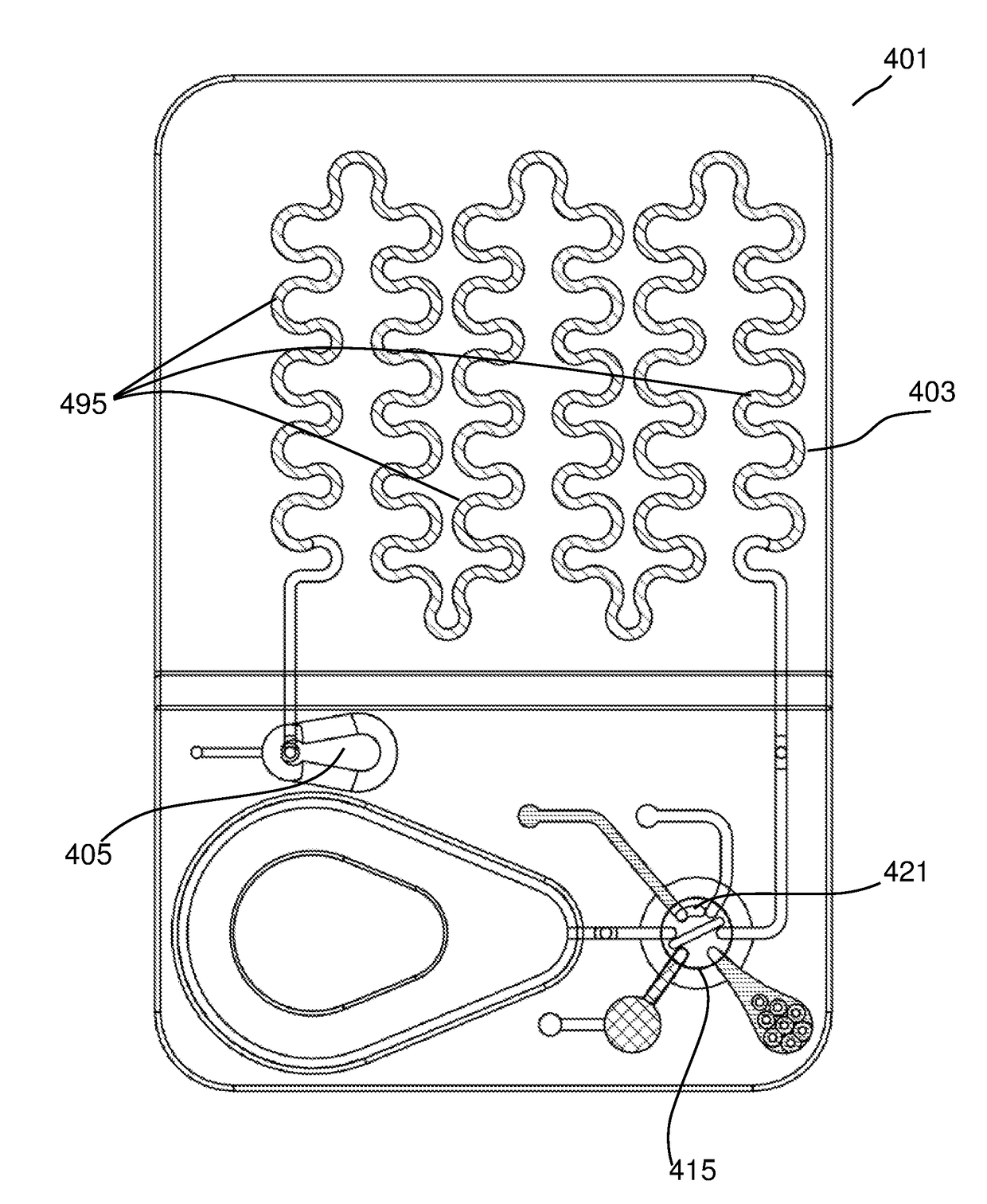
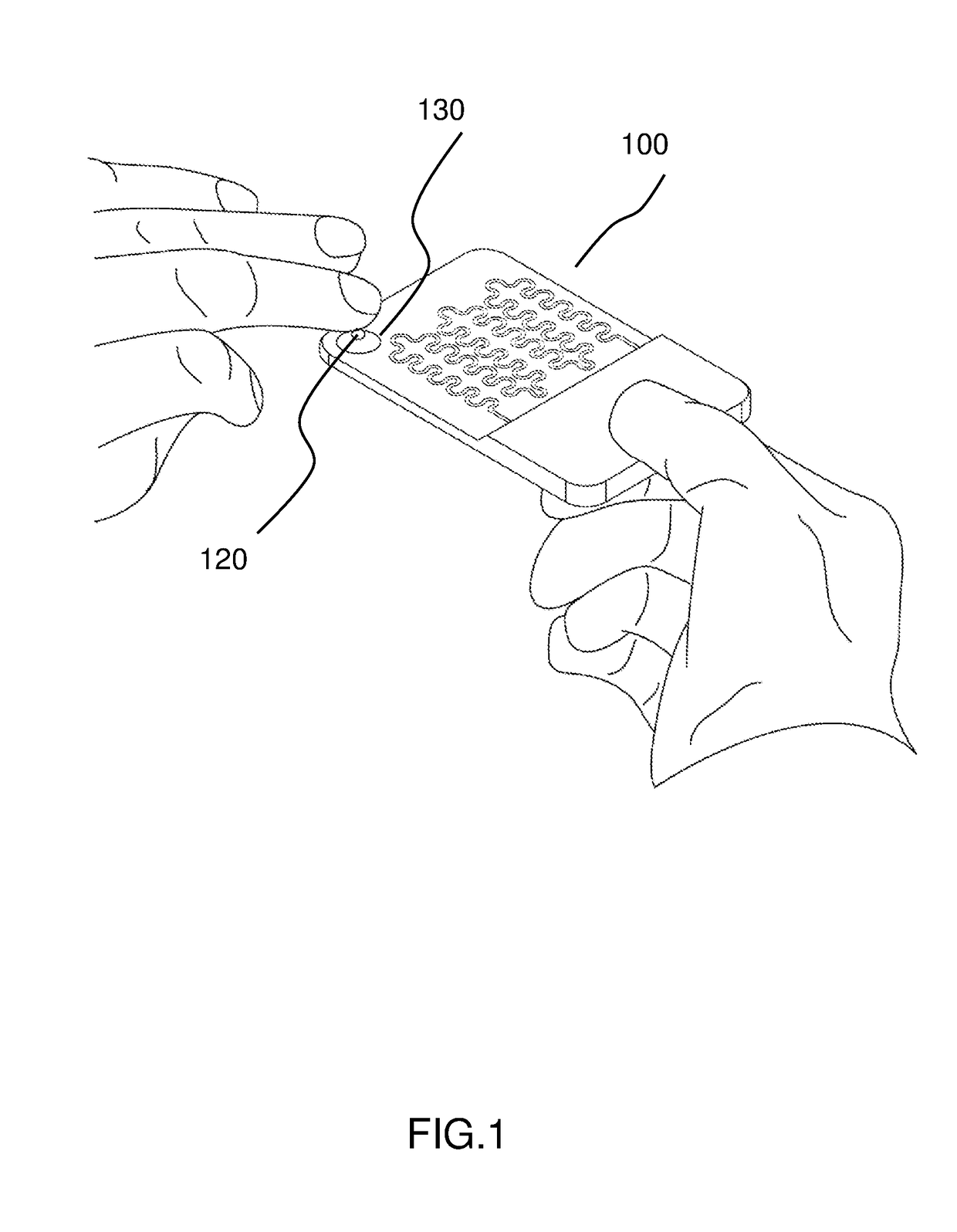
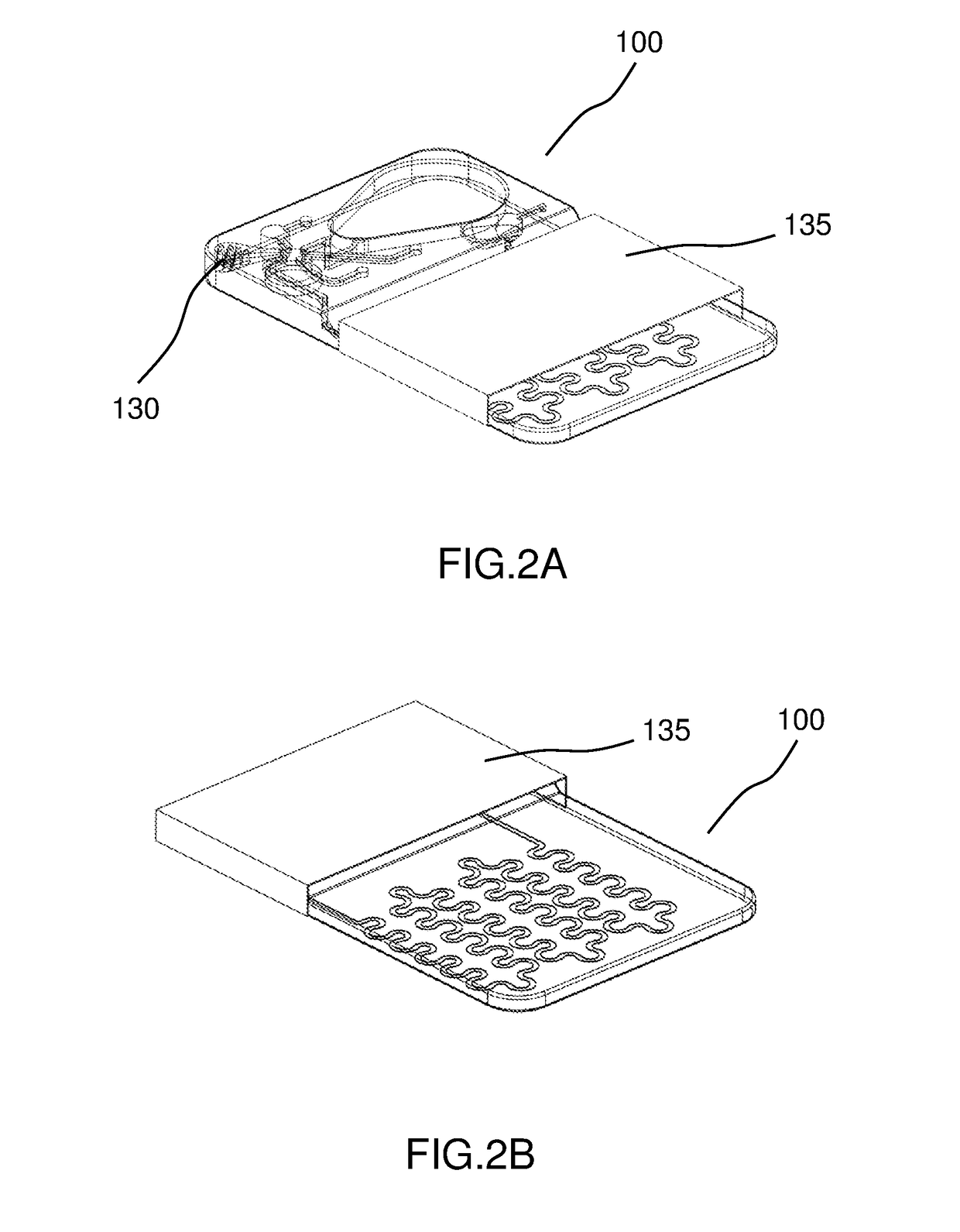
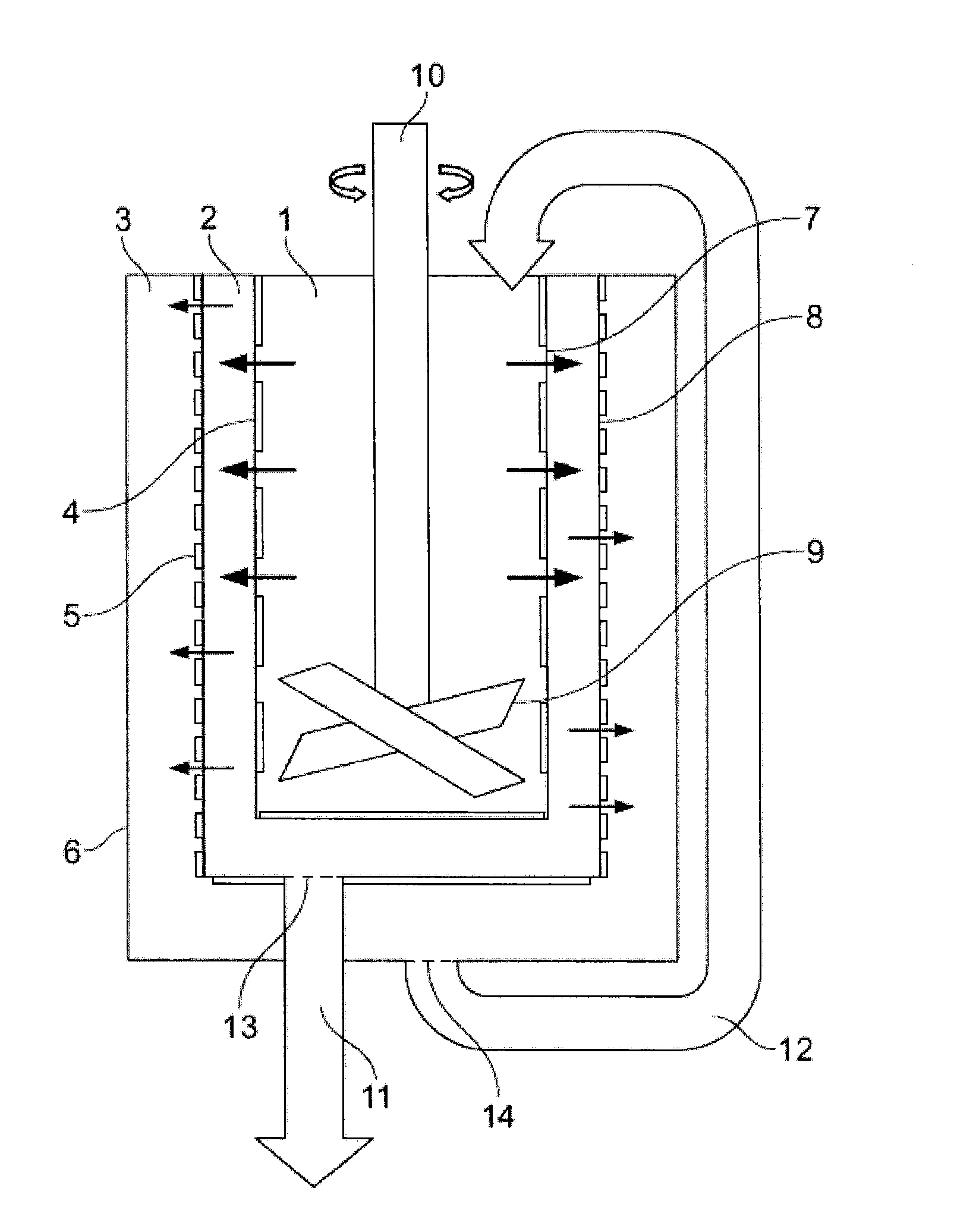
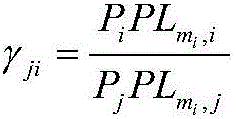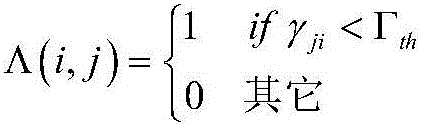Patents
Literature
96 results about "Cell clustering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cell clustering and scattering play important roles in cancer progression and tissue engineering. While. the extracellular matrix (ECM) is known to control cell clustering, much of the quantitative work has. focused on the analysis of clustering between cells with strong cell-cell junctions.
