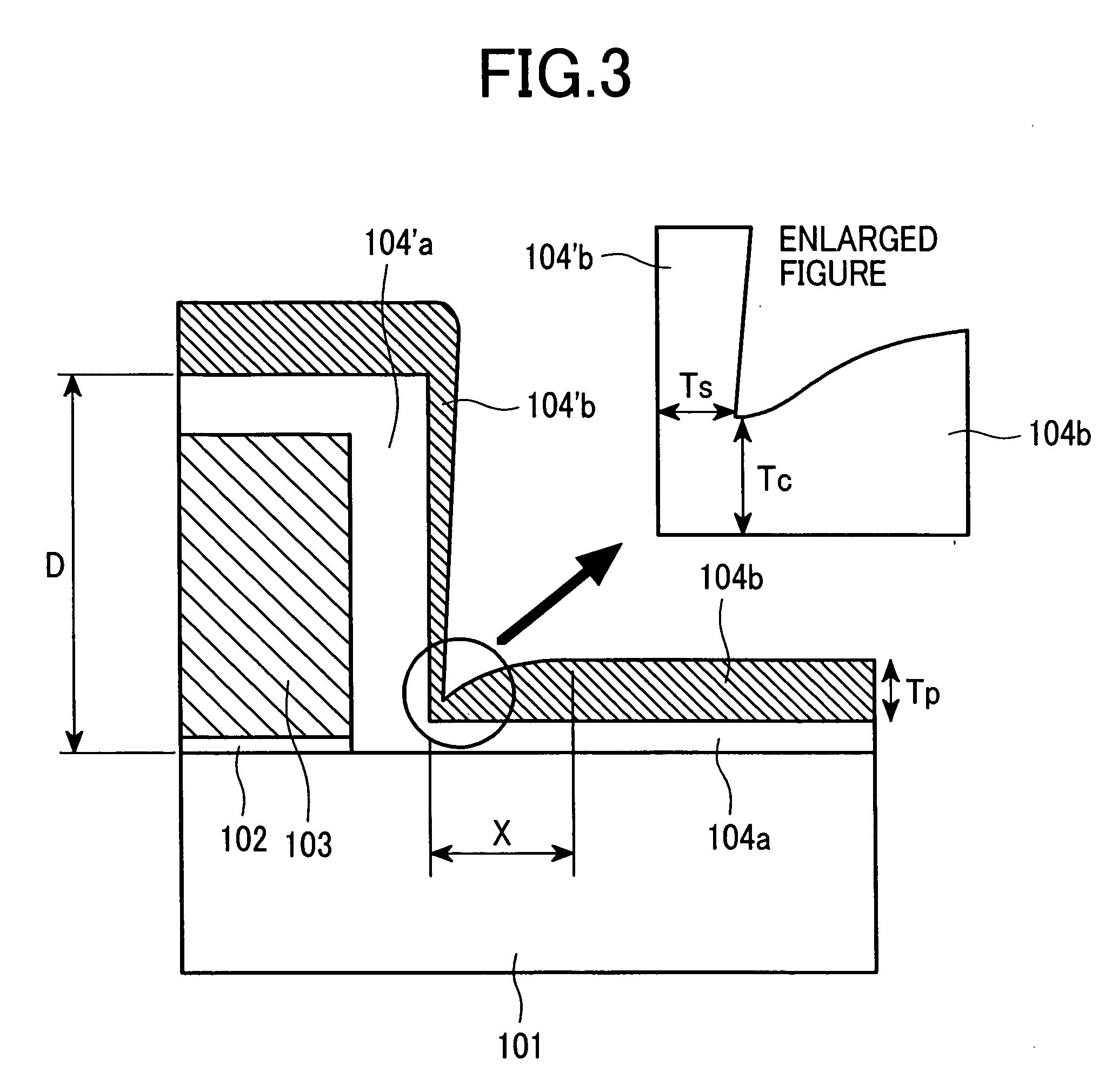
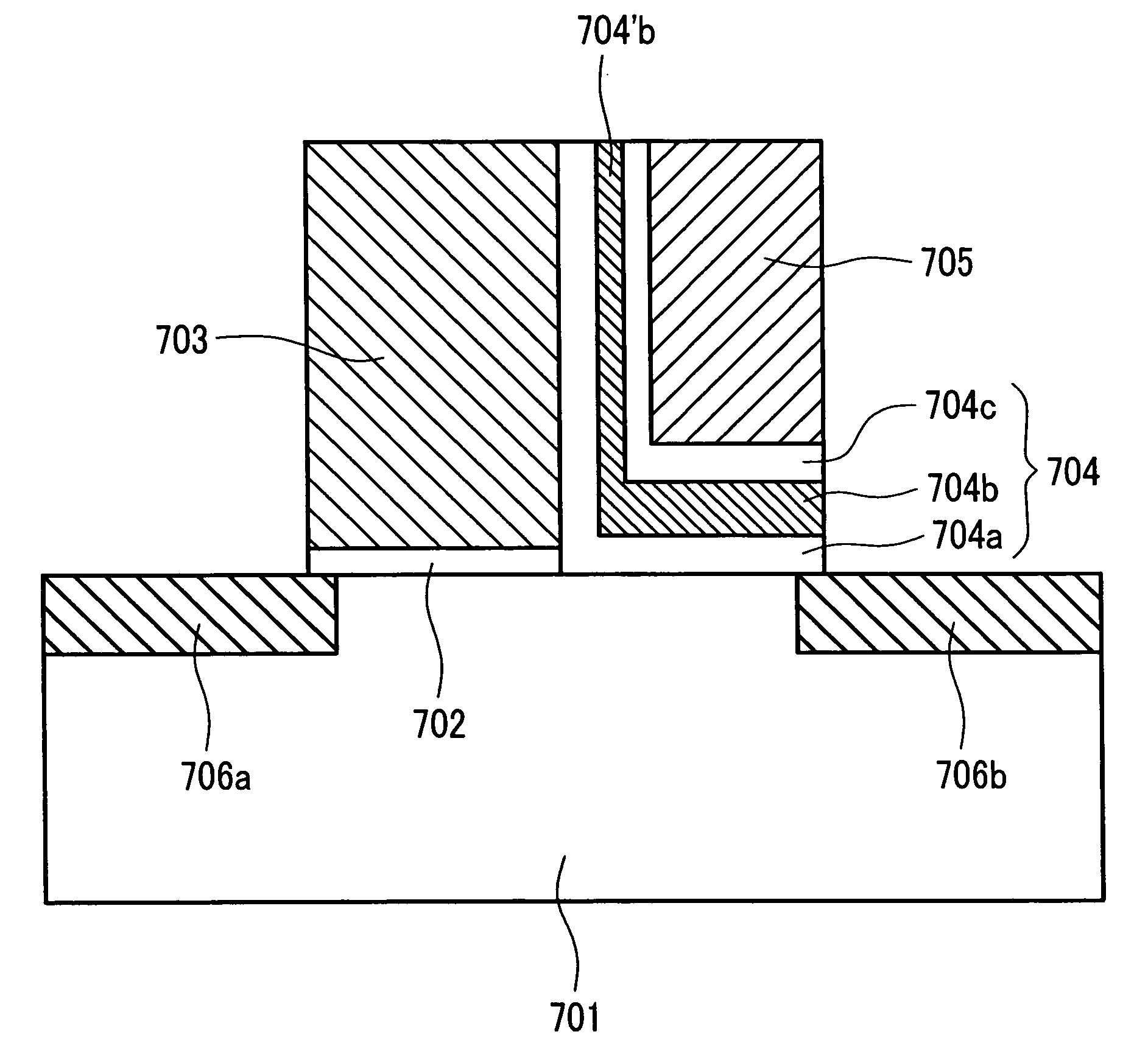
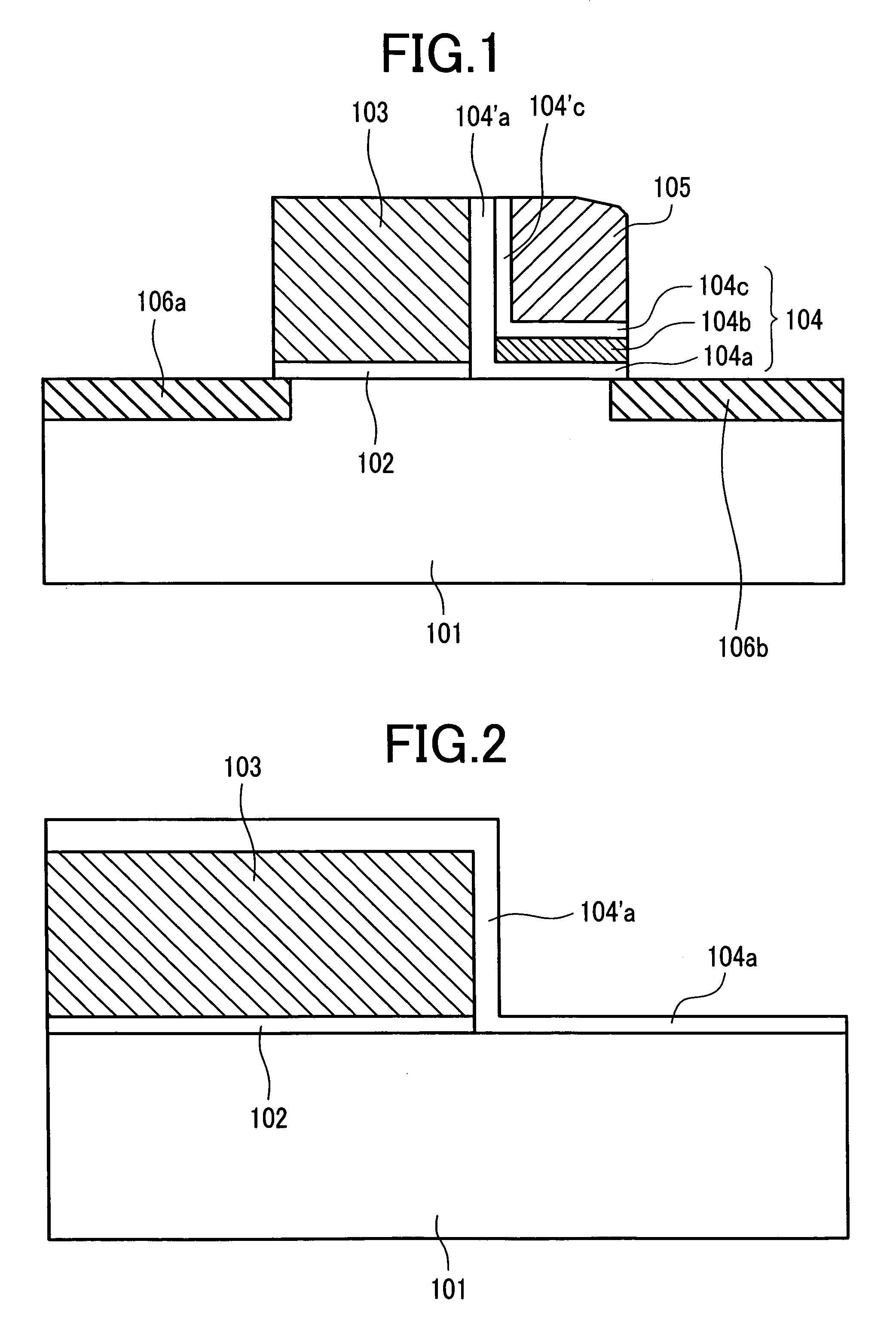
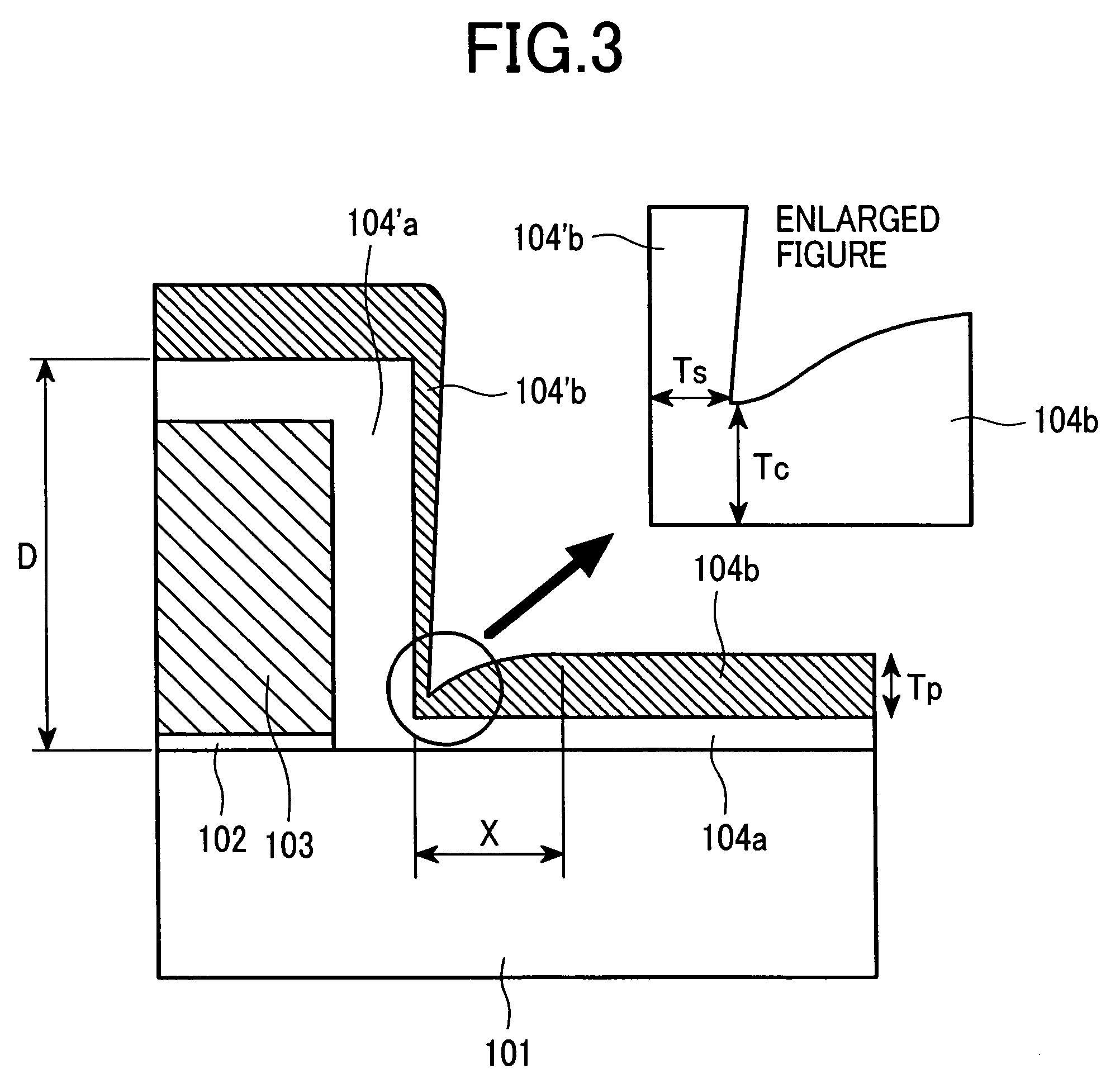
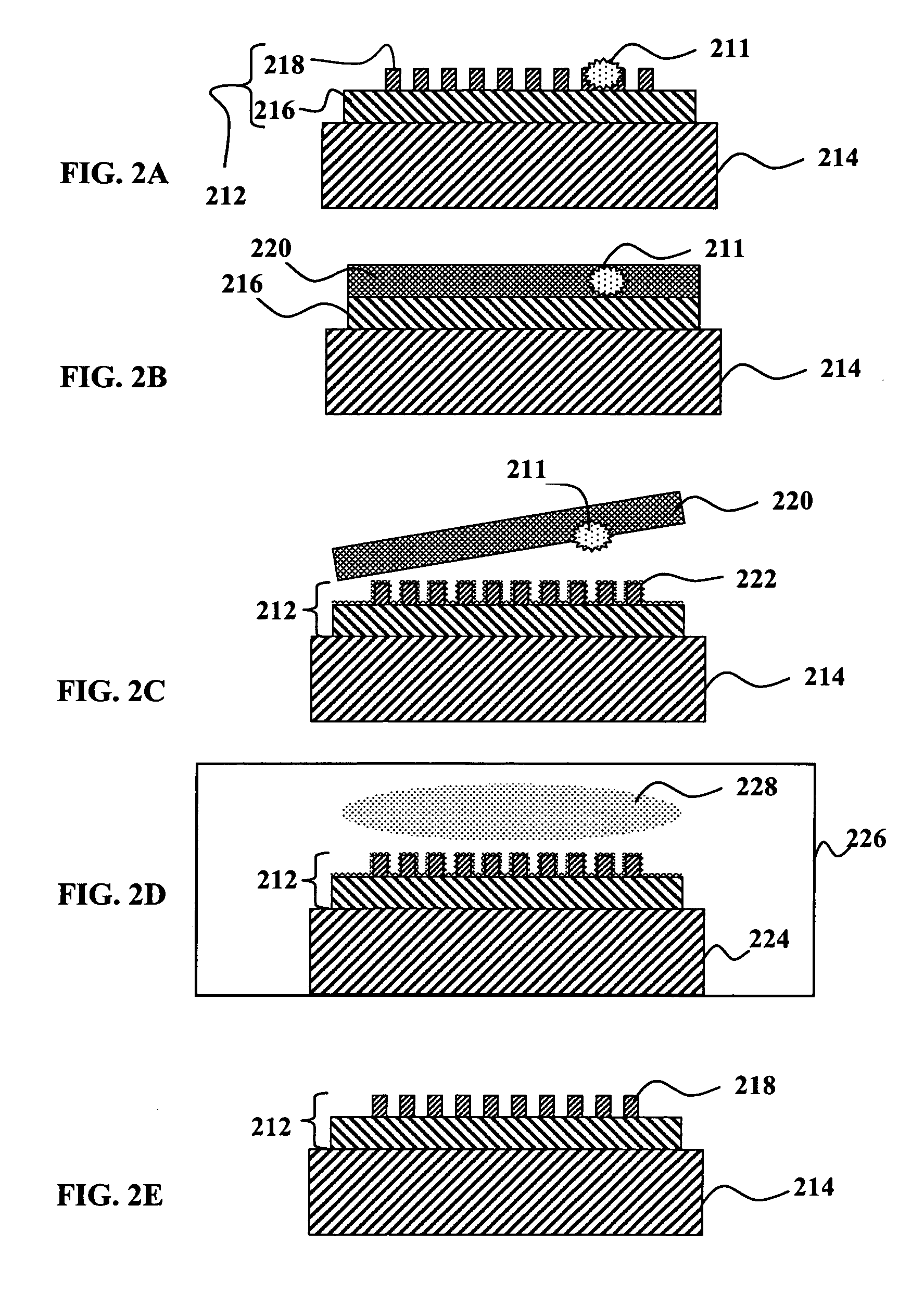
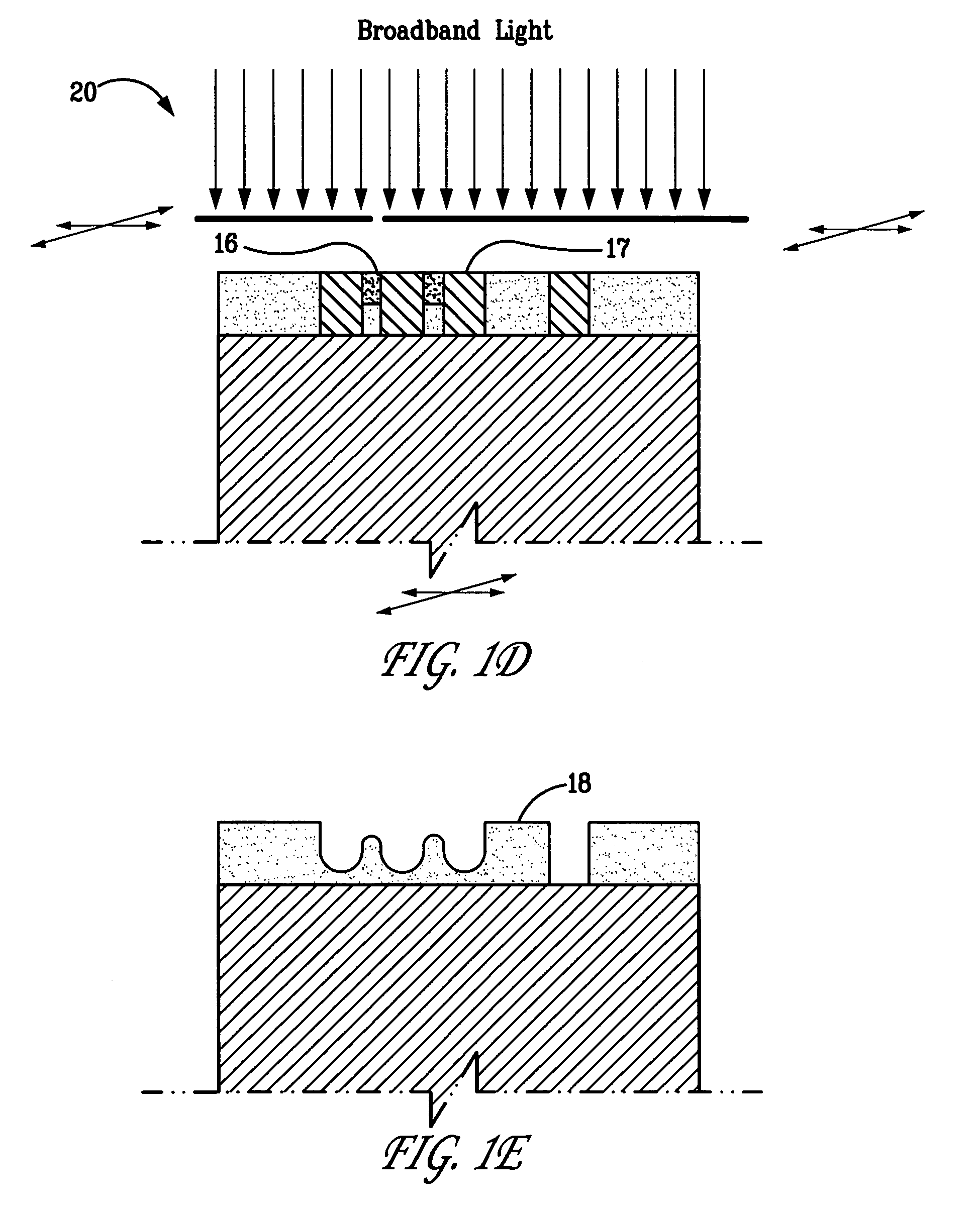
Patents
Literature
118 results about "Reactive plasma" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
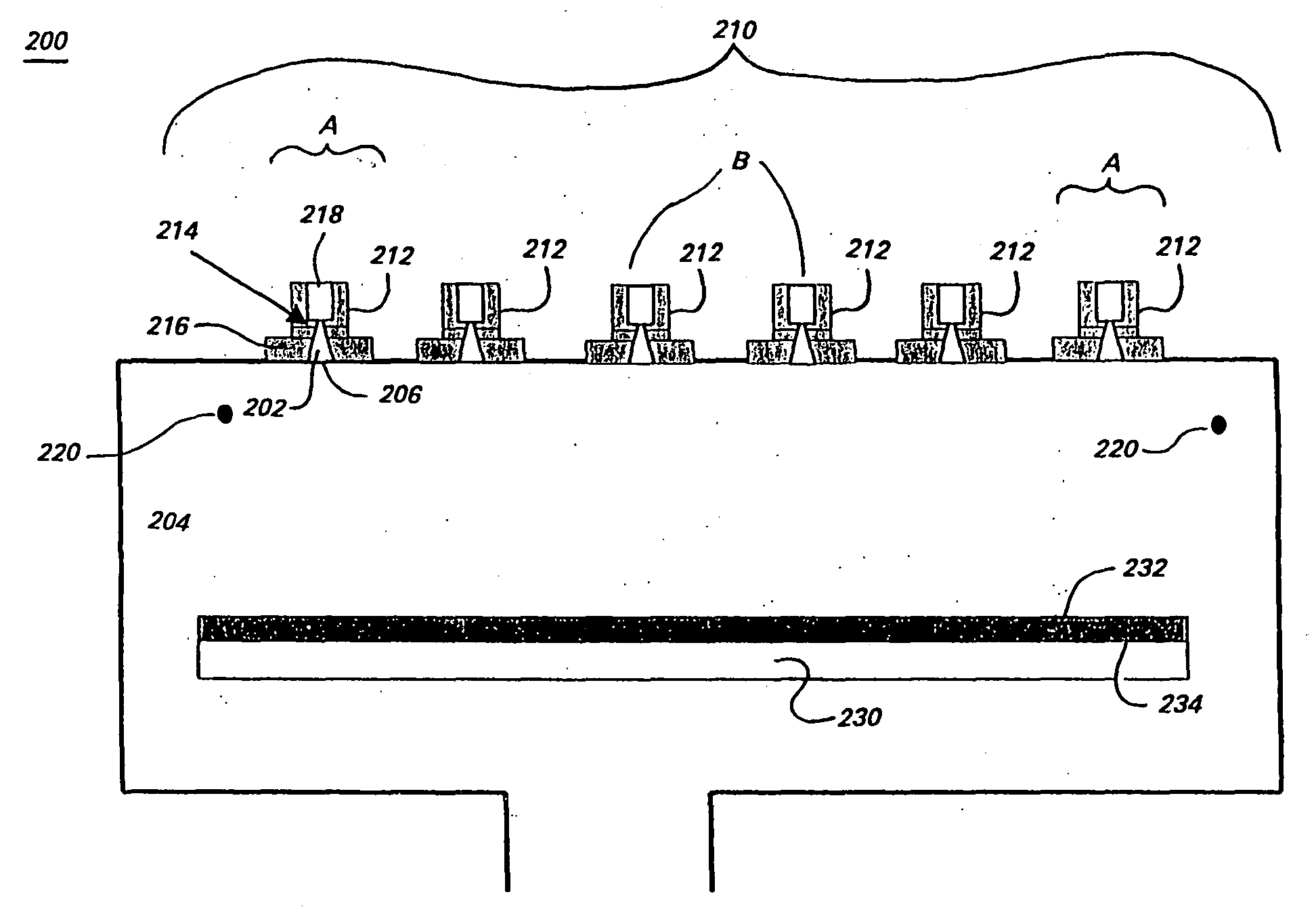
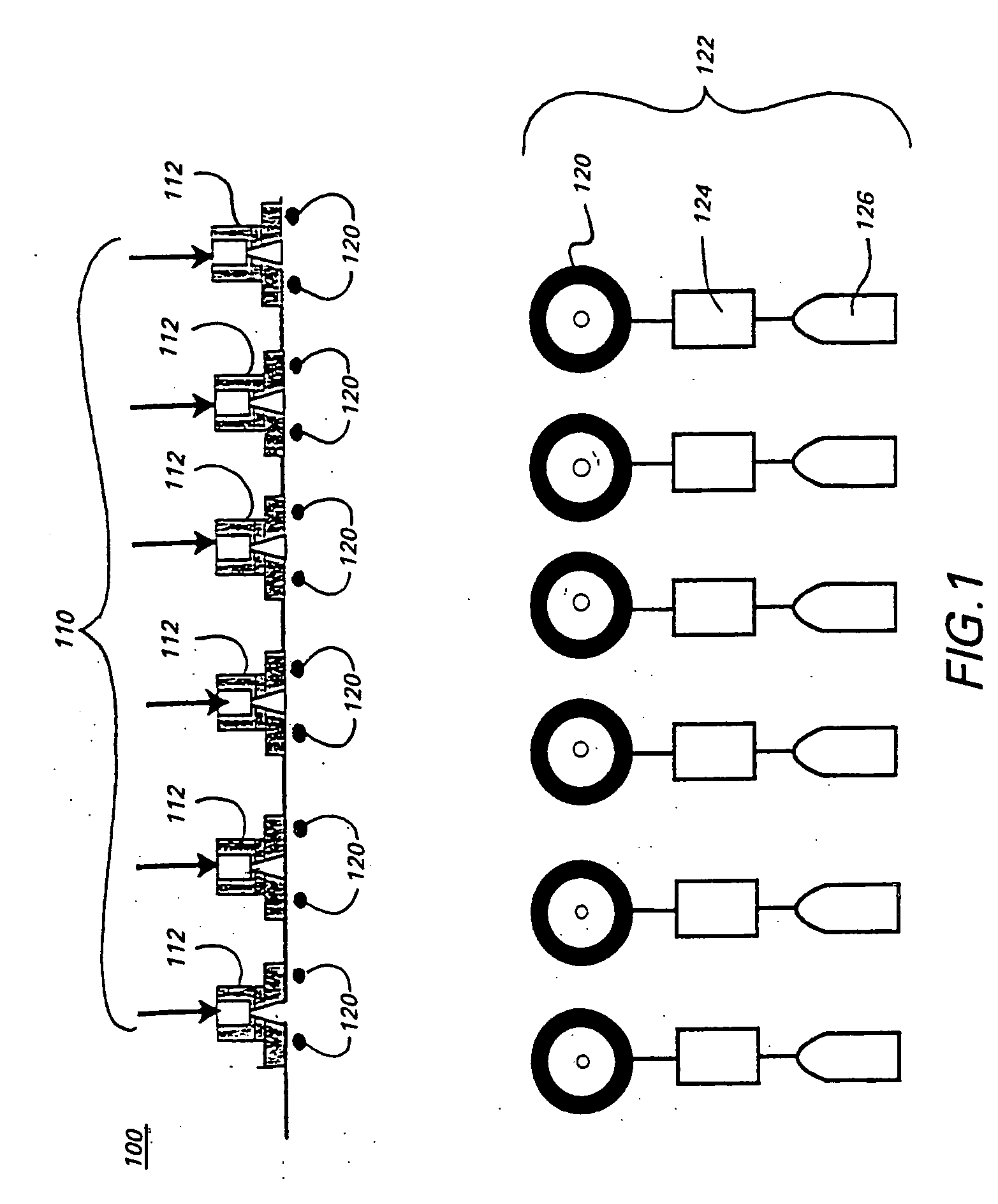
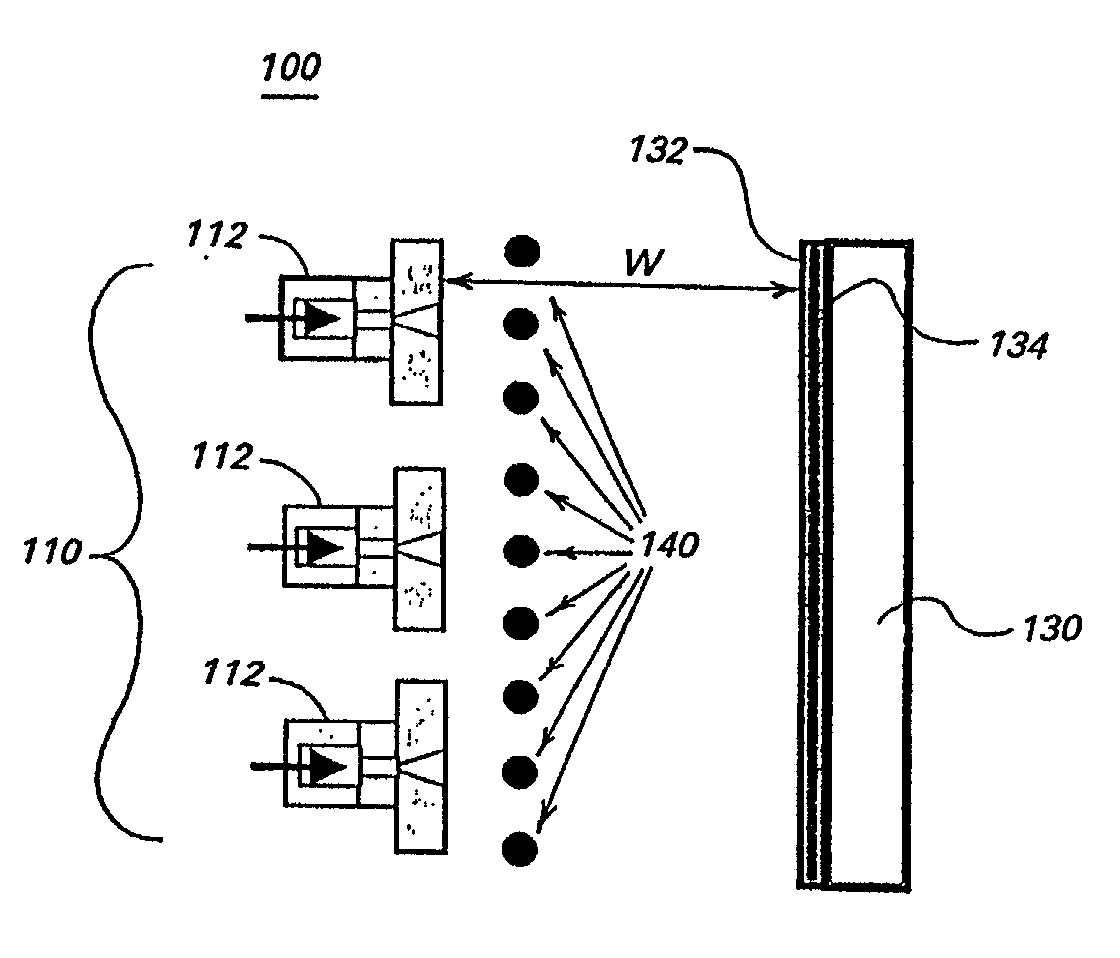
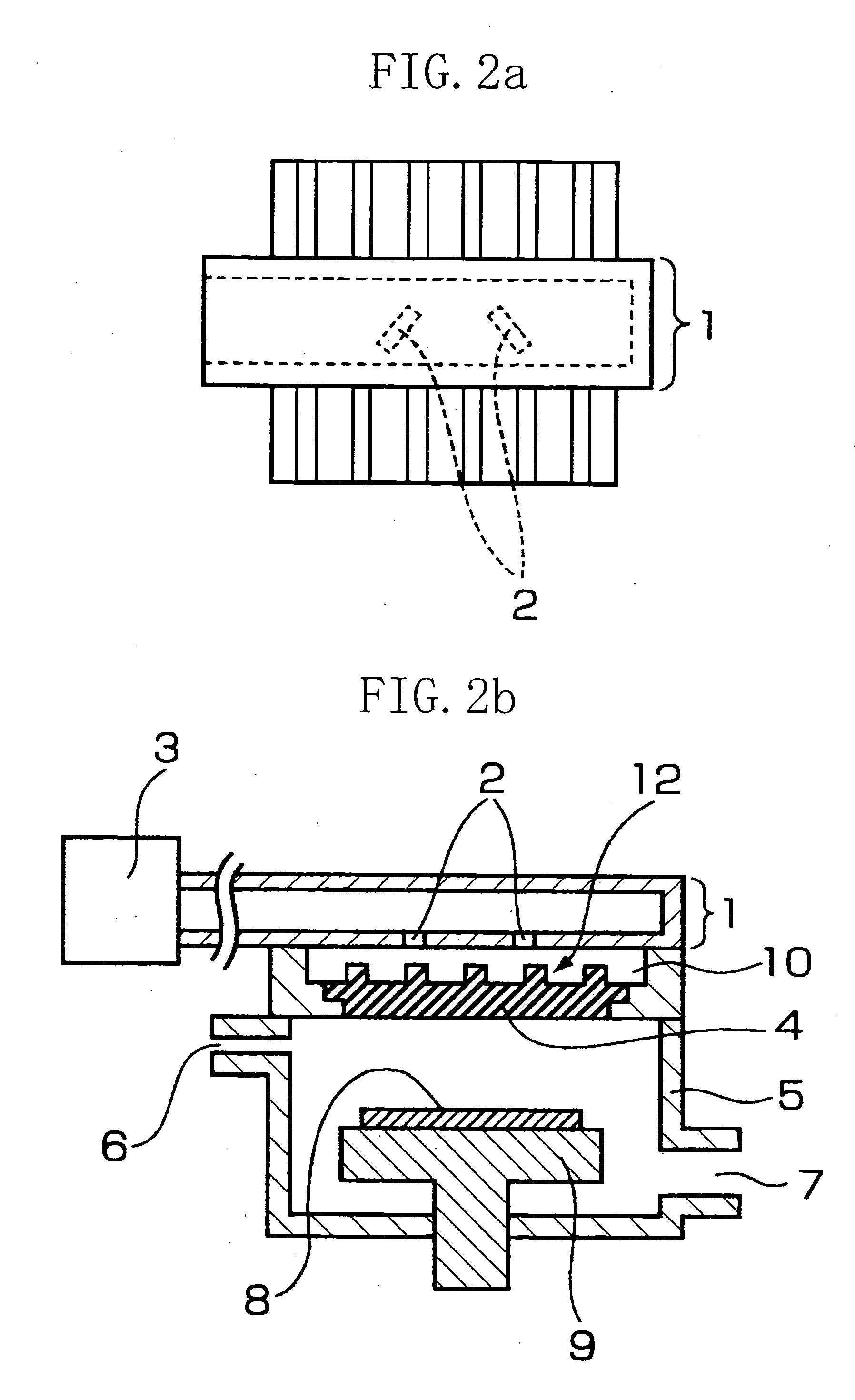
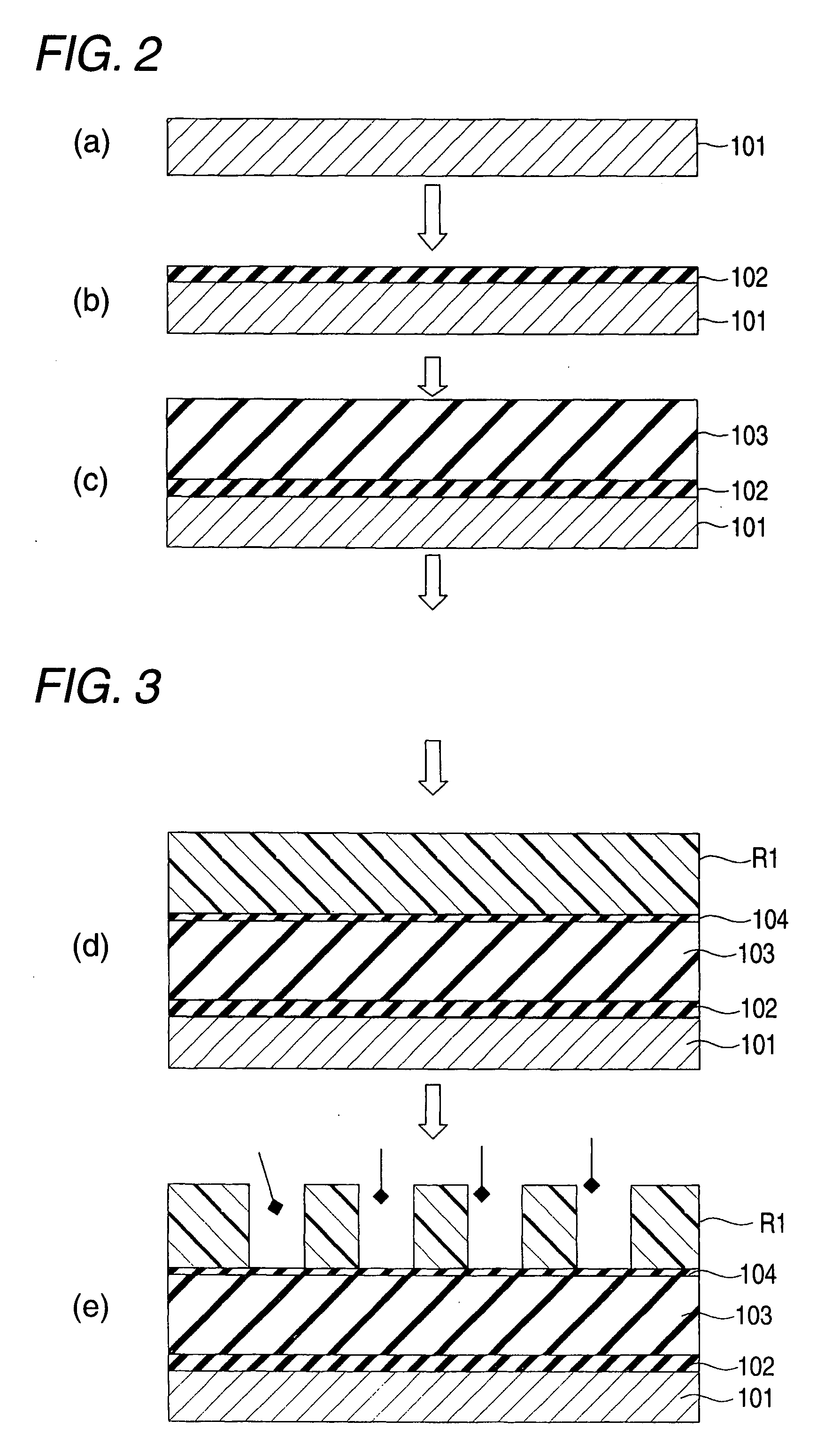
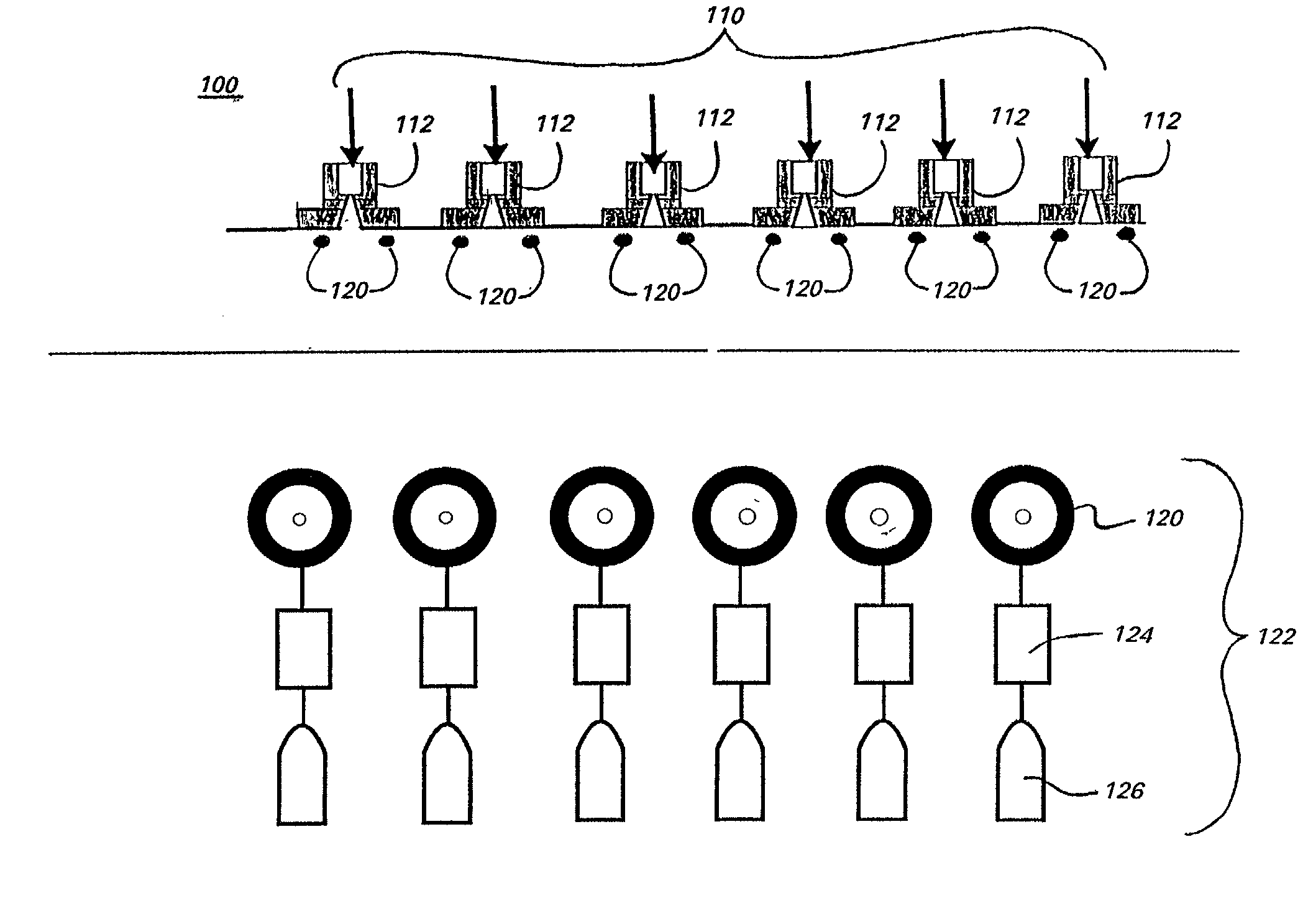
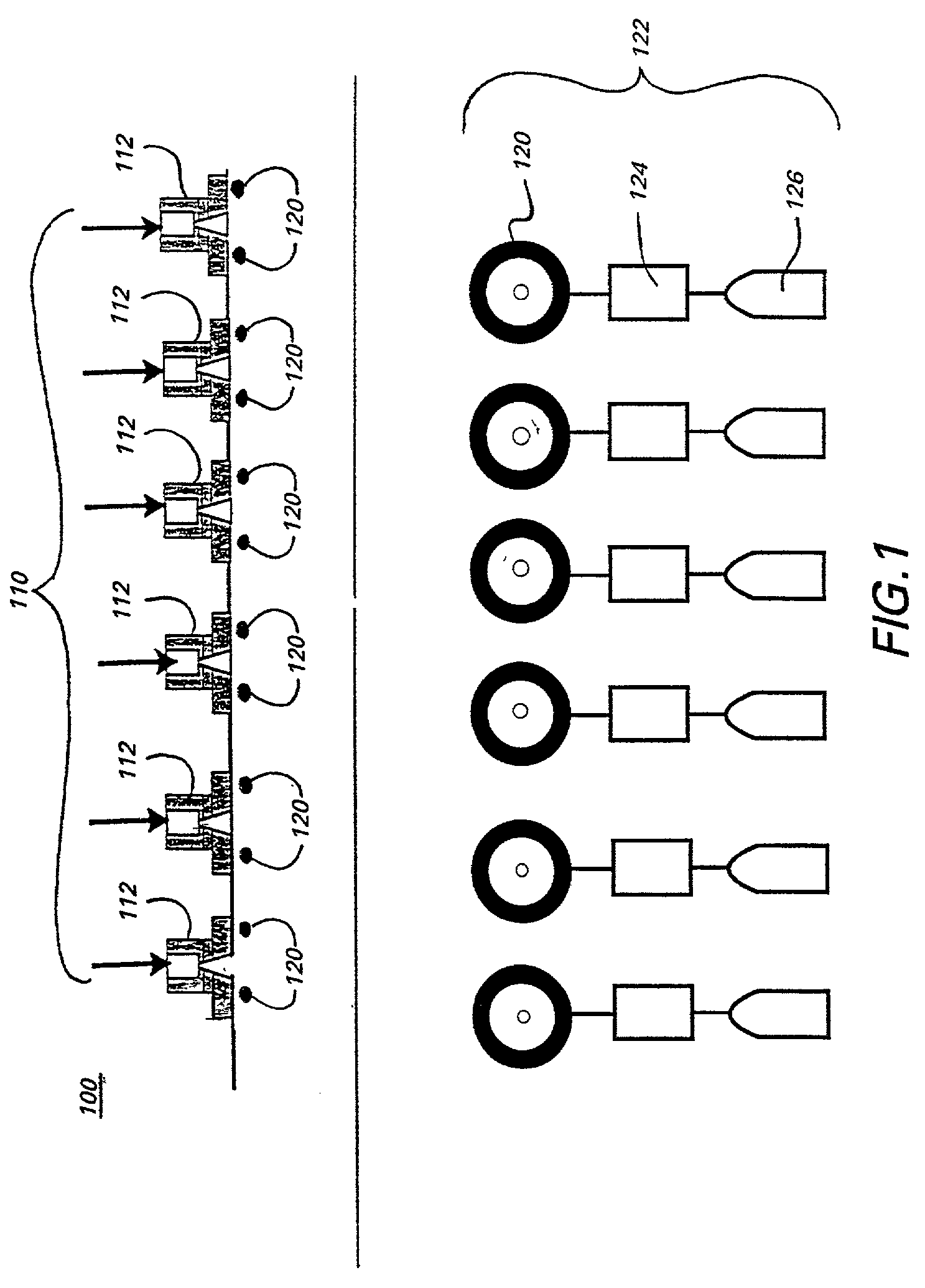
Enhanced reactive DC sputtering system
InactiveUS6024844ASpeed up the processDissipate any charge build-upCellsElectric discharge tubesReactive plasmaInductor
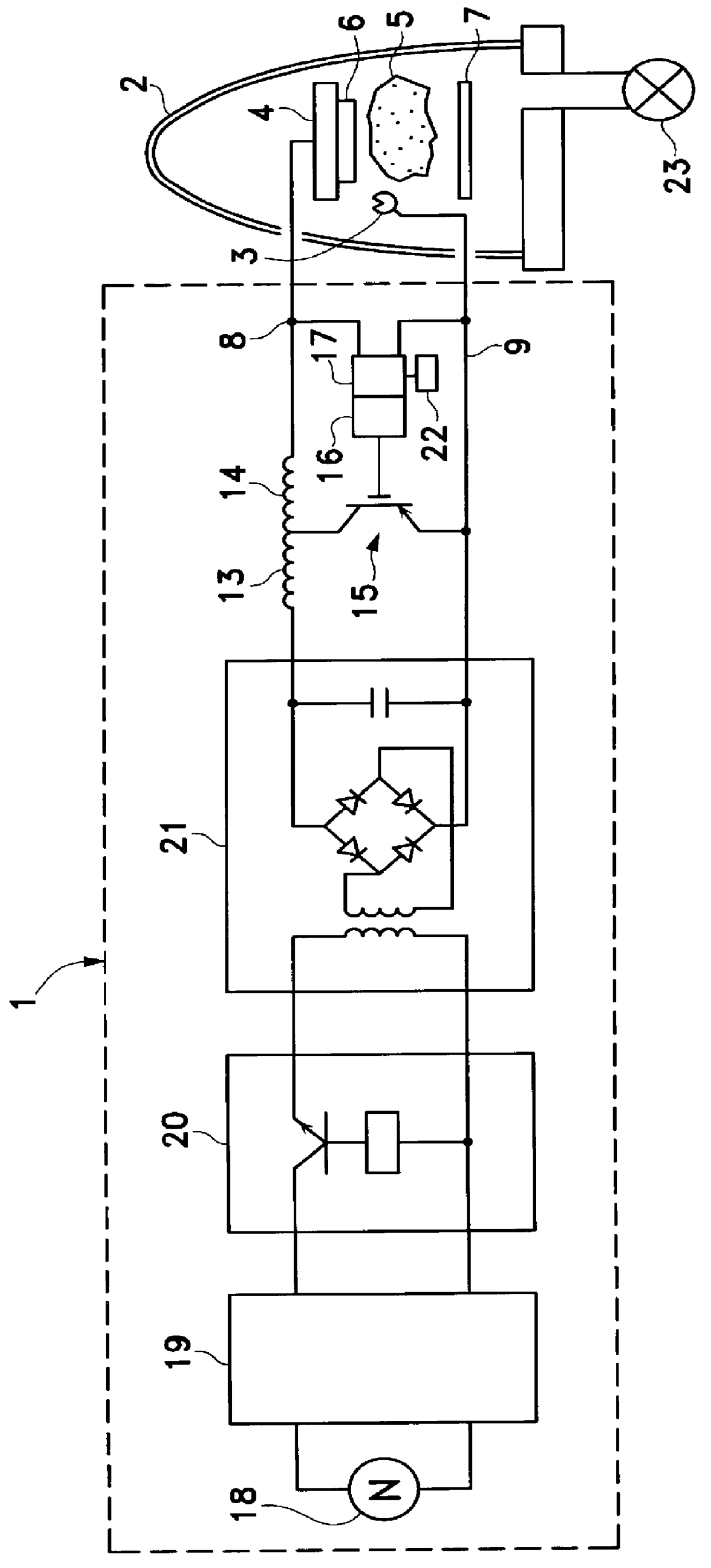
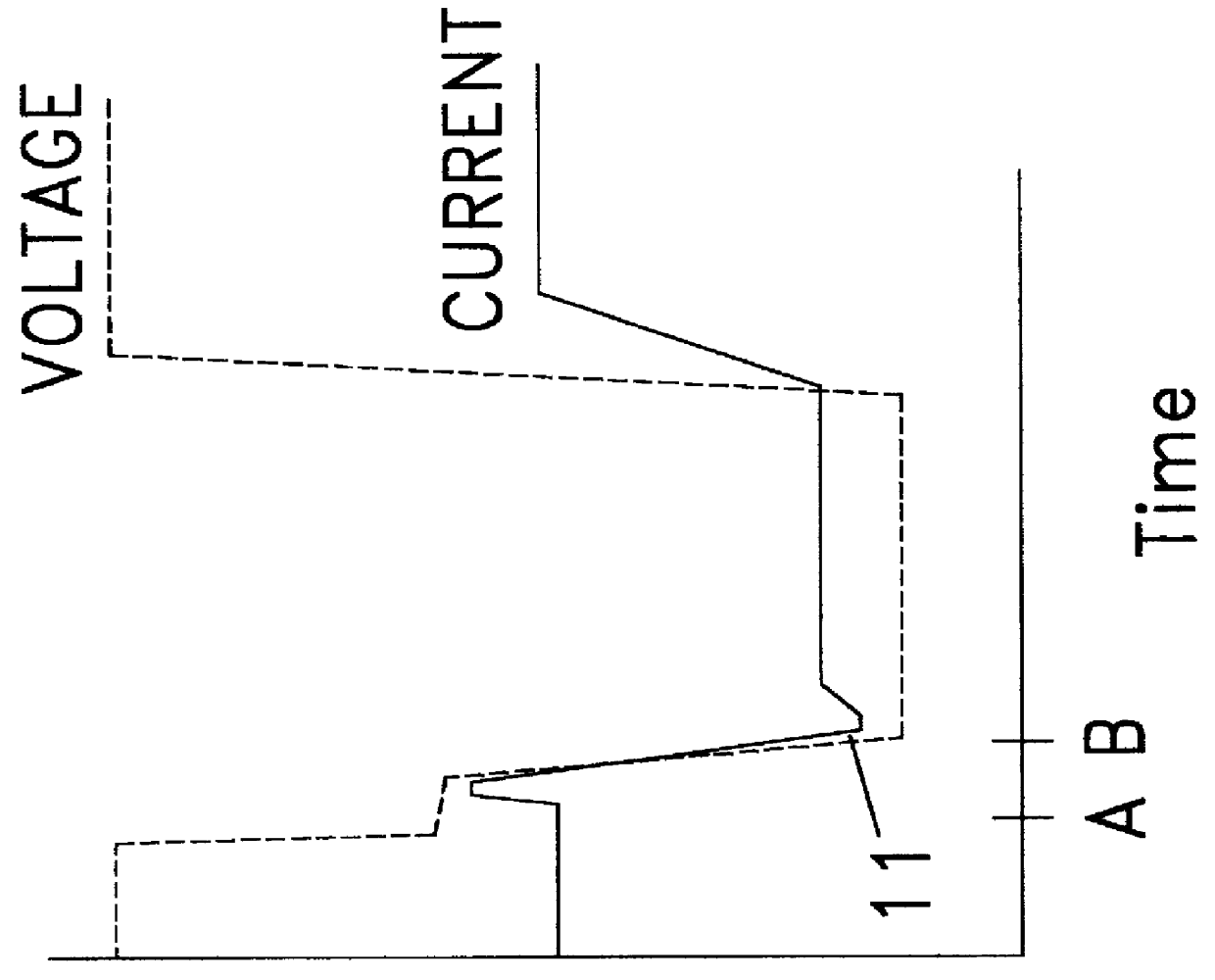
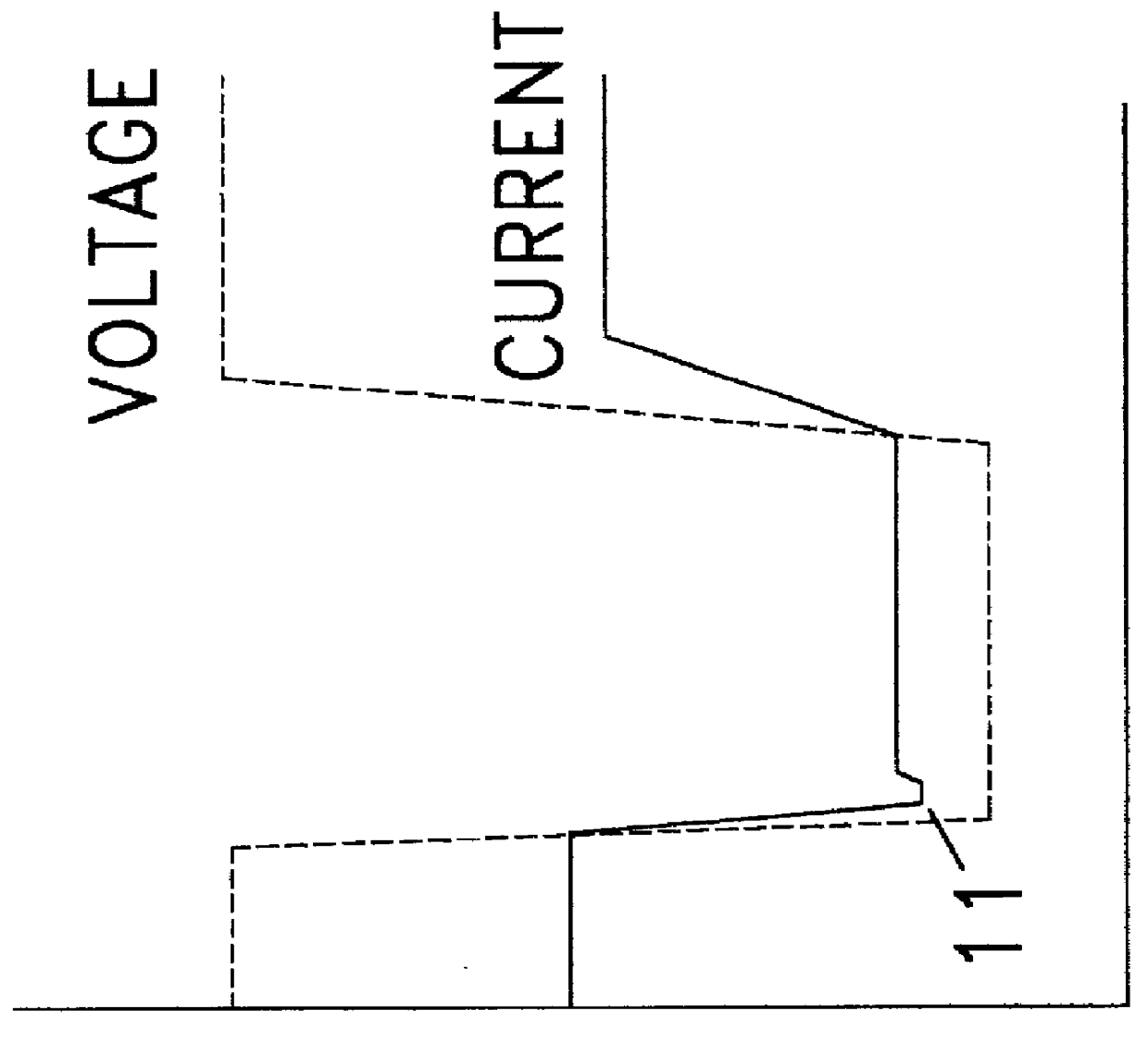
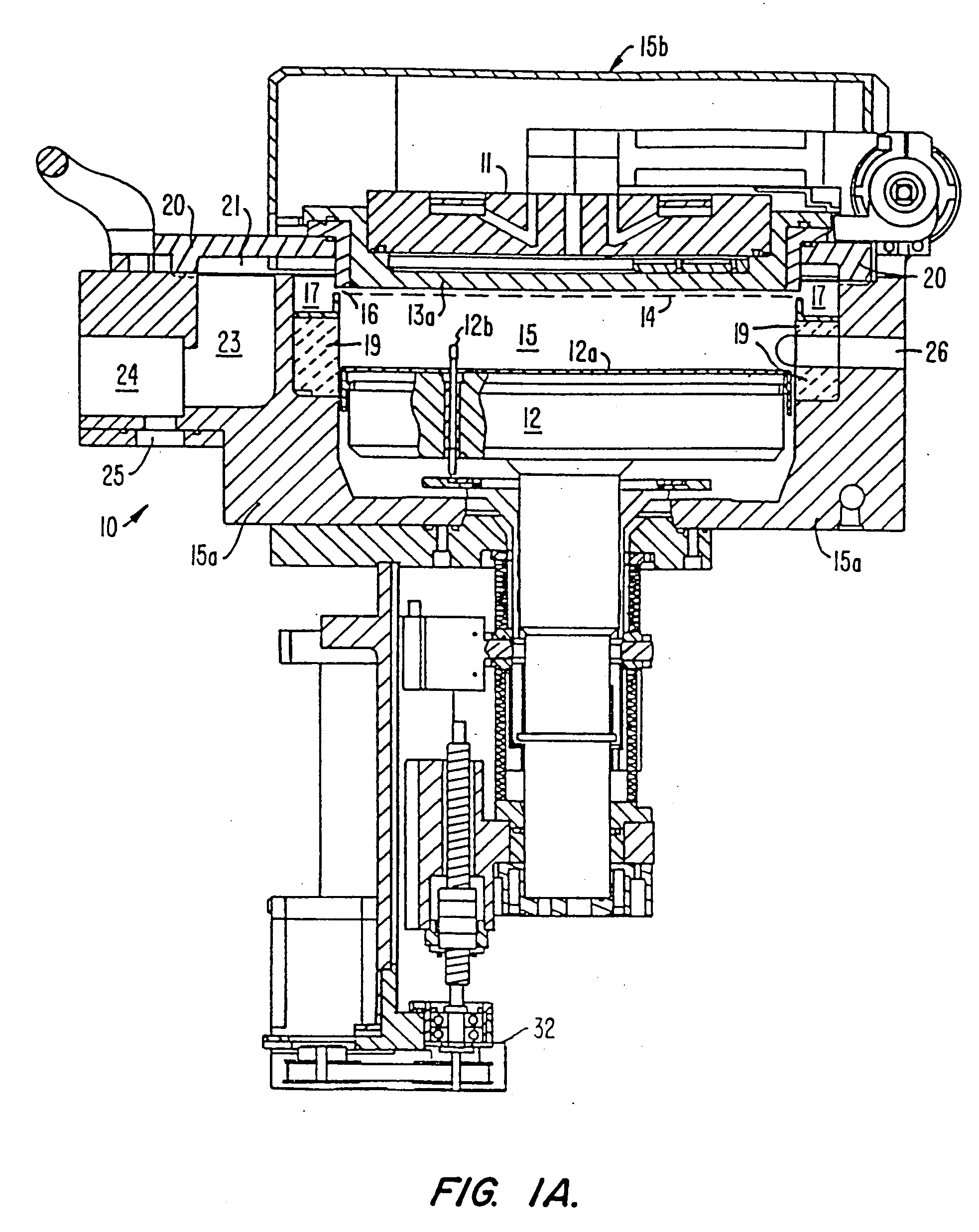
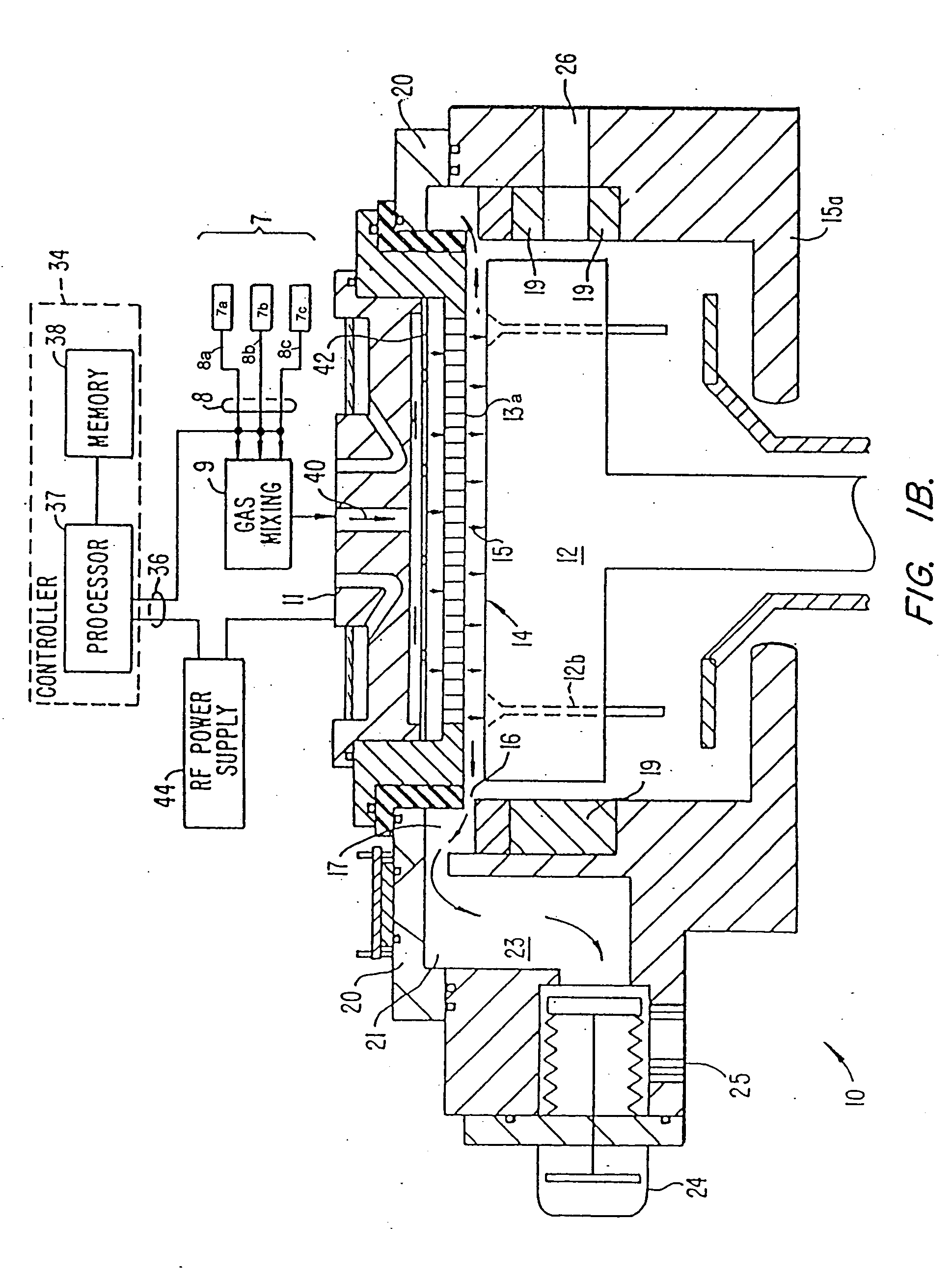
An enhanced reactive plasma processing method and system useful for deposition of highly insulating films. A variety of alternative embodiments are allowed for varying applications. In one embodiment, a tapped inductor is switched to ground or some common level to achieve substantial voltage reversal of about 10% upon detection of an arc condition. This reversal of voltage is maintained long enough to either afford processing advantages or to allow restoration of uniform charge density within the plasma prior to restoration of the initial driving condition. A technique for preventing arc discharges involving periodically either interrupting the supply of power or reversing voltage is effected through a timer system in the power source.
Owner:ADVANCED ENERGY IND INC
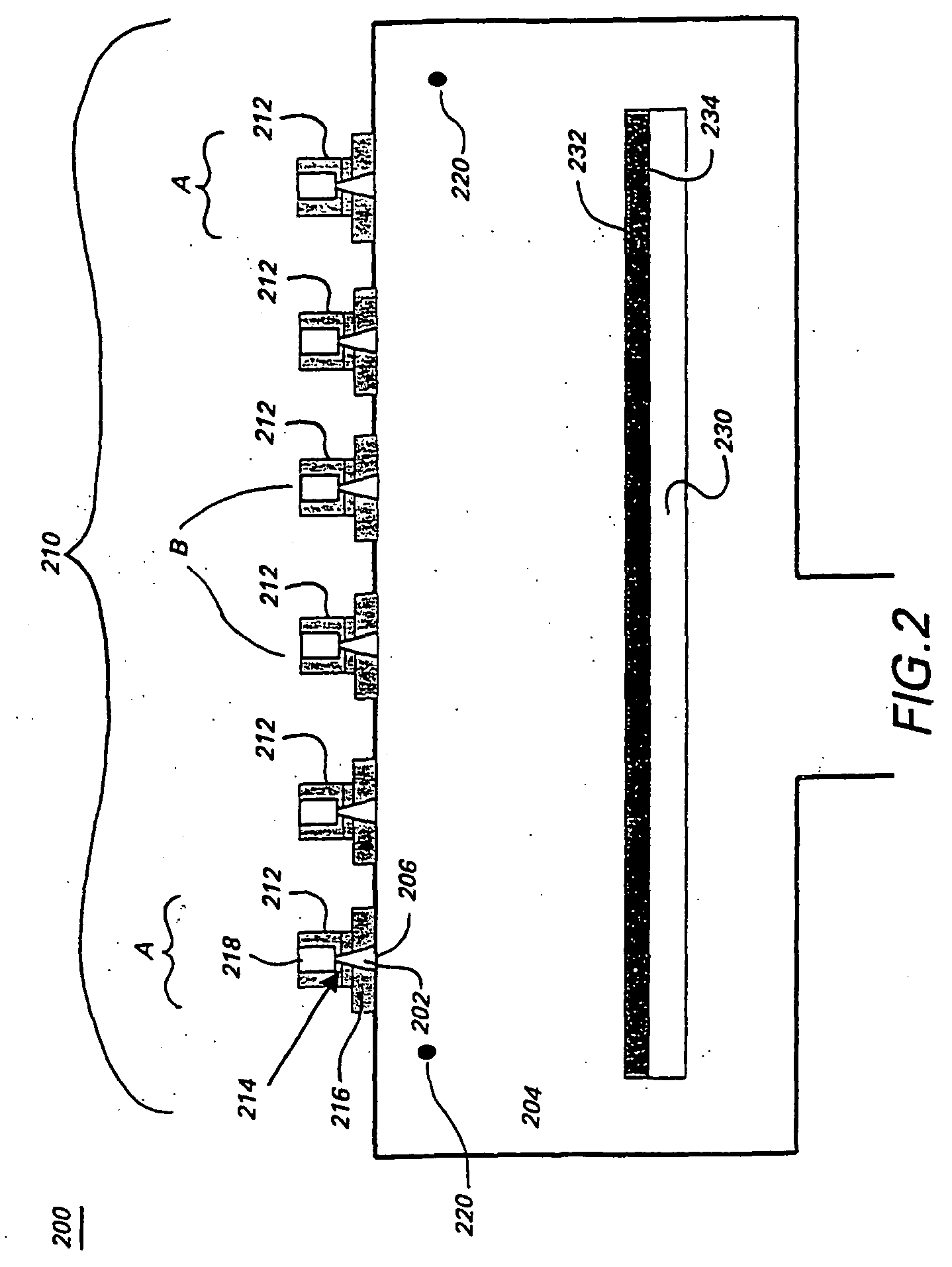
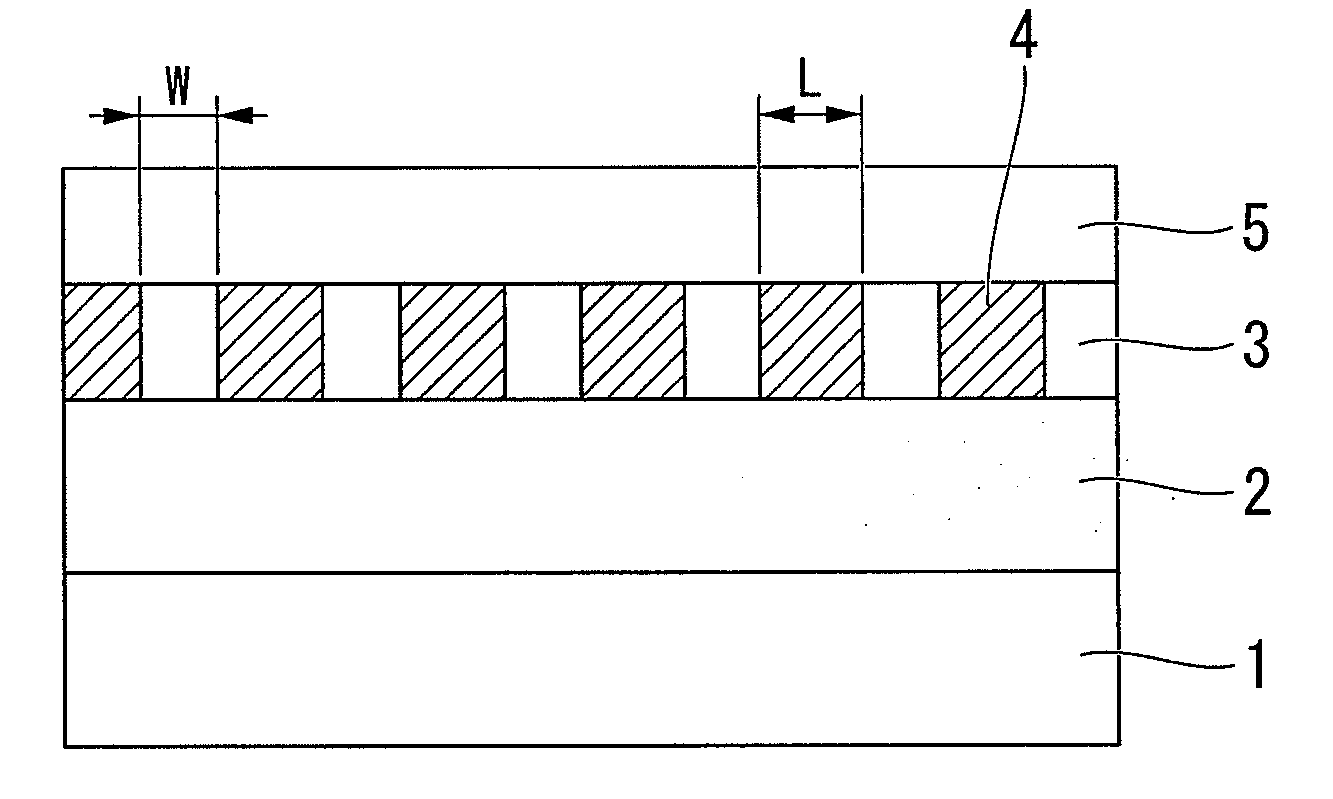
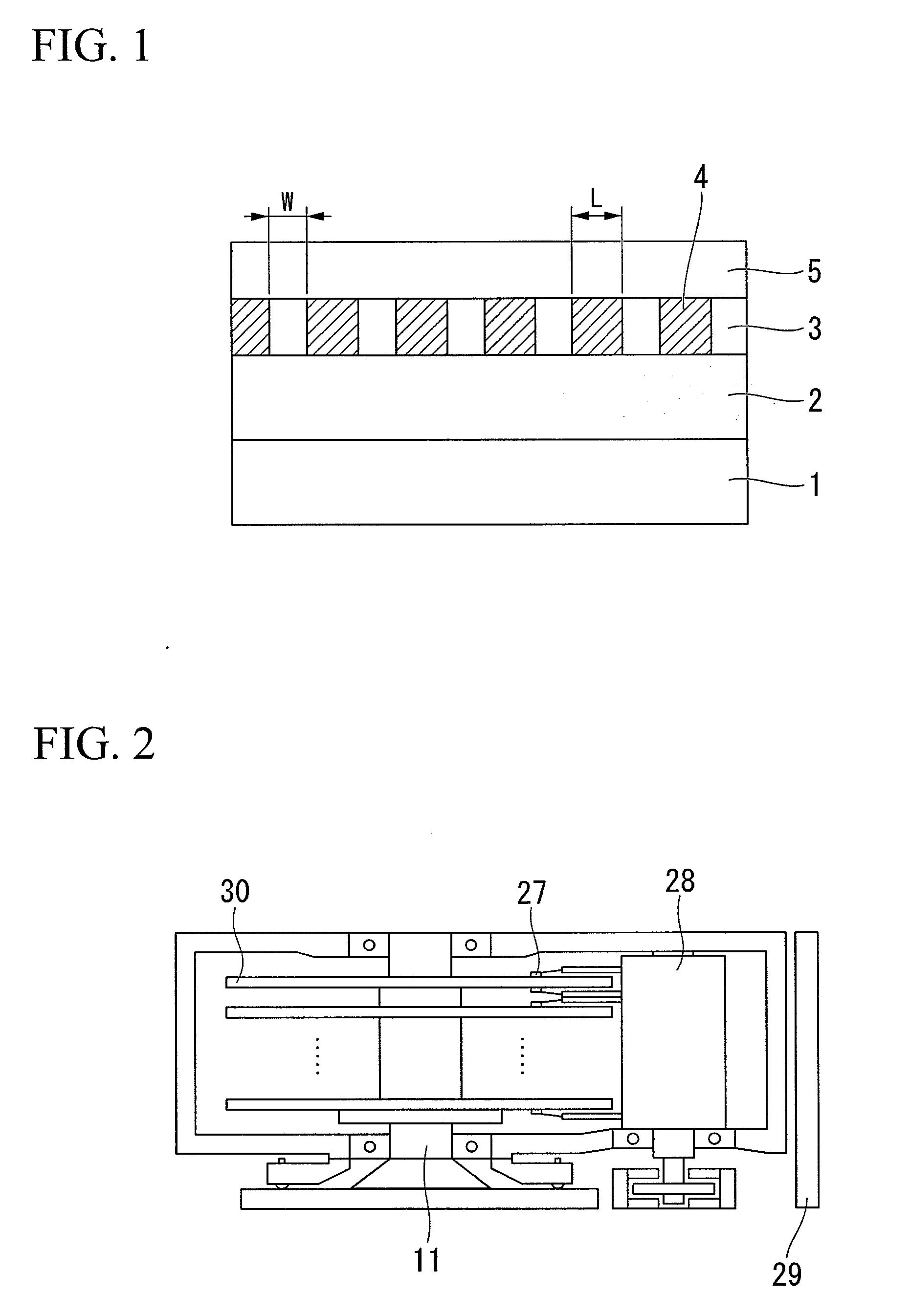
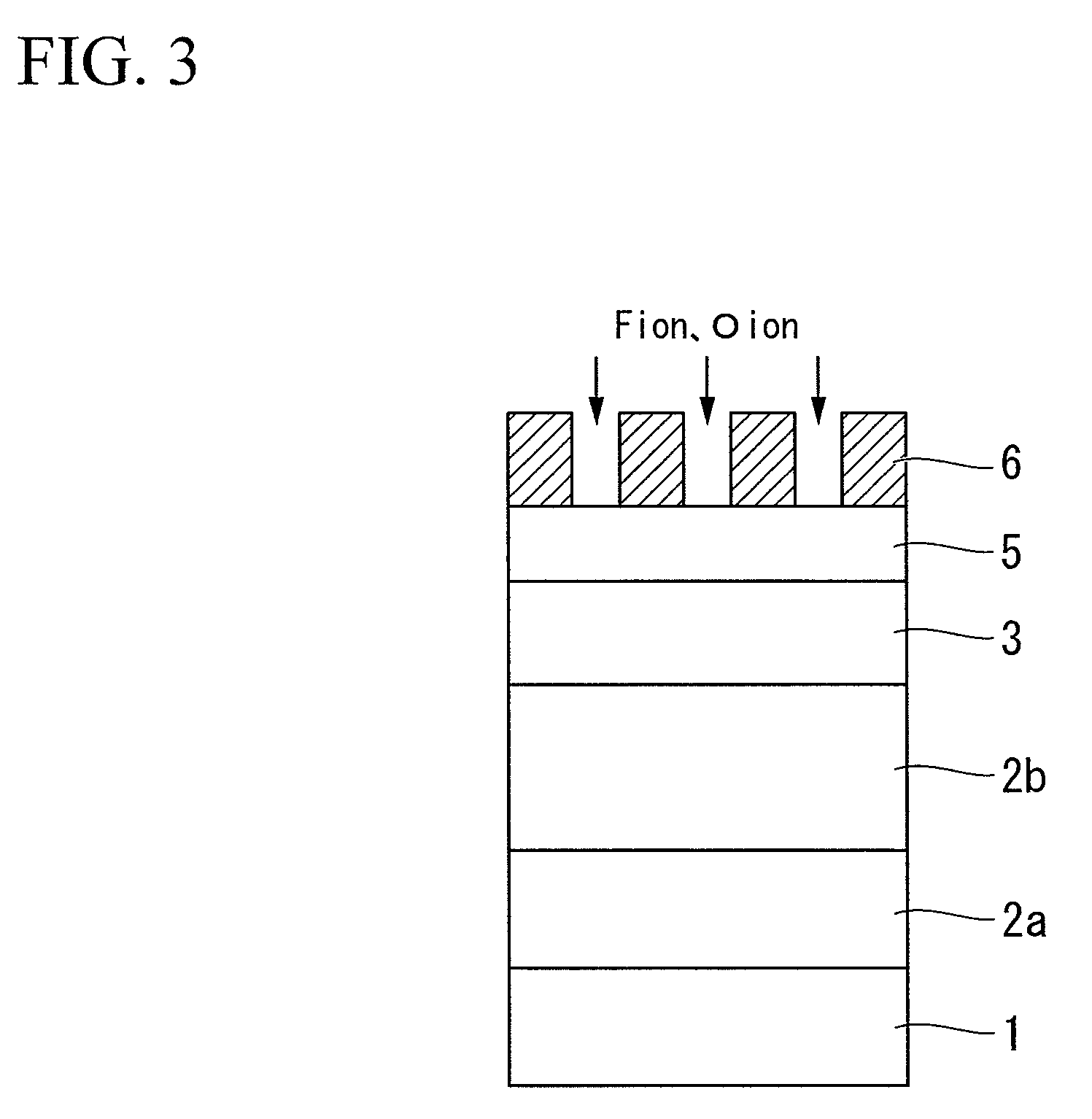
Apparatus and method for depositing large area coatings on non-planar surfaces
InactiveUS6681716B2Low deposited thicknessUniform profileSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingChemical physicsReactive plasma
A method and apparatus for depositing a uniform coating on a large area, non-planar surface using an array of multiple plasma sources. The apparatus comprises at least one array of a plurality of plasma sources for generating a plurality of plasmas, wherein each of the plurality of plasma sources has a cathode, anode, and an inlet for a non-reactive plasma source gas disposed in a plasma chamber, and at least one reactant gas injector for differentially injecting at least one reactant gas into the plurality of plasmas. The reactant gas injector and substrate are located in a deposition chamber in fluid communication with each plasma chamber. Individual adjustment of the flow of deposition precursor into each of the plasmas generated by the multiple plasma array compensates for changes in substrate processing conditions due to local variations in the working distance between the plasma source and the surface of the substrate.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
