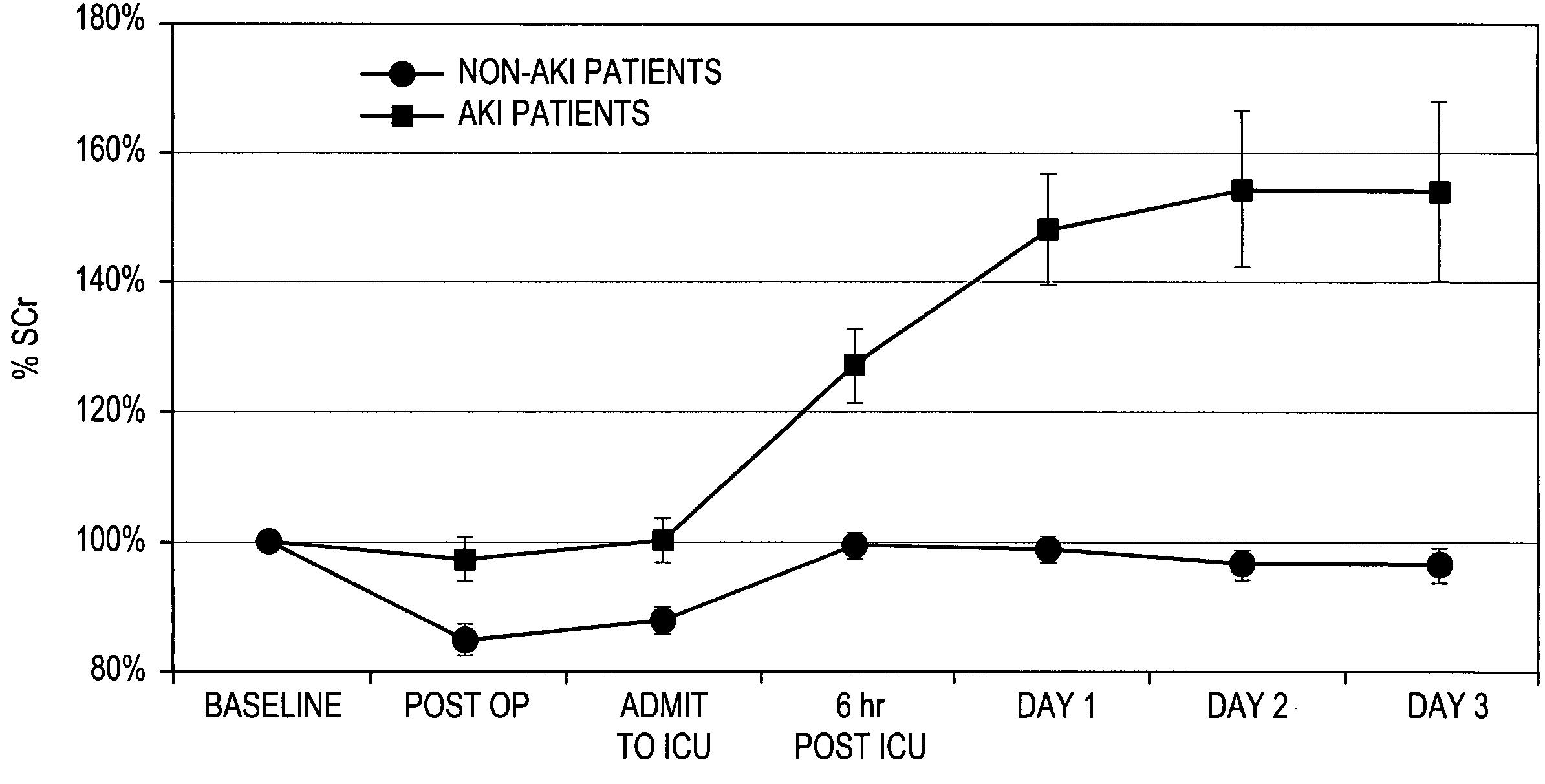
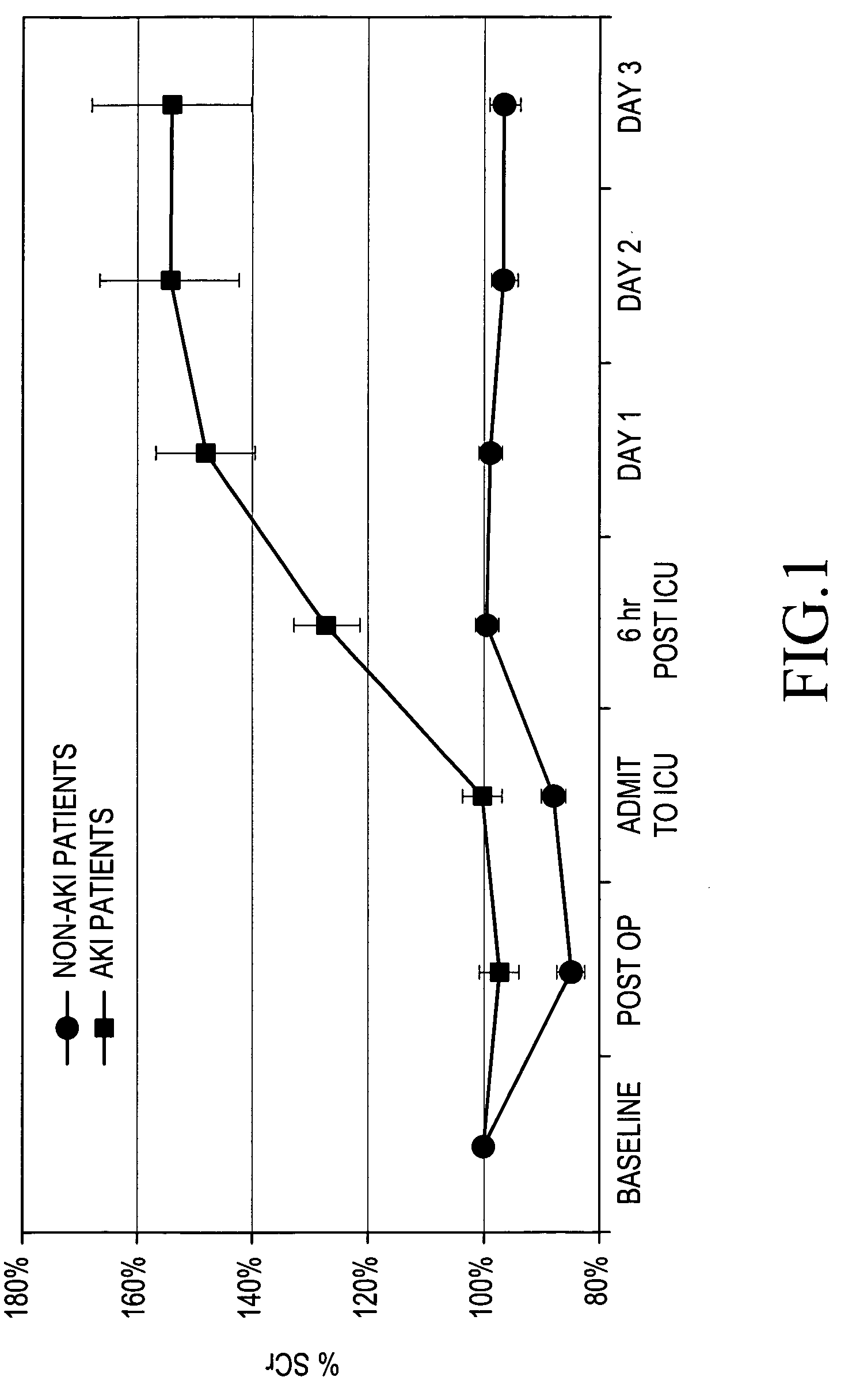
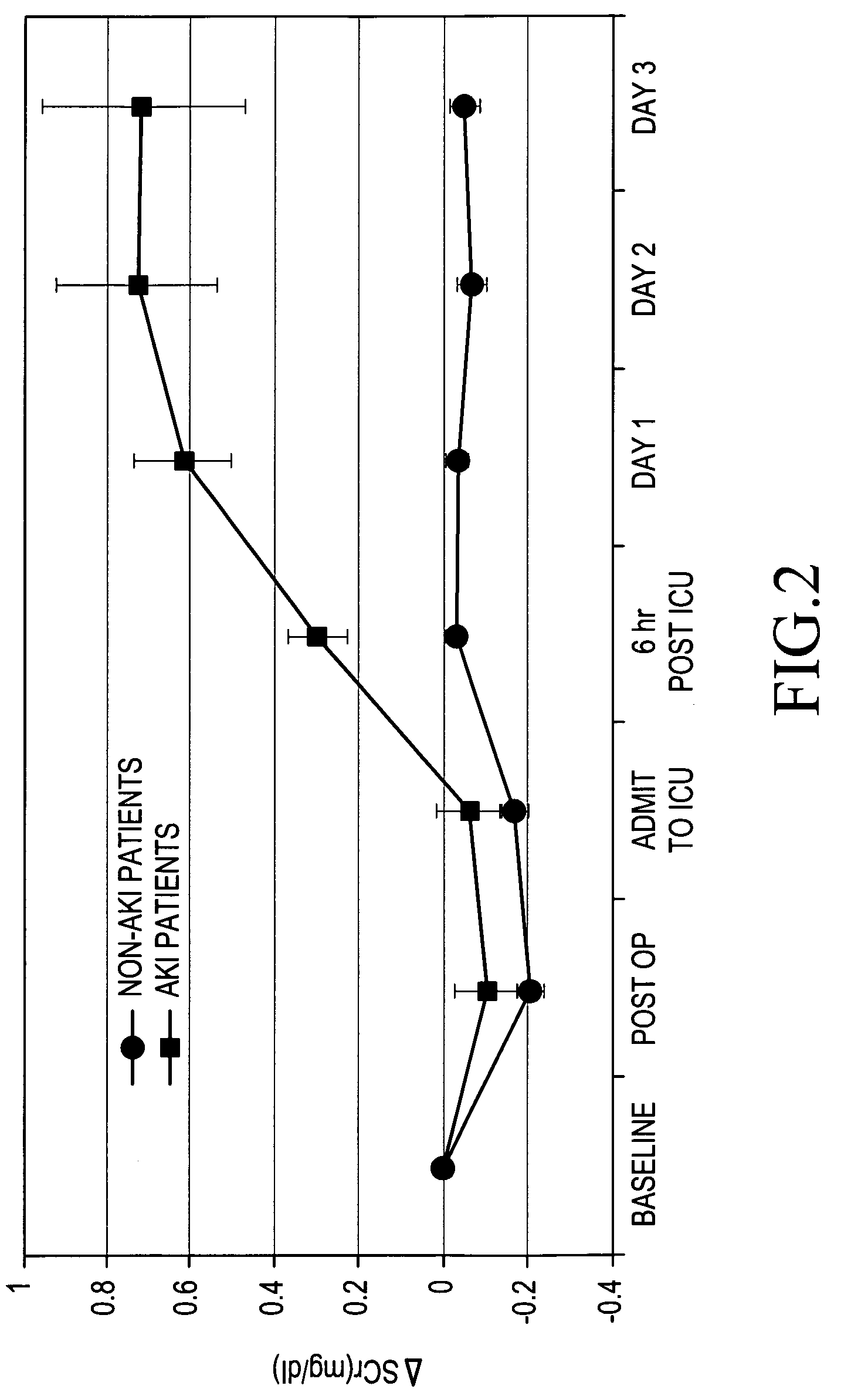
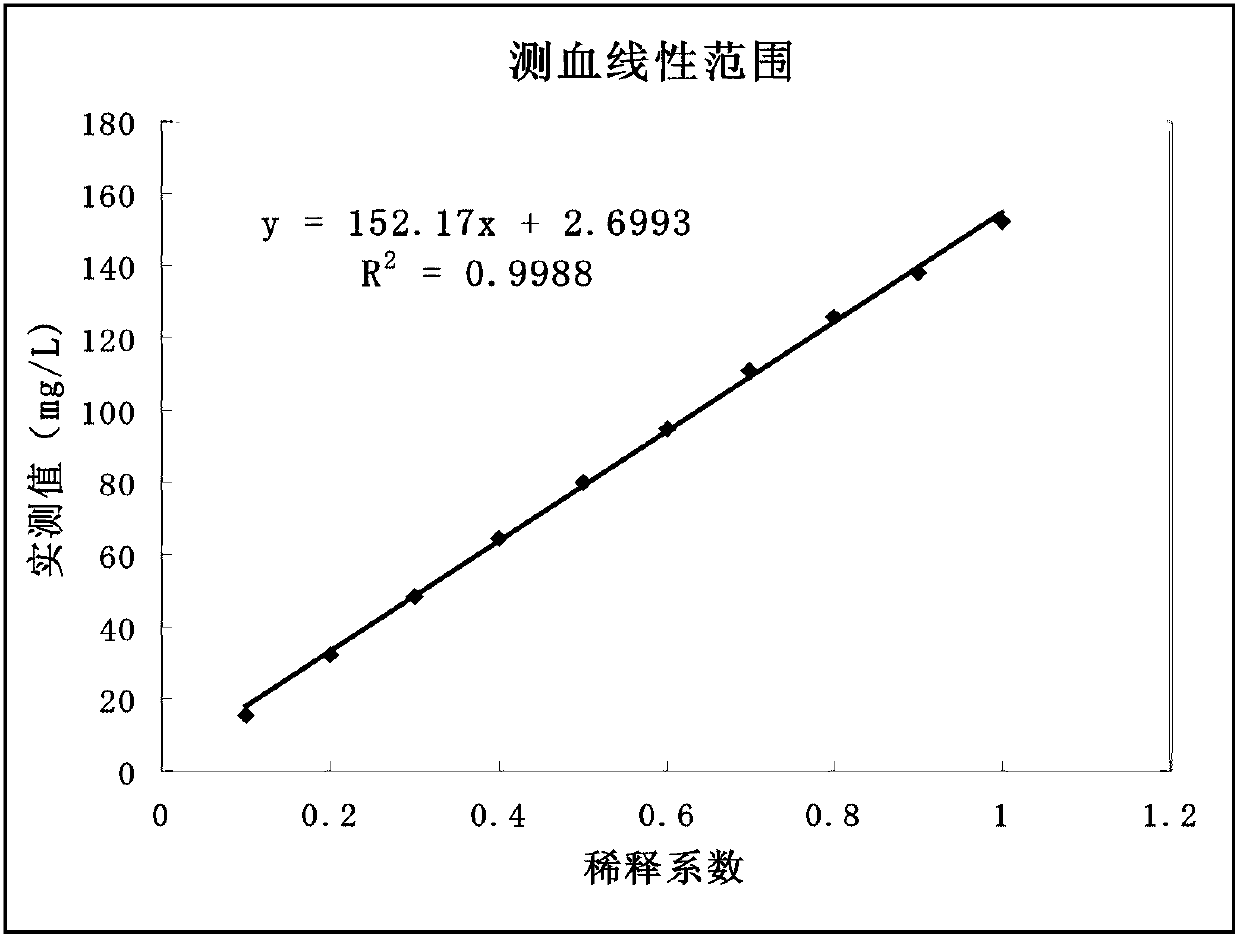
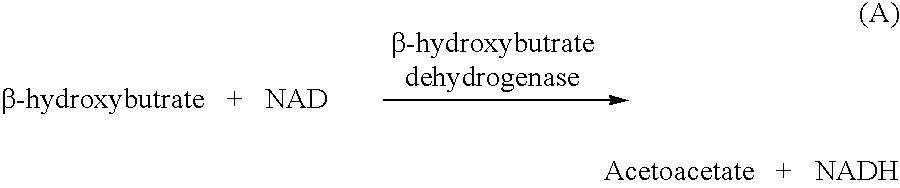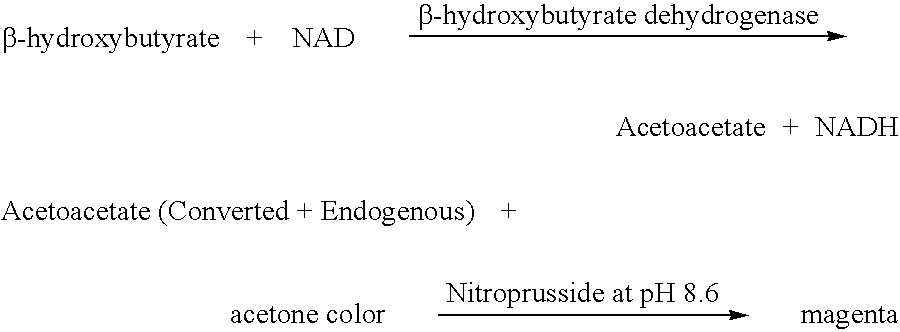Patents
Literature
1281 results about "Urine sample" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The types of urine sample you might be asked for include a random specimen, first morning specimen or timed collection. To collect a urine sample you should: label a sterile, screw-top container with your name, date of birth and the date. wash your hands. start to pee and collect a sample of urine "mid-stream" in the container.
Methods, compositions, and automated systems for separating rare cells from fluid samples
InactiveUS7166443B2Aid in diagnosis and prognosisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCancer cellRed blood cell
The present invention recognizes that diagnosis and prognosis of many conditions can depend on the enrichment of rare cells from a complex fluid sample. In particular, the enrichment of fetal cells from maternal samples, such as maternal blood samples, can greatly aid in the detection of fetal abnormalities or a variety of genetic conditions. In addition, the present invention recognizes that the enrichment of rare malignant cells from patient samples, can aid in diagnosis, prognosis, and development of therapeutic modalities for patients. The invention includes microfabricated filters for filtering fluid samples and methods of enriching rare cells of fluid samples using microfabricated filters of the present invention. The invention also includes solutions for the selective sedimentation of red blood cells (RBCs) from a blood sample and methods of using selective RBC sedimentation solutions for enriching rare cells of a fluid sample. Yet another aspect of the invention is an automated system for processing a fluid sample that includes: at least one filtration chamber that includes a microfabricated filter; automated means for directing fluid flow through at least one filtration chamber of the automated system, and means for collecting enriched rare cells. The present invention also includes methods of using automated systems for separating rare cells from fluid samples. Preferred fluid samples are blood, effusion, or urine samples, and rare cells that can be enriched from such sample include nucleated red blood cells and cancer cells.
Owner:AVIVA BIOSCI
System for Conducting the Identification of Bacteria in Urine
ActiveUS20110008825A1Rapid diagnosisImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCuvettePipette
A system for conducting the identification and quantification of micro-organisms, e.g., bacteria in urine samples which includes: 1) several disposable cartridges for holding four disposable components including a centrifuge tube, a pipette tip having a 1 ml volume, a second pipette tip having a 0.5 ml volume, and an optical cup or cuvette; 2) a sample processor for receiving the disposable cartridges and processing the urine samples including transferring the processed urine sample to the optical cups; and 3) an optical analyzer for receiving the disposable cartridges and configured to analyze the type and quantity of micro-organisms in the urine sample. The disposable cartridges with their components including the optical cups or cuvettes are used in the sample processor, and the optical cups or cuvettes containing the processed urine samples are used in the optical analyzer for identifying and quantifying the type of micro-organism existing in the processed urine samples.
Owner:POCARED DIAGNOSTICS
Methods, compositions, and automated systems for separating rare cells from fluid samples
InactiveUS6949355B2Aid in diagnosis and prognosisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCancer cellRed blood cell
The present invention recognizes that diagnosis and prognosis of many conditions can depend on the enrichment of rare cells from a complex fluid sample. In particular, the enrichment of fetal cells from maternal samples, such as maternal blood samples, can greatly aid in the detection of fetal abnormalities or a variety of genetic conditions. In addition, the present invention recognizes that the enrichment of rare malignant cells from patient samples, can aid in diagnosis, prognosis, and development of therapeutic modalities for patients.A first aspect of the present invention is a microfabricated filter for filtering a fluid sample. A microfabricated filter of the present invention comprises at least one tapered pore, and preferably comprises at least two tapered pores whose variation in size is 20% or less. The present invention also includes a method of enriching rare cells of a fluid sample using a microfabricated filter of the present invention.Another aspect of the invention is solutions for the selective sedimentation of red blood cells (RBCs) from a blood sample comprising a red blood cell aggregating agent and at least one specific binding member that selectively binds RBCs. Solutions of the present invention include a combined solution for rare cell enrichment that comprise RBC aggregating agents, at least one specific binding member that selectively binds RBCs, and at least one additional specific binding member for the removal of undesirable sample components other than RBCs. The invention also includes methods of using selective RBC sedimentation solutions and combined solutions for enriching rare cells of a fluid sample.Yet another aspect of the invention is an automated system for processing a fluid sample that includes: at least one filtration chamber that comprises or engages one or more microfabricated filters of the present invention; automated means for directing fluid flow through the one or more filtration chambers of the automated system, and means for collecting enriched rare cells. The present invention also includes methods of using an automated system for separating rare cells from a fluid sample. Preferred fluid samples are effusion, blood, or urine samples, and rare cells that can be enriched from such sample include nucleated red blood cells and cancer cells.