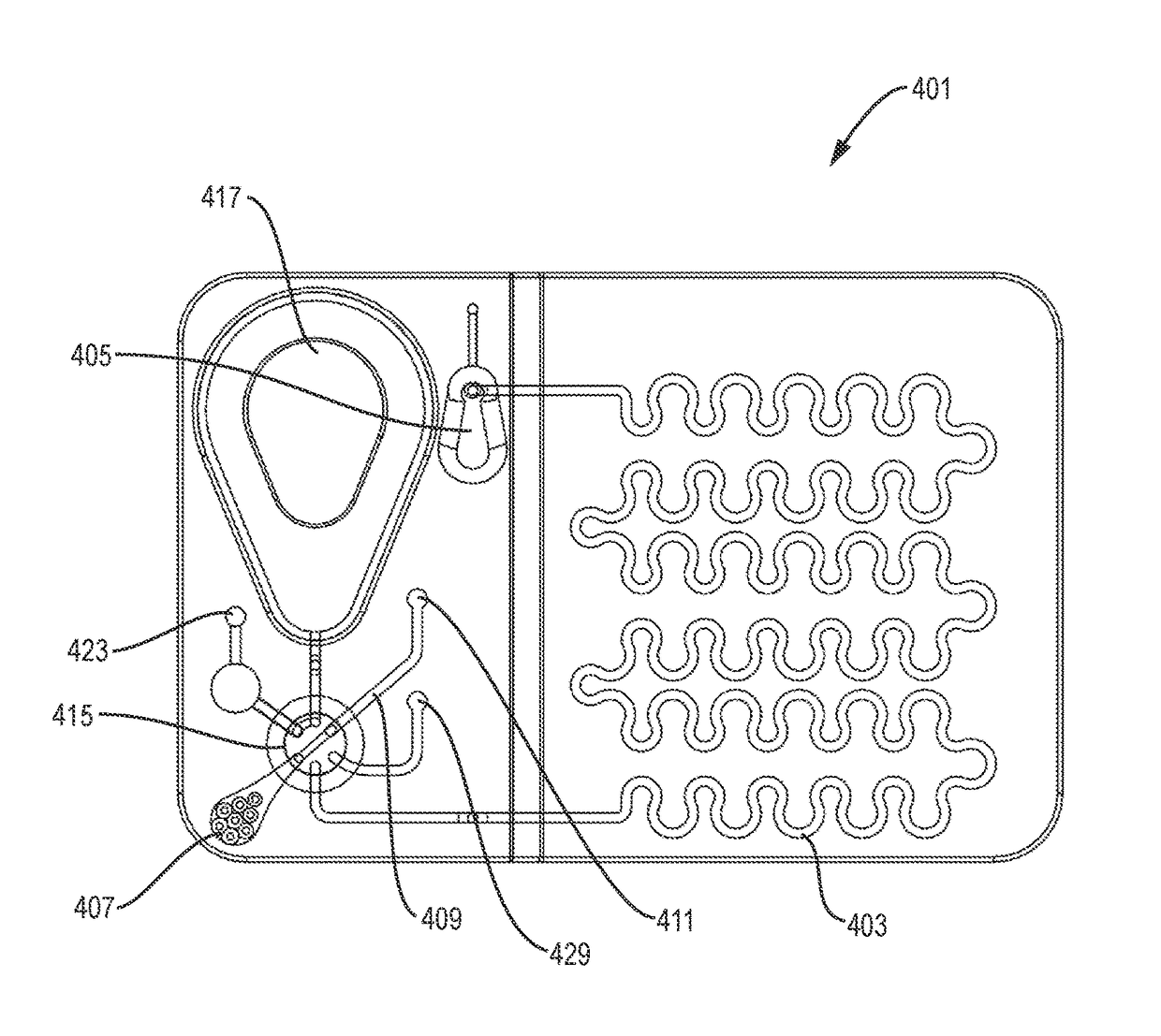
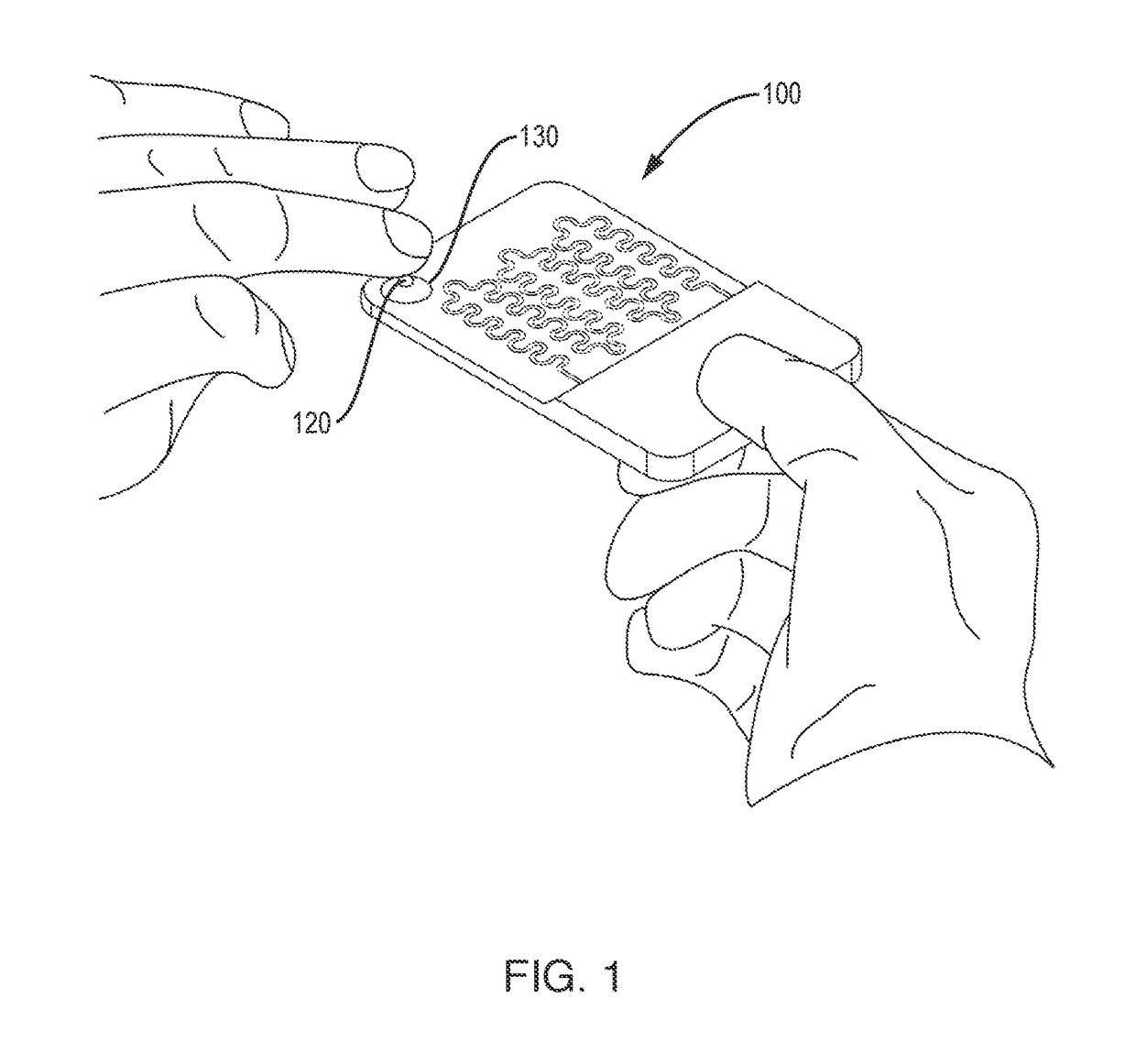
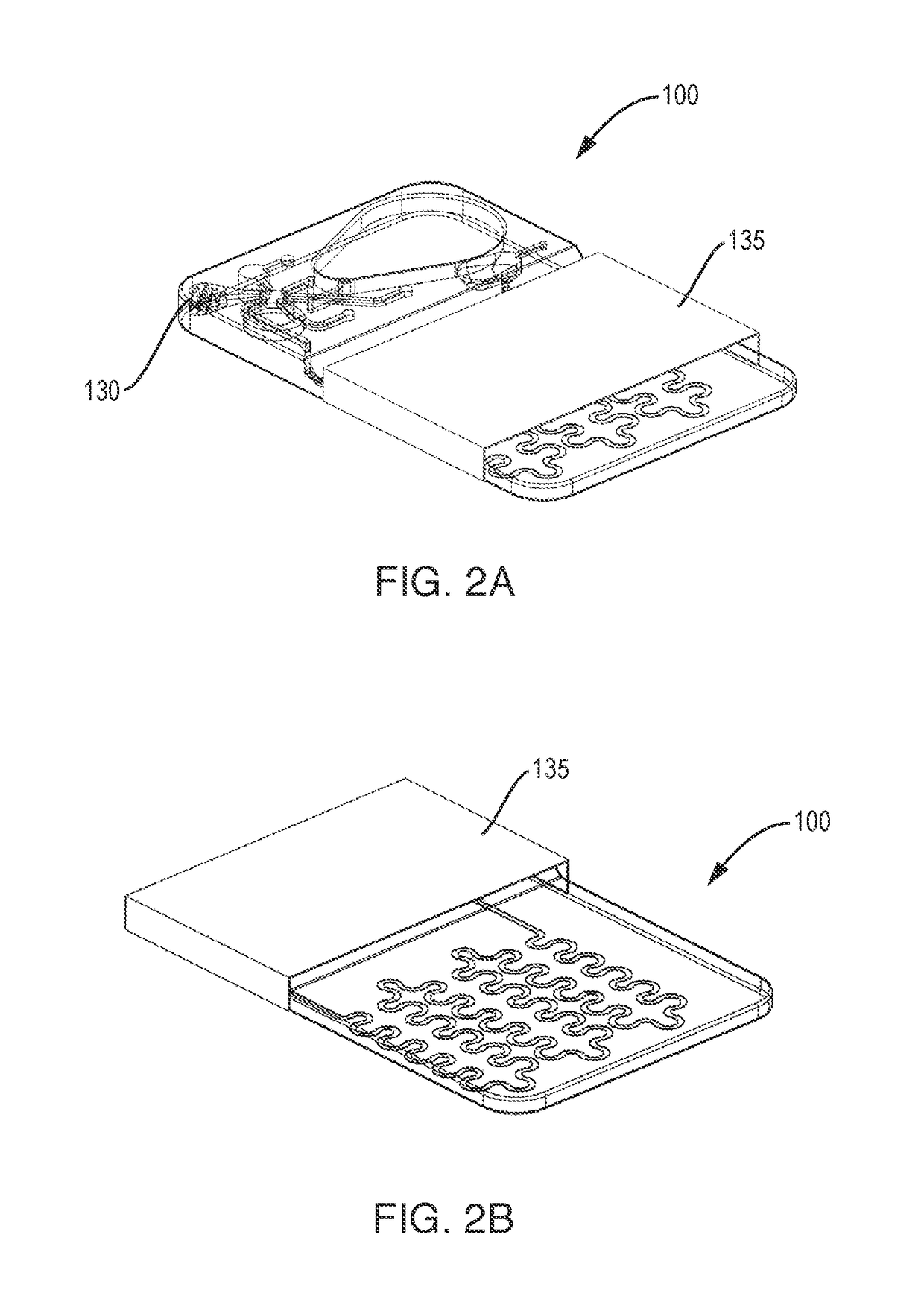
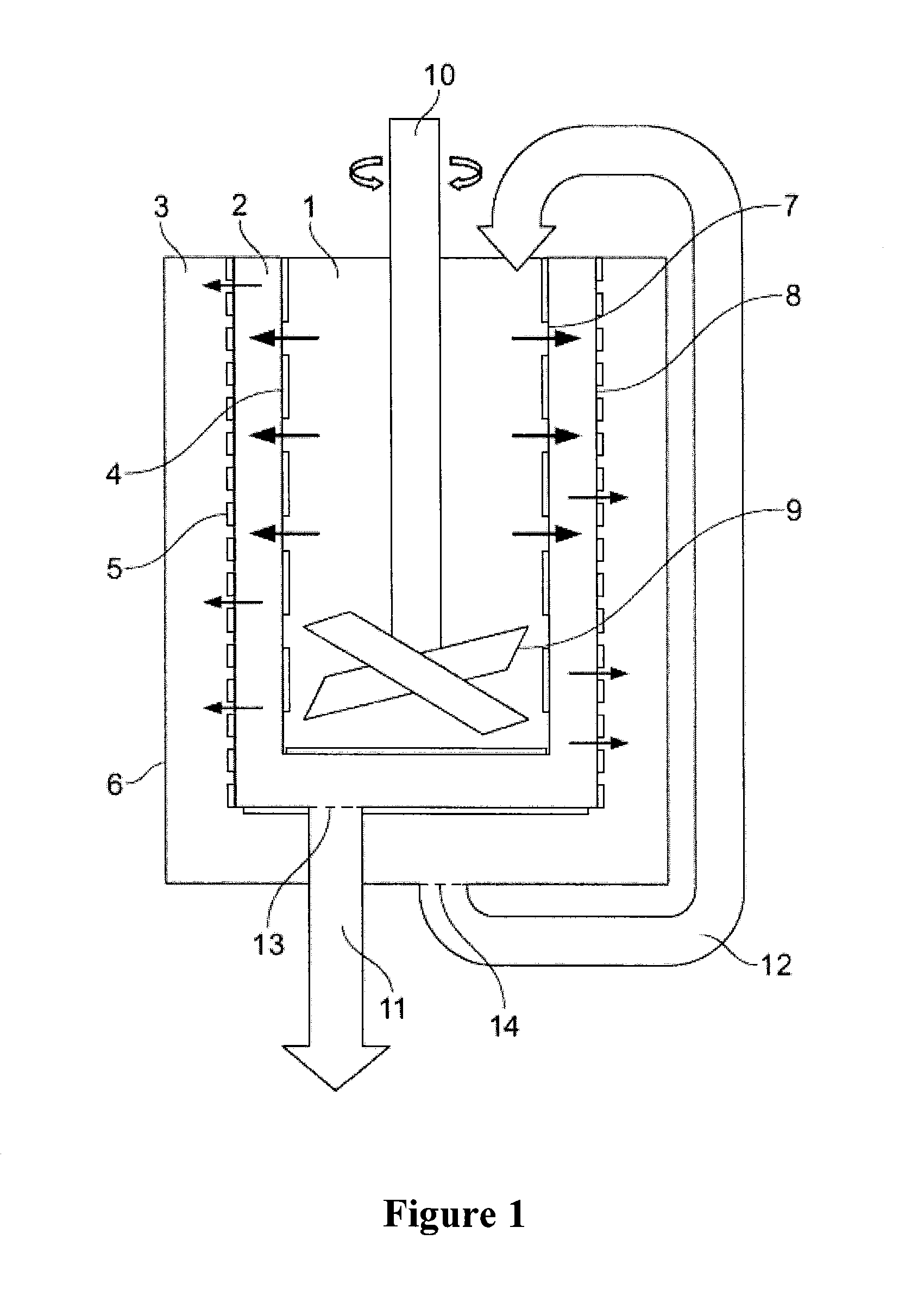
Methods, compositions, and automated systems for separating rare cells from fluid samples
InactiveUS6949355B2Aid in diagnosis and prognosisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCancer cellRed blood cell
The present invention recognizes that diagnosis and prognosis of many conditions can depend on the enrichment of rare cells from a complex fluid sample. In particular, the enrichment of fetal cells from maternal samples, such as maternal blood samples, can greatly aid in the detection of fetal abnormalities or a variety of genetic conditions. In addition, the present invention recognizes that the enrichment of rare malignant cells from patient samples, can aid in diagnosis, prognosis, and development of therapeutic modalities for patients.A first aspect of the present invention is a microfabricated filter for filtering a fluid sample. A microfabricated filter of the present invention comprises at least one tapered pore, and preferably comprises at least two tapered pores whose variation in size is 20% or less. The present invention also includes a method of enriching rare cells of a fluid sample using a microfabricated filter of the present invention.Another aspect of the invention is solutions for the selective sedimentation of red blood cells (RBCs) from a blood sample comprising a red blood cell aggregating agent and at least one specific binding member that selectively binds RBCs. Solutions of the present invention include a combined solution for rare cell enrichment that comprise RBC aggregating agents, at least one specific binding member that selectively binds RBCs, and at least one additional specific binding member for the removal of undesirable sample components other than RBCs. The invention also includes methods of using selective RBC sedimentation solutions and combined solutions for enriching rare cells of a fluid sample.Yet another aspect of the invention is an automated system for processing a fluid sample that includes: at least one filtration chamber that comprises or engages one or more microfabricated filters of the present invention; automated means for directing fluid flow through the one or more filtration chambers of the automated system, and means for collecting enriched rare cells. The present invention also includes methods of using an automated system for separating rare cells from a fluid sample. Preferred fluid samples are effusion, blood, or urine samples, and rare cells that can be enriched from such sample include nucleated red blood cells and cancer cells.
Owner:AVIVA BIOSCI
Method and apparatus for performing coordinated multi-point transmission and reception in wireless communication system
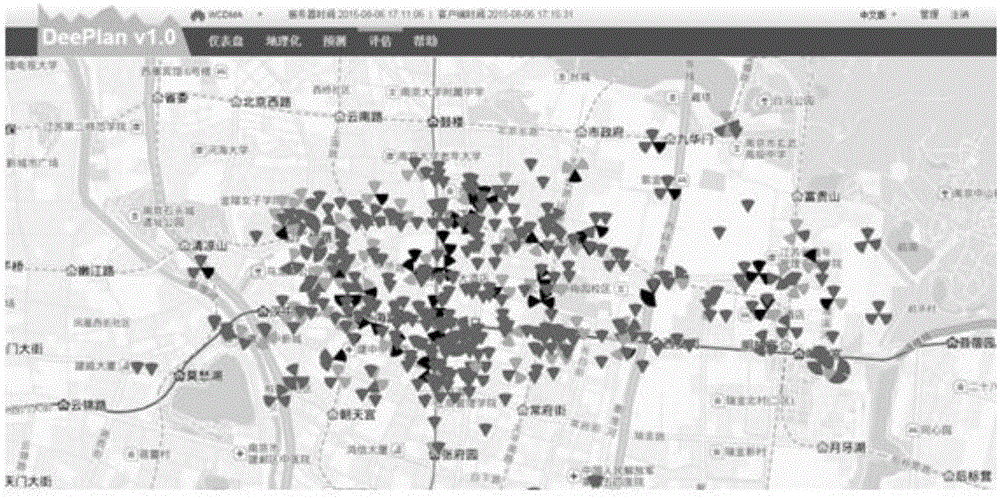
ActiveUS20110124345A1Improve system efficiencyAssess restrictionNetwork planningCommunications systemCell ID
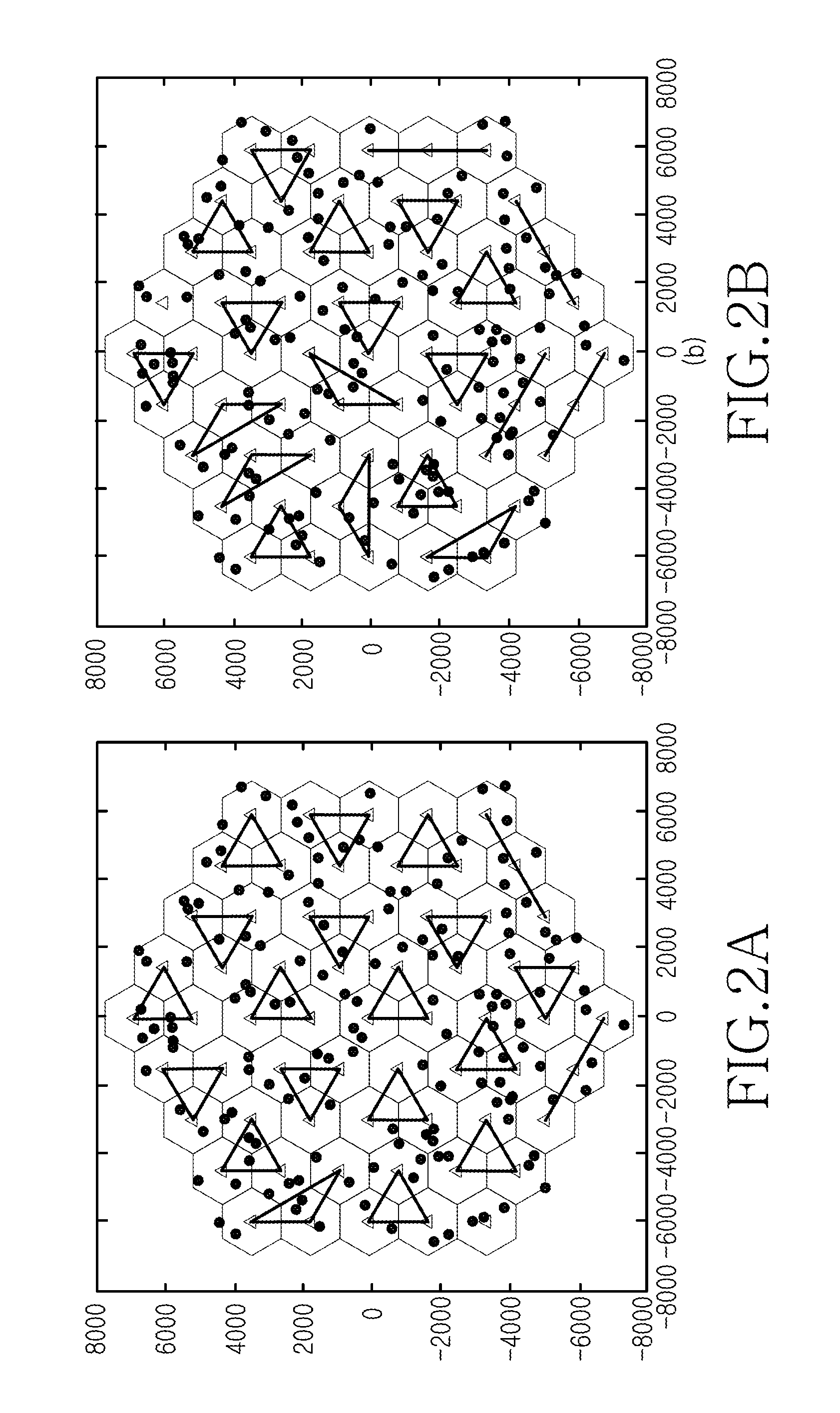
A method and an apparatus for performing a Coordinated Multi-Point (CoMP) transmission in a wireless communication system are provided. An operating method of a base station for the CoMP transmission in a wireless communication system includes performing a cell clustering for CoMP transmission of a terminal, receiving a reference signal from the terminal, determining cell IDentifier (ID) information of the terminal, when the terminal uses a cell ID for the CoMP transmission, comparing a Channel Quality Indicator (CQI) value of the reference signal with a threshold, and when the CQI value of the reference signal is greater than or equal to the threshold, participating in the CoMP transmission of the terminal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Automated microscopic cell analysis
ActiveUS9767343B1High quantitative accuracySample preparation is improvedWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationCellular componentCell analyzer
This disclosure describes single-use test cartridges, cell analyzer apparatus, and methods for automatically performing microscopic cell analysis tasks, such as counting blood cells in biological samples. A small unmeasured quantity of a biological sample such as whole blood is placed in the disposable test cartridge which is then inserted into the cell analyzer. The analyzer isolates a precise volume of the biological sample, mixes it with self-contained reagents and transfers the entire volume to an imaging chamber. The geometry of the imaging chamber is chosen to maintain the uniformity of the mixture, and to prevent cells from crowding or clumping, when it is transferred into the imaging chamber. Images of essentially all of the cellular components within the imaging chamber are analyzed to obtain counts per unit volume. The devices, apparatus and methods described may be used to analyze a small quantity of whole blood to obtain counts per unit volume of red blood cells, white blood cells, including sub-groups of white cells, platelets and measurements related to these bodies.
