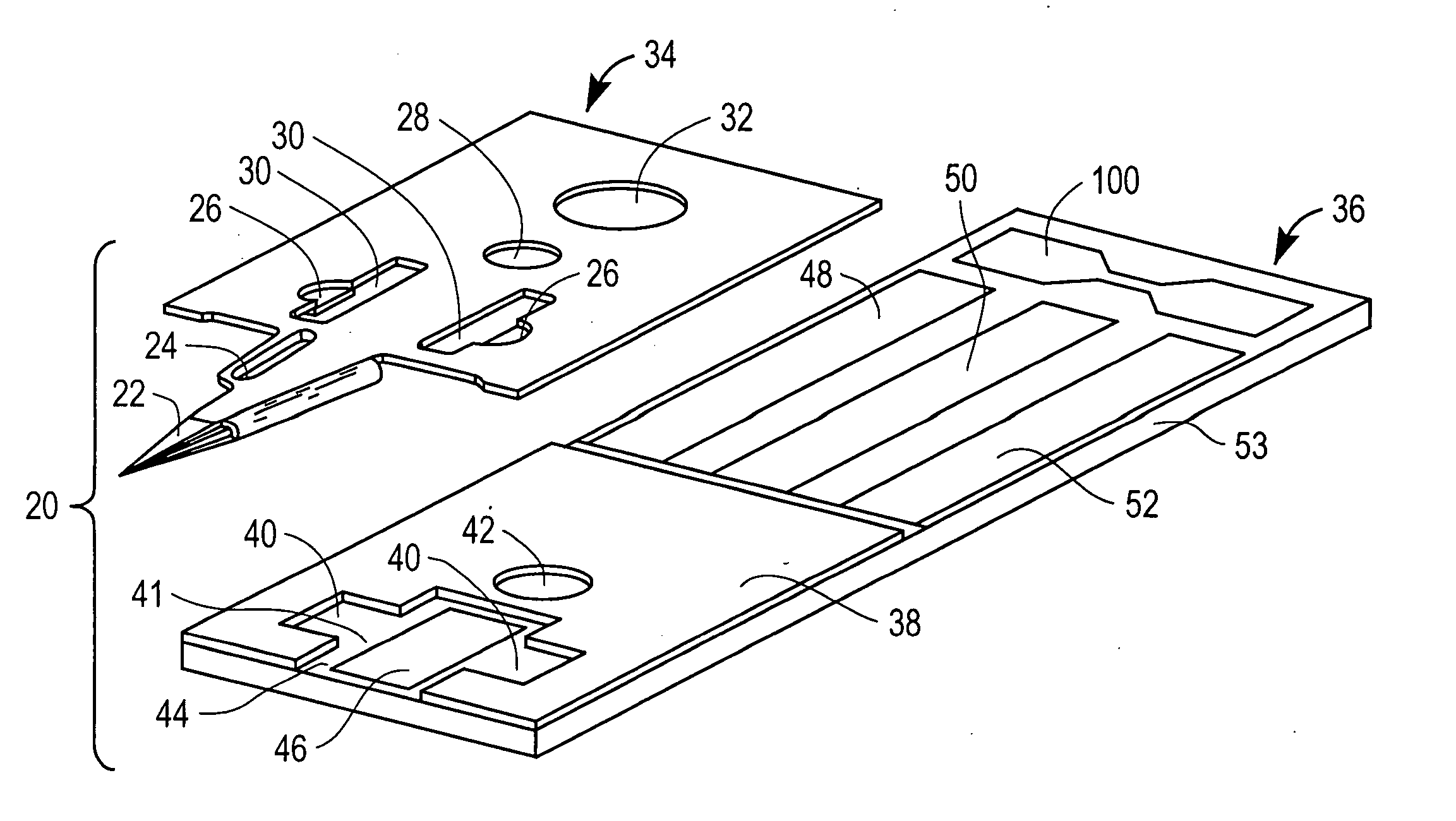
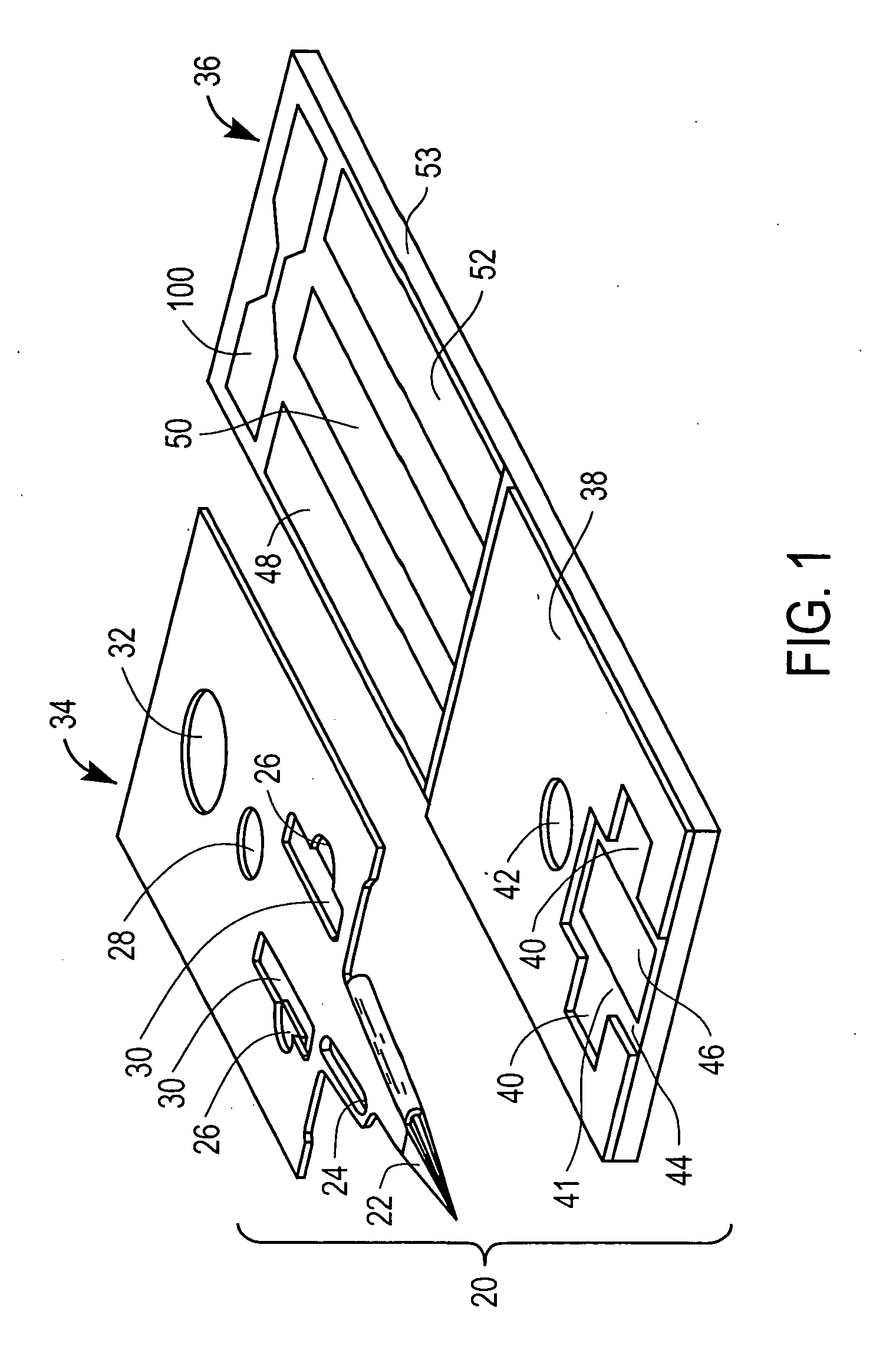
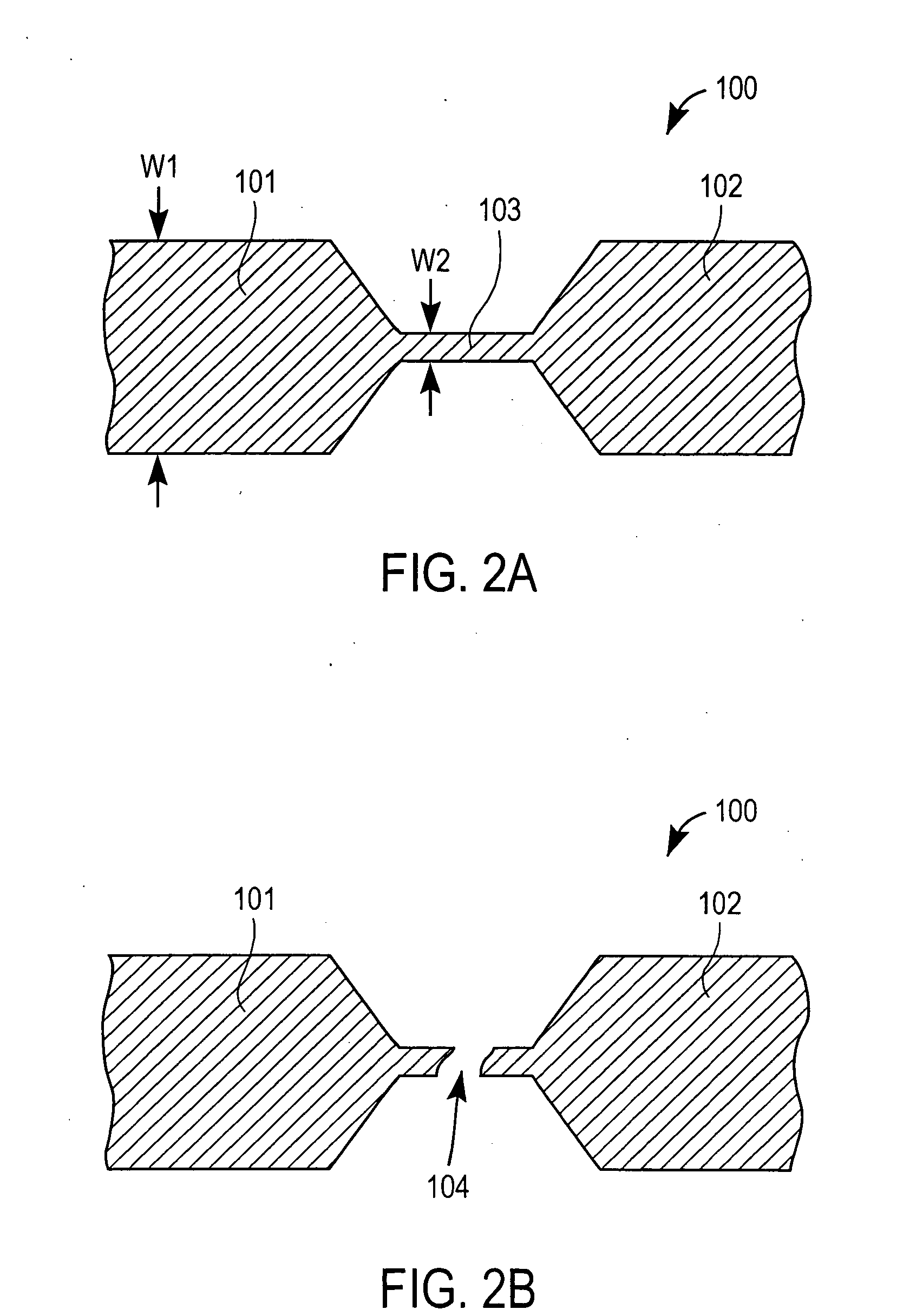
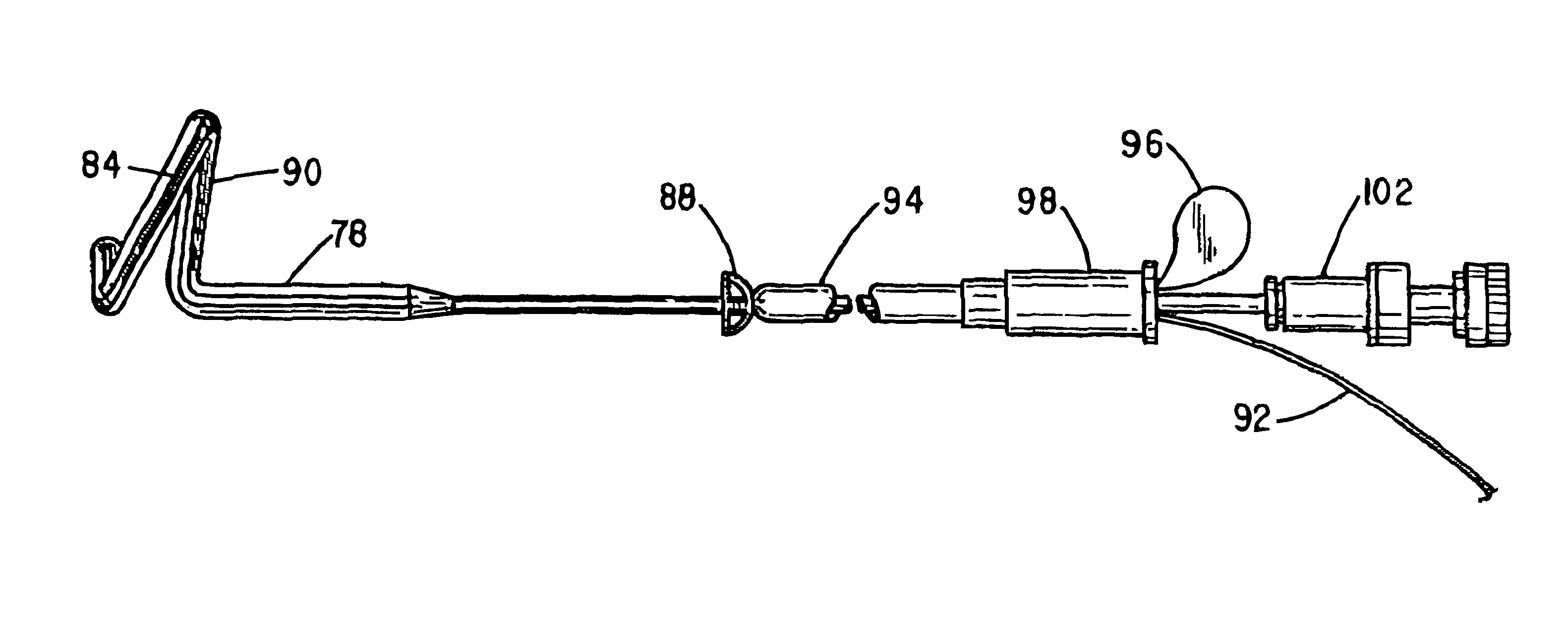
Patents
Literature
3220 results about "Spot urine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
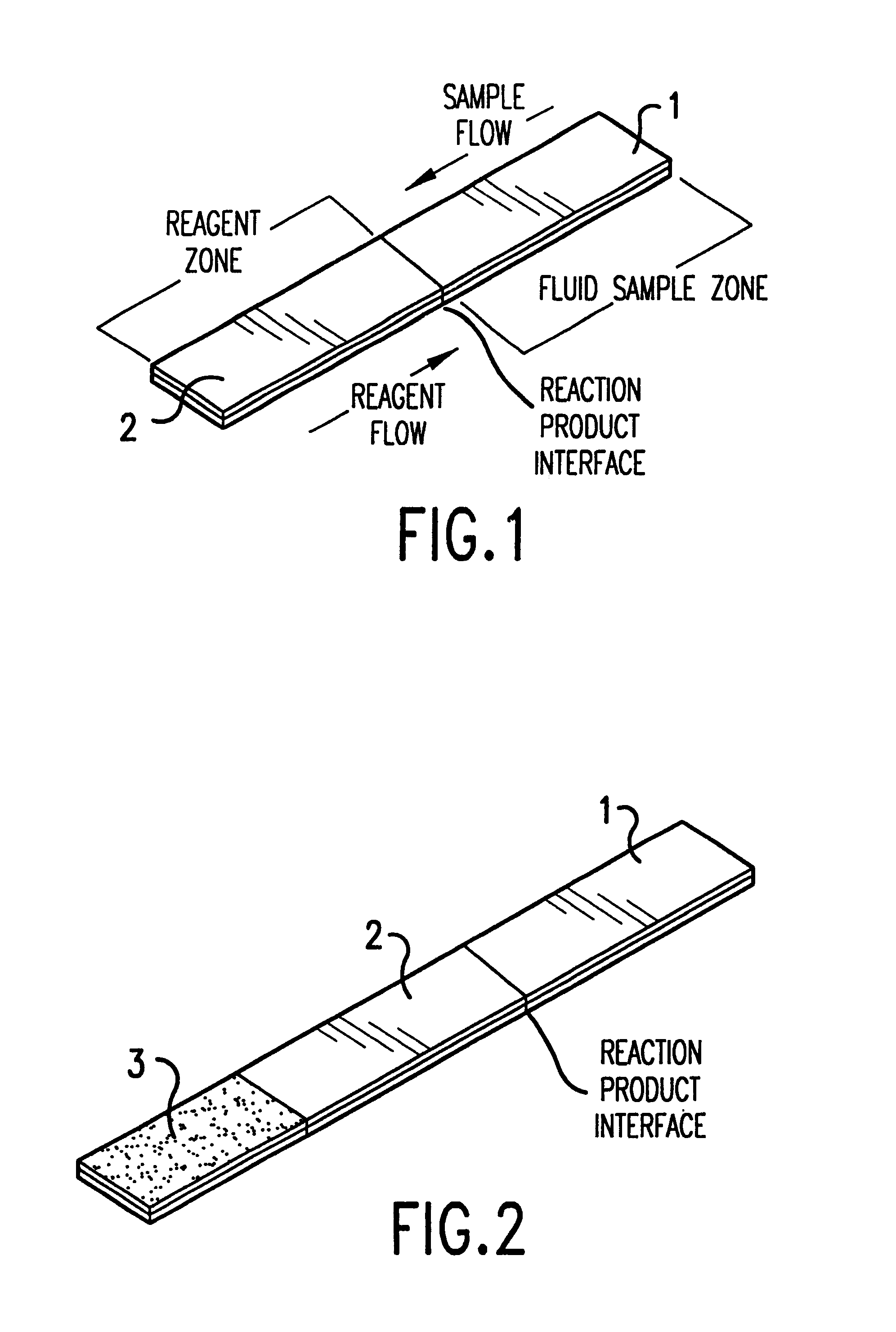
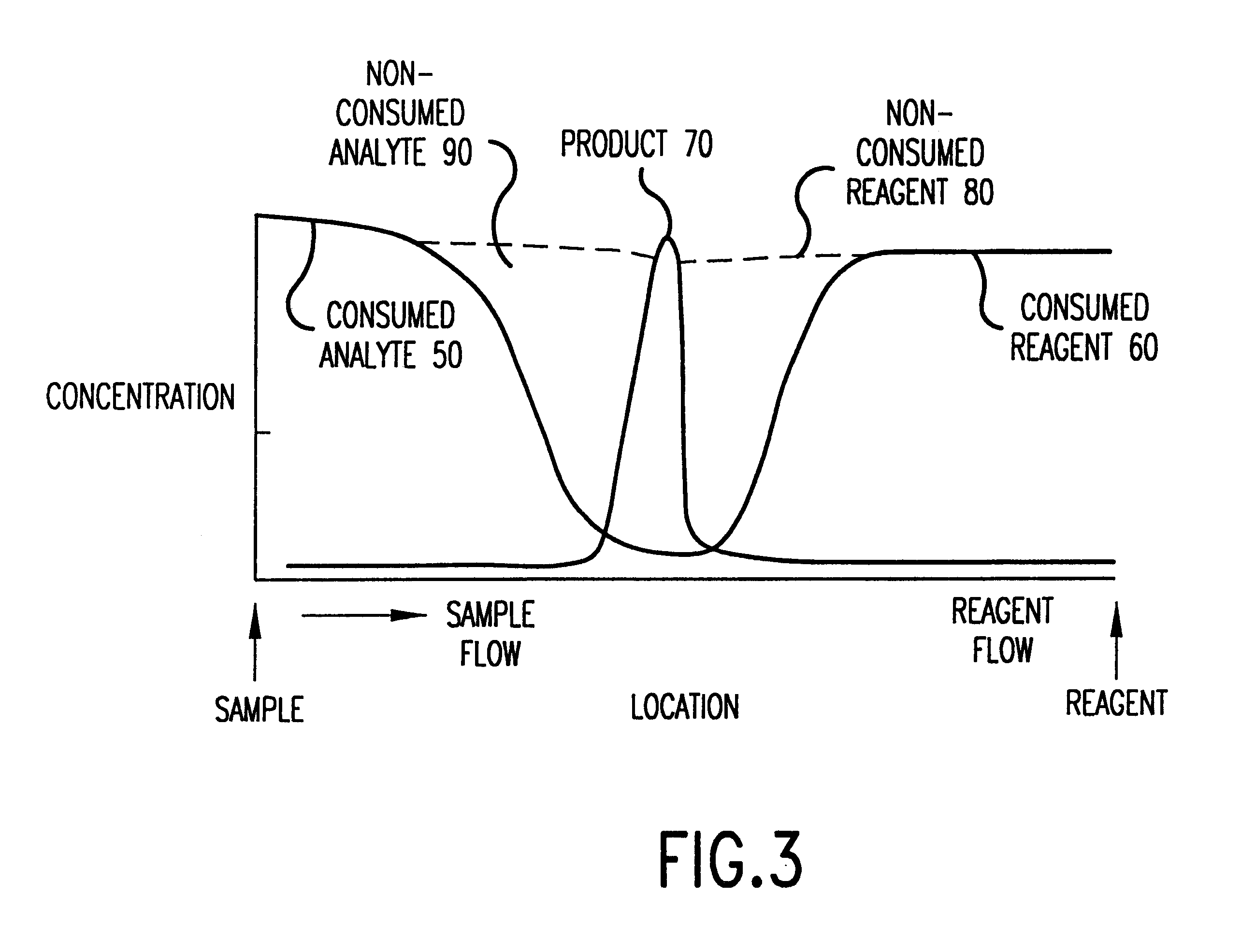
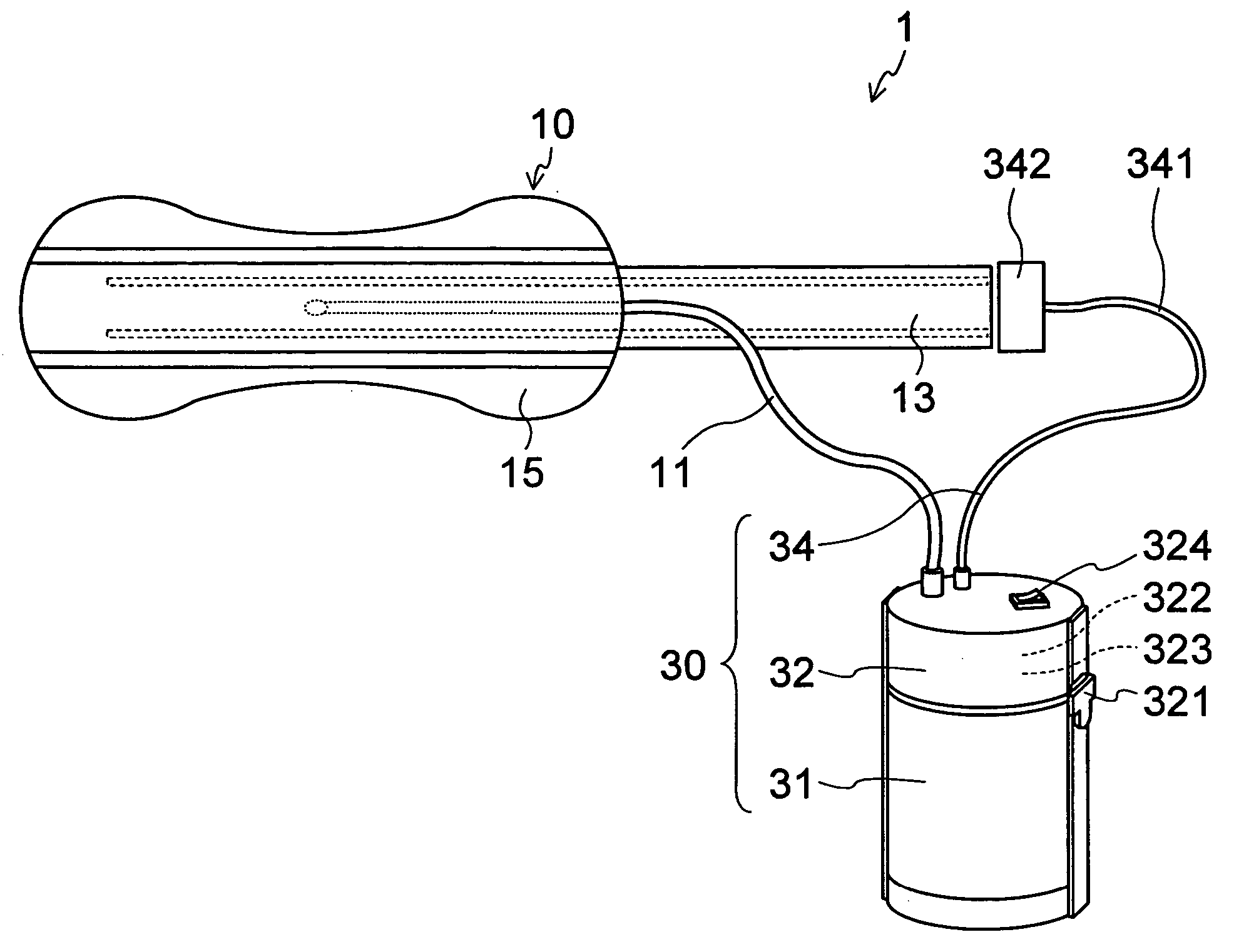
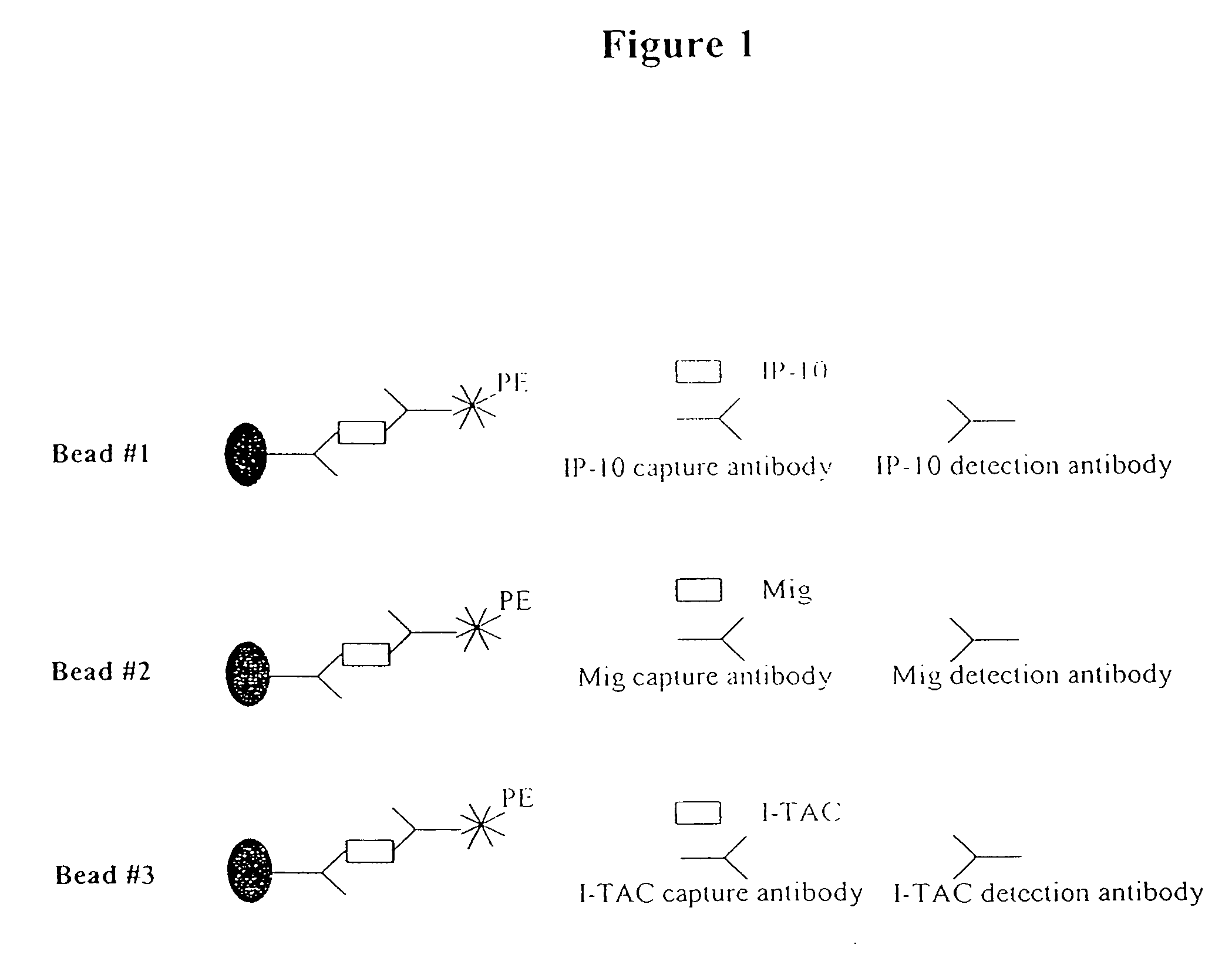
Collection, spot urine The sampling of a single, untimed urine specimen, voided spontaneously by the patient. The sample is analyzed to determine its protein, creatinine, or electrolyte content.
