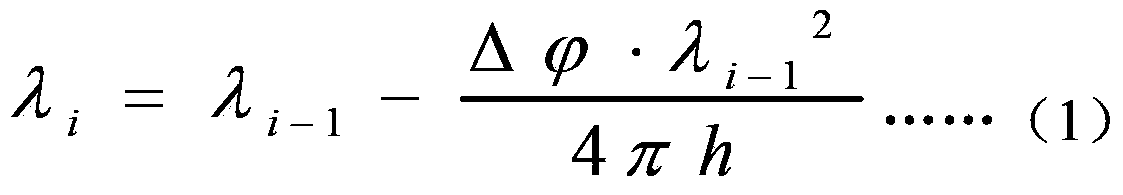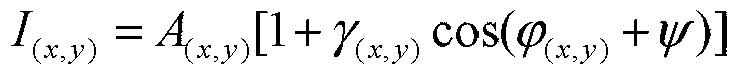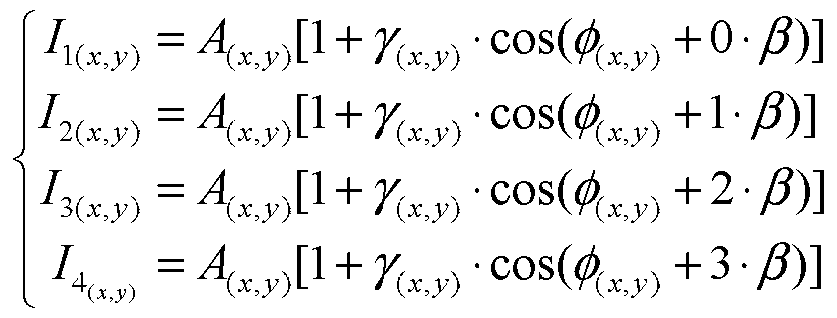Patents
Literature
79 results about "Point diffraction interferometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
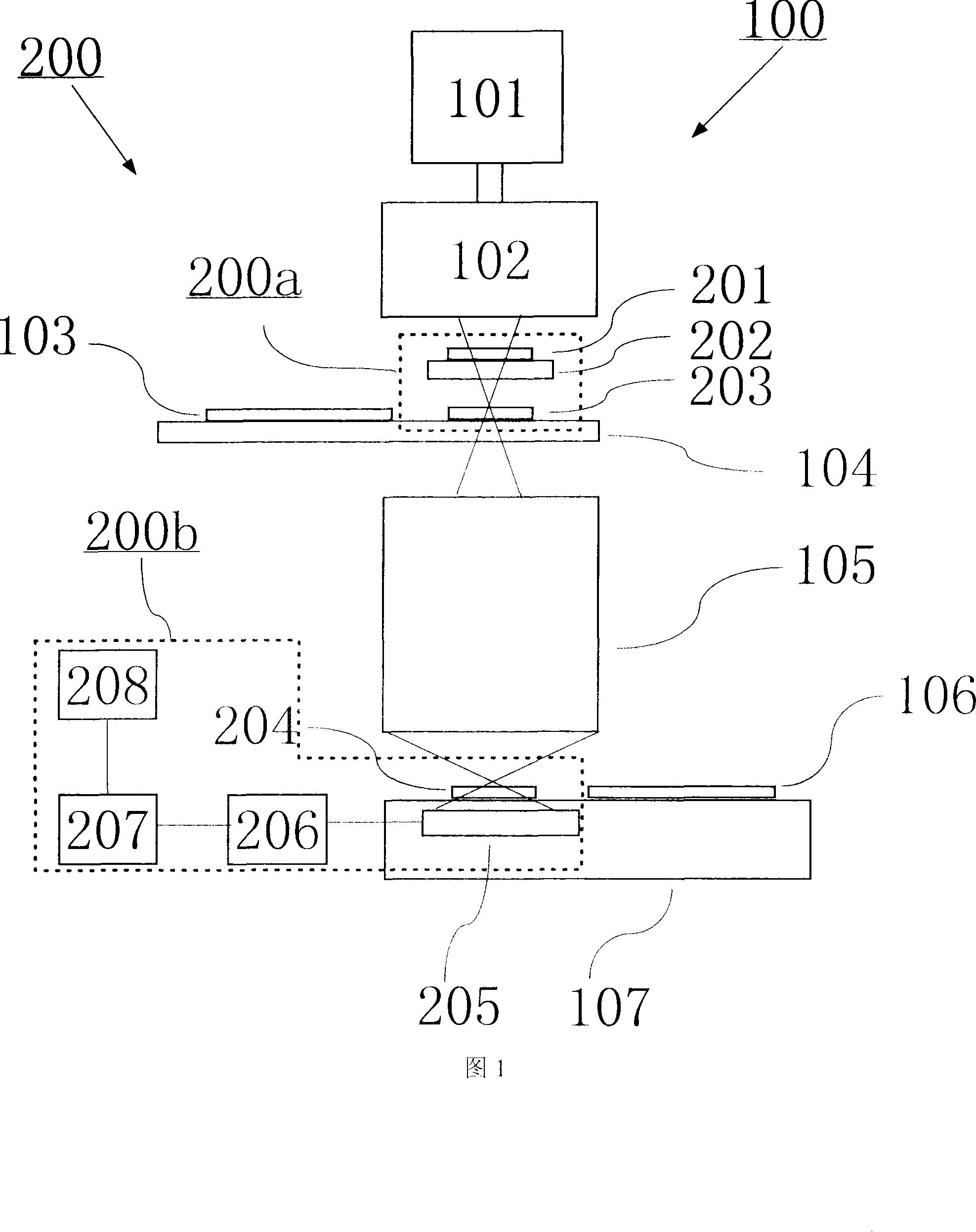
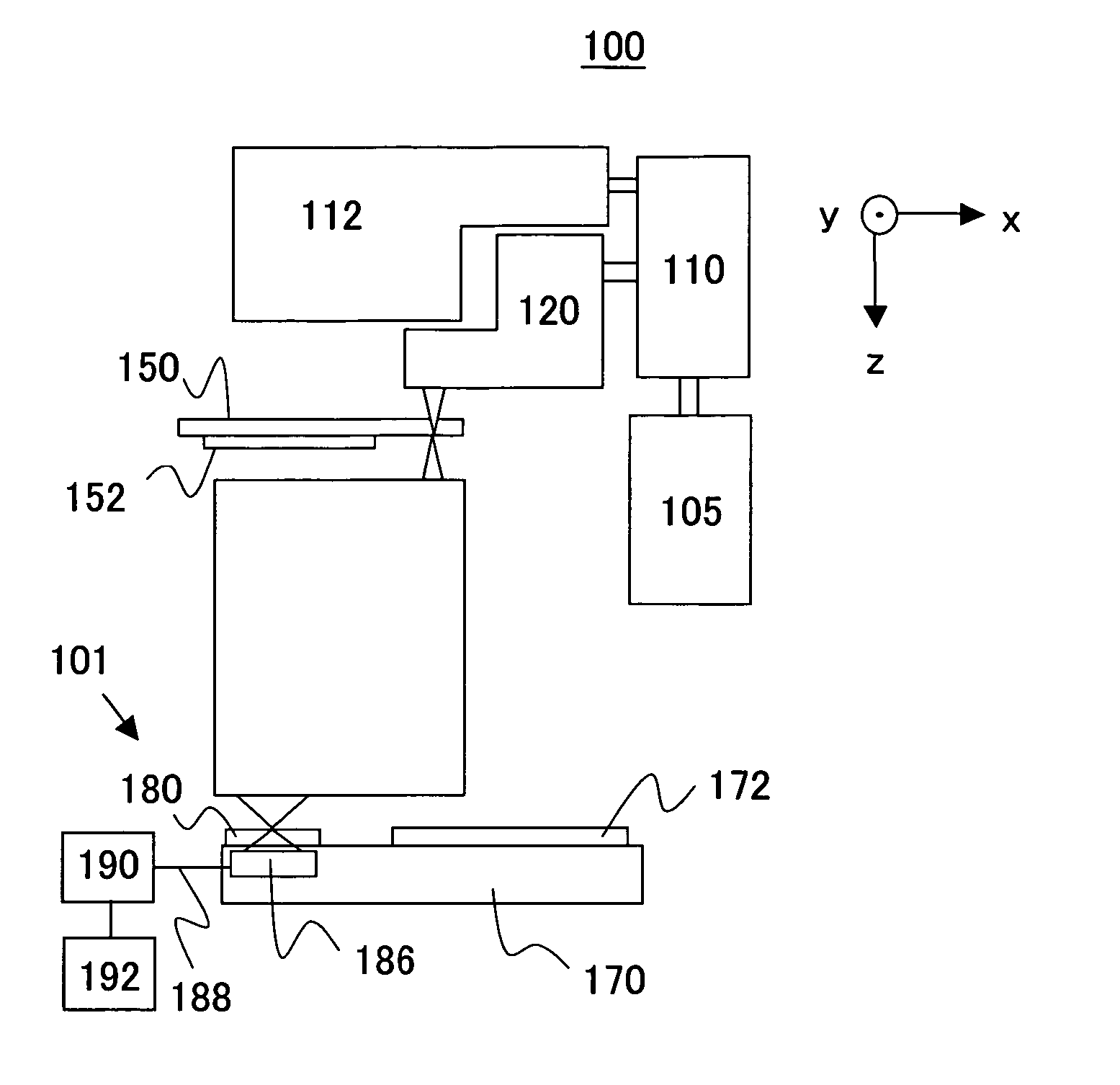
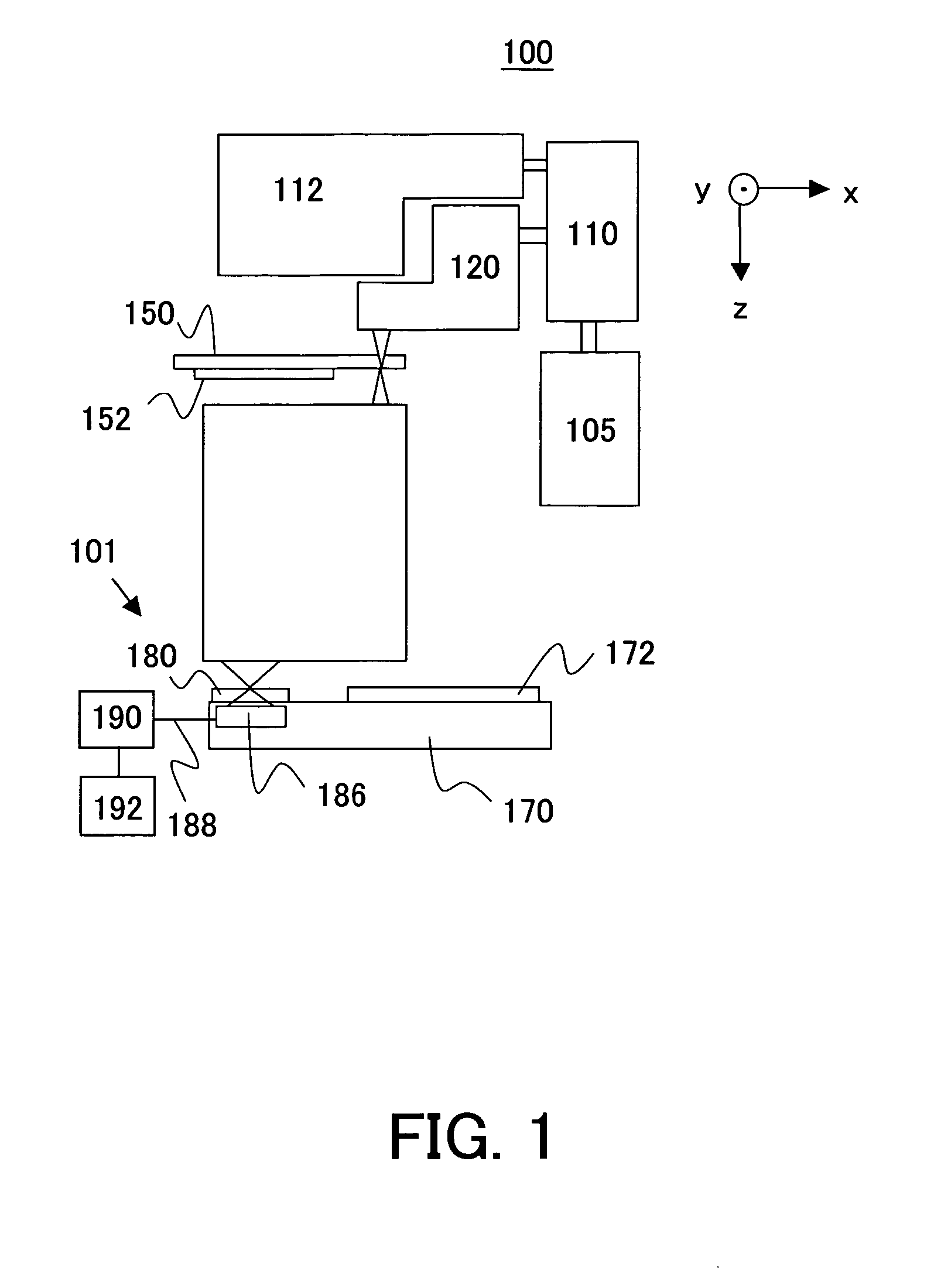
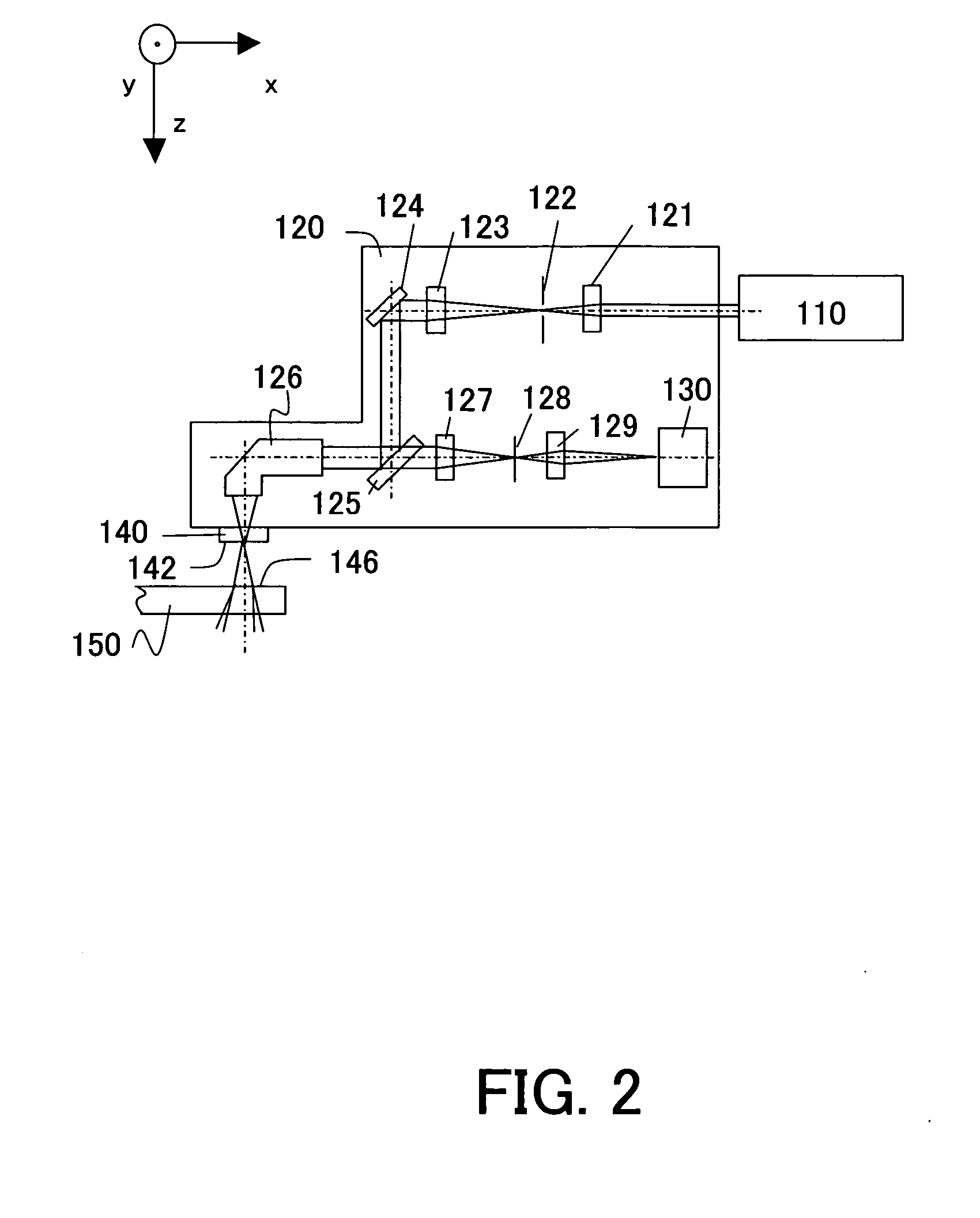
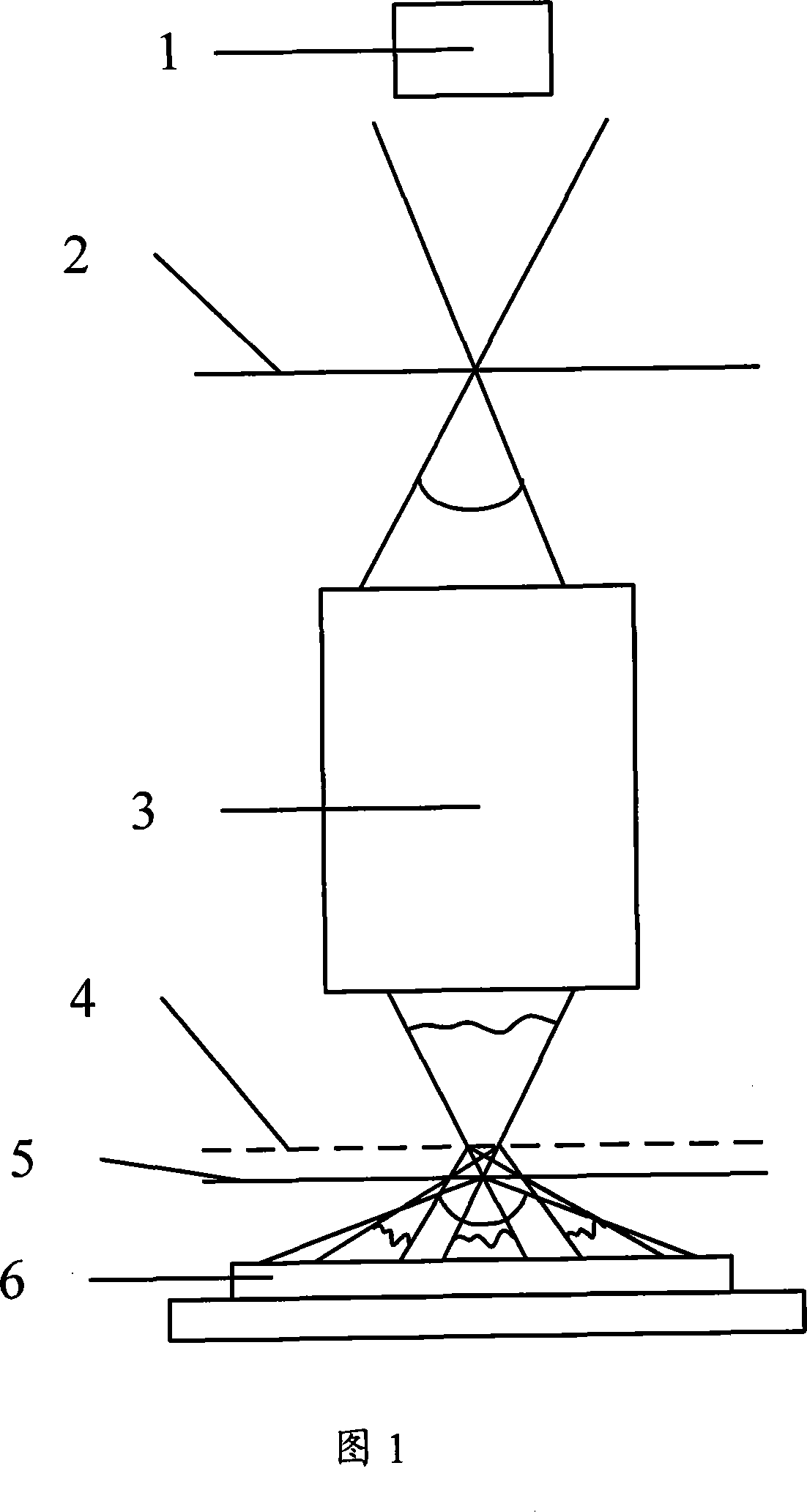
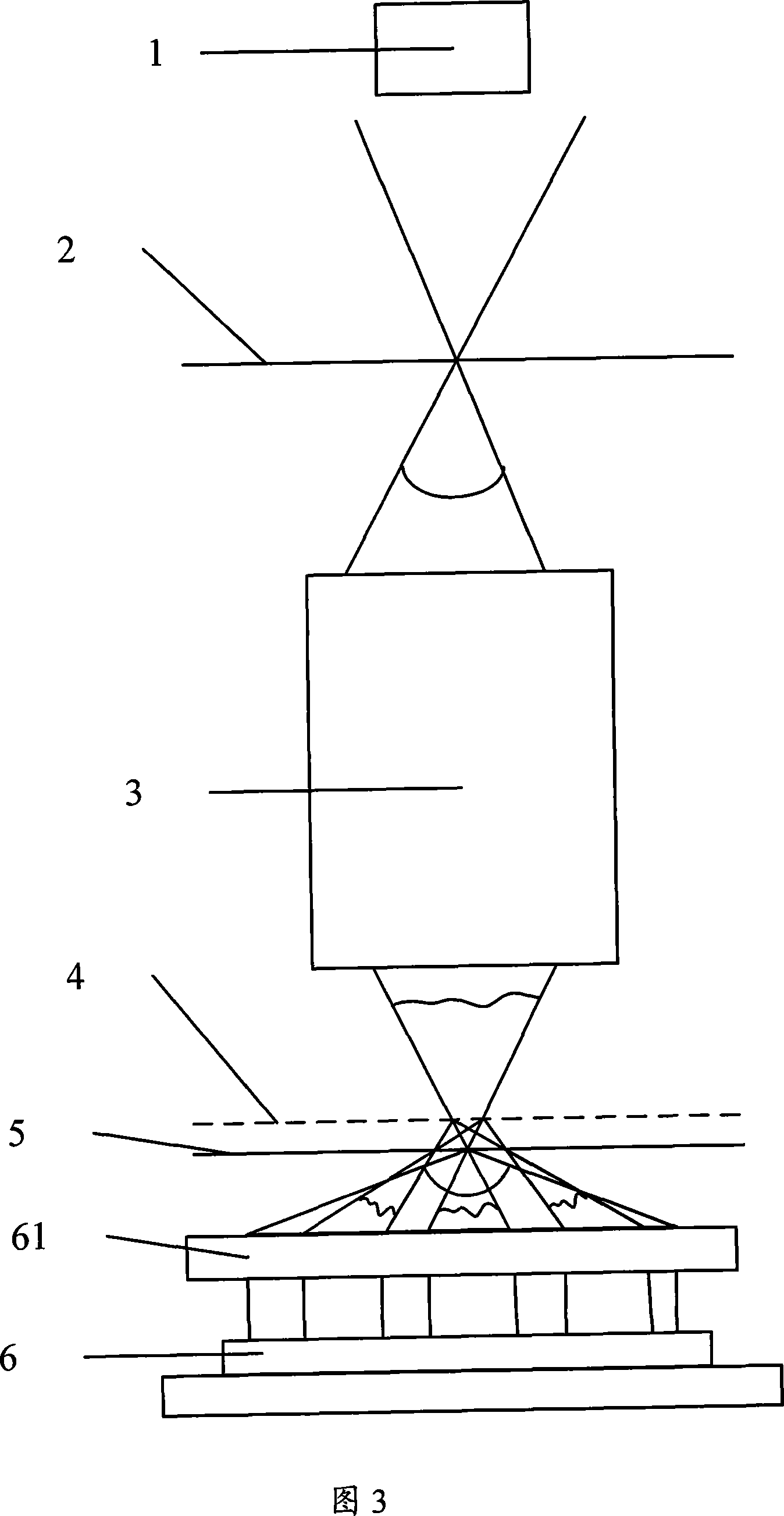
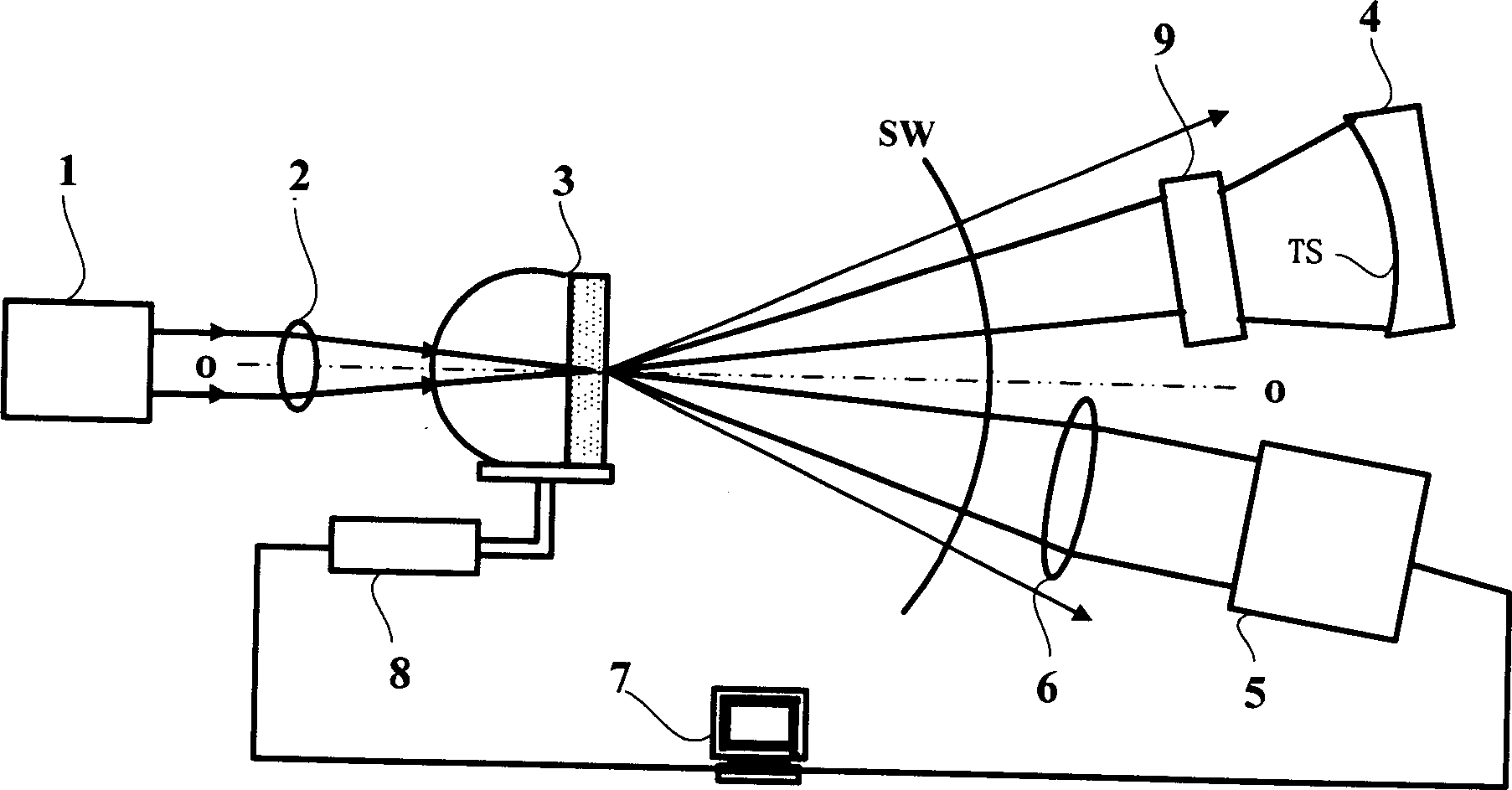
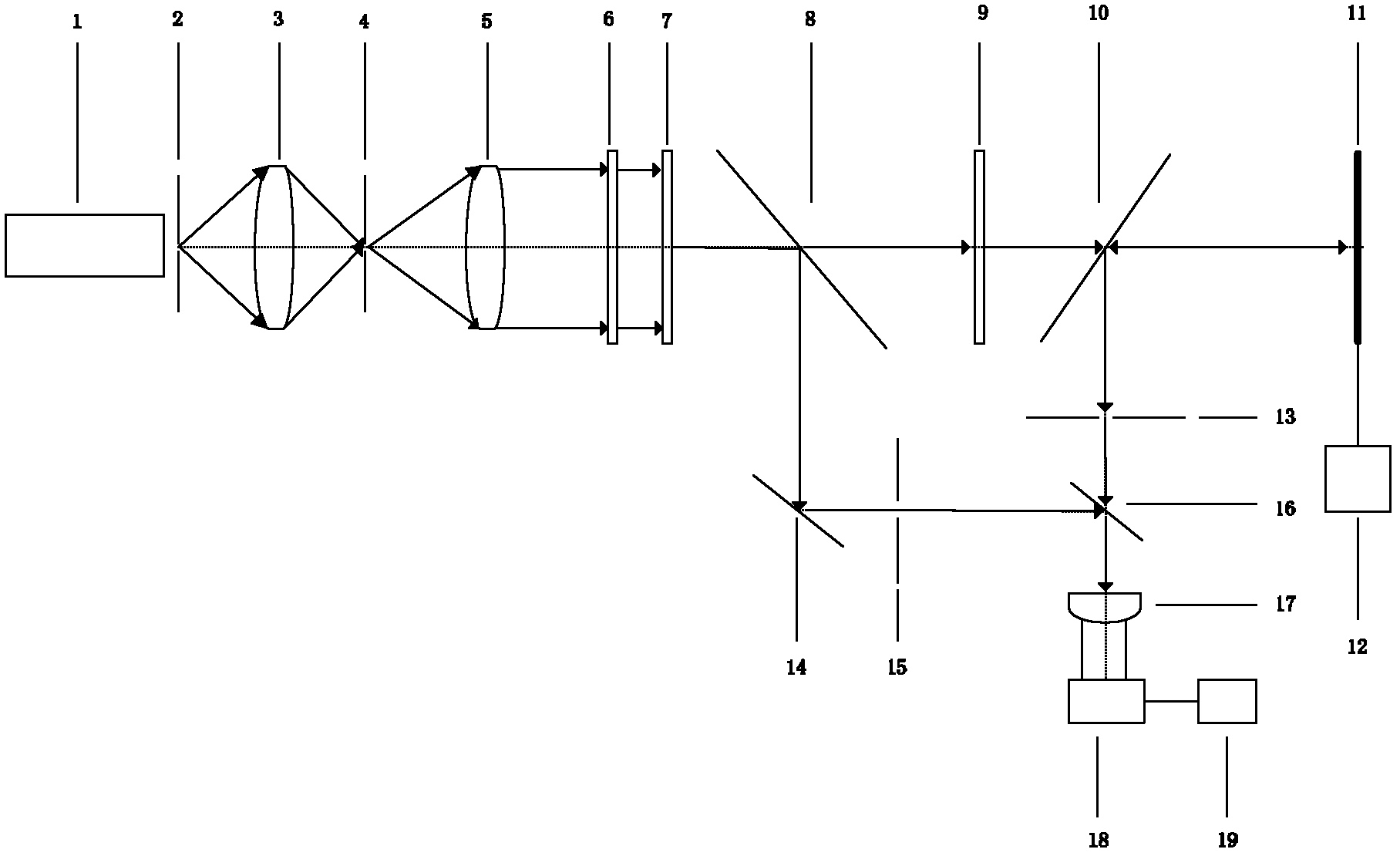
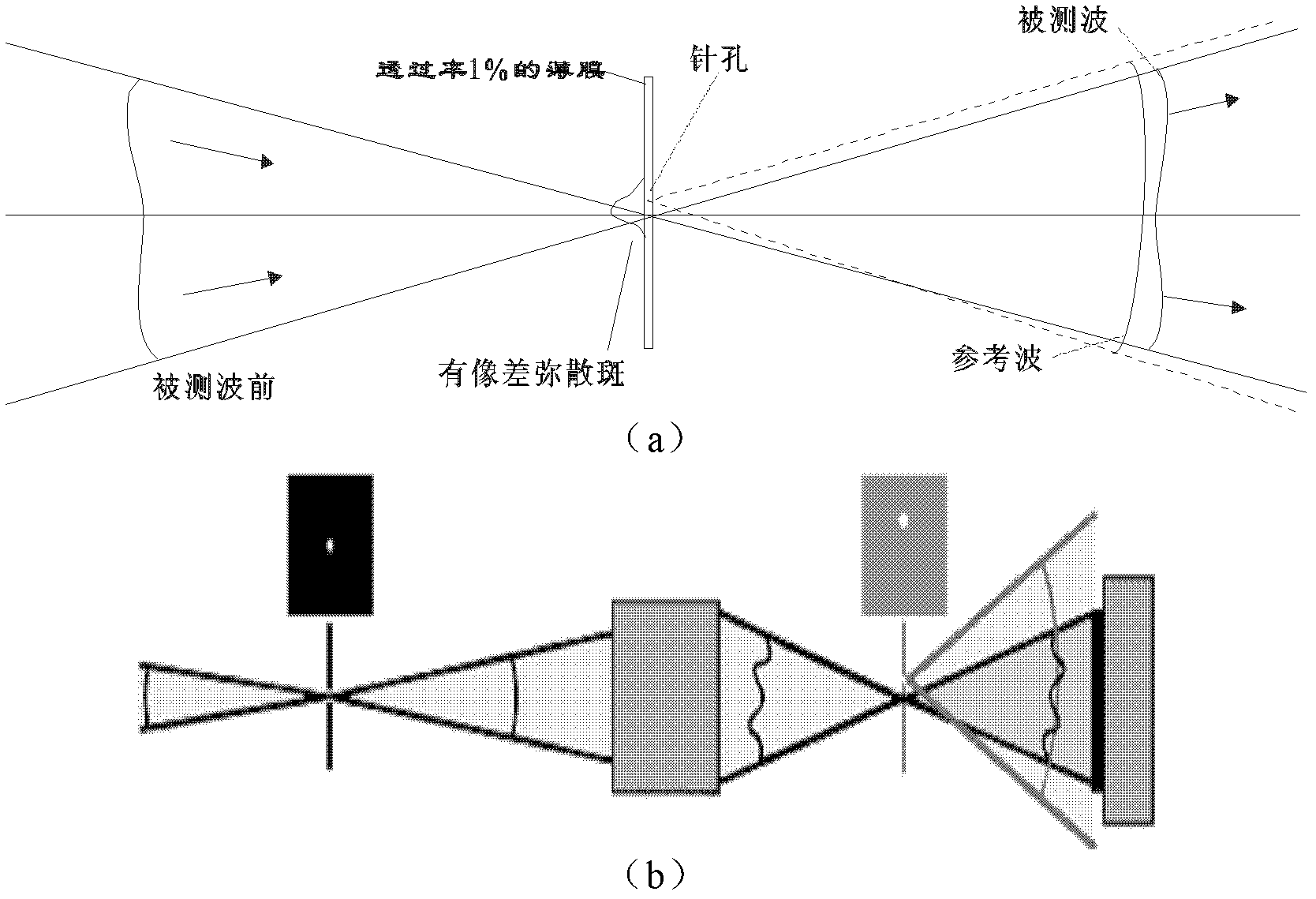
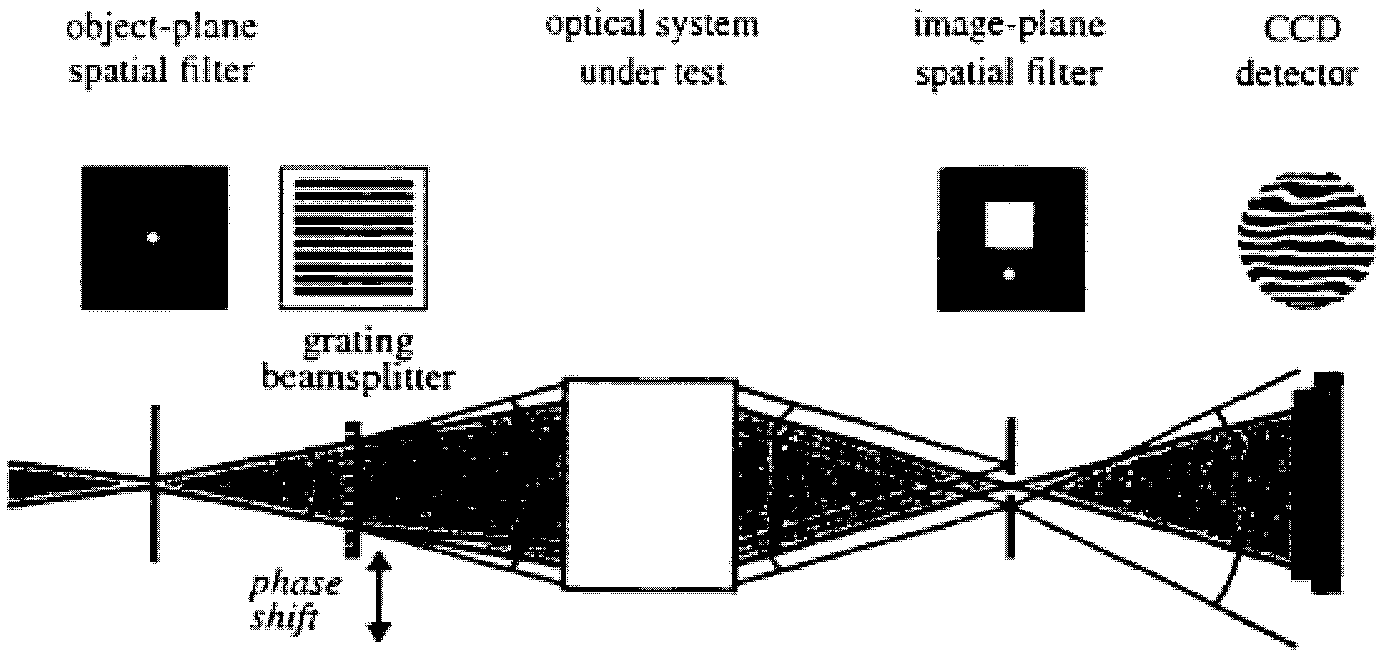
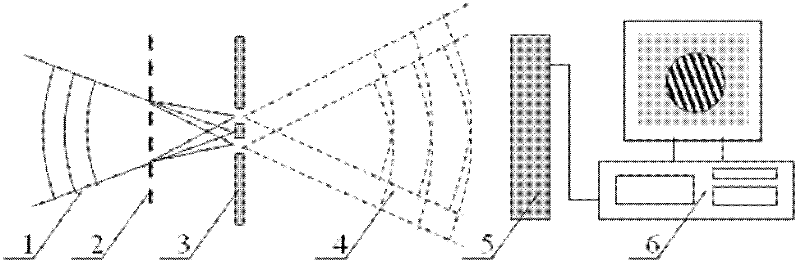
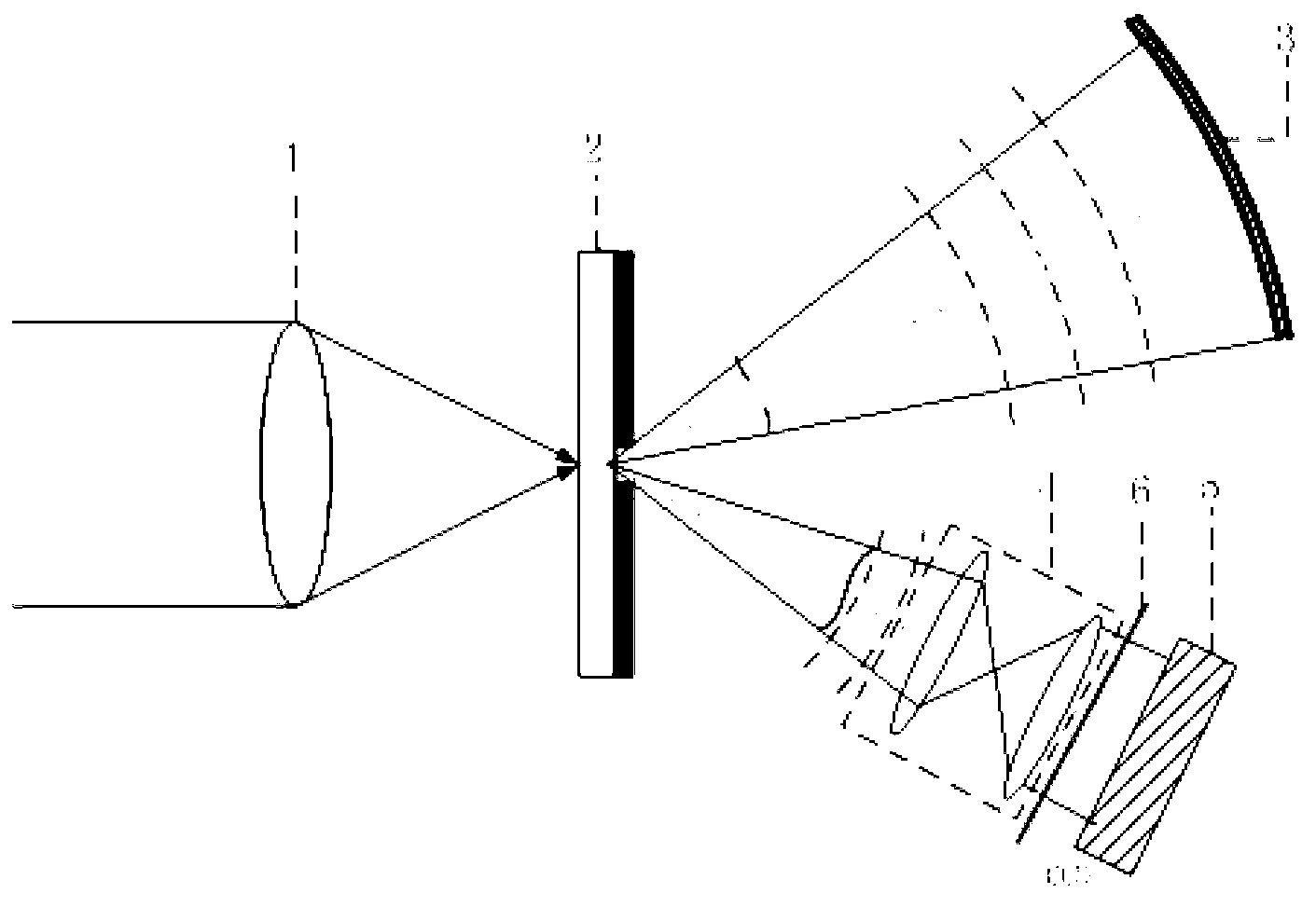
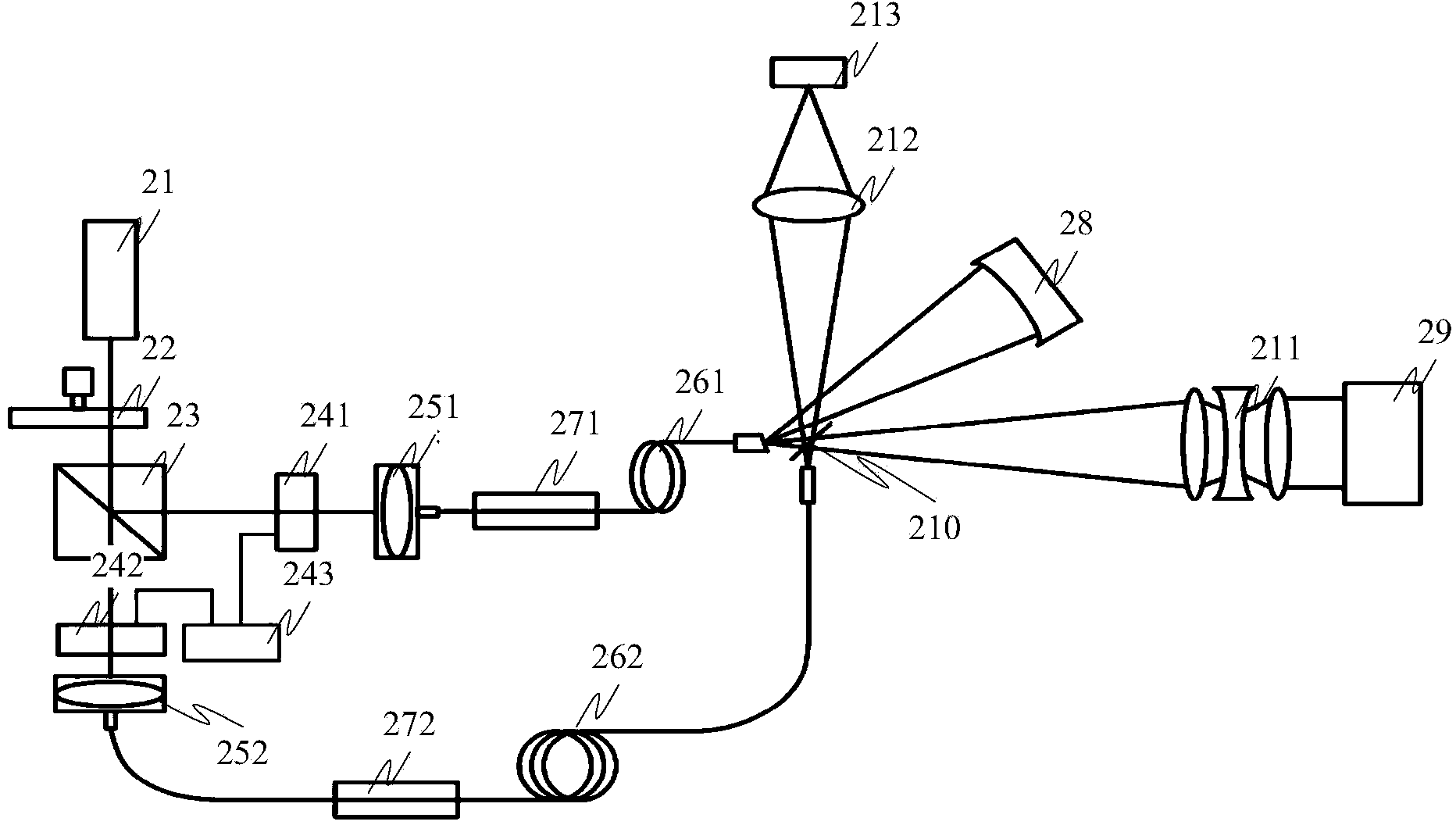
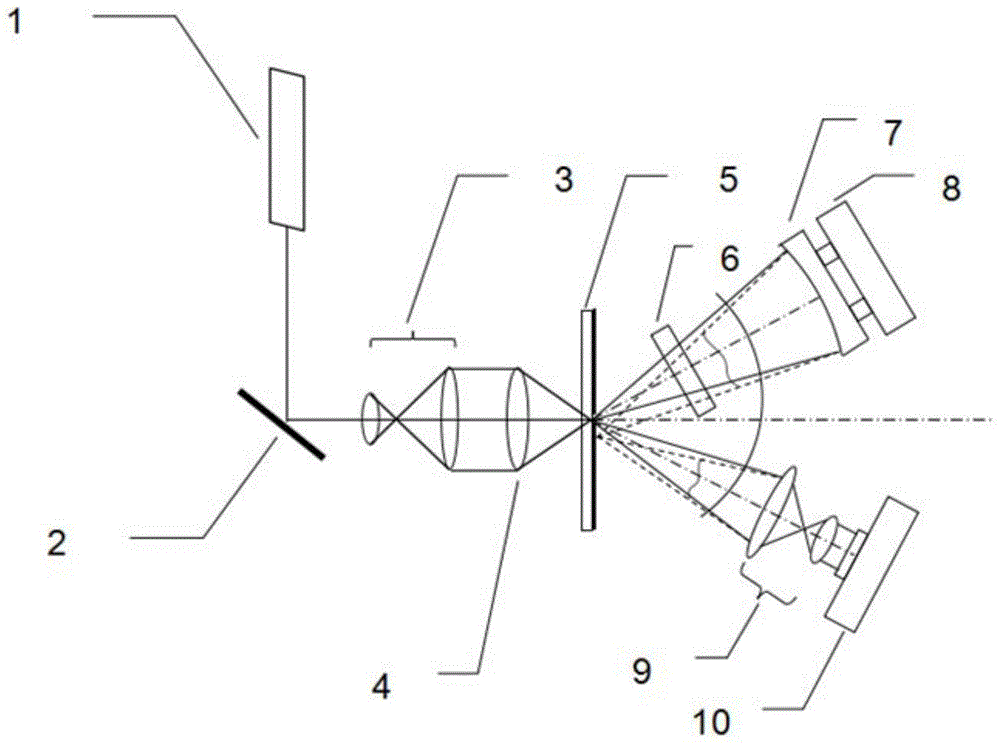
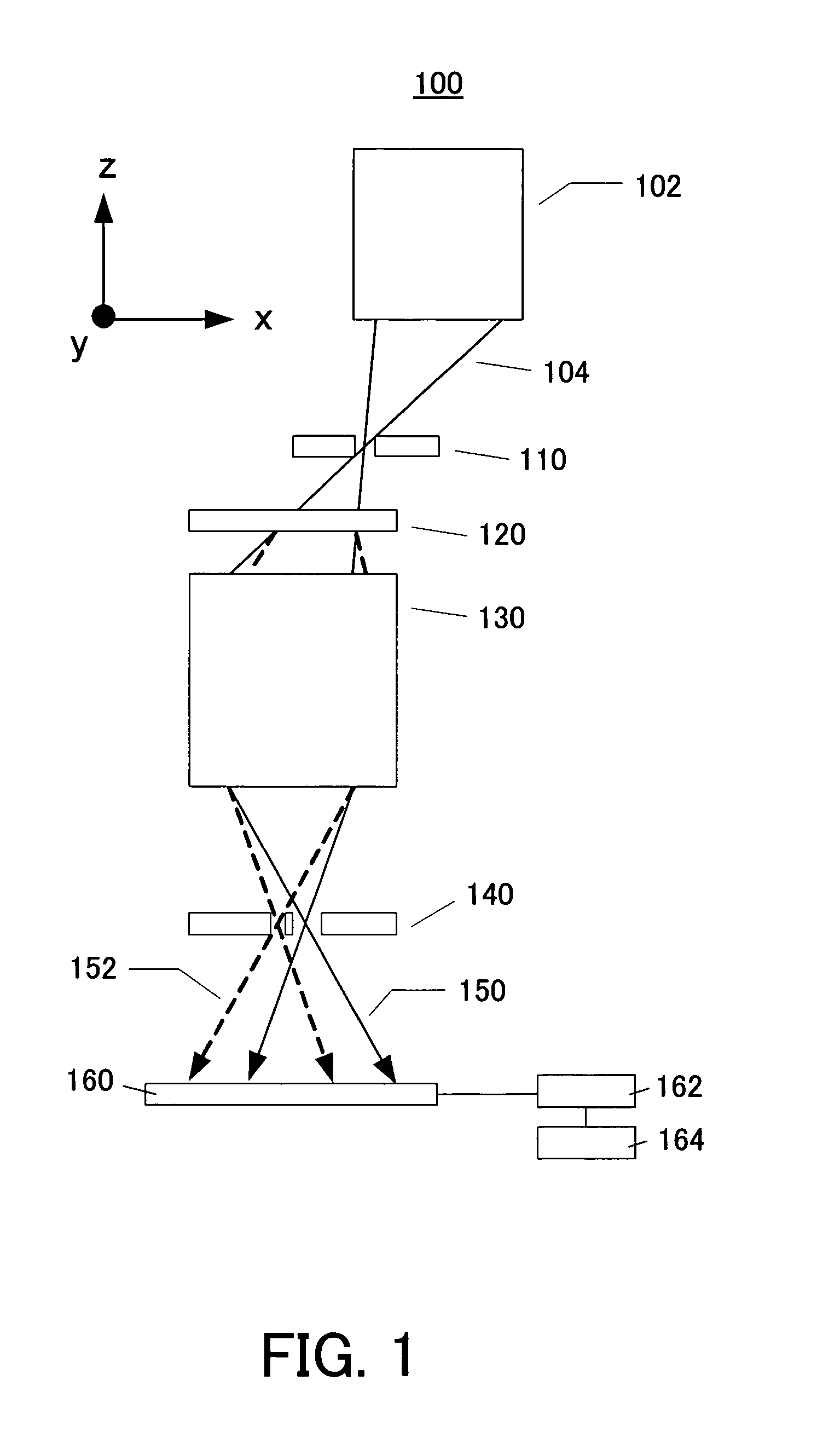
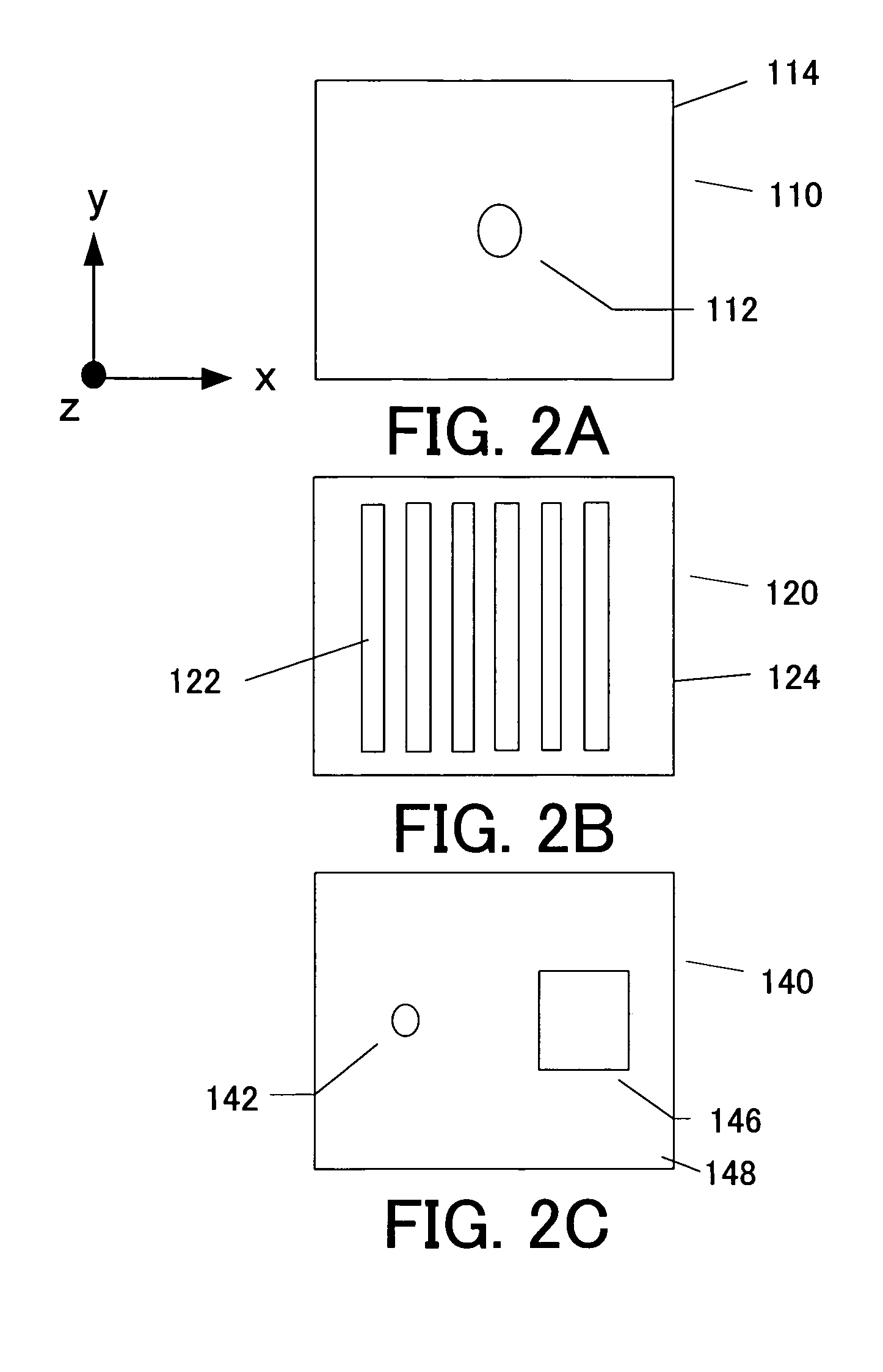
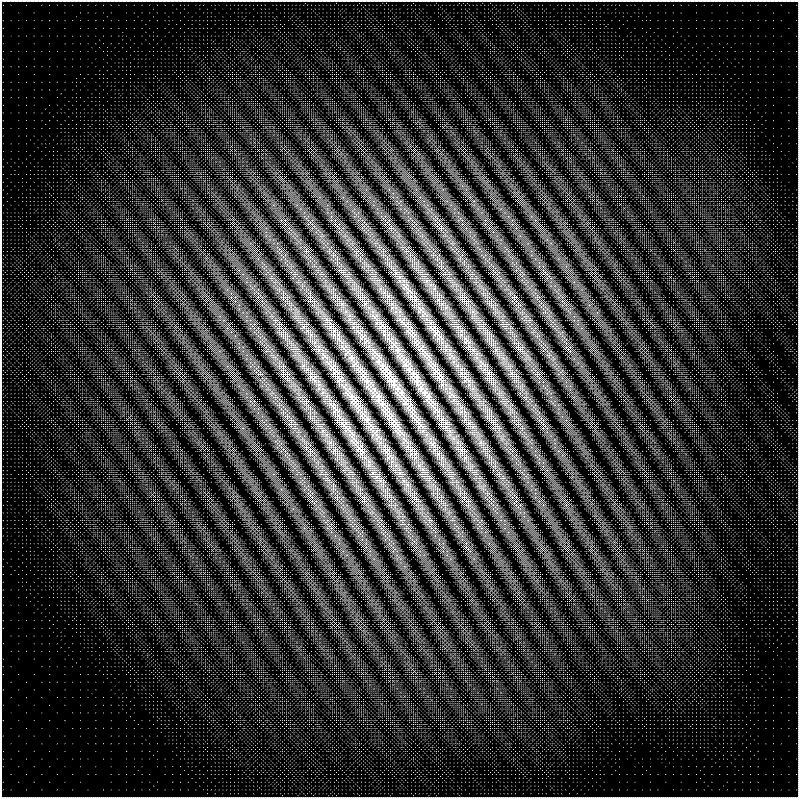
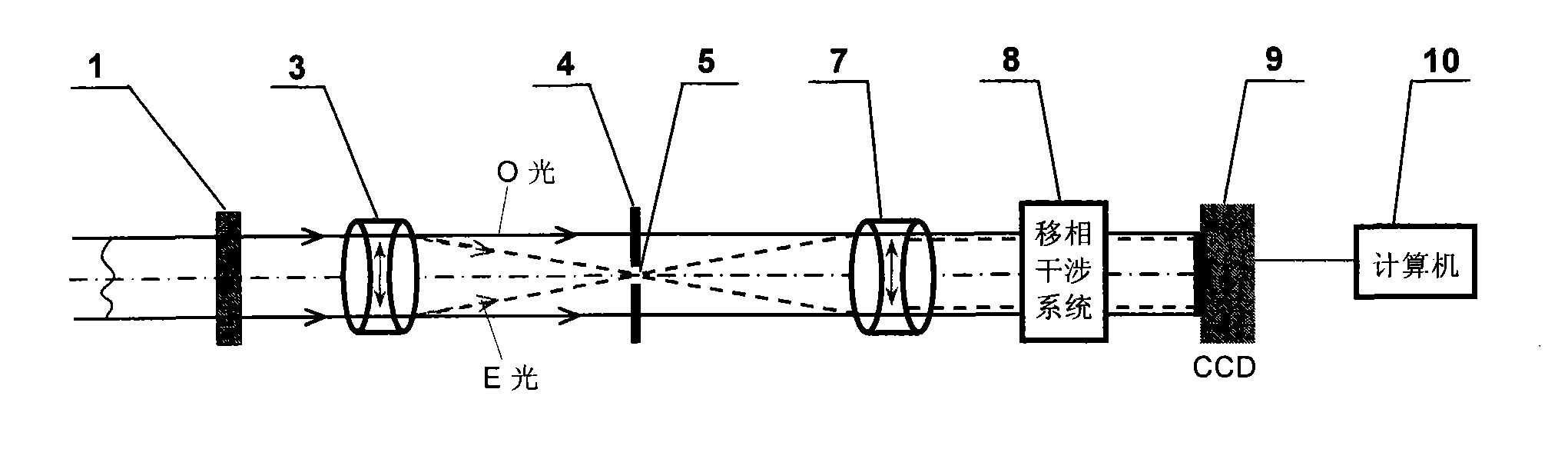
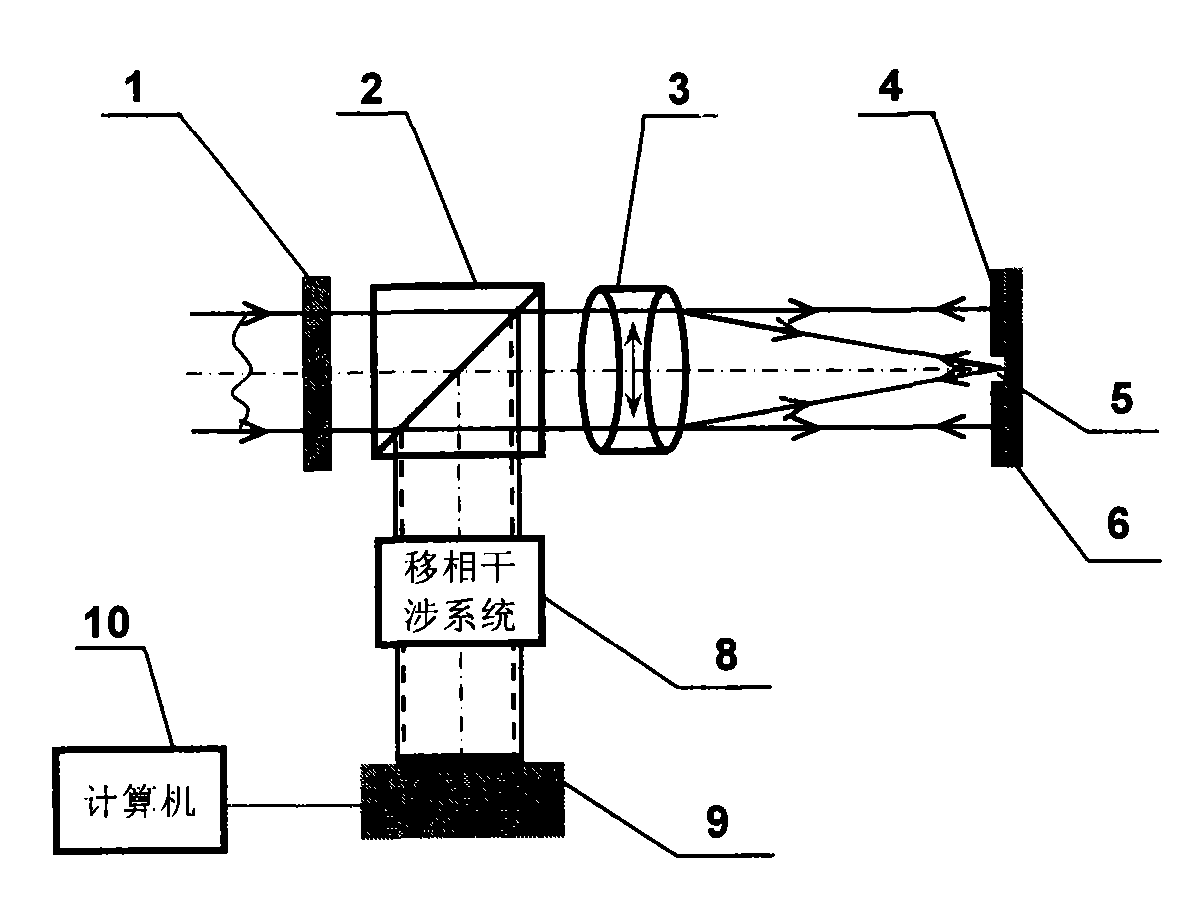
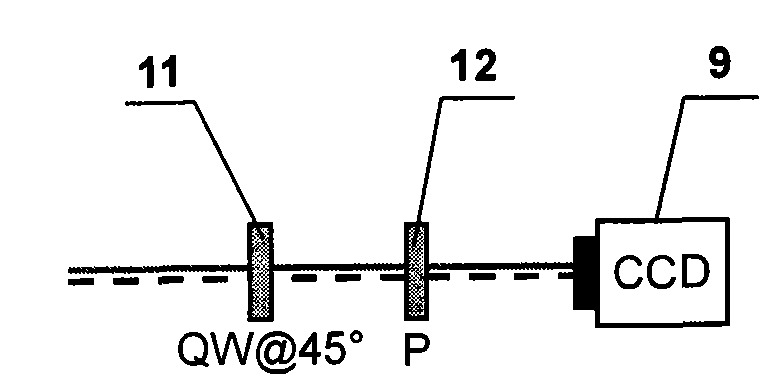
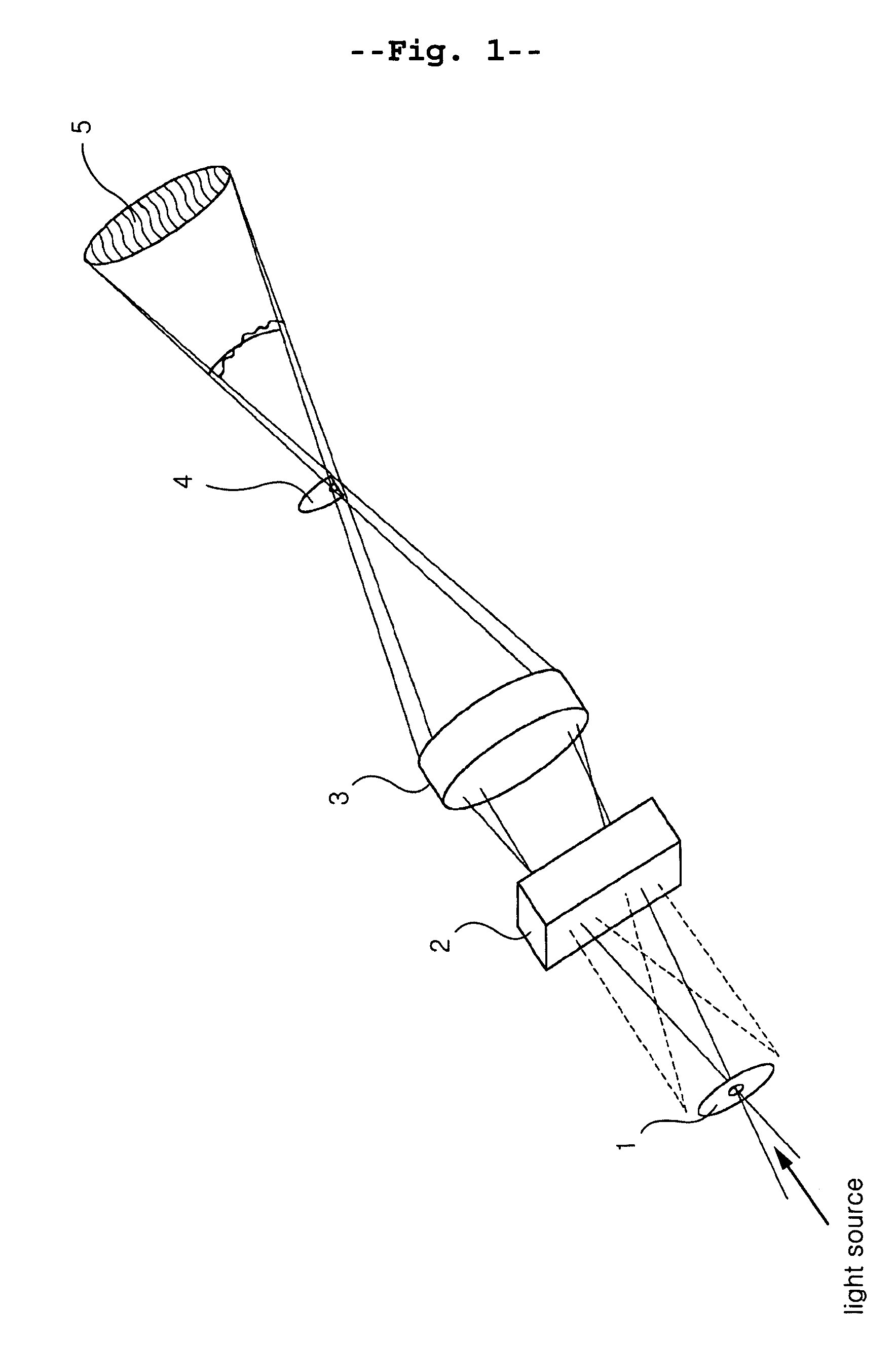
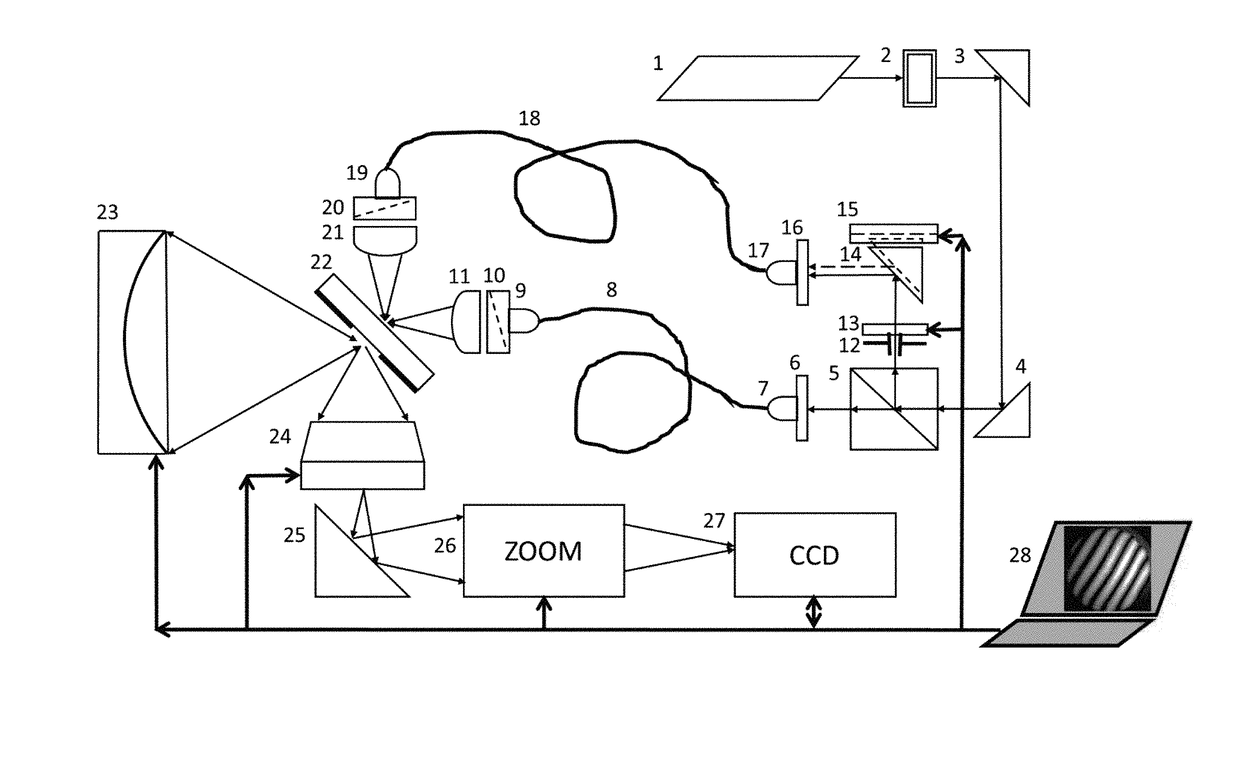
