Patents
Literature
61 results about "Cost metric" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
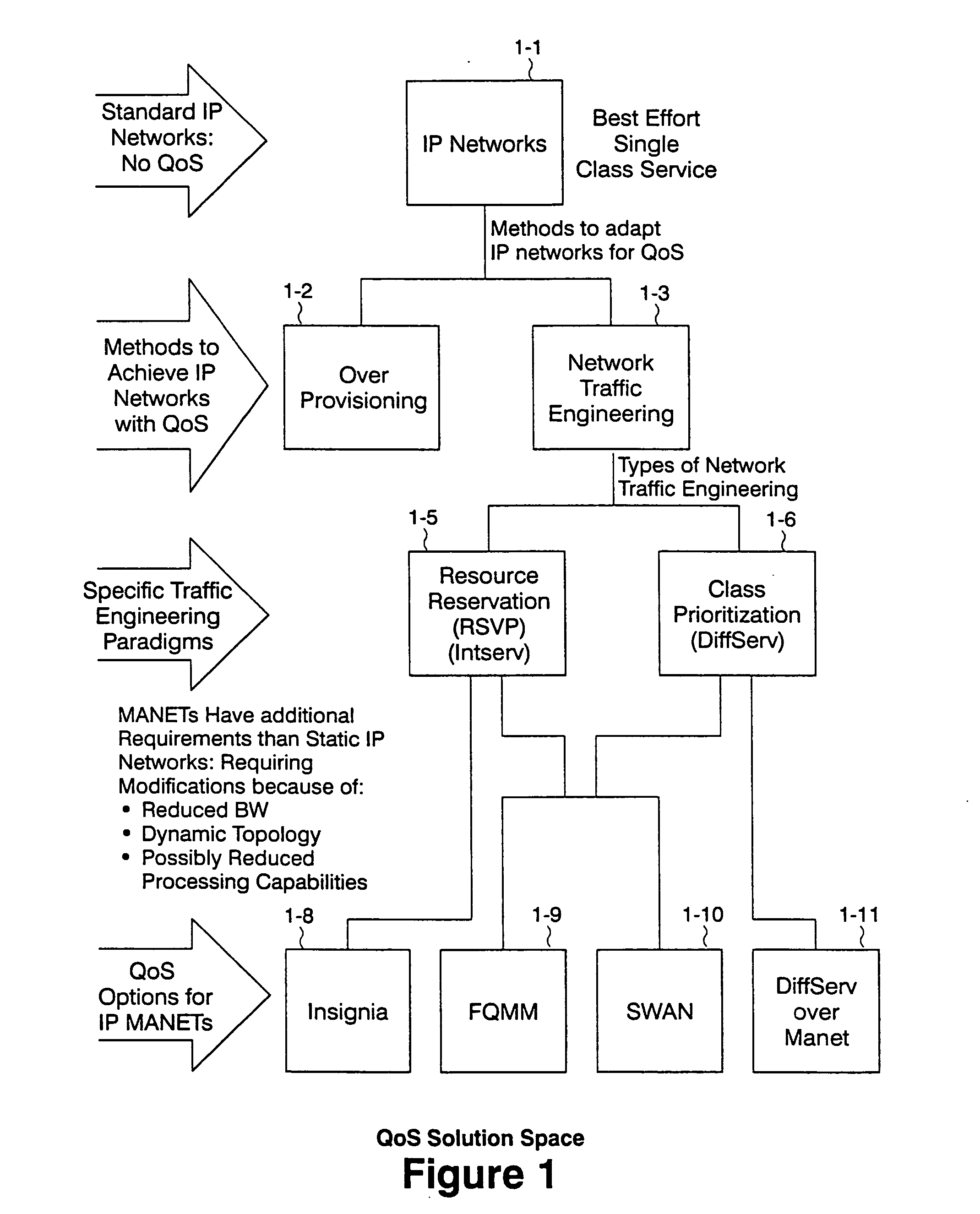
Cost (Total) is the most commonly used metric for your cloud spend analysis. It is reported on a cashflow-based accounting method, and for AWS is the unblended cost.
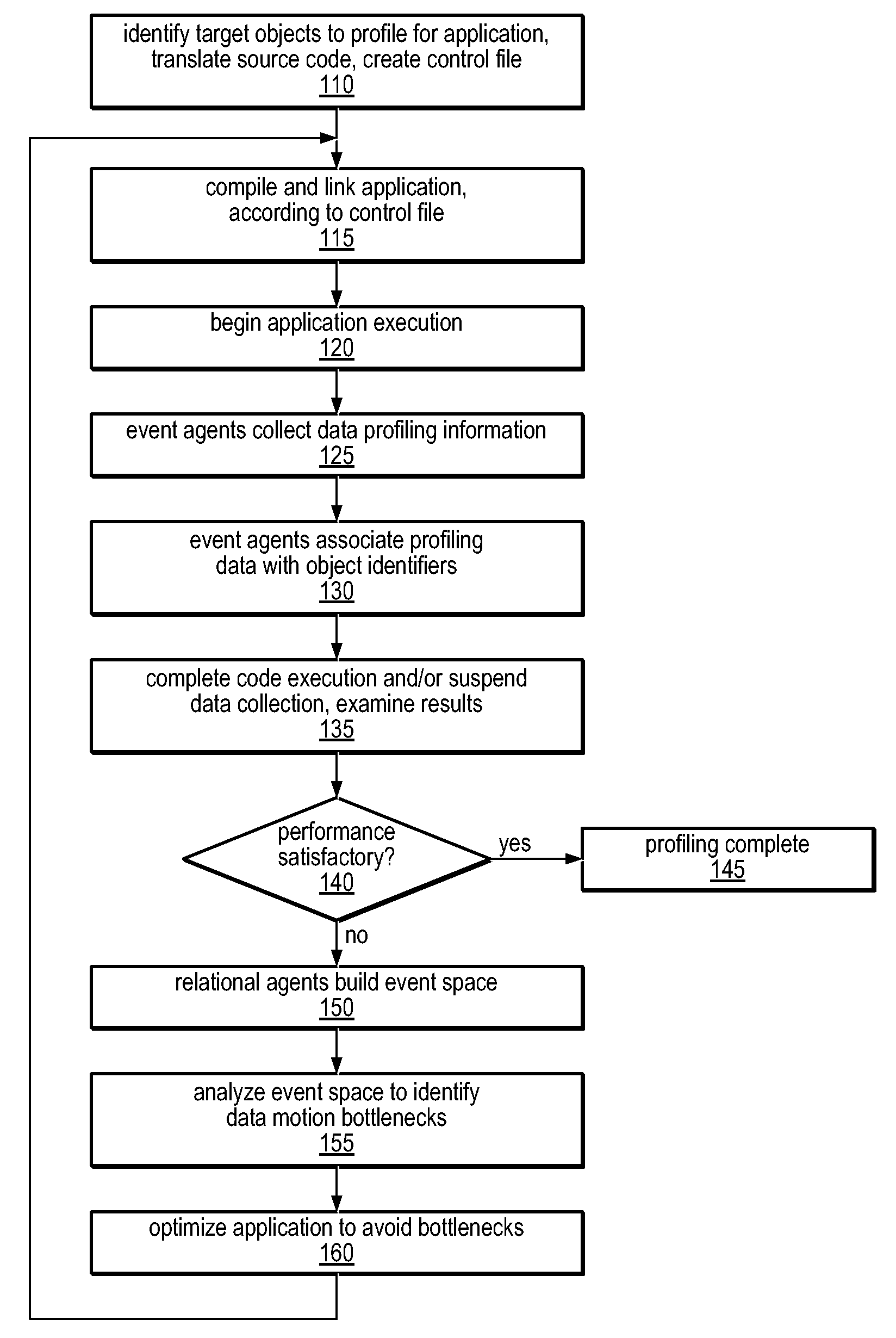
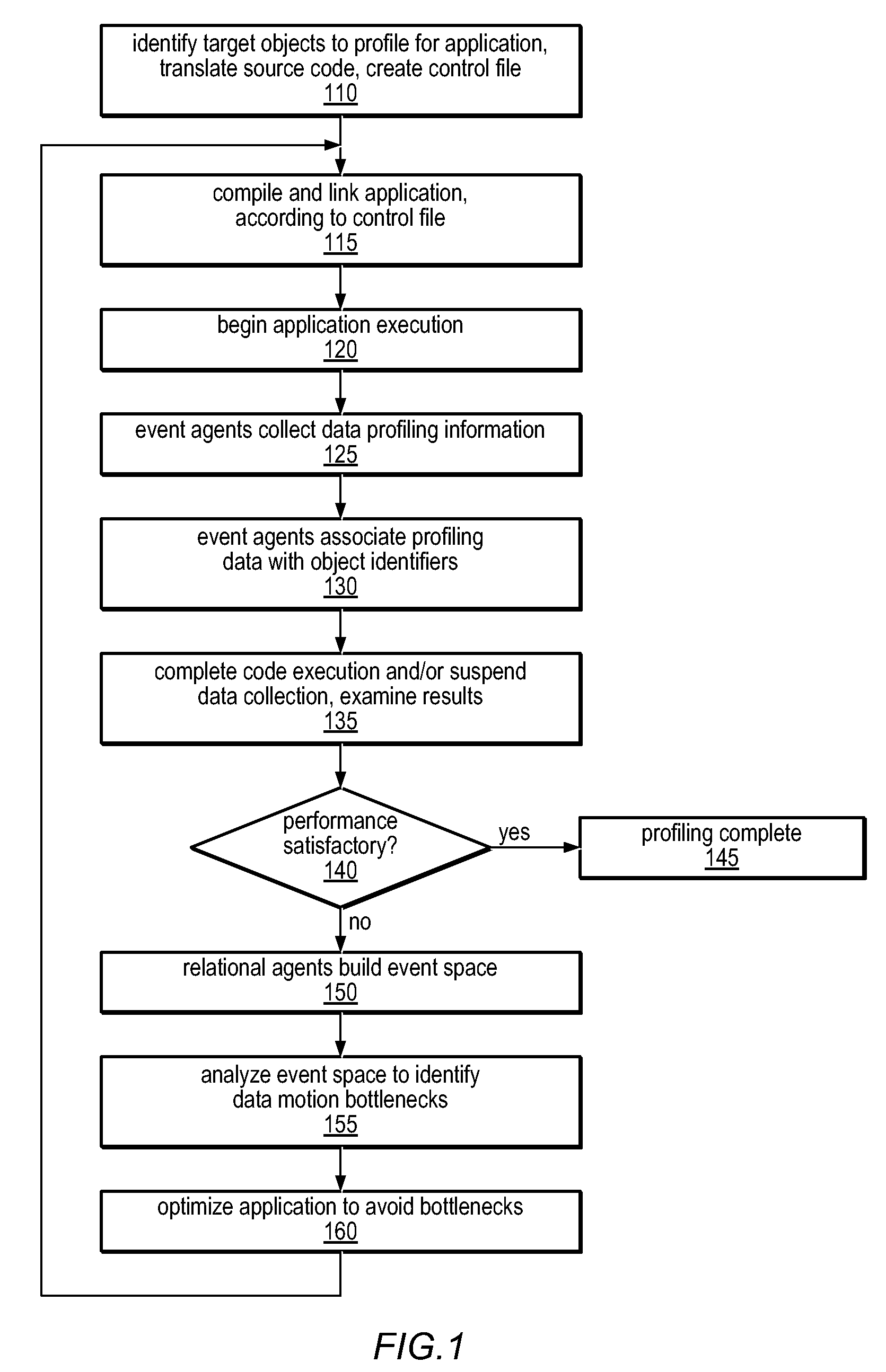
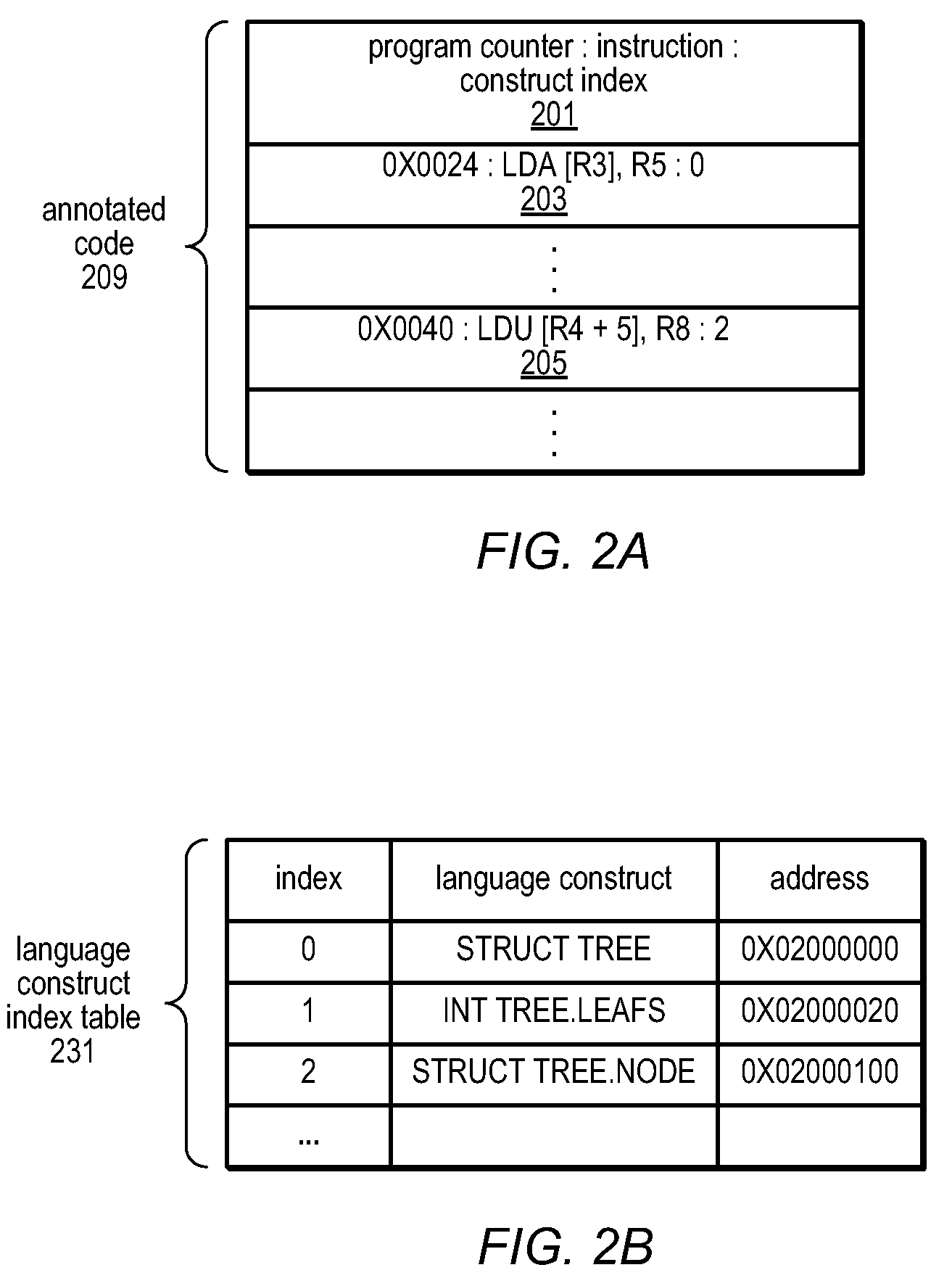
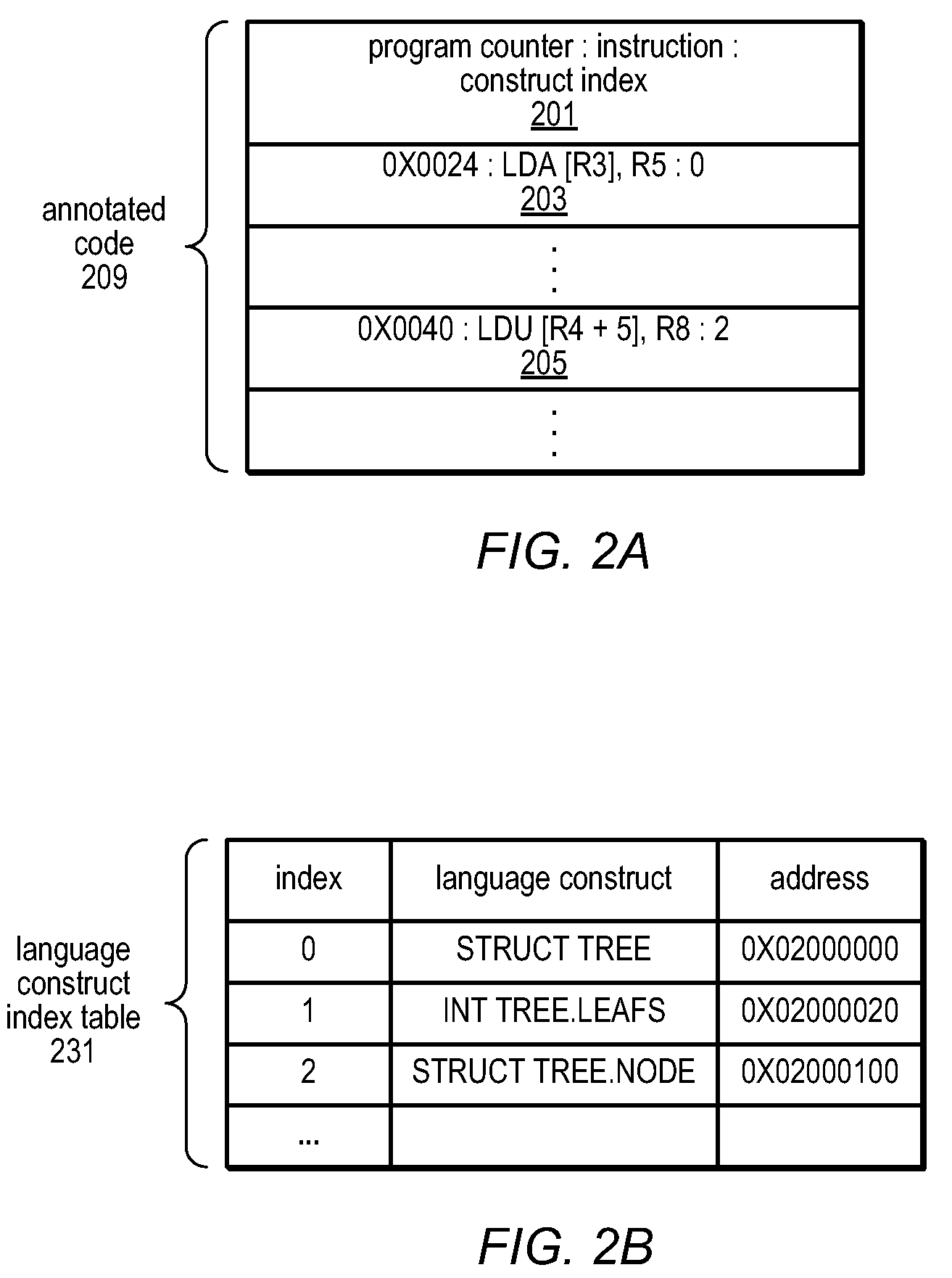
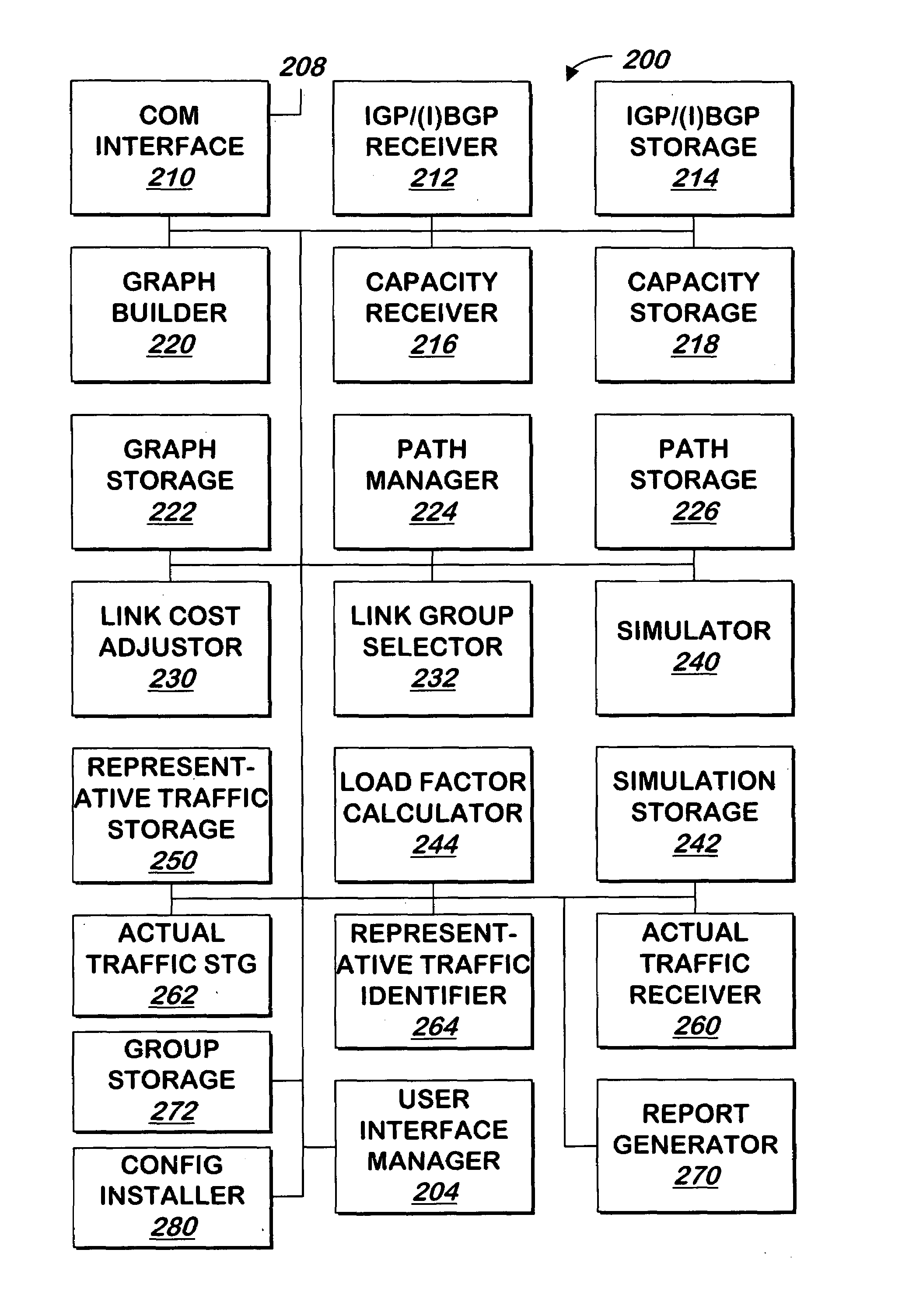
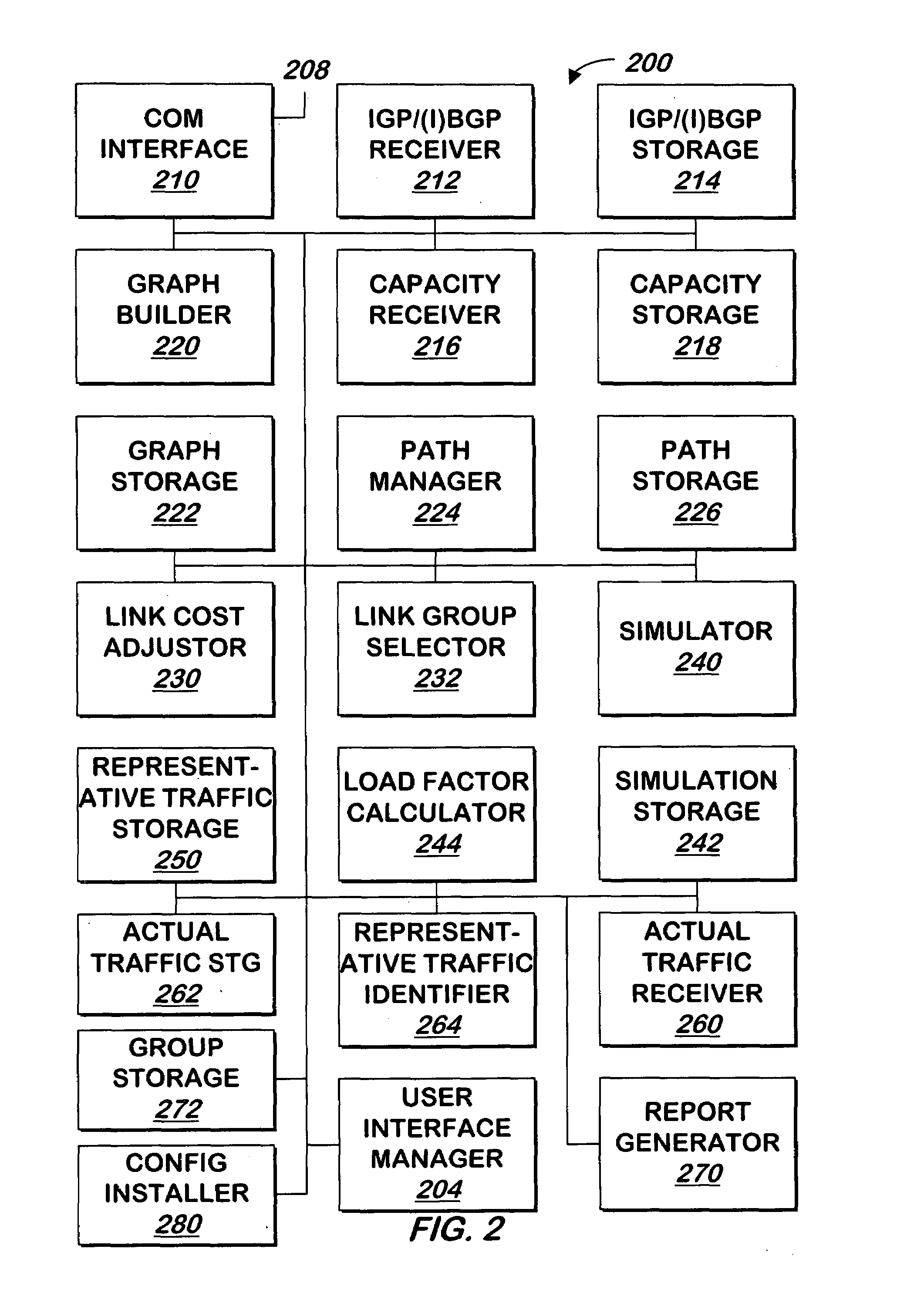
Method and Apparatus for Computing User-Specified Cost Metrics in a Data Space Profiler
ActiveUS20080127149A1Software engineeringSpecific program execution arrangementsCost metricData space
A system and method for profiling a software application may include means for defining a custom cost metric that includes a cost metric identifier and a cost function. The cost function may apply a mathematical formula to data extracted from an event set to calculate a respective cost metric value for each of one or more events in the event set. The data extracted from the event set may include one or more respective profiling object identifiers and one or more other respective costs associated with each of the one or more events. A cost associated with an event in the event space may be associated with a function or basic block of instructions. The cost function may include a distribution formula for attributing at least a portion of the cost associated with a function or basic block to each of the instructions comprising the function or basic block.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
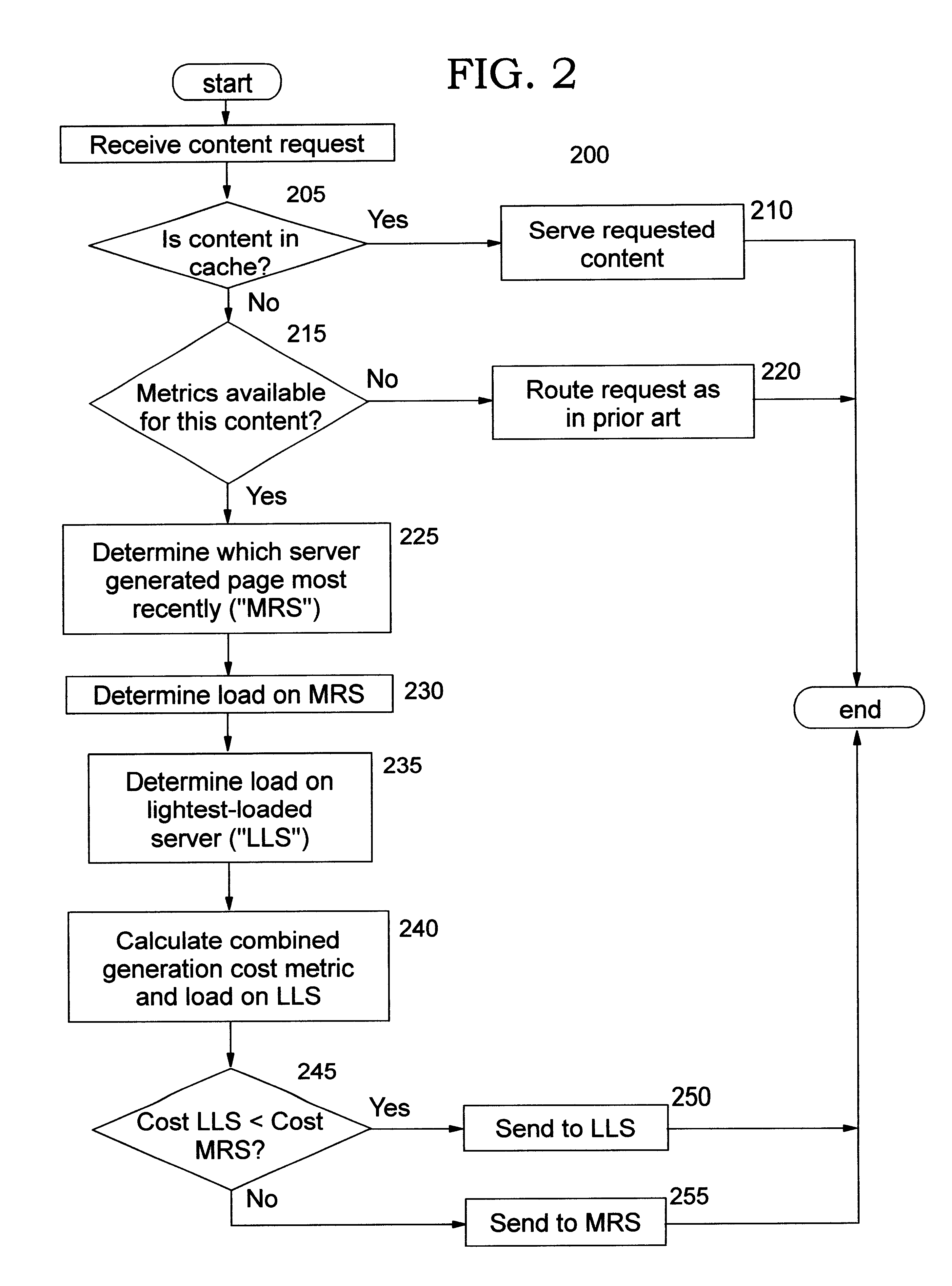
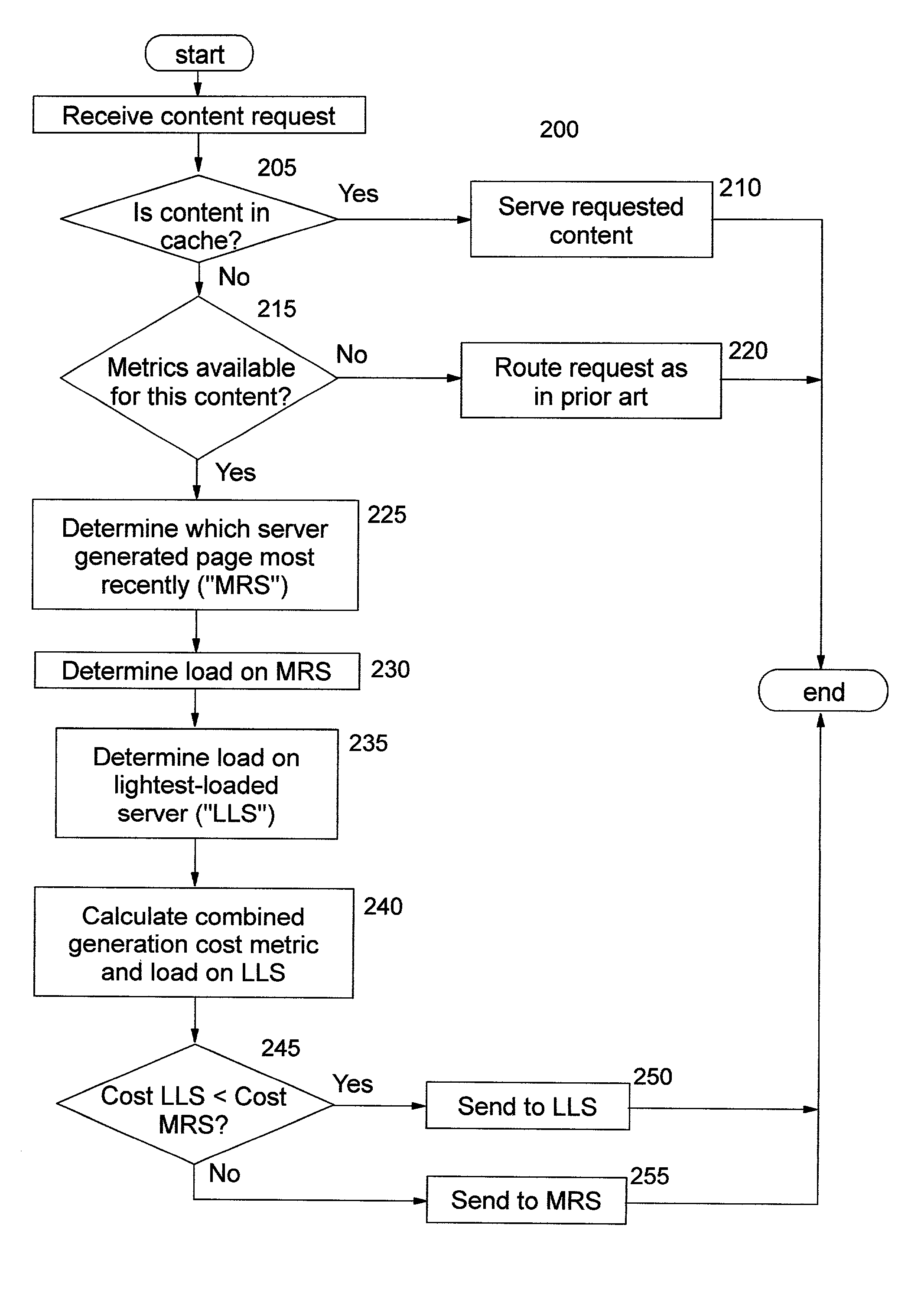
Load balancing content requests using dynamic document generation cost information
InactiveUS6839700B2Simple technologyEfficiently routedData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsCurrent loadCost metric
Methods, systems, computer program products, and methods of doing business by performing load balancing of content requests using information regarding the cost of dynamically creating the requested document content. Cost metrics are gathered by a server which generates requested content, and may reflect processing at one or more other servers. This cost information is provided to a load balancing host. Several alternative approaches for providing