Owner:MEDICA CORP
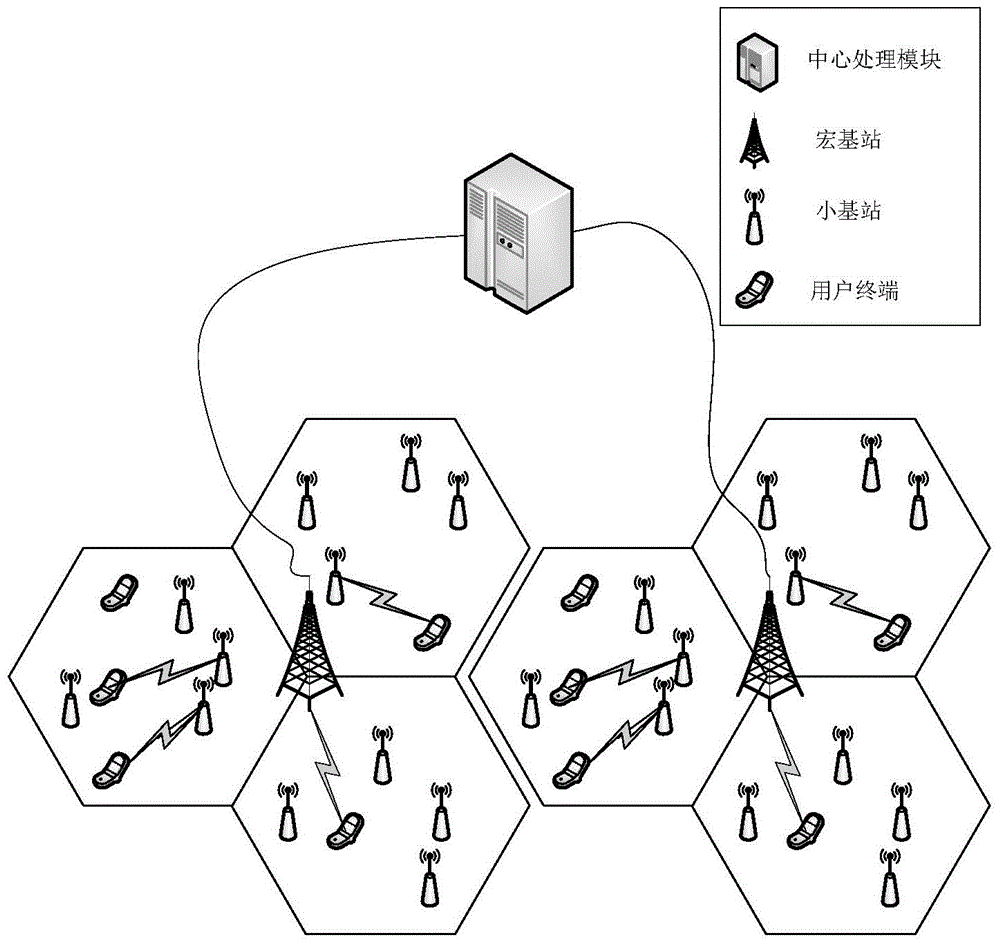
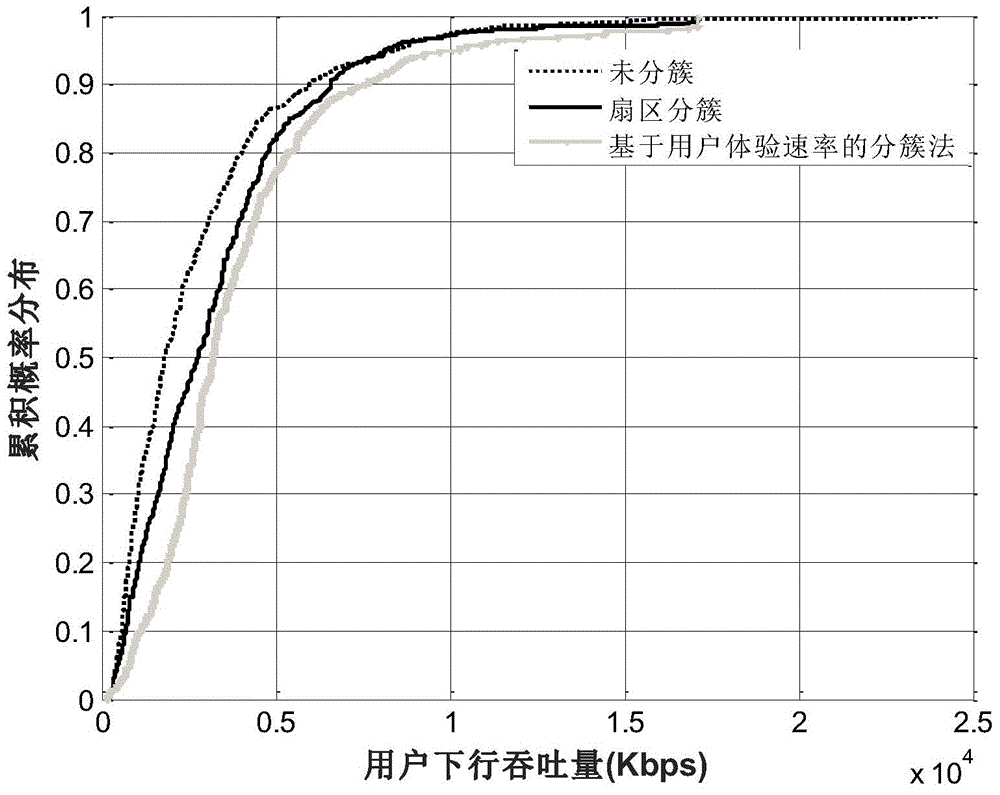
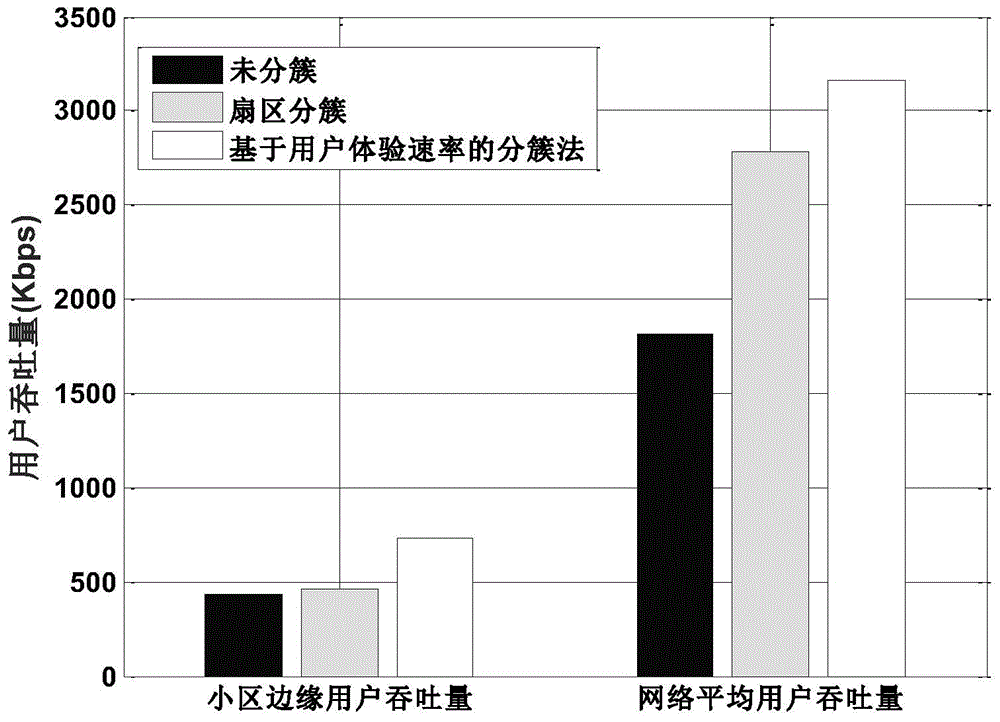
Heterogeneous network cell clustering method and device based on user experience speed
InactiveCN104955077AImprove throughputReduce the impact of interferenceWireless communicationCell clusteringHeterogeneous network
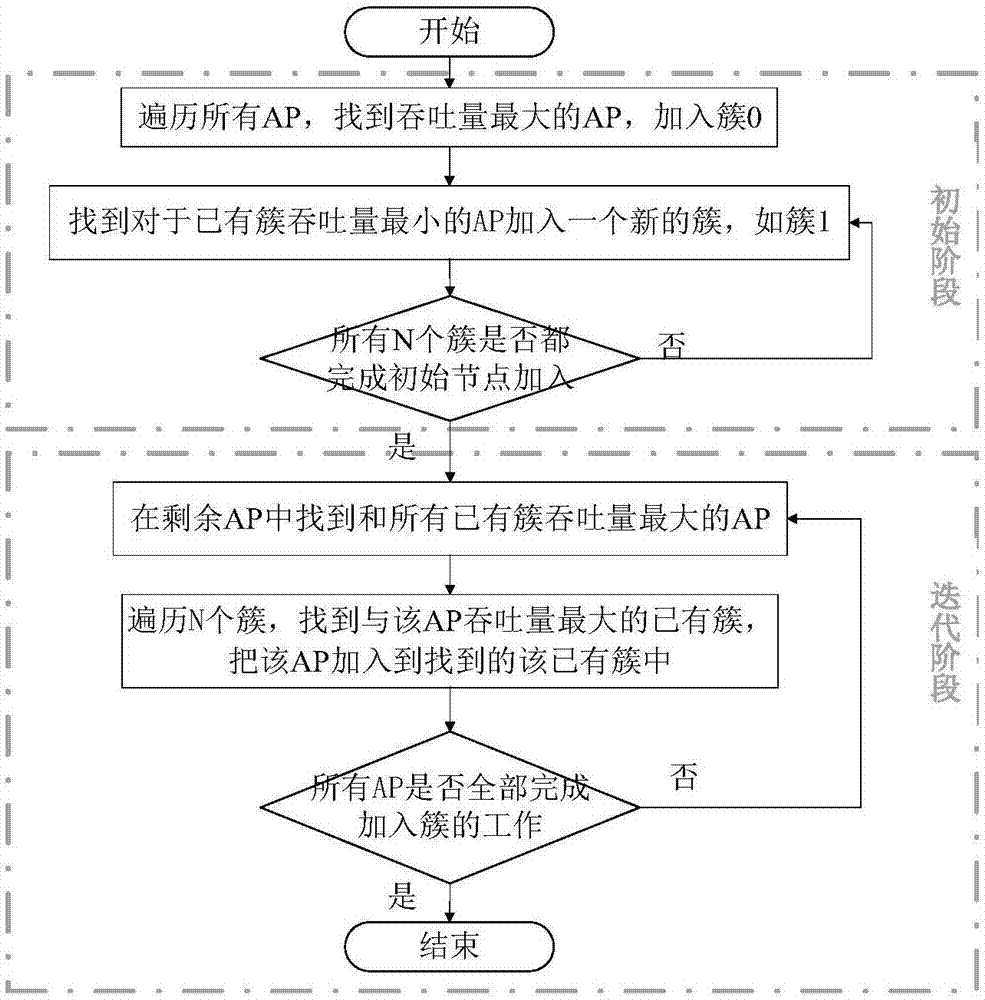
The invention relates to a heterogeneous network cell clustering method and device based on user experience speed and belongs to the technical field of radio communication. By means of K-means method, a plurality of base stations to be distributed are classified into several different types so as to meet transmission needs of different users, the base stations in the same type are high in similarity, and objects in different clusters are low in similarity; similarity is calculated by a 'central object' obtained by signal strength average of the base stations in various types. In the heterogeneous network cell clustering method, the above process is repeated until convergence, that is, until reasonable user distribution base station clusters are found. Compared with the prior art, the heterogeneous network cell clustering method has the advantages that interference to users in the intensive coverage environment is remarkably reduced, average network throughput and throughput of cell edge users are remarkably increased, and user experience quality is remarkably improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
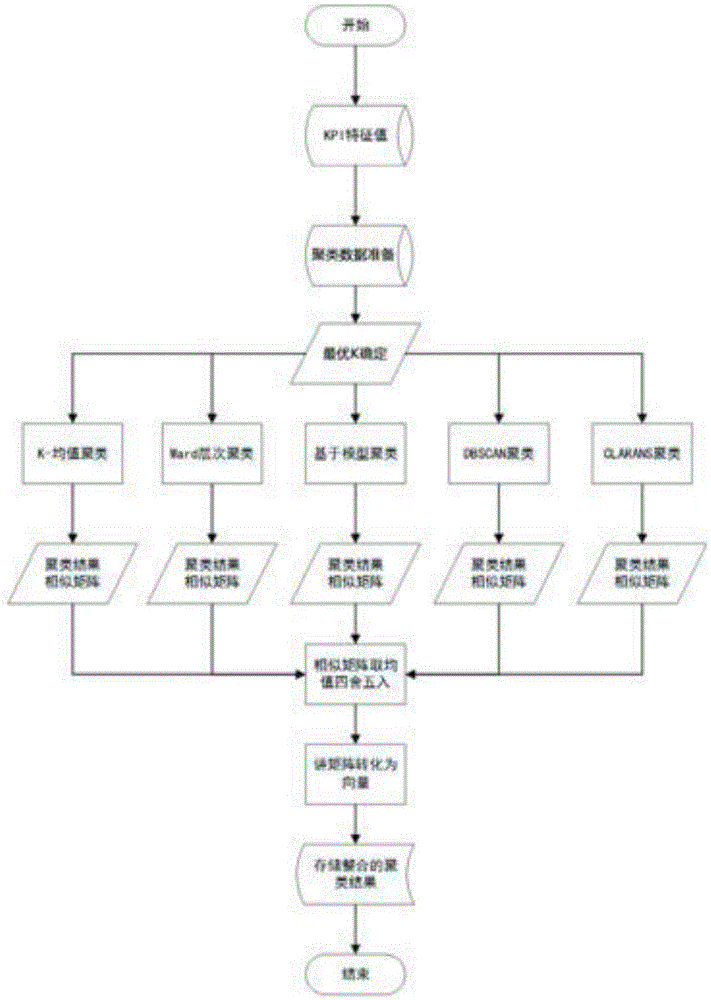
Cell clustering method and system based on wireless network traffic features
The invention provides a cell clustering method based on wireless network traffic features. The method comprises the following five steps: S1, selecting to-be-processed data; S2, extracting feature parameters of all to-be-processed data; S3, carrying out clustering optimal K value selection on the to-be-processed data; S4, carrying out clustering integration on the to-be-processed data with the selected optimal K value by means of five kinds of clustering algorithms; and S5, combining a clustering result with geographic information in a geographic information system and displaying a combined clustering result. According to the invention, a cell with similar traffic data is obtained based on clustering. And thus an auxiliary scheme for evaluating and planning a network capacity can be provided for a mobile operator.
Owner:NANJING HOWSO TECH
Isolated mammalian neural stem cells, methods of making such cells
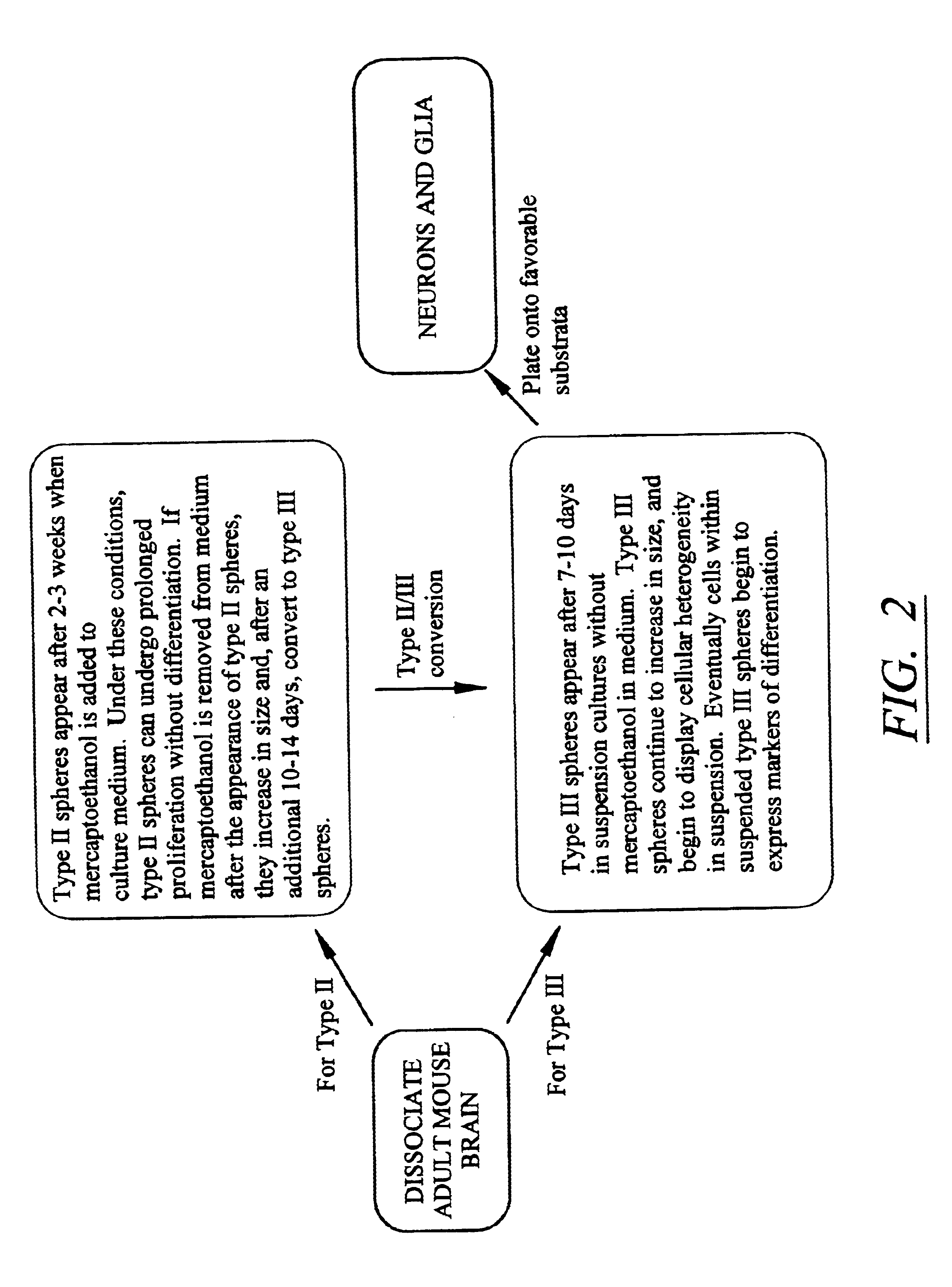
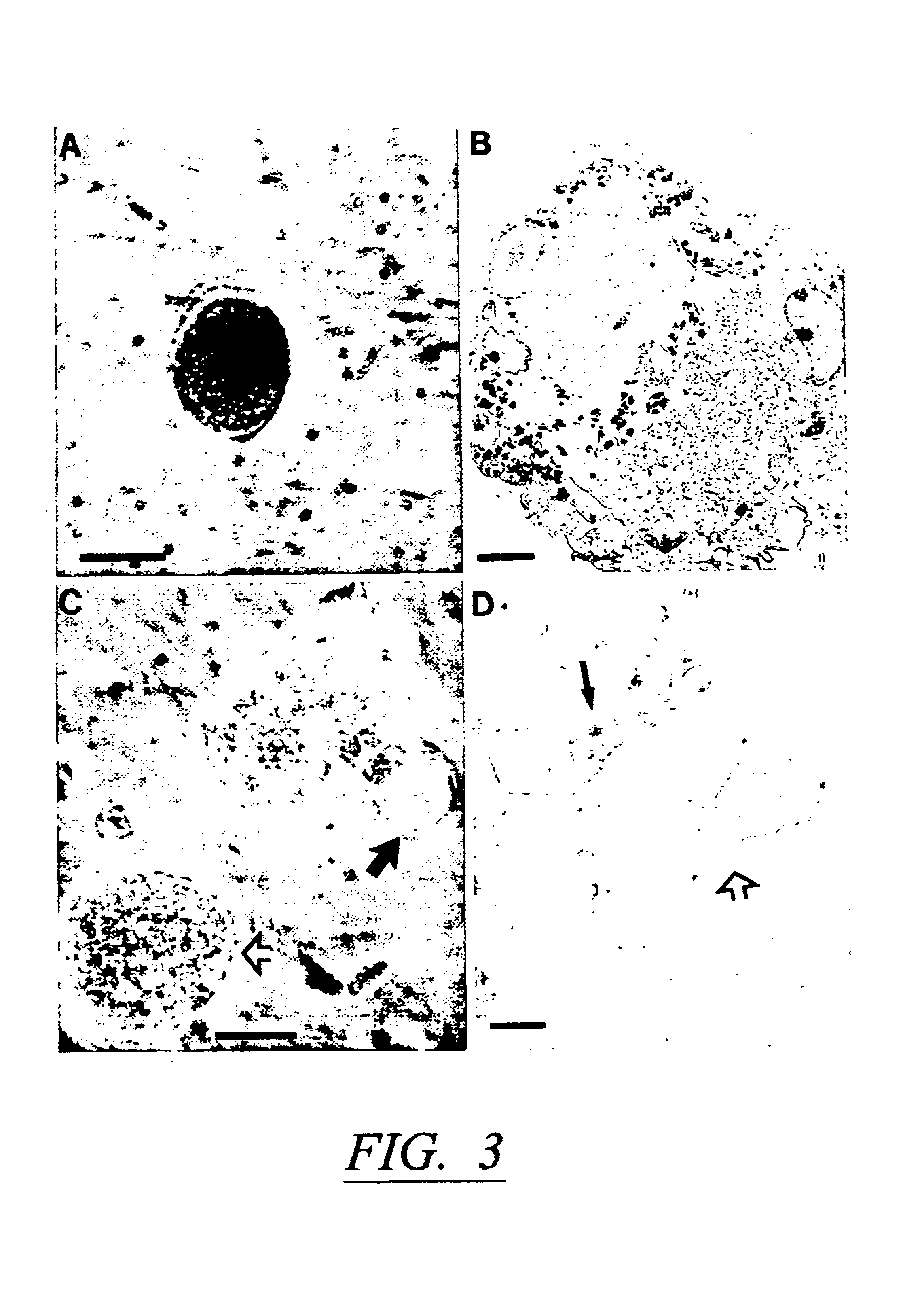
Using a novel culture approach, previously unknown populations of neural progenitor cells have been found within an adult mammalian brain. By limiting cell-cell contact, dissociated adult brain yields at least two types of cell aggregates. These aggregates or clones of stem / precursor cells can be generated from adult brain tissue with significantly long postmortem intervals. Both neurons and glia arise from stem / precursor cells of these cultures, and the cells can survive transplantation to the adult mammalian brain.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Devices and methods for production of cell aggregates
InactiveUS20110086375A1Efficiently generate tissue-level organizationReduce chaosBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh densityCell clustering
The present application provides methods and devices for the production and recovery of cell aggregates. In one embodiment, the device is a microwell device with a high density of microwells. The application also provides a device for extracting cell aggregates such as stem cells or embryoid bodies from well plates. Such cell aggregates are used for the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells such as embryonic stem cells, in the fields of developmental biology and regenerative medicine / tissue engineering.