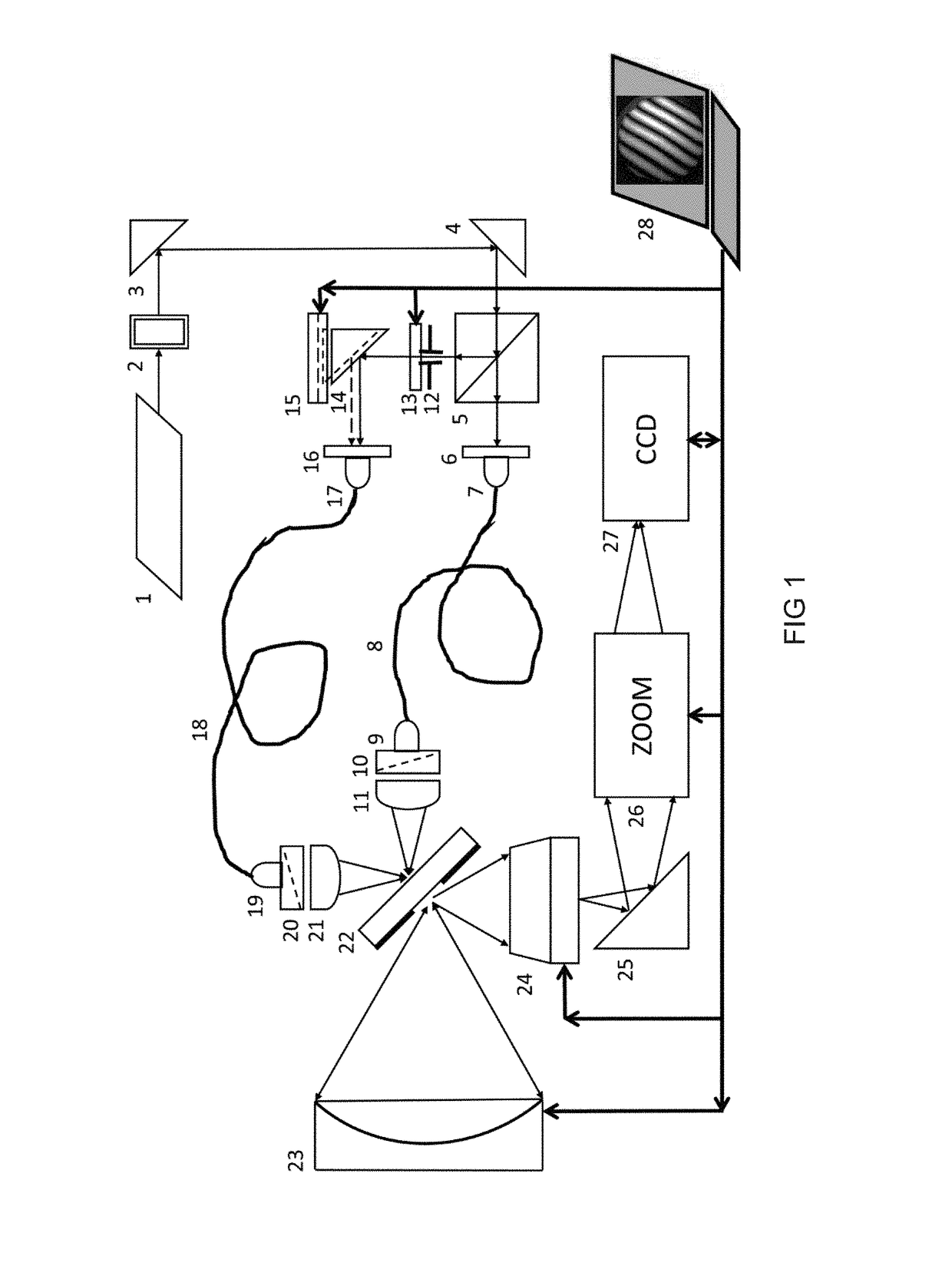
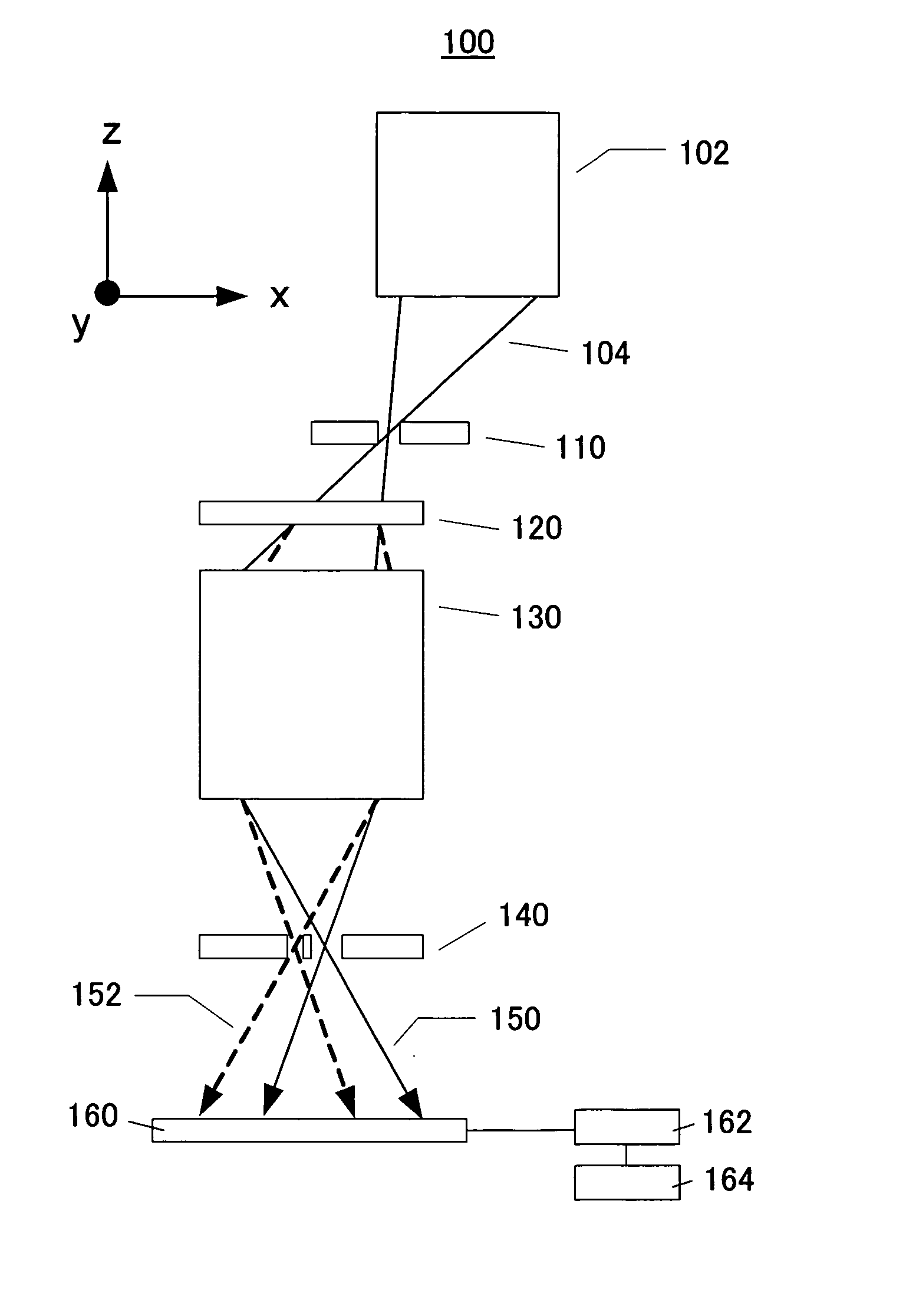
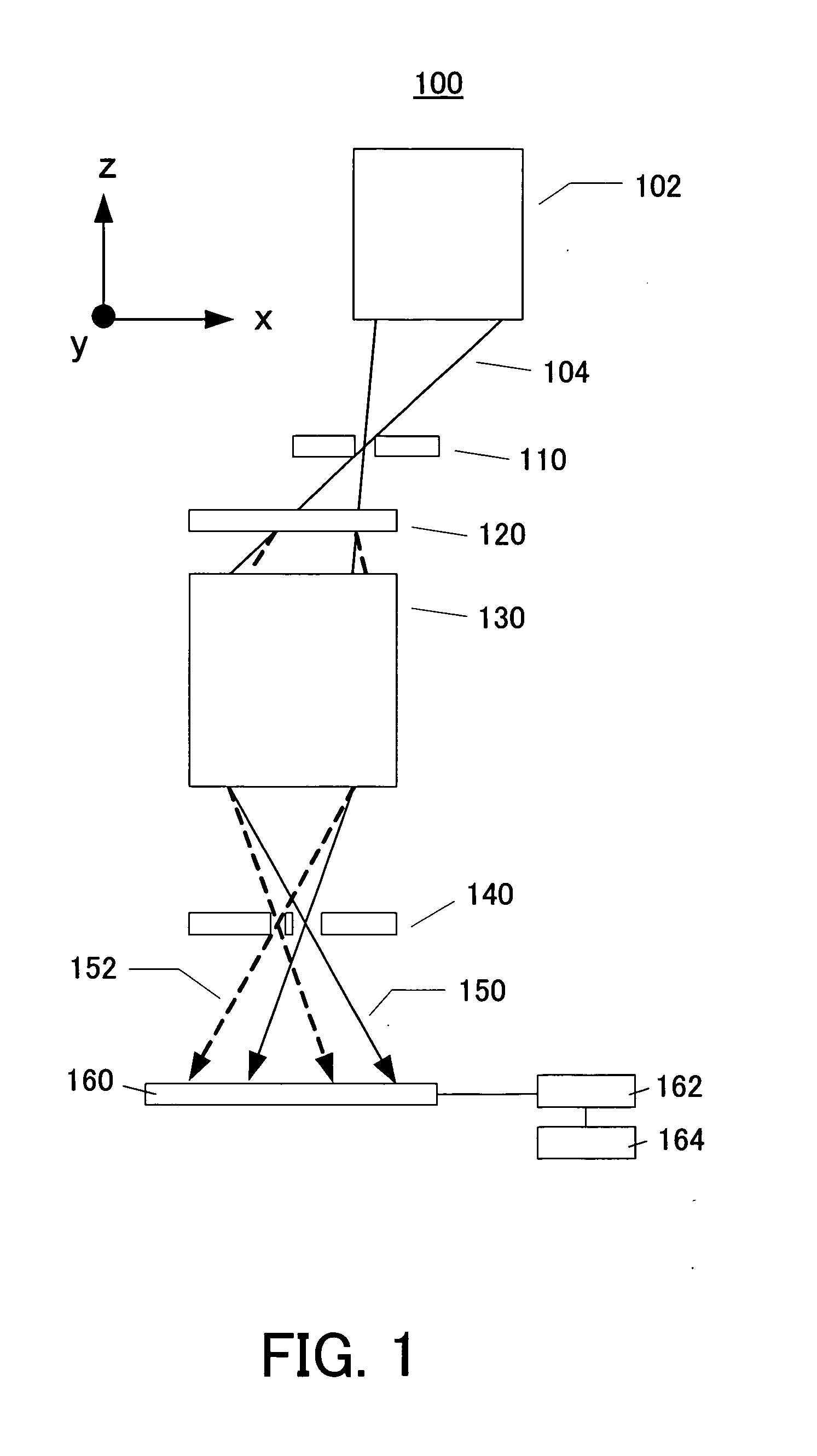
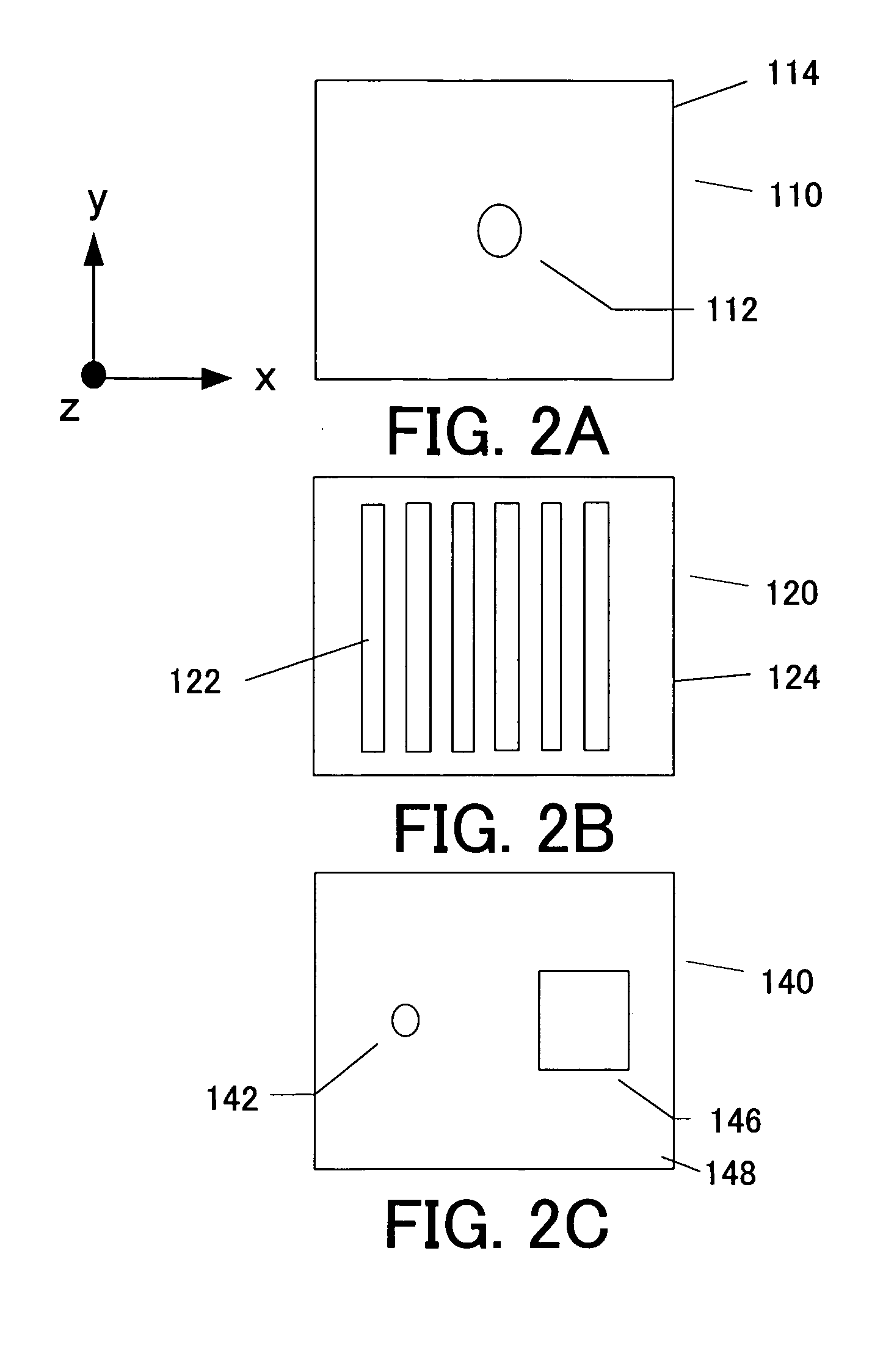
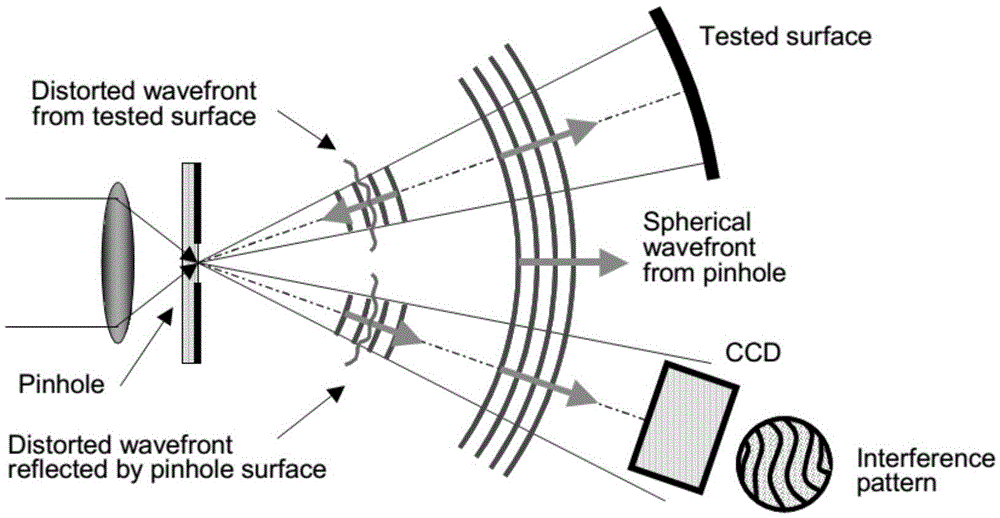
A point diffraction interferometer (PDI) is a type of common-path interferometer. Unlike an amplitude-splitting interferometer, such as a Michelson interferometer, which separates out an unaberrated beam and interferes this with the test beam, a common-path interferometer generates its own reference beam. In PDI systems, the test and reference beams travel the same or almost the same path. This design makes the PDI extremely useful when environmental isolation is not possible or a reduction in the number of precision optics is required. The reference beam is created from a portion of the test beam by diffraction from a small pinhole in a semitransparent coating. The principle of a PDI is shown in Figure 1.
Photo-etching machine projection objective wave aberration on-line detection method
InactiveCN101236362AHigh measurement accuracyGood repeatabilityPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusPoint diffraction interferometerWave aberration