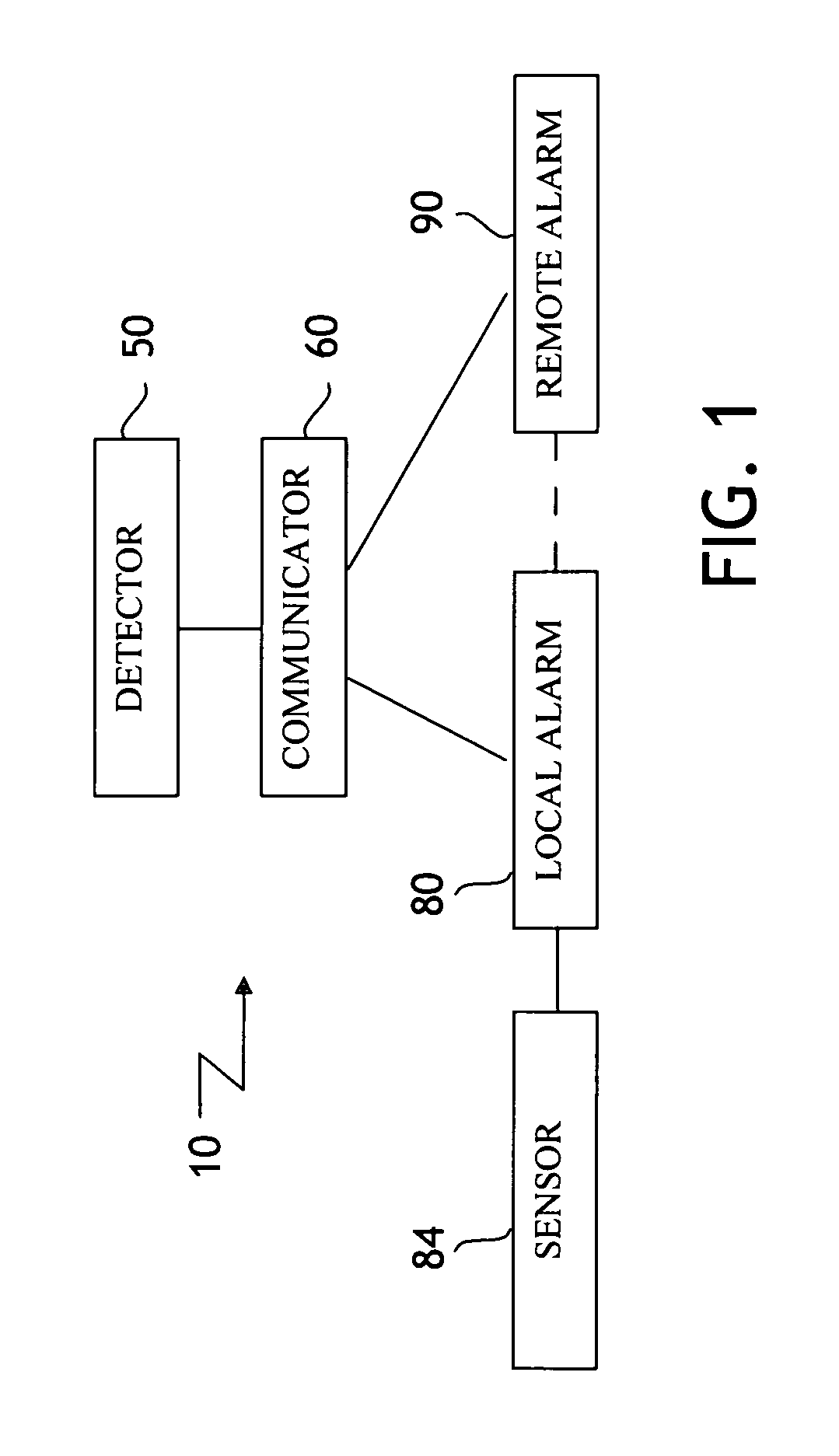
Elimination-absorber monitoring system
InactiveUS6246330B1Complicating power requirementEffectively overcome problemBaby linensAlarmsMonitoring systemEngineering
An elimination-absorber monitoring system addresses diaper-monitoring problems with a unique, low cost, multi-layer disposable sensor structure that absorbs small volumes of urine, yet allows most urine volume to flow unimpeded through it, and into the diaper below. When connected with a reusable, miniature monitor / indicator unit, the sensor presents a clear and on-going change of measurement condition upon experiencing a rapid influx into the diaper of a significant volume of urine, and / or upon a significant reduction in the available absorbency of the diaper's top surface. The sensor additionally provides recessed, protected elements for similarly presenting a clear and on-going change in measurement condition upon experiencing the presence of fecal matter. Further provided is the monitor unit employing narrow, widely-spaced, fast rise-time, fast transition-time pulses for conductivity measurement and alarm activation. The monitor and sensor are interconnected and attached to a diaper by particularly effective and unique means, and the monitor is equipped with a highly intuitive and convenient control interface, as well as improved assemblies for the transmission of audible and visual alarm indications. Also described is a convenient test-strip device which, when connected to the monitor / alarm unit of the system, can selectively simulate either a soiled or unsoiled elimination-absorber / sensor for test, caregiver-training or demonstration purposes.
Owner:NIELSEN WYN Y
Process for discriminating between biological states based on hidden patterns from biological data
The invention describes a process for determining a biological state through the discovery and analysis of hidden or non-obvious, discriminatory biological data patterns. The biological data can be from health data, clinical data, or from a biological sample, (e.g., a biological sample from a human, e.g., serum, blood, saliva, plasma, nipple aspirants, synovial fluids, cerebrospinal fluids, sweat, urine, fecal matter, tears, bronchial lavage, swabbings, needle aspirantas, semen, vaginal fluids, pre-ejaculate.), etc. which is analyzed to determine the biological state of the donor. The biological state can be a pathologic diagnosis, toxicity state, efficacy of a drug, prognosis of a disease, etc. Specifically, the invention concerns processes that discover hidden discriminatory biological data patterns (e.g., patterns of protein expression in a serum sample that classify the biological state of an organ) that describe biological states.
Owner:ASPIRA WOMENS HEALTH INC +1
Methods, compositions, and automated systems for separating rare cells from fluid samples
InactiveUS7166443B2Aid in diagnosis and prognosisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCancer cellRed blood cell
The present invention recognizes that diagnosis and prognosis of many conditions can depend on the enrichment of rare cells from a complex fluid sample. In particular, the enrichment of fetal cells from maternal samples, such as maternal blood samples, can greatly aid in the detection of fetal abnormalities or a variety of genetic conditions. In addition, the present invention recognizes that the enrichment of rare malignant cells from patient samples, can aid in diagnosis, prognosis, and development of therapeutic modalities for patients. The invention includes microfabricated filters for filtering fluid samples and methods of enriching rare cells of fluid samples using microfabricated filters of the present invention. The invention also includes solutions for the selective sedimentation of red blood cells (RBCs) from a blood sample and methods of using selective RBC sedimentation solutions for enriching rare cells of a fluid sample. Yet another aspect of the invention is an automated system for processing a fluid sample that includes: at least one filtration chamber that includes a microfabricated filter; automated means for directing fluid flow through at least one filtration chamber of the automated system, and means for collecting enriched rare cells. The present invention also includes methods of using automated systems for separating rare cells from fluid samples. Preferred fluid samples are blood, effusion, or urine samples, and rare cells that can be enriched from such sample include nucleated red blood cells and cancer cells.
Owner:AVIVA BIOSCI
Analyte test system for determining the concentration of an analyte in a physiological or aqueous fluid
InactiveUS20050196747A1Cheap productionReliable resultsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSmall sampleQuality control system
This invention provides a device for determining the concentration of an analyte like glucose, cholesterol, free fatty acids, triglycerides, proteins, ketones, phenylalanine or enzymes, in a physiological or aqueous fluid like blood, serum, plasma, saliva, urine, interstitial and / or intra-cellular fluid, the device having an integrated calibration and quality control system suitable for dry reagent test strips with a very small sample volume of about 0.5 μL based on to a new sample distribution system. The production of the inventive analyte test element involves only a small number of uncomplicated production steps enabling an inexpensive production of the strips.
Owner:EGOMEDICAL SWISS
System for Conducting the Identification of Bacteria in Urine
ActiveUS20110008825A1Rapid diagnosisImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCuvettePipette
A system for conducting the identification and quantification of micro-organisms, e.g., bacteria in urine samples which includes: 1) several disposable cartridges for holding four disposable components including a centrifuge tube, a pipette tip having a 1 ml volume, a second pipette tip having a 0.5 ml volume, and an optical cup or cuvette; 2) a sample processor for receiving the disposable cartridges and processing the urine samples including transferring the processed urine sample to the optical cups; and 3) an optical analyzer for receiving the disposable cartridges and configured to analyze the type and quantity of micro-organisms in the urine sample. The disposable cartridges with their components including the optical cups or cuvettes are used in the sample processor, and the optical cups or cuvettes containing the processed urine samples are used in the optical analyzer for identifying and quantifying the type of micro-organism existing in the processed urine samples.
Owner:POCARED DIAGNOSTICS
Diagnostic assay device
This invention relates to assays for an analyte in a liquid sample such as a body fluid. More particularly, the invention relates to a method and apparatus for the detection of a ligand in a body fluid such as urine or blood, which includes an immobilization zone for interfering agents in a sample.
Owner:SEKISUI DIAGNOSTICS
Method and system for microfluidic manipulation, amplification and analysis of fluids, for example, bacteria assays and antiglobulin testing
A microfluidic system for isolation and amplification of DNA or RNA from aqueous solutions and detection of the DNA or RNA on a lateral flow detection strip, including a disposable microfluidic card for use in analysis of bacteria in platelets and an analysis of sexually transmitted diseases (STD) in urine. The card will include an embedded membrane that filters out cells and cellular debris. Any biological debris on the membrane will be lysed and the DNA or RNA amplified via PCR amplification protocol, including appropriate reagents and thermal cycling conditions. The amplified DNA or RNA are transferred to a lateral flow detection strip for a visual diagnostic read out. An alternate embodiment includes a microfluidic card for use in typing antiglobulin assays.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Methods for detecting early cancer
InactiveUS7090983B1Easy to implementSensitive highPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteriuriaUrine production
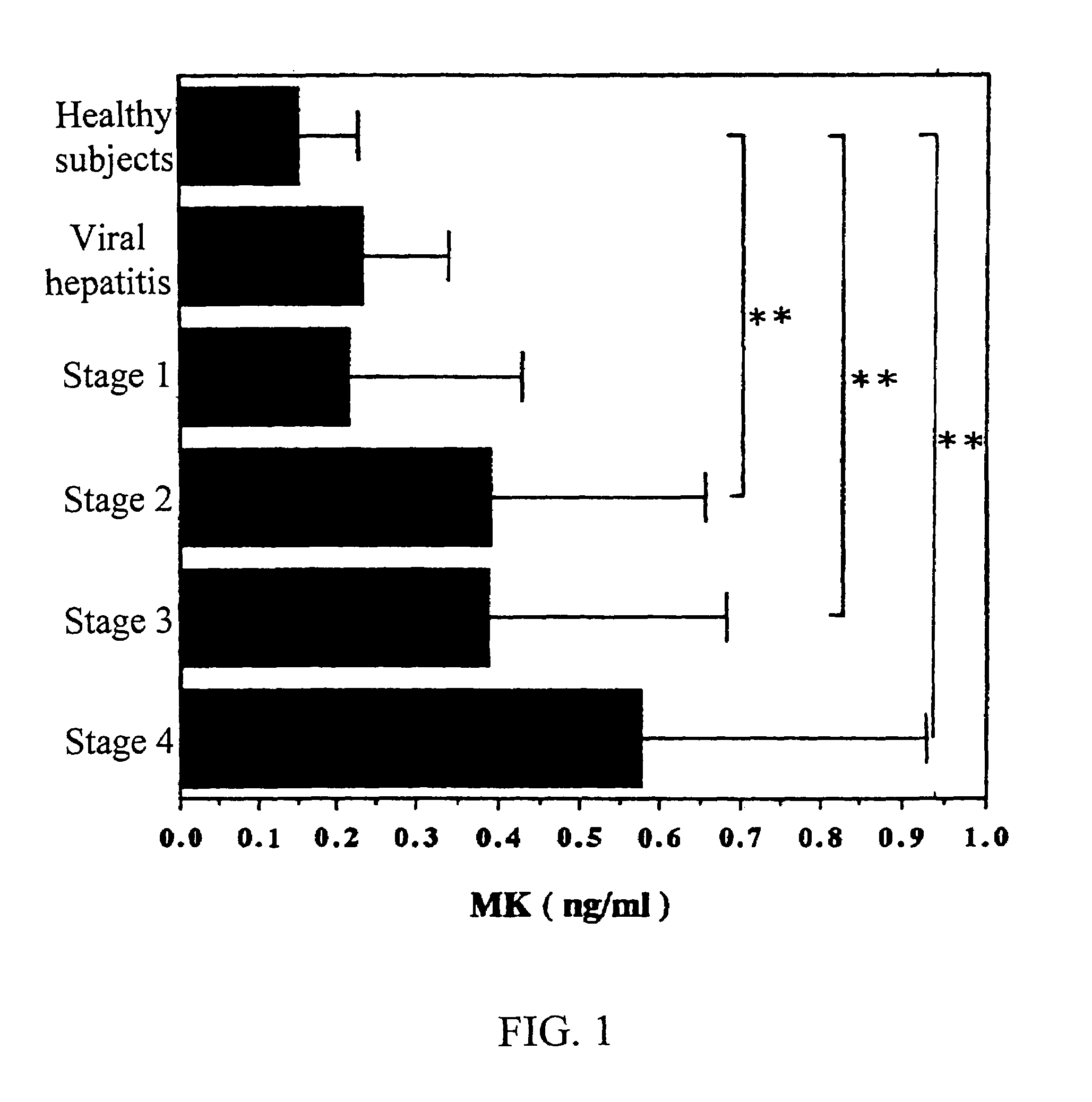
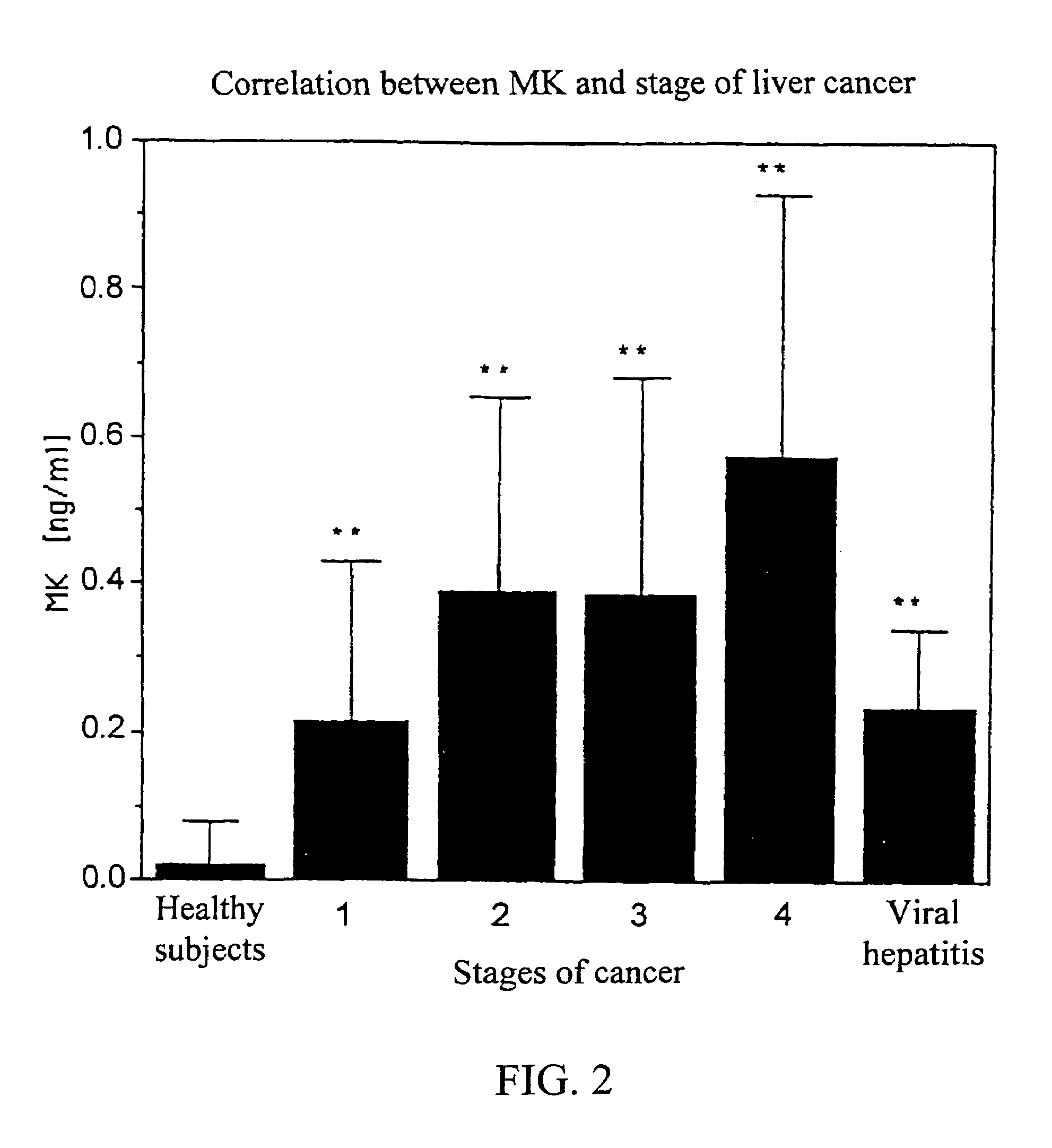
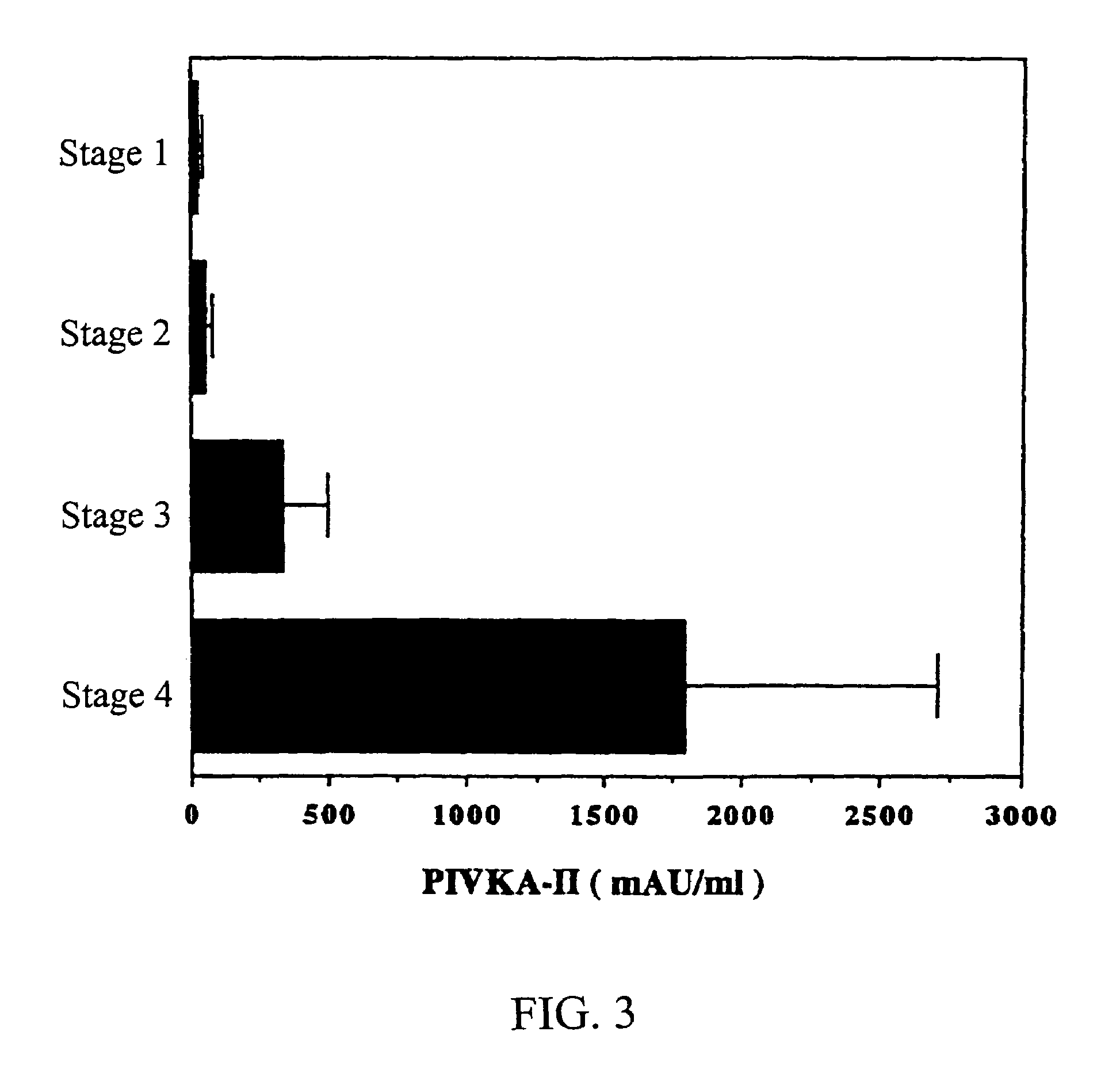
MK (midkine) was found to rise in the blood or urine of patients with various types of cancers at early stage. Based on this finding, a method for detecting early cancer, comprising the step of measuring MK in blood or urine was completed.