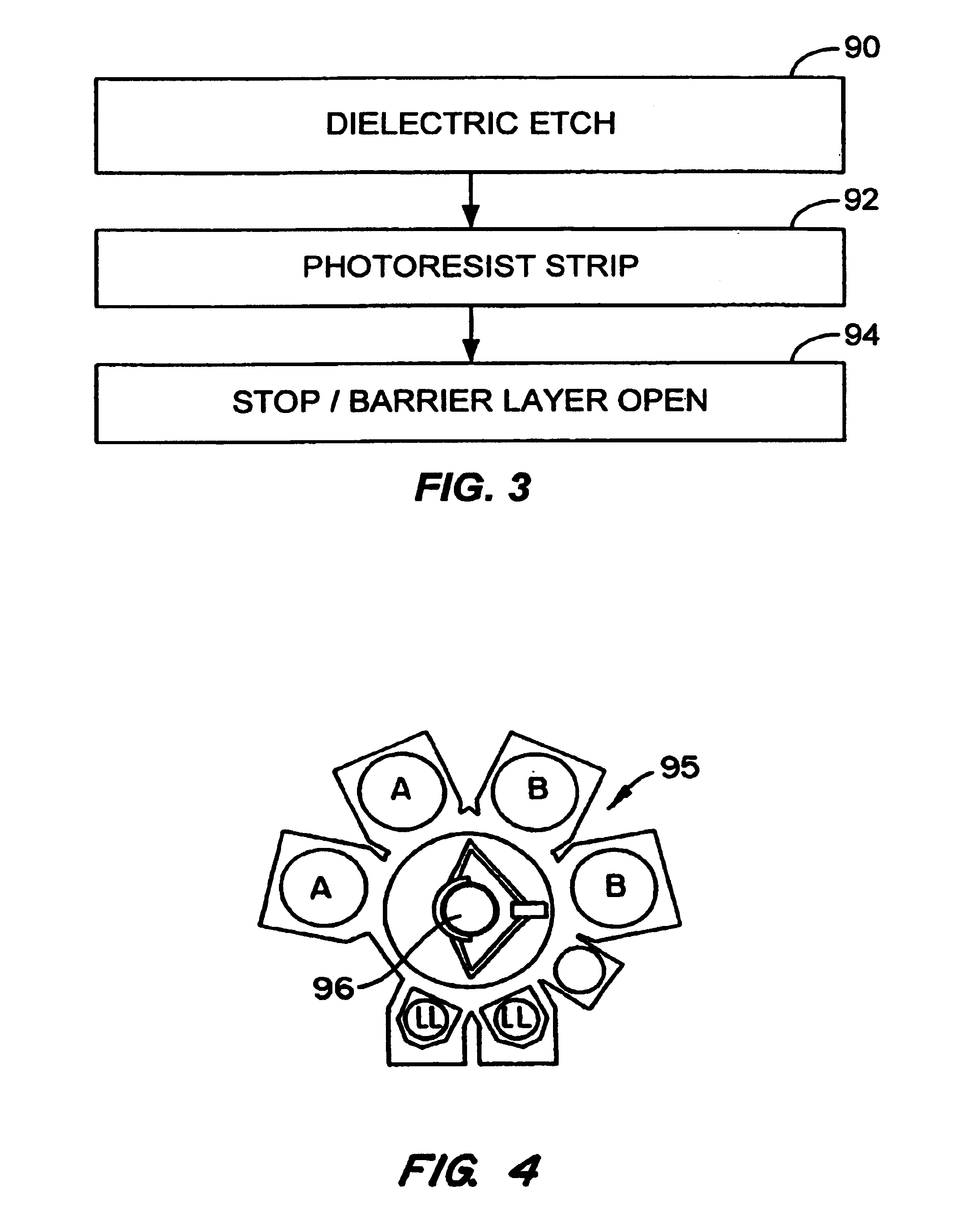
System level in-situ integrated dielectric etch process particularly useful for copper dual damascene
InactiveUS6949203B2Low costImproved etch resultElectric discharge tubesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsResistReactive plasma
An integrated in situ etch process performed in a multichamber substrate processing system having first and second etching chambers. In one embodiment the first chamber includes an interior surface that has been roughened to at least 100 Ra and the second chamber includes an interior surface that has a roughness of less than about 32 Ra. The process includes transferring a substrate having formed thereon in a downward direction a patterned photoresist mask, a dielectric layer, a barrier layer and a feature in the substrate to be contacted into the first chamber where the dielectric layer is etched in a process that encourages polymer formation over the roughened interior surface of the chamber. The substrate is then transferred from the first chamber to the second chamber under vacuum conditions and, in the second chamber, is exposed to a reactive plasma such as oxygen to strip away the photoresist mask deposited over the substrate. After the photoresist mask is stripped, the barrier layer is etched through to the feature to be contacted in the second chamber of the multichamber substrate processing system using a process that discourages polymer formation over the relatively smooth interior surface of the second chamber. All three etching steps are performed in a system level in situ process so that the substrate is not exposed to an ambient between steps. In some embodiments the interior surface of the first chamber has a roughness between 100 and 200 Ra and in other embodiments the roughness of the first chamber's interior surface is between 110 and 160 Ra.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for generating a highly reactive plasma for exhaust gas aftertreatment and enhanced catalyst reactivity
InactiveUS6190507B1Lower impedanceImprove responseInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusMicrowaveReactive plasma