The invention relates to an on-line detection method for detecting the wave aberration of a projection objective of a photoetching machine. The on-line detection, revising, and controlling are done to the wave aberration of the projection objective by integrating an interferometer device on the photoetching machine. The interferometer device is a point-diffraction interferometer or a slit-diffraction interferometer and is provided with two measuring modules: a PSI measuring module and an FTM measuring module. The PSI measuring module adopts phase shifting interferometry with high measuring precision and is mainly used to detect the error calibration in an interferometer device system; the FIM measuring module adopts fourier transform method to treat with interference fringes with high measuring speed, and is mainly used to on-line detect and control the wave aberration of the projection objective. The method improves the measuring precision without reducing the measuring speed, and improves the measuring precision and reproducibility of the interferometer device by adopting a higher quality spherical reference wave to calibrate the systematic error caused by each component of the interferometer device without reducing the contrast ratio of the interference fringes.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Exposure apparatus mounted with measuring apparatus
InactiveUS20050190378A1Simple structureShort timeOptical measurementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPoint diffraction interferometerMeasurement device
An exposure apparatus for exposing a pattern of a mask onto an object using light from a light source, includes a projection optical system for projecting the pattern onto the object, and a measuring apparatus for measuring, as an interference fringe, optical performance of the projection optical system using the light, wherein the measuring apparatus is a point diffraction interferometer that has a pinhole to form an ideal spherical wave, a line diffraction interferometer that has a slit to form an ideal cylindrical wave or an ideal elliptical wave, or a shearing interferometer that utilizes a shearing interferometry.
