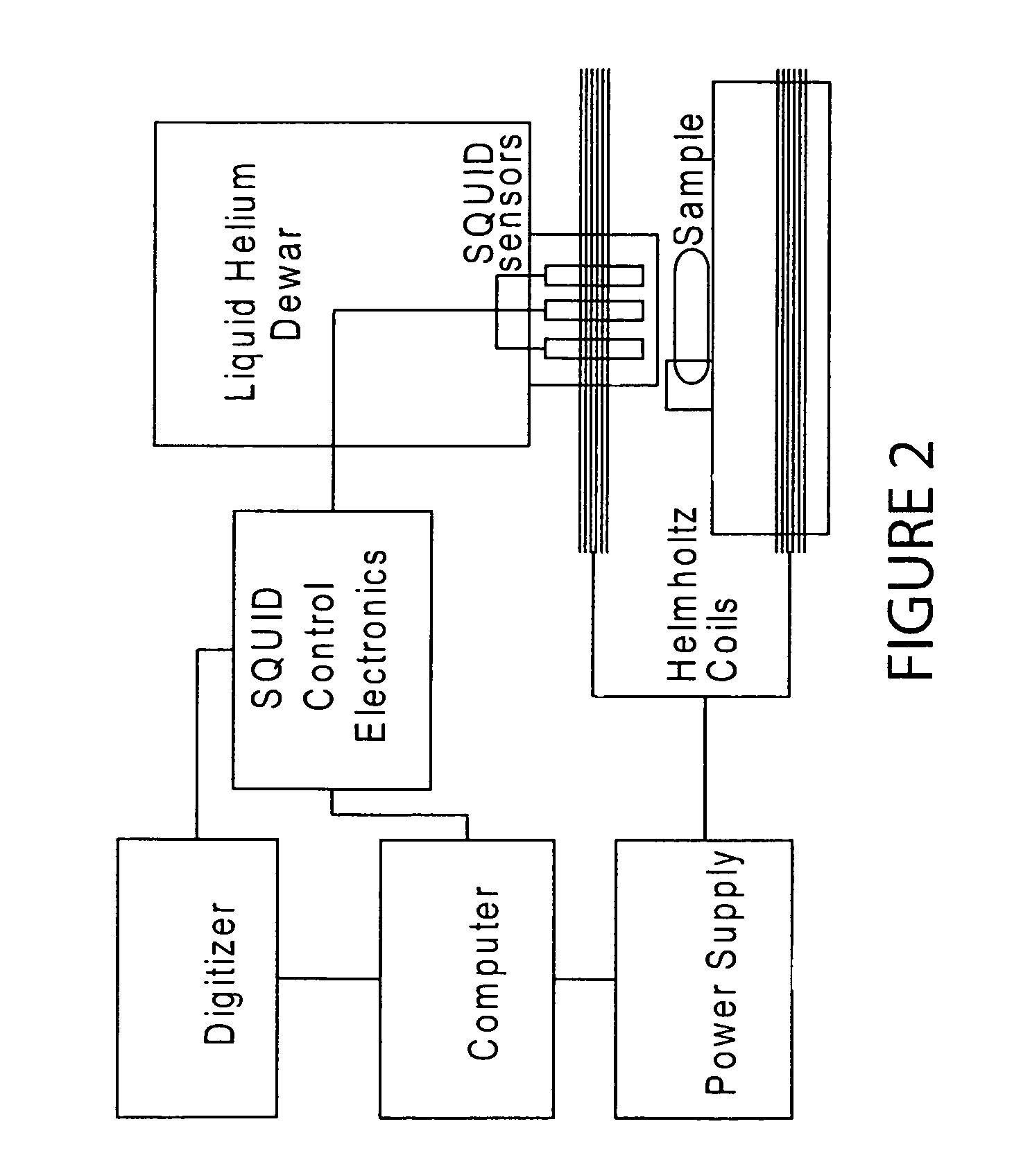
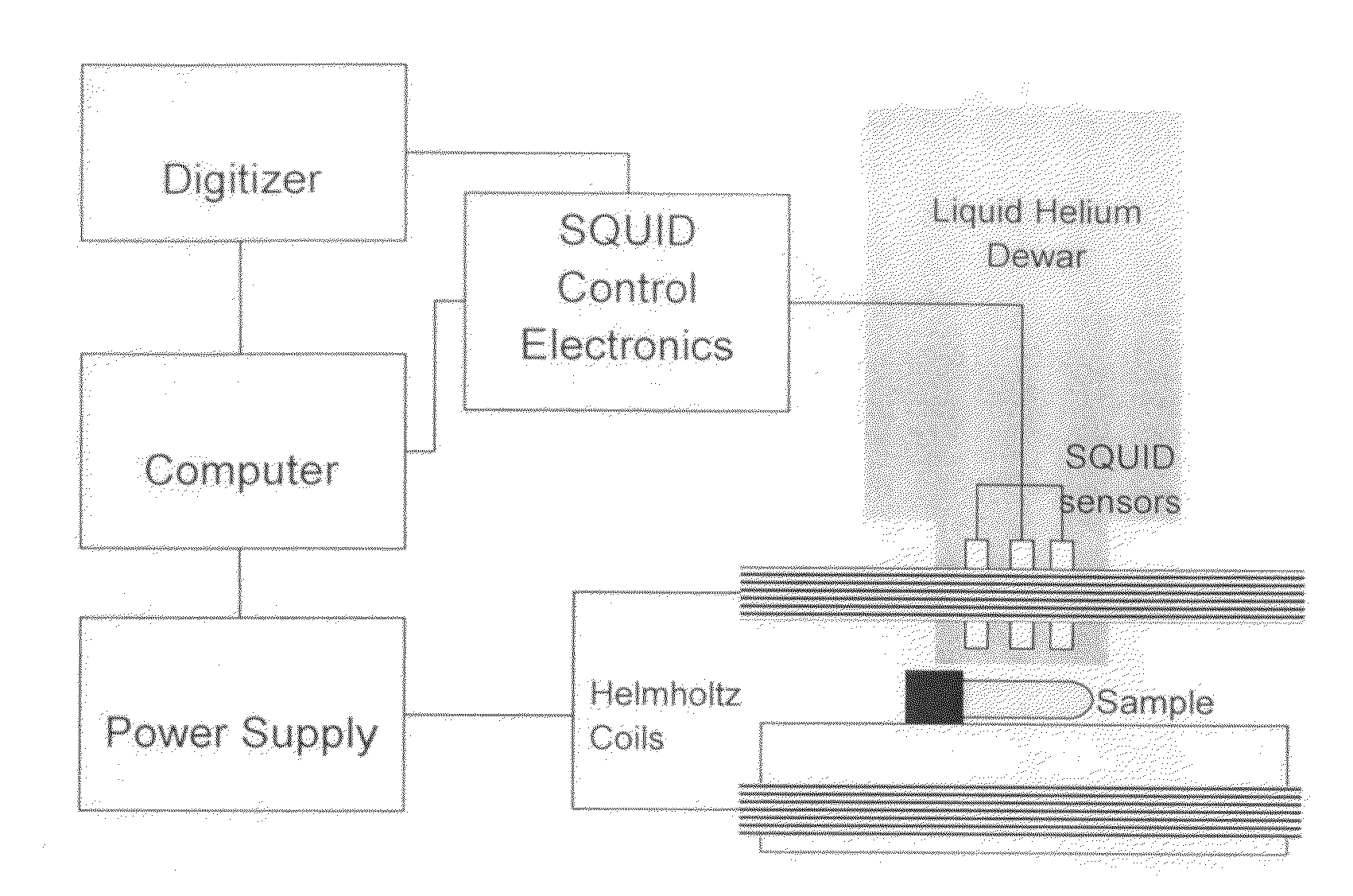
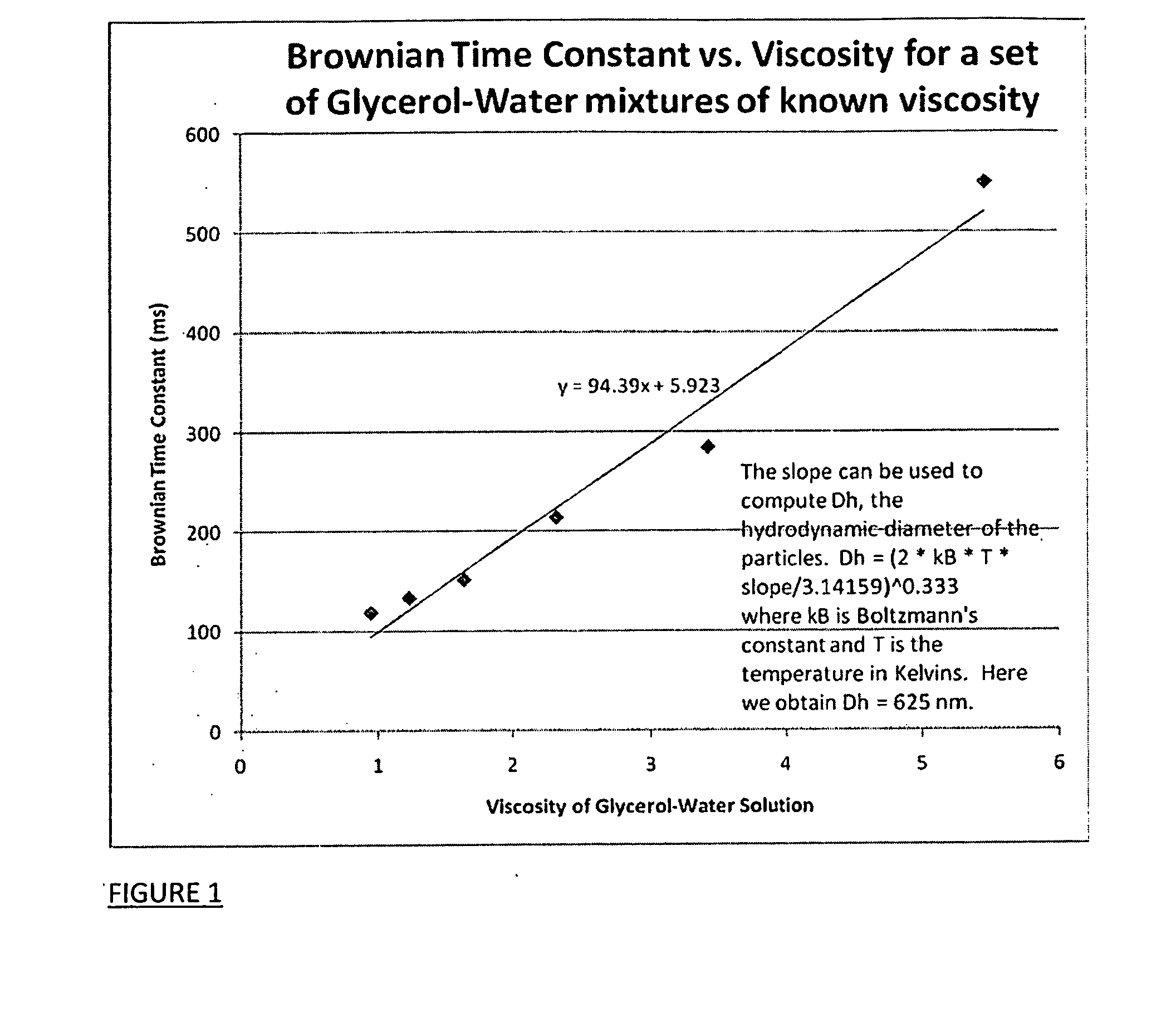
Viscosity measuring method
InactiveUS9074976B2Reduce and eliminate relaxation effectFlow propertiesNanosensorsRoom temperatureMagnetite Nanoparticles
A method for measuring the average viscosity of a test fluid uses calibrated magnetic nanoparticles, with certain chosen hydrodynamic diameters and actual lateral dimensions (e.g. diameters), that are mixed into a small volume of the test fluid and a single magnetic relaxation curve measurement to provide data for viscosity determination. The distribution of hydrodynamic particle sizes of an ensemble of magnetic nanoparticles that are magnetically blocked at room temperature can be determined. Modifications of the method can be used to determine the distribution of viscosities in a complex fluid at the sub-microscopic level providing a novel type of viscosity measurement.