the cost metrics may be used, including defining new headers for response messages, specifying cookie values, and so forth. The load balancing host may choose to route a subsequent request for that content to the server which most recently generated the content, or to another available server, depending on the cost of re-generating the content and the current load on those servers.
Owner:IBM CORP
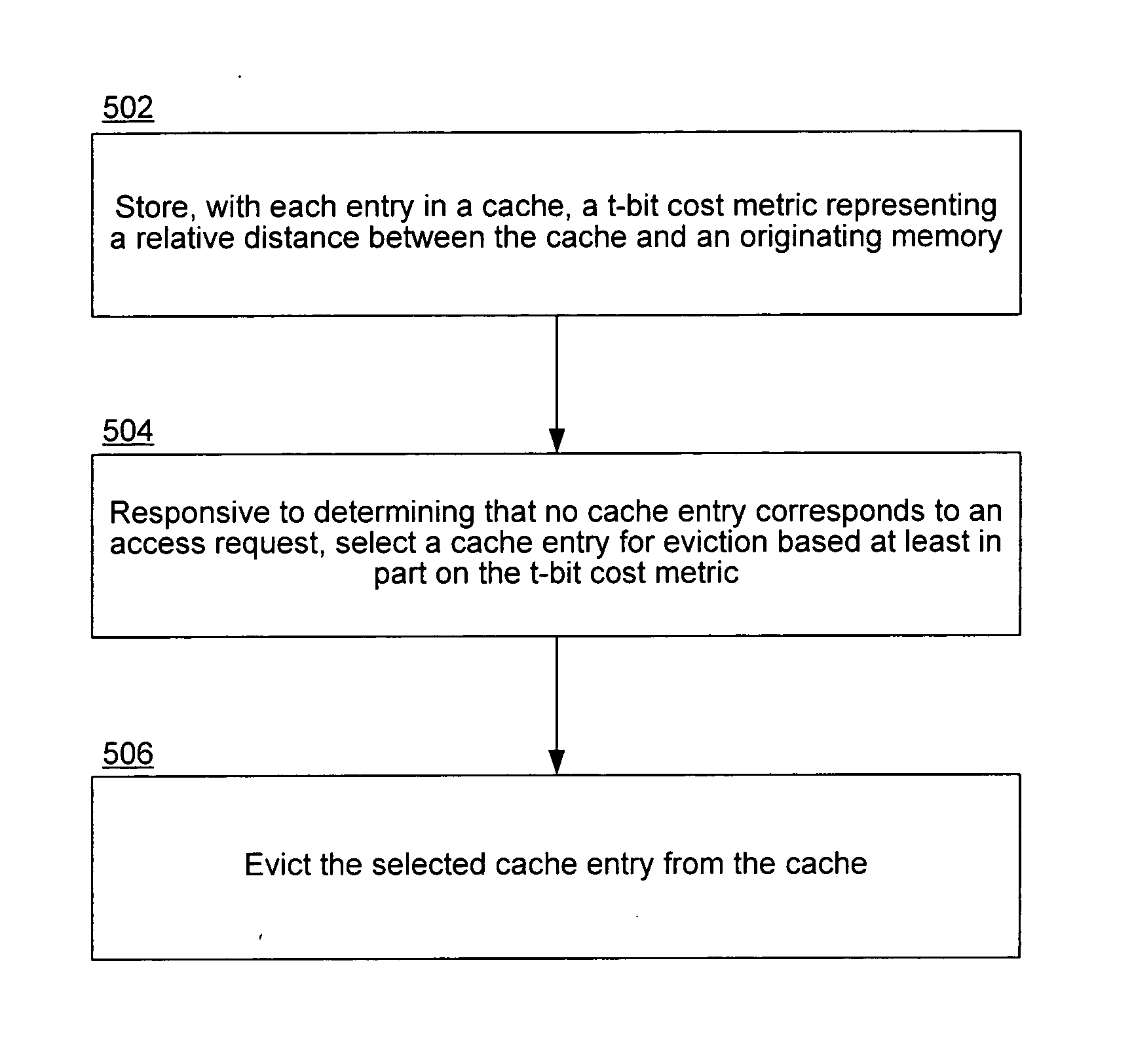
Home node aware replacement policy for caches in a multiprocessor system
InactiveUS20070156964A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsCost metricMulti processor
A home node aware replacement policy for a cache chooses to evict lines which belong to local memory over lines which belong to remote memory, reducing the average transaction cost of incorrect cache line replacements. With each entry, the cache stores a t-bit cost metric (t≧1) representing a relative distance between said cache and an originating memory for the respective cache entry. Responsive to determining that no cache entry corresponds to an access request, the replacement policy selects a cache entry for eviction from the cache based at least in part on the t-bit cost metric. The selected cache entry is then evicted from the cache.
Owner:INTEL CORP
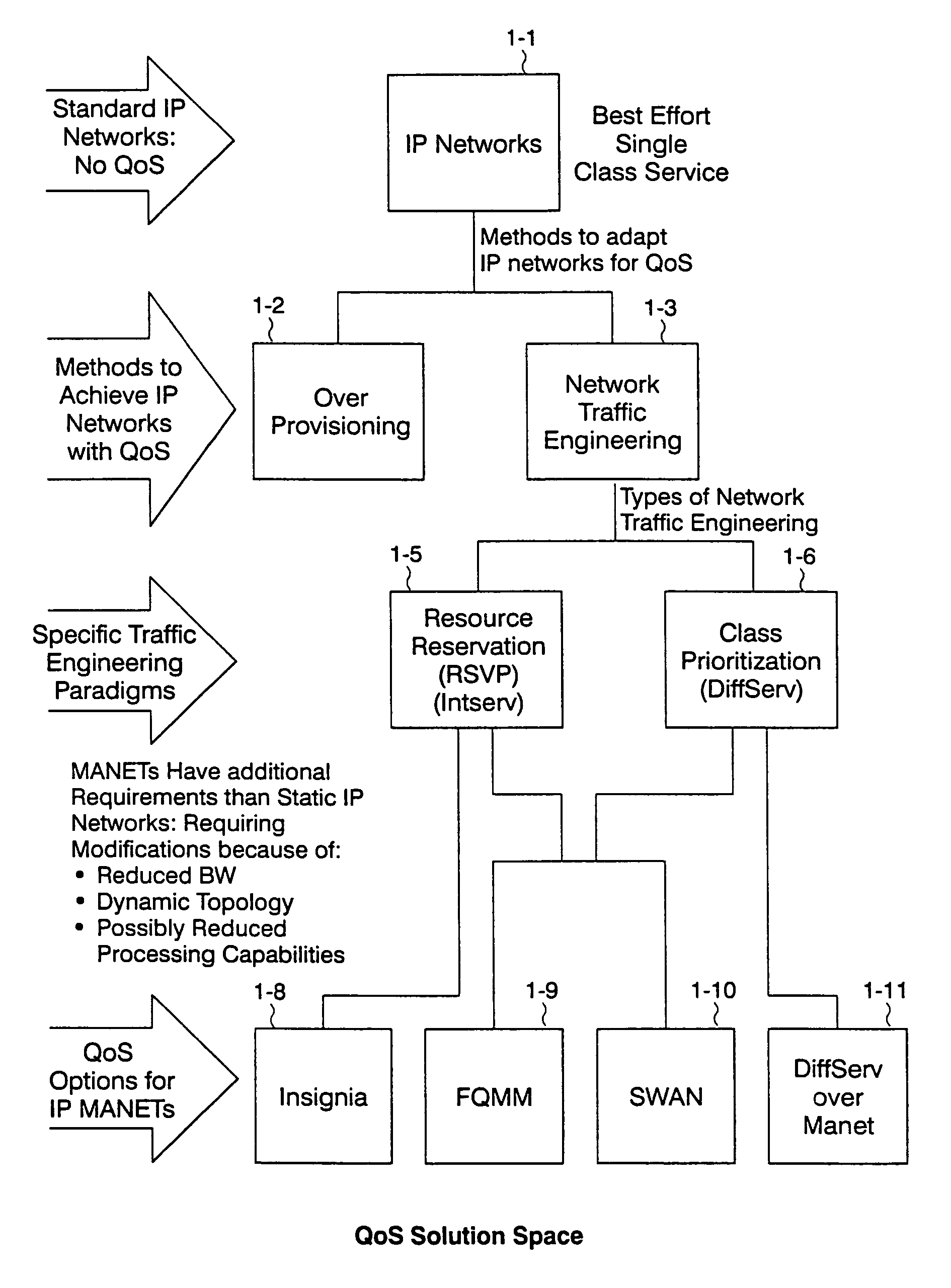
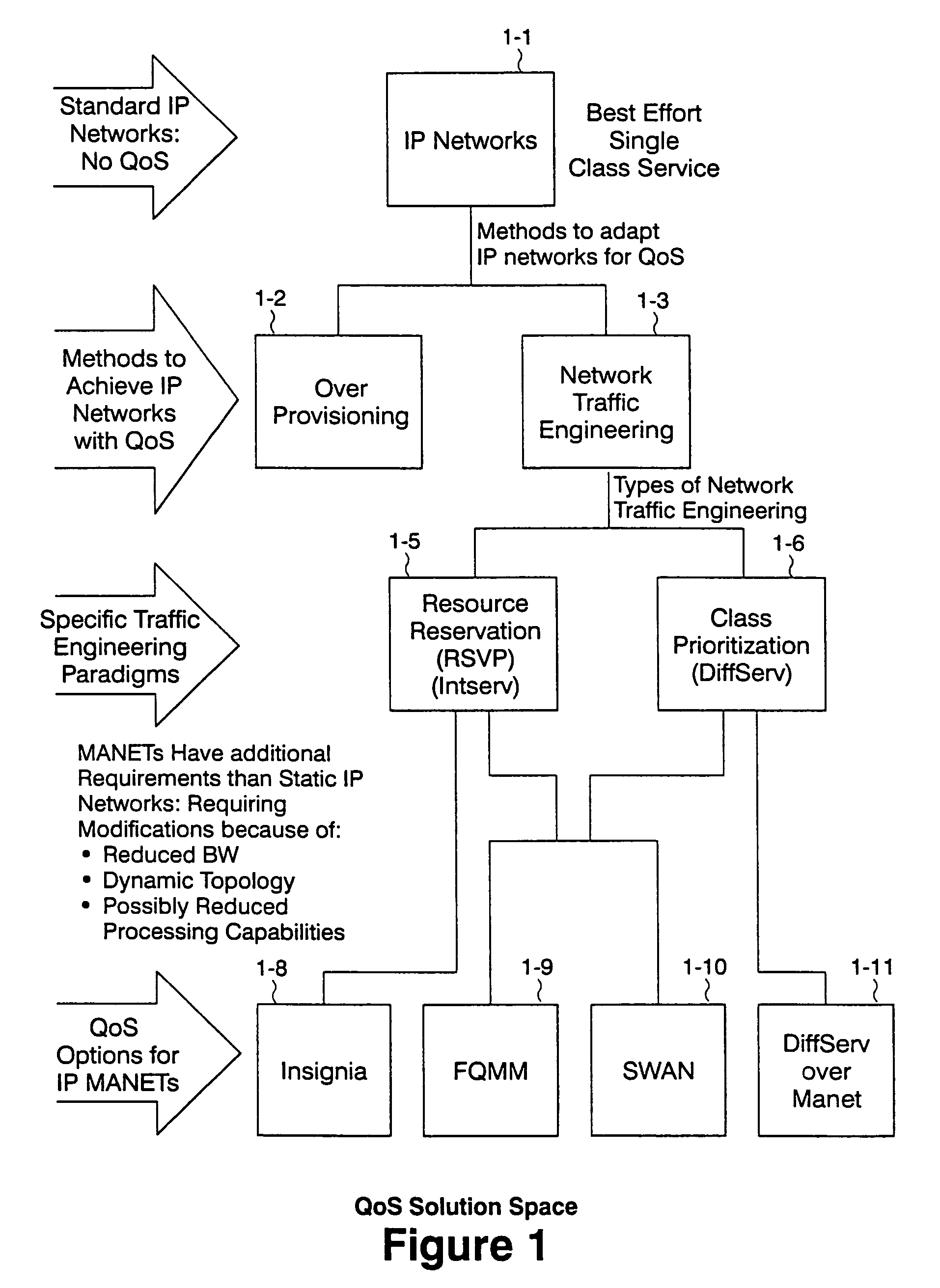
Method and Apparatus for Mesh Routing
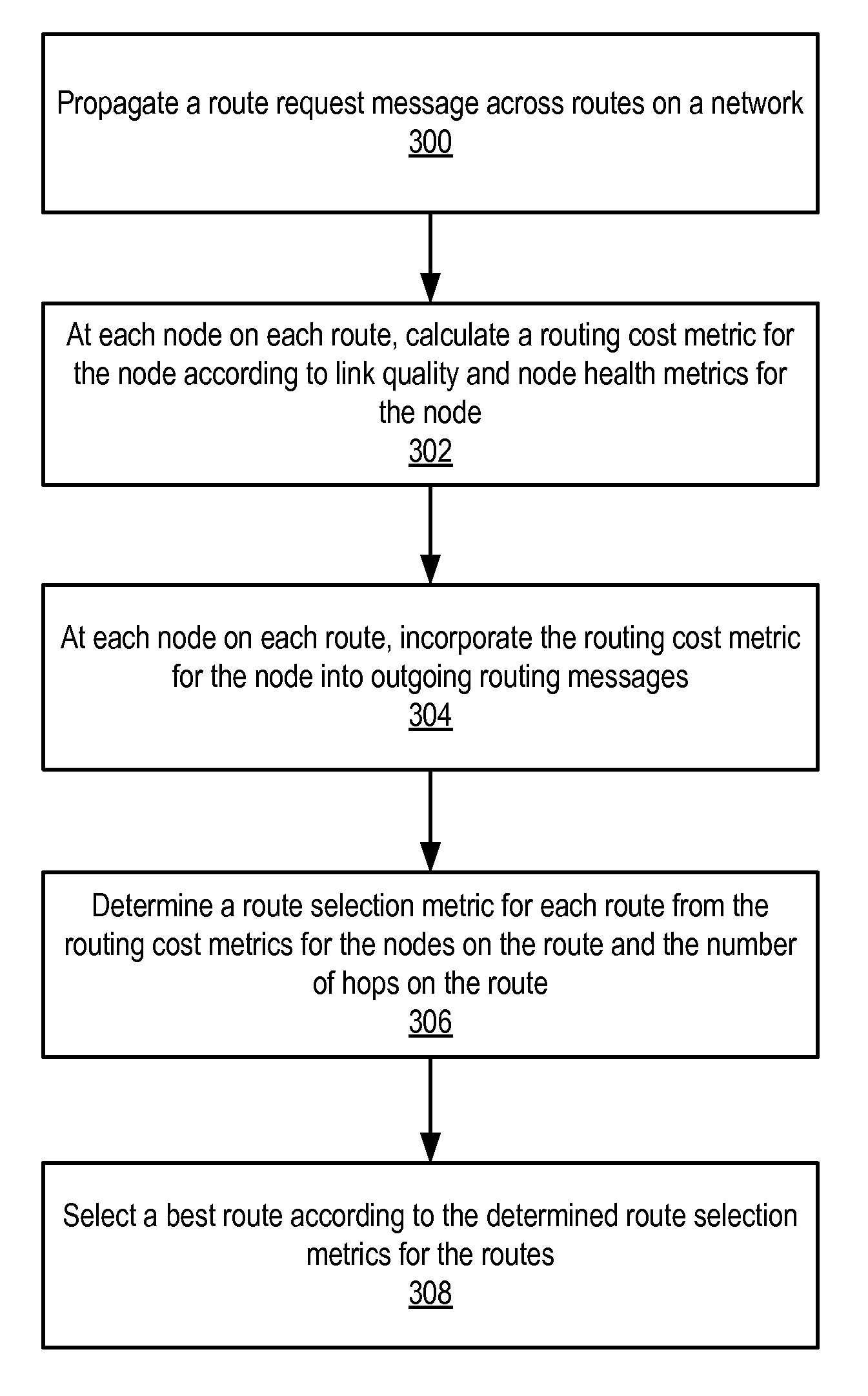
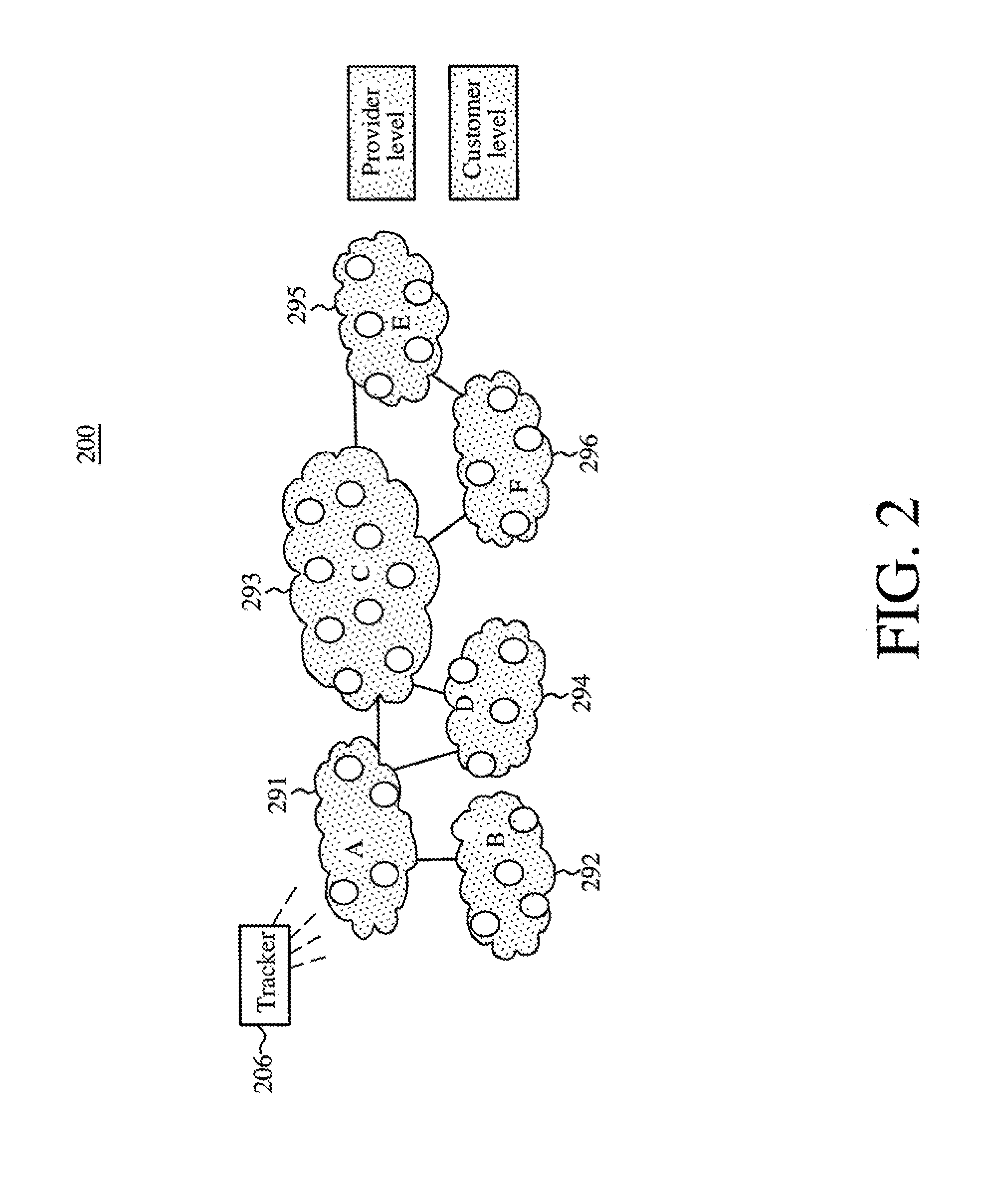
ActiveUS20090168653A1Good for healthProlong lifeError preventionTransmission systemsCost metricMesh routing
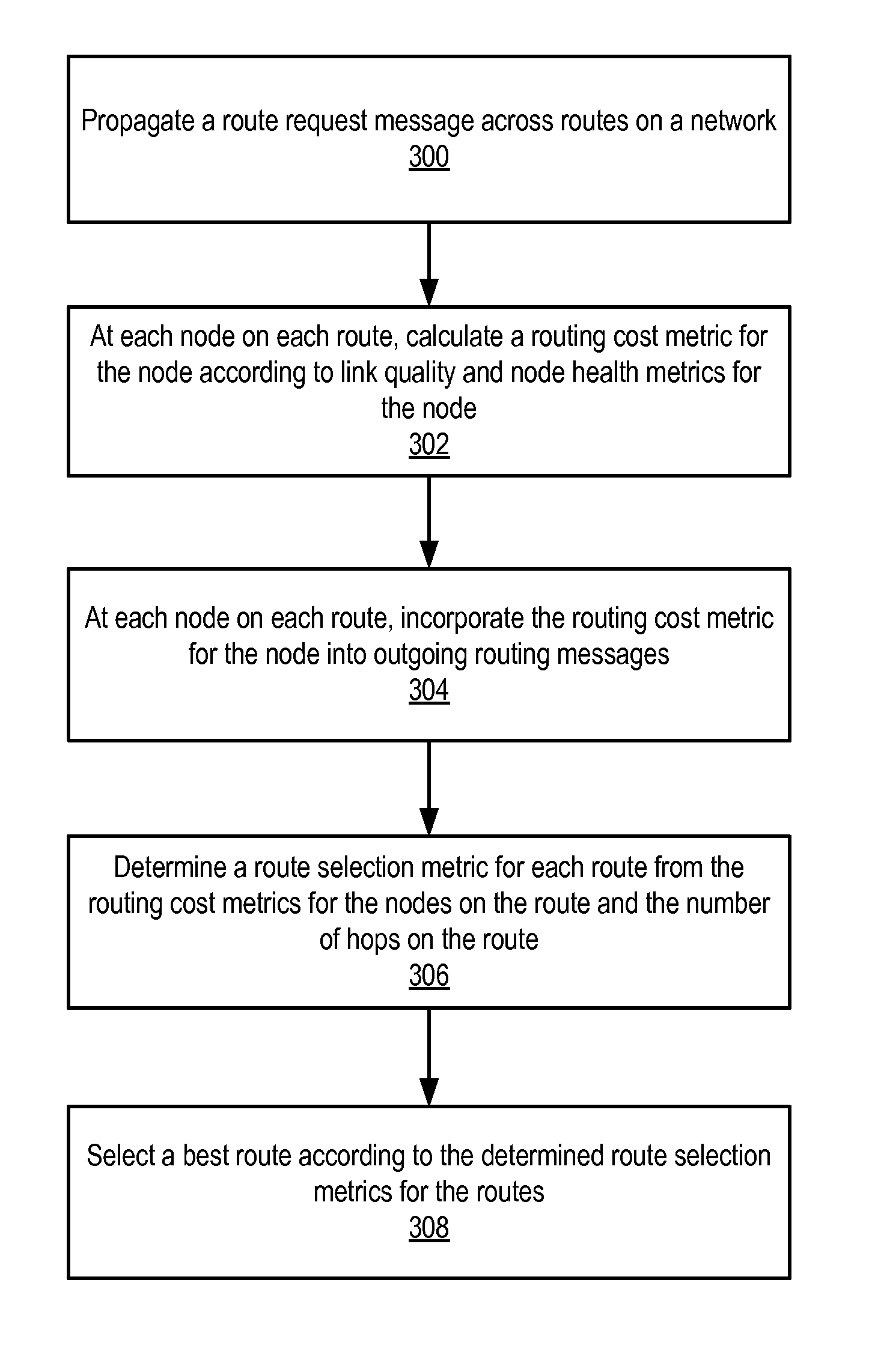
Method and apparatus for optimizing mesh routing for stability and system lifetime maximization in networks, for example in wireless networks. A routing module may be instantiated in nodes on the network. The routing module may implement a link quality and node health aware routing protocol on the network that considers a combination of link quality and node health / residual lifetime metrics in the calculation of the desirability of nodes and links between nodes as parts of an overall route. A route selection metric for each route may be determined from routing cost metrics for the nodes on the route and the number of hops on the route. A node may then select a best route according to the determined route selection metrics for the routes.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