A method for non-thermal plasma aftertreatment of exhaust gases the method comprising the steps of providing short risetime (about 40 ps), high frequency (about 5G hz), high power bursts of low-duty factor microwaves sufficient to generate a dielectric barrier discharge and passing a gas to treated through the discharge so as to cause dissociative reduction of the exhaust gases. The invention also includes a reactor for generating the non-thermal plasma.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Apparatus and method for depositing large area coatings on planar surfaces
InactiveUS20050079295A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingReactive plasmaDelivery system
A method and apparatus for depositing a uniform coating on a large area, planar surface using an array of multiple plasma sources and a common reactant gas injector. The apparatus includes at least one array of a plurality of plasma sources, wherein each of the plurality of plasma sources includes a cathode, an anode, and an inlet for a non-reactive plasma source gas disposed in a plasma chamber, and a common reactant gas injector disposed in a deposition chamber that contains the substrate. The common reactant gas injector provides a uniform flow of at least one reactant gas to each of the multiple plasmas generated the multiple plasma sources through a single delivery system. The at least one reactant gas reacts with the plurality of plasmas to form a uniform coating on a substrate.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Apparatus and method for depositing large area coatings on non-planar surfaces
InactiveUS20030097988A1Compensation changesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingReactive plasmaIndividual Adjustment
A method and apparatus for depositing a uniform coating on a large area, non-planar surface using an array of multiple plasma sources. The apparatus comprises at least one array of a plurality of plasma sources for generating a plurality of plasmas, wherein each of the plurality of plasma sources has a cathode, anode, and an inlet for a non-reactive plasma source gas disposed in a plasma chamber, and at least one reactant gas injector for differentially injecting at least one reactant gas into the plurality of plasmas. The reactant gas injector and substrate are located in a deposition chamber in fluid communication with each plasma chamber. Individual adjustment of the flow of deposition precursor into each of the plasmas generated by the multiple plasma array compensates for changes in substrate processing conditions due to local variations in the working distance between the plasma source and the surface of the substrate.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20050199940A1Reduce the impactReduce in quantityTransistorSolid-state devicesReactive plasmaSputter deposition
