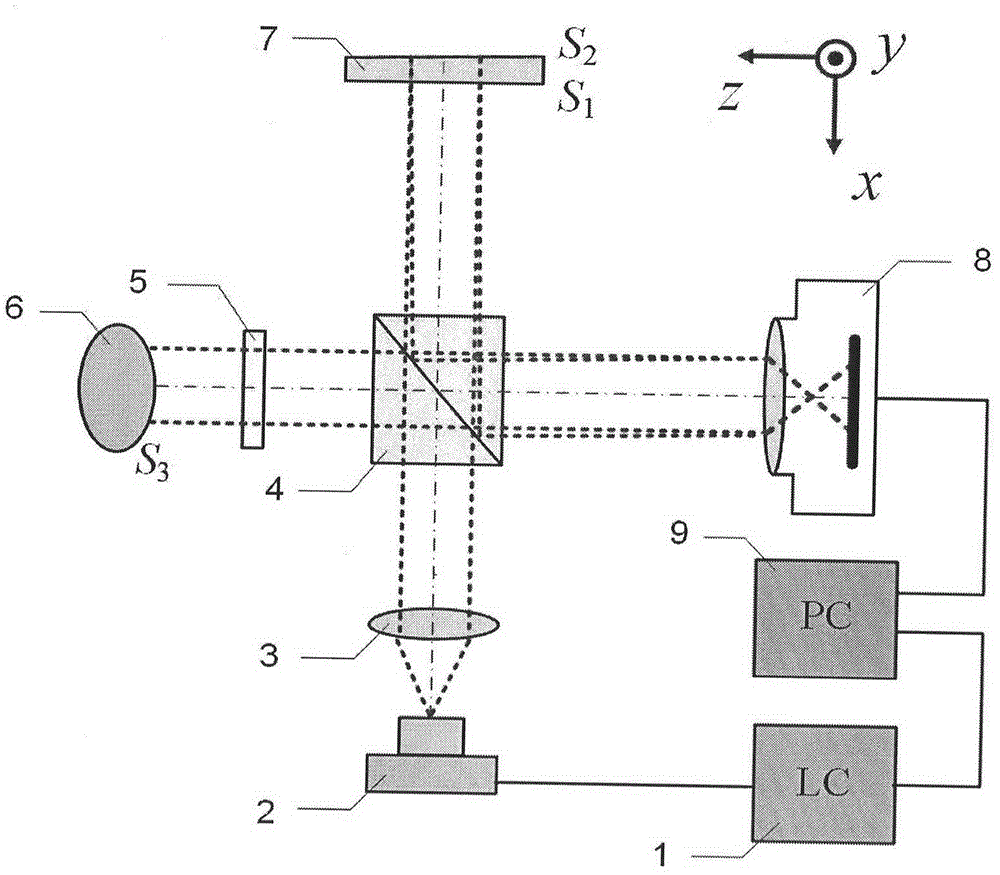
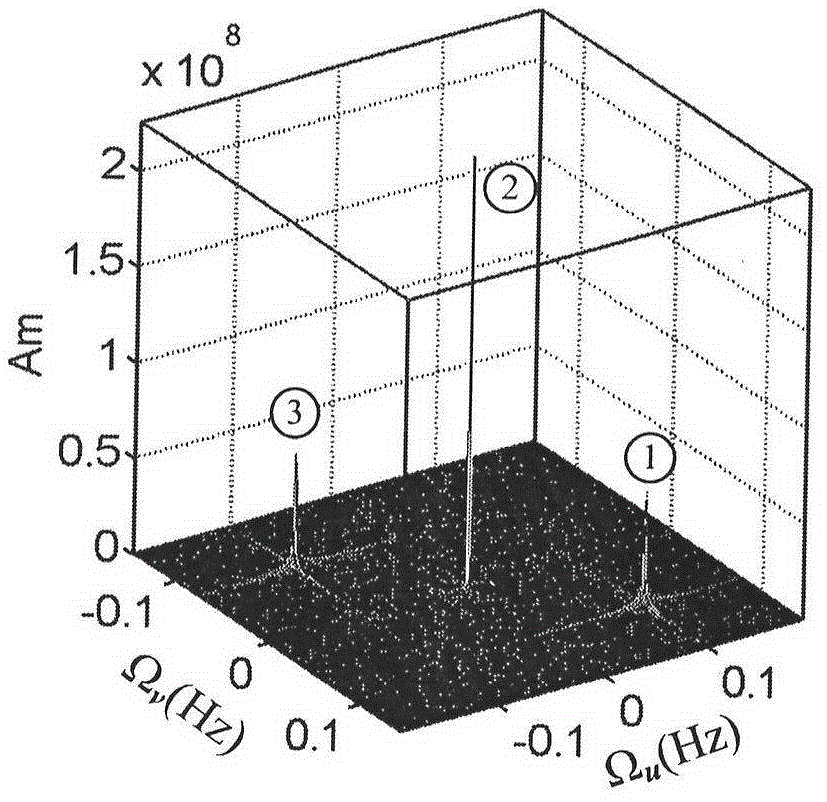
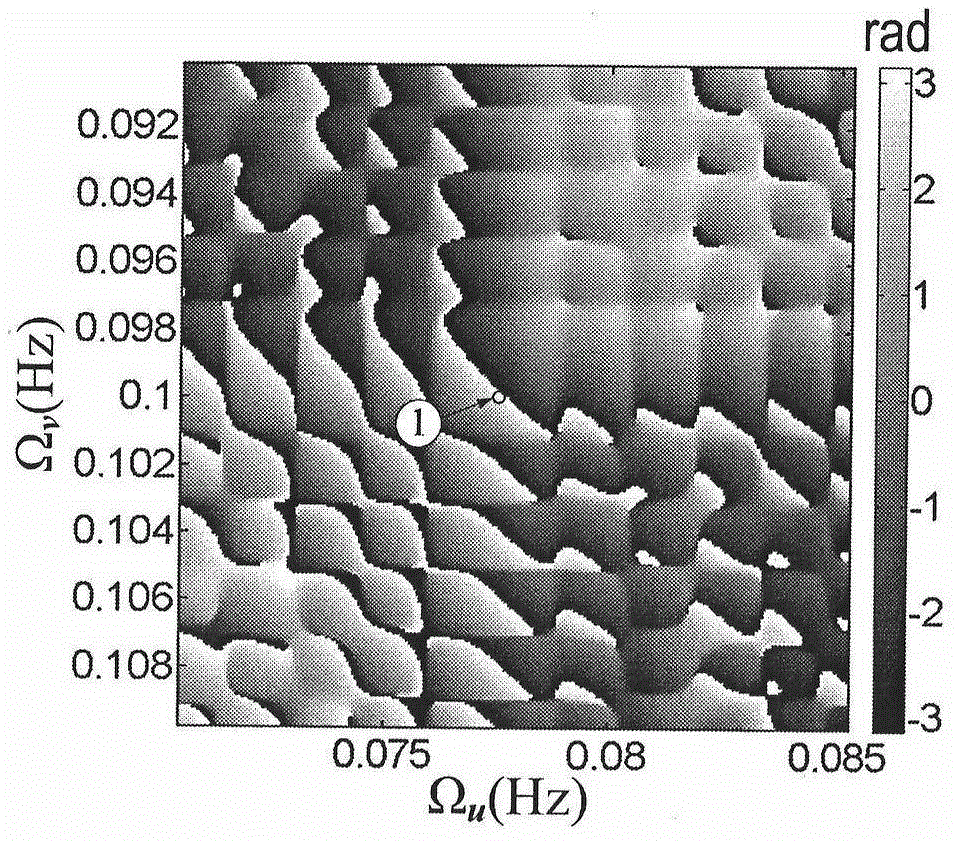
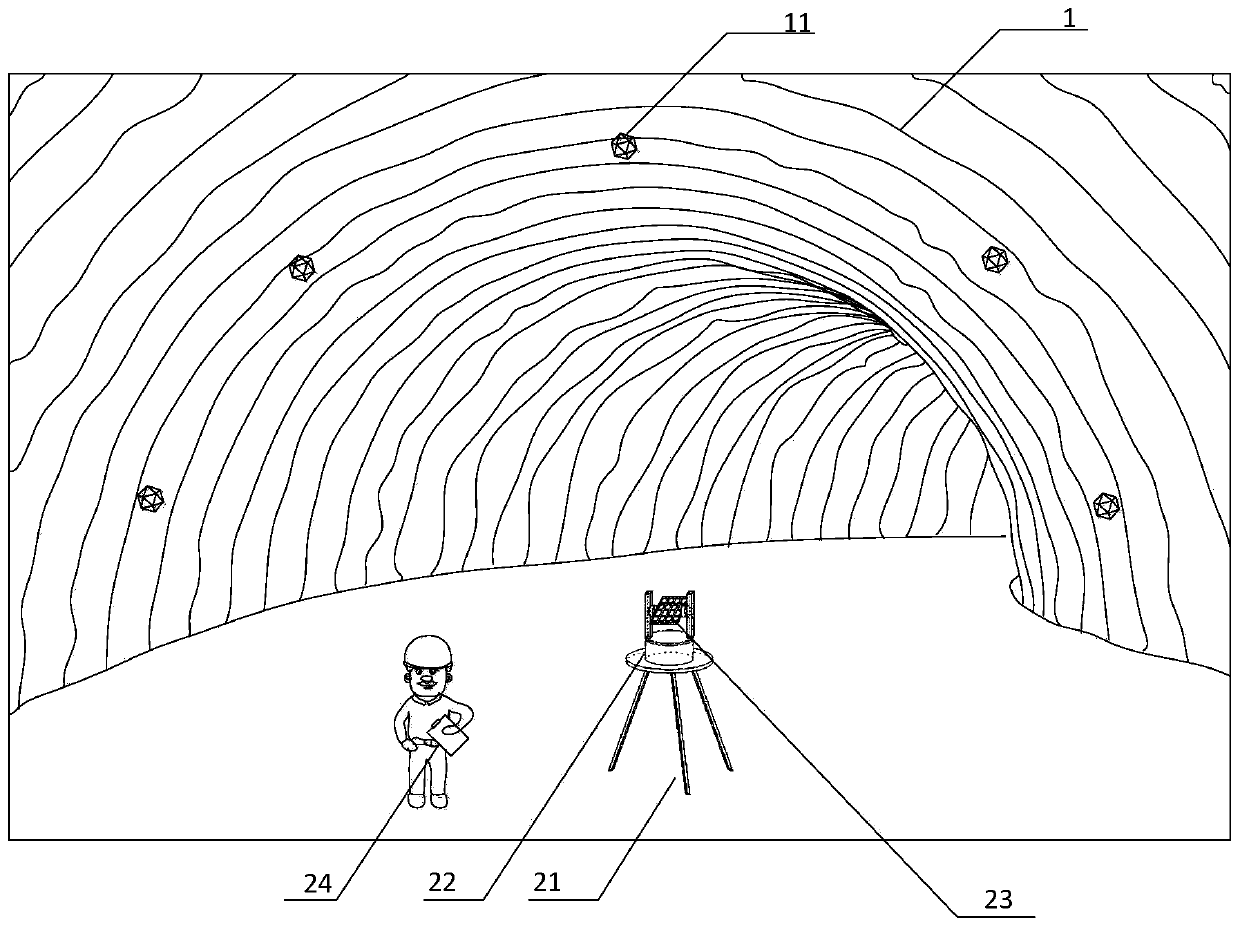
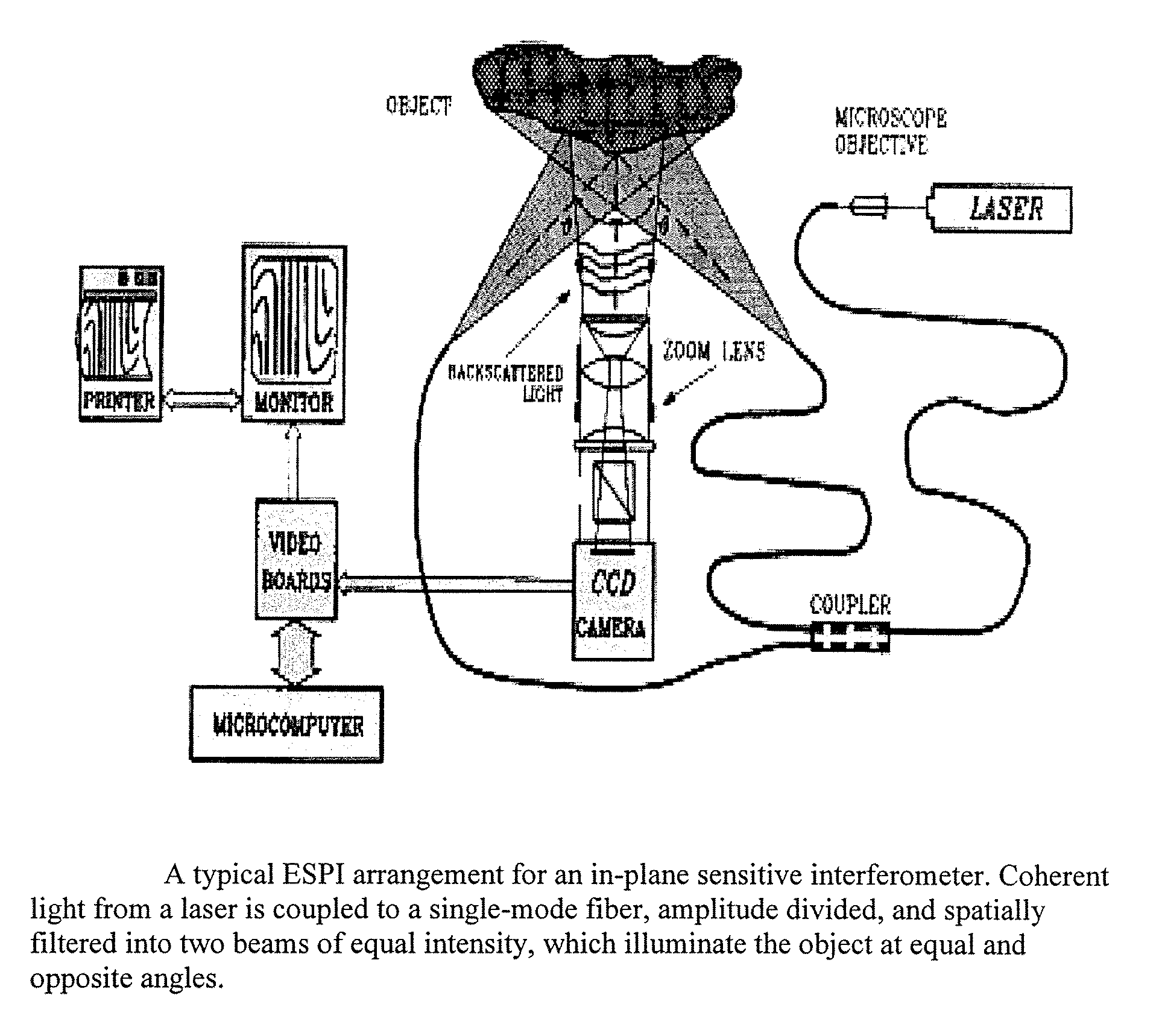
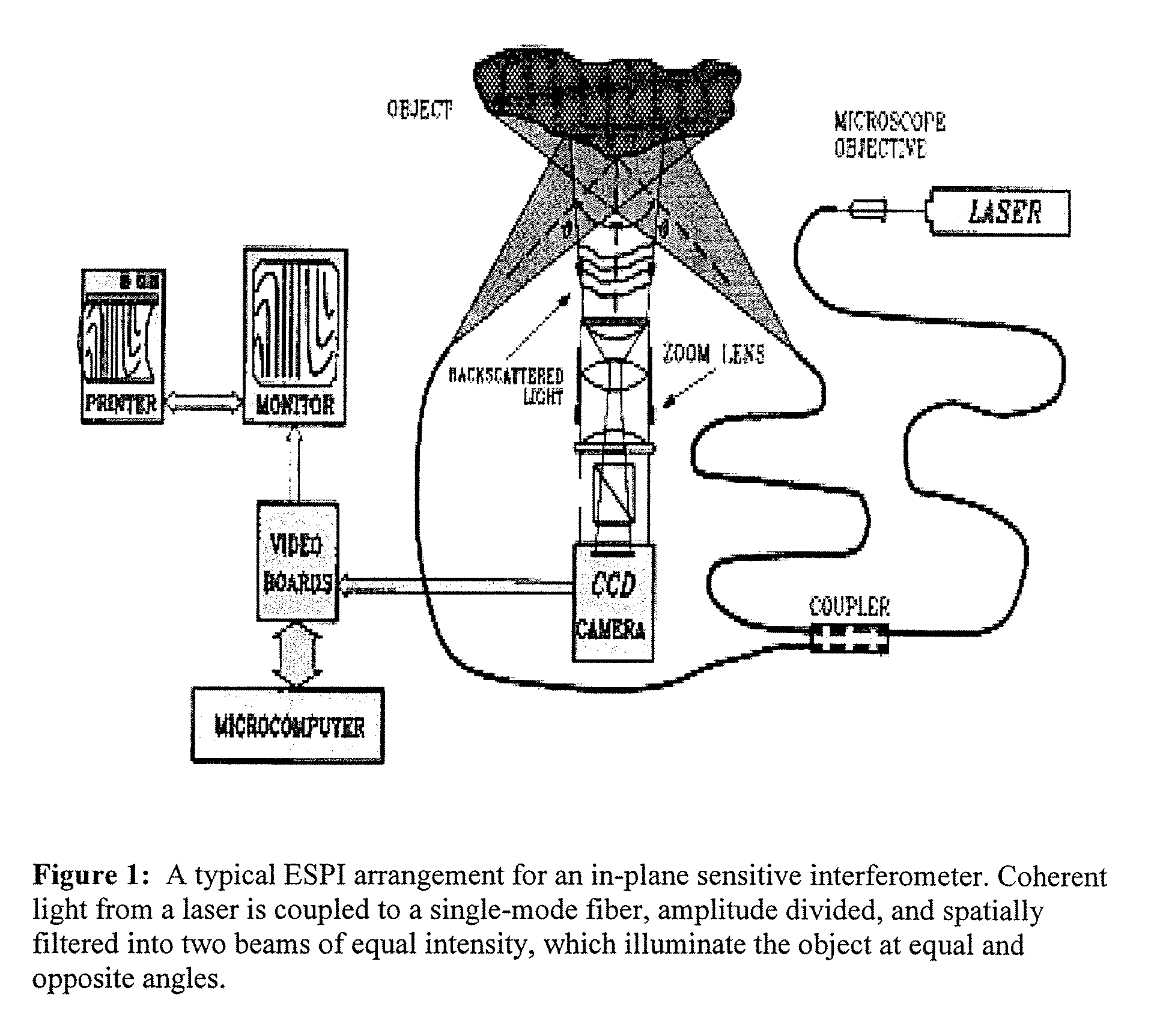
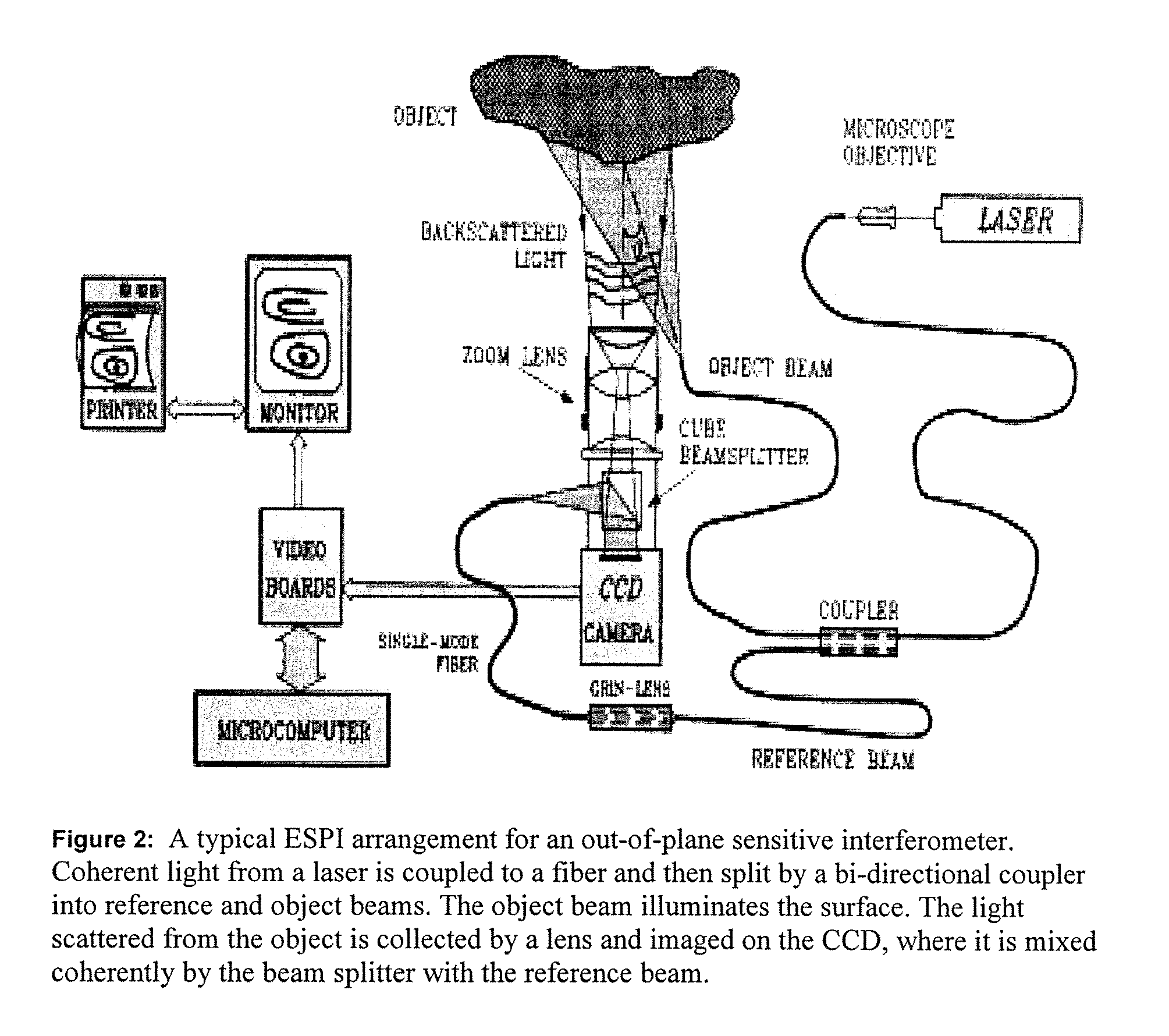
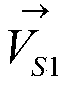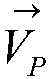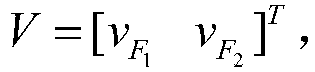Patents
Literature
274 results about "Interference graph" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
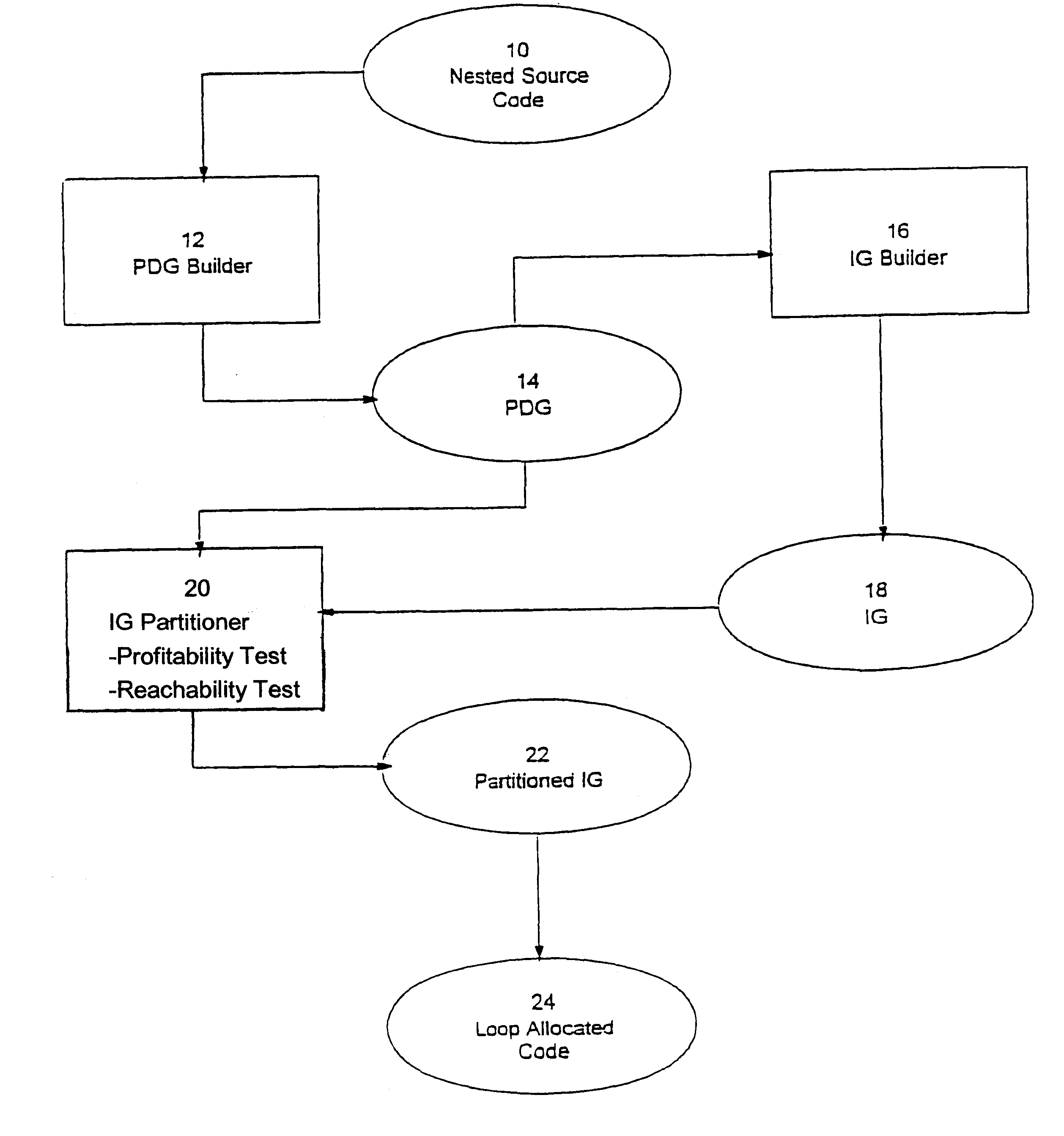
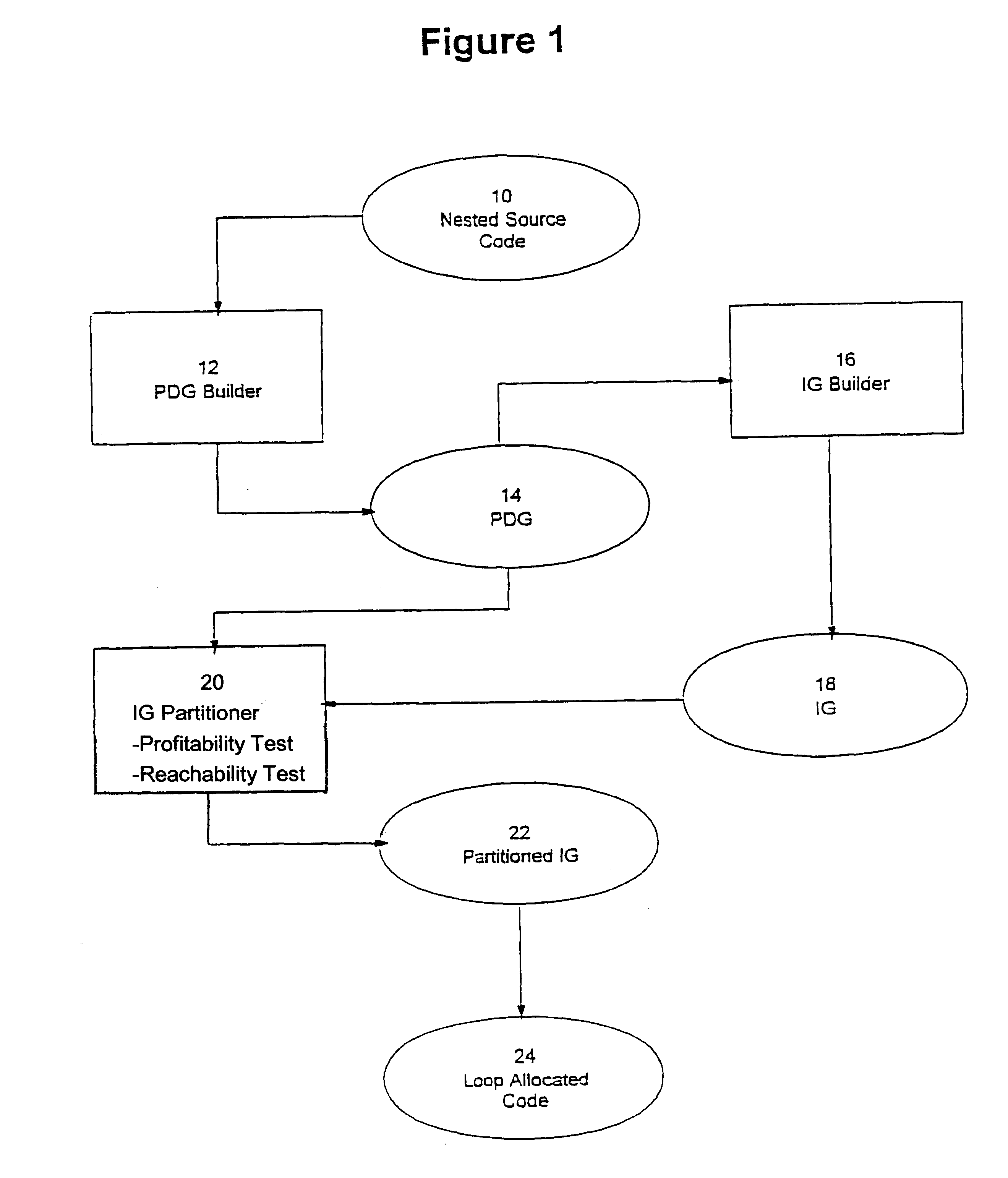
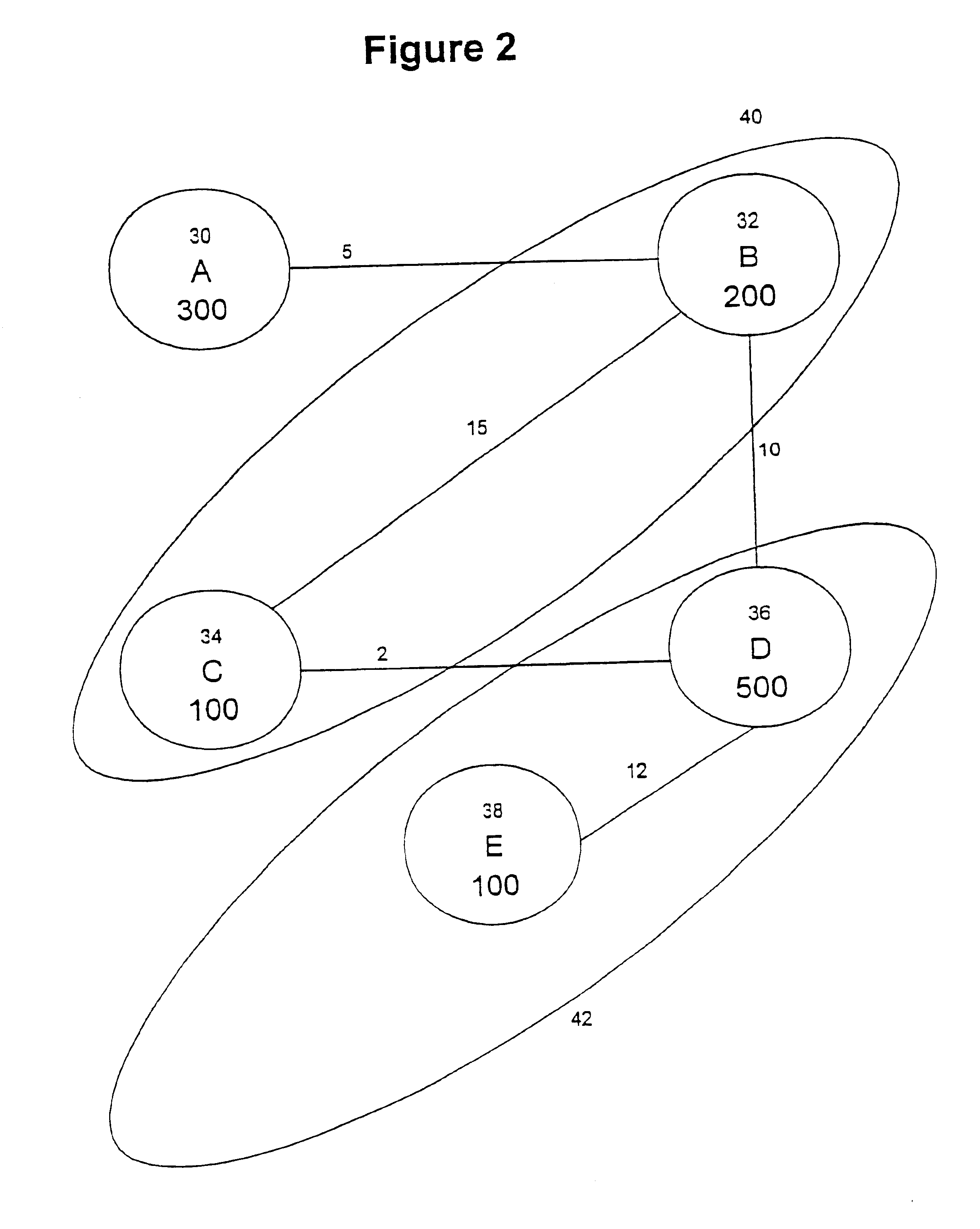
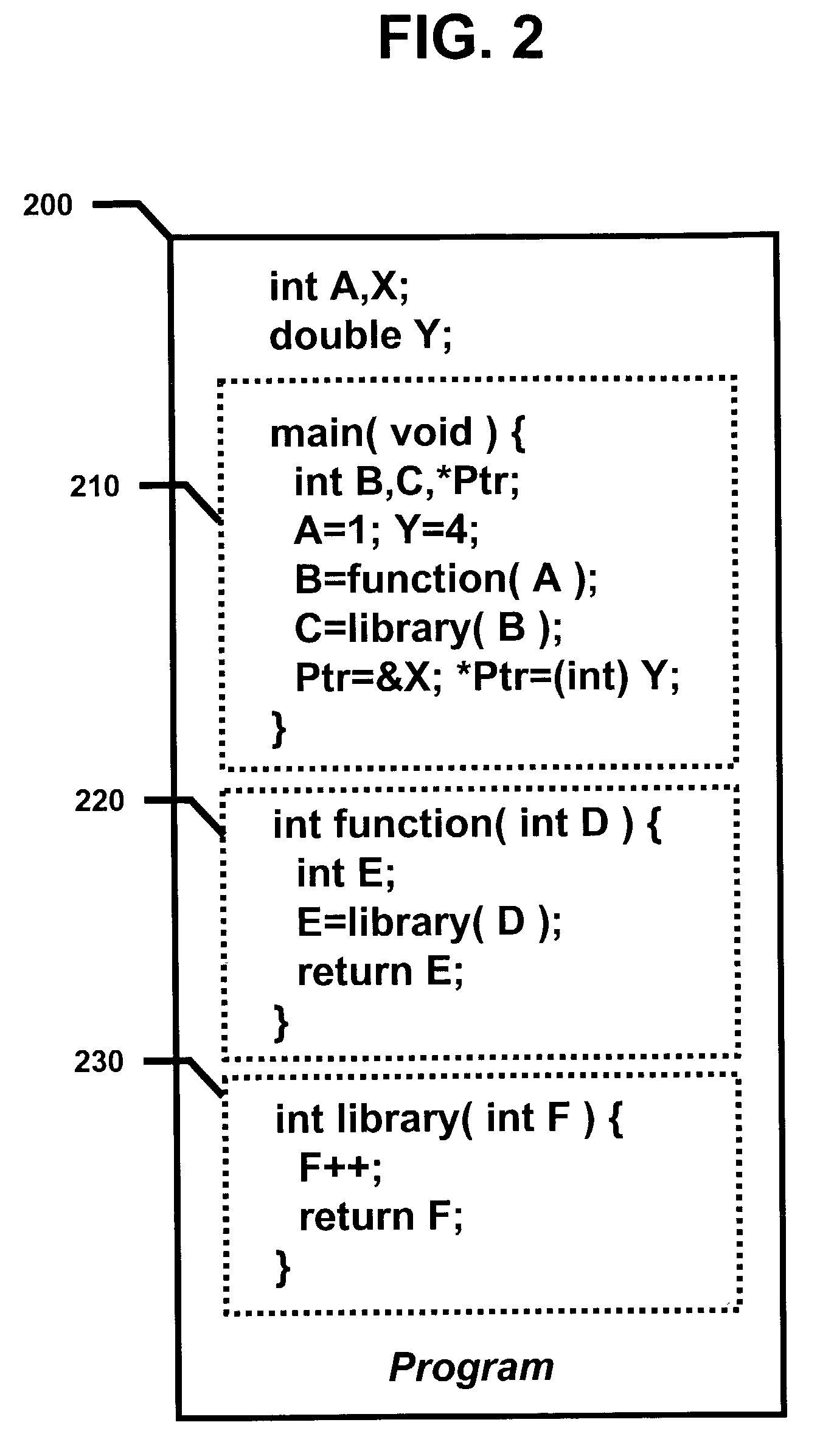
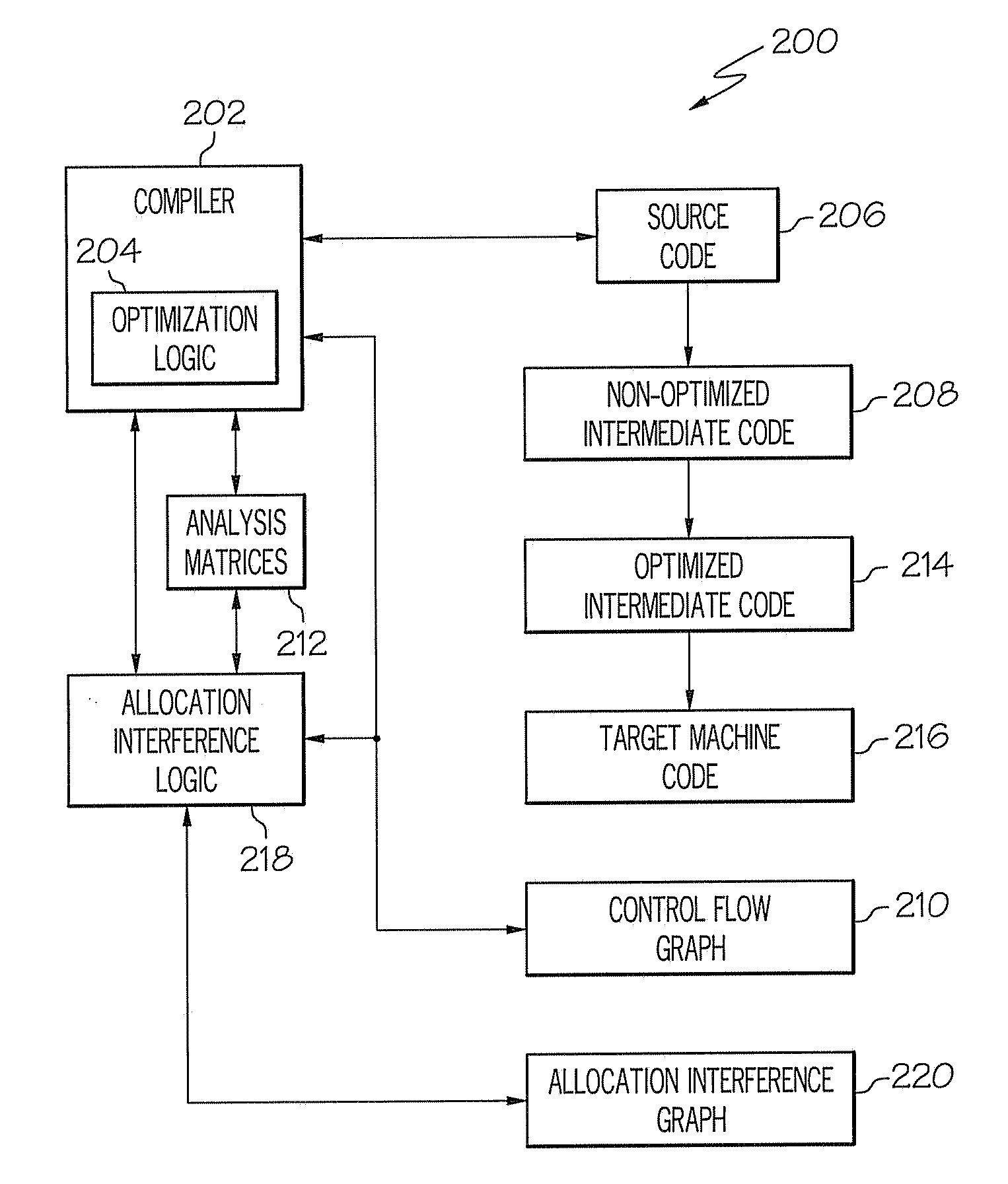
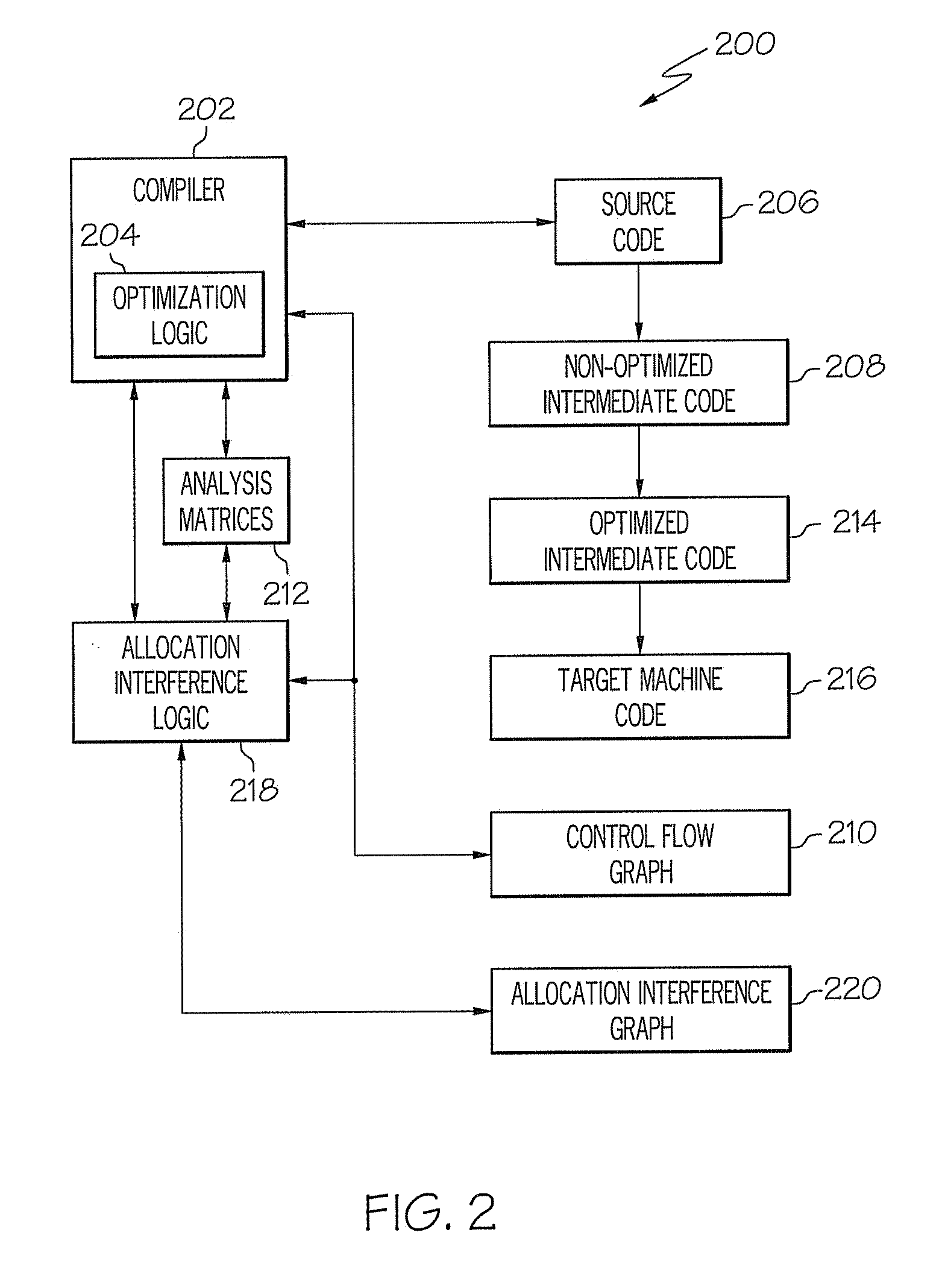
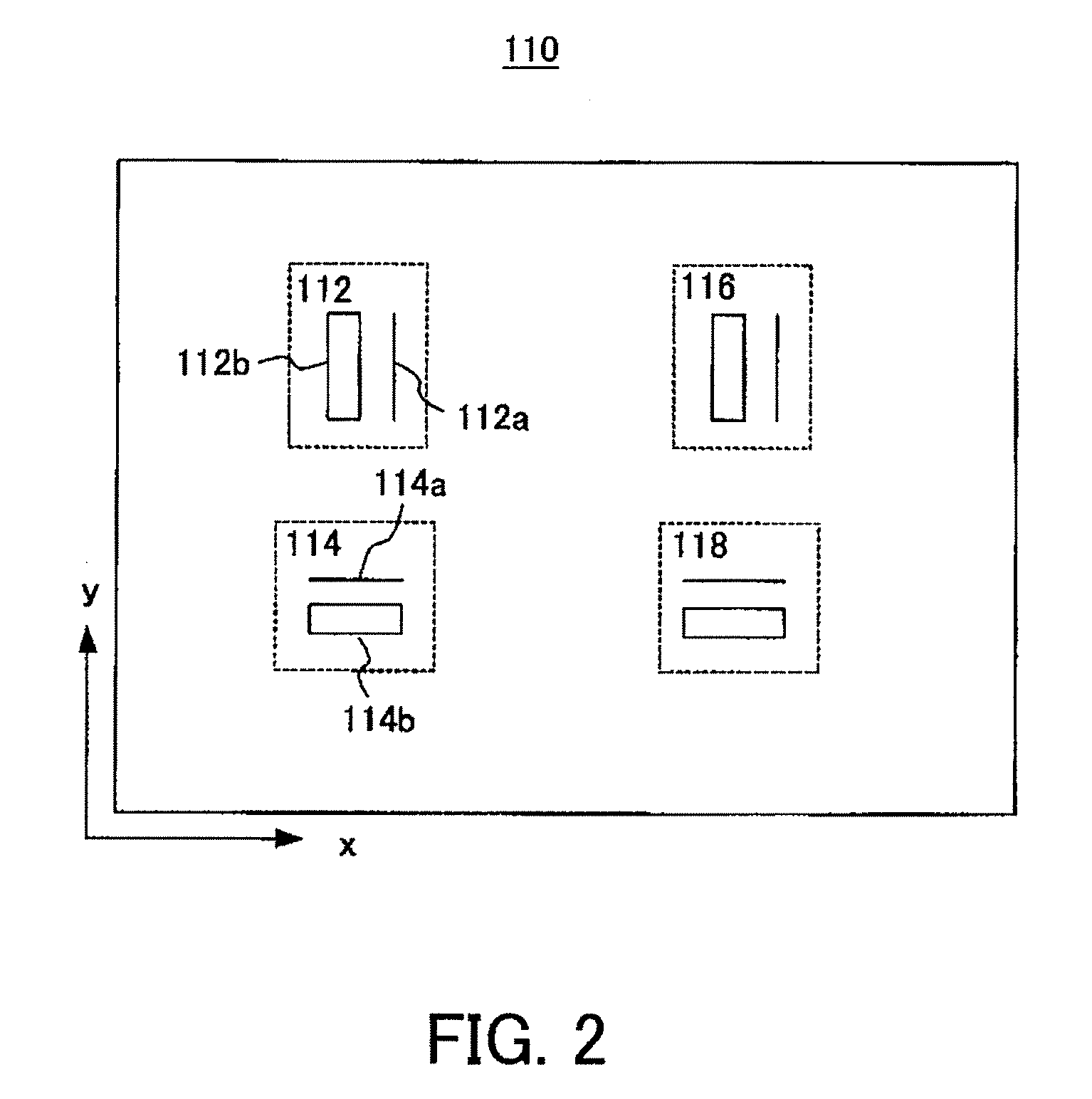
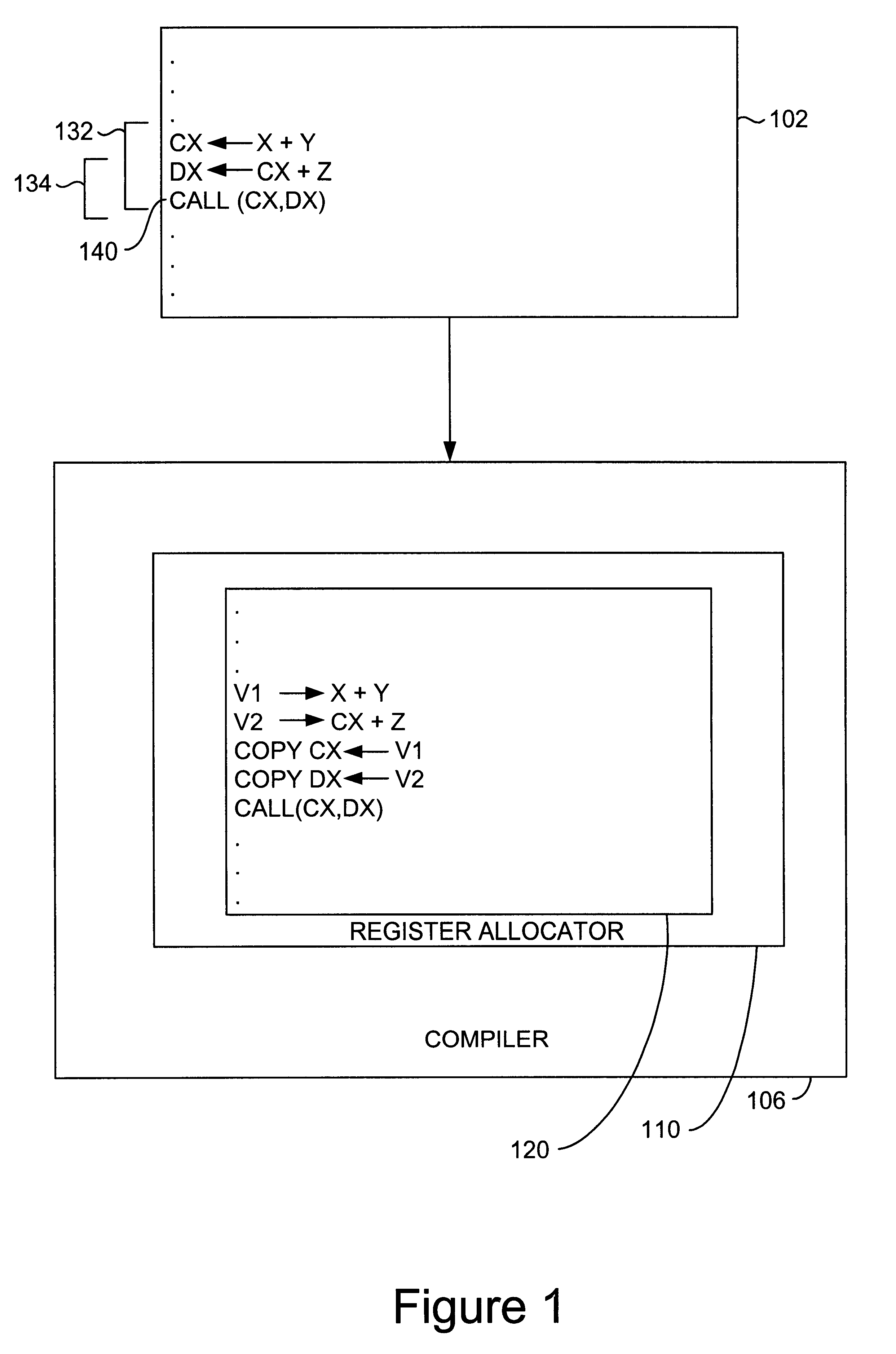
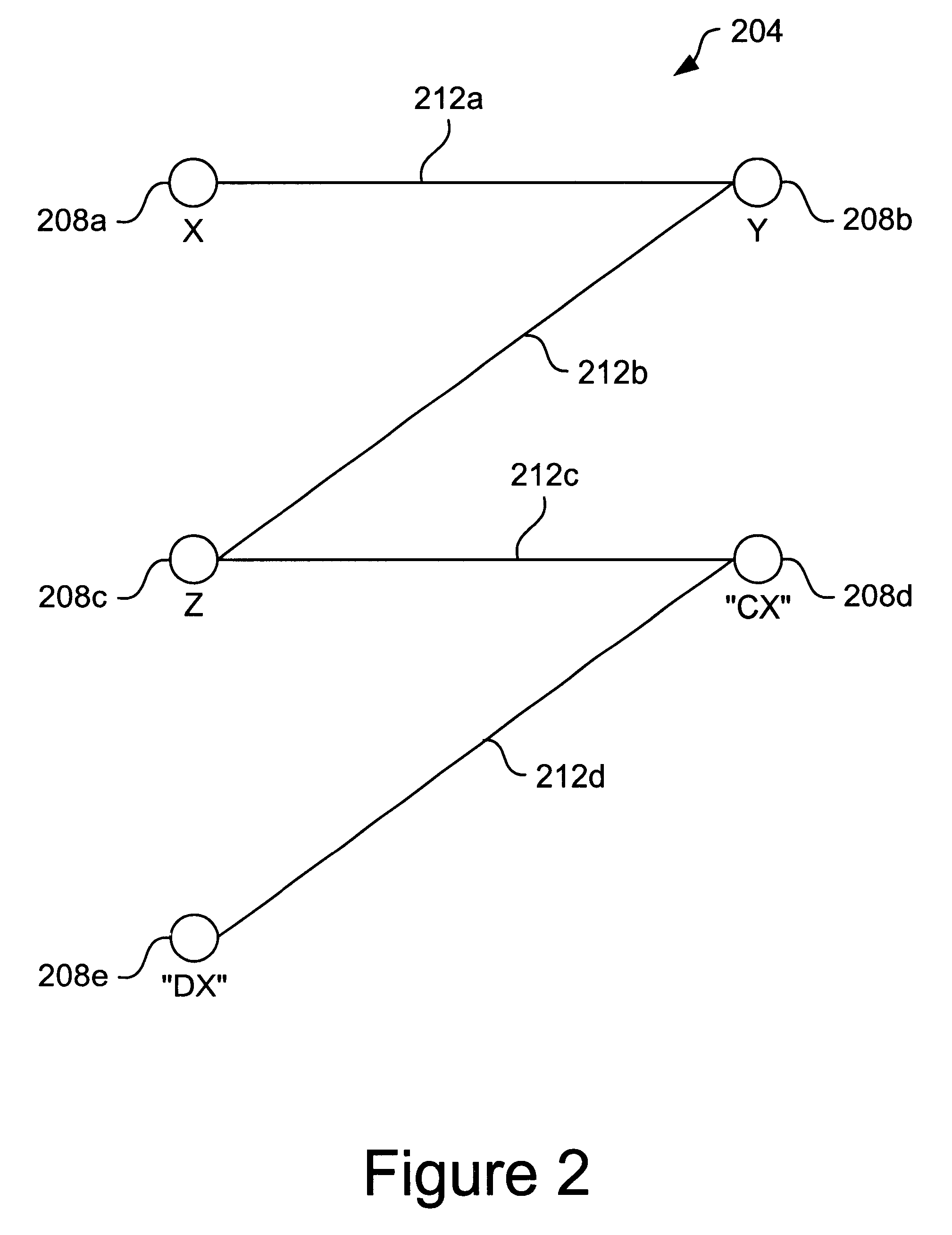
Loop allocation for optimizing compilers
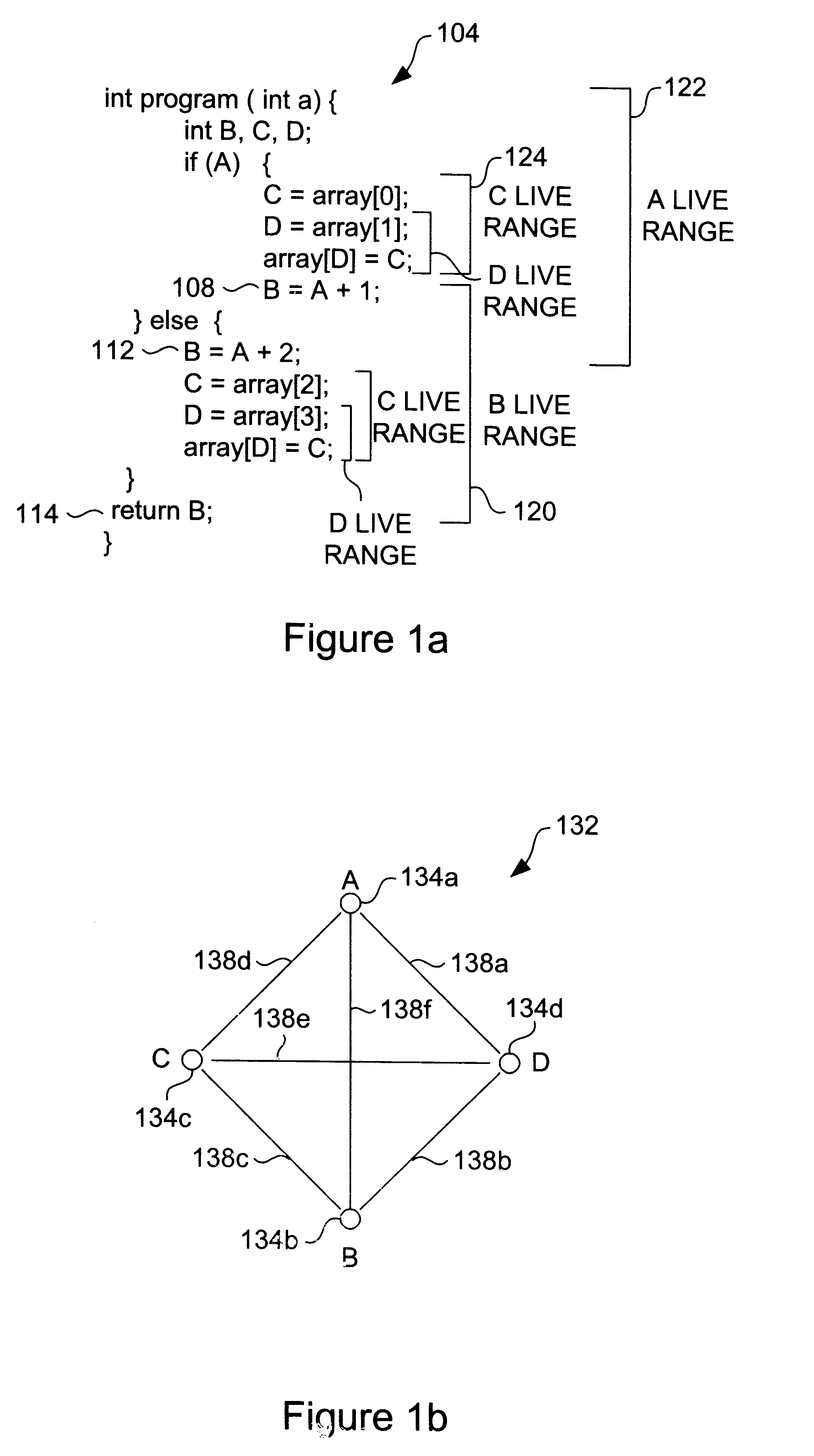
Loop allocation for optimizing compilers includes the generation of a program dependence graph for a source code segment. Control dependence graph representations of the nested loops, from innermost to outermost, are generated and data dependence graph representations are generated for each level of nested loop as constrained by the control dependence graph. An interference graph is generated with the nodes of the data dependence graph. Weights are generated for the edges of the interference graph reflecting the affinity between statements represented by the nodes joined by the