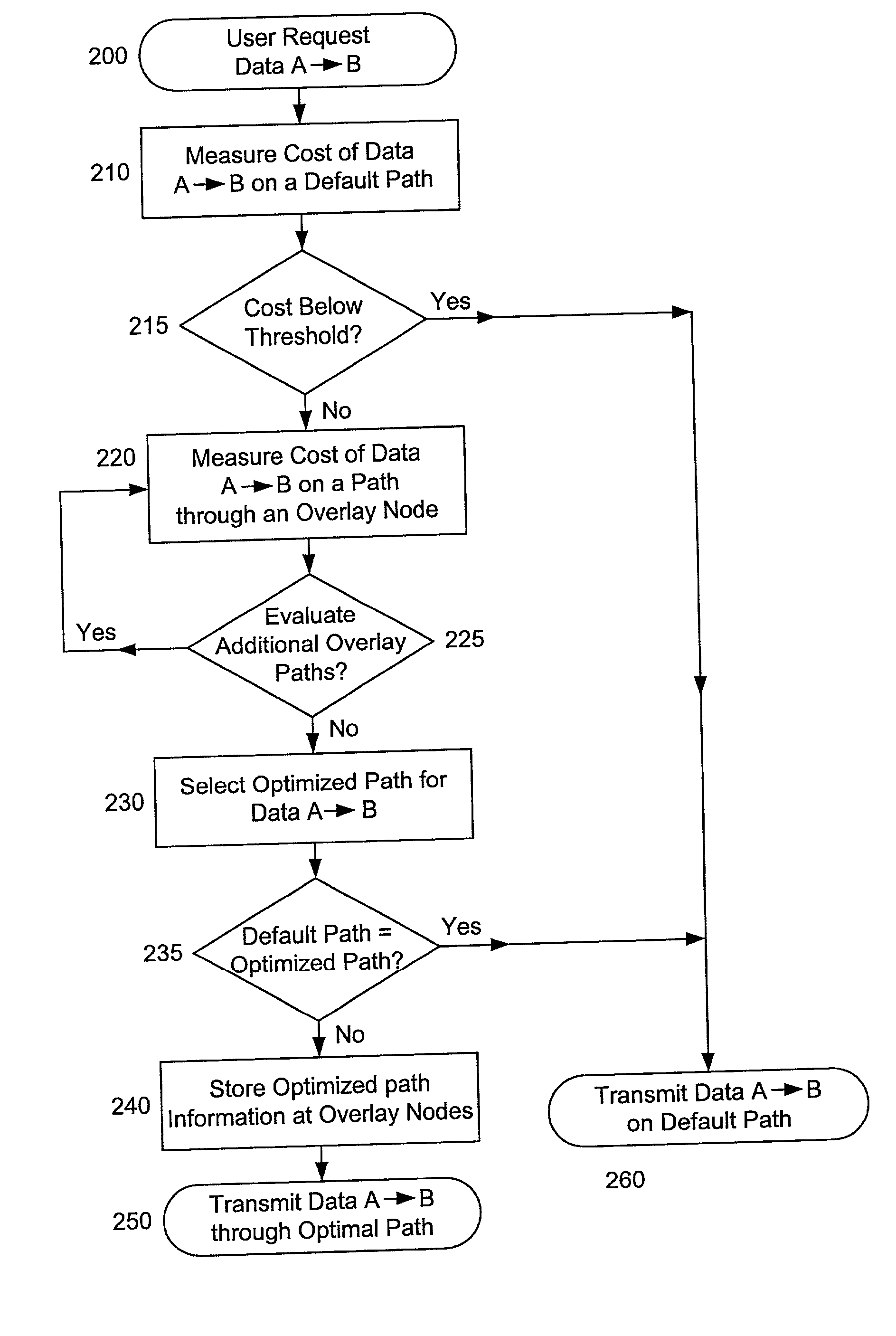
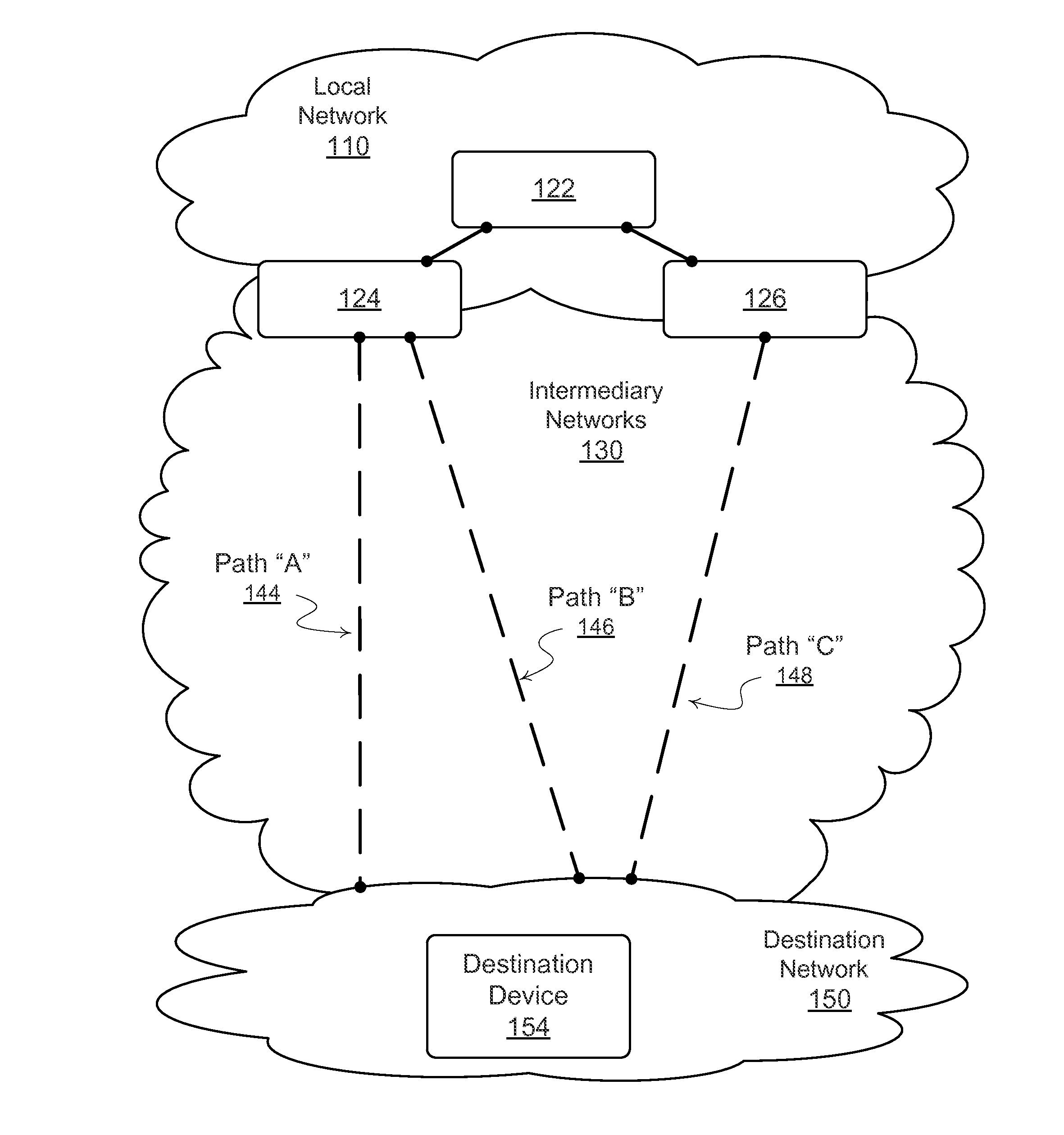
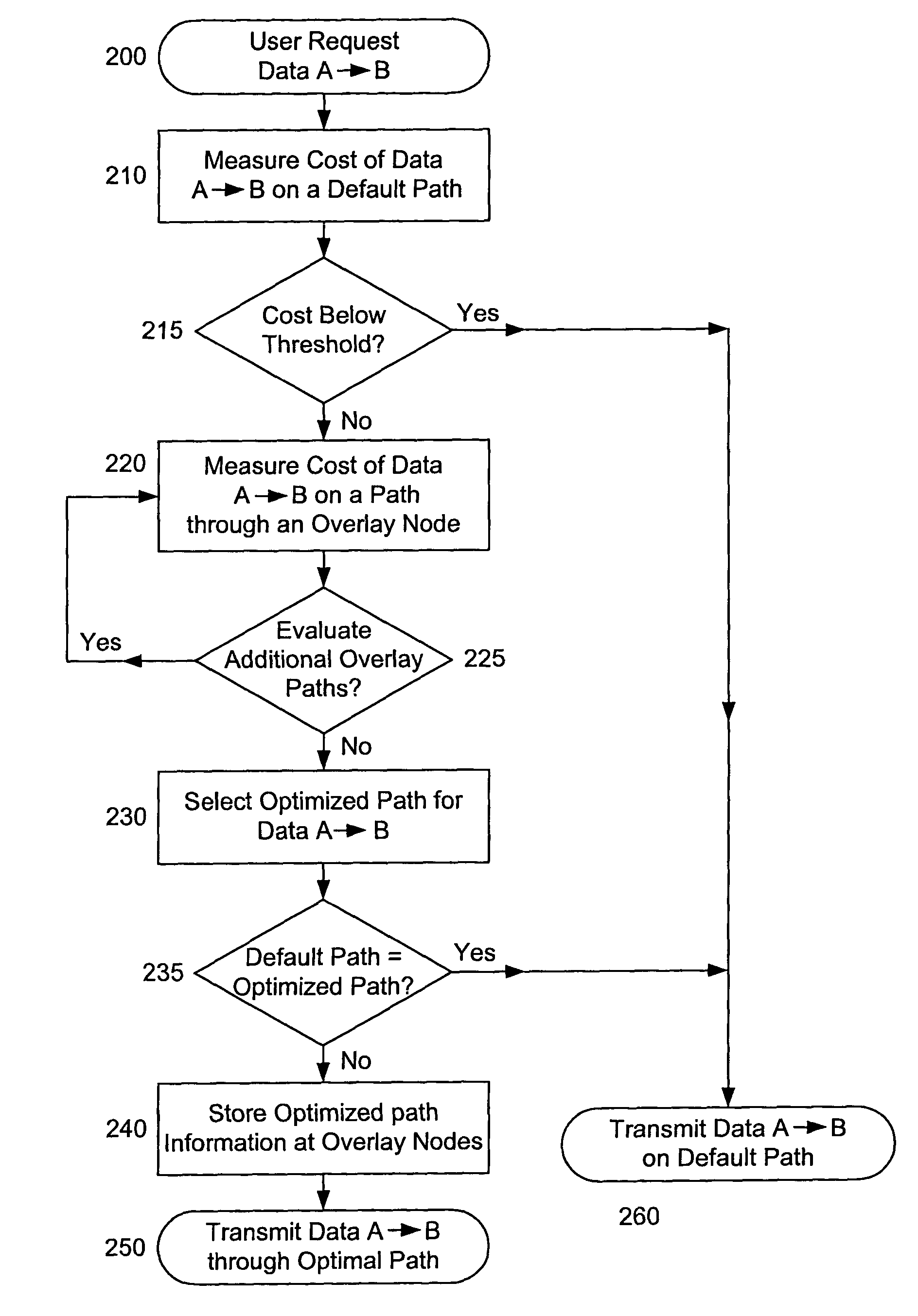
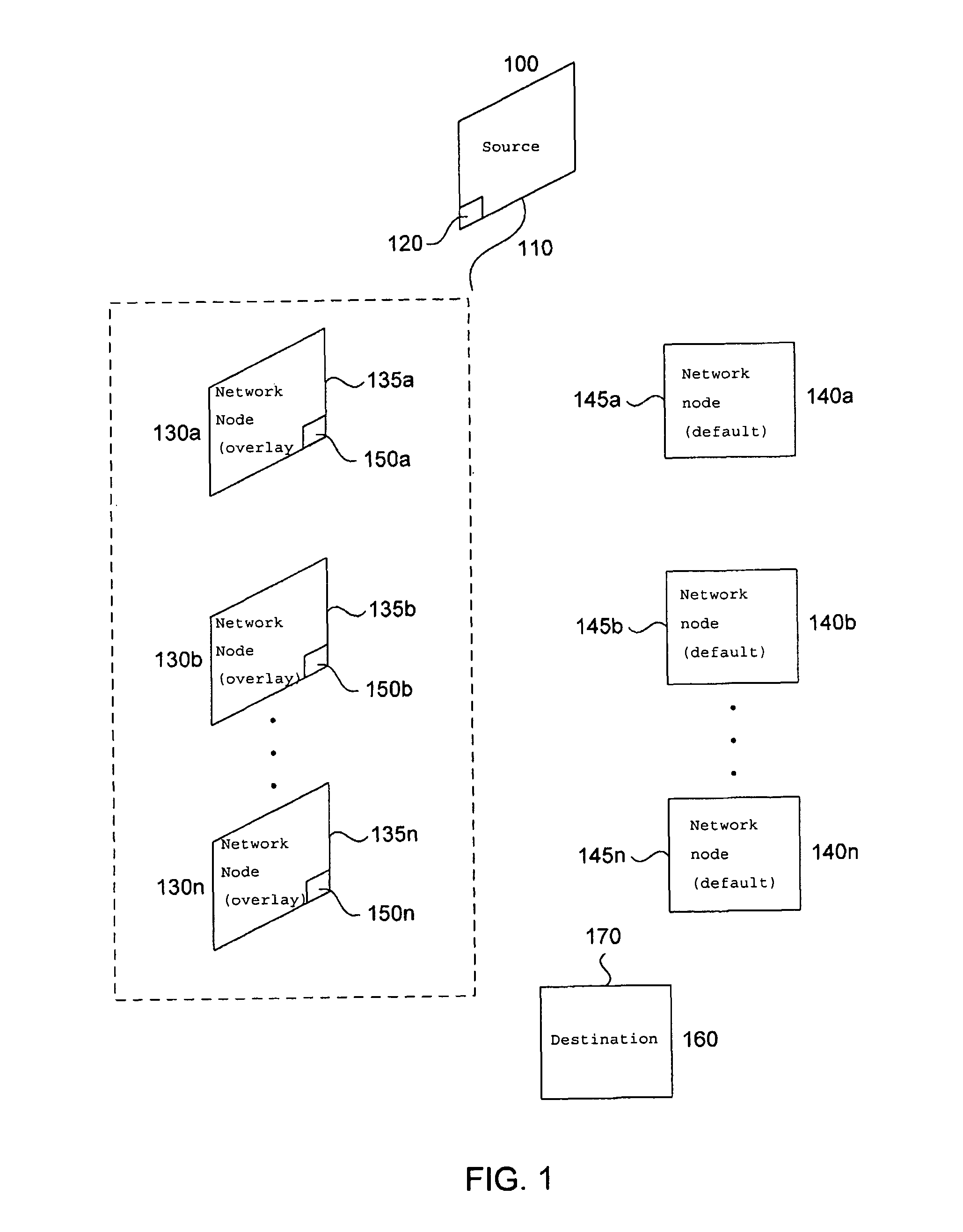
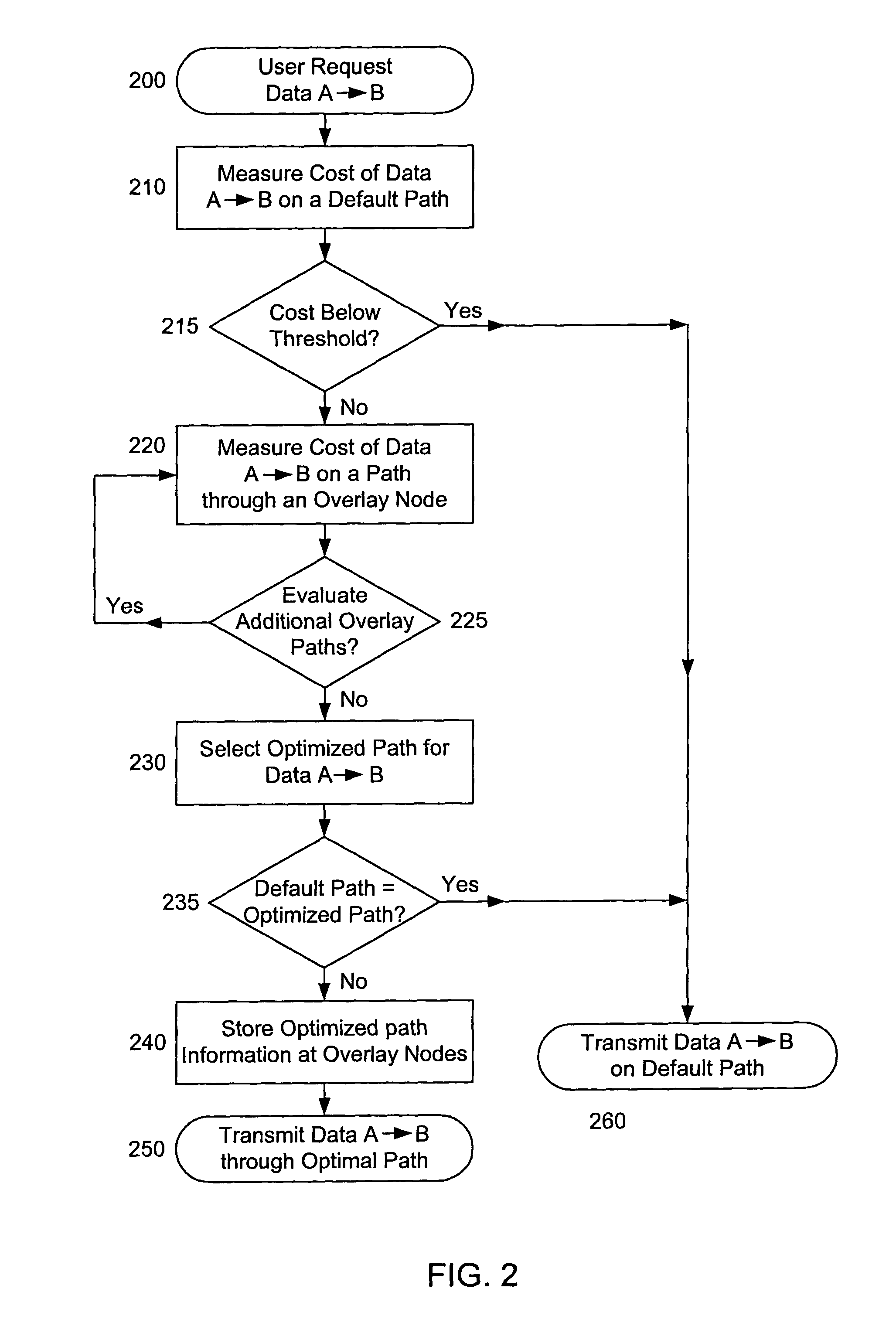
On-demand overlay routing for computer-based communication networks
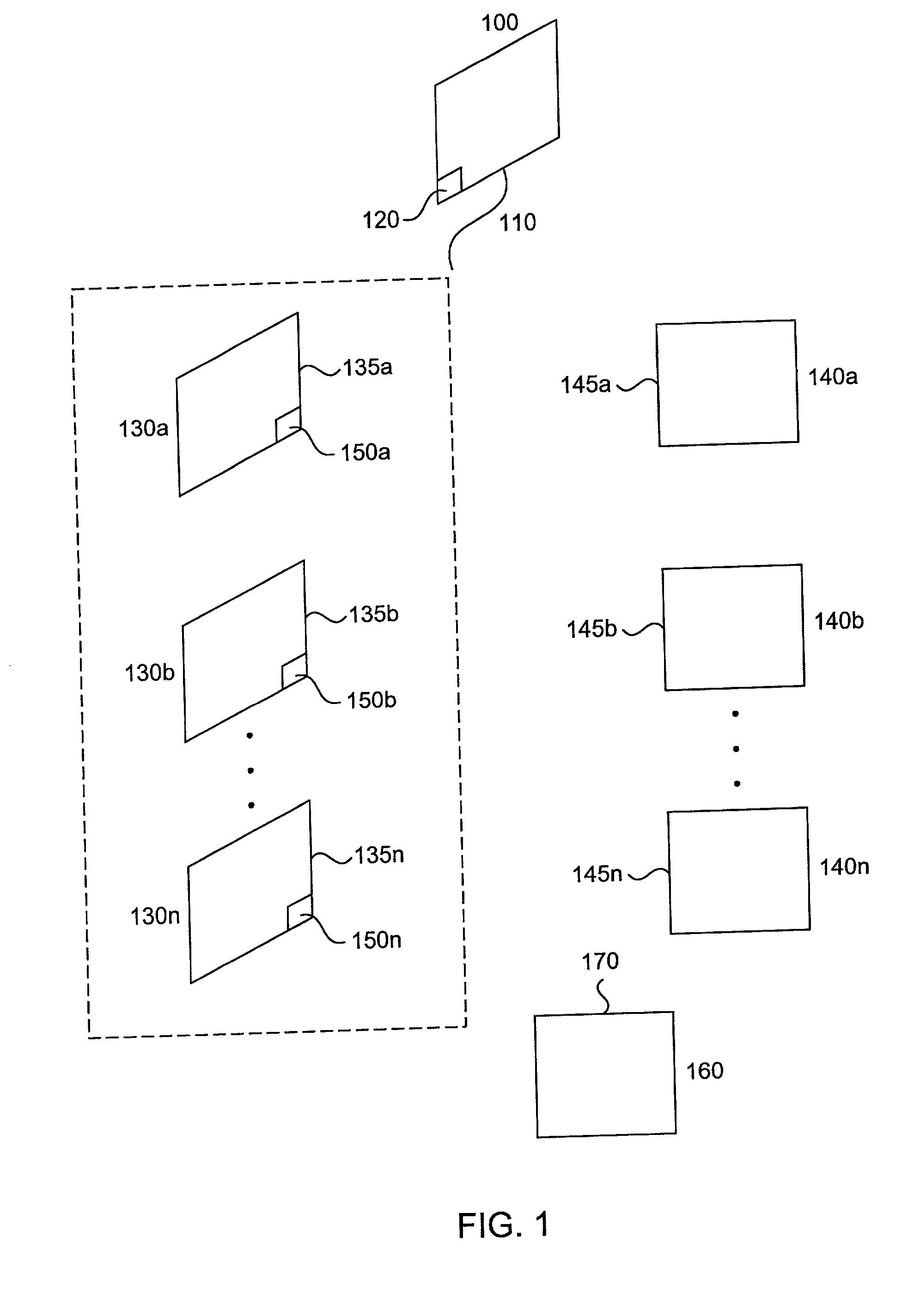
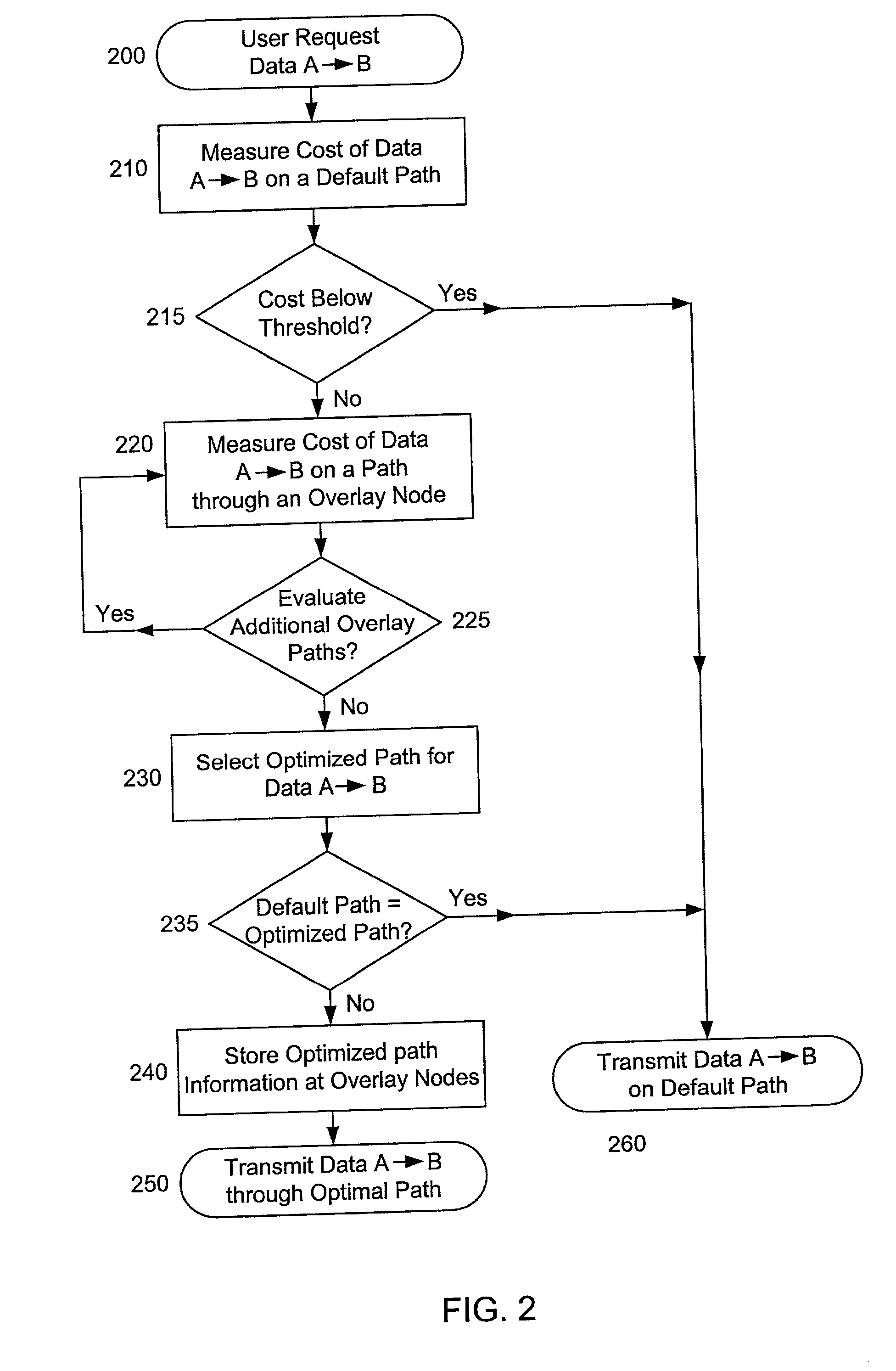
InactiveUS20020018449A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationCost metricNetwork Communication Protocols
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for dynamically discovering and utilizing an optimized network path through overlay routing for the transmission of data. A determination whether to use a default network path or to instead use an alternate data forwarding path through one or more overlay nodes is based on real-time measurement of costs associated with the alternative paths, in response to a user request for transmission of message data to a destination on the network. Cost metrics include delay, throughput, jitter, loss, and security. The system chooses the best path among the default forwarding path and the multiple alternate forwarding paths, and implements appropriate control actions to force data transmission along the chosen path. No modification of established network communication protocols is required.
Owner:LEVEL 3 COMM LLC
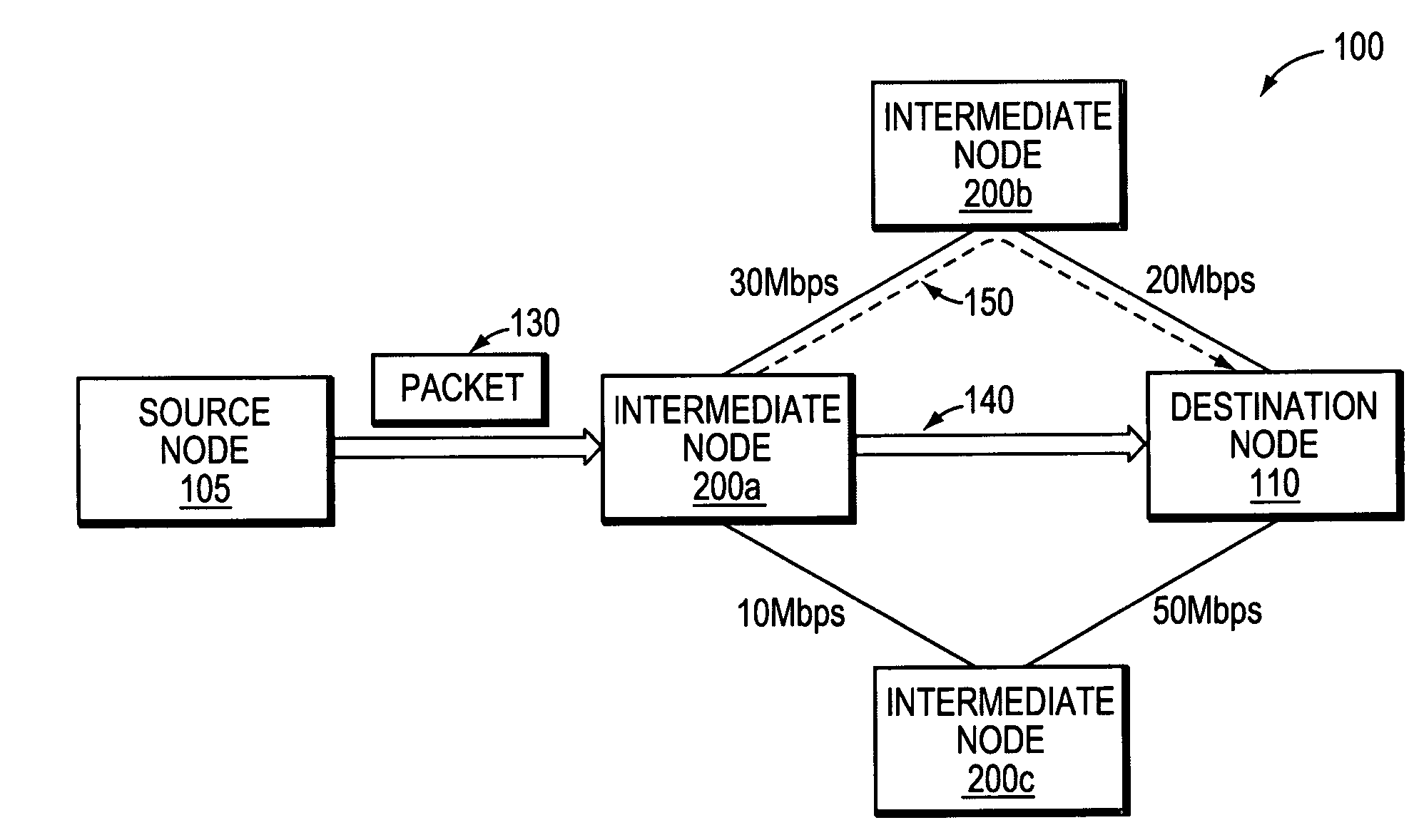
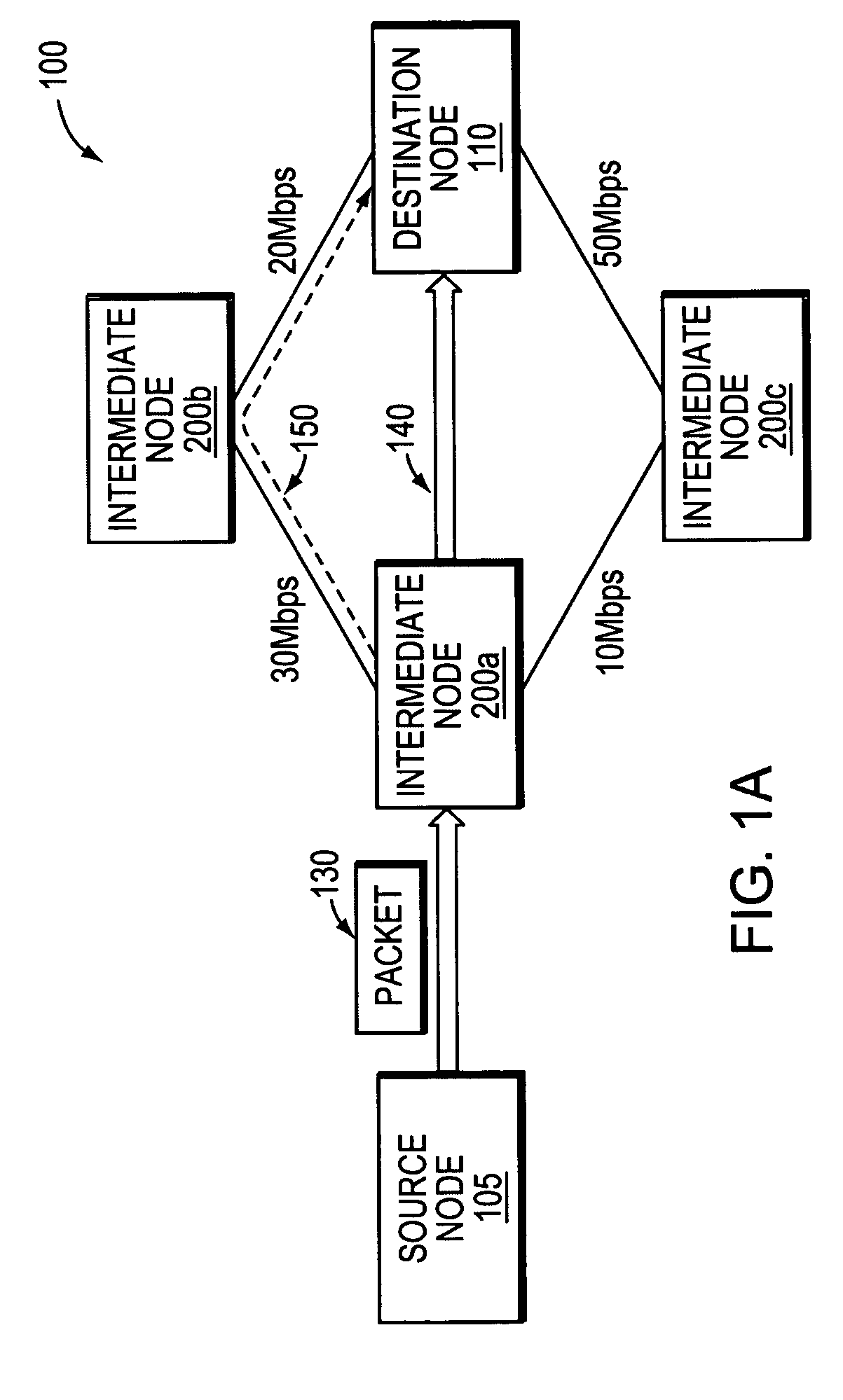
Method and apparatus to compute local repair paths taking into account link resources and attributes
A technique for calculating local repair paths through a computer network using one or more dynamically measured parameters in place of, or in addition to, statically assigned cost metrics. The dynamically measured parameters include various statistical measures of resources and attributes associated with data links and / or network nodes in the computer network. In operation, an intermediate node monitors a set of local link and / or node parameters. The node may generate an advertisement in response to at least one of its monitored parameters crossing a predetermined threshold value or changing value by a predetermined percentage or amount. The advertisement is “flooded” so as to advertise the dynamically measured parameter value to other neighboring intermediate nodes. After receiving the advertisement, each node may recalculate one or more local repair paths based on the advertised parameter value. The node may utilize a recalculated repair path if it provides an appreciably lower-cost path, e.g., by a predetermined percentage, as compared with the currently deployed repair path.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