Owner:UNGRIN MARK +1
Method for producing ciliary marginal zone-like structure
ActiveUS20150132787A1Improve efficiencyBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementSerum igeSerum free media
The invention provides a method for producing a cell aggregate containing a ciliary marginal zone-like structure by culturing a cell aggregate containing a retinal tissue in which Chx10 positive cells are present in a proportion of 20% or more of the tissue in a serum-free medium or serum-containing medium, each containing a substance acting on the Wnt signal pathway for only a period before the appearance of a RPE65 gene expressing cell, followed by culturing the “cell aggregate in which a RPE65 gene expressing cell does not appear” thus obtained in a serum-free medium or serum-containing medium, each not containing a substance acting on the Wnt signal pathway and so on.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD +1
Three-dimensional complex cell aggregate model as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104651300AOvercoming heterogeneous growthOvercome inhibitionSkeletal/connective tissue cellsEmbryonic cellsChemical synthesisCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention provides a three-dimensional complex cell aggregate model as well as a preparation method and application thereof. According to the model, a natural or chemically synthesized polymer is used as a matrix material to prepare submicron-scale microspheres, and cell factors are embedded in or fixed on the surface of the submicron-scale microspheres and are co-cultured with cells to form a complex cell aggregate containing the microspheres, so that the biological activity of the cells in the aggregate can be regulated and controlled from inside to outside. The model can be used for researches of propagation and differentiation of stem cells in a three-dimensional state, overcomes the problems that the cell aggregate is heterogeneous in composition / structure, the cell proliferation efficiency is low and the directional induced differentiation efficiency is low due to non-uniform mass transfer and short acting time of liquid factors in a culture medium during the traditional three-dimensional culture of the stem cells, can be used for stimulating interaction between cells and cells, cells and an extracellular matrix as well as cells and soluble factors, thereby providing a theoretical and technical support for in vitro construction and optimization of a stem cell culture technology, and tissue engineering construction of various tissue and organ analogs or equivalents.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
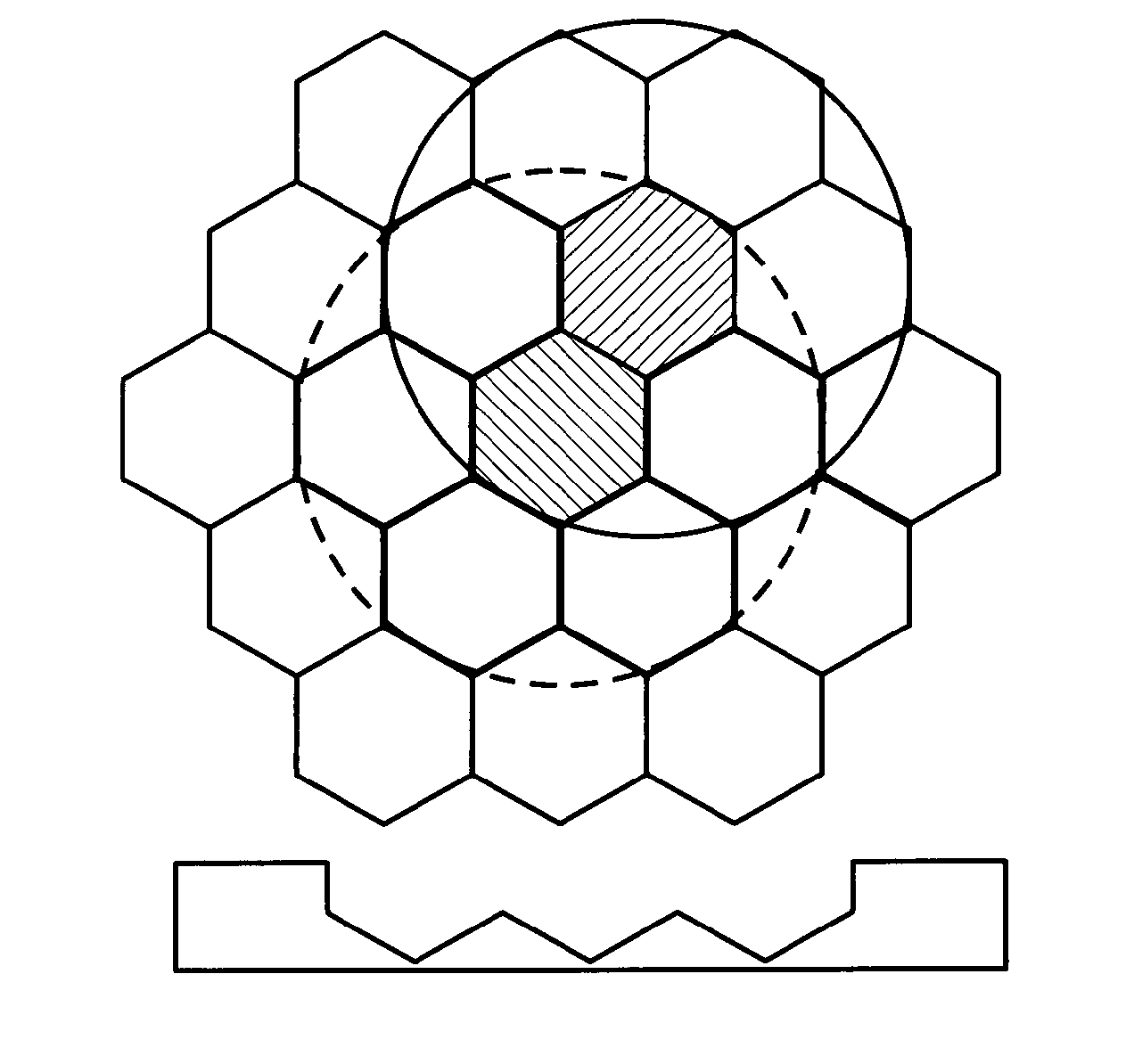
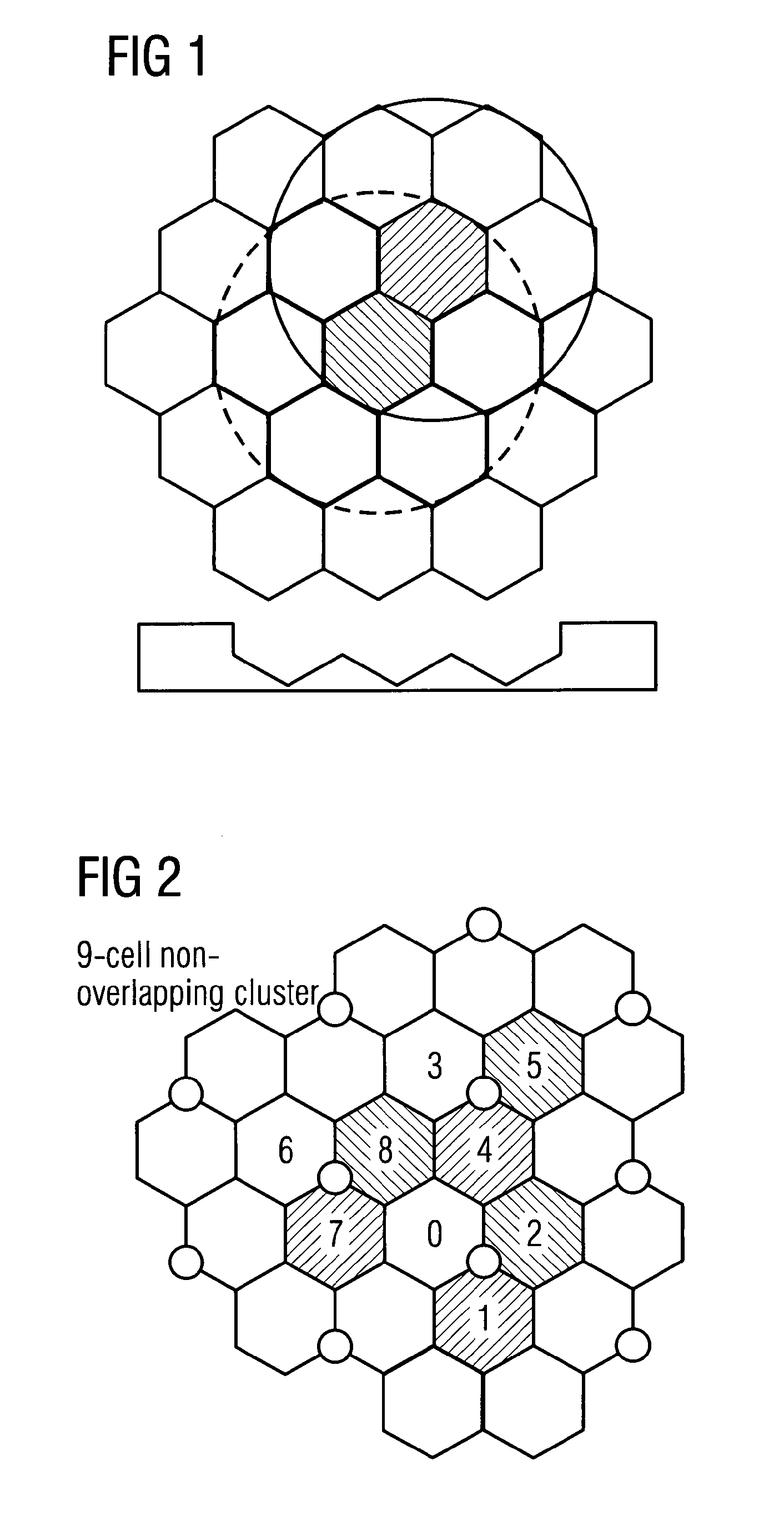
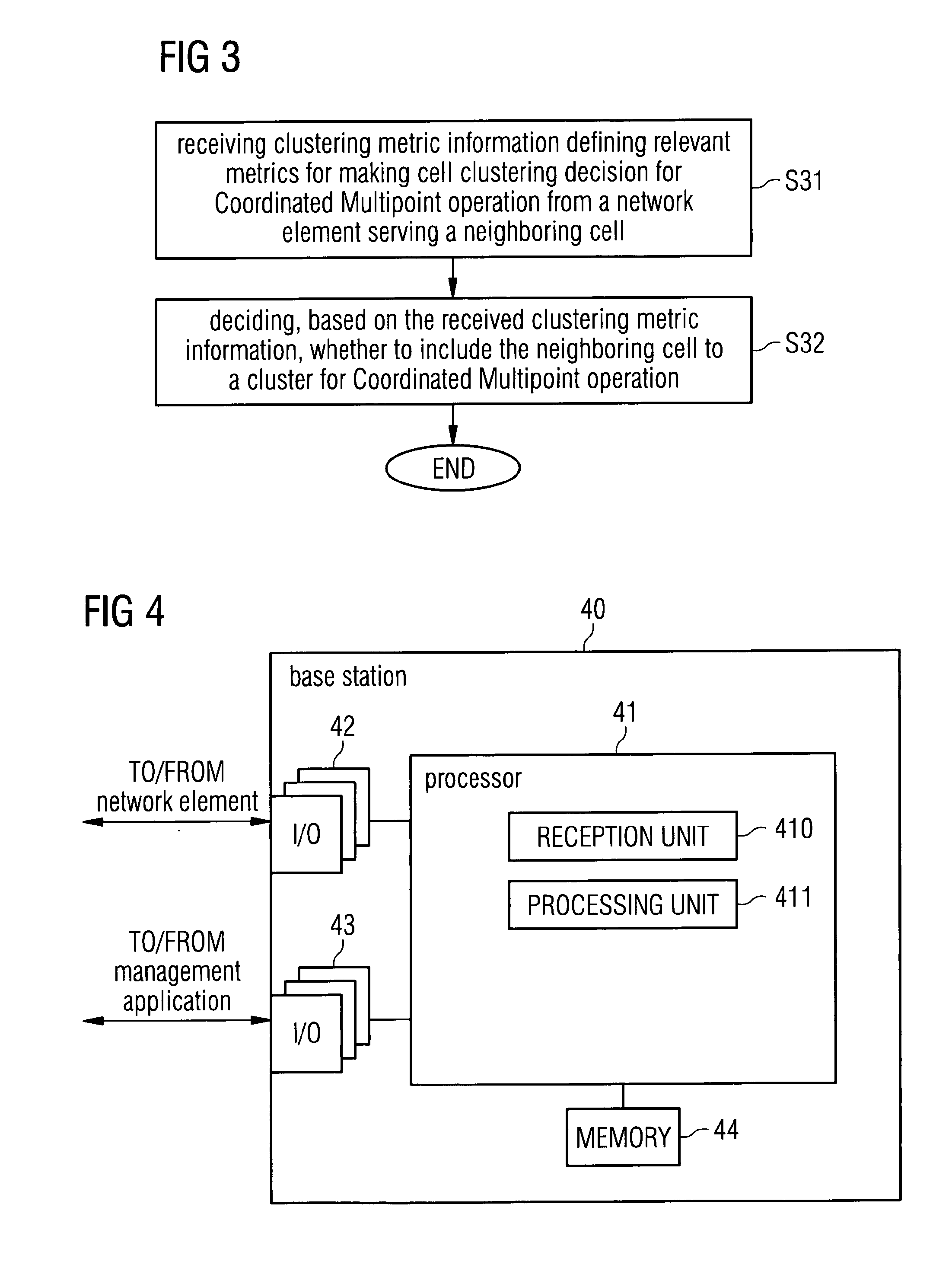
Dynamic cell clustering for coordinated multipoint operation
InactiveUS20170054477A1Increase in sum utilitySite diversityOrthogonal multiplexCell clusteringData mining
The present invention addresses method, apparatus and computer program product for dynamic cell clustering for Coordinated Multipoint operation. Clustering metric information defining relevant metrics for making cell clustering decision for Coordinated Multipoint operation are received from a network element serving a neighboring cell, and based on the received clustering metric information, it is decided whether to include the neighboring cell to a cluster for Coordinated Multipoint operation.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
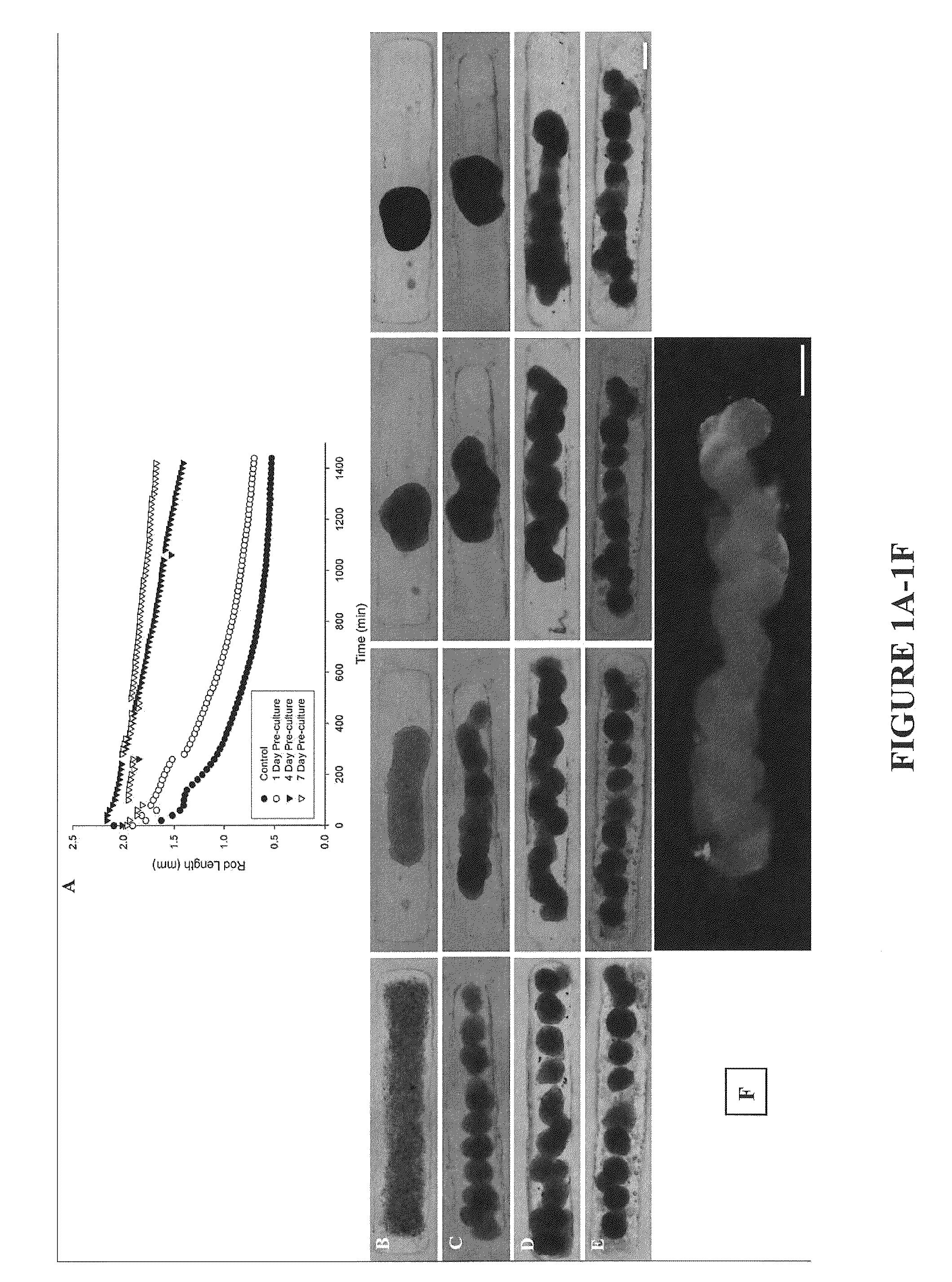
Assays and methods for fusing cell aggregates to form proto-tissues
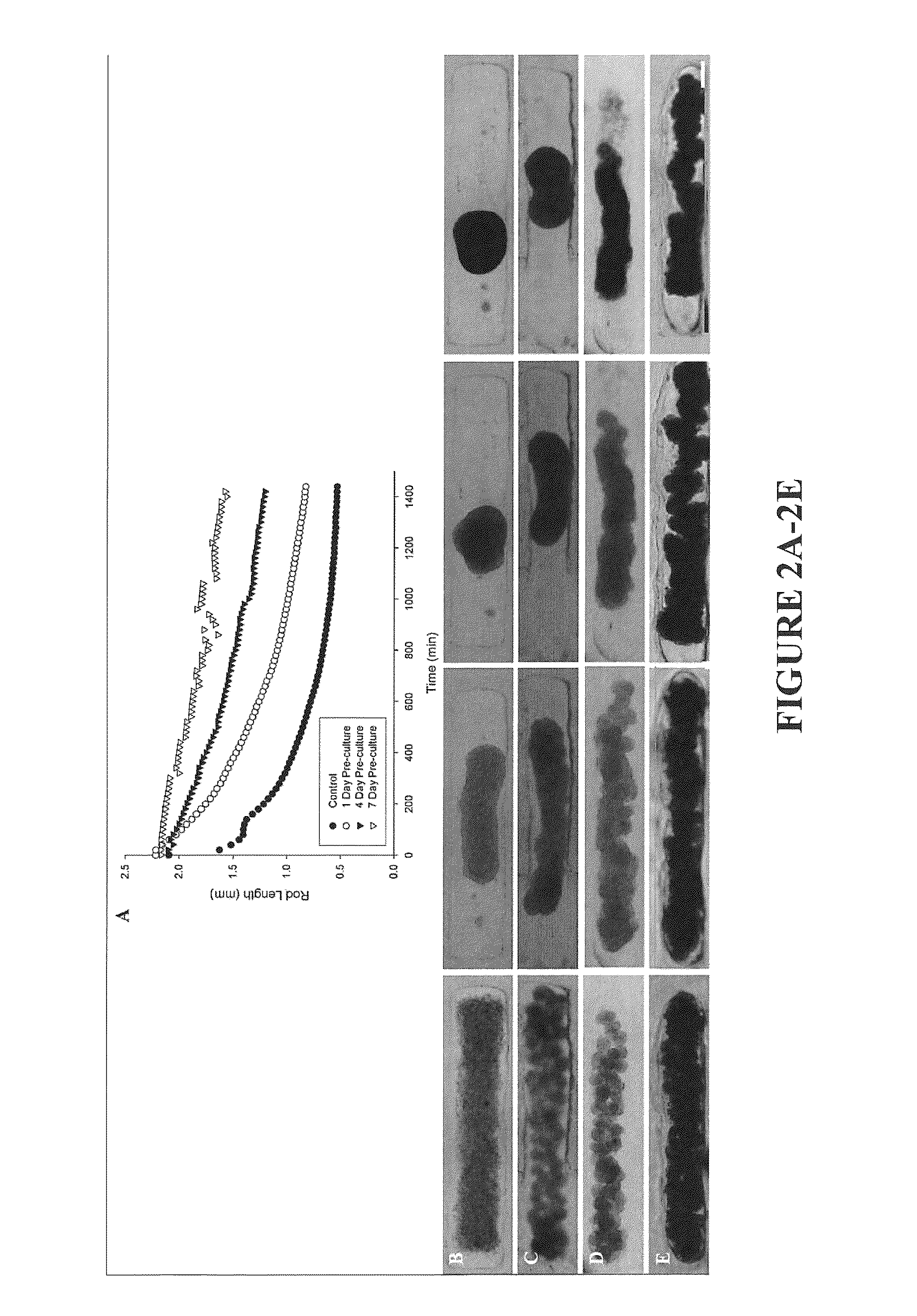
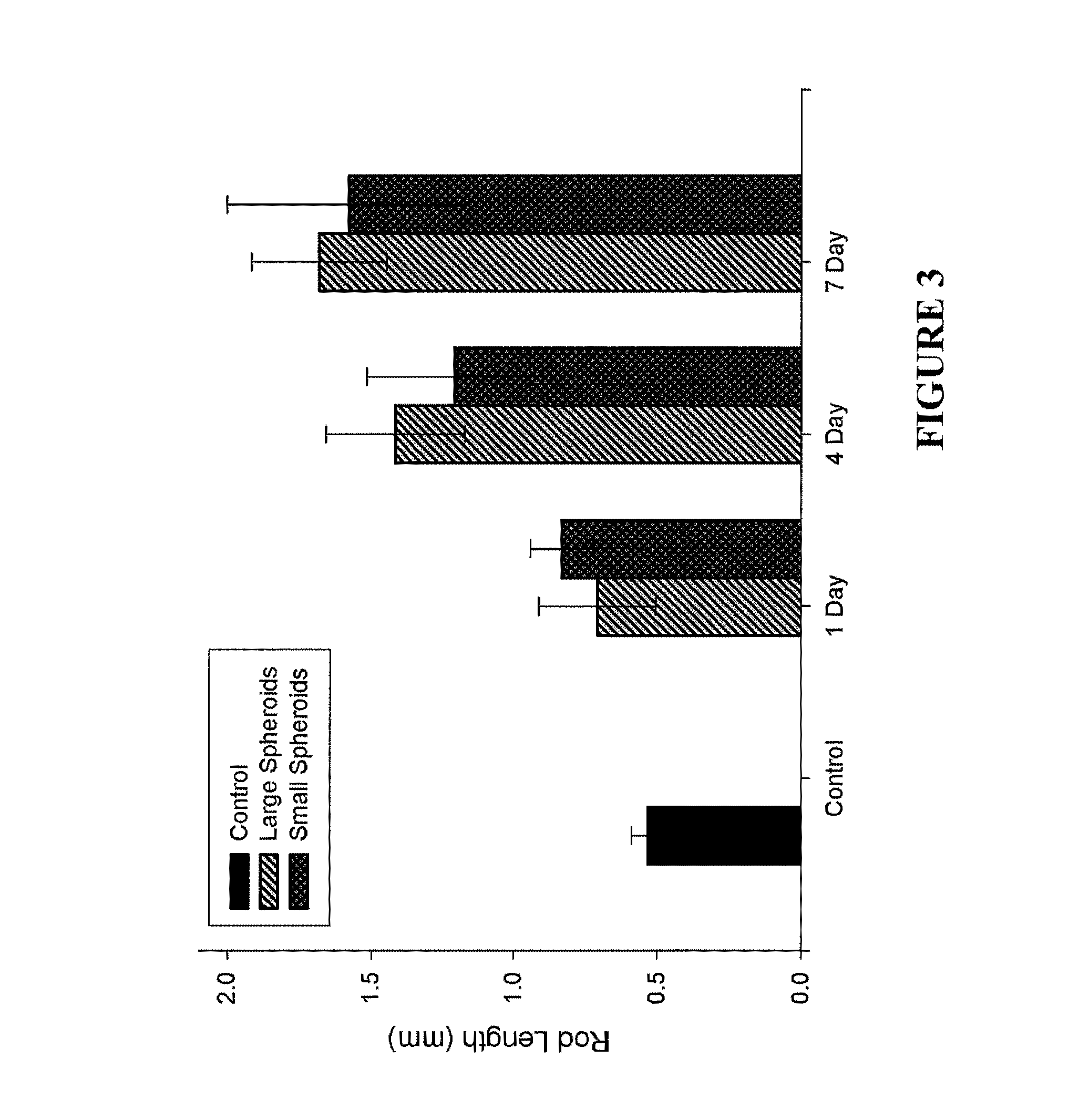
Provided are assays and methods for creating proto-tissues from aggregates of cells. The invention concerns assays and methods useful in tissue engineering and reconstruction techniques, specifically in the formation of macrotissues from microtissues using microtissue pre-culture time as a controlling parameter.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
