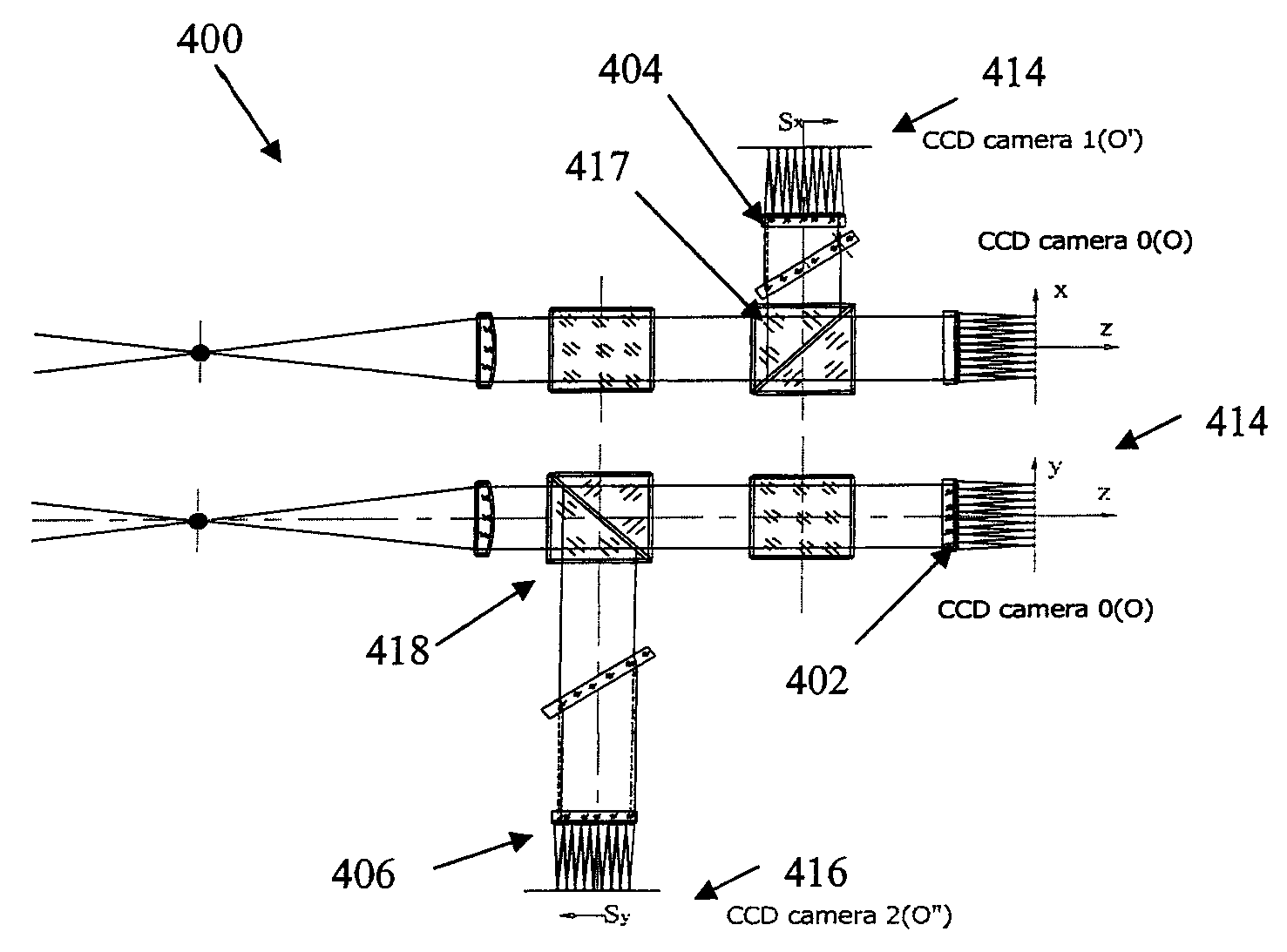
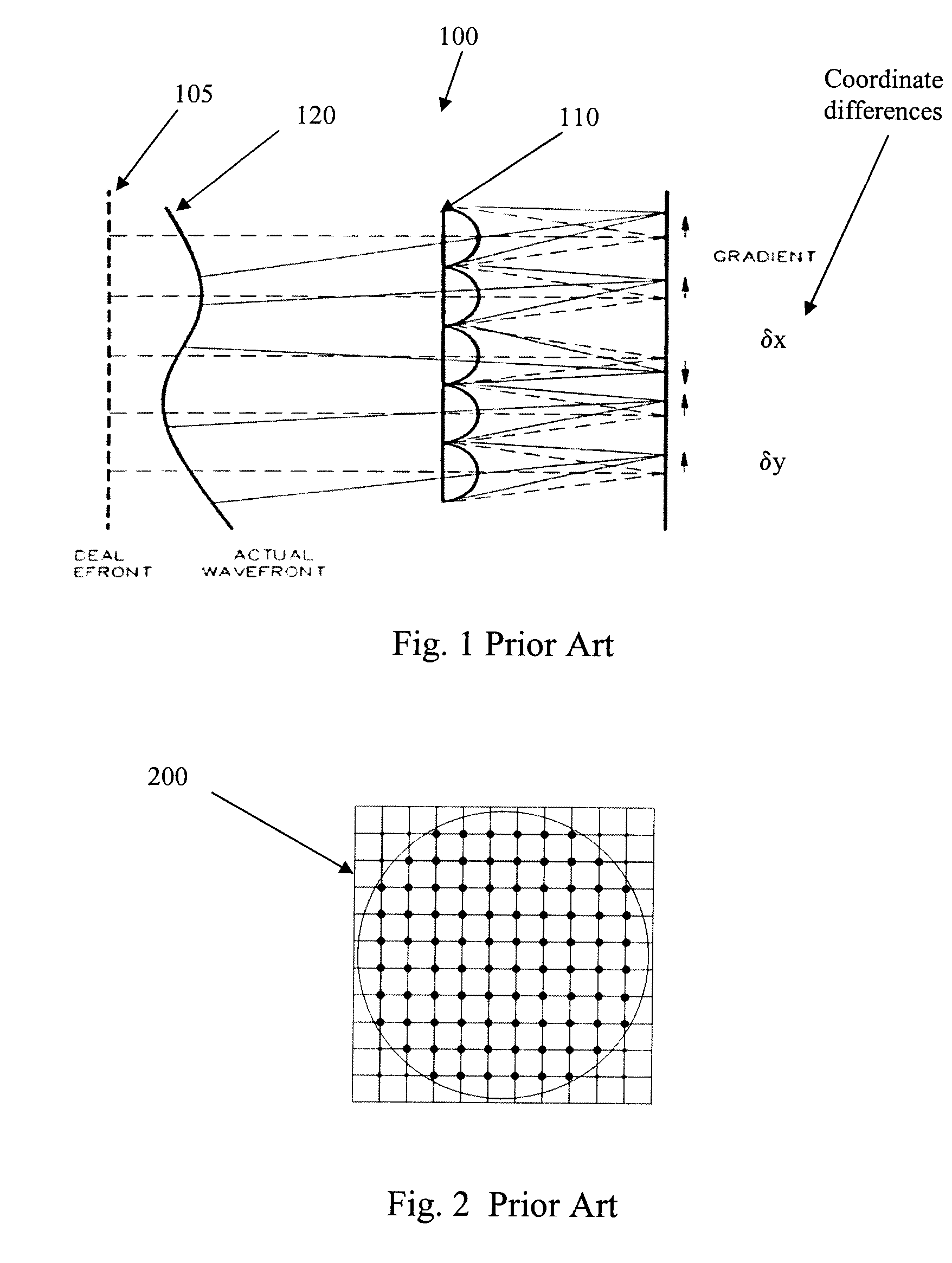
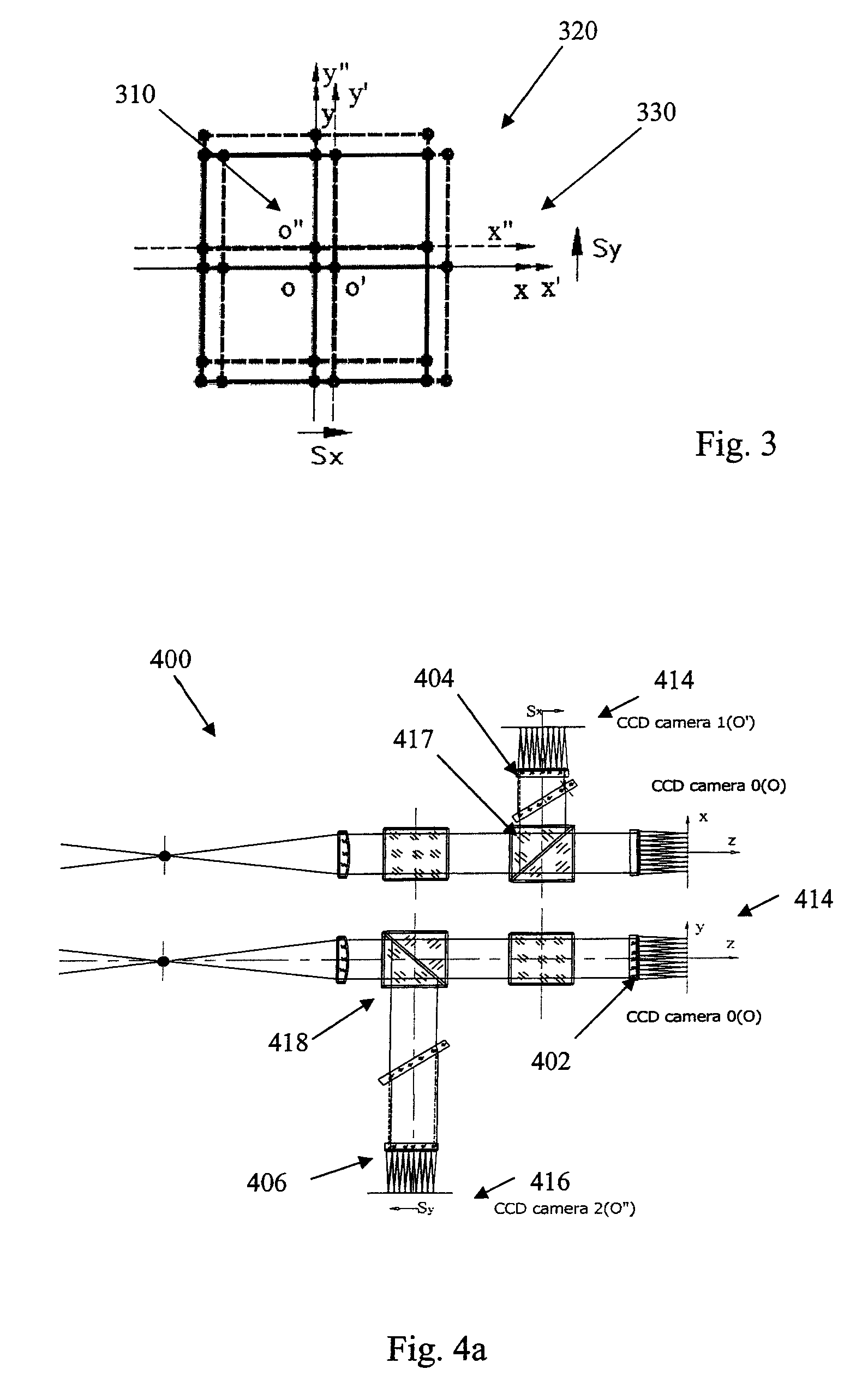
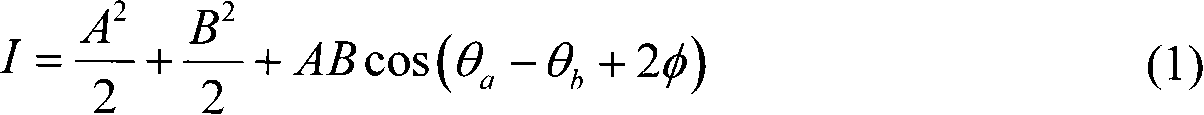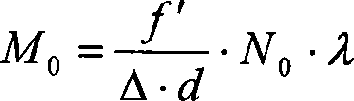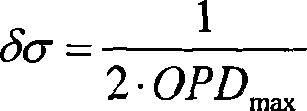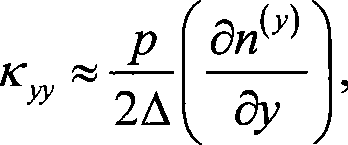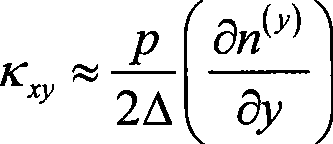Patents
Literature
146 results about "Shearing interferometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
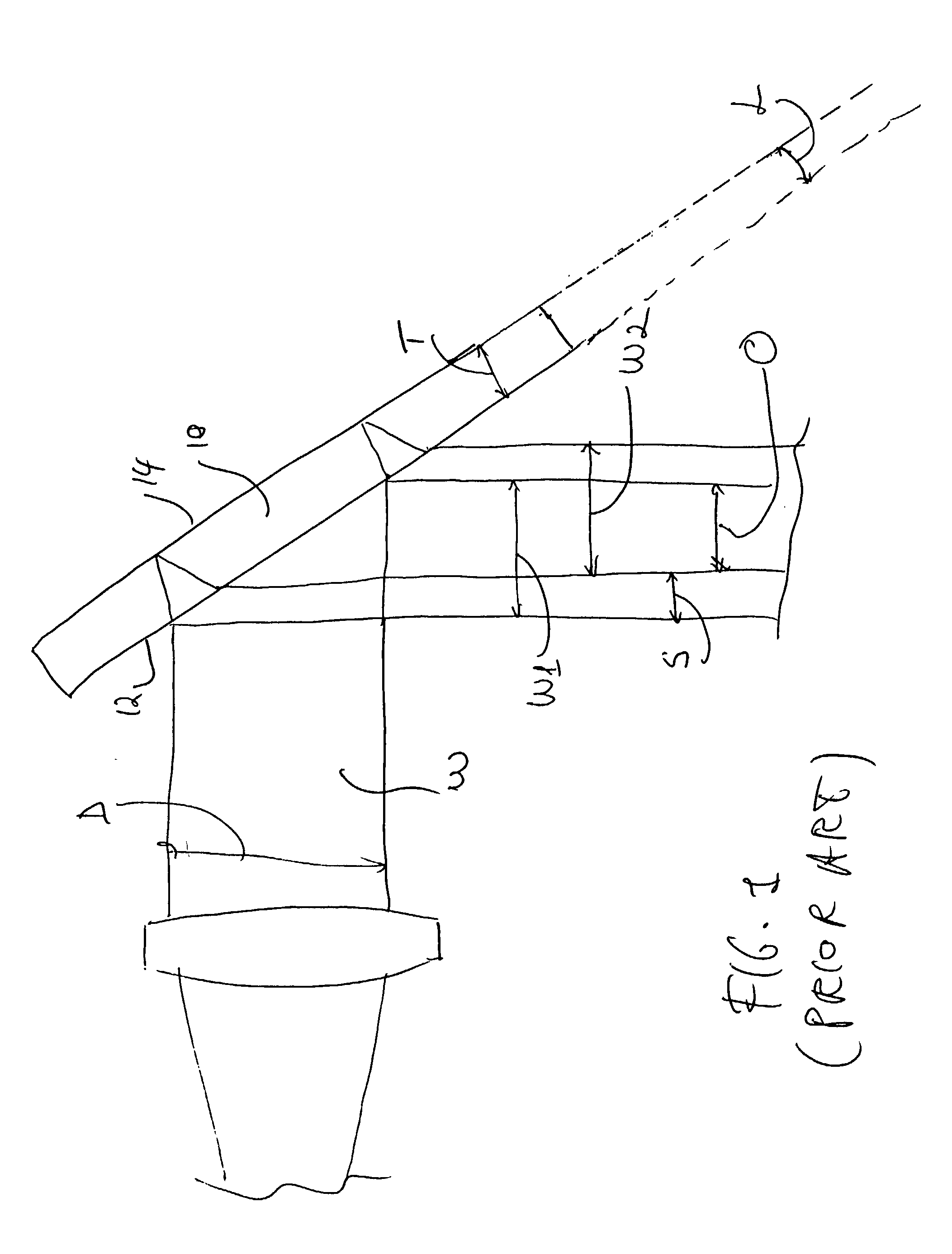
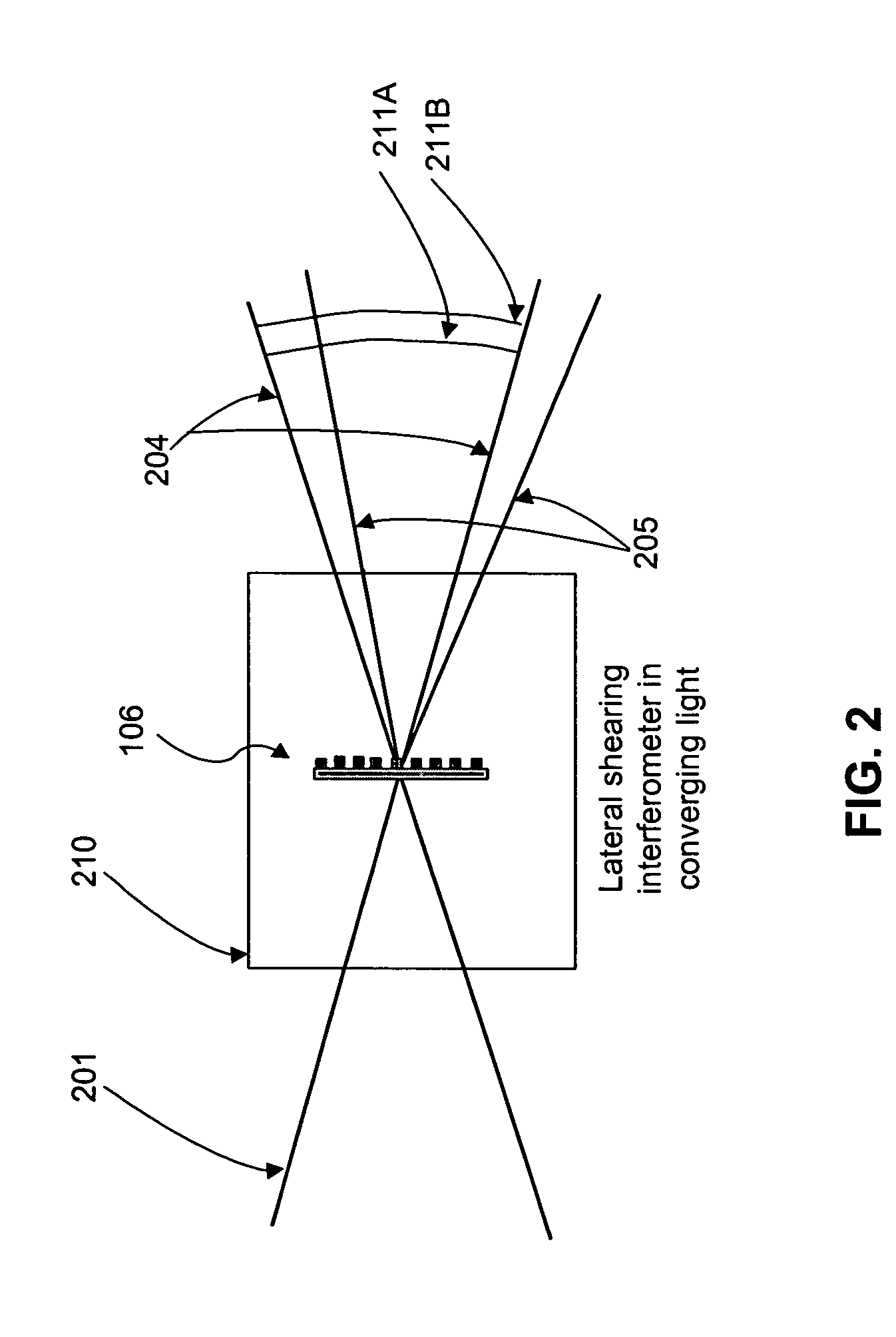
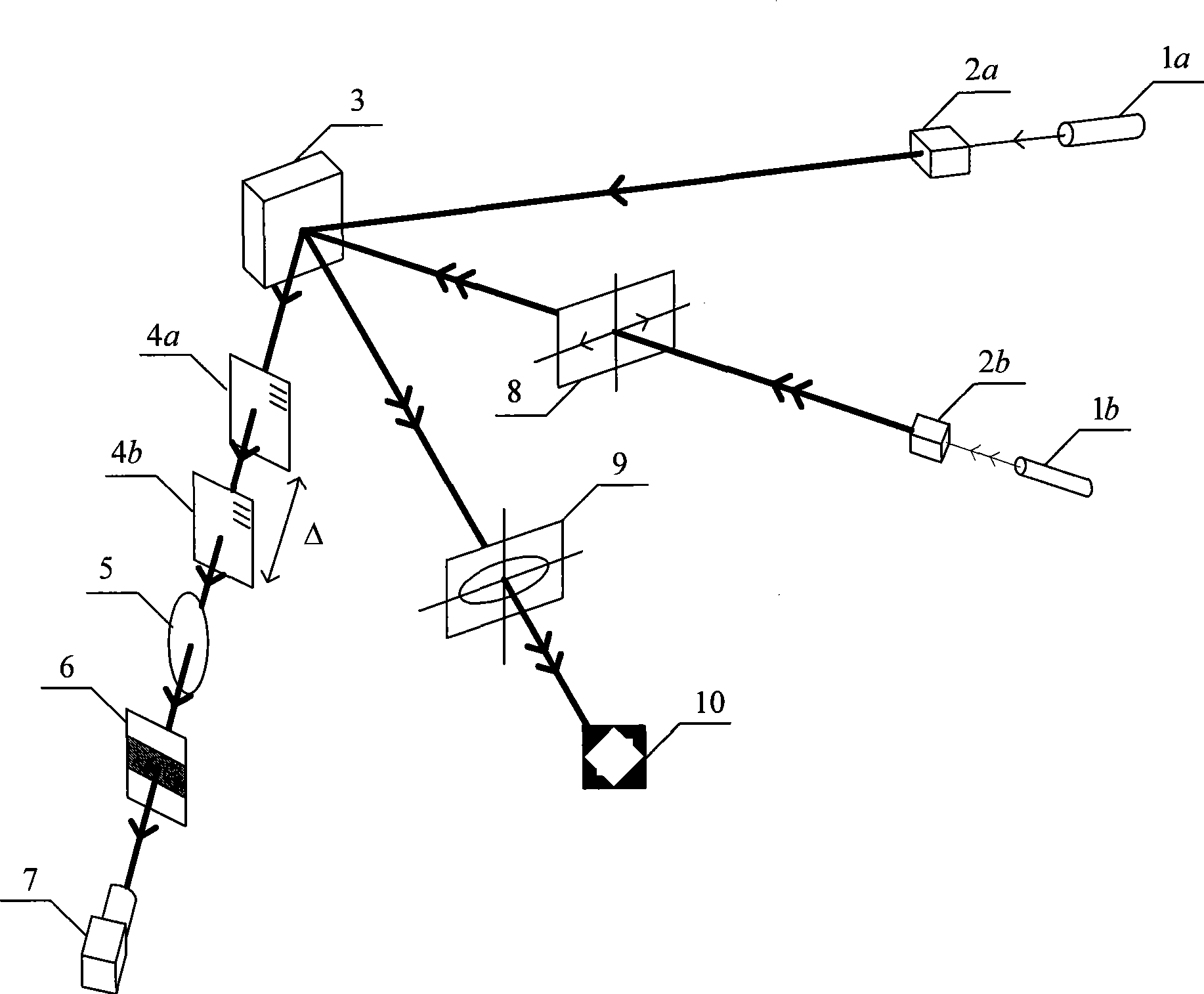
The shearing interferometer is an extremely simple means to observe interference and to use this phenomenon to test the collimation of light beams, especially from laser sources which have a coherence length which is usually significantly longer than the thickness of the shear plate (see graphics) so that the basic condition for interference is fulfilled.
