Common-optical path polarization point diffraction phase-shift interference wavefront sensor
A wavefront sensor, point diffraction phase-shifting technology, applied in optical radiation measurement, instruments, optics, etc., can solve the problem of strong resistance to environmental vibration and atmospheric interference, test light waves and reference light waves do not share the same path, and difficulty in PDI mask processing Advanced problems, to achieve the effect of large measurement dynamic range, strong anti-atmospheric interference and environmental vibration capabilities, and simple wavefront reconstruction algorithm
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
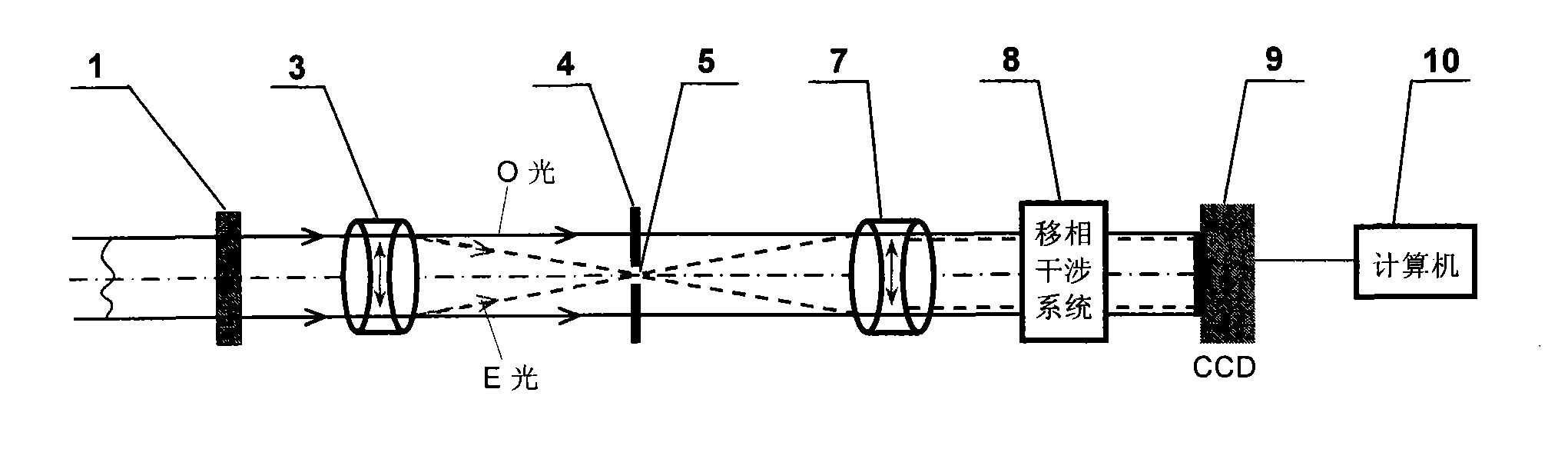
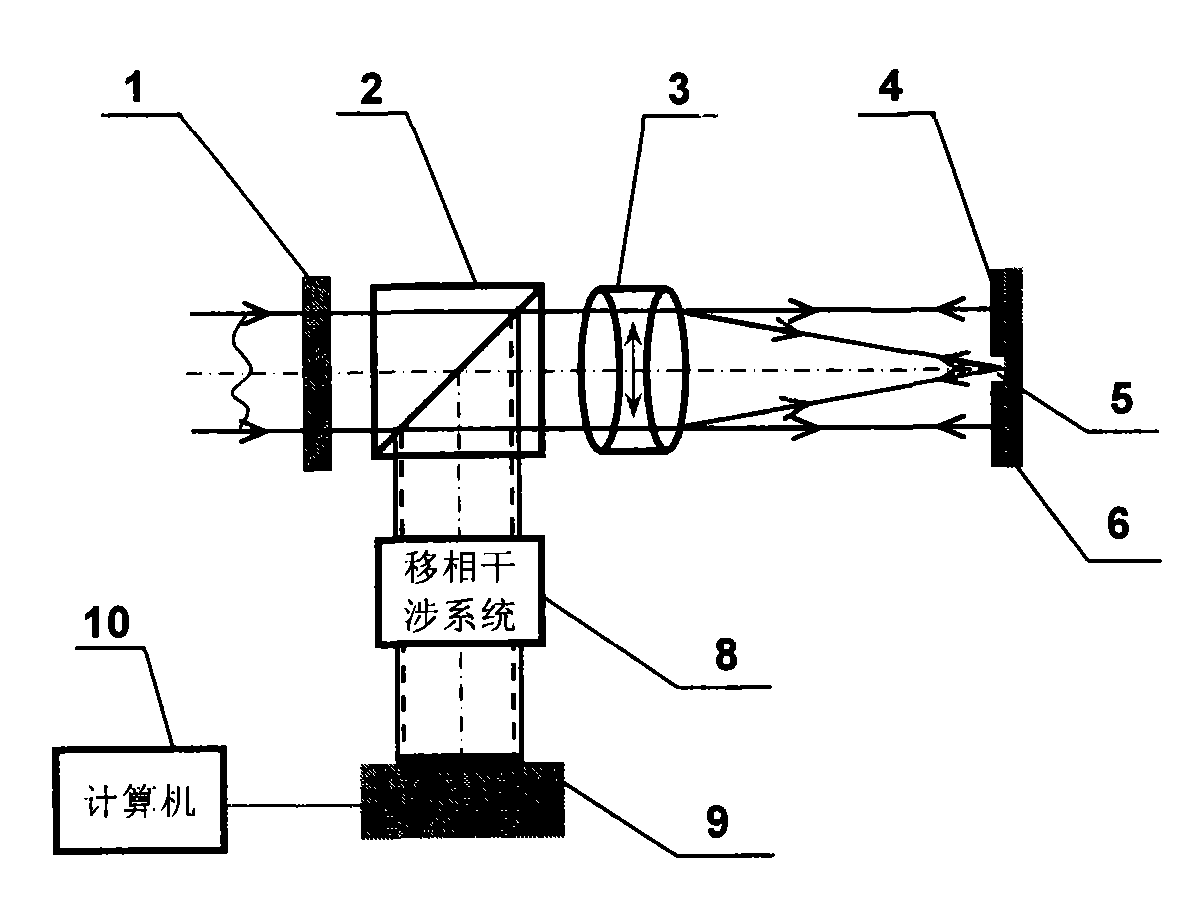
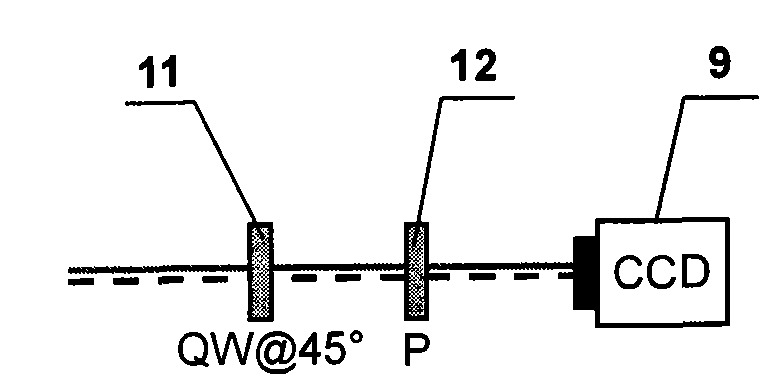
[0024] The common optical path polarization point diffraction phase-shifting interference wavefront sensor of the present invention, such as figure 1 As shown, it includes a polarizer 1, a first birefringent lens 3 and a second birefringent lens 7, a phase-shifting interference system 8, a CCD sensor 9, and a computer 10; A polarized PDI mask 4 containing a pinhole 5 is added, the vibration direction of which is perpendicular to the vibration direction of the converged light beam passing through the first birefringent lens 3 . The first birefringent lens 3 and the second birefringent lens 7 are a symmetrical birefringent triplet lens, composed of a calcite biconcave lens located in the middle and two glass biconvex lenses, and the optical axis of the calcite is located at the lens plane Inside, the focal points of the two lenses coincide and the directions of the fast axes are parallel; the birefringent lenses 3 and 7 can divide a beam of linearly polarized parallel beams into...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com