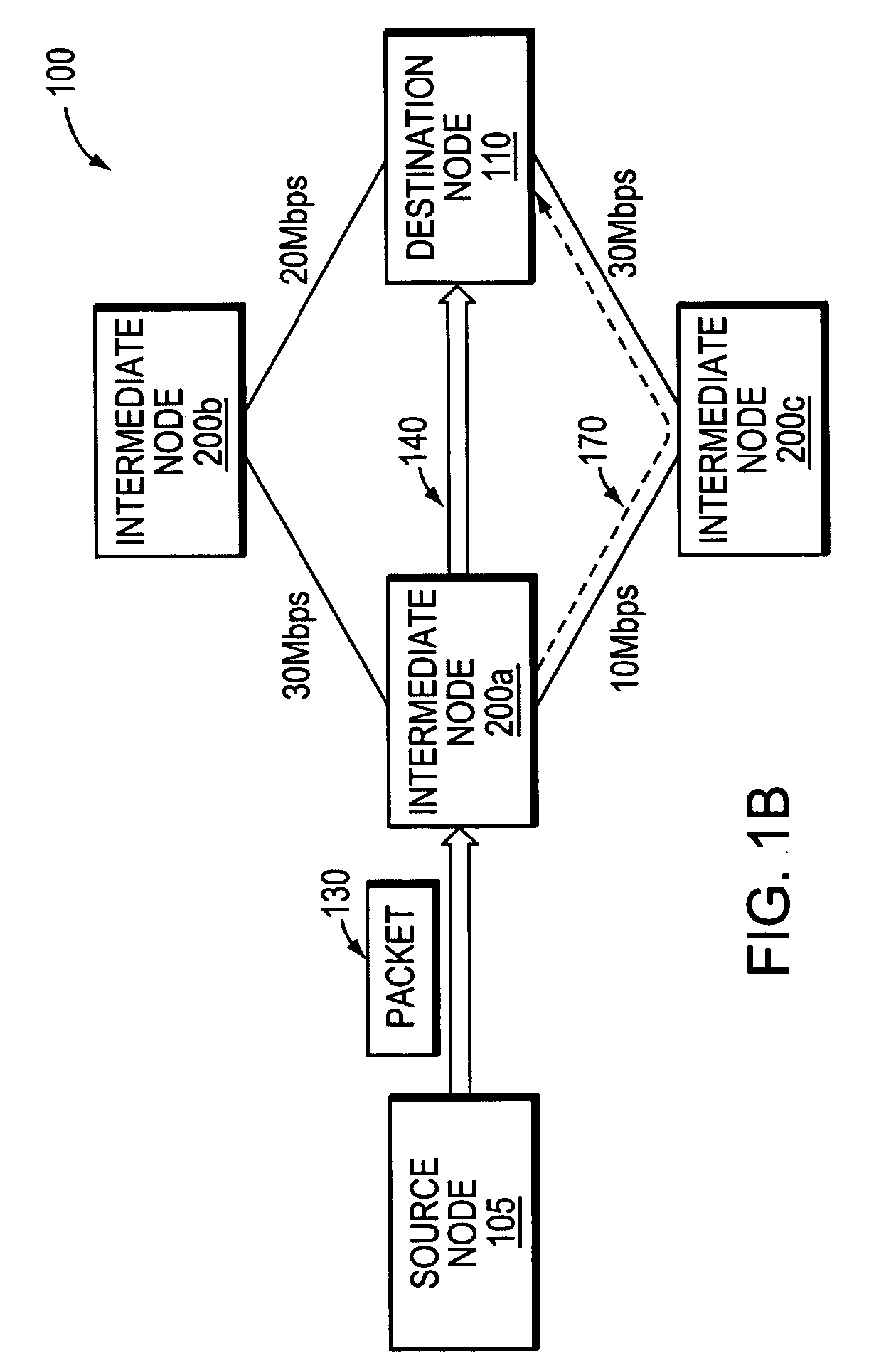
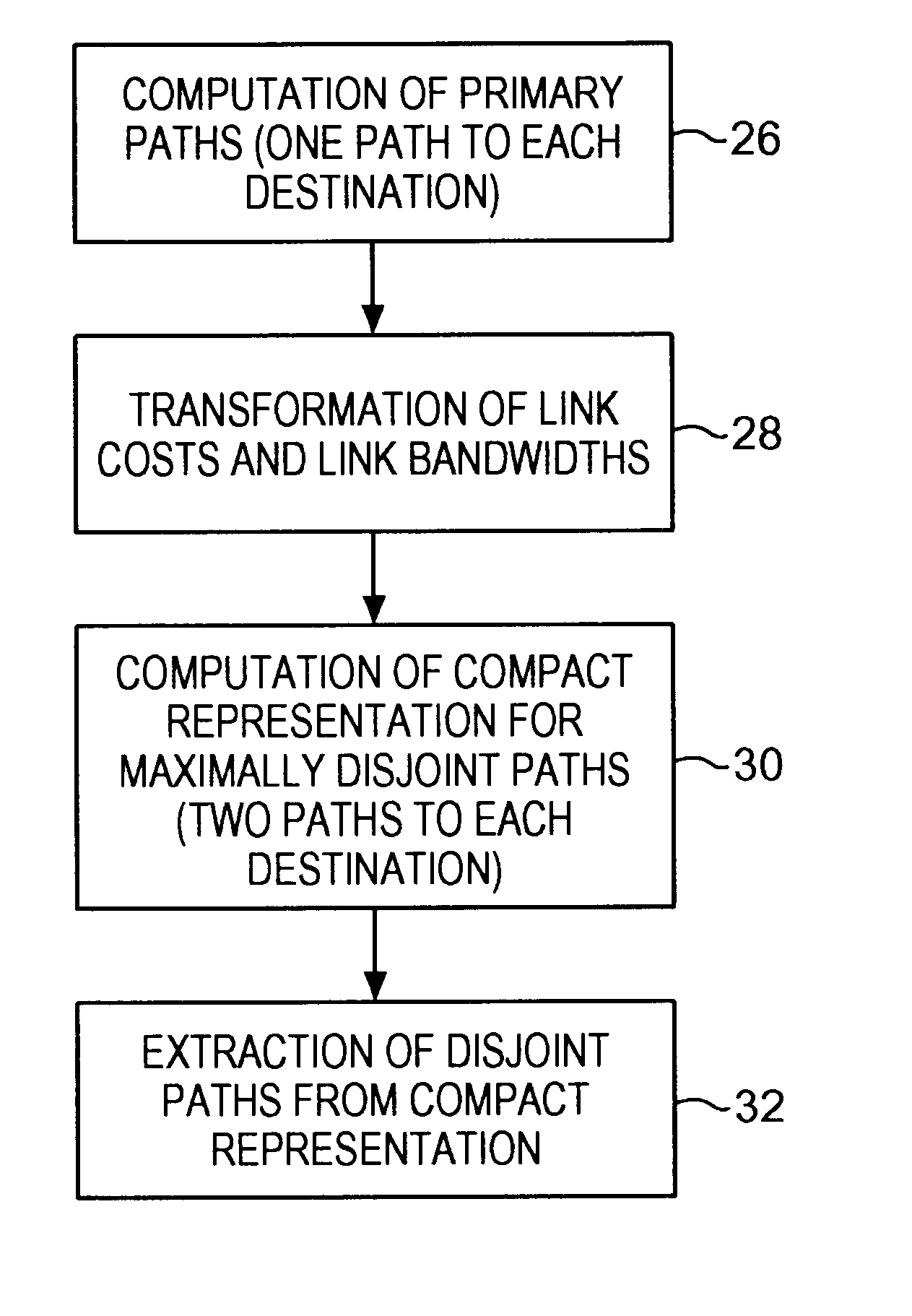
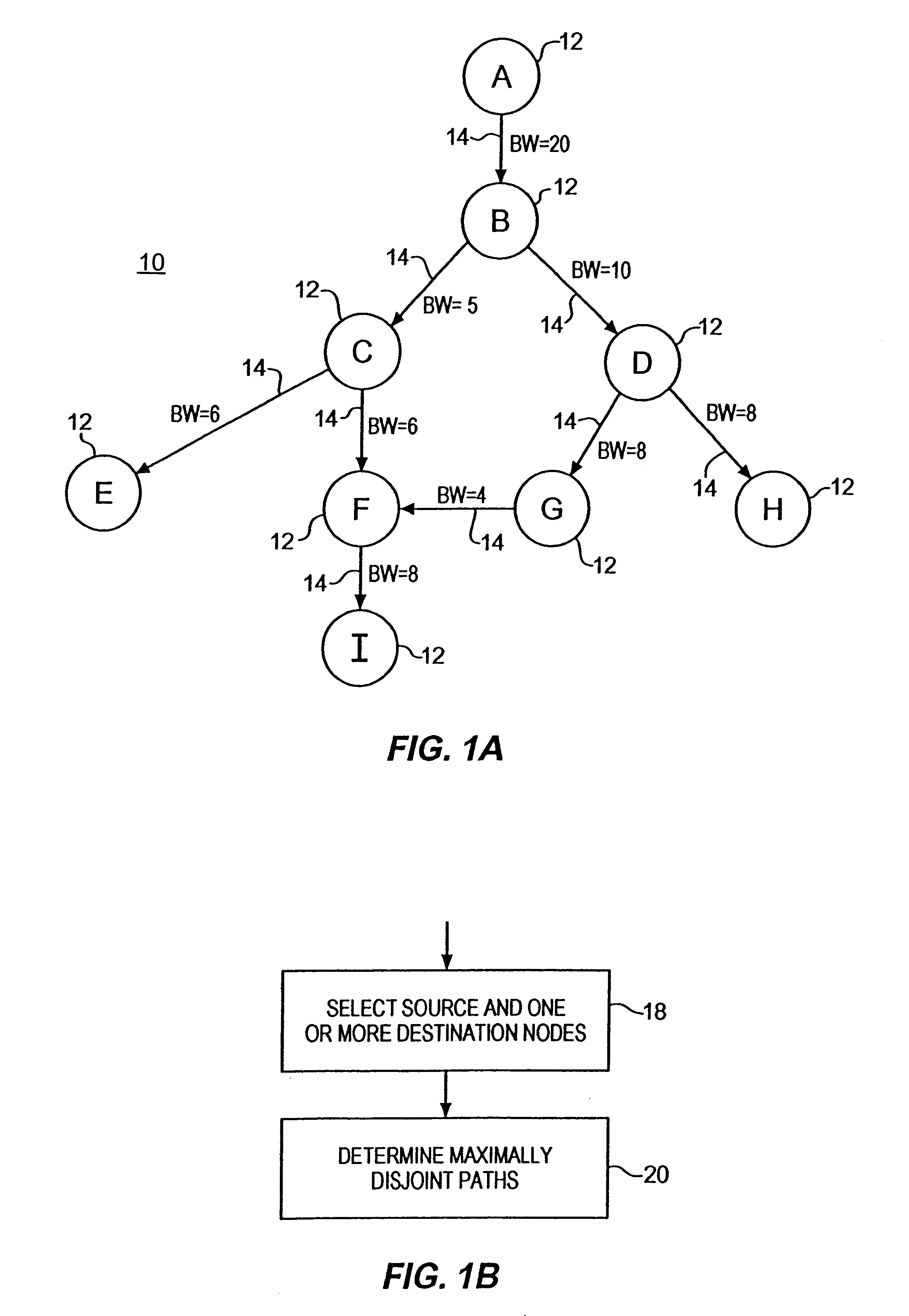
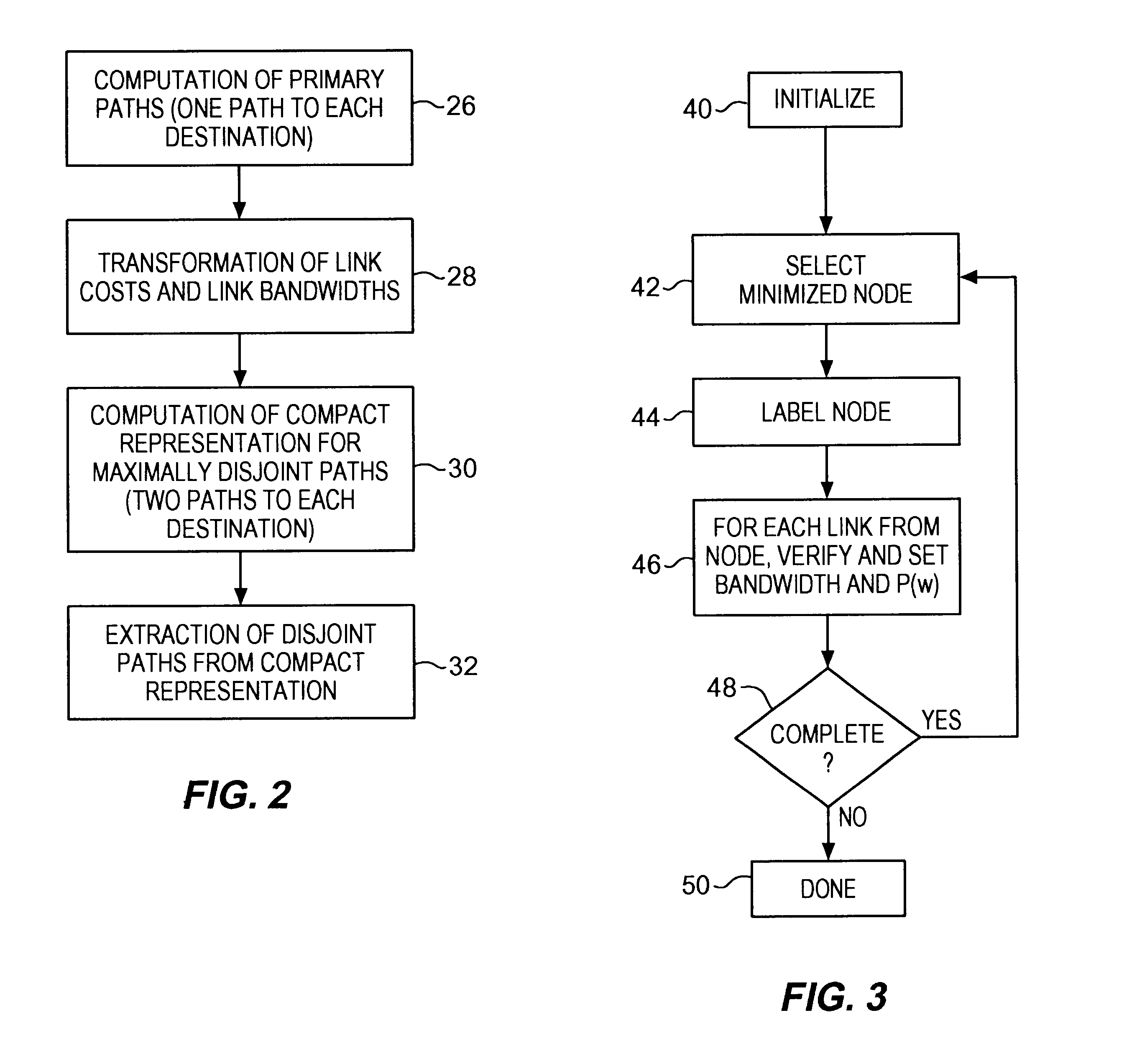
Communications network system and method for routing based on disjoint pairs of paths
InactiveUS6804199B1Raise the possibilityMinimizes probabilityError preventionTransmission systemsCost metricHigh bandwidth
Owner:SPRINT CORPORATION
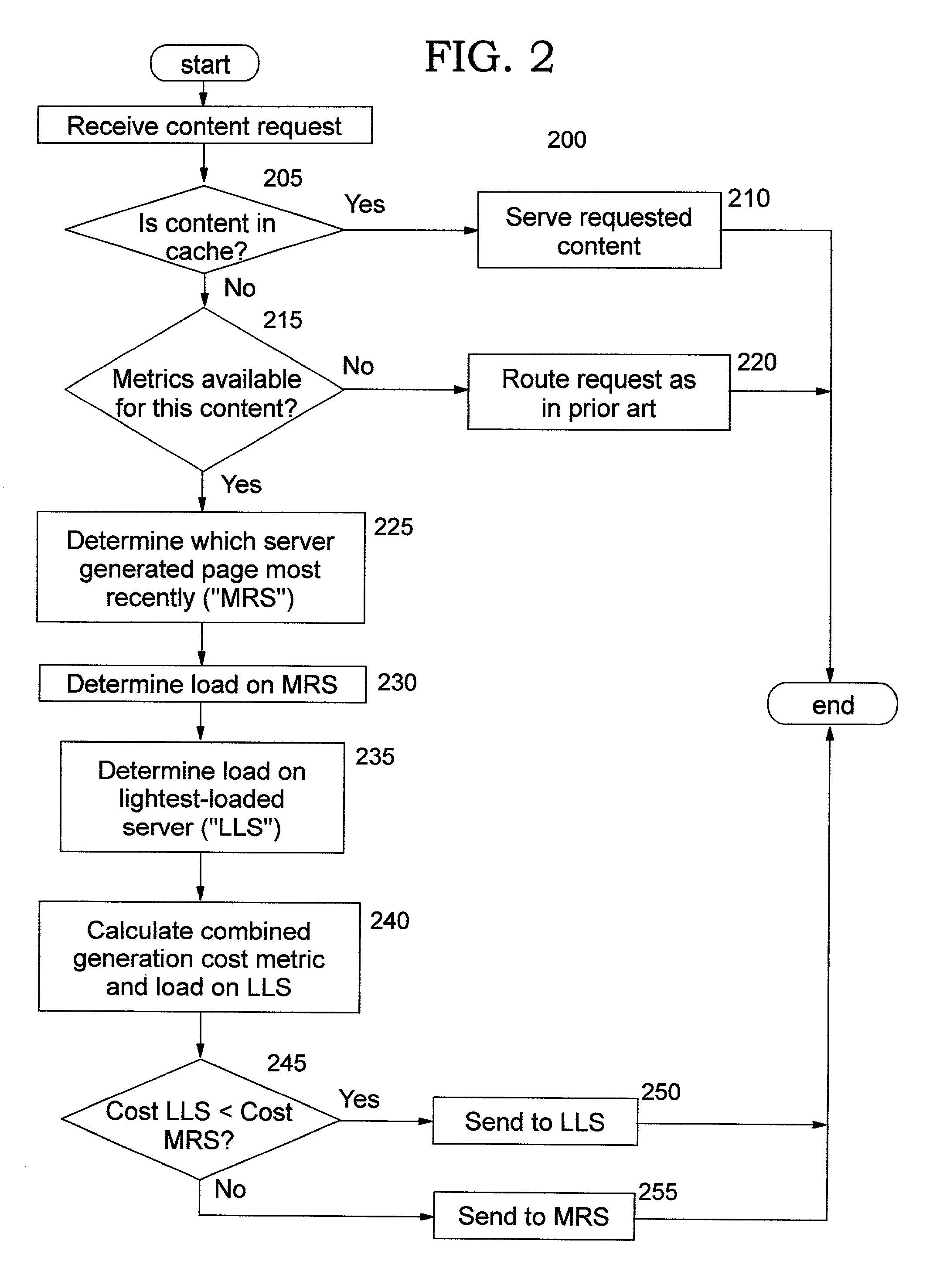
Load balancing content requests using dynamic document generation cost information
InactiveUS20020178259A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsCurrent loadCost metric
Methods, systems, computer program products, and methods of doing business by performing load balancing of content requests using information regarding the cost of dynamically creating the requested document content. Cost metrics are gathered by a server which generates requested content, and may reflect processing at one or more other servers. This cost information is provided to a load balancing host. Several alternative approaches for providing the cost metrics may be used, including defining new headers for response messages, specifying cookie values, and so forth. The load balancing host may choose to route a subsequent request for that content to the server which most recently generated the content, or to another available server, depending on the cost of re-generating the content and the current load on those servers.
Owner:IBM CORP
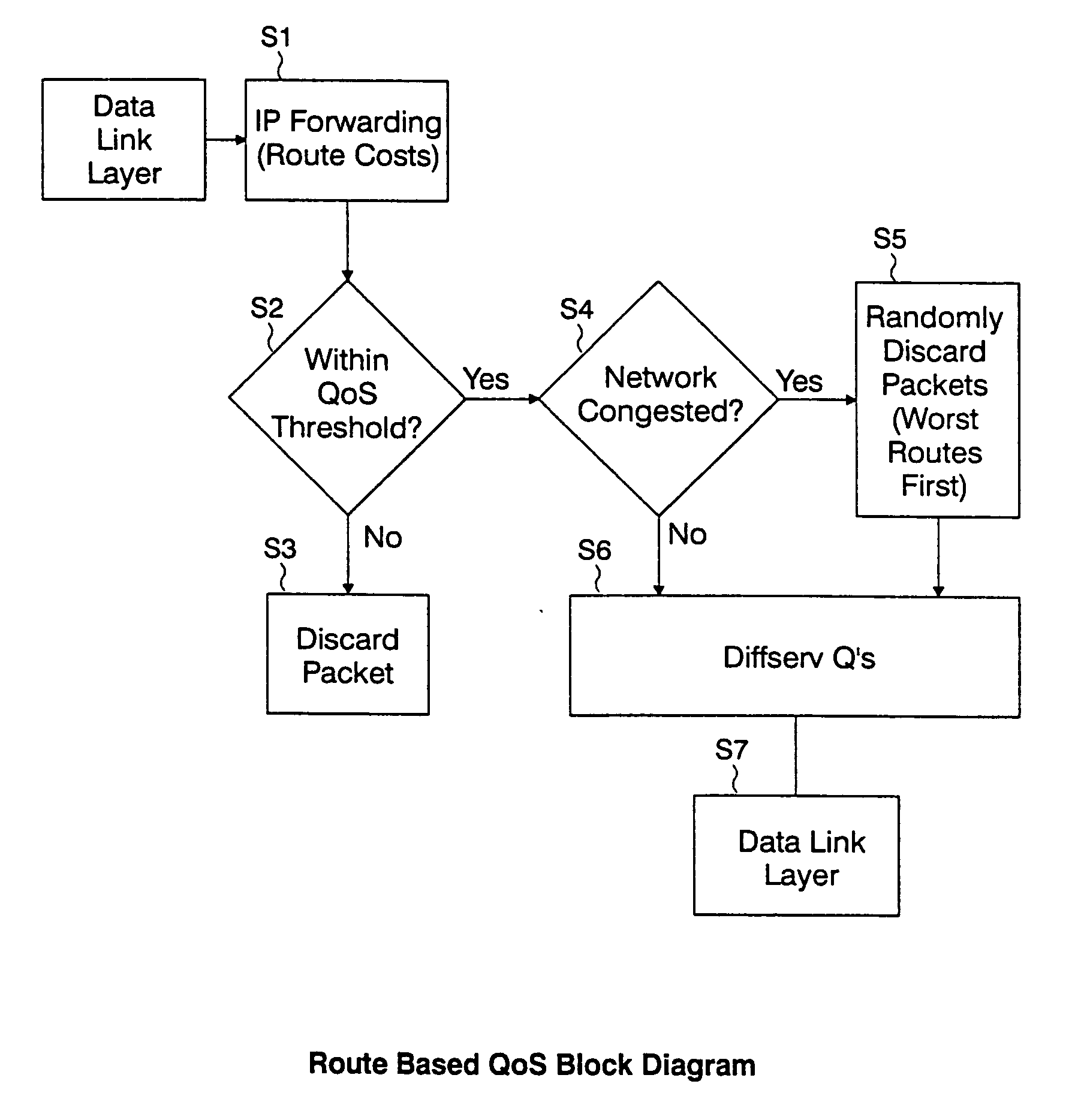
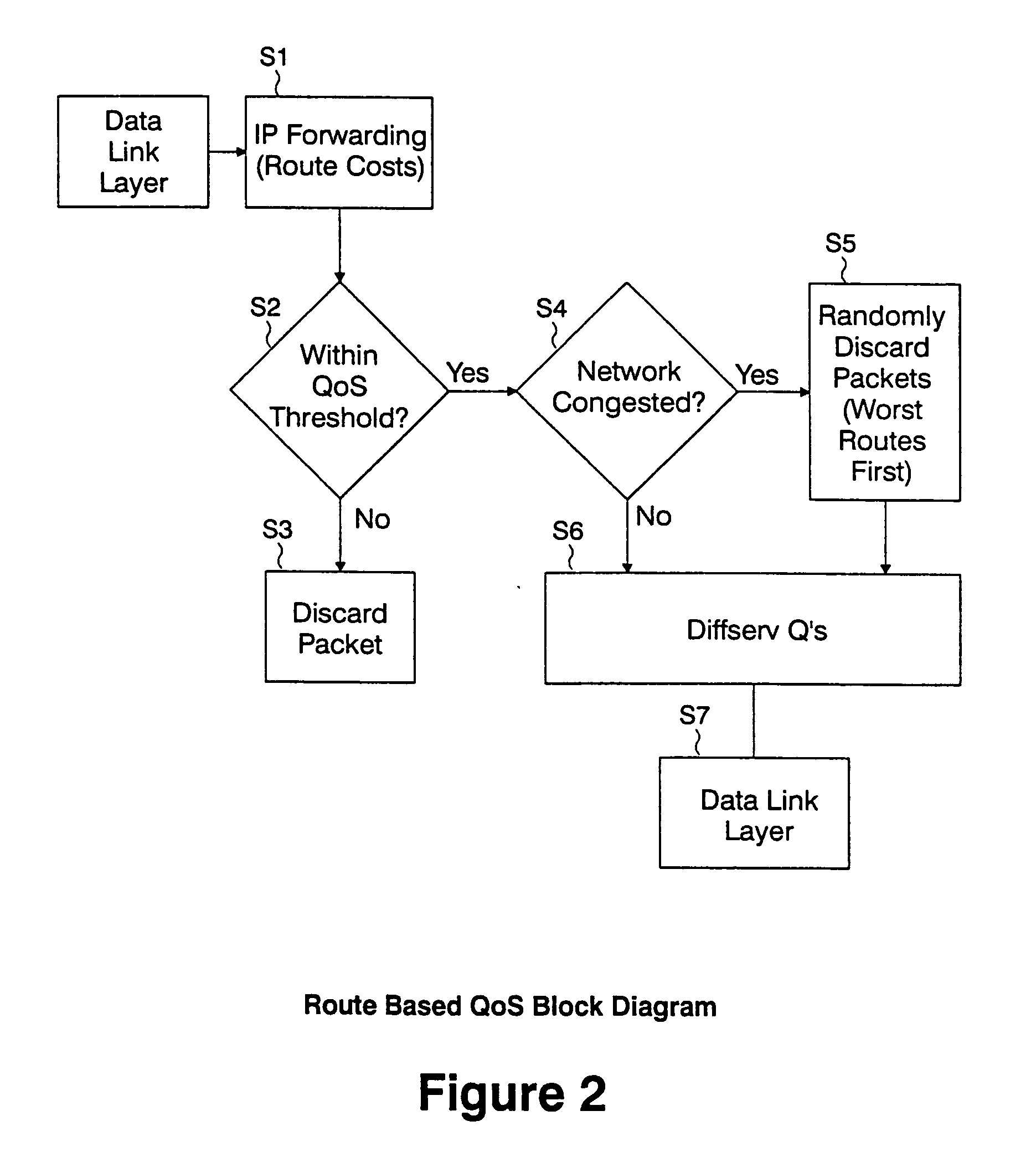
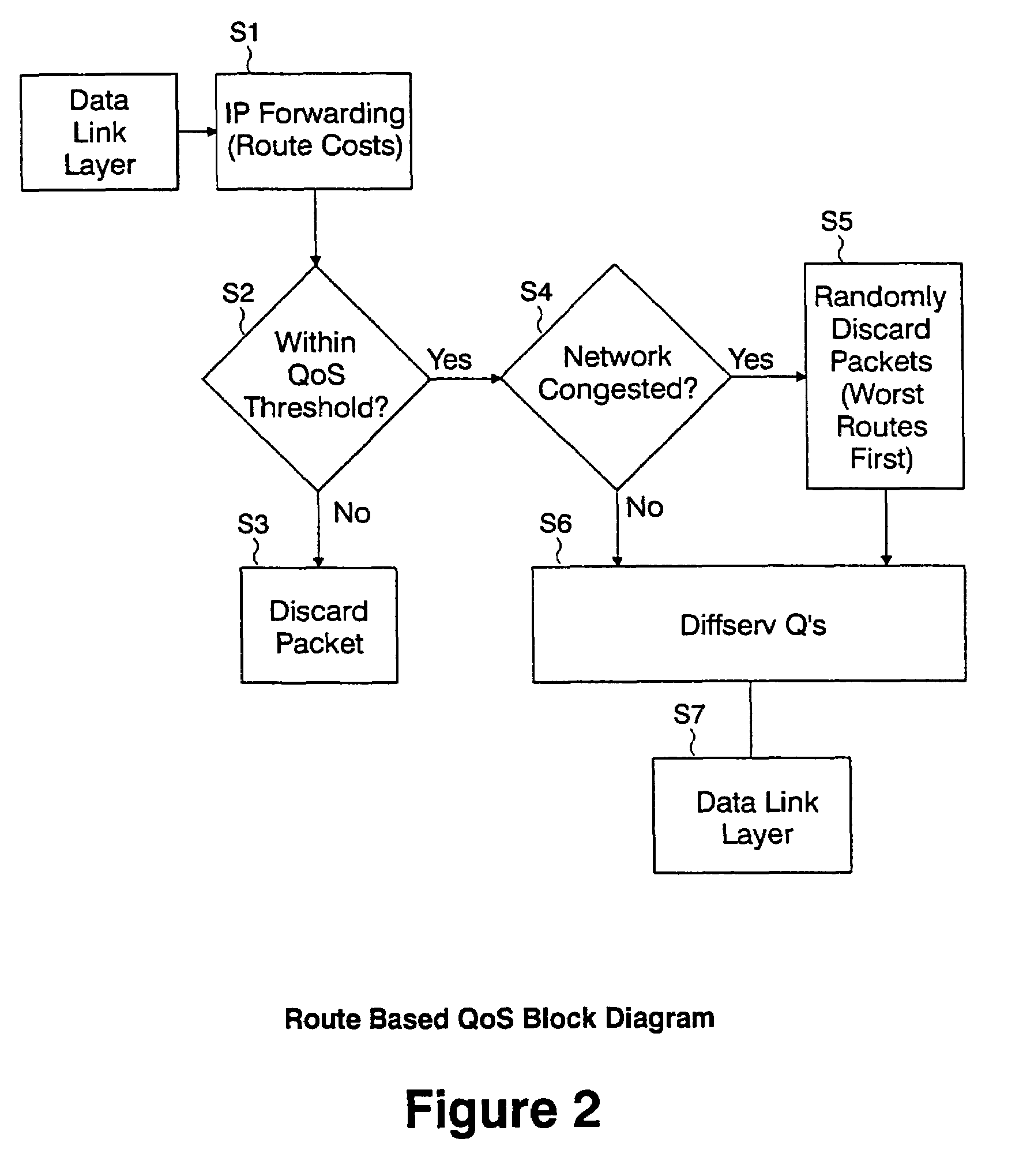
Routing cost based network congestion control for quality of service
ActiveUS20060067213A1Reduce loadError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCost metricQuality of service