edges. Nodes in the interference graph are given weights reflecting resource usage by the statements associated with the nodes. The interference graph is partitioned using a profitability test based on the weights of edges and nodes and on a correctness test based on the reachability of nodes in the data dependence graph. Code is emitted based on the partitioned interference graph.
Owner:IBM CORP
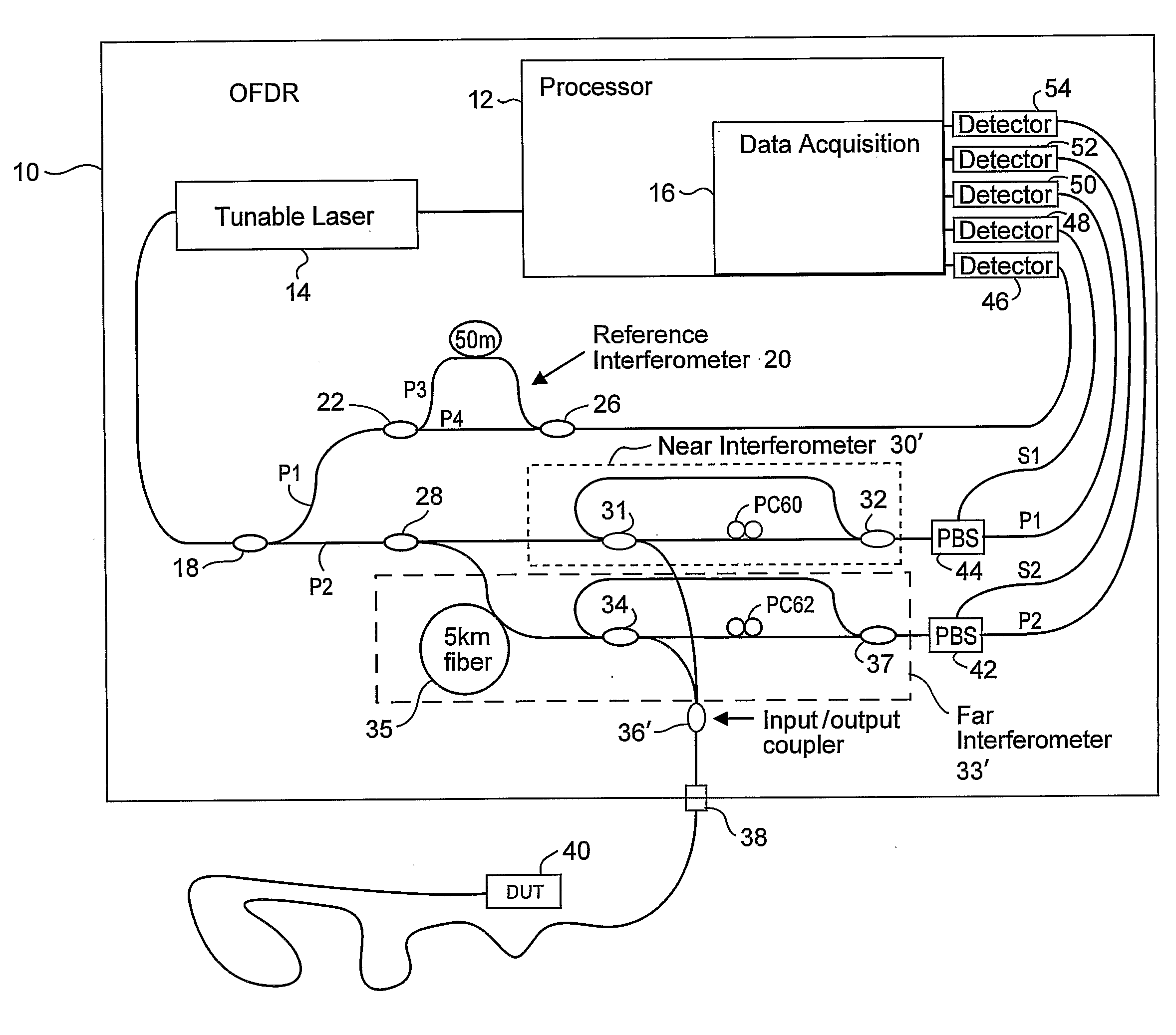
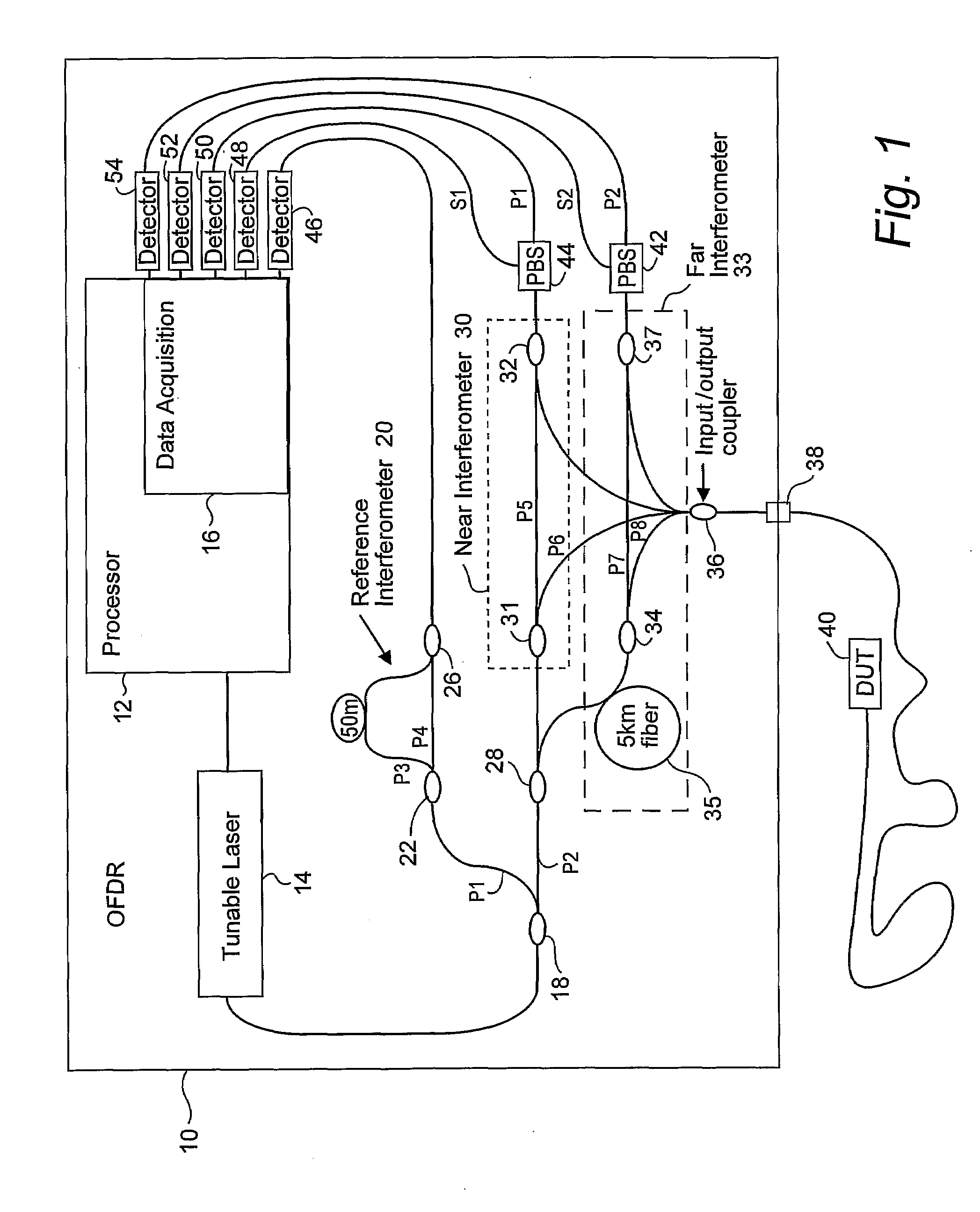
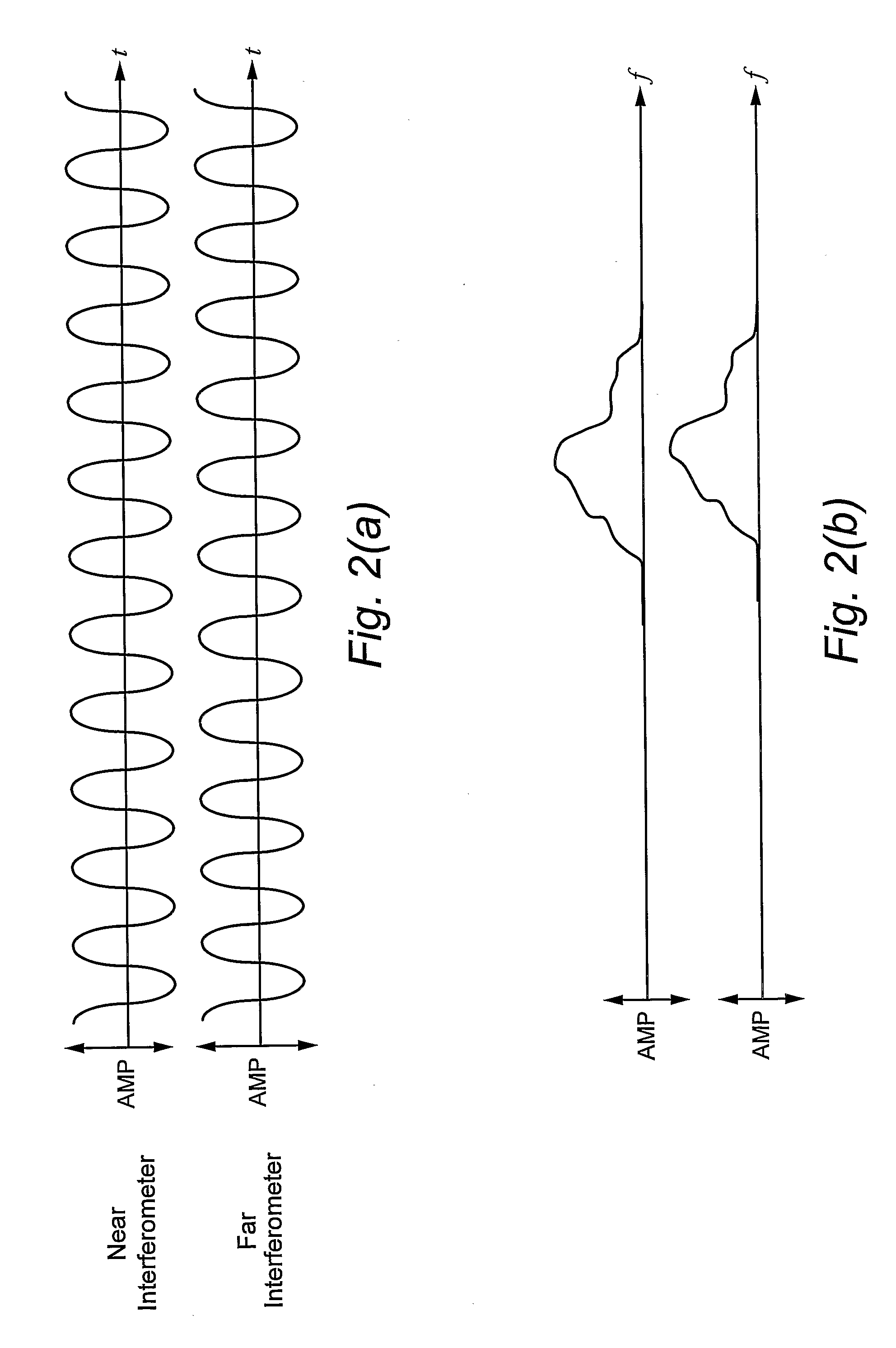
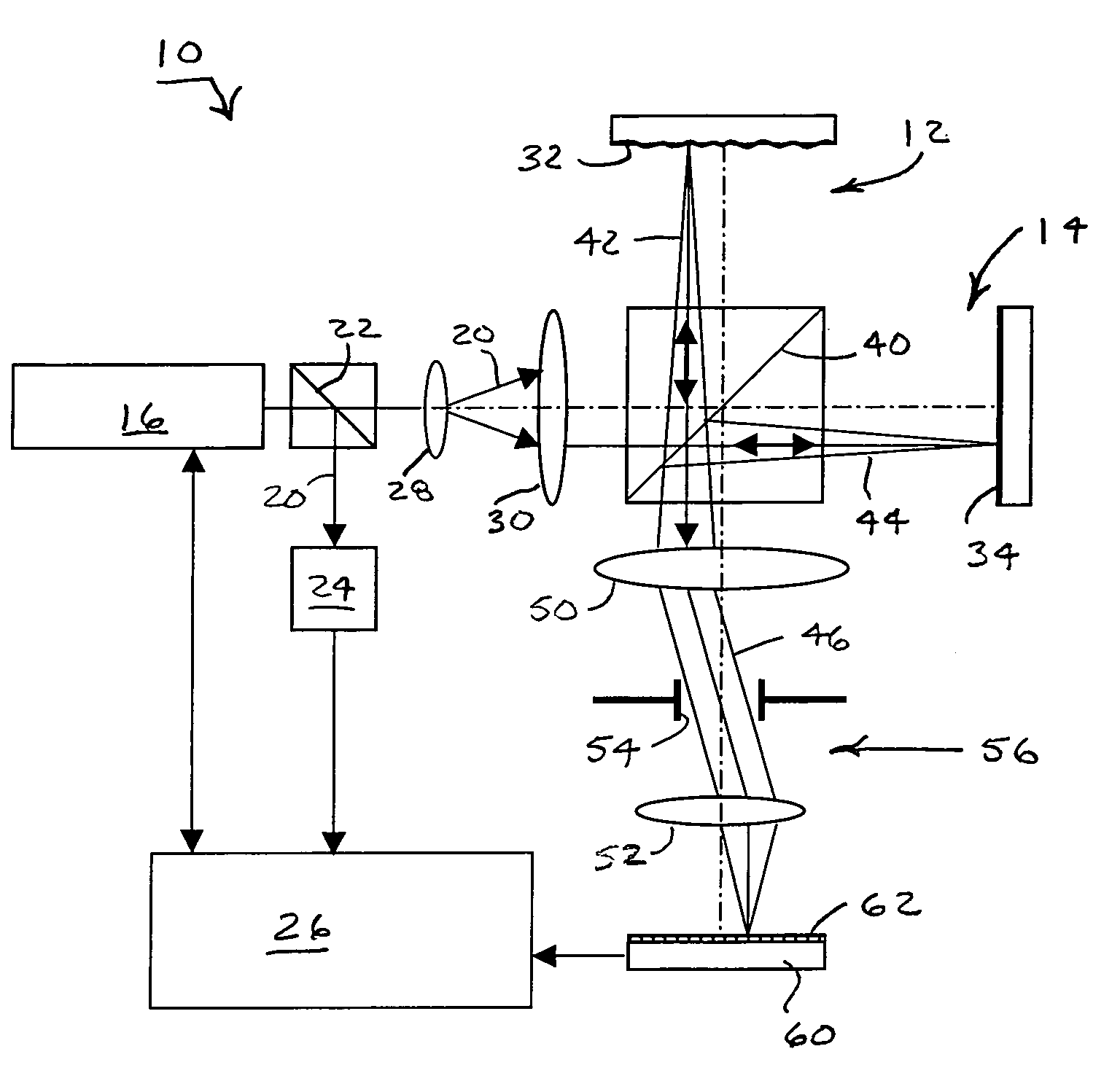
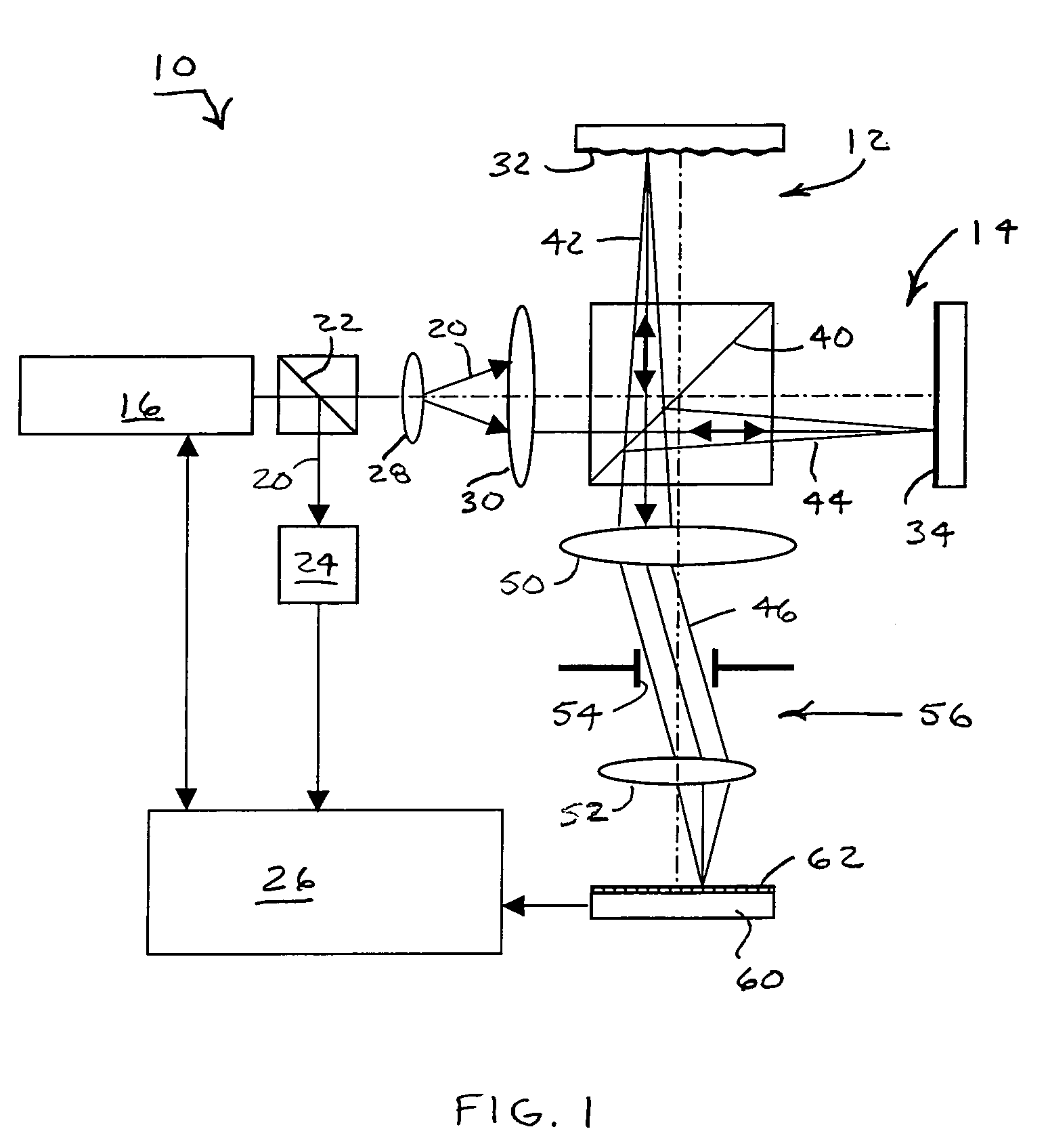
Compensating for Time Varying Phase Changes in Interferometric Measurements
ActiveUS20090103100A1Precise location and determinationIncrease spaceAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsPhase varianceEngineering
An optical device under test (DUT) is interferometrically measured. The DUT can include one or more of an optical fiber, an optical component, or an optical system. First interference pattern data for the DUT is obtained for a first path to the DUT, and second interference pattern data for the DUT is obtained for a second somewhat longer path to the DUT. Because of that longer length, the second interference pattern data is delayed in time from the first interference pattern data. A time varying component of the DUT interference pattern data is then identified from the first and second interference pattern data. The identified time varying component is used to modify the first or the second interference pattern data to compensate for the time-varying phase caused by vibrations, etc. One or more optical characteristics of the DUT may then be determined based on the modified interference pattern data.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Method for identifying an object
InactiveUS20030156294A1Paper-money testing devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansObject basedPhysics
The invention concerns a method for identifying an object comprising the following steps: (a) selecting an intrinsic surface of an object to be identified; (b) illuminating at least an identification zone in the intrinsic surface of the object to be identified with a coherent light and intercepting at least part of the light reflected by the identification zone, so as to obtain an interference figure in specific illuminating and intercepting conditions; (c) preserving said interference figure as reference interference figure of the object to be identified; (d) placing a candidate object which could possibly be the object to be identified in similar illuminating and intercepting conditions as those used to obtain the reference interference figure and obtain from said candidate object an interference figure; (e) comparing the reference interference figure with the interference figure of the candidate object; and (f) assessing the probability of identity between the object to be identified and the candidate object based on the degree of correspondence between the reference interference figure and the interference figure of the candidate object.