Cell analysis apparatus and cell analysis method
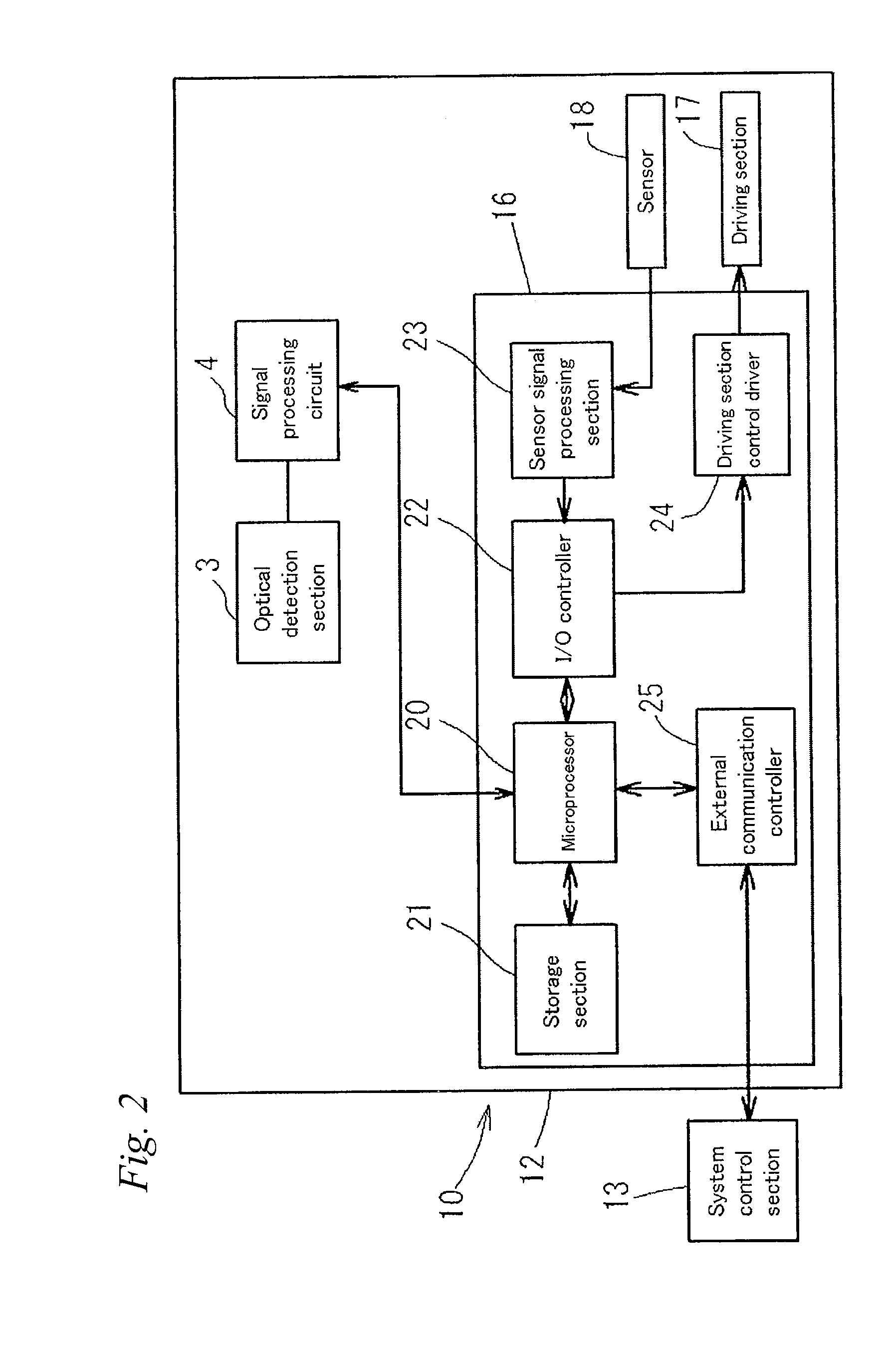
ActiveUS20100196917A1Accurate distinctionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFlow cellSignal processing circuits
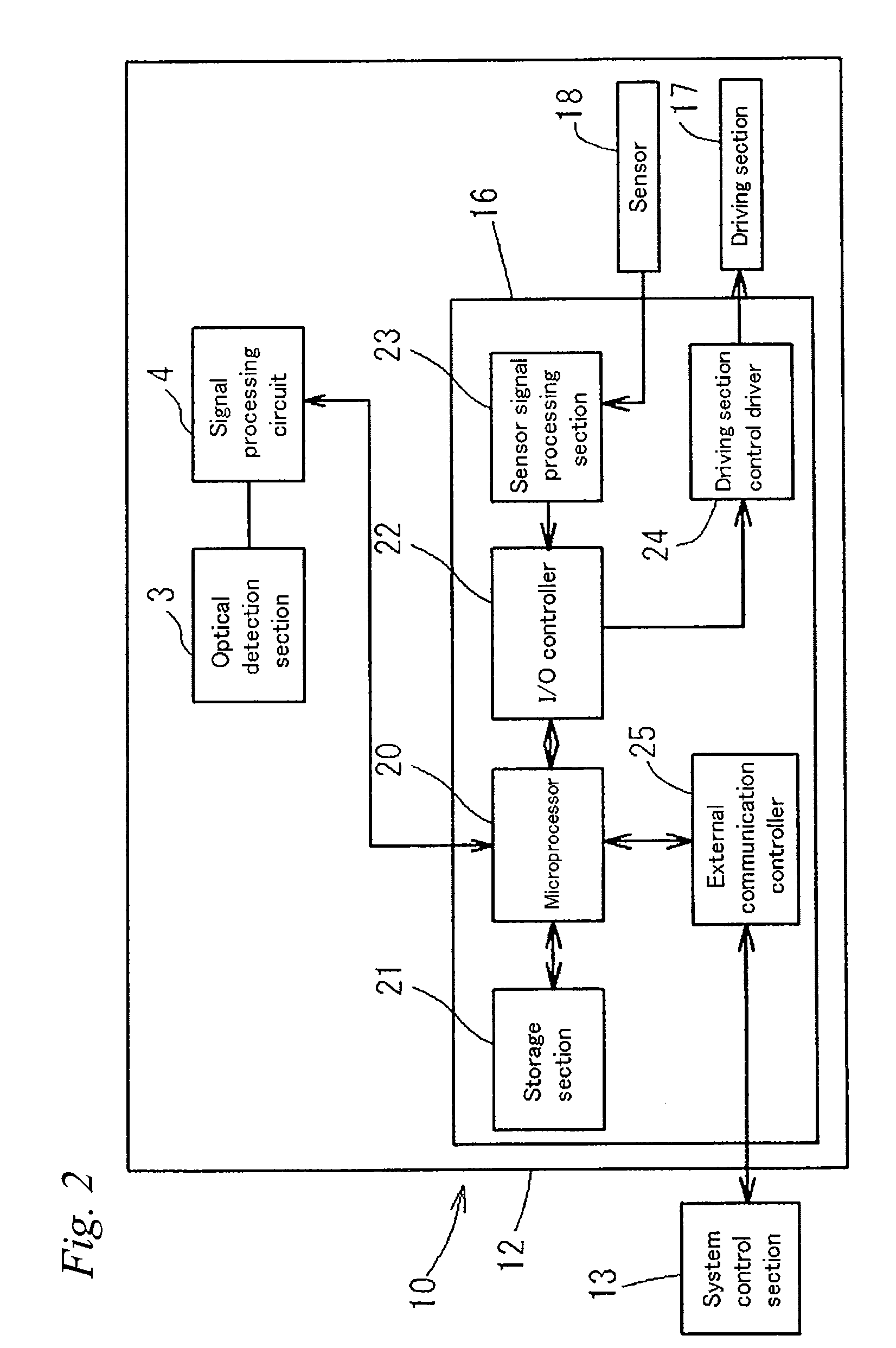
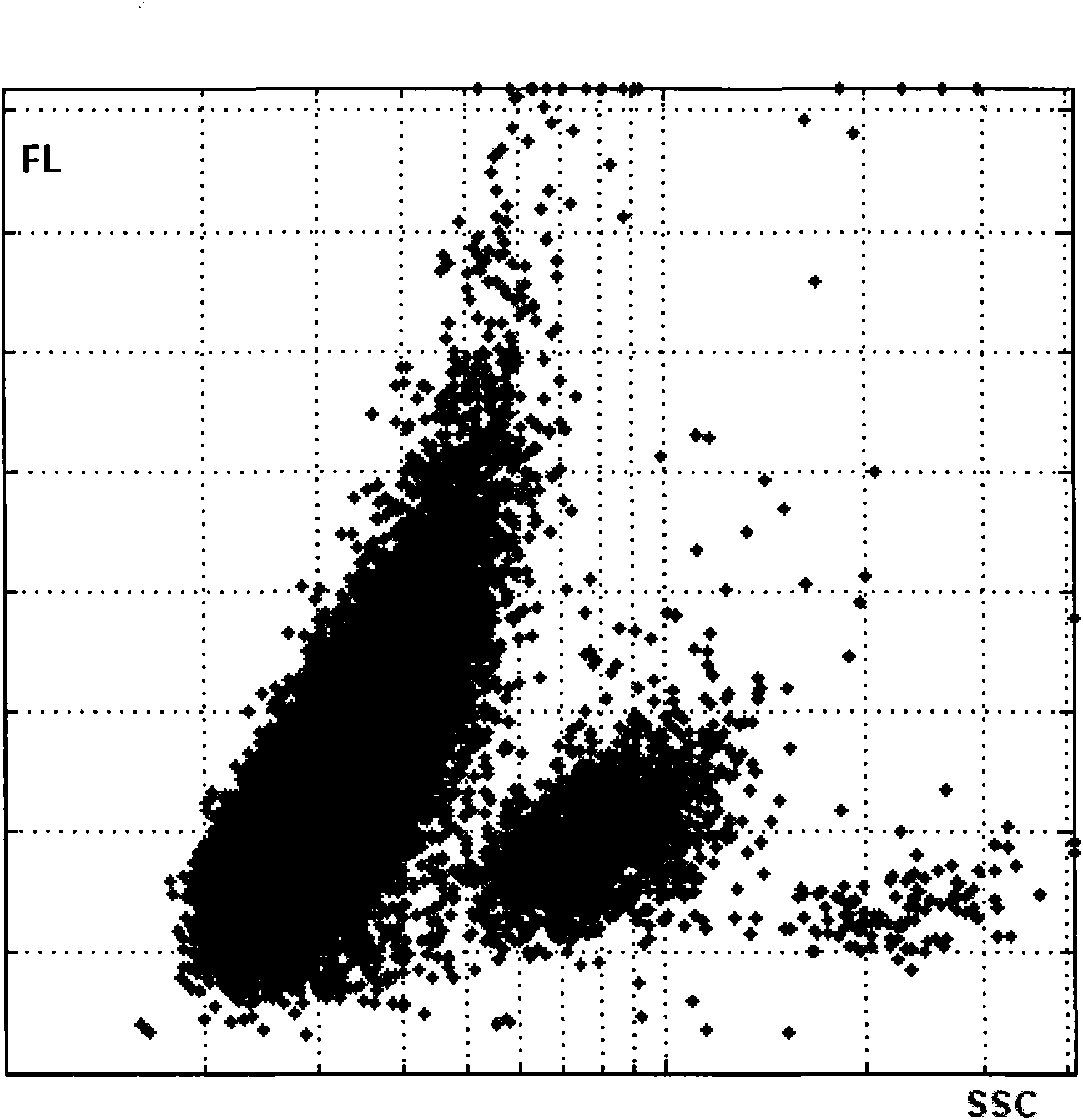
A cell analysis apparatus that can accurately distinguish between an aggregating cell and a non-aggregating cell is provided. The cell analysis apparatus (10) includes: an optical detection section (3) for flowing a measurement sample obtained from a biological sample and a pigment into a flow cell (51), irradiating the measurement sample flowing in the flow cell (51) with laser beam and detecting fluorescence from the measurement sample; a signal processing circuit (4) for acquiring, based on a fluorescence signal outputted from the detection section (3), a value reflecting the height of a waveform of the signal and a value reflecting the length of a ridge line of the waveform of the signal; and a system control section (13) for distinguishing between an aggregating cell formed by aggregation of a plurality of cells and a non-aggregating cell, based on the value reflecting the height of the waveform of the fluorescence signal and the value reflecting the length of the ridge line of the waveform of the fluorescence signal obtained by the signal processing circuit (4).
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Clustering method and device for support vector machine
ActiveCN101923648AReduce in quantityAdaptableScattering properties measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionOriginal dataAlgorithm
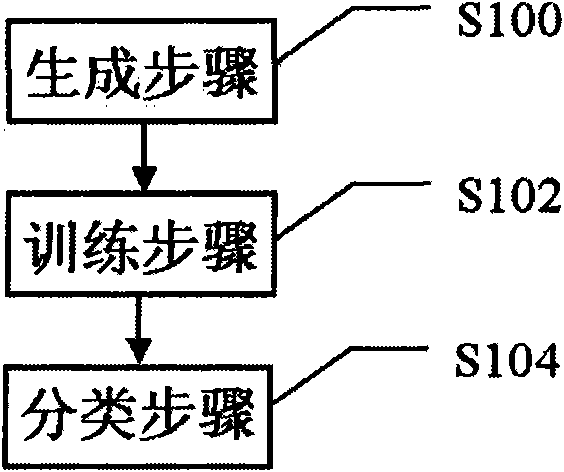
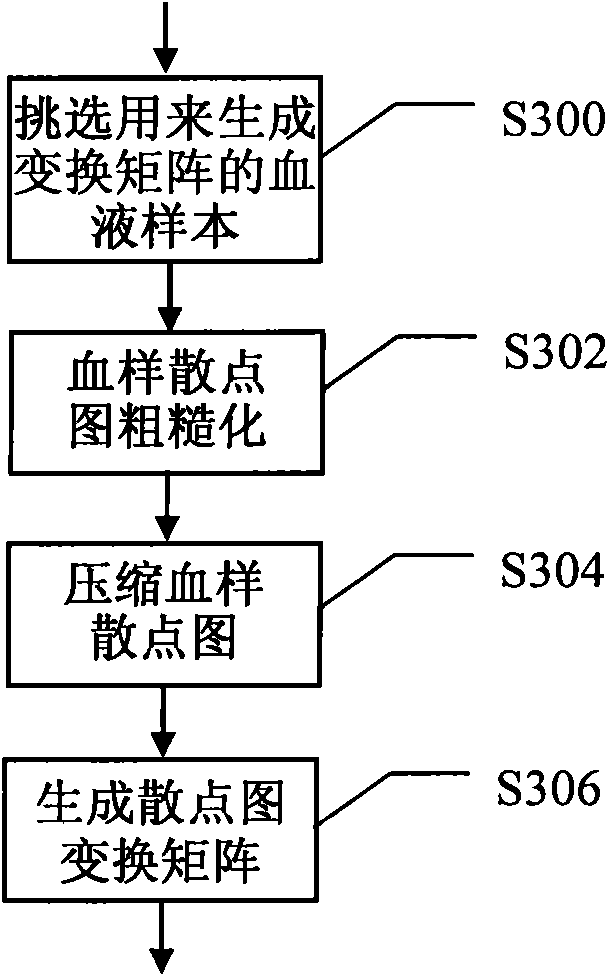
The invention discloses a cell clustering method and a device. The method comprises a generating step of generating a transformation matrix by using a collected blood sample, a training step of obtaining a support vector machine classified model of a support vector machine through training by using the chosen training blood sample, and a classifying step of transforming a scatter diagram formed by roughing an original data with the transformation matrix, obtaining a feature attribute vector of the cell by adding the data of a cell channel, and inputting the feature attribute vector to the trained support vector machine model so as to obtain a classifying result of the cell. The method and device of the embodiment of the invention have strong adaptability, are capable of classifying various types of samples and can be easily transplanted and applied to other related classifications.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Automated microscopic cell analysis
ActiveUS20170326549A1Easy to operateAvoid cross contaminationWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationCellular componentWhite blood cell
This disclosure describes single-use test cartridges, cell analyzer apparatus, and methods for automatically performing microscopic cell analysis tasks, such as counting blood cells in biological samples. A small unmeasured quantity of a biological sample such as whole blood is placed in the disposable test cartridge which is then inserted into the cell analyzer. The analyzer isolates a precise volume of the biological sample, mixes it with self-contained reagents and transfers the entire volume to an imaging chamber. The geometry of the imaging chamber is chosen to maintain the uniformity of the mixture, and to prevent cells from crowding or clumping, when it is transferred into the imaging chamber. Images of essentially all of the cellular components within the imaging chamber are analyzed to obtain counts per unit volume. The devices, apparatus and methods described may be used to analyze a small quantity of whole blood to obtain counts per unit volume of red blood cells, white blood cells, including sub-groups of white cells, platelets and measurements related to these bodies.