Owner:MEDICAL THERAPIES
Analyte measuring system which prevents the reuse of a test strip
InactiveUS20050284757A1Microbiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresAnalytePhysiological fluid
The present invention may be used in test strips for measuring an analyte or indicator such as glucose in a physiological fluid such as blood, interstitial fluid, or urine. The present invention also relates to test strips incorporating an integrated lance such as a needle, blade, or other sharp or skin puncturing device. In particular, in one embodiment of the present invention, a fused link is incorporated into the test strip. The fused link may be destroyed once the test is completed, preventing reuse of the strip.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
Self-cleansing bladder drainage device
An urethral drain having deep external drainage channels, a low-profiled bladder retention segment, and a reversibly detachable collection segment, facilitates the draining of urine and fluids from the bladder. The low-profiled retention means minimizes bladder irritations and the deep external channels reduce the occurrence of infections. Incorporation of a reduced diameter smooth segment on the catheter, proximate the location of the external urethral sphincter allows the patient to void normally and at will. Modifying the size of this smooth segment aids the function of a defective sphincter in controlling urine leakage. The drain can be worn concealed within the urethra. Flushing action from normal voiding washes out particulate matters in the urethra and the concealed drain further minimizes contamination. Together, these features improve quality of life for patients needing catheterization.
Owner:CONSERT INC
Apparatus and method for rapid spectrophotometric pre-test screen of specimen for a blood analyzer
InactiveUS6195158B1The process is fast and accurateWithdrawing sample devicesTransmissivity measurementsLipid formationHematology analyzer
A method and apparatus for use in respect of samples which are assessed for quality prior to testing in a clinical analyzer. The method and apparatus identify parameters such as gel level and height of fluid above the gel in blood samples, where appropriate, for the purposes of positioning the specimen for determination of interferents. Such interferents include hemoglobin (Hb), total bilirubin and lipids. These interferents are determined by measurement of absorption of different wavelengths of light in serum or plasma, or other specimens, which are then compared with values obtained through calibration using reference measurements for the respective interferents in serum or plasma or other type of specimen. Determinations of temperature of the specimen, as well as specimen type, for example whether the specimen is urine or plasma or serum, may also be carried out.
Owner:NELLCOR PURITAN BENNETT LLC
Automated Sampling And Analysis Using A Personal Sampler Device
InactiveUS20090093970A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImaging processingMedicine
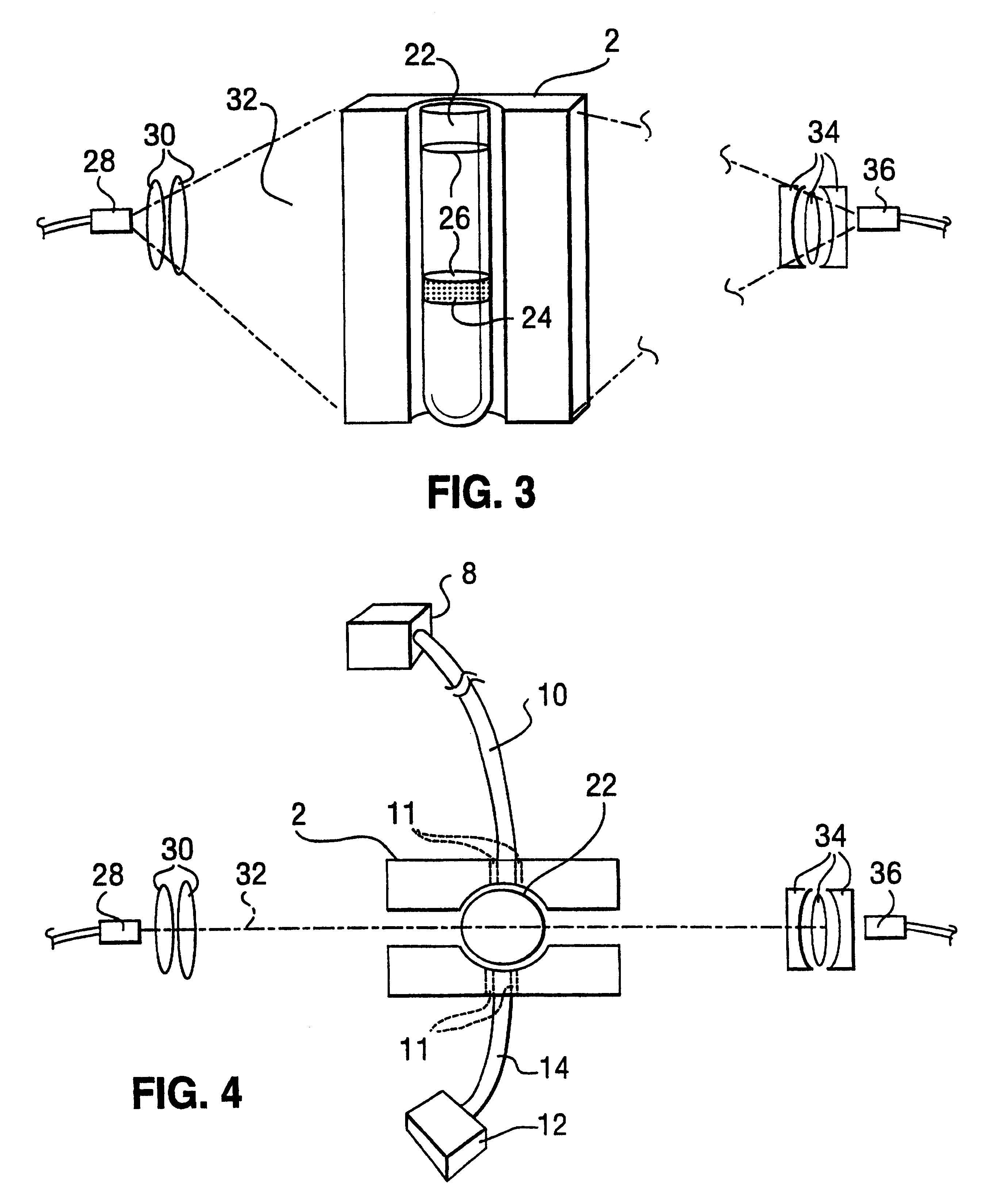
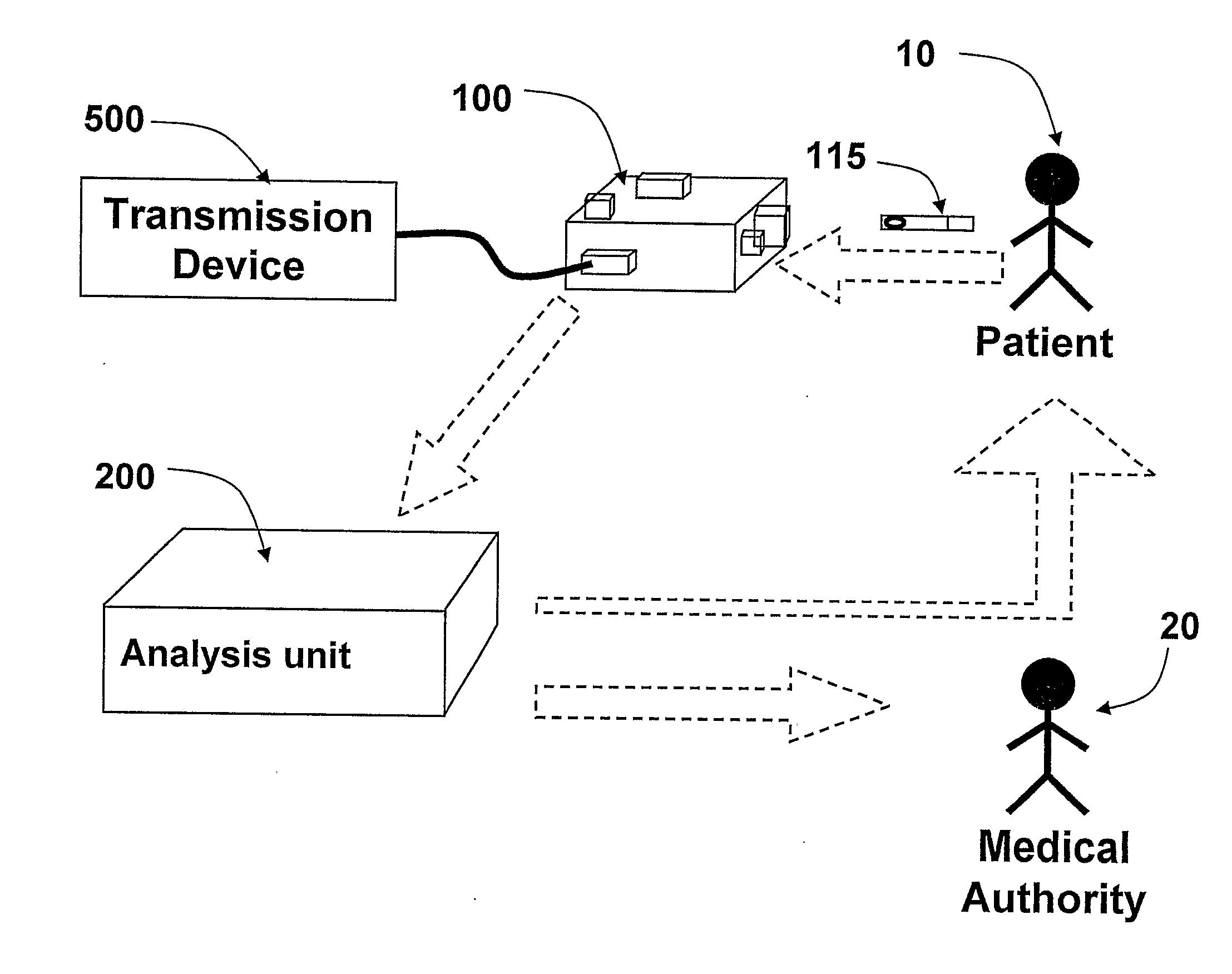
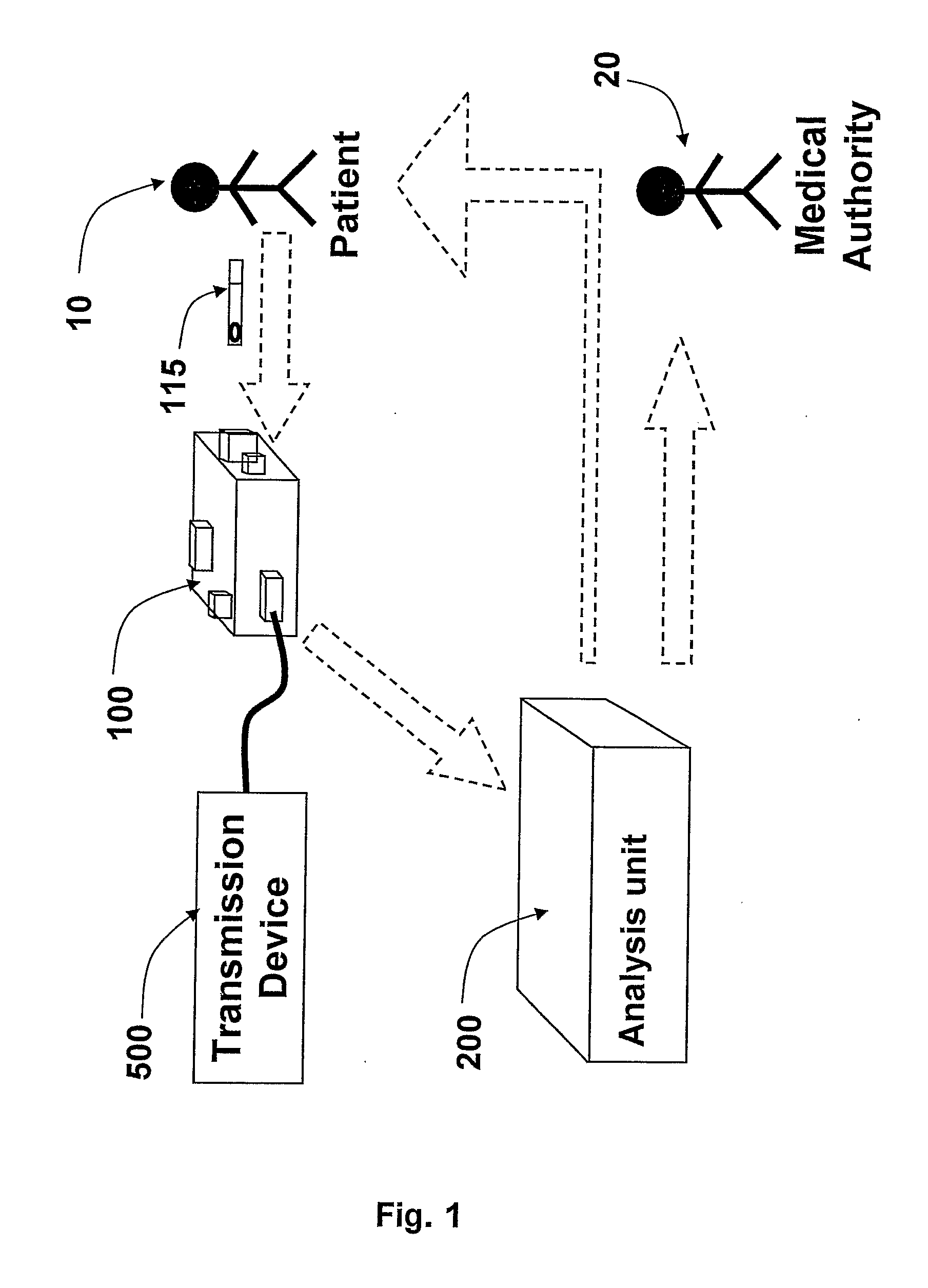
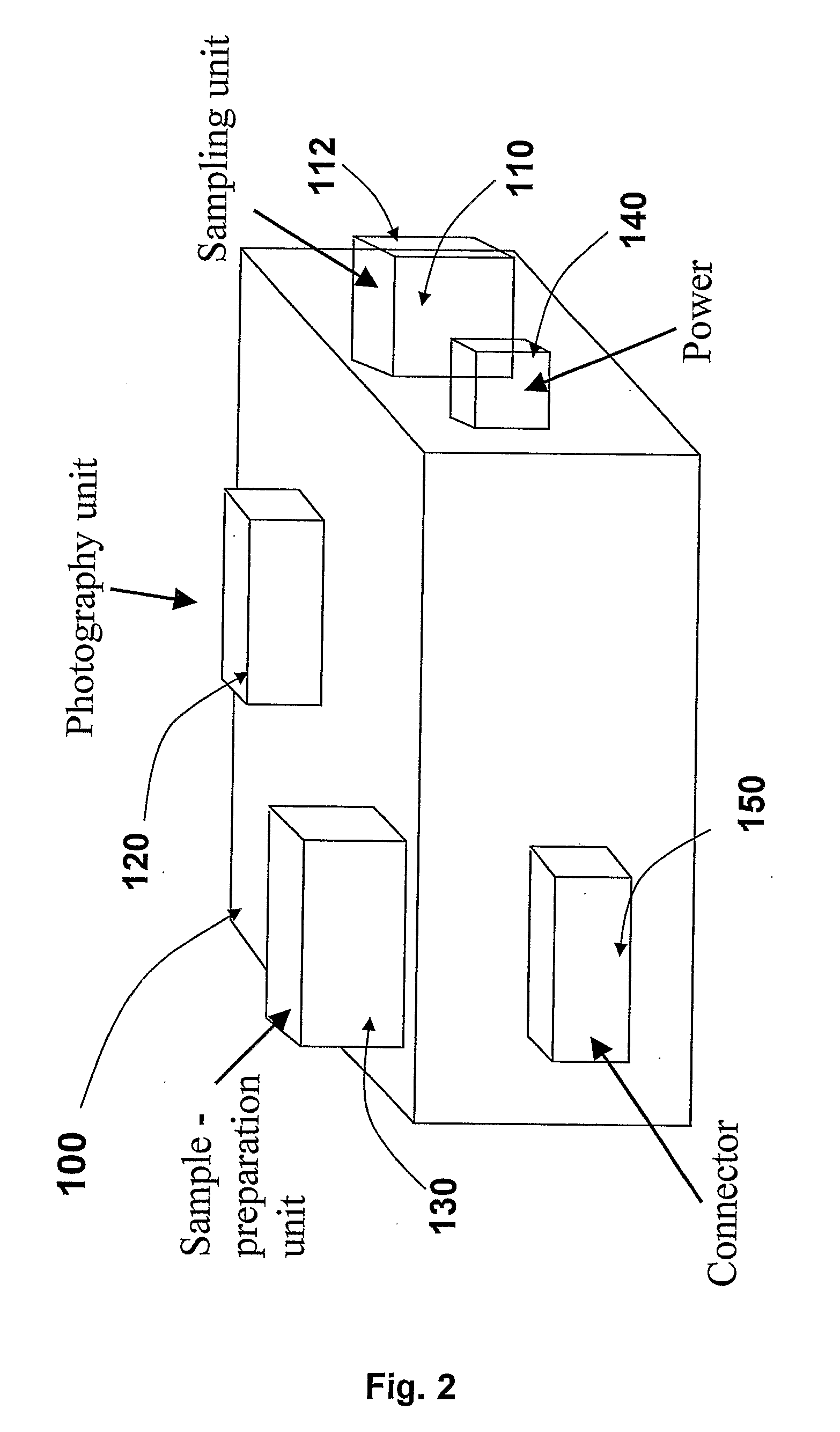
The present invention is a system and a method for blood or urine sampling and sample-analysis, through a sampler that is a self blood-testing device or a urine-testing device. The system comprises a sampler, a transmission unit and an analysis unit. A patient may place a sampled blood drops on a sample strip and insert the strip into the sampler. The sampler may automatically prepare the sample and photograph it using a sample-preparation unit and a photography unit respectively. After the sample has been photographed, the resulting sample image may be transmitted to the analysis unit that may analyze the image through an image-processing algorithm. The analysis results may be automatically transmitted to the patient and to a medical authority, such as the patient's physician, a nurse, a clinic and the like, for further analysis, decision-making and treatment.