Owner:EURON COMMUNITY EC
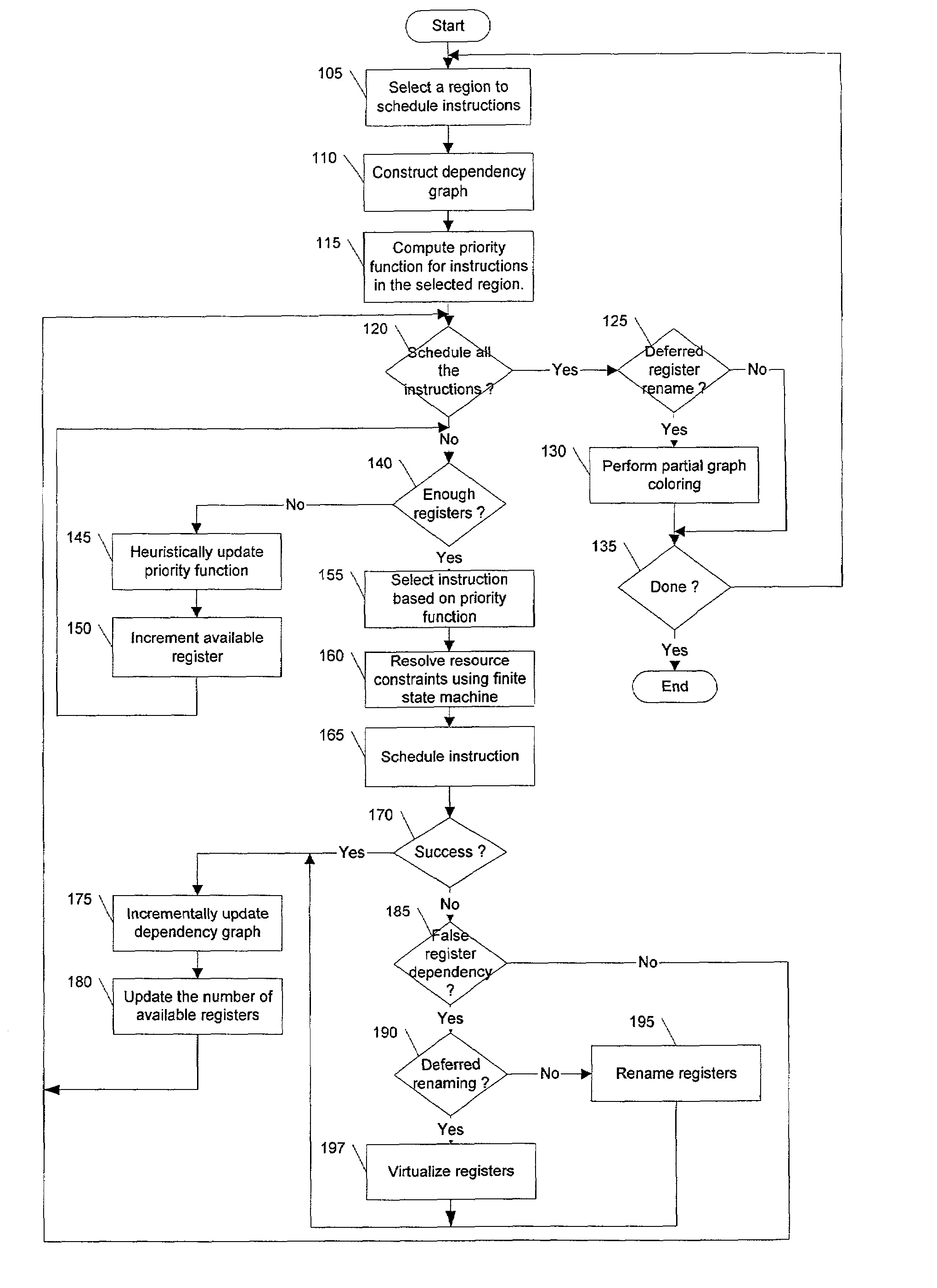
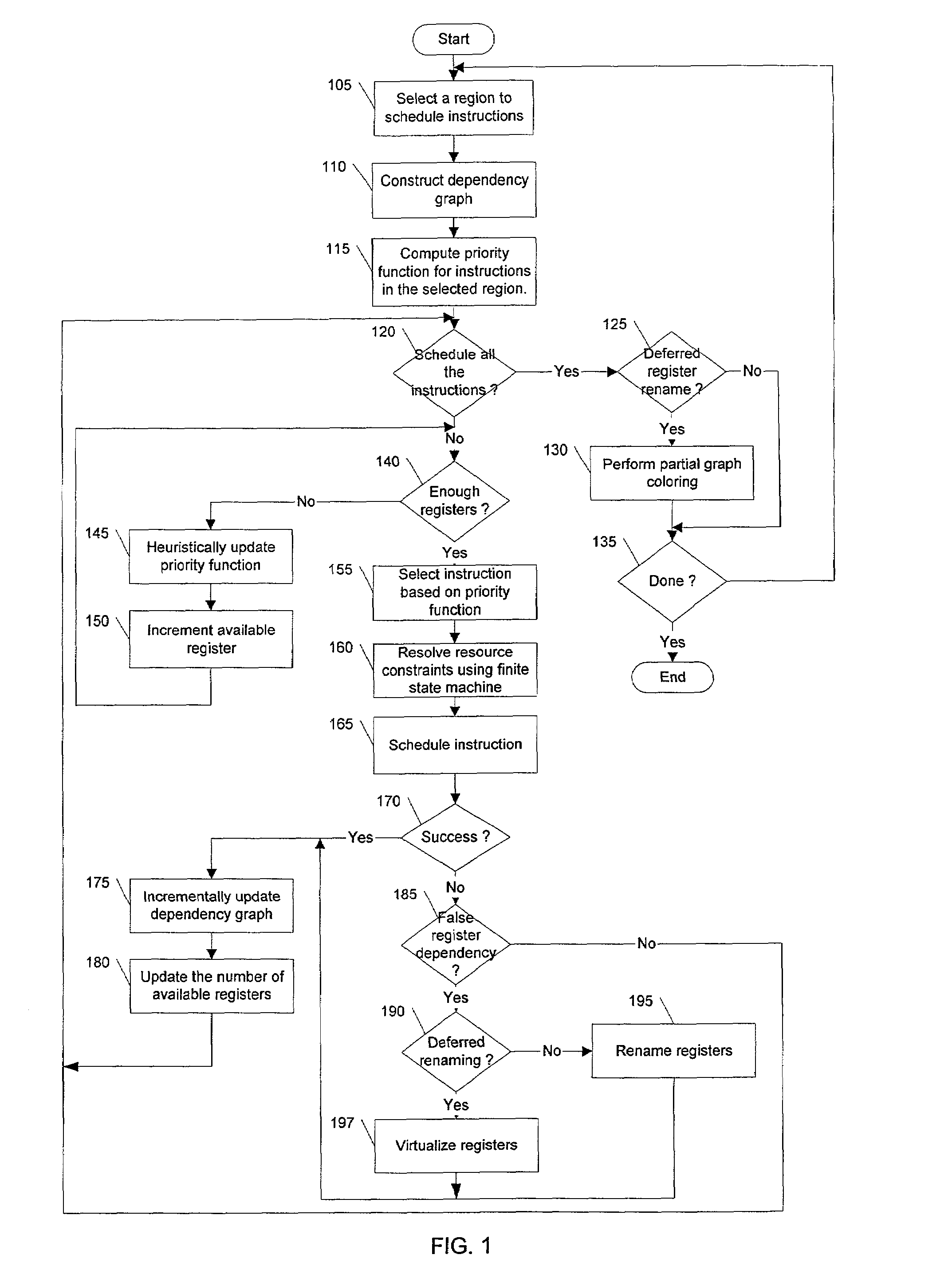
Method and apparatus for integrated instruction scheduling and register allocation in a postoptimizer
The present invention describes a method of efficiently optimizing instruction scheduling and register allocation in a post optimizer. The method removes false register dependencies between pipelined instructions by building an incremental (partial) interference graph of register allocation for scheduled instructions. False dependency graph indicates the amount of parallelism in the data flow graph. The incremental interference graph uses a mix of virtual and physical registers. The interference graph is built incrementally as an instruction schedular schedules each instruction. The optimization is done incrementally on localized code. The physical register mapping is maximized and virtual registers are created on demand basis.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and apparatus for allocating stack slots
Methods and apparatus for allocating and using stack space are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, a computer-implemented method for allocating stack space in an object-based system includes obtaining source code that is suitable for compilation and includes a definition associated with a variable. During register allocation, stack slots and machine registers are treated substantially similarly. This includes the steps of building an interference graph, copy coalescing, attempting to color the interference graph, and determining if the attempt to color the interference graph is successful. If the coloring attempt is not successful, then in lieu of normal spill code being inserted, register-to-register copies, e.g., "reg-reg" copies, are inserted in the source code. The "reg-reg" copies include copies associated with both stack slots and machine registers.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Inter-procedure global register allocation method
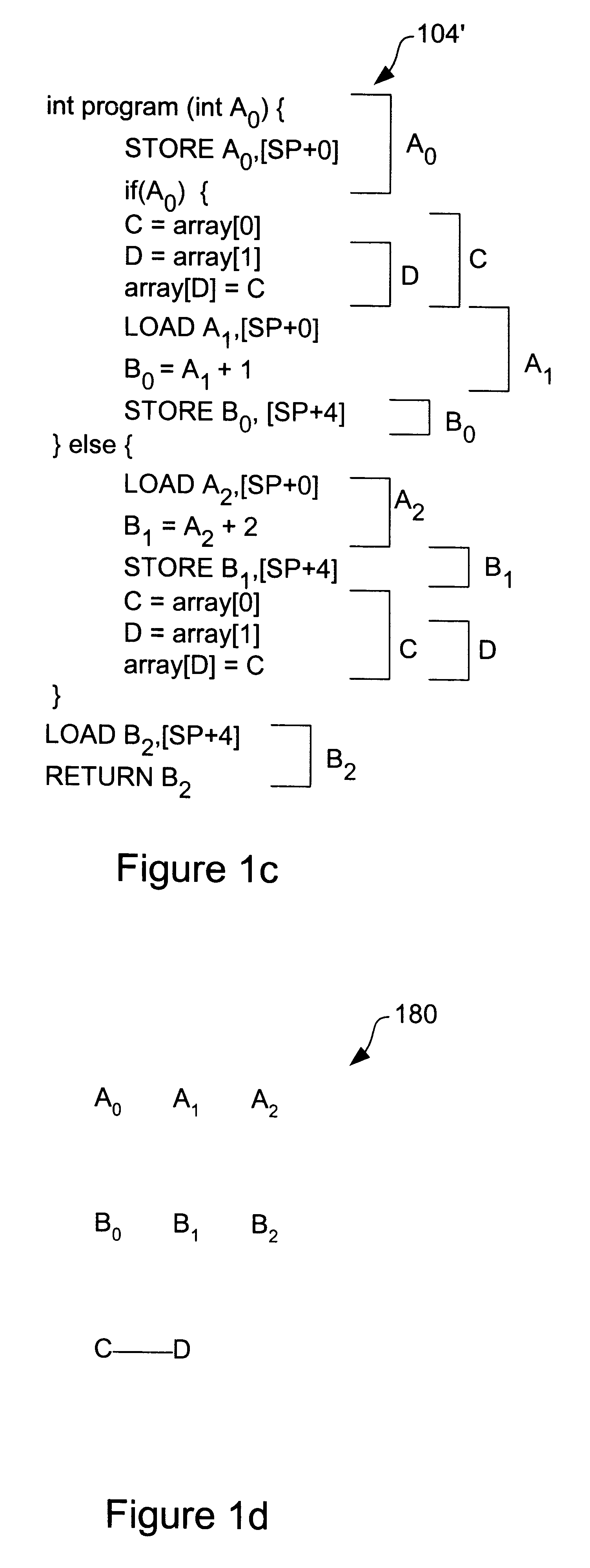
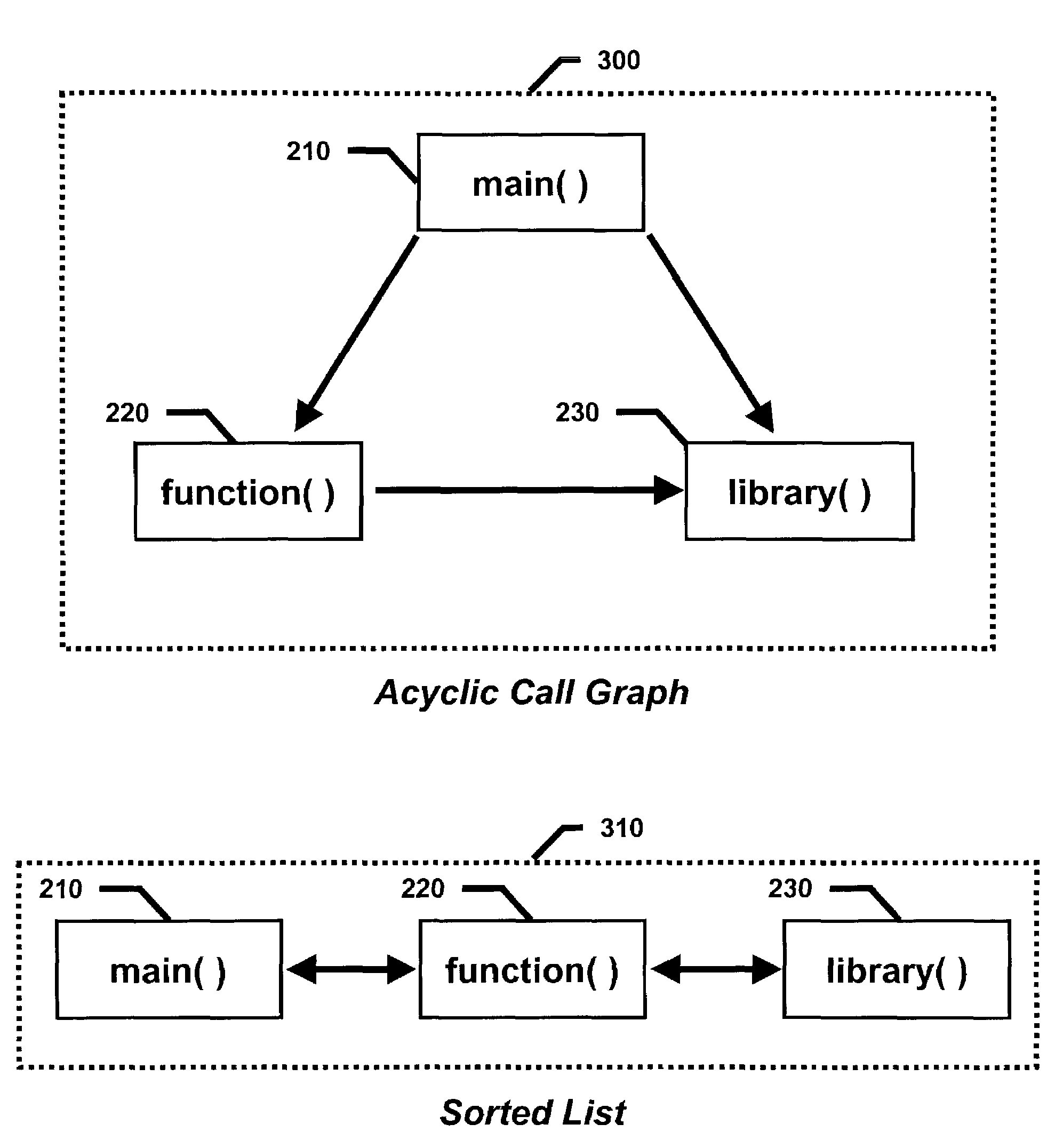
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method and system for optimizing processor register allocation. Variables from an acyclic call graph having a plurality of functions may be identified and a plurality of virtual registers may be created by assigning each of the identified variables to at least one virtual register. An interference graph may be constructed based on the plurality of virtual registers and may be colored with a plurality of physical registers. If the interference graph is not colorable, then at least one virtual register may be spilled from the interference graph.
Owner:INTEL CORP
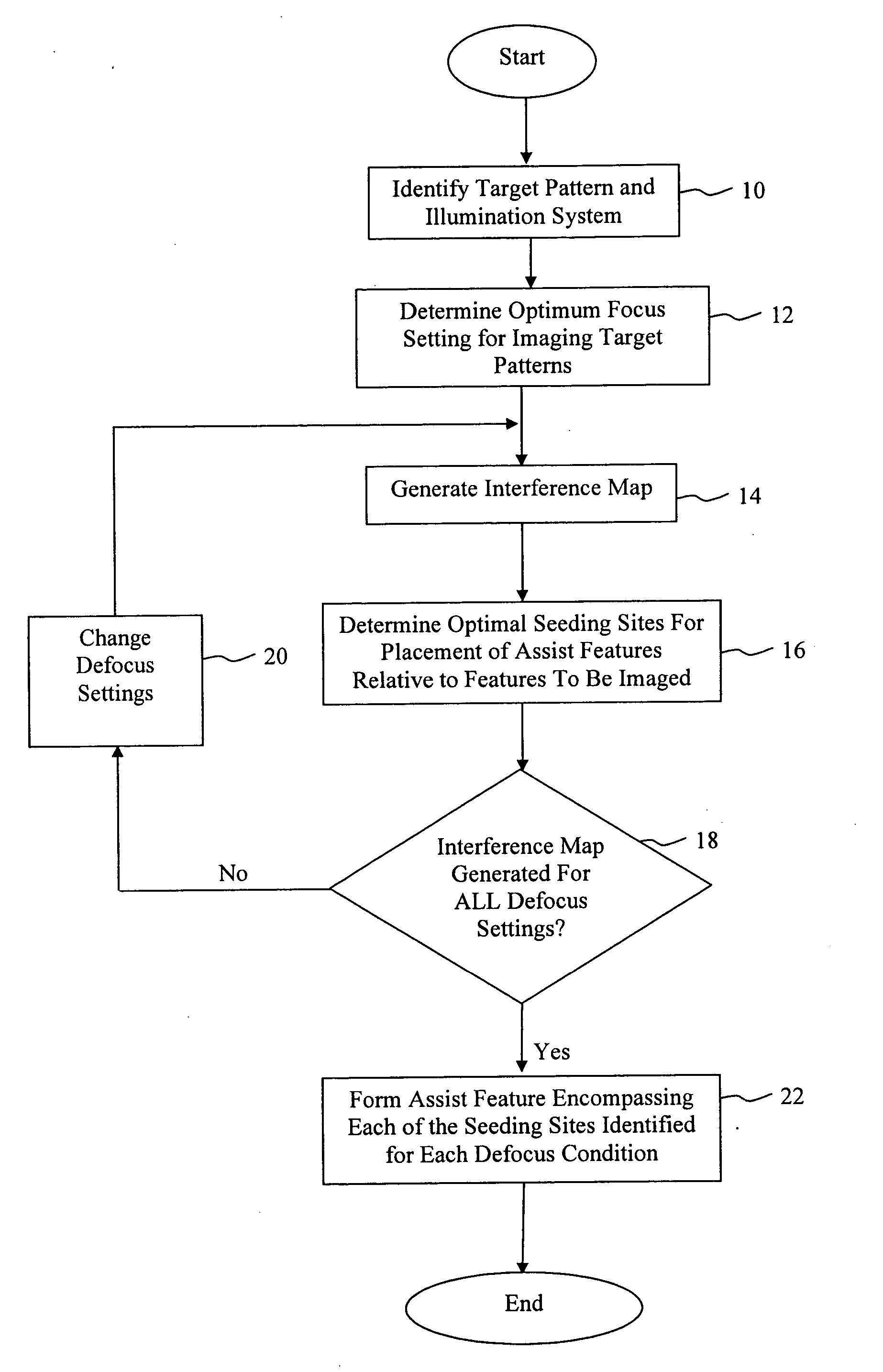
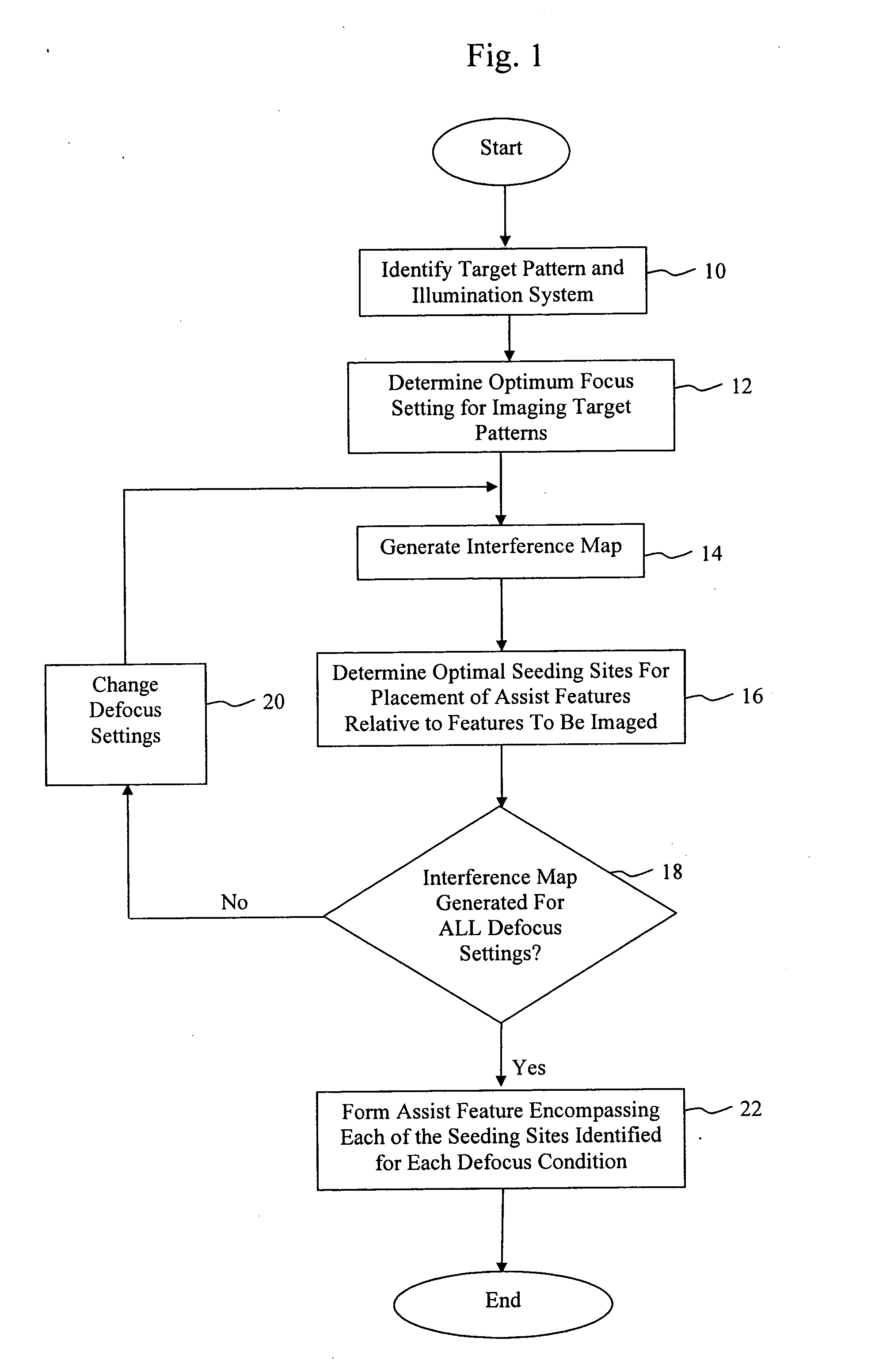
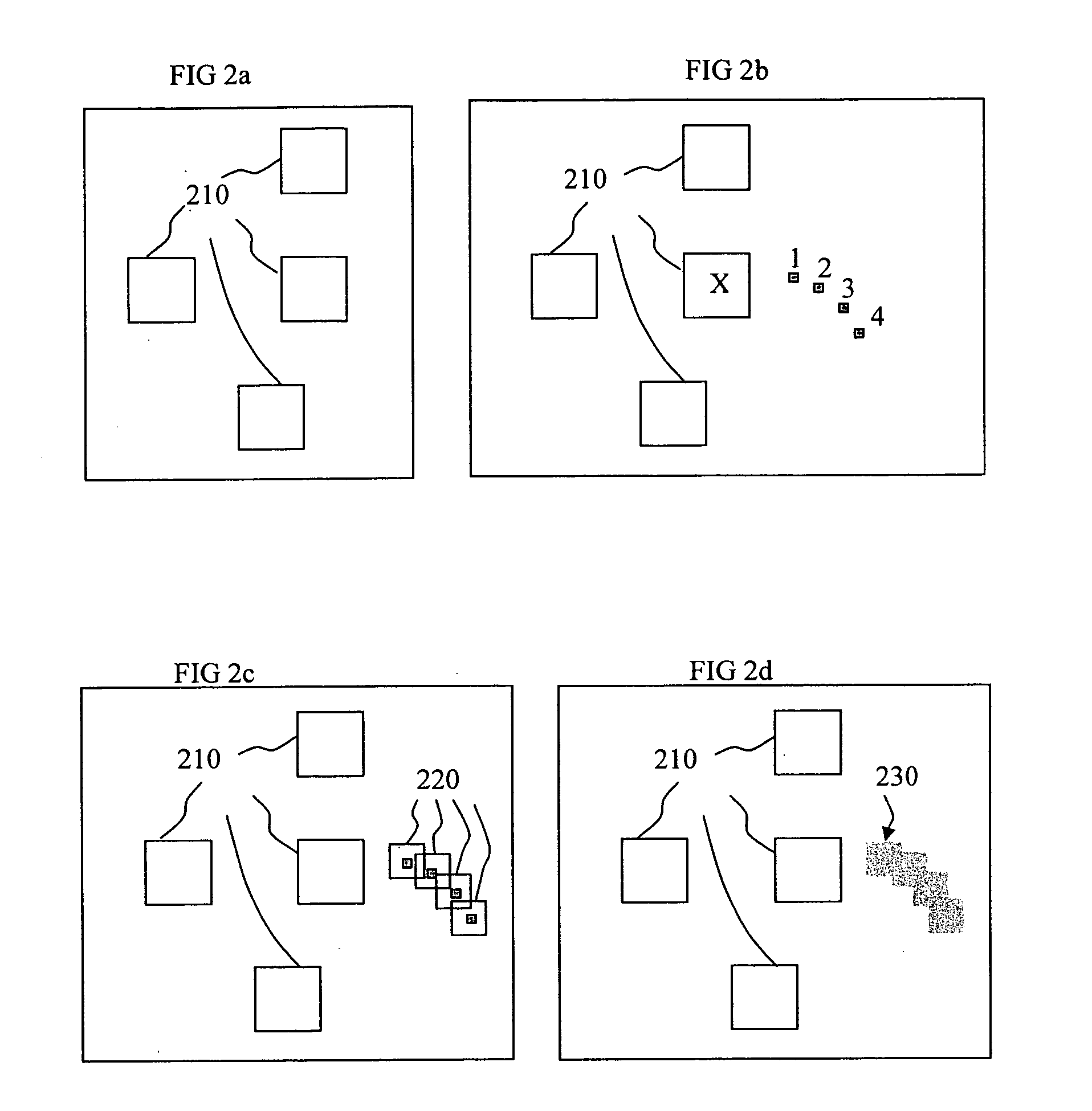
Method, program product and apparatus for model based scattering bar placement for enhanced depth of focus in quarter-wavelength lithography
ActiveUS20060075377A1Improve performanceSimple methodPhotomechanical exposure apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentLithographic artistWavelength
A method of generating a mask having optical proximity correction features. The method includes the steps of: (a) obtaining a desired target pattern having features to be imaged on a substrate; (b) determining a first focus setting to be utilized when imaging the mask; (c) determining a first interference map based on the target pattern and the first focus setting; (d) determining a first seeding site representing the optimal placement of an assist feature within the mask relative to a feature to be imaged on the basis of the first interference map; (e) selecting a second focus setting which represents a predefined amount of defocus relative to the first focus setting; (f) determining a second interference map based on the target pattern and the second focus setting; (g) determining a second seeding site representing the optimal placement of an assist feature within the mask relative to the feature to be imaged on the basis of the second interference map; and (h) generating an assist feature having a shape which encompasses both the first seeding site and the second seeding site.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
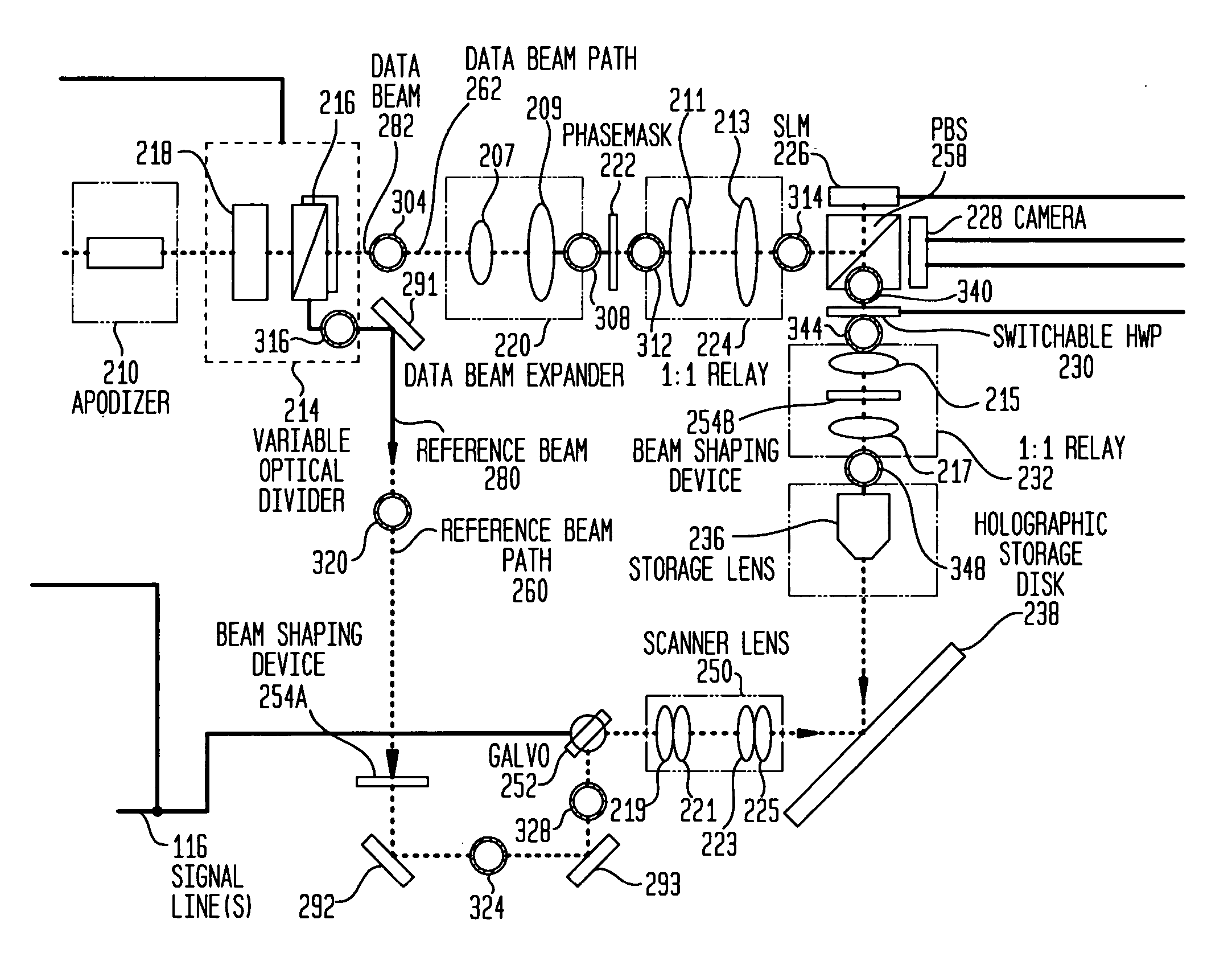
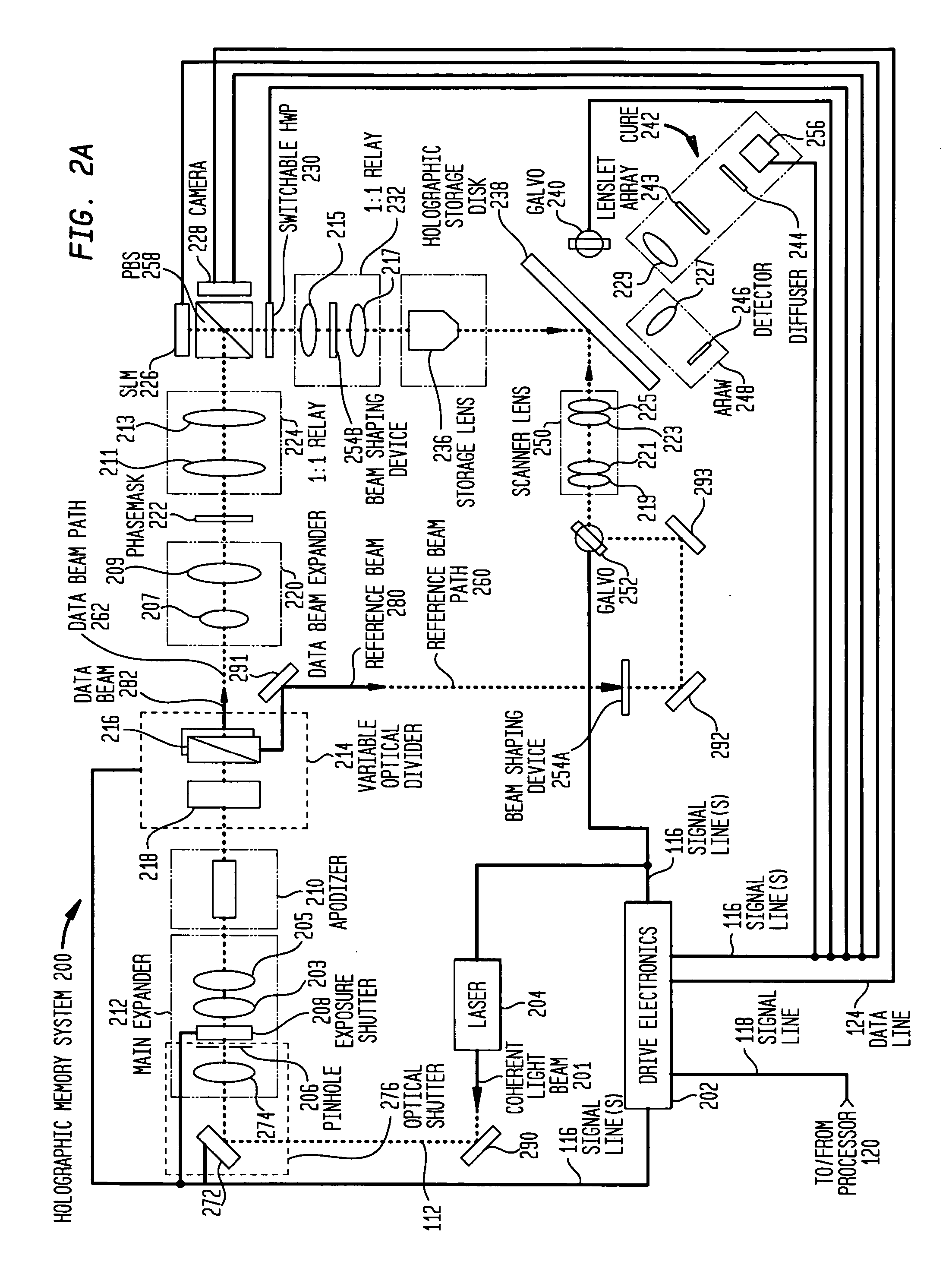
Optical delay line in holographic drive
InactiveUS20060291022A1Holographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic optical componentsPhysicsOptical path