Owner:IMAGION BIOSYST INC +1
Tissue-like organization of cells and macroscopic tissue-like constructs, generated by macromass culture of cells and the method of macromass culture
InactiveUS20080026461A1Sectioned easilySimple processEpidermal cells/skin cellsMammal material medical ingredientsHigh cellHuman body
Three-dimensional tissue-like organization of cells by high cell-seeding-density culture termed as macromass culture is described. By macromass culture, cells can be made to organize themselves into a tissue-like form without the aid of a scaffold and three-dimensional macroscopic tissue-like constructs can be made wholly from cells. Tissue-like organization and macroscopic tissue-like constructs can be generated from fibroblastic cells of mesenchymal origin (at least), which can be either differentiated cells or multipotent adult stem cells. In this work, tissue-like organization and macroscopic tissue-like constructs have been generated from dermal fibroblasts, adipose stromal cells-derived osteogenic cells, chondrocytes, and from osteoblasts. The factor causing macroscopic tissue formation is large scale culture at high cell seeding density per unit area or three-dimensional space, that is, macromass culture done on a large scale. No scaffold or extraneous matrix is used for tissue generation, the tissues are of completely cellular origin. No other agents (except high cell-seeding-density) that aid in tissue formation such as tissue-inducing chemicals, tissue-inducing growth factors, substratum with special properties, rotational culture, etc, are employed for tissue formation. These tissue-like masses have the potential for use as tissue replacements in the human body. Tissue-like organization by high cell-seeding-density macromass culture can also be generated at the microscopic level.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
High elasticity graphene membrane
The invention discloses a high elasticity graphene membrane, which is obtained by subjecting oxidized graphene to solution film forming and chemical reduction. The graphene membrane is prepared by physically crosslinking macroscopic multilayer-wrinkle graphene having microscopic level wrinkles; in the macroscopic level, the membrane is composed of many macroscopic wrinkles, and thus the membrane has an extremely high horizontal elasticity. The membrane has an extremely good flexibility, and can be repeatedly folded for more than 100,000 times without any fold. The high flexibility graphene heat conductive membrane can be repeatedly folded for more than 100,000 times, the elastic breaking elongation rate is 20 to 50%, the conductivity is 600 to 1000 S / cm, and the graphene membrane can be used as a high elasticity flexible conductive device.
Owner:杭州德烯科技集团有限公司
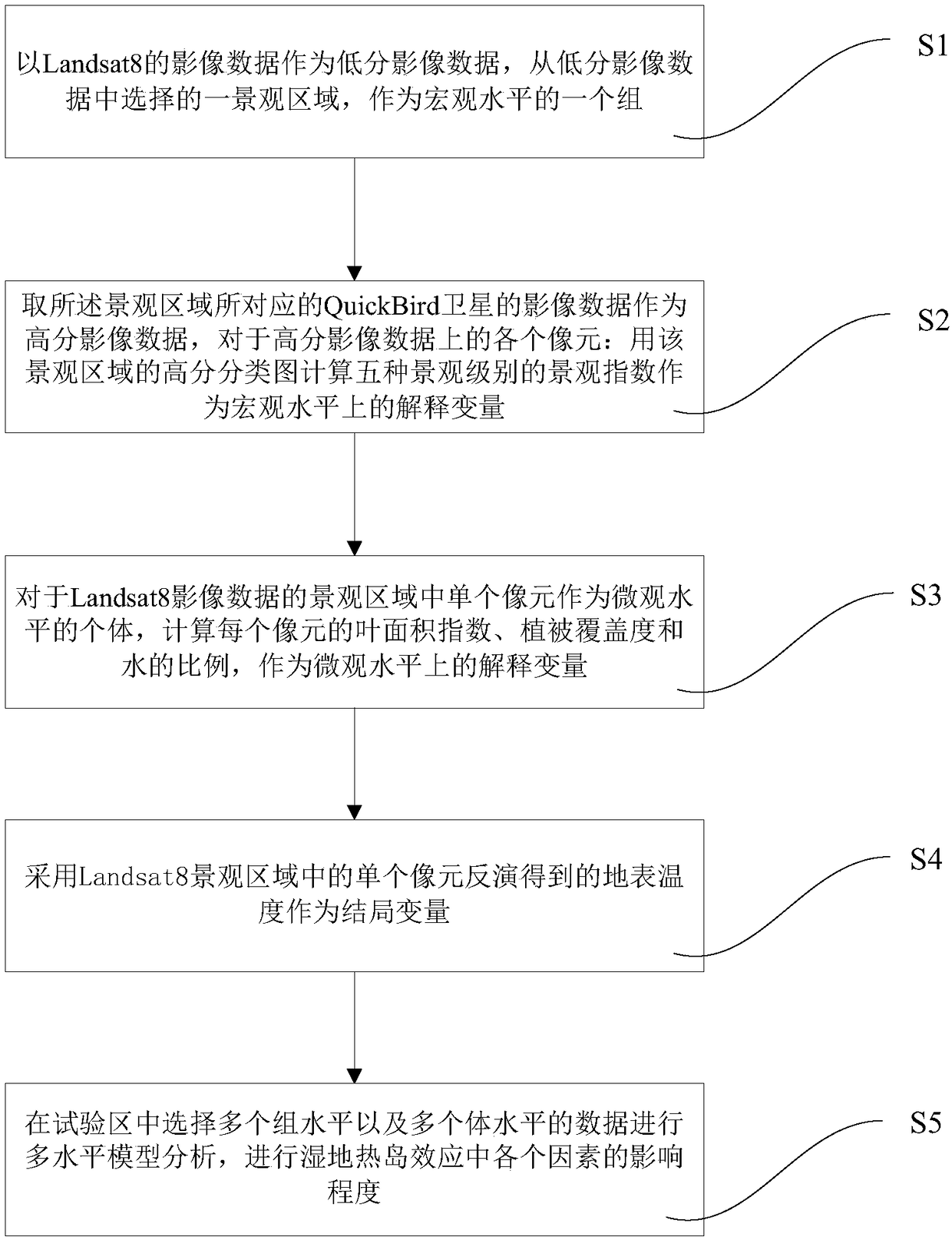
Method and system for analyzing urban wetland heat island effect based on multi-source remote-sensing image
InactiveCN108320285AStable supportThe result is stable and accurateImage enhancementImage analysisHigh resolution imageModelling analysis
A method and system for analyzing an urban wetland heat island effect based on a multi-source remote-sensing image. The method comprises using a Landsat8 image data as low-resolution image data, selecting a landscape area therefrom as a group at a macroscopic level; obtaining the image data of a QuickBird satellite corresponding to the landscape area as high-resolution image data, for each pixelon the high-resolution image data: calculating the landscape index of the landscape level as an explanatory variable at the macroscopic level by using the high-resolution classification map of the landscape area; for a single Landsat8 pixel as an individual at the microscopic level, calculating the explanatory variable at the microscopic level of each pixel; inverting the surface temperature as anoutcome variable by using a single pixel in the Landsat8 landscape area; selecting multiple group level and multiple body level data in the experimental area for multi-level model analysis to analyzethe degree of influence of various factors in the wetland heat island effect. The method and system can simultaneously study the relationship between various factors at the microscopic and macroscopic levels and the surface temperature, and is more accurate and stable in result.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Micro-devices for improved disease detection
ActiveUS9689863B2High and much improved degreeGuaranteed simplicity and practicalityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyMicro devices
Among others, the present invention provides micro-devices for detecting or treating a disease, each comprising a first sorting unit capable of detecting a property of the biological subject at the microscopic level and sorting the biological subject by the detected property; a first detection unit capable of detecting the same or different property of the sorted biological subject at the microscopic level; and a first layer of material having an exterior surface and an interior surface, wherein the interior surface defines a first channel in which the biological subject flows from the first sorting unit to the first detection unit.