Owner:AVIVA BIOSCI
Spectrophotometric system and method for the identification and characterization of a particle in a bodily fluid
InactiveUS7027134B1Rapid and inexpensive and convenient for diagnosisRapidly and inexpensively disease diagnosisScattering properties measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringTurbidimetryWavelength
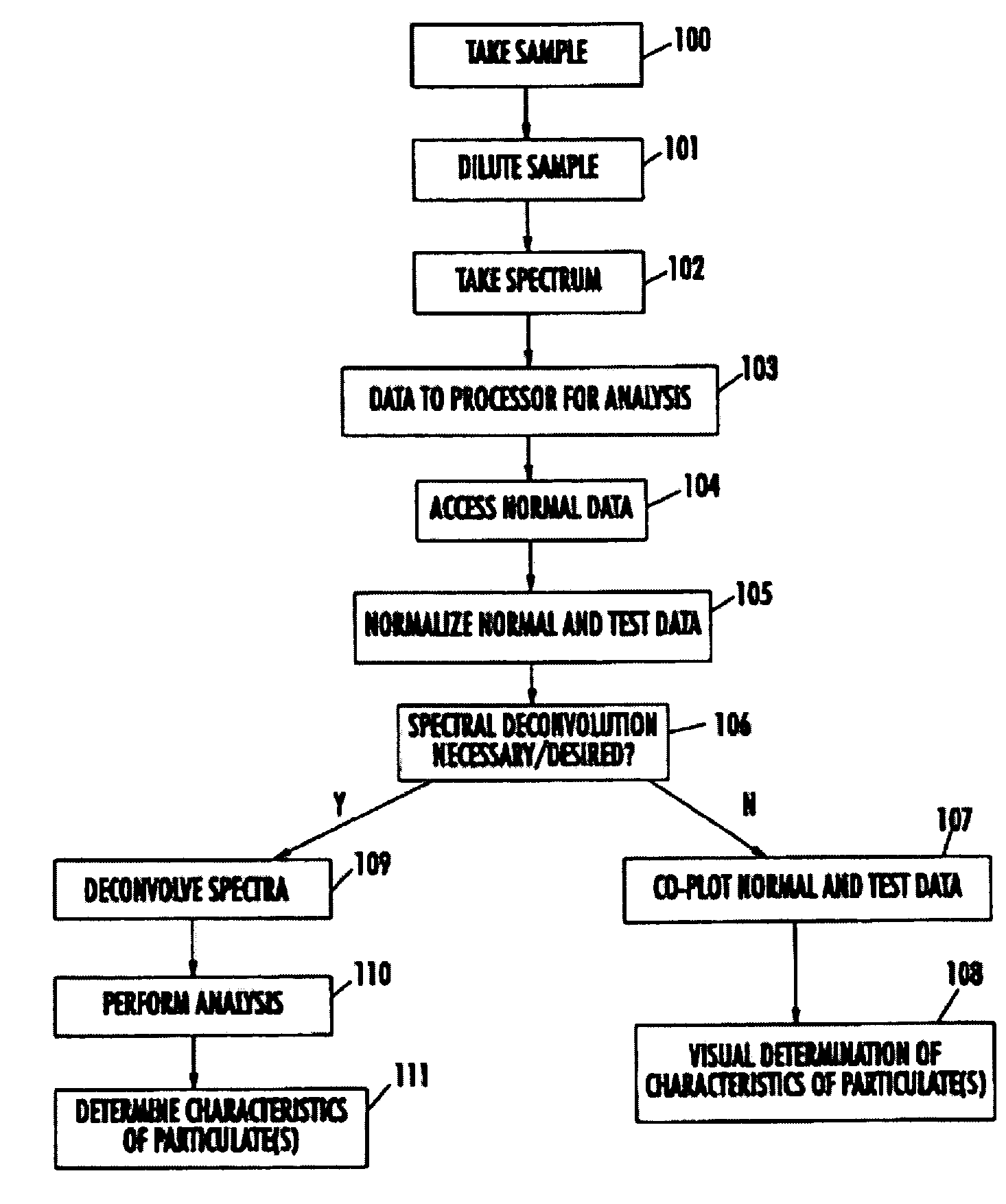
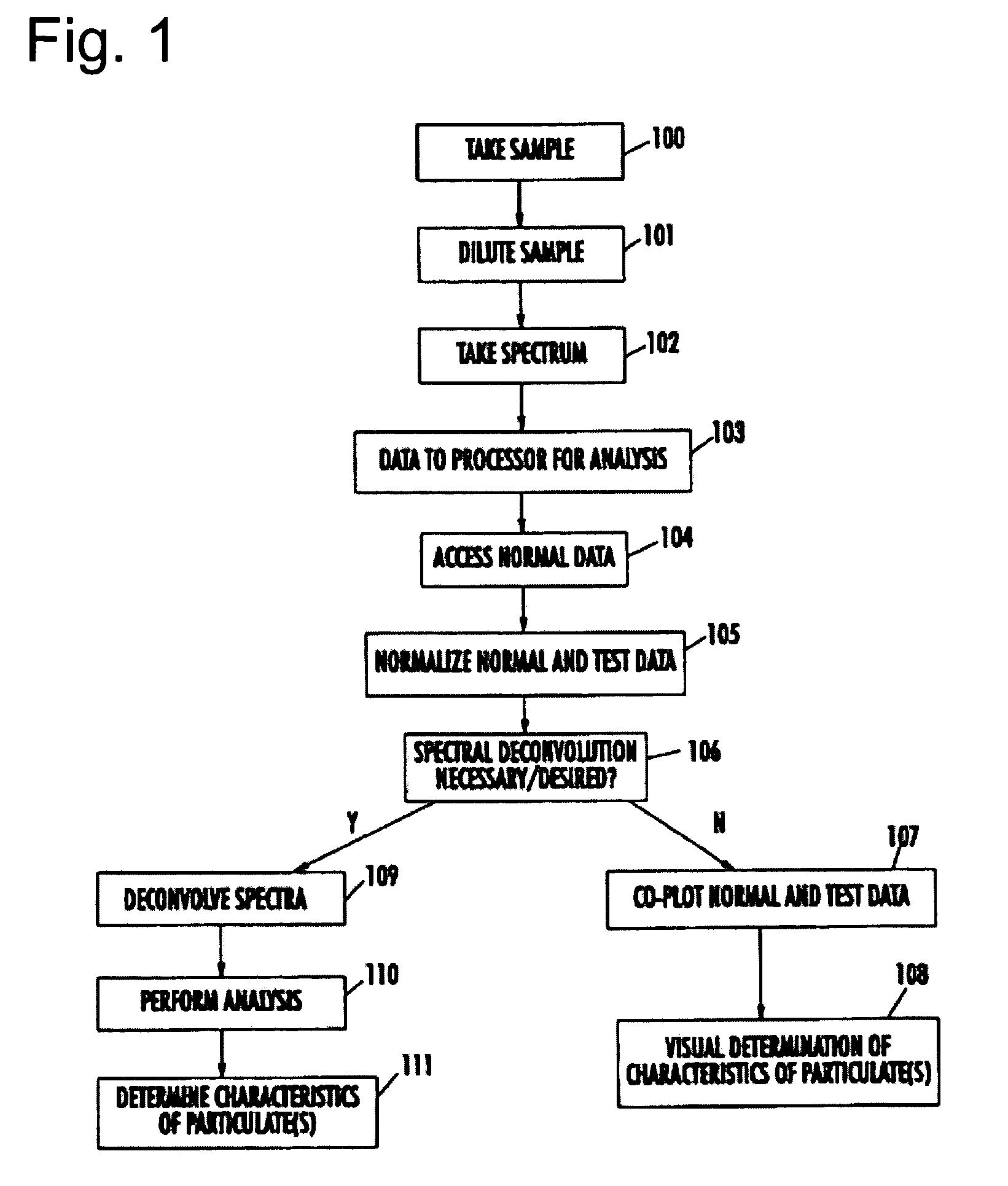
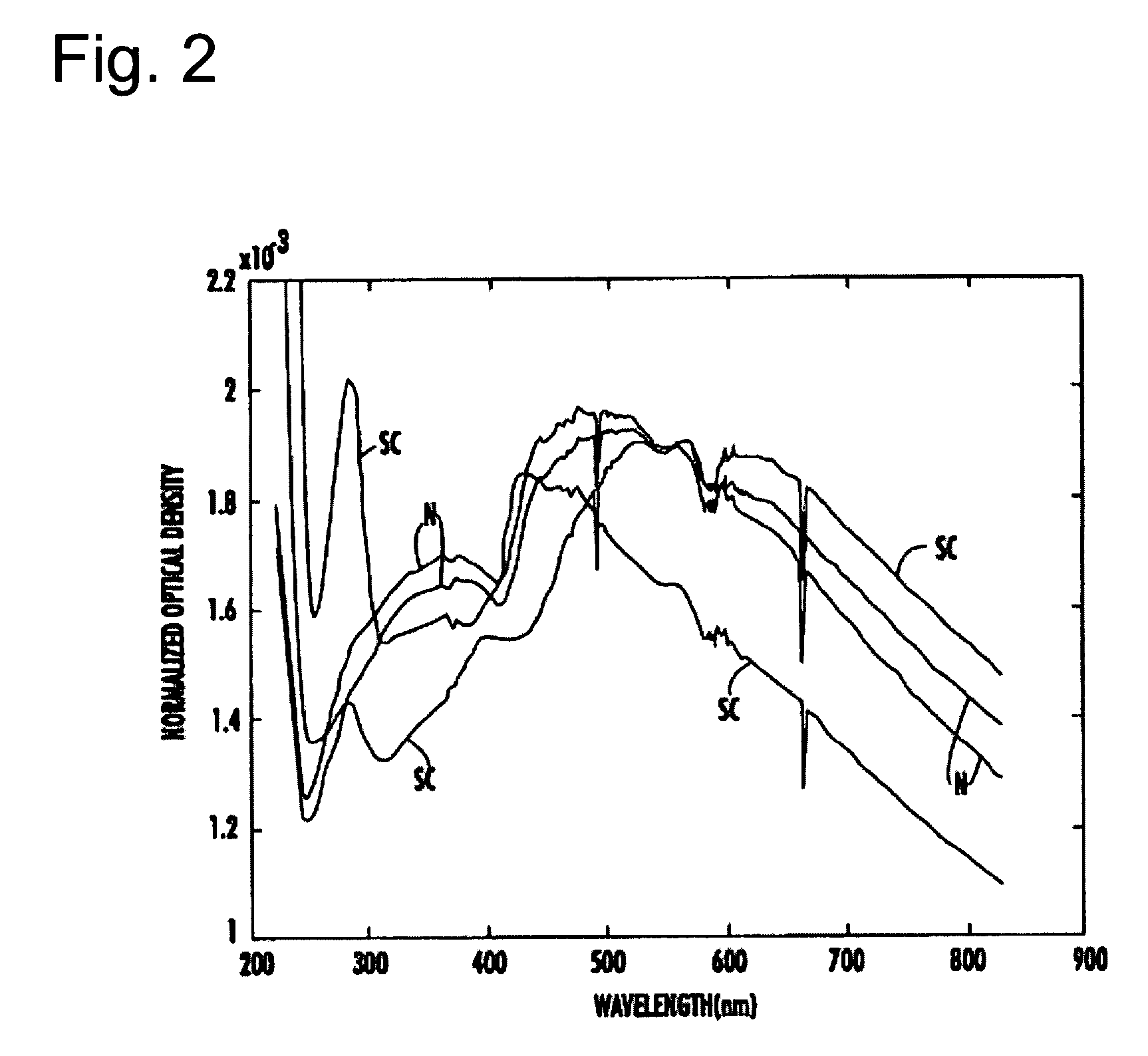
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for the detection of an infectious disease or disorder in a fluid, such as a mammalian blood sample, the detection of a specific protein in a urine sample, or the detection of a particle in a plasma. The identification of the particles of interest is enable by taking a transmission spectrum of a test sample in at least a portion of the ultraviolet, visible, near-infrared portion of the spectrum and comparing the spectrum with a standard sample spectrum. From the comparison it is then determined whether the fluid from the test sample contains an particle of interest, and an identity of the particle of interest is determined. Spectroscopic and multiwavelength turbidimetry techniques provide a rapid, inexpensive, and convenient means for diagnosis. The comparison and determination steps may be performed visually or by spectral deconvolution.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Cyr61 as a Biomarker for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Cancers of Epithelial Origin
ActiveUS20080286811A1Easy diagnosisRaise the possibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisBacteriuriaOncology
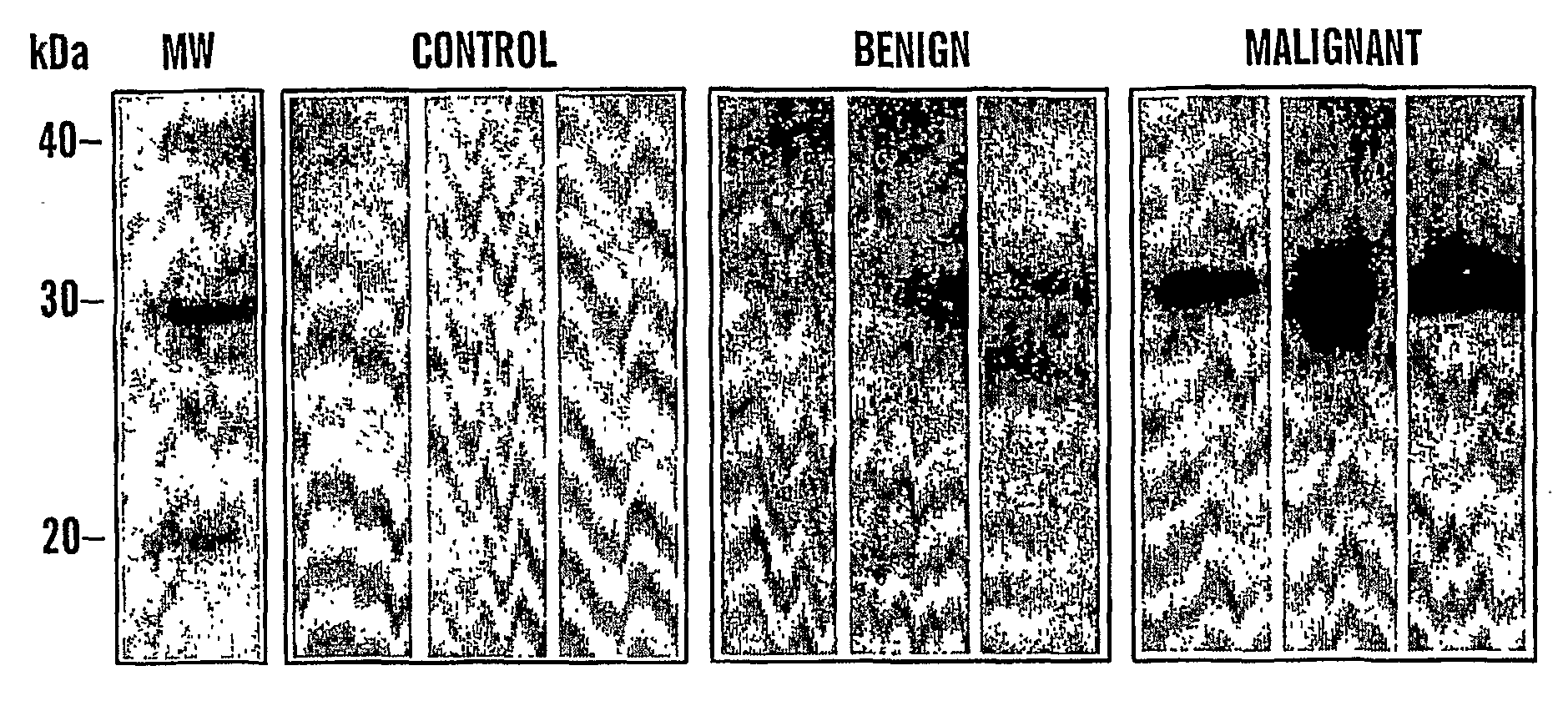
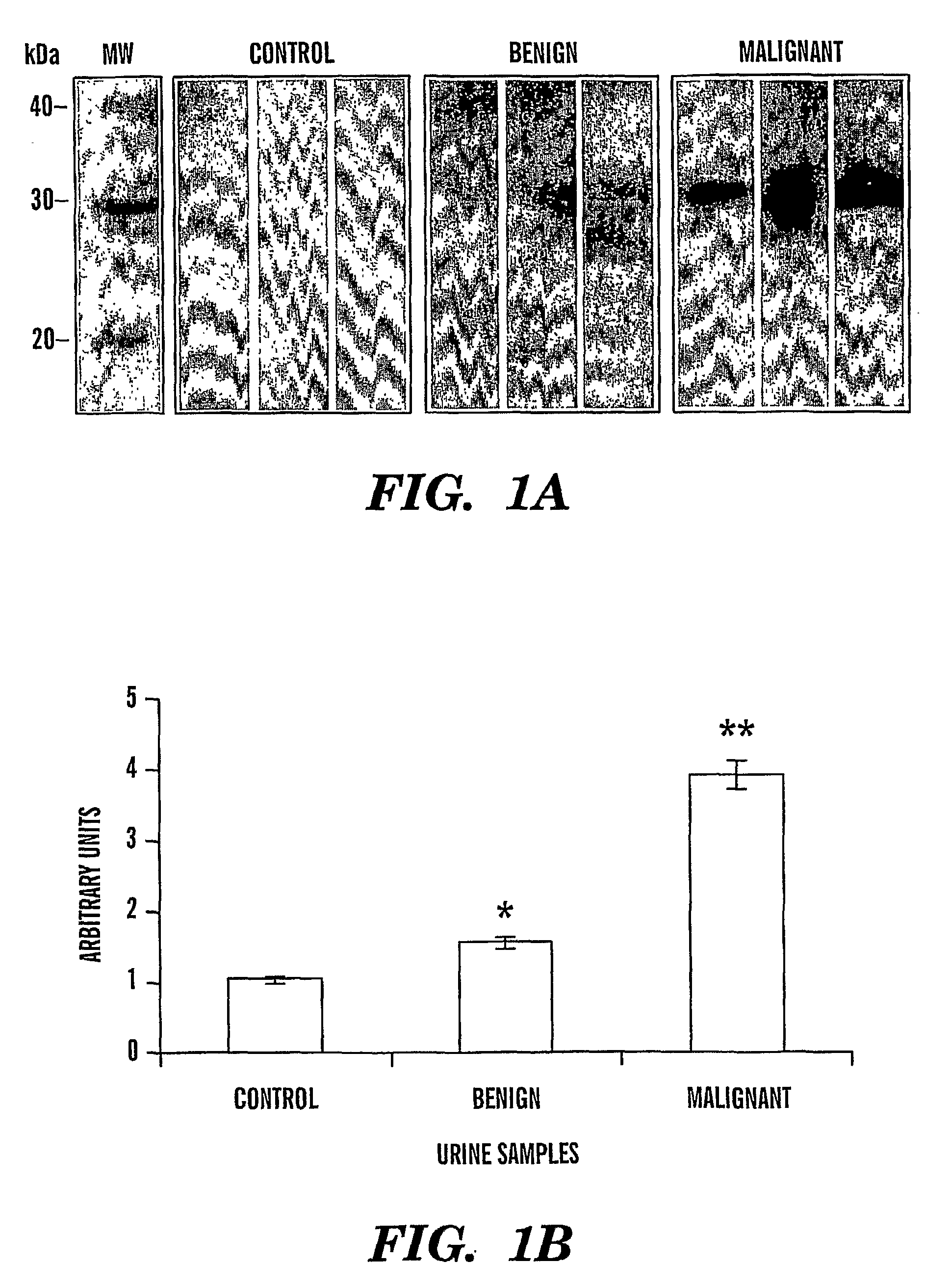
Urinary Cyr61 protein levels are up regulated in patients that have cancers of epithelial origin, i.e. breast cancer and ovarian cancer. Accordingly, the present invention is directed to methods for prognostic evaluation, and diagnosis of cancers of epithelial origin. Further, the amount of Cyr61 protein detected in a urine sample correlates with disease status such that Cyr61 levels can be used to predict the presence of, as well as the metastatic potential of cancer. Thus, measuring the level of Cyr61 in urine provides a quick, easy, and safe screen that can be used to both diagnose and prognose cancer in a patient.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Hydration/dehydration sensor
InactiveUS20100159611A1Reduce and eliminate errorAnalysis using chemical indicatorsChemical analysis using titrationUltimate tensile strengthColor transition
A fluidic assay device or test format that can regulate or control the sample flow rate and modulate the manifestation of test results to reduce or eliminate errors is described. The assay device has a substrate with a flow-rate control zone that regulates the amount of time needed for development and appearance of a visual signal in the observation-feedback zone until the color transition in the detection zone reaches color stability. The present invention also describes absorbent articles incorporating such an assay device and methods of monitoring dehydration or testing ion strength of a urine sample using such a test format.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Urine sample collection device
InactiveUS20060184064A1Easy to useReduce manufacturing costSurgeryBathroom accessoriesUrine CollectionsUrine collection device
Owner:SAMPLE RITE
Diagnosis of preeclampsia
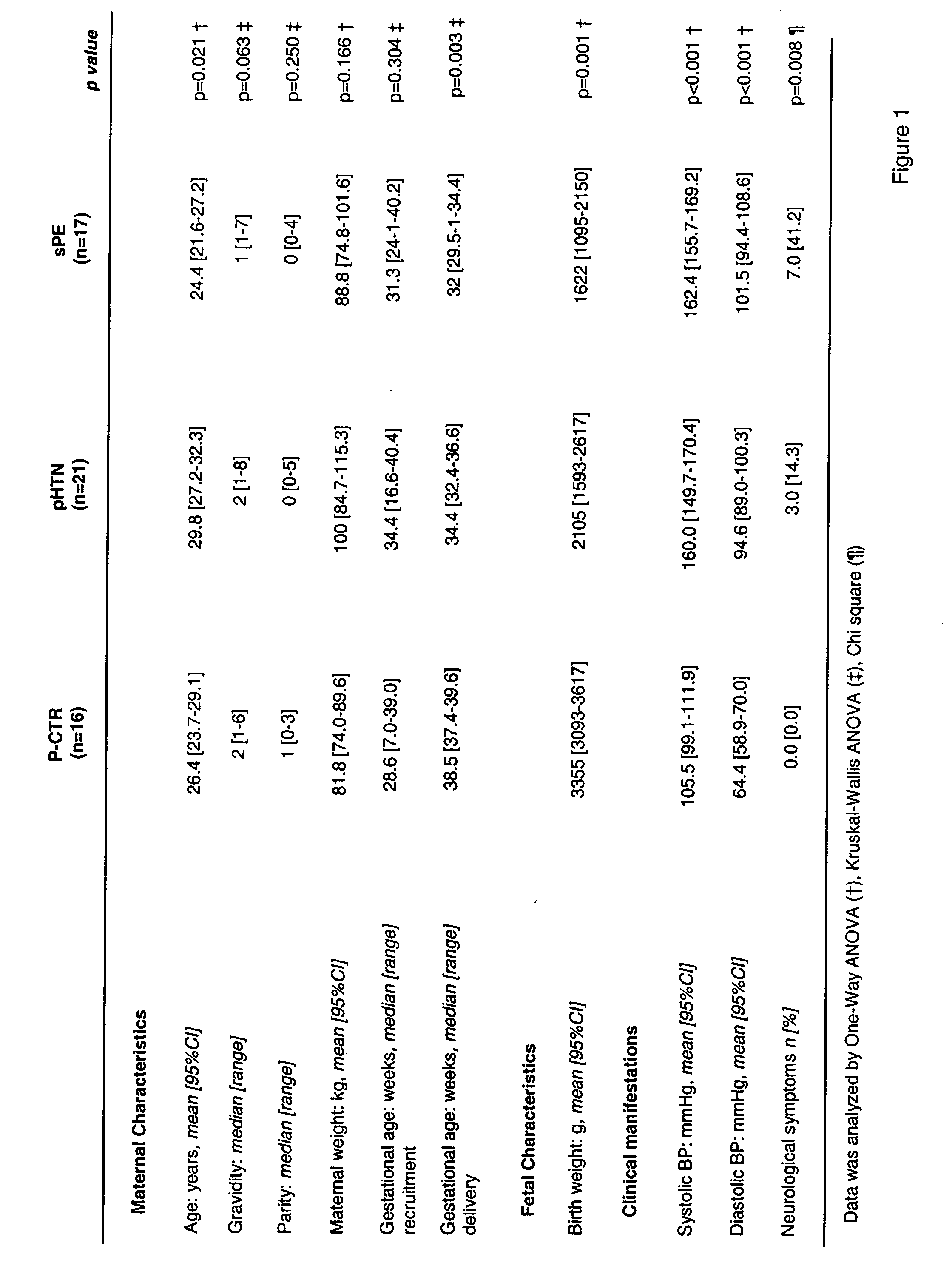
ActiveUS20060183175A1Reduce needRaise the possibilityPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide sourcesDiseaseThird trimester
The present invention provides methods and compositions related to the detection and / or monitoring of the levels of angiogenic factors, specifically VEGF, PlGF and sFlt-1, in urine samples obtained from pregnant women and the effects of such levels on the risk of developing complications of pregnancy, including hypertensive disorders such as preeclampsia, in the first, second, and / or third trimester of pregnancy. The present invention also provides kits for identifying and screening patients at risk of developing a complication of pregnancy, such as preeclampsia.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Methods for detection of nucleic acid sequences in urine
InactiveUSRE39920E1Reduce DNA degradationReducing DNA degradationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetics predispositionNon invasive
Described are non-invasive methods of detecting the presence of specific nucleic acid sequences as well as nucleic acid modifications and alterations by analyzing urine samples for the presence of transrenal nucleic acids. More specifically, the present invention encompasses methods of detecting specific fetal nucleic acid sequences and fetal sequences that contained modified nucleotides by analyzing maternal urine for the presence of fetal nucleic acids. The invention further encompasses methods of detecting specific nucleic acid modifications for the diagnosis of disease, such as cancer and pathogen infections, and detection of genetic predisposition to various disease. The invention specifically encompasses methods of analyzing specific nucleic acid modifications for the monitoring of cancer treatment. The invention further encompasses methods of analyzing specific nucleic acids in urine to track the success of transplanted cells, tissues and organs. The invention also encompasses methods for evaluating the effects of environmental factors and aging on the genome.