The present invention relates to a system comprising a holographic data storage drive that records holographic digital data in a holographic recording medium, and which comprises: a data beam path having a first optical path length; and a reference beam path having a second optical path length; wherein one of the data beam and reference beams paths comprise an optical delay line so that the difference between the first and second optical path lengths is less than the laser coherence length. The present invention further relates to a method for operating a laser in the holographic data storage drive in a multi-mode state during the recording of holographic digital data the holographic medium without adverse effects on the strength of the interference patterns formed.
Owner:AKONIA HOLOGRAPHICS
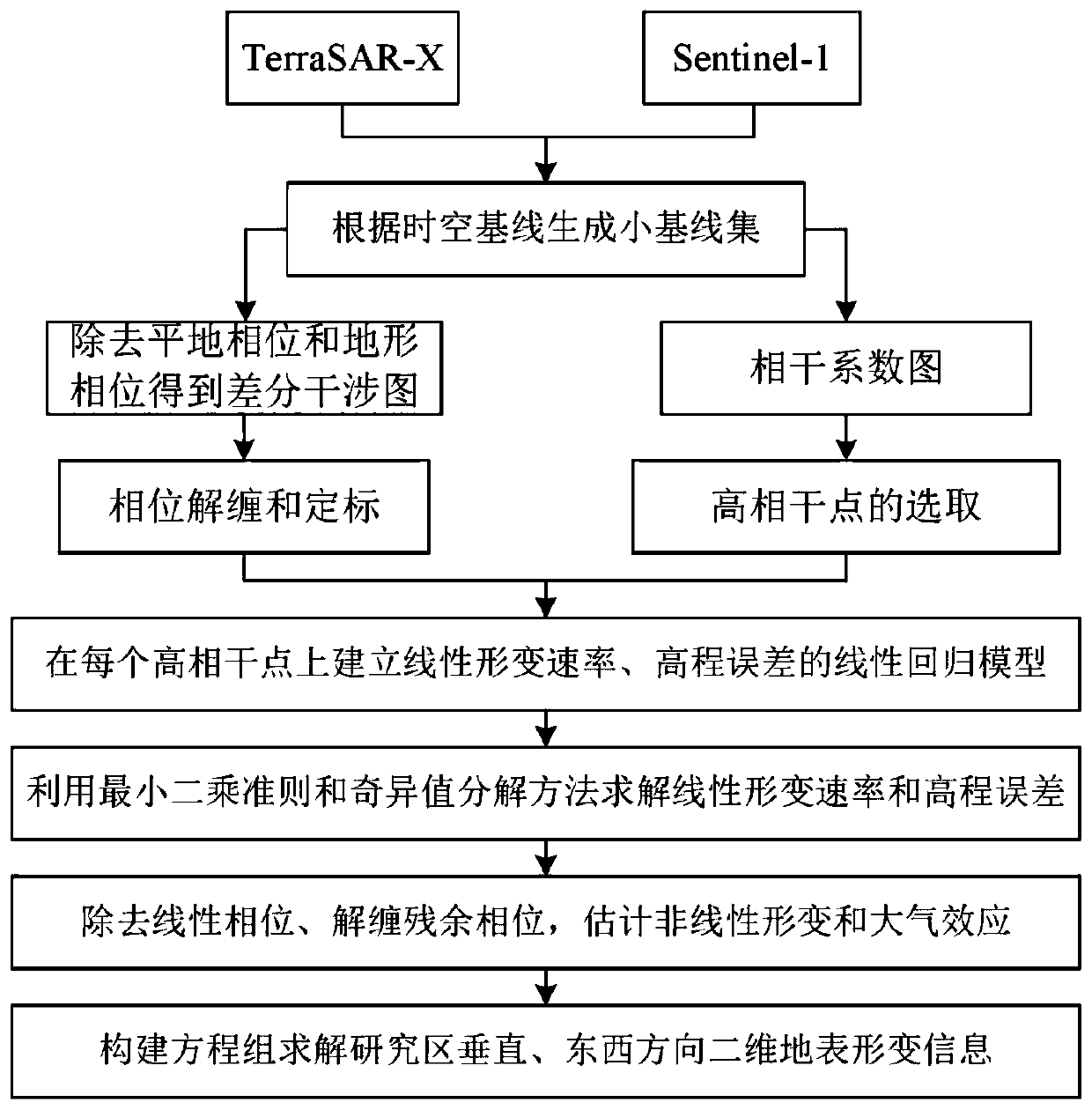
Coal mine area surface deformation monitoring method based on lifting rail time sequence InSAR
InactiveCN110888130ASolve the workloadSolve the costRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarDeformation monitoring
The invention discloses a coal mine area surface deformation monitoring method based on a lifting rail time sequence InSAR. The coal mine area surface deformation monitoring method is characterized bycomprising the steps of acquiring a plurality of scene SAR images of C and X wave bands, generating a short baseline set, differentiating an interference pattern, acquiring a high coherence point, constructing an equation, acquiring surface deformation information and the like. Compared with the prior art, the coal mine area surface deformation monitoring method has the advantages of breaking through the limitation that a single SAR satellite platform InSAR technology can only obtain deformation information in a radar sight line direction, effectively weakens the influences of space-time incoherence, phase unwrapping errors, atmospheric delay errors and the like, improves the precision and reliability of the InSAR technology for monitoring surface deformation information, and promotes thewide application of the InSAR technology in the field of deformation monitoring.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Centralized channel selection method and apparatus for wireless networks in a dense deployment environment
ActiveUS20110292898A1Rapid and significant increaseEasy to useTransmission control/equalisingAssess restrictionWireless mesh networkTelecommunications
A method and apparatus are described including scanning a channel, generating a report for the scanned channel, transmitting the channel report to an associated access point and receiving a channel assignment responsive to said channel report. Also described are a method and apparatus including scanning a channel, generating a first channel report, receiving a second channel report from an associated client, transmitting the first channel report and the second channel report to a server, receiving a channel assignment message from the server responsive to the first and second channel reports and transmitting the channel assignment message to the associated client. Further described are a method and apparatus including receiving a channel report from an associated access point, building an interference graph responsive to the channel report, determining channel assignments based on the interference graph and transmitting a channel assignment message to the associated access point.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
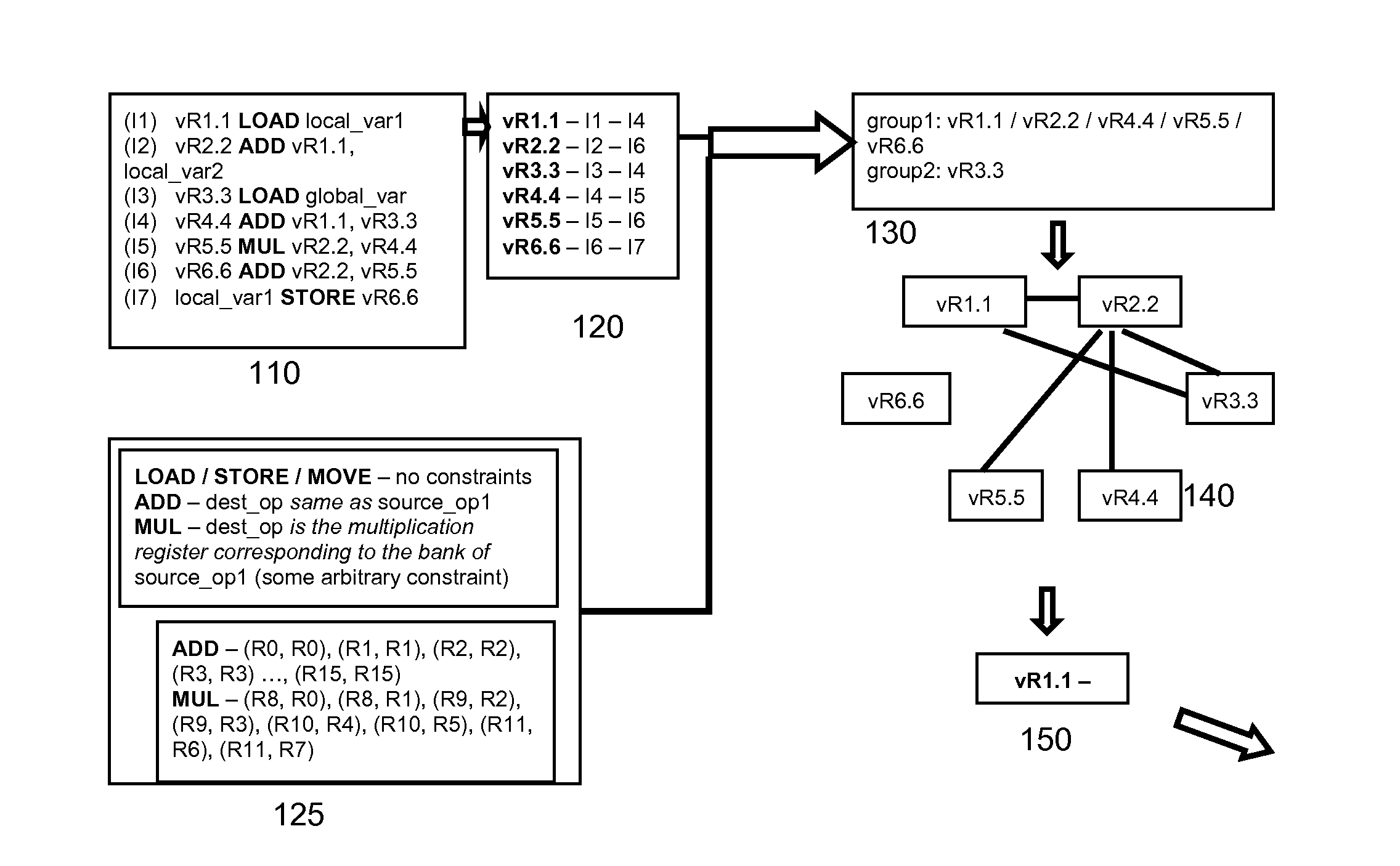
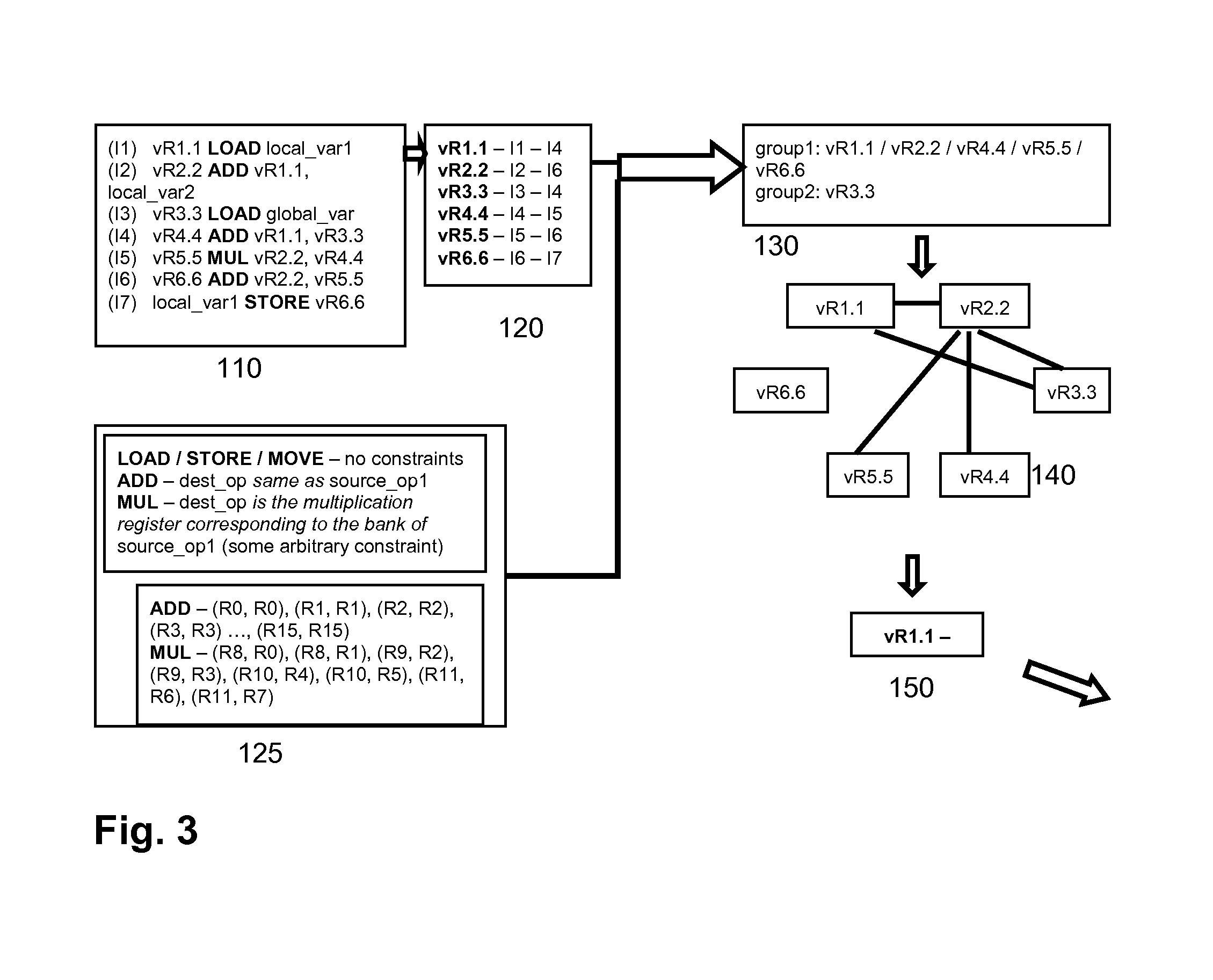
Optimization method for compiler, optimizer for a compiler and storage medium storing optimizing code
The invention pertains to an optimization method for a compiler, comprising providing a model of inter-operand constraints of physical registers of a target-platform of a compilation; and a) providing an intermediate representation of a source code using virtual registers; b) grouping the virtual registers of the intermediate representation based on the model of inter-operand constraints into two or more groups, each group comprising at least one virtual register; c) if for at least one group at least one interference of virtual registers within the group occurs, amending the intermediate representation to resolve at least one interference and jumping to step b); otherwise d) providing a representation of a group interference graph of interferences between the groups; and e) allocating virtual registers to physical registers using a coloring scheme on the representation of the group interference graph. The invention also refers to a corresponding optimizer for a compiler and a computer-readable storage medium storing optimizing code.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Graph-Based Method for Allocating Resources in OFDMA Networks
InactiveUS20090245085A1Easy to solveError preventionCriteria allocationSystem capacityInterference graph
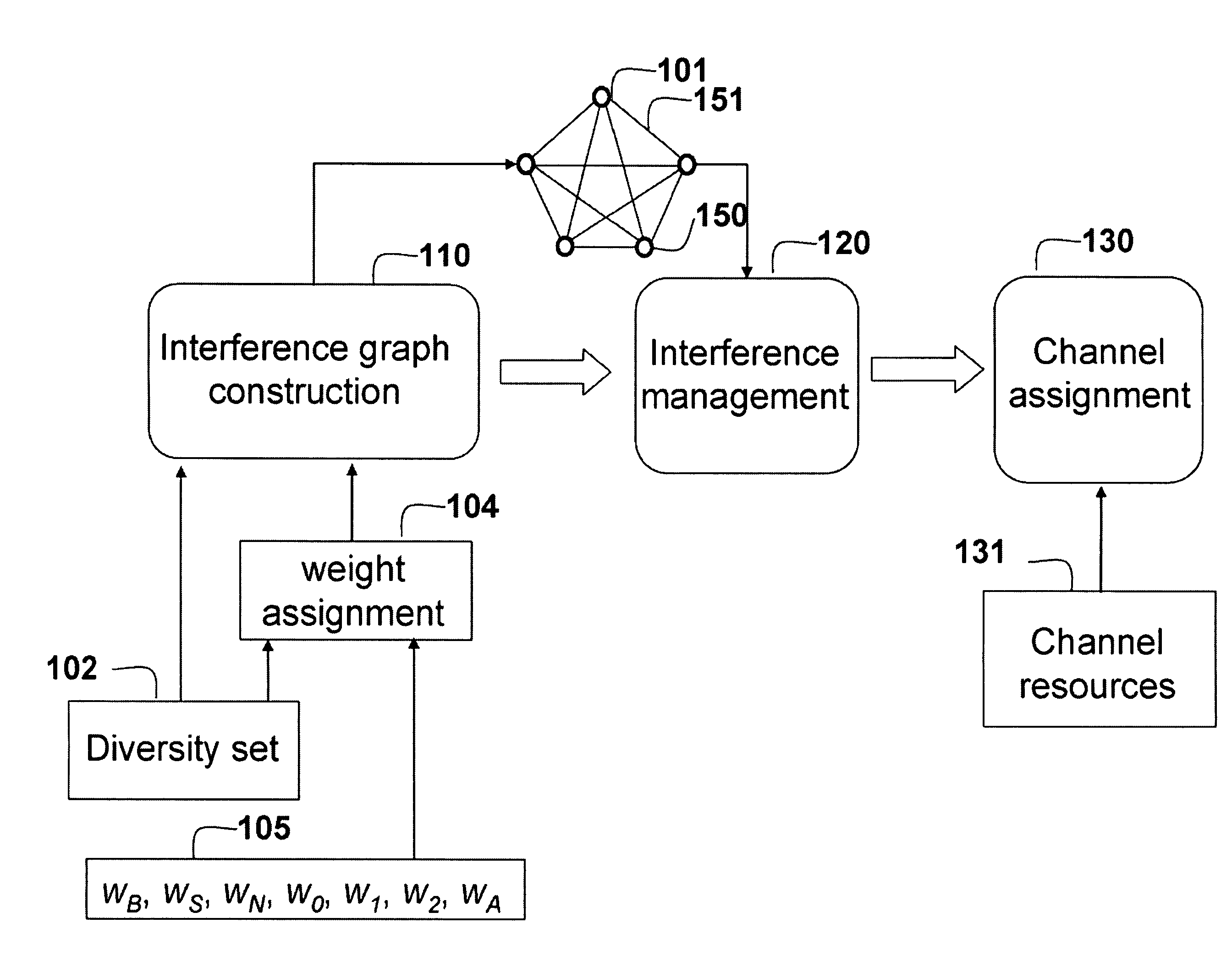
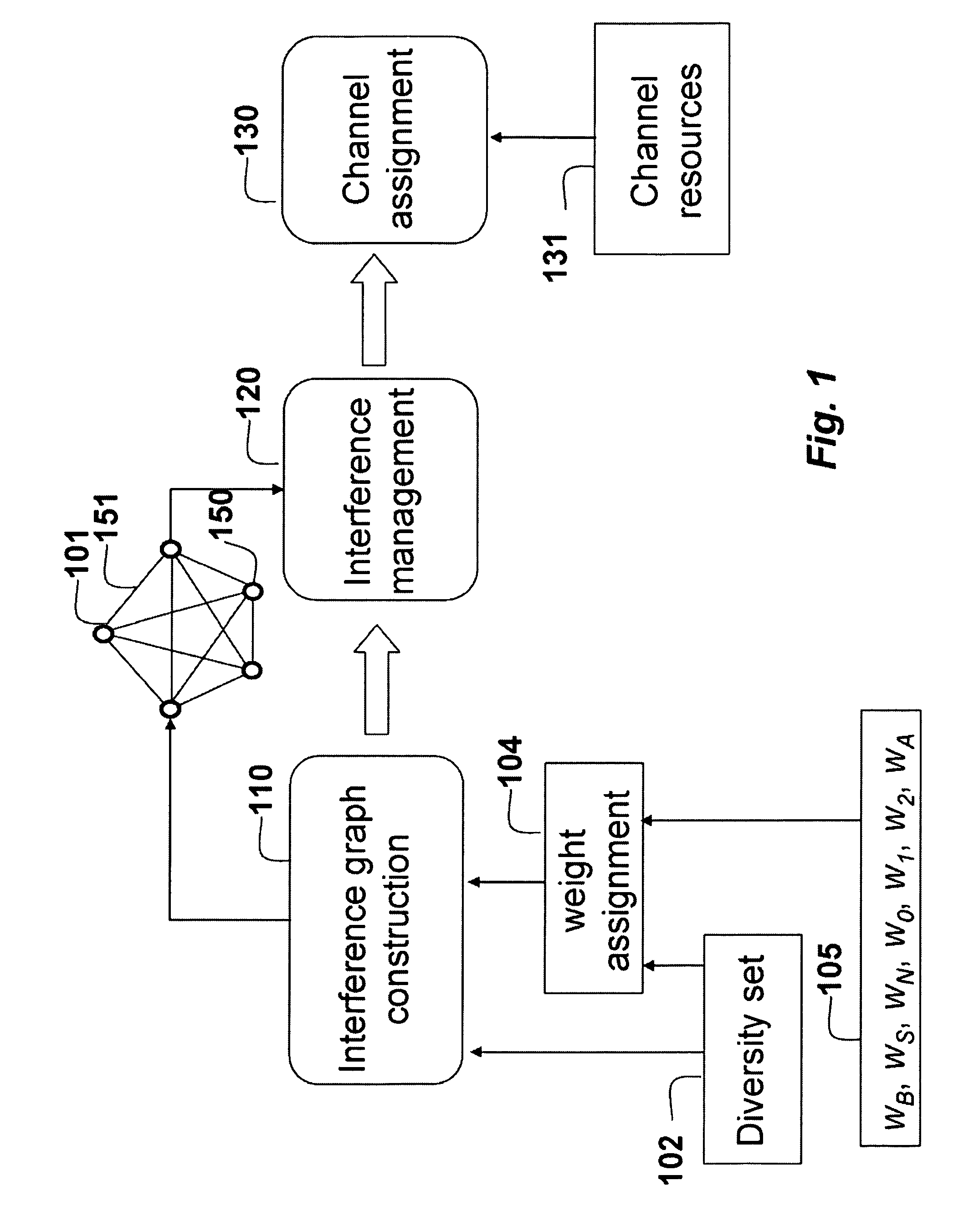
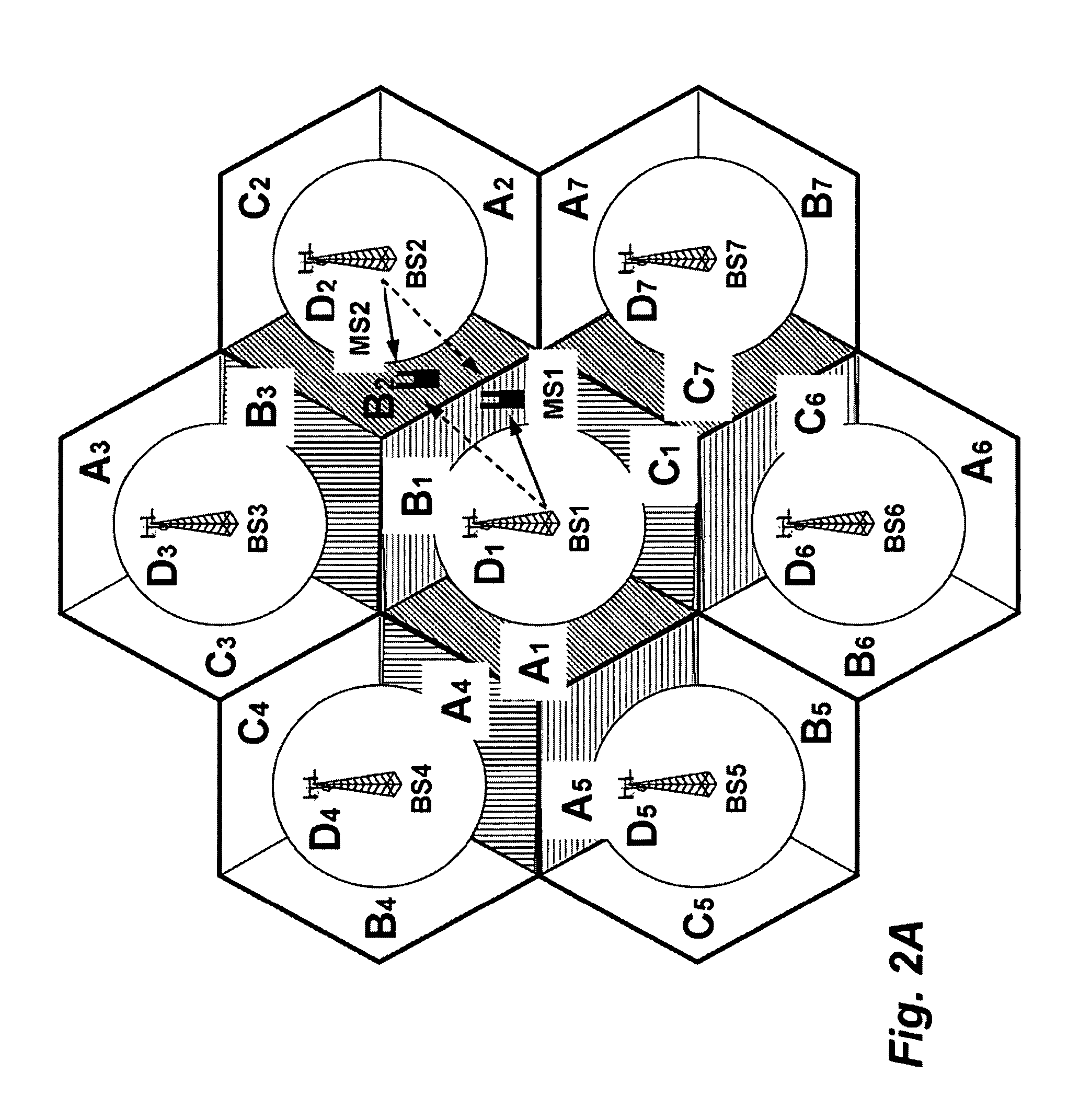