Owner:NING KASAI TECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Burner for combustion of a low-calorific fuel gas and method for operating a burner
InactiveCN101040149AImprove spatial uniformityAvoid installationBurnersContinuous combustion chamberLow nitrogenProcess engineering
The invention relates to a burner (1), for the combustion of a low-calorific fuel gas (SG), with an air channel (2), running along a burner axis (12), for the introduction of combustion air (10) and a fuel gas channel (26), embodied for a high volumetric flow of low-calorific fuel gas (SG), whereby the fuel gas channel (26) and the air channel (2) open out into a mixing region (27). According to the invention, a low-nitrogen oxide synthesis gas operation of the burner (1) may be achieved, whereby a swirl element (4) is arranged in the air channel (2) for the generation of turbulent combustion air (10). The swirling element is provided in an opening region (28) directly adjacent to the flow of the mixing region (27). The invention further relates to a method of operation of a synthesis gas burner (1), whereby, directly before the mixing of the synthesis gas (SG) with the combustion air (10), the level of turbulence of the mass air flow is significantly increased on the microscopic level and a temporally and spatially homogenous mixing of the synthesis gas / air mixture is achieved.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method for characterizing three-dimensional pore network structure parameters of coal rock
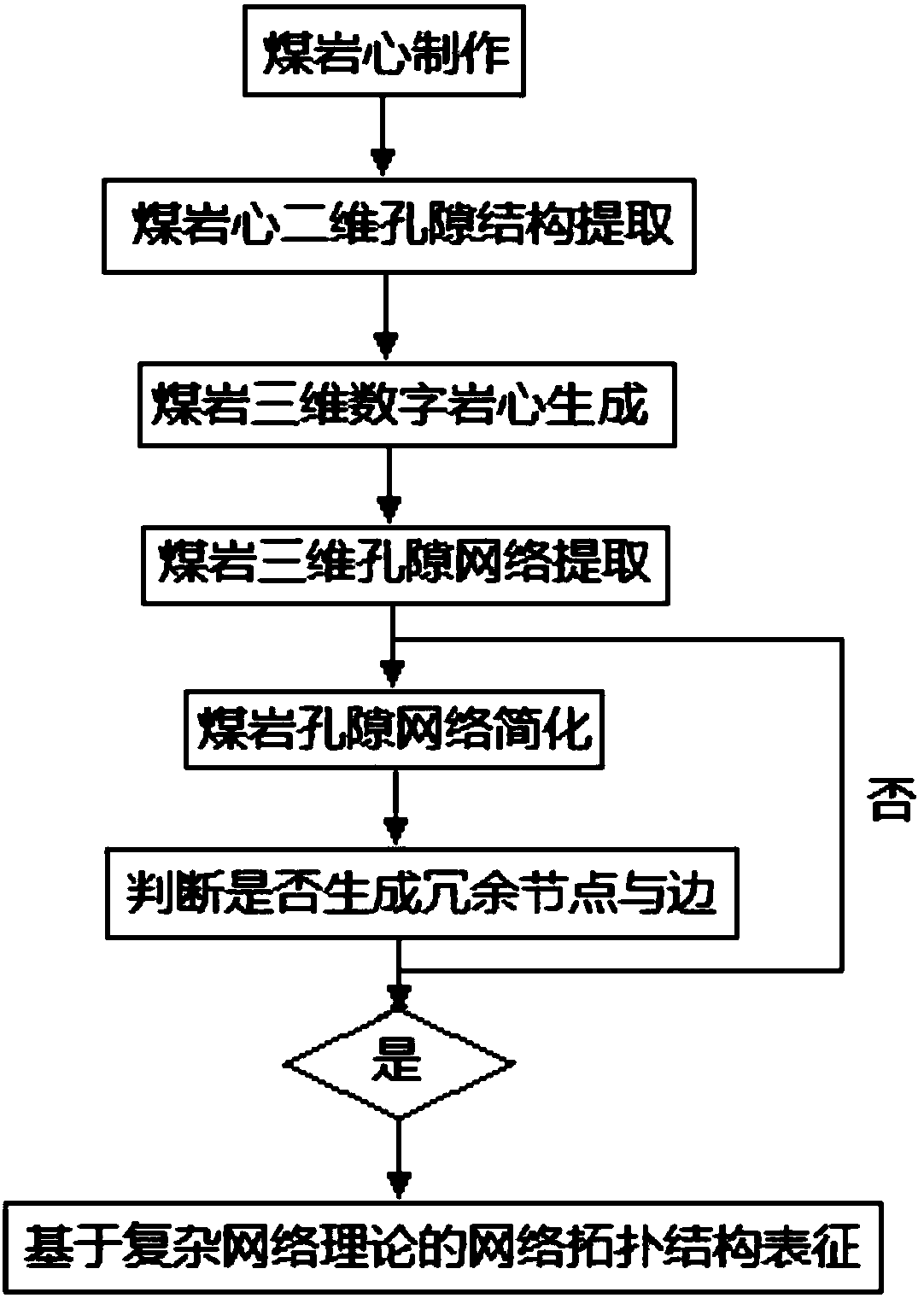
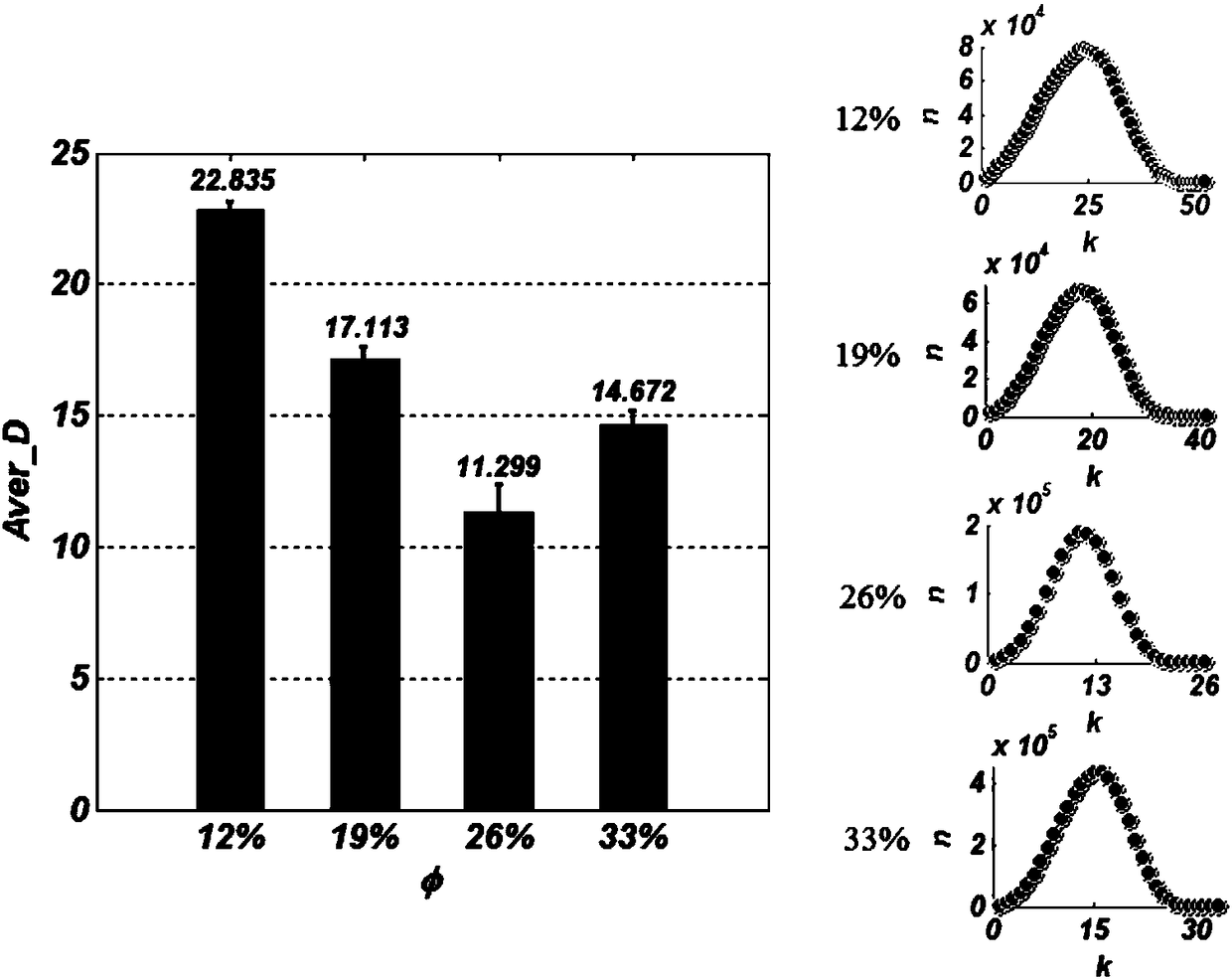
ActiveCN108303360AImprove analysisEnhanced overall recoveryPermeability/surface area analysisPorosityStructure analysis
A method for characterizing the pore network structure of a coal rock comprises the following steps: obtaining three-dimensional data of a coal rock core pore structure by a CT technology, establishing a three-dimensional digital rock core, and establishing a three-dimensional pore network by using a central axis algorithm; simplifying the model data of the pore network, simplifying pores into nodes, simplifying pore passages into edges, marking the pores, and deriving pore communication information; and using a complex network to characterize the basic information of the network, comprising the total number of the nodes, the total number of the edges, node distribution, the average degree of the nodes, the average path length of the network, the network clustering coefficient, the networkmedia, the network density and the network robustness. Compared with traditional coal rock pore structure analysis methods, the method in the invention increases network property analysis, can analyze the seepage law of different pore network communication structures having the same porosity to achieve the purpose of improving the existing gas recovery rate at the microscopic level, and adopts acomplex network theory to quantitatively characterize the pore structure network parameters of the coal rock in order to accurately and comprehensively characterize the pore network communication property of the coal rock.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Graphene/nickel hydroxide composite material and preparation method thereof, and electrode material