A method and system of congestion control in a network are provided. A required quality of service (QoS) parameter, such as a maximum allowable latency, for a packet received at a queue in the network, and a route cost metric, such as accumulated and estimated latency, are determined, and the packet is either discarded if the route cost metric exceeds the required QoS parameter, or a discard bias value is set for the packet. Also, if the required QoS parameter exceeds the route cost metric, the method includes determining whether a congestion condition exists in the network, and if the congestion condition exists, biasing the packet for discard based on its latency if the route cost metric for the packet exceeds a threshold. The network may be an IP network, and a network such as a mobile ad hoc network (MANET).
Owner:GE LIGHTING SOLUTIONS LLC
Method and apparatus for computing user-specified cost metrics in a data space profiler
A system and method for profiling a software application may include means for defining a custom cost metric that includes a cost metric identifier and a cost function. The cost function may apply a mathematical formula to data extracted from an event set to calculate a respective cost metric value for each of one or more events in the event set. The data extracted from the event set may include one or more respective profiling object identifiers and one or more other respective costs associated with each of the one or more events. A cost associated with an event in the event space may be associated with a function or basic block of instructions. The cost function may include a distribution formula for attributing at least a portion of the cost associated with a function or basic block to each of the instructions comprising the function or basic block.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Routing cost based network congestion control for quality of service
A method and system of congestion control in a network are provided. A required quality of service (QoS) parameter, such as a maximum allowable latency, for a packet received at a queue in the network, and a route cost metric, such as accumulated and estimated latency, are determined, and the packet is either discarded if the route cost metric exceeds the required QoS parameter, or a discard bias value is set for the packet. Also, if the required QoS parameter exceeds the route cost metric, the method includes determining whether a congestion condition exists in the network, and if the congestion condition exists, biasing the packet for discard based on its latency if the route cost metric for the packet exceeds a threshold. The network may be an IP network, and a network such as a mobile ad hoc network (MANET).