A method allocates radio channel resources in an orthogonal frequency-division multiple access network including a set of base stations (BS) and a set of mobile stations (MS). For each BS, a diversity set is maintained for the sets of MS. Each BS determines possible interference at the MS based on the diversity set. A graph is constructed, in which nodes represent the sets of MS, mid each edge between a pair of nodes represents channel interference between the MS represented by the pair of nodes. A weight is assigned to each edge, which reflects interference between the two MSs connected by the edge. The interference graph is partitioned into non-overlapping clusters of nodes based on a structure of the interference graph, the potential interference, so that a sum of the weights of the edges between each cluster is maximized. Based upon the graph partitioning, the channel resources are allocated to the mobile stations in order to maximize the system capacity.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
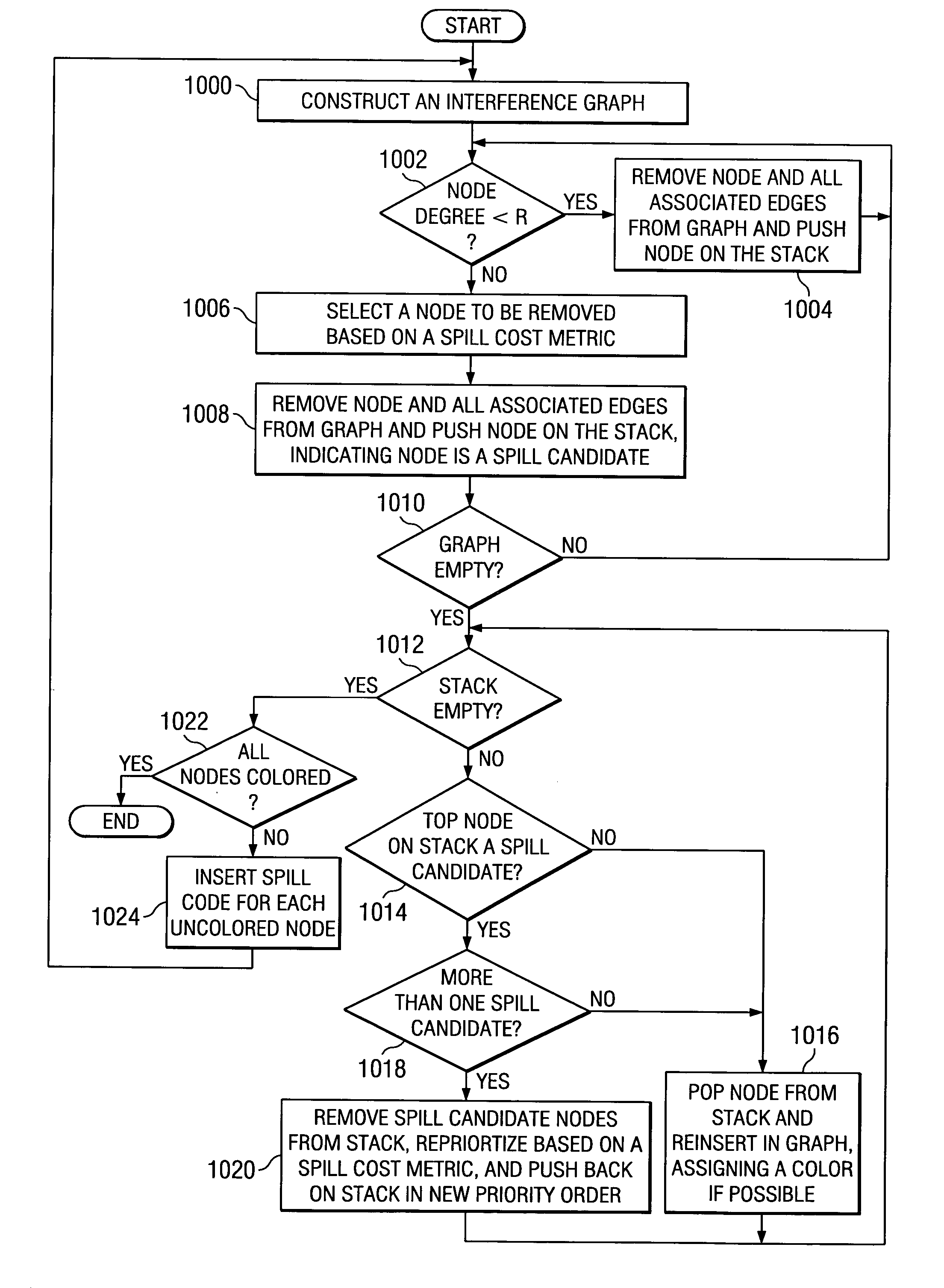
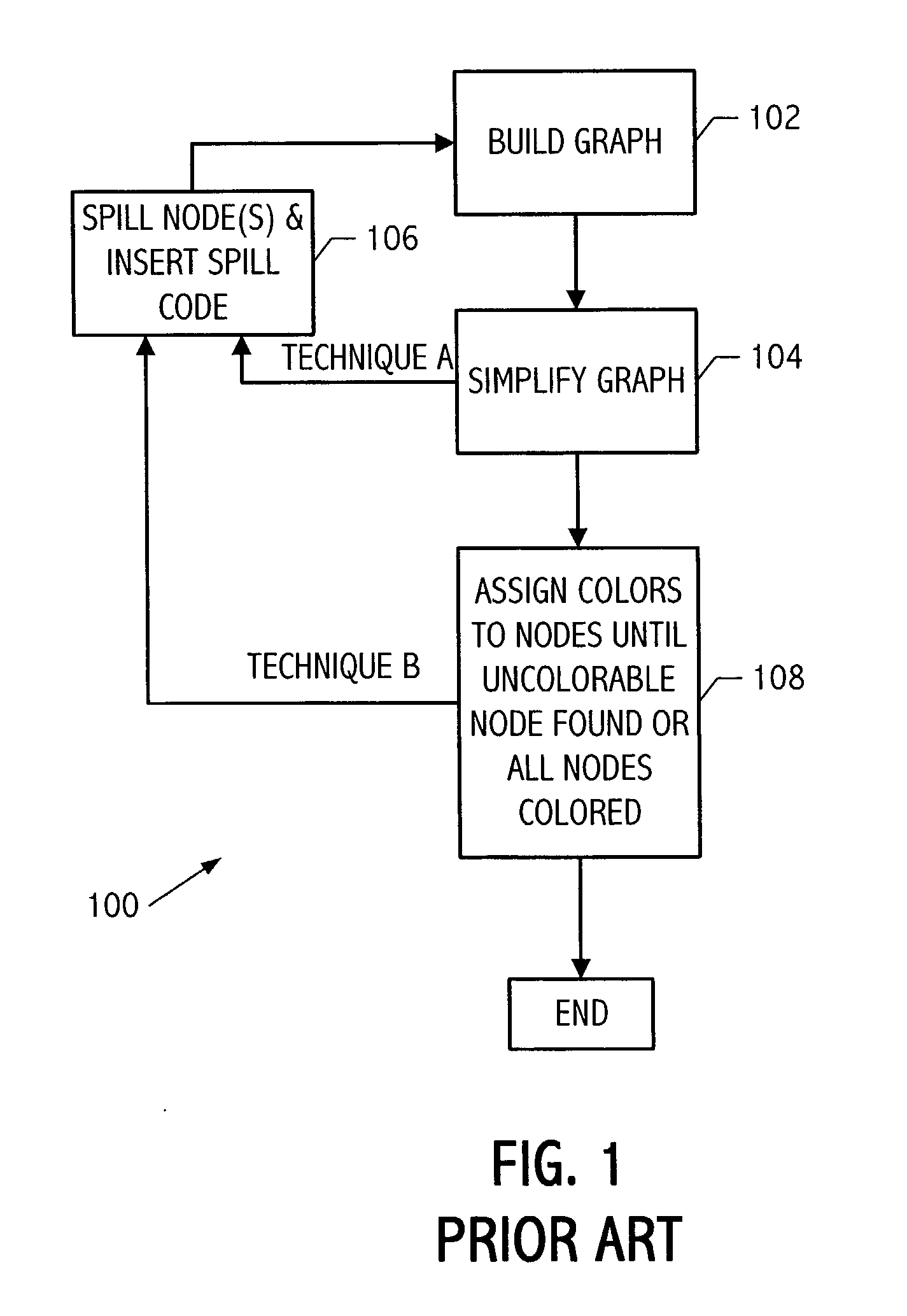
Register allocation and code spilling using interference graph coloring
ActiveUS20050039175A1Achieve colorColor interferenceSoftware engineeringSpecific program execution arrangementsRegister allocationCost metric
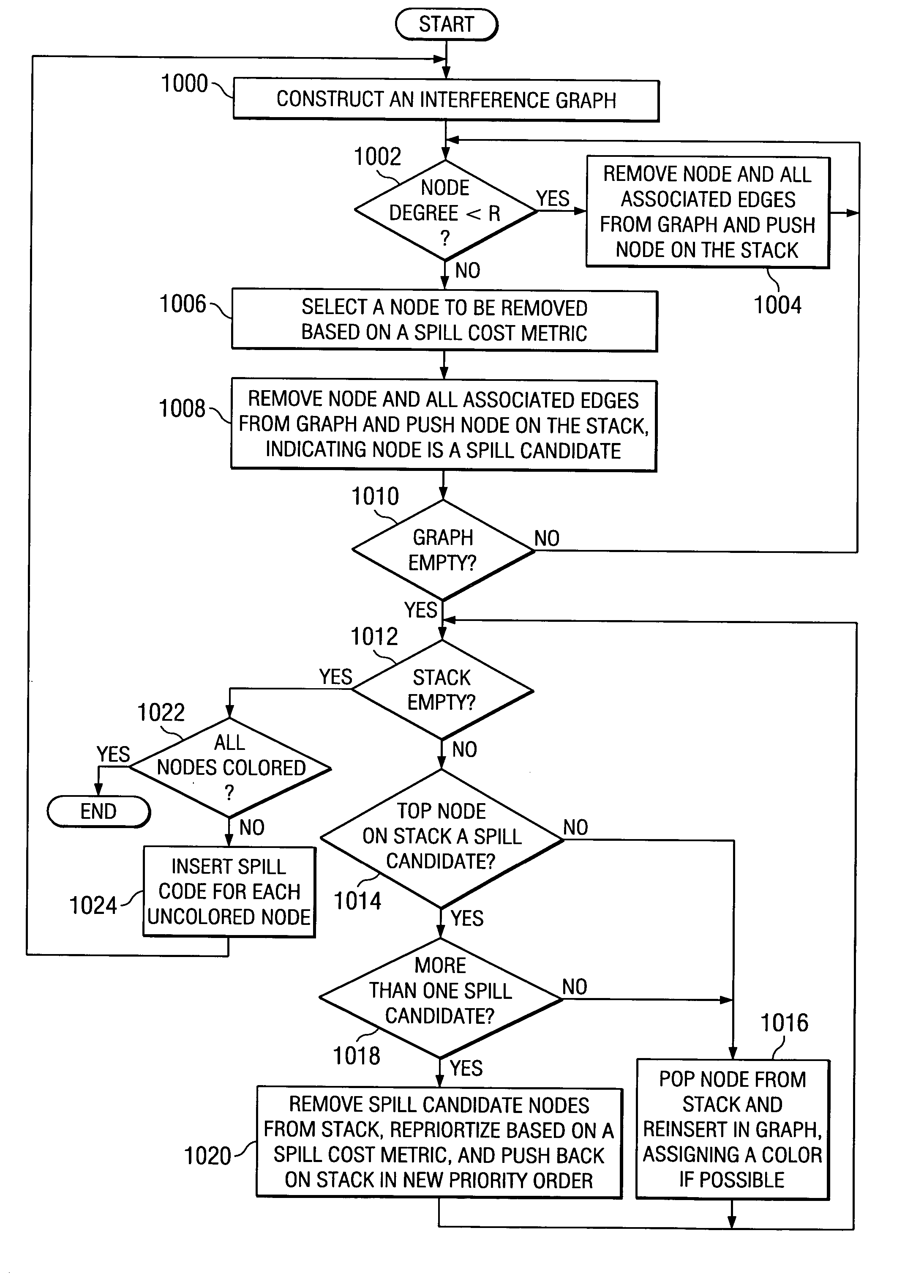
An improved method is provided for performing register allocation in a compiler. This method determines the allocation of a plurality R of registers of a processor for use during the execution of a software program. The register allocation process is treated as a graph-coloring problem, such that an interference graph is constructed for the software program, the graph is simplified, and an R-coloring the interference graph to the extent possible is attempted. Then, spill code is inserted in the software program each for each uncolored node of the graph, a new interference graph is constructed, and the process is repeated. During the simplification process, nodes with degree greater than or equal to R are removed from the graph in an order dictated by a spill cost metric. During the coloring process, these same nodes are reinserted in the graph in an order dictated by reapplying the spill cost metric.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Point diffraction interferometer
ActiveCN101183042AAvoid motion errorsHigh sampling frequencyUsing optical meansTesting optical propertiesOptical diffractionPoint diffraction interferometer
The invention provides a point diffraction interferometer and comprises a light source module, a mask which can produce an ideal spherical wave, an optical diffraction component which can produce multi-level sub-diffraction light, an image sensor and an optical component. The measured optical component is arranged between the mask and the optical diffraction component and the diffraction light of some levels can permeate the optical component completely, wherein, the diffraction light of a certain level can permeate the optical component partly while being diffracted partly; the diffraction light of some levels can permeate the optical component completely, wherein, the diffraction light of a certain level can be diffracted or the optical component consists of a plurality of windows and a plurality of small holes; diffraction light of some levels can selectively permeate the window, however, the non-diffracted light can be diffracted through the small hole on the optical component. The point diffraction interferometer of the invention conducts measurement through a plurality of interference graphs which are produced at the same time and the sampling frequency is improved, moreover, the design and operation of the whole system is simplified and the motion error of a phase-shift component can be avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
System and Method for Optimizing Compiler Performance by Object Collocation
A computer-implemented method, system, and computer program product for performing object collocation on a computer system are provided. The method includes analyzing a sequence of computer instructions for object allocations and uses of the allocated objects. The method further includes creating an allocation interference graph of object allocation nodes with edges indicating pairs of allocations to be omitted from collocation. The method also includes coloring the allocation interference graph such that adjacent nodes are assigned different colors, and creating an object allocation at a program point prior to allocations of a selected color from the allocation interference graph. The method additionally includes storing an address associated with the created object allocation in a collocation pointer, and replacing a use of each allocation of the selected color with a use of the collocation pointer to collocate multiple objects.