Owner:TROVAGENE
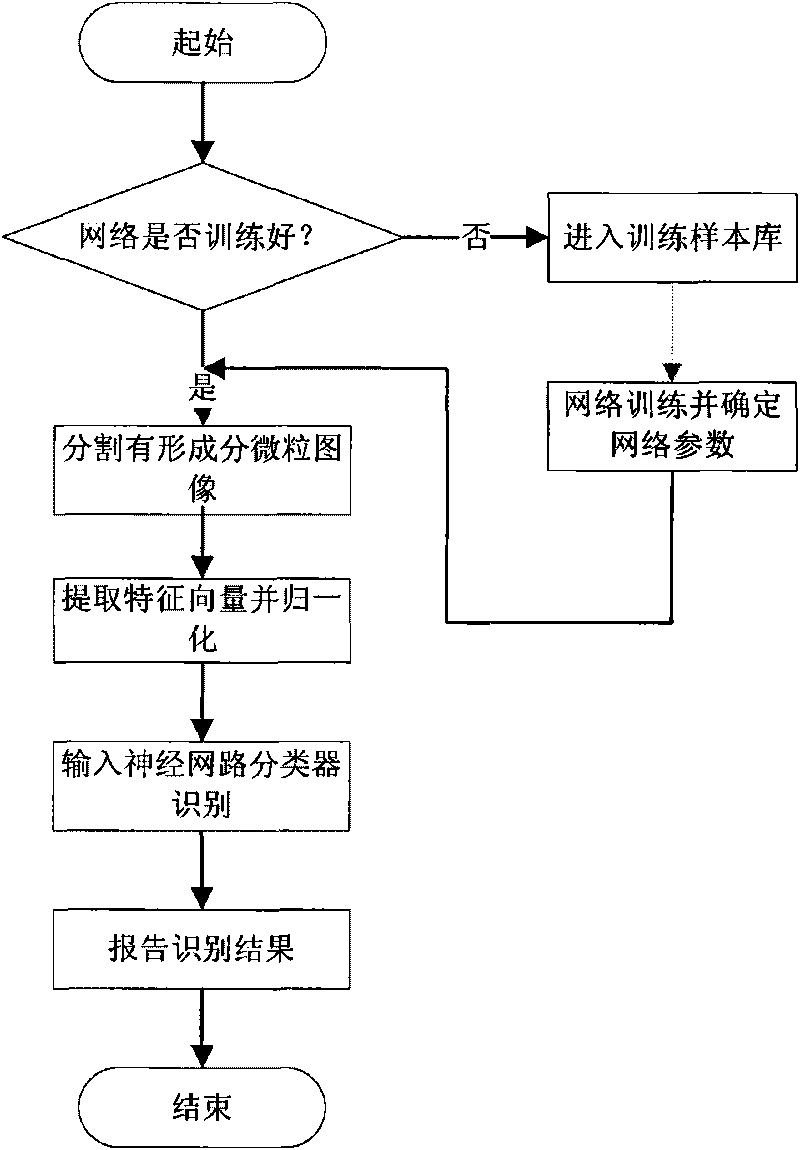
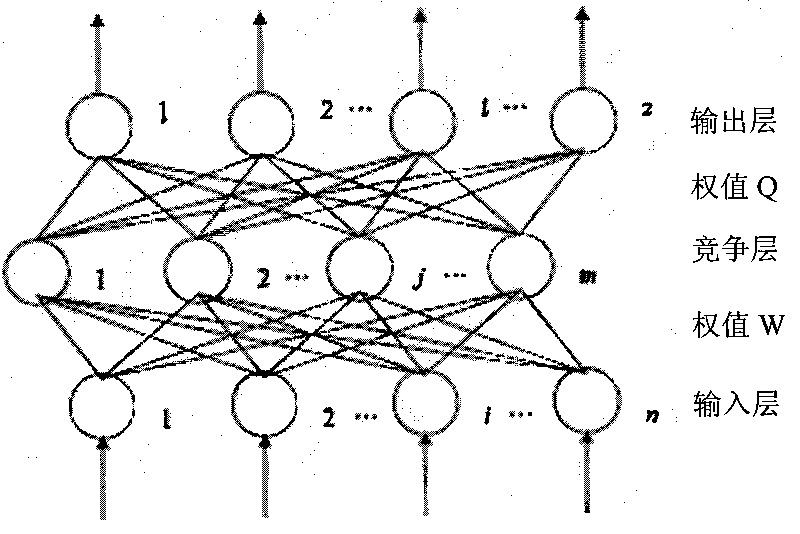
Neural network-based method for identifying and classifying visible components in urine
ActiveCN101713776AQuick Auto DetectHigh speedImage analysisNeural learning methodsNerve networkClassification methods
The invention relates to a neural network-based method for identifying and classifying visible components in urine, and belongs to a method for identifying and classifying the visible components in the urine. The method comprises the following steps: shooting an image of a urine sample with a flowing microscope system in urinary sediment detection equipment, and transmitting the image to a memoryof a urinary sediment image workstation; segmenting the shot image in the step 1 to form visible component particle images of the urine, calculating shape and texture feature vectors of the segmentedvisible component particle images in the step 2, and taking the vectors as input of an intelligent neural network; and receiving the feature vectors of the visible component particle images to be identified, normalizing to a range of [0,1], and inputting the trained intelligent neural network for identification. The method has high identification rate and low false positive rate, and greatly improves the accuracy and objectiveness of identifying the visible components in the clinical urine. Meanwhile, the workload of doctors is greatly lightened, and the standardization and automation of detecting the visible components in the urine are realized.
Owner:DIRUI MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Methods of detecting cancer cells in biological samples
InactiveUS20040197839A1Preparing sample for investigationBiological testingBladder cancerBacteriuria
The invention provides methods of detecting cancerous cells in biological samples using a double staining / dual imaging approach, which can be used to diagnose cancer. More specifically, the present invention provides methods of diagnosing bladder cancer by a simultaneous scanning of cell morphology and FISH signals of cells derived from a urine sample.
Owner:BIOVIEW
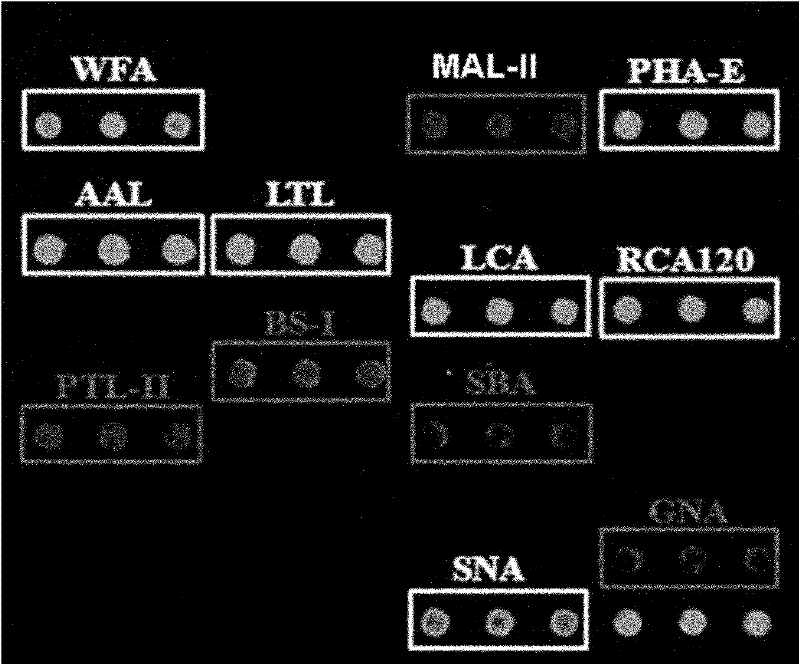
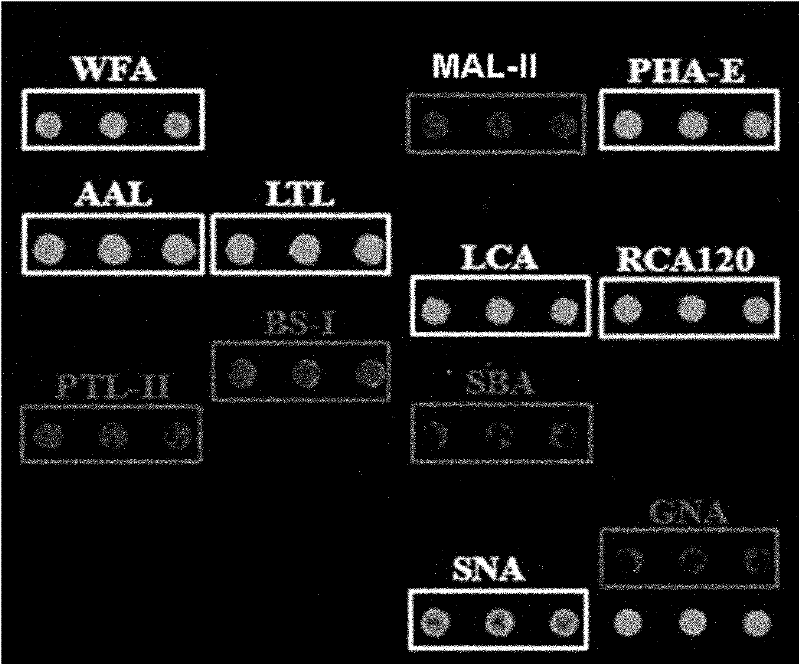
Method for detecting alternative biological markers of liver neoplasms in saliva, serum and urine
The invention provides a method for detecting alternative biological markers of liver neoplasms in saliva, serum and urine so as to detect expression information of alternative biological markers of liver neoplasms in a rapid, convenient and accurate manner. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: 1) preparing agglutinin chips corresponding to detection of saliva, serum and urine samples respectively; 2) pretreating stock solutions of saliva, serum and urine samples, removing impurities and purifying proteins, labeling by using a fluorescent reagent and removing redundant fluorescence by using G-25 columns to obtain corresponding samples to be detected; and 3) respectively loading three samples to be detected onto corresponding agglutinin chips to obtain respective glycoprotein sugar chain spectrum in each sample to be detected, and obtain information of the alternative biological markers according to reaction results of any sample to be detected. By the method, the sensibility during detection is high and detection results are accurate; moreover, the method has the advantages of safety, no damage, convenience for sample collection, simplicity in storage and the like.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Detection of biological molecules
InactiveUS20060096870A1Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHigh concentrationCorrelation coefficient
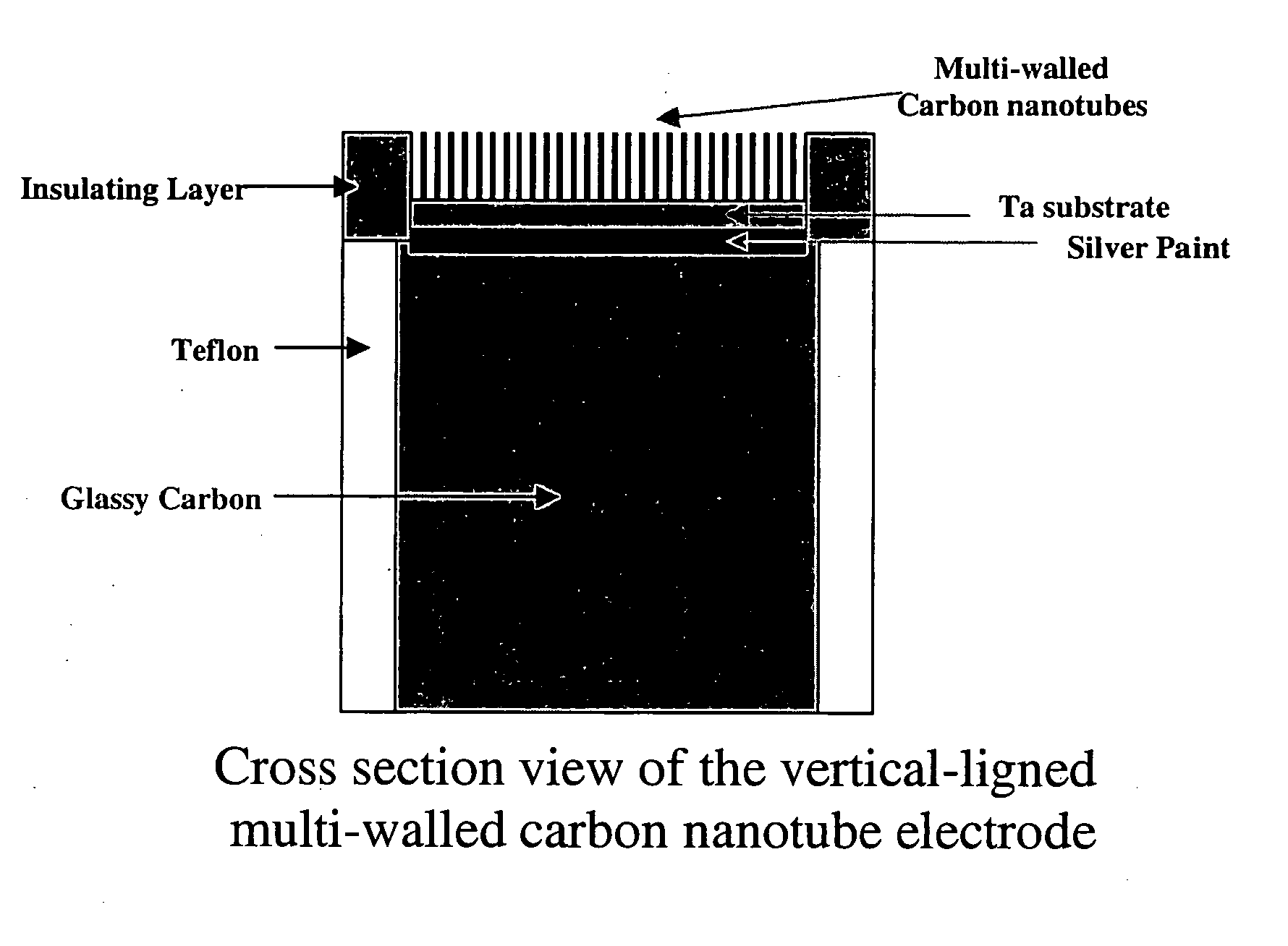
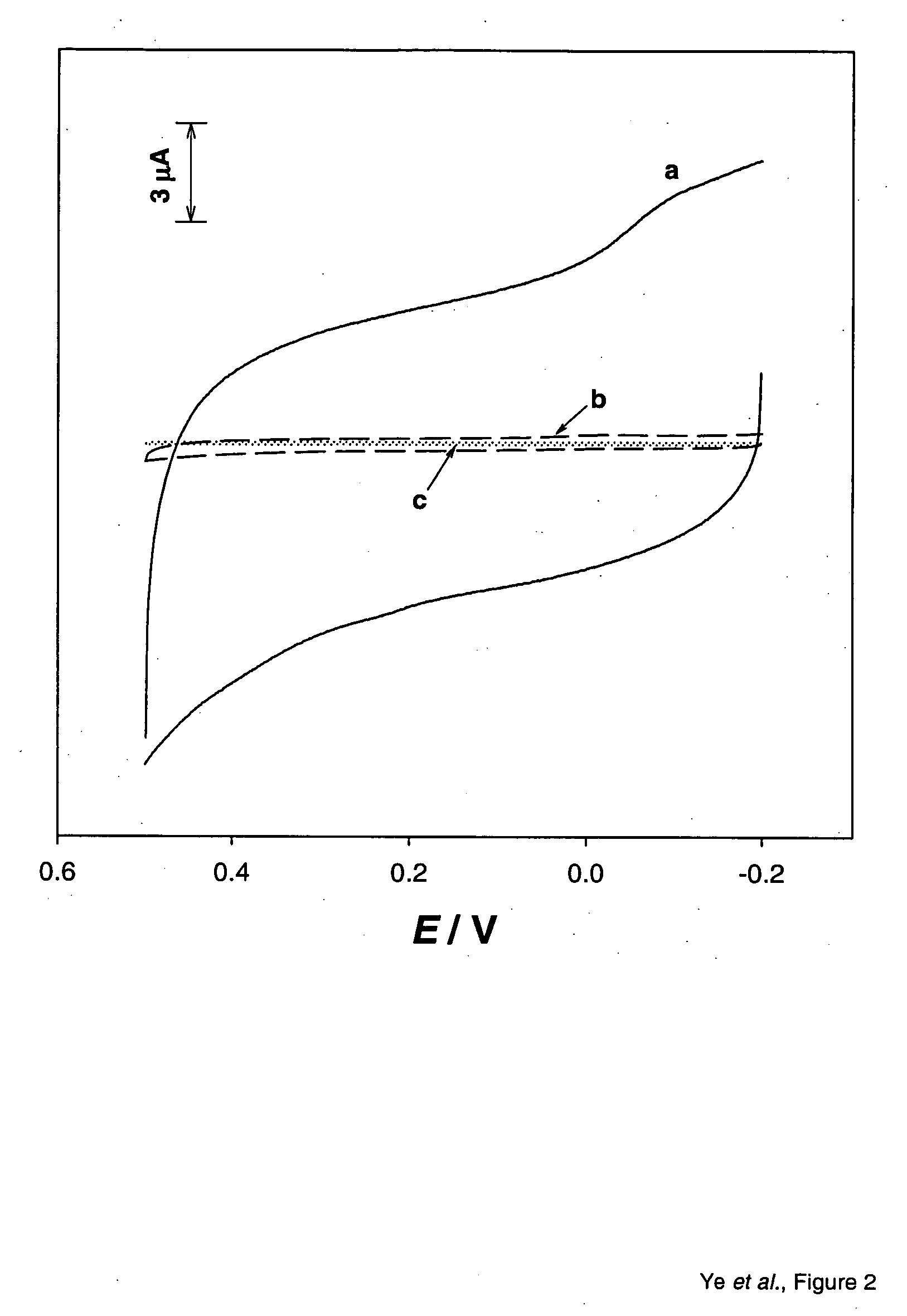
An apparatus uses carbon nanotubes for electrochemical analysis of biological molecules of interest such as Uric Acid, illustrating how the voltammetric behaviors of uric acid (UA) and L-ascorbic acid (L-AA) at a well-aligned, carbon nanotube, electrode may be used in a biochemical assay. Compared to glassy carbon, a carbon nanotube electrode reduces troublesome overpotentials. Based on its differential catalytic function toward the oxidation of UA and L-AA, the carbon nanotube electrode can be used for a selective determination of UA in the presence of L-AA. The peak current obtained from DPV was linearly dependent on the UA concentration in the range of 0.2 μM to 80 μM with a correlation coefficient of 0.997. The detection limit (3δ) for UA was found to be 0.1 μM. The device allows for detection of UA in a human urine sample, even in the presence of high concentrations of L-AA, using only simple dilution.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
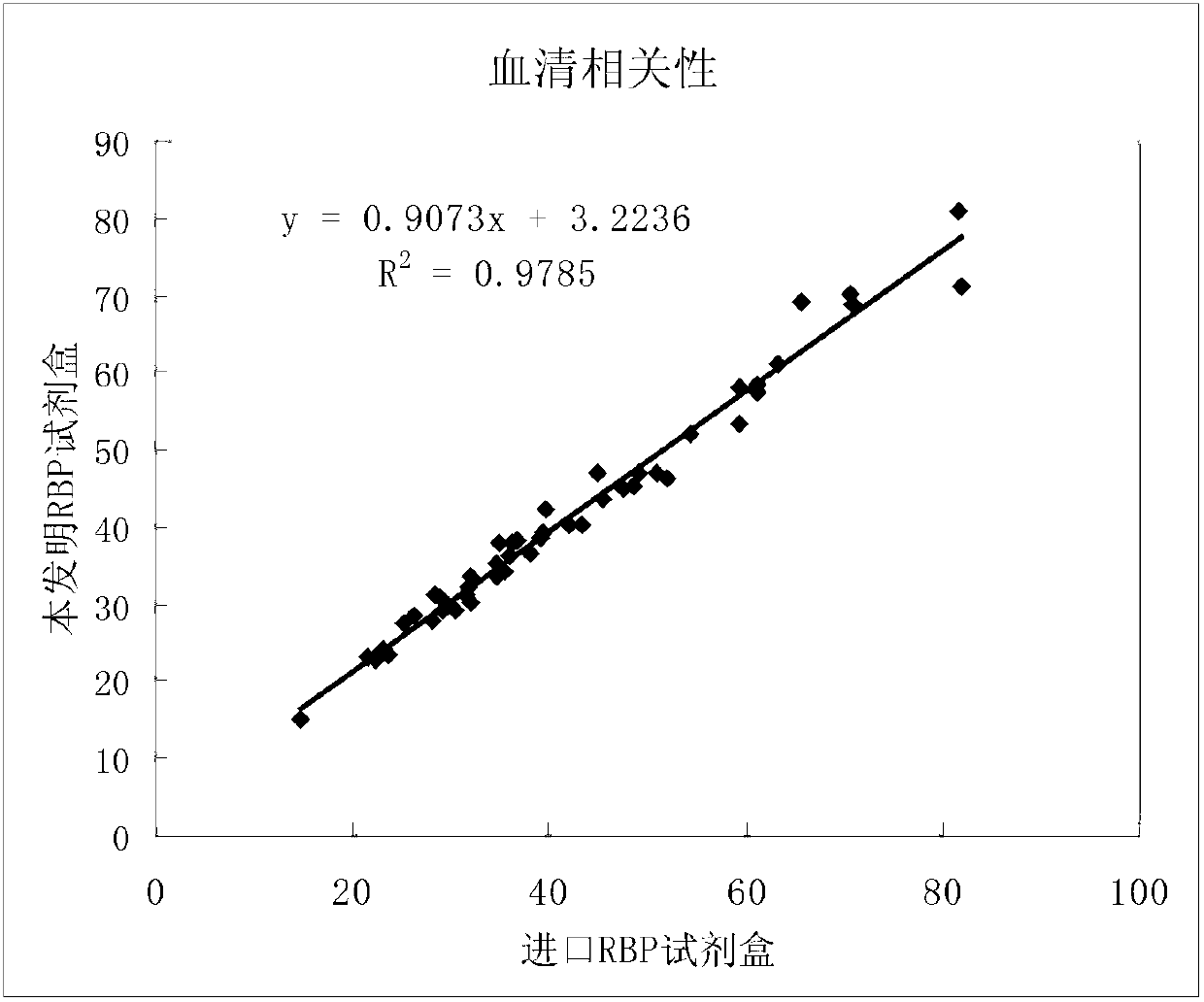
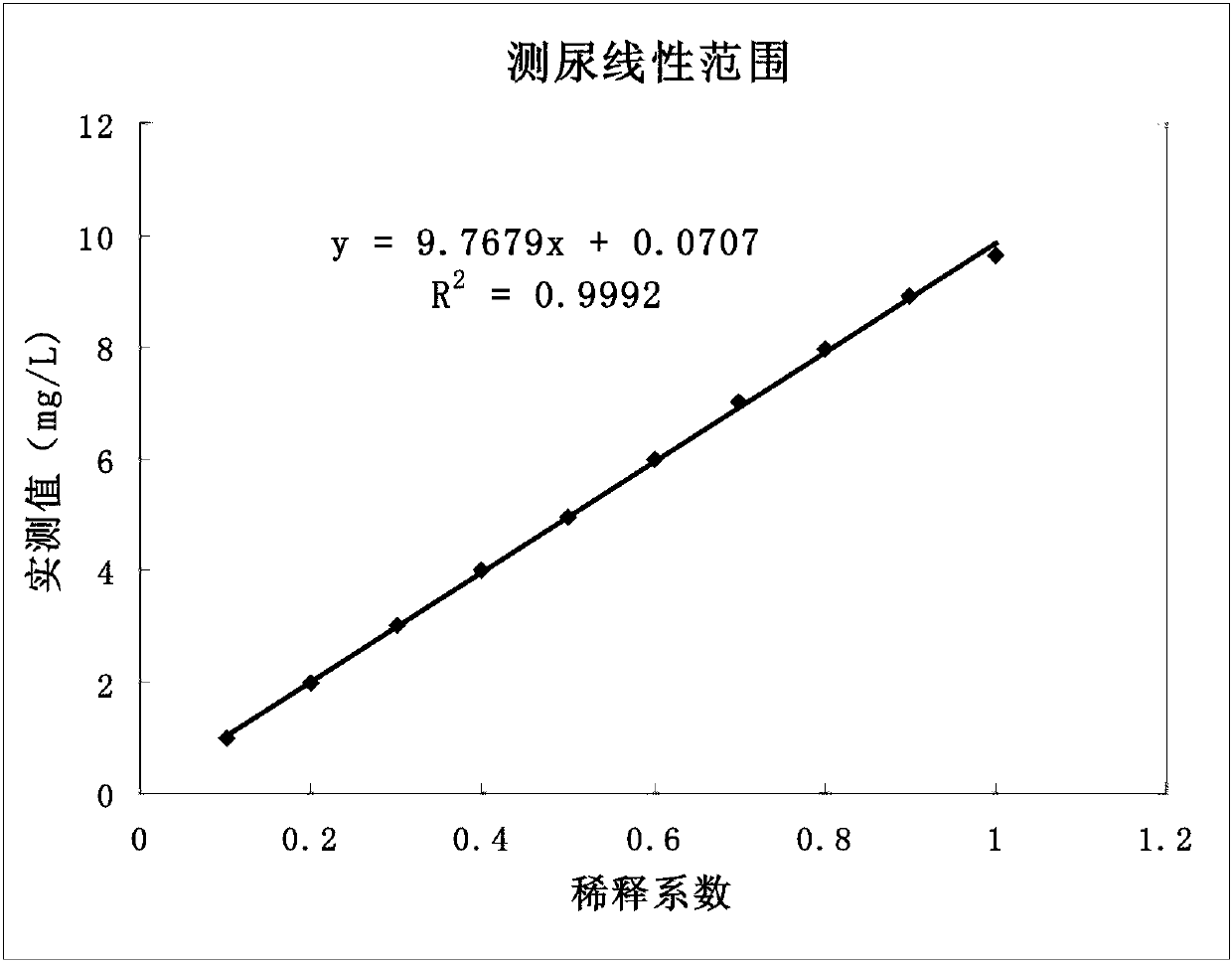
Double antibody latex enhanced retinol binding protein detection kit
The invention relates to a double antibody latex enhanced retinol binding protein detection kit. More specifically, the invention discloses a double antibody coating latex enhanced immunoturbidimetry kit for detecting retinol binding protein. The kit contains a reagent 1, a reagent 2 and a calibrator. Paring monoclonal antibody A and B are respectively coated on latex particles. Coated antibody is bonded with RBP to be detected, and a plurality of bonders are aggregated together to form detectable turbidity change. The detection kit provided by the invention has high sensitivity, can be used to detect urine samples and serum samples and can be used as nutritive index to detect RBP in serum. Simultaneously, through the detection of RBP in urine, the kit is sensitive to the damage degree of renal proximal tubule.