Lateral-scanning interferometer with tilted optical axis
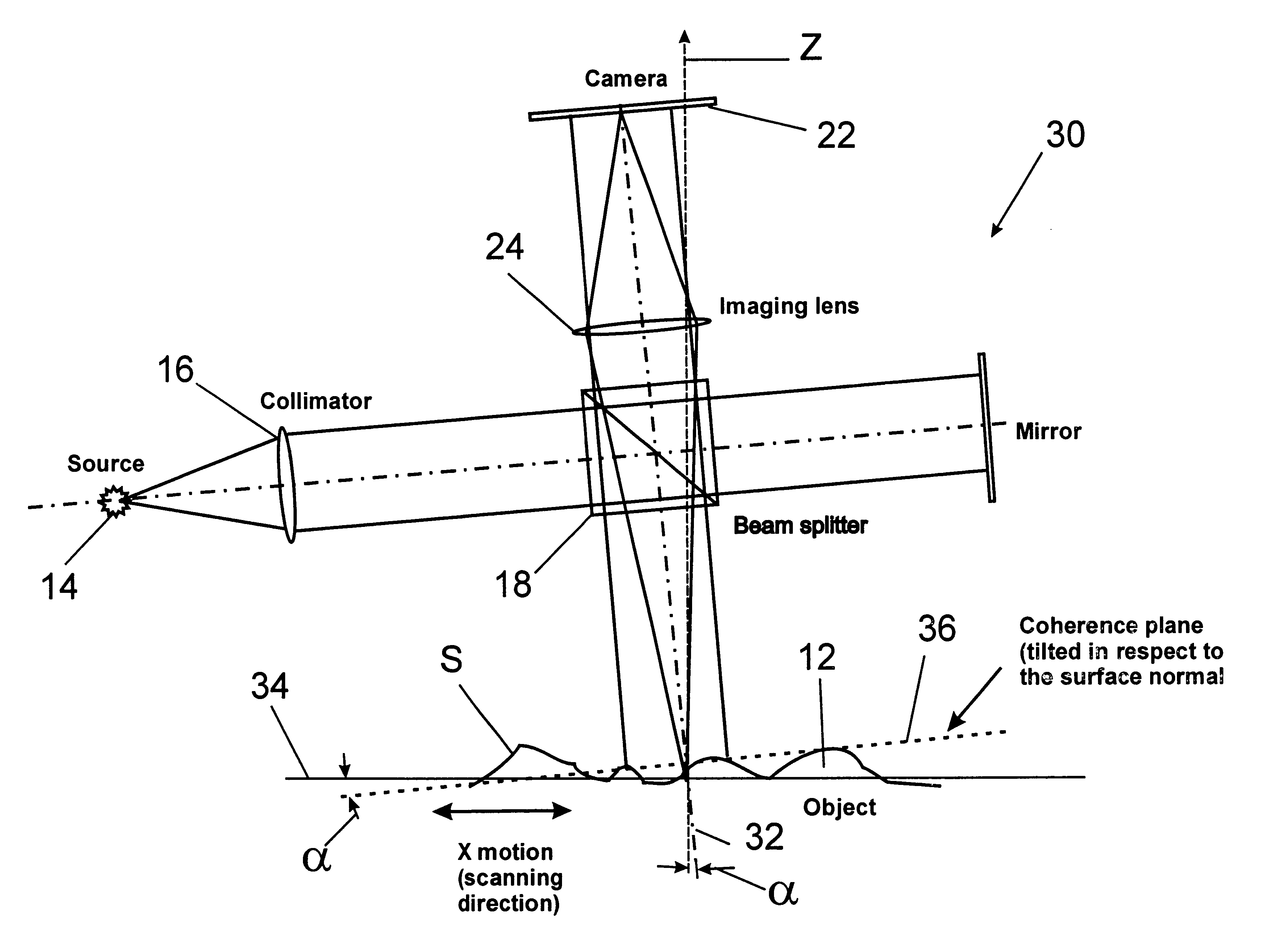
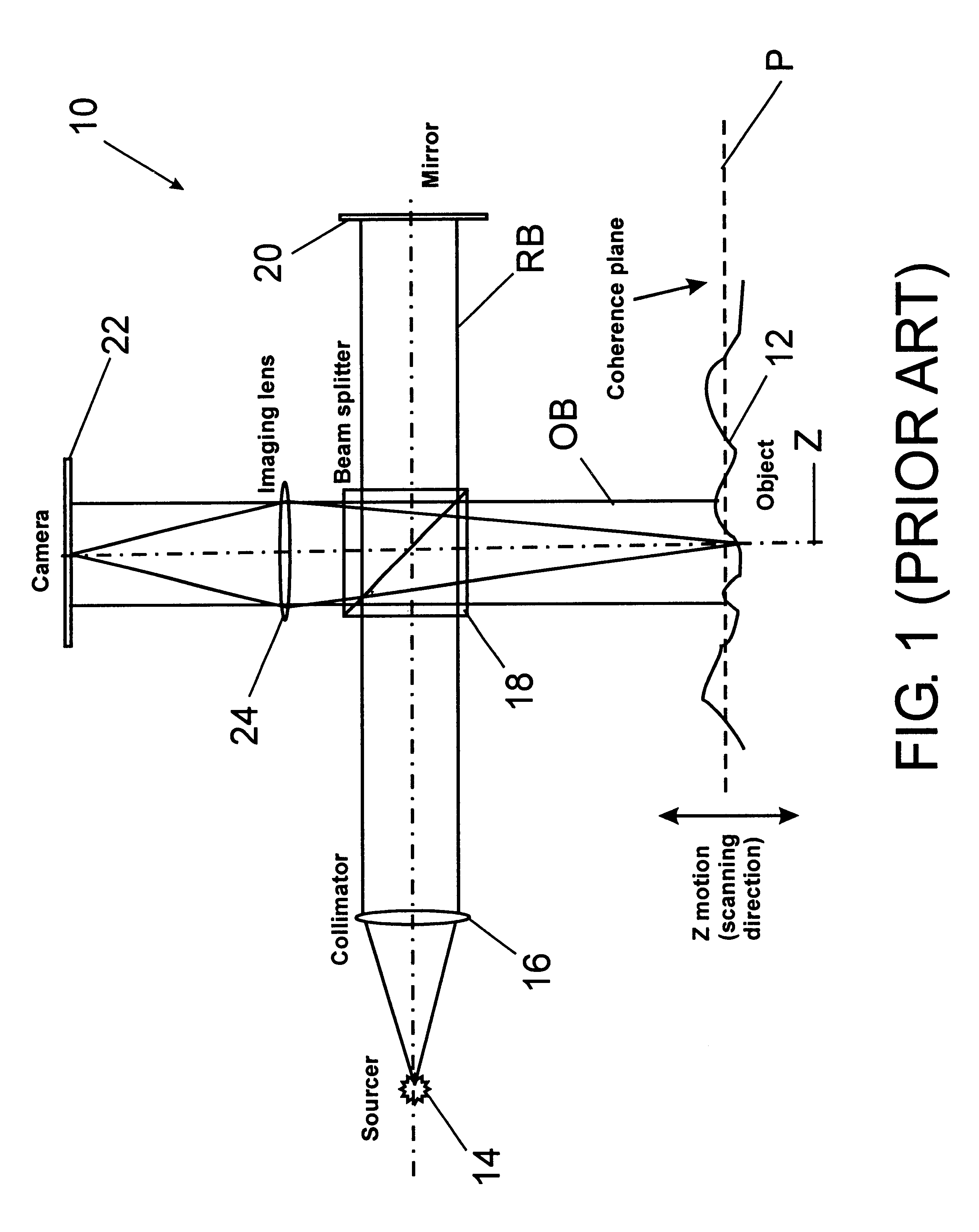
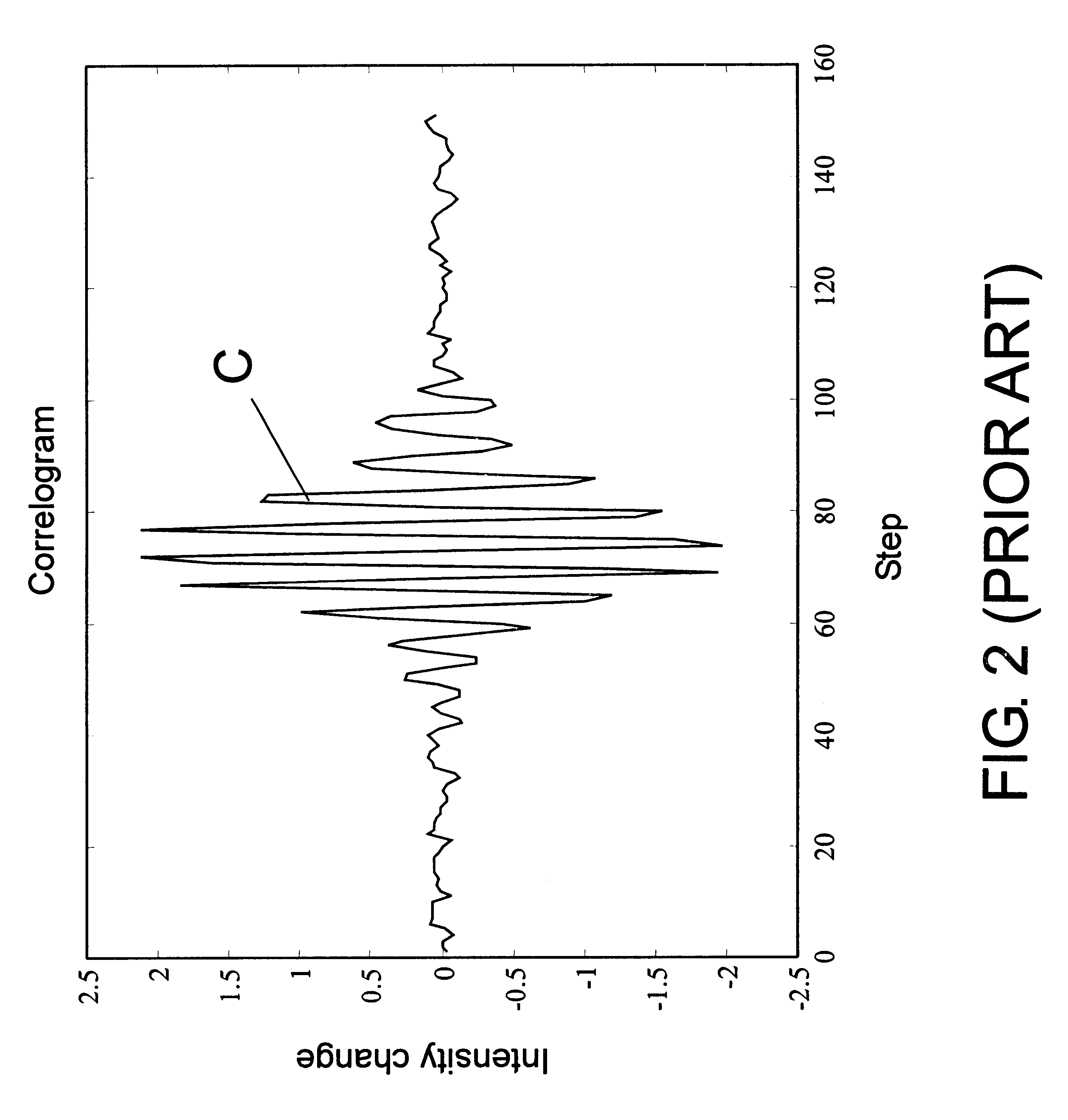
An interferometer scans the sample surface laterally with respect to the optical axis of the interferometric objective. The objective is tilted, so that the sample surface is placed at an angle with respect to the maximum coherence plane of the instrument. By moving the sample stage laterally, at an angle, through a point at a set distance from the objective on the objective's optical axis, rather than vertically along the optical axis, different parts of the object intersect the maximum coherence plane at different times as the surface passes through the coherence plane, the precise time depending on the profile of the surface. When the OPD of a point on the object's surface is greater than the coherence length of the light source, the intensity of light reflected from this point does not produce interference fringes. Therefore, the intensity registered by the detector is approximately constant. However, when the object point enters the zone of coherence, the interference effects modulate the intensity the same way as in a regular VSI procedure. As the object moves along the scanning direction, it also has a relative vertical speed with respect to the objective because of the tilt of the objective's optical axis with respect to the scanning plane; therefore, the lateral scanning motion produces an OPD variation as the vertical scan in a conventional system. As a result, light intensity data are acquired continuously as the test surface is scanned, thus elimination the need for stitching multiple sub-sets of data.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Passive zero shear interferometers
InactiveUS6847452B2Beam shear (e.g.Relative beam shear) can be reducedInterferometersPhotomechanical apparatusLight beamClassical mechanics
Beam shear can be reduced in an interferometric system by conditioning an input beam prior to directing the input beam to an interferometer. Accordingly, apparatus and methods for conditioning an interferometer input beam are disclosed.
Owner:ZYGO CORPORATION
Spectrum shearing interferometer suitable for measuring shaped pulses
The invention relates to the field of shaped pulse measurement, in particular to a spectrum shearing interferometer suitable for measuring shaped pulses. A plane grating, a first concave face reflecting mirror, a double-slit baffle, a first reflecting mirror and a second reflecting mirror are used for forming a special 4f zero dispersion compressor, the distance between the plane grating, the first reflecting mirror and the second reflecting mirror and the first concave face reflecting mirror is equal to the focal length of the first concave face reflecting mirror in the 4f zero dispersion compressor, the mode that the 4f zero dispersion compressor is added with the double-slit baffle is used for acquiring two quasi monochromatic long pulses, the two quasi monochromatic long pulses and a pulse to be measured are made to be in sum frequency. According to the mode, a shearing amount omega and the band width delta omega of an auxiliary pulse segment participating in sum frequency can be prevented from varying along with the change of the characteristics of the pulses to be measured, the shearing amount omega can be changed conveniently to measure the same pulse, the corresponding phase difference of each frequency of the pulse can be solved independently, and therefore the shaped pulses with various characteristics can be measured accurately.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