Owner:CANON KK
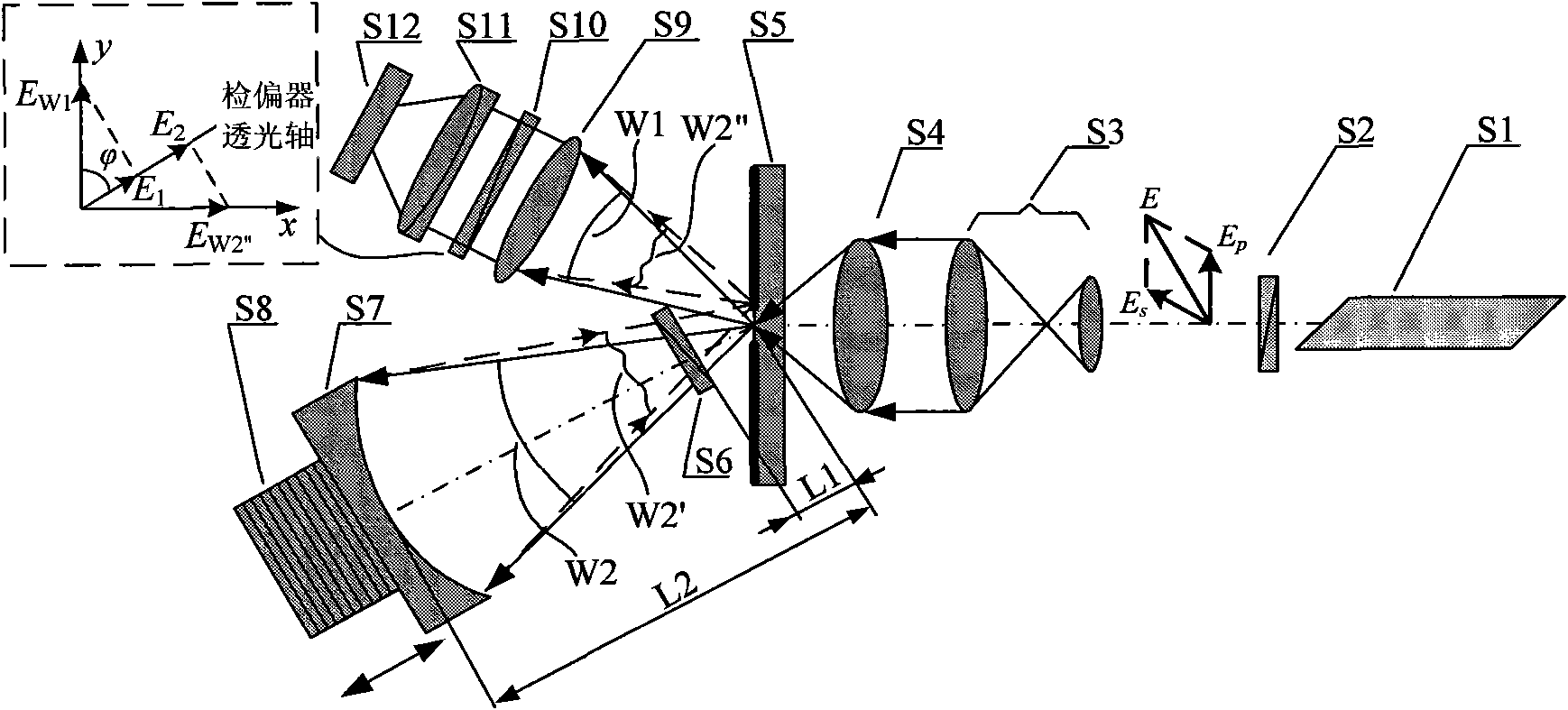
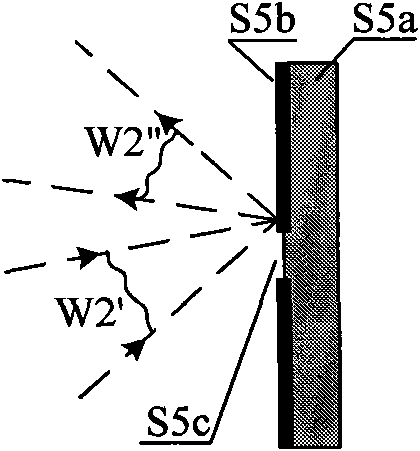
Polarized point diffraction interferometer system for test of low-reflectivity optical spherical surfaces
InactiveCN101915556AAdjustable contrastSimple structureUsing optical meansPoint diffraction interferometerVisibility
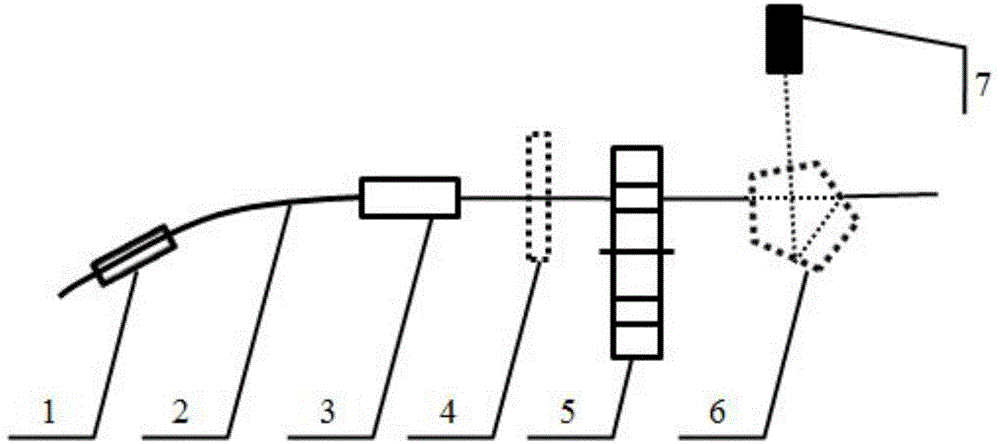
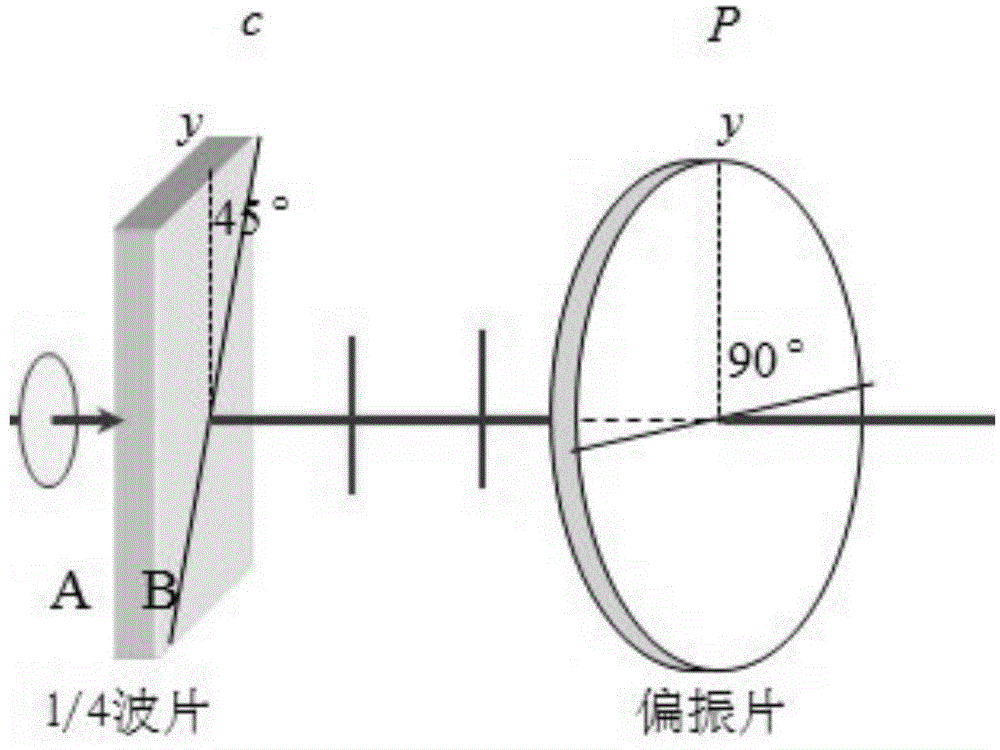
The invention discloses a polarized point diffraction interferometry system for test of low-reflectivity optical spherical surfaces. As the reflectivity of the optical spherical surface is low in the actual polishing process, a high-precision interference test system needs to have the function of adjusting visibility of fringes to obtain the ideal visibility of interference fringes. The invention solves the problem of realizing adjusting the visibility of interference fringes while ensuring the test precision of the spherical surface. The invention is technically characterized by establishing the polarized point diffraction interferometer system capable of realizing adjusting the visibility of interference fringes by introducing a polarization optical element to adjust the polarization states of light beams based on a point diffraction interferometer system capable of realizing high-precision test; and putting forward corresponding structure design and system error correction methods by analyzing the function characteristics of each element in the interferometer system to realize high-precision test of the spherical surfaces. The invention provides a feasible method for high-precision test of the low-reflectivity optical spherical surfaces.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
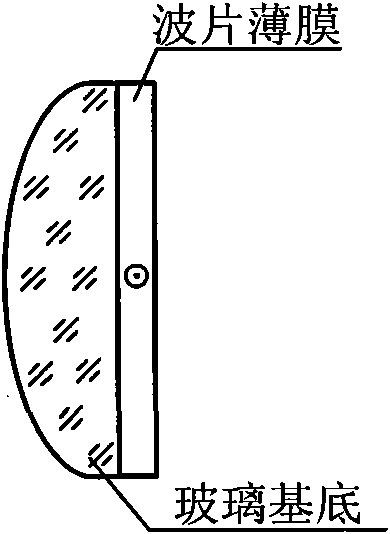
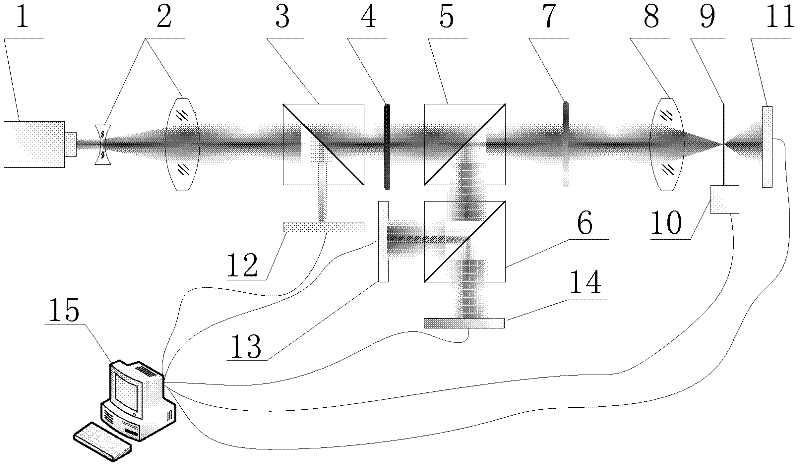
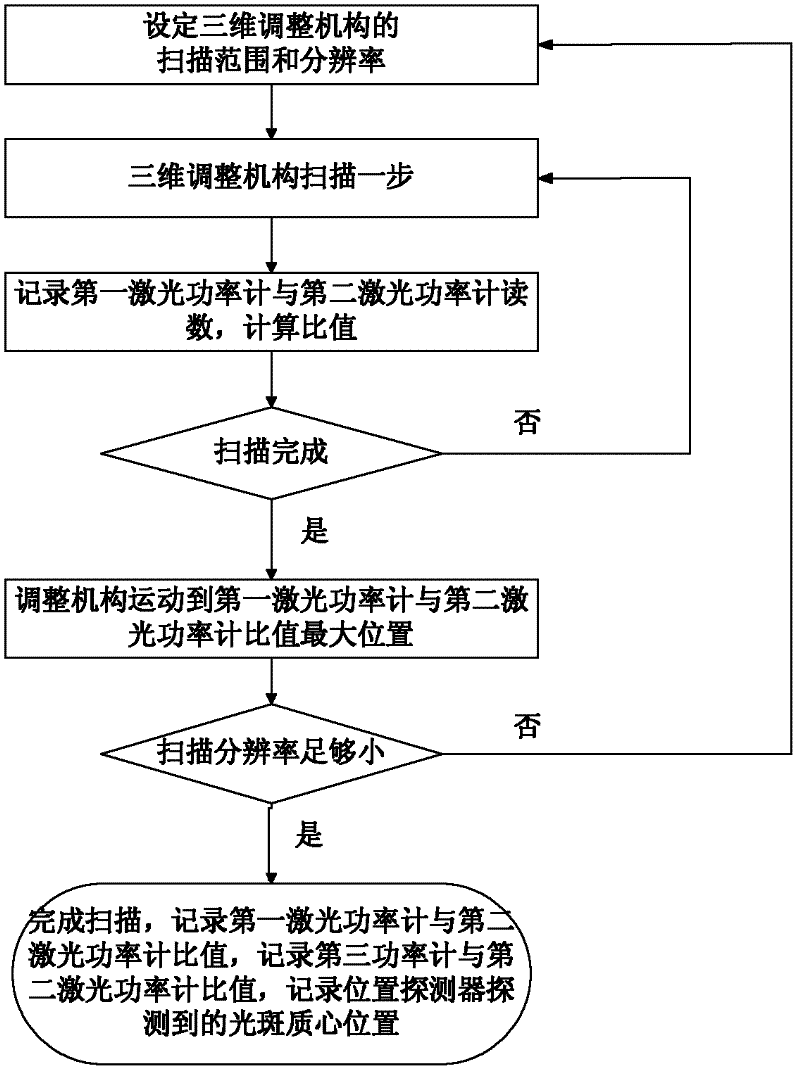
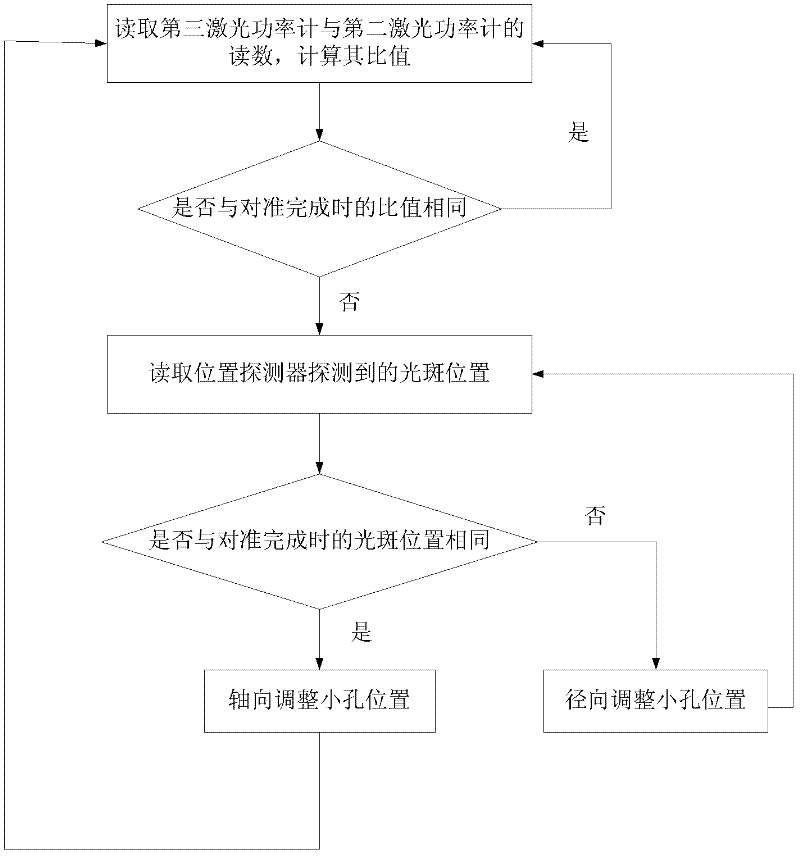
Device and method for aligning pinhole of point-diffraction interferometer
InactiveCN102564301AAvoid misjudgmentFast alignmentUsing optical meansPoint diffraction interferometerOptical power meter
The invention discloses a device and a method for aligning a pinhole of a point-diffraction interferometer, belonging to the technical field of optical precise debugging, namely a device and a method for aligning the pinhole of the point-diffraction interferometer provided to realize real-time monitoring of precise aligning and aligning states of a focusing spot and a diffraction pinhole in the point-diffraction interferometer. The device comprises a laser device, a laser beam expander, a first dispersion prism, a half-wave plate, a second dispersion prism, a third dispersion prism, a quarter-wave plate, a focus lens, a pinhole plate, a three-dimensional scanning and micro-adjusting mechanism, a first laser power meter, a second laser powder meter, a third laser power meter, a position detector and a computer. According to the device and the method disclosed by the invention, the aligning speed is increased; the pinhole aligning state is quickly aligned again when being monitored; power change of the laser device is detected by a sole laser power meter in the invention and the aligning state is reflected by a ratio of the laser power instead of an absolute value so that error judgment on the aligning state of the pinhole caused by laser power change is overcome.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Point diffraction interferometer
ActiveCN101183042AAvoid motion errorsHigh sampling frequencyUsing optical meansTesting optical propertiesOptical diffractionPoint diffraction interferometer
The invention provides a point diffraction interferometer and comprises a light source module, a mask which can produce an ideal spherical wave, an optical diffraction component which can produce multi-level sub-diffraction light, an image sensor and an optical component. The measured optical component is arranged between the mask and the optical diffraction component and the diffraction light of some levels can permeate the optical component completely, wherein, the diffraction light of a certain level can permeate the optical component partly while being diffracted partly; the diffraction light of some levels can permeate the optical component completely, wherein, the diffraction light of a certain level can be diffracted or the optical component consists of a plurality of windows and a plurality of small holes; diffraction light of some levels can selectively permeate the window, however, the non-diffracted light can be diffracted through the small hole on the optical component. The point diffraction interferometer of the invention conducts measurement through a plurality of interference graphs which are produced at the same time and the sampling frequency is improved, moreover, the design and operation of the whole system is simplified and the motion error of a phase-shift component can be avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
High-numerical-aperture optical fiber point diffraction interference device used for three-coordinate measurement and method thereof
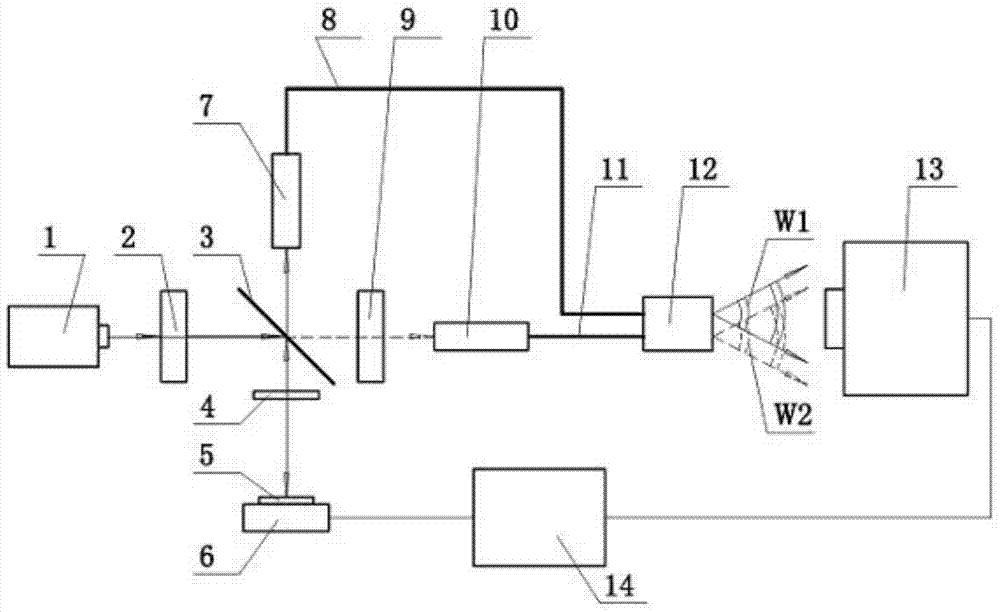
ActiveCN104330039ASimplify adjustment difficultyReduced photosensitivity requirementsUsing optical meansBeam splittingHigh energy
The invention provides a high-numerical-aperture optical fiber point diffraction interference device used for three-coordinate measurement and a method thereof, and relates to optical measurement. Light emitted by a laser device is divided into transmission light and reflected light via a polarized beam splitting prism. Point diffraction spherical wave front W2 is generated at a sub-wavelength aperture optical fiber emergent end by transmission light, and point diffraction spherical wave front W1 is generated at the sub-wavelength aperture optical fiber emergent end by reflected light after being reflected by a moving reflecting mirror. A CCD detector acquires W1 and W2 interference fringes, and three-dimensional coordinate measurement of a measured object is realized via multi-step phase-shifting and a double iteration algorithm of an L-M algorithm. A problem in the prior art that high-numerical-aperture and high-energy diffraction spherical wave front is difficult to realize simultaneously by a point diffraction interferometer used for three-coordinate measurement is solved. The beneficial effects are that probes of two sub-wavelength aperture optical fibers act as measuring probe heads, the high-brightness and high-numerical-aperture point diffraction spherical wave front is acquired, the requirement of light sensitivity is reduced and measurement range of an optical fiber point diffraction interference system used for three-coordinate measurement is enlarged.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Spot diffraction interferometer for measuring surface shape
InactiveCN1431477AFocusEasy to assembleInterferometric spectrometryPhase-affecting property measurementsData acquisitionOptoelectronics
The interferometer includes the optical part and the data acquisition, process and control parts. The optical part includes the laser, the convergent lens, the lens soaked by the solid coated with super resolving power mask arranged in optical axis in sequence along the traveling direction of the laser beam. The part to be measured is positioned above the optical axis and the image lens is in lower part. The data acquisition, process and control parts include the CCD camera, the computer and the displacement controller. The key technique in the invention is the lens soaked by the soild and the mask with supper resolving power. Thus, the smaller pinhole can be obtained as the ideal light source with spherical wave. The position and size of the pinhole are adjustable, providing high transmittance of light and low requirement for the quality of the light beam.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Detection device and method for small hole calibration
InactiveCN102445280AHigh measurement accuracyRealize high-precision optical surface inspectionOptical measurementsBeam splitterProcessing cost
The invention provides a detection device and method for small hole calibration, wherein light emitted by a laser is divided into two paths of light after passing through a filter hole, a condenser lens, a spatial filter, a beam expanding lens, a lambda / 2 wave plate, a lambda / 4 wave plate and a semi-transmitting semi-reflecting mirror; the first path of light is reflected by a reflector after passing through an attenuation plate and a beam splitter, and the reflected light is further reflected by the beam splitter to a first small hole so that diffracted spherical wave is produced by the first small hole and then is transmitted through the beam splitter; the second path of light passing through the semi-transmitting semi-reflecting mirror is reflected by the reflector to irradiate a second small hole; the diffracted spherical wave produced by the second small hole is reflected by the beam splitter before forming interference with the diffracted spherical wave produced by the first small hole; interference fringes pass through the condenser lens and then are collected by an optical detector; and finally, the errors of the diffracted spherical waves produced by three small holes areobtained through predetermined replacement operations. The detection device and the detection method provided in the invention are capable of improving the measurement accuracy of a point-diffractioninterferometer and reducing the processing cost of a high-accuracy small hole.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Device and method for detecting reference spherical wave deviation in visible light point diffraction interferometer
InactiveCN102297725ARealize high-precision detectionAchieving Shearing InterferenceOptical measurementsPoint diffraction interferometerWavefront sensor