Owner:GE LIGHTING SOLUTIONS LLC
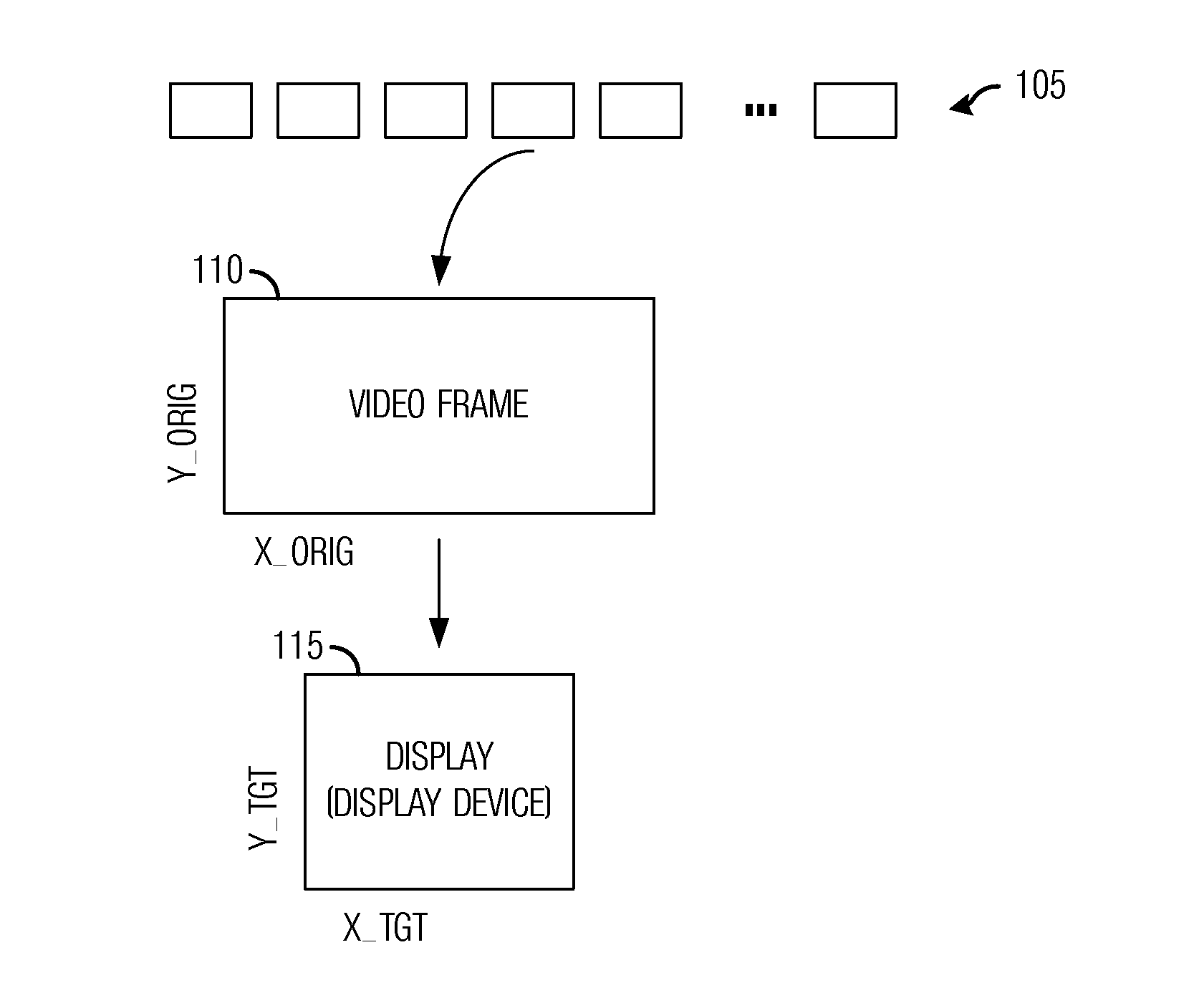
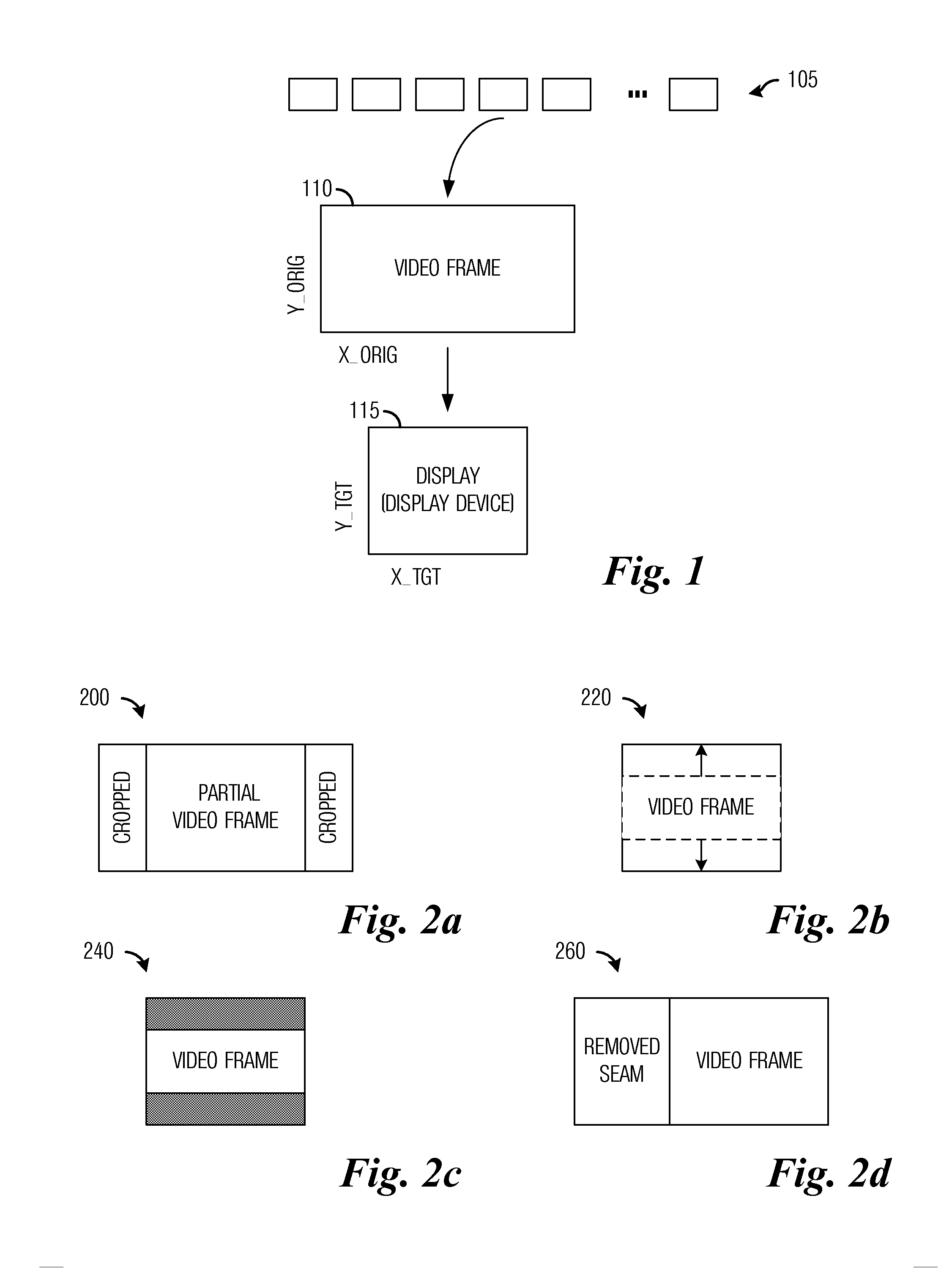
System and Method for Retargeting Video Sequences
InactiveUS20130050574A1Promote resultsImprove viewing experiencePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningCost metricVideo sequence
A system and method for retargeting video sequences are provided. A method for retargeting a video includes a plurality of frames includes determining saliency information for the plurality of frames, determining a cost metric for the video, and retargeting the video based on the cost metric to produce a retargeted video. The cost metric considers loss due to cropping, scaling, temporal factors, and spatial factors. The retargeting makes use of a crop window for each frame in the plurality of frames.
Owner:VID SCALE INC
Apparatus and methods for compressing video content using adaptive projection selection
ActiveUS20180084257A1Low rate-distortion costRate-distortion costDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionCost metric
Apparatus and methods for encoding panoramic content, such as by a wide field of view and large image size. In one implementation, a panoramic image may be mapped to a cube, equirectangular or any other projection e.g., icosahedron or octahedron. Projection may be selected adaptively based on evaluation of the panoramic content. Content evaluation may include obtaining rate distortion cost metric for a given projection configuration including projection type, projection arrangement, and projection orientation. Projection configuration with the lowest cost may be selected as target projection for encoding content. As content composition changes (e.g., object motion, texture presence and / or location) projection may be adaptively selected to match changes in the content. Adaptive content selection methodology may provide for a lower encoded bitrate for a given encoded quality and / or higher quality for a given bitrate.
Owner:GOPRO
Price-aware neighborhood selection for peer-to-peer networks
A method and apparatus for peer-to-peer file sharing is provided. In some embodiments, the method includes receiving a request for a list of neighbor peers, where the request is made by a requesting peer device, and where the requesting peer device has a local internet service provider (ISP). The method may also include employing a server device to rank each neighbor peer in a plurality of neighbor peers based on whether the respective neighbor peer is external to the local ISP, and if the respective neighbor peer is external to the ISP, further based on a cost metric associated with a next ISP hop from the requesting peer device to the respective neighbor peer. The method may also include generating the list of neighbor peers based on the ranking of the neighbor peers, and enabling transmission of the list of neighbor peers to the requesting peer device.
Owner:DEUTSCHE TELEKOM AG
Method and apparatus for mesh routing
ActiveUS7881206B2Good for healthProlong lifeError preventionTransmission systemsCost metricMesh routing
Method and apparatus for optimizing mesh routing for stability and system lifetime maximization in networks, for example in wireless networks. A routing module may be instantiated in nodes on the network. The routing module may implement a link quality and node health aware routing protocol on the network that considers a combination of link quality and node health / residual lifetime metrics in the calculation of the desirability of nodes and links between nodes as parts of an overall route. A route selection metric for each route may be determined from routing cost metrics for the nodes on the route and the number of hops on the route. A node may then select a best route according to the determined route selection metrics for the routes.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