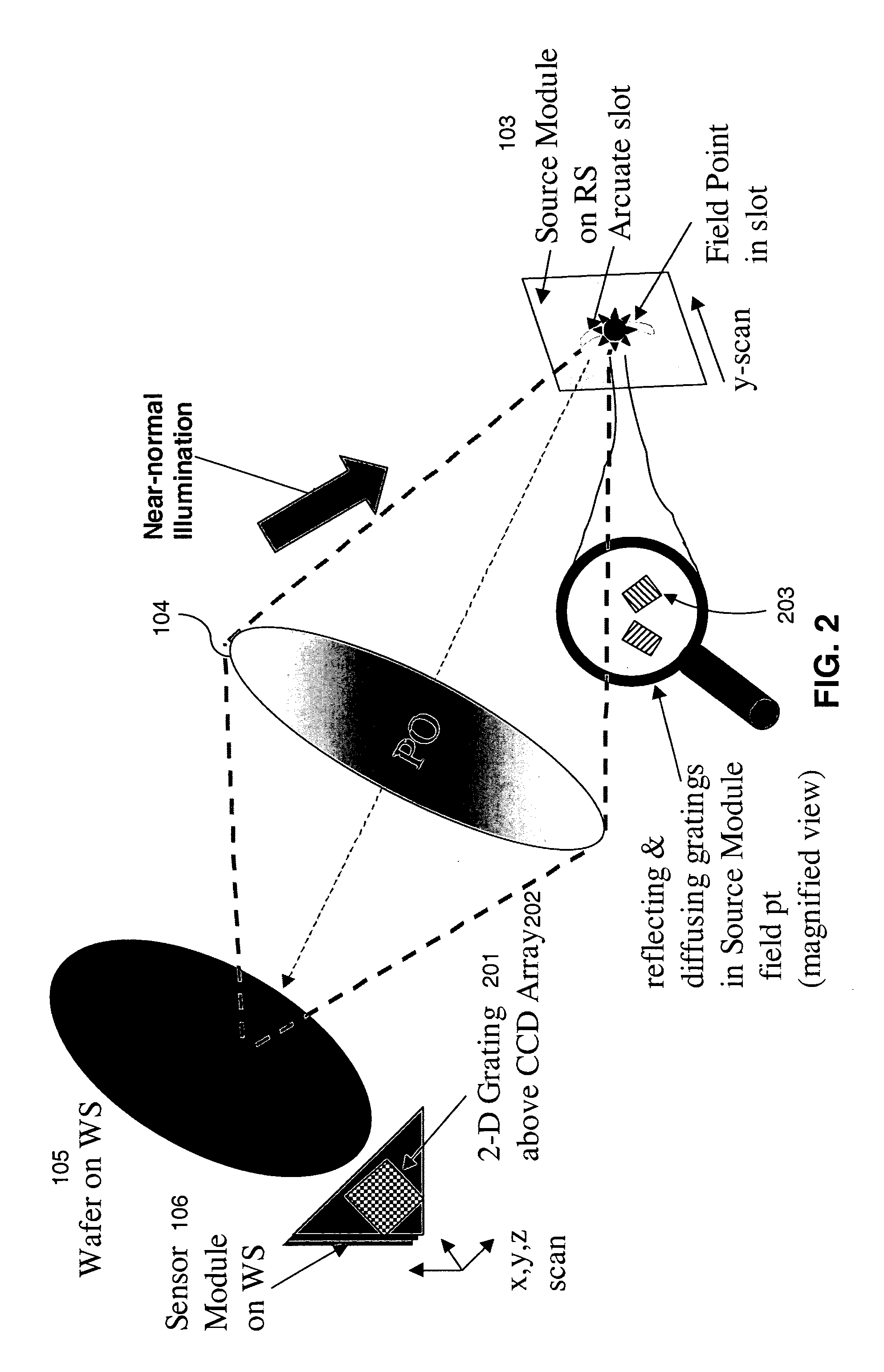
Projection objective lens wave aberration detection device and method
InactiveCN102681365AReduced measurement timeFlexible adjustmentPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusGratingWave aberration
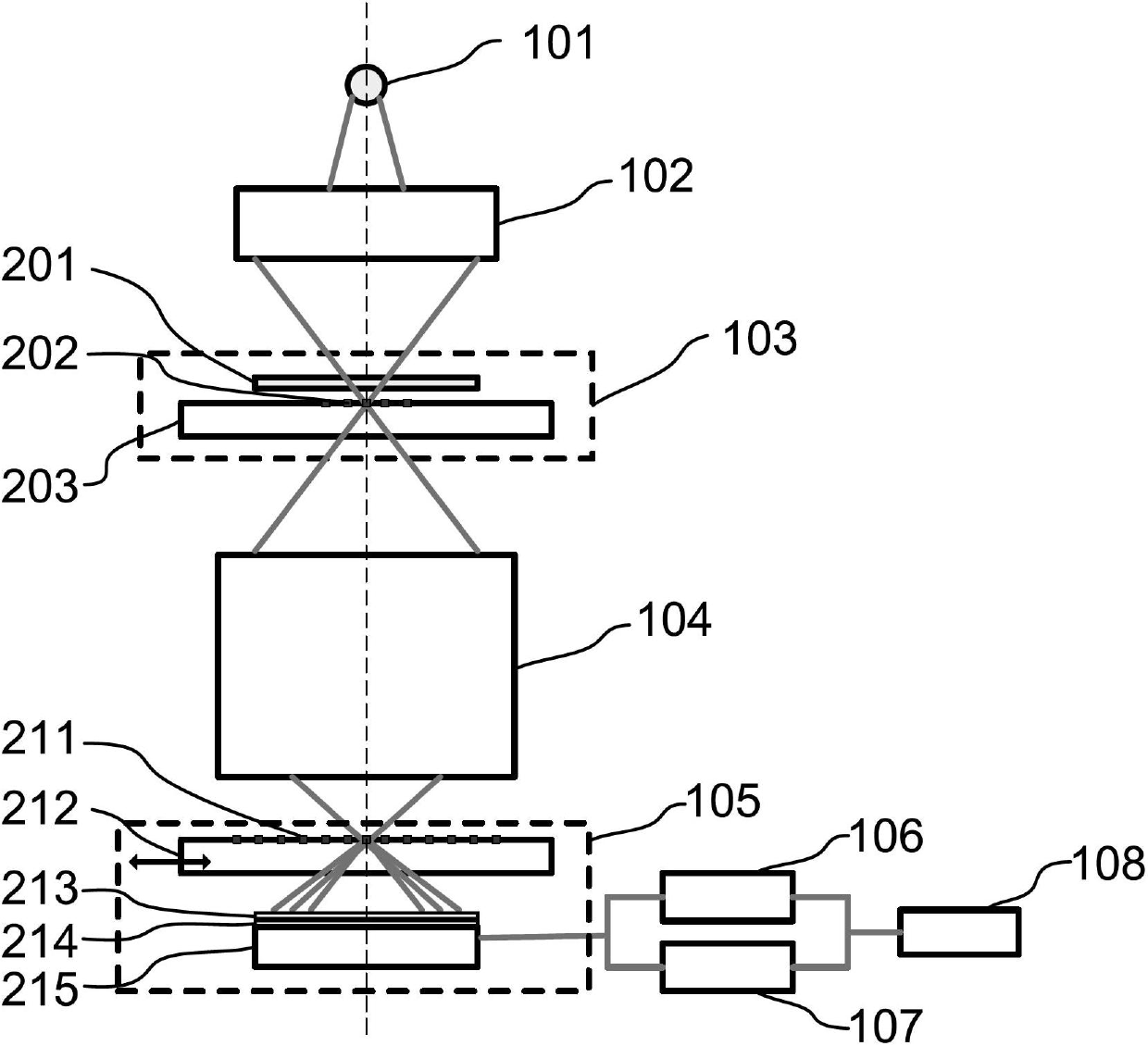
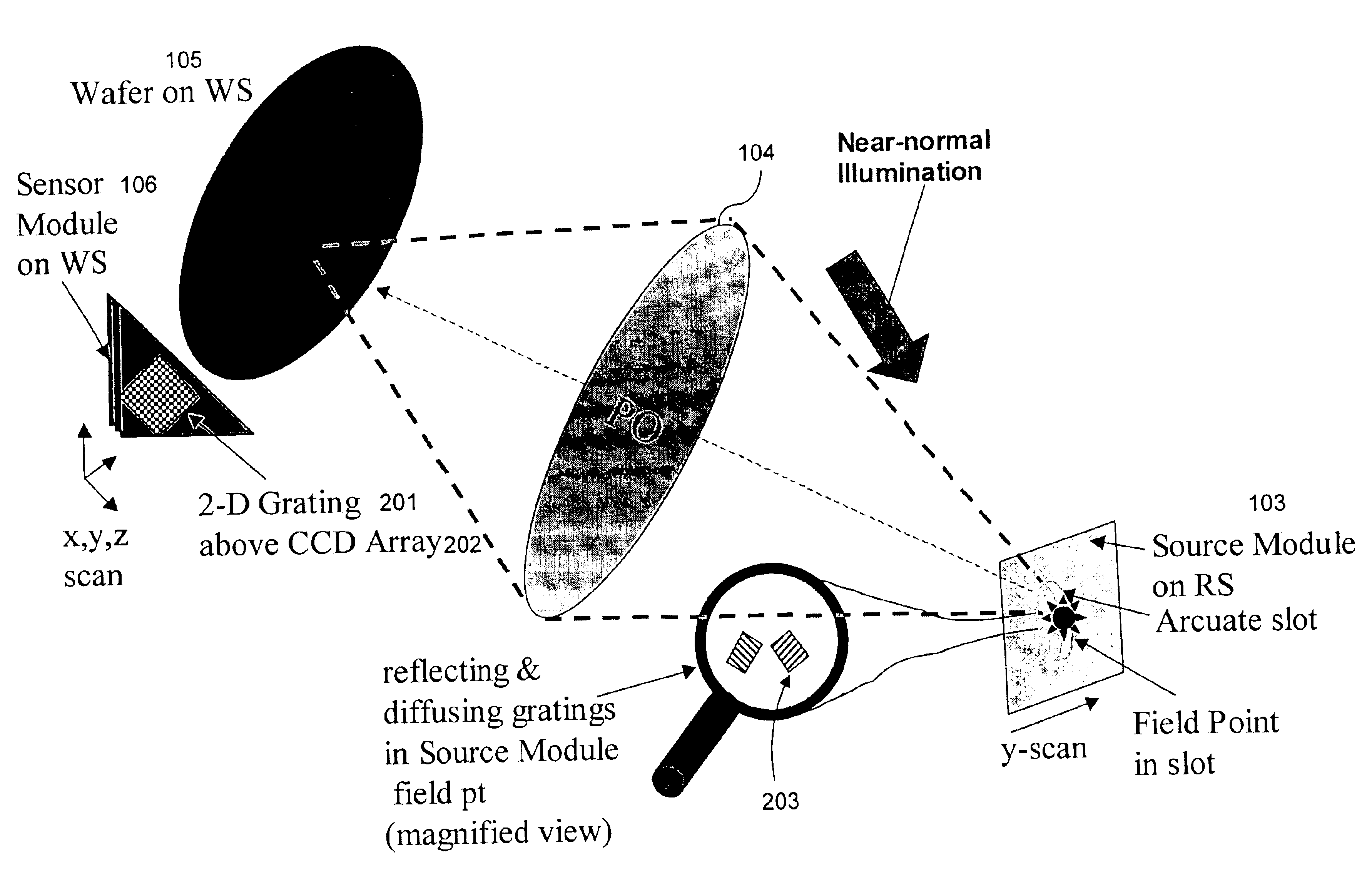
The invention relates to a projection objective lens wave aberration detection device and method. Light emitted by a light source is uniformly radiated on a projection objective lens object plane, a scatter plate and a needle hole are installed on a masking stage, the needle hole is arranged on an object plane of a projection objective lens, the field of view is selected through the movement of the masking stage, a shearing grating is arranged on an image plane of the projection objective lens, the shearing grating is installed on a wafer stage together with a detector, the phase shifting function is realized through the transverse precise movement of the grating by the wafer stage, and simultaneously each frame of a shearing interference figure in the phase shifting process is recorded by utilizing the detector. Two-dimensional shearing is realized by utilizing the two-dimensional grating, the phase shifting function is integrated into the shearing interference instrument, and the high-precise measurement of the projection objective lens wave aberration is realized by adopting the characteristics of the phase space vector.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Exposure apparatus mounted with measuring apparatus
InactiveUS20050190378A1Simple structureShort timeOptical measurementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPoint diffraction interferometerMeasurement device
An exposure apparatus for exposing a pattern of a mask onto an object using light from a light source, includes a projection optical system for projecting the pattern onto the object, and a measuring apparatus for measuring, as an interference fringe, optical performance of the projection optical system using the light, wherein the measuring apparatus is a point diffraction interferometer that has a pinhole to form an ideal spherical wave, a line diffraction interferometer that has a slit to form an ideal cylindrical wave or an ideal elliptical wave, or a shearing interferometer that utilizes a shearing interferometry.
Owner:CANON KK
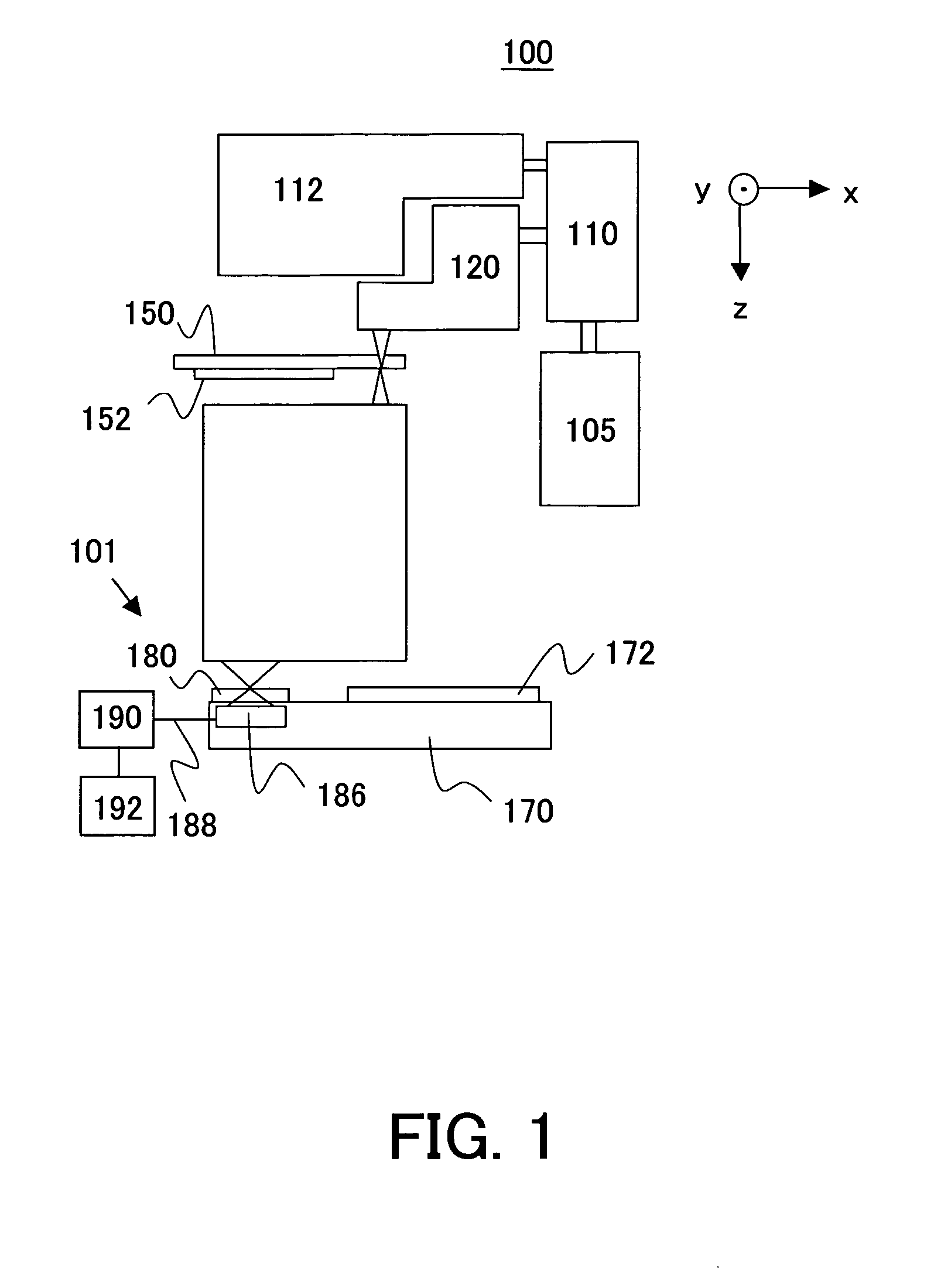
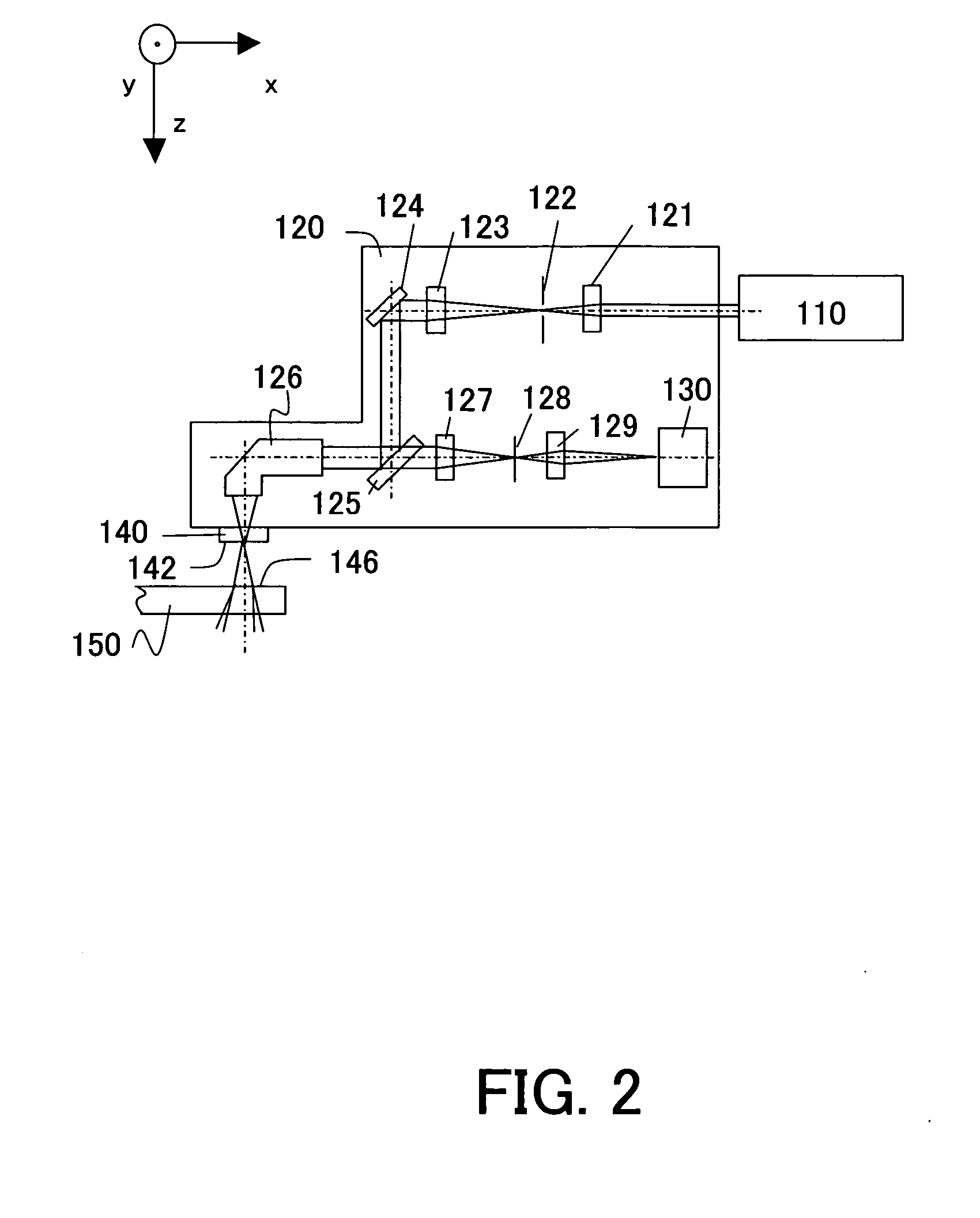
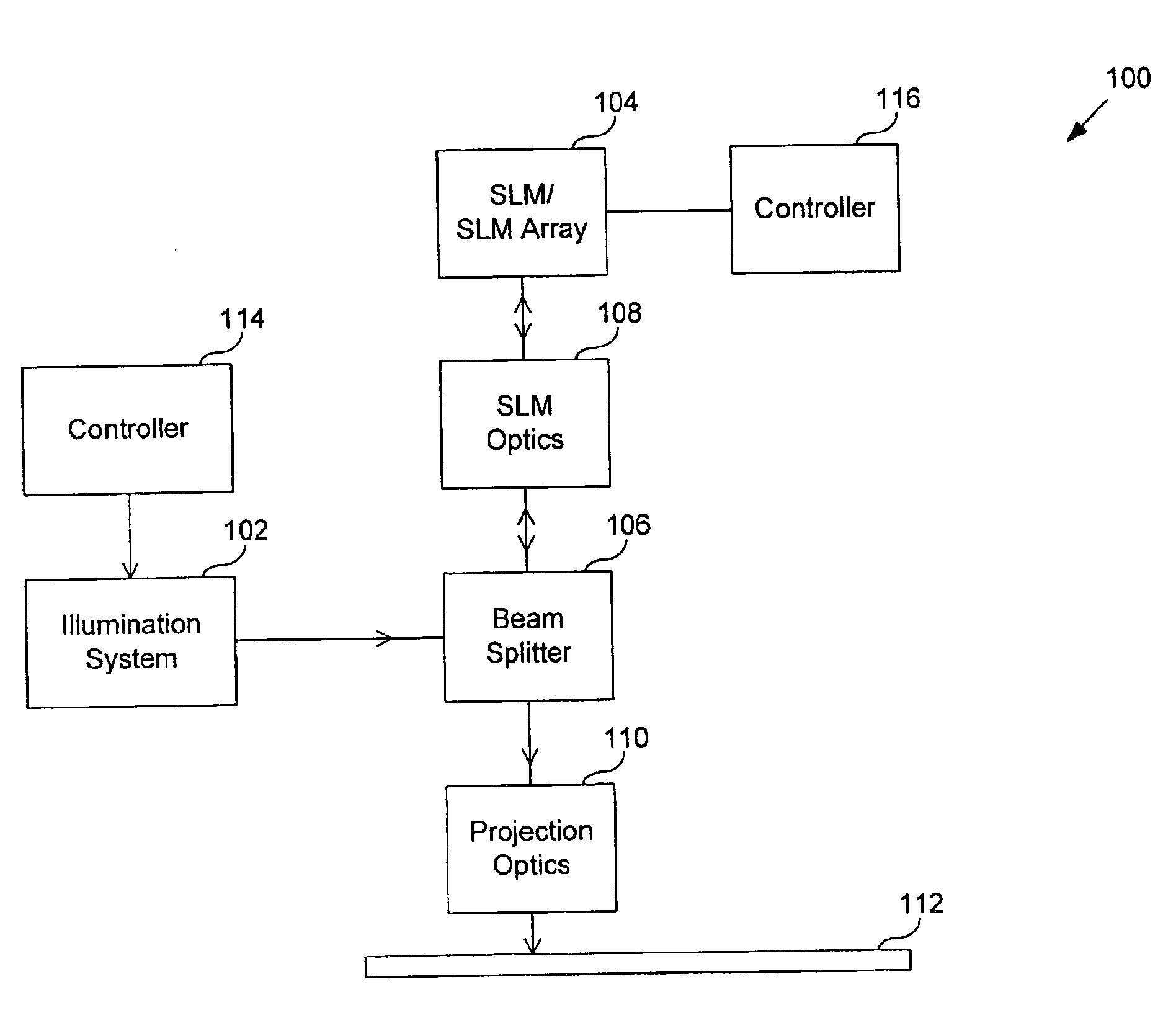
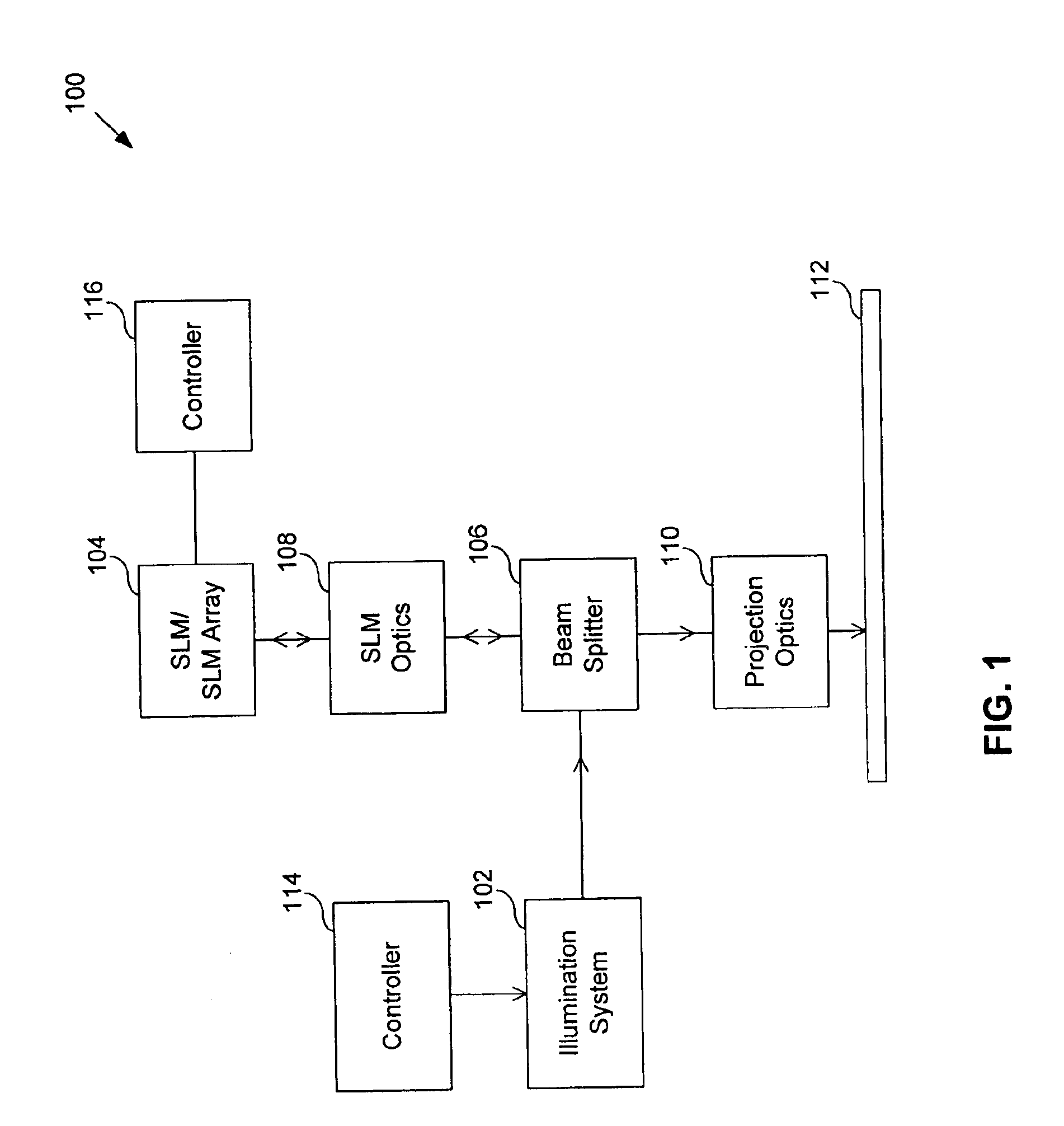
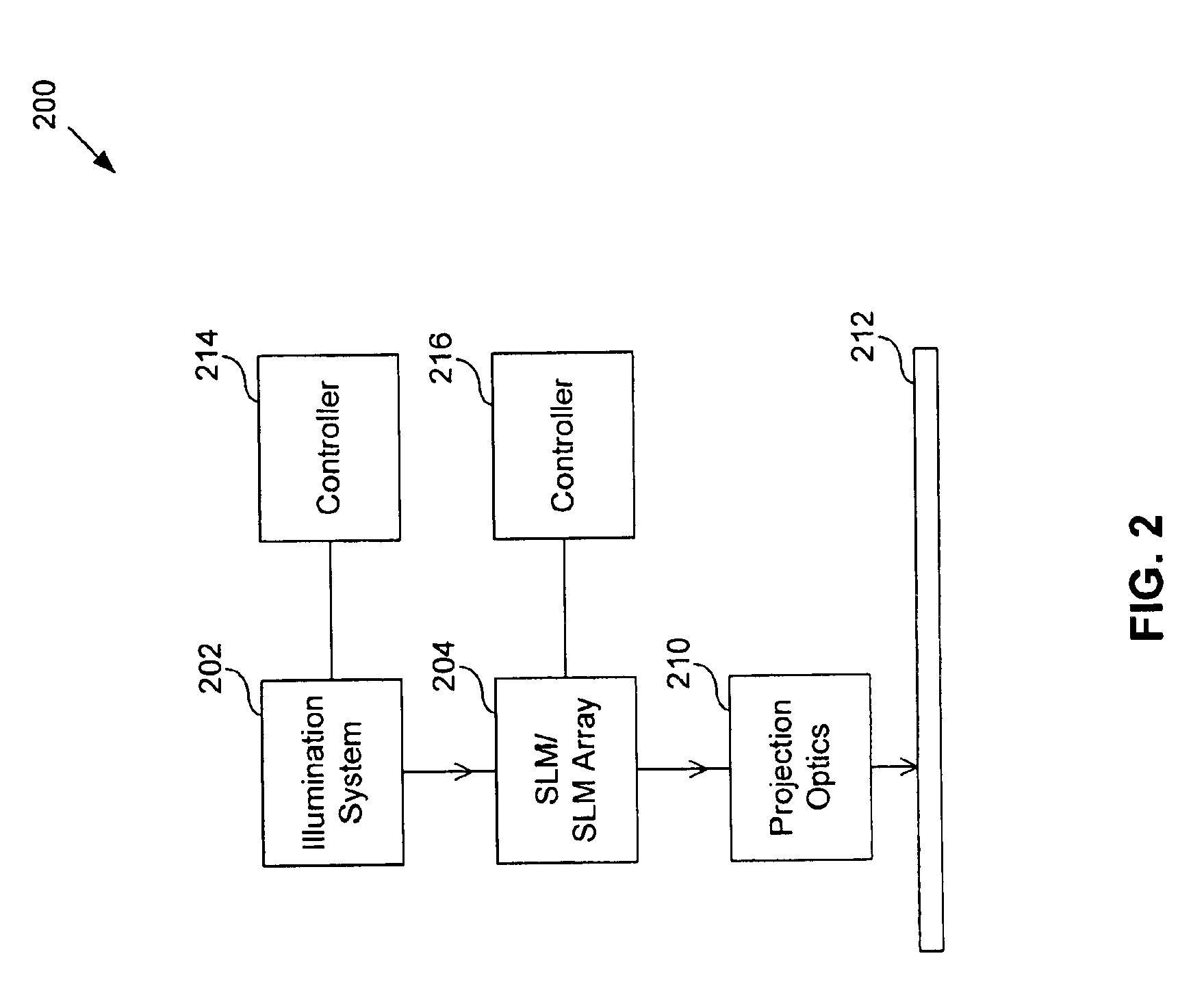
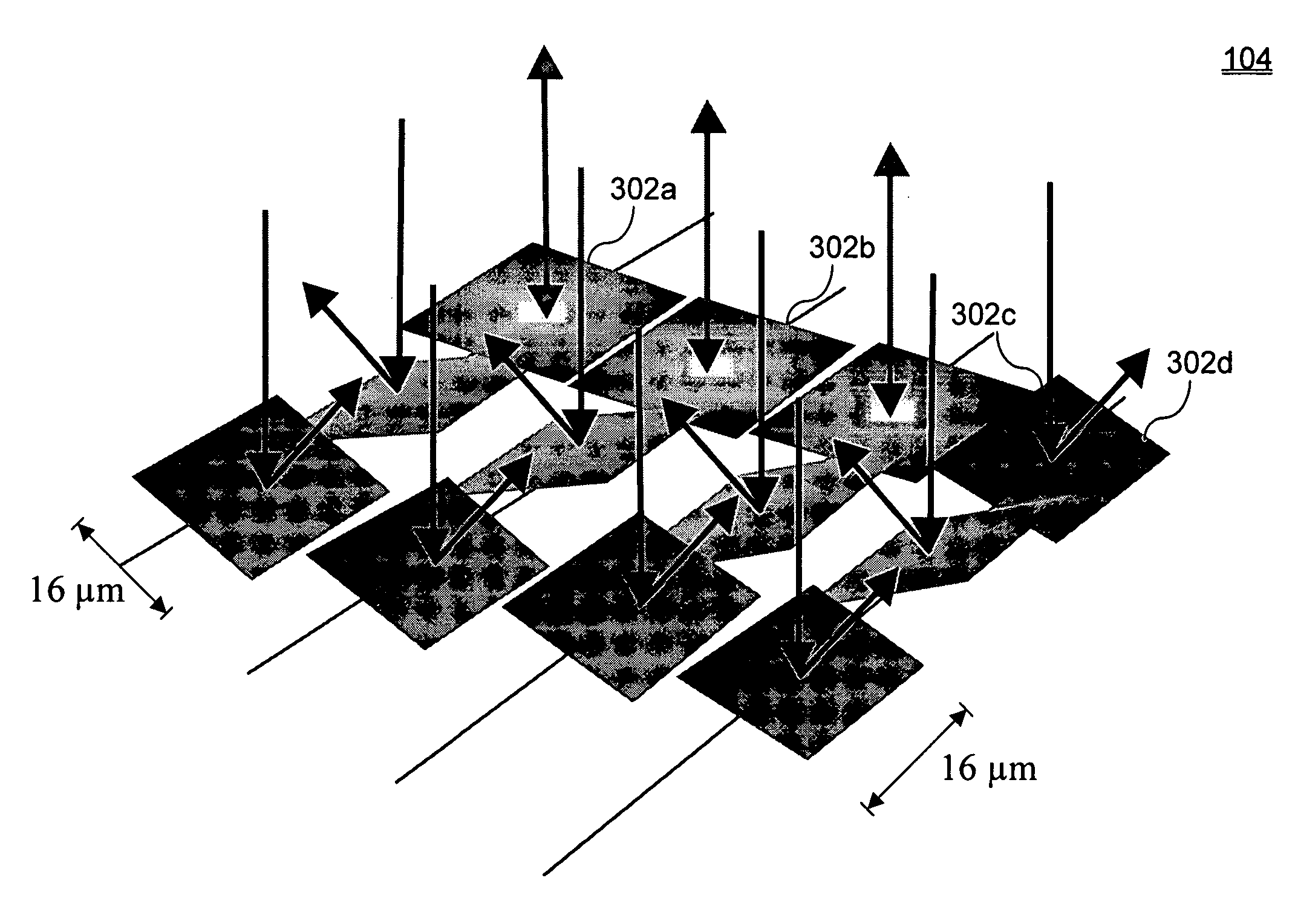
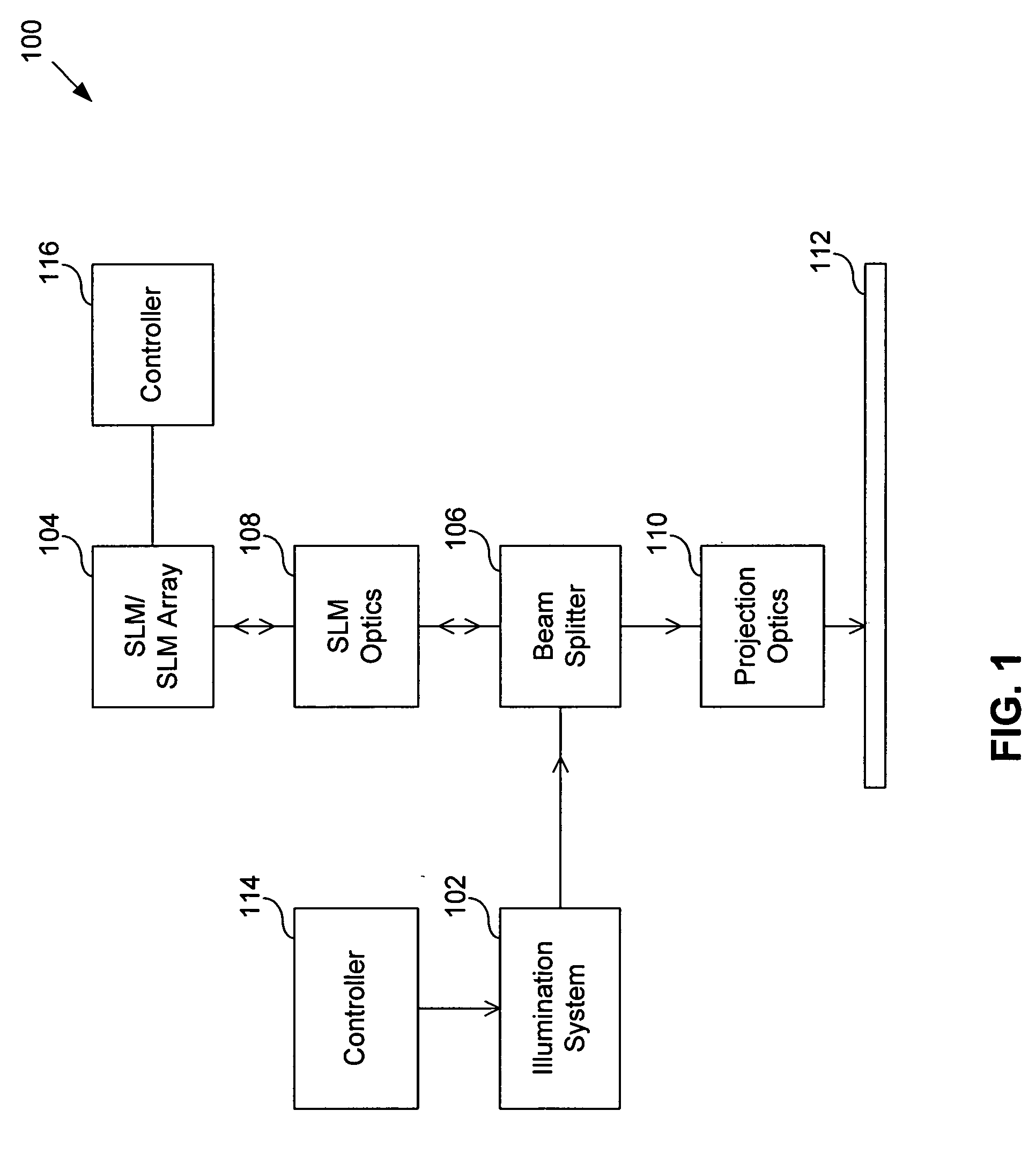
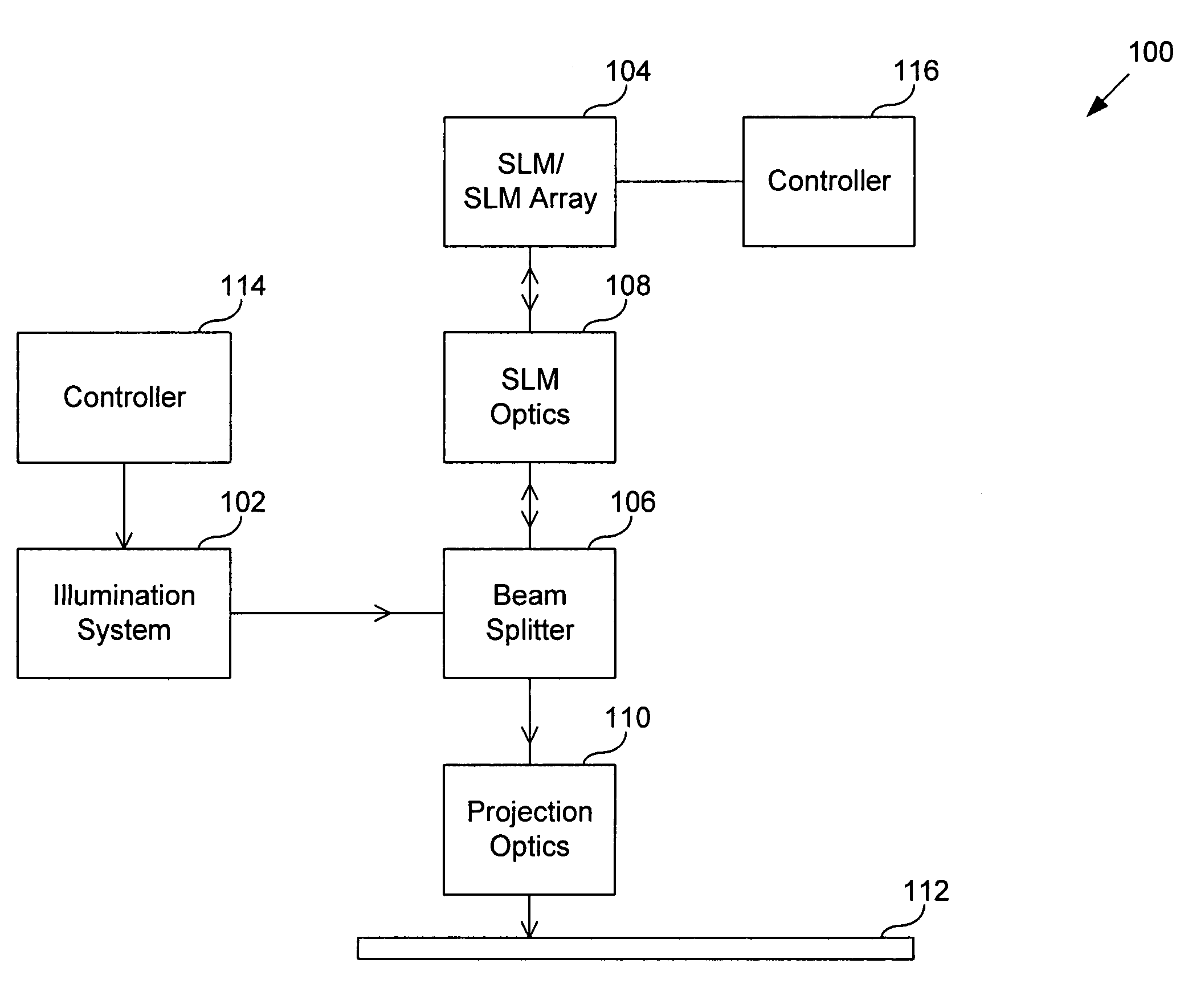
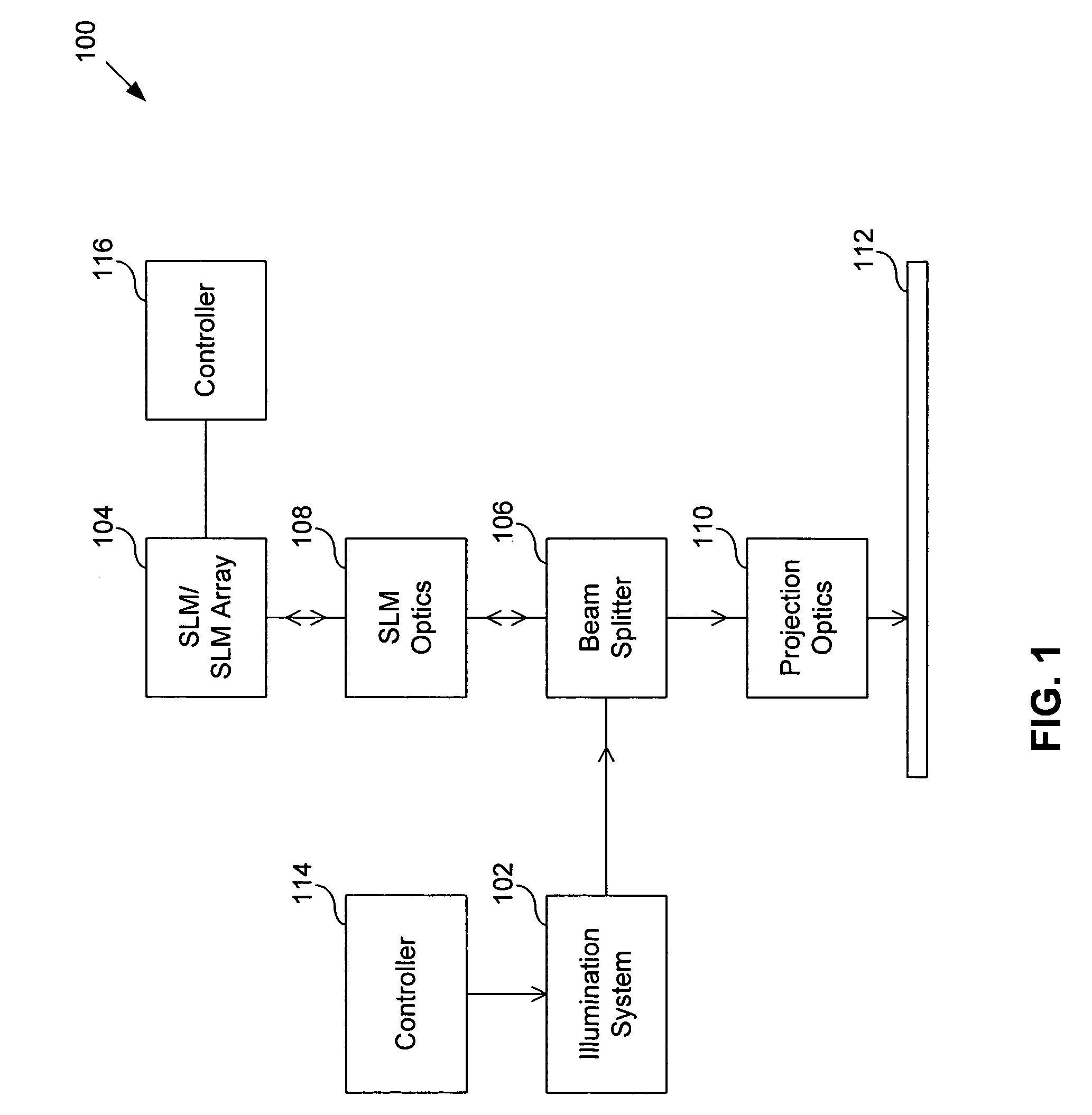
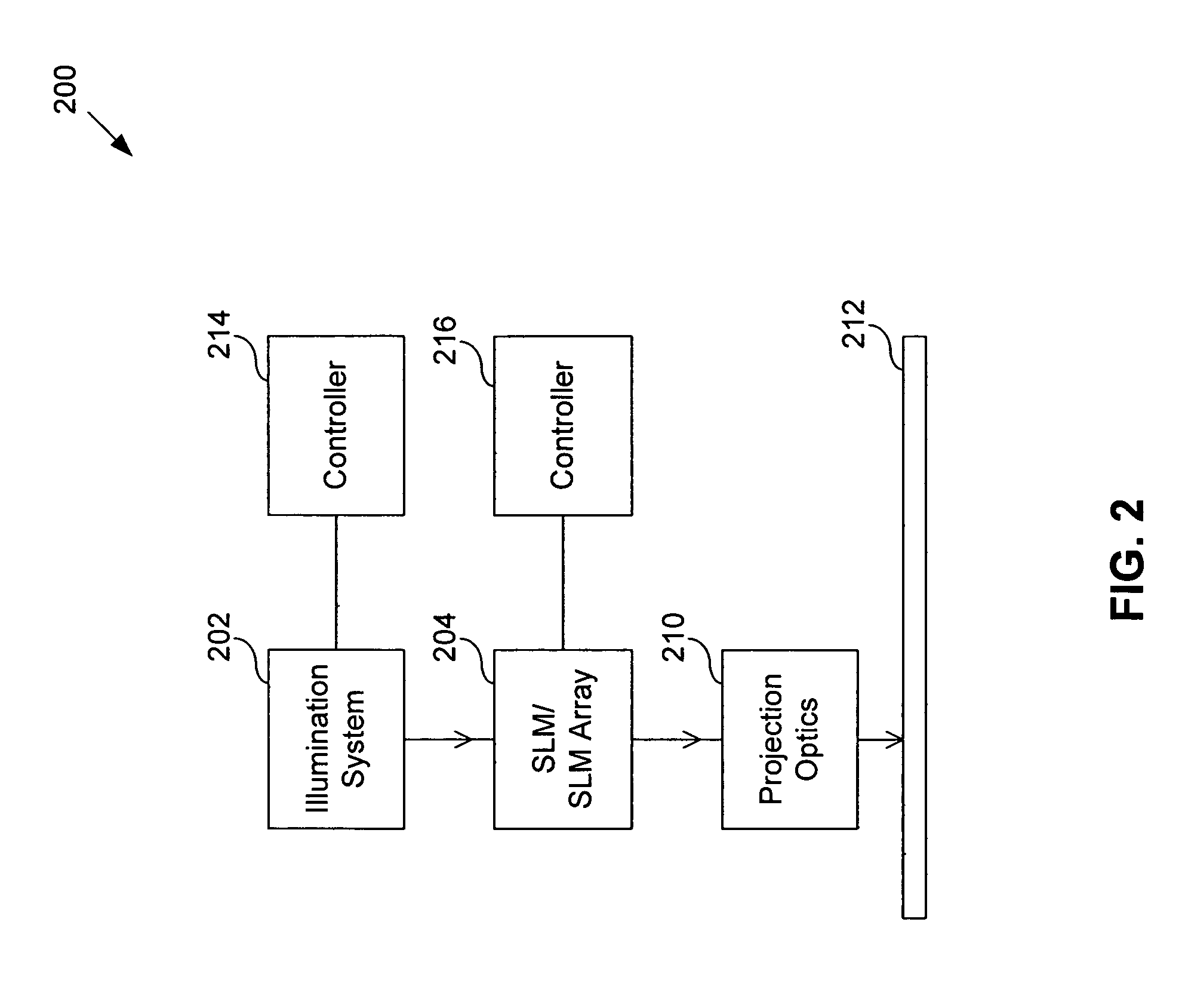
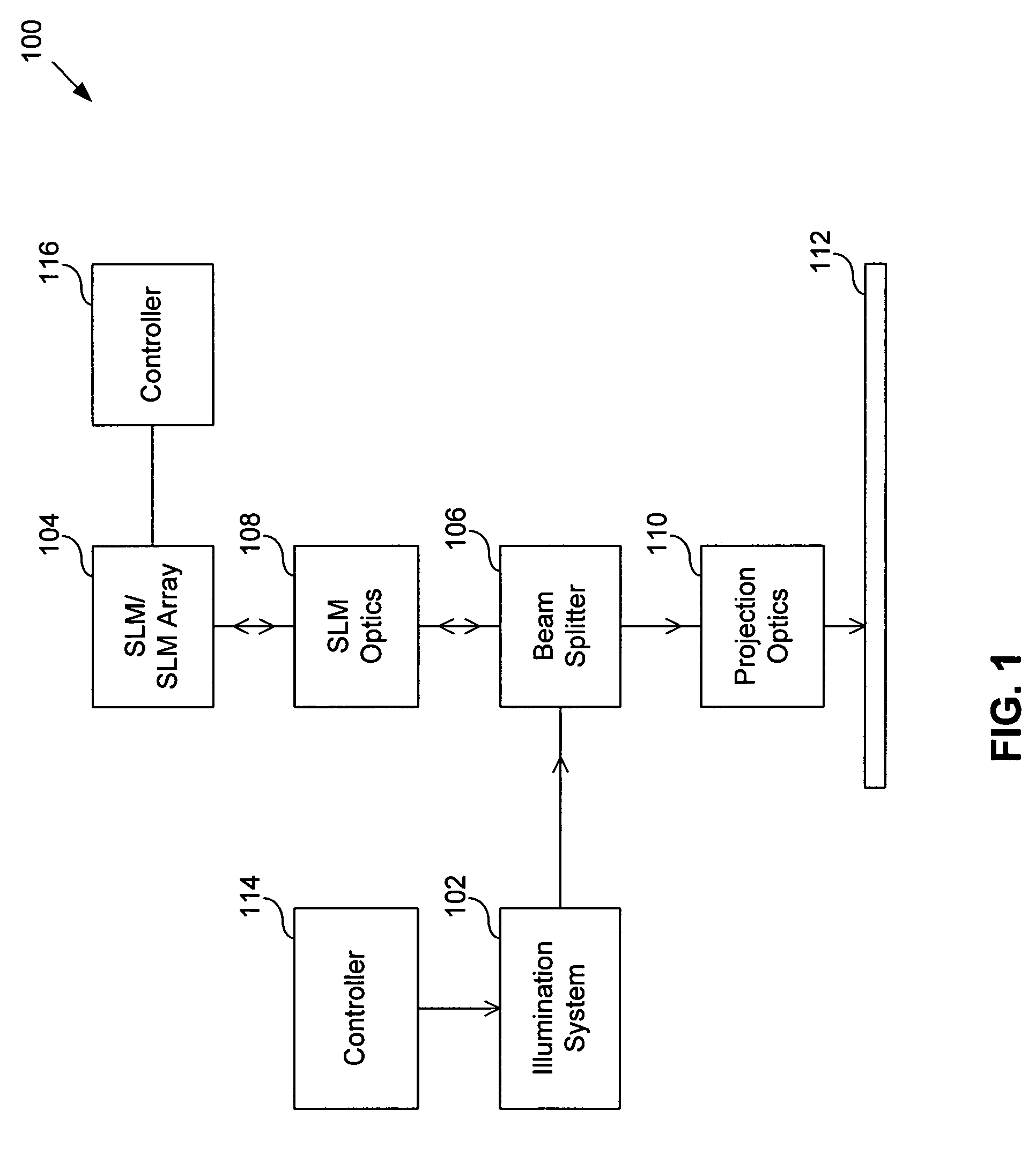
System and method for calibrating a spatial light modulator array using shearing interferometry
ActiveUS6847461B1Photometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansProjection opticsSpatial light modulator