A MONOS nonvolatile memory of a split gate structure, wherein writing and erasing are performed by hot electrons and hot holes respectively, is prone to cause electrons not to be erased and to remain in an Si nitride film on a select gate electrode sidewall and that results in the deterioration of rewriting durability. When long time erasing is applied as a measure to solve the problem, drawbacks appear, such as the increase of a circuit area caused by the increase of the erasing current and the deterioration of retention characteristics. In the present invention, an Si nitride film is formed by the reactive plasma sputter deposition method that enables oriented deposition and the Si nitride film on a select gate electrode sidewall is removed at the time when a top Si oxide film is formed.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS7115943B2Improve performanceReduce in quantityTransistorSolid-state devicesReactive plasmaSputter deposition
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
In-situ process layer using silicon-rich-oxide for etch selectivity in high AR gapfill
ActiveUS7951683B1Reduce morbiditySmall sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHigh densityReactive plasma
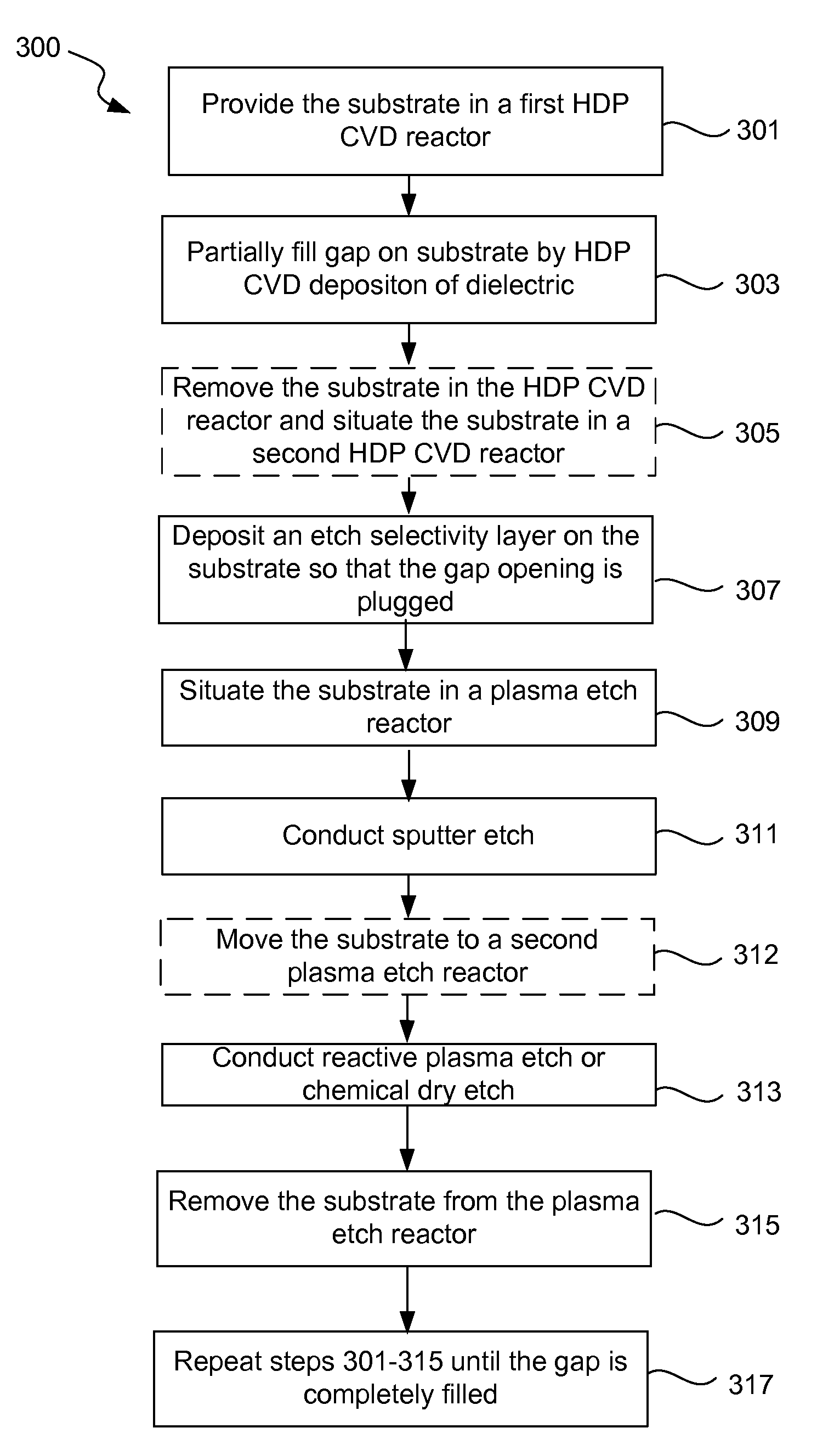
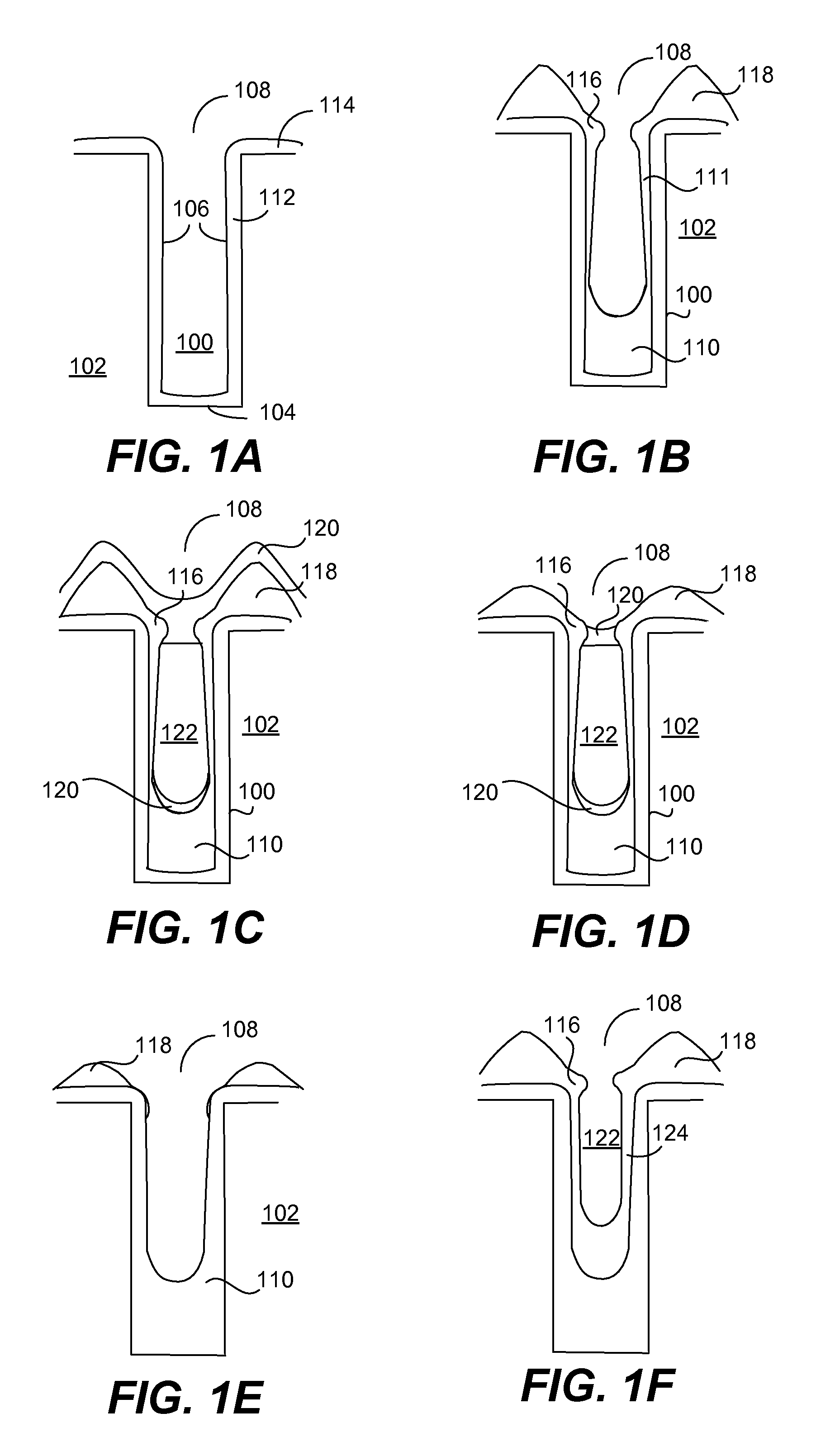
In-situ semiconductor process that can fill high aspect ratio (typically at least 6:1, for example 7:1 or higher), narrow width (typically sub 0.13 micron, for example 0.1 micron or less) gaps with significantly reduced incidence of voids or weak spots is provided. This deposition part of the process may involve the use of any suitable high density plasma chemical vapor deposition (HDP CVD) chemistry. Prior to etch back, the feature gap is plugged with an etch selectivity layer. The etch back part of the process involves multiple steps including a sputter etch to reduce the top hat formations followed by a reactive plasma etch to open the gap. This method improves gapfill, reduces the use of high cost fluorine-based etching and produces interim gaps with better sidewall profiles and aspect ratios.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method for cleaning plasma etch chamber structures
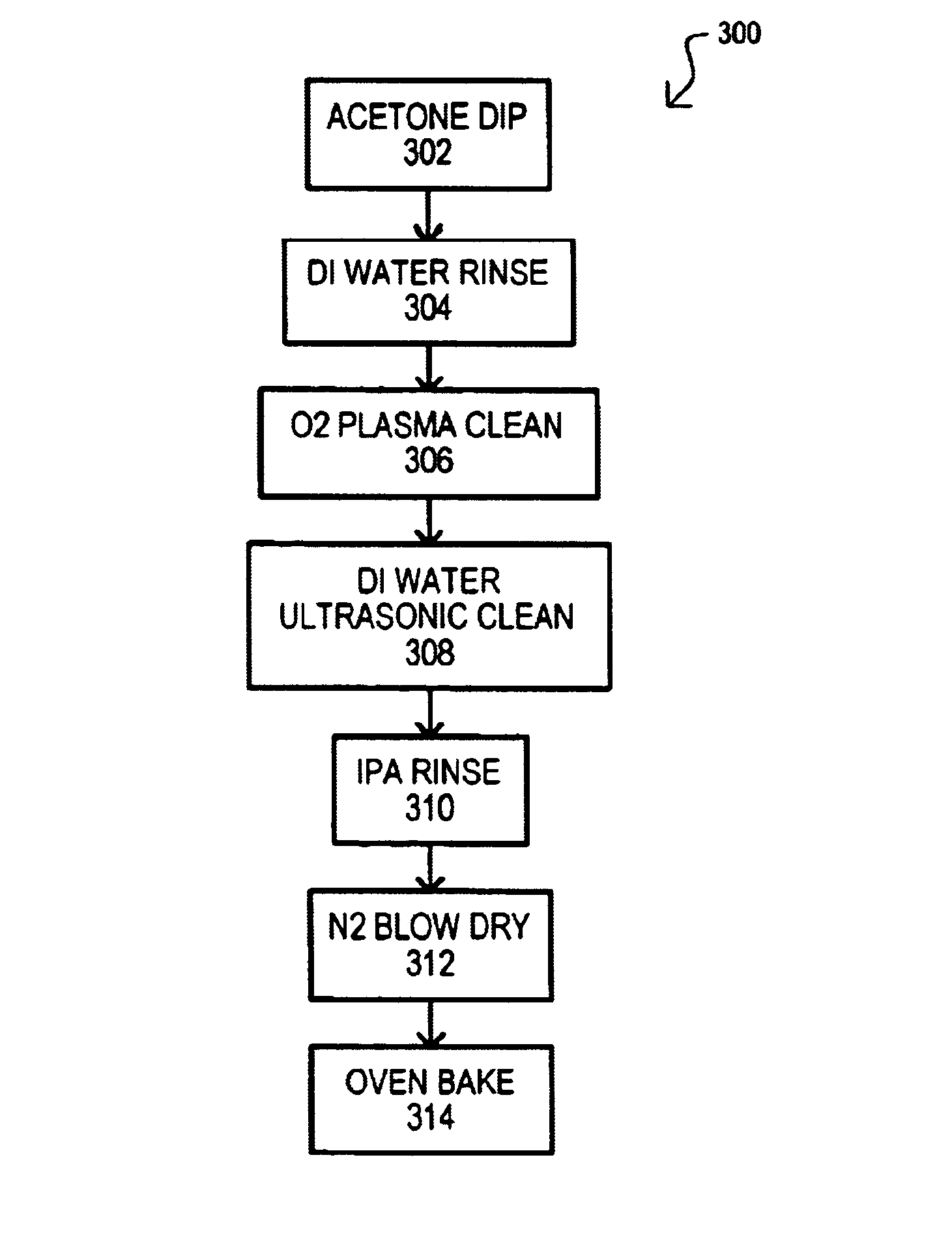
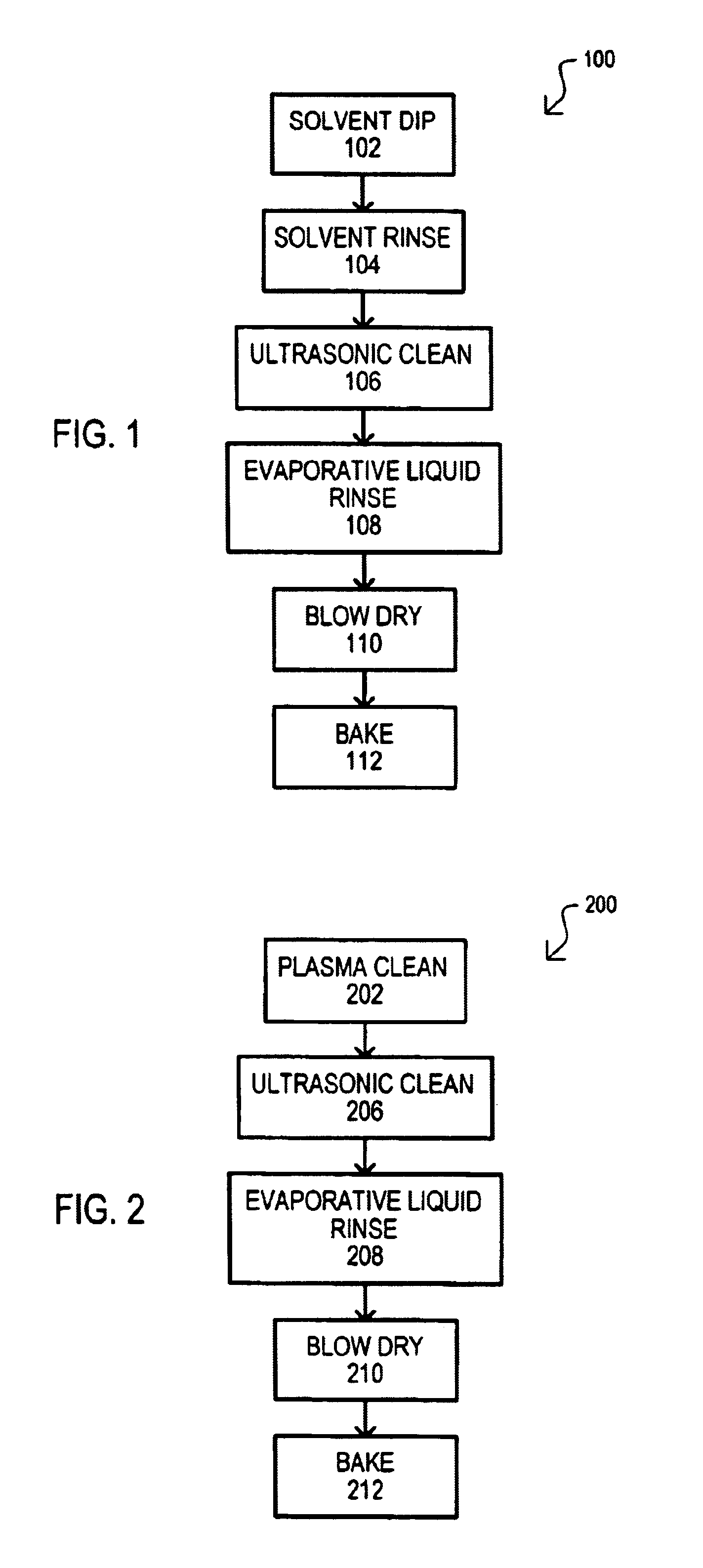
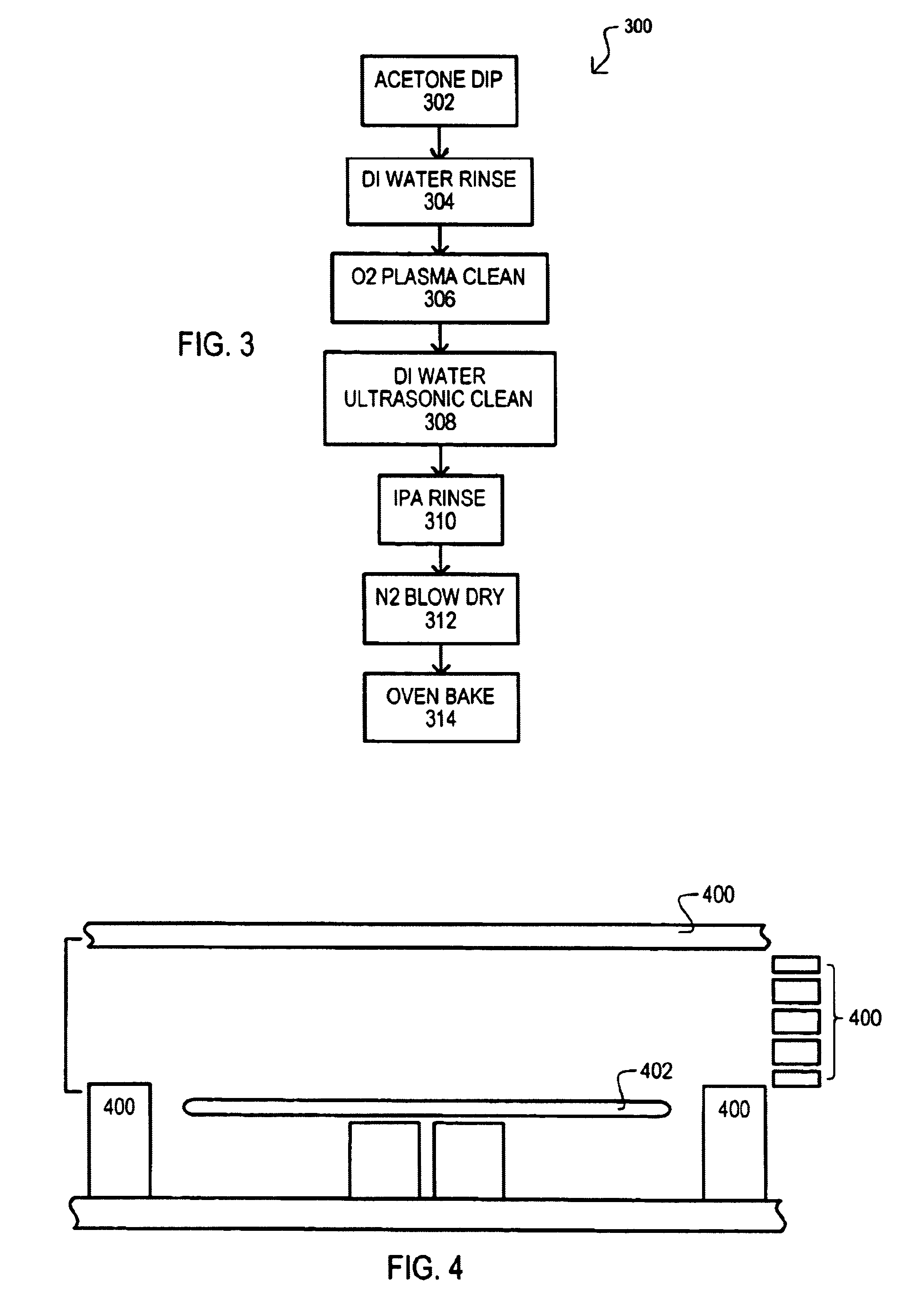
A method for cleaning a plasma reactor clamber part (100) may include dipping the chamber part in a solvent (102) that may dissolve a material that has been redistributed on the chamber part by a reactive plasma. A chamber part may then be rinsed (104), ultrasonically cleaned (106) in a ultrasonic cleaning liquid, and then rinsed again with a liquid that may evaporate at a lower temperature than an ultrasonic cleaning liquid (108). A chamber part may then be blown dry (110) and baked (112). In addition, or alternatively, a method may also include plasma cleaning a chamber part (202).