Owner:BEIJING STRONG BIOTECH INC
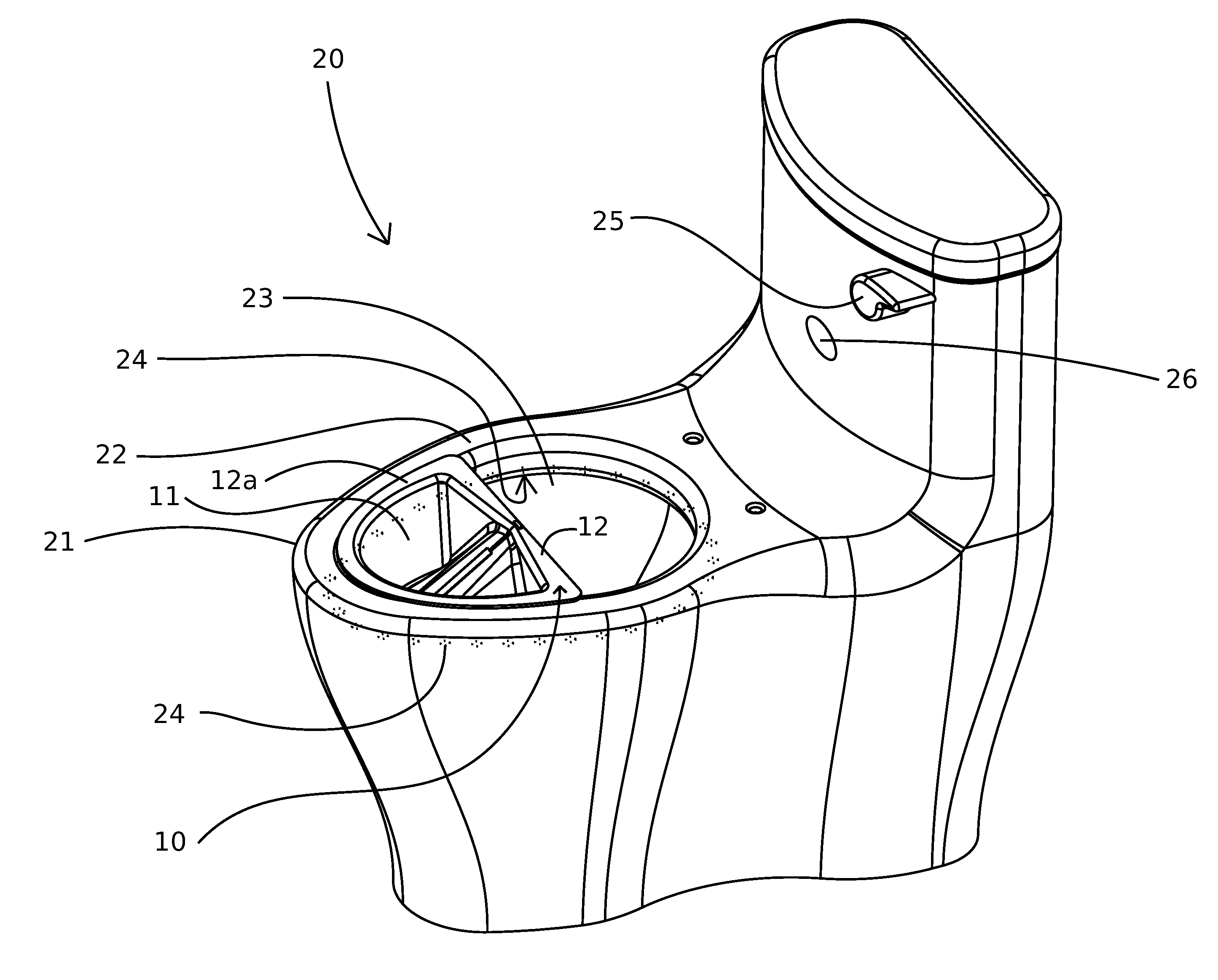
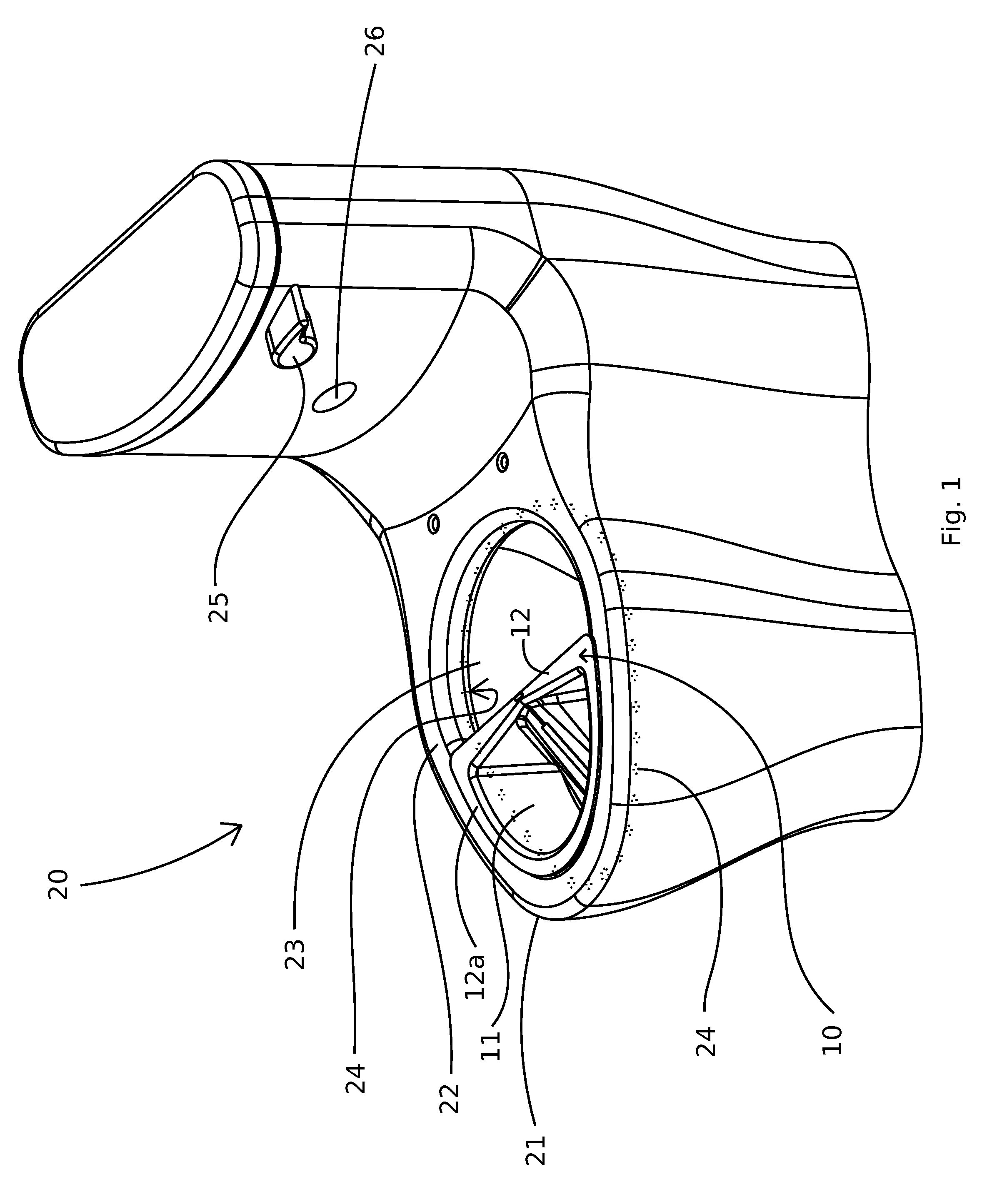
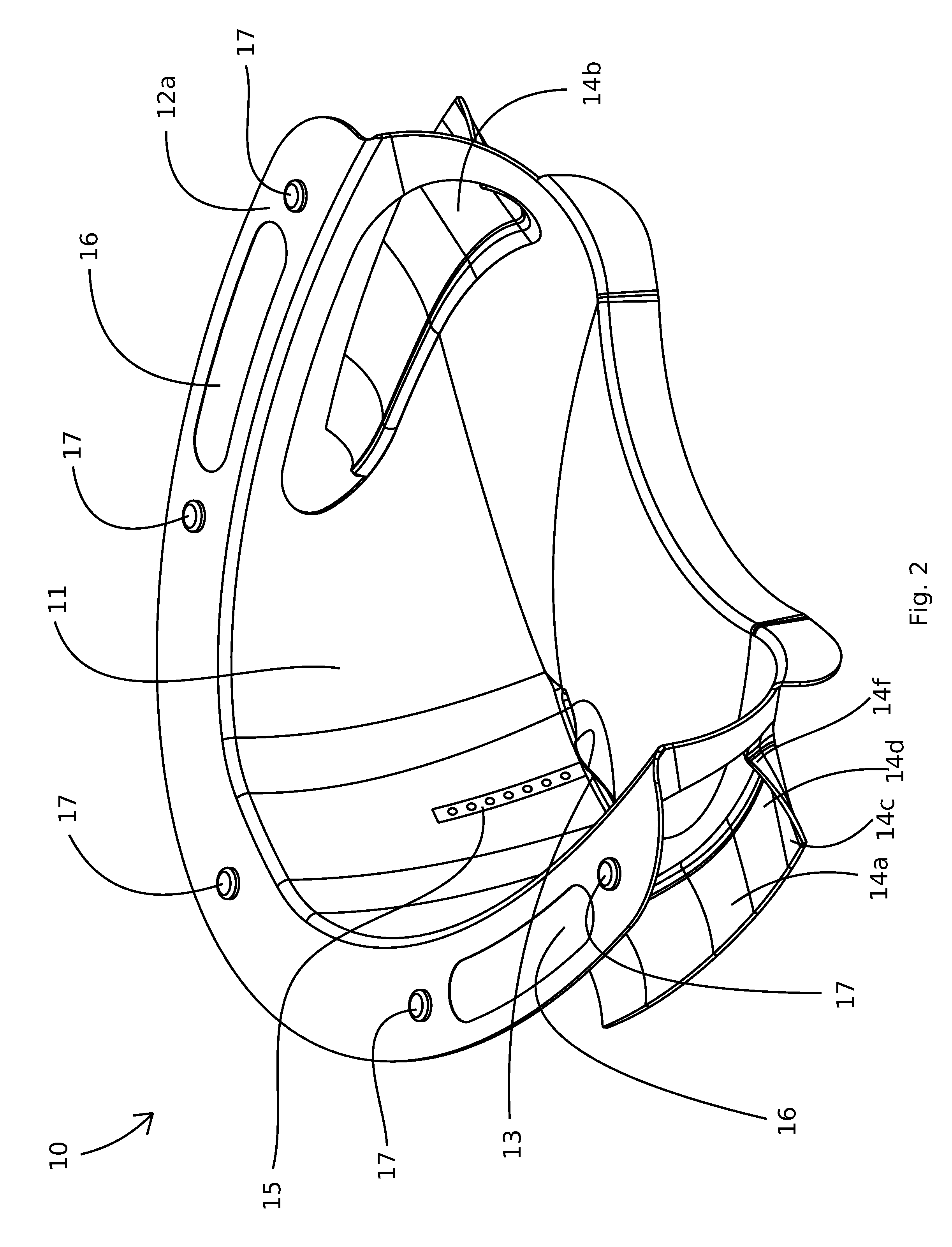
Toilet based urine analysis system
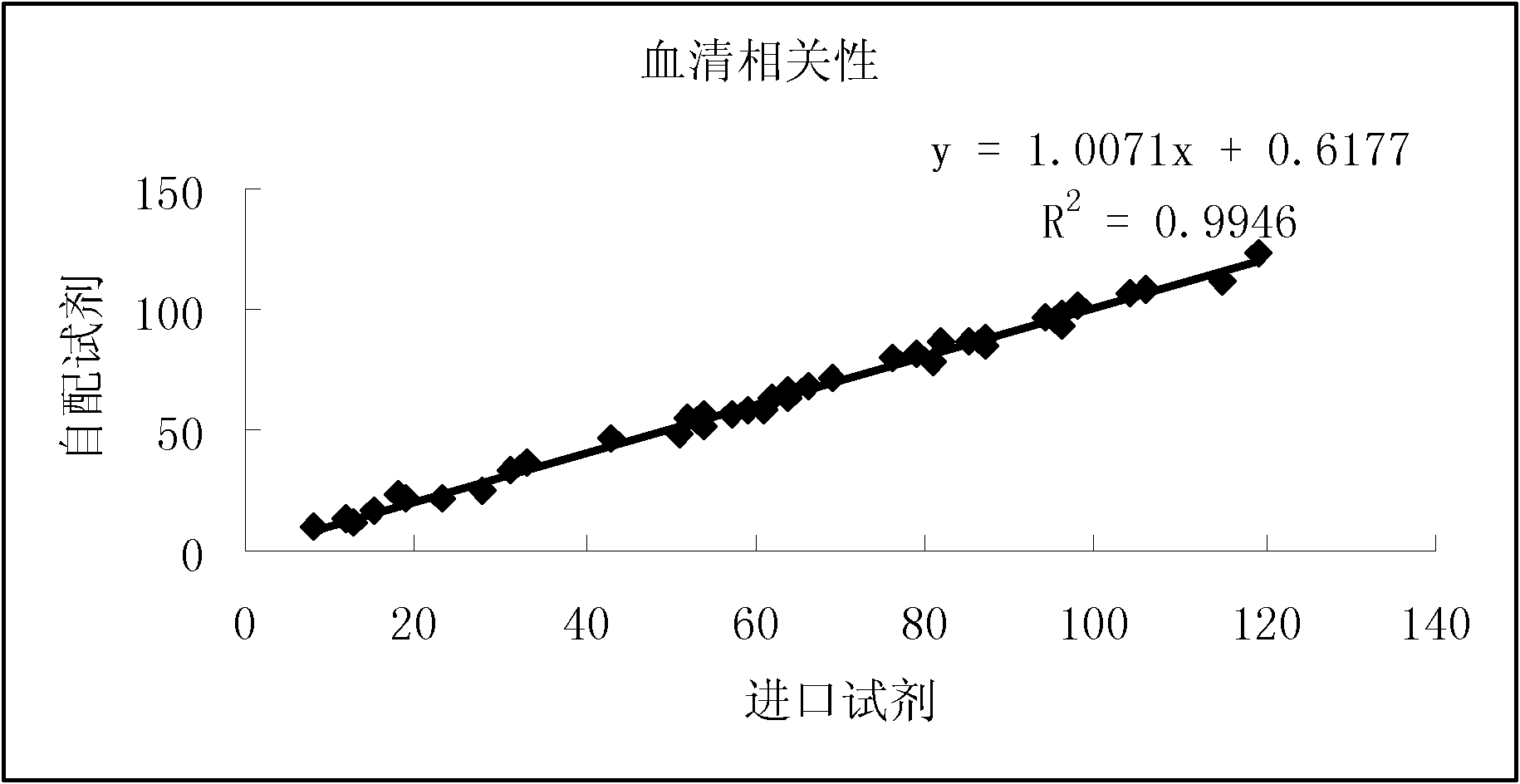
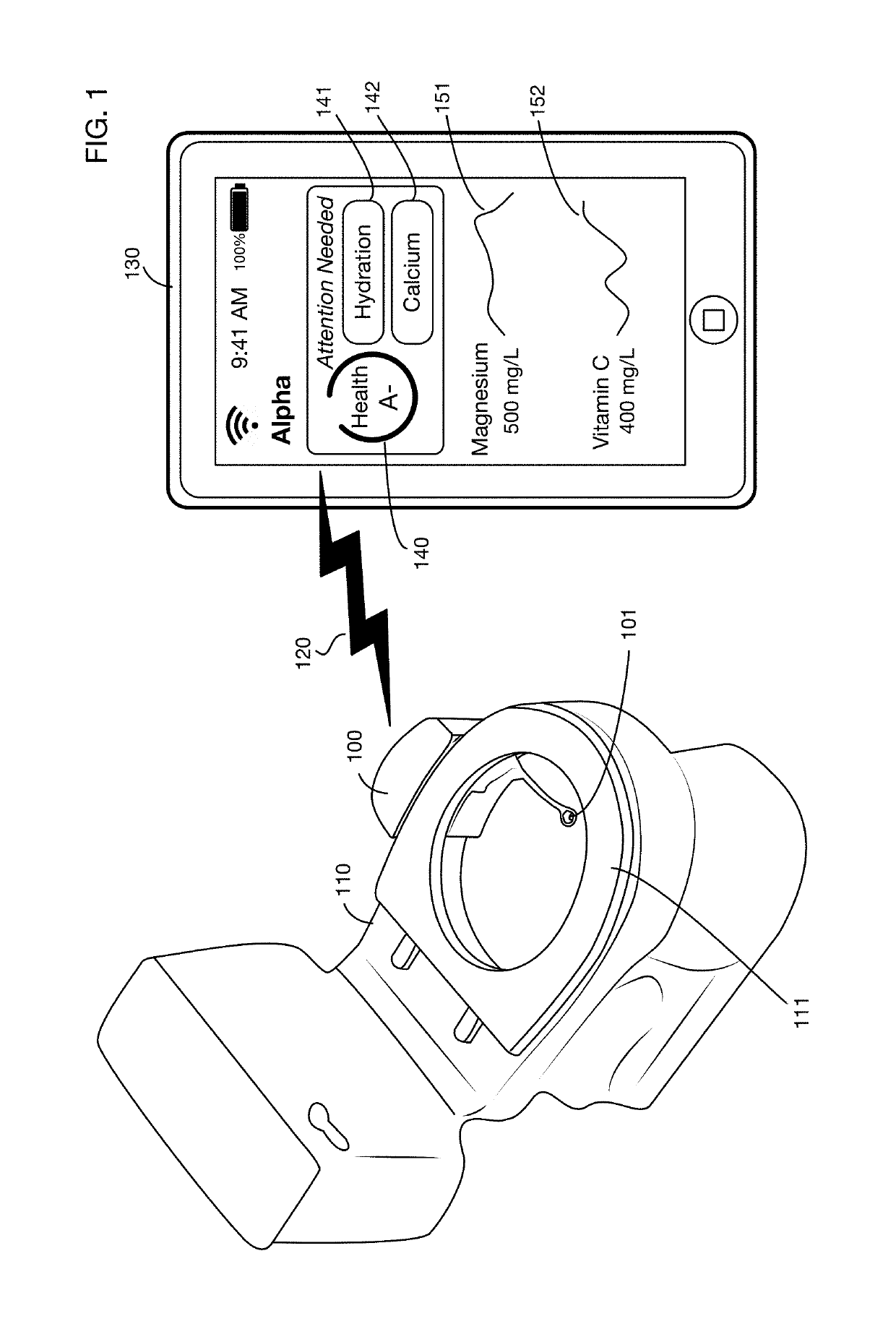
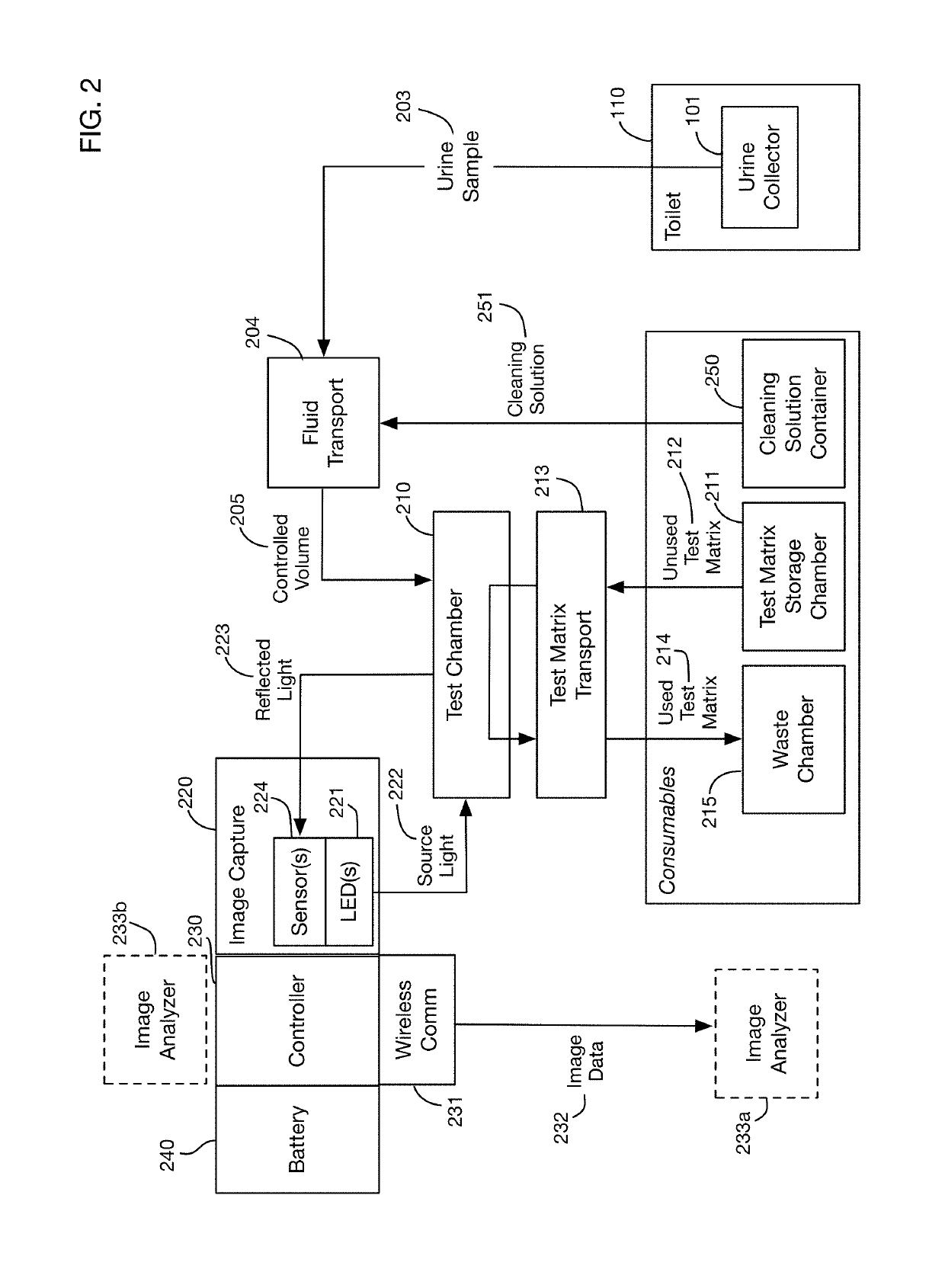
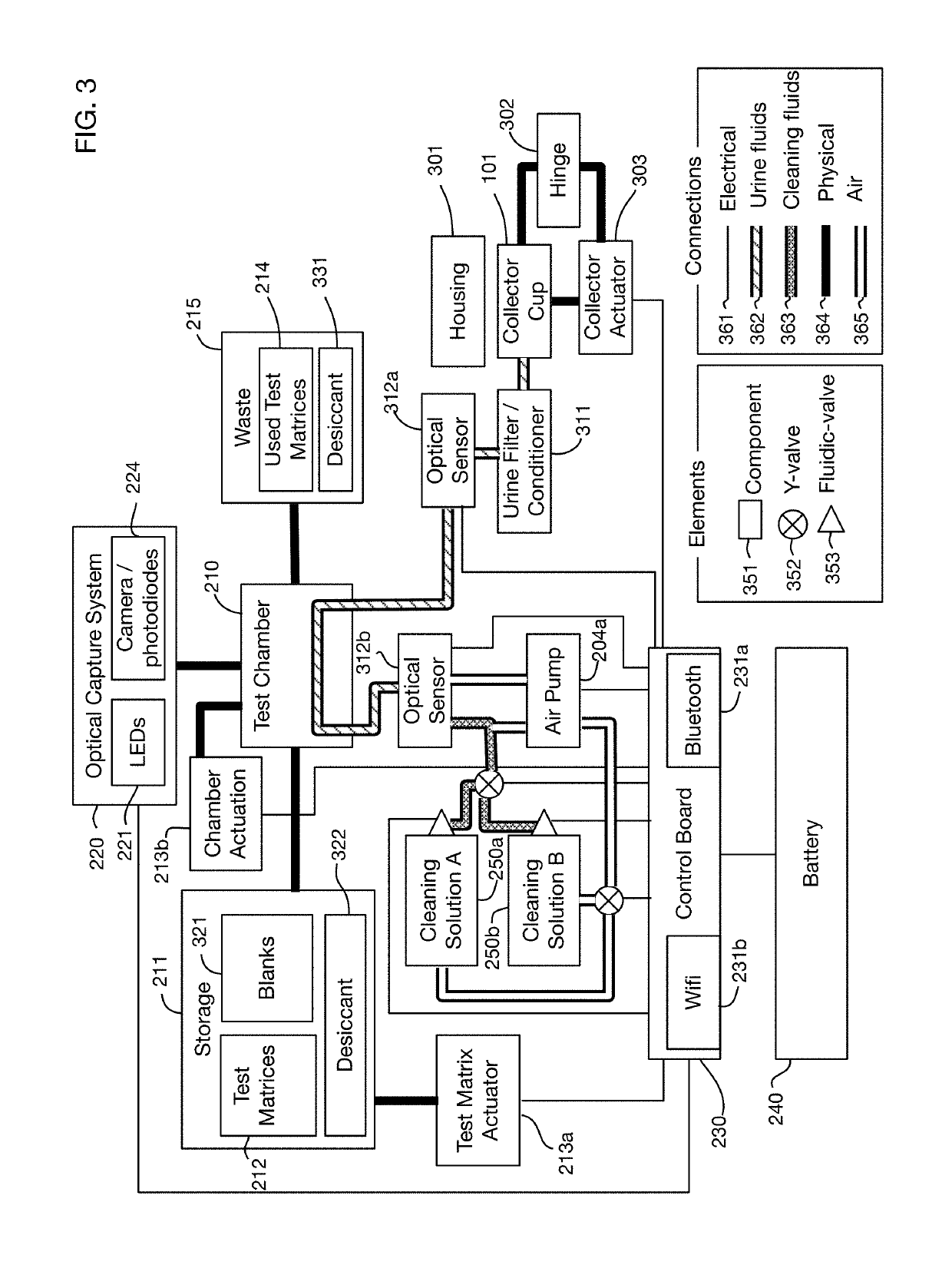
Urine analysis system that couples or integrates with a toilet. Wirelessly links to a computer, such as a user's mobile device to accept control inputs and report urine test results. Accepts user input to initiate testing and deploys a urine collector into the toilet bowl above the water to collect a urine sample. The collected urine sample is dispensed onto multiple regions of a test matrix that may perform many urine tests simultaneously. A single test matrix may include multiple types of tests, such as immunochromatography and colorimetric assays. An optical imaging system detects reaction of the urine with reagents integrated into the test matrix. Analysis of images may be performed locally or on a remote server. The system may store an inventory of test matrices to support daily testing for long durations, for example 6 months or more before refilling.
Owner:BLOOM HEALTH INC
Methods of identifying responders to dopamine agonist therapy
The present invention is directed to a method of identifying patients to be treated by dopamine agonist therapy comprising the step of analyzing a plasma or urine sample from said patient for concentrations of norepinephrine (NE), norepinephrine metabolites (NE metabolites), dopamine, dopamine metabolites, serotonin, serotonin metabolites, or fasting triglycerides, wherein one or more of: (a) NE metabolites, (b) NE / NE metabolites: dopamine / dopamine metabolites, (c) NE and serotonin, (d) NE / NE metabolites and serotonin, (e) NE and serotonin