A system for calibrating a spatial light modulator array includes an illumination system and a spatial light modulator array that reflects or transmits light from the illumination system. A projection optical system images the spatial light modulator array onto an image plane. A shearing interferometer creates an interference pattern in the image plane. A controller controls modulation of elements of the spatial light modulator array. The shearing interferometer includes a diffraction grating, a prism, a folding mirror or any other arrangement for generating shear. The shearing interferometer can be a stretching shearing interferometer, a lateral shearing interferometer, or a rotational shearing interferometer. The shearing interferometer may include a diffraction grating with a pitch corresponding to a shear of the light by an integer number of elements. The projection optics resolves each element of the spatial light modulator array in the image plane. The controller can modulate alternate columns of elements of the spatial light modulator array.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
Phase shifting lateral direction shearing interferometer
InactiveCN101113927AAutomate processingImprove performanceOptical measurementsUsing optical meansPhase shiftedParallel plate
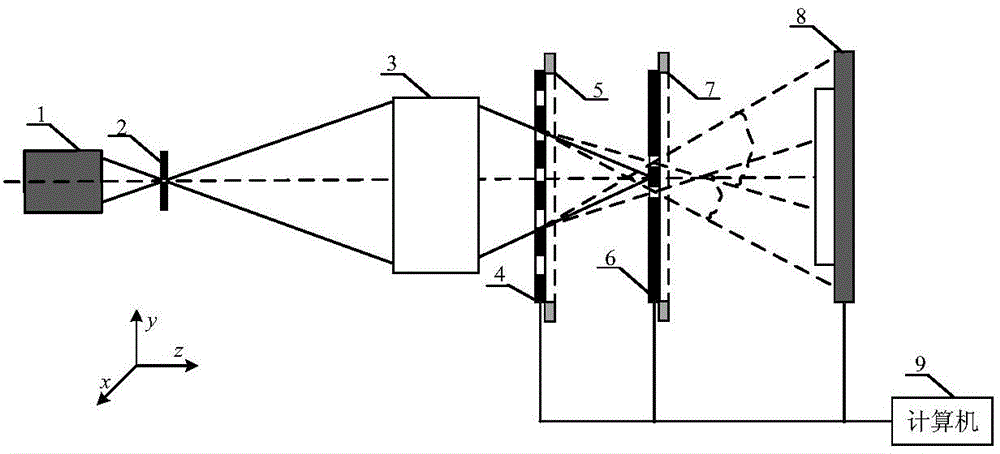
A phase shift transverse shear interferometer consists of a first polarizer, an input parallel plate, a second polarizer, a third polarizer, a first shear plate, a second shear plate, an output parallel plate, a quarter wave plate, a detecting deflection machine, a CCD camera and a computer, the phase shift transverse shear interferometer is an equal optical path interference optical system, the shear quantity can be continuously adjusted, which is very applicable to the wavefront measurement of the short interference length, and satisfies the wavefront measurement of the different light beam bore and the measurement precision.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Defect detection method and defect detection apparatus
ActiveUS20170350690A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansThree-phaseLaser light
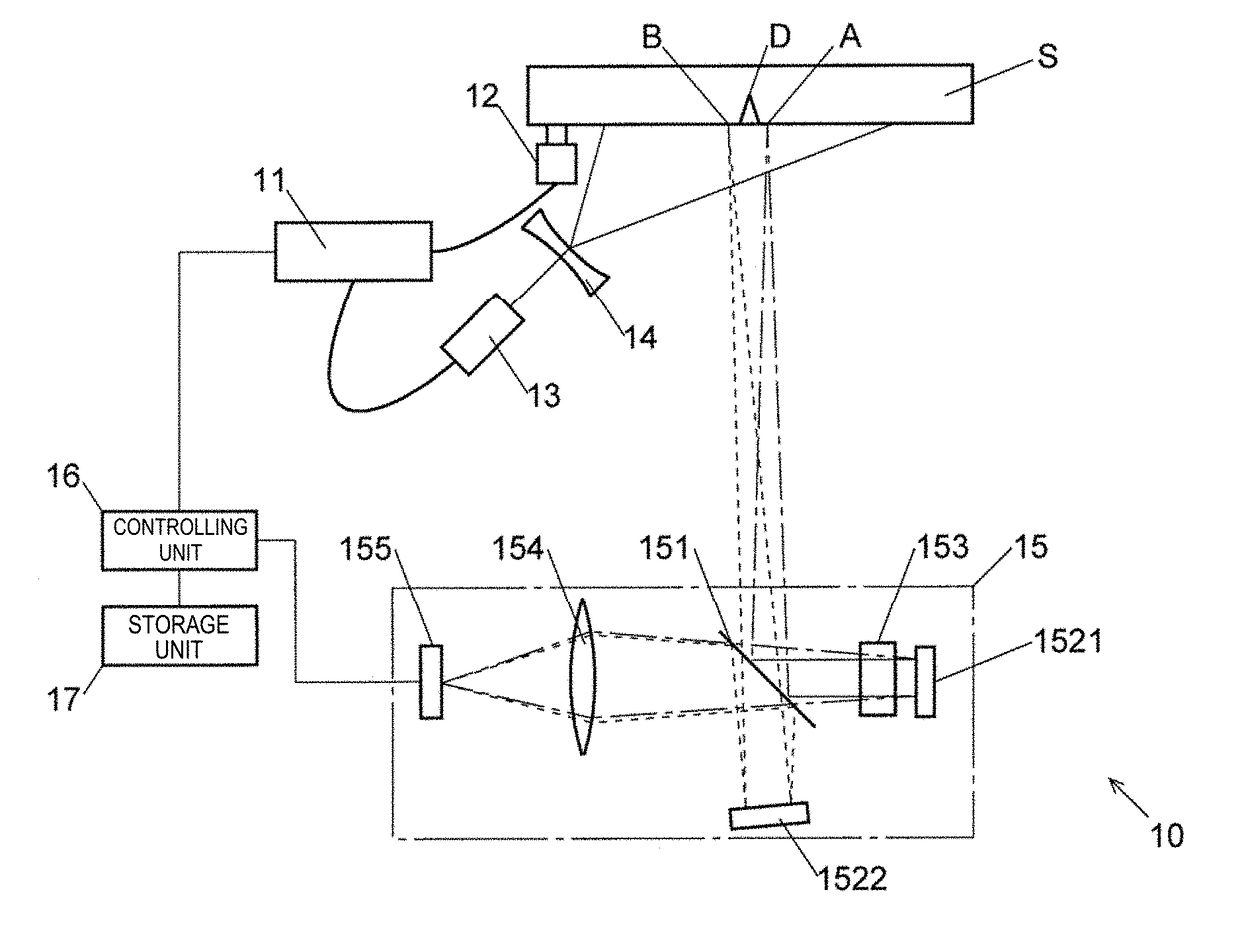
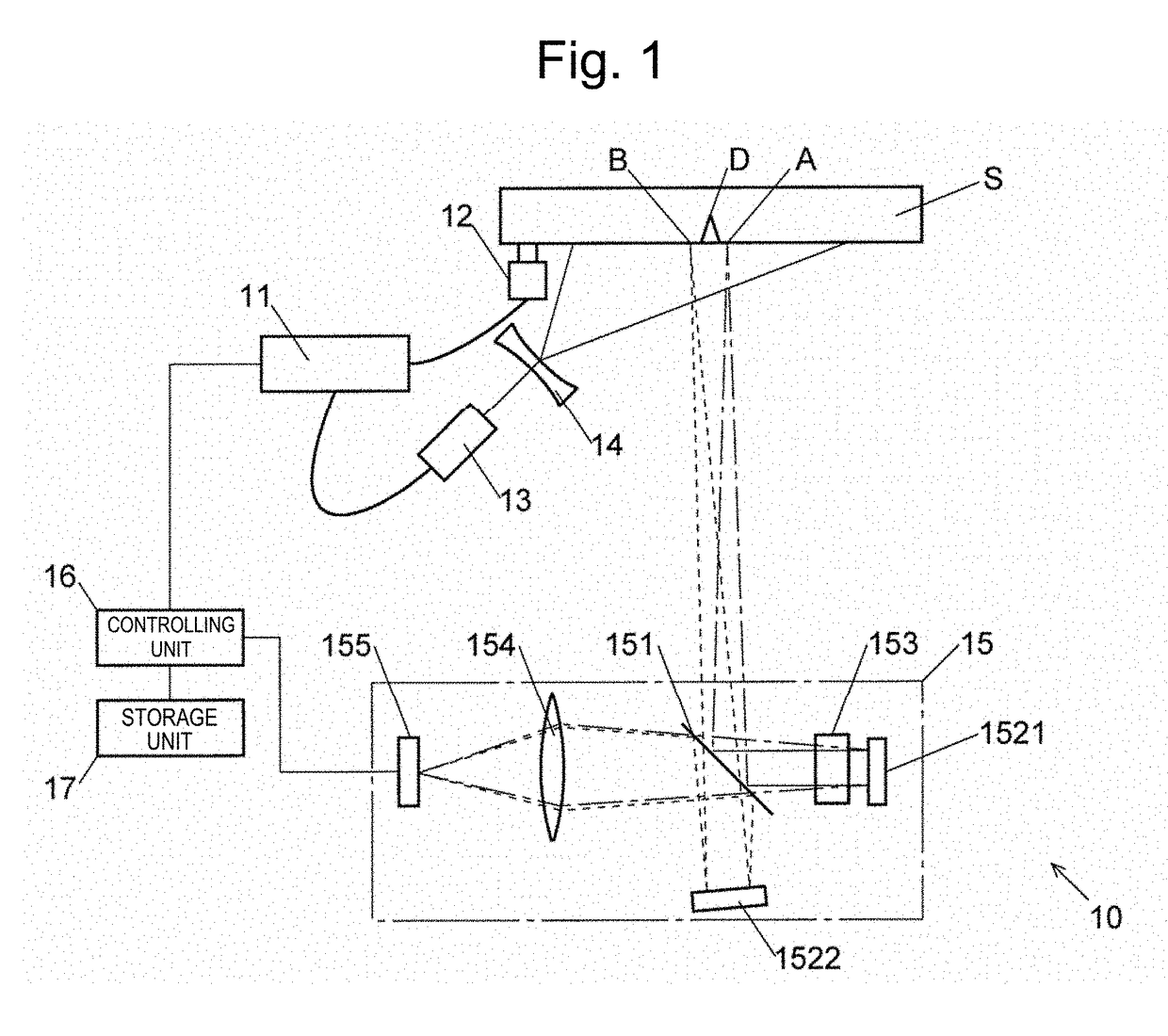
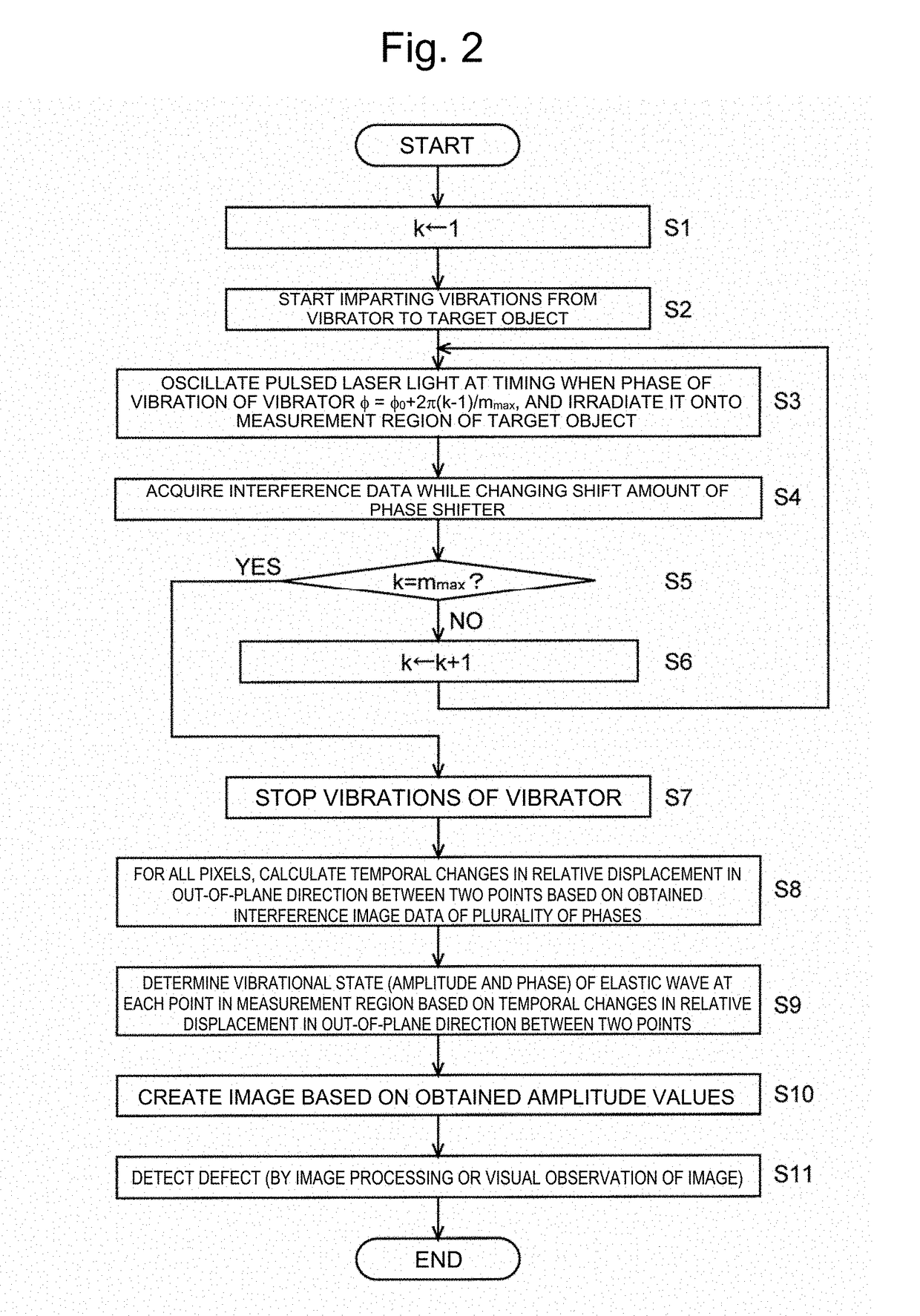
A defect detection apparatus is provided that can inspect a measurement region of a target object at one time and without inconsistencies arising within the measurement region. A defect detection apparatus 10 includes: a generation unit (signal generator 11 and vibrator 12) for generating an elastic wave in a target object S; an illumination unit (pulsed laser light source 13 and illumination light lens 14) for performing stroboscopic illumination onto a measurement region of a surface of the target object S; and a displacement measurement unit (speckle shearing interferometer 15) for collectively measuring displacements in a normal direction at each point of the measurement region with respect to at least three mutually-different phases of the elastic wave by controlling a phase of the elastic wave and a timing of the stroboscopic illumination. Defects in the measurement region are detected based on the displacements in the normal direction at each point of the measurement region with respect to at least three phases that are obtained by the displacement measurement unit.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
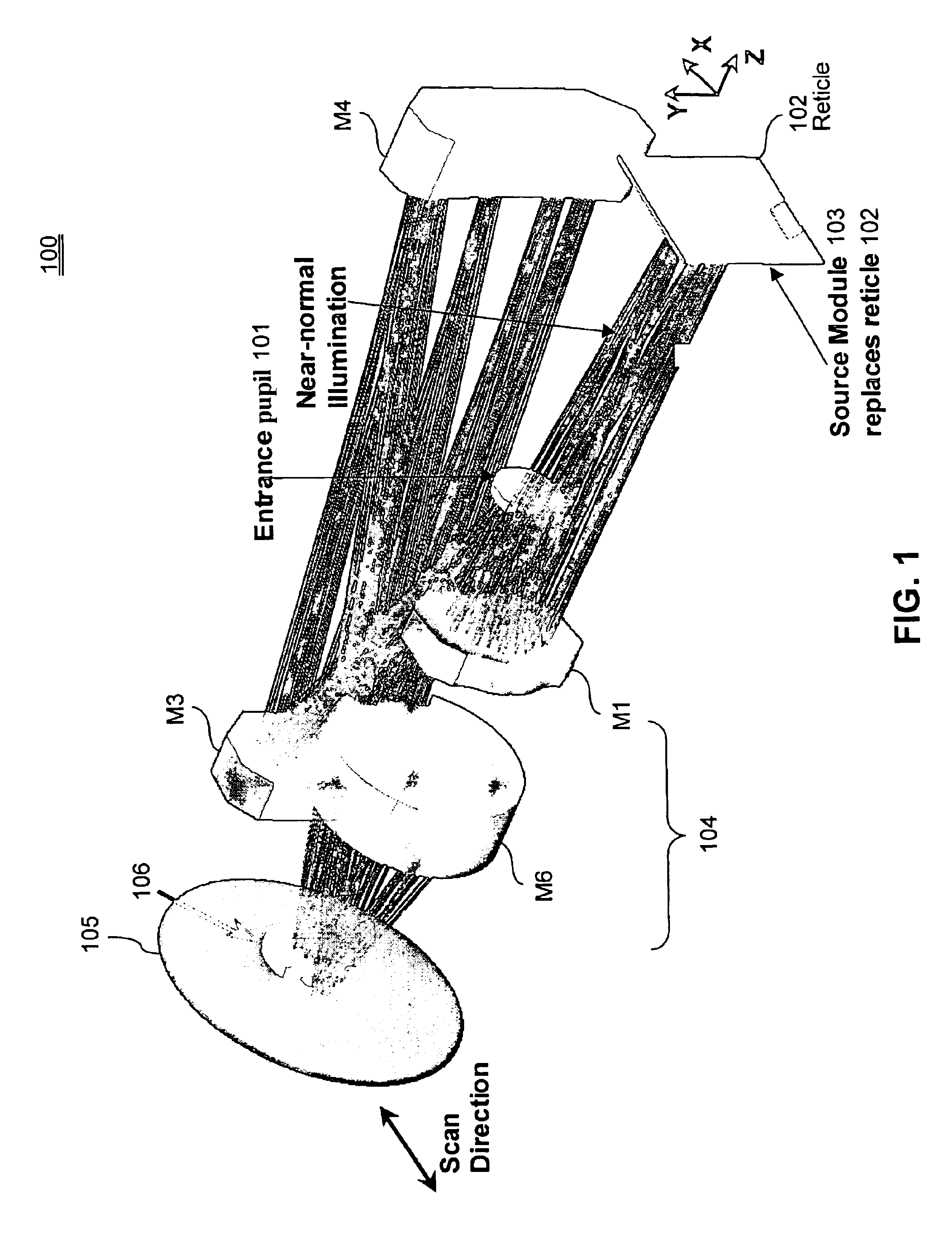
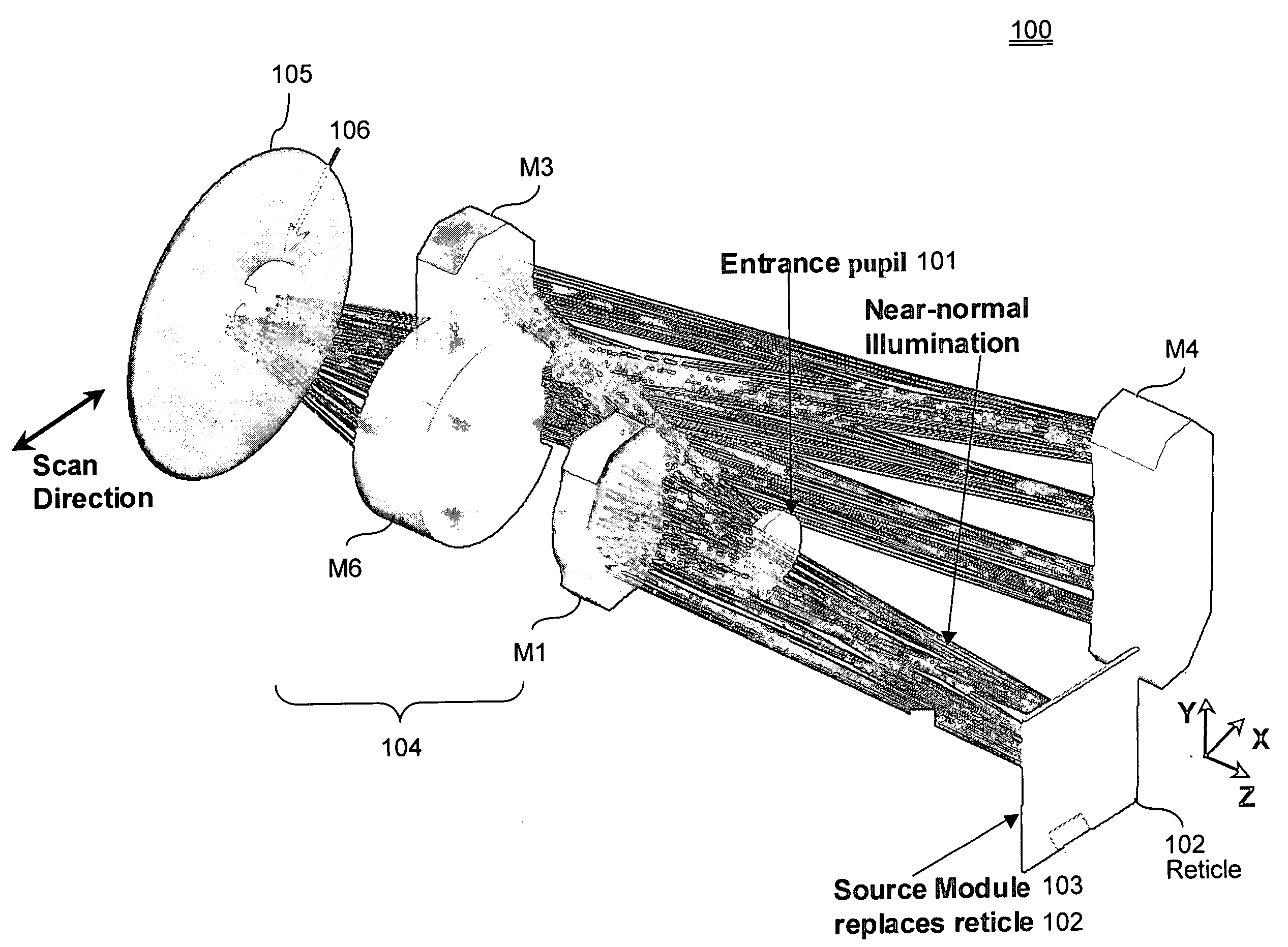
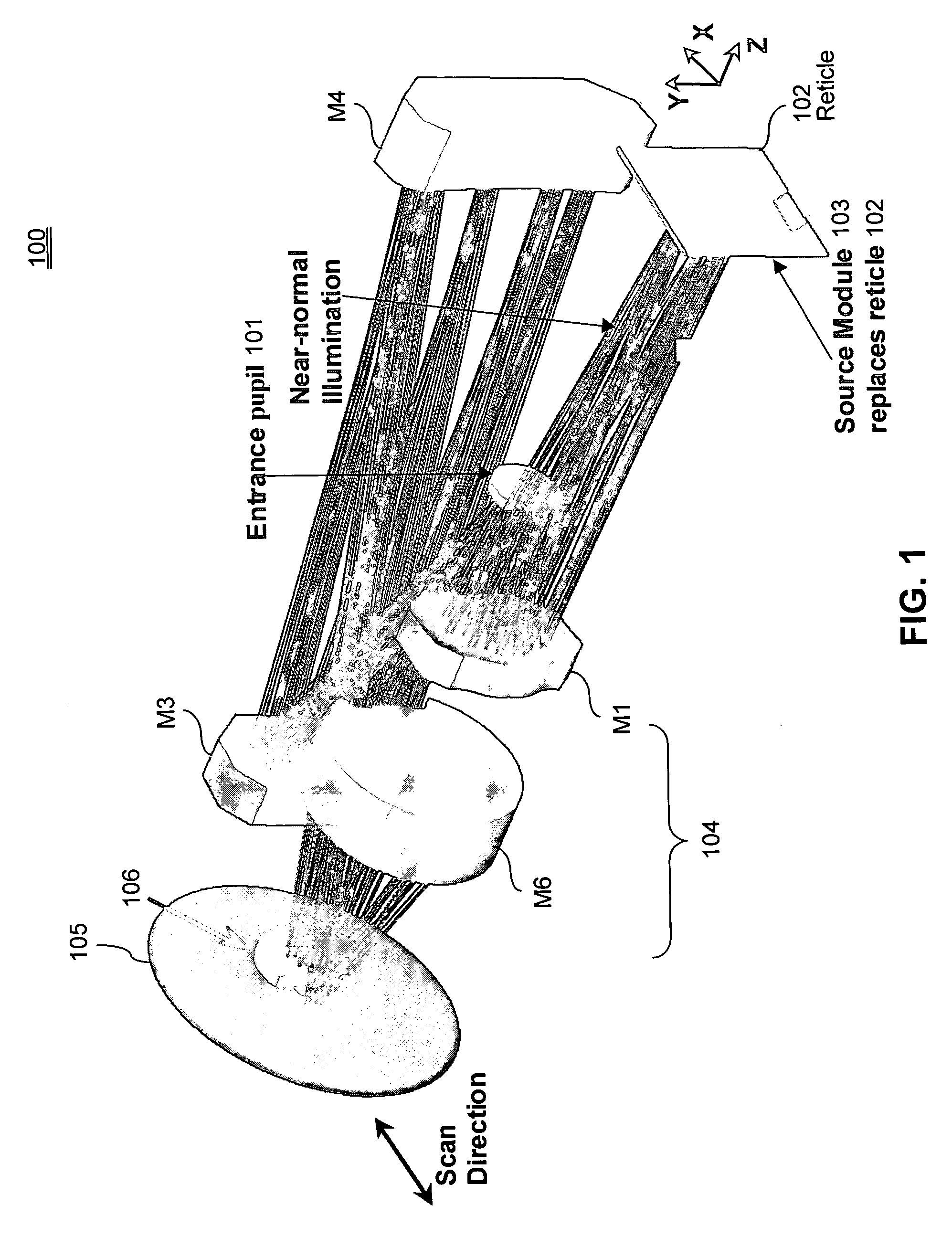
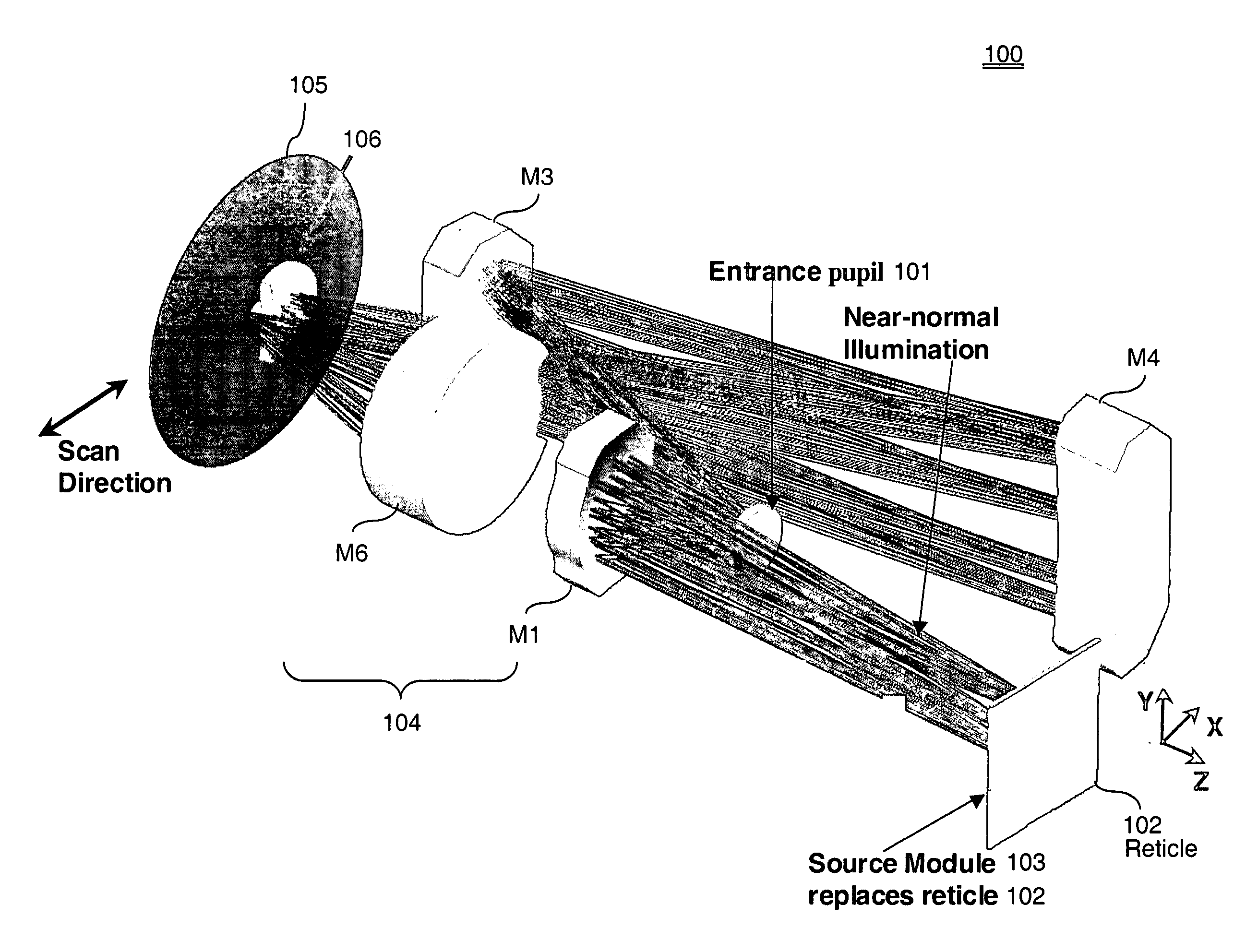
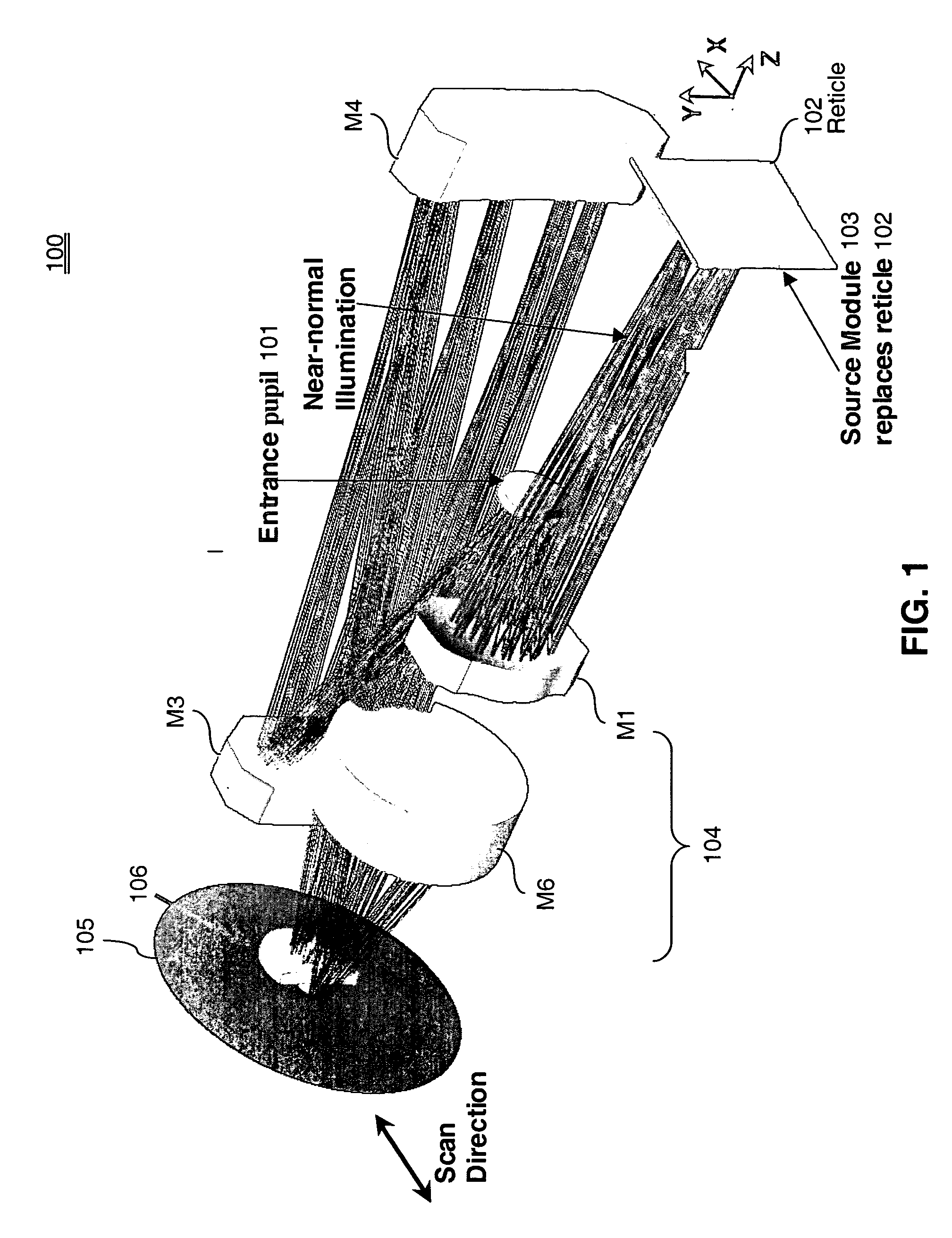
Tailored reflecting diffractor for EUV lithographic system aberration measurement
ActiveUS6867846B2Improve performanceOptical measurementsDiffraction gratingsGratingShearing interferometer
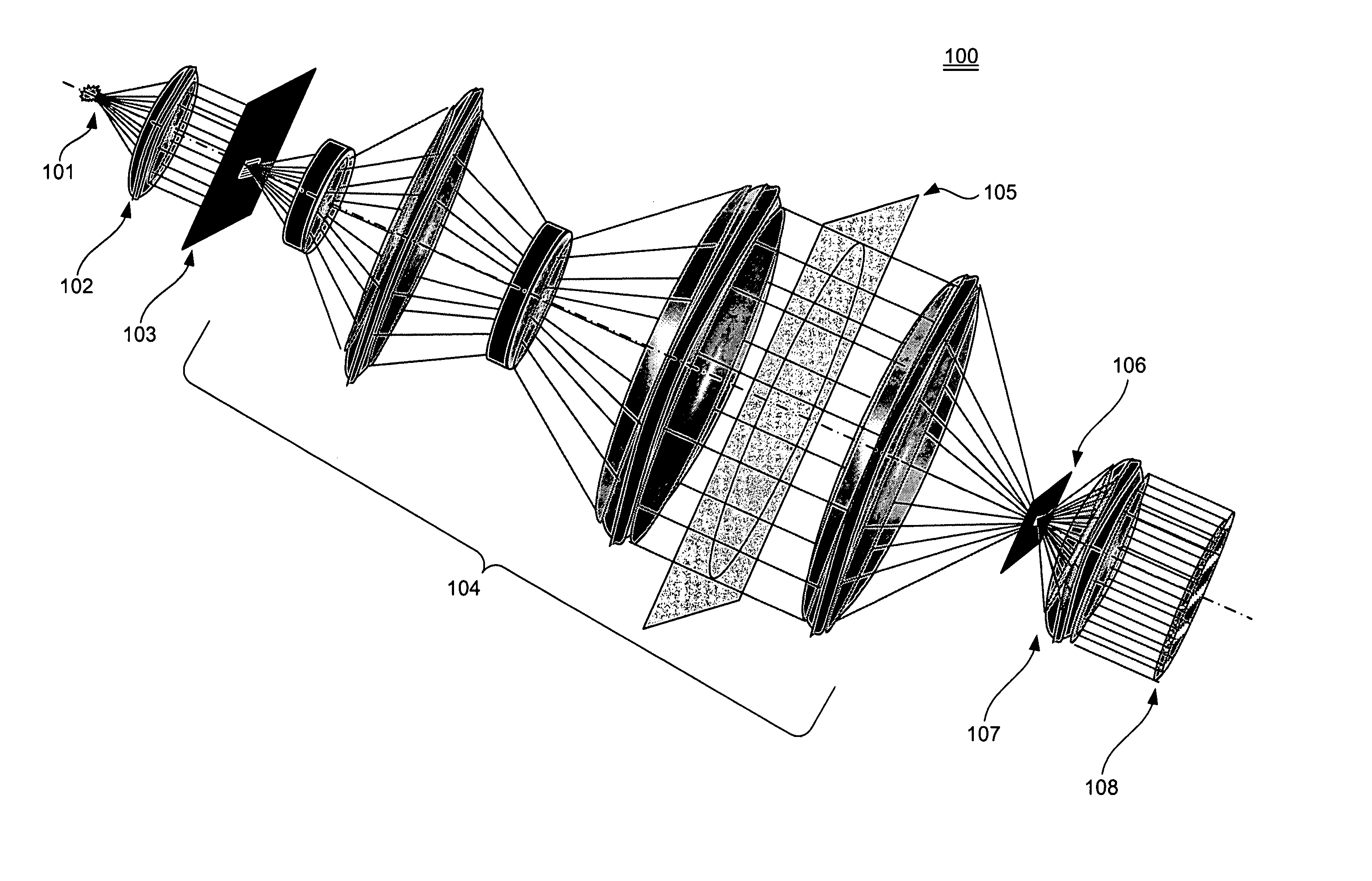
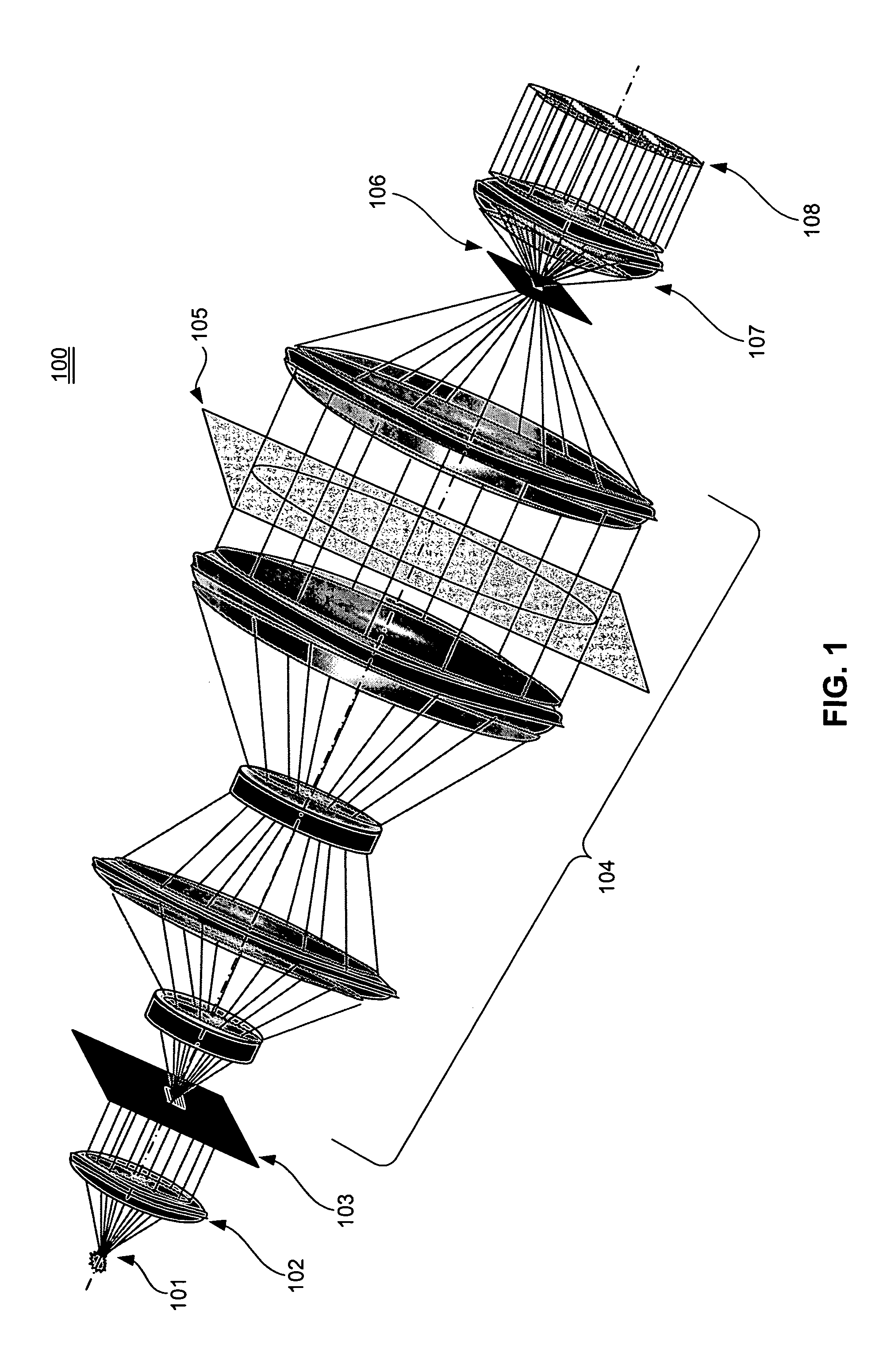