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
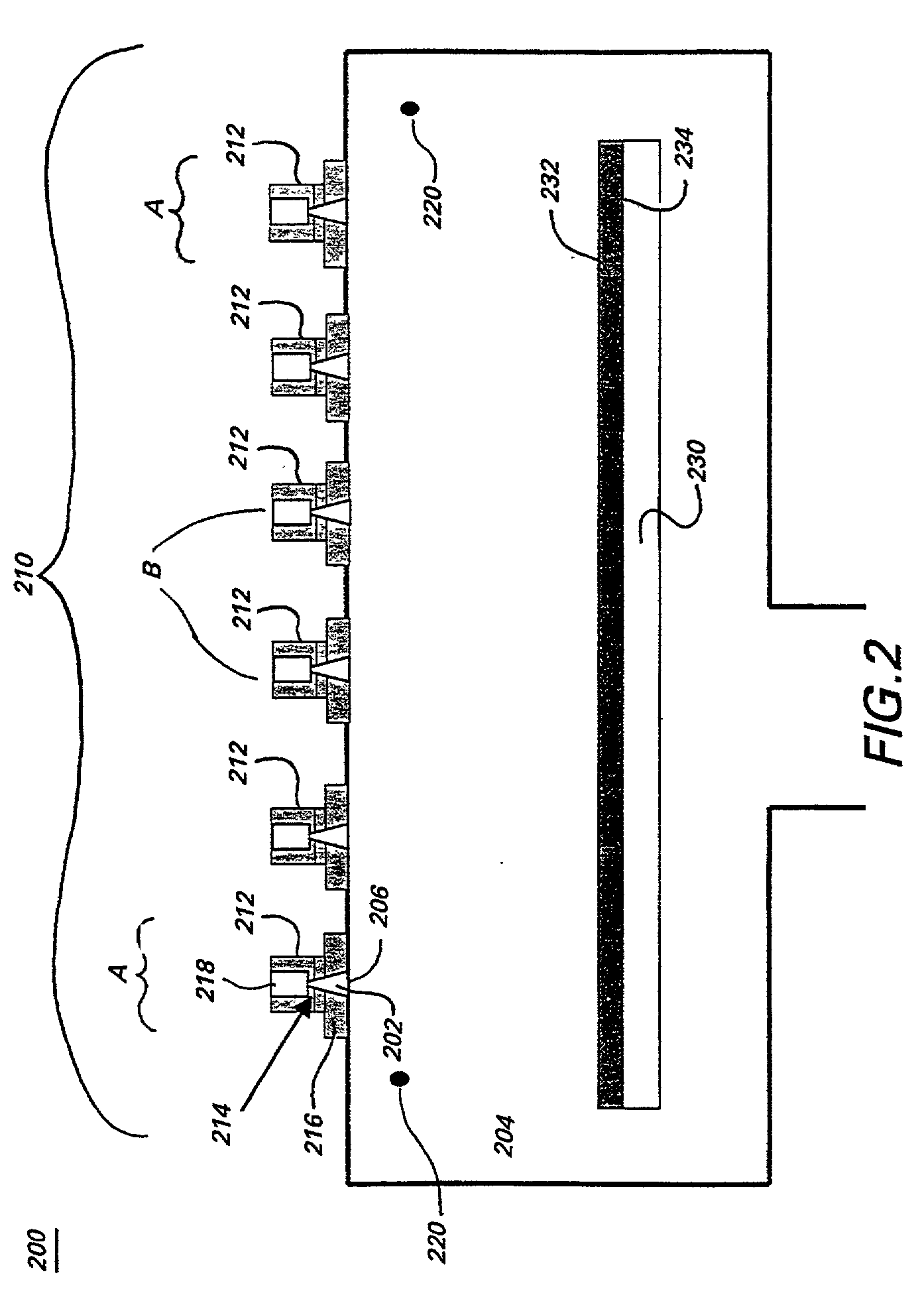
Plasma processing apparatus
InactiveUS20050257891A1Improve uniformityEffective radiationElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricReactive plasma
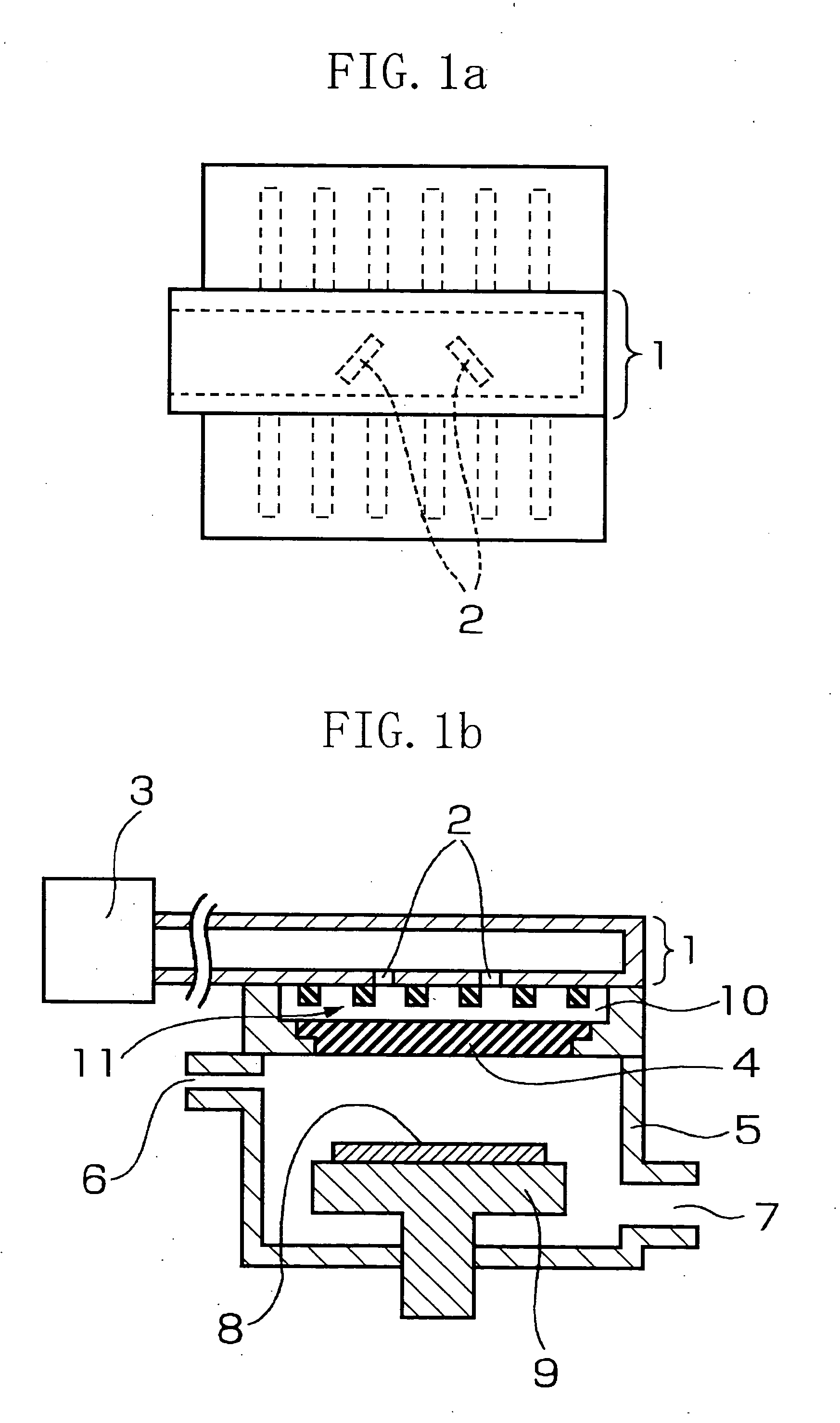
There is provided a plasma treatment apparatus capable of treating a square shaped substrate having a large area even in the case of using reactive plasma, the plasma treatment apparatus including a waveguide 1, a waveguide antenna 2 made up of slots provided on the H-surface of the waveguide 1, an electromagnetic wave radiation window 4 made of a dielectric, a dielectric space 10 sandwiched between the waveguide 2 and the electromagnetic wave radiation window 4, and generating plasma by using the electromagnetic wave radiated from the waveguide antenna 2 through the electromagnetic wave radiation window 4, wherein an uneven portion 11 is provided on the surface of the waveguide 1 opposite to the electromagnetic wave radiation window 4.
Owner:ADVANCED LCD TECH DEVMENT CENT
Apparatus and method for depositing large area coatings on planar surfaces
A method and apparatus for depositing a uniform coating on a large area, planar surface using an array of multiple plasma sources and a common reactant gas injector. The apparatus includes at least one array of a plurality of plasma sources, wherein each of the plurality of plasma sources includes a cathode, an anode, and an inlet for a non-reactive plasma source gas disposed in a plasma chamber, and a common reactant gas injector disposed in a deposition chamber that contains the substrate. The common reactant gas injector provides a uniform flow of at least one reactant gas to each of the multiple plasmas generated the multiple plasma sources through a single delivery system. The at least one reactant gas reacts with the plurality of plasmas to form a uniform coating on a substrate.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Plasma resistant curable fluoroelastomer composition
A fluoroelastomer composition comprising a) a fluoroelastomer, b) a curative and c) barium sulfate having an average particle size less than 200 nm is disclosed. This composition loses less weight and produces fewer particles when exposed to reactive plasmas than do similar compositions which contain larger particle size barium sulfate.
Owner:DUPONT DOW ELASTOMERS LLC
Manufacturing Method Of Semiconductor Device And Semiconductor Device Produced Therewith
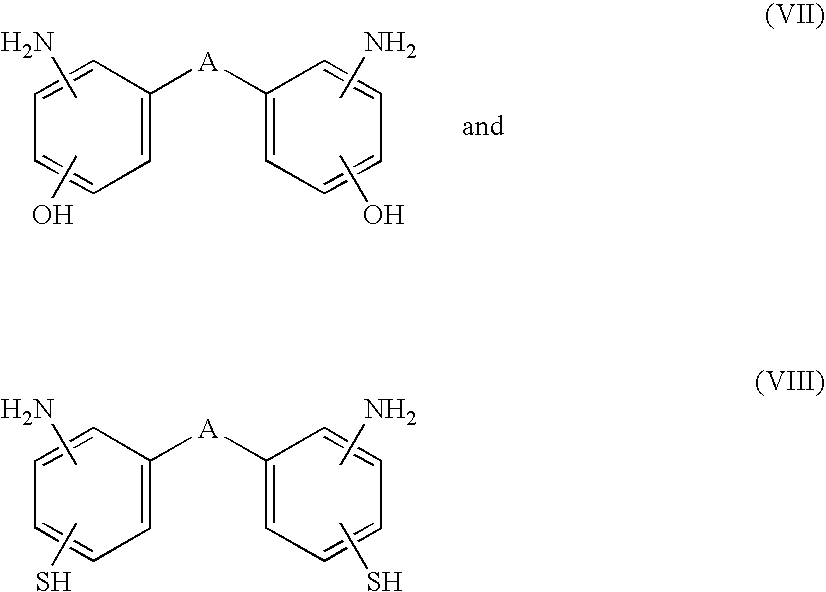
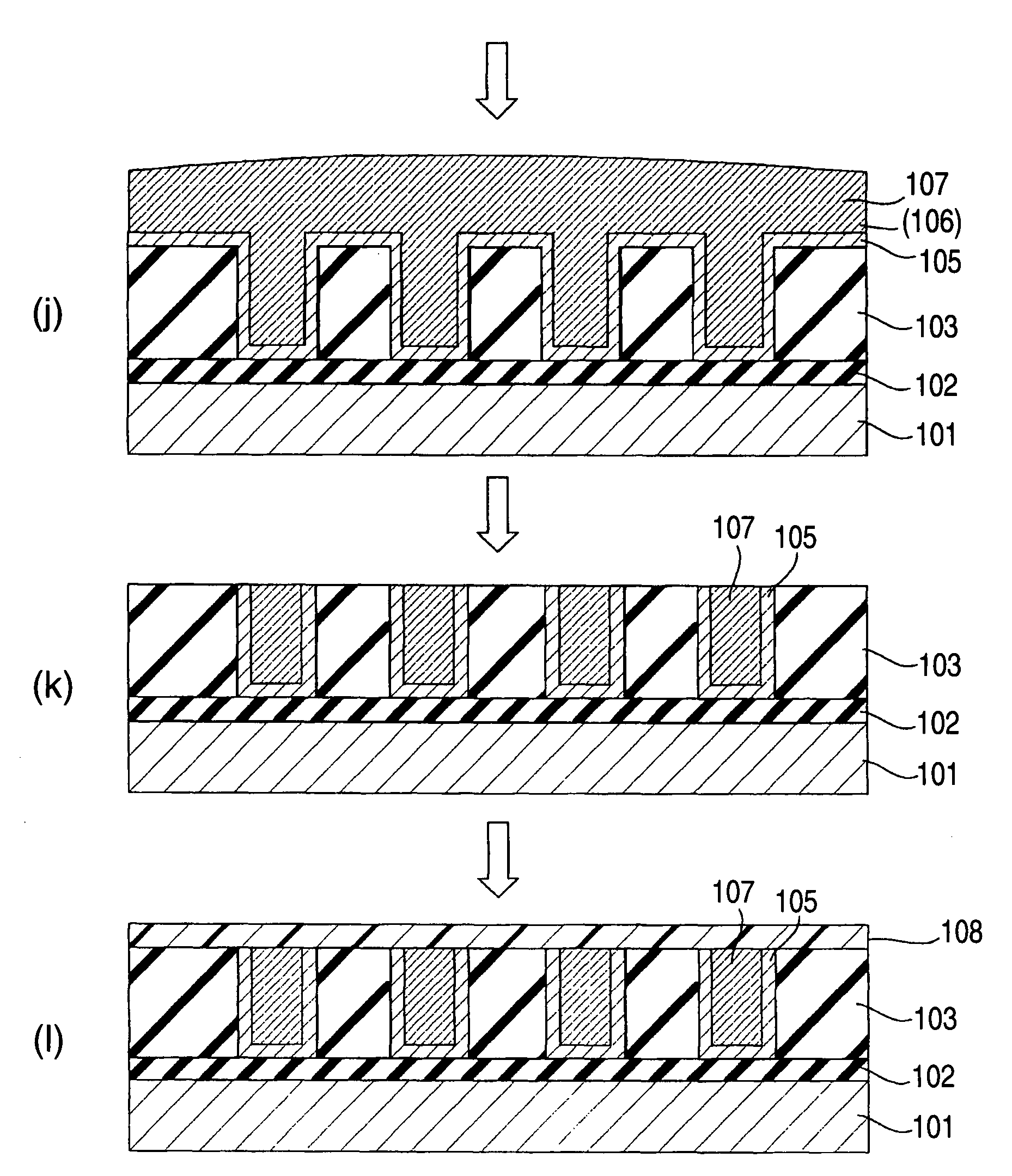
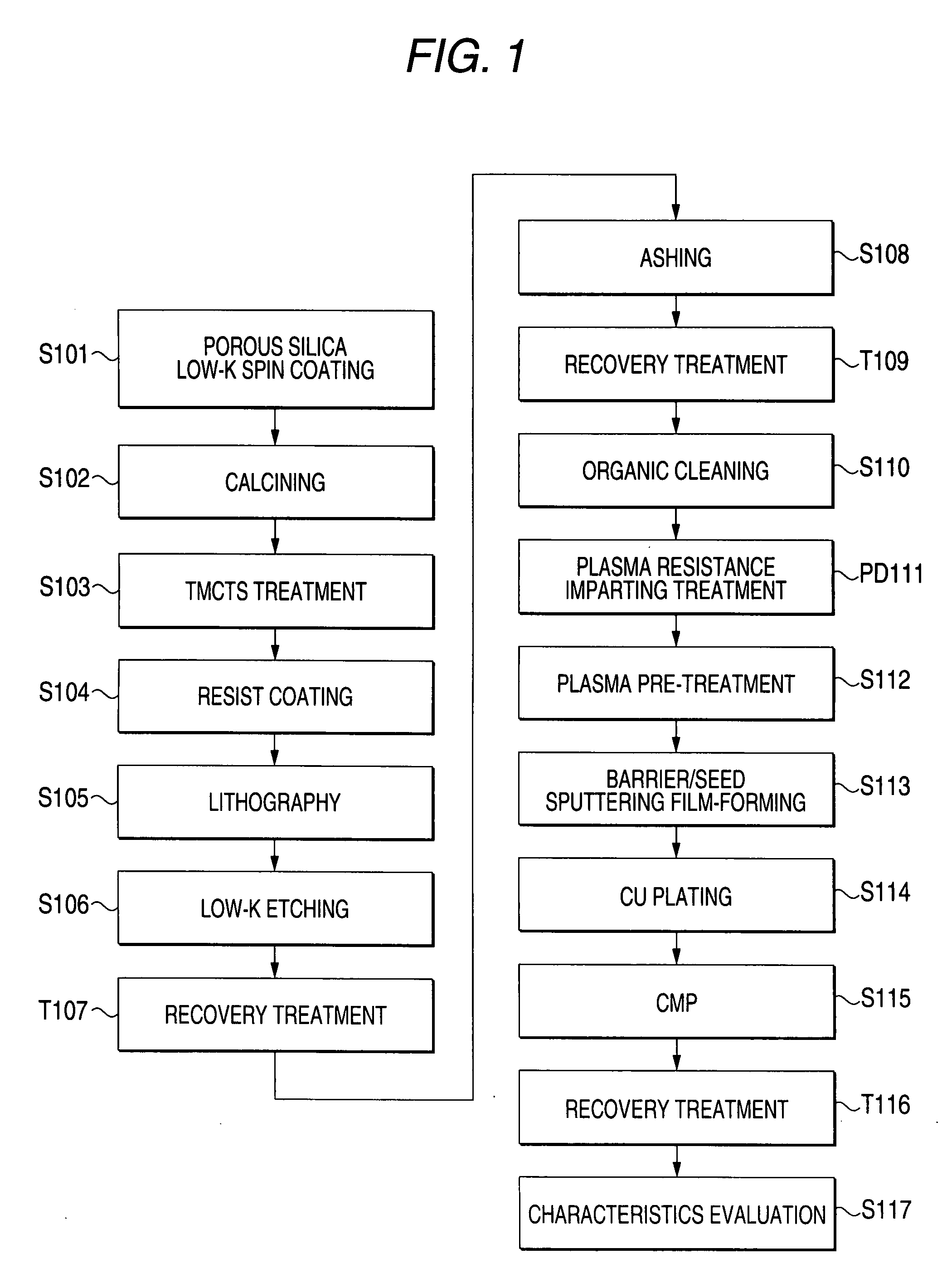
ActiveUS20080122101A1Improve adhesionPrevent processing damageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTrimethylsilyl chlorideReactive plasma
A semiconductor device having a wiring structure that is enhanced in adhesion between a dielectric thin film and a conductive layer and has high reliability is provided.A method of the invention includes: a step of supplying reactive plasma on a surface of a dielectric thin film in which a plurality of pores are arranged around a skeleton mainly made of a Si—O bond, to perform a pretreatment; a step of forming a conductive film on the surface of the pretreated dielectric thin film by a sputtering method; and before the pretreatment step, bringing a gas containing at least one kind of tetramethylcyclotetrasiloxane (TMCTS), hexamethylsilazane (HMDS) and trimethylchlorosilane (TMCS) molecules into contact with the surface of the dielectric thin film.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD +1
Method of producing magnetic recording medium, and magnetic recording and reading device
ActiveUS20100165504A1Maintain good propertiesExcellent high recording-density propertyDriving/moving recording headsVacuum evaporation coatingReactive plasmaNon magnetic
The present invention aims to provide a method of producing a magnetic recording medium which is a method of producing a magnetic recording medium having a magnetically-separated magnetic recording pattern, the method including: forming a magnetic layer on a non-magnetic substrate; then exposing a surface of the magnetic layer partially to reactive plasma, or a reactive ion generated in the plasma to amorphize the portion of the magnetic layer.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Accelerated plasma clean
InactiveUS20050103266A1Shorten the timeOvercome problemsHollow article cleaningSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingReactive plasmaEngineering
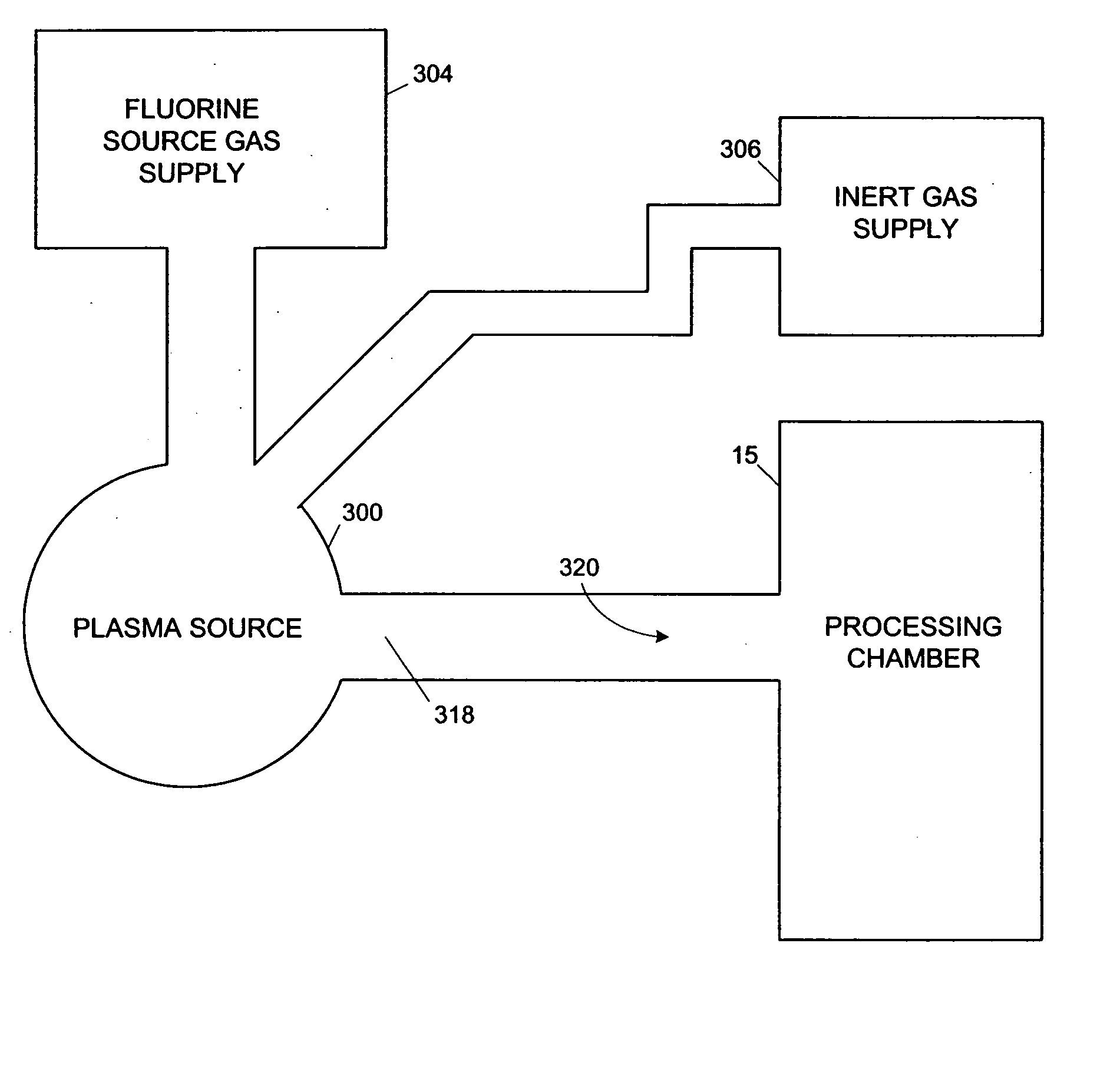
A method and apparatus that reduces the time required to clean a processing chamber employing a reactive plasma cleaning process. A plasma is formed in an Astron fluorine source generator from a flow of substantially pure inert-source gas. After formation of the plasma, a flow of a fluorine source gas is introduced therein such that the fluorine source flow accelerates at a rate no greater than 1.67 standard cubic centimeters per second2 (scc / s2). In this fashion, the plasma contains a plurality of radicals and dissociated inert-source gas atoms, defining a cleaning mixture. The ratio of inert-source gas to fluorine source is greater than 1:1.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Establishing a hydrophobic surface of sensitive low-k dielectrics of microstructure devices by in situ plasma treatment
InactiveUS20100304566A1Improve surface propertiesDegree of reductionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenReactive plasma
Silicon oxide based low-k dielectric materials may receive superior hydrophobic surface characteristics on the basis of a plasma treatment using hydrogen and carbon containing radicals. For this purpose, the surface of the low-k dielectric material may be exposed to these radicals, at least in one in situ process in combination with another reactive plasma ambient, for instance used for patterning the low-k dielectric material. Consequently, superior surface characteristics may be established or re-established without significantly contributing to product cycle time.