Owner:MEDICA CORP
Preparation of cells, cell aggregates and tissue fragments
ActiveUS8871159B1Withdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationAngiogenesis growth factorCell clustering
This invention provides compositions and methods useful for the processing of a tissue sample and the preparation of cells, cell aggregates and / or tissue fragments. The invention provides two-stage filer devices and two-membrane devices. Cell aggregates and / or tissue fragments prepared using such devices and according to methods of the present invention can be used in a variety of assay systems, including, but not limited to, drug validation assays, drug screening assays, proliferation assays, metabolic assays, metastasis assays, angiogenesis assays, binding assays, biochemical assays, cellular assays, genetic assays, and the like.
Owner:APFEL CHRISTIAN
Behavior-based network optimization through cell clustering
InactiveUS20130329588A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsUser deviceRadio access network
The techniques and systems described herein are directed, in part, to optimizing network performance by clustering cell sites of the network based on performance patterns and then optimizing each cluster of cell sites, thereby optimizing performance of a network as a whole. The cell sites may be base stations, radio access networks, and / or other hardware that directly or indirectly exchanges communications with user devices such as mobile telecommunication devices (e.g., user handsets, user hardware, etc.). By optimizing the clusters of cell sites, a service provider (e.g., a telecommunications company, etc.) may improve network performance in less time and / or with less capital resources than attempting to optimize each cell site on an individual basis.
Owner:T MOBILE USA
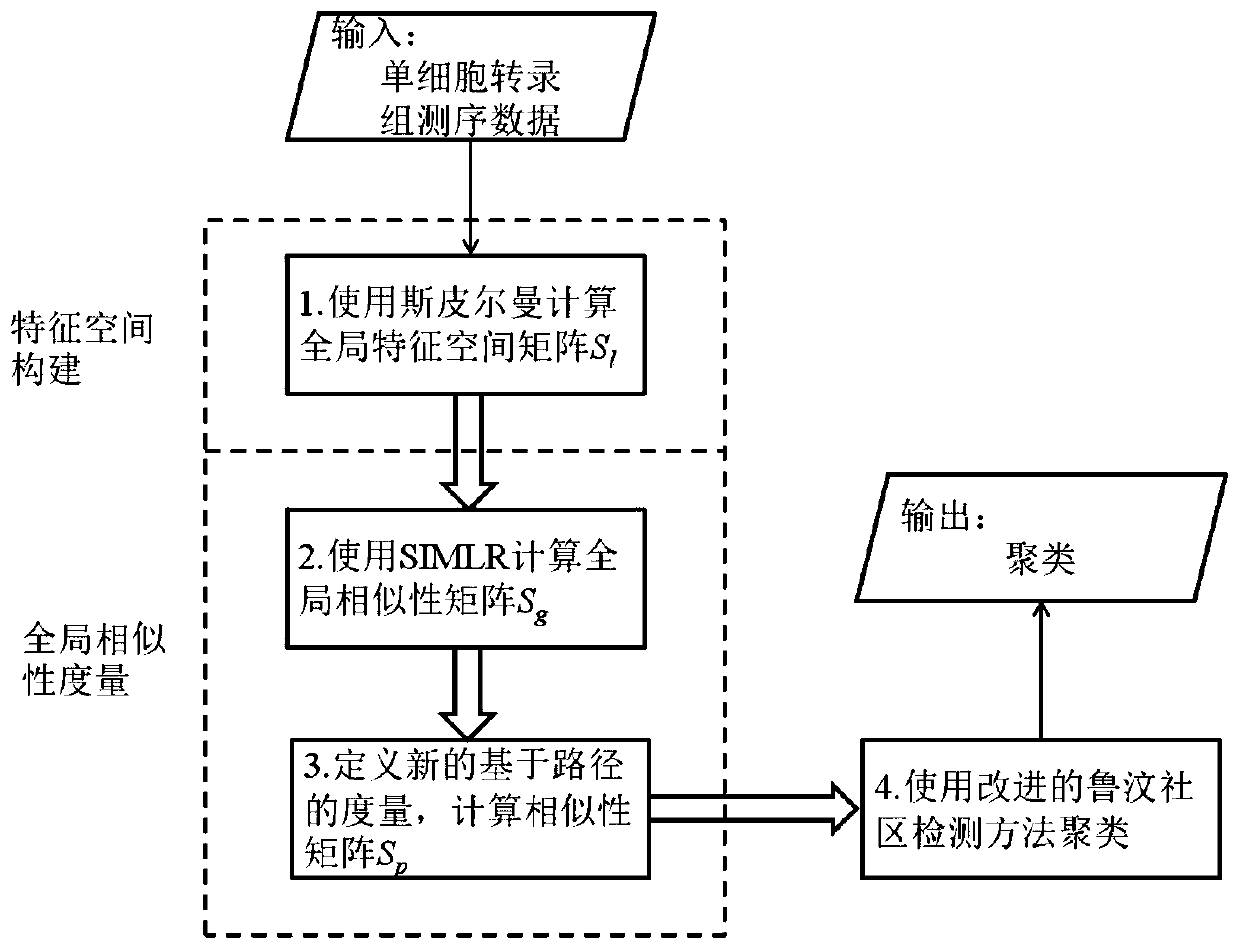
Single cell clustering method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
The invention discloses a single cell clustering method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium. On the basis of calculating local similarity between node pairs based on distance information, a global feature space is constructed. Based on the global feature space, the global similarity between the node pairs is calculated by using a multi-core learning method. Then, nodes on all second-order paths of the node pairs are expanded and considered, more relevant node information is added, and a more effective global similarity calculation method is constructed. Finally, by sorting the nodes according to the node degrees, and determining an initial association joining sequence of the nodes, a Louvain association detection method is improved, and clustering is carried out by usingthe method. The method is simple and effective, and compared with other methods, tests on a public single cell transcriptome sequencing data set show that the method has good prediction performance inthe aspect of single cell transcriptome sequencing data clustering.
Owner:YULIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Serum-free medium for full-suspension culture of MDCK cells (madin-darby canine kidney cells) and preparation method of serum-free medium
ActiveCN106119186ALow costClear ingredientsCulture processCell culture mediaMadin Darby canine kidney cellSerum free media
The invention discloses a serum-free medium for full-suspension culture of MDCK cells (madin-darby canine kidney cells) and a preparation method of the serum-free medium. The serum-free medium for full-suspension culture of the MDCK cells consists of a basic metabolism nutrient, nucleotide, vitamins, inorganic salt, a shear force protective agent, a cell clustering resisting agent, a pH buffer agent, a pH indicator, an influenza virus proliferation accelerant and other additives; and the preparation method of the serum-free medium for full-suspension culture of the MDCK cells comprises the following steps: 1) preparing mixed liquid: dissolving and mixing the raw materials; and 2) regulating pH: regulating pH of the mixed liquid to 6.3-6.7, and setting a constant volume, so that the serum-free medium for full-suspension culture of the MDCK cells is obtained. The medium supports the high-density full-suspension culture of the MDCK single cells and is capable of greatly shortening a time of domesticating the MDCK cells from adherent cells into the serum-free full-suspension cells; and the medium is applicable to the large-scale production of biological products, in particular veterinary biological products.
Owner:ZHAOQING DAHUANONG BIOLOGIC PHARMA +2
Cell clustering algorithm based on interference coordination
ActiveCN107426825AEliminate distractionsHigh throughput gainOrthogonal multiplexNetwork planningTime domainMaximum level
The invention discloses a cell clustering algorithm based on interference coordination. Compared with prior art, according to the invention, the user-based algorithm enables each user to freely select most appropriate coordination cluster in such a manner that from the user's perspective, once the cell turns to a coordination cell, the interference among cells can be eliminated at the maximum level, and higher system turnout gain can be obtained. The theory of cell clustering algorithm iteratively allocates nodes to clusters, ensures minimization of distance gains among nodes which are allocated to the cluster in each iteration process, performs processing by placing users which have strong interference to the same cluster, applies the interference avoiding technology which is based on time domain or frequency domain to intra-cluster interferences; and applies intra-cell interference coordination technology to intra-cluster interference.