Owner:IBM CORP
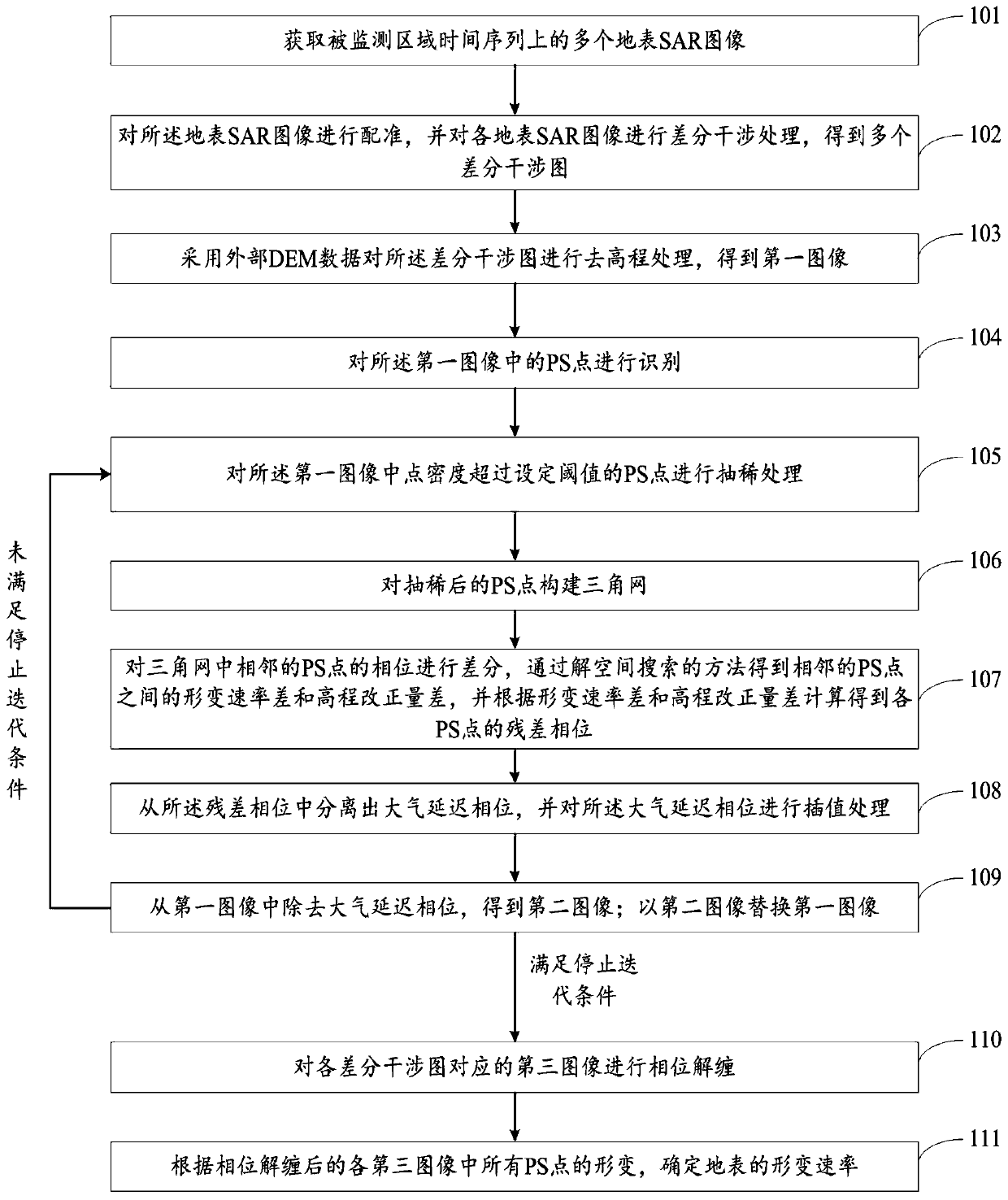
Time sequence InSAR deformation monitoring method and system based on high resolution
ActiveCN111059998AShorten the timeEasy to handleWave based measurement systemsElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementImaging processingDeformation monitoring
The invention discloses a time sequence InSAR deformation monitoring method and system based on high resolution. The method comprises the steps of carrying out registration, differential interferenceprocessing and elevation removal processing on a surface SAR image; identifying PS points in the image; thinning the PS points of which the point density exceeds a set threshold value; constructing atriangulation network for the thinned PS points; differentiating the phases of the adjacent PS points in the triangulation network, obtaining a deformation rate difference and an elevation correctiondifference between the adjacent PS points through a solution space search method, and calculating the residual phase of each PS point according to the deformation rate difference and the elevation correction difference; separating an atmospheric delay phase from the residual phase, and carrying out interpolation processing on the atmospheric delay phase; removing the atmospheric delay phase from the differential interferogram, repeating the above steps for iteration, obtaining an image after the atmospheric delay phase is removed for many times, carrying out the phase unwrapping of the image,carrying out analysis on all PS points, and determining the deformation rate of the ground surface. According to the invention, the image processing rate is improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING) +1
Computing optimal channel allocations using decomposition methods and related devices
ActiveUS20060067258A1OptimizationNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesAlgorithmDecomposition
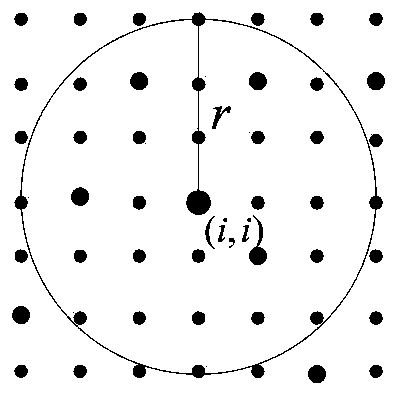
By decomposing (i.e., dividing) an interference graph into subgraphs, it becomes feasible to compute close approximations of an optimal channel allocation scheme within a reasonable amount of time. The channel allocation scheme may be used to allocate specific channels to access points (APs) in a wireless, local area network (WLAN).
Owner:RPX CORP +1
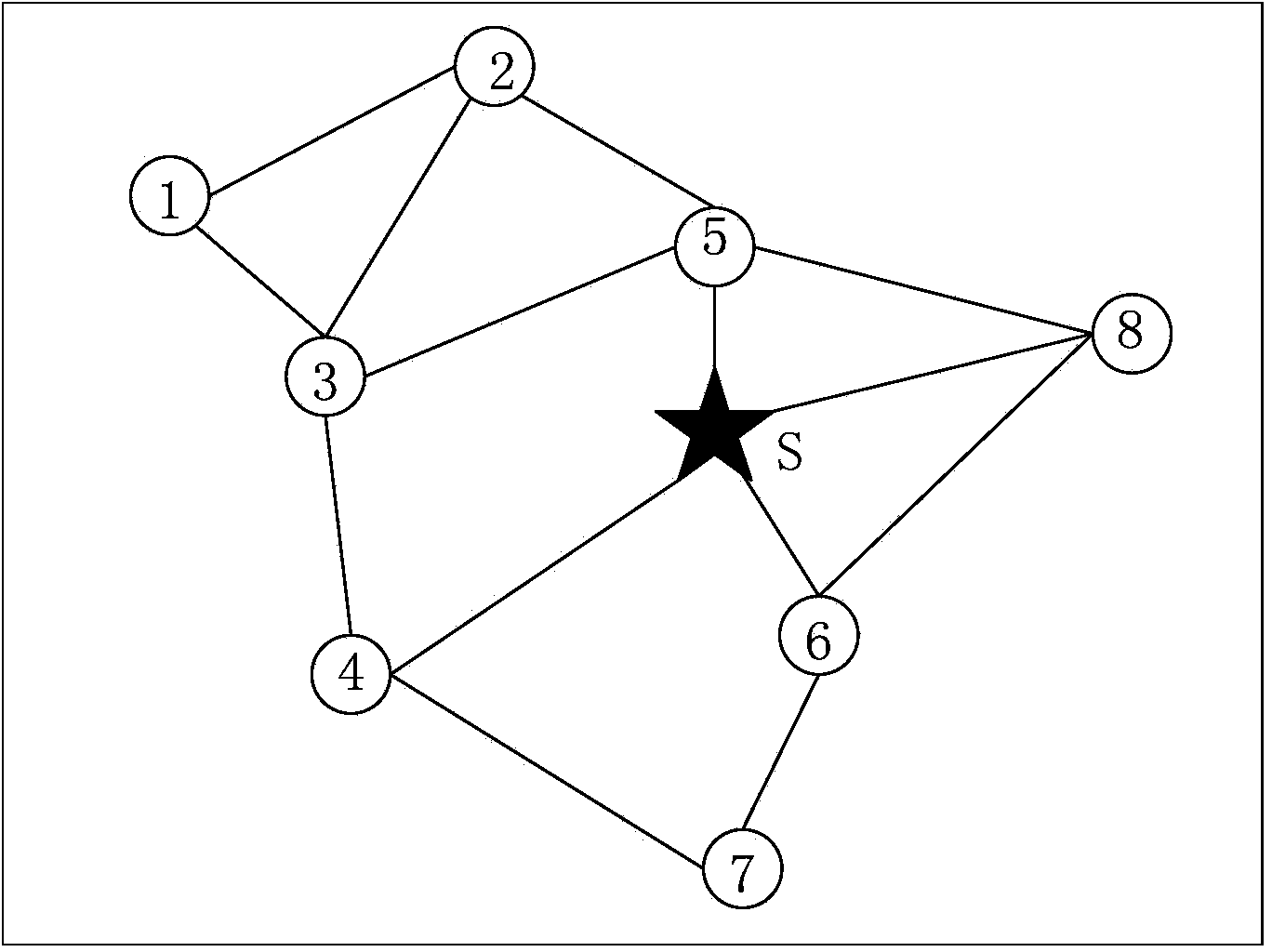
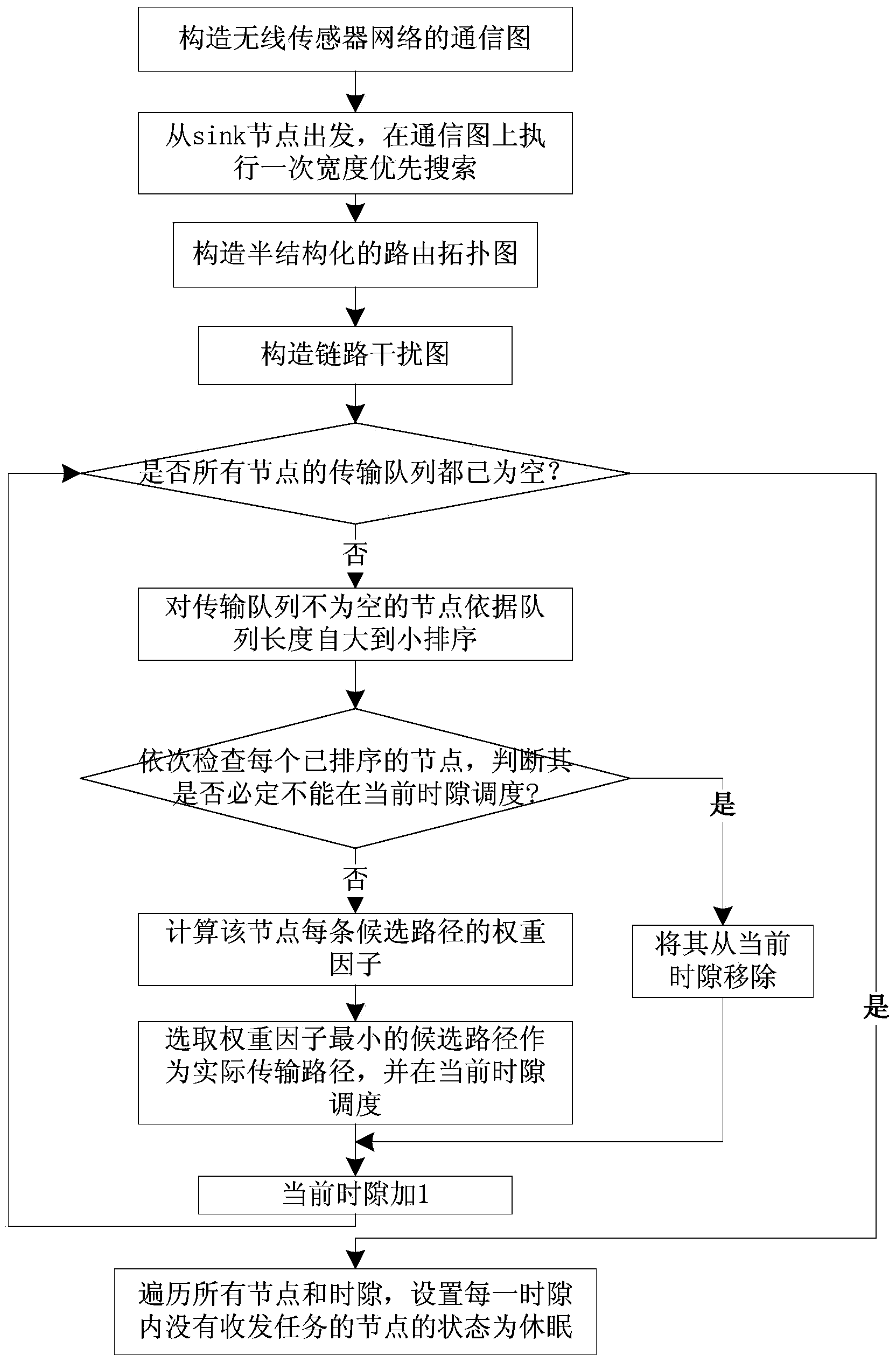
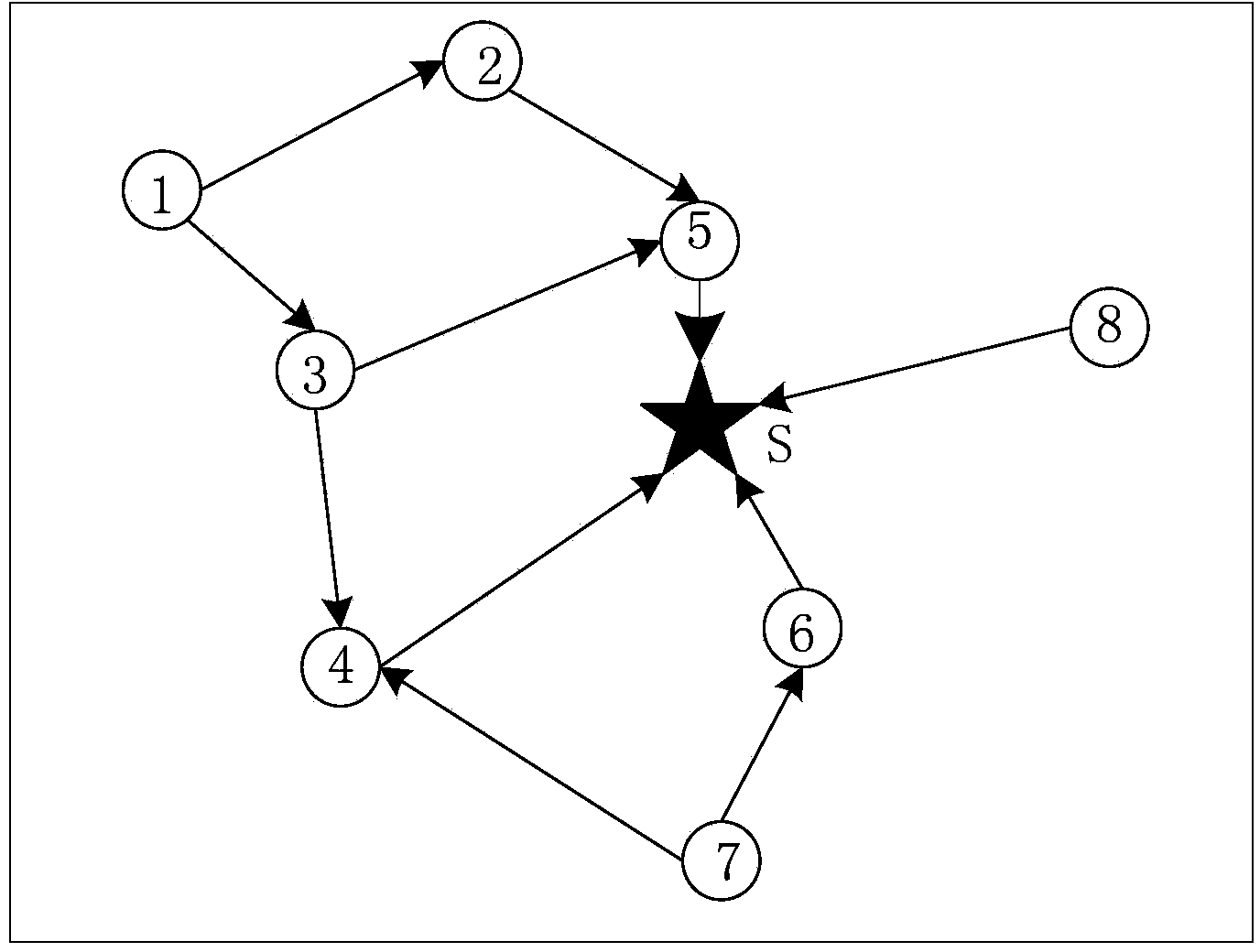
Semi-structured transmission dispatching method orienting wireless sensor network data collection
ActiveCN104301966AReduce energy consumptionExtend the life cyclePower managementHigh level techniquesSemi-structured dataInterference factor
The invention discloses a semi-structured transmission dispatching method orienting wireless sensor network data collection. The method is characterized by comprising the steps that 1, breadth-first search is carried out on a network communication graph, so that a slack semi-structured data collection route topological graph is constructed; 2, a link interference graph is constructed according to the main interference and subsidiary interference relation between transmission links in a network; 3, link weight interference factors are defined, so that the interference intensity caused to other links of the network from transmission loads of sending nodes and sending links is comprehensively weighed; 4, the dynamic link selection and time slot allocation strategy based on preference of the minimum weight is carried out; 5, a node dormant state is controlled in an explicit mode, and a data collection period is adjusted in a self-adaptive mode. According to the method, routing and dispatching are designed in a unified mode on the basis of a cross-layer design idea, the time slot utilization rate of dispatching is increased by fully utilizing the redundancy of a path, time delay of data collection is shortened, and the handling capacity of the network is improved. The method is applied to the wireless sensor network with the high requirement for the real-time property.
Owner:中科水研(江西)科技股份有限公司
Optimal register allocation in compilers
An improved register allocation technique is provided. An interference graph coloring is attempted multiple times prior to spilling one or more nodes. Each node has a spill cost derived from the time it takes to store and recall the variable's data combined with how often the compiler thinks the variable is needed. Similarly, each coloring failure has a spill cost which is the accumulation of the spill costs of the remaining un-colorable nodes. If any solutions are found, the process is complete. If only failures are found, the cheapest node(s) to spill is evaluated based on the multiple failures. In one embodiment, the cheapest node of the cheapest failure is spilled. In another embodiment, the cheapest node is evaluated across all failures. This process is repeated until a solution is found (all nodes are colored or spilled).
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
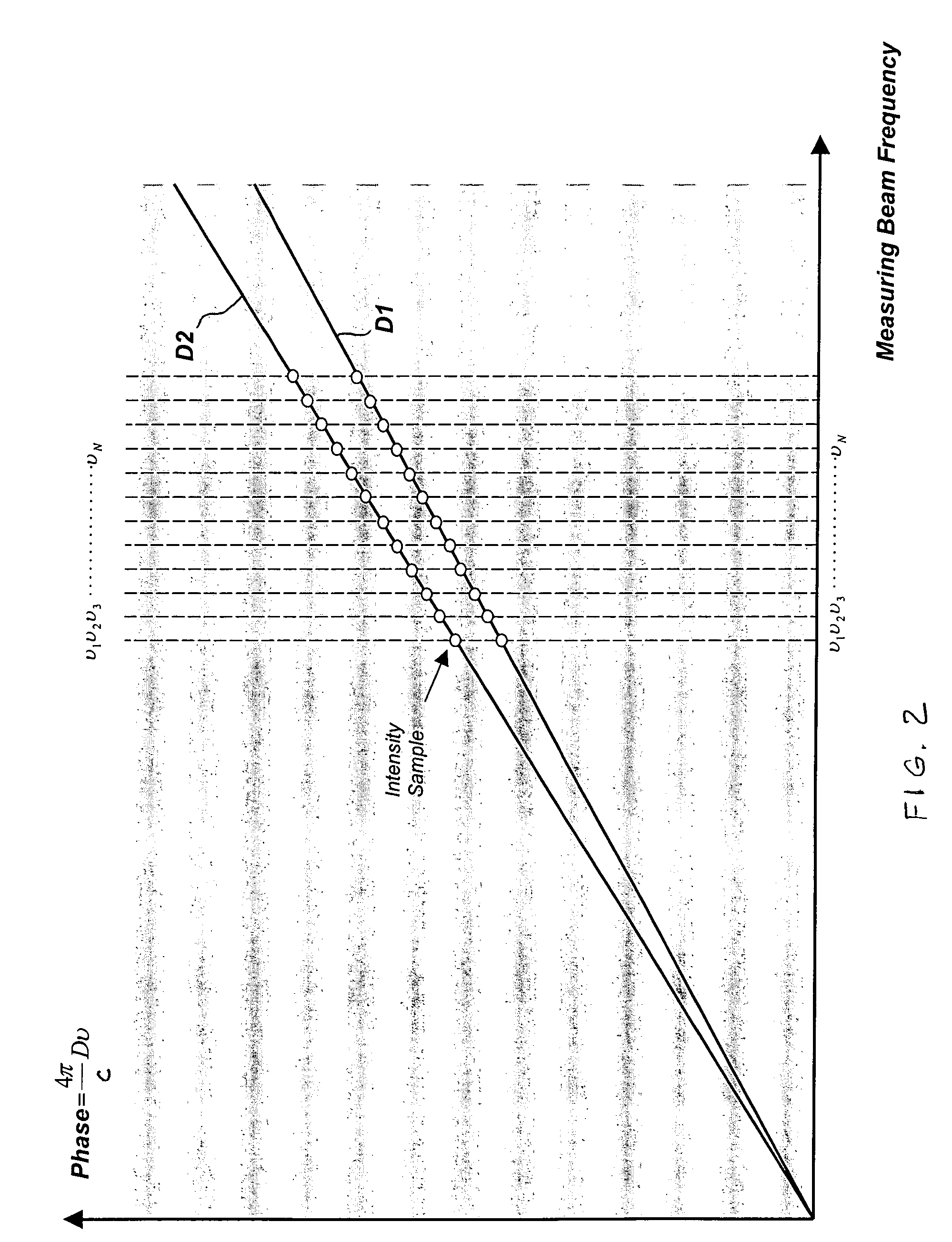
Phase-resolved measurement for frequency-shifting interferometry
ActiveUS7268889B2Reduce correlationHigh correlationInterferometersUsing optical meansLight beamInterference graph
A frequency-shifting interferometer gathers intensity data from a set of interference patterns produced at different measuring beam frequencies. A periodic function is matched to the intensity data gathered from the set of interference patterns over a corresponding range of measuring beam frequencies. Localized correlations involving phase offsets between the interfering portions of the measuring beam are used to inform a determination of a rate of phase change with measuring beam frequency corresponding to the optical path length difference between the interfering beam portions.
Owner:CORNING INC
X-ray recording system for x-ray imaging at high image frequencies of an object under examination by way of direct measurement of the interference pattern
InactiveCN104068875AAccurately determineReal-time Capability Phase Contrast ImagingAngiographyRadiation detection arrangementsPhase gratingImage resolution
An x-ray recording system is disclosed for x-ray imaging of an object under examination by way of direct measurement of an interference pattern, especially for differential, real-time capable phase-contrast imaging. In at least one embodiment, the system includes with at least one x-ray emitter for creating quasi-coherent x-ray radiation; an x-ray image detector, including a detector layer and detector pixels arranged in a matrix; and a diffraction or phase grating, disposed between the object under examination and the x-ray image detector, configured to create an interference pattern, directly detectable in the nth Talbot order by an x-ray image detector with a very high achievable local resolution, which amounts to at least half the wavelength of the interference pattern in accordance with the Nyquist theory arising in the nth Talbot order.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
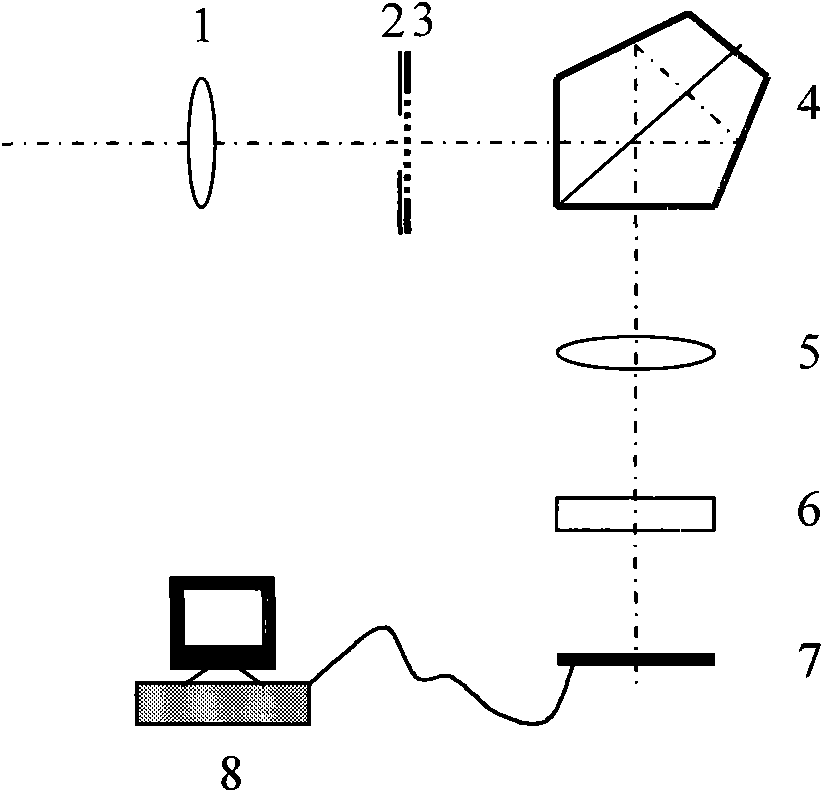
Three-surface interference type high-accuracy curved surface profile measuring system and method
The invention discloses a three-surface interference type high-accuracy curved surface profile measuring system and method. According to the measuring system, the 3D profile information of the surface of a measured part is obtained by using the Michelson interference principle. According to the system and method of the invention, a computer is utilized to control a semiconductor laser to carry out wave number scanning, and at the same time, a CCD camera continuously captures interference images under different wave numbers; wave number online monitoring is performed on the interference image of the front surface and back surface of an optical wedge in an optical path; Fourier transformation is performed on each pixel of the interference image along the time axis, wrapping phase information is extracted at the peaks of the interference signals of the profile of the curved surface of the measured part and the front surface of the optical wedge; and after the wrapping phase information is unwrapped, the 3D profile information of the surface of the measured part can be obtained. With the system and method adopted, the 3D profile measuring accuracy of the curved surface can achieve + / -10nm, and the system and method are stable and reliable and do not need frequent real-time verification and a reference hook surface, and can maintain high accuracy.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Foundational interference virtual aperture deformation monitoring radar system and working method thereof
ActiveCN110645886ADeformation judgmentElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementRadio wave reradiation/reflectionData displayRadar systems
The invention discloses a foundational interference virtual aperture deformation monitoring radar system and a working method thereof. The foundational interference virtual aperture deformation monitoring radar system comprises a tripod, a two-dimensional turntable, a radar sub-system and a data display sub-system, wherein the radar sub-system is used for achieving scanning of a special region, and the two-dimensional turntable is used for global scanning. The working method comprises the steps of radiating broadband frequency modulation continuous wave signals at millimeter wave bands to a tunnel through uniform sparse linear arrays distributed at four edges of a rectangle by the radar sub-system, and receiving an echo signal to obtain initial radar echo data; performing first-time virtual aperture processing, namely MIMO processing, to achieve aperture expansion; executing distance to Fourier transform; performing second-time virtual aperture processing, namely forecast extrapolation, to further achieve aperture expansion; and obtaining a high-resolution three-dimensional radar complex image after two-dimensional digital wave beam formation, acquiring an interference map containing a differential phase from primary and secondary images, obtaining inner wall deformation condition of the tunnel after interference map unwrapping and correction, and transmitting the inner wall deformation condition to a data display sub-system.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Measurement method and apparatus, exposure apparatus
InactiveUS20070229848A1Accurate measurementOptical measurementsPhotomechanical apparatusMeasurement deviceWavefront aberration
A measurement method for measuring a wavefront aberration of a target optical system using a measurement apparatus that measures the wavefront aberration of the target optical system by detecting an interference pattern includes the steps of measuring as a system parameter a shift from a design value of a value that defines a structure of the measurement apparatus and the target optical system, and measuring the wavefront aberration of the target optical system using the system parameter.