Owner:LEWY HADAS +2
Kit for determining heart-type fatty acid binding protein in serum or urine by latex enhanced turbidimetric immunoassay
ActiveCN102628864AStrong specificityImprove accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingLatex particlePHA granule
The invention relates to a kit for determining heart-type fatty acid binding protein in serum or urine by latex enhanced turbidimetric immunoassay. Specifically, the kit for determining the heart-type fatty acid binding protein comprises a reagent R1, a reagent R2 and a calibrator, wherein the reagent R1 contains a reaction promoter, an antiseptic, a surfactant, a stabilizing agent, an electrolyte and a buffer; the reagent R2 contains latex particles with binding of anti-heart-type fatty acid binding protein monoclonal antibody and polyclonal antibody, an antiseptic, a surfactant, a stabilizing agent, an electrolyte and a buffer; and the calibrator contains an antiseptic, an electrolyte, a stabilizing agent, a heart-type fatty acid binding protein pure product and a buffer. By the complex coating method of latex particles with the monoclonal antibody and the polyclonal antibody, high sensitivity and wide linear range of the kit are guaranteed. Simultaneously, the kit also has advantages of high accuracy, good repeatability, strong singularity, easy operation and the like, and is applicable to an automatic biochemical analyzer which is commonly used in clinic.
Owner:BEIJING STRONG BIOTECH INC
Spectrophotometric system and method for the identification and characterization of a particle in a bodily fluid
InactiveUS7027134B1Rapid and inexpensive and convenient for diagnosisRapidly and inexpensively disease diagnosisScattering properties measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringTurbidimetryWavelength
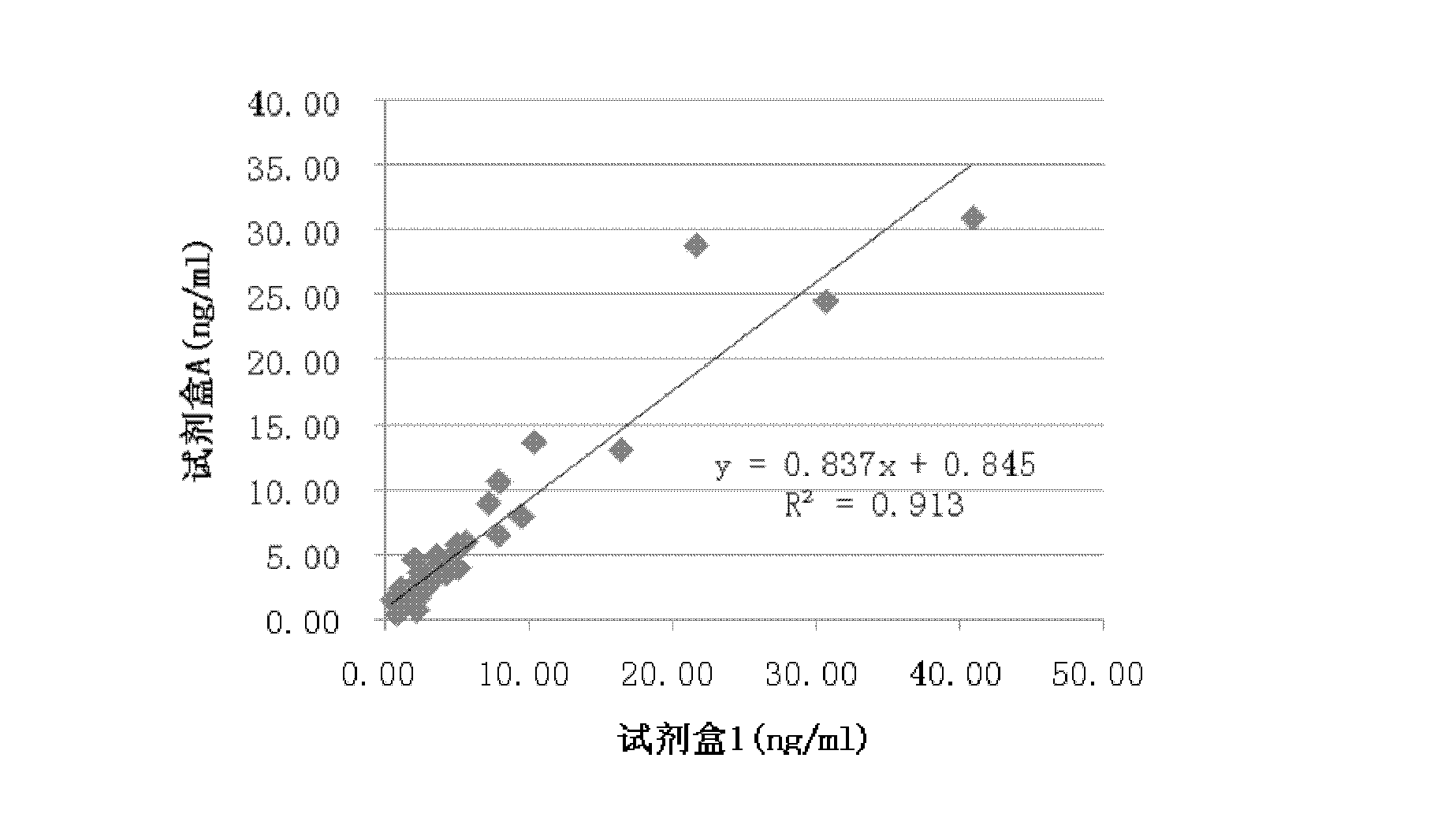
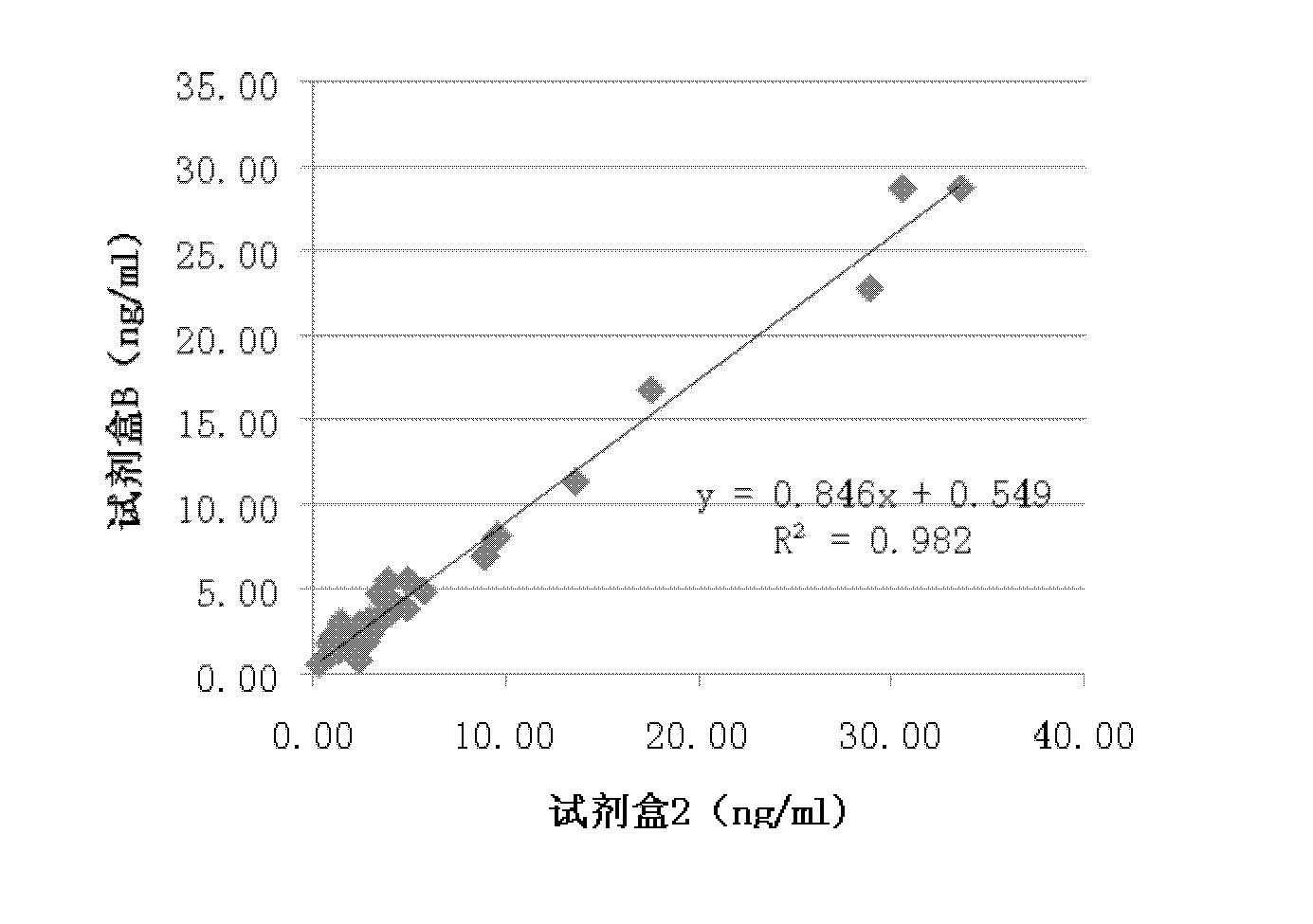
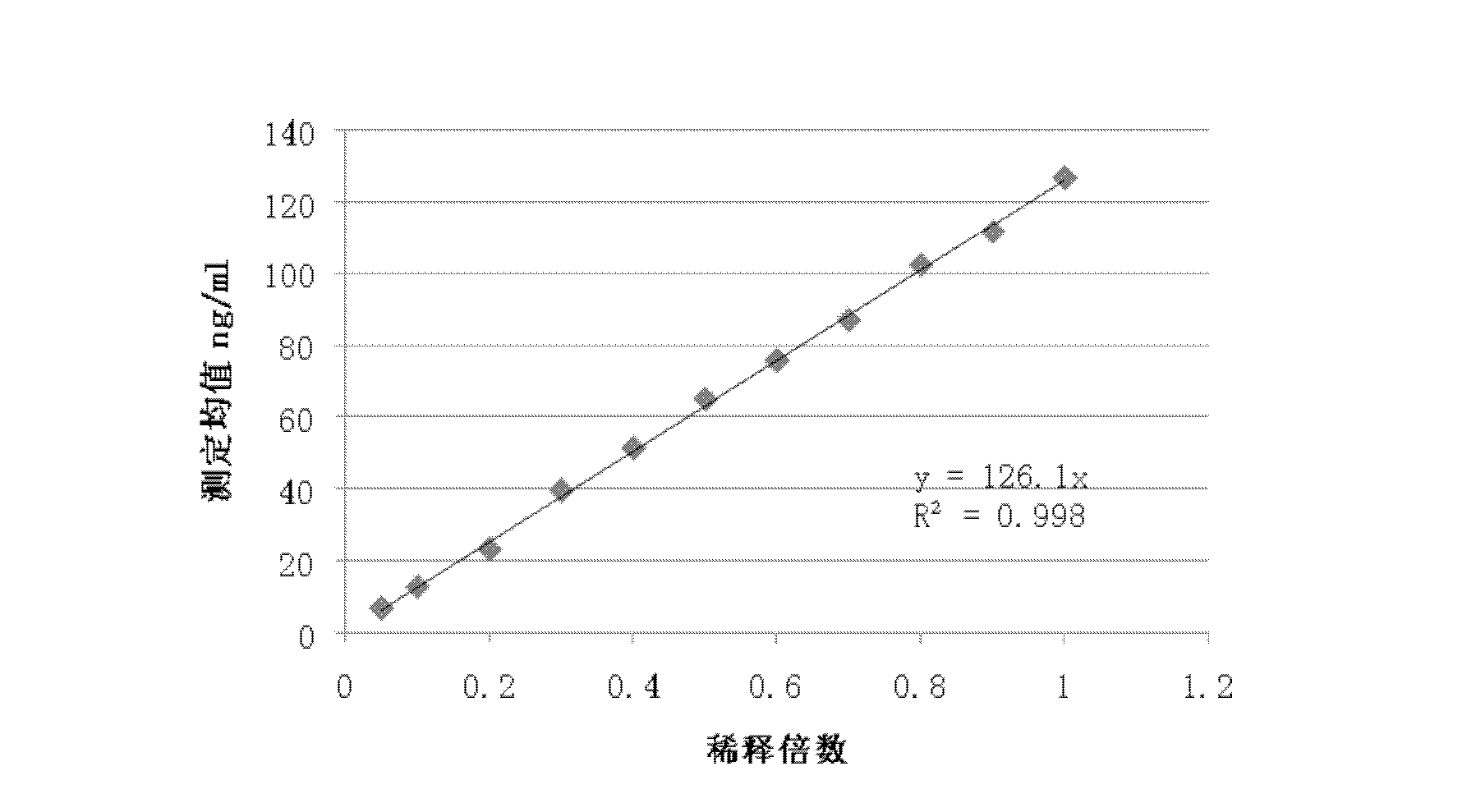
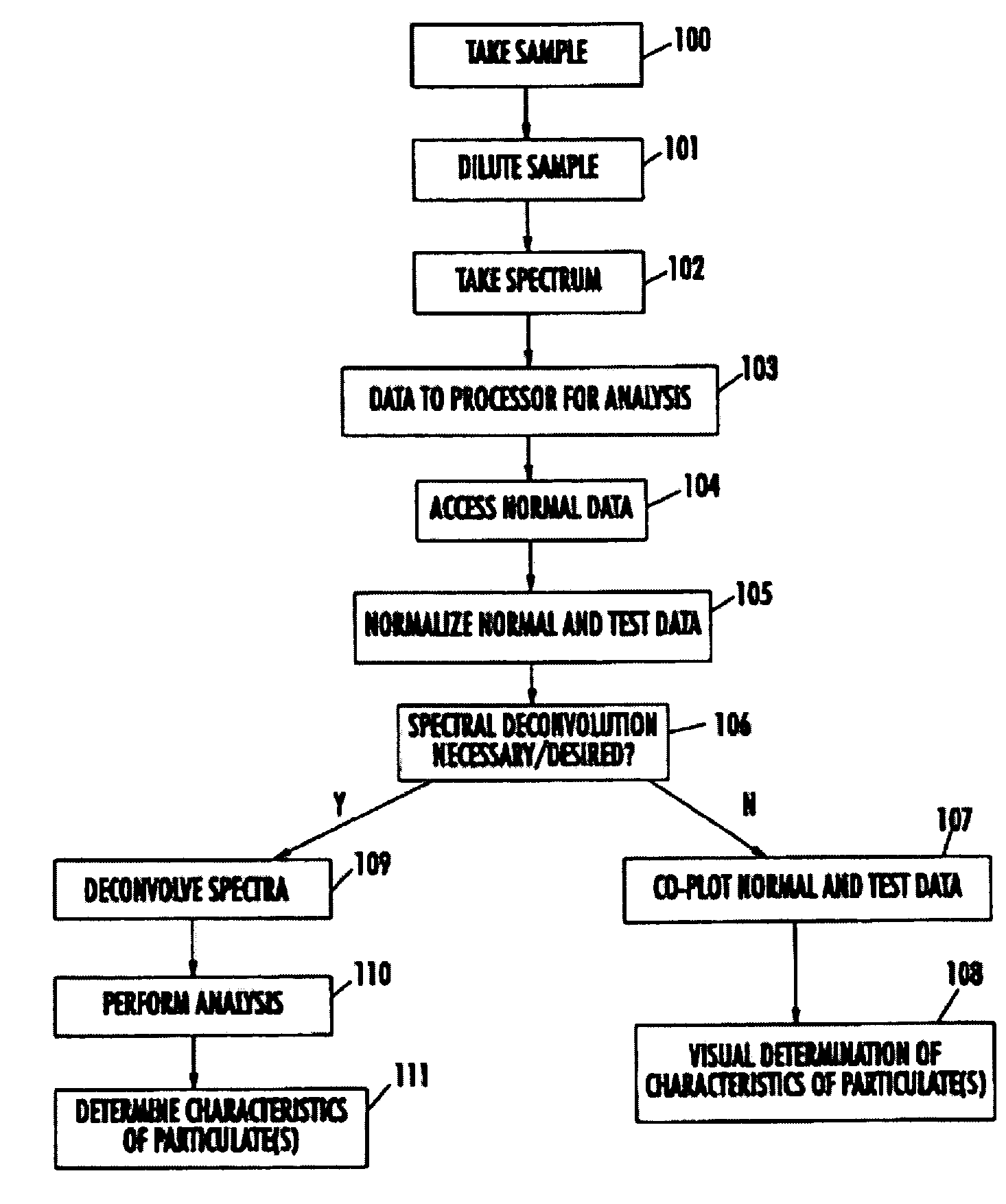
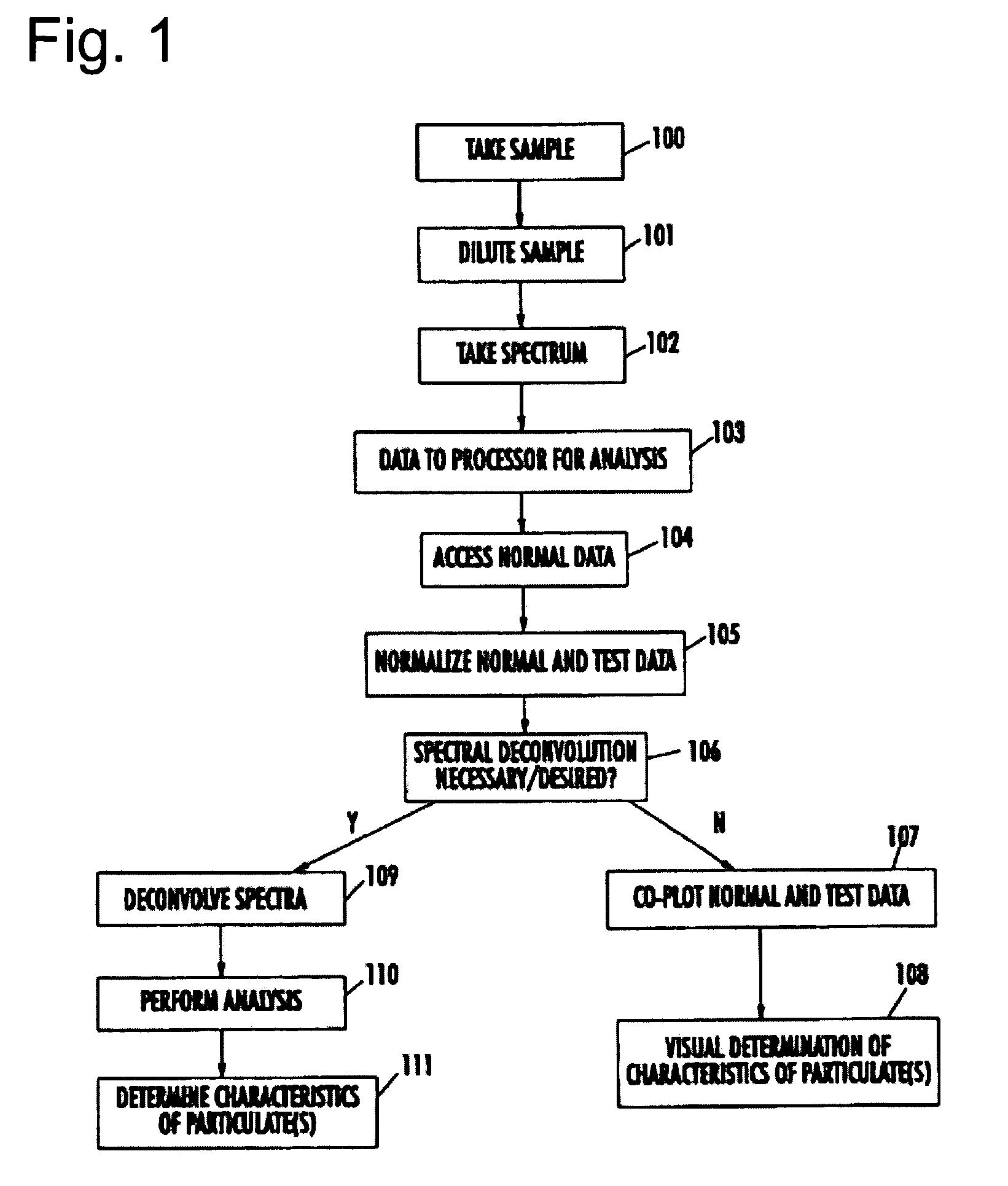
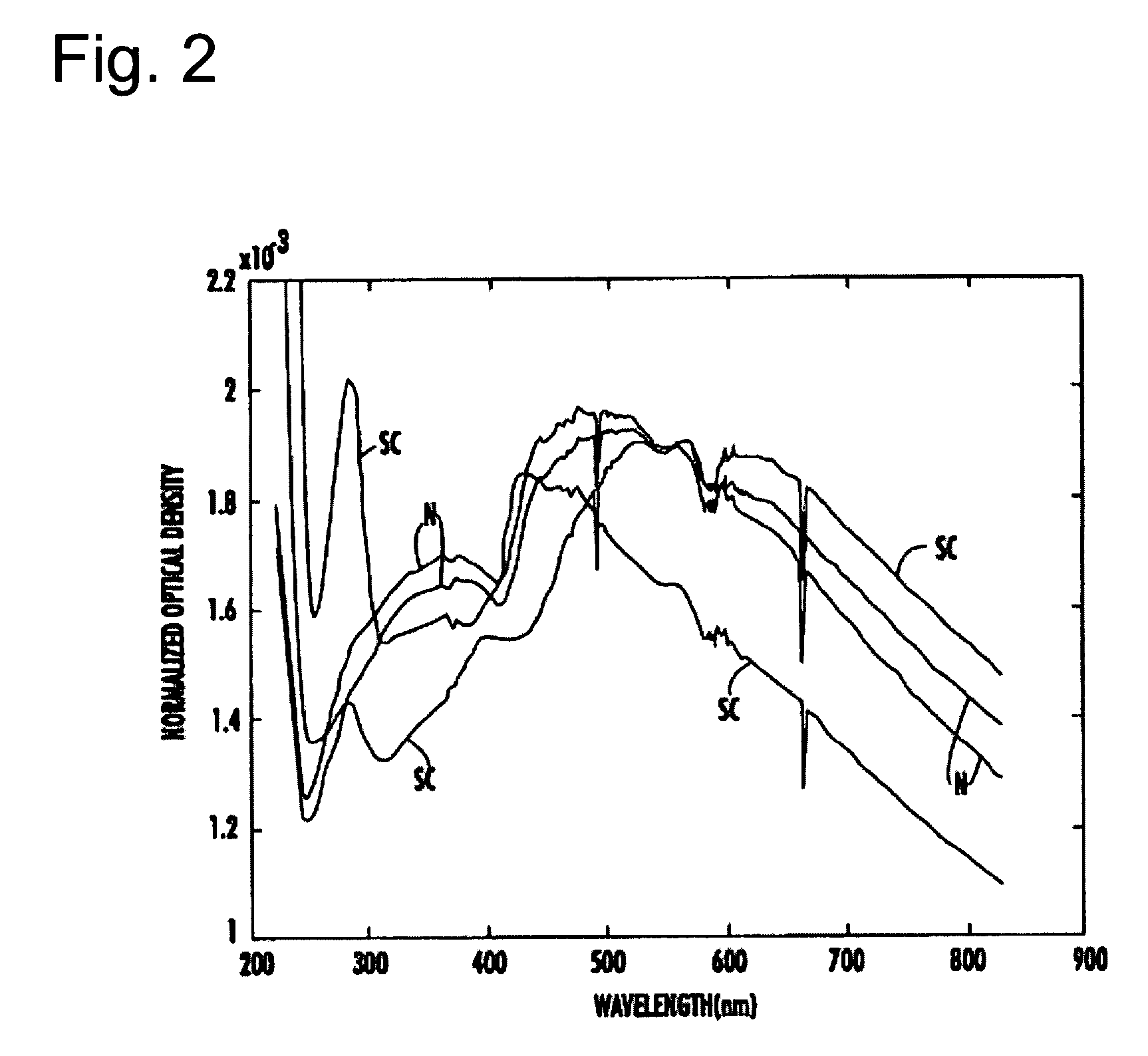
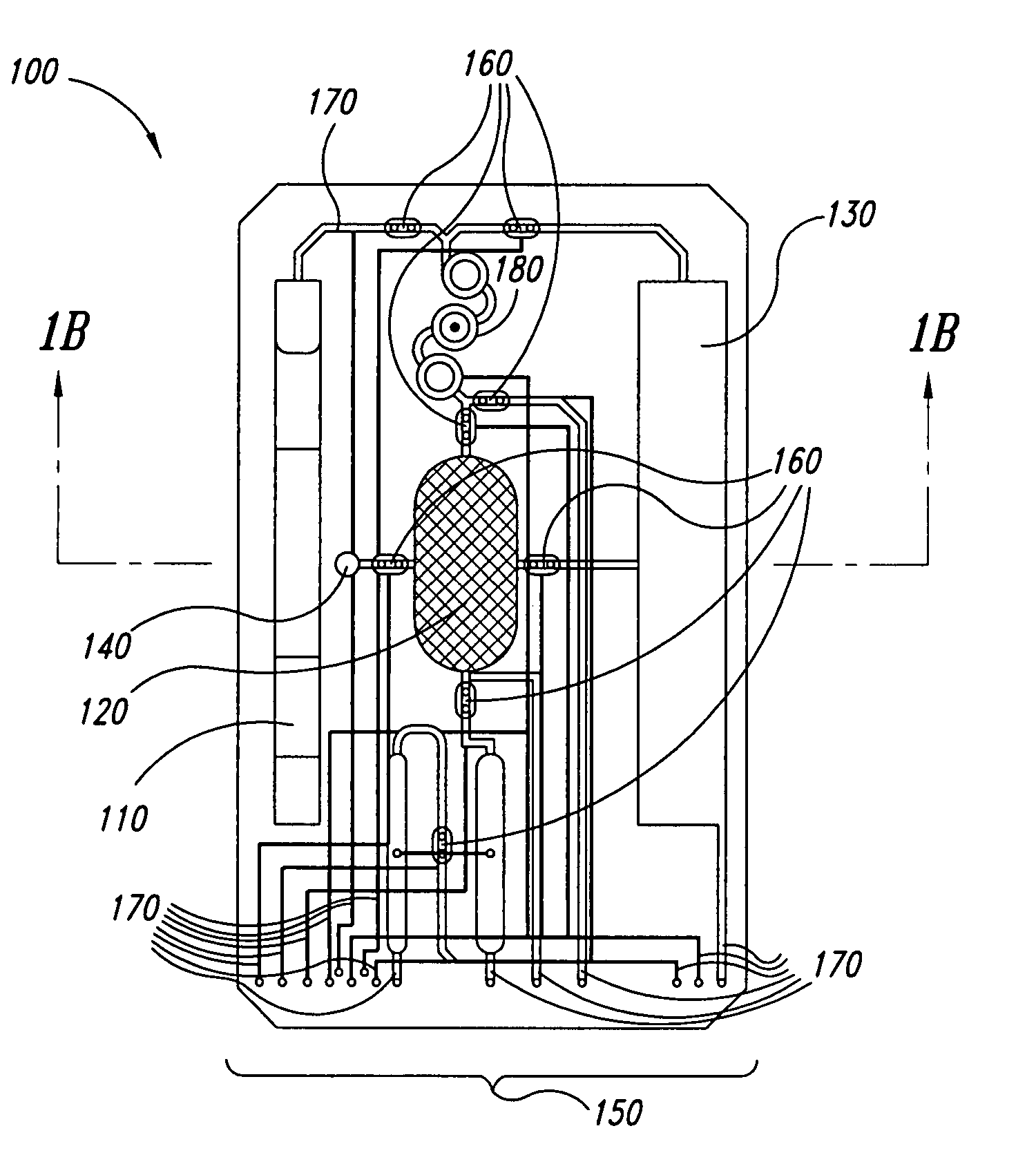
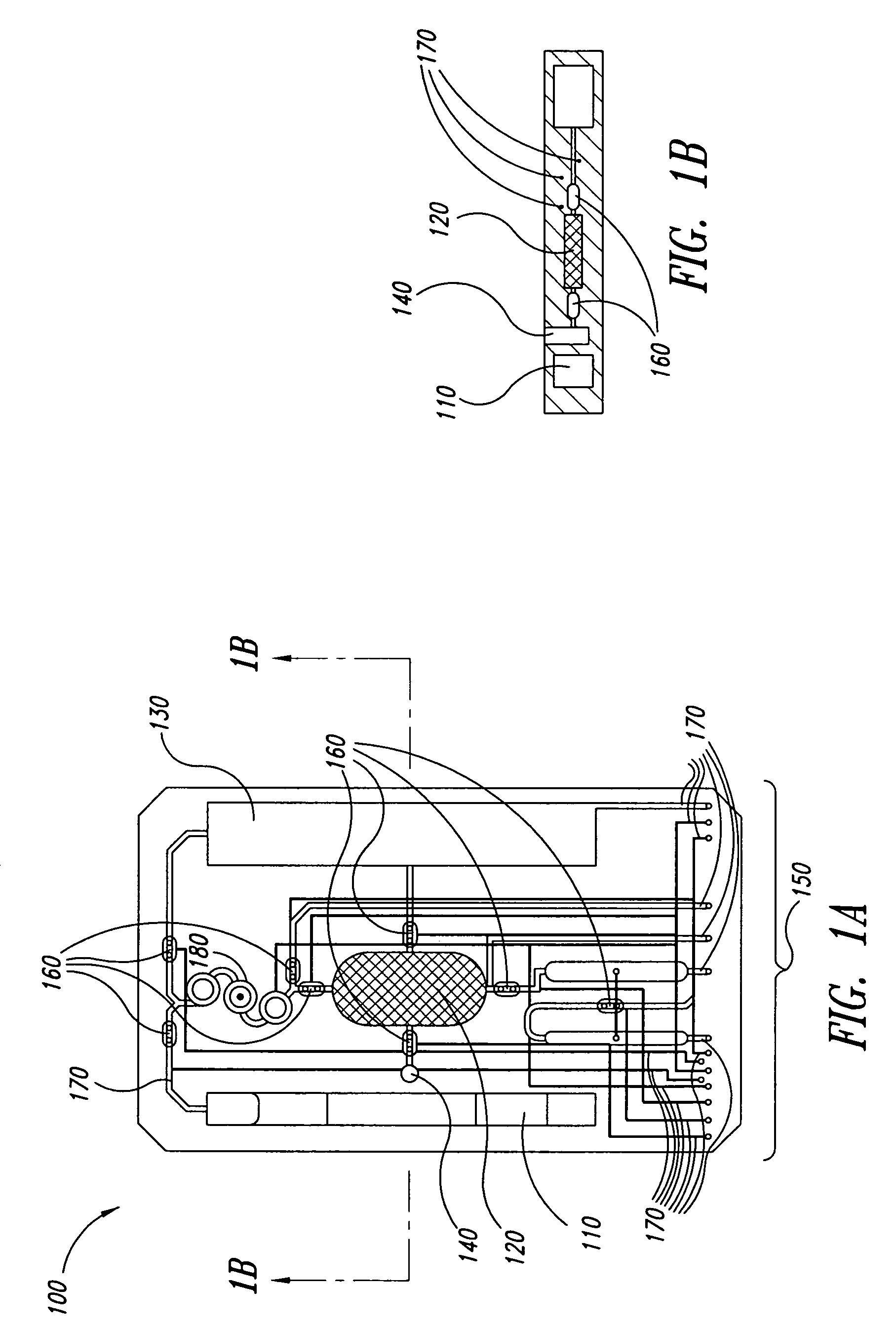
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for the detection of an infectious disease or disorder in a fluid, such as a mammalian blood sample, the detection of a specific protein in a urine sample, or the detection of a particle in a plasma. The identification of the particles of interest is enable by taking a transmission spectrum of a test sample in at least a portion of the