The invention discloses a device and a method for detecting reference spherical wave deviation in a visible point diffraction interferometer and belongs to the field of reference spherical wave ultra-high precision detection methods. The limitation of a Hartmann wavefront sensor on wavefront micro-deviation detection is overcome so that the wavefront high-precision detection can be realized. A light path comprises an incidence convergent light wave, a grating, a small pore plate with three circular holes along an orthogonal direction and a charge coupled device. The output end of the charge coupled device is connected to a computer. After being diffracted through the grating, the incidence convergent light wave is divided into a plurality of diffraction orders; + / -1 order of diffraction light respectively passes through two small holes; after the light is diffracted by the small holes, approximately ideal spherical waves are generated; two spherical waves are subjected to shear interference; an interference image is recorded on a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) detector; and after the interference image is collected, the diffraction wavefront deviation can be obtained. According to the device and method disclosed by the invention, the diffraction wavefront high-precision detection is realized by performing the shear interface of the spherical waves generated through double-hole diffraction in a visible light band.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Wavelength turning phase-shift point-diffraction interference measuring device and method thereof
A wavelength turning phase-shift point-diffraction interference measuring device and a method thereof belong to the field of surface profile measuring devices and methods for optical elements based on phase-shift point-diffraction interferometers. The device comprises a tunable laser light source module, a point-diffraction interference module and a control system; the tunable laser light source module comprises a tunable laser, a first spectroscope, a second spectroscope, a wavemeter and a dynamometer; the point-diffraction interference module comprises a beam adjusting mirror assembly, a needle hole plate, an interferometer imaging mirror assembly and a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera; the control system comprises a tunable laser control module, a CCD camera collection control module and a main-control computer. The device can realize phase shift and accomplish phase-shift point-diffraction interference measurement by using a wavelength-tunable laser, does not adopt a piezoceramic phase shifter PZT (Piezoe-lectric Transducer) or utilize a piezoceramic moving pyramid reflecting mirror or other mechanical moving components for phase shift, overcomes the technical problems that a mechanical phase shift device is high in manufacturing difficulty and high in cost, and stress deformation errors is caused by dead weight of a mechanical phase-shift device.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method used for improving measuring accuracy of point-diffraction interferometer
InactiveCN102798341ASolve the problem of reducing the number of digits in analog-to-digital conversionImprove test accuracyOptical measurementsUsing optical meansUltrasound attenuationPoint diffraction interferometer
The invention relates to a method used for improving measuring accuracy of a point-diffraction interferometer, and belongs to the test field of point-diffraction interferometers. The method comprises the following steps of: placing a gathering lens and a foraminule plate on a same optical axis, enabling a parallel light source to gather through the gathering lens, and exit through the foraminule plate; enabling part of rays to form testing light, enabling the other part of rays to be used as reference light, and enabling the testing light and the reference light to share a light path on an ocular circle position of an imaging lens of a camera; and marking the light intensity maximum value of ocular circle on the ocular circle position of the imaging lens as A, placing an attenuation piece for which A point is taken as a centre and the transmissibility is gradually improved, wherein the attenuation piece is used for adjusting the light intensity distribution of an ocular circle light beam of the imaging lens, and the image intensities of the centre and an edge interference fringe are consistent. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the design and structure are simple, the cost is cheap, the processing and manufacturing are easy, the problem that the rim light intensity of the point-diffraction interferometer is dropped so as to cause analog-digital conversion digit reduction is solved with lower cost, and the measuring accuracy of the point-diffraction interferometer is improved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Equal optical path position adjusting method of optical fiber point diffraction interferometer
ActiveCN104792424AHigh precisionImprove efficiencyOptical measurementsPoint diffraction interferometerOptical measurements
An equal optical path position adjusting method of an optical fiber point diffraction interferometer relates to the technical field of optical measurement. The method can effectively judge whether reference light and testing light have the equal optical path or not and has a relatively low price. A polarization splitting prism, two polarization sheets, two coupling lenses and two optical fibers are additionally arranged behind a first polarization splitting prism; optical path conditions of the reference light and the testing light are reflected on an interference pattern and the optical path difference of the reference light and the testing light is judged by the contrast ratio of the interference pattern, which is a direct physical amount; an optical method, but not a mechanical method, is used for adjusting an equal optical path position, so that the optical path conditions of the reference light and the testing light are quantitatively given; the equal optical path position adjusting method has the advantages of high precision, high efficiency, simplicity in operation and the like.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
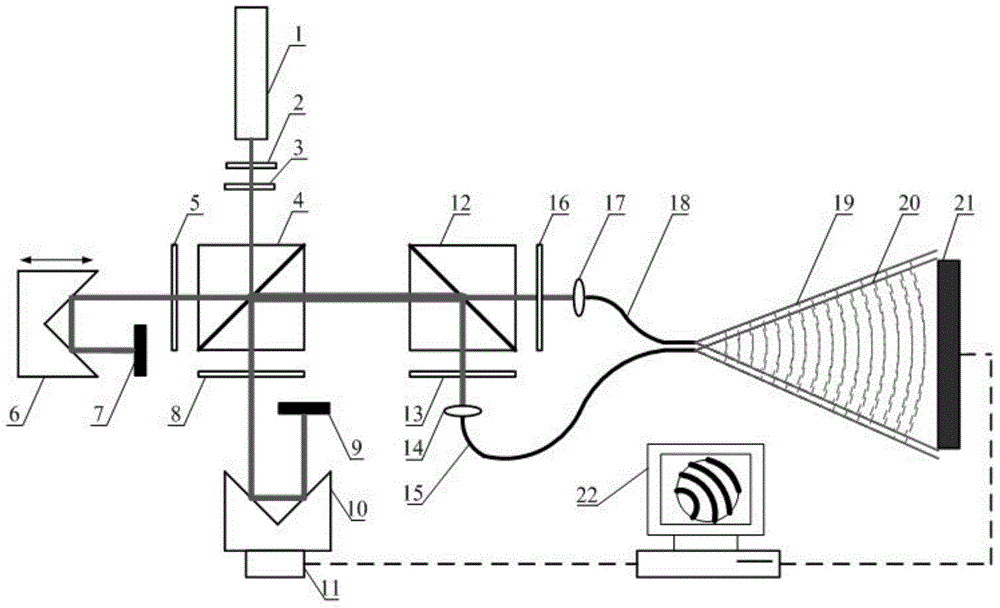
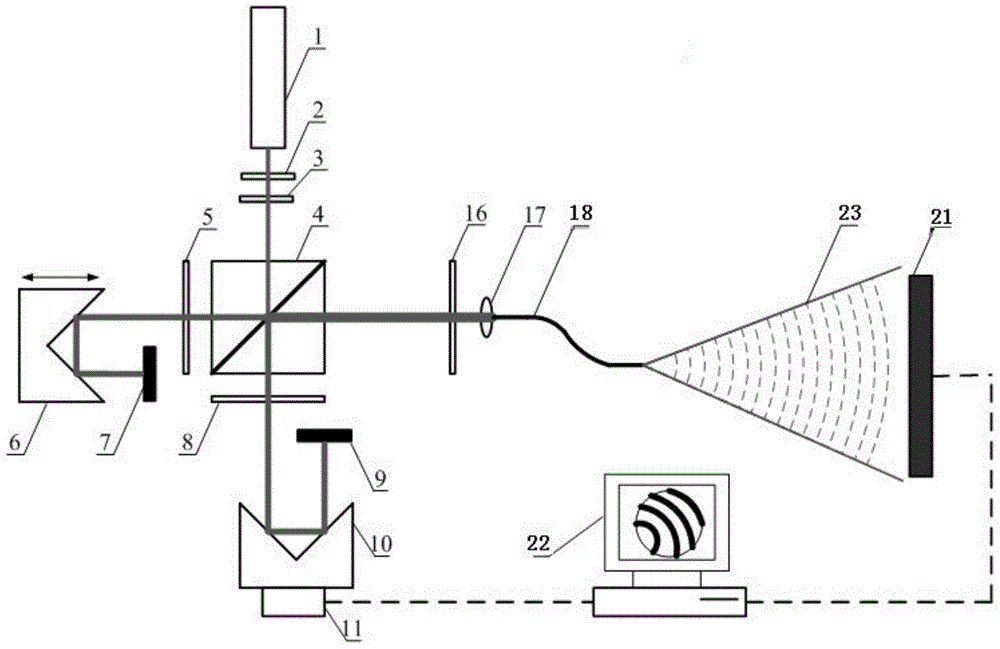
Heterodyne point diffraction interferometer based on phase shift of low-frequency-difference acousto-optic frequency shifter
ActiveCN104296676AAvoid problemsHigh measurement accuracyUsing optical meansPoint diffraction interferometerPhase shifted
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
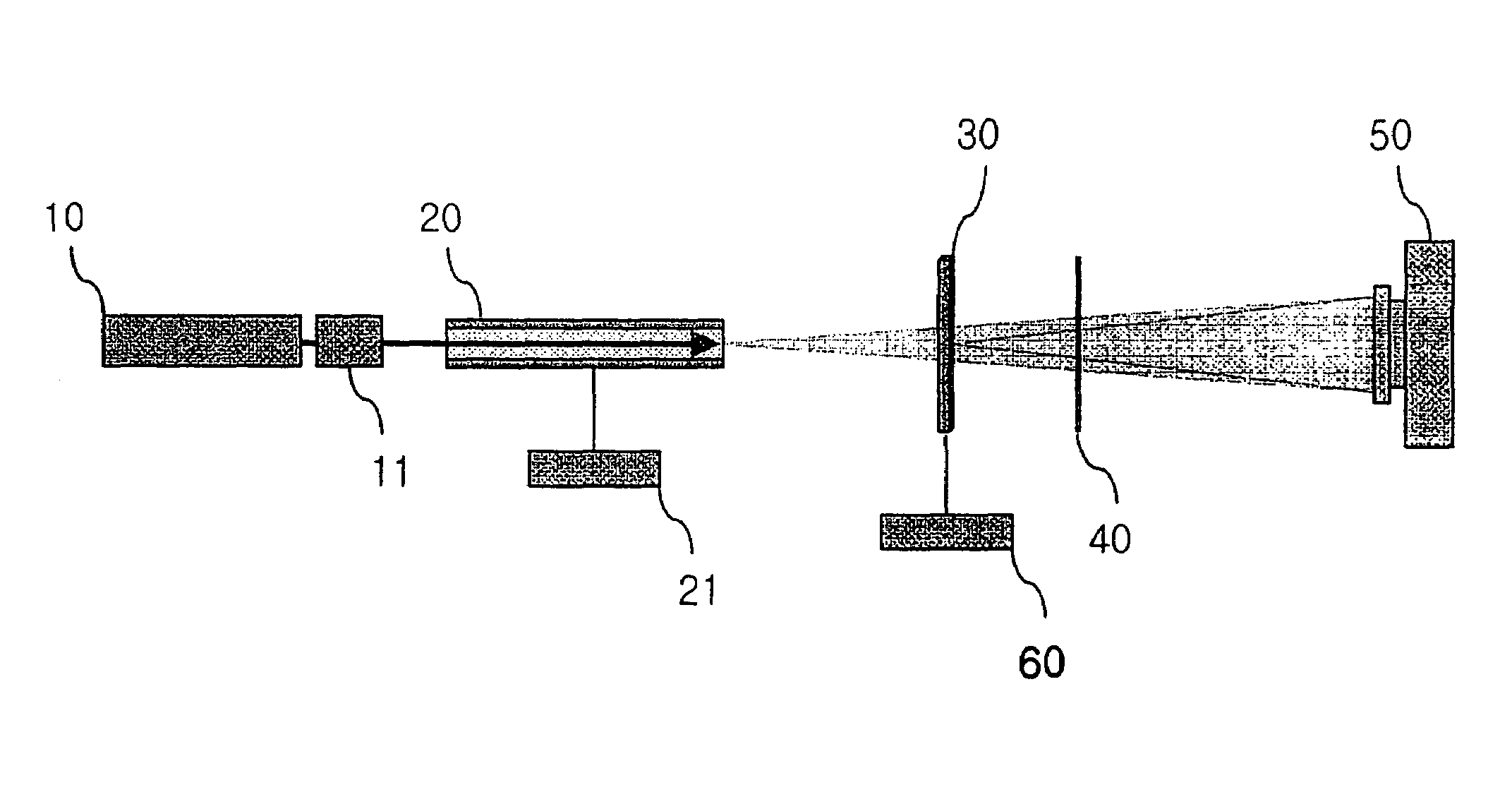
Point diffraction interferometer with enhanced contrast
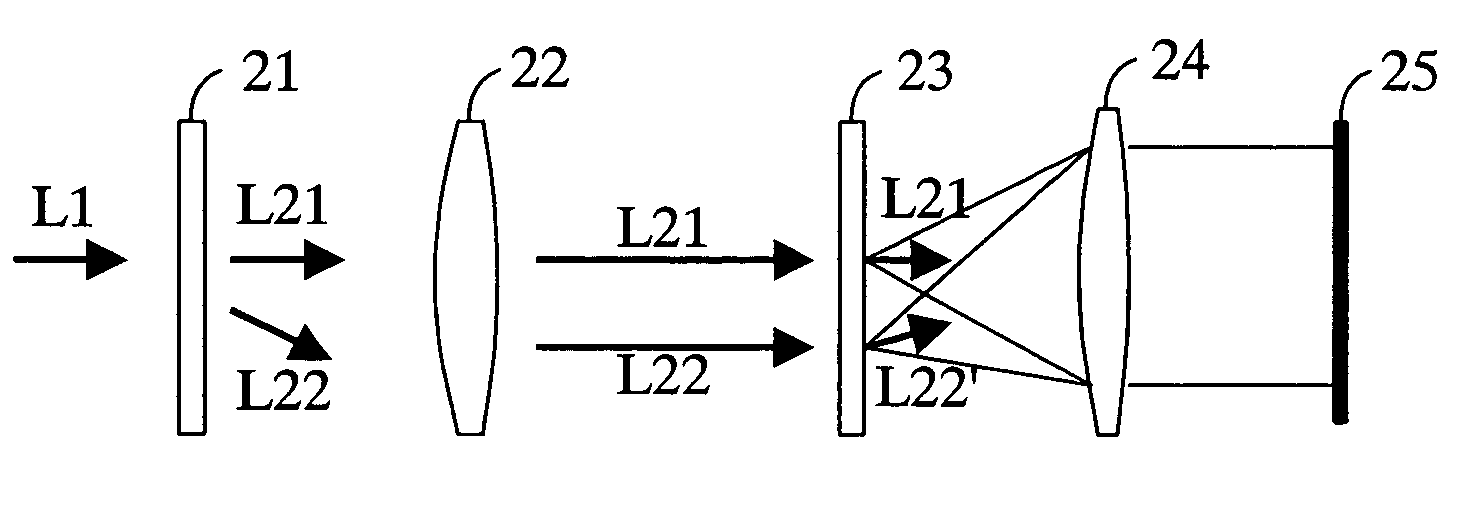
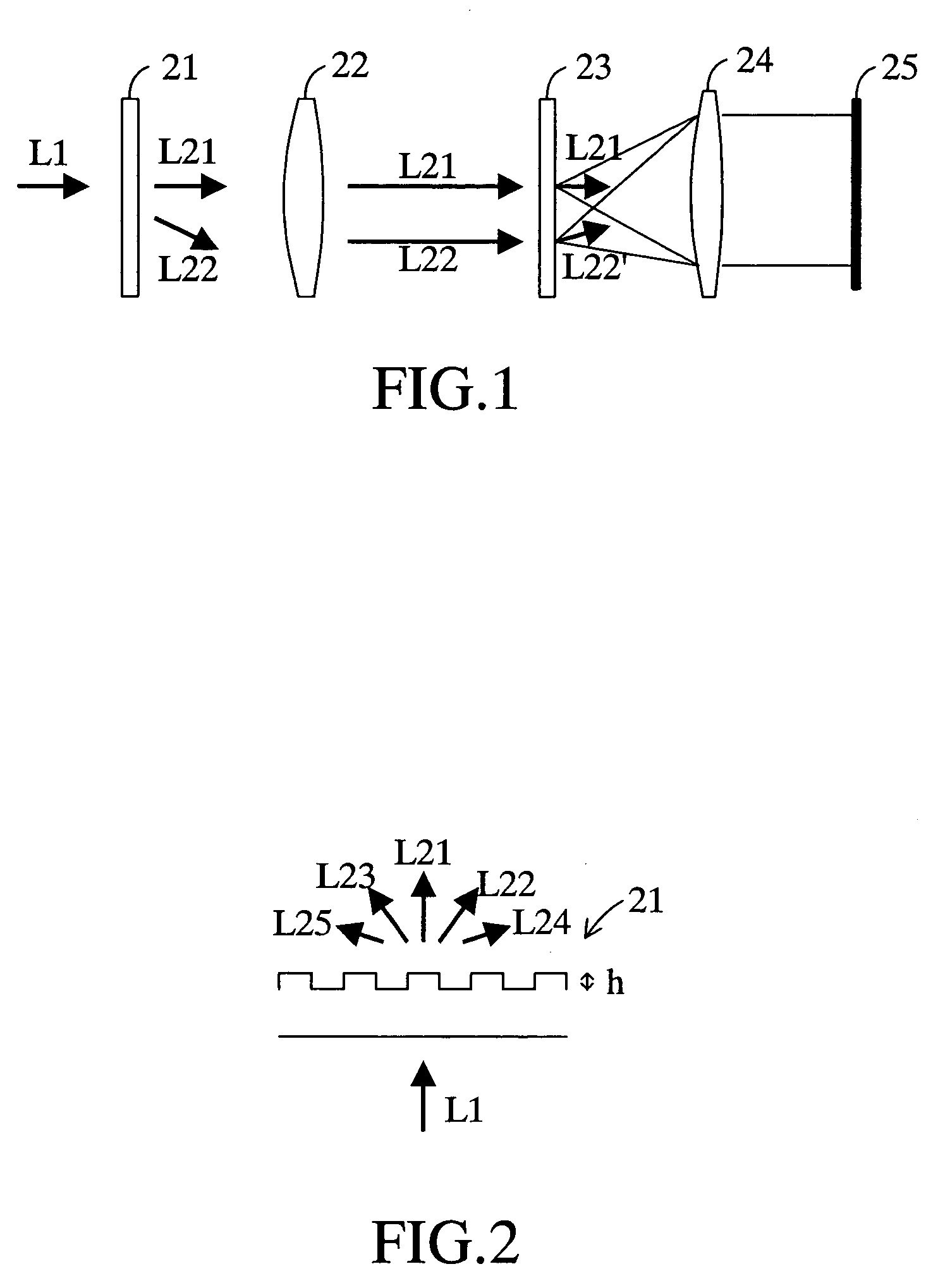
InactiveUS7095510B2Improve accuracyIncrease contrastOptical measurementsUsing optical meansZeroth orderPoint diffraction interferometer
The interferometer has a diffraction grating 21, a condenser lens 22, a transparent substrate 23, a field lens 24 and an imaging device 25 arranged in this order. The transparent substrate 23 is arranged at the position in the optical axis direction where both focal spots of a zeroth-order diffracted light L21 and a first-order diffracted light L22 are formed. Formed on the transparent substrate 23 is a circular opaque zone 23a whose central position is the central position of the focal spot of the first-order diffracted light L22. Formed at the center of the opaque zone 23a is a pinhole 23b whose central position is the central position of the focal spot of the first-order diffracted light L22. The contrast of the interference fringes observed on the image device 25 is enhanced by the optical interference between the first-order diffracted light L22 passing through the pinhole 23b and the zeroth-order diffracted light L21 passing through the transparent substrate 23.
Owner:PULSTEC IND
Device and method for measuring curvature radius of spherical mirror based on pinhole type point diffraction interferometer
InactiveCN104655053AAvoid damageAvoid synchronous measurementsUsing optical meansPoint diffraction interferometerNon destructive
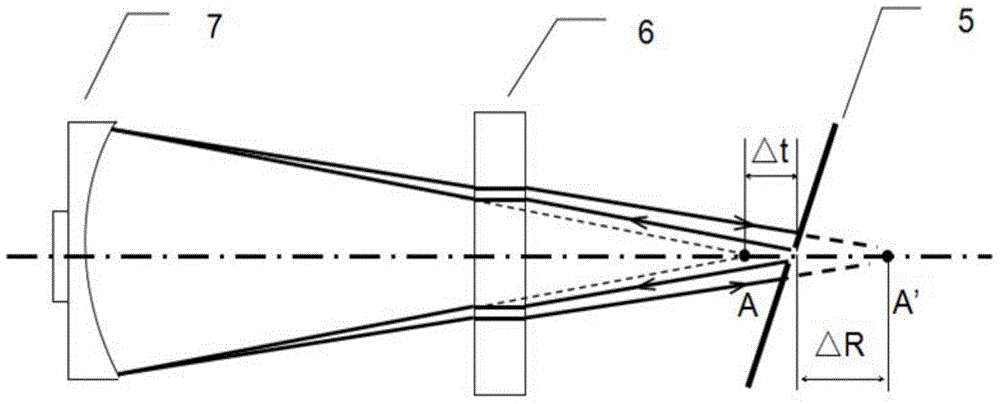
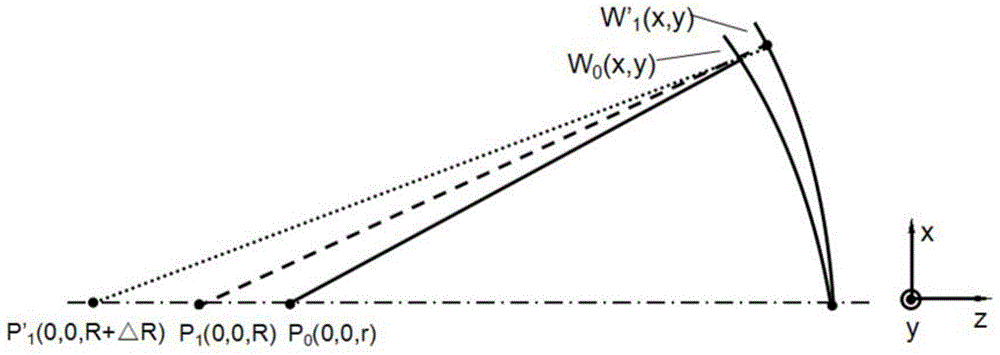
The invention discloses a device and method for measuring the curvature radius of a spherical mirror based on a pinhole type point diffraction interferometer. Double quantitative defocusing is realized through sequentially inserting two parallel flat plates with different thicknesses in an interfering cavity of the pinhole type point diffraction interferometer. When the parallel flat plates are not placed in a test optical path, wavefront data W0 are obtained through phase shifting measurement. After the two parallel flat plates with different thicknesses are respectively placed in the test optical path, two different wavefronts W1 and W2 are obtained through phase shifting measurement, and the calculating formula of the curvature radius of the spherical mirror is derived through the difference between the defocusing coefficients of the W1 and the W0, the difference between the defocusing coefficients of the W2 and the W0 and a Gaussian imaging formula. When the non-contact type measurement method is adopted, the damage of the surface of the spherical mirror is avoided, a feasible method is provided for the non-destructive measurement of the curvature radius of the spherical mirror with a large numerical aperture. Meanwhile, the method is suitable for the surface shape test of the spherical mirror with the large numerical aperture.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Point diffraction interferometer and exposure apparatus and method using the same
InactiveUS7304749B2Measure the optical performance of a target optical systemAccurate performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUsing optical meansPoint diffraction interferometerComputational physics
A point diffraction interferometer measures optical performance of a target optical system based on a light intensity distribution of an interference fringe through an interference between a wave front that passes the target optical system and a reference wave front generated from a pinhole, wherein the pinhole satisfies 1.05≦ellipticity≦1.16, where the ellipticity is defined as a diameter of a pinhole in a direction perpendicular to a linear polarization direction of light incident upon the pinhole, divided by a diameter of the pinhole in the linear polarization direction.