InactiveCN106340391AImprove electrochemical performanceHybrid capacitor electrodesHybrid/EDL manufactureTetramineNickel oxide hydroxide
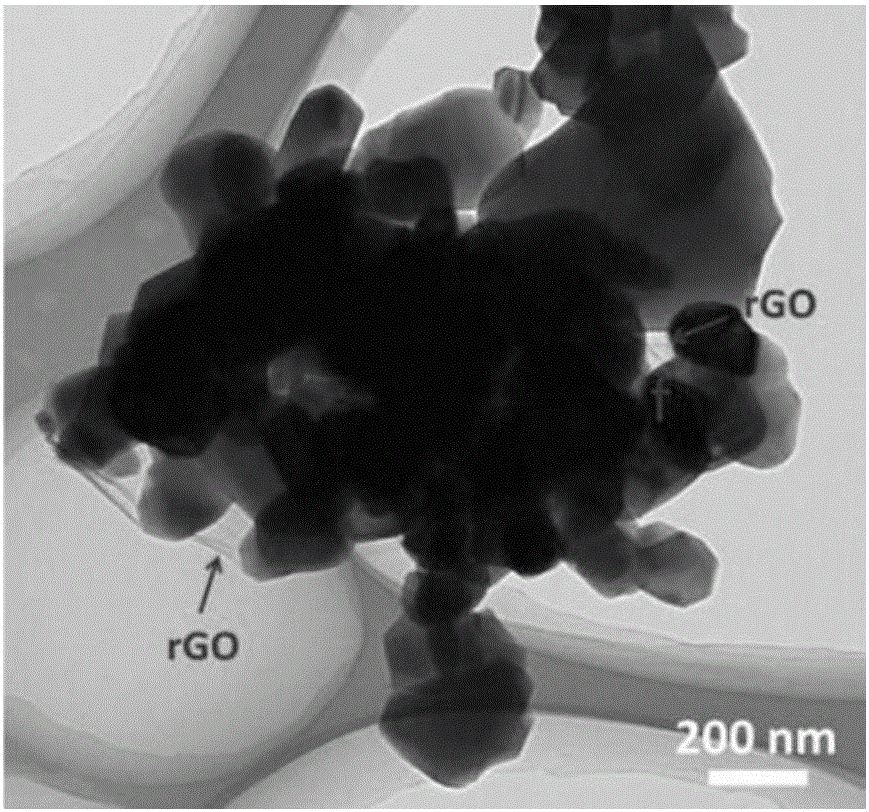
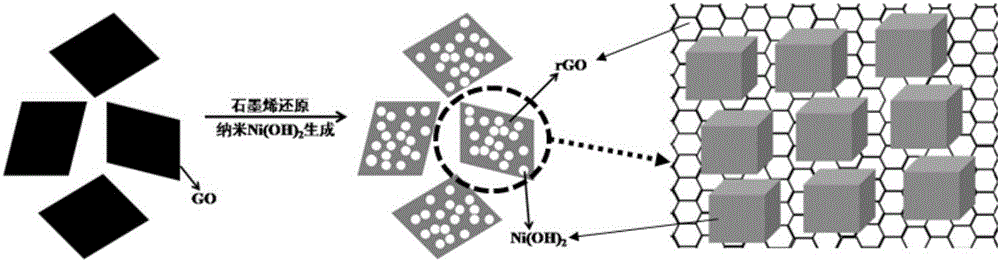
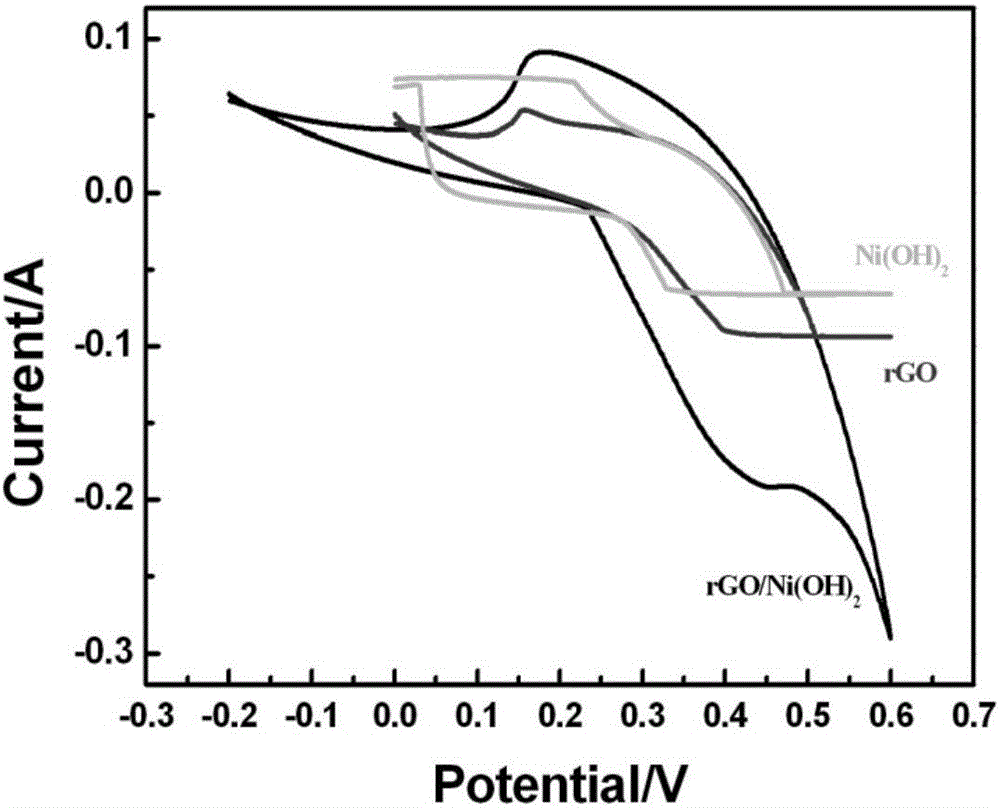
The invention provides a preparation method of a graphene / nickel hydroxide composite material. The method comprises that oxidized graphene, water, hexamethylene tetramine and a nickel source are mixed, heated and reacted to obtain the graphene / nickel hydroxide composite material. A simple hydrothermal method is used to synchronize generation of nanometer nickel hydroxide with reduction of oxidized graphene, two-phase combination is carried out in source and microscopic levels, and the composite material in which nanometer nickel hydroxide is attached to the sheet-shaped graphene uniformly is prepared. The composite material combines the advantages that graphene has a large specific surface area and high conductivity with that nanometer nickel hydroxide is high in the specific capacity, and the composite material has high integrated performance when being used for a super capacitor.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
Coke microscopic structure analysis method based on microscopic-level panoramagram
InactiveCN105957091AComprehensive observation of microstructureImprove and improve qualityImage enhancementImage analysisStructure analysisLow-power electronics
The present invention belongs to the coke microscopic structure analysis technology field, in particular to a coke microscopic structure analysis method based on a microscopic-level panoramagram. The method comprises the following steps of S10 shooting the surface of a coke sample to obtain a low-power electronic picture set; S20 using a median filtering method to smooth the digital photographs; S30 splicing and fusing the low-power electronic picture set to obtain a microscopic-level panoramagram; S40 appointing the local amplification areas based on the microscopic-level panoramagram, shooting the surfaces of the local amplification areas to obtain high-power electronic picture sets; S50 using the median filtering method to smooth the digital photographs; S60 splicing and fusing the high-power electronic picture sets to obtain the microscopic-level local amplification pictures; S70 linking the microscopic-level local amplification pictures and the local amplification areas. The method provides a path for analyzing the coke microscopic structure comprehensively and deeply, and provides the bases for searching a mineralization mechanism and a solution method and improving the coke product and the quality.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Starch-hyaluronic acid hemostatic agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102988407ARich varietyAbundant productionOrganic active ingredientsGranular deliveryMedicineMicroscopic level