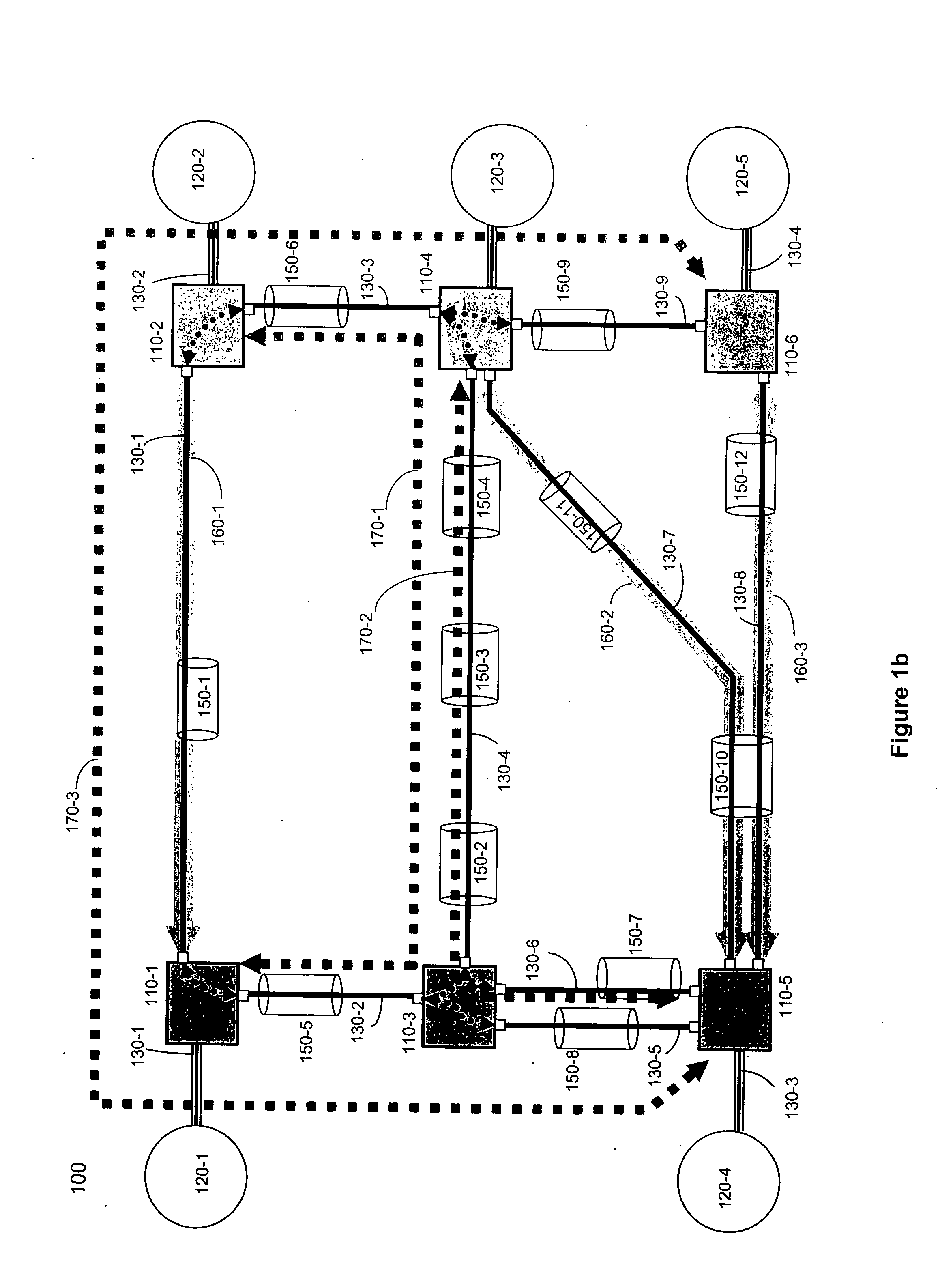
System and method for identifying cost metrics for a network
A system and method identifies the costs to be assigned to each link in a network that can more evenly balance the utilization of links in the network.
Owner:CIENA
Prefix-aware weighted cost multi-path group reduction
ActiveUS20150326476A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic characteristicCost metric
Methods and systems for generating a forwarding table for a packet switch. The system includes a route manager for the packet switch, configured to identify a plurality of multi-path groups each corresponding to a respective initial set of routing entries in the forwarding table and generate, for one or more multi-path groups, at least one replacement set of routing entries with fewer routing entries than the initial set corresponding to the respective multi-path group. The route manager selects, based on a traffic reduction cost metric, one or more of the replacement sets of routing entries, each corresponding to a different respective multi-path group, and updates the forwarding table with the selected replacement sets. In some implementations, the traffic reduction cost metric includes a traffic characteristic. In some implementations, the packet switch participates in a software-defined network (SDN) and the route manager is part of an SDN controller.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method for stochastic selection of improved cost metric backup paths in shared-mesh protection networks
InactiveUS20050025058A1Efficient sharingReduce the amount requiredError preventionTransmission systemsCost metricBackup path
A method of path selection in shared-mesh restoration networks that results in efficient use of network resources, using only the network state information available locally at each network element. The method uses probability theory to develop an estimate of protection channel sharing opportunities and encourages sharing of protection channels if possible
Owner:SUMMIT TECH SYST LP
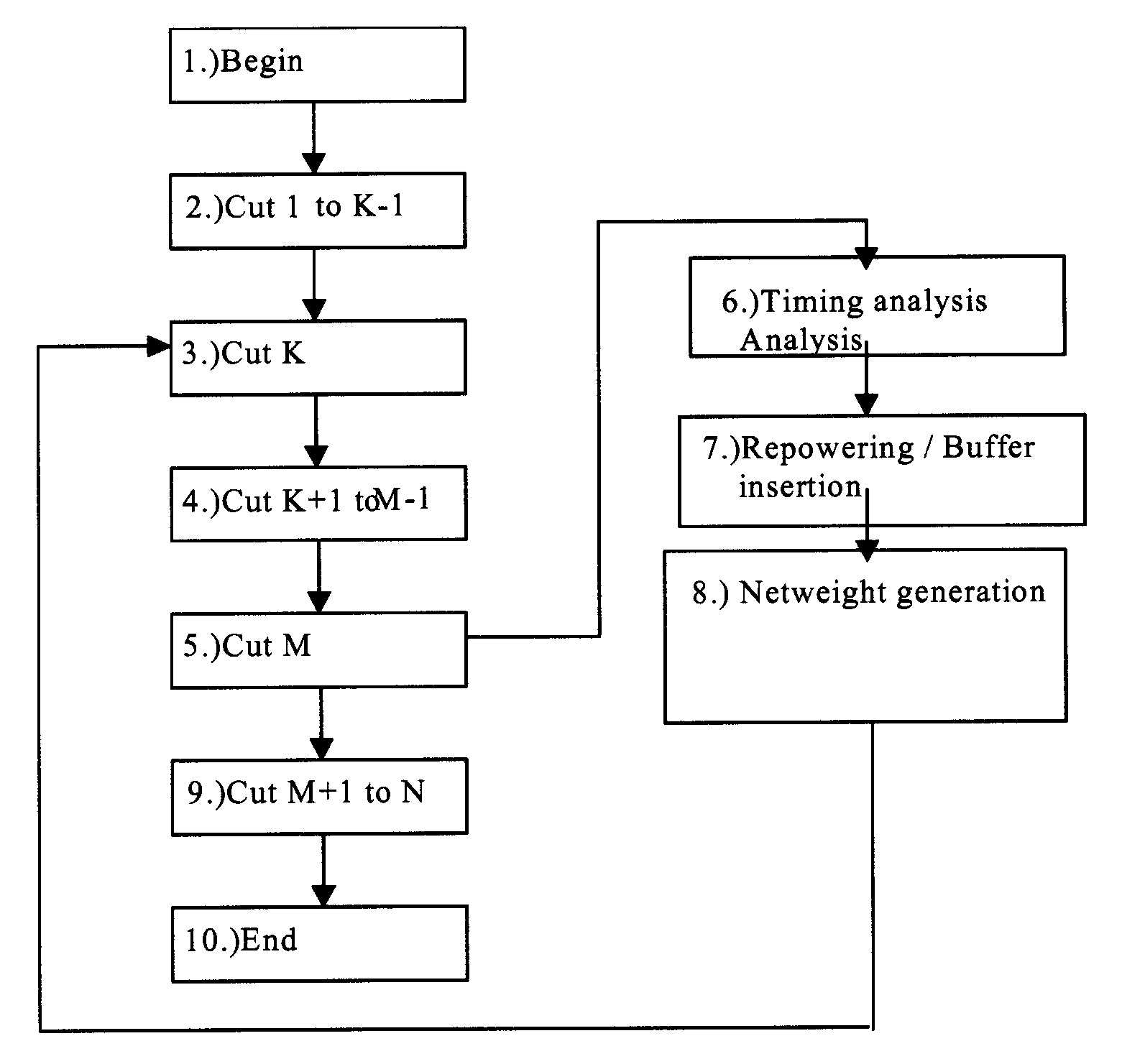
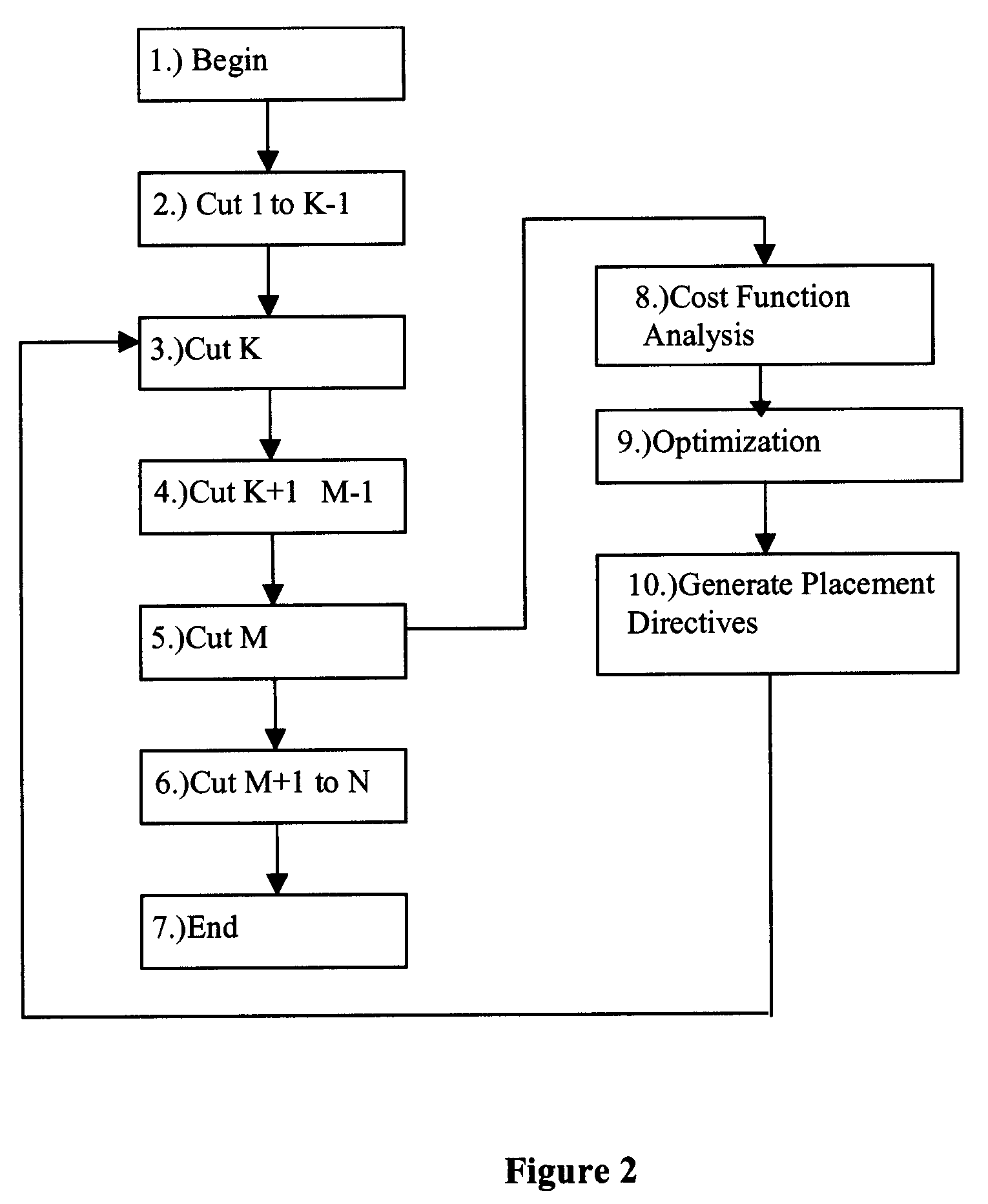
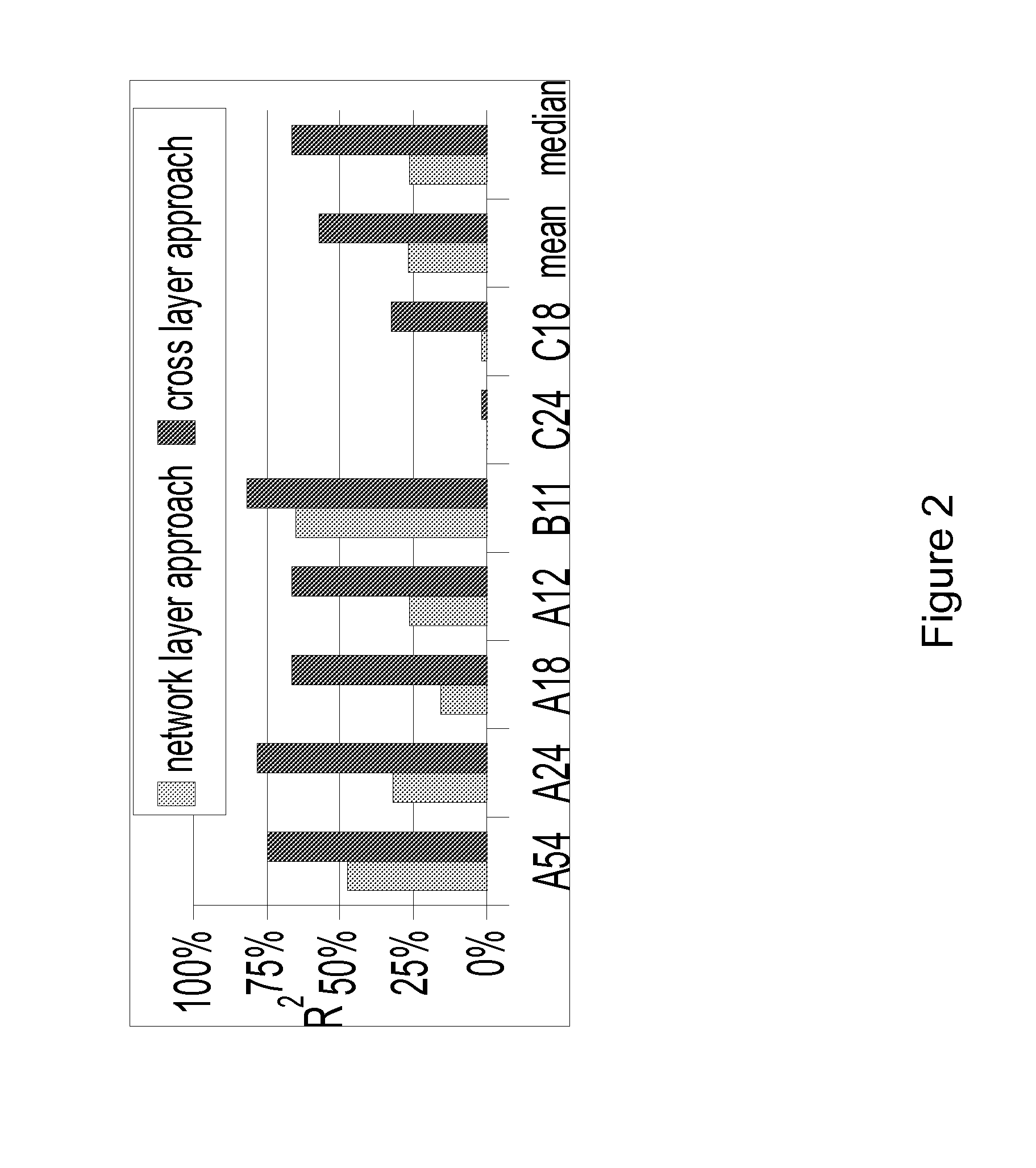
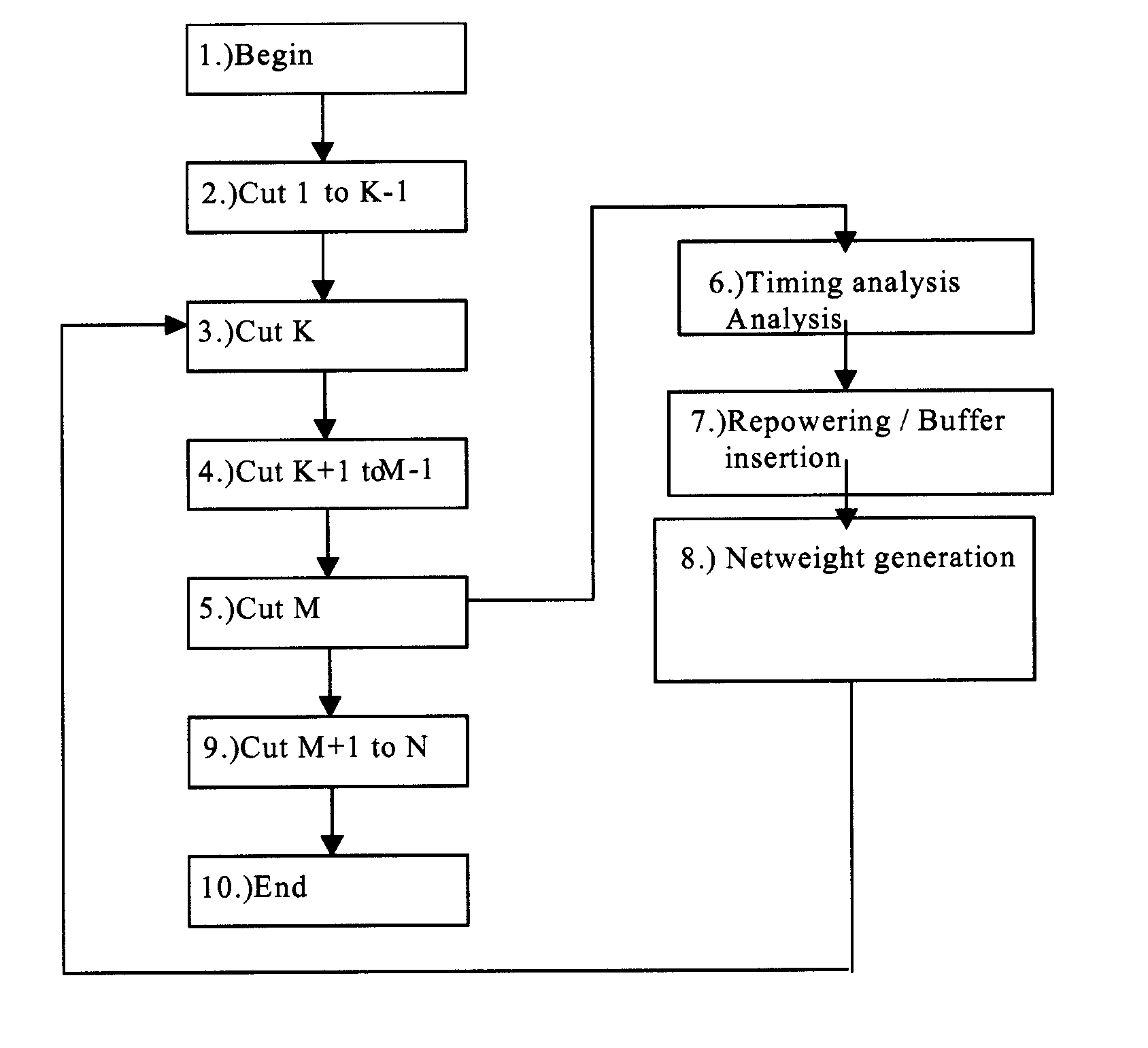
Method for successive placement based refinement of a generalized cost function
InactiveUS7076755B2Quality improvementEasy to placeMulti-objective optimisationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationCost metricComputer science
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
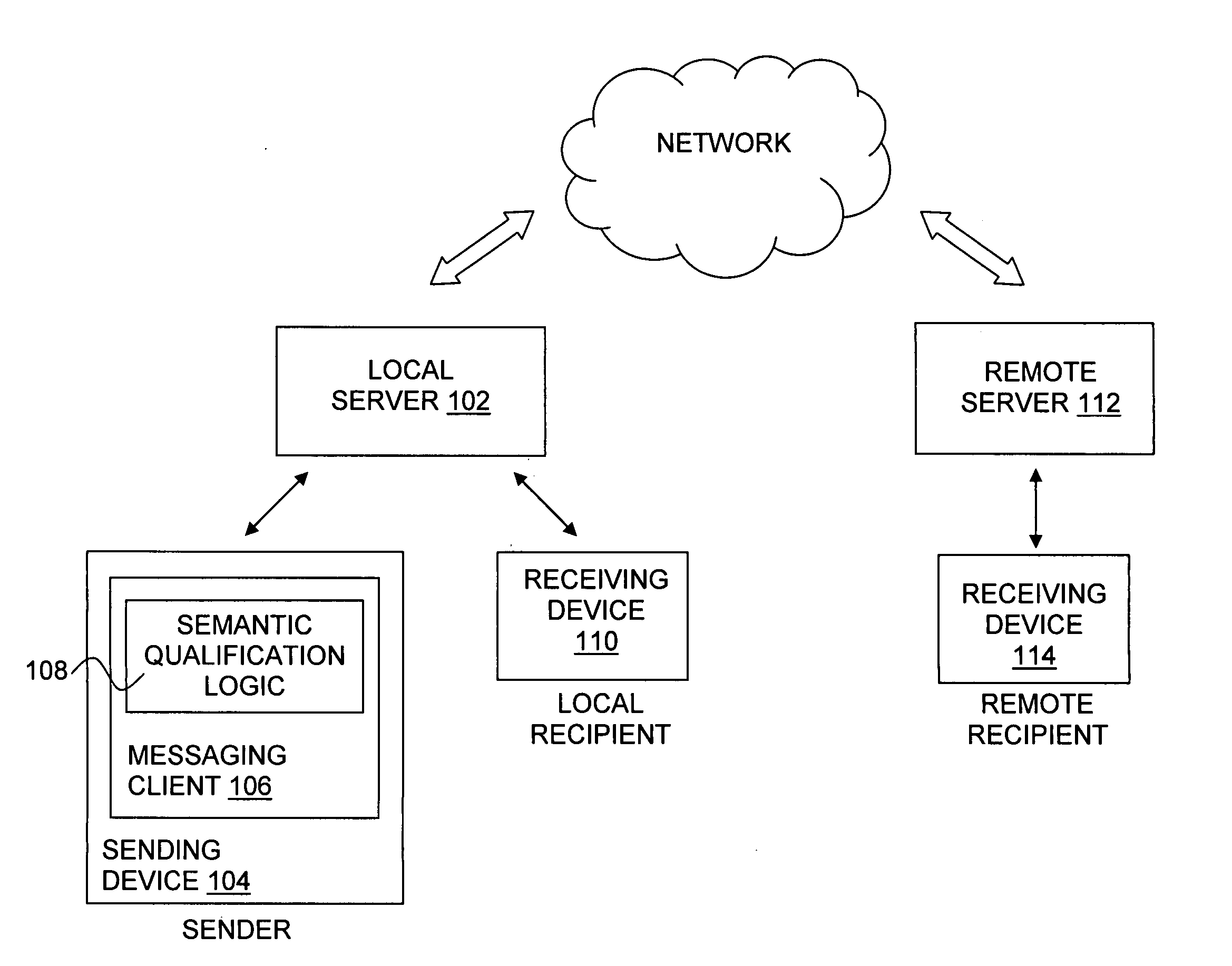
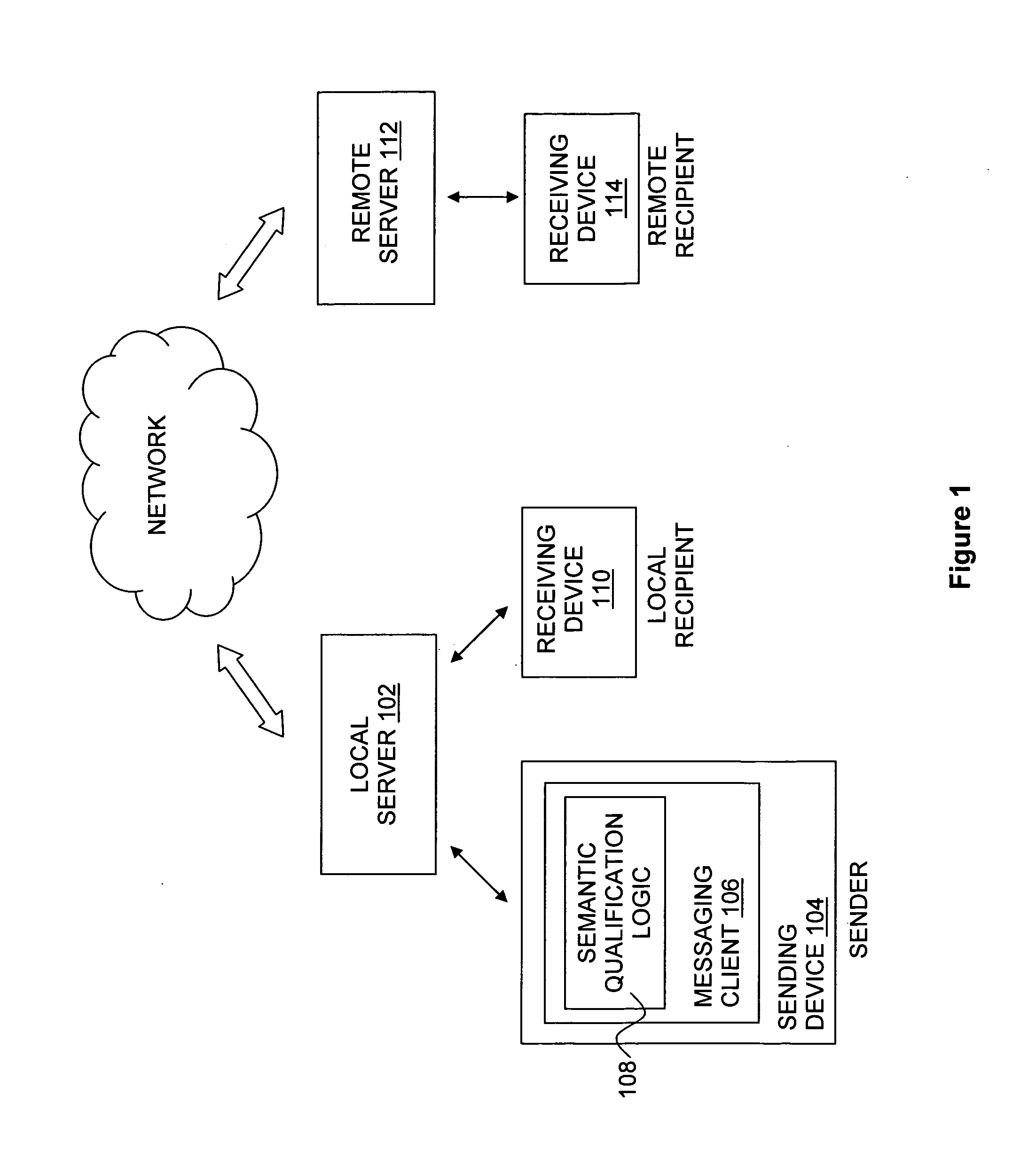
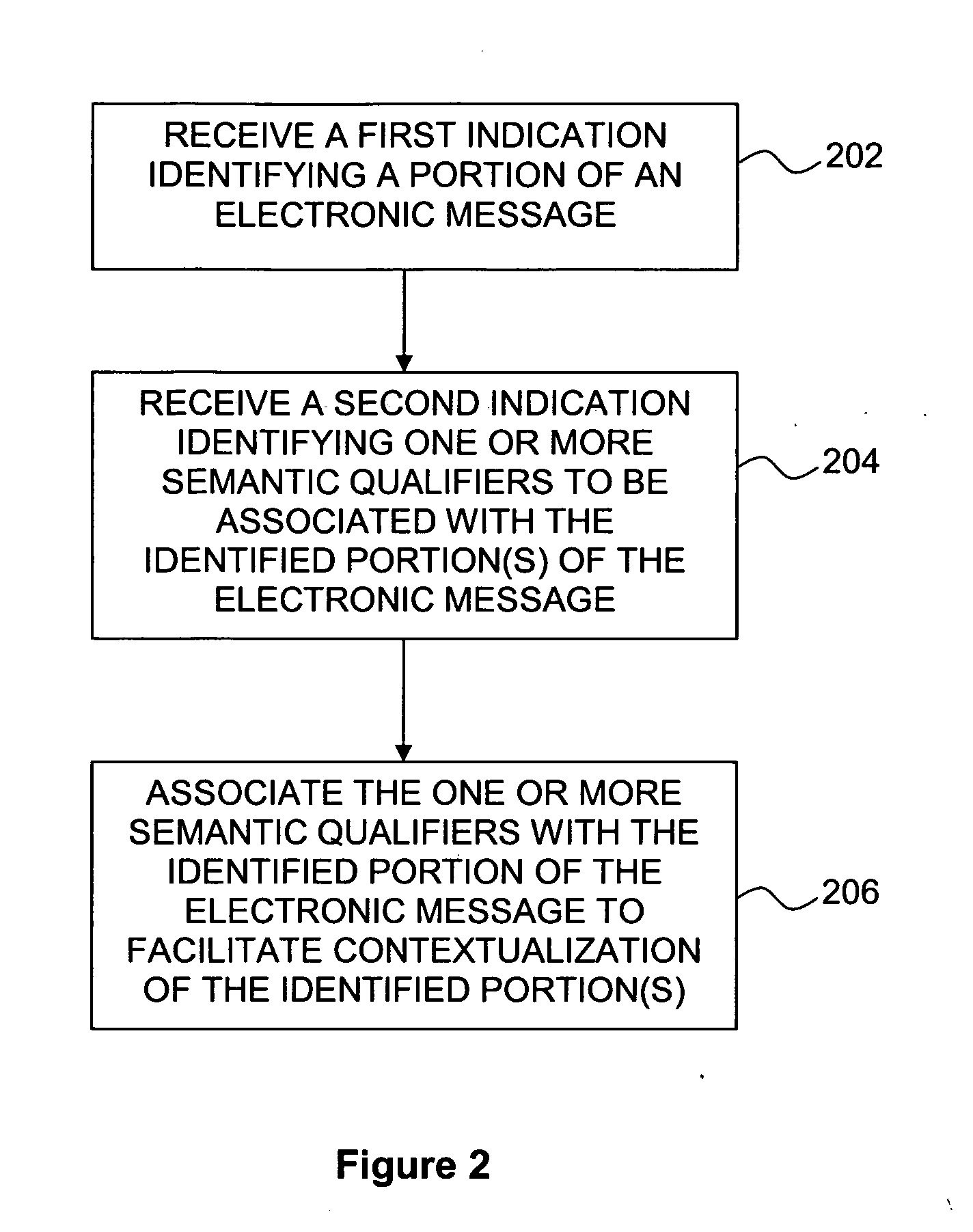
Method and apparatus for assigning cost metrics to electronic messages
ActiveUS20060092920A1Improve connectivityGood suitMultiple digital computer combinationsOffice automationCost metricElectronic mail
The present invention provides methods and apparatuses for contextualization of electronic messages, for example, by determining at least one cost metric for an electronic mail message based at least in part upon an identified context, automatically generating metadata representing the at least one cost metric, and associating the metadata with the electronic mail message.
Owner:SURESCRIPTS
On-demand overlay routing for computer-based communication networks
InactiveUS7953888B2Mechanical apparatusDigital computer detailsCost metricNetwork Communication Protocols
Owner:LEVEL 3 COMM LLC
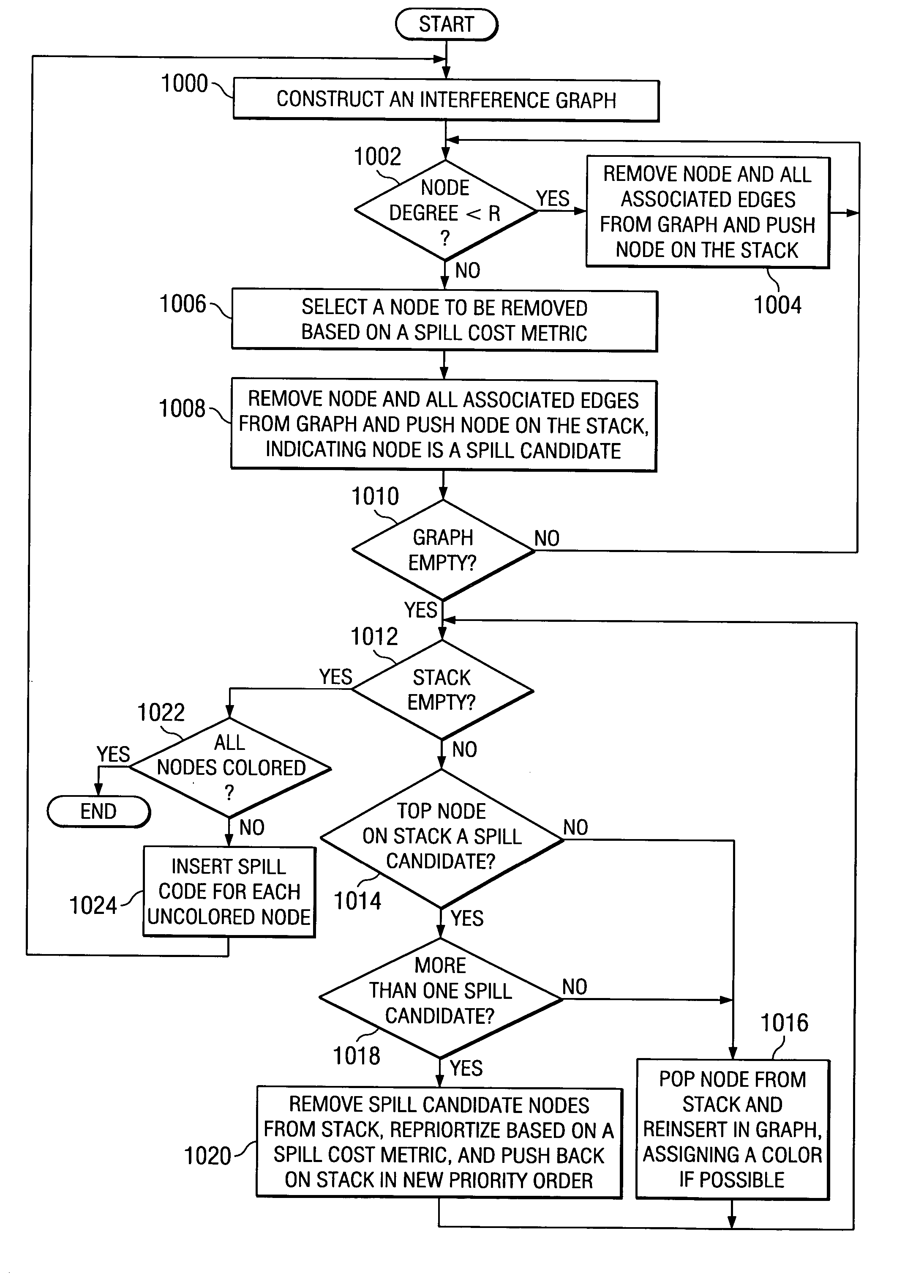
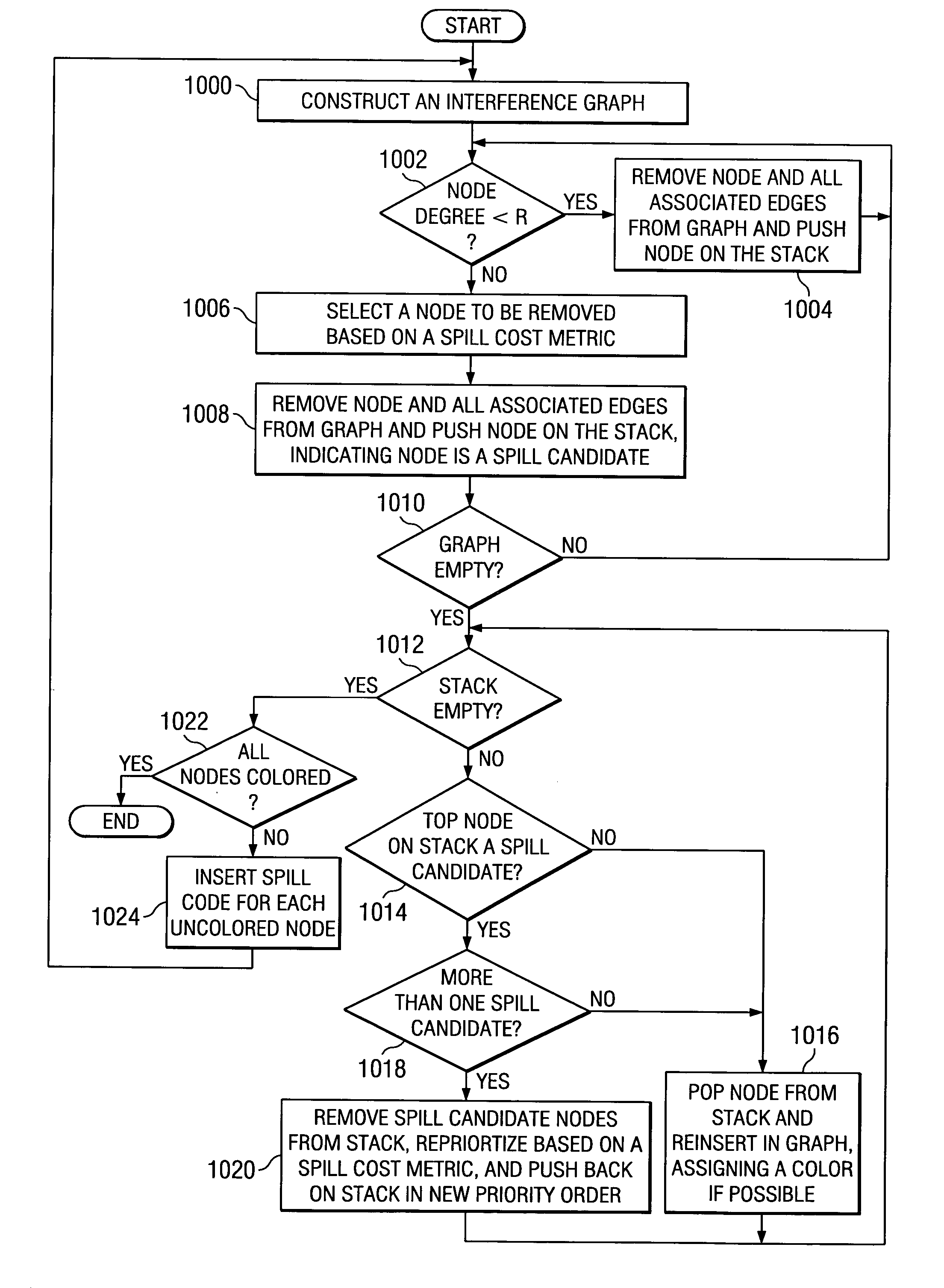