metabolites, (f) NE / NE metabolites and serotonin metabolites, or (g) NE is / are greater than about 30% over normal level; or dopamine / dopamine metabolites are less than about 30% below normal; or said patient has hypertriglyceridemai and / or hypertension . The present invention is also directed to treating identified patients with dopamine agonist therapy.
Owner:VEROSCI
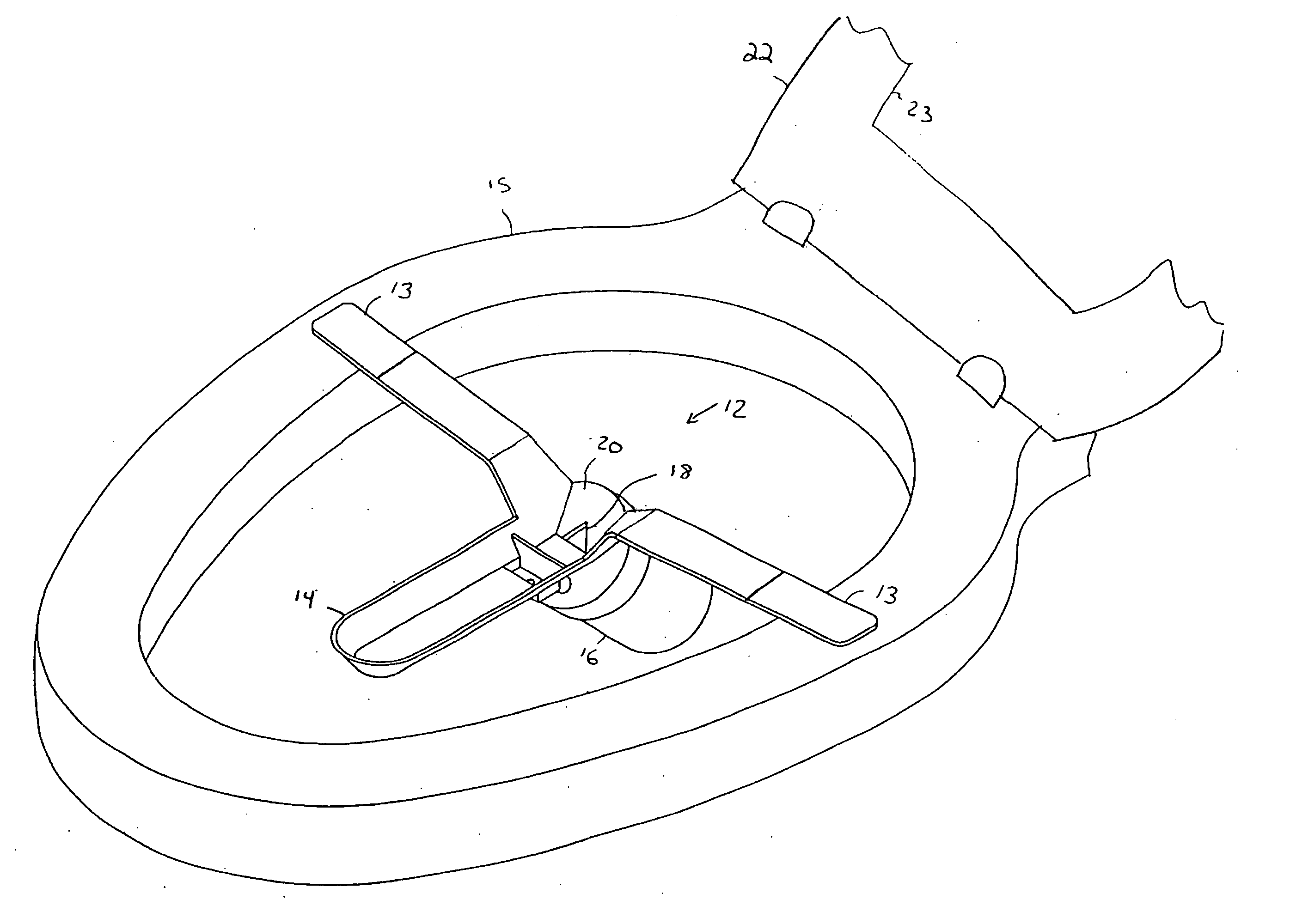
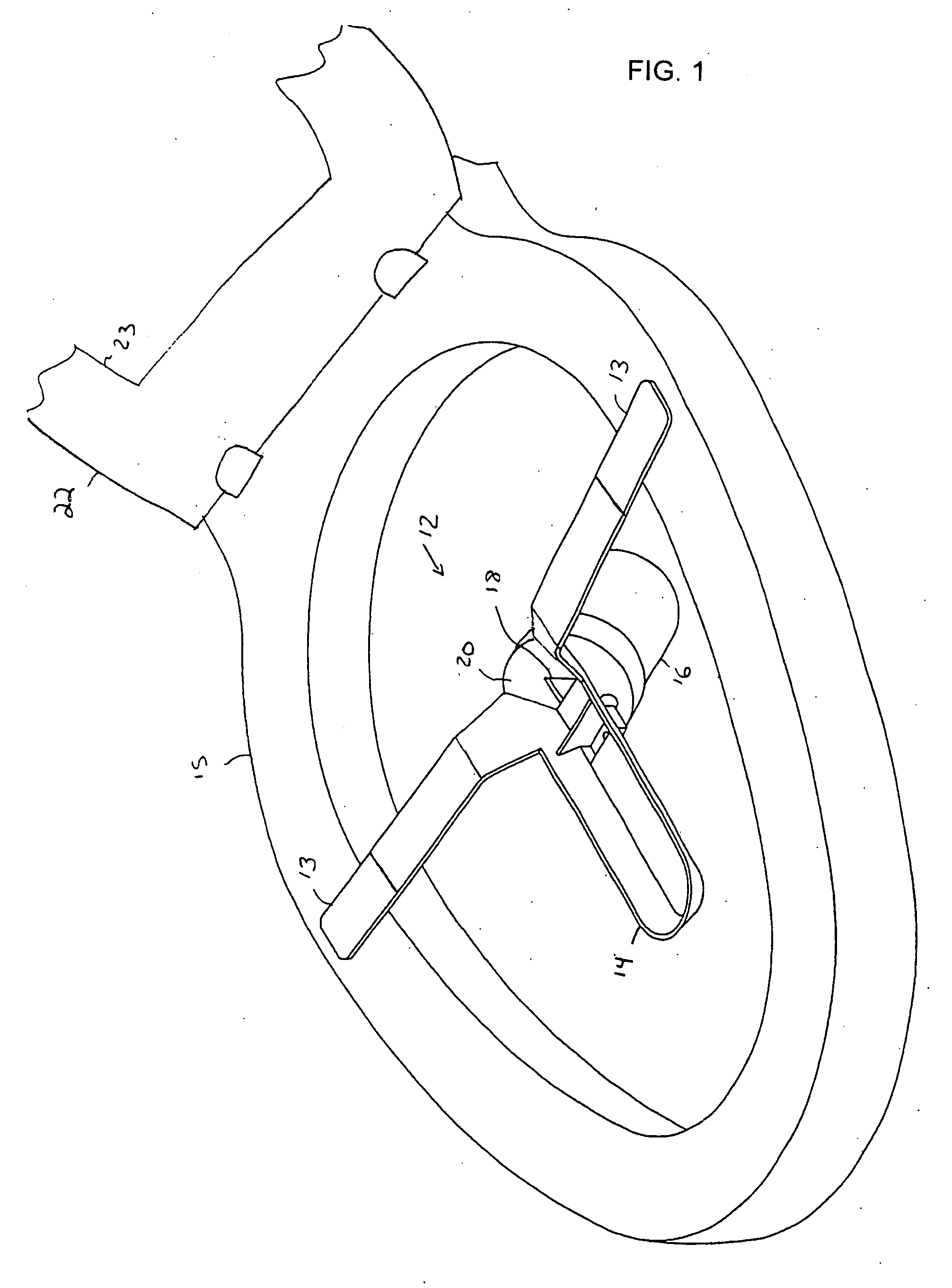
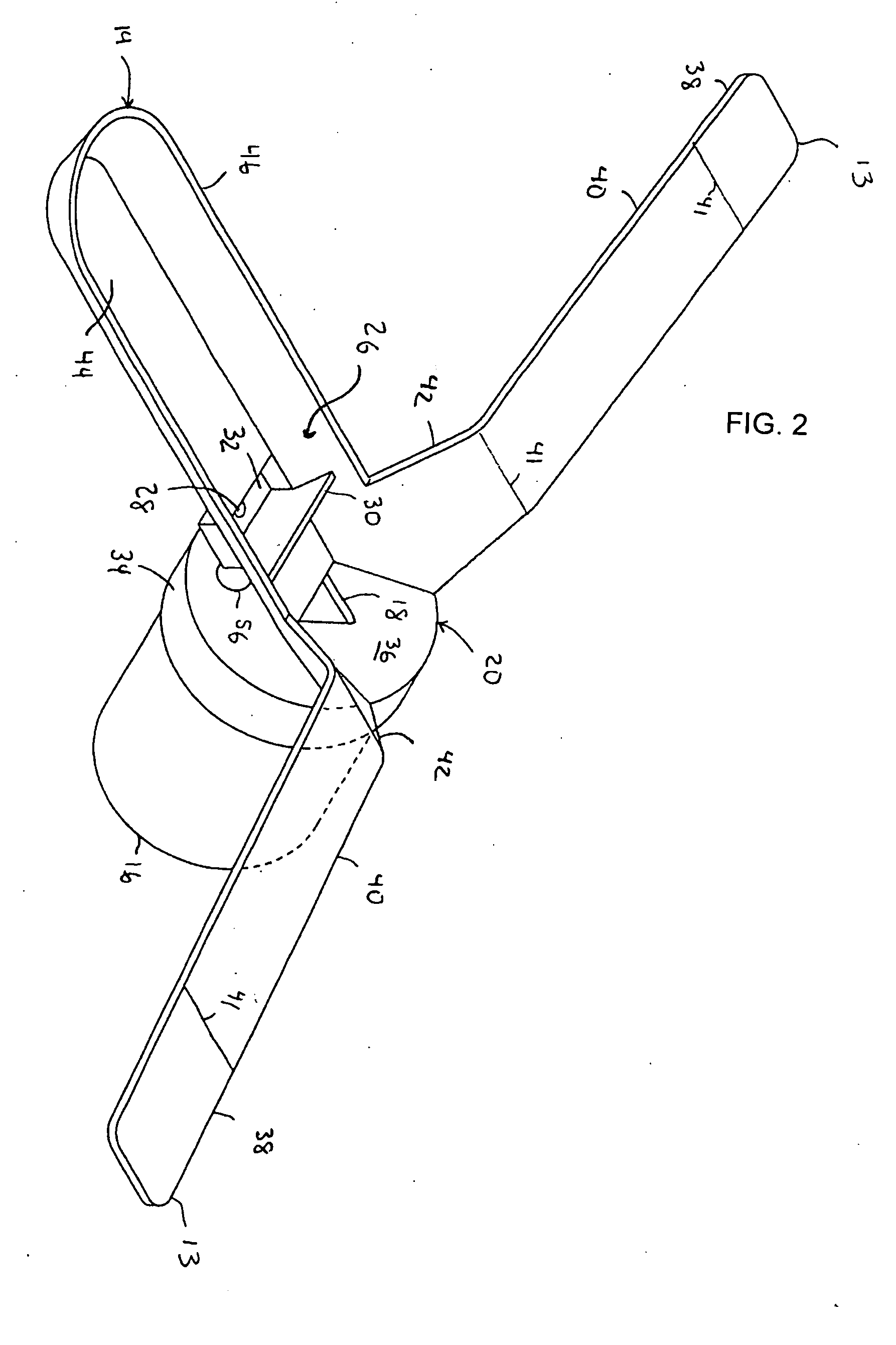
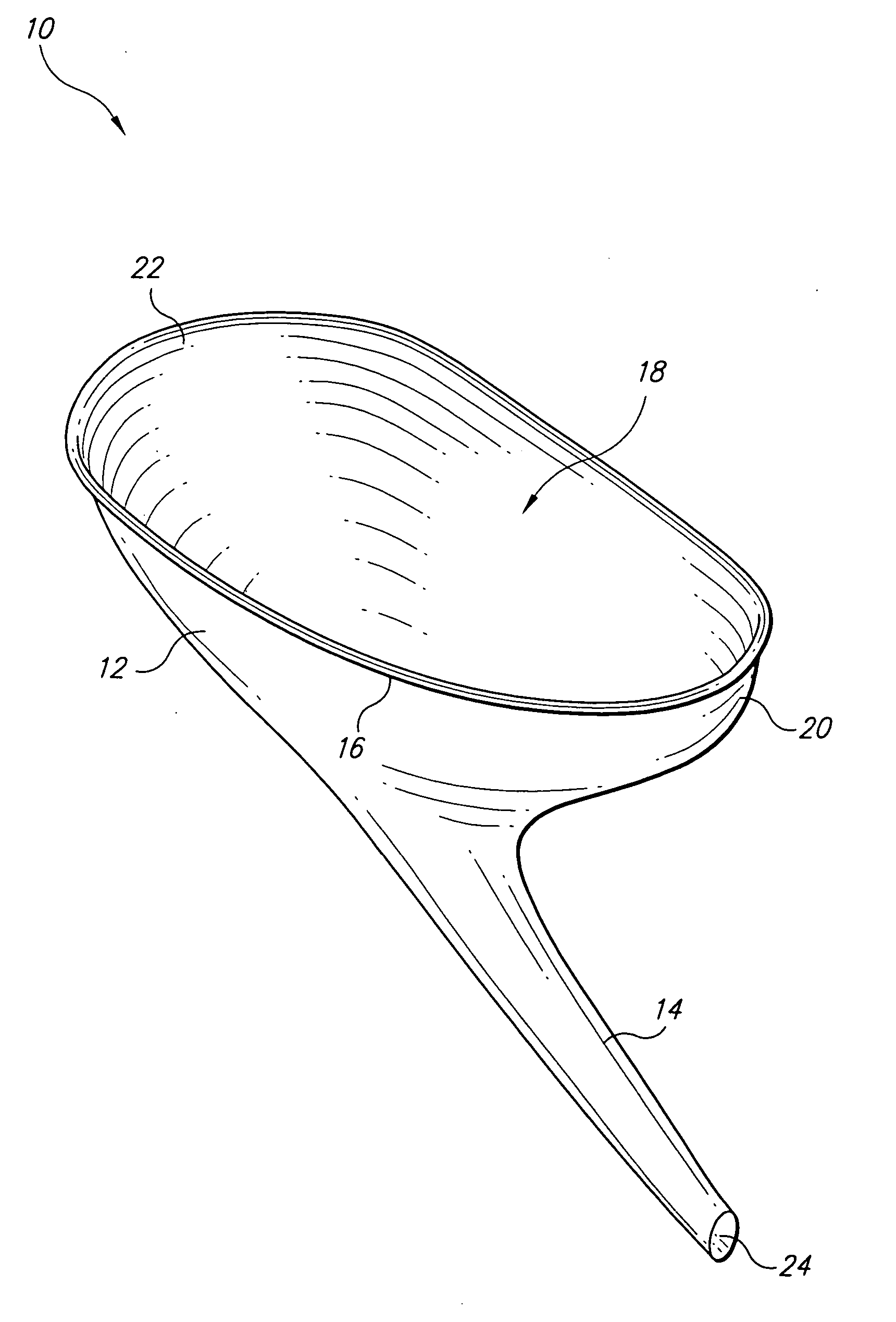
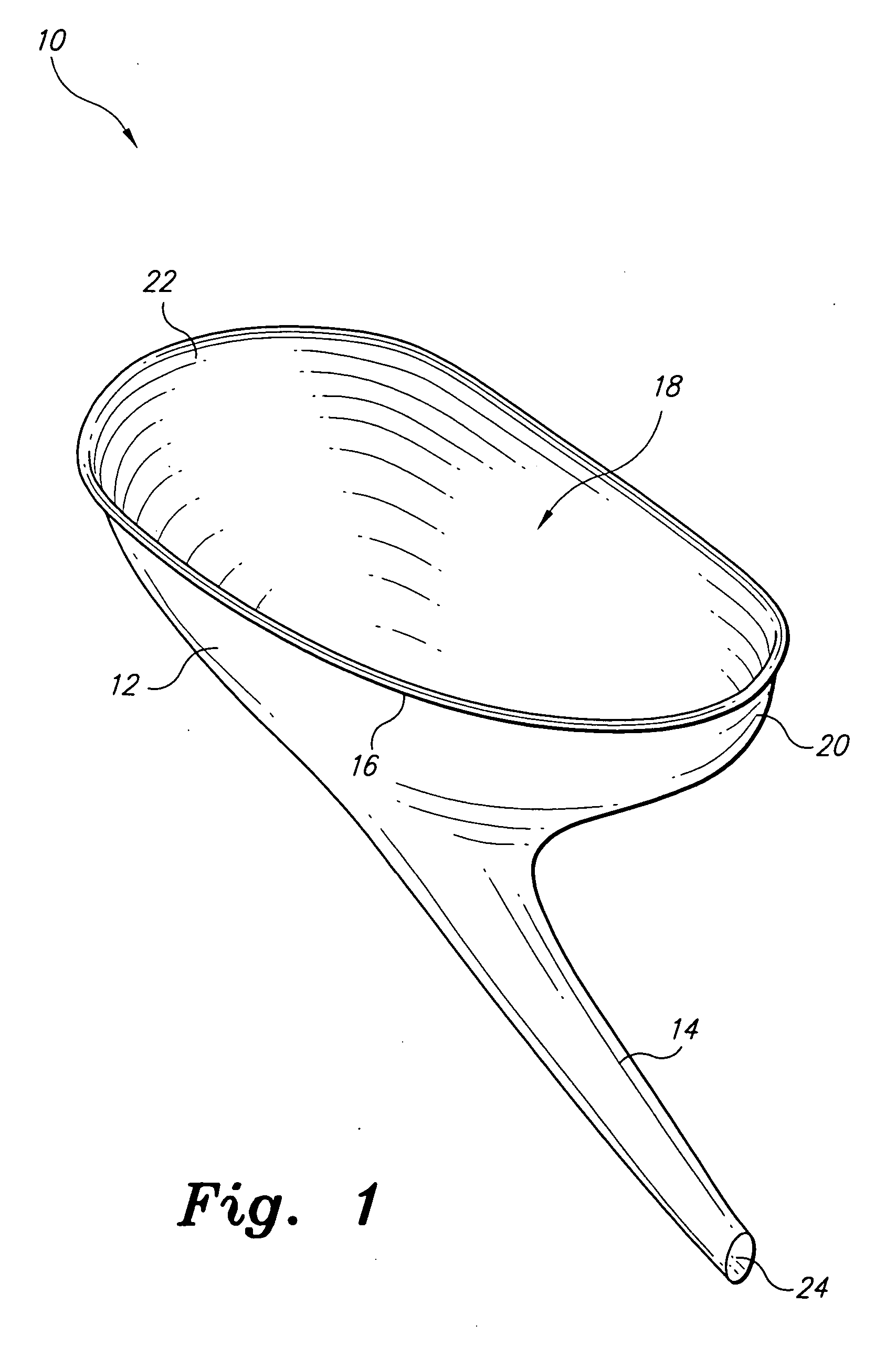
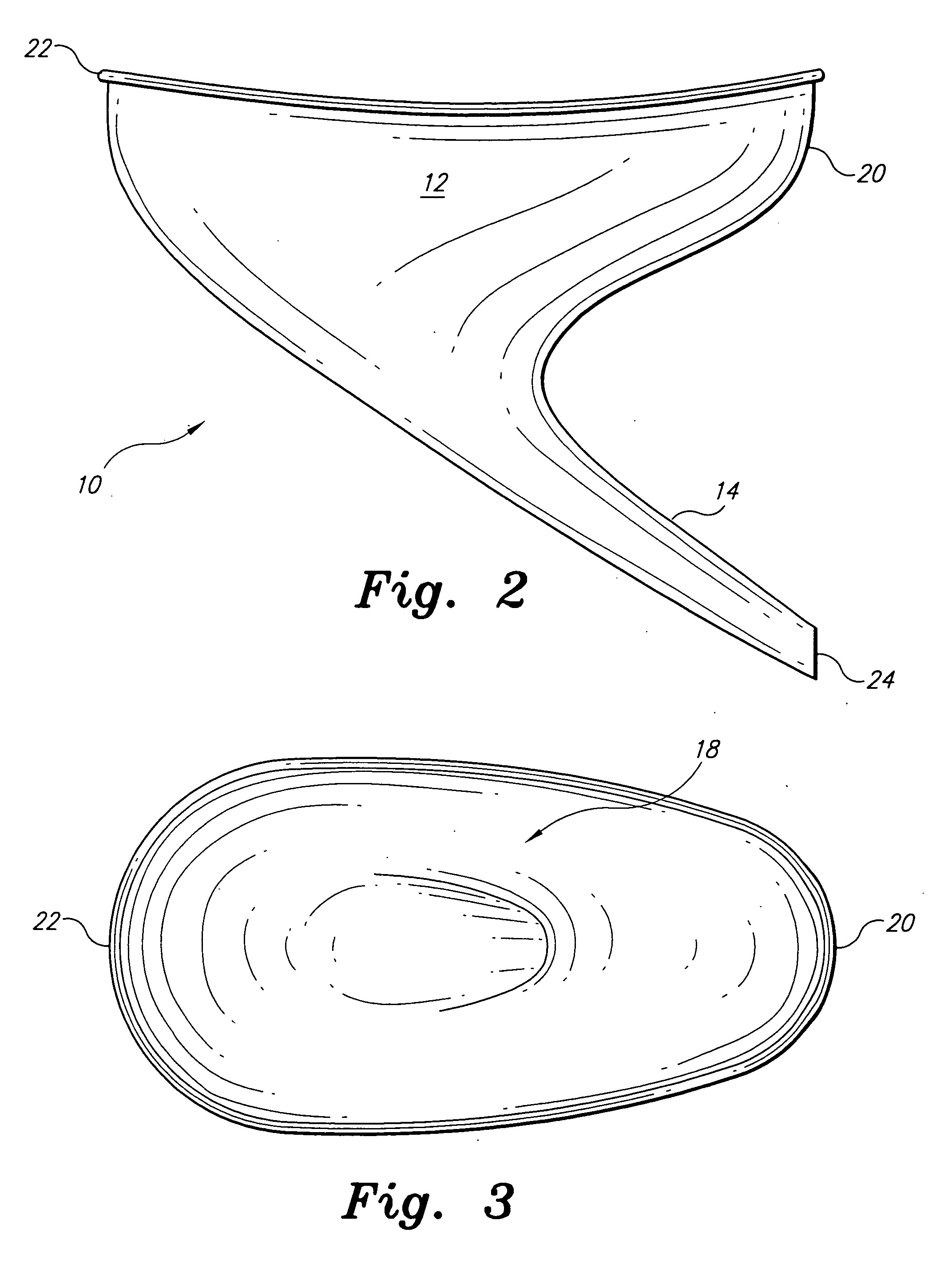
Disposable funnel for urine samples
InactiveUS20070006368A1Easy to collectExpand coverageBathroom accessoriesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsUpper lipUrine production
The disposable urine funnel is a urinary aid device that is placed upon a vaginal opening when the user is seated in order to guide urine into a urine sample cup. The disposable urine funnel is a bowl-shaped container that may be integrally connected to a tube, or the tube may be omitted entirely. The container has an upper lip that defines a mouth of the container. The mouth of the container has a first end and a second end, the first end being narrower from one side of the mouth to the other than the second end. The tube is optionally attached to the container and extends angularly downward from the container and in the direction of the first end of the mouth of the funnel, terminating in a discharge opening from which urine passes.
Owner:KEY LORI A
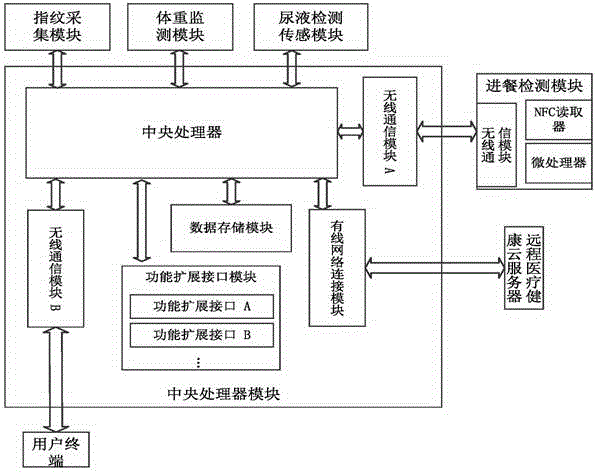
Health monitoring system based on intelligent closestool
InactiveCN104452926ASuitable for useEasy to returnCo-operative working arrangementsLavatory sanitoryMonitoring systemGeneral family