The invention relates to the field of medical devices and in particular relates to a starch-hyaluronic acid hemostatic agent and a preparation method thereof. The starch-hyaluronic acid hemostatic agent is characterized in that porous microspheres which are formed by cross-linking of starch-hyaluronic acid and are of a certain particle size are taken as hemostatic materials, and the starch-hyaluronic acid hemostatic agent is an absorbable blood factor concentrating agent. The preparation method of the starch-hyaluronic acid hemostatic agent, disclosed by the invention, comprises the following steps: heating a mixed solution of starch and hyaluronic acid, then adding an initiator, and then putting into a spray dryer for spray drying so as to prepare the starch-hyaluronic acid porous microspheres, wherein the porous microspheres are characterized by showing a surface porous structure at a microscopic level and being of solid powdery substances at a macroscopic level. The starch-hyaluronic acid hemostatic agent is stored after radiation sterilization and directly applied at the bleeding part for hemostasis. The hemostatic agent has the advantages of high hemostatic performance and biodegradability.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
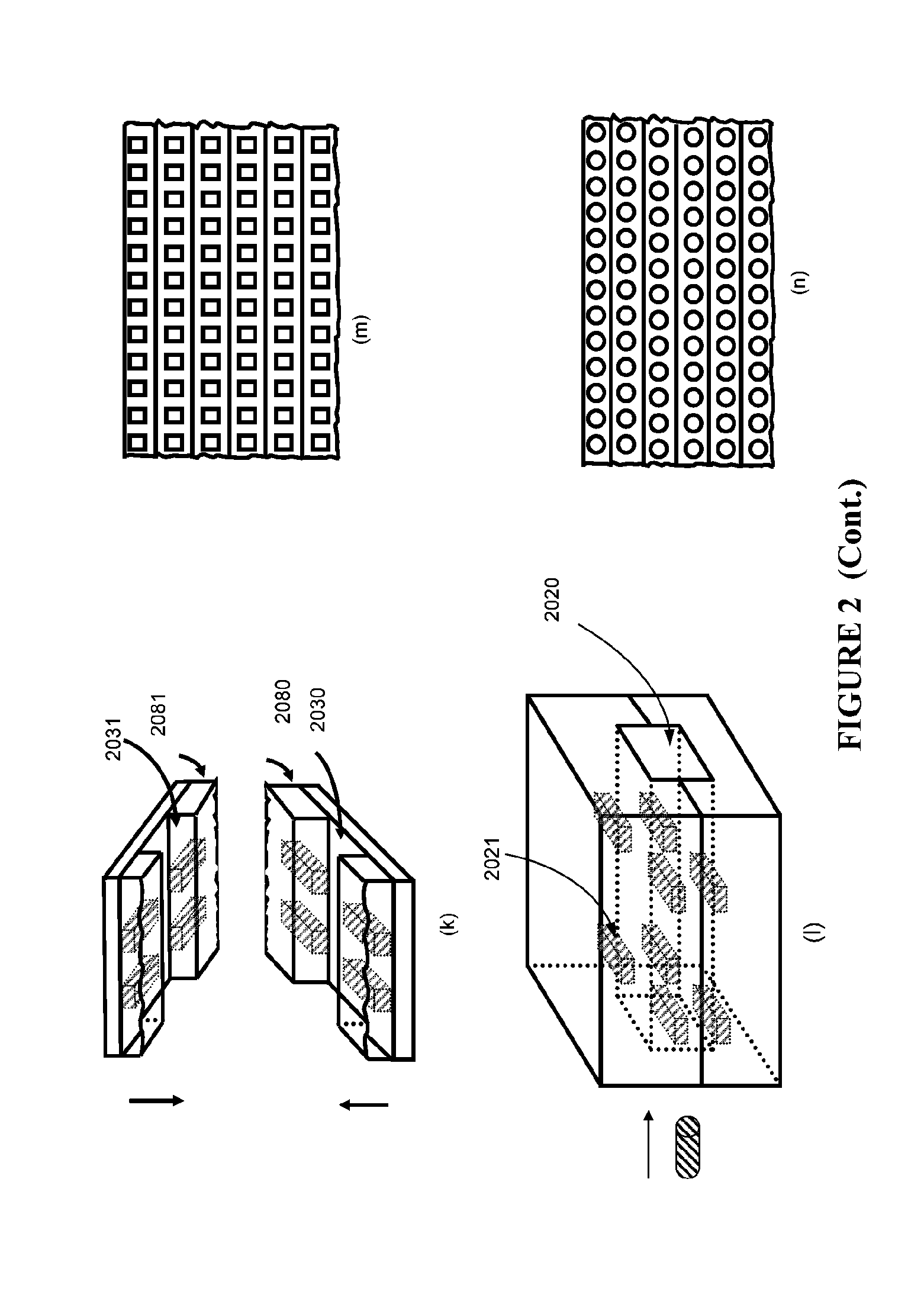
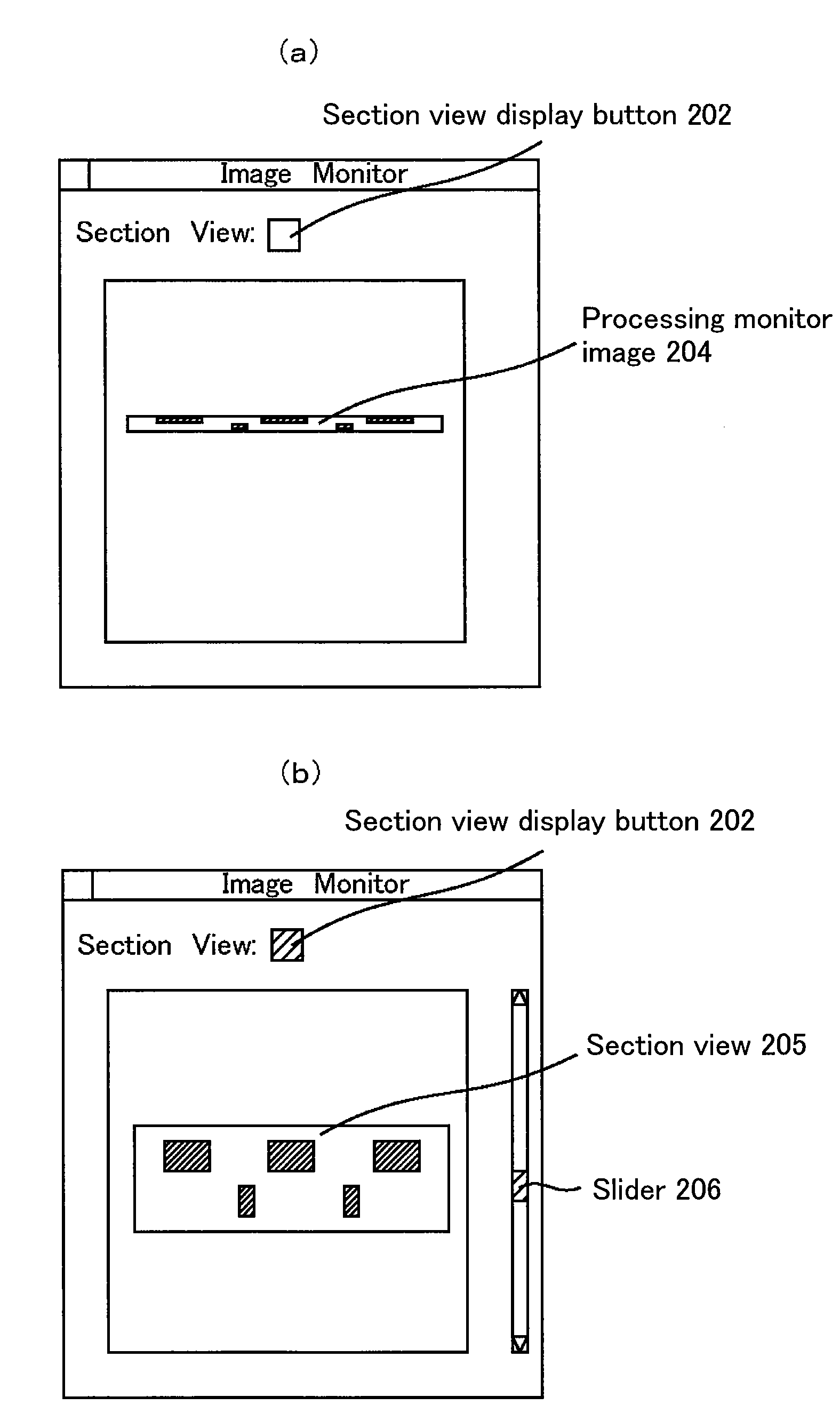
Micro-sample processing method, observation method and apparatus
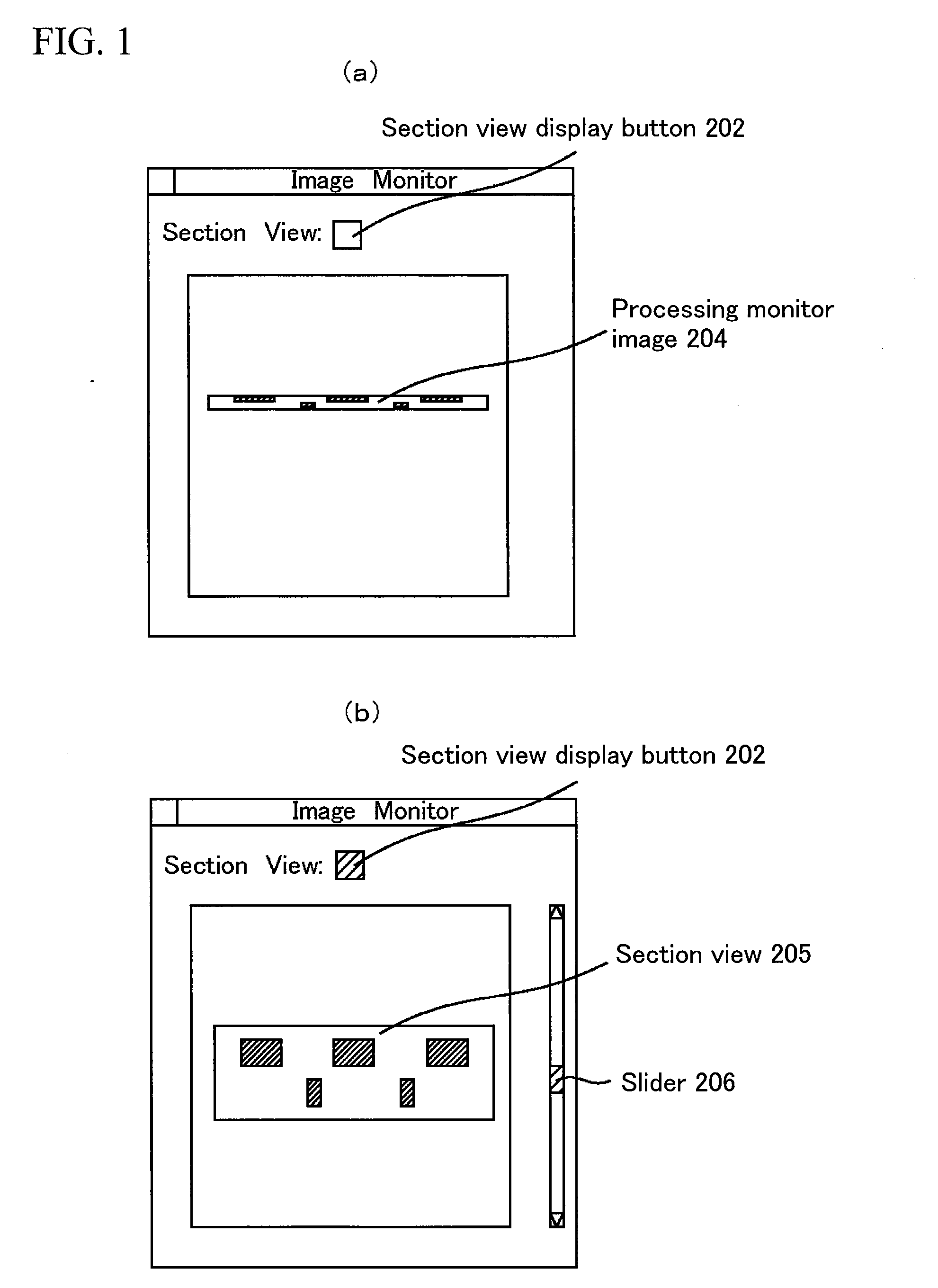
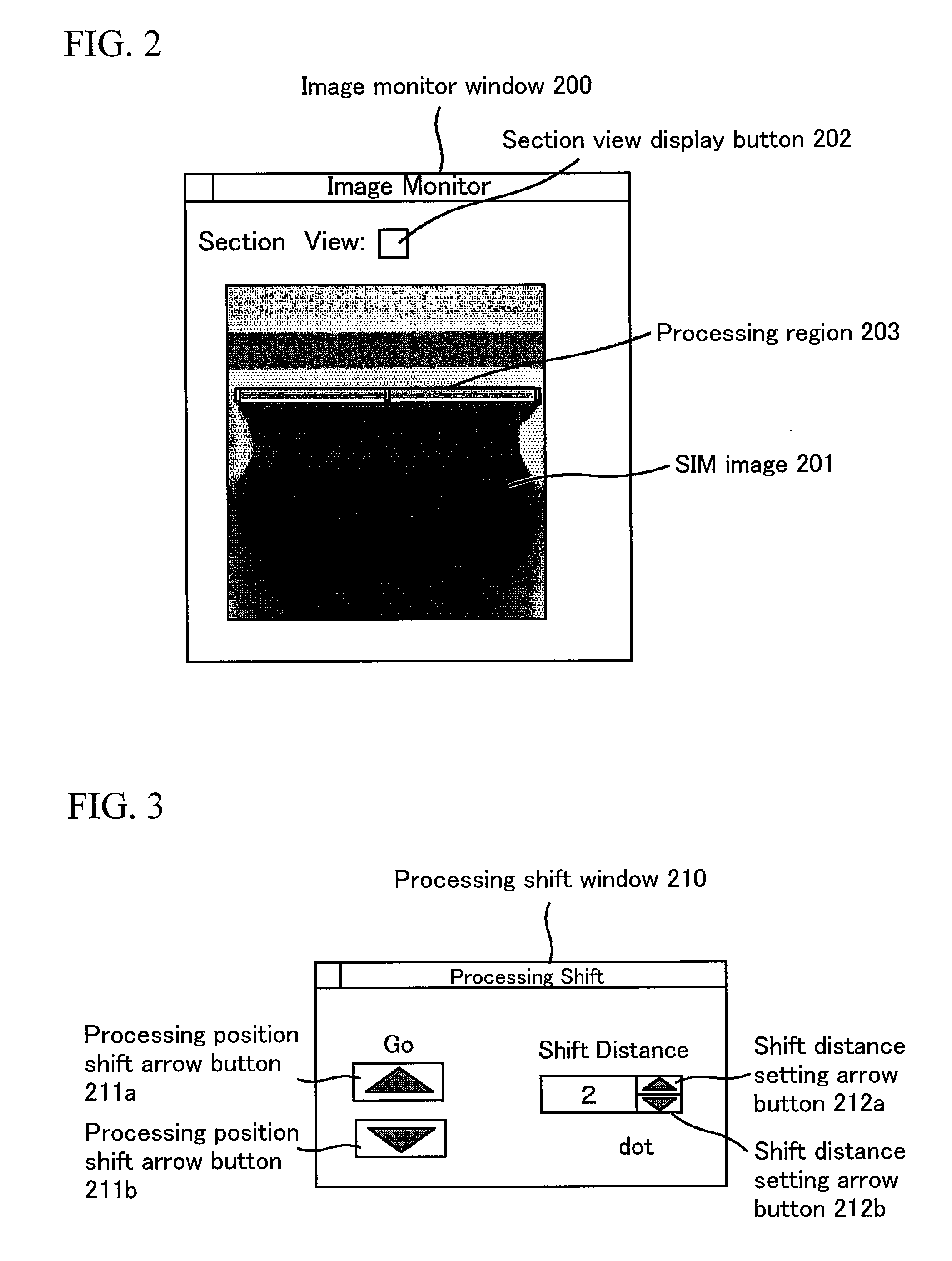
ActiveUS20080283746A1Reduced sample damageSuppressing damageMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesPerformed ObservationProcess region
As sample sizes have decreased to microscopic levels, it has become desirable to establish a method for thin film processing and observation with a high level of positional accuracy, especially for materials which are vulnerable to electron beam irradiation. The technological problem is to judge a point at which to end FIB processing and perform control so that the portion to be observed ends up in a central portion of the thin film. The present invention enables display of structure in cross-section by setting a strip-like processing region in an inclined portion of a sample cross-section and enlarging the display of the strip-like processing region on a processing monitor in a short-side direction. It is then possible to check the cross-sectional structure without additional use of an electron beam. Since it is possible to check the processed section without using an electron beam, electron beam-generated damage or deformation to the processed section is avoided. Further, performing the observation using a high-speed electron beam after forming the thin film enables observation with suppressed sample damage. Processing of even thinner thin films using the FIB while observing images of the sample generated using an electron beam is then possible.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Apparatus for detecting tumor cells
PendingUS20140073884A1Multiple and enhanced functionalityHigh degree of sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationBiological bodyEngineering