A wavefront measurement system includes a source of electromagnetic radiation. An imaging system directs the electromagnetic radiation at an object plane that it uniformly illuminates. A first grating is positioned in the object plane to condition the radiation entering the input of a projection optic. A projection optical system projects an image of the first grating onto the focal plane. A second grating is positioned at the focal plane that receives a diffracted image of the source to form a shearing interferometer. A CCD detector receives the image of the first grating through the projection optical system and the second grating that forms a fringe pattern if there are aberrations in the projection optical system. Phaseshift readout of fringe pattern can be accomplished by stepping the first grating in a lateral direction and reading each frame with the CCD detector. The first grating includes a plurality of reflecting lines each formed by a plurality of reflecting dots. The first grating has a pitch that is ½ times the magnification of the projection system times the pitch of the second grating for achromatic operation.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
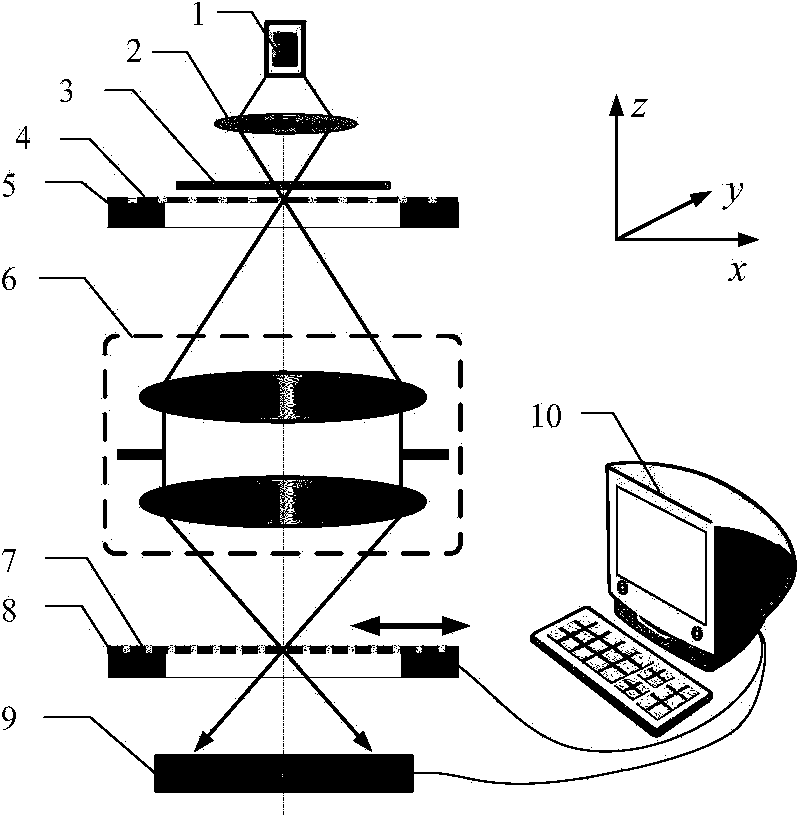
Ronchi shearing interferometer based phase extraction method
ActiveCN104111120AHigh measurement accuracyAccurate measurementOptical measurementsWave aberrationShearing interferometer
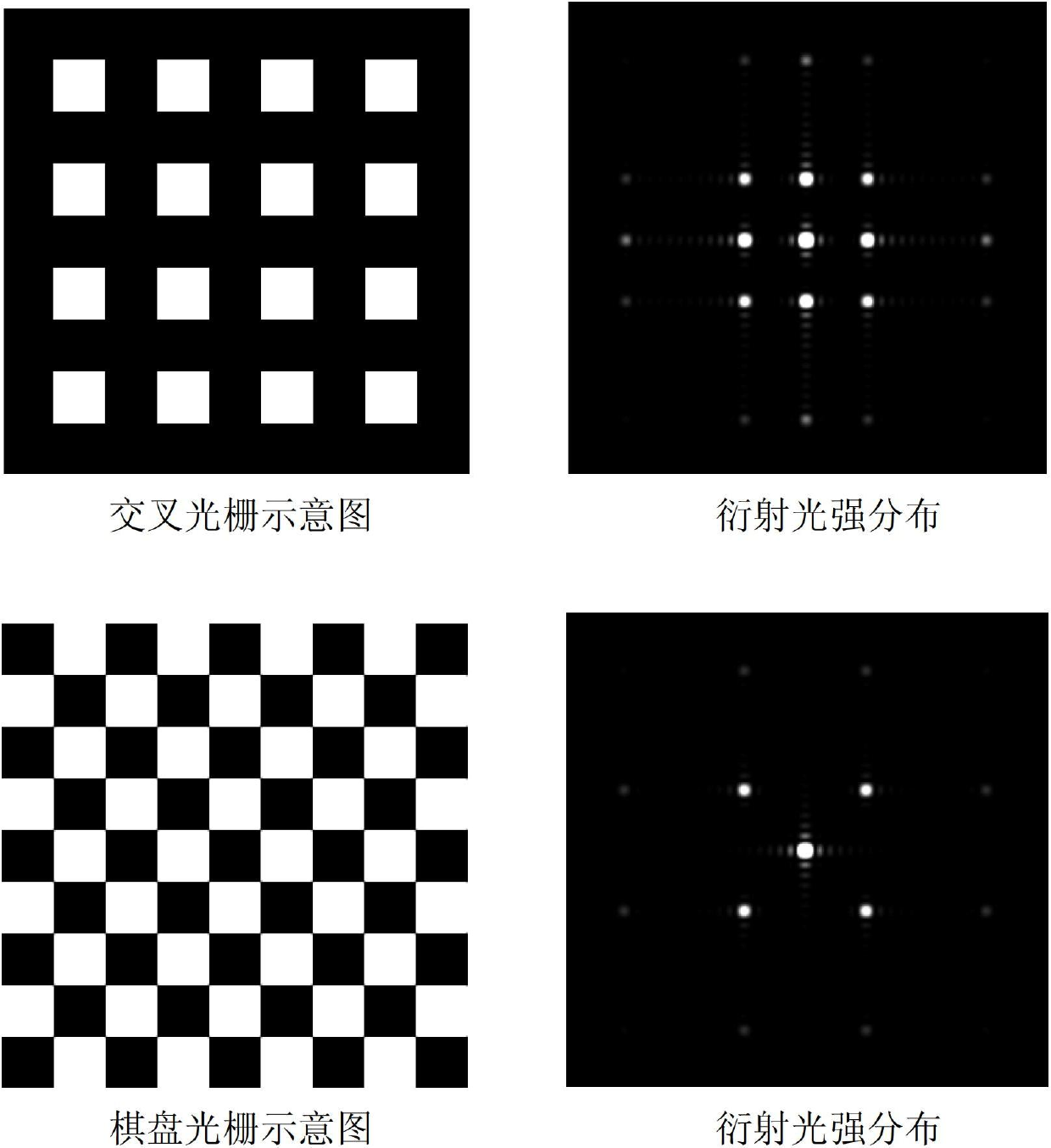
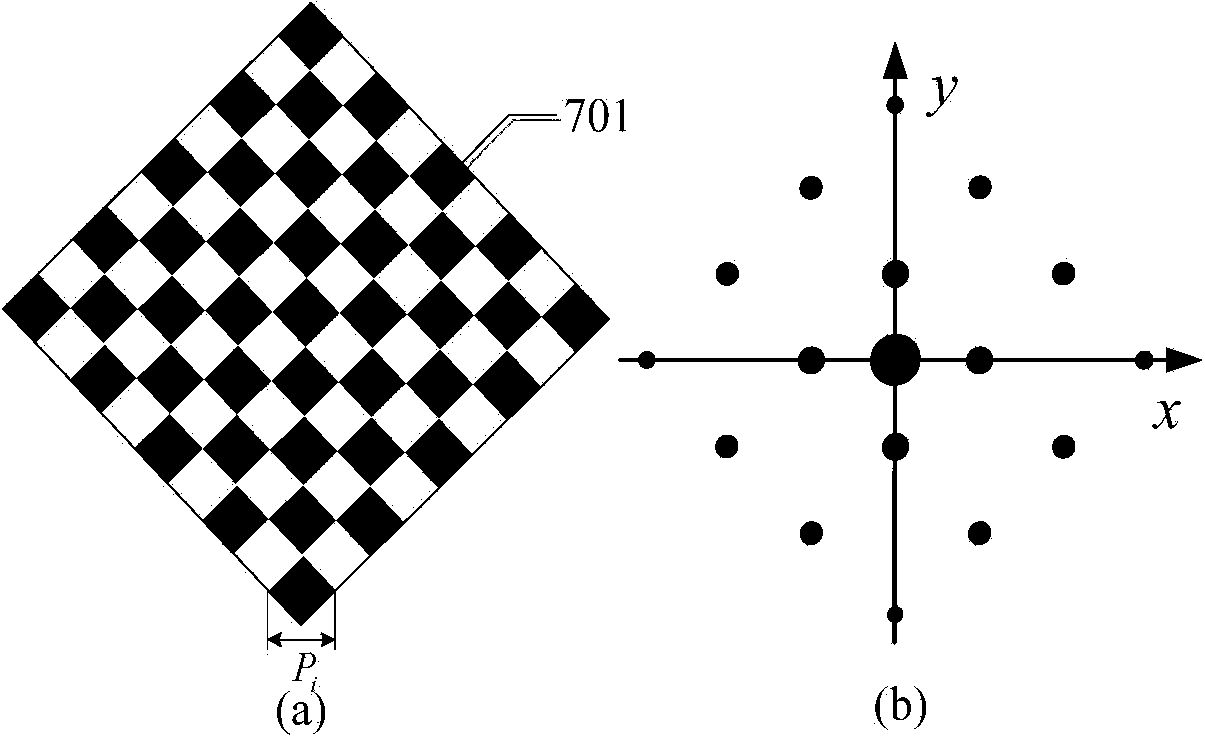
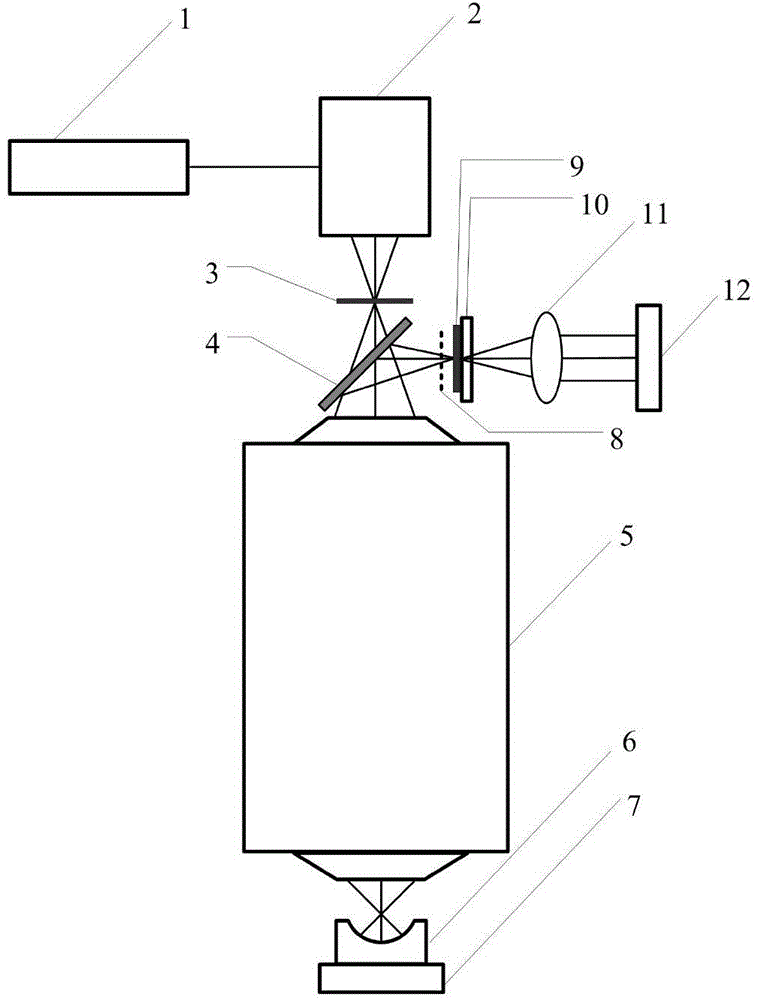
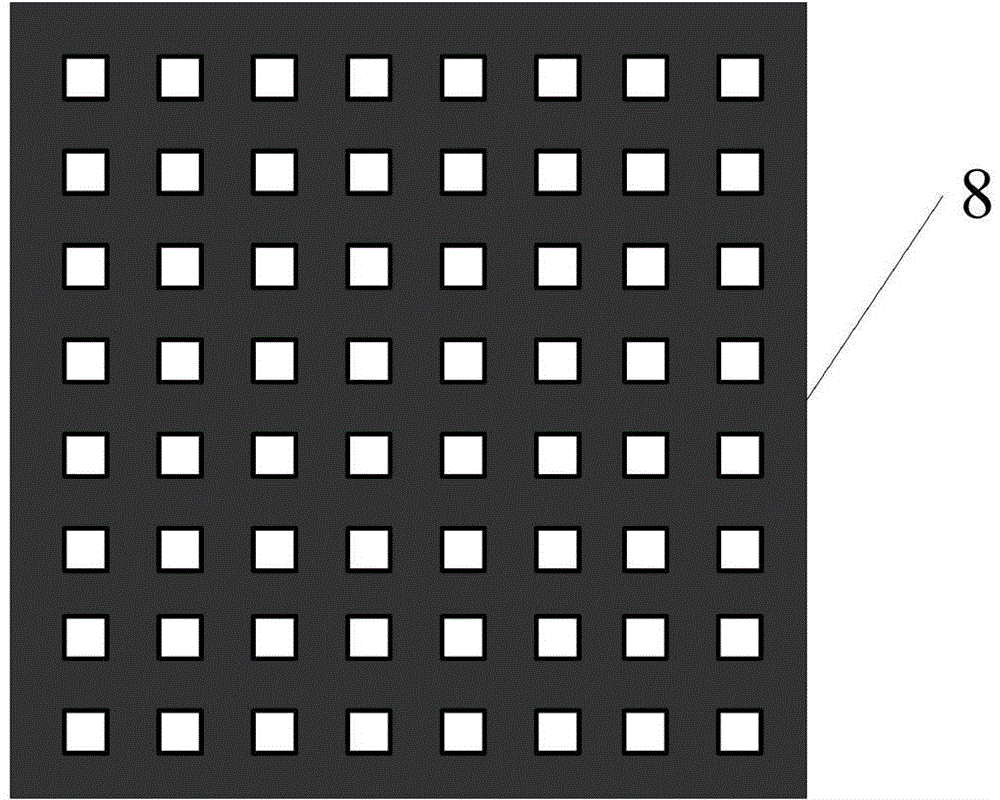
The invention discloses a Ronchi shearing interferometer based phase extraction method. A Ronchi shearing interferometer structure used in the Ronchi shearing interferometer based phase extraction method comprises a light source, a focusing lens, a scattering optical element, one-dimensional diffraction grating plates, a measured optical system platform, chessboard gratings, a two-dimensional photoelectric sensor and a computer. The one-dimensional diffraction grating plates and the chessboard gratings are arranged on an object plane and an image plane of the measured optical system and the phase is calculated due to collection of 9 interferometric fringe patterns with the shifting interval to be a quarter of pi to eliminate influences to the phase extraction accuracy from multi-level diffraction light in Ronchi shearing interference. The Ronchi shearing interferometer based phase extraction method has the advantages of eliminating the influences of diffraction items in higher levels other than the levels 0, 1 and minus 1, reducing the phase extraction system error in wave aberration detection and improving the wave aberration detection accuracy of the optical system.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
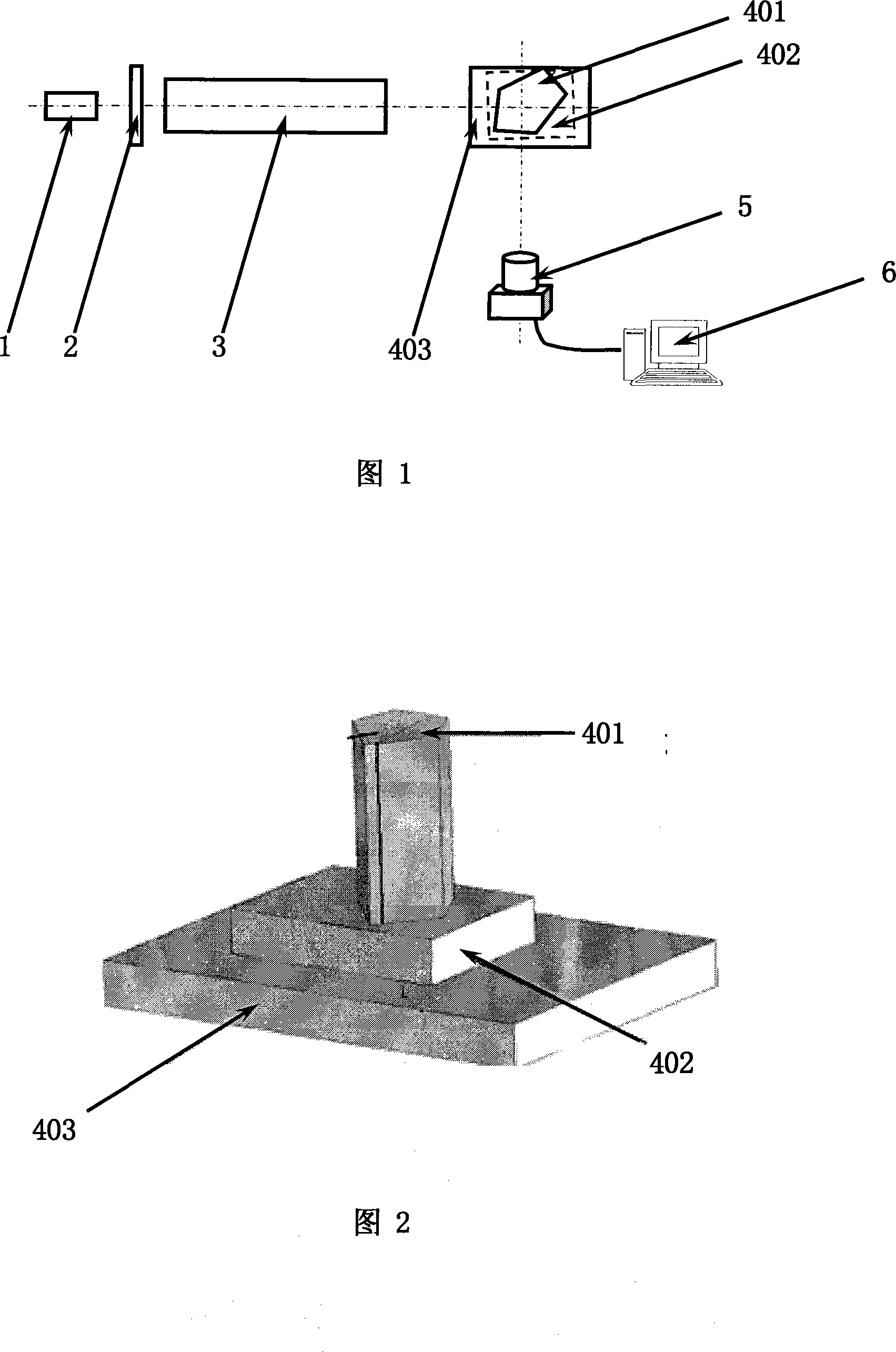
Device and method for integrally machining and measuring optical parts
ActiveCN102303224AReduce intermediate linksRealize feedback compensation machiningMeasurement/indication equipmentsNumerical controlInformation processingOptical axis
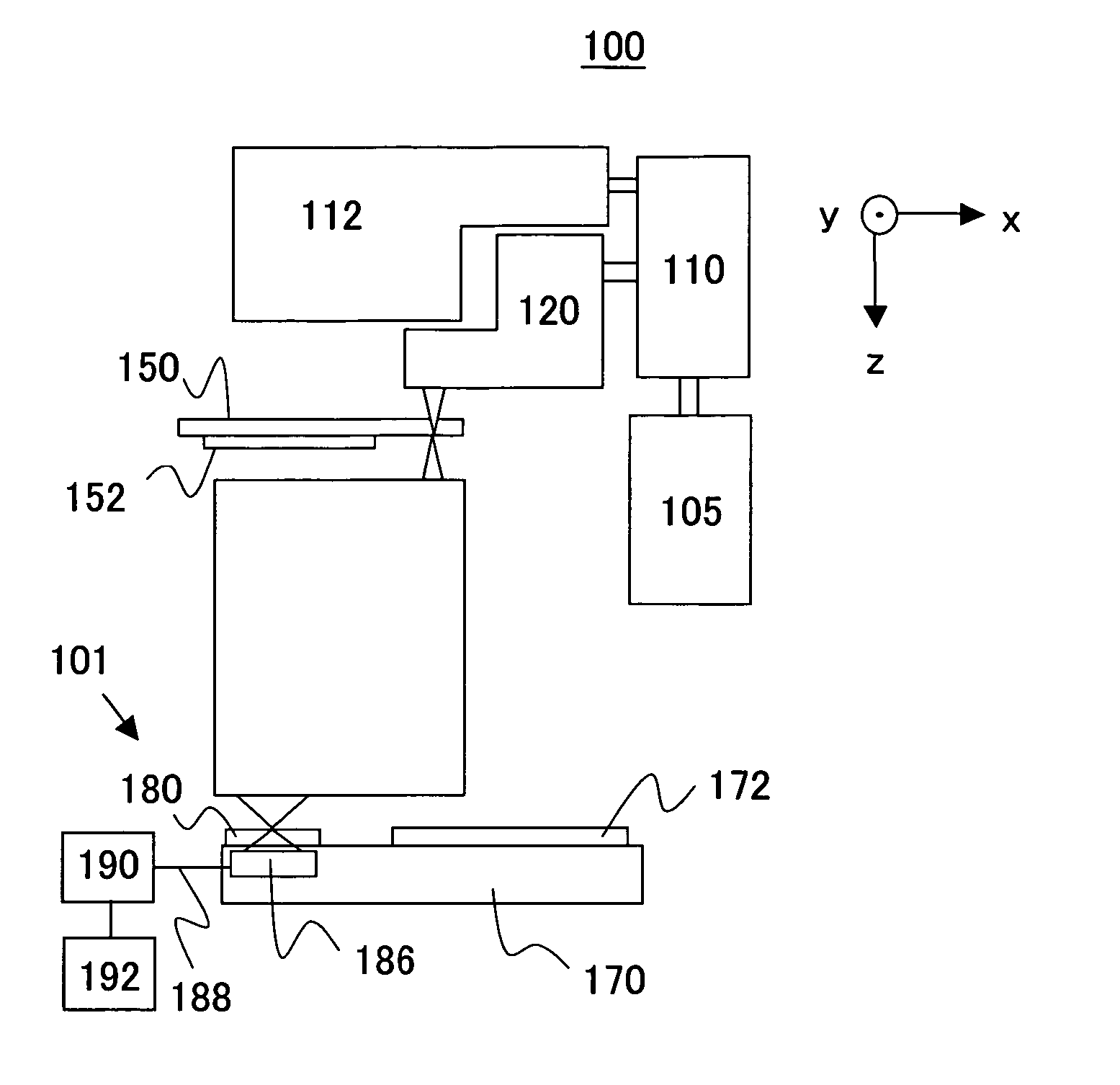
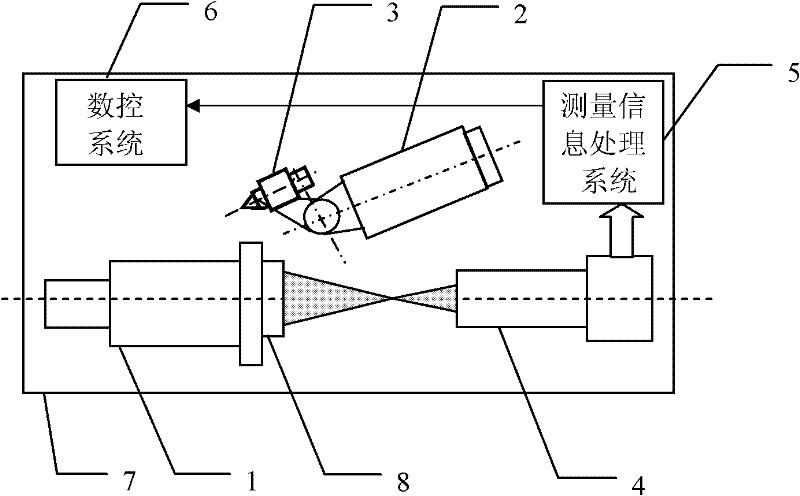
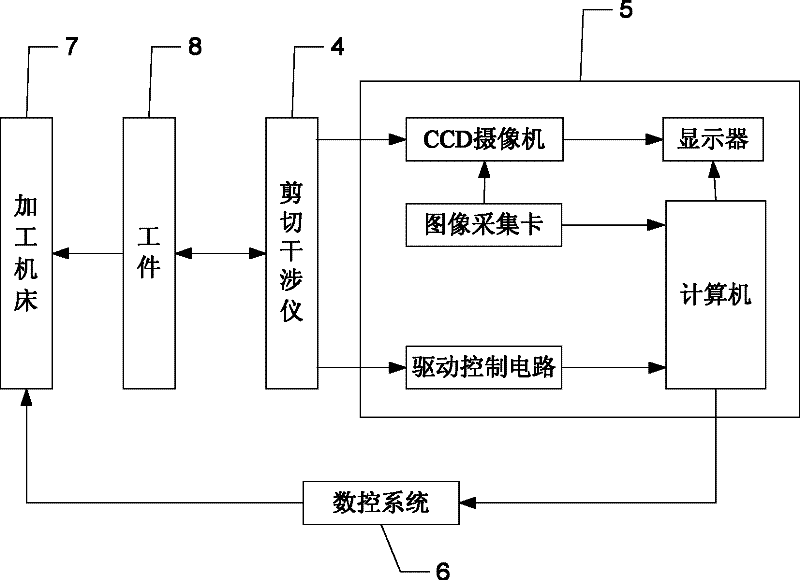
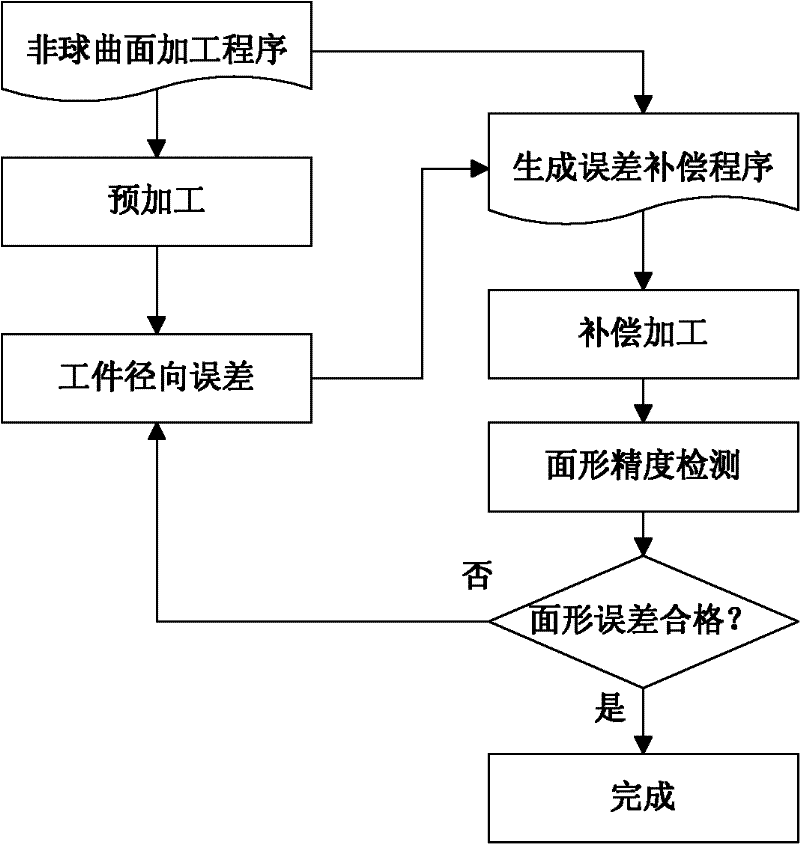
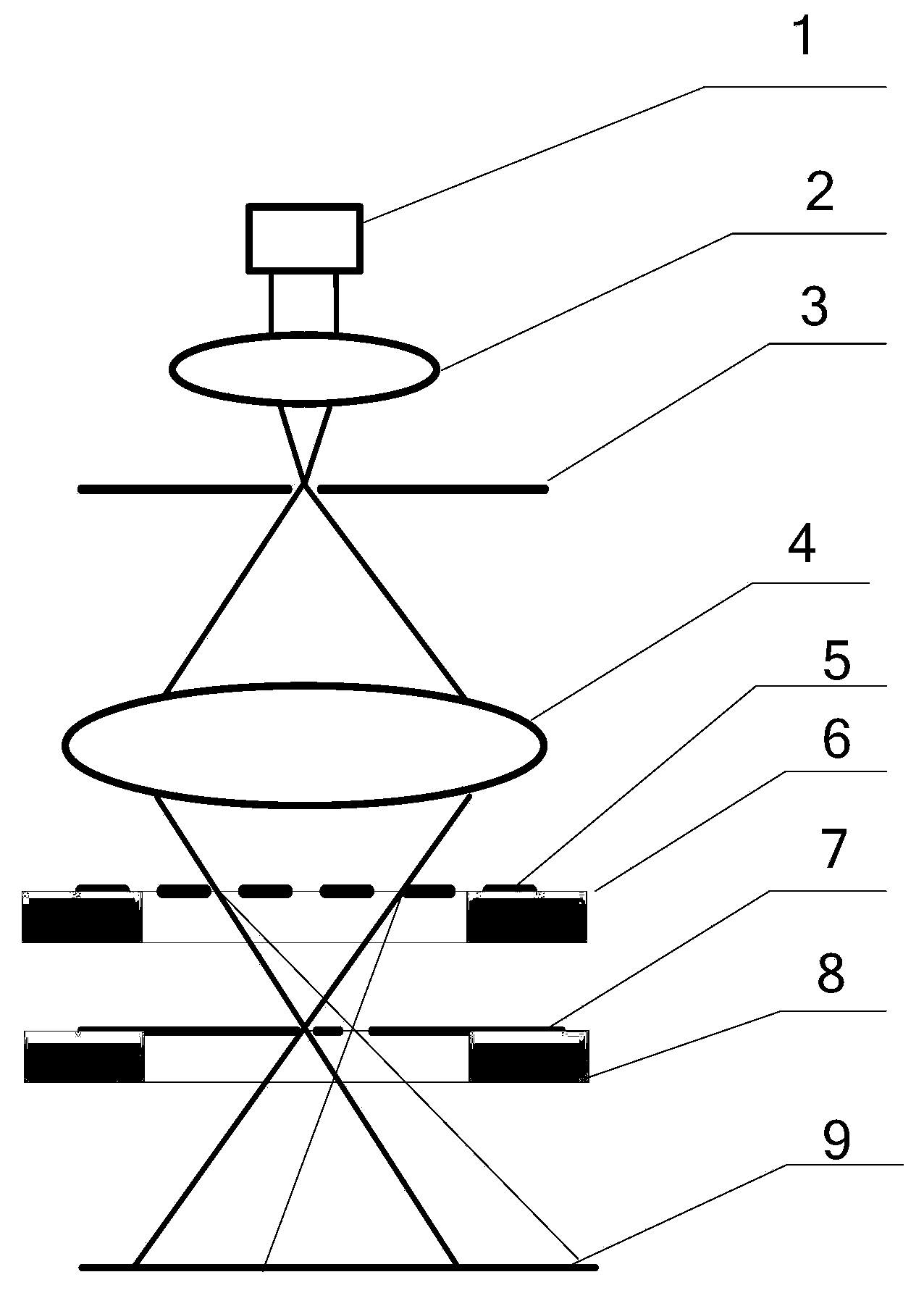
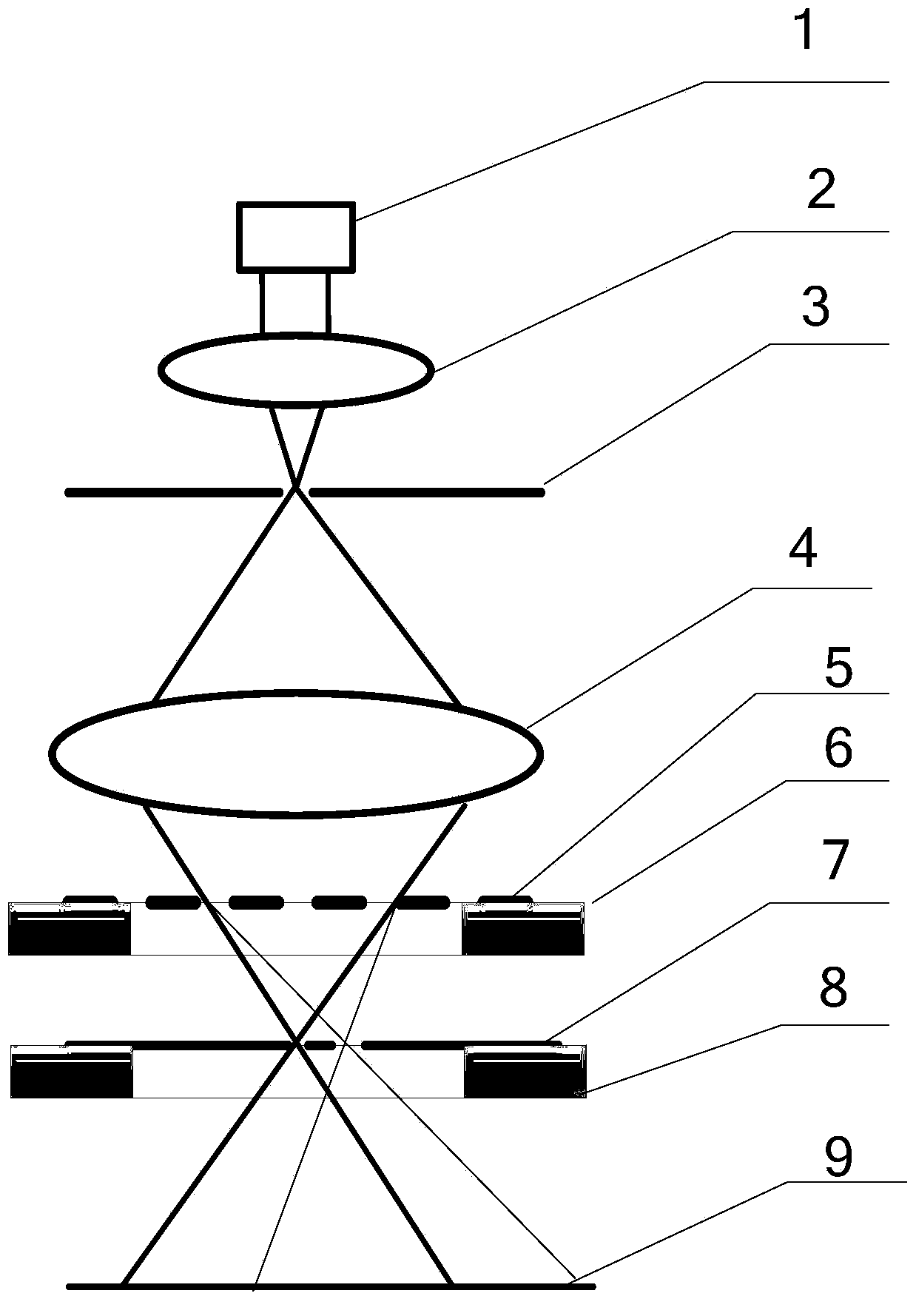