The invention discloses a health monitoring system based on an intelligent closestool. Physical indexes of a user are obtained by extracting and sampling urine of the user and conducting various types of index urine detection and analysis on a urine sample through sensors, and returned to a user terminal. The user terminal conducts inquiry or consultation on a remote medical health cloud server according to information such as the urine detection result and the dining time, and the inquiry or consultation result can be conveniently and rapidly returned to the user. In the specific configuration of the health monitoring system, no more auxiliary devices are needed, sampling, detecting and the like of the sample are all designed in the closestool, the sampling and detecting accuracy is quite accurate, space and cost can be greatly saved, and the health monitoring system is suitable for ordinary families.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Methods and Compositions for Diagnosing Urological Disorders
InactiveUS20100166739A1Aid in diagnosisOrganic active ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsDiseaseCCL2
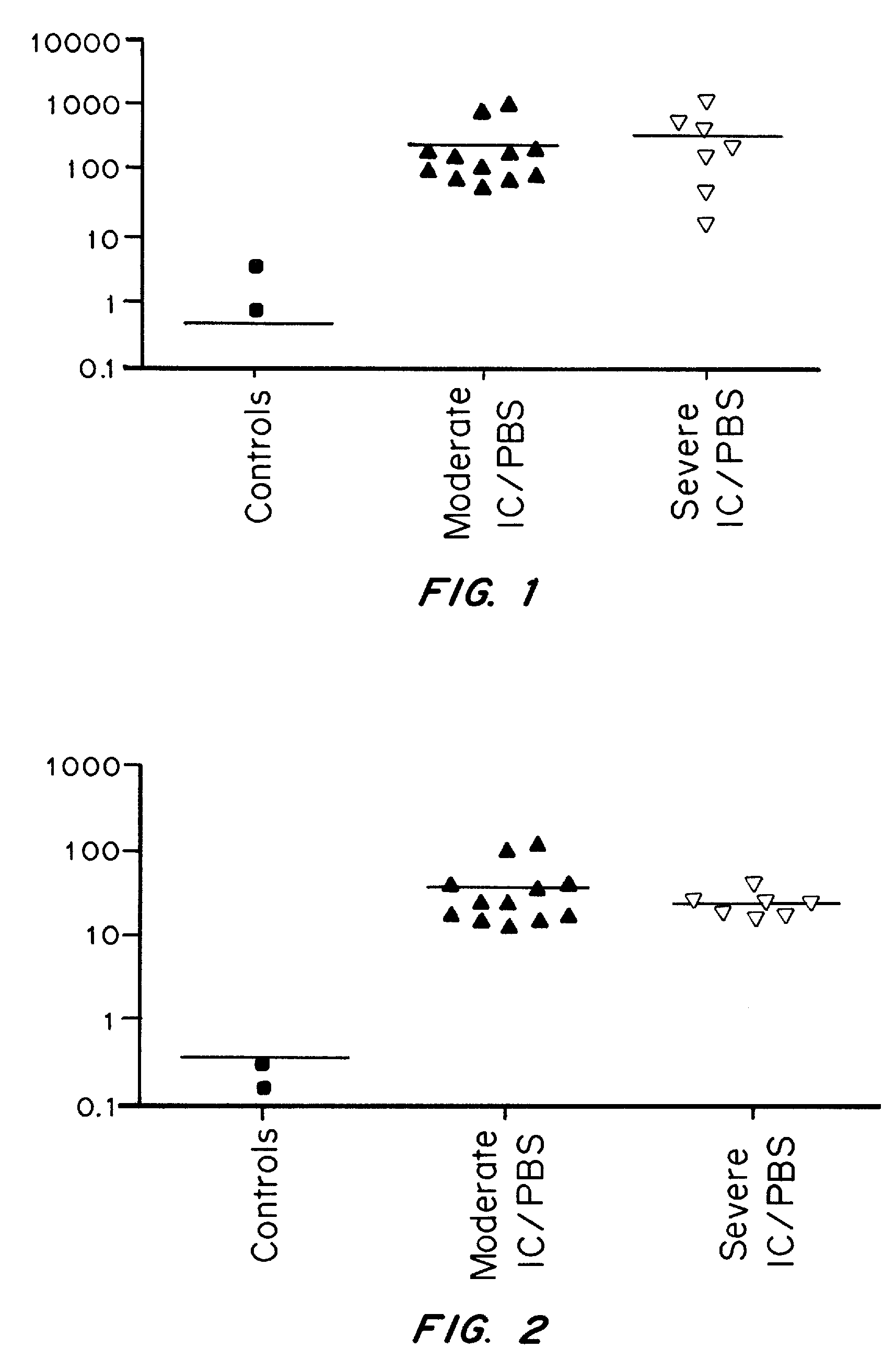
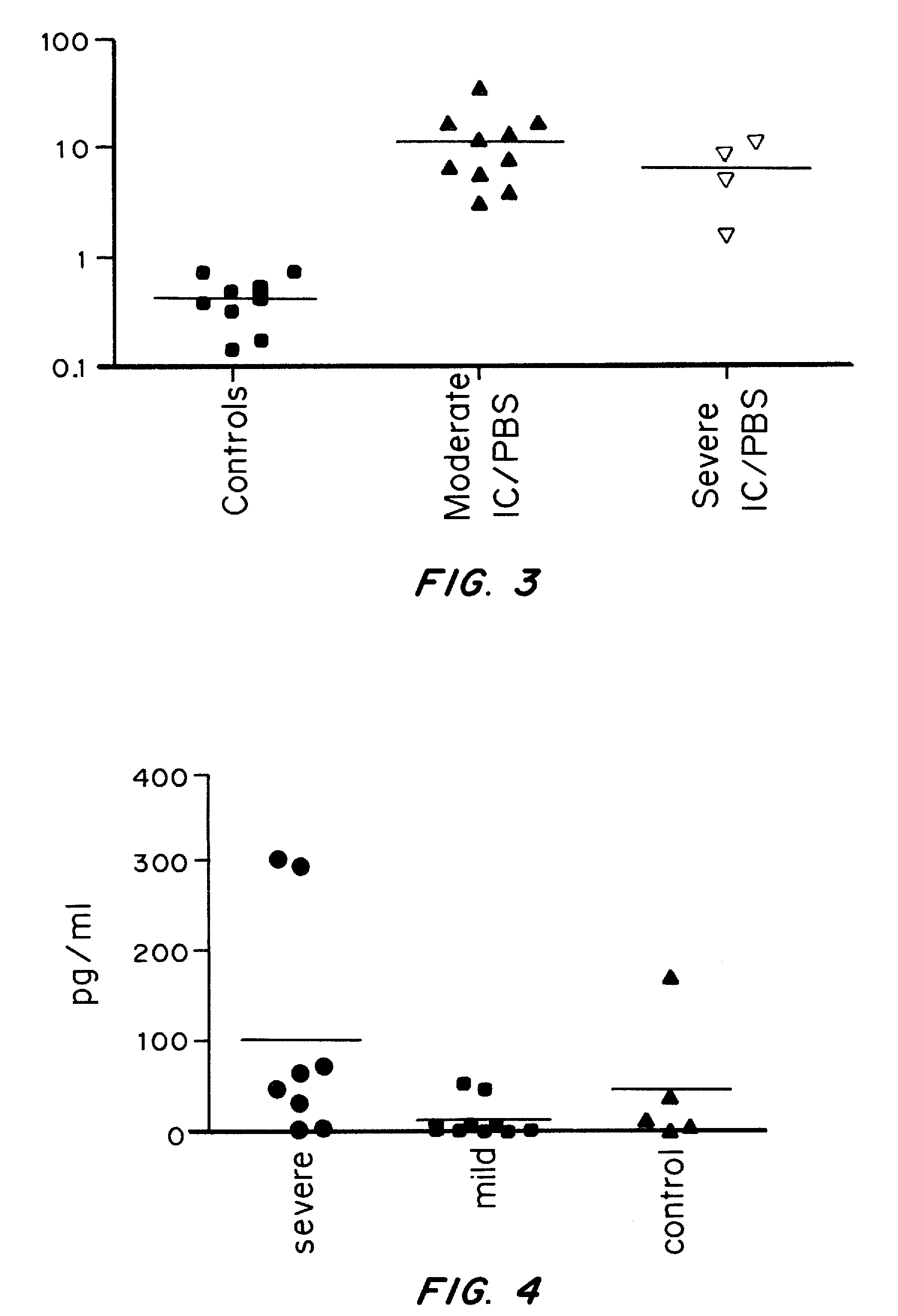
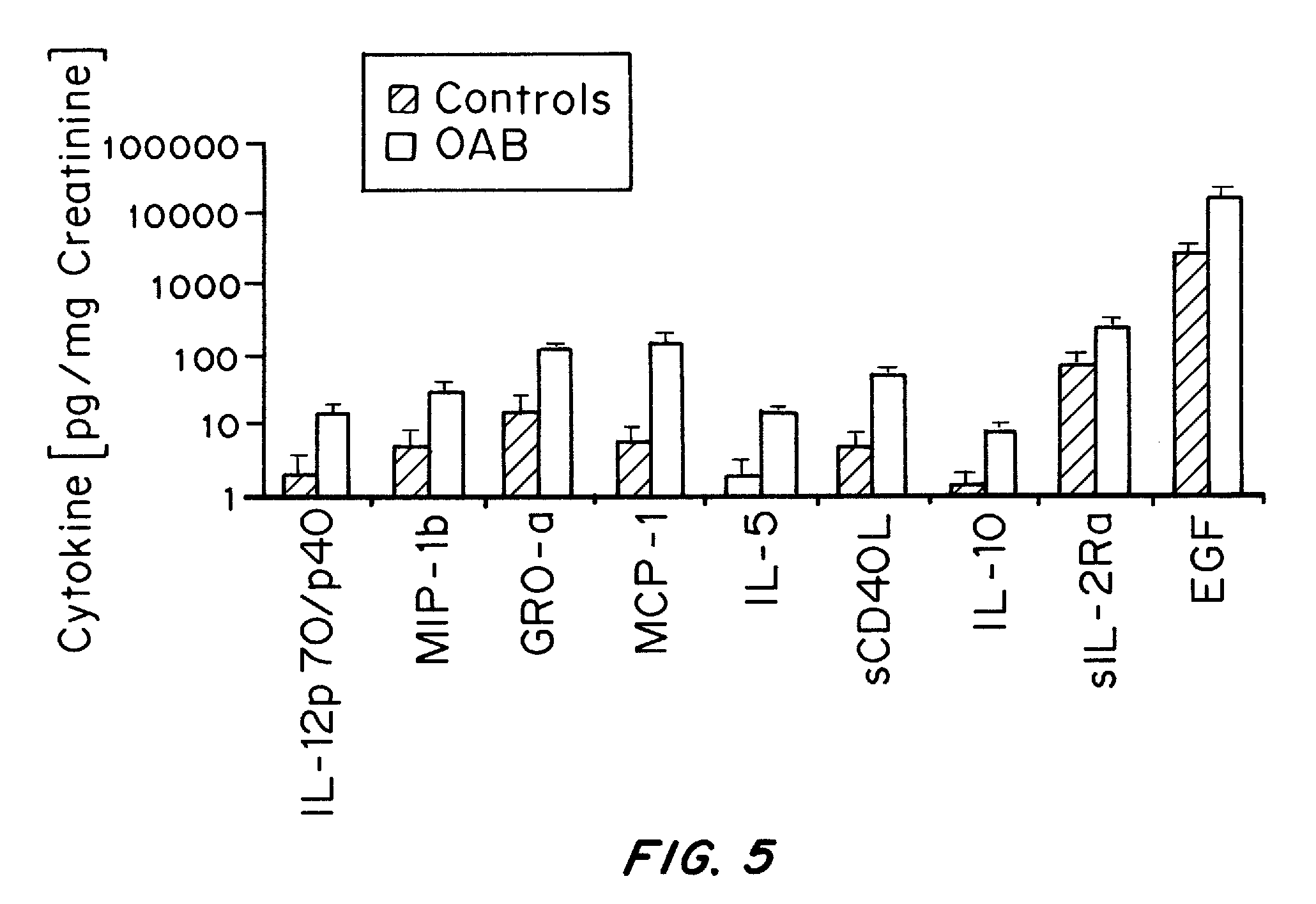
It has been discovered that cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors in urine are biomarkers indicative of urological disorders including interstitial cystitis / painful bladder syndrome and overactive bladder syndrome. Preferred chemokine biomarkers are CCL2, CCL4 (MIP-1β), CCL11, CXCL1 (GRO-α), sCD40L, IL-12p70 / p40, IL-5, sIL-2Rα, IL-6, IL-10, IL-8, and EGF. The concentration of one or more of these chemokines in an urine sample can be used to assist in the diagnosis of urological disorders. Methods for evaluating the effectiveness of treatments for urological disorders and for assessing the severity of urological disorders are also provided.