Among others, the present invention provides apparatus for detecting circulating tumor cells, comprising a system delivery biological subject and a probing and detecting device, wherein the probing and detecting device includes a first micro-device and a first substrate supporting the first micro-device, the first micro-device contacts a biologic material to be detected and is capable of measuring at the microscopic level an electrical, magnetic, electromagnetic, thermal, optical, acoustical, biological, chemical, electro-mechanical, electro-chemical, electro-optical, electro-thermal, electro-chemical-mechanical, bio-chemical, bio-mechanical, bio-optical, bio-thermal, bio-physical, bio-electro-mechanical, bio-electro chemical, bio-electro-optical, bio-electro-thermal, bio-mechanical-optical, bio-mechanical thermal, bio-thermal-optical, bio-electro-chemical-optical, bio-electro-mechanical-optical, bio electro-thermal-optical, bio-electro-chemical-mechanical, physical or mechanical property, or a combination thereof, of the biologic subject.
Owner:ANPAC BIO MEDICAL SCI (LISHUI) CO LTD
Conducting paste for device level interconnects
InactiveUS20120069531A1Prevent sinteringLine/current collector detailsConductive materialConductive pasteInterconnection
A conducting paste and method of forming the paste for device level interconnection. The conducting paste contains metal loading in the range 80-95% that is useful for making five micron device level interconnects. The conducting paste is made by mixing two different conducting pastes, each paste maintaining its micro level individual rich region in the mixed paste even after final curing. One paste contains at least one low melting point alloy and the other paste contains noble metal fillers such as gold or silver flakes. In general, average flake size below five micron is suitable for five micron interconnects. However, 1 micron or smaller silver flakes and an LMP mixture is preferred for five micron interconnects. The amount of LMP based paste in the final mixture is preferably 20-50% by weight. The nano micro paste embodiment shows good electrical yield (81%) and low contact resistance.
Owner:TTM TECH NORTH AMERICA LLC
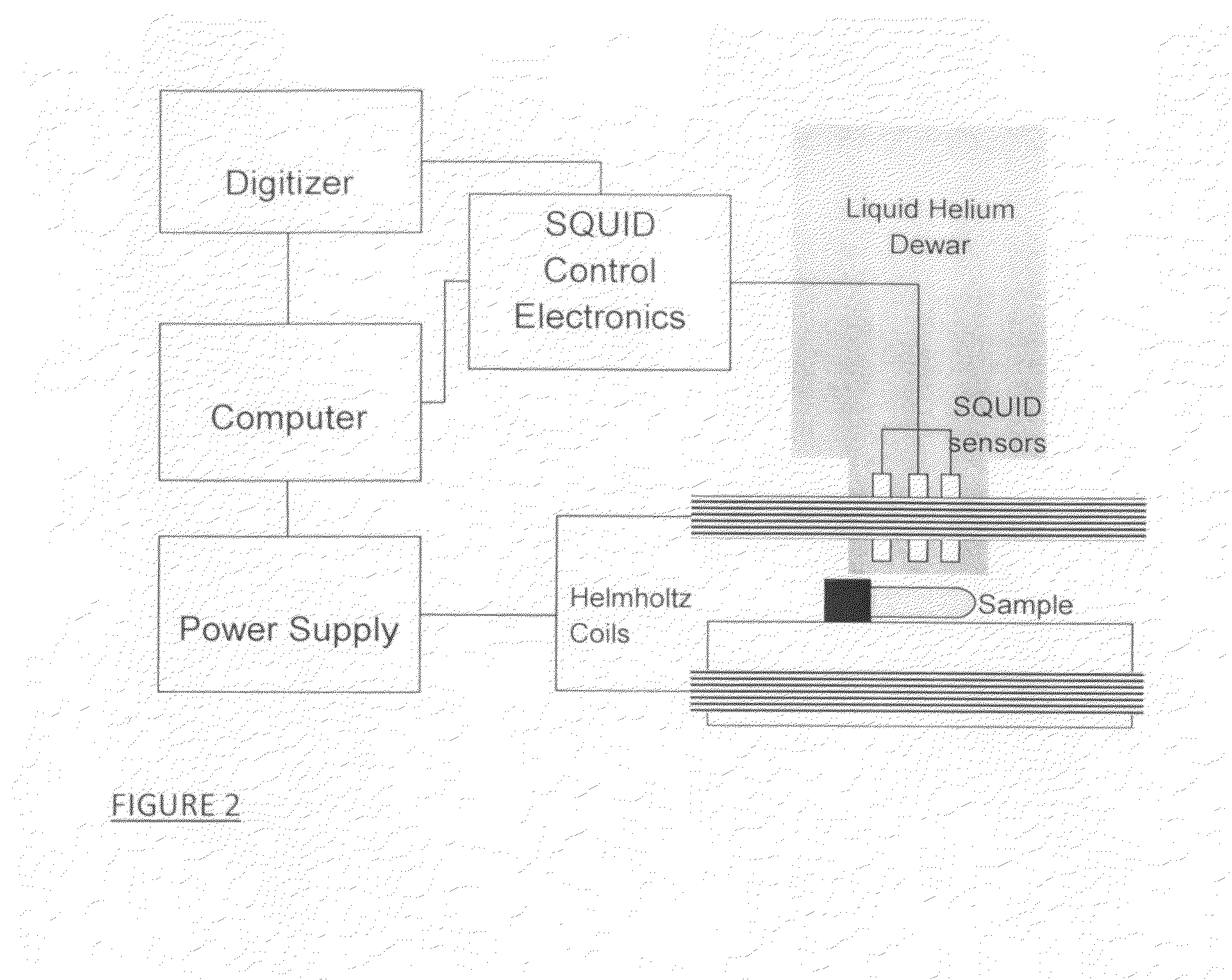
Viscosity measuring method
InactiveUS20150293004A1Reduce and eliminate relaxation effectFlow propertiesNanosensorsMeasurement testRoom temperature
A method for measuring the average viscosity of a test fluid uses calibrated magnetic nanoparticles, with certain chosen hydrodynamic diameters and actual lateral dimensions (e.g. diameters), that are mixed into a small volume of the test fluid and a single magnetic relaxation curve measurement to provide data for viscosity determination. The distribution of hydrodynamic particle sizes of an ensemble of magnetic nanoparticles that are magnetically blocked at room temperature can be determined. Modifications of the method can be used to determine the distribution of viscosities in a complex fluid at the sub-microscopic level providing a novel type of viscosity measurement.