Owner:CANON KK
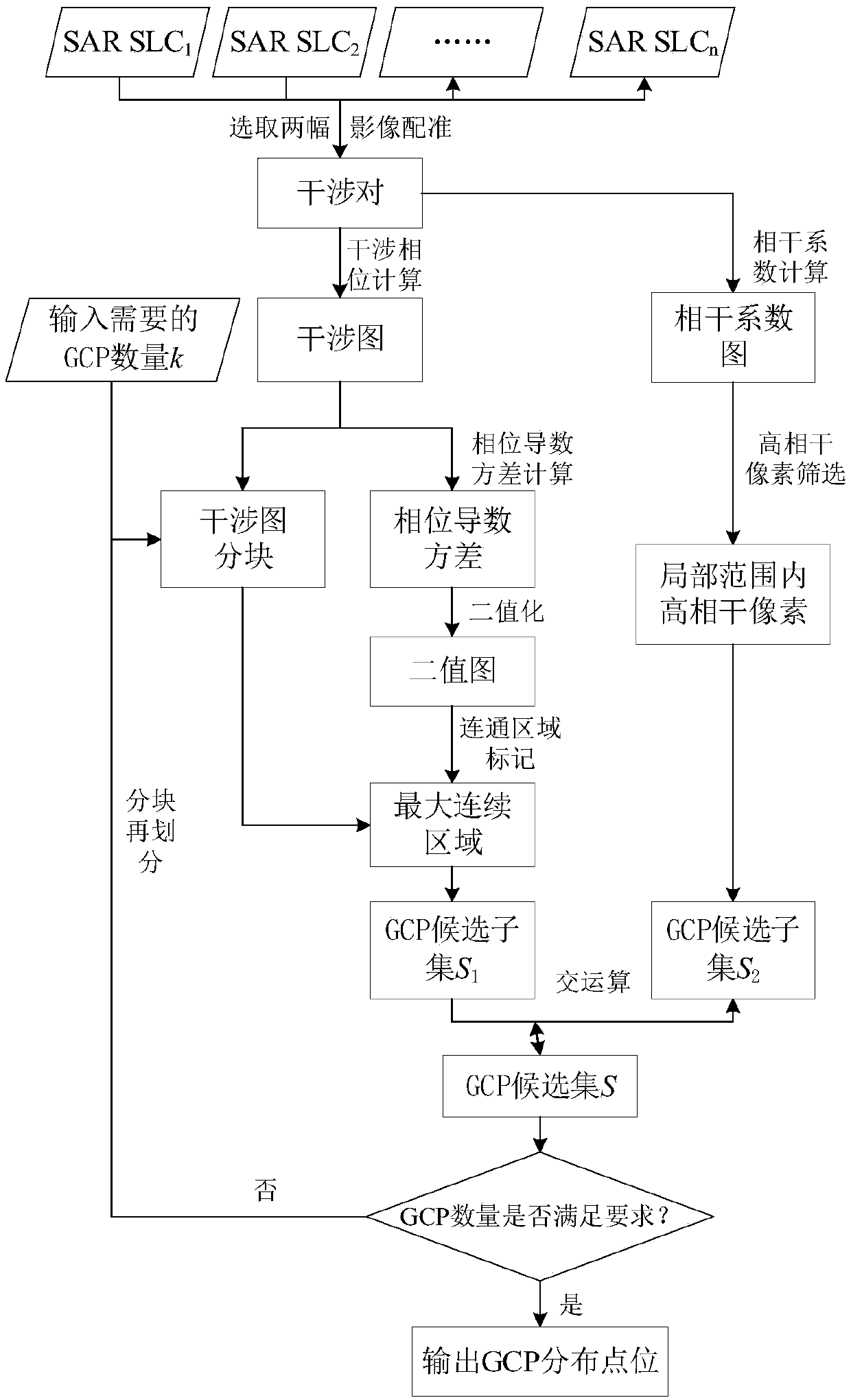
Method for automatically selecting ground control points during interference measurement of synthetic aperture radar
ActiveCN108387899AMeet needsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarInterference graph
The invention discloses a method for automatically selecting ground control points during the interference measurement of a synthetic aperture radar. The method comprises the steps of randomly selecting two images in a multi-time-sequence SAR SLC image sequence to be subjected to interference measurement to form an interference pair, obtaining an interference graph through interference phase calculation, and calculating a coherence coefficient graph; segmenting the interference graph according to the number of required GCPs, figuring out an interference phase derivative of each pixel in the interference pair, carrying out statistics on the variance of all interference phase derivatives in each pixel local window, and searching a region in each block to form a candidate subset S1 of GCPs, wherein all searched regions are stable in interference phase or continuously and uniformly changing in interference phase; on the basis of the coherence coefficient graph, screening out pixels high inboth own coherence coefficient and coherence coefficient in the pixel local window, and forming a candidate subset S2 of GCPs; obtaining the intersection set of the candidate subset S1 and the candidate subset S2 of GCPs and obtaining a preliminary GCP selection result; optimizing the preliminary GCP selection result according to the number and the distribution of GCPs, and obtaining a final GCPselection result of GCPs. According to the invention, the method has an important value for improving the automation degree and the precision of the radar interference measurement of different modes.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
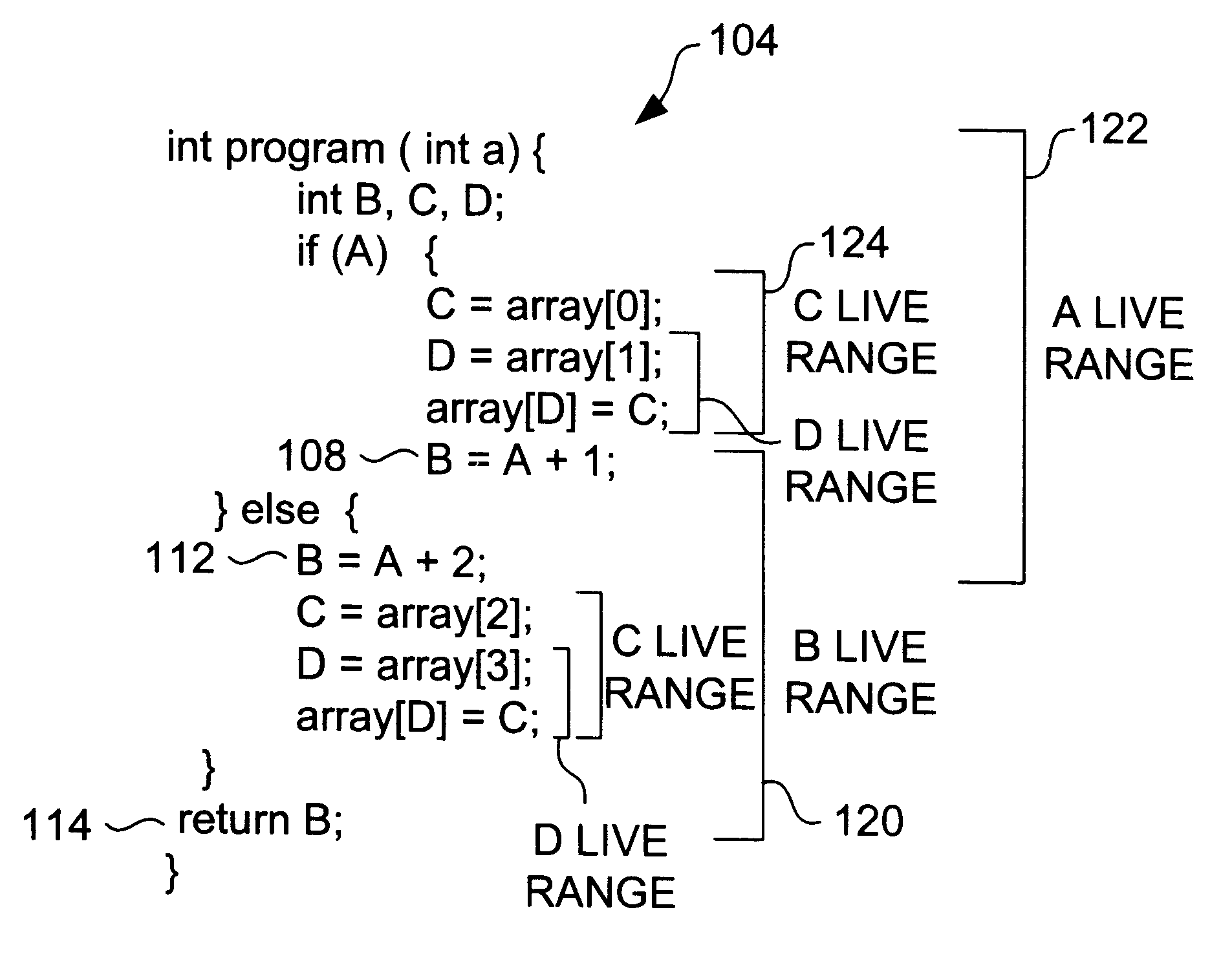
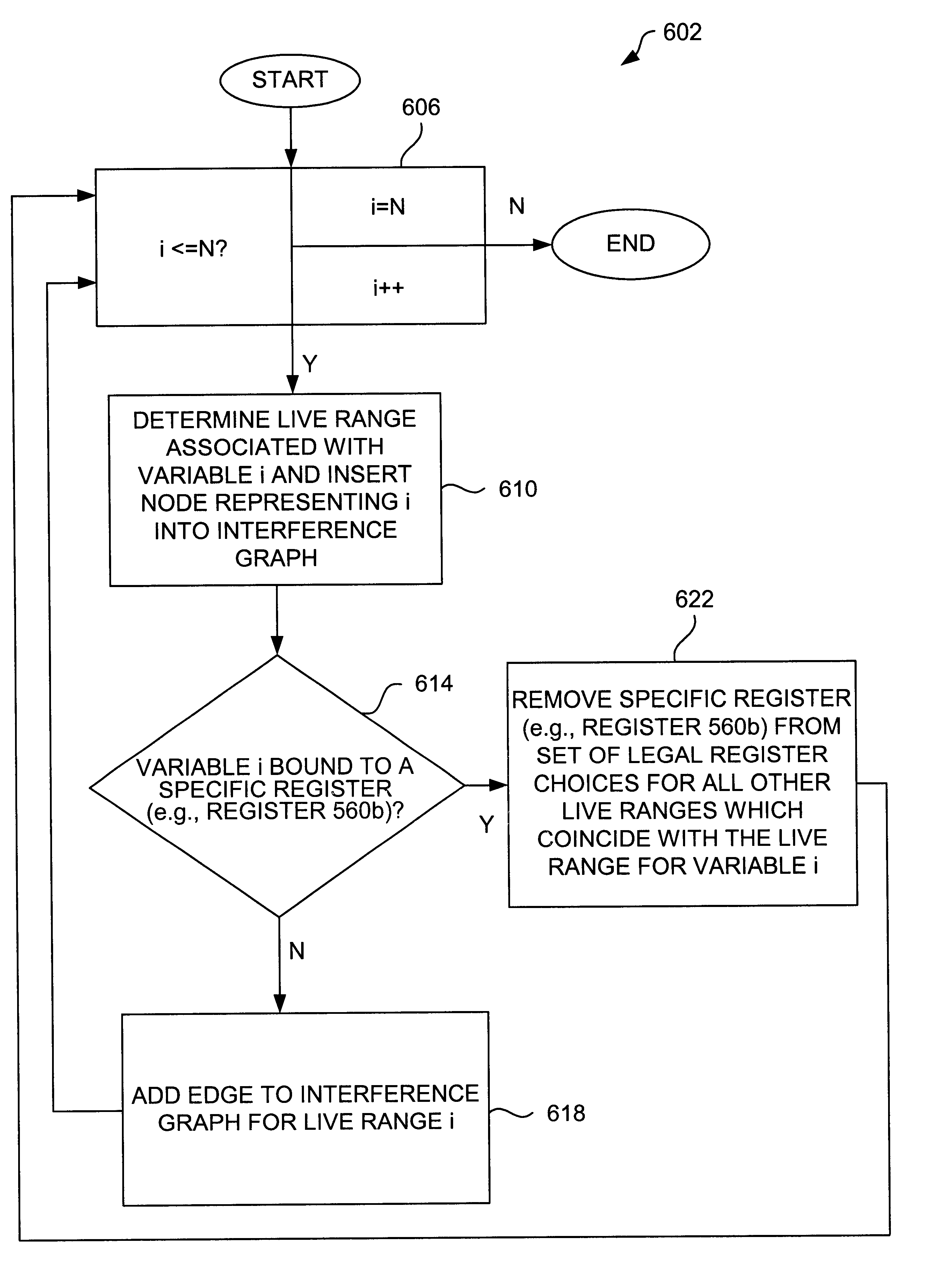
Method and apparatus for producing a sparse interference graph
Methods and apparatus for reducing the number of edges described by an interference graph are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, a computer-implemented method for allocating memory space in an object-based computing system includes obtaining source code that includes a code segment associated with a first variable and a code segment associated with a second variable. The method also includes binding the first variable to a specific register, and obtaining a live range for the second variable. Once the live range for the second variable is obtained, a register allocation is performed. Performing the register allocation includes creating an interference graph that includes a representation of the second variable and does not to include a representation of the first variable. In one embodiment, obtaining source code that includes the code segment associated with the first variable includes obtaining a call to a subroutine which includes the first variable as an argument in the call.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Hadamard transform interferometric spectral imaging method and Hadamard transform interferometric spectral imaging equipment
InactiveCN101526400ASimple structureReduce volumeInterferometric spectrometryPhysicsSystem structure
The invention relates to a Hadamard transform interferometric spectral imaging method comprising the following steps: (1) a target is imaged on the surface of a Hadamard template; (2) a field range taking part in the Hadamard transform coding is limited and vagabond ray is filtered; (3) the Hadamard template is cut into two void Hadamard templates in the direction vertical to the ray axis, and the two void Hadamard templates are parallel to and have the same width direction with the Hadamard template; (4) the two void Hadamard templates interfere with each other and the interferometric fringe direction is vertical to the cutting direction; (5) an interference pattern signal is sent in a computer processing system; (6) the coding is completed after the Hadamard template transforms coding for n times; (7) Fourier transform is performed for the interference pattern signal to obtain n target spectral images coded by the Hadamard template, the two-dimensional space information and the one-dimensional spectral information of the target are finally obtained after the images are decoded, and the imaging is completed. The invention is not limited by the size of the Hadamard templates and has simple formed system structure.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Interference baseline estimation method based on SRTM DEM
InactiveCN109242872AReduce inaccurate location informationReduce location informationImage analysisComplex mathematical operationsEstimation methodsInterference graph
The invention discloses an interference baseline estimation method based on SRTM DEM, which solves the problem of poor accuracy of real-time orbit rapid generation DEM. Realization steps: real-time trajectory fitting of two interferometric SAR images is carried out by Lagrange interpolation; the elevation value of SRTM DEM on the oblique plane is obtained; the unwrapped phase of two SAR interferometric images is used to perform phase-elevation conversion, to obtain the elevation value of the interference image in the oblique plane; The height error on the oblique plane is obtained by subtracting the height of SRTM DEM on the oblique plane from the height of the oblique plane obtained by interferometry of two SAR images; the baseline error in the scene is obtained by using the relationshipamong the fuzzy height, elevation error and baseline error; the real-time orbit error is corrected by the baseline error, and the DEM is reconstructed by the corrected orbit information; the baselineestimation results are verified by comparing the DEM with SRTM DEM. The invention obviously alleviates the precision loss of DEM reconstruction of real-time orbit, effectively observes topography andgeomorphology, and can be used for signal processing such as InSAR.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
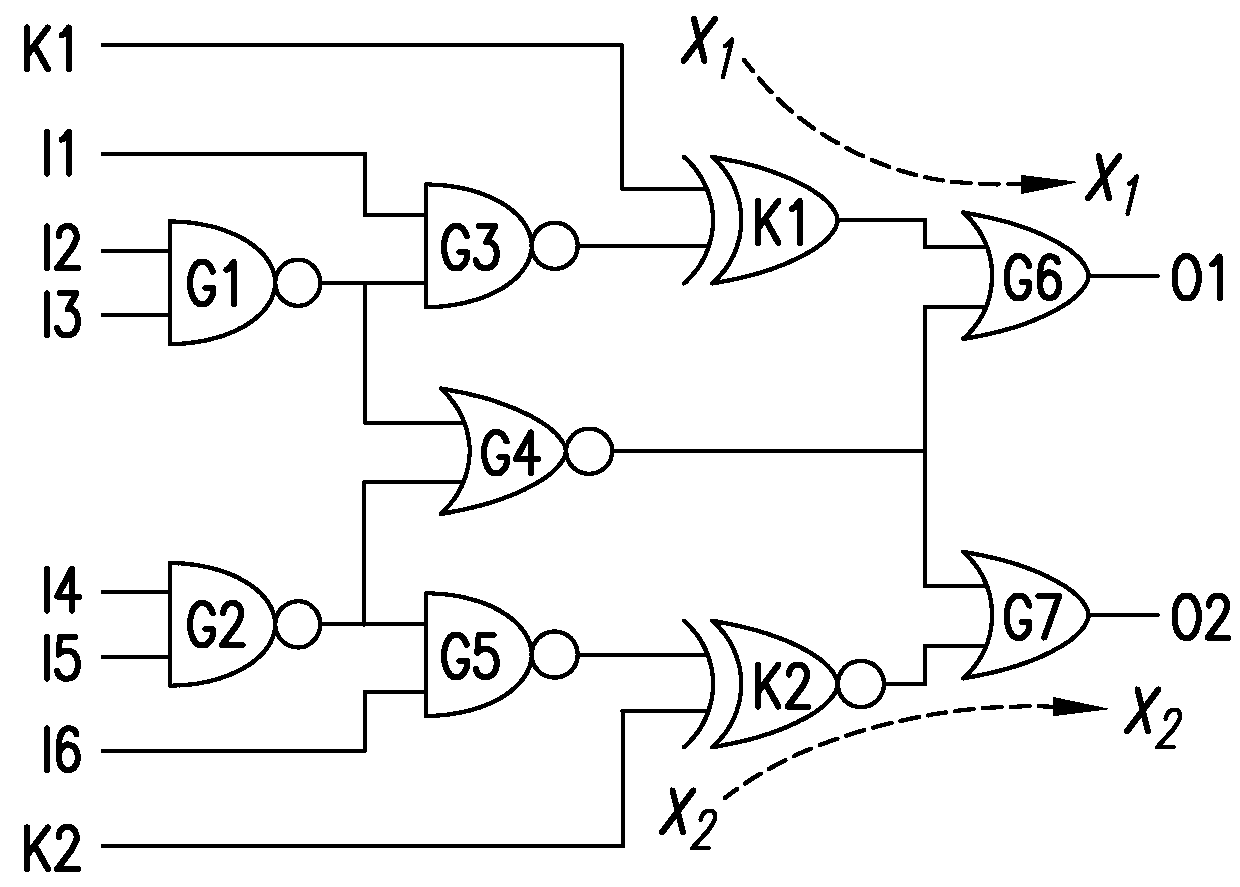
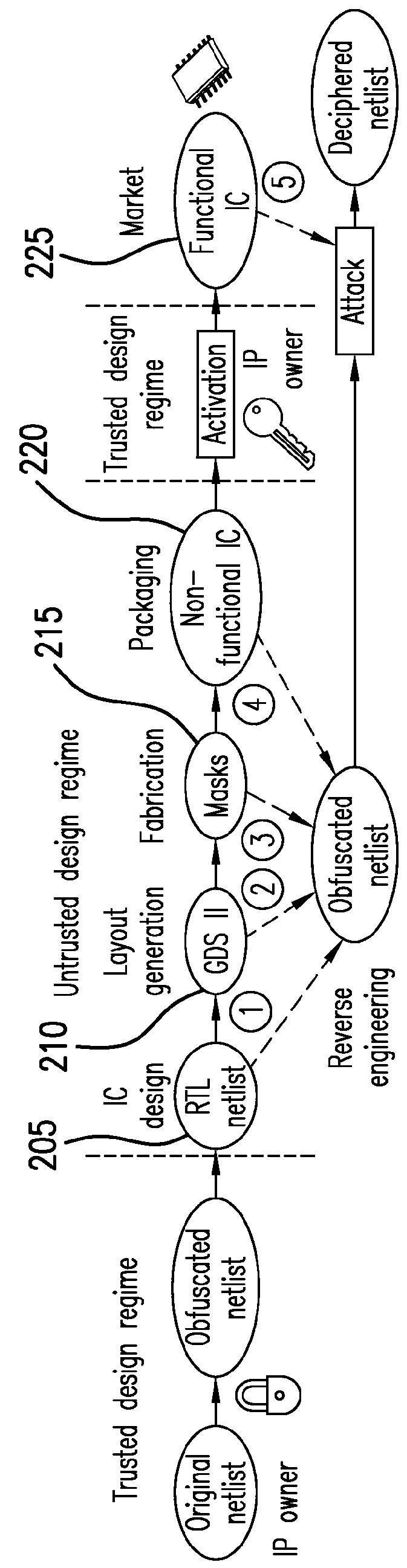
System, method and computer-accessible medium for facilitating logic encryption
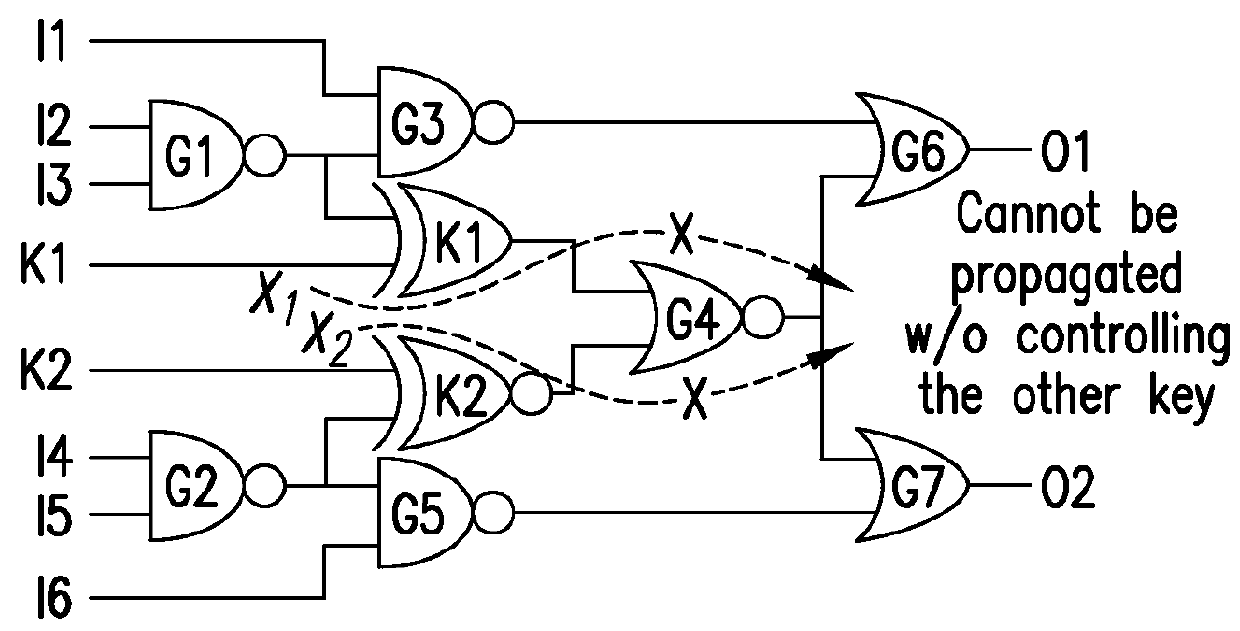
ActiveUS20160034694A1Unauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringInterference graphComputer science
Exemplary systems, methods and computer-accessible mediums for encrypting at least one integrated circuit (IC) can include determining, using an interference graph, at least one location for a proposed insertion of at least one gate in or at the at least one IC, and inserting the gate(s) into the IC(s) at the location(s). The interference graph can be constructed based at least in part on an effect of the location(s) on at least one further location of the IC(s).
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Method for resolving phase in electronic speckle interferometry
ActiveUS7280187B1Force measurement by measuring optical property variationUsing optical meansData setPhase difference
The invention is a method of determining the phase difference between two interferometric images. The method includes the steps of measuring the intensities of the two beam arms, and measuring the intensities of the interfering beam arms at two different times (two frames). From the recorded data, the phase angle between the arms can be determined for each frame. These frame phase angles subtracted, and the sine of the difference is taken. The resulting data set is examined to determine a multiplicative factor that converts the minimum and maximum to the bounds of the sine function (−1, +1). This multiplicative factor is applied to a bounded trig function of the difference of the frame angles, and the inverse of the bounded trig function is taken, resulting in the phase difference between frames.
Owner:SOUTHEASTERN LOUISIANA UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com