Owner:ALSEPHINA INNOVATIONS INC
Super-hydrophobic microstructure and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN106809795AHigh strengthScratch resistantSemi-permeable membranesVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsReactive plasmaRoom temperature
The invention discloses a super-hydrophobic microstructure and a manufacturing method thereof. The method comprises: using colloid crystalline grains as an etching mask film, using a colloid crystalline grain etching technology to form nanoscale or micron grade microstructures on the surface of a silicon wafer; using ICP-PECVD to deposit fluorine-doped diamond film on the microstructures. The thickness of the diamond film is 1-100 nm, and mass proportion of fluorine in the diamond film is 1-50%. The colloid crystalline grain etching technology is used, and expensive optical equipment is not needed. Colloid crystalline grains in different grain diameters are used as the etching mask film, and micron and nano meter microstructures in different feature sizes are obtained. The ICP-PECVD is helpful to improve density of reactive plasma in a cavity and increase density of the fluorine-doped DLC film, so as to improve quality of the formed film. The ICP-PECVD can realize to deposit films at room temperature, and the DLC film can be formed on an organic polymer substrate which is not resistant to high temperature, and the DLC film has hydrophobic property.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
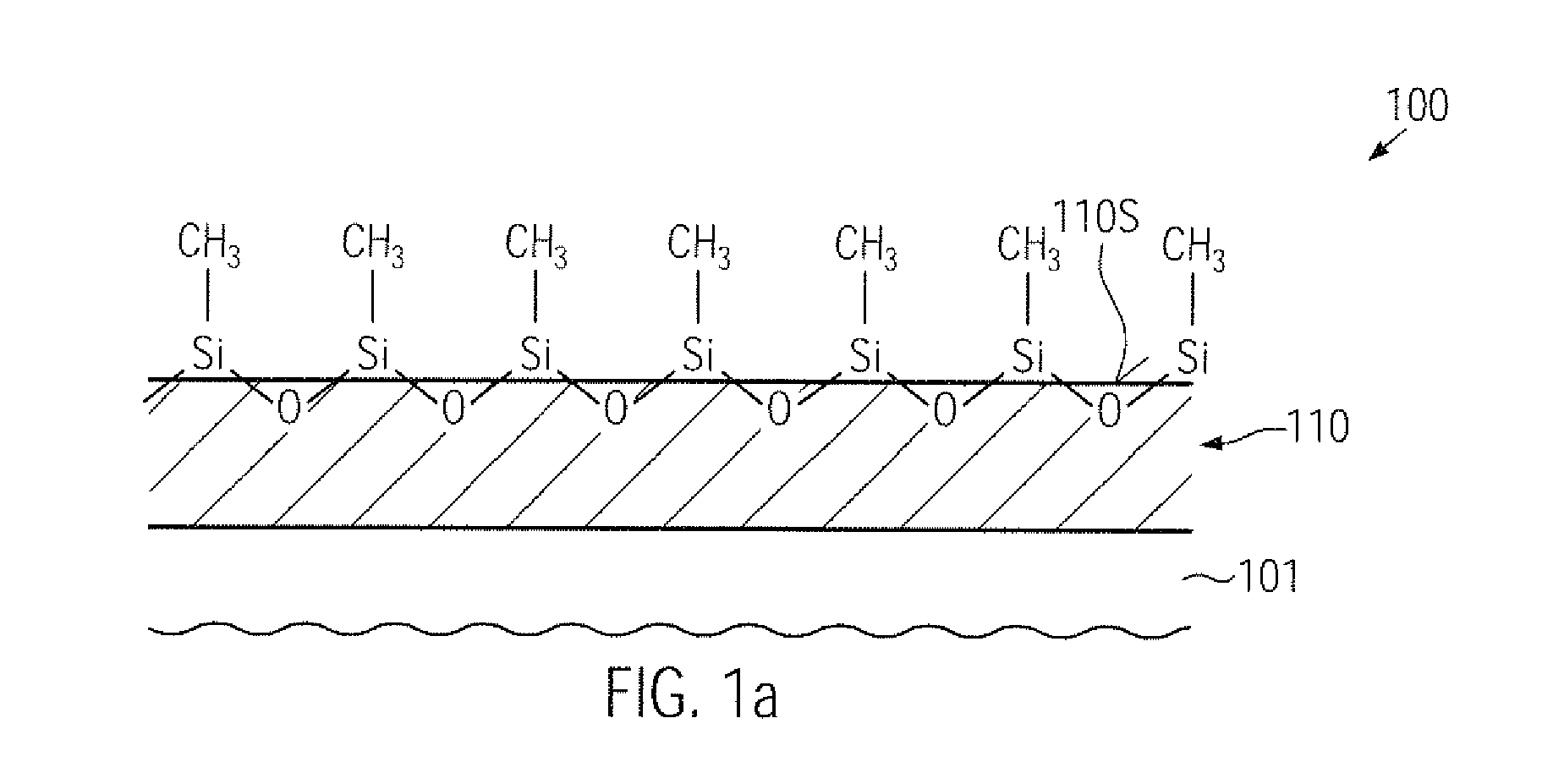
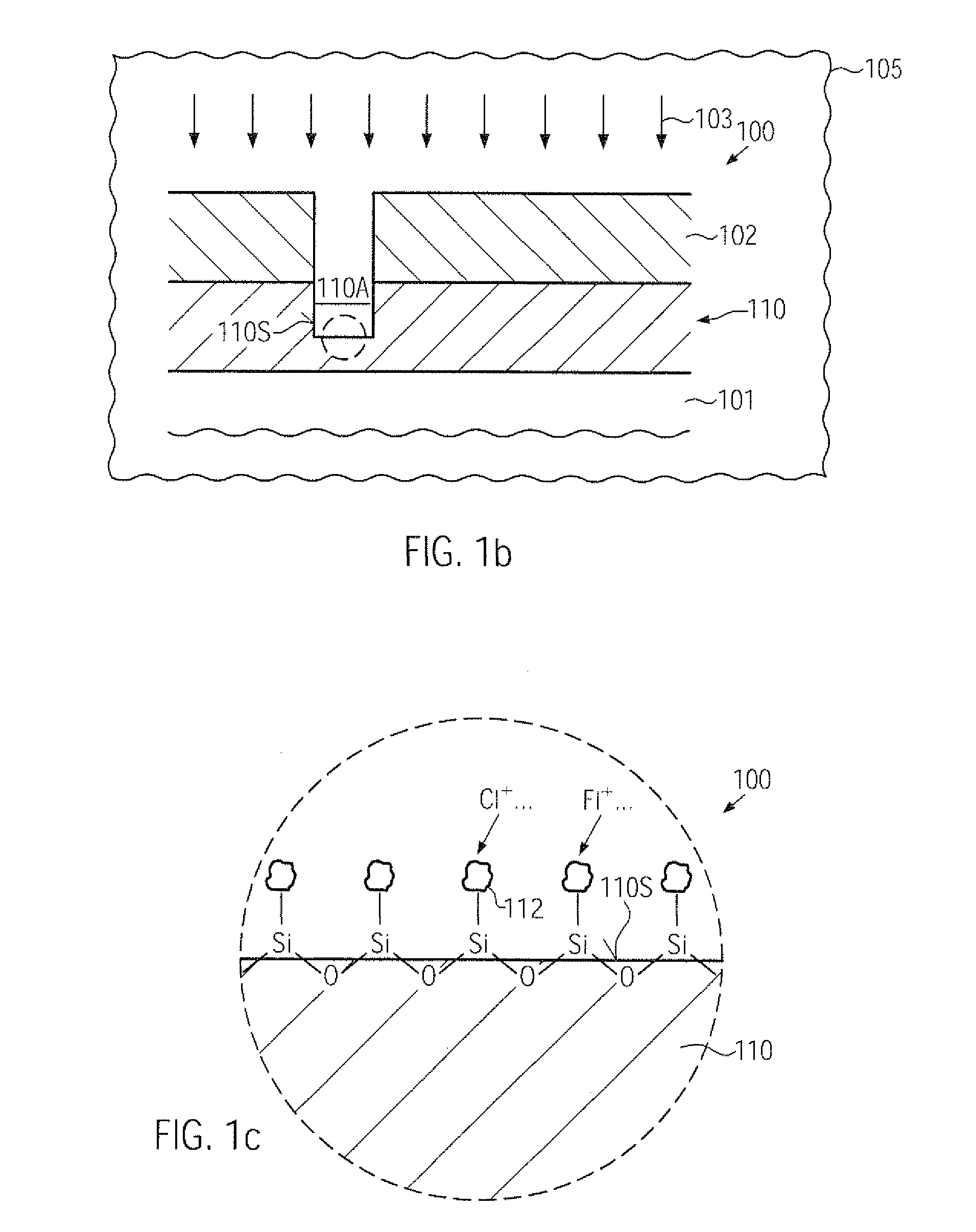
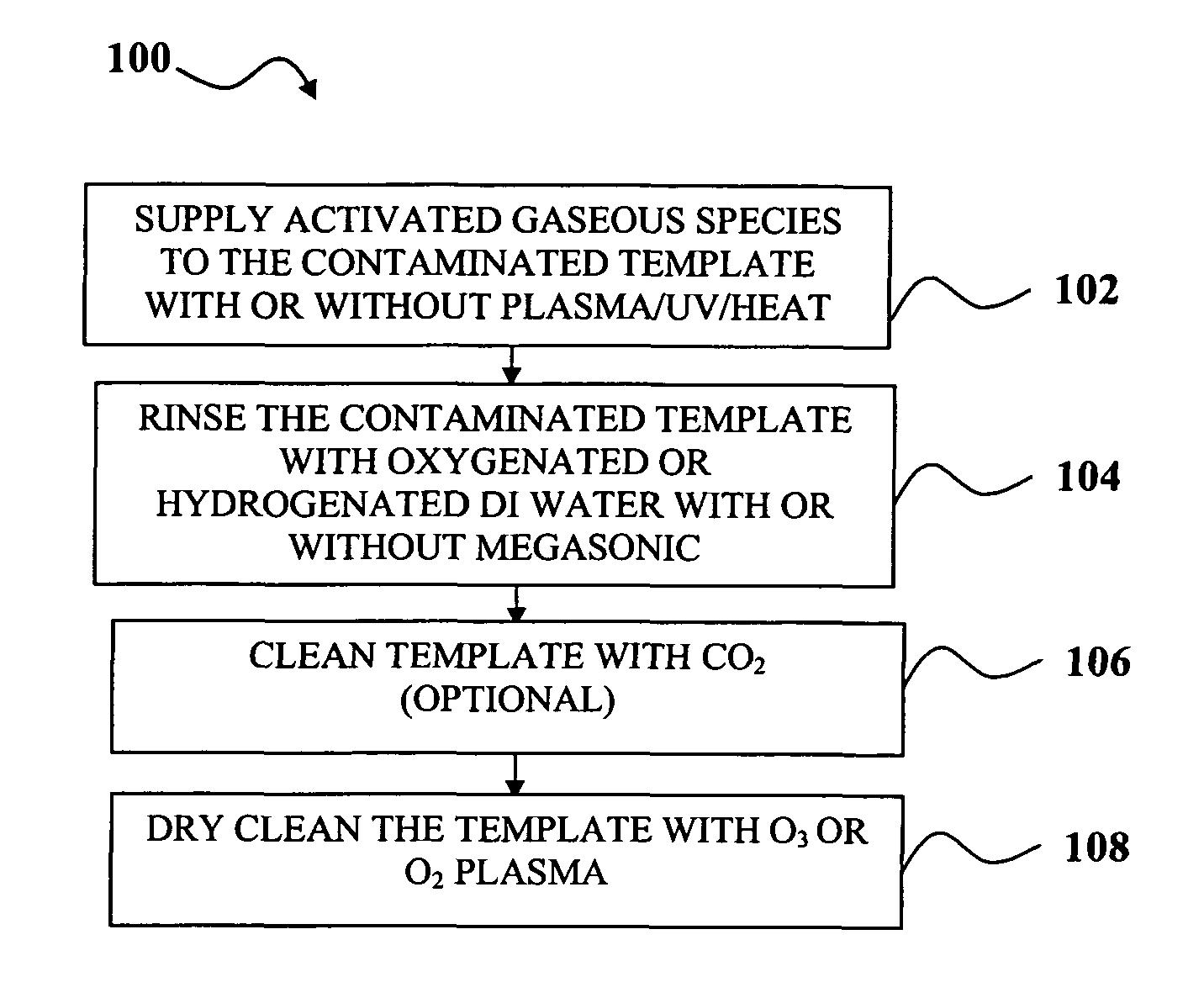
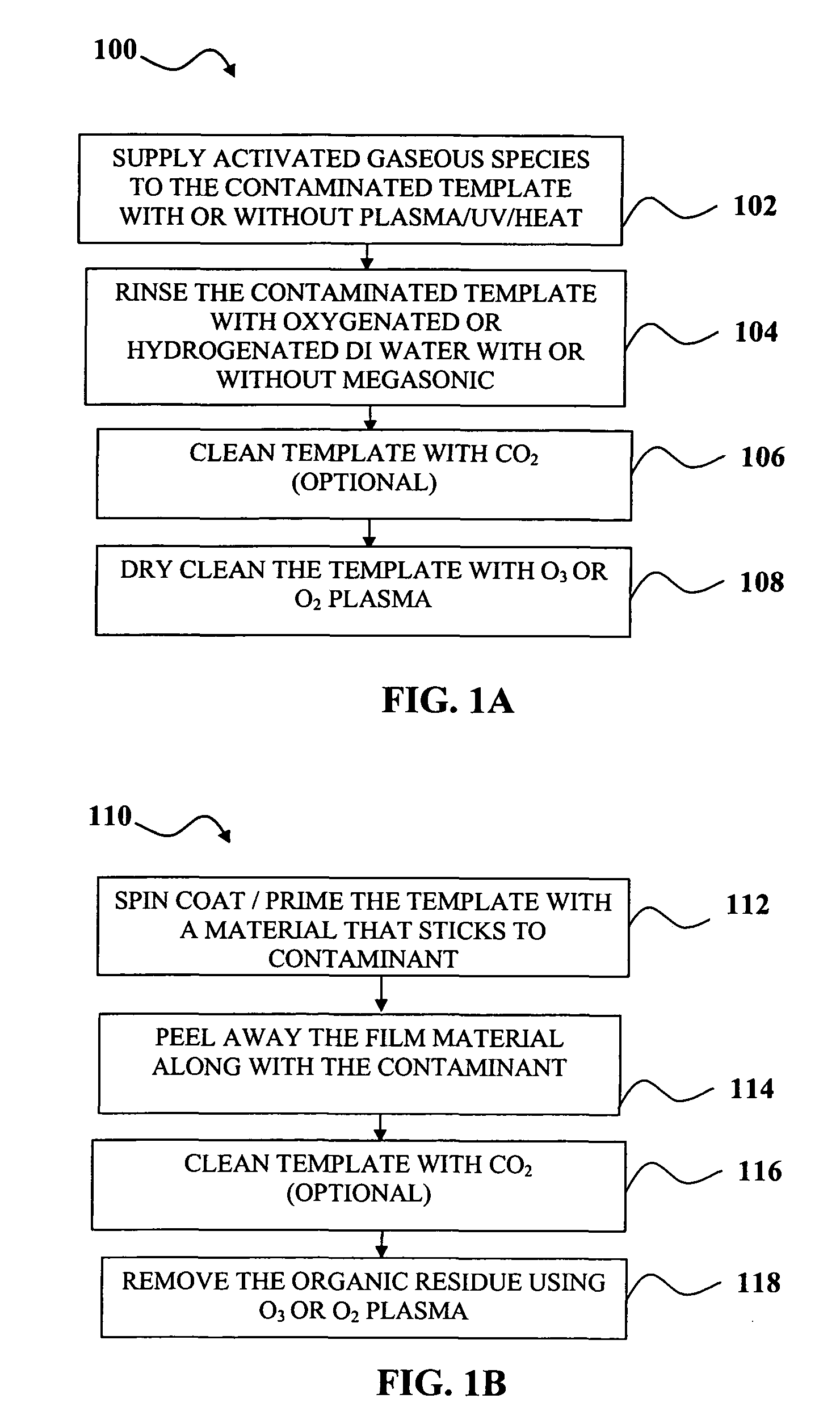
Environment friendly methods and systems for template cleaning and reclaiming in imprint lithography technology
InactiveUS7846266B1Repeatable quality outputDetergent mixture composition preparationElectrostatic cleaningLithographic artistReactive plasma
Cleaning and reclaiming nano-imprint templates using environment friendly methods and systems is disclosed. A template may be cleaned by a combination of exposure to activated gaseous species followed by rinsing with oxygenated or hydrogenated DI water and exposure to reactive plasma to remove organic contaminant. Contaminant may be removed by forming a coating film of a water soluble polymer on the template and then peeling off the coating film. Organic residue from the film may be removed using oxygenated plasma.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Apparatus and method for producing transparent conductive oxide film
InactiveCN101509126AQuality improvementReduce air intakeVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingVacuum pumpingOxygen ions
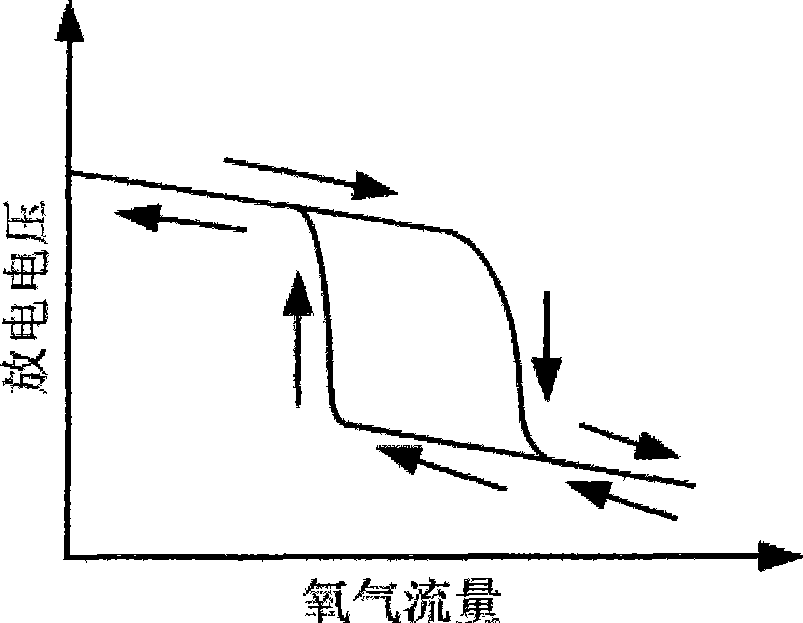
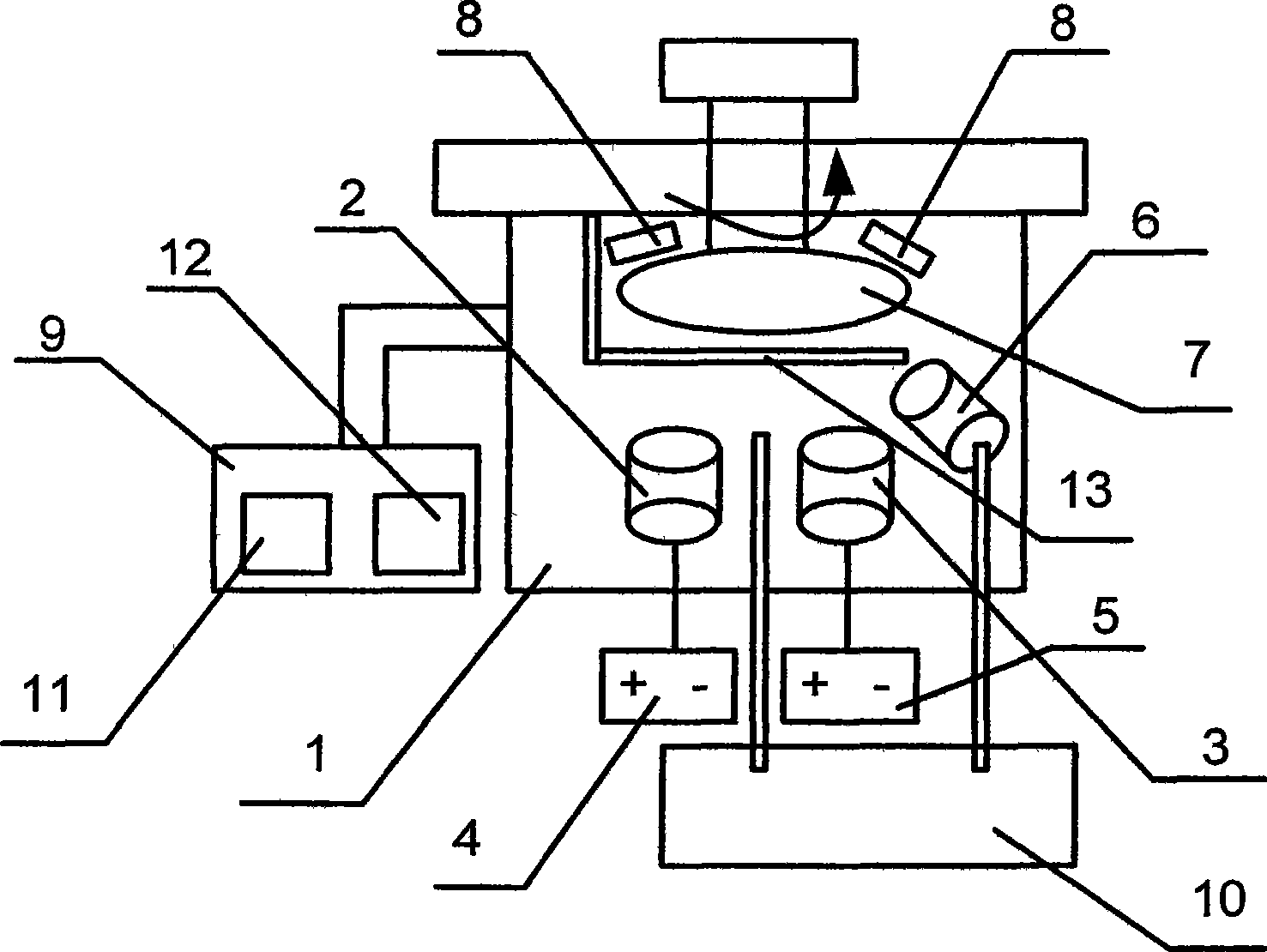
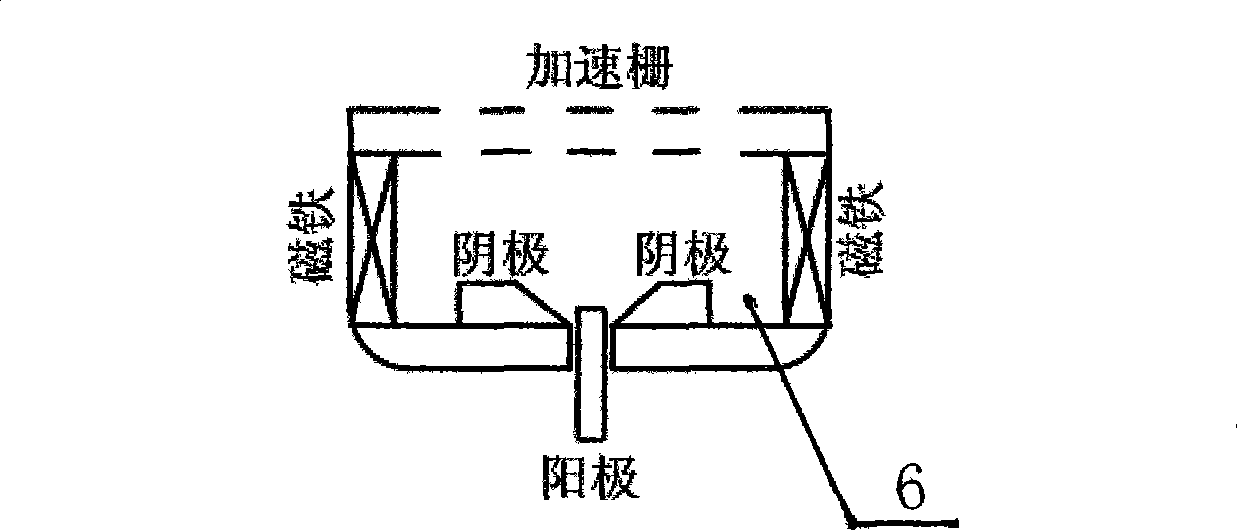
The invention relates to a transparent conducting oxide thin film, in particular to preparation equipment of the transparent conducting oxide thin film and a method thereof. The preparation equipment comprises a closed reaction chamber with a vacuum-pumping system and an air inlet system; wherein, a base plate frame capable of moving or rotating is arranged inside the closed reaction chamber, furnished with a heater, a baffle and a sputtering source arranged opposite to the base plate frame. The difference lies in that an oxygen ion source is arranged between the substrate frame and the sputtering source. The centric angles of the oxygen ion source and the base plate frame are adjustable within the range from 0 degree to 180 degrees. In the invention, reactive plasma oxygen is used as a reactant replacing the oxygen, thus greatly reducing the probability of anode disappearing and cathode poisoning and the frequency of arc starting and enhancing the operating stability of the system. In addition, the structure is simple, the manufacturing cost and the operation and maintenance cost is low.