Owner:陕西云瑞创智科技有限公司
Cell clustering method
InactiveCN103458414AUplink and downlink interference avoidanceAvoid interferenceNetwork planningAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
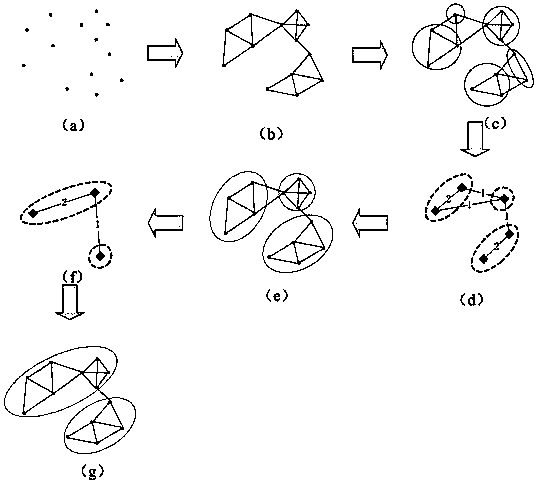
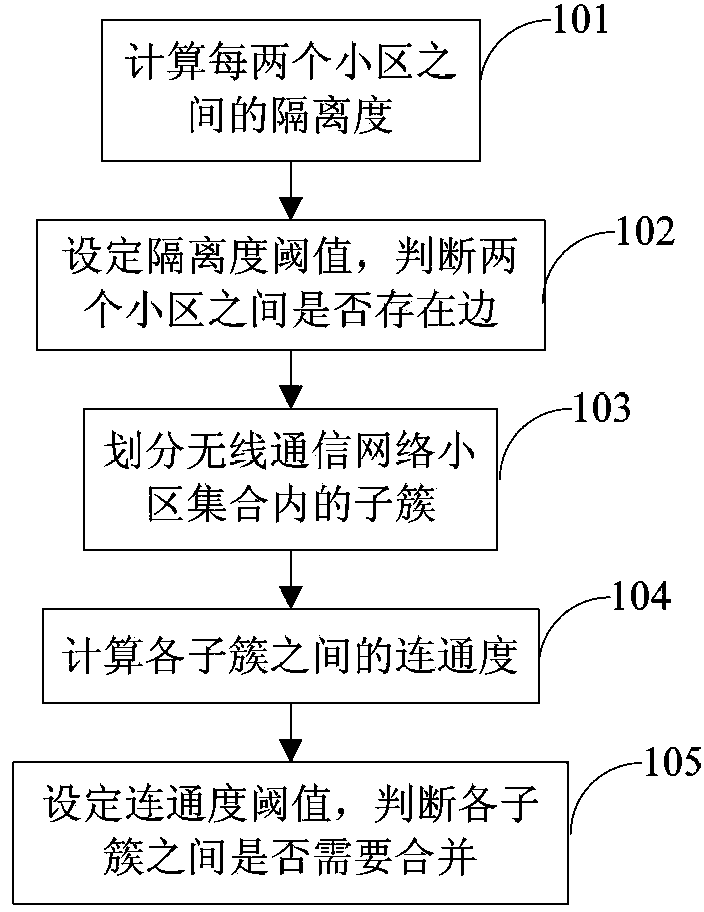
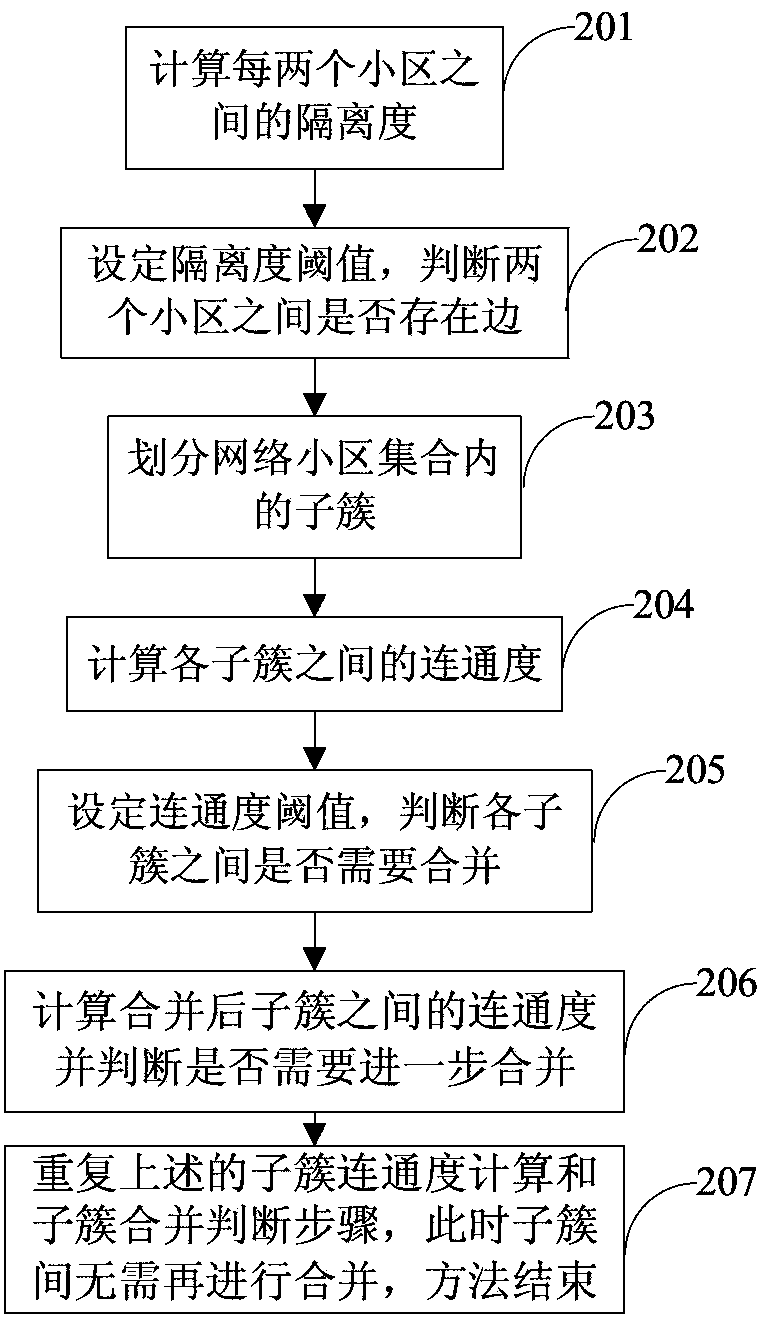
The invention provides a cell clustering method. The cell clustering method is characterized by comprising the step of calculating isolation between every two adjacent cells in a wireless communication network cell aggregation; the step of setting the isolation threshold value theta and judging whether a boundary exists between the two cells; the step of dividing the cell aggregation in which the boundaries exist between every two adjacent cells into sub-clusters Si in the wireless communication network cell aggregation U, wherein i=1, 2,...,m and the sub-clusters Si meet the formula: U=S1 UpsilonS2 Upsilon...Upsilon Sm; the step of calculating the connectivity among the sub-clusters; the step of setting a connectivity threshold value N and judging whether the sub-clusters need to be combined or not according to the connectivity threshold value N; when the connectivity degree between every two adjacent sub-clusters is larger than the connectivity threshold value N, the two sub-clusters are combined. The limitation tolerance for an interference link is ruled according to the connectivity threshold value among the sub-clusters, and on the premise that the interference among cell base stations is effectively avoided, the requirement for improving the self-adaptability of the cell network service can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Super dense networking cell clustering method
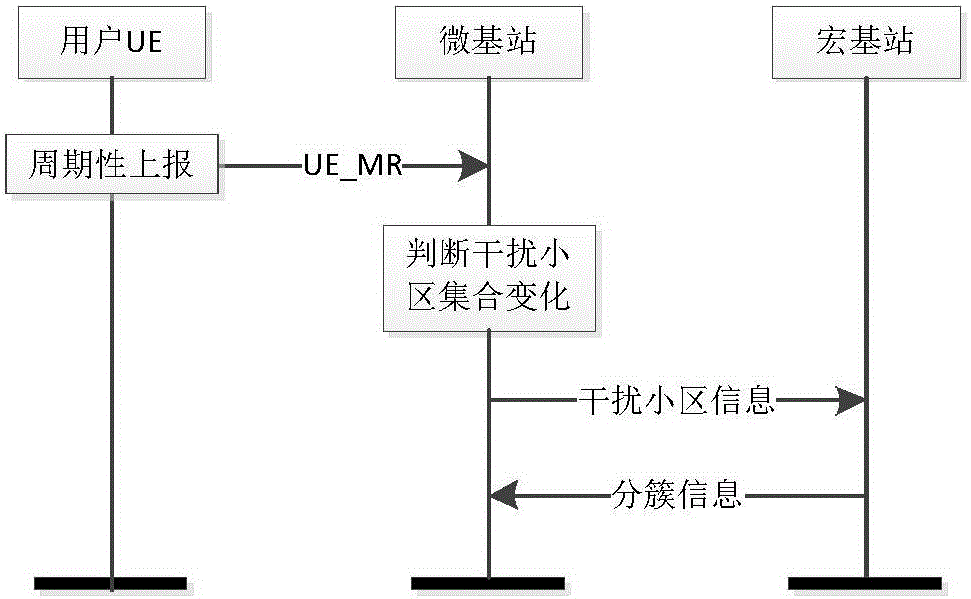
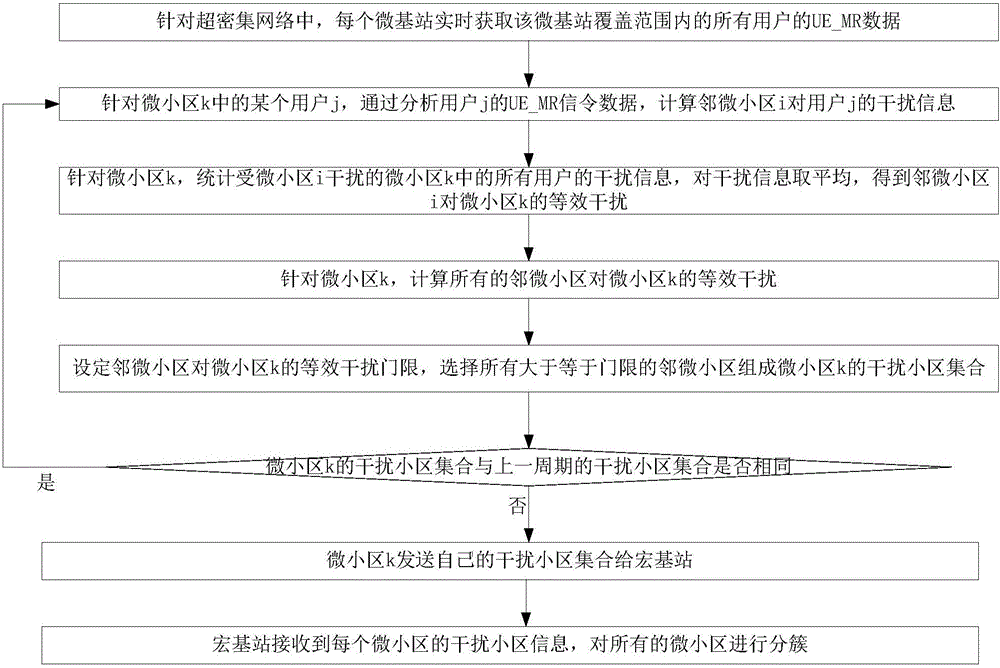
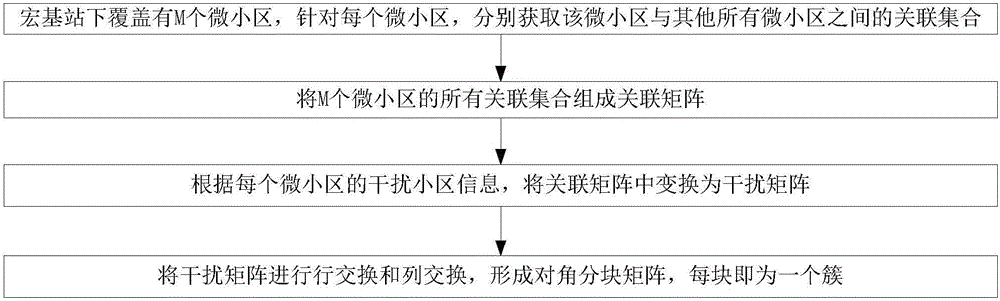
ActiveCN105933923AReliable resultsIn line with the actual situation of the constructionNetwork traffic/resource managementMacro base stationsMicro cell
The invention provides a super dense networking cell clustering method, belonging to the field of mobile communication. The method comprises that steps that each micro base station obtains the UE_MR data of all users in real time and calculates the interference information to a user j by an adjacent micro cell i; then the interference information average value of all users in a micro cell is calculated as equivalent interference; the equivalent interference to the micro cell by all adjacent micro cells is calculated; an equivalent interference threshold EIth is set, and the interference cell set of the micro cell is selected; finally, whether the interference cell set of the micro cell is same as a previous period or not is judged, and the interference information is recalculated if so; otherwise, the micro cell sends the interference cell set of the micro cell to a macro base station; the macro base station carries out clustering and notifies each micro cell. The method has the advantages that a network overall division is employed to carry out clustering without the selection of an original clustering or original point, the clustering result is stable, the micro base stations are responsible for UE_MR preprocessing working, the macro base station is responsible for micro cell clustering, and the purpose of balancing a load is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for culturing pluripotent stem cell
InactiveUS20140329317A1Easy to controlSmall sizeArtificial cell constructsCell culture supports/coatingInduced pluripotent stem cellCell clustering
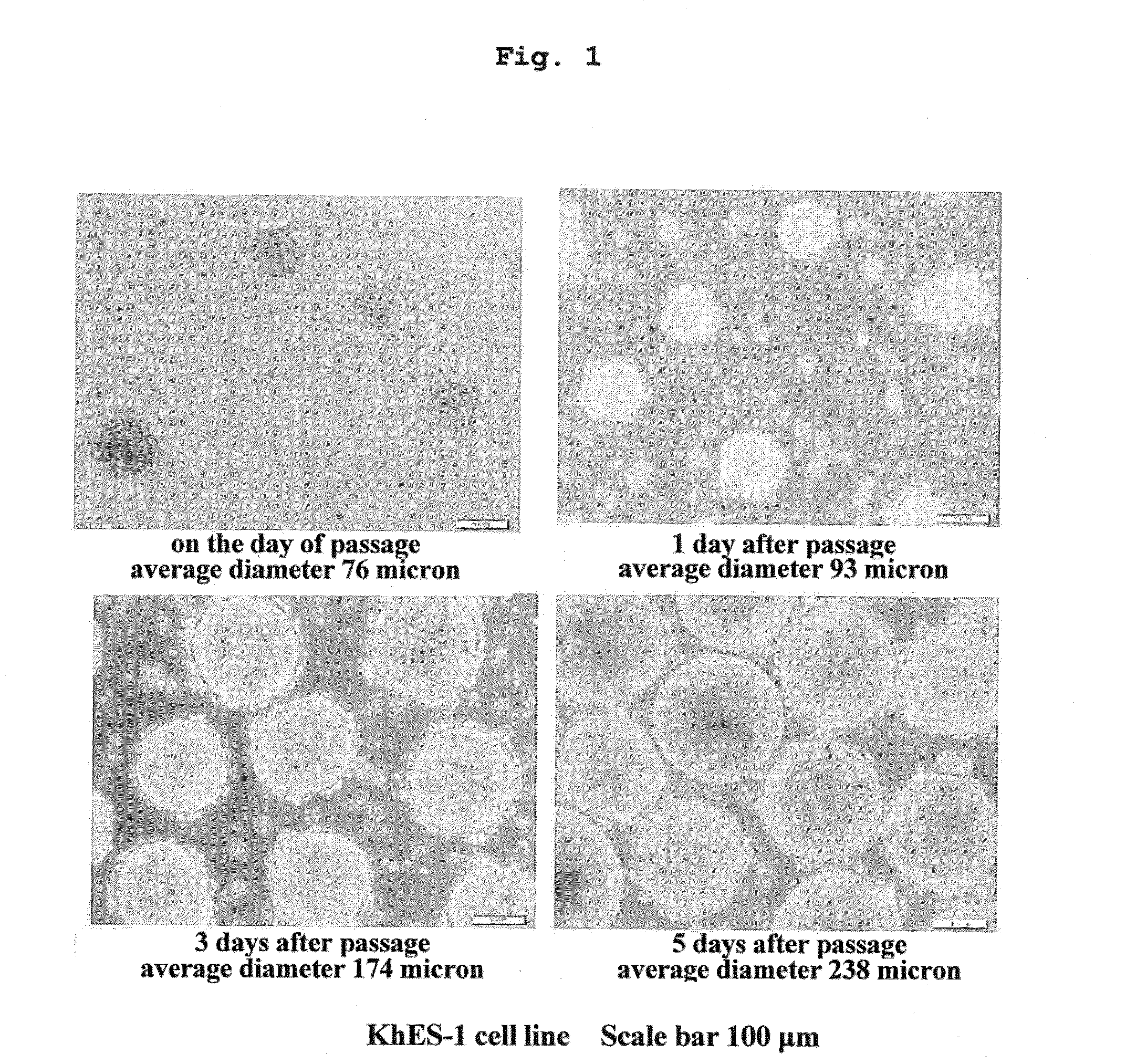
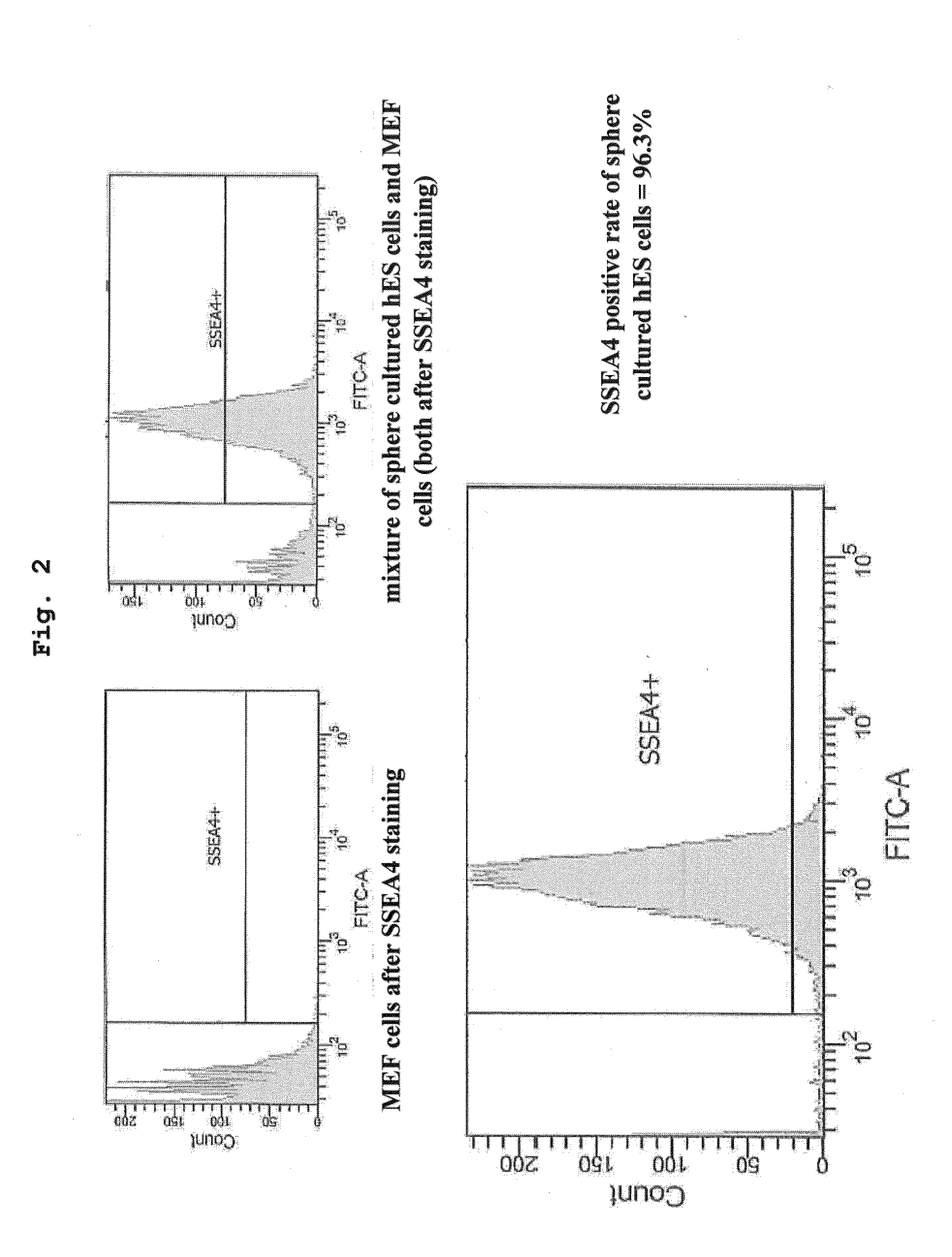
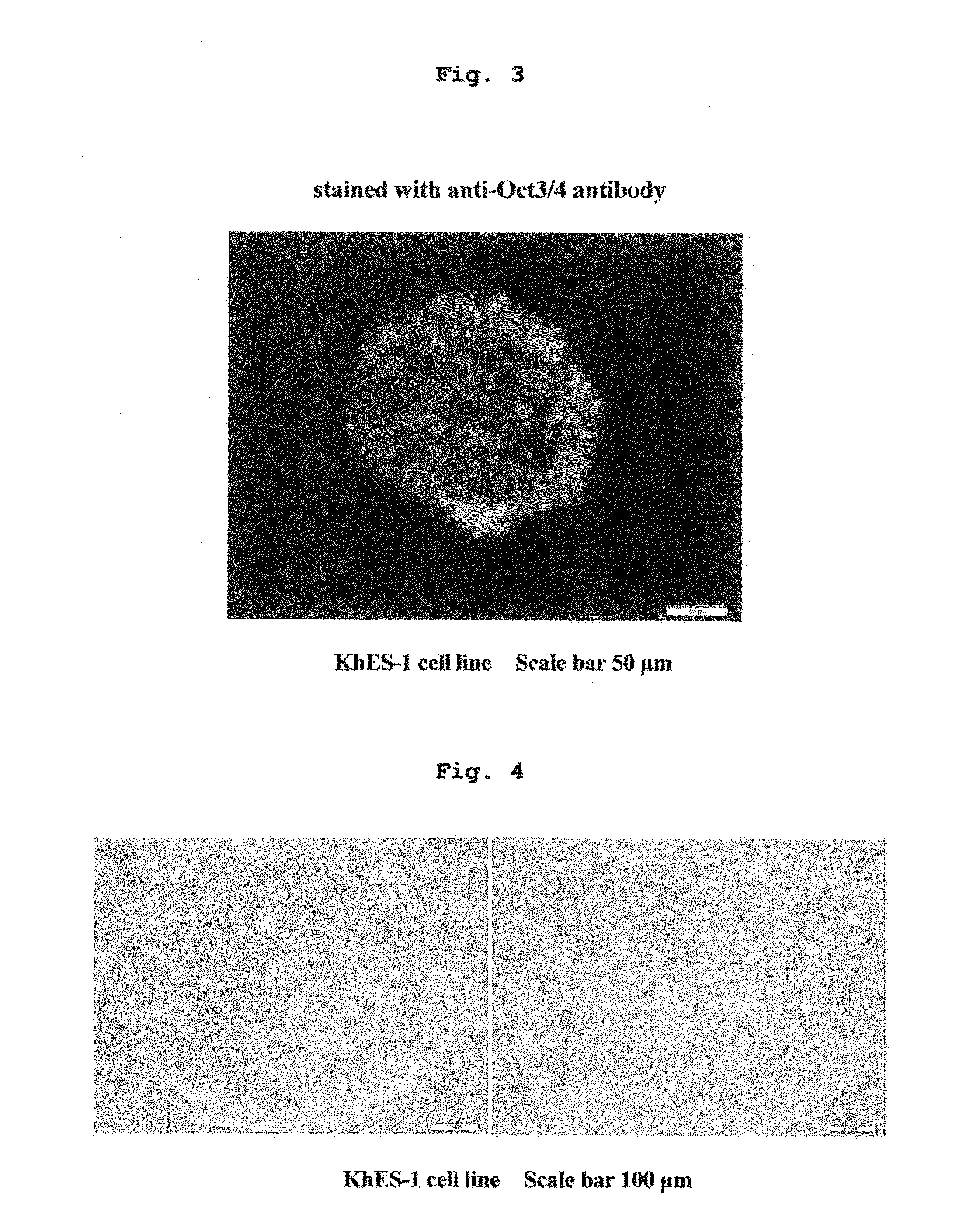
The present invention provides a method of maintaining and amplifying pluripotent stem cells, including repeating the following steps:(i) suspension culturing pluripotent stem cells until cell aggregates have an average diameter of about 200-about 300 μm,(ii) fragmenting the cell aggregates obtained by step (i) into cell aggregates having a uniform average diameter of about 80-about 120 μm. In step (i), a suitable viscosity is conferred to the medium to prevent movement of floating cell aggregates and adhesion and fusion of cell aggregates. In step (ii), the cell aggregates are mechanically fragmented into smaller uniform cell aggregates by passing the cell suspension through a mesh.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Cell analysis apparatus and cell analysis method
ActiveUS20140154677A1Accurate distinctionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFlow cellSignal processing circuits
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Devices for the production of cell clusters of defined cell numbers and cluster sizes
ActiveUS20120149051A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell clusteringCell cluster
Devices for the in vitro aggregation of cells. The devices are characterized by containing special ground cavities allowing cluster formation to take place when a cell suspension is seeded onto the device. Further, the present invention relates to a method for aggregating cells and the use of the devices of the present invention for the aggregation of cells.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH
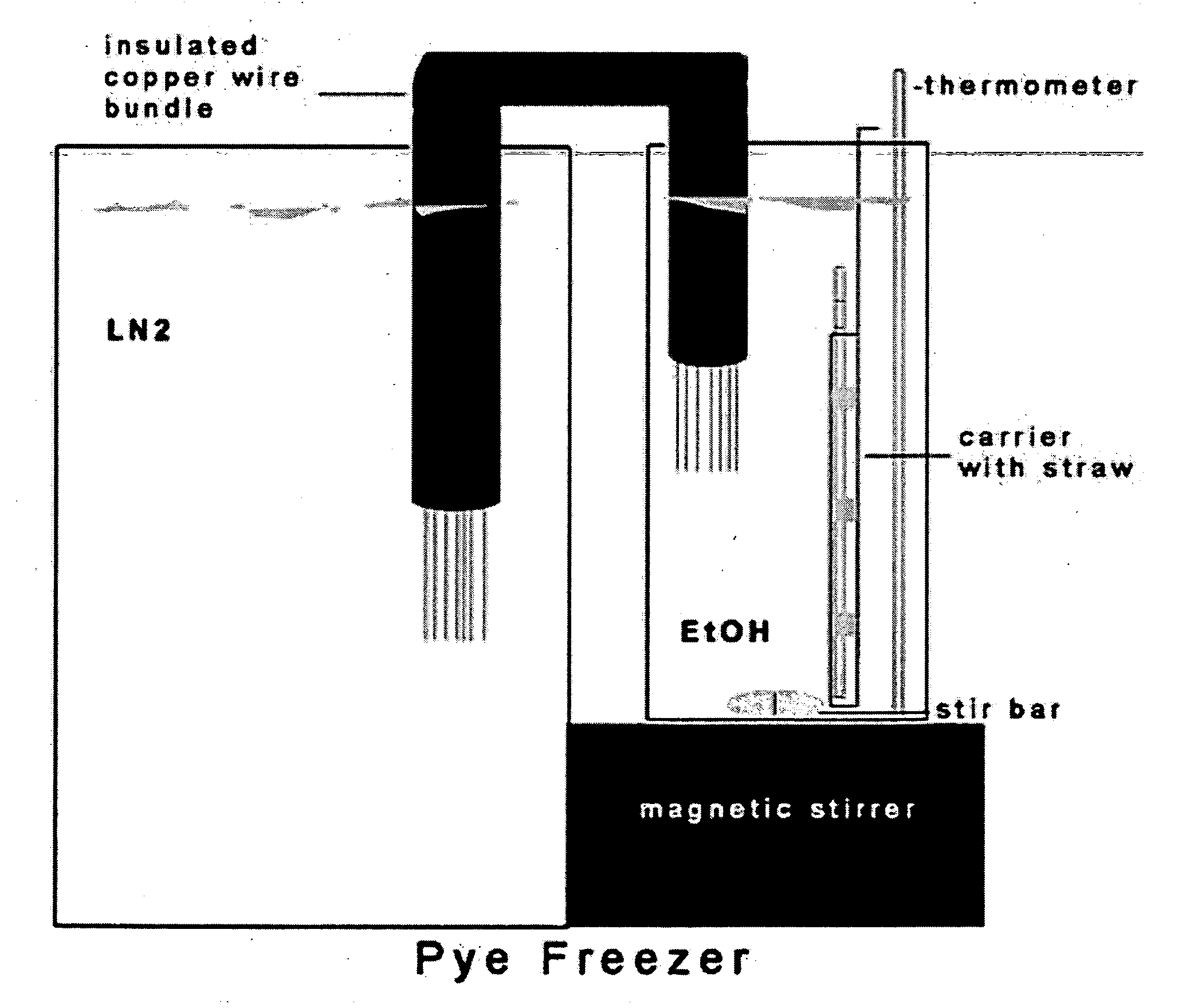
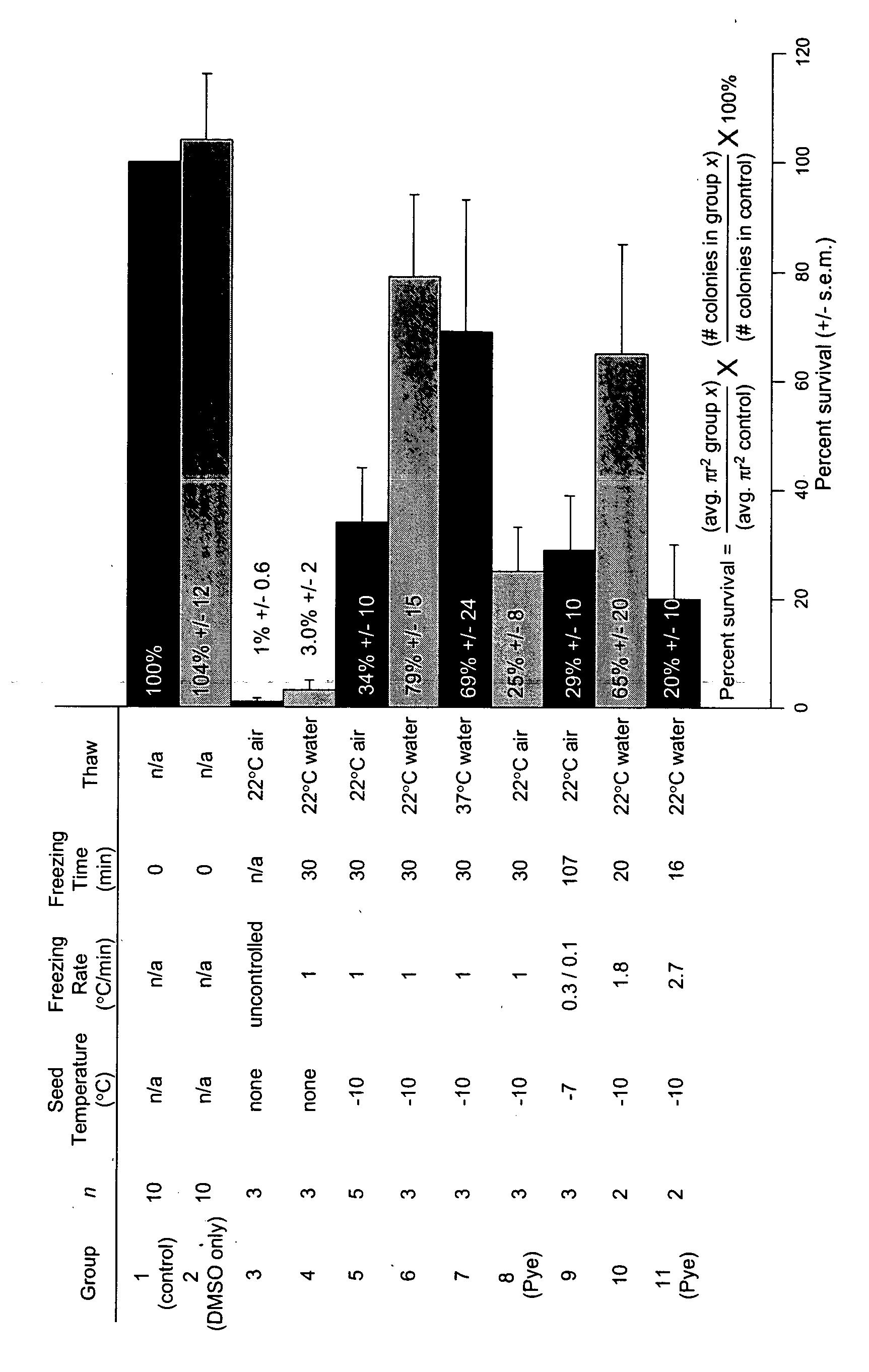
Cryopreservation of primate embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20060269908A1Improve survivabilityVertebrate cellsDead animal preservationCell specificPrimate