Owner:LIPELLA PHARMA
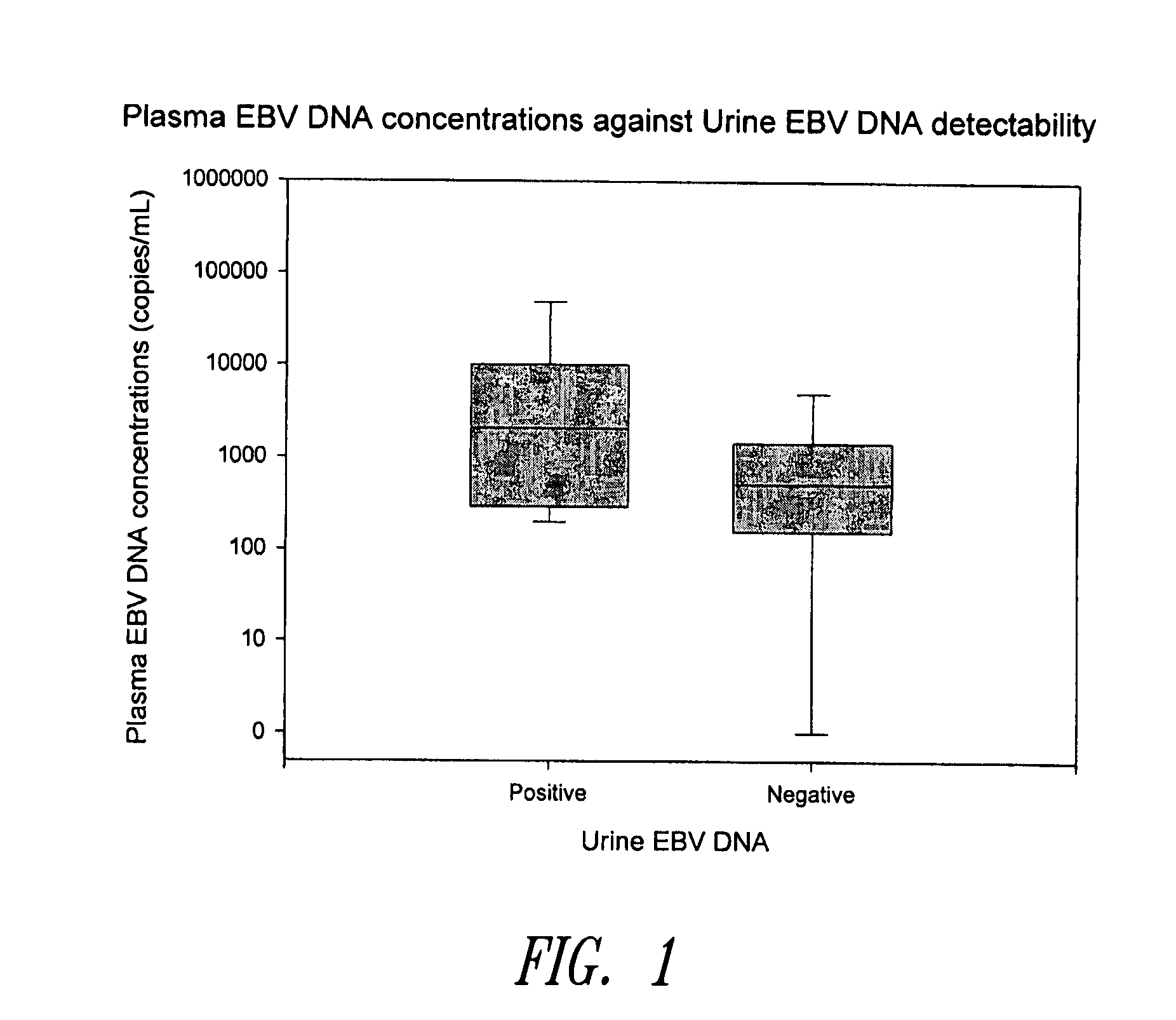
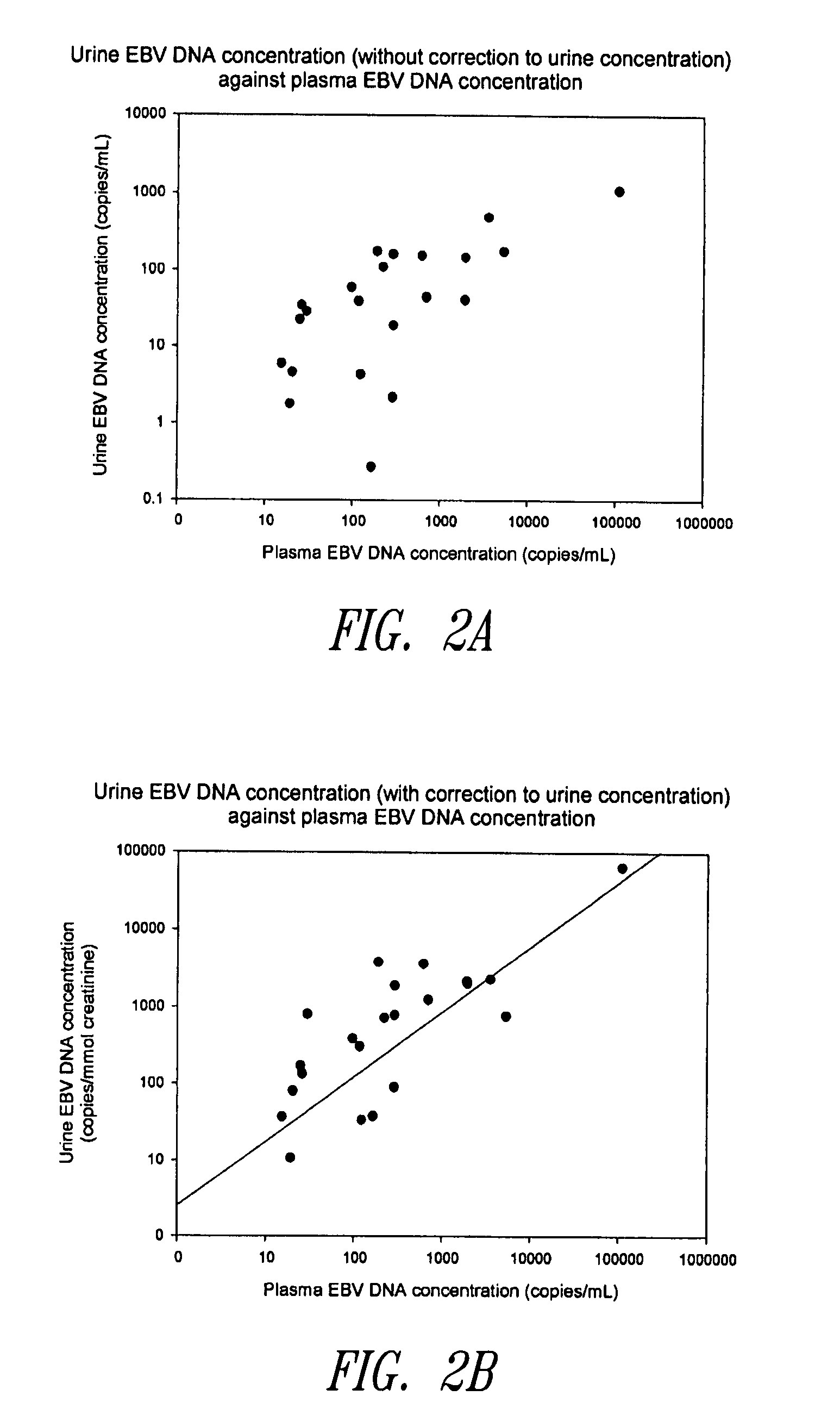
Methods and kits for diagnosis, prognosis or monitoring of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated cancer
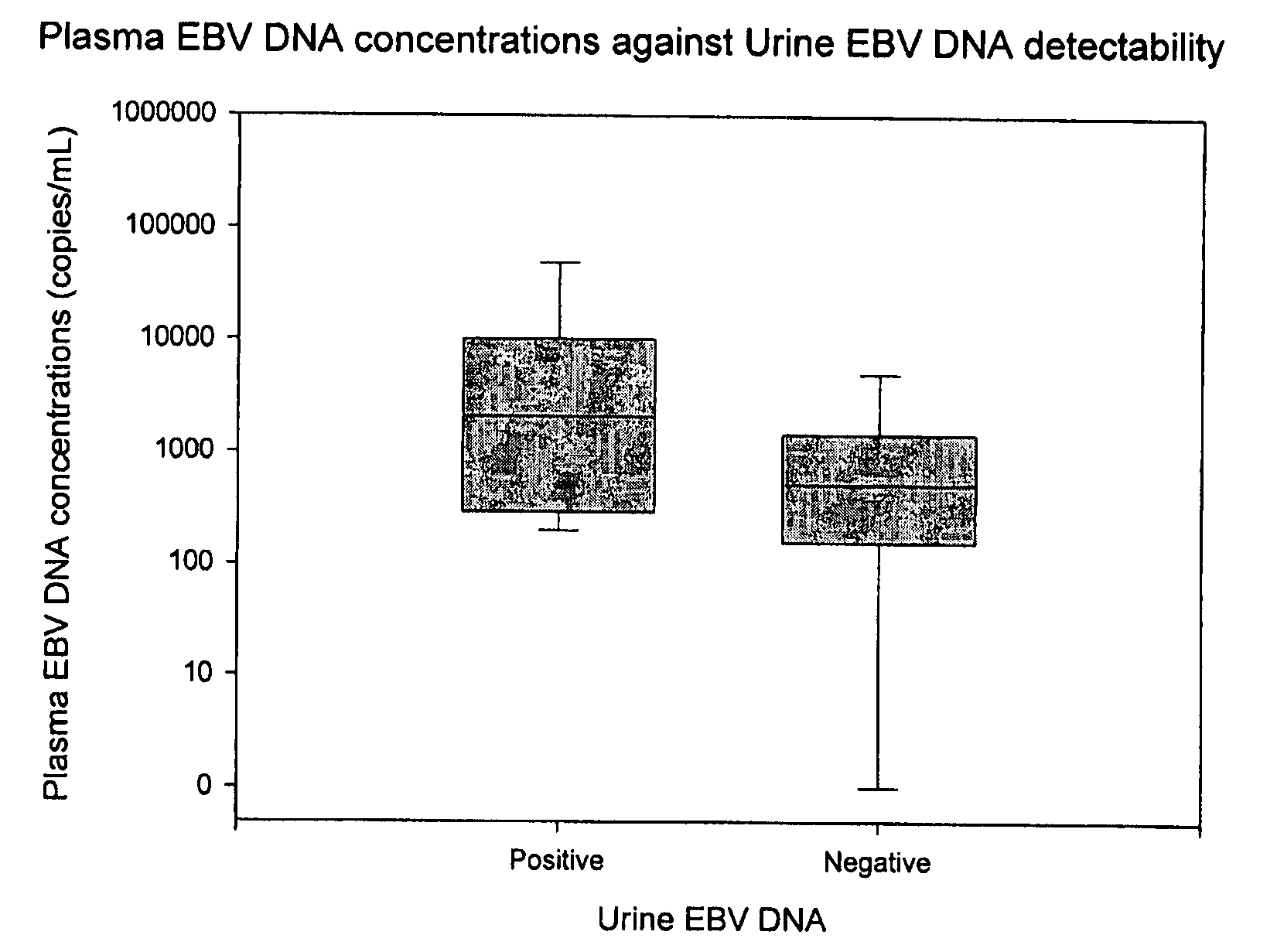
InactiveUS20080206749A1Lower Level RequirementsEliminate false positive caseMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBacteriuriaNon invasive
Disclosed is a non-invasive method for diagnosis, prognosis or monitoring of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated cancer by detecting and / or quantifying EBV associated nucleic acid fragments in a urine sample from an individual. Kits for diagnosis, prognosis or monitoring of cancer are also disclosed.
Owner:HONG KONG THE CHINESE UNIV OF
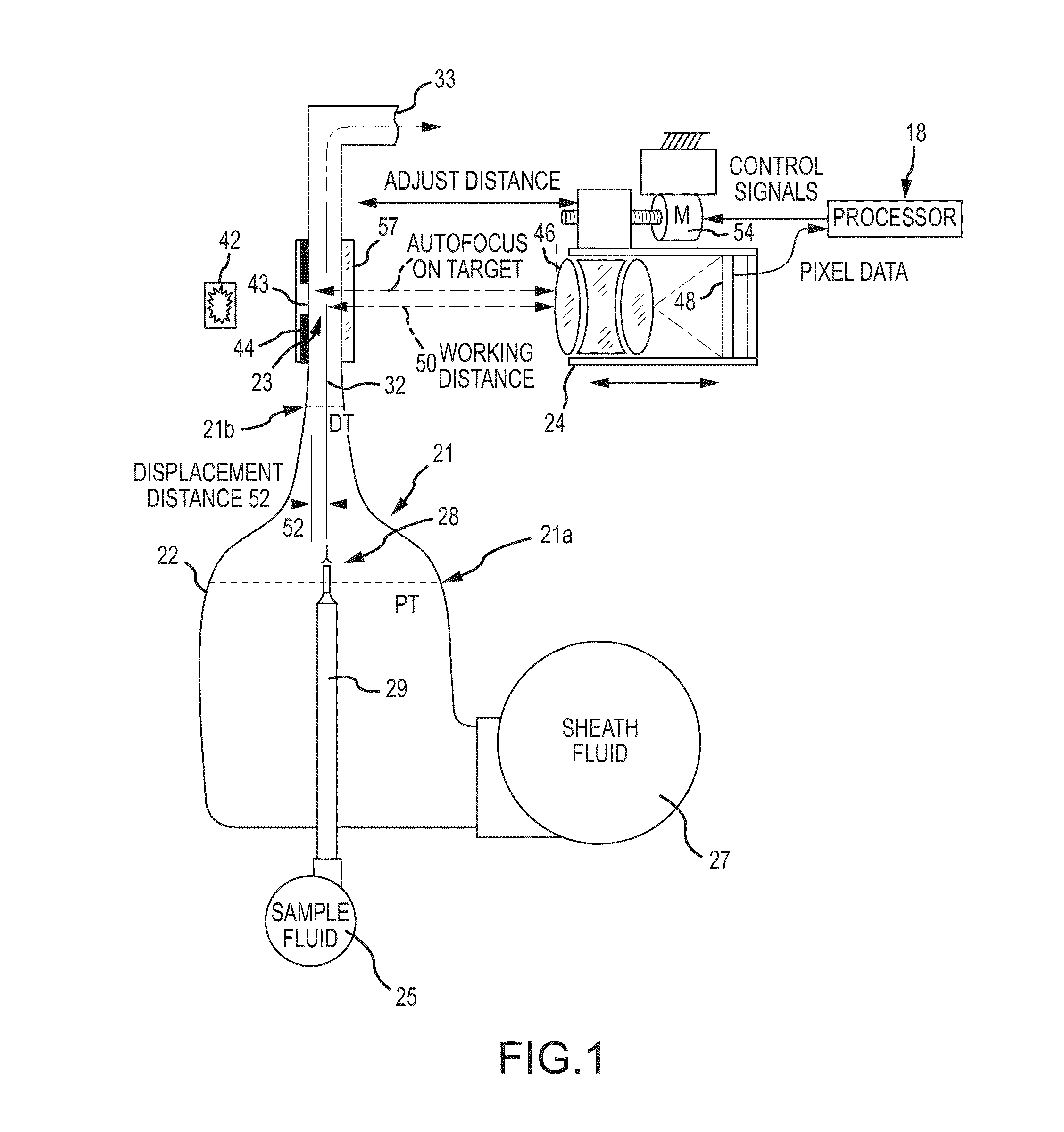
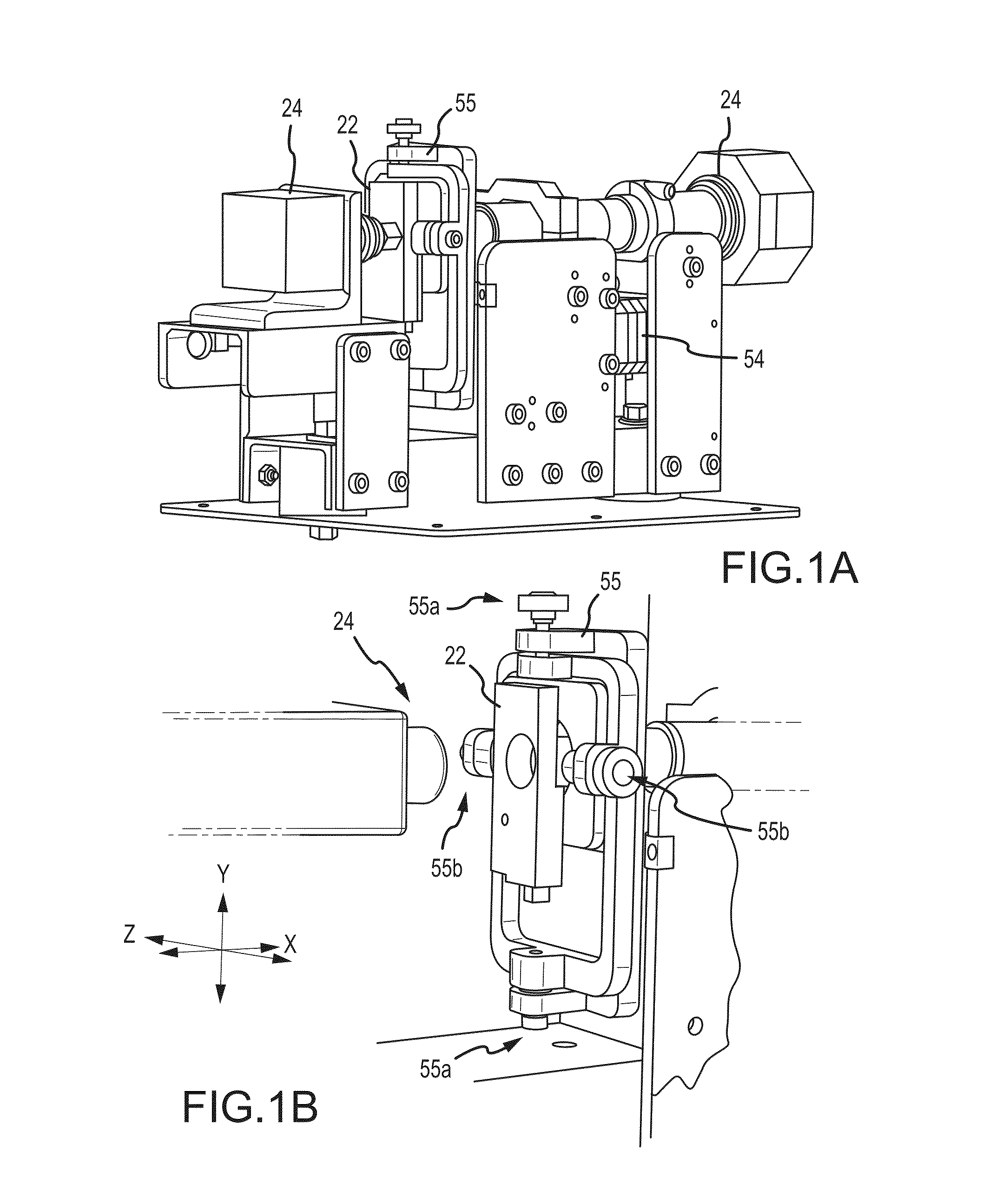
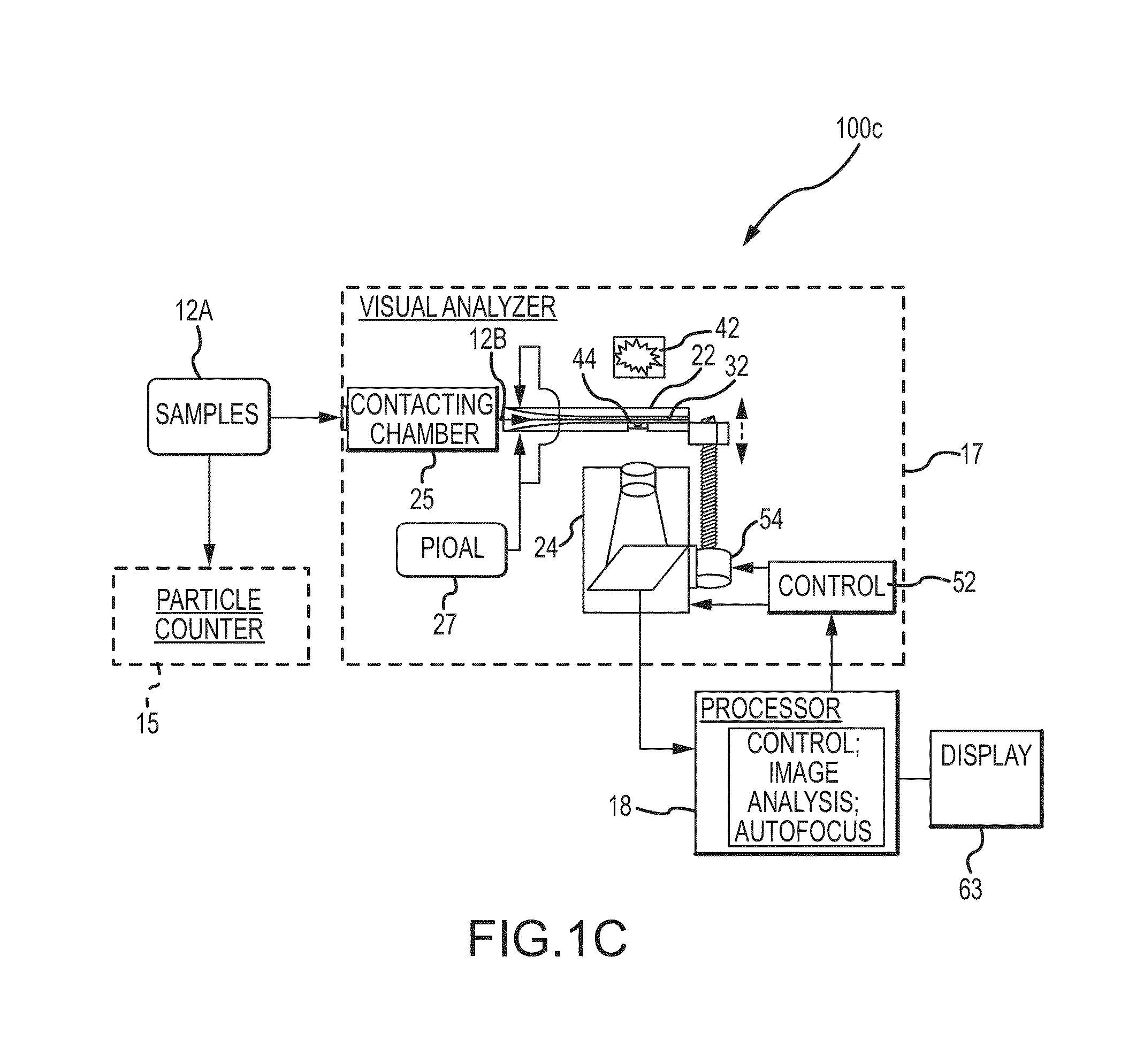
Flowcell, sheath fluid, and autofocus systems and methods for particle analysis in urine samples
ActiveUS20140329265A1Efficiently provideBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsUrine sampleImaging data
The present disclosure relates to apparatus, systems, compositions, and methods for analyzing a sample containing particles. A particle imaging system or analyzer can include a flowcell through which a urine sample containing particles is caused to flow, and a high optical resolution imaging device which captures images for image analysis. A contrast pattern for autofocusing is provided on the flowcell. The image processor assesses focus accuracy from pixel data contrast. A positioning motor moves the microscope and / or flowcell along the optical axis for autofocusing on the contrast pattern target. The processor then displaces microscope and flowcell by a known distance between the contrast pattern and the sample stream, thus focusing on the sample stream. Cell or particle images are collected from that position until autofocus is reinitiated, periodically, by input signal, or when detecting temperature changes or focus inaccuracy in the image data.
Owner:IRIS INT
Urine specimen capture and analysis device
The present invention relates to a urine specimen capture device comprising a capture bowl for collecting a urine specimen, a mounting frame for supporting the capture bowl within a toilet bowl, and an analytic device connected to the capture bowl to analyze a property of the urine specimen in the capture bowl.
Owner:MEDIC INC
Method for the early identification and prediction of kidney injury
InactiveUS20090239242A1Convenient treatmentTransferasesDisease diagnosisCreatinine riseElevated blood
A method for the early identification and prediction of elevated blood creatinine levels resulting from a reduction in kidney function in a subject, comprises contacting a urine sample from the subject with a capture molecule for a biomarker specific for the distal region of the renal tubule and which biomarker is released from said region when there is damage to said region indicative and predictive of elevated blood creatinine levels resulting from a reduction in kidney function. The method can be used to detect Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) caused by many conditions or diseases or through the administration of drugs. The method can indicate and / or predict a reduction in kidney function significantly earlier than the current standard creatinine test. Methods for predicting a need for renal replacement therapy (RRT) are also disclosed.