ultraviolet, visible, near-infrared portion of the spectrum and comparing the spectrum with a standard sample spectrum. From the comparison it is then determined whether the fluid from the test sample contains an particle of interest, and an identity of the particle of interest is determined. Spectroscopic and multiwavelength turbidimetry techniques provide a rapid, inexpensive, and convenient means for diagnosis. The comparison and determination steps may be performed visually or by spectral deconvolution.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Method and system for microfluidic manipulation, amplification and analysis of fluids, for example, bacteria assays and antiglobulin testing
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Method for the rapid detection of whole microorganisms on retaining membranes by use of chaotropic agents
InactiveUS6846648B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAntigenThiourea
Owner:ANDA BIOLOGICALS
Diagnostic assay device
ActiveUS7465587B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteBody fluid
This invention relates to assays for an analyte in a liquid sample such as a body fluid. More particularly, the invention relates to a method and apparatus for the detection of a ligand in a body fluid such as urine or blood, which includes an immobilization zone for interfering agents in a sample.
Owner:SEKISUI DIAGNOSTICS
Device for maintaining a passage for urine through the prostate
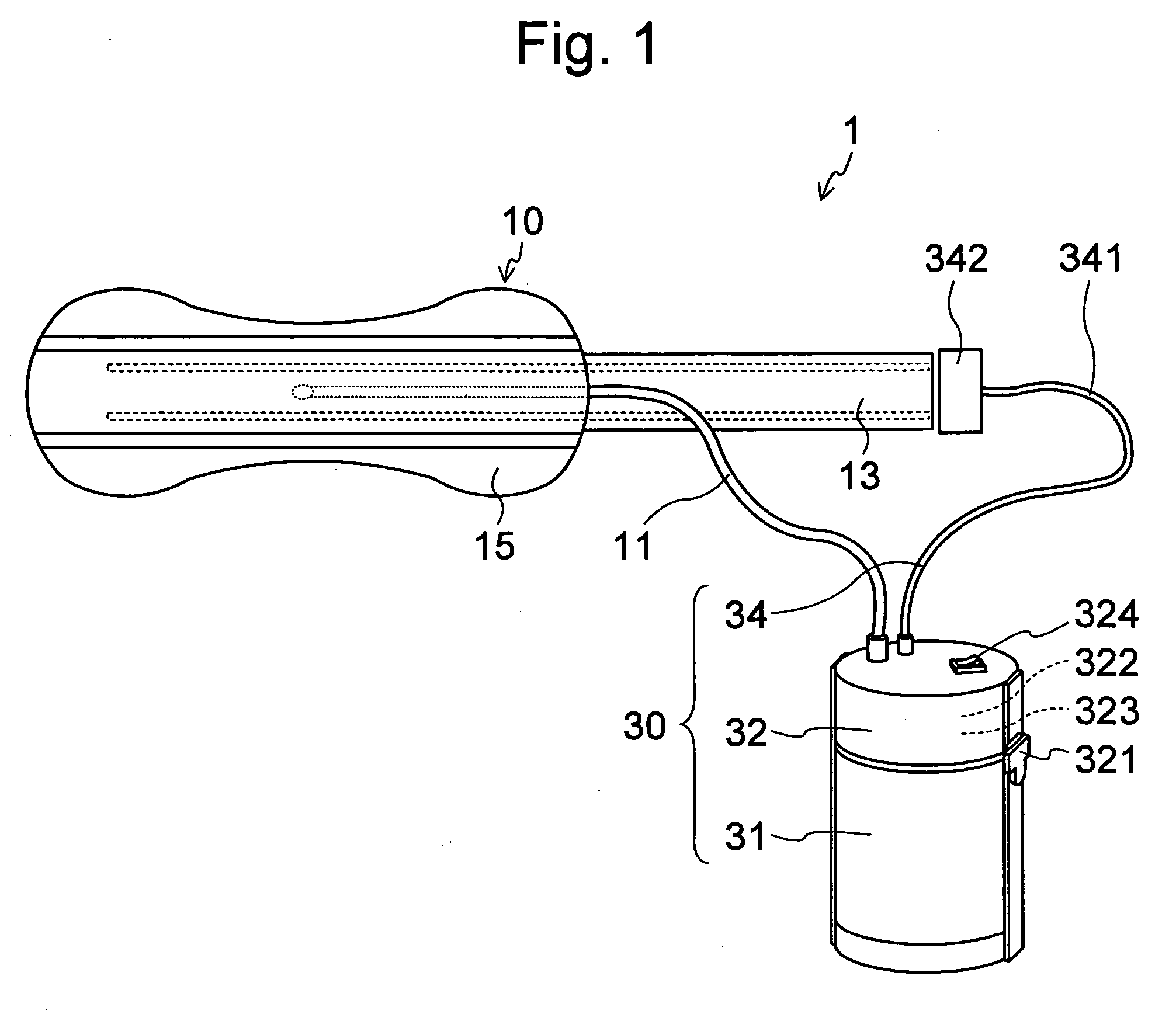
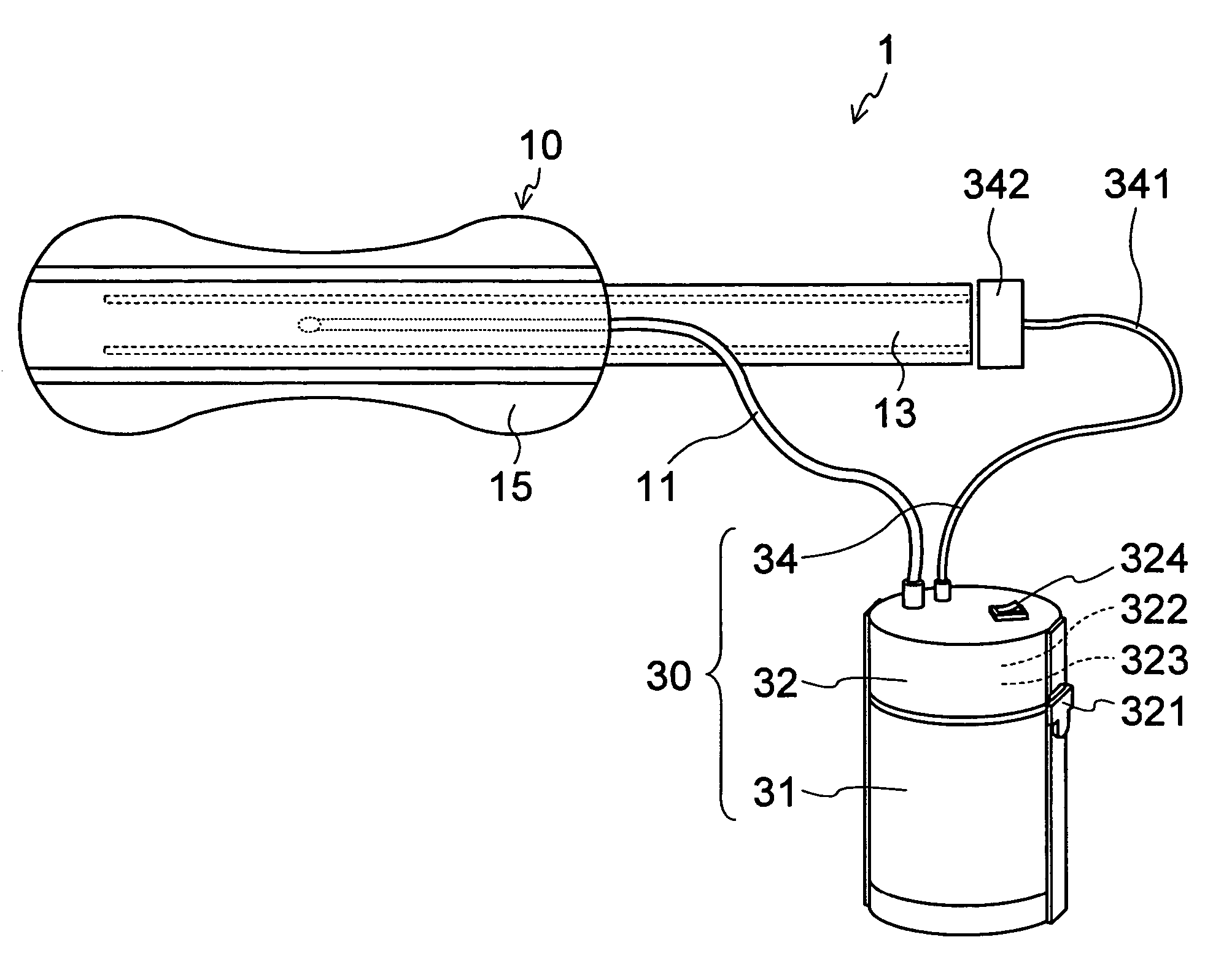
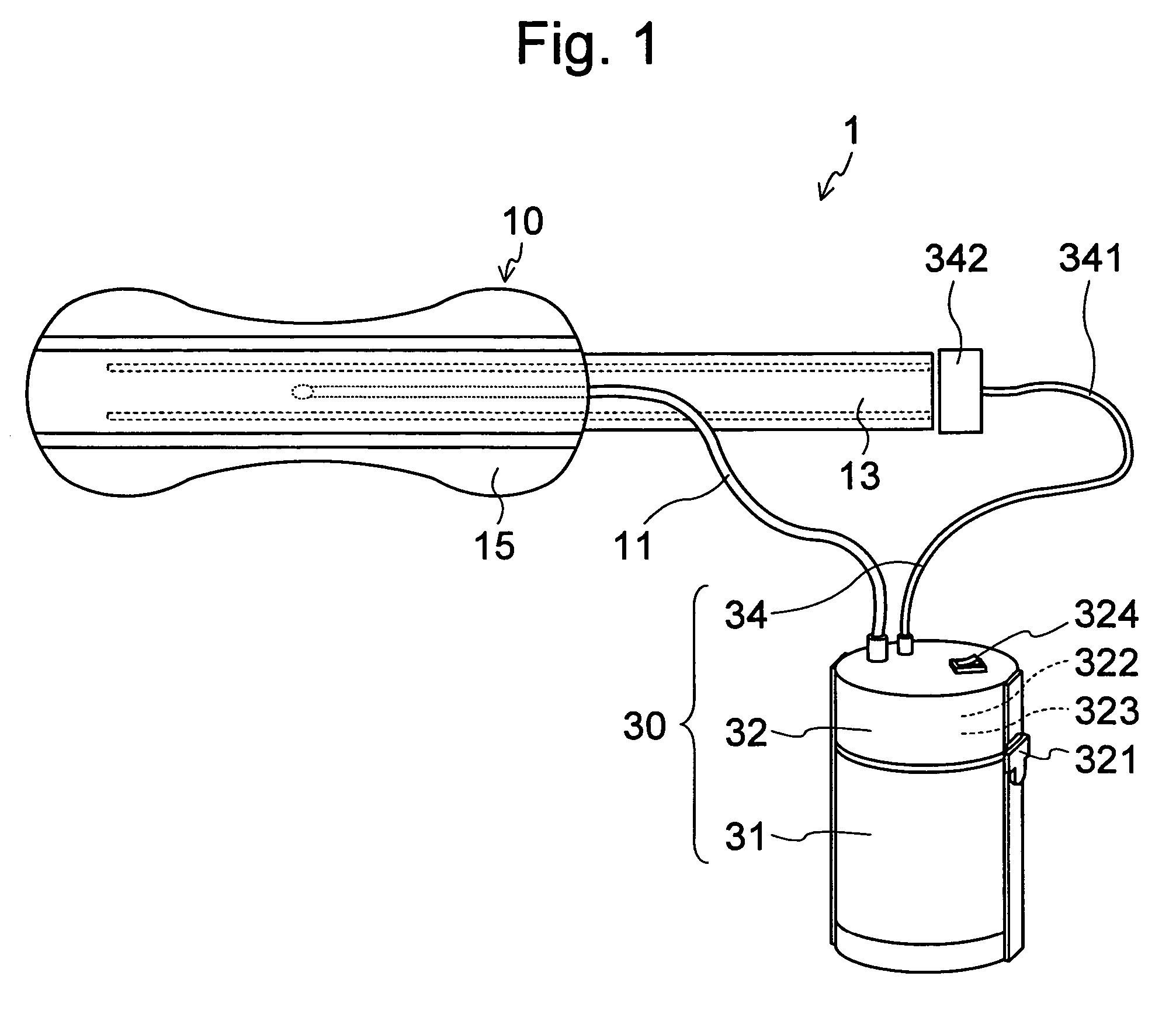
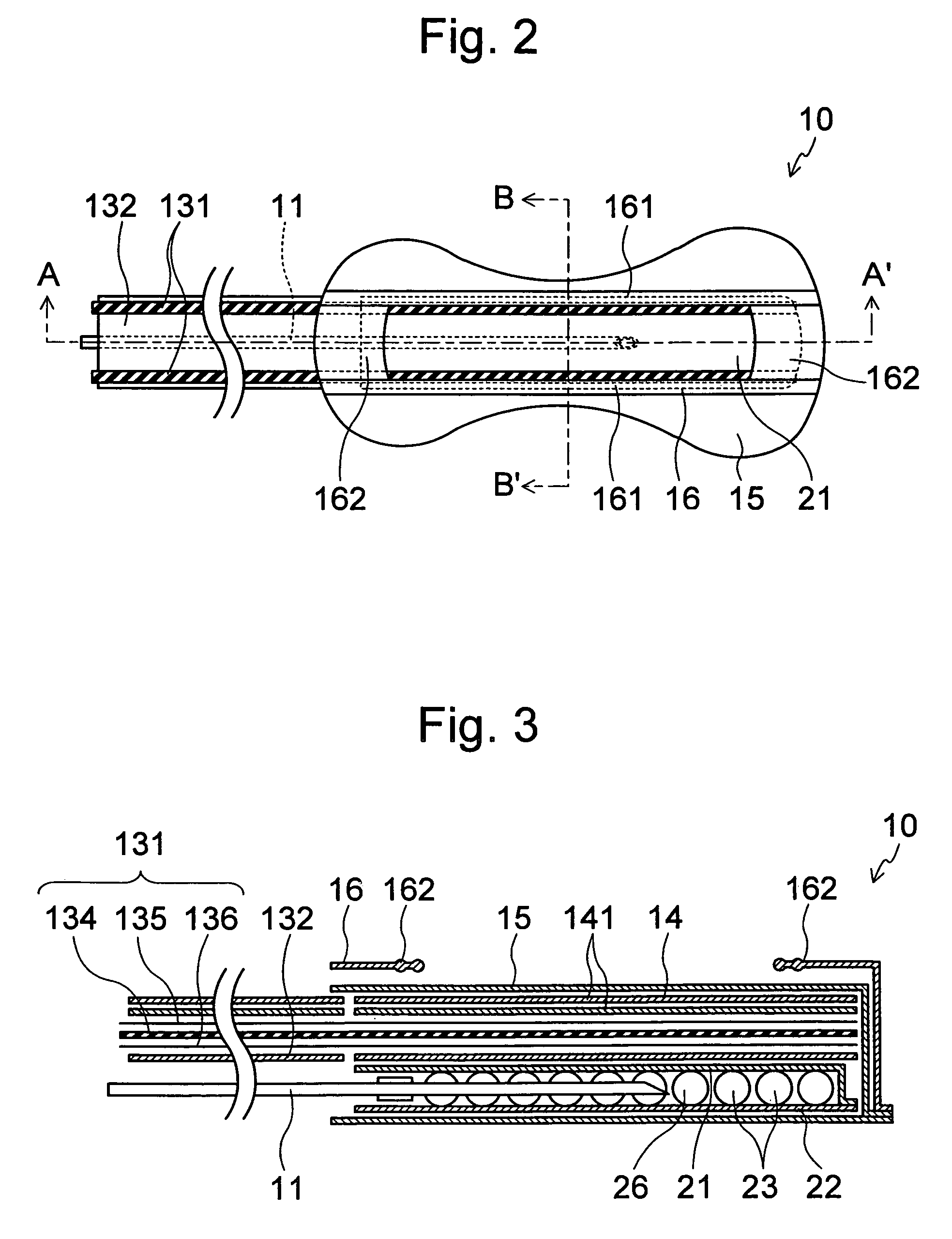
PCT No. PCT / SE96 / 00607 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 12, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 12, 1997 PCT Filed May 9, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 35395 PCT Pub. Date Nov. 14, 1996A device for maintaining a passage through the prostate gland (13) after treatment of a catheter (10) inserted through the urethra into the prostate gland, the catheter (10) being provided with means (11) for heating the prostate gland. A sleeve (12) is received over the catheter (10) so as to follow the catheter (10) during insertion into a desired position within the prostate gland, and the sleeve (12) is formed to remain in the desired position when the catheter is removed from the prostate gland, thereby maintaining a passage having a predetermined lower inner diameter through the prostate gland when tissue in the prostate gland swells.