Register allocation and code spilling using interference graph coloring
ActiveUS20050039175A1Achieve colorColor interferenceSoftware engineeringSpecific program execution arrangementsRegister allocationCost metric
An improved method is provided for performing register allocation in a compiler. This method determines the allocation of a plurality R of registers of a processor for use during the execution of a software program. The register allocation process is treated as a graph-coloring problem, such that an interference graph is constructed for the software program, the graph is simplified, and an R-coloring the interference graph to the extent possible is attempted. Then, spill code is inserted in the software program each for each uncolored node of the graph, a new interference graph is constructed, and the process is repeated. During the simplification process, nodes with degree greater than or equal to R are removed from the graph in an order dictated by a spill cost metric. During the coloring process, these same nodes are reinserted in the graph in an order dictated by reapplying the spill cost metric.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and apparatus to compute local repair paths taking into account link resources and attributes
ActiveUS8068411B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCost metricDistributed computing
A technique for calculating local repair paths through a computer network using one or more dynamically measured parameters in place of, or in addition to, statically assigned cost metrics. The dynamically measured parameters include various statistical measures of resources and attributes associated with data links and / or network nodes in the computer network. In operation, an intermediate node monitors a set of local link and / or node parameters. The node may generate an advertisement in response to at least one of its monitored parameters crossing a predetermined threshold value or changing value by a predetermined percentage or amount. The advertisement is “flooded” so as to advertise the dynamically measured parameter value to other neighboring intermediate nodes. After receiving the advertisement, each node may recalculate one or more local repair paths based on the advertised parameter value. The node may utilize a recalculated repair path if it provides an appreciably lower-cost path, e.g., by a predetermined percentage, as compared with the currently deployed repair path.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
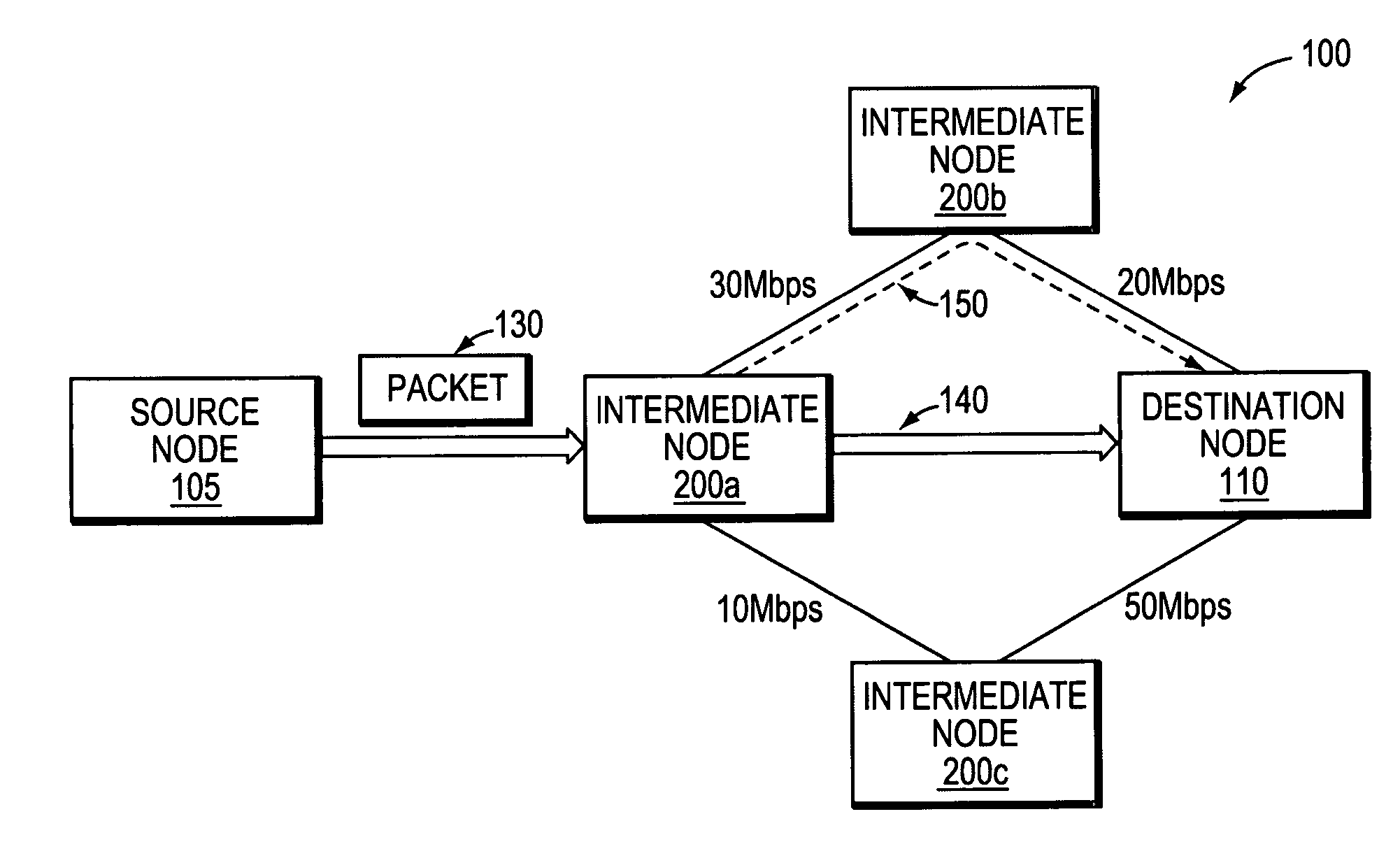
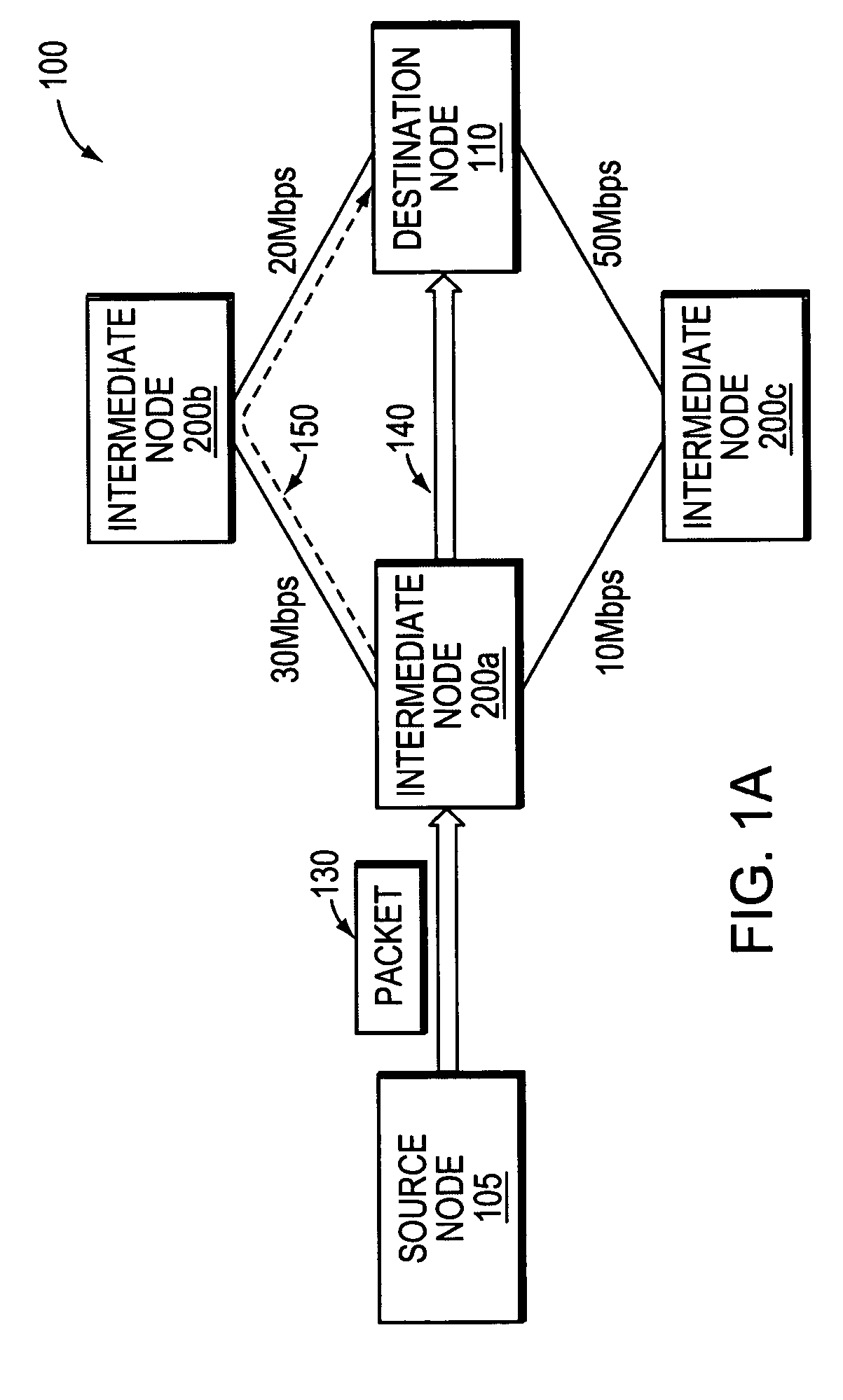
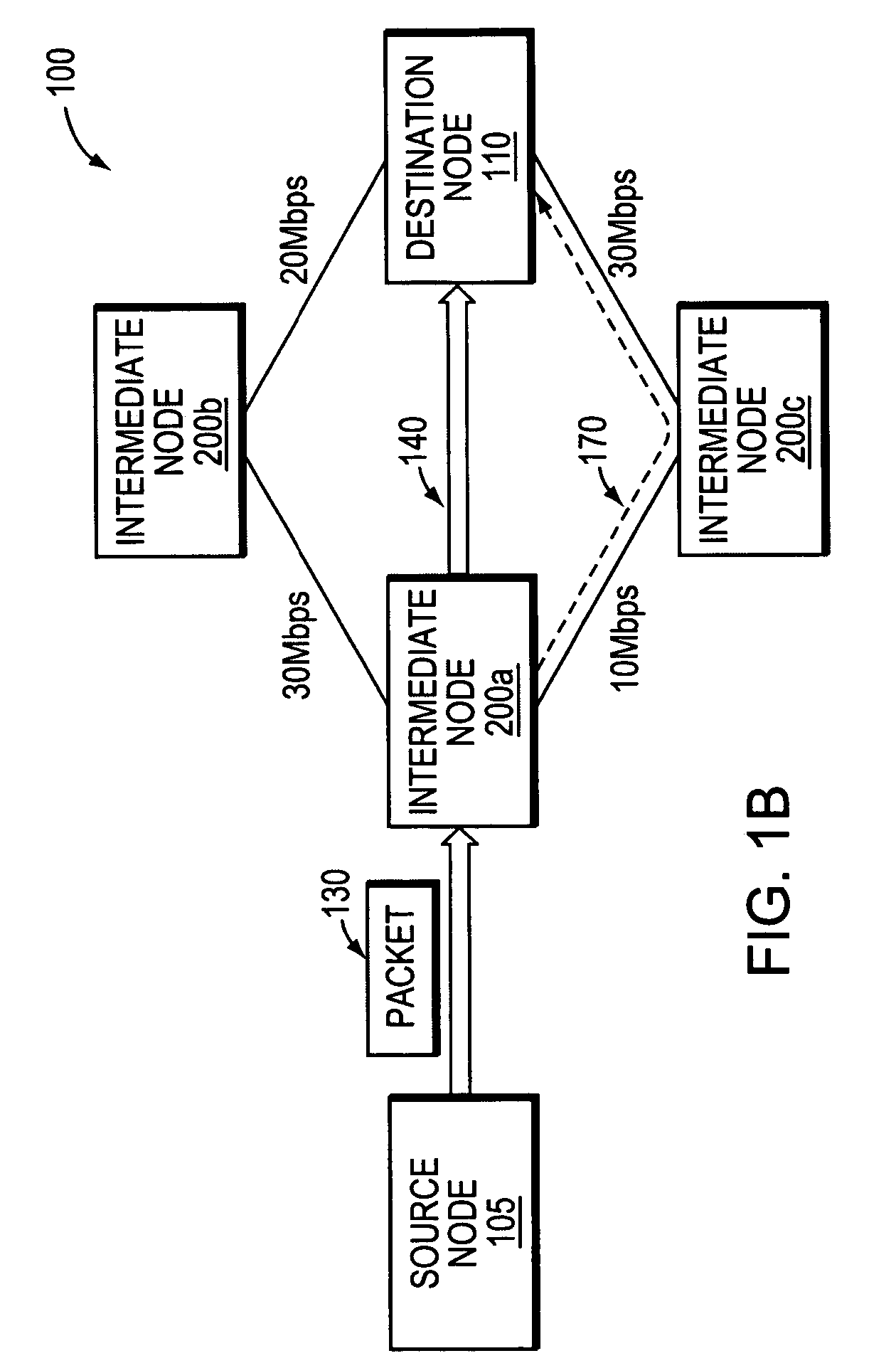
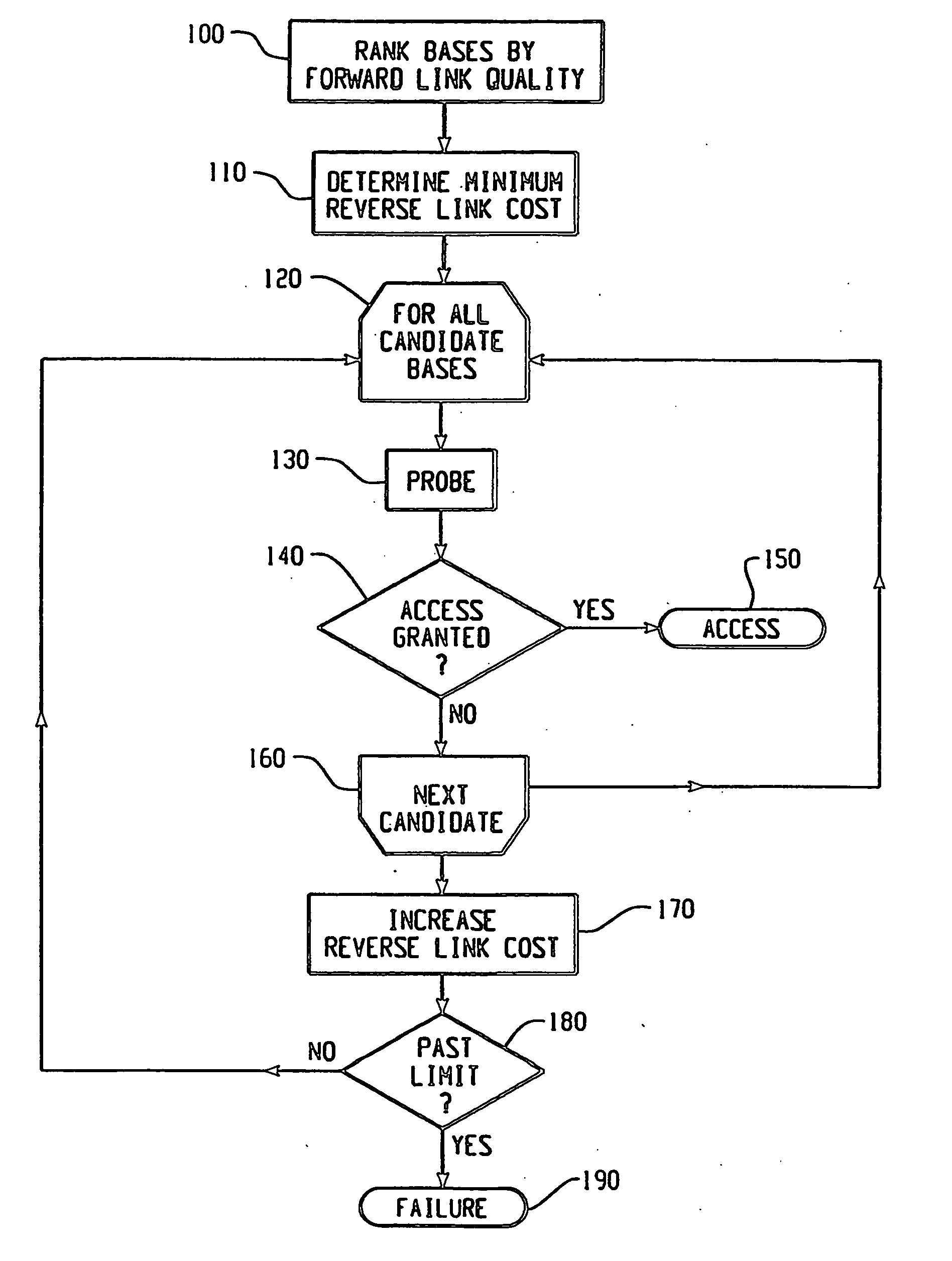
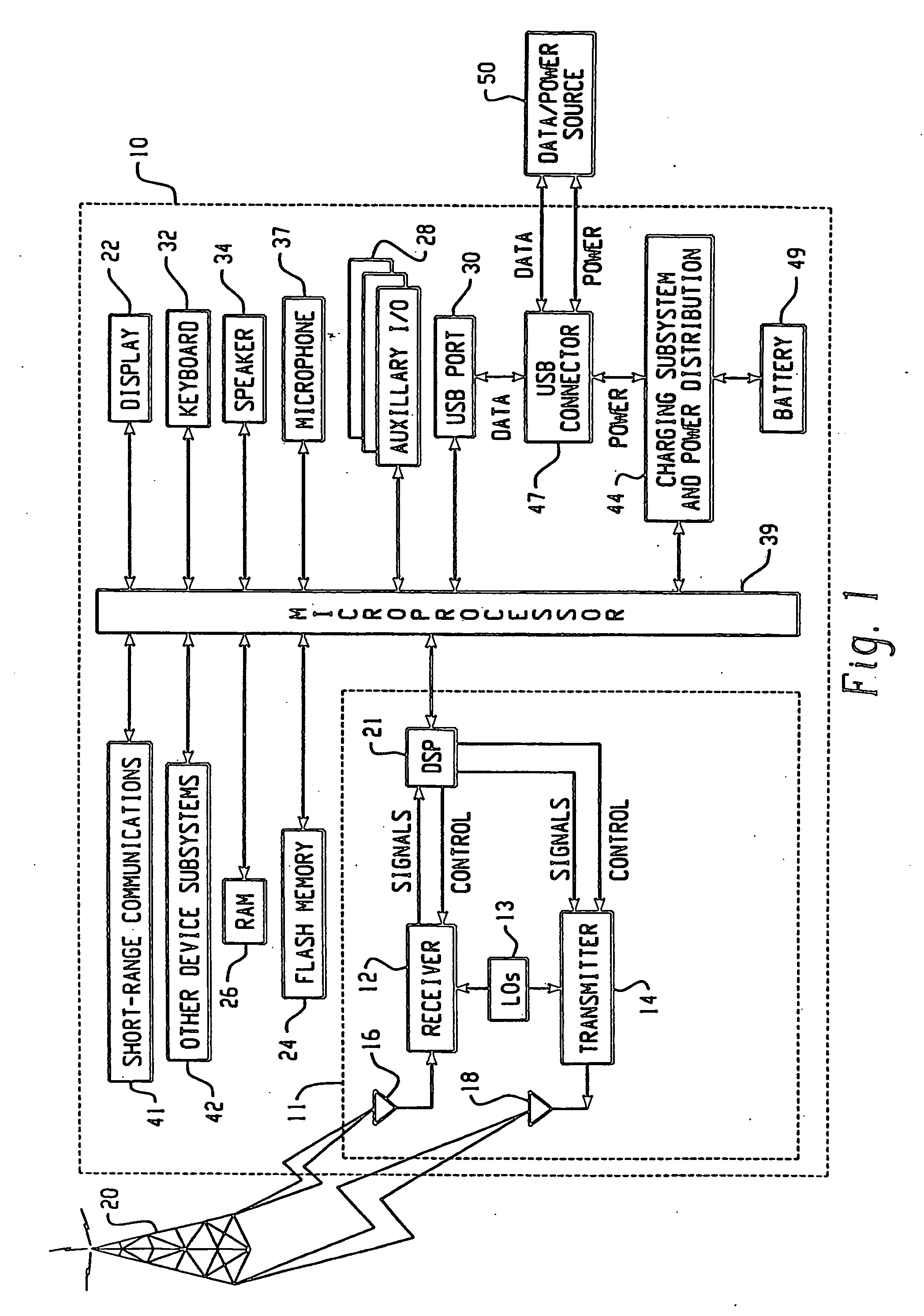
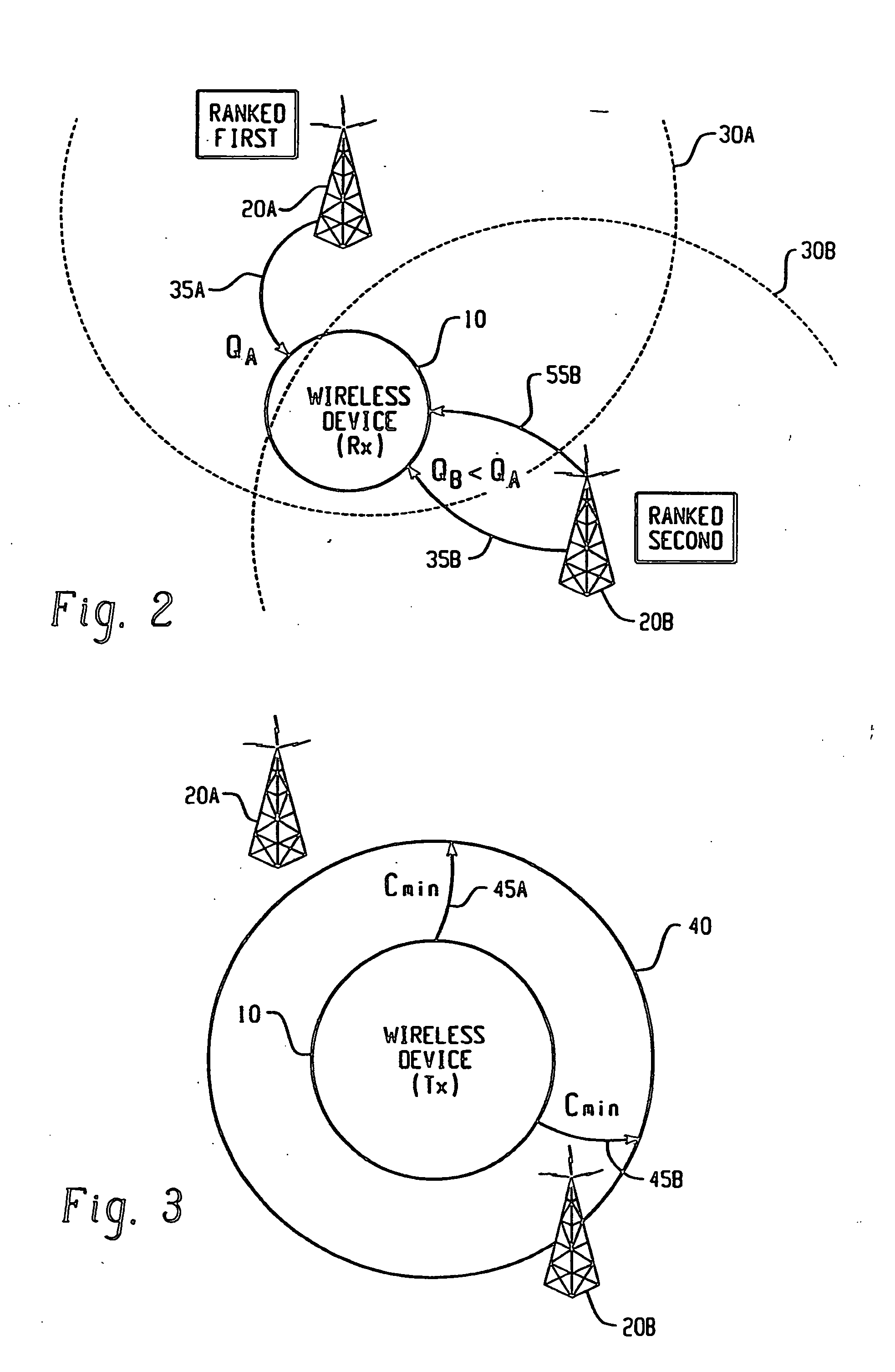
Method of system access to a wireless network
A method of system access from a wireless device to a wireless network, the network having a plurality of base stations includes the steps of: selecting at least one reverse link cost metric from a list of predetermined reverse link cost metrics; determining a reverse link cost according to the selected at least one reverse link cost metric; selecting a candidate base station from the plurality of base stations; sending a probe signal at the reverse link cost to the candidate base station; waiting for a response from the candidate base station within a timeout period; and repeating steps until timeout, or until the condition that a response is received from at least one candidate base station so that at least one candidate base station can be used to provide system access from the wireless device to the wireless network.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
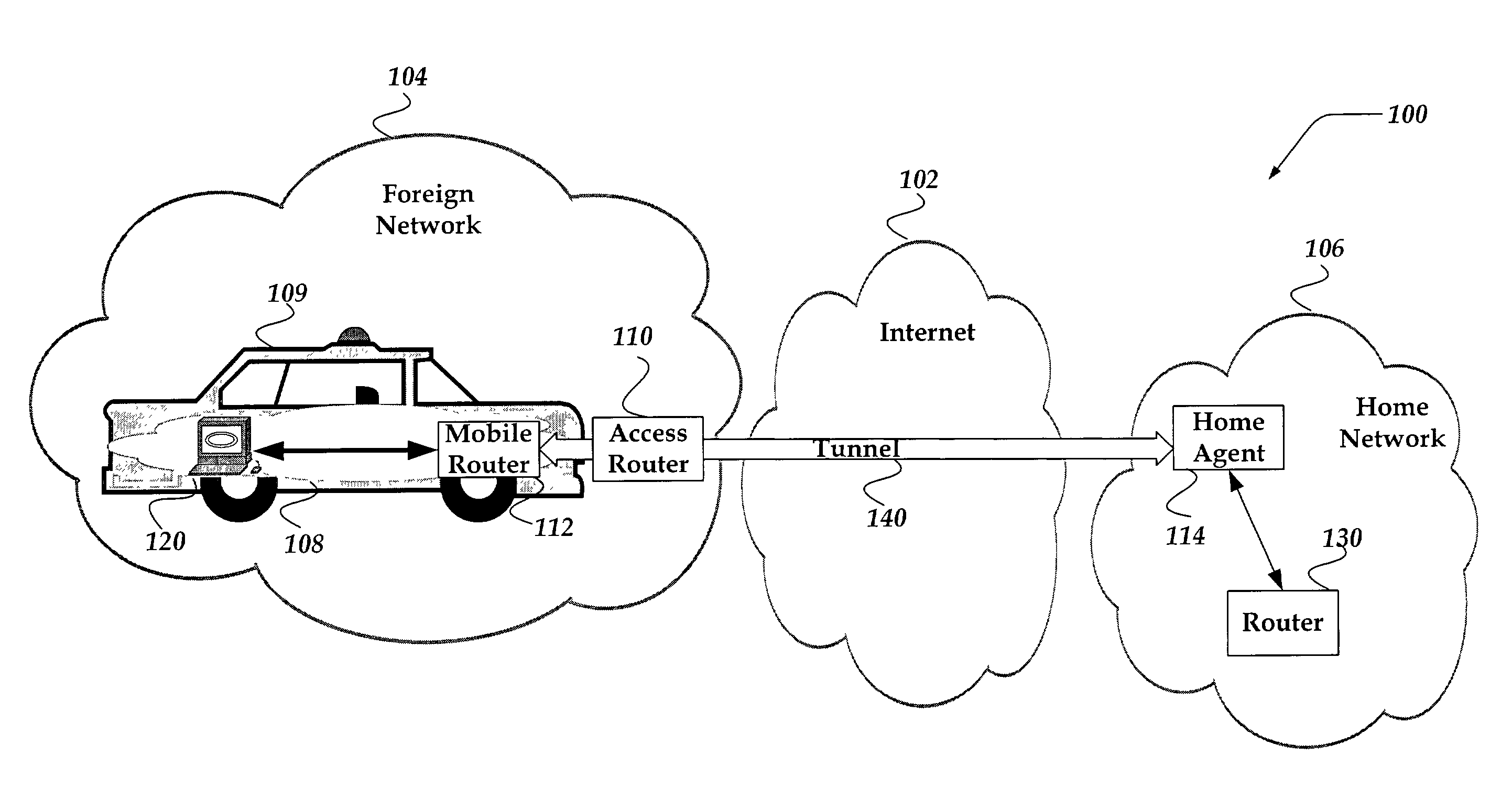