Owner:王凯 +1
Method of manufacturing a semiconductor device
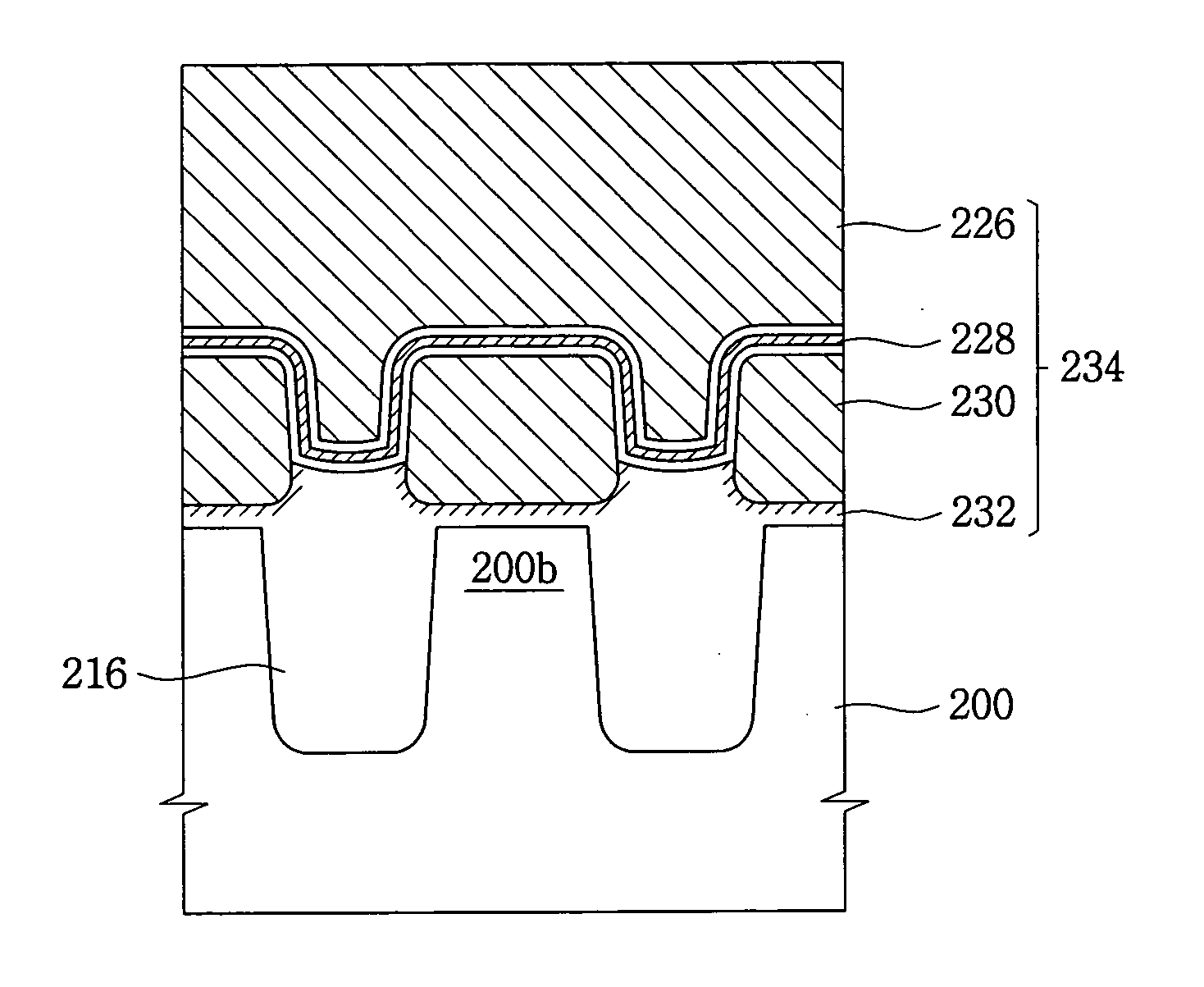
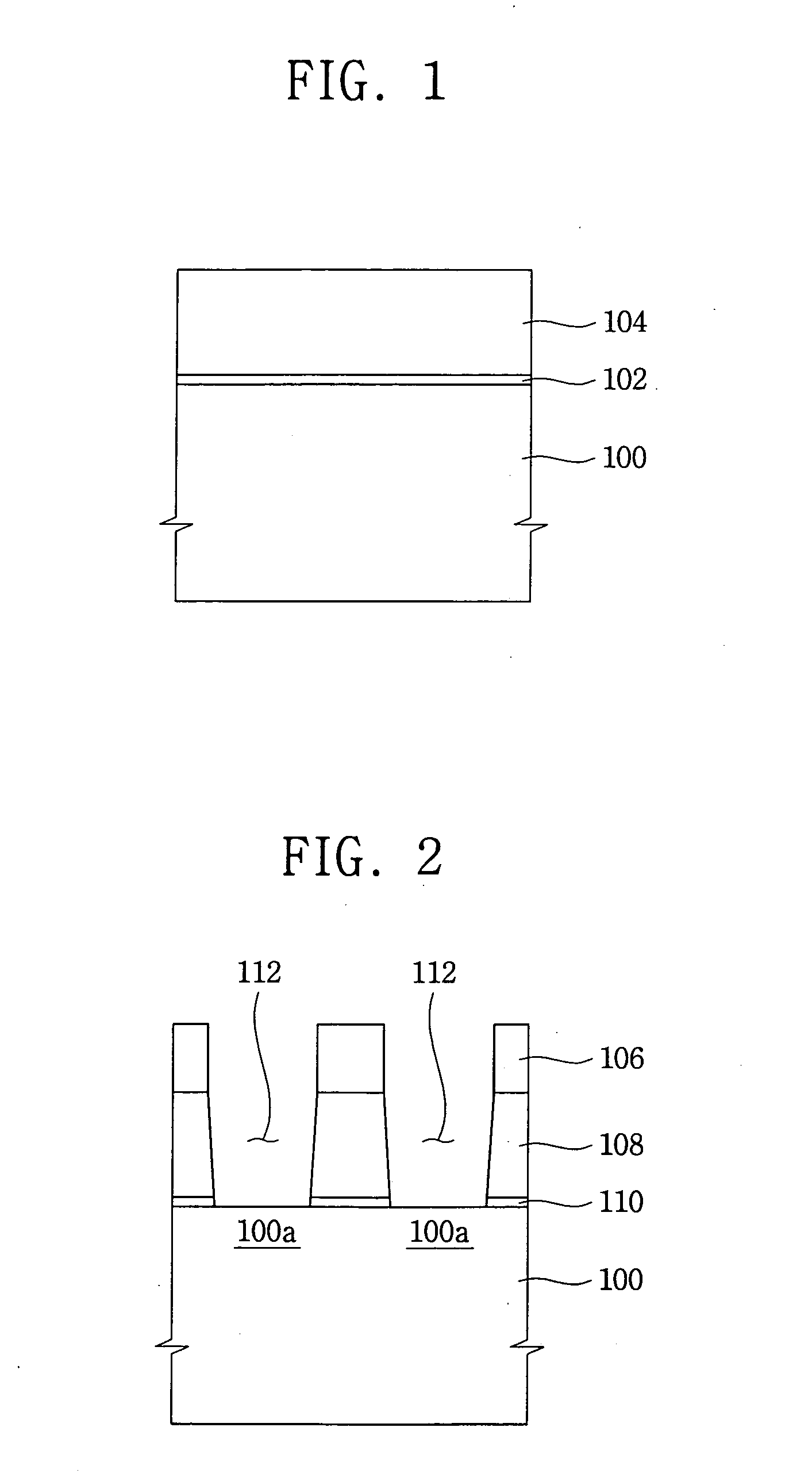
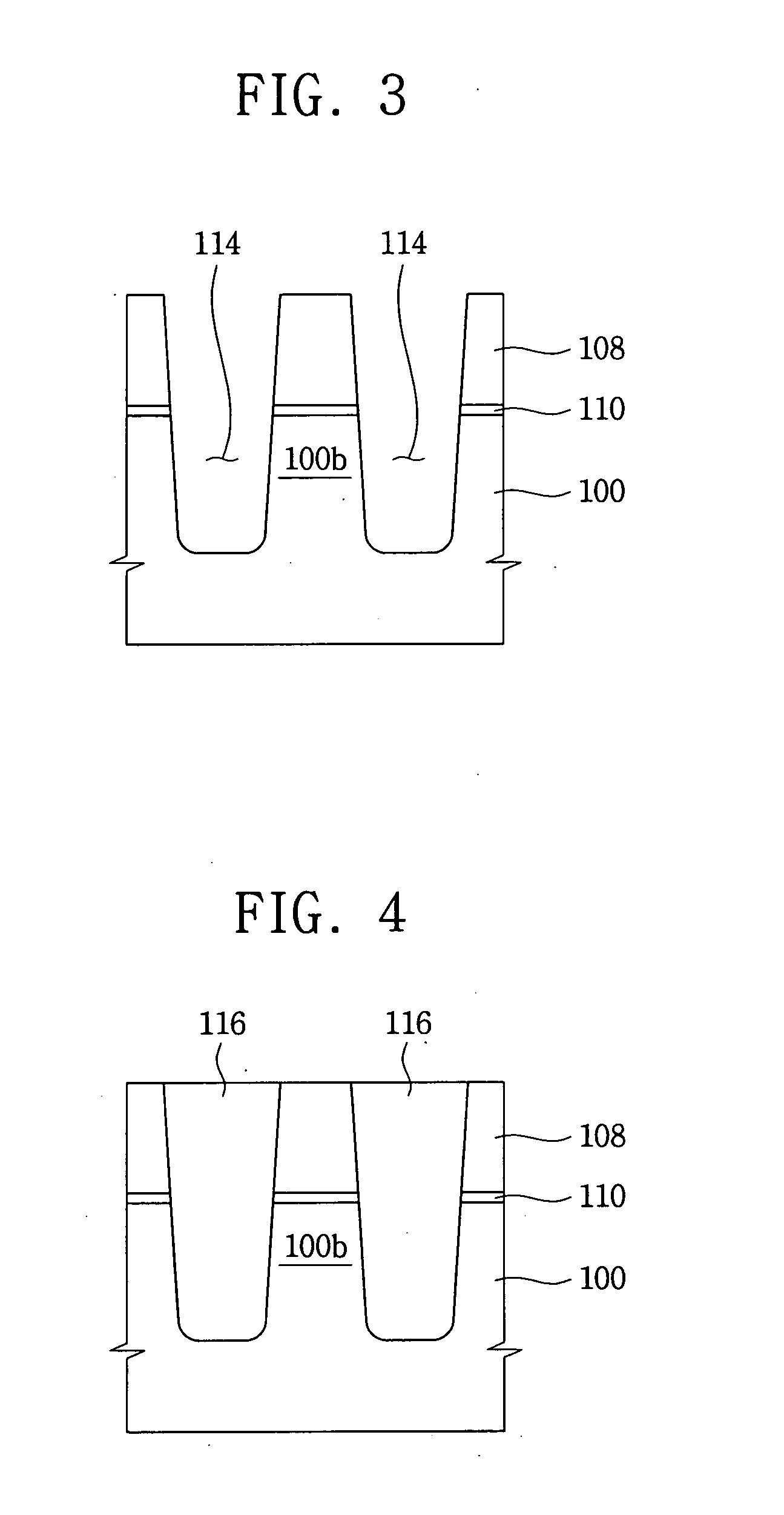
InactiveUS20070026655A1Improve thickness uniformityEnhance layeringSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialActivation energy
In a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device for use in such applications as a flash memory device, a field insulating pattern defines an opening that exposes an active region of a semiconductor substrate. The field insulating pattern includes a first portion protruding from the substrate and a second portion buried in the substrate. An oxide layer is formed on the active region by an oxidation process using a reactive plasma including an oxygen radical and a conductive layer is then formed on the oxide layer to sufficiently fill up the opening. The oxide layer is formed by an oxidation reaction of a surface portion of the active region with the oxygen radical having a relatively low activation energy, resulting in an improved thickness uniformity of the oxide layer. As a result, various performance characteristics of the semiconductor device when used in flash memory and similar applications are improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Etching methods
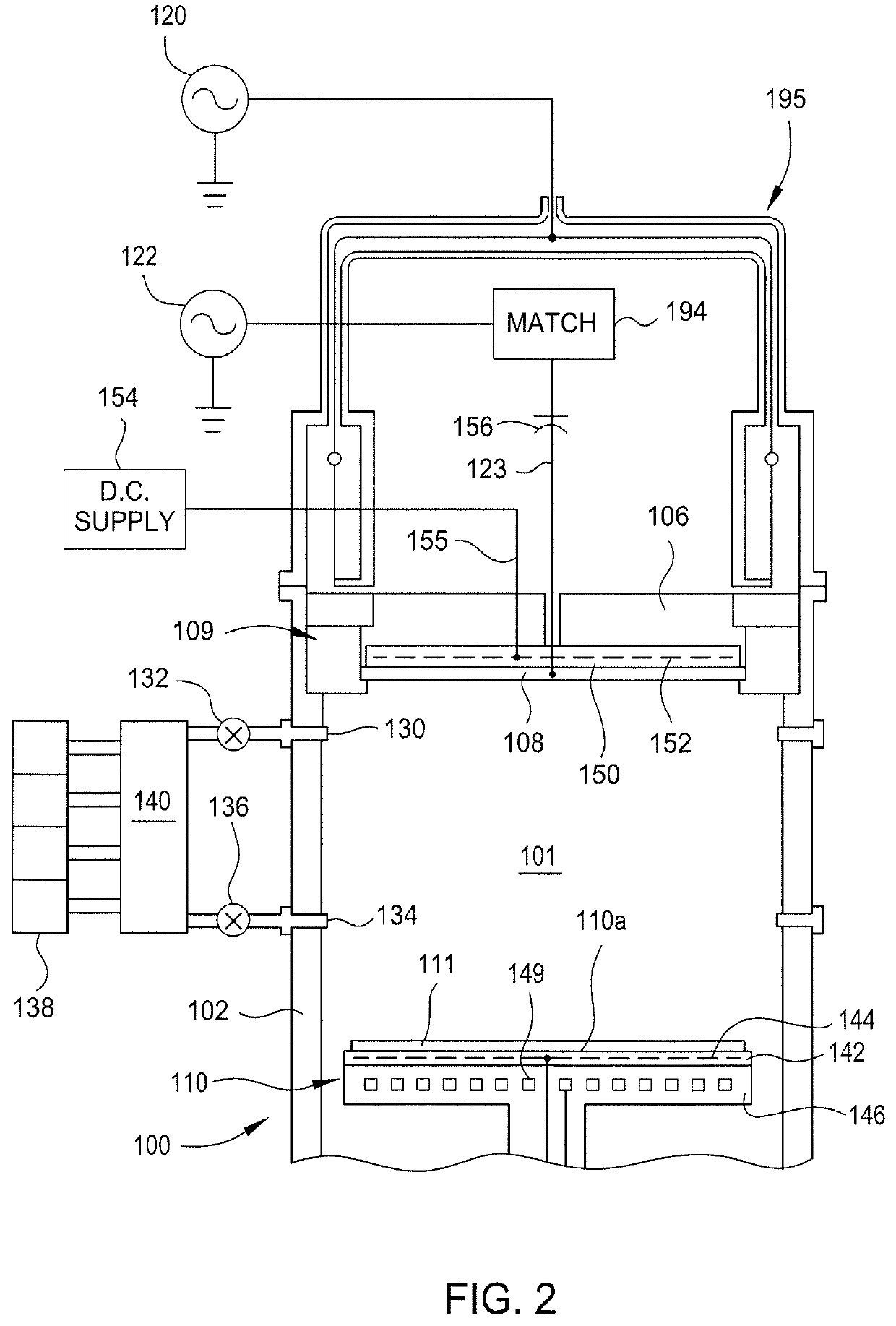
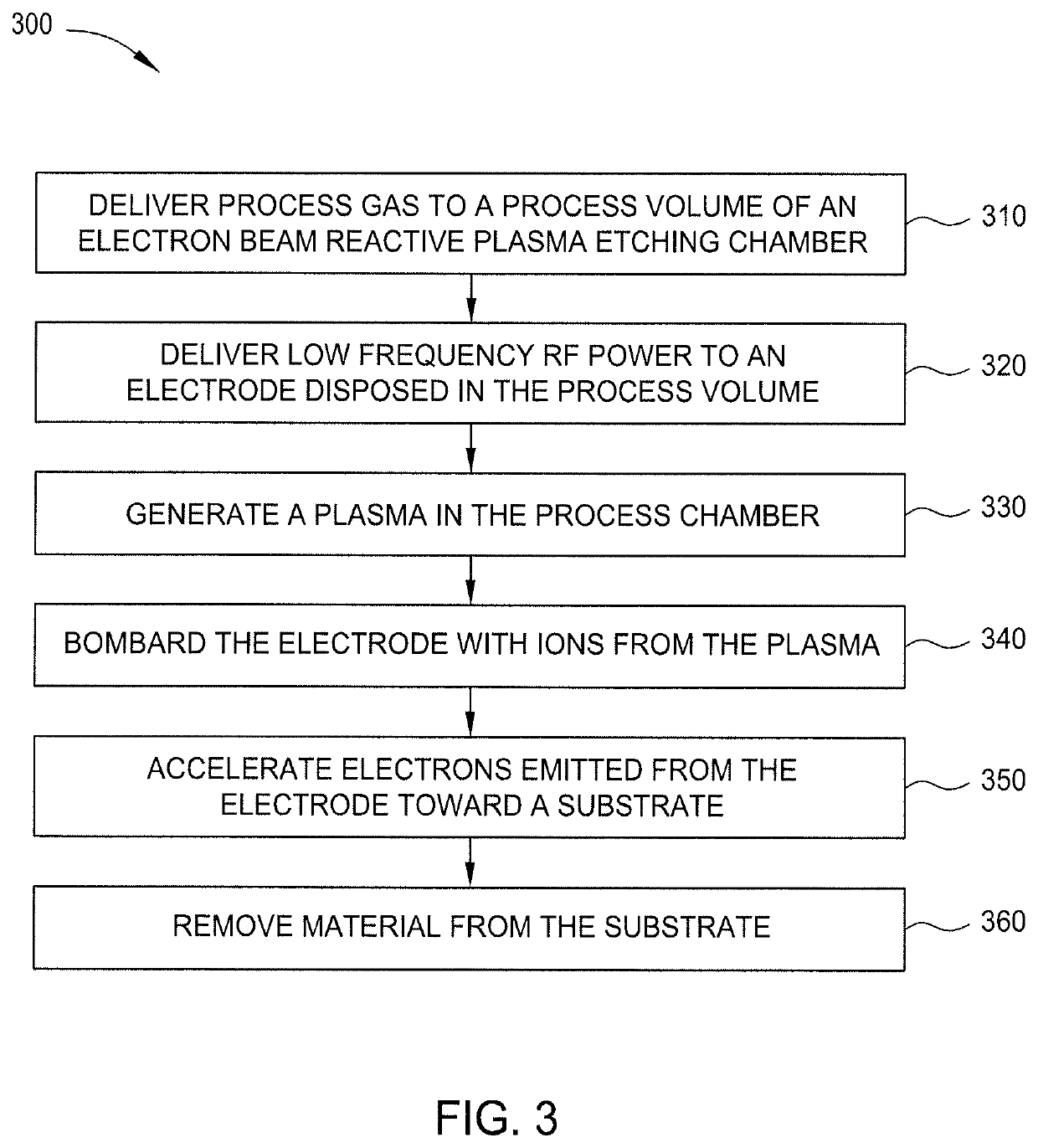
ActiveUS10707086B2Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingReactive plasmaSecondary electron emission coefficient
Embodiments described herein relate to apparatus and methods for performing electron beam reactive plasma etching (EBRPE). In one embodiment, an apparatus for performing EBRPE processes includes an electrode formed from a material having a high secondary electron emission coefficient. In another embodiment, methods for etching a substrate include generating a plasma and bombarding an electrode with ions from the plasma to cause the electrode to emit electrons. The electrons are accelerated toward a substrate to induce etching of the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for manufacturing magnetic recording medium, and magnetic recording/reproducing device
InactiveUS20100232056A1Improve environmental resistanceDecorative surface effectsRecord information storageSurface layerReactive plasma
Provided is a process for manufacturing a magnetic recording medium having a magnetically partitioned magnetic recording patterns, which comprises the following steps, conducted in the order: (1) step of forming a magnetic layer on a non-magnetic substrate, (2) step of exposing the surface of regions of the magnetic layer to a reactive plasma or a reactive ion, which regions are to magnetically partition the magnetic layer for forming a magnetically partitioned magnetic recording pattern, and (3) step of exposing the magnetically partitioned magnetic layer to an inert gas irradiation. Preferably, a step of removing surface layer portions of said regions of the magnetic layer is carried out after the step (1) but before the step (2). The surface of the magnetic layer of produced magnetic recording medium exhibits good resistance to corrosion caused by oxidation or halogenation.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Supersonic reaction plasma spray gun
InactiveCN101289744AExtended service lifeImprove cooling effectMetallic material coating processesLiquid spraying apparatusCeramic coatingReactive plasma
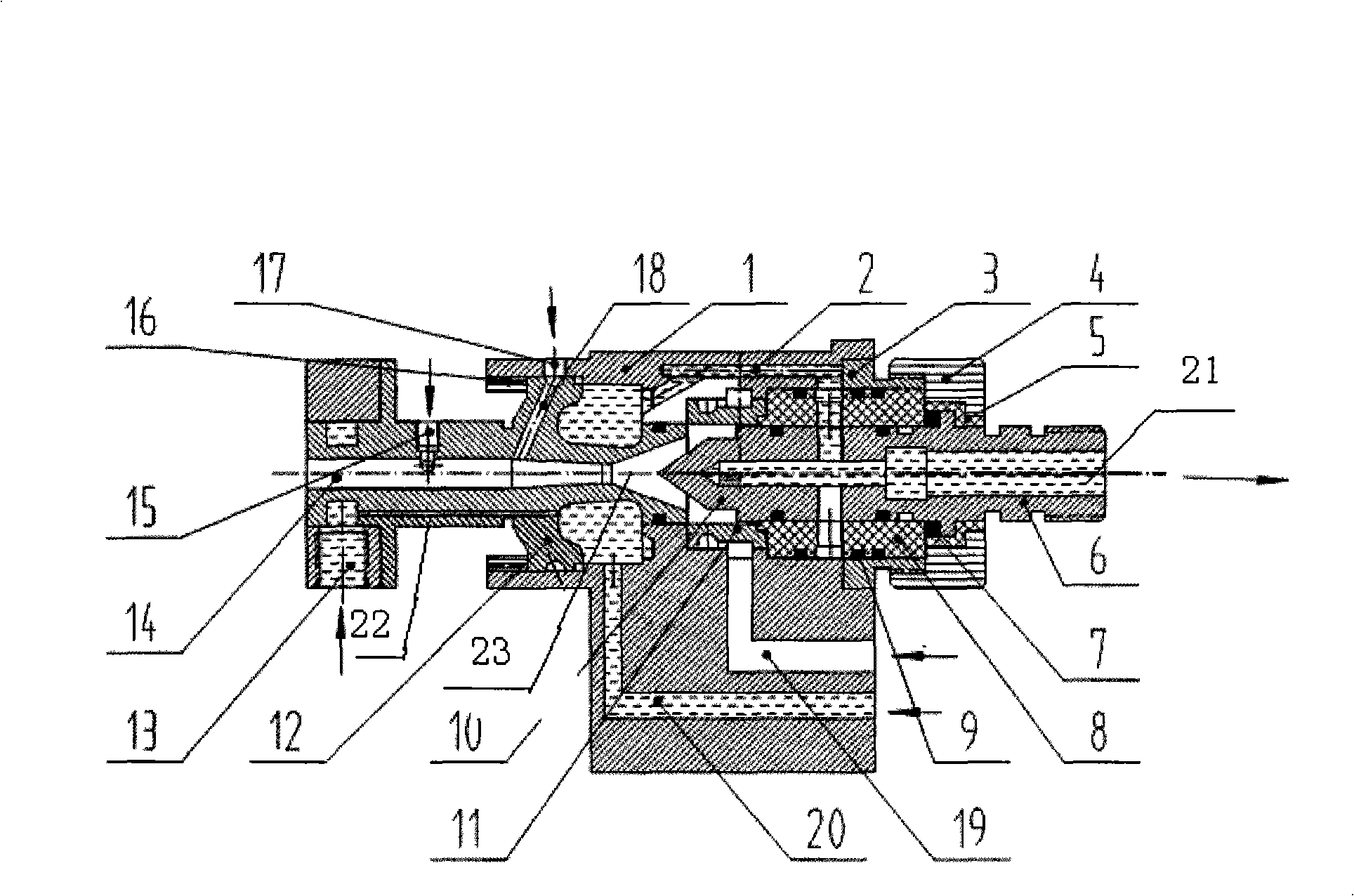
The invention provides a supersonic reactive plasma spray gun, belonging to the welding field. The spray gun mainly comprises a gun body (1), an insulator (8), a gas swirling ring (11), a cathode body (6), an in-situ reaction Laval anode nozzle (12), a fastening sleeve (3), a front fixing cap (16), a back pressing cap (14) and an insulating gasket (5), which are in the following connection mode that: the in-situ reaction Laval anode nozzle (12) is connected with the gun body (1) through the front pressing cap (16); the gas swirling ring (11) and the insulator (8) are fixed inside the gun body (1) through the fastening sleeve (3); the fastening sleeve (3) and the gun body (1) are connected through tight fit; the cathode body (6) is fixed inside the gun body (1) through the insulator (8), the fastening sleeve (3), the back pressing cap (14) and the insulating gasket (5). The in-situ reaction Laval anode nozzle (12) is in an integrated structure on which a powder feeding hole (18), a reaction gas inlet (15), an auxiliary cooling water inlet (18) and an auxiliary cooling water channel (22) are arranged. The spray gun allows in-situ synthesis and supersonic plasma spraying to be accomplished in one step, thereby realizing the high performance, high efficiency and low cost of ceramic coating spraying and the long life-span of the spray gun.