Owner:CANON KK
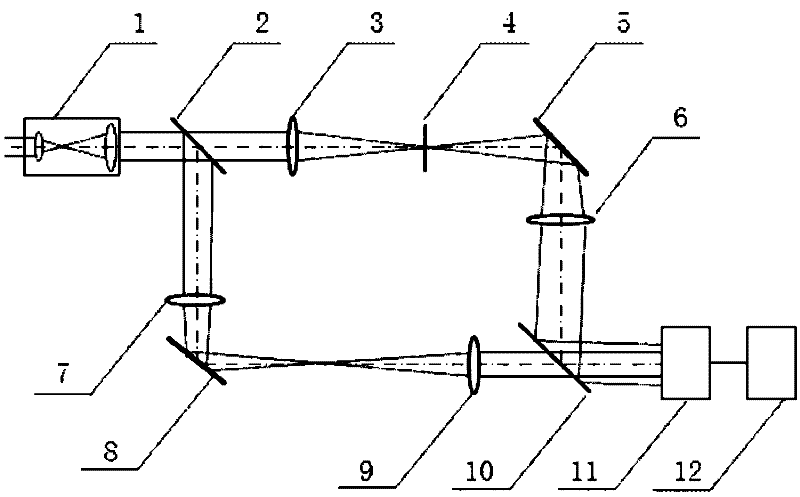
Mach-Zehnder point diffraction interferometer and method for reconstructing laser complex amplitudes
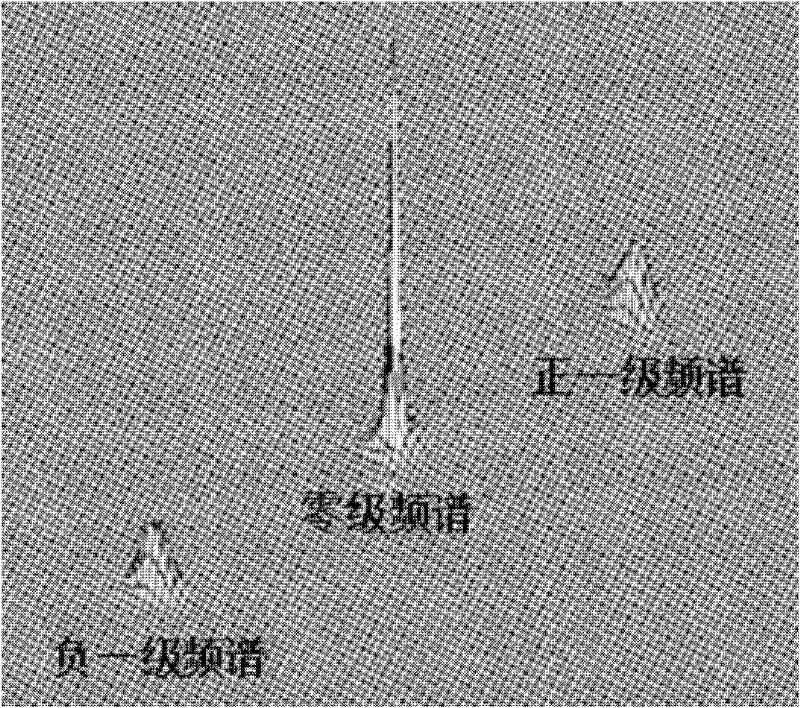
InactiveCN102230827AImprove detection accuracySolve the detection speed is slowOptical measurementsFrequency spectrumCharge couple device
The invention provides a Mach-Zehnder point diffraction interferometer, comprising an optical matching system, a first optical spectroscope, a second optical spectroscope, a first reflector, a second reflector, a first Fourier lens, a second Fourier lens, a third Fourier lens, a fourth Fourier lens, a pinhole filter, a CCD (charge coupled device) detector and a computer system. A method for reconstructing laser complex amplitudes comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out Fourier transform on collected carrier frequency interference fringes to acquire spectral distribution of the interference fringes; carrying out frequency-domain filtering to acquire zero-level frequency spectrum components and one-level frequency spectrum components, carrying out Fourier transform on one-level frequency spectrums to acquire wavefront phase distribution of lasers to be measured and amplitude modulation degree functions of the interference fringes, and carrying out Fourier transform on the zero-level frequency spectrums to acquire background light intensity of the interference fringes; and combining the amplitude modulation degree functions with the background light intensity to acquire amplitude distribution of lasers to be measured. The interferometer and the method provided by the invention are in no need of special reference light, and can be applied to detecting complex amplitudes of various lasers dynamically and evaluating light beam quality.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Octave type phase-shifting diffraction interferometer and measurement method used for detecting micro spherical surface profile
ActiveCN103344198ARealize secondary modulationTo achieve phase shift operationUsing optical meansOctavePrism
The invention discloses an octave type phase-shifting diffraction interferometer and measurement method used for detecting a micro spherical surface profile and relates to the field of optical detection. The problems that the single measurement and detection range is extremely narrow and the measurement accuracy is low in a traditional time domain phase-shifting interference measurement device are solved. The interferometer comprises a comprises a short coherence laser, a spatial filter, a beam splitter prism, a corner cube mirror, a polarization splitting prism, a lambda / 4 wave plate, a 4f beam-expanding system, a micro objective, a plane mirror, a cube-corner prism, a phase shifter, an optical fiber coupling mirror, a single mode optical fiber, an optical fiber collimating lens, a lambda / 2 wave plate, a polarization splitting prism, a polarizing film, an area array charge coupled device (CCD) and a computer. The phase shifter is controlled through the computer, so that the area array CCD acquires four interference patterns, the computer acquires a positioning relationship among interference images through the interference patterns, the initial phase difference which corresponds to each pixel point in an interference field is solved, the optical path difference is further solved, and the spherical morphology is measured. The interferometer is suitable for detecting the micro spherical surface profile.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Common-optical path polarization point diffraction phase-shift interference wavefront sensor
InactiveCN103245423AHigh precisionImprove spatial resolutionOptical measurementsOptical elementsWavefront sensorFrame time
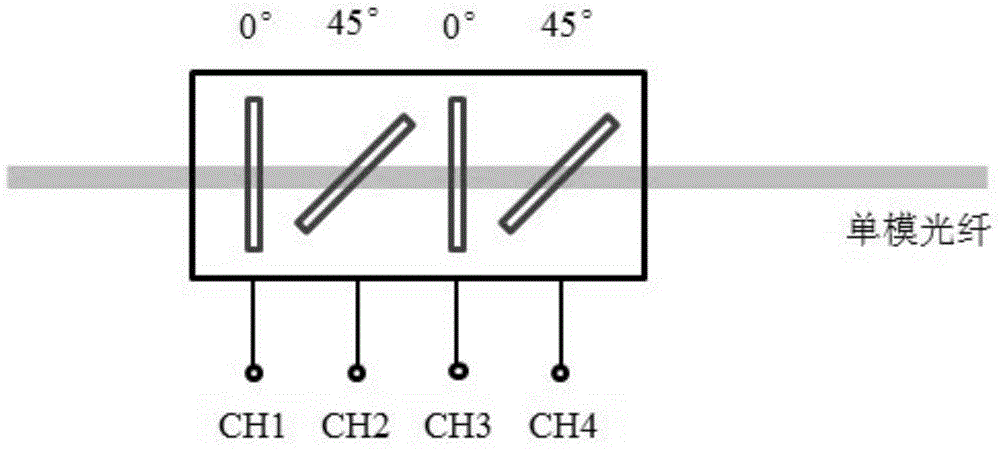
The invention relates to a common-optical path polarization point diffraction phase-shift interference wavefront sensor, which comprises a polaroid, a first double refraction lens, a second double refraction lens, a phase-shift interference system, a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) sensor and a computer, as well as a polarization PDI (Point-diffraction Interferometer) mask plate provided with a needle hole and additionally arranged at a confocal plane of the first and second double refraction lenses, wherein a linearly polarized light beam to be detected is divided into two beams by the first double refraction lens, E light is converged at the needle hole of the polarization PDI mask plate to be subjected to small hole diffraction so as to serve as reference light, and O light passes through the polarization PDI mask plate nearly without decrement to serve as testing light; the reference light and the testing light pass through the phase shift interference system to form a four-frame time or space phase shift interference figure; streak contrast gradient is adjusted through rotating the polaroid; and then a phase shift algorithm is adopted to re-establish a phase position of a wavefront to be detected. According to the invention, the wavefront sensor adopts a common-optical path, dispenses with special reference light, is strong in system stability and adjustable in streak contrast gradient, and is suitable for high-precision detection for dynamic and static stage of various wavefront phase positions.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF TECH
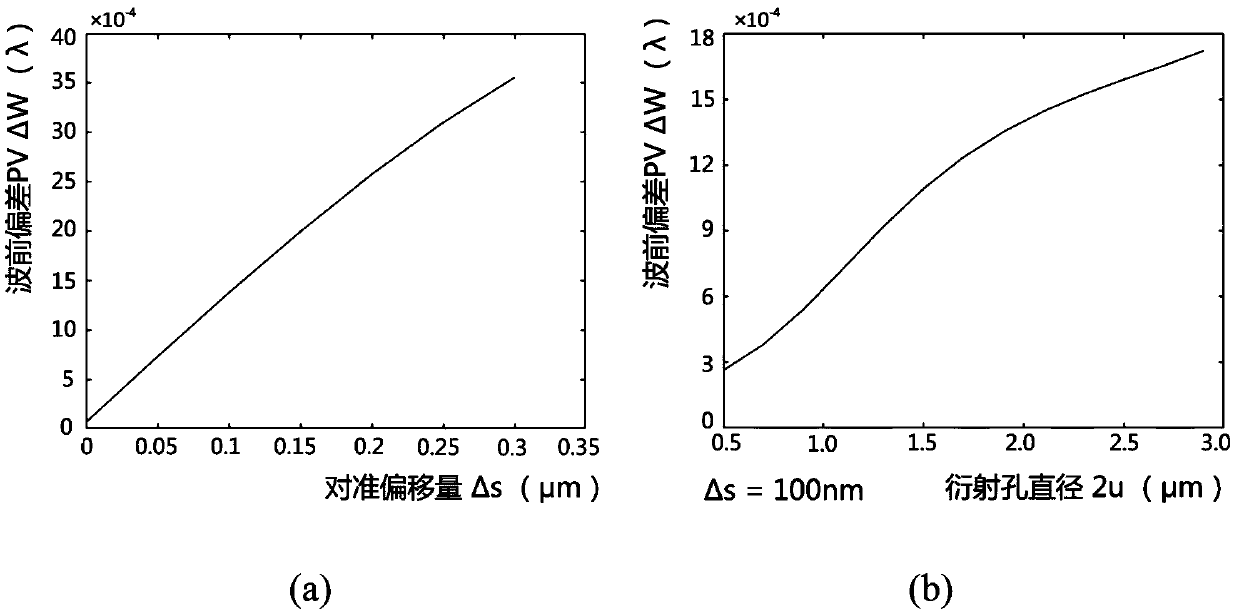
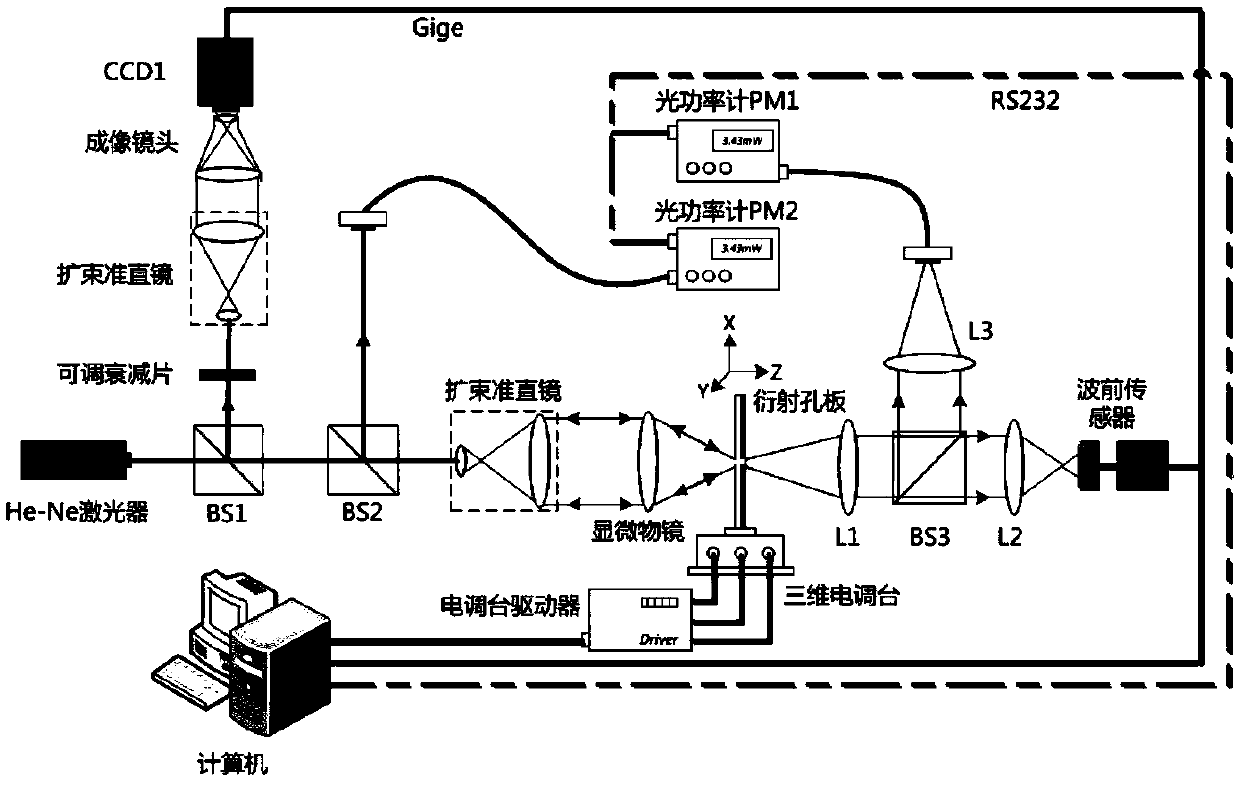
System and method for accurately calibrating optical path of point diffraction interferometer based on image information
ActiveCN109556531AAvoid damageRealize visualizationUsing optical meansOptical power meterWavefront sensor
The invention discloses a system and a method for accurately calibrating an optical path of a point diffraction interferometer based on image information. The system comprises spectroscopic prisms, abeam expanding collimation system, a diffraction orifice plate, a wave-front sensor, lenses, an optical power meter, three-dimensional precision electronically controlled translation stage and driverthereof, a CCD1 (charge-coupled device), and a computer. The method comprises the following steps of: analyzing and obtaining a mathematical relationship between an alignment error and a diffraction wave-front deviation by using the Rayleigh-Sommerfeld diffraction theory; designing an accurate optical path calibration system according to requirements to obtain a spot-hole alignment image and lightintensity before and after the diffraction orifice plate; then analyzing and measuring alignment deviation information through an image processing algorithm to establish a mathematical model betweenthe measurement quantity and the control quantity; and finally, achieving accurate calibration according to a system implementation principle. According to the system and the method for accurately calibrating the optical path of the point diffraction interferometer based on the image information, the precise alignment of the diffraction holes and the spot in the visual environment is realized, andthe influence of the alignment deviation on the detection precision of the point diffraction interferometer to some extent is eliminated. The system and the method have characteristics of high precision and high efficiency, and reduce the damage of the laser to the vision of operators during experimental operation.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
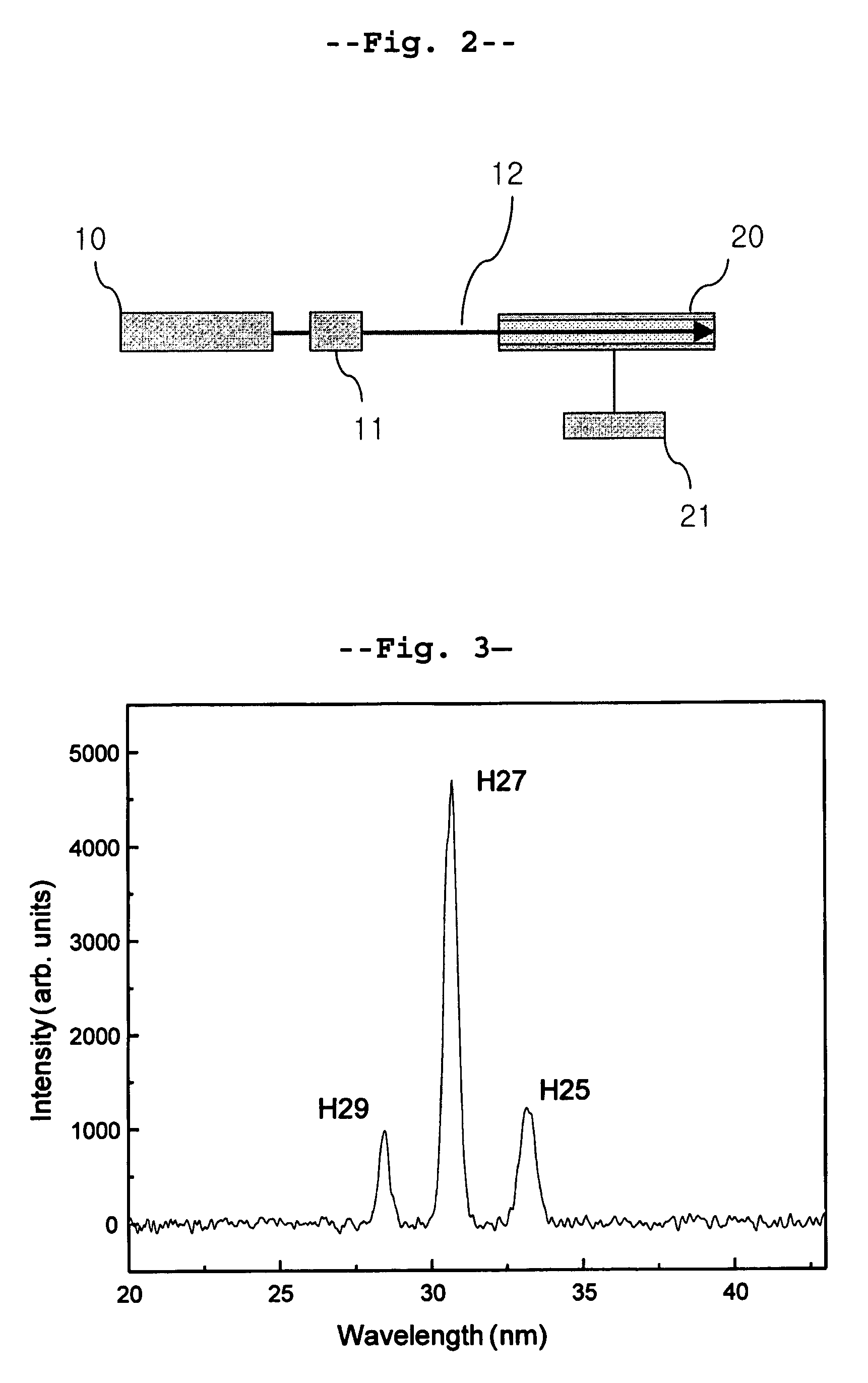
Apparatus and method for generating high-order harmonic X-ray, and point-diffraction interferometer using high-order harmonic X-ray
InactiveUS6968038B2Reduce intensityImprove fluencyWave amplification devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionPoint diffraction interferometerHigher order harmonics
Disclosed herein is a point-diffraction interferometer which can inspect a surface quality of an optical system for extreme ultraviolet lithography using a high-order harmonic X-ray source with excellent coherence, and an apparatus and method for generating a high-order harmonic X-ray. The present invention uses a high-order harmonic X-ray beam as a coherence light source, thus remarkably reducing the size of an apparatus for generating a light source to approximately 1 / 100 of a device using a light source generated in a conventional synchrotron. Further, the present invention simplifies the construction of an interferometer by employing a thin foil in which a pinhole is formed through a drilling technique using high power femtosecond laser, thus increasing the industrial utility of the interferometer.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Digital phase shift point diffraction interferometer and optical system wave aberration measuring method
ActiveCN105092056APrecise phase shiftEasy to phase shiftOptical measurementsTesting optical propertiesSpatial light modulatorDiffraction order
The invention relates to a digital phase shift point diffraction interferometer and an optical system wave aberration measuring method. The interferometer comprises a light source, a small-hole mask, a first spatial light modulator, a second spatial light modulator, a two dimension photoelectric detector and a computer, wherein the first spatial light modulator is set as a raster through the computer, and is used as a splitter; the second spatial light modulator is set as a pin hole window mask, and is used as a filter for filtering diffraction orders except 0 order and +1 (or -1) order to enable the 0-order light to realize diffraction production through the pin hole to generate a quasi-ideal spherical wave so as to use the quasi-ideal spherical wave as the reference light wave; the +1 (or -1) order light is used as the object light wave through the window; then interference occurs between the reference light wave and the object light wave so that an interferogram is obtained; and the optical system wave aberration to be measured can be extracted from the interferogram. For the digital phase shift point diffraction interferometer, the distance among image plane convergent points for the object light wave and the reference light wave is adjustable, and great interference fringe density can be realized without reducing the interference fringe contrast.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
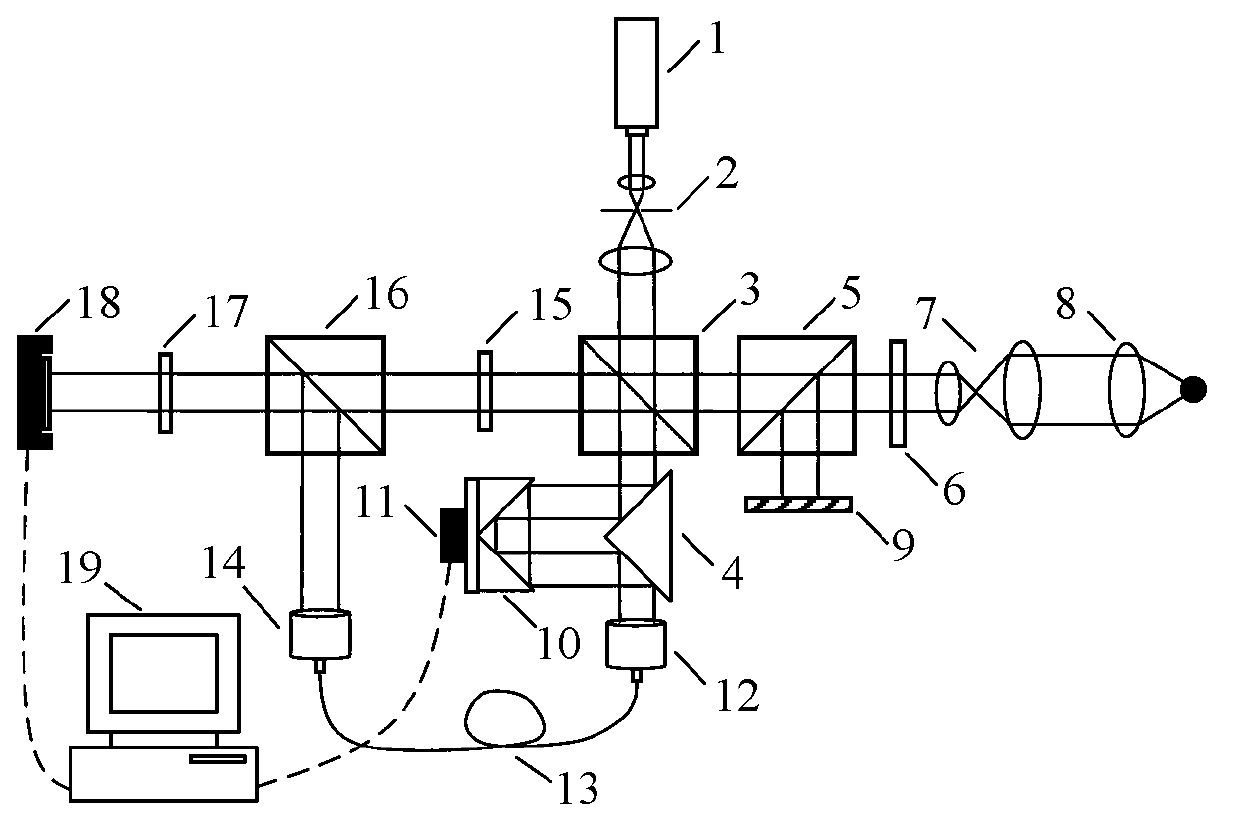
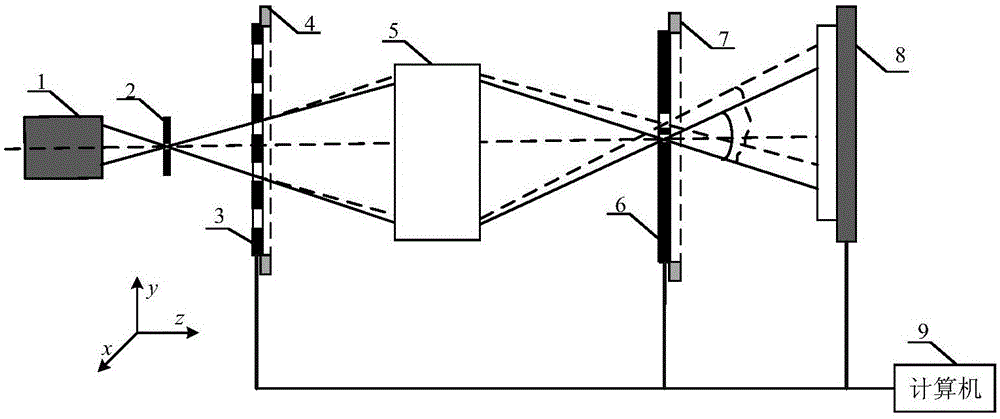
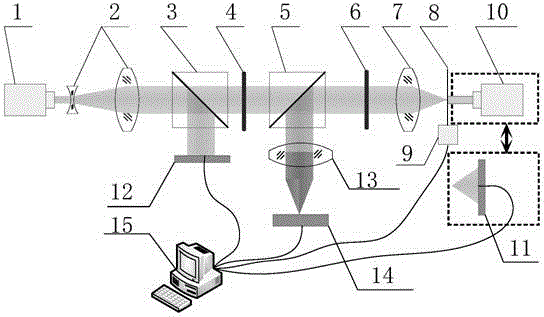
Device and method for pinhole alignment of point diffraction interferometer
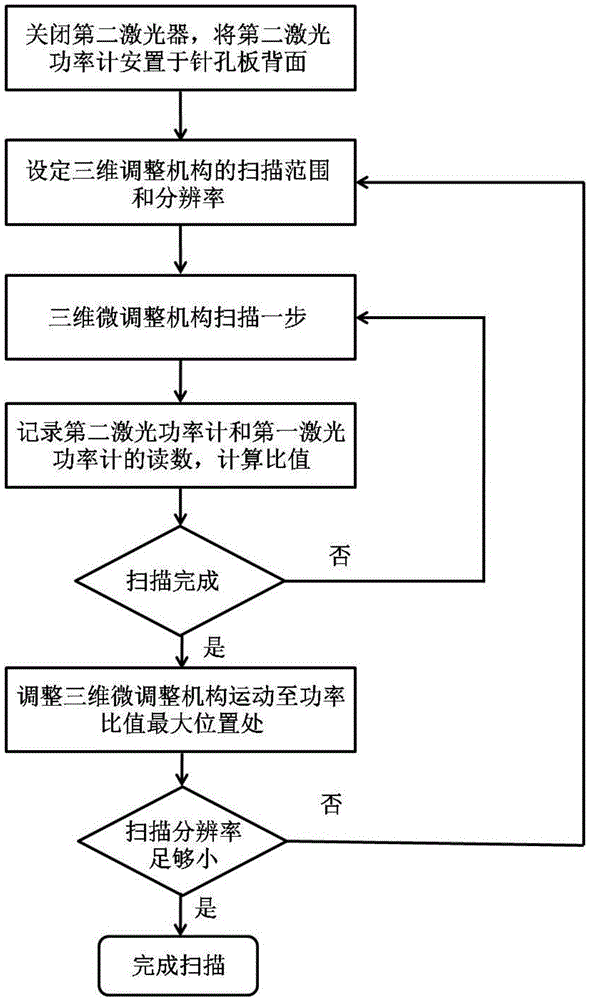
The invention provides a device for pinhole alignment of a point diffraction interferometer. The device comprises a first laser device, laser beam expanders, a first beam splitting prism, a half-wave plate, a second beam splitting prism, a quarter-wave plate, a focusing mirror, a pinhole plate, a three-dimensional adjusting mechanism, a second laser device, a second laser power meter, a first laser power meter, a rear group of lenses for imaging, a CMOS camera and a computer. The invention further provides a method for pinhole alignment of the point diffraction interferometer. The method comprises the steps of rapid coarse alignment and precise alignment, the coarse alignment process is intuitive, convenient and rapid, the precise alignment process can achieve0.1 mu m precision alignment by just two rounds of scanning, and the method has the advantages of short time consumption and high precision.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Variable-resolution phase unwrapping method based on point diffraction interferometer