Owner:STC UNM +1
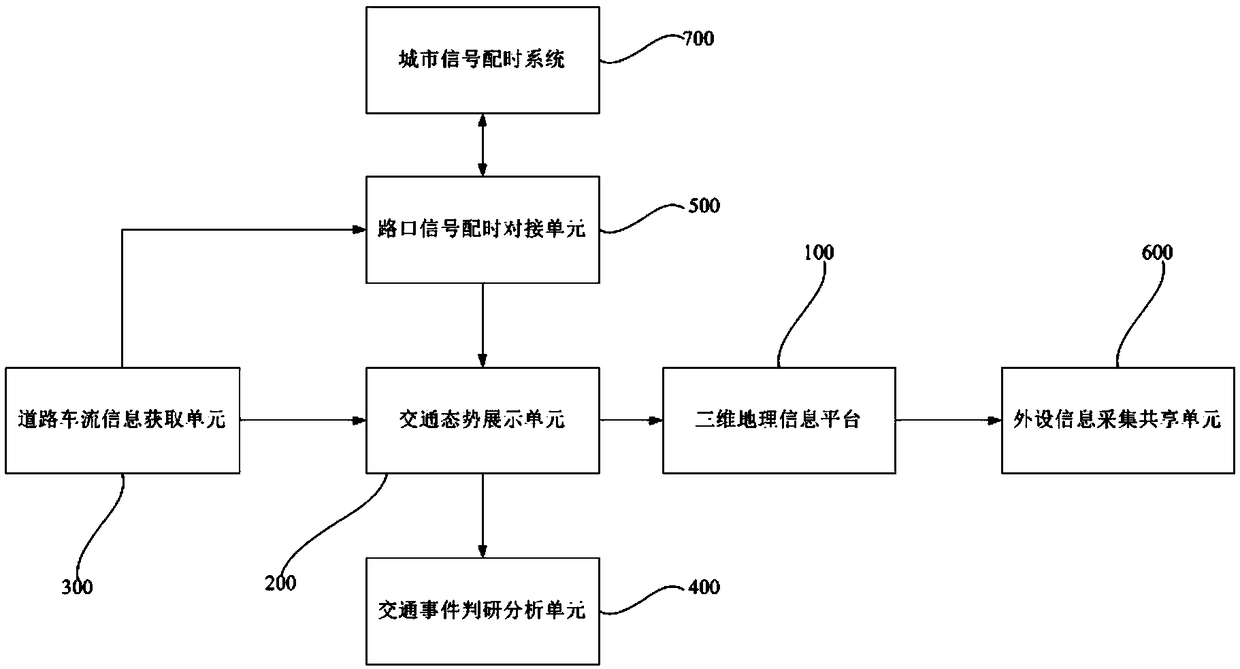
Road holographic induction-based traffic service and management system
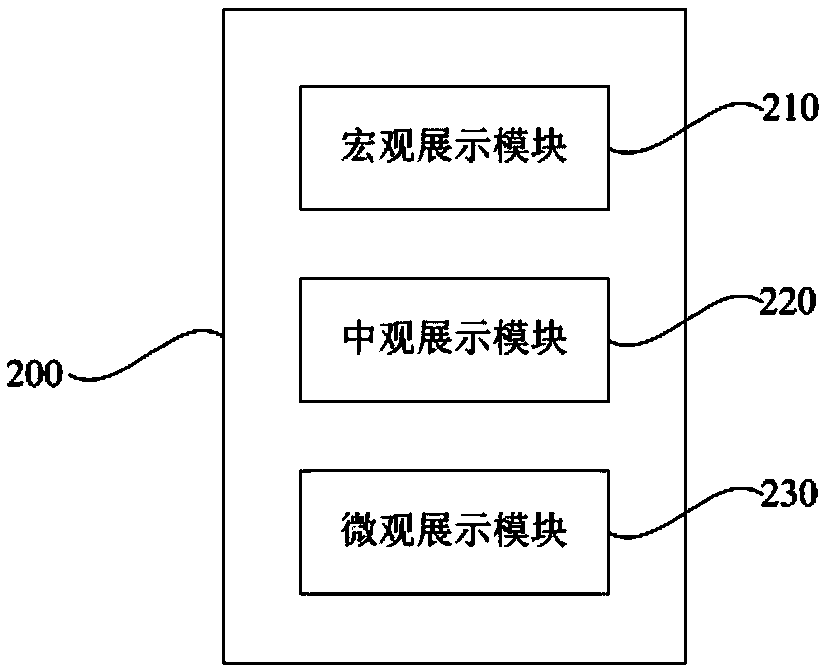
ActiveCN109410573AEasy to manageAchieve refinementDetection of traffic movementMicroscopic levelIntermediate level
The invention discloses a road holographic induction-based traffic service and management system. The system comprises a three-dimensional geographic information platform, a traffic situation displayunit, a road traffic information acquisition unit, a traffic event judgment analysis unit, an intersection signal timing docking unit, and a peripheral information collection and sharing unit; the three-dimensional geographic information platform is used for providing the road network map layer information of a lane level; the traffic situation display unit is used for fully presenting urban traffic operation situations from a macroscopic level, an intermediate level and a microscopic level; the road traffic information acquisition unit is used for acquiring traffic flow information on roads;the traffic event judgment analysis unit is used for judging whether a traffic event exists according to the traffic operation status of the traffic situation display unit and sending alarm information; the intersection signal timing docking unit is used for obtaining intersection signal timing information; and the peripheral information collection and sharing unit is used for collecting traffic facility information on a road network, and sharing the information displayed by the three-dimensional geographic information platform with a cloud server. With the road holographic induction-based traffic service and management system of the invention, the urban traffic conditions can be comprehensively presented from the macroscopic level, the intermediate level and the microscopic level, urban traffic management capabilities can be effectively improved, and the refinement of urban traffic information services can be realized.
Owner:中电科新型智慧城市研究院有限公司
Apparatus for disease detection
ActiveUS20140342441A1Low costHigh degree of sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsVacuum evaporation coatingBiological bodyEngineering
The present invention provides, among others, apparatus for detecting a disease, comprising a system delivery biological subject and a probing and detecting device, wherein the probing and detecting device includes a first micro-device and a first substrate supporting the first micro-device, the first micro-device contacts a biologic material to be detected and is capable of measuring at the microscopic level an electric, magnetic, electromagnetic, thermal, optical, acoustical, biological, chemical, physical, or mechanical property of the biologic material.
Owner:CHANGWEI SYST TECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Micro-devices for disease detection
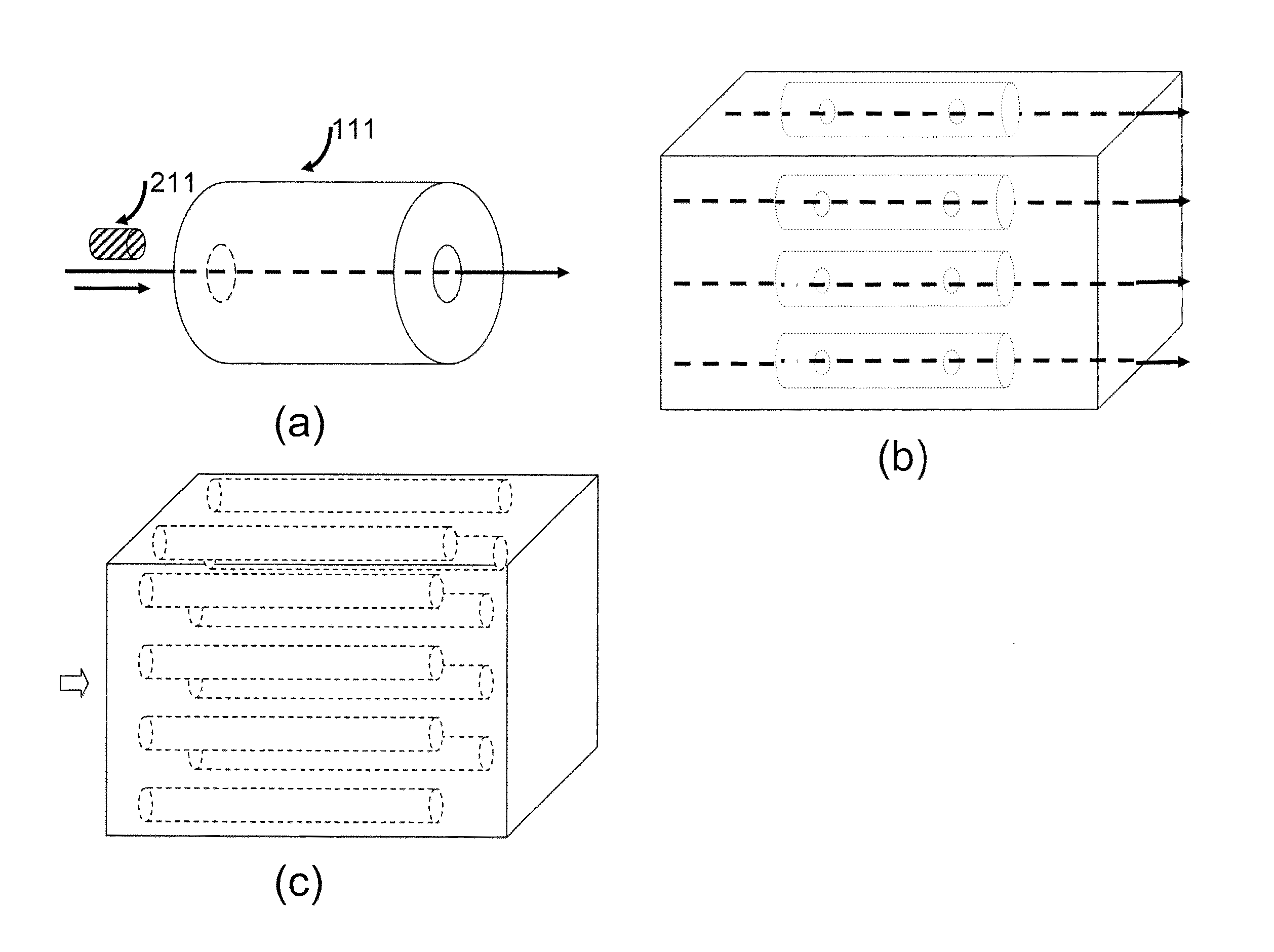