The invention relates to a device and method for integrally machining and measuring optical parts, belonging to the field of optical part machining. The invention aims at solving the problems that: an off-line measuring manner is mostly adopted in the traditional optical part machining, thus the machining efficiency is low; and the traditional optical part machining equipment cannot satisfy with the requirement of online measuring. According to the invention, a workpiece main shaft, a cutting tool main shaft and a shearing interferometer are mounted on a worktable surface of a machining machine; a workpiece is mounted on the workpiece main shaft; a cutting tool is mounted on the cutting tool main shaft through an oscillating arm and a tool carrier; a numerical control system is used for driving the cutting tool main shaft to rotate and driving the cutting tool to machine the workpiece; the optical axis of a measuring light beam which is emitted by the shearing interferometer and the central line of the workpiece main shaft are the same straight line; the shearing interferometer is used for emitting the measuring light beam to the workpiece; the shearing interferometer is used for acquiring image information which is returned by the measuring light beam and is used for sending the image information to a measured information processing system; the measured information processingsystem is used for acquiring surface error information of the surface of the workpiece according to the image information and is used for sending the information to the numerical control system; and the numerical control system is used for carrying out compensation machining on the workpiece.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
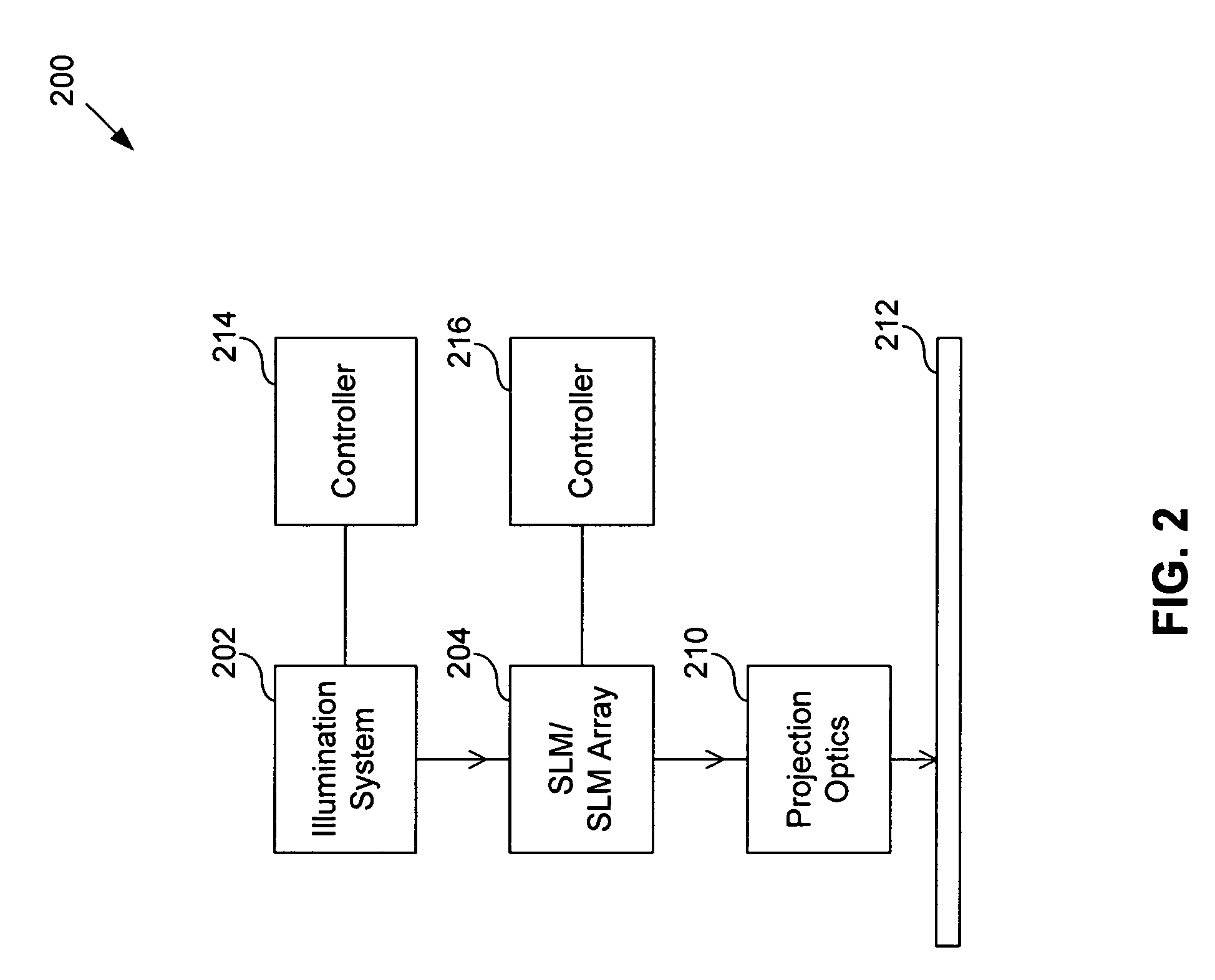
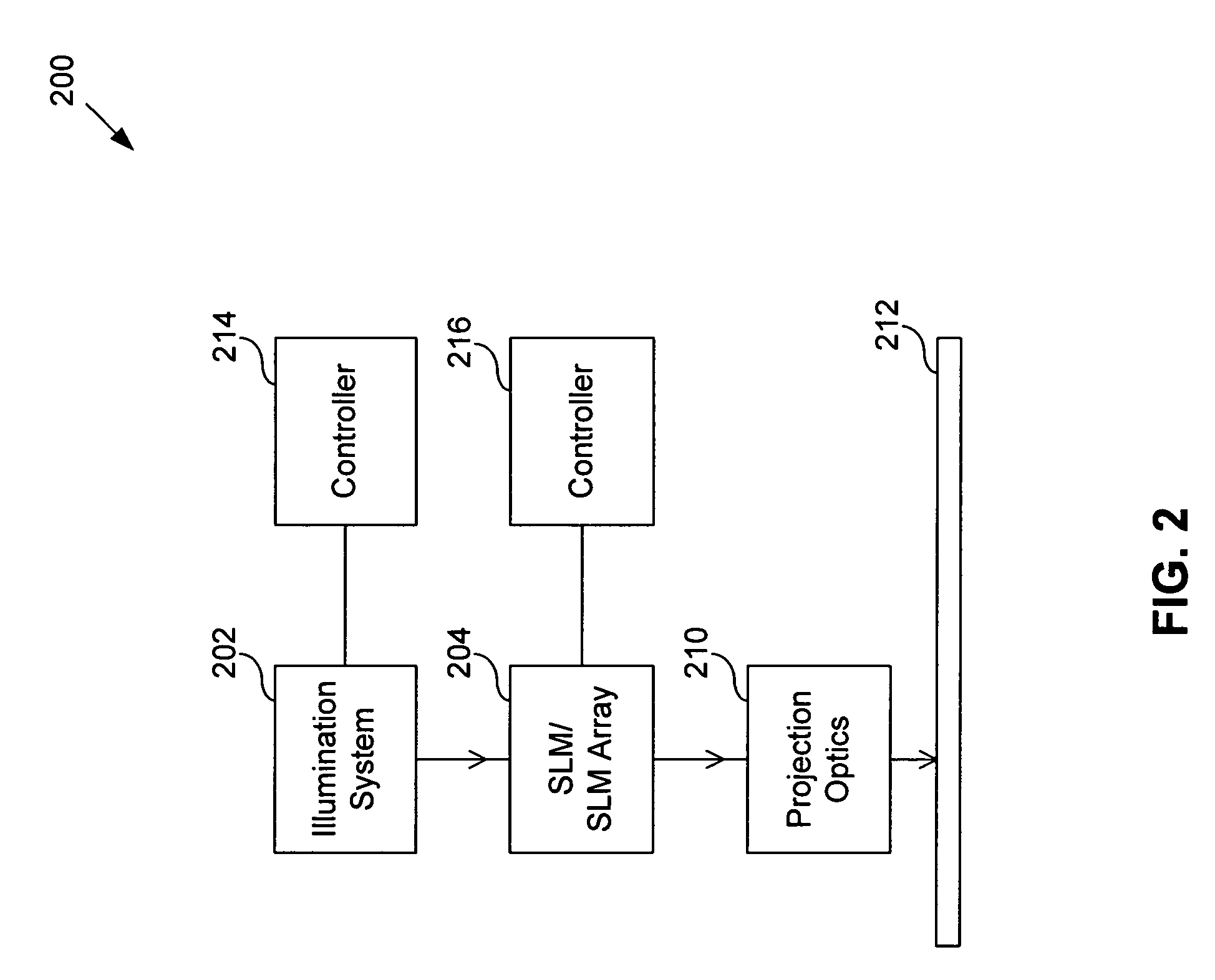
System and method for calibrating a spatial light modulator array using shearing interferometry
InactiveUS20050225859A1Photometry using reference valueOptical measurementsProjection opticsSpatial light modulator
A system for calibrating a spatial light modulator array includes an illumination system and a spatial light modulator array that reflects or transmits light from the illumination system. A projection optical system images the spatial light modulator array onto an image plane. A shearing interferometer creates an interference pattern in the image plane. A controller controls modulation of elements of the spatial light modulator array. The shearing interferometer includes a diffraction grating, a prism, a folding mirror or any other arrangement for generating shear. The shearing interferometer can be a stretching shearing interferometer, a lateral shearing interferometer, or a rotational shearing interferometer. The shearing interferometer may include a diffraction grating with a pitch corresponding to a shear of the light by an integer number of elements. The projection optics resolves each element of the spatial light modulator array in the image plane. The controller can modulate alternate columns of elements of the spatial light modulator array.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
Small-beam lateral-shear interferometer
ActiveUS20040051877A1Eliminate DiffractionOptical measurementsUsing optical meansPhase shiftedLight beam
A lateral-shear interferometer utilizes two relatively thick glass plates bonded together in a single block with a tilted air gap between opposing inner surfaces. The thickness of the glass plates is selected to be sufficiently large to separate the output beams from the light reflected from the top and bottom surfaces of the block, thereby eliminating the need for antireflection coatings. The shear interferometer is combined with an external mirror mounted on a tilt stage actuated by a computer-controlled tilt actuator to perform phase-shifting interferometric analysis in conventional manner.