Primate embryonic stem cells are cryopreserved by resuspension in a freezing medium and slow cooling at a controlled rate. In some embodiments, prior to the controlled freezing step, the suspension of cells is cooled to a temperature just below freezing, and ice crystal formation is induced. The cryopreserved cell aggregates are useful in transplantation, for experimental evaluation, and as a source of lineage and cell specific products, and as targets for the discovery of factors or molecules that can affect them.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
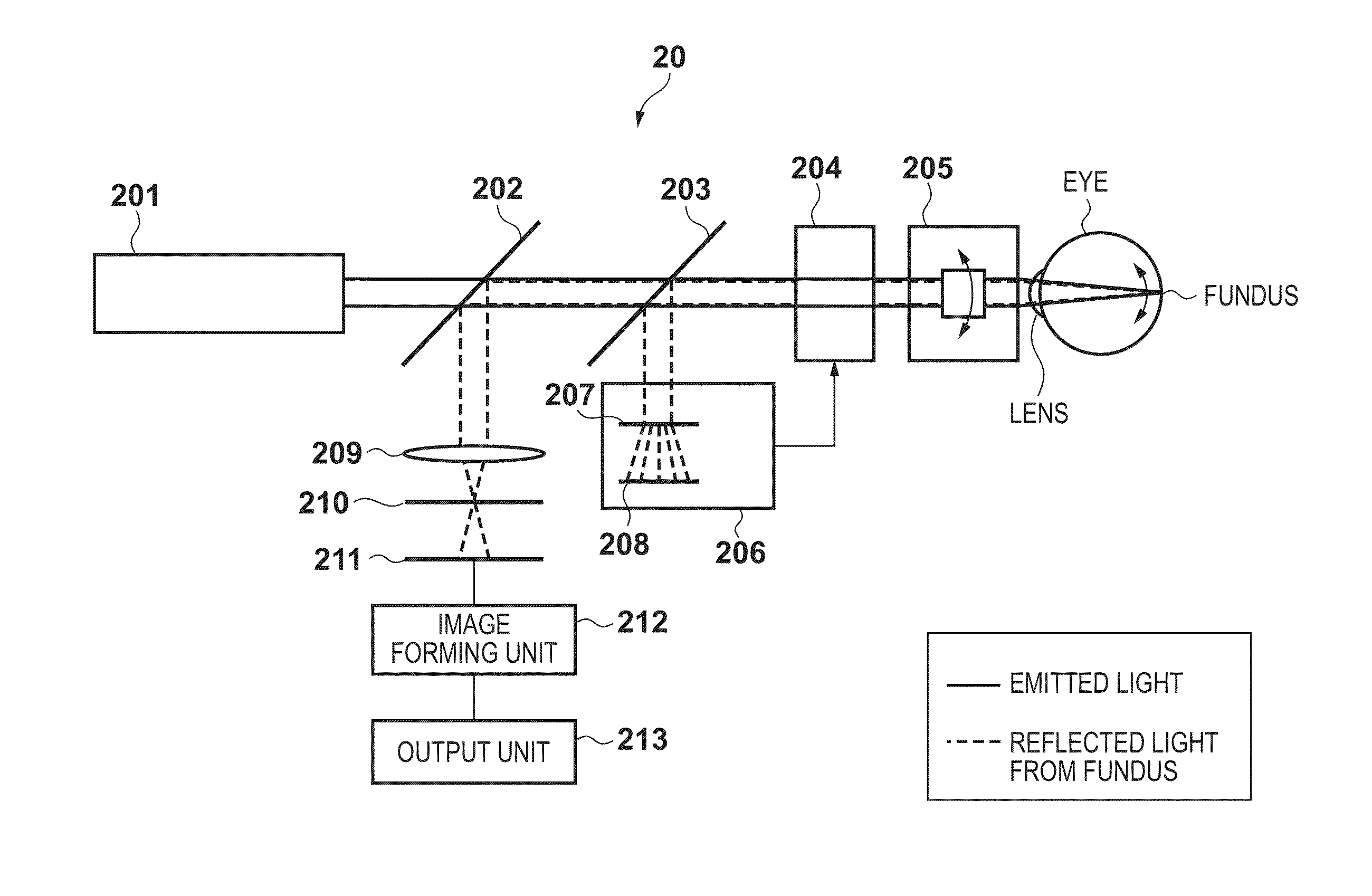
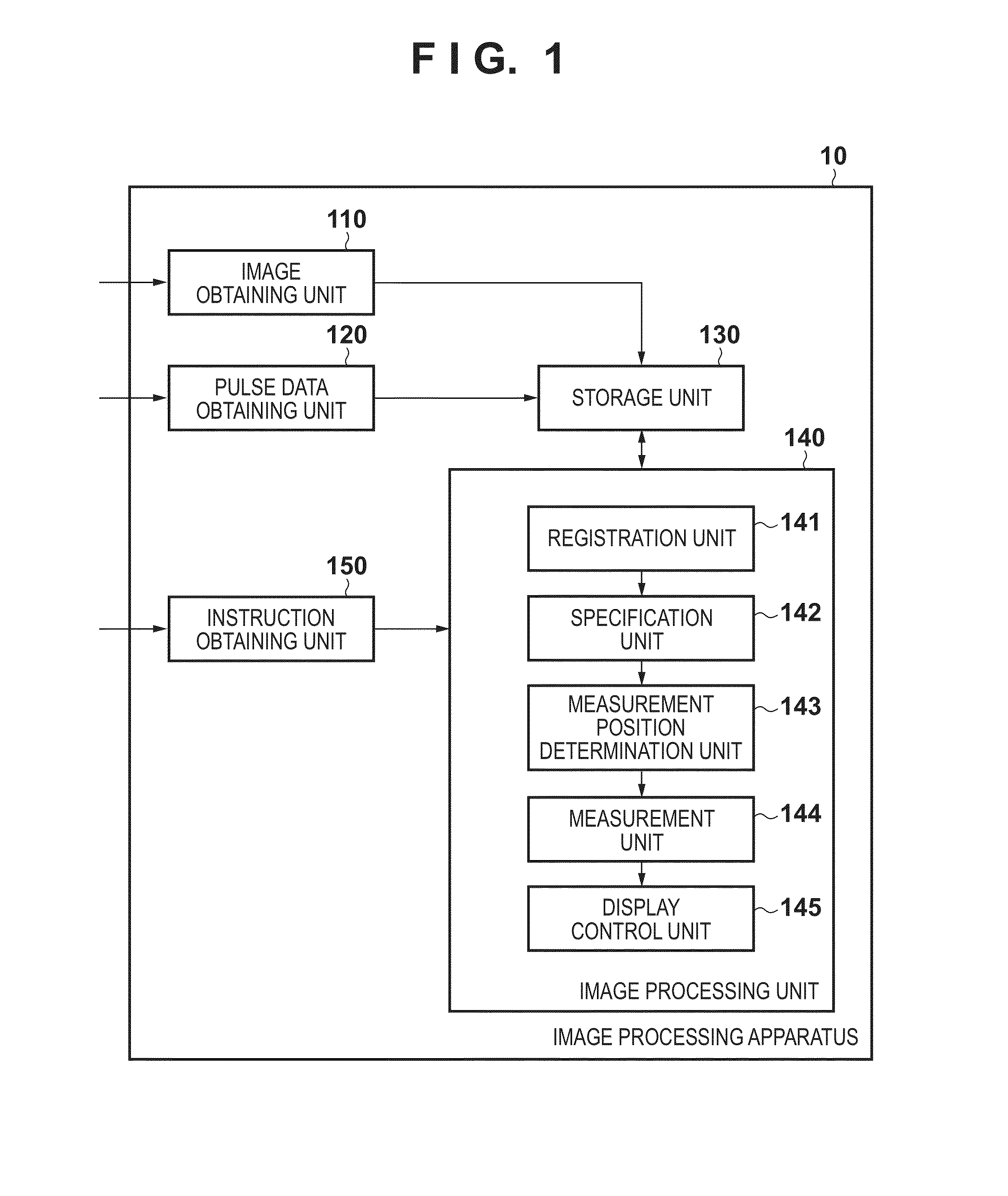
Image processing apparatus and image processing method
ActiveUS20140240668A1Acquiring/recognising microscopic objectsSensorsImaging processingCell clustering
An image processing apparatus obtains an image of an eye area, determines a measurement target among multiple vascular branches based on information regarding multiple vascular branches that include multiple vascular bifurcations in the obtained image, and measures the size of a blood cell aggregate in the determined measurement target.
Owner:CANON KK
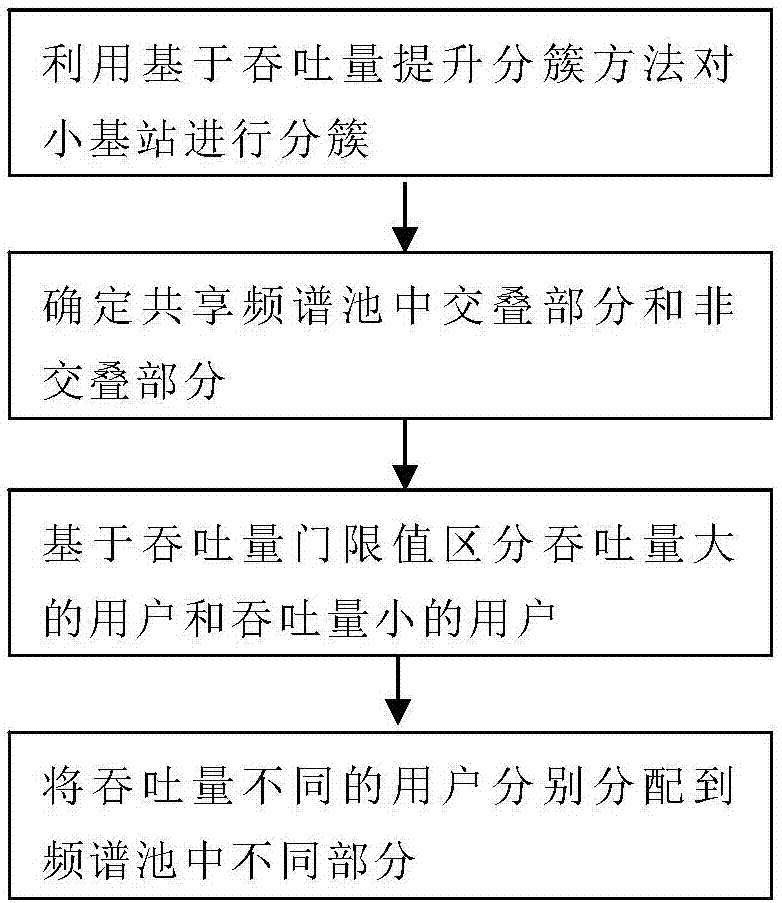
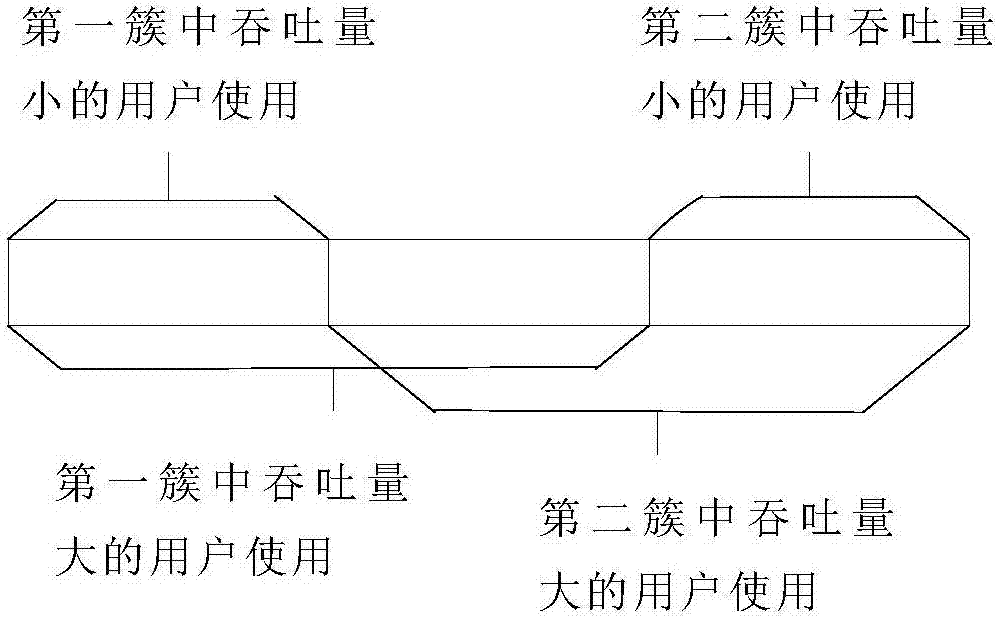
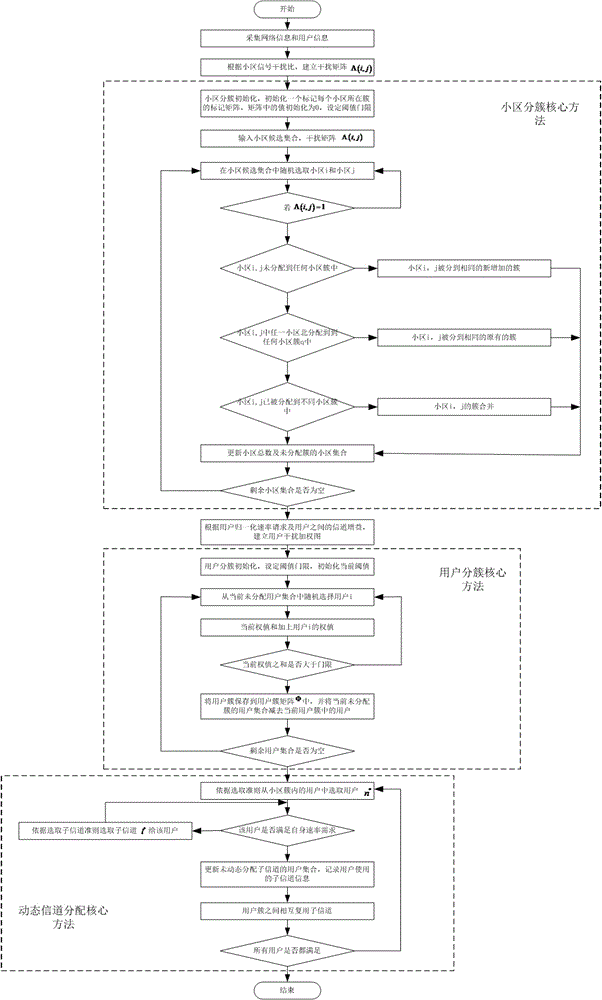
Cell clustering method and frequency spectrum overlapping multiplexing method based on same
InactiveCN107371167AImprove average spectral efficiencyNetwork planningMultiplexingFrequency spectrum
Owner:SHANGHAI RES CENT FOR WIRELESS COMM
Improved weighted graph-based super dense heterogeneous network interference coordination method
ActiveCN106412988AReduce complexityReduce distractionsNetwork traffic/resource managementMultiplexingRound complexity
The invention discloses an improved weighted graph-based super dense heterogeneous network interference coordination method. With maximizing the network spectrum efficiency as a target and in a condition of ensuring a changed rate request along with changes of a service type for cell users, cells are firstly clustered according to cell interference environments in the actual super dense heterogeneous network scene; a user interference weighted graph is built in each cell cluster, users in the cluster adopt a low-complexity dynamic sub-channel multiplexing method, the method joins cell clustering and user clustering, and a weighted interference graph is built for the user. The purposes of increasing the network spectrum efficiency and reducing the interference are realized, the low complexity and good convergence performance are realized, the interference problem in the whole network is converted to the interference problem in each small cell cluster, the interference problem is simplified, interference in the network is suppressed on the basis of ensuring the user rate, and the maximization of the network spectrum efficiency is realized.
Owner:上海瀚芯实业发展合伙企业(有限合伙)
Cell clustering based configuration of flexible time division duplex communication
ActiveCN105165084AGuaranteed normal transmissionEasy to adaptTransmission path divisionNetwork topologiesNetwork deploymentCell clustering
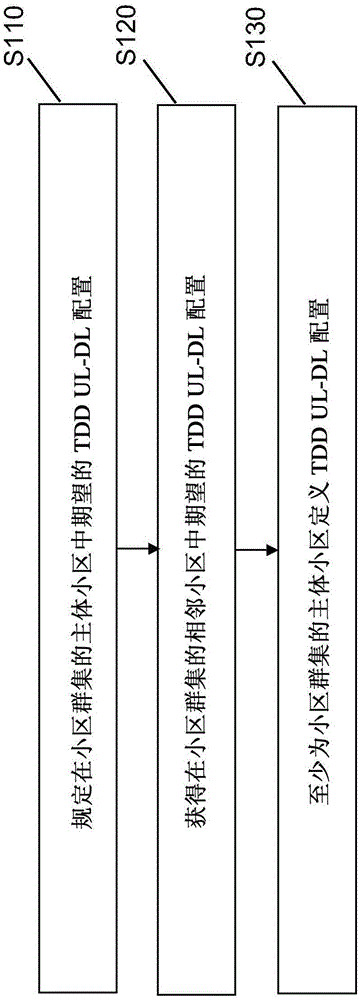
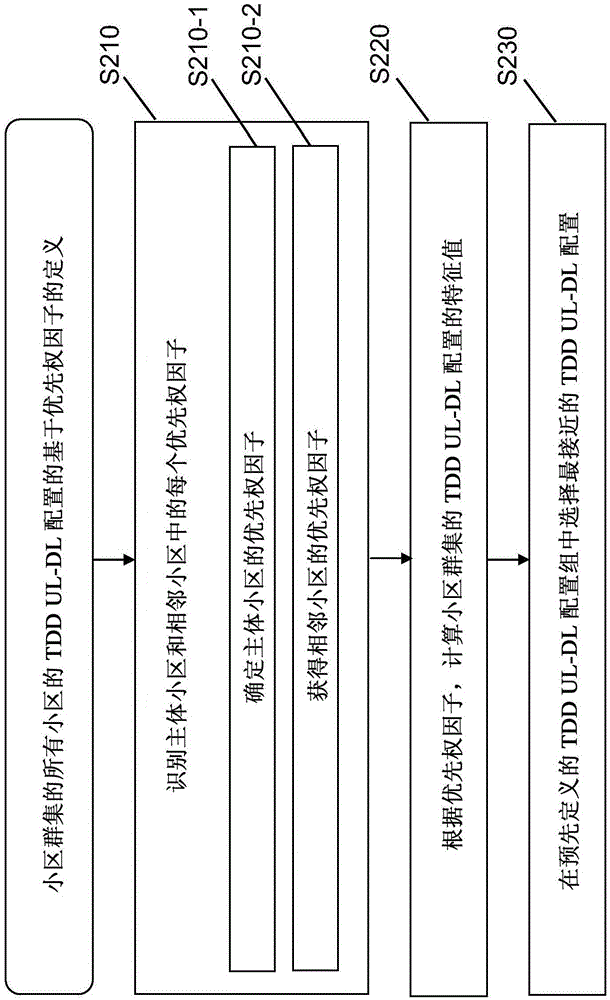
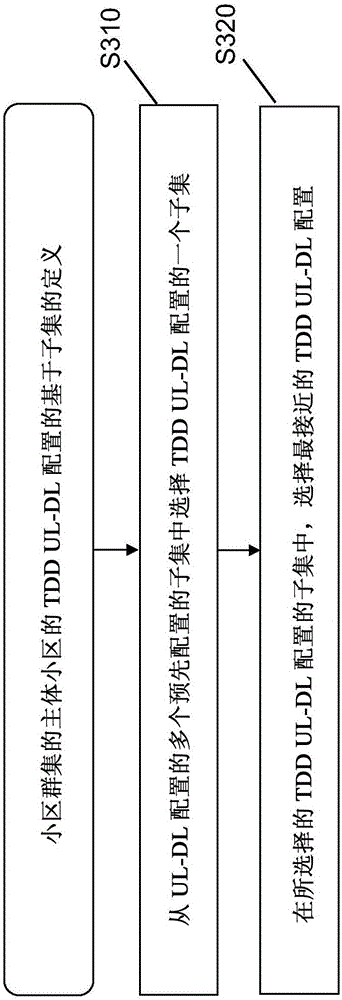
There are provided measures for cell clustering based configuration of flexible time division duplex communication, such as e.g. in layered heterogeneous network deployments. Such measures may exemplarily comprise measures for specifying a desired uplink-downlink configuration for time division duplex communication in a subject cell of a cellular communication system, obtaining at least one desired uplink-downlink configuration for time division duplex communication in at least one neighboring cell of the cellular communication system, wherein the at least one neighboring cell and the subject cell belong to the same cell cluster, and defining an uplink-downlink configuration for time division duplex communication in at least the subject cell of the cell cluster out of a set of predefined uplink-downlink configurations with flexible subframe patterns for flexible time division duplex communication on the basis of the specified desired uplink-downlink configuration for the subject cell and the obtained at least one desired uplink-downlink configuration for the at least one neighboring cell.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Single cell integrated clustering method based on subspace randomization
The invention relates to the field of data mining in bioinformatics, in particular to a single cell integrated clustering method based on subspace randomization. The method mainly comprises the following steps: (1) data preprocessing; (2) random subspace sampling is carried out to carry out cell similarity measurement; (3) subspace fusion is performed; and (4) single cell clustering is performed by measuring the overall similarity based on spectral clustering to obtain a final result. Compared with the prior art, the single cell clustering method provided by the invention is used for characterizing the novel cell type and detecting the heterogeneity in the population, and has stronger statistical ability and better stability. The method provided by the invention is feasible and effective, can achieve a good effect in the aspect of identifying the single cell cluster, and has important significance for researching cell type classification and identification of a complex data set.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com