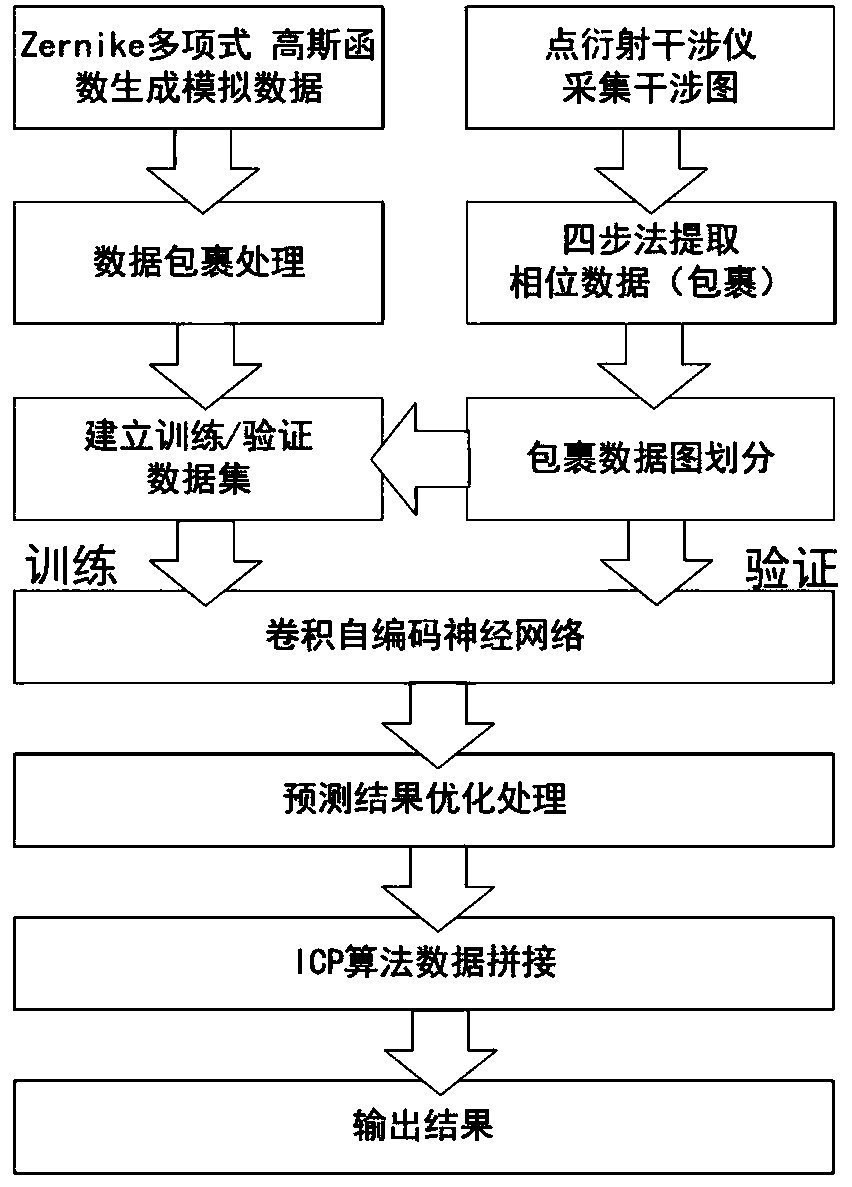
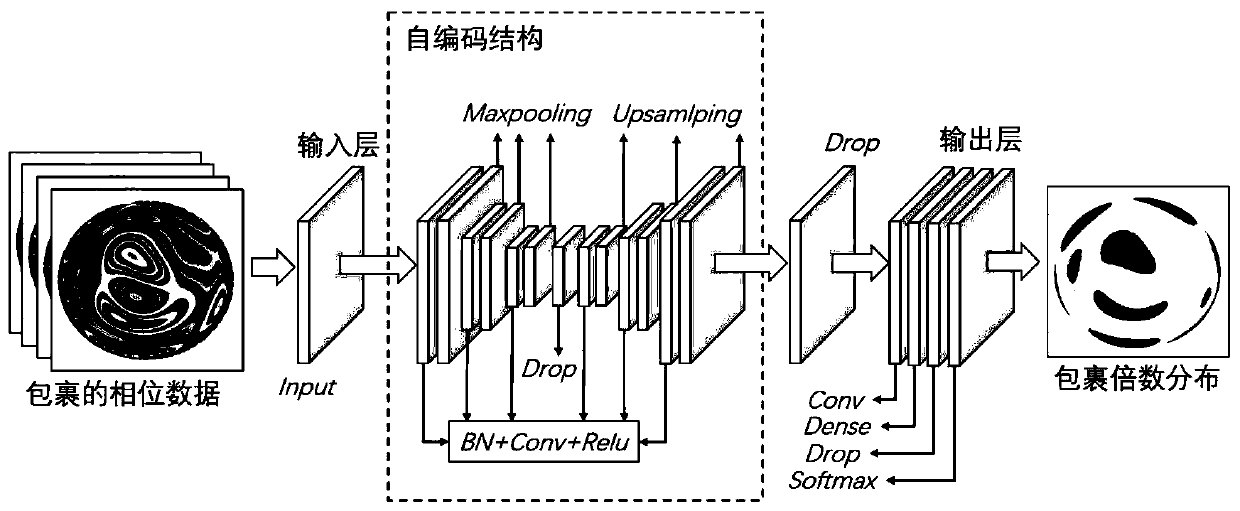
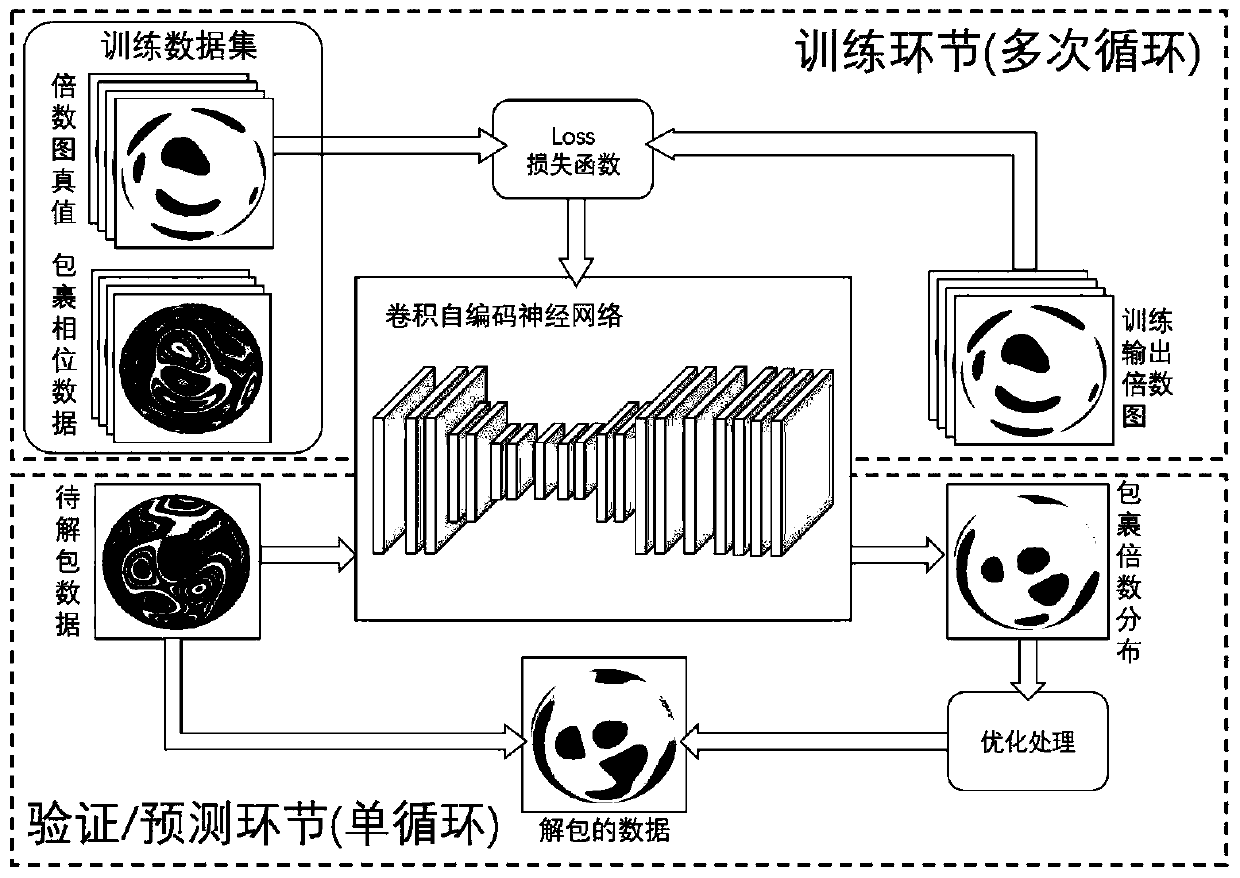
ActiveCN111561877ARealize splicingHigh precisionUsing optical meansNeural architecturesPoint diffraction interferometerData set
The invention discloses a variable-resolution phase unwrapping method based on a point diffraction interferometer. The method comprises the following steps: generating network model training and verification data by actually acquiring by the interferometer; establishing a training / verification data set after carrying out wrapping processing, and extracting interferogram phase data by adopting a four-step phase shift method; establishing a convolutional self-encoding neural network model, inputting the training data into the model, iterating the training network for multiple times until the network is in an optimal state, and then predicting to-be-processed data acquired by the instrument; carrying out region division on a wrapped phase diagram according to the resolution before prediction,and carrying out full-width unpacking through a subsequent splicing strategy; taking the original wrapping phase as a reference, extracting data jump points to obtain a wrapping region contour, usingan initial prediction result, denoising by taking the region as a unit, and optimizing the prediction result to improve the unpacking accuracy; and splicing a plurality of groups of adjacent phase data by using an Iterative Closest Point algorithm to realize adjustable resolution. And the unpacking precision is high, the universality is strong, and the real-time processing capability is strong.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Two-channel point-diffraction interferometer
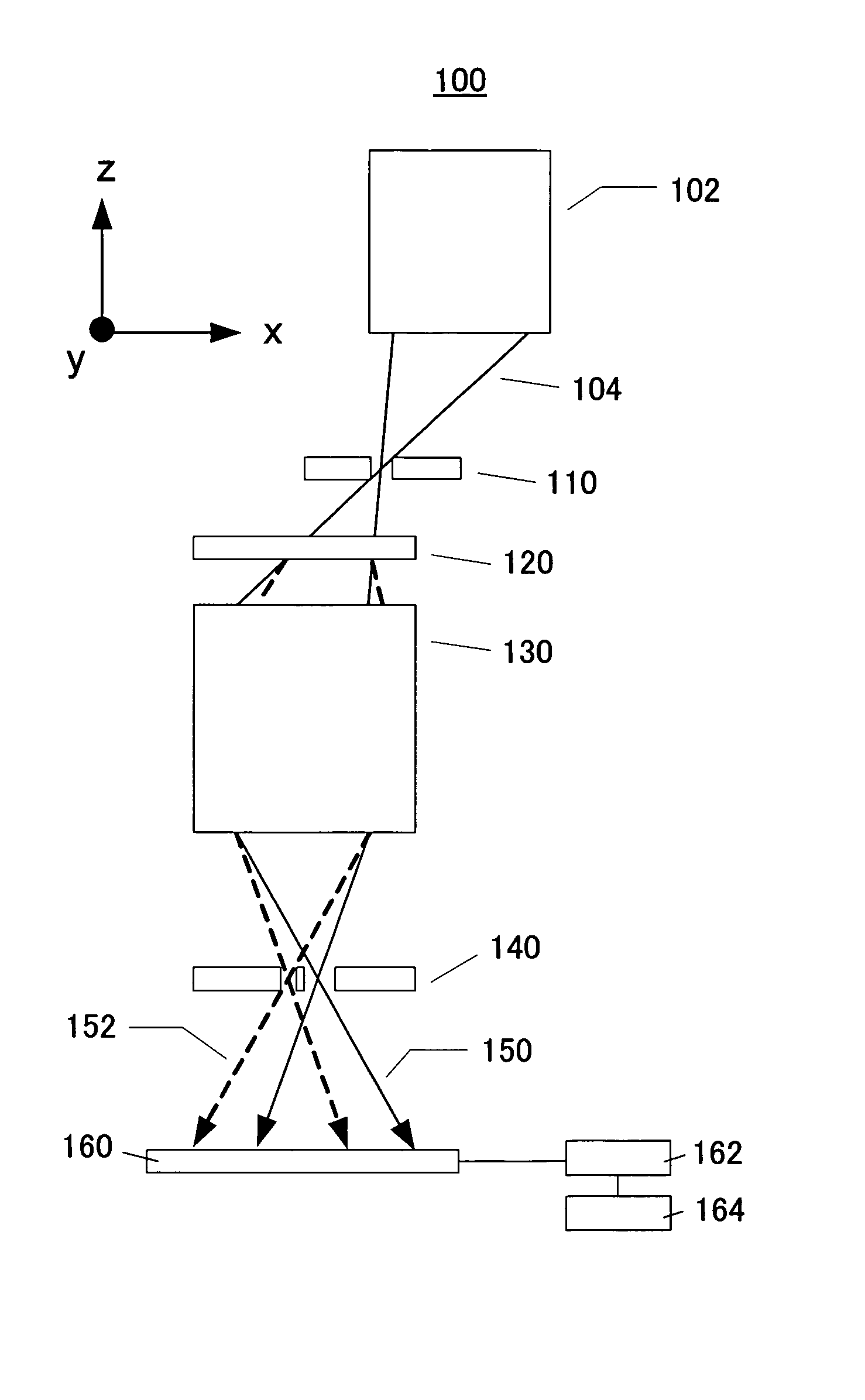
ActiveUS20170191820A1Improve stabilityReduce vibration sensitivityInterferometersUsing optical meansPoint diffraction interferometerBeam splitter
The present invention is related with the two-channel point-diffraction interferometer for testing the optical systems or optical elements. The two-channel point-diffraction interferometer comprising a laser source inducing a linearly polarized laser beam which is divided by a beam splitter to a working channel and to a reference channel whereas the one half of light as working channel is directed from the first collimator to the working collimator by a first single-mode optical fibre to keep polarization of light unchanged, and another half of light as reference channel is directed from the second collimator to the reference collimator by a second single-mode optical fibre to keep polarization of light unchanged.
Owner:DIFROTEC OU
Point diffraction interferometer and exposure apparatus and method using the same
InactiveUS20050190377A1Measure the optical performance of a target optical systemAccurate performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUsing optical meansPoint diffraction interferometerEllipse
A point diffraction interferometer measures optical performance of a target optical system based on a light intensity distribution of an interference fringe through an interference between a wave front that passes the target optical system and a reference wave front generated from a pinhole, wherein the pinhole satisfies 1.05≦ellipticity≦1.16, where the ellipticity is defined as a diameter of a pinhole in a direction perpendicular to a linear polarization direction of light incident upon the pinhole, divided by a diameter of the pinhole in the linear polarization direction.
Owner:CANON KK
Full visual field low frequency heterodyne point diffraction interferometer
ActiveCN105674875AHigh measurement accuracyIncreased measurement numerical aperture rangeUsing optical meansFiberLight spot
The invention discloses a full visual field low frequency heterodyne point diffraction interferometer. An acousto-optic frequency shifter is adopted to shift phase by heterodyne interference so that moving members of the interferometer are avoided, and measurement accuracy is further increased. The interferometer has good anti-interference performance, reduced development difficulty and cost, and compared with mechanical drive, the interferometer has more obvious advantages. Two optical fibers are used to respectively generate measuring light and reference light instead of part of emitting light; the interferometer combines the advantages that optical fiber point diffraction light is easy to access and flexible to adjust; compared with typical optical fiber point diffraction interferometer system, the measurement value aperture diameter range is increased. Besides, beam combination of point diffraction measurement light and reference light is realized by gluing angle ground fiber tips with light splitting plain films, wherein the beam combination is realized through outer sides of the semi-transparent and semi-reflection plain films, interference of diffraction opening edges on wave front of convergence light spots is avoided. The interferometer is easy to operate and has low cost.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
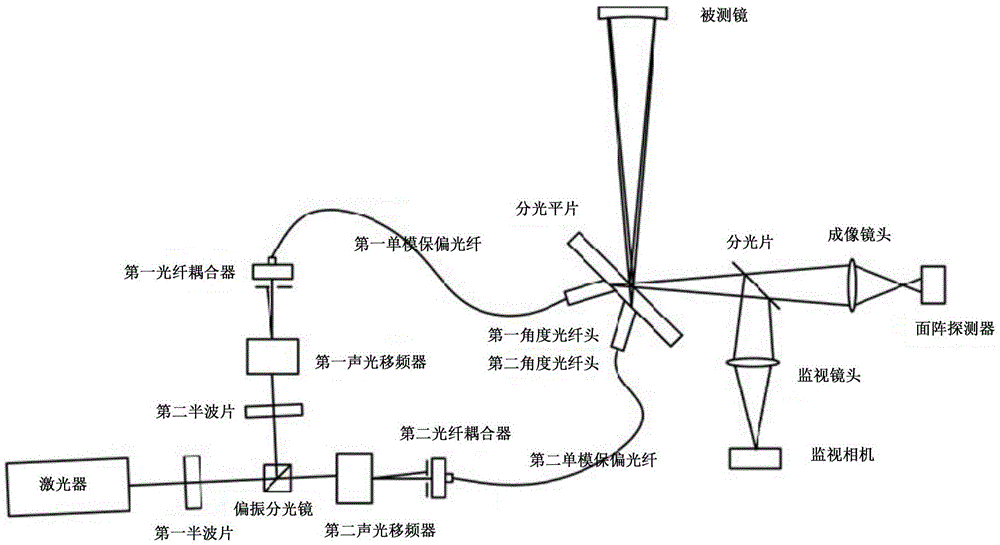
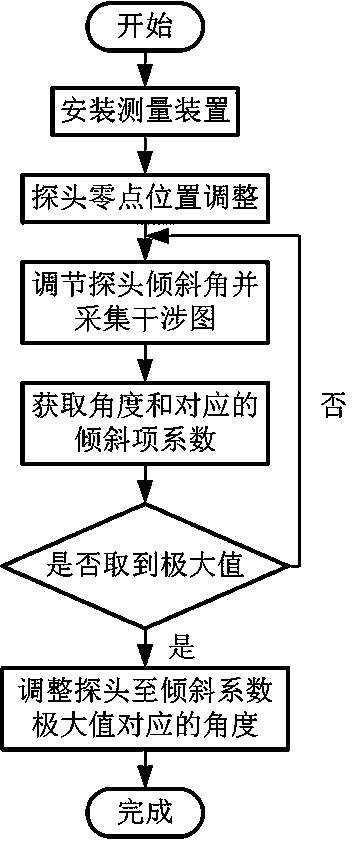
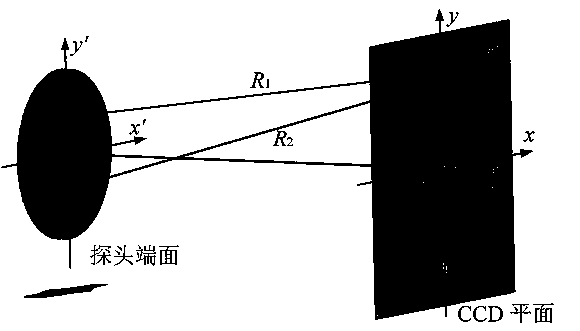
Method for leveling end surface of probe of three-coordinate measuring device based on point diffraction interferometer
ActiveCN109341523AFast and precise reconstruction resultsSatisfy the solution requirementsUsing optical meansPoint diffraction interferometerMeasurement device
The invention provides a method for leveling the end surface of a probe of a three-coordinate measuring device based on the point diffraction interferometer, and relates to the technical field of measurement. The method for adjusting zero position of the probe based on the wave surface symmetry is adopted. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring the initial wave surface data by a detector; rotating the probe by 180 degree, and panning the probe to acquire the wave surface again; making the difference with the initial wave surface data after rotating the wave surface data by 180degree; panning the probe to the middle position, which is the zero position of the probe, between the initial position and the position in which the difference is the minimum value, and adjusting thetilt angle of the probe and obtaining the wave surface data; and fitting the wave surface by using the Zernike polynomial fitting method to obtain a x-y direction tilt term coefficient, and adjustingthe angle to which the coefficient is the maximum value to achieve leveling the end surface of the probe. According to the method for leveling the end surface of the probe of the three-coordinate measuring device based on the point diffraction interferometer, the technical problem of the measurement accuracy is affected in the prior art because the end face of the probe is difficult to level withrespect to the detecting surface. The beneficial effect of the invention is as follows: the state of the end face of the probe is determined, and the requirements for solving a measurement model is satisfied, so that the reconstruction result of the three-dimensional coordinate is more accurate and can be obtained more quickly.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV +1
Dynamic point diffraction interferometer on the basis of micro-polaroid array
InactiveCN105300272ATo achieve the effect of real-time detectionReduced vibration requirementsUsing optical meansPoint diffraction interferometerPhase shifted
The present invention discloses a dynamic point diffraction interferometer on the basis of a micro-polaroid array. The dynamic point diffraction interferometer on the basis of micro-polaroid array comprises: a laser, a beam spread collimation system, a polarizer, a first quarter wave plate, a focusing lens, a diffraction template located at the focus of the focusing lens, a second quarter wave plate in a diffraction light path, a measured piece, an imaging lens, a micro-polaroid array and a photosensitive element. A part of light diffracted in the small hole of the diffraction template reaches the measured piece through the second quarter wave plate, and the light reflected by the measured piece is reflected by the diffraction template through the second quarter wave plate and is received by the photosensitive element through the imaging lens and the micro-polaroid array; and the other part of the light diffracted in the small hole of the diffraction template is directly received by the photosensitive element through the imaging lens and the micro-polaroid array. One time exposure of the dynamic point diffraction interferometer on the basis of the micro-polaroid array may obtain four phase shift images, so that real time detection effect is reached; and devices for generating phase shift are simplified, and the vibration resistance requirement is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Polarization control method used in fiber point-diffraction interferometer wave surface reference source
ActiveCN104536146ALess freedomFast regulationPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusOptical power meterBeam polarization
The invention relates to a polarization control method used in a fiber point-diffraction interferometer wave surface reference source. The polarization control method includes the steps that optical fiber diffraction spherical wave is collimated through a high-quality collimator lens, and then passes through a rotatable polarizing film placed on a single-axis displacement platform, a double-layer density disk located in a through hole, a pentaprism, and an optical power meter, wherein the pentaprism and the optical power meter are placed on the single-axis displacement platform, and the polarization state of an initial light beam can be determined by theoretical calculation through the rotatable polarizing film; the rotatable polarizing film is then moved out of the light path through the single-axis displacement platform, the double-layer density disk is turned to be in the circularly polarized light detection state, namely, a 1 / 4 wave plate and a polarizing film, the control voltages of two control channels of a polarization controller are calculated through the polarization state of the initial light beam, which is obtained in the previous step, and then the circular polarization state is obtained through fine adjustment and observation of the optical power meter reading till extinction. The system has the advantages of being capable of achieving quick adjustment of the circular polarization state under the premise that extra error is not introduced to the wave surface reference source and effectively improving contrast ratio and detection precision of interference fringe.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com