Owner:PLA AIR FORCE RADAR COLLEGE
Exposure method and tool
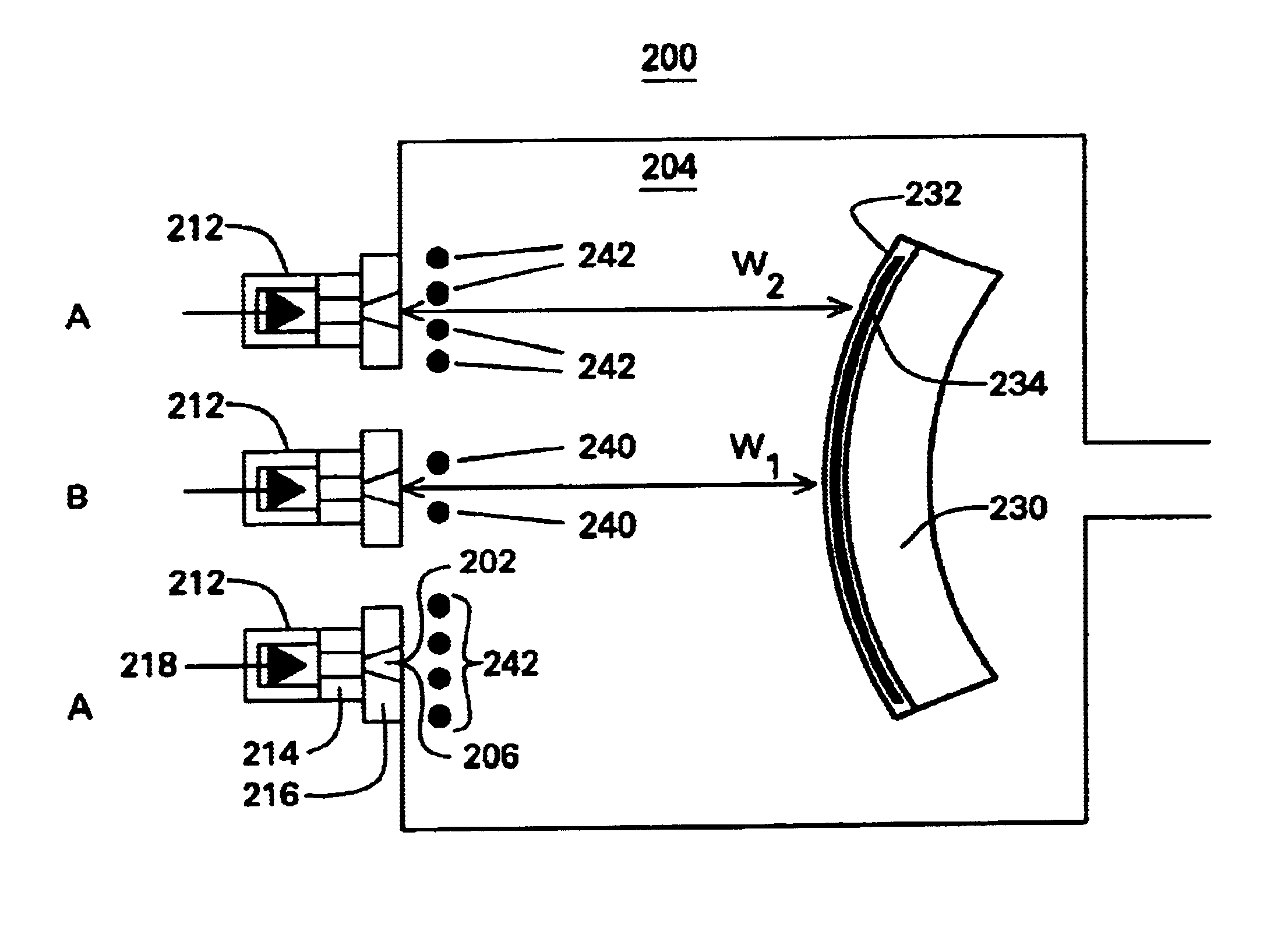
InactiveUS20090098479A1Easy constructionAvoid problemsPhotosensitive materialsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusResistUltraviolet
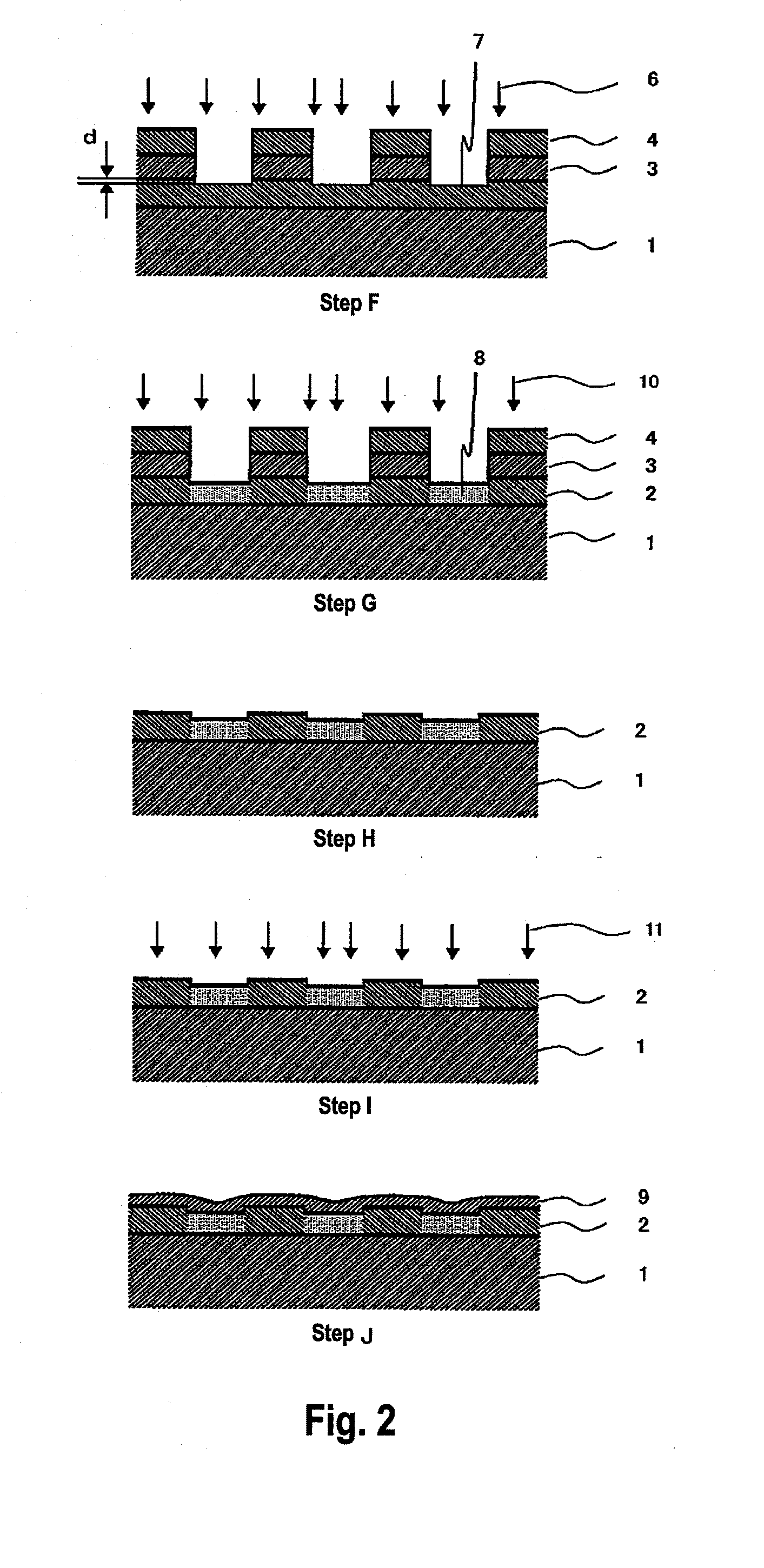
A method for forming a regularly repeating pattern on to a substrate comprising the steps of: applying a resist on a surface of a substrate to be processed; imprinting on the applied resist a pattern formed by exposing it to a beam of ultra violet (‘UV’) light, which has been caused to pass through a suitable mask delineating the pattern and then trough a focusing lens on to the resist, so as to cause chemical changes in the resist which makes it more or less soluble in a suitable developer solution; the imprinting step being carried out: in a repetitive series of discrete exposure steps using a mask held stationery with respect to the beam and the lens that represents only a small area of the total area of the substrate and using a single short pulse of UV radiation at each step to illuminate the mask, the radiation pulse having such an energy density at the substrate that it is below the threshold value for ablation of the resist; and the series of discrete exposure steps being repeated over the full area of the surface of a substrate, to give a full structure comprising a plurality of pixels, by moving the substrate in a direction parallel to one axis of the structure to be formed on the substrate and activating the pulsed mask illumination light source at the instant that the substrate has moved over a distance equivalent to a complete number of periods of the repeating pattern on the substrate; treating the exposed resist with a developer to cause either exposed regions (for positive resists) or unexposed regions (for negative resists) to be dissolved and subsequently washed away by the developer solution to reveal the pattern formed by the remaining resist; treating the substrate with a suitable chemical etching solution, reactive plasma or abrasive particles that removes the substrate in resist free areas; and removing remaining resist from the substrate with a suitable solvent to leave a finished patterned substrate.The invention further comprises a scanning exposure tool for carrying out the method as aforesaid.
Owner:EXITECH
Method for producing magnetic recording medium and producing apparatus thereof
InactiveUS20110059235A1Improve environmental resistanceImprove recording densityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingEnvironmental resistanceReactive plasma
Provided are a method of producing a magnetic recording medium with improved environmental resistance, especially, corrosion resistance and an apparatus used therefor. In producing a magnetic recording medium having a magnetic recording pattern on a magnetic recording layer formed on at least a surface of a nonmagnetic substrate using an in-line film formation apparatus, the method comprising: mounting a nonmagnetic substrate on the carrier, the nonmagnetic substrate having at least the magnetic recording layer and a mask layer corresponding to the magnetic recording pattern laminated thereon in this order; forming the magnetic recording pattern by having areas of the magnetic recording layer that are not covered with the mask layer subjected to a reactive plasma treatment or an ion irradiation treatment; removing the mask layer from the magnetic recording layer; and removing the nonmagnetic substrate from the carrier, wherein each of the chambers has a decompressed atmosphere inside while the carrier passes through each of the chambers and each of the processes are conducted continuously while being blocked from the ambient air.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
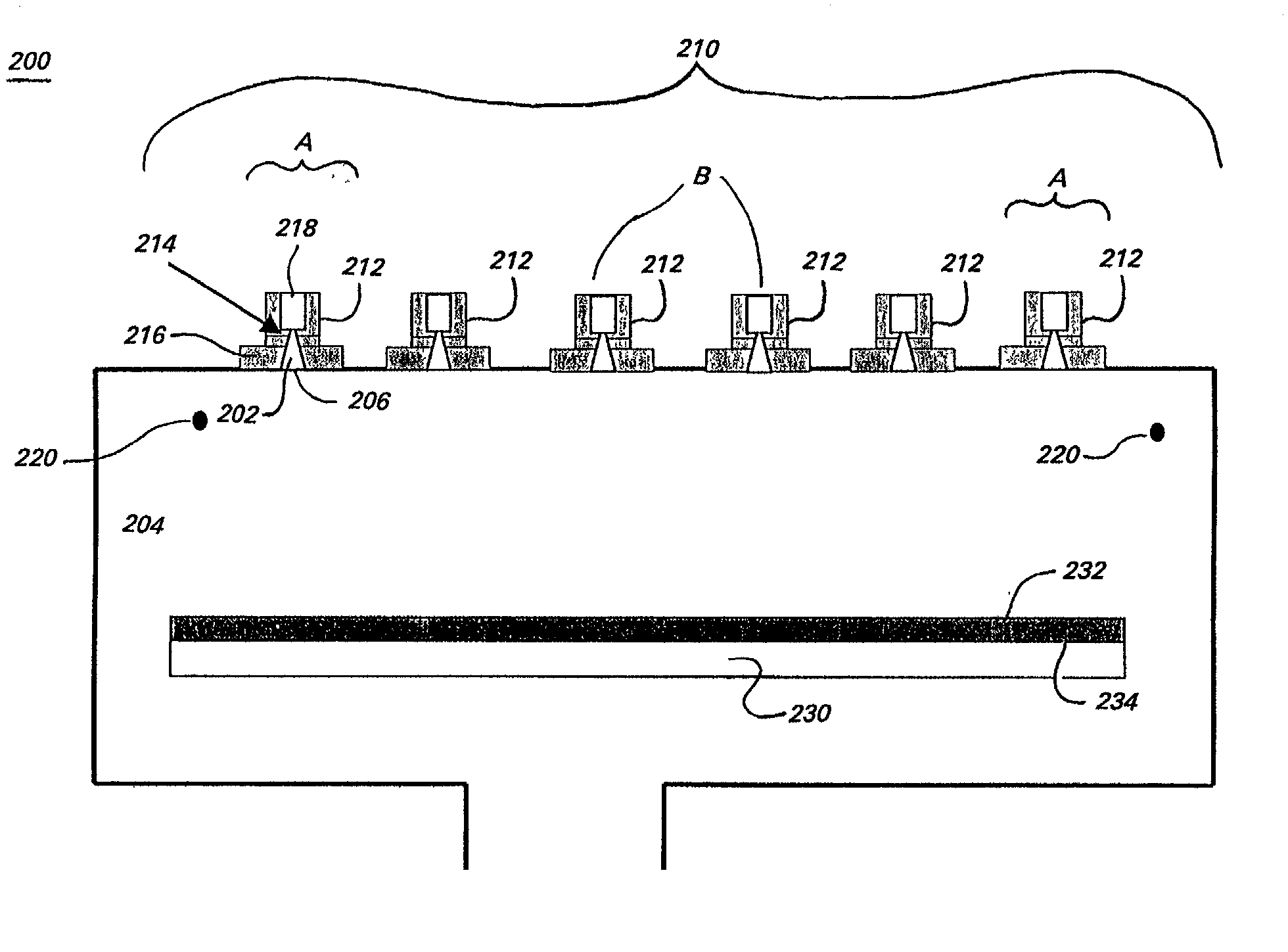
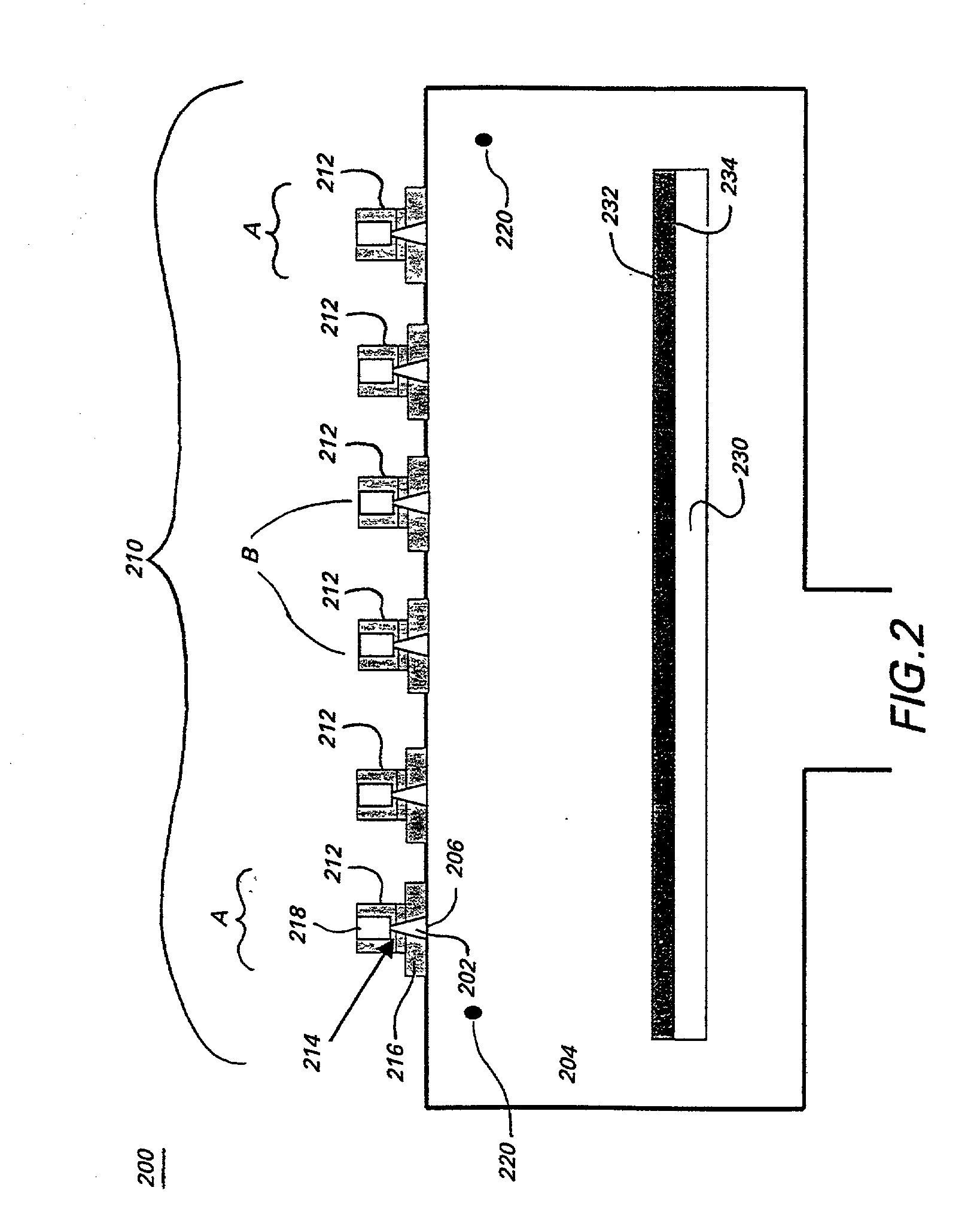
Processes and systems for determining the identity of metal alloys
A method and apparatus for depositing a uniform coating on a large area, planar surface using an array of multiple plasma sources and a common reactant gas injector. The apparatus includes at least one array of a plurality of plasma sources, wherein each of the plurality of plasma sources includes a cathode, an anode, and an inlet for a non-reactive plasma source gas disposed in a plasma chamber, and a common reactant gas injector disposed in a deposition chamber that contains the substrate. The common reactant gas injector provides a uniform flow of at least one reactant gas to each of the multiple plasmas generated the multiple plasma sources through a single delivery system. The at least one reactant gas reacts with the plurality of plasmas to form a uniform coating on a substrate.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
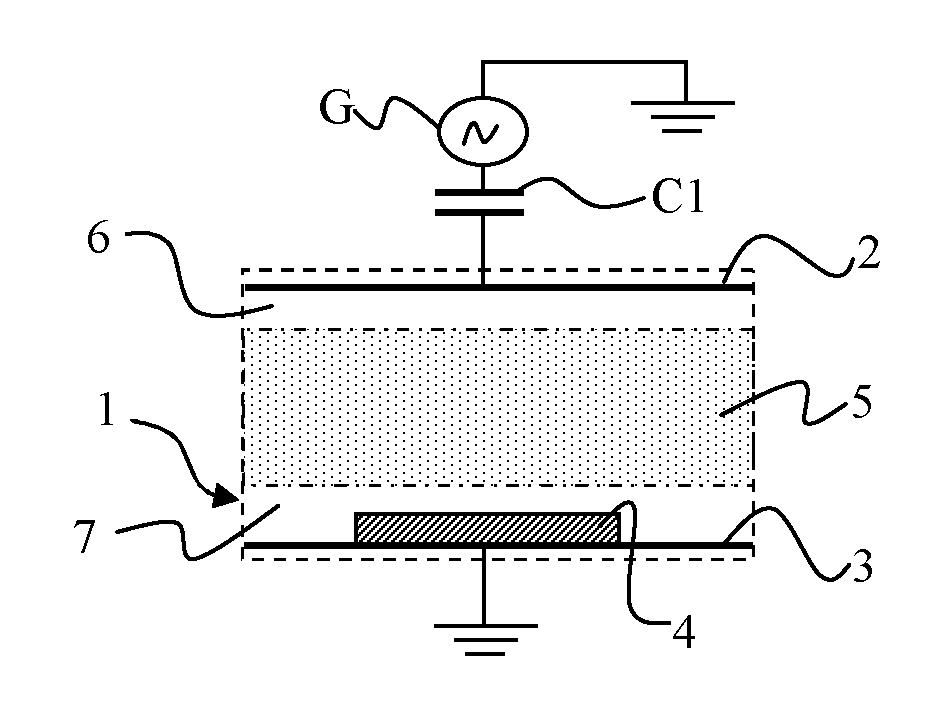
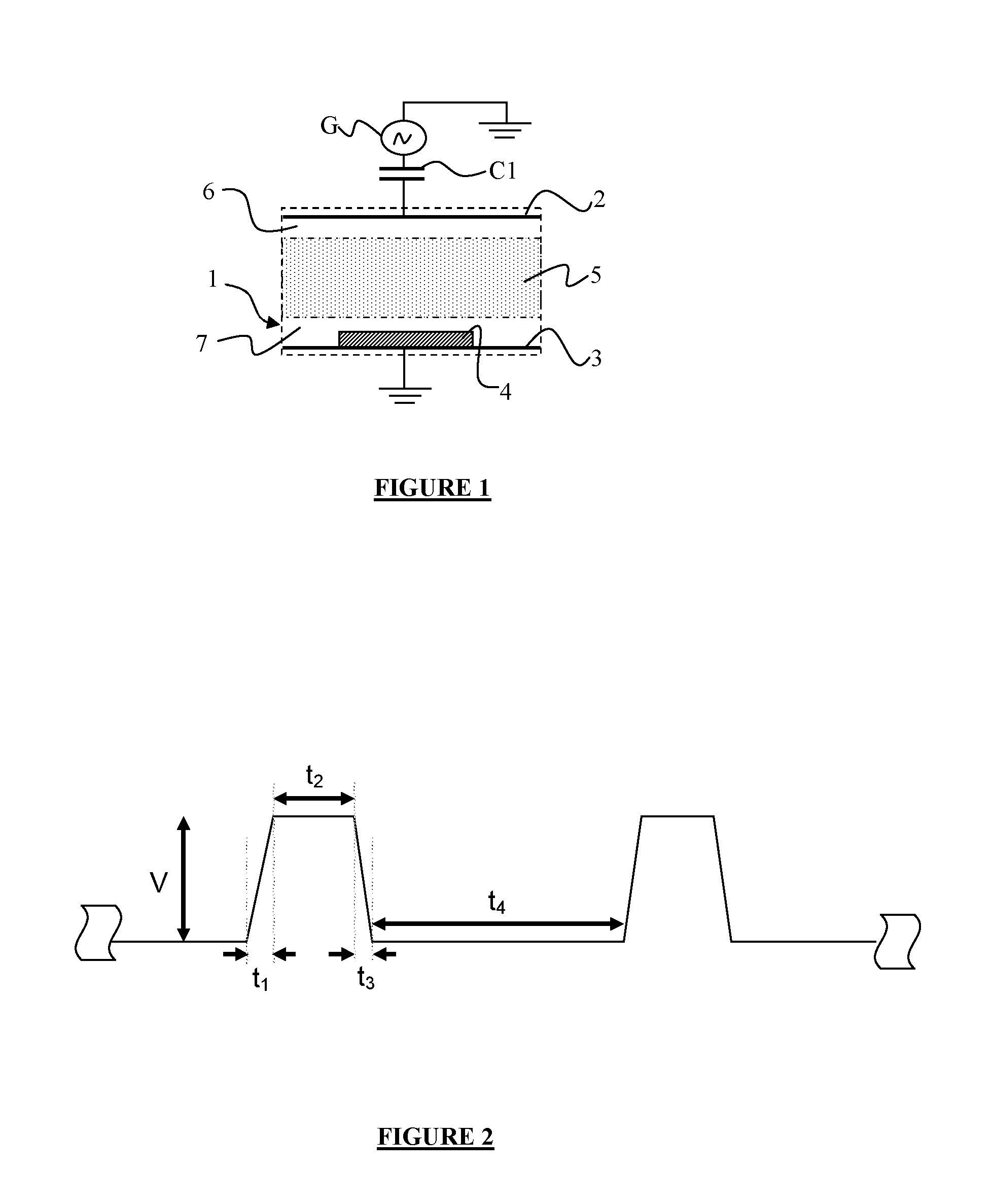
Plasma processing in a capacitively-coupled reactor with trapezoidal-waveform excitation
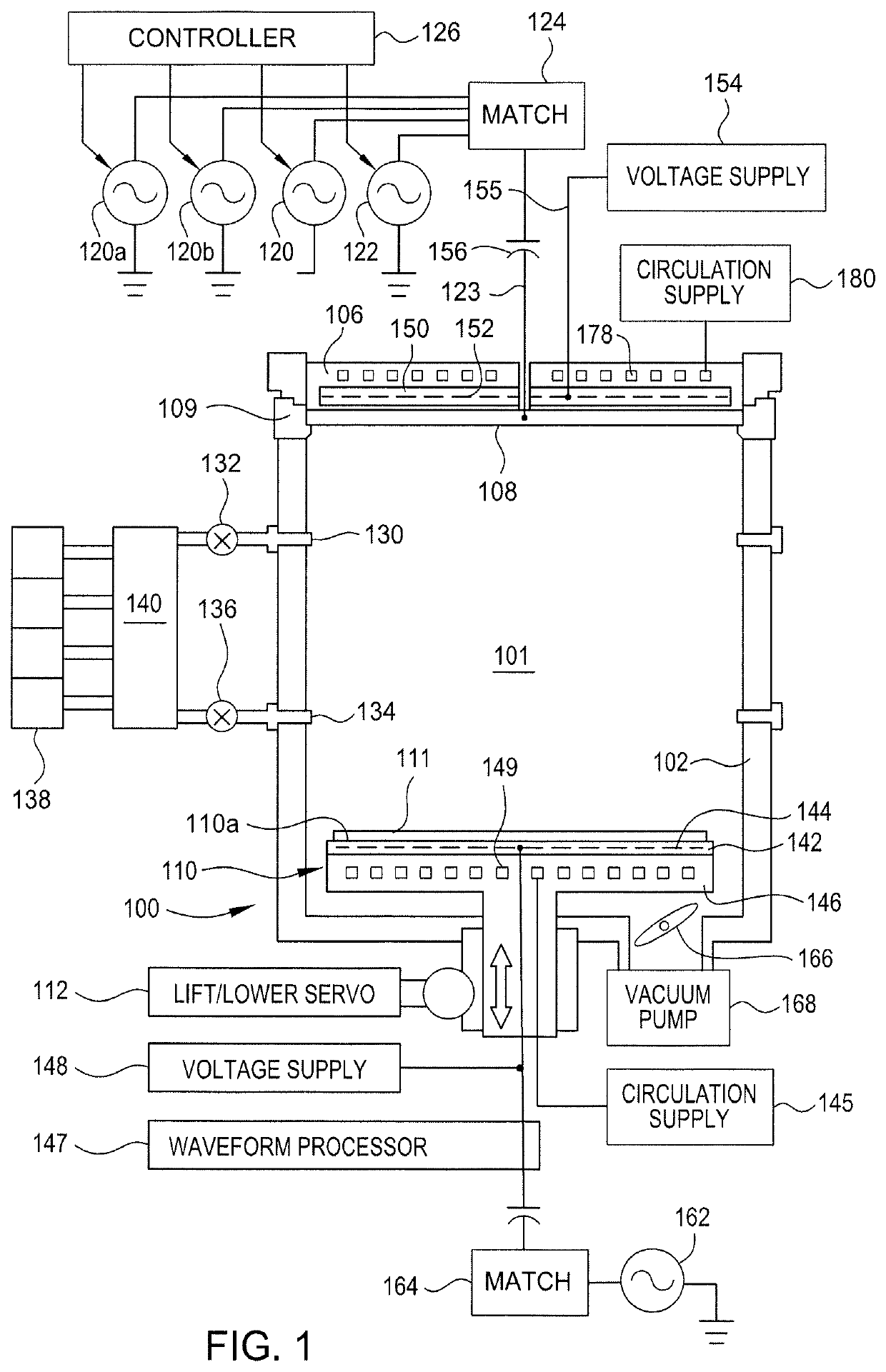
ActiveUS20130136872A1Optimal plasma cleaningHigh rateElectric discharge tubesChemical vapor deposition coatingCapacitancePlasma density
A method is provided for exciting at least one electrode of a capacitively coupled reactive plasma reactor containing a substrate. The electrode is excited by applying a RF voltage with a trapezoidal waveform comprising a ramp-up, a high plateau, a ramp-down and a low plateau. The plasma density can be controlled by adjusting the duration of the ramp-up, the duration of the ramp-down, the amplitude and the repetition rate of the trapezoidal waveform. The ion energy distribution function at the substrate can be controlled by adjusting the amplitude and the relative duration between the high plateau and the low plateau of the trapezoidal waveform.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE +1
Gray scale x-ray mask
InactiveUS7008737B2Easy to manufactureSimple to provideElectric discharge tubesRadiation applicationsResistX-ray
The present invention describes a method for fabricating an embossing tool or an x-ray mask tool, providing microstructures that smoothly vary in height from point-to-point in etched substrates, i.e., structure which can vary in all three dimensions. The process uses a lithographic technique to transfer an image pattern in the surface of a silicon wafer by exposing and developing the resist and then etching the silicon substrate. Importantly, the photoresist is variably exposed so that when developed some of the resist layer remains. The remaining undeveloped resist acts as an etchant barrier to the reactive plasma used to etch the silicon substrate and therefore provides the ability etch structures of variable depths.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Composite electrode material containing reactive plasma spraying nanometer TiN middle layer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103345958AImprove corrosion resistanceImprove conductivityMolten spray coatingMetal/alloy conductorsComposite electrodeMicrometer
The invention discloses a composite electrode material containing a reactive plasma spraying nanometer TiN middle layer. The material comprises a base body, a bonding bottom layer arranged on the base body, the reactive plasma spraying nanometer TiN middle layer arranged on the bonding bottom layer and an oxide catalytic layer arranged on the middle layer. The base body is an iron-based or Ti-based base body, the bonding bottom layer is a nickel aluminum self-fluxing alloy layer containing Ni 95wt. % or an iron aluminum self-fluxing alloy layer containing Fe 50 wt. %, the thickness of the bonding bottom layer is 30-70 micrometers, the thickness of the reactive plasma spraying nanometer TiN middle layer is 300-500 micrometers, and the thickness of the oxide catalytic layer is 10-30 micrometers. Compared with a conventional Ti-based and iron-based electrode, a composite electrode is remarkably improved by 20%-25% in oxygen evolution potential, the fortified life of a Ti / TiN / Sb-SnO2 composite electrode is 3 times as long as that of the conventional electrode without the middle layer, and the fortified life of a Fe / TiN / PbO2 composite electrode is 360 times as long as that of the Ti / TiN / Sb-SnO2 composite electrode.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com