Owner:ARGUTUS INTPROP
Kit for simultaneously detecting retinol-binding protein (RBP) in urine sample and serum sample
ActiveCN103134934AReduce dosageStrong specificityColor/spectral properties measurementsLatex particlePromotion effect
The invention provides a kit for simultaneously detecting RBP in a urine sample and a serum sample. The kit comprises a reagent R1 and a reagent R2, the reagent R1 is a polymer buffer solution having an agglomeration promotion effect, the reagent R2 is a buffer solution containing a latex-antibody crosslink, and the latex-antibody crosslink comprises anti-RBP polyclonal antibody marked large latex particles and anti-RBP monoclonal antibody marked small latex particles. The kit which adopts a composite monoclonal and polyclonal antibody sensitized latex enhanced immune detection method has the advantages of simultaneous satisfying of the requirements comprising good specificity, high sensitivity and wide linear range, small antibody application amount, and cost reduction, and can be simultaneously used for the clinic detection of the RBP in human blood and urine.
Owner:NINGBO MEDICAL SYSTEM BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Glycoprotein Profiling of Bladder Cancer
InactiveUS20100184049A1Simple and rapid and reliable and accurate and cost-effectiveEasy to identifyElectrolysis componentsMicrobiological testing/measurementHaptoglobinBiomarker (petroleum)
The present invention relates to a method for the diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring of bladder cancer, such as early or late stage bladder cancer, by detecting in a urine sample from a subject at least one biomarker for bladder cancer identified herein, such as alpha-1B-glycoprotein, haptoglobin, serotransferrin, or alpha-1-antitrypsin. The biomarkers may be detected and, optionally, measured using an agent that detects or binds to the biomarker protein or an agent that detects or binds to encoding nucleic acids, such as antibodies specifically reactive with the biomarker protein or a portion thereof. The invention further relates to kits for carrying out the methods of the invention. The invention further relates to a device for the rapid detection of one or more bladder cancer biomarkers in urine and methods for rapidly measuring bladder cancer biomarkers in urine.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Multi-layer slides for analysis of urine sediments
ActiveUS8462332B2Less-expensiveSimple processWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansPipetteCapillary channel
Visual analysis of urine samples is carried out with the use of a slide consisting of three layers containing an enclosed viewing chamber which receives a urine sample deposited by pipette into an opening on the outer layer of the slide. From the inlet opening the sample enters an inlet chamber in the middle layer and passes through a capillary passageway into the viewing chamber where it is inspected for particles and sediments.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Apparatus for analyzing particles in urine and method thereof
ActiveCN101173888AMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological particle analysisFluorescenceRed Cell
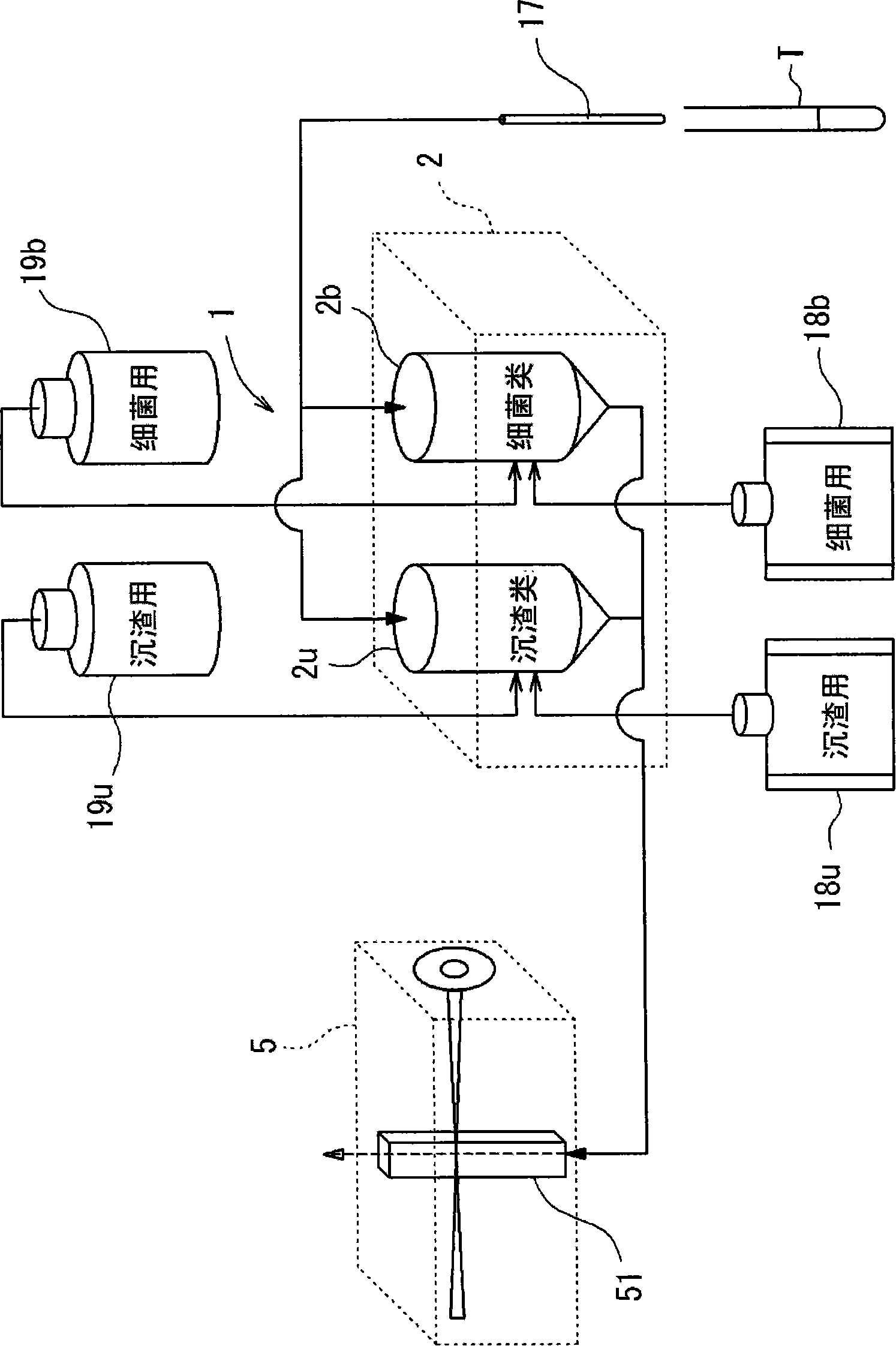
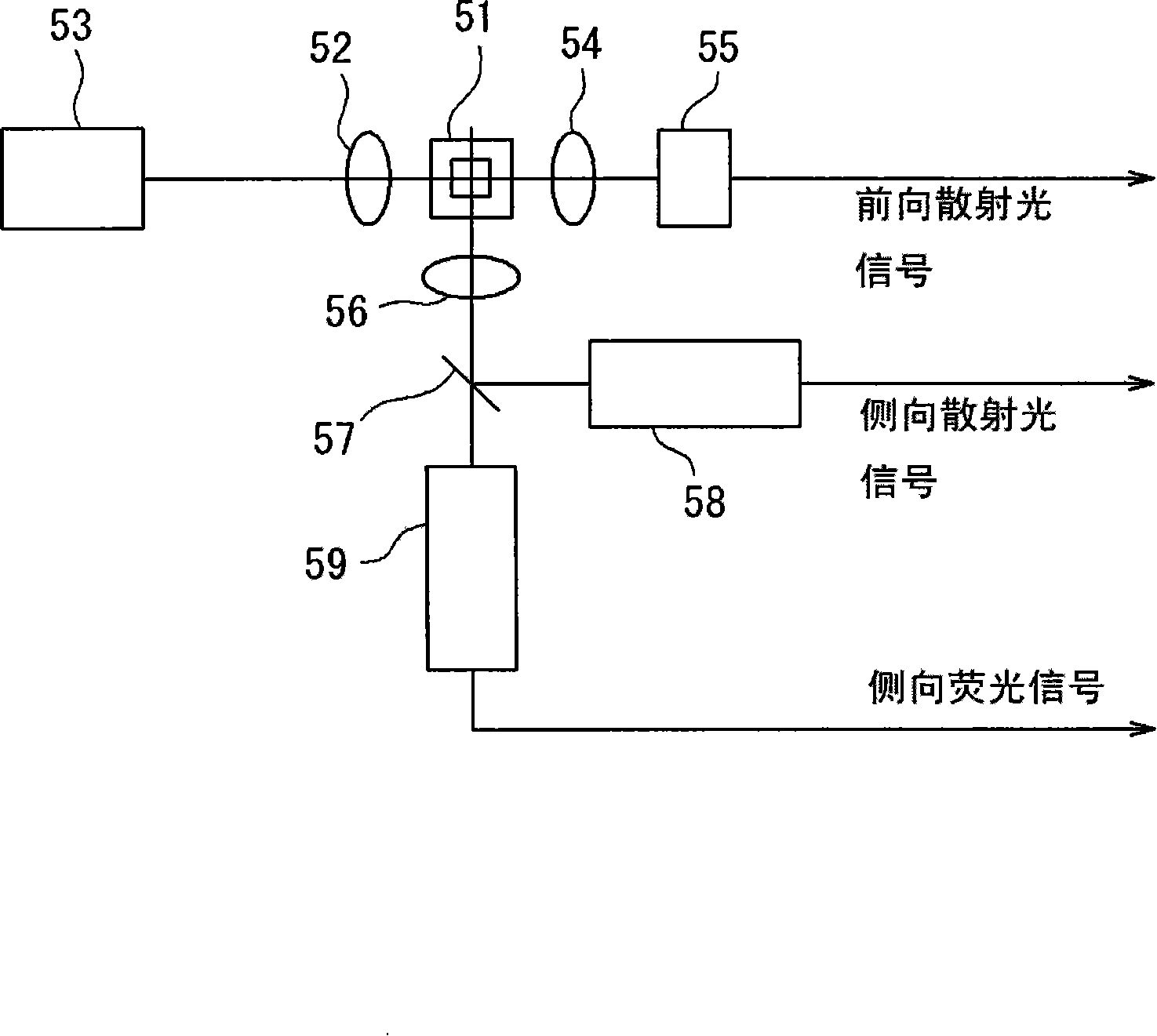
An apparatus, intended for use in analyzing particles in urine is disclosed, that comprising: a sample distribution section for distributing urine samples to a first aliquot and a second aliquot; a first specimen preparing section for preparing a first specimen for measuring urinary particles, containing at least erythrocytes, by mixing a first stain reagent and the first aliquot; a second specimen preparing section for preparing a second specimen for measuring bacteria by mixing a second stain reagent and the second aliquot; and an optical detecting section comprising a light source for irradiating a light to a specimen being supplied, a scattered light receiving element for detecting scattered light emitted from the specimen, and a fluorescence receiving element for detecting fluorescence emitted from the specimen. A method intended for use in analyzing particles in urine is also disclosed.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Urine sample retrieval device
ActiveUS7762596B1Facilitates tray manipulationEasy to collectVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringEngineeringBottle
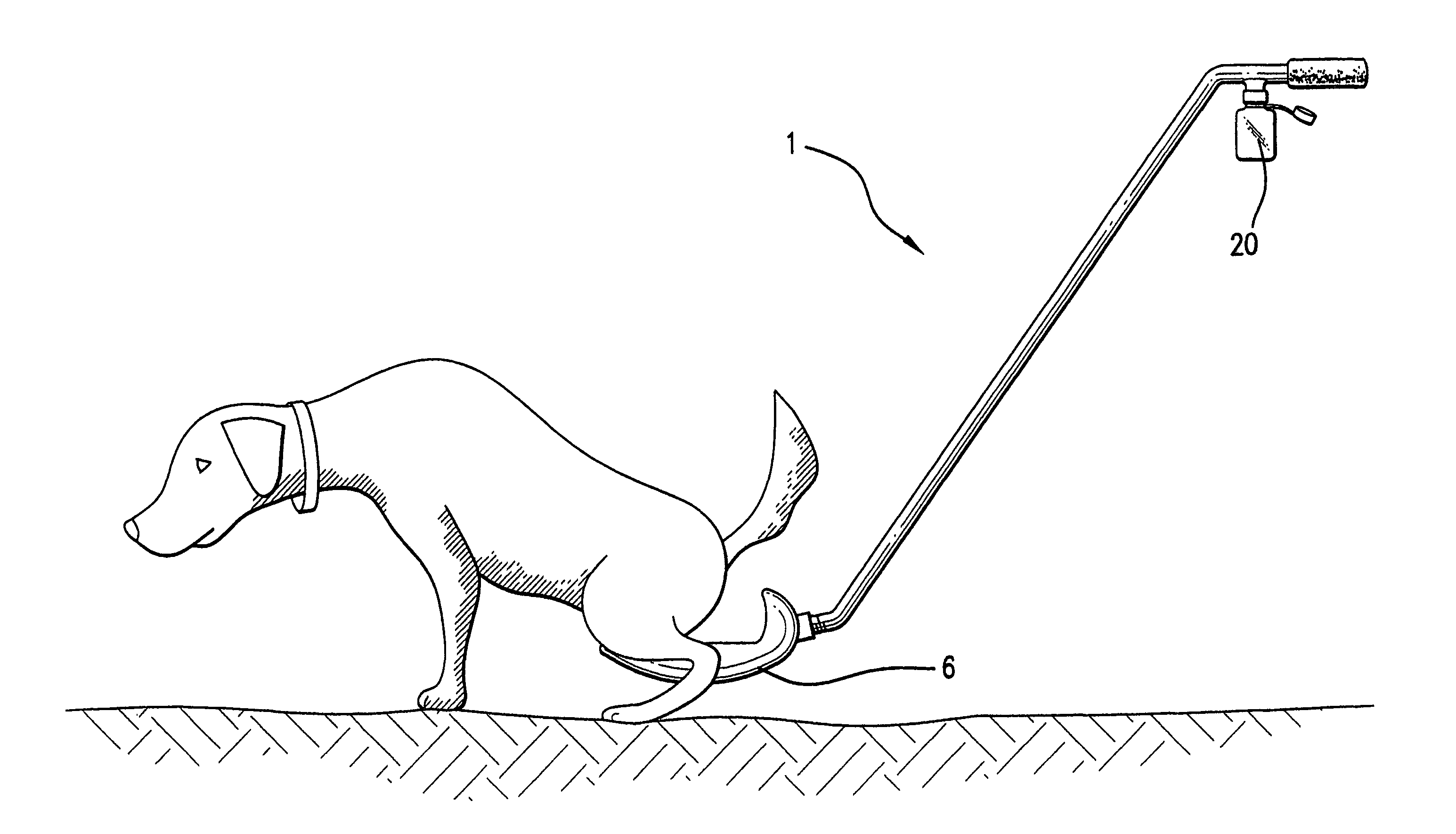
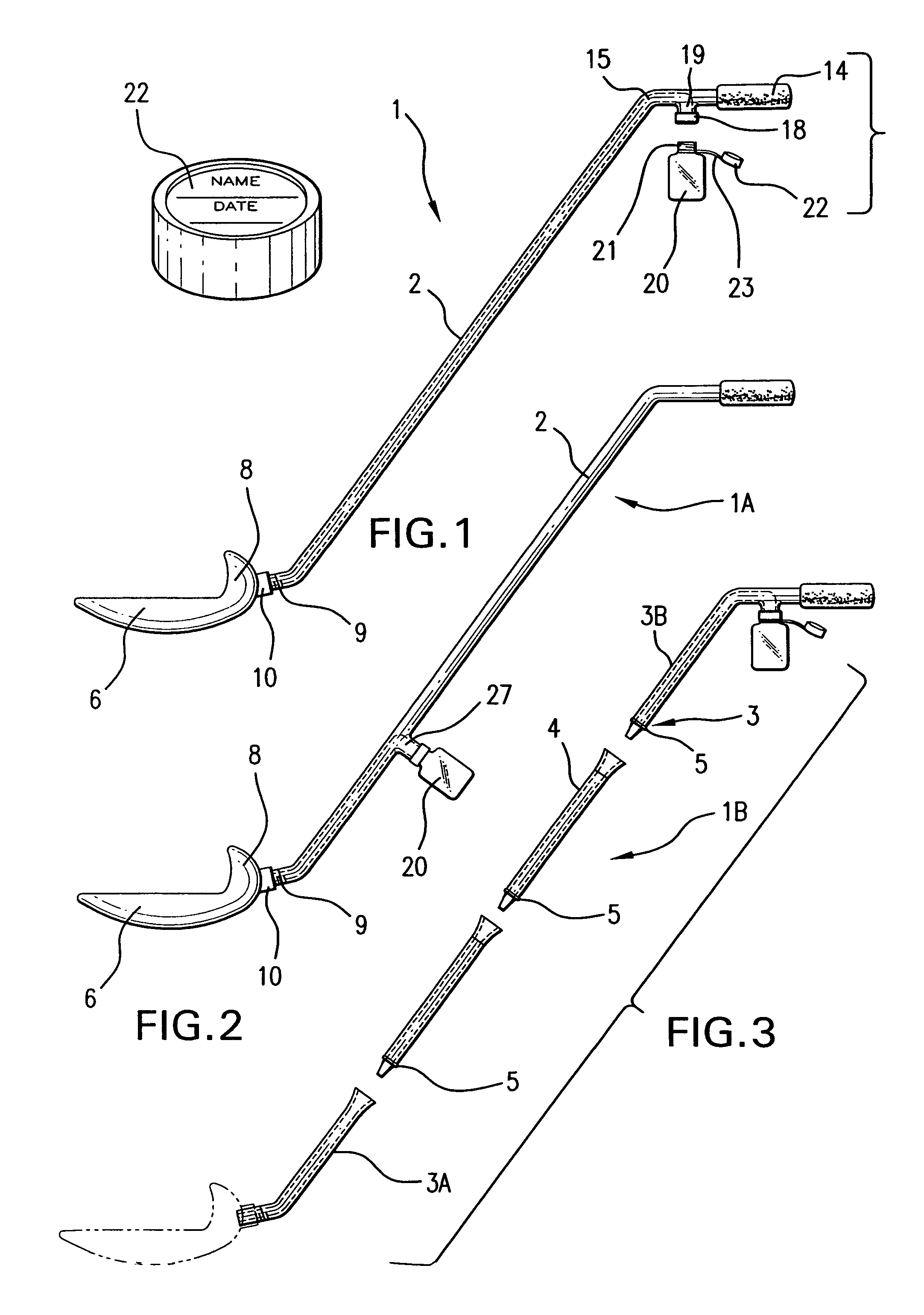
Device and method for collecting animal urine including a tray mounted to an elongated handle which is at least partially hollow. The handle, at one end, is interconnected to a tray to be deployed beneath the animal in advance of urination. At its other end, the handle is configured as a hand grip. Located at a point along the handle and spaced away from the tray, is a collection bottle mount to which is connected a specimen collection bottle within direct flow connection with the tray via the partially hollow handle. The bottle and mount serve as a second handle for steadying control of the device. By tipping the handle such that the tray is raised above the handle, urine collected in the tray is drained directly to the bottle. The bottle includes a slit wafer ensuring against spillage when the bottle is removed for recapping and transport for analysis.
Owner:GAYDOS KELLY M +1
Device and method for the collection of a urine sample
ActiveUS7833169B2Avoid bacterial contaminationVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsAnimal teeth treatmentContaminationUrine sample
A device and method for collection of a urine sample is disclosed which comprises a channel, an opening in the channel, and a collector associated with the opening. The channel is formed so that urine can flow through it from a first end to a second end thereof. The opening is provided in the channel at a point between the first and the second ends thereof. The collector is associated with the opening in the channel to be able to receive urine therein. In one embodiment, a member can cover the opening to permit urine to pass through it after contact with urine. Specifically, the member may dissolve or otherwise permit urine to pass through the opening after a period of time to test a urine sample which is not from the initial flow of urine to avoid bacteria contamination.
Owner:HOLLISTER INCORPORAED
Method and test strips for the measurement of fat loss during weight loss programs
InactiveUS20040043376A1Great advantageEasy to manufactureMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementPhysiologyAcyl CoA dehydrogenase
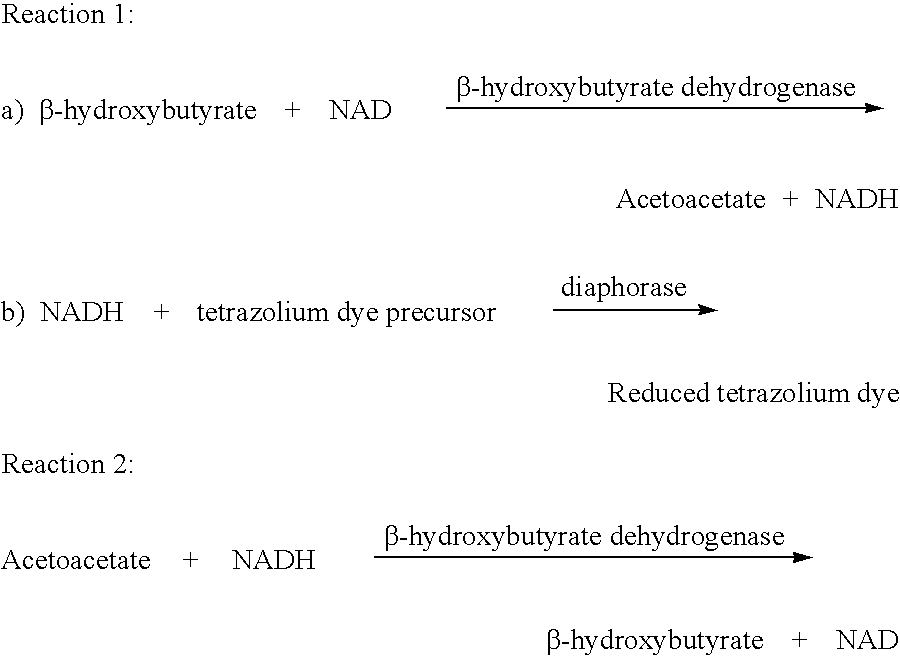
Disposable test strips and a wet chemistry method for measuring each of beta-hydroxybutyrate alone, combined beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate or total ketone bodies (i.e., beta-hydroxybutyrate, acetoacetate and acetone) in human bodily fluid samples, including but not limited to urine, saliva or sweat are described. The test strips need only be dipped in the sample and can be used by anyone in almost any milieu. Measurement can be made electrochemically, spectrophotometrically, fluorometrically or by comparision to a color standard. Combined acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate which account for 97-98% of total ketone bodies and may be measured in a cyclic reaction that occurs at pH about 7.0 to about 8.3 with beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, (beta-HBD), nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, a tetrazolium dye precursor and an electron mediator. Using this reaction, false positive results obtained from urine samples taken from patients on sulfhydryl drugs are avoided. beta-HBD from some sources was found to cause false negative results in samples (e.g. urine) containing high chloride content due to chloride inhibition of beta-HBD. Using a simple test for chloride inhibition, it was found that beta-HBD from Alcaligenes is not so inhibited. Using either beta-HBD that is not inhibited by chloride or using 10-20 times the normal concentration of this enzyme eliminates false negatives in samples having substantial chloride content, such as urine, both in the reaction described above and in other reactions disclosed for measuring each of beta-hydroxybutyrate alone, combined beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate and total ketone bodies, all of which reactions occur in the pH range of about 8.6 to about 9.5.
Owner:GUPTA SURENDRA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com