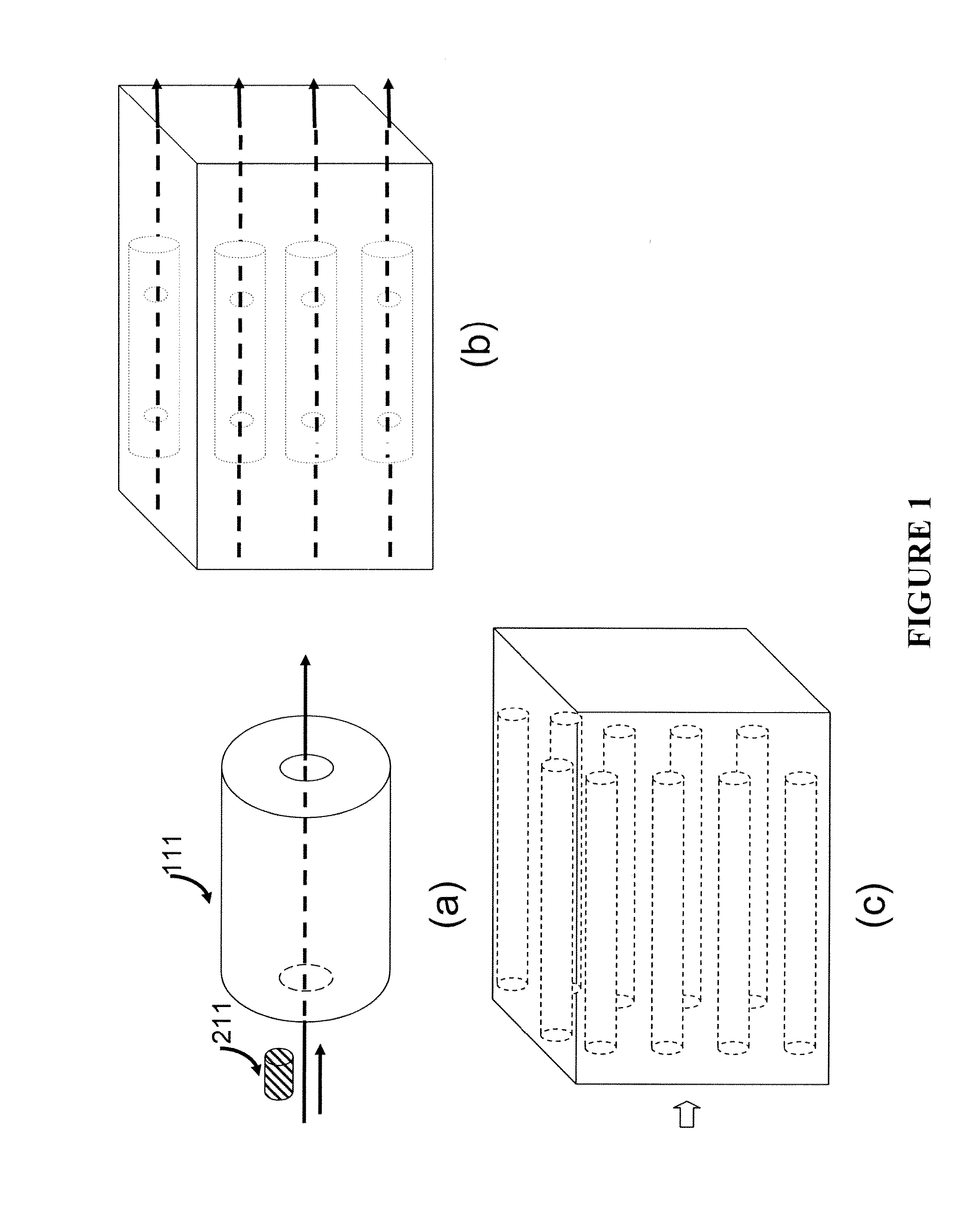
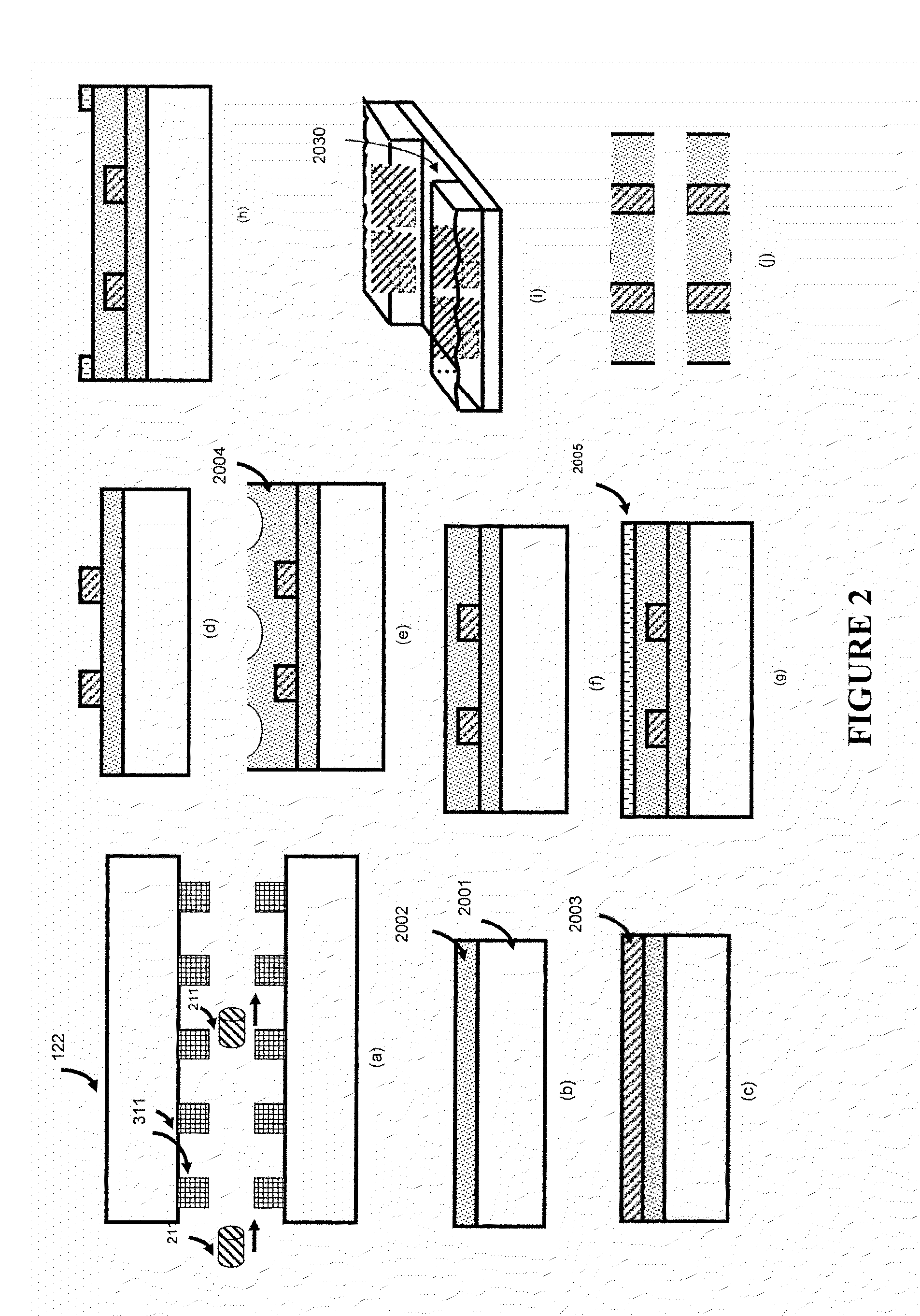
ActiveUS9651542B2High degree of sensitivityImprove convenienceLaboratory glasswaresBiological testingDiseaseMicro devices
Among others, the present invention provides micro-devices for detecting or treating a disease, each comprising a first micro sensor for detecting a property of the biological sample at the microscopic level, and an interior wall defining a channel, wherein the micro sensor is located in the interior wall of the micro-device and detects the property of the biological sample in the microscopic level, and the biological sample is transported within the channel.
Owner:NINGKASAI TECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Evaluation method for uniformity of continuous-fiber-reinforced composite resin
The invention provides an evaluation method for the uniformity of continuous-fiber-reinforced composite resin. According to a technical scheme in the invention, the method comprises the following main steps: step 1, acquiring a continuous-fiber-reinforced composite, cutting out samples at to-be-detected positions, wherein when the samples are to be cut out, it is required that the axial direction of most fibers on each selected cross section is perpendicular to the cross section; step 2, randomly selecting a sample, selecting test areas on a polished cross section; and step 3, after selection of the test areas, successively testing the nanometer mechanical hardness of each test area, wherein when one test area is to be tested, a nanometer indentation probe is used for scanning the three-dimensional morphology of the test area, then test points are selected from the test area, and the nanometer hardness of each test point is tested successively. Thus, the method can test the performance of the composite resin in a nano-scale microscopic level for evaluation of microscopic uniformity of the resin; and the method has a wide application scope and is applicable to acquisition of microscopic mechanical data of samples located at different areas and positions, so multiple information of integral, local and microscopic uniformity of composite samples can be obtained.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING AERONAUTICAL MFG TECH RES INST +1
Micro-devices for disease detection
ActiveUS9823209B2High degreeReduce device sizeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsVacuum evaporation coatingBiophysical chemistryMedicine
Among others, the present invention provides piezo-electric micro-devices for detecting at the microscopic level an electric, magnetic, electromagnetic, thermal, optical, acoustical, biological, chemical, physical, bio-chemical, bio-physical, physical-chemical, bio-physical-chemical, bio-mechanical, bio-electro-mechanical, electro-mechanical, or mechanical property of the biologic subject.
Owner:NING KASAI TECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com