Owner:PROSTALUND OPERATIONS
Urine sample collection device
InactiveUS20060184064A1Easy to useReduce manufacturing costSurgeryBathroom accessoriesUrine CollectionsUrine collection device
Owner:SAMPLE RITE
Method and device for detecting analytes in fluids
InactiveUS6602719B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh concentrationBlood plasma
Owner:IDEXX LABORATORIES
Urine receiver and urine collection processing system implementing urine receiver
InactiveUS20060015081A1Good adhesionPrevent leakageNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSuction devicesUrine leakageSkin surface
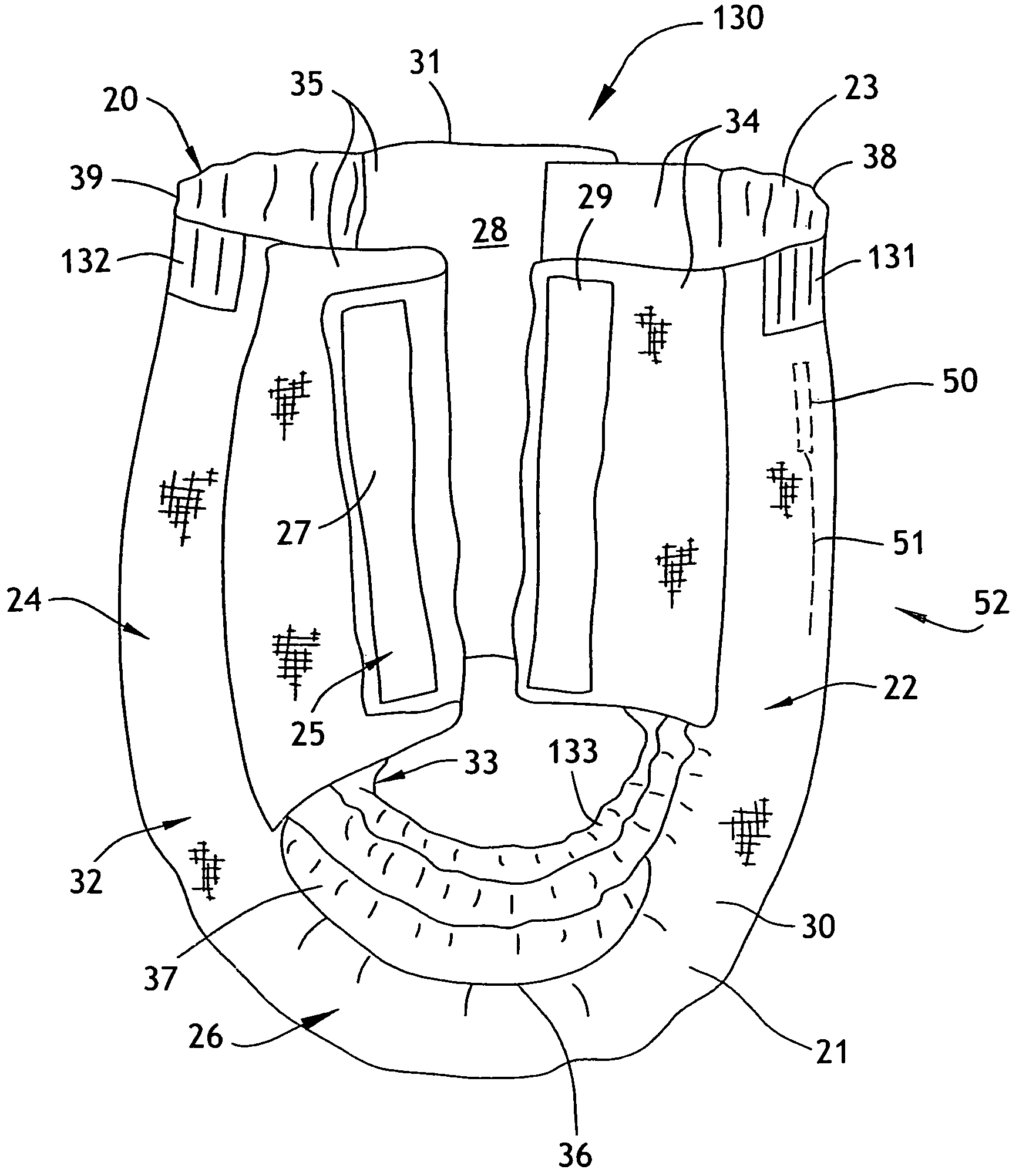
A urine receiver which is sanitary, easy to attach, and furthermore, prevents urine leakage even when a wearer repeatedly changes positions is provided. A urine receiver 10 is implemented in a urine collection processing system wherein urine discharged from the wearer is suctioned into a urine tank via a urethral tube. The urine receiver 10 comprises, at the least: a liquid permeable, air-impermeable sheet 21 which is placed opposite of and covering the urethral meatus of the wearer; a leak-proof sheet 22 which is placed on the surface of the air-impermeable sheet 21 opposite to the urethral meatus and bonds to the outer border of the air-impermeable sheet 21; a suction part 26 which is provided between the air-impermeable sheet 21 and the leak-proof sheet 22 and to which the urethral tube 11 is connected; and a gathers part 16 for sealing the space between the air-impermeable sheet 21 and the wearer's skin surface which is provided on the outer border part of the air-impermeable sheet 21 on the urethral meatus side.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
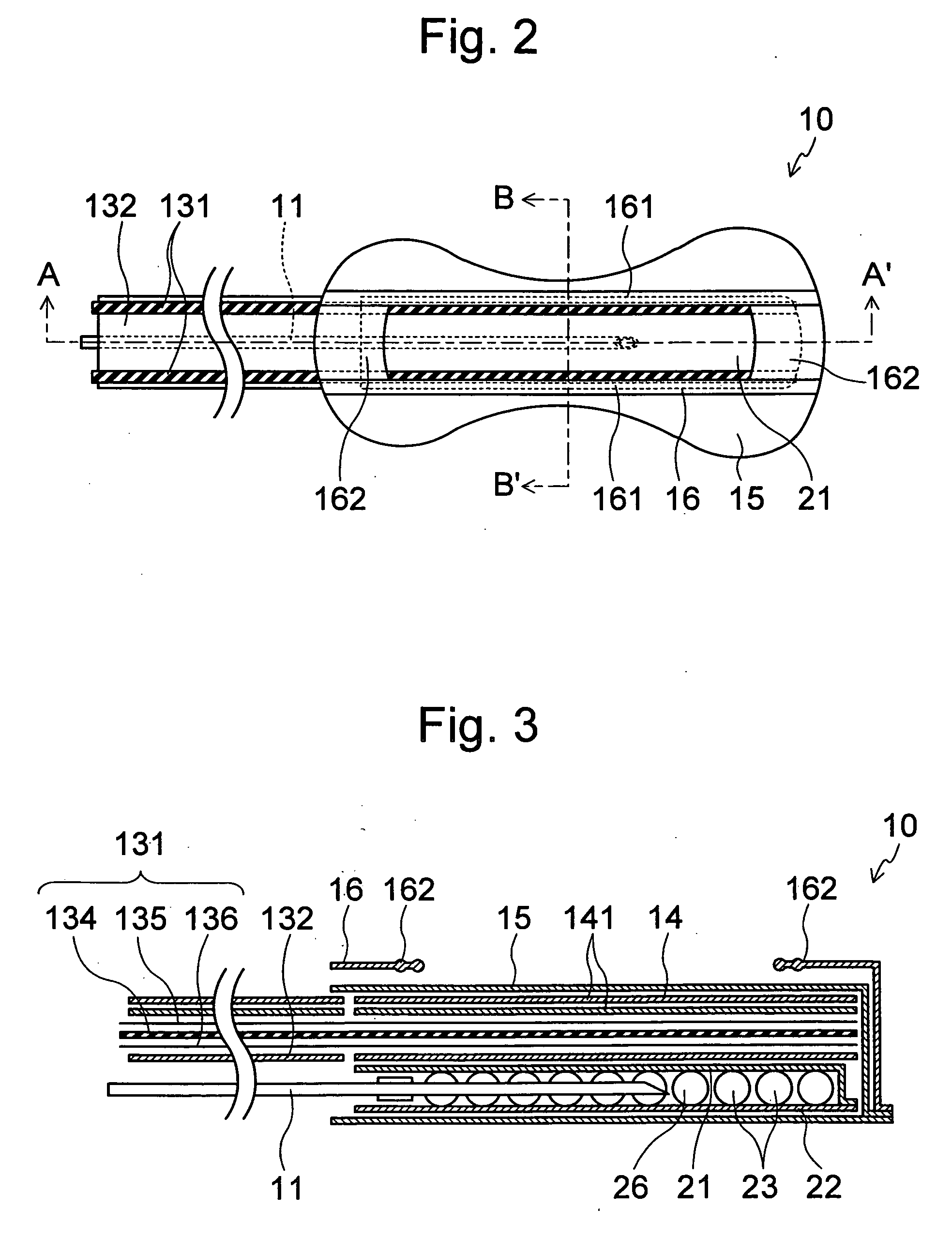
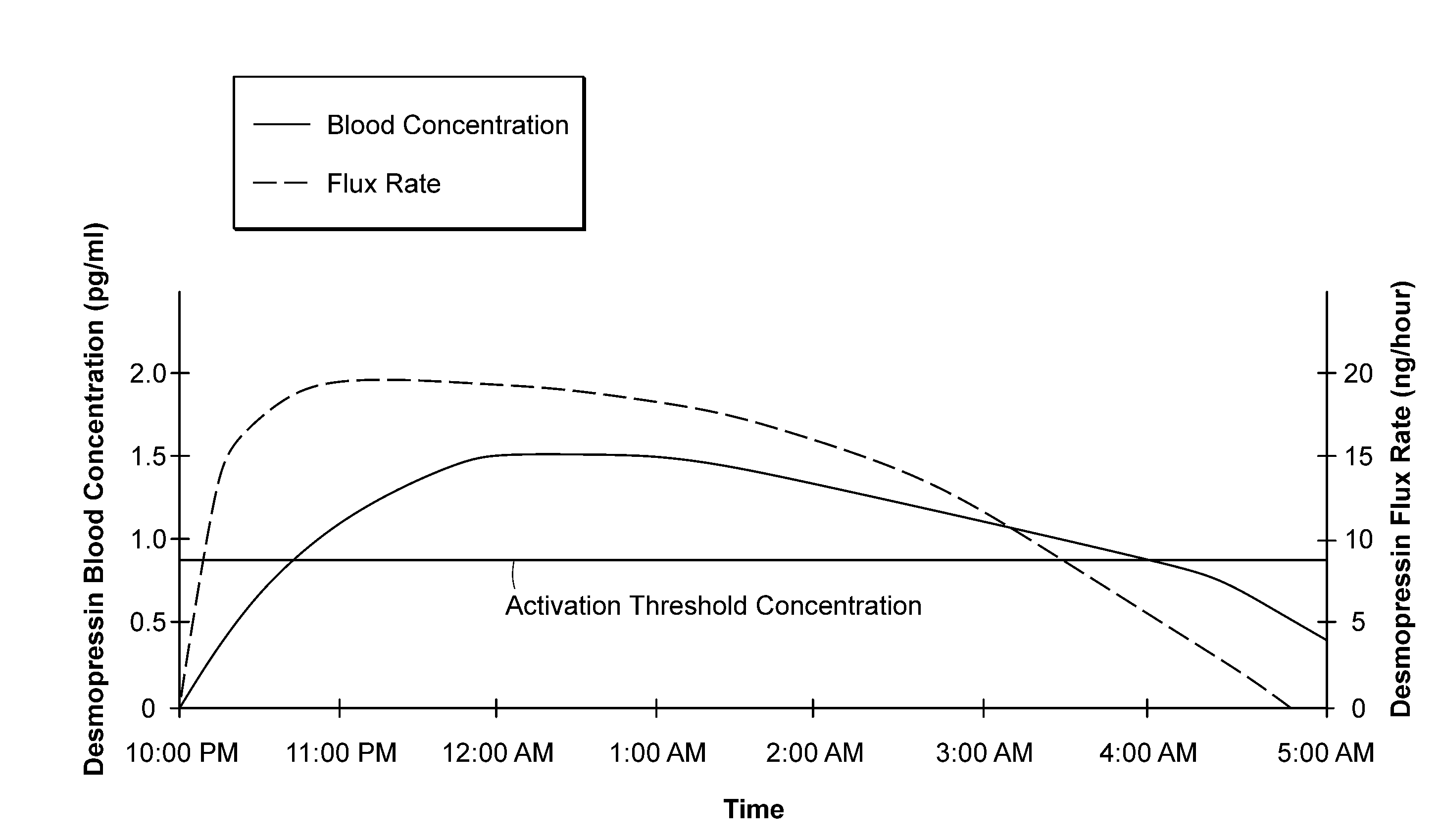
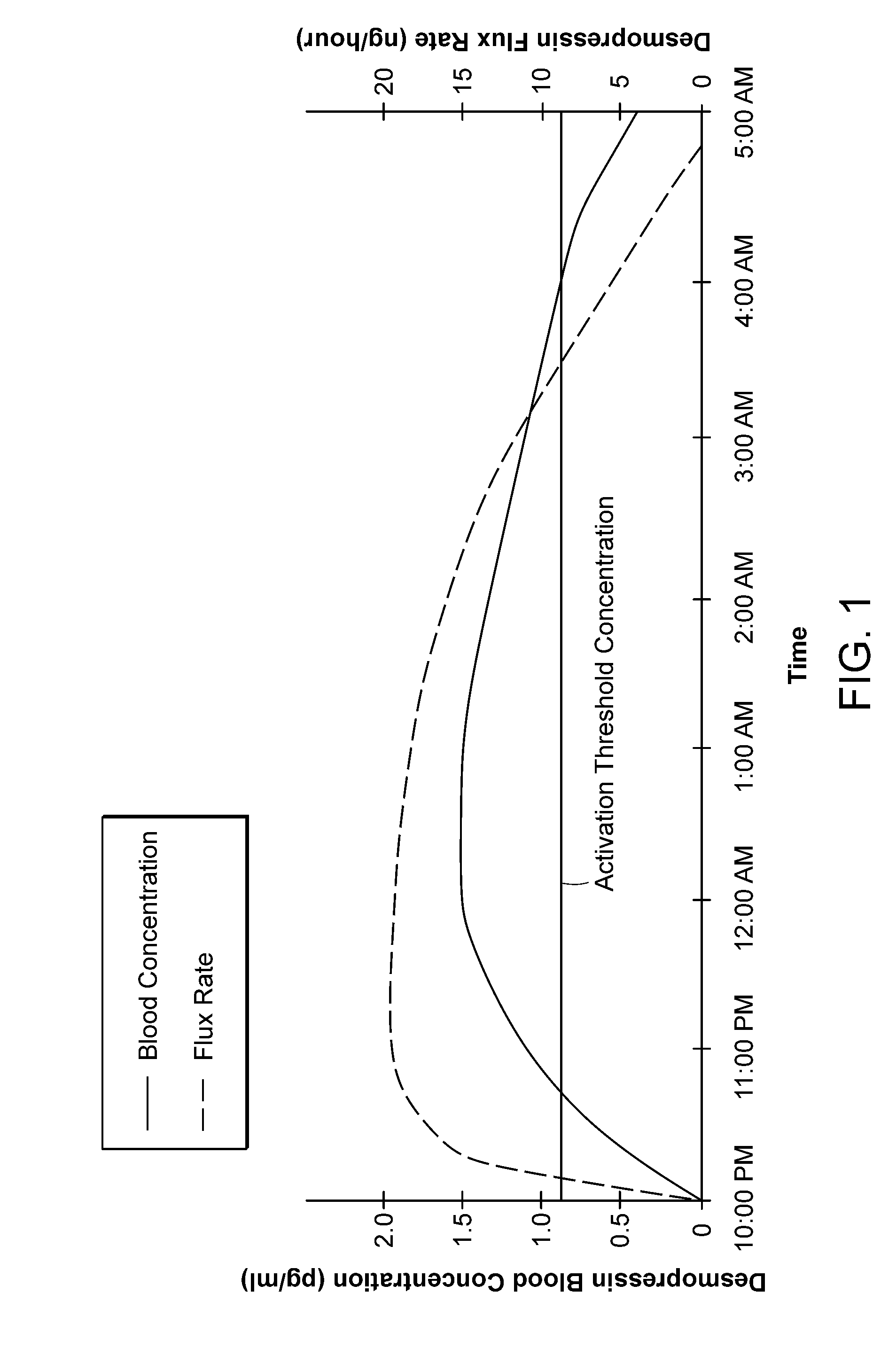
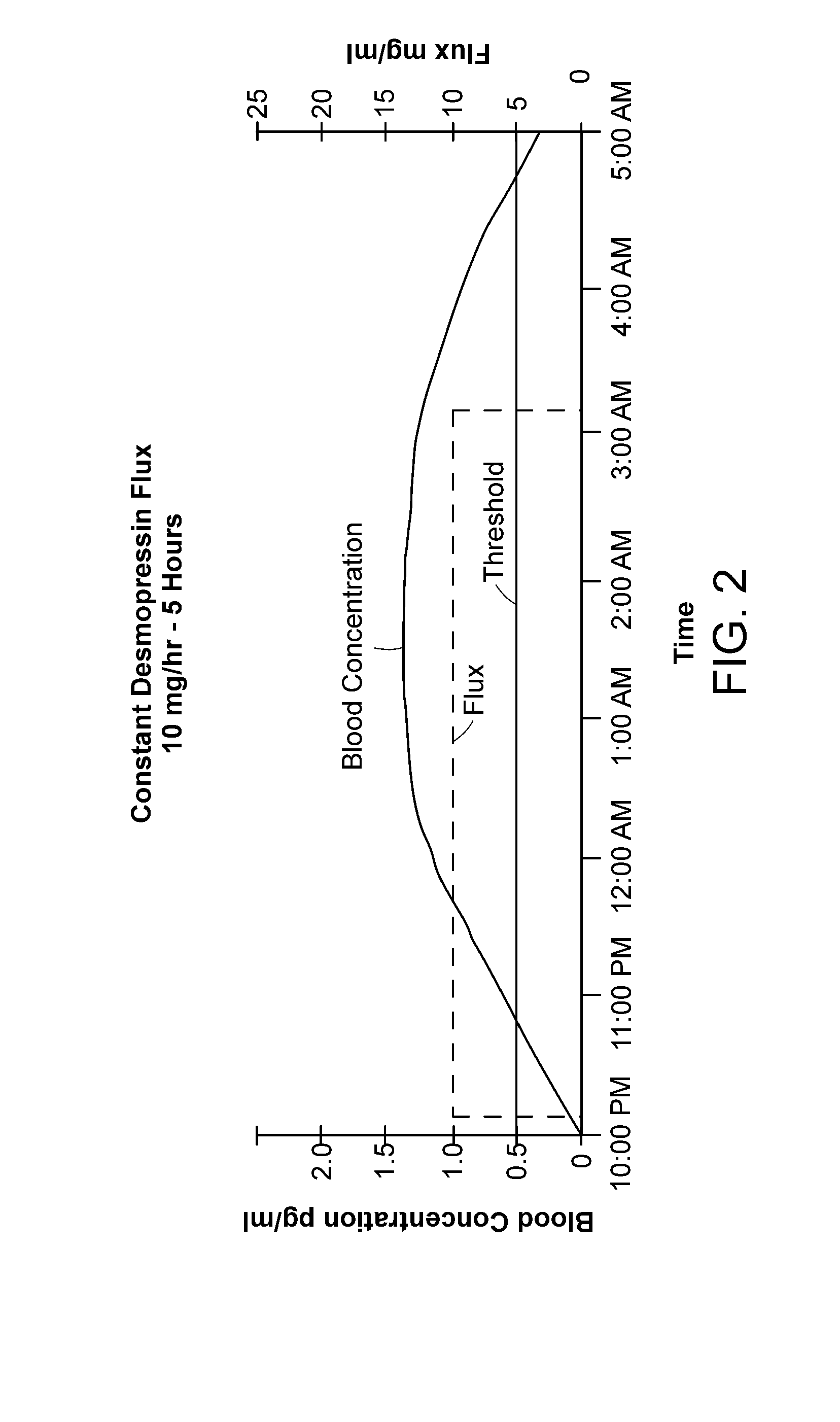
Methods and devices for desmopressin drug delivery
InactiveUS20090042970A1Reduce urine productionRestore normal urine productionBiocidePowder deliveryDecreased sodiumSide effect
Disclosed are devices for urine voiding postponement, and methods for treating conditions such as central diabetes insipidus, enuresis, nocturia, urinary frequency or incontinence. The devices deliver a desmopressin flux through the skin of a patient in a low dose amount just necessary to achieve a desired anti-diuretic effect without undesirable side effects such as hyponatremia. The devices are designed to permit a state of normal urinary production to return quickly after the desmopressin flux is terminated.