Owner:ENG SYNTHESIS DESIGN
Device for detecting system wave aberration of photoetchingprojection objective
InactiveCN104483817AAvoid restrictionsReduce noisePhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusGratingFull field
A device for detecting system wave aberration of a photoetchingprojection objective comprises a light source, an illuminating system, a pinhole space filter, a beamsplitter, a to-be-detected projection objective, a spherical reflector, a two-dimensional grating, a space filter and an image sensor. According to the device, a level selection window is taken as the space filter, so that noise is reduced, the measuring accuracy is improved, and the defect of limitation of Talbot distance to the image sensor position is overcome. The spherical reflector is added to a light path, can be used for detection of system wave aberration of an immersedprojection objective and can also be used for detection of system wave aberration of a non-immersedprojection objective; full-field system wave aberration of the projection objective can be detected, and wave aberration represented by 36 Zernike coefficients is obtained; and with adoption of a light path structure of a shearing interferometer, the device has the advantages of high detecting accuracy, good repeatability and the like.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Digital phase-shifting lateral shearing interferometer and optical system wave aberration measurement method
InactiveCN104807548AEnhanced inhibitory effectThe effect of high-level diffracted light above level 2 is goodOptical measurementsTesting optical propertiesSpatial light modulatorPhase shifted
Disclosed are a digital phase-shifting lateral shearing interferometer and an optical system wave aberration measurement method. The interferometer is composed of a light source, a small-hole mask, a first spatial light modulator, a second spatial light modulator, a two-dimensional photoelectric detector and a computer. The first spatial light modulator is arranged as a grating by computer programming to serve as a shearing light splitter, the second spatial light modulator is arranged as a double-window mask to serve as a filter for filtering high-order diffraction light at zero order and more than two orders, and only diffraction light at +1 order and -1 order takes part in interference. The problem that the high-order diffraction light takes part in interference is solved, the interferometer has the advantage that changeable shearing direction and adjustable shearing rate can be realized without replacing or rotating any device.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
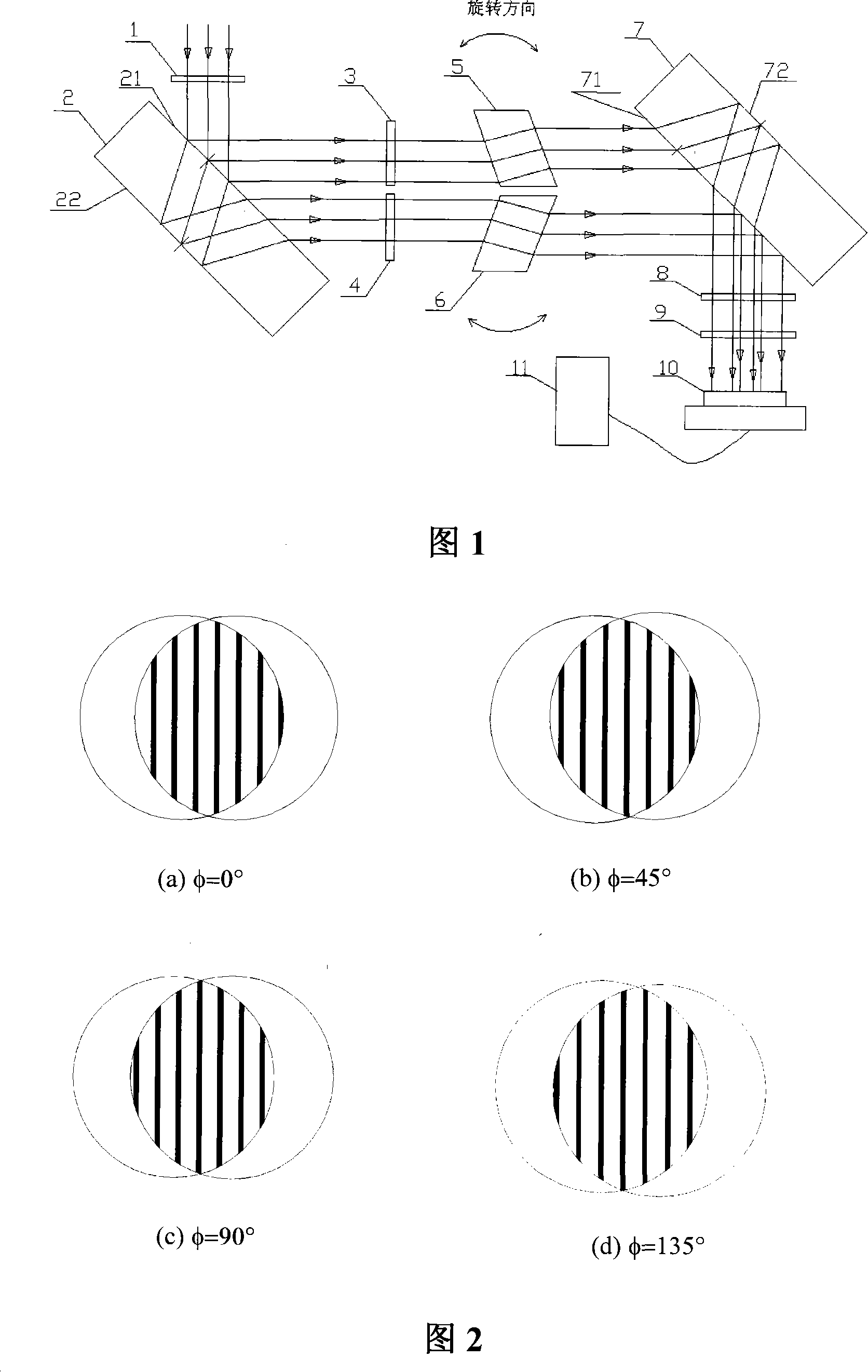
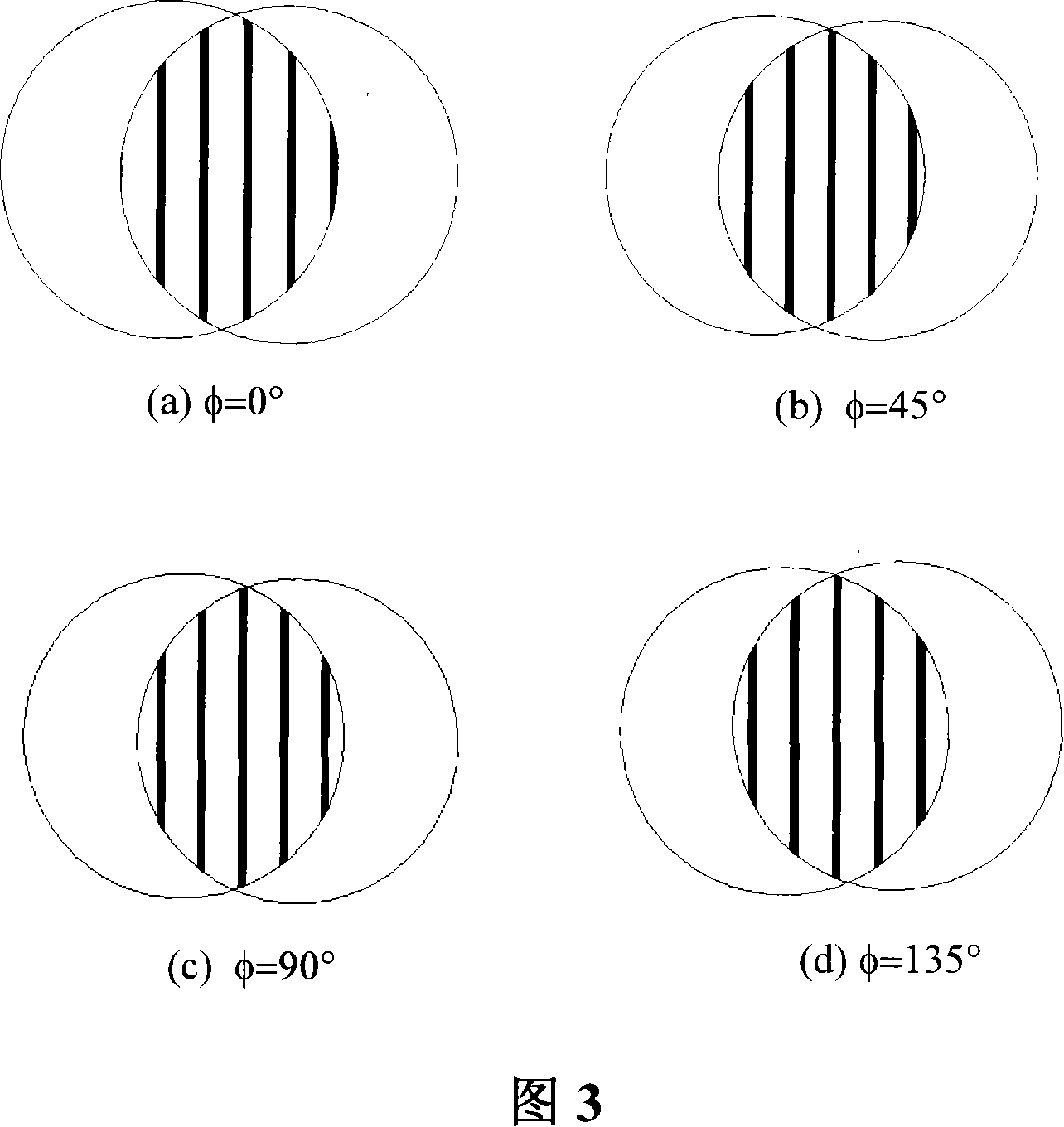
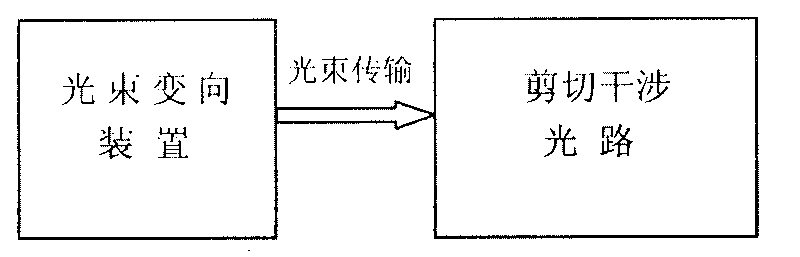
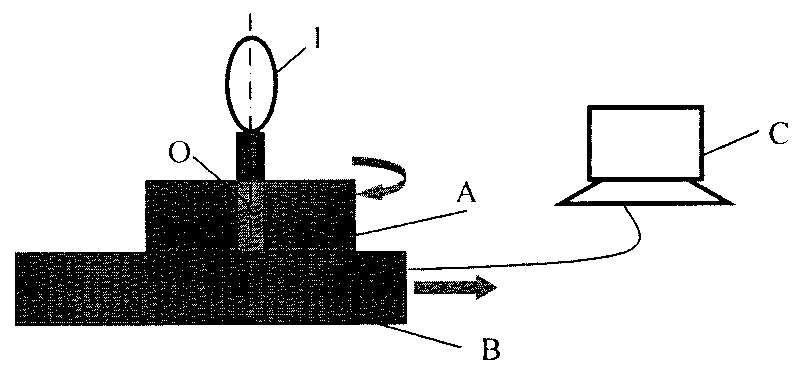
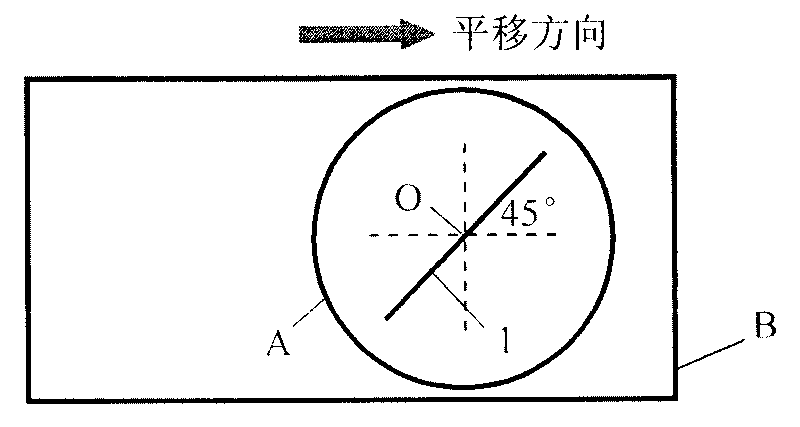
Wave-front measuring instrument of collimation deflection beam and measuring method thereof
The invention relates to a wave-front measuring instrument of a collimation deflection beam and a measuring method thereof, relating to the wave-front measurement of a collimation deflection beam in the optical field. The measuring instrument comprises a beam deviation device and a hearing interference light path, wherein the beam deviation device comprises a reflector and an electric combined platform controlled by a computer. The measuring method comprises the following steps: using a stripe generated by a collimation laser through the measuring instrument as a reference stripe chart; setting the action parameter of the combined platform by the computer according to the deflection angle of a beam to be measured; controlling the reflector to rotate and translate to change the propagation direction of the beam into a direction perpendicular to the translation direction of the combined platform; measuring a distorted stripe chart; and calculating the wave-front distribution of the deflected beam at an incidence hole according to a stripe-processing algorithm. By adding a device capable of changing the propagation direction of the deflected beam on a basis of a radial shearing interferometer in the quadrilateral structure, the invention can conveniently and rapidly measure the wave-front distribution of the collimation deflection beam and solve the problem that the traditional instrument can not directly measure the wave-front distribution of the collimation deflection beam.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Transverse shearing interferometer agglutination checking method
InactiveCN101122456AImprove control accuracyReduce interpretation errorUsing optical meansMountingsLaser lightAgglutination
A scuffing detection method for a lateral shearing interferometer is provided. The lateral shearing interferometer to be scuffed is coated evenly with photosensitive glues and is vertically put on a high precision optical plate of a precision adjusting platform. The laser light output by a laser forms into even parallel light on the lateral shearing interferometer to be scuffed. Interference fringes formed on the send out end of the lateral shearing interferometer to be scuffed are received by a digital camera and are displayed in real time on a computer. The CCD pixel number M0 of the digital camera occupied by N0 interference fringes is calculated. Two prisms are moved slightly to read CCD pixel number M of the digital camera occupied by N0 interference fringes. When the CCD pixel number M becomes to be M0, the two prisms are set not to move. The two scuffed prisms are solidified. The invention solves a technical problem in background technology that the lateral shearing amount of the lateral shearing interferometer is hard to be precisely controlled. The error of the lateral shearing amount of the invention can be controlled within 1%.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System and method for calibrating a spatial light modulator array using shearing interferometry
InactiveUS6965436B2Photometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansSpatial light modulatorGrating
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
Tailored reflecting diffractor for EUV lithographic system aberration measurement
A wavefront measurement system includes a source of electromagnetic radiation. An imaging system directs the electromagnetic radiation at an object plane that it uniformly illuminates. A first grating is positioned in the object plane to condition the radiation entering the input of a projection optic. A projection optical system projects an image of the first grating onto the focal plane. A second grating is positioned at the focal plane that receives a diffracted image of the source to form a shearing interferometer. A CCD detector receives the image of the first grating through the projection optical system and the second grating that forms a fringe pattern if there are aberrations in the projection optical system. Phaseshift readout of fringe pattern can be accomplished by stepping the first grating in a lateral direction and reading each frame with the CCD detector. The first grating includes a plurality of reflecting lines each formed by a plurality of reflecting dots. The first grating has a pitch that is ½ times the magnification of the projection system times the pitch of the second grating for achromatic operation.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
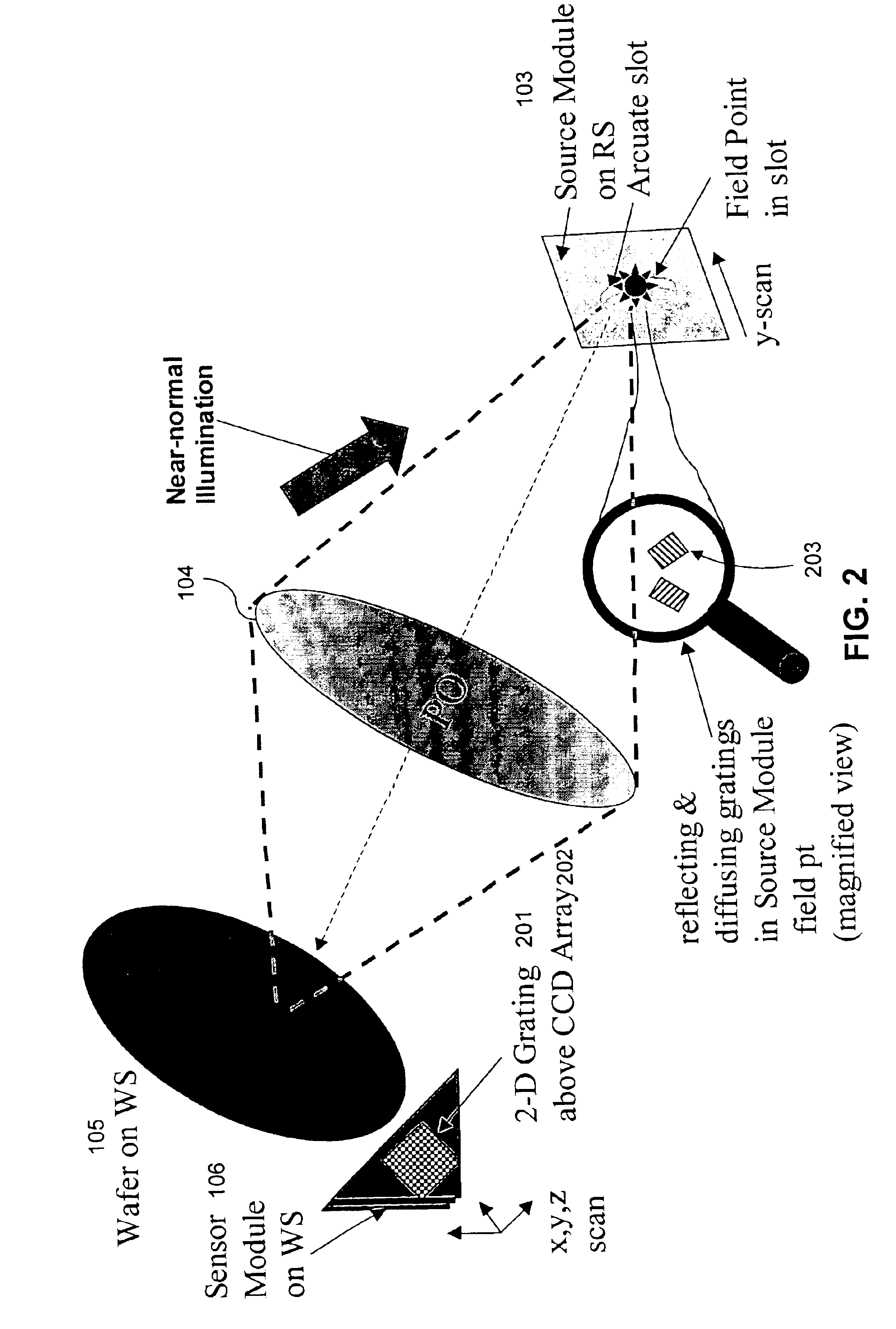
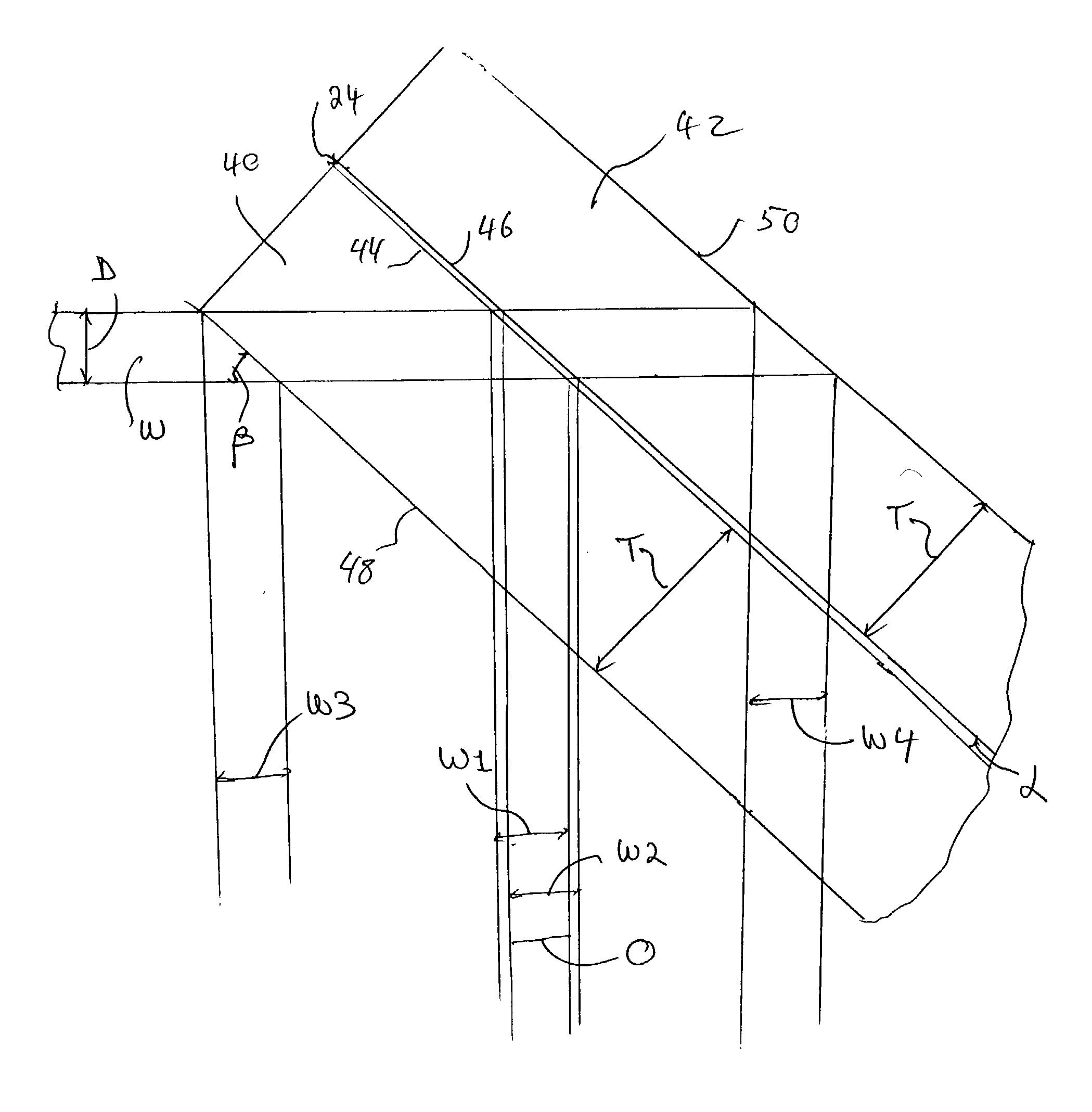
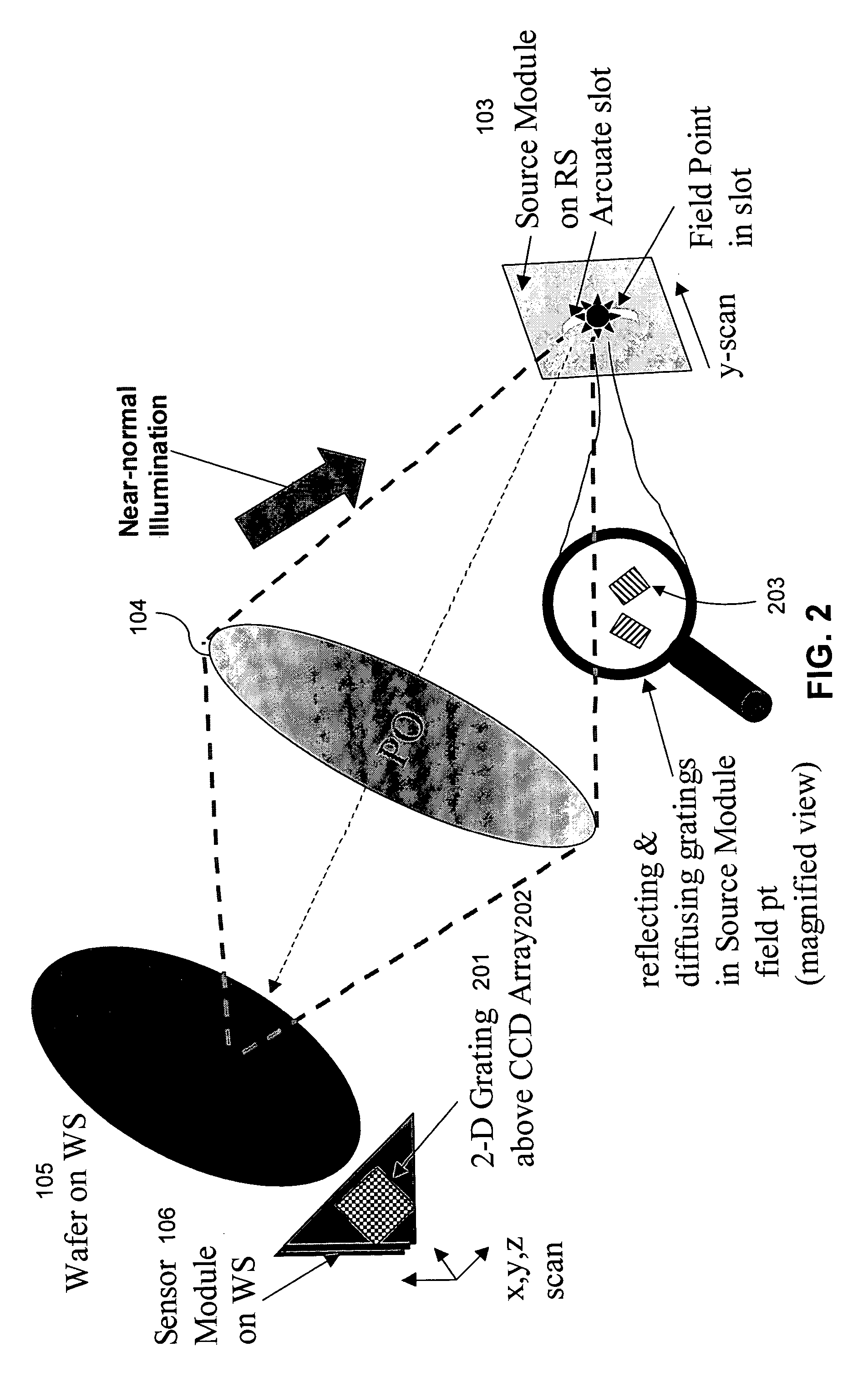
Shearing interferometer with dynamic pupil fill
InactiveUS20050259269A1Optical measurementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGratingEntire pupil
A wavefront measurement system includes a source of electromagnetic radiation. An illumination system delivers the electromagnetic radiation to an object plane. A source of a diffraction pattern is in the object plane. A projection optical system projects the diffraction pattern onto an image plane, which includes a mechanism (e.g., a shearing grating) to introduce the lateral shear. A detector is located optically conjugate with the pupil of the projection optical system, and receives an instant fringe pattern, resulting from the interference between sheared wavefronts, from the image plane. The diffraction pattern is dynamically scanned across a pupil of the projection optical system, and the resulting time-integrated interferogram obtained from the detector is used to measure the wavefront aberration across the entire pupil.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
Small-sized radial shearing interferometer based on four-step phase-shifting theory
ActiveCN102967378ASuppress disturbanceLow environmental requirementsOptical measurementsOptical elementsPolarizerShearing interferometer
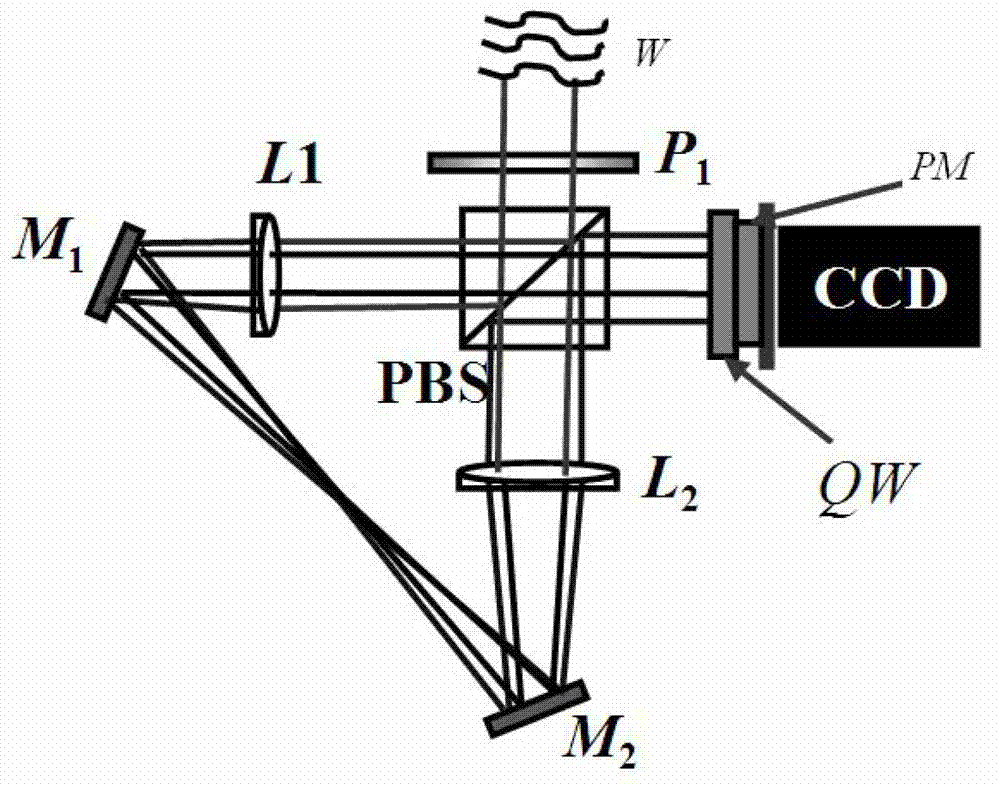
The invention provides a small-sized radial shearing interferometer based on the four-step phase-shifting theory, comprising a polarizer (P1), a polarizing beam splitter (PBS), a beam reducer or expander system, a quarter-wave (QW) plate, a binary micro-polarizer array and a photosensor CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) camera, wherein the beam reducer or expander system comprises a first lens (L1) with the focus f1, a second lens (L2) with the focus f2 (f1 is not equal to f2), a first reflector (M1) and a second reflector (M2). According to the interferometer, an aberrated beam enters the small-sized radial shearing interferometer to form a pair of beams which are arranged on the same optical axis and have polarization directions vertical to each other and beam sizes reduced and expanded according to the same proportion, and the pair of beams are projected on the photosensitive surface of the CCD camera to form a single-frame interferogram after passing through a four-step phase shifter which comprises the quarter-wave plate (QW) and the binary micro-polarizer array. The small-sized radial shearing interferometer based on the four-step phase-shifting theory does not need a fully-flattened reference mirror, can be used in the field of wavefront sensing application such as adaptive optics, and can effectively suppress environmental disturbance due to the adoption of a complete common path structure, and has low environment requirements and stable interferogram.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
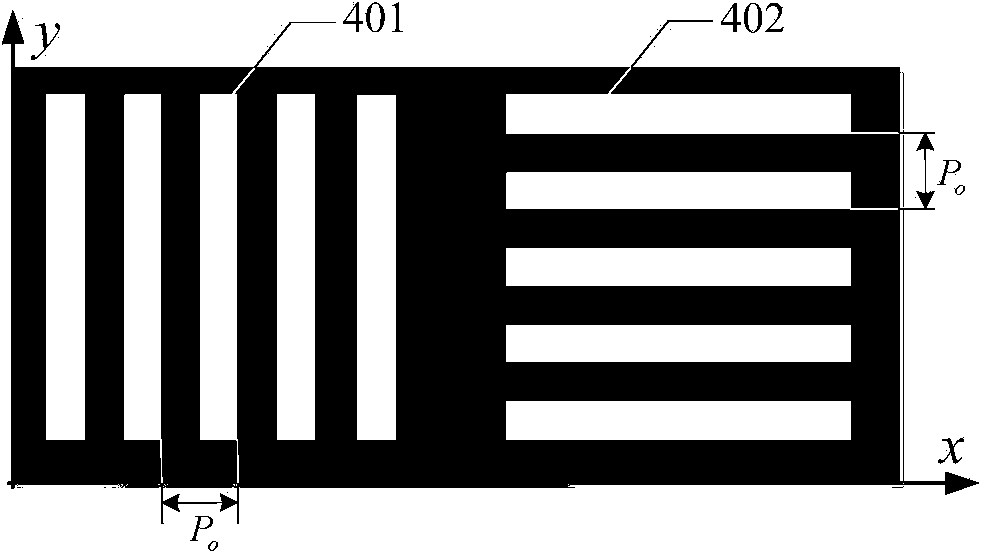
Grating shear wave aberration detection interferometer and detection method thereof
ActiveCN104165755AEliminate tilt errorsImprove detection accuracyTesting optical propertiesPath lengthGrating
The invention provides a grating shear wave aberration detection interferometer. The grating shear wave aberration detection interferometer comprises a light source, a focus lens, a filtering pinhole, a two-dimensional grating, a grating displacement platform, a diaphragm plate, a diaphragm alignment displacement platform and a two-dimensional photoelectric sensor. According to the grating shear wave aberration detection interferometer, the wave aberration of an optical system to be detected is detected; when the optical system to be detected is illuminated by the light source, the wavefront of the optical system to be detected generates an interference pattern through grating separation and shear, wavefront reconstruction is conducted on differential information generated by multiple diffraction levels in different directions through shear and interference, so that a system error correlative is obtained, and then the relevant parameters, namely, the distance between every two adjacent focusing points of different levels of diffraction light and the inclination angle of a detector, of main system error terms influencing the wave aberration detection precision of the grating shear interferometer are obtained; in this way, geometric path-length errors and detector inclination errors existing in wave aberration detection are eliminated, and the precision of wavefront reconstruction and the accuracy of wave aberration detection are improved. By the adoption of the grating shear wave aberration detection interferometer, wave aberration detection of the optical system to be detected is conducted, system errors existing during detection are eliminated, and the detection precision is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Eliminating method of system errors in raster shearing interferometer wave aberration detecting
ActiveCN103674493AImprove detection accuracyReduce mistakesTesting optical propertiesGratingWave aberration
Provided is an eliminating method of system errors in raster shearing interferometer wave aberration detecting. According to the method, + / - one-level diffraction light is used for carrying out shearing interferometry with zero-level diffraction light respectively, difference information is subjected to wave-front reconstruction and turning processing, relevant parameters, namely the space distance of rendezvous points of diffraction light of different levels and the inclination angle of a detector of main system error terms which affect raster shearing interferometer wave aberration detecting accuracy are obtained by numerical calculation, geometry optical-distance errors and detector inclination errors in wave aberration detecting are eliminated, and wave aberration detecting accuracy is improved. The geometry optical-distance errors and the detector inclination errors in wave-front reconstruction are eliminated according to practical situations, and the accuracy of raster shearing interferometer wave aberration detecting is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
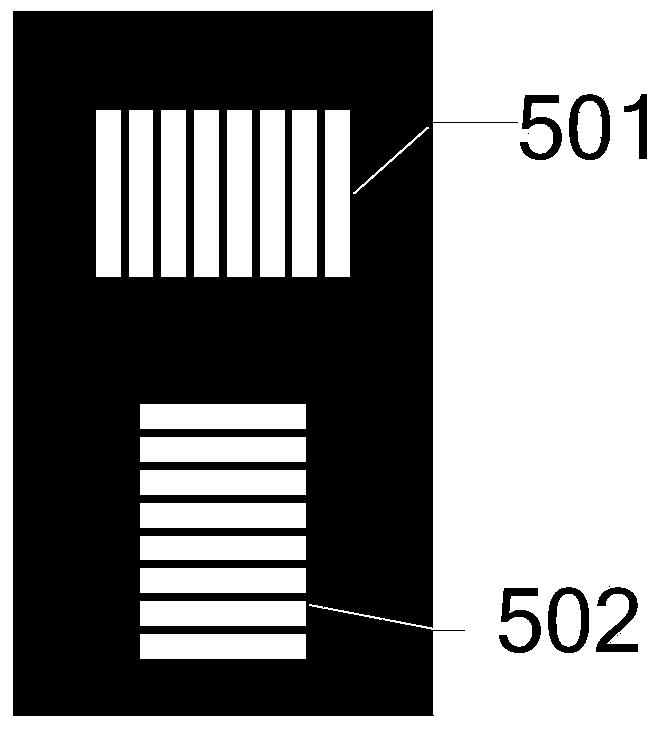
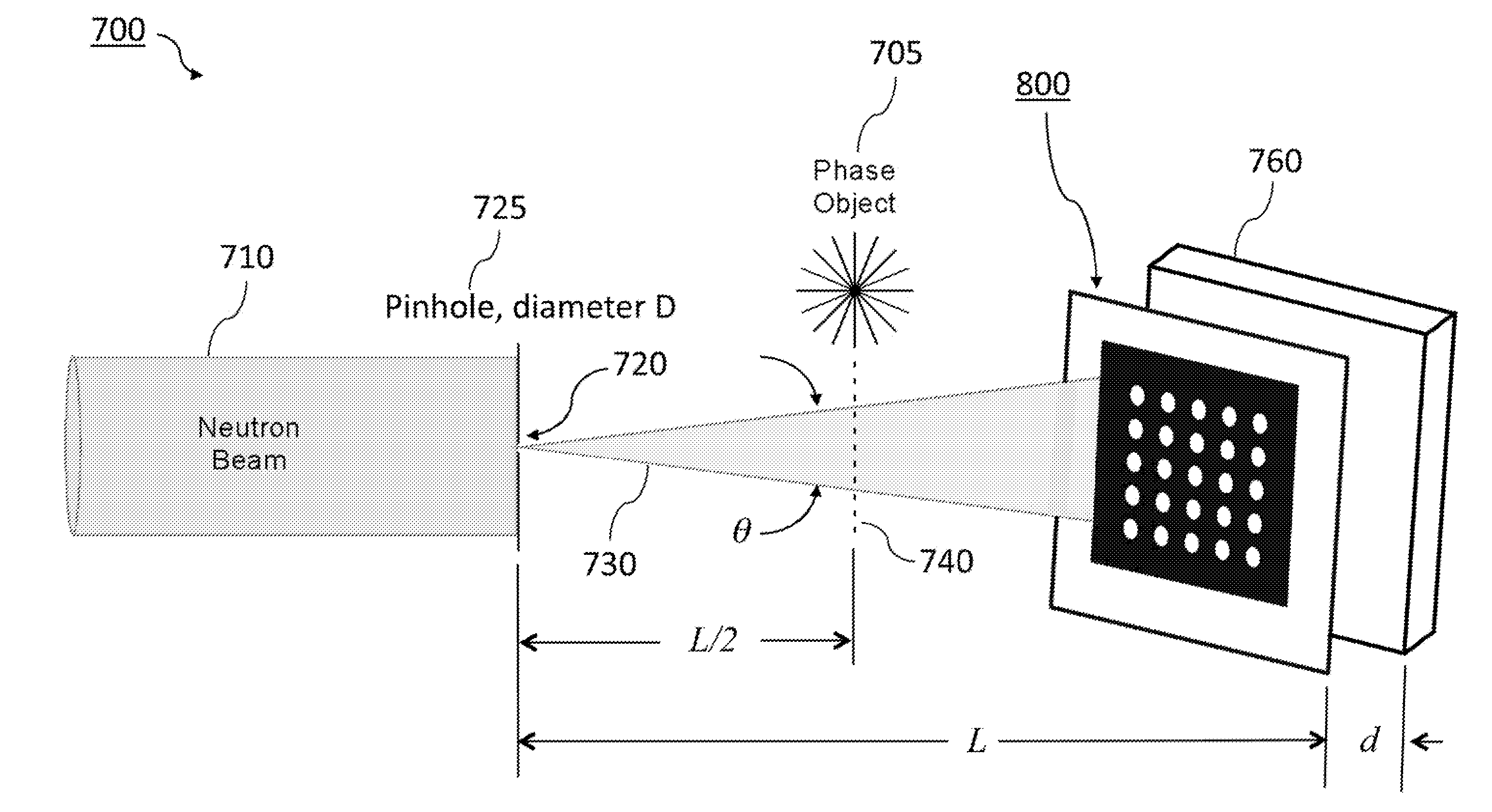
Phase-sensitive two-dimensional neutron shearing interferometer and hartmann sensor
A neutron imaging system detects both the phase shift and absorption of neutrons passing through an object. The neutron imaging system is based on either of two different neutron wavefront sensor techniques: 2-D shearing interferometry and Hartmann wavefront sensing. Both approaches measure an entire two-dimensional neutron complex field, including its amplitude and phase. Each measures the full-field, two-dimensional phase gradients and, concomitantly, the two-dimensional amplitude mapping, requiring only a single measurement.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
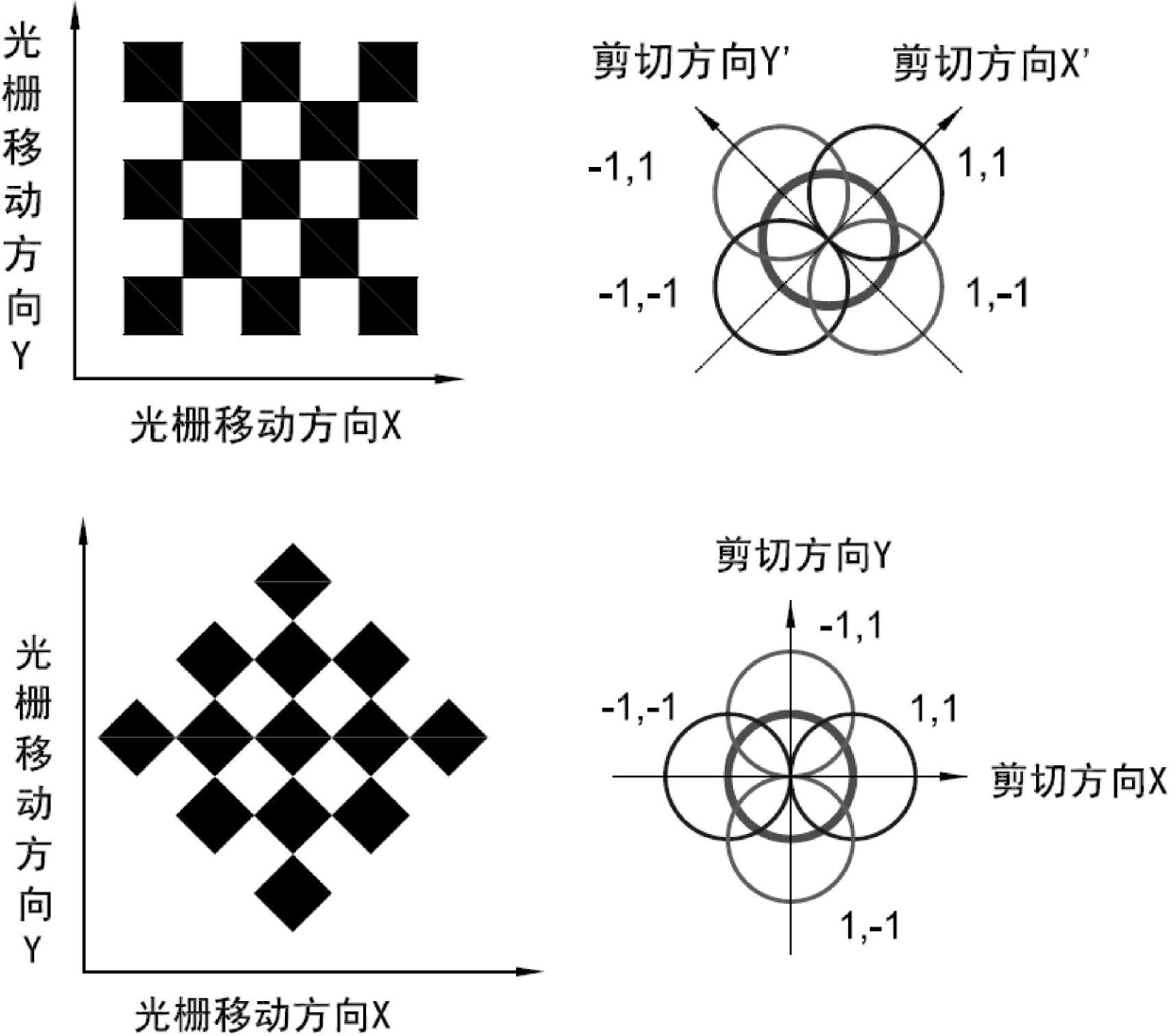
Transmission shear grating in checkerboard configuration for EUV wavefront sensor
ActiveUS20040169866A1Optical measurementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProjection opticsGrating
A wavefront measurement system includes a source of electromagnetic radiation. An imaging system directs the electromagnetic radiation at an object plane that it uniformly illuminates. A first grating is positioned in the object plane to condition the radiation entering the input of a projection optic. A projection optical system projects an image of the first grating onto the focal plane. A second grating is positioned at the focal plane that receives a diffracted image of the object plane to form a shearing interferometer. A CCD detector receives the image of the pupil of the projection optical system through the projection optical system and the second grating that forms a fringe pattern if there are aberrations in the projection optical system. Phaseshift readout of fringe pattern can be accomplished by stepping the first grating in a lateral direction and reading each frame with the CCD detector.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
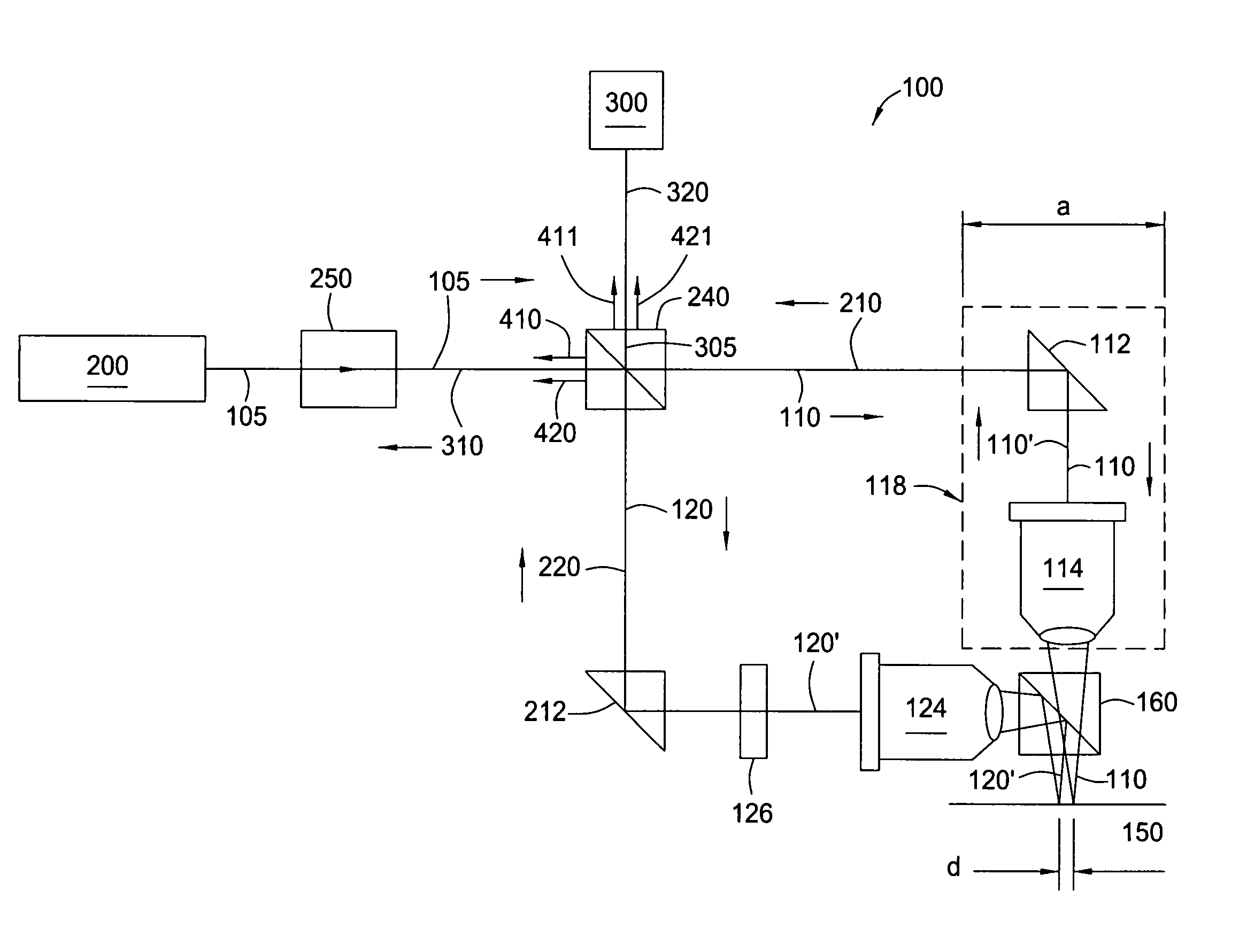
Dual-beam interferometer for ultra-smooth surface topographical measurements
InactiveUS7019840B2Reduce sensitivityEfficient and accurateRecord information storageUsing optical meansBeam splitterShearing interferometer
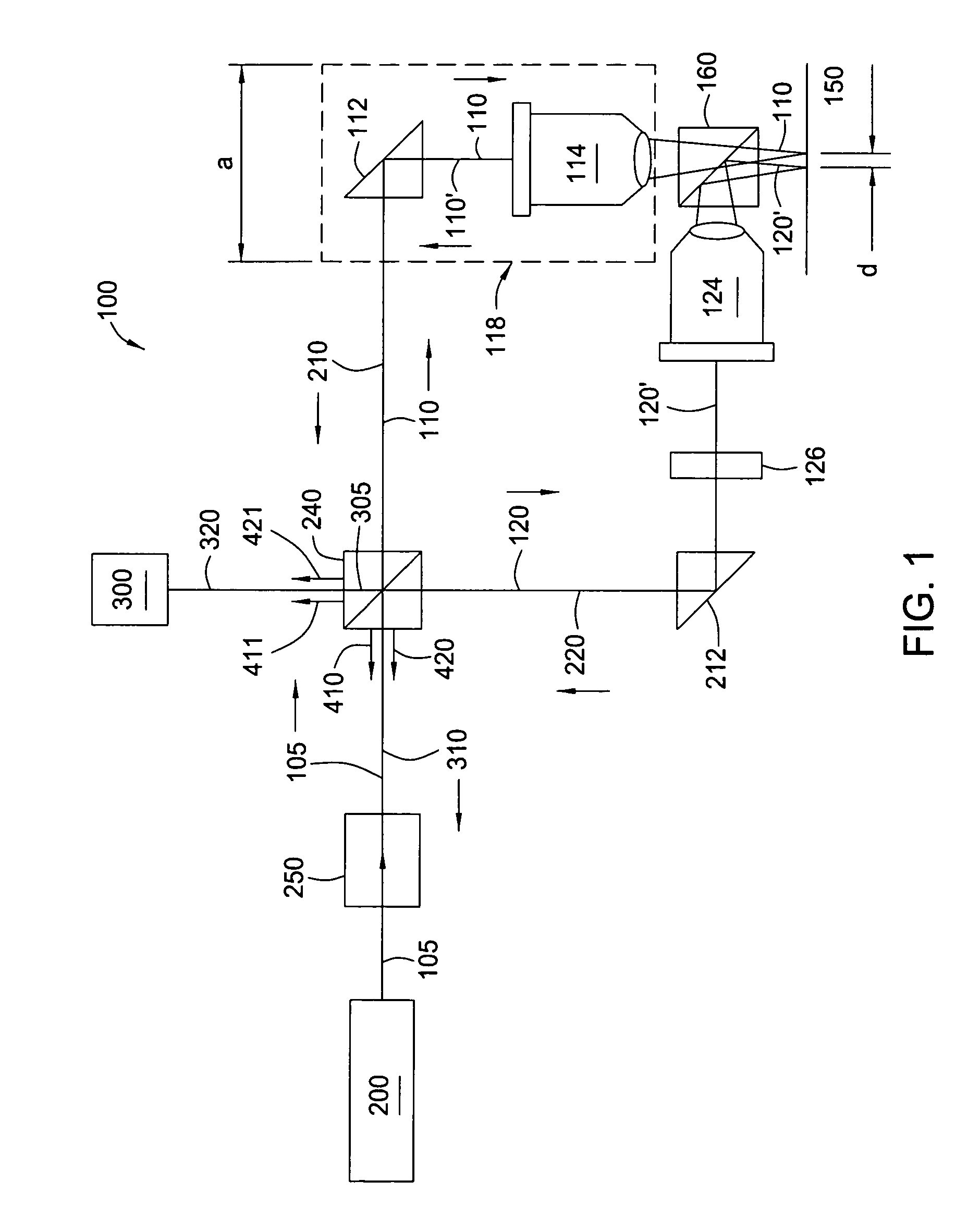
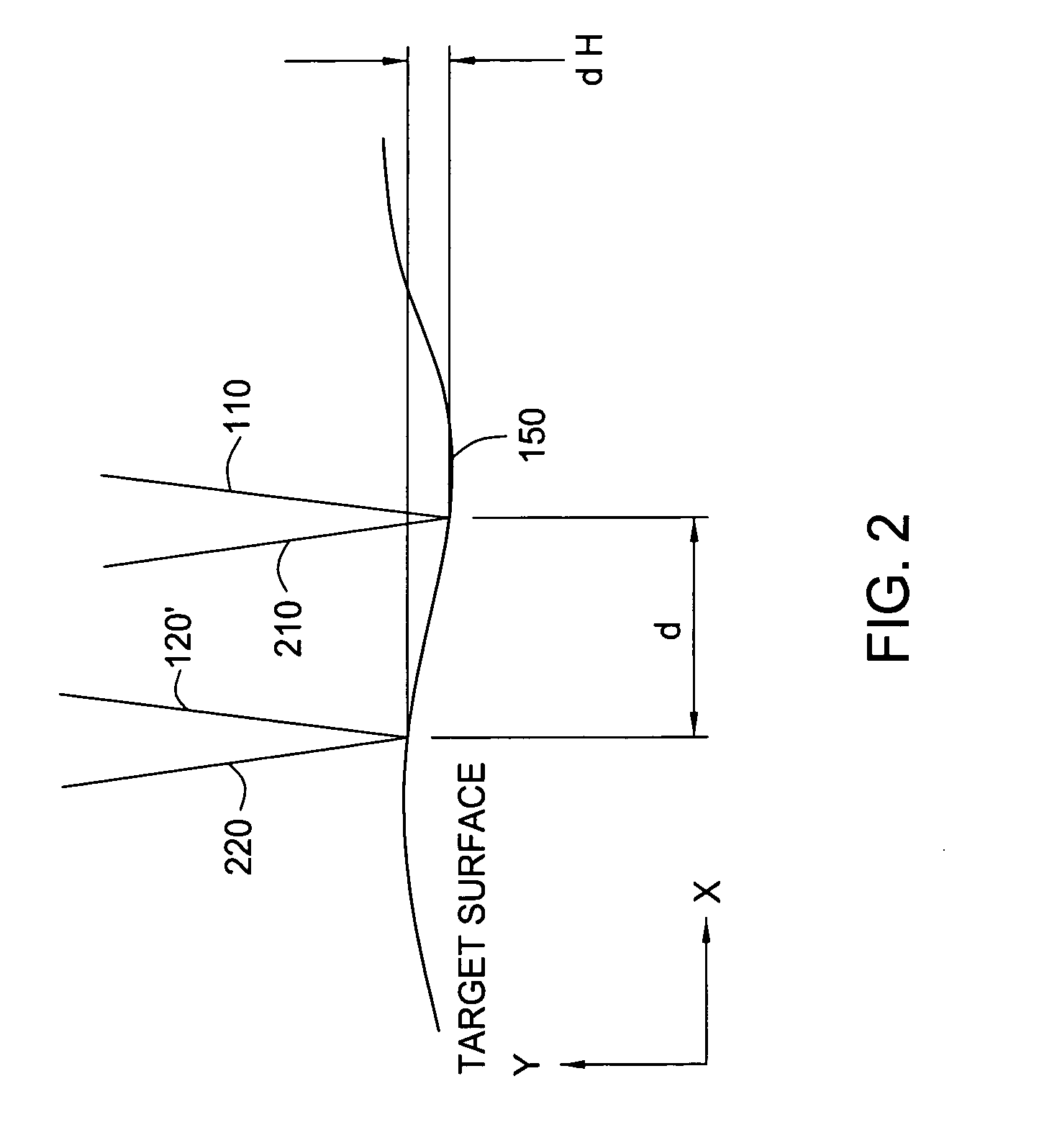
A method and apparatus for using a dual-beam interferometer to test surface flatness is provided. The interferometer directs two beams focused at distinct points on a testing surface, such as the surface of a magnetic recording disc. An offset distance “d” between the two beams is provided on the target surface. In the present invention, the separation distance “d” is adjustable. The feature of adjustable separation distance in the interferometer allows the interferometer to meet the different spatial frequency requirements of various applications. In operation, first and second reflected beams are returned to an intensity beam splitter, where they are split and then recombined into two new beams of substantially equal intensity. The second of the two new light beams is constructed by the interference of half intensity of the first and half intensity of second beams, and is sent to a photodiode. The photodiode generates signals in response to the changing interference fringes caused as a result of the modulation of the optical path length difference between the original first and second beams. A local height difference on the reflective surface is calculated relative to the separation distance “d”.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Spatial phase shift lateral shearing interferometer
InactiveCN103256991ASimple structureCompact structureOptical measurementsOptical elementsPhase shiftedShearing interferometer
The invention relates to a spatial phase shift lateral shearing interferometer which is characterized in that the interferometer is composed of a polarization light splitting shearing plate, a polarization phase shift device, a first image sensor, a second image sensor, a third image sensor and a computer. According to the spatial phase shift lateral shearing interferometer, polarization shearing interference is introduced to achieve spatial phase shift, influences caused by environmental vibration are eliminated and the spatial phase shift lateral shearing interferometer has the advantages of being simple and compact in structure, easy and convenient to operate and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Increase spatial sampling for wave front mid-spatial frequency error recovery
InactiveUS7619191B1Improve reliabilityOptical measurementsPhotometry using reference valueMeasurement deviceLight beam
A differential curvature sensing device for measuring a wavefront curvature by employing increased spatial sampling for wavefront testing with mid-frequency error recovery. The device includes a sampling sensor having an output beam, an optical element to split said output beam, a lenslet array in the path of each beam to generate corresponding sampling grids, a shearing element for shifting the grid points in horizontal and vertical directions to produce plural sampling grids having plural grid points for use generating a spatial sampling grid having a density for mid-spatial frequency recovery. The displacement of the shifting less than a pitch size of the lenslet array, and a measuring device measuring plural slopes of plural wavefronts at each grid point to obtain a wavefront normal curvature and corresponding twist curvature terms to determine a principal curvature and directions. The sensor is a Shack-Hartman sensor, shearing interferometer sensor and other discrete-point sampling sensors.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Magnetoelasticity performance simultaneous on-line detecting method of iron magnetic thin film
InactiveCN101441195ANon-uniform stressAvoiding Curvature Measurement EffectsMaterial magnetic variablesMagnetoelastic couplingHysteresis
An online detection method for magnetoelasticity performance of thin-ferromagnetic-film, which belongs to the field of engineering materials, structure deformation, and mechanical test. The device implementing the method of the invention comprises a thin-ferromagnetic-film non-uniform stress measuring light path and a film hysteresis loop measuring light path, wherein, the film non-uniform stress measuring light path comprises a laser, a beam expander, a grating, a lens, a filter screen, and a CCD camera; and the film hysteresis loop measuring light path comprises a laser, a beam expander, a polarizer, an analyzer, and a photodetector. The method of the invention comprises the steps of measuring non-uniform curvature of the thin-ferromagnetic-film surface by shearing interferometer to obtain the non-uniform stress in film, and measuring the hysteresis loop of the film by using magnetooptic Kerr effect of the thin-ferromagnetic-film surface. The method can simultaneously online measure the non-uniform stress and the hysteresis loop of thin-ferromagnetic-film, so as to provide experimental basis for the research on magnetoelasticity coupling behavior of the thin-ferromagnetic-film.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com