Owner:SERENITY PHARMA CORP
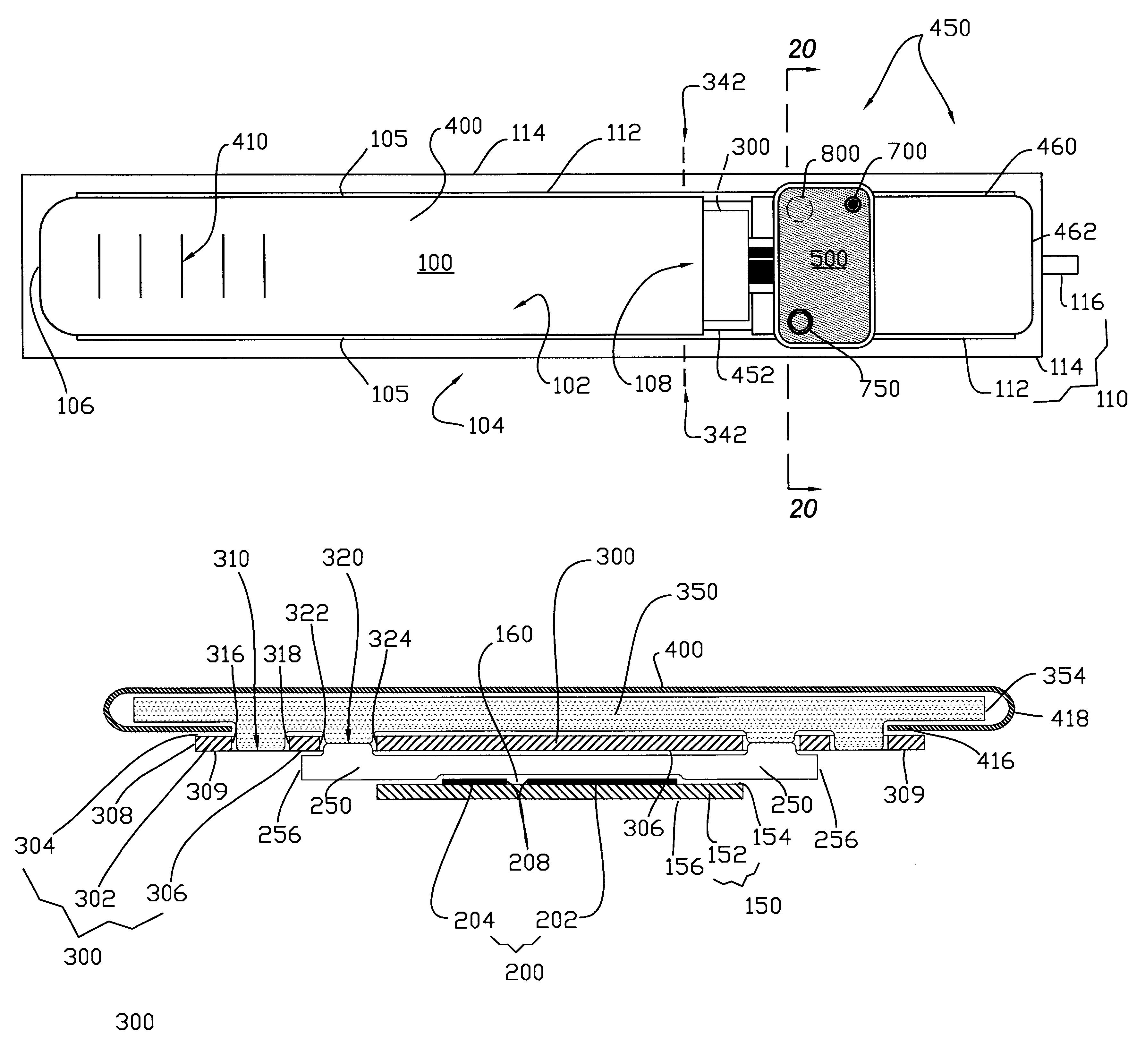
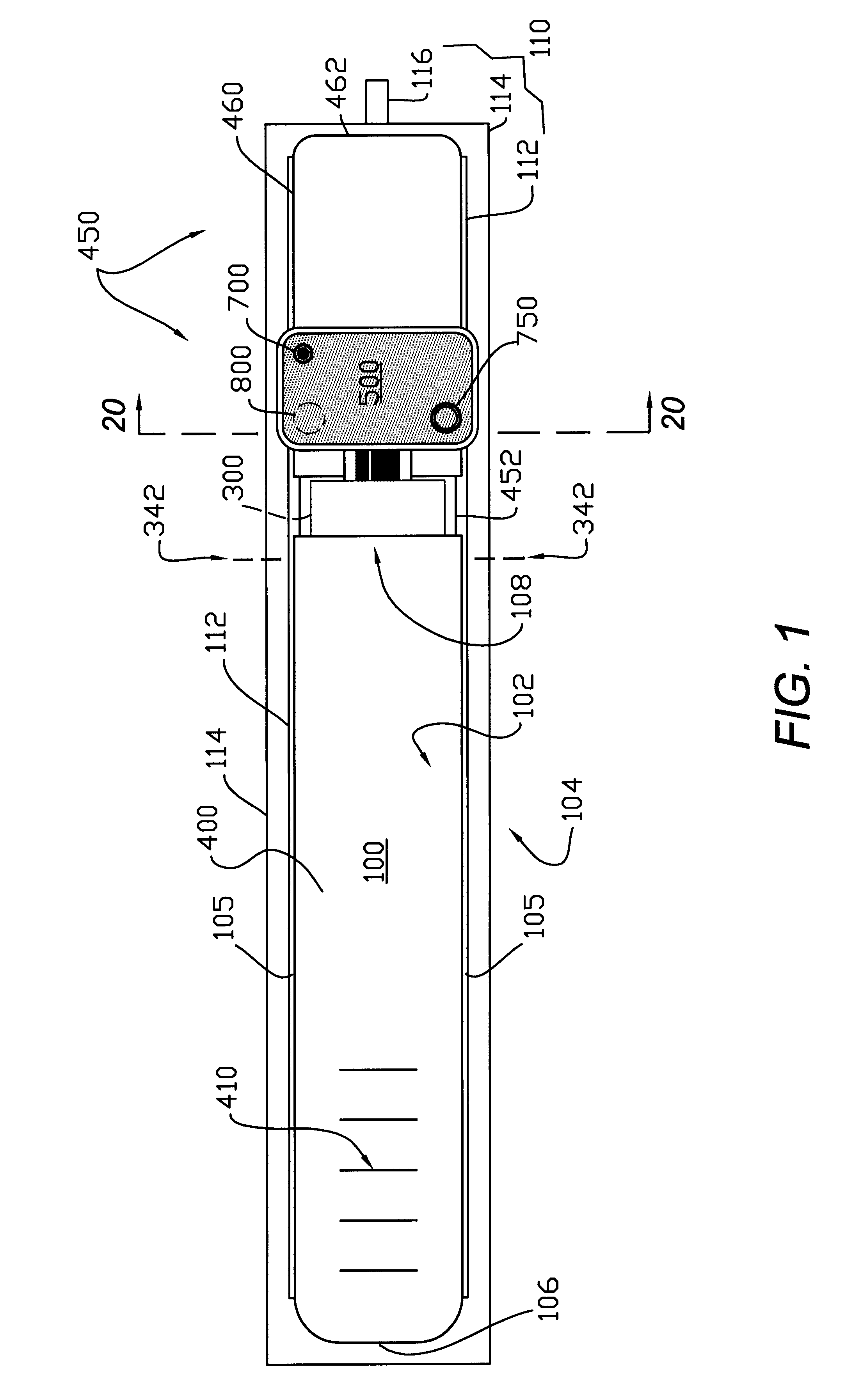
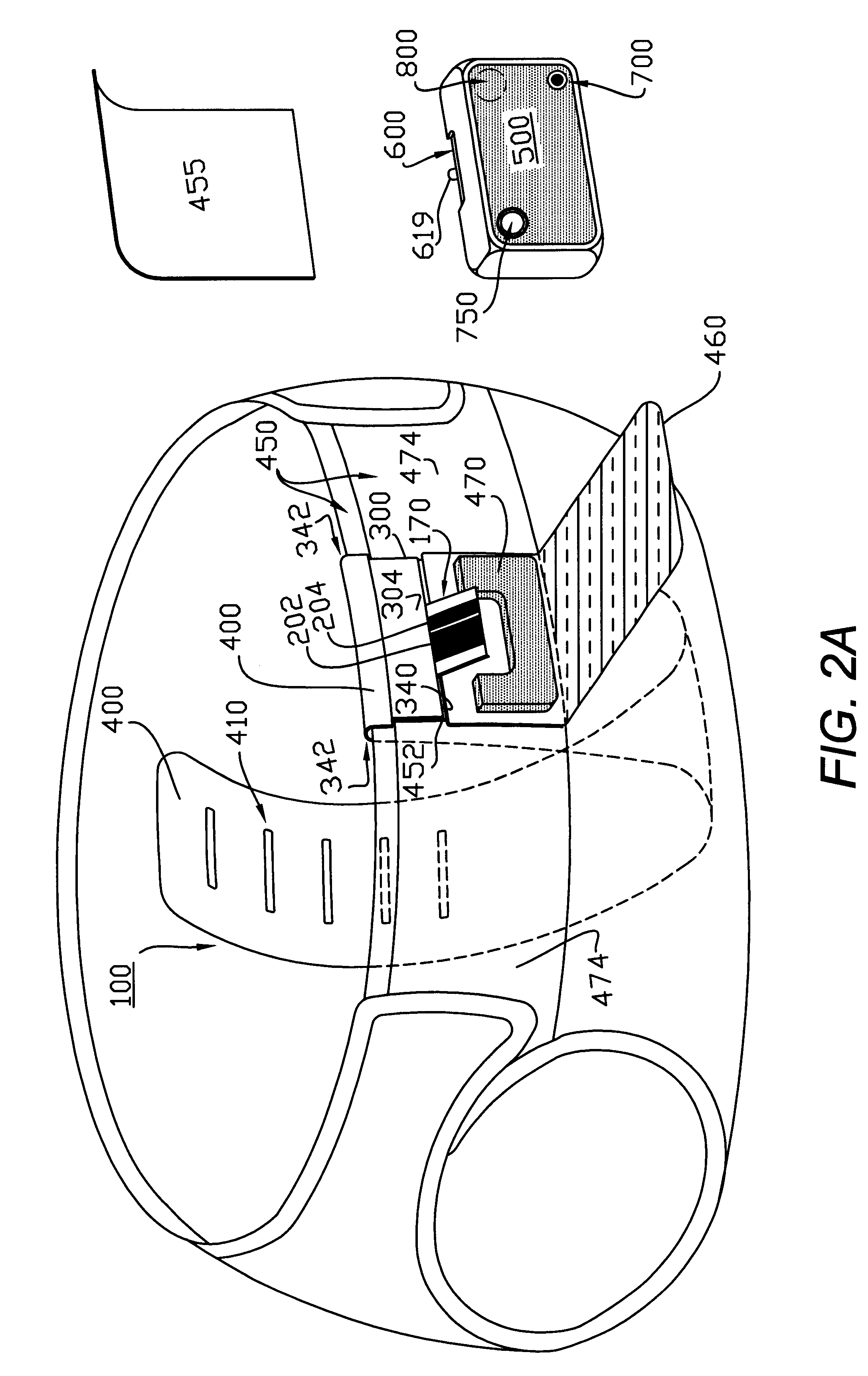
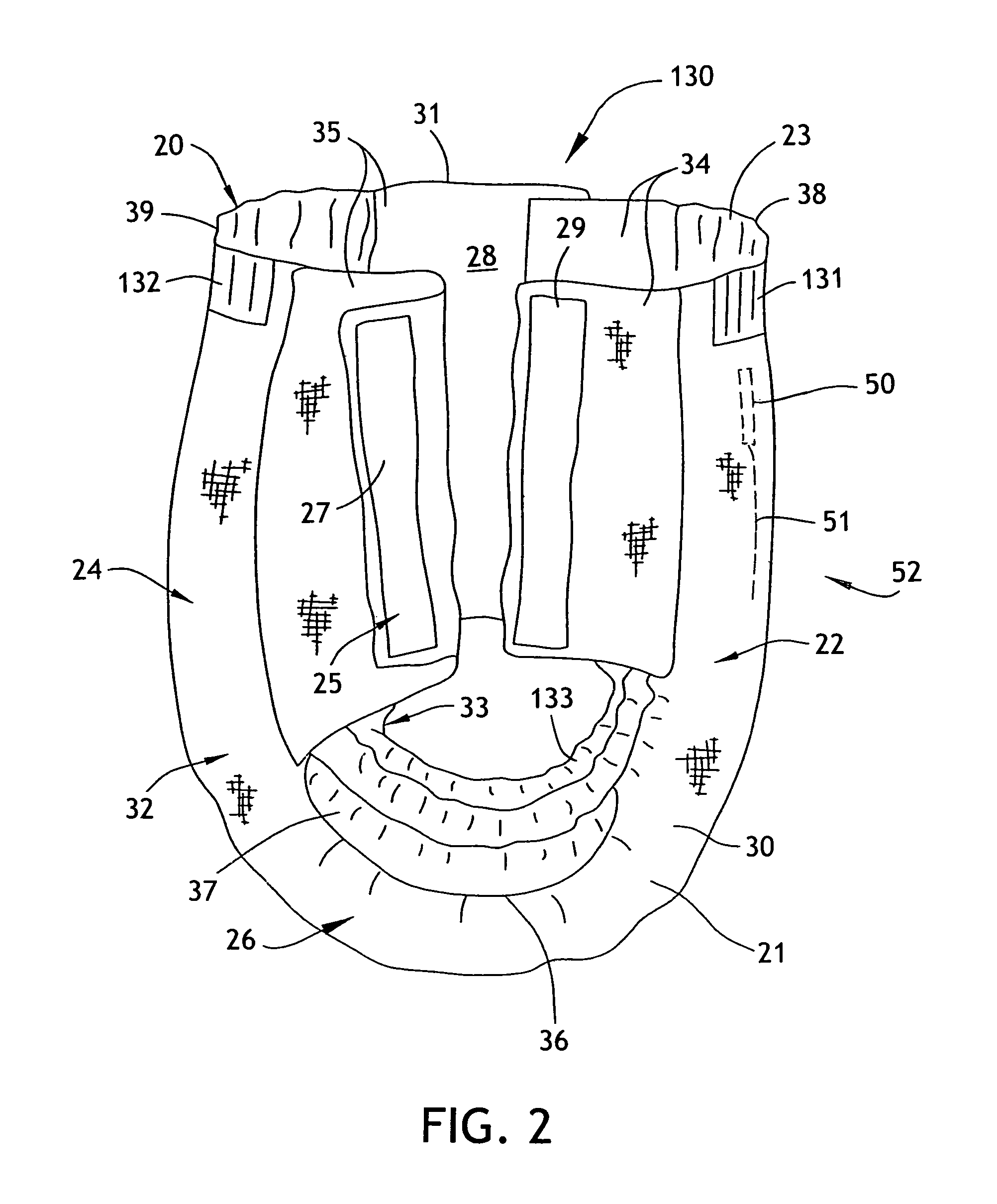
Absorbent articles
The present invention provides an improved disposable article for the absorption and containment of urine or other body exudates, for example a diaper, training pants or an adult incontinence article, that has a high fecal fluid intake rate as measured by the Fecal Fluid Intake Test.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Urine Sensor
InactiveUS20070035405A1Lose their capabilityReliable detectionAbsorbent padsAlarmsUrine productionTissue skin
Here is disclosed a urine receiver. The urine receiver comprises a container member adapted to suck urine discharged from a wearer of the urine receiver and a urine sensor provided with a pair of electrodes interposed between the container member and the wearer's skin and serving to detect the urine. The paired electrodes covered with insulating coating. The coating is formed with through-holes adapted to expose a limited area of the electrodes.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN INST FOR BIOMEDICAL ENG AT THE UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
Methods for detection of nucleic acid sequences in urine
InactiveUSRE39920E1Reduce DNA degradationReducing DNA degradationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetics predispositionNon invasive
Described are non-invasive methods of detecting the presence of specific nucleic acid sequences as well as nucleic acid modifications and alterations by analyzing urine samples for the presence of transrenal nucleic acids. More specifically, the present invention encompasses methods of detecting specific fetal nucleic acid sequences and fetal sequences that contained modified nucleotides by analyzing maternal urine for the presence of fetal nucleic acids. The invention further encompasses methods of detecting specific nucleic acid modifications for the diagnosis of disease, such as cancer and pathogen infections, and detection of genetic predisposition to various disease. The invention specifically encompasses methods of analyzing specific nucleic acid modifications for the monitoring of cancer treatment. The invention further encompasses methods of analyzing specific nucleic acids in urine to track the success of transplanted cells, tissues and organs. The invention also encompasses methods for evaluating the effects of environmental factors and aging on the genome.
Owner:TROVAGENE
Urine receiver and urine collection processing system implementing urine receiver
InactiveUS7220250B2Good adhesionPrevent leakageNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSuction devicesUrine leakageSkin surface
A urine receiver which is sanitary, easy to attach, and furthermore, prevents urine leakage even when a wearer repeatedly changes positions is provided. A urine receiver 10 is implemented in a urine collection processing system wherein urine discharged from the wearer is suctioned into a urine tank via a urethral tube. The urine receiver 10 comprises, at the least: a liquid permeable, air-impermeable sheet 21 which is placed opposite of and covering the urethral meatus of the wearer; a leak-proof sheet 22 which is placed on the surface of the air-impermeable sheet 21 opposite to the urethral meatus and bonds to the outer border of the air-impermeable sheet 21; a suction part 26 which is provided between the air-impermeable sheet 21 and the leak-proof sheet 22 and to which the urethral tube 11 is connected; and a gathers part 16 for sealing the space between the air-impermeable sheet 21 and the wearer's skin surface which is provided on the outer border part of the air-impermeable sheet 21 on the urethral meatus side.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
System for interactively training a child and a caregiver to assist the child to overcome bedwetting
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
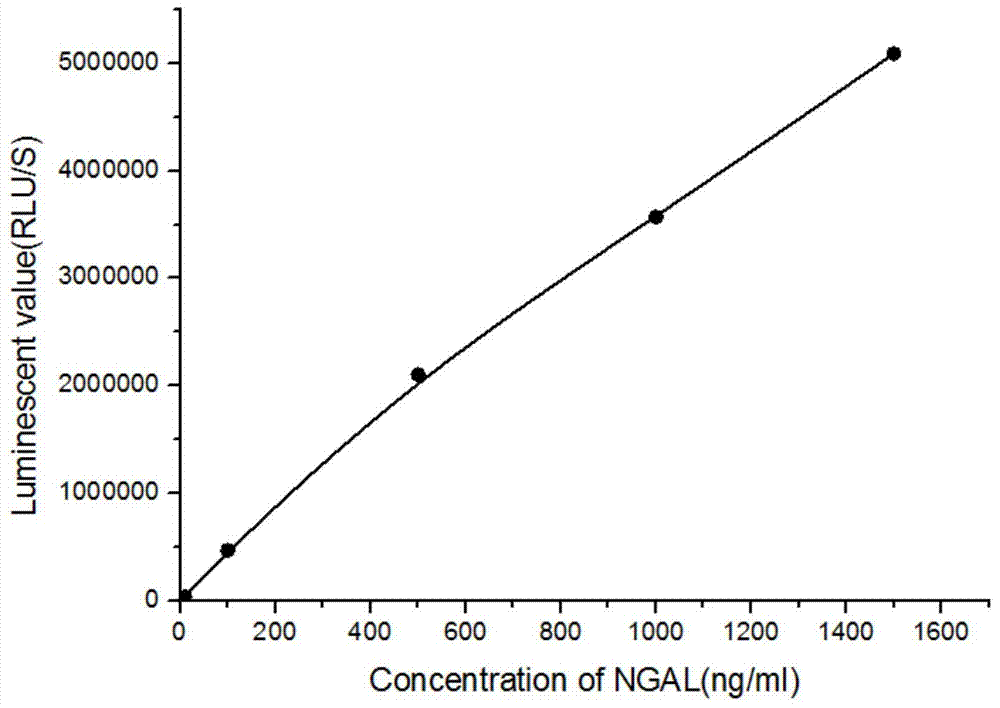
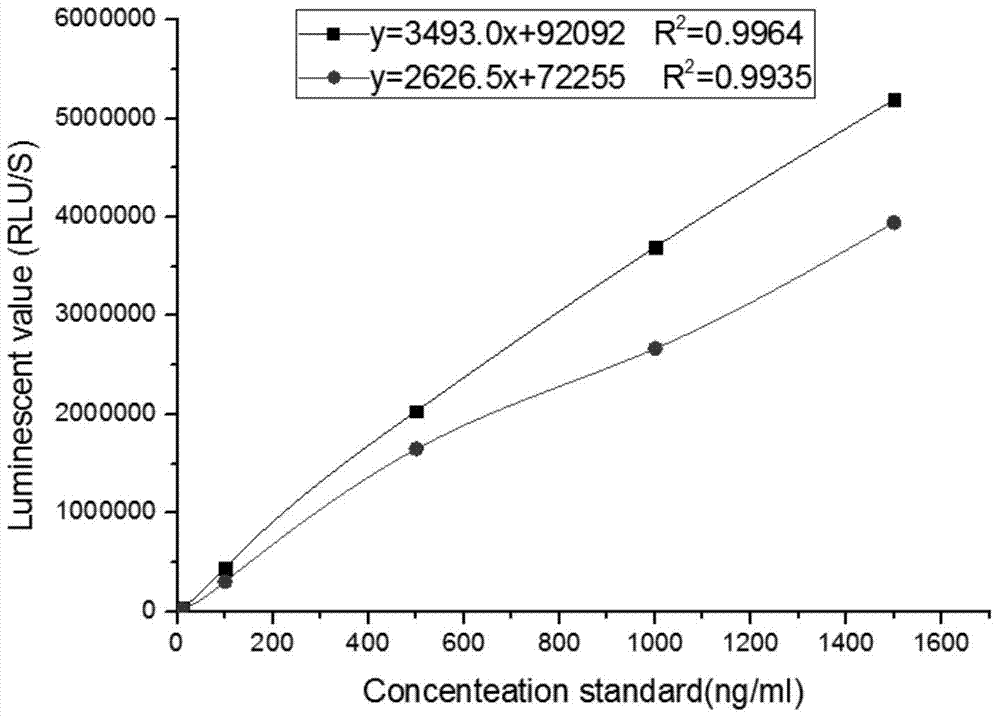
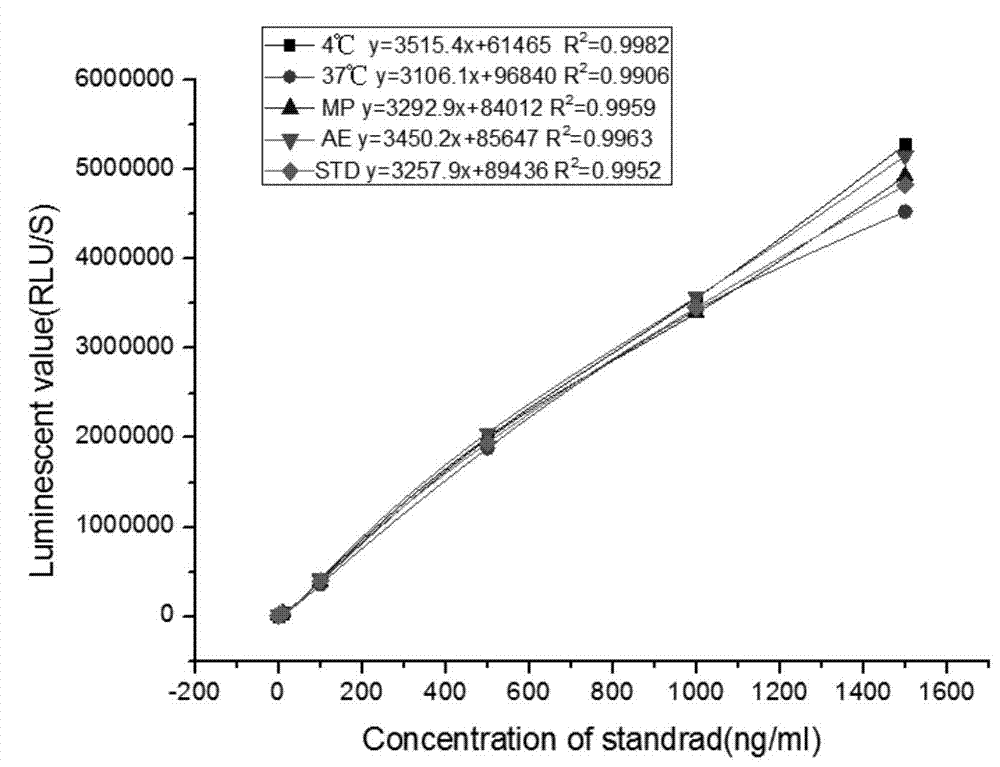
Kit for detecting NGAL content and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a kit for detecting neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin content based on chemiluminescence immunoassay. According to the invention, by employing a double-antibody sandwich immunization analysis method, a chemiluminescence magnetic microspheres immunization technology is used, anti-NGAL antibody-coated magnetic microspheres for specifically combining with NGAL antigen of a standard substance / sample in a reaction cup, then are reacted to another strain anti-NGAL antibody labelled with acridine salt to form an immunization compound, through an acid-base chemical reaction of a pre-Trigger and a Trigger, relative light unit (RLU / s) of the chemiluminescence reaction can be measured; the NGAL antigen content in the sample is in direct proportion to the relative light unit (RLU / s) measured by an optical system, determination of NGAL content in an urine specimen can be determined through standard curve fitting; and the method has the obvious advantages of high sensitivity, strong specificity, good stability, simple operation and low cost.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DARUI BIOTECH
Secretion-monitoring article
InactiveUS20070003993A1Overcome disadvantagesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBacterial vaginosisAmniotic fluid
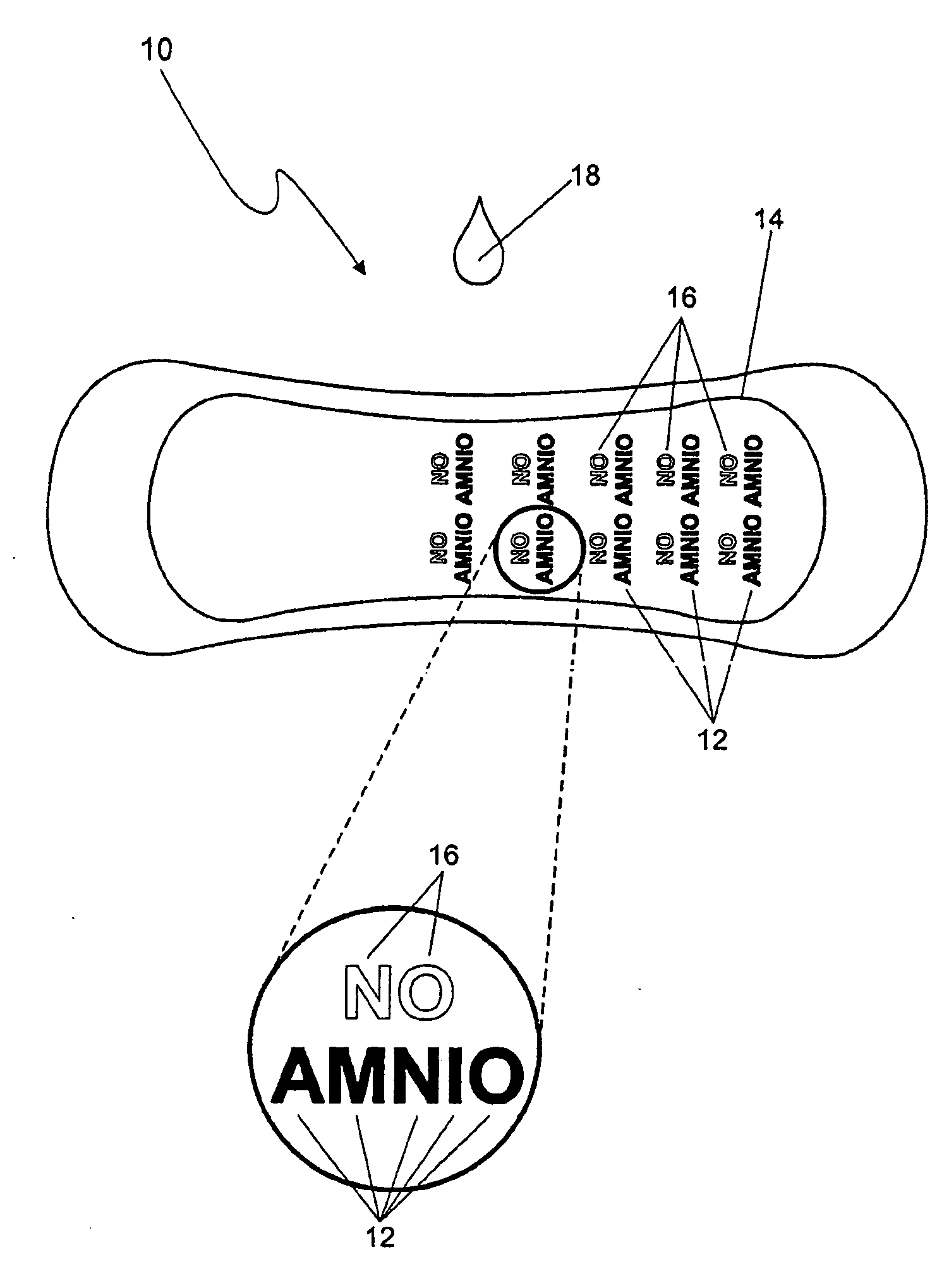
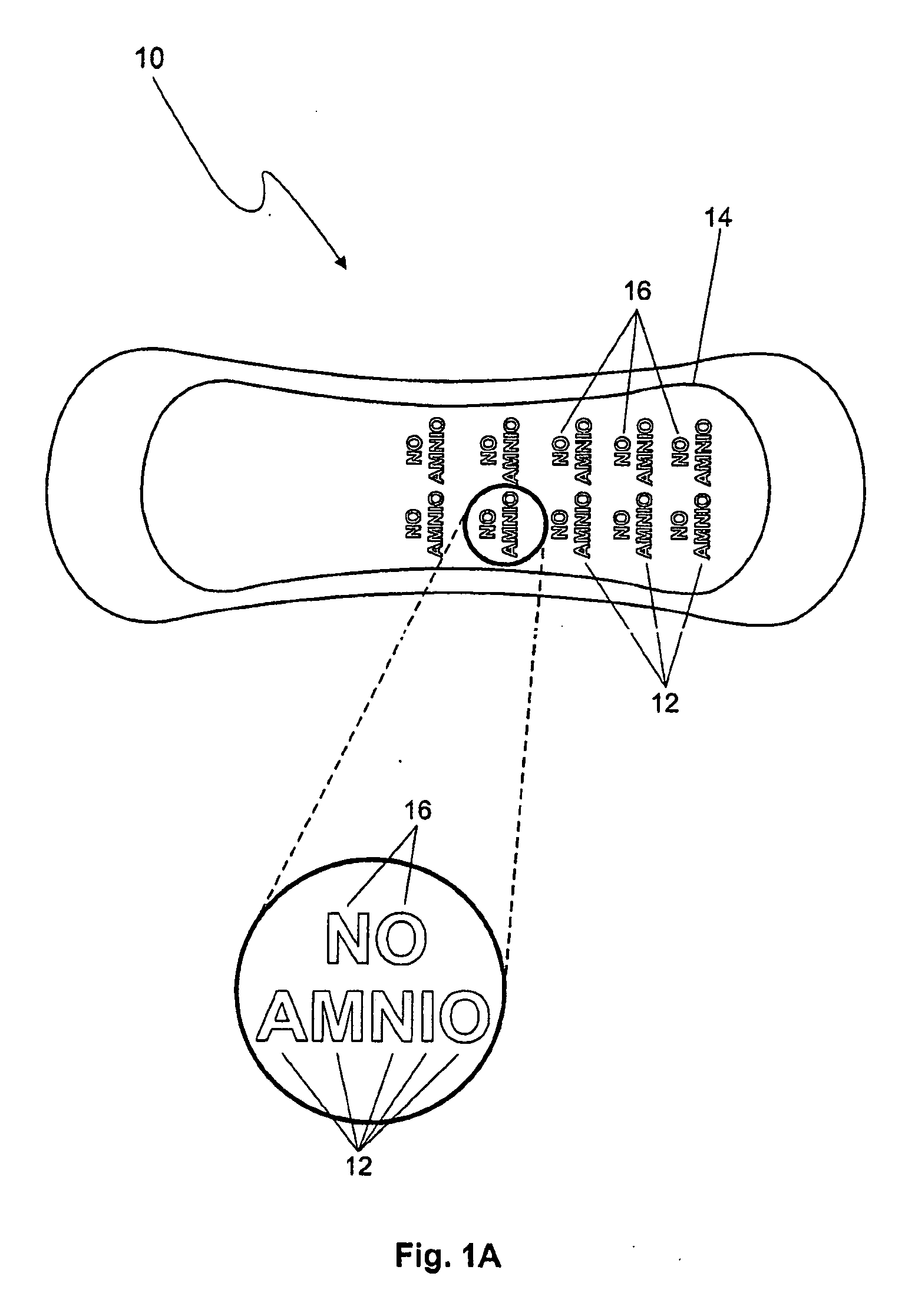
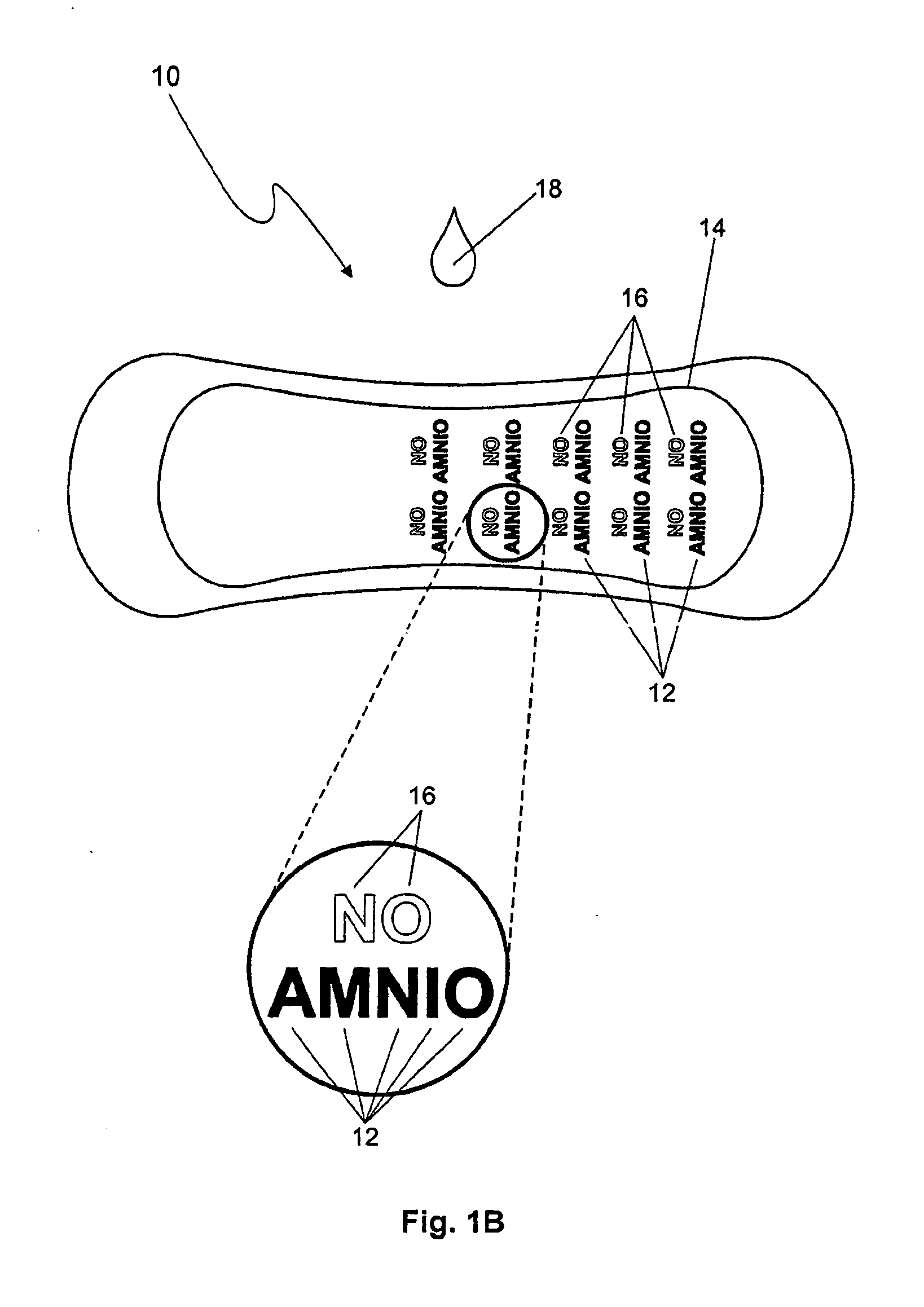
A secretion-monitoring article for identifying a secreted biological fluid comprising a body with an absorbent material for absorbing a biological fluid secreted from a person and an indicator system. The indicator system comprises an indicator agent and an ion-balance reagent, wherein the indicator system provides an indication of physiological conditions associated with the pH or the buffer capacities of the biological fluid, which indication is stable for at least 48 hours, preferably at least 72 hours. The article can be embodied as a swab, gauze, shield, hygienic napkin, diaper or interlabial absorbent structure and can be used to indicate the presence of amniotic fluid, or secretions associated with bacterial vaginosis without giving a false positive result upon exposure to urine or drying out.
Owner:COMMON SENSE
Systems and methods for characterizing kidney diseases
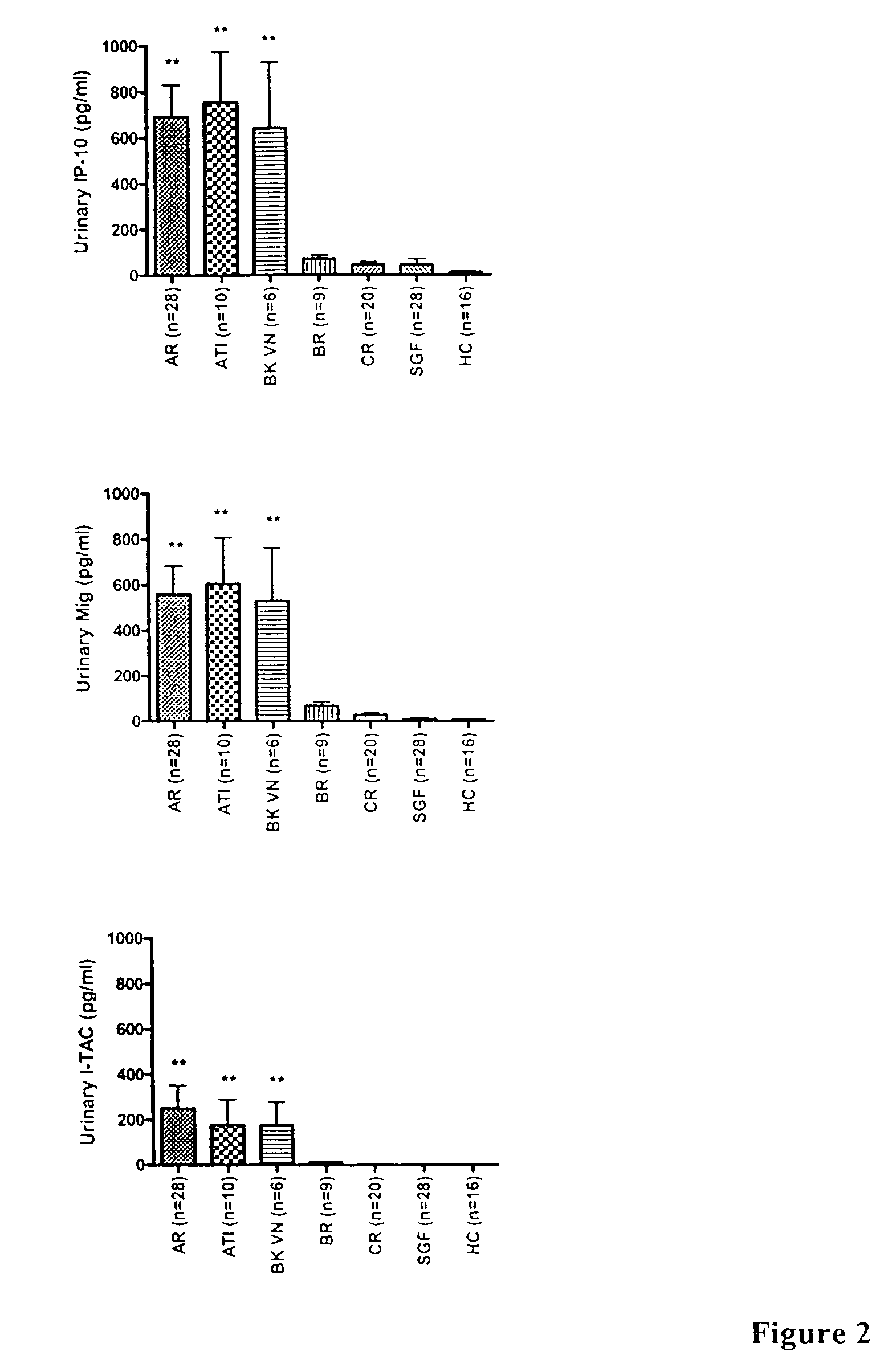
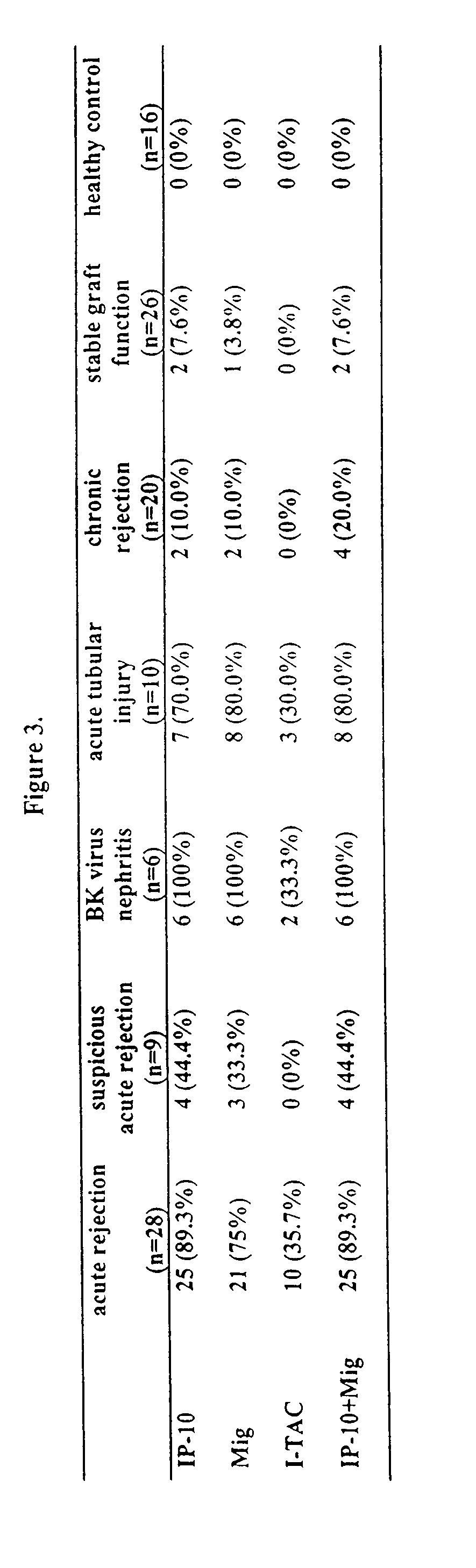
The present invention relates to methods of diagnosing, predicting and monitoring kidney disorders. In particular, the present invention relates to the diagnosis, prediction and monitoring of kidney disorders by detection of cytokines, cytokine-related compounds and chemokines in urine. The present invention further relates to methods and compositions for assessing the efficacy of agents and interventions used to treat kidney disorders.
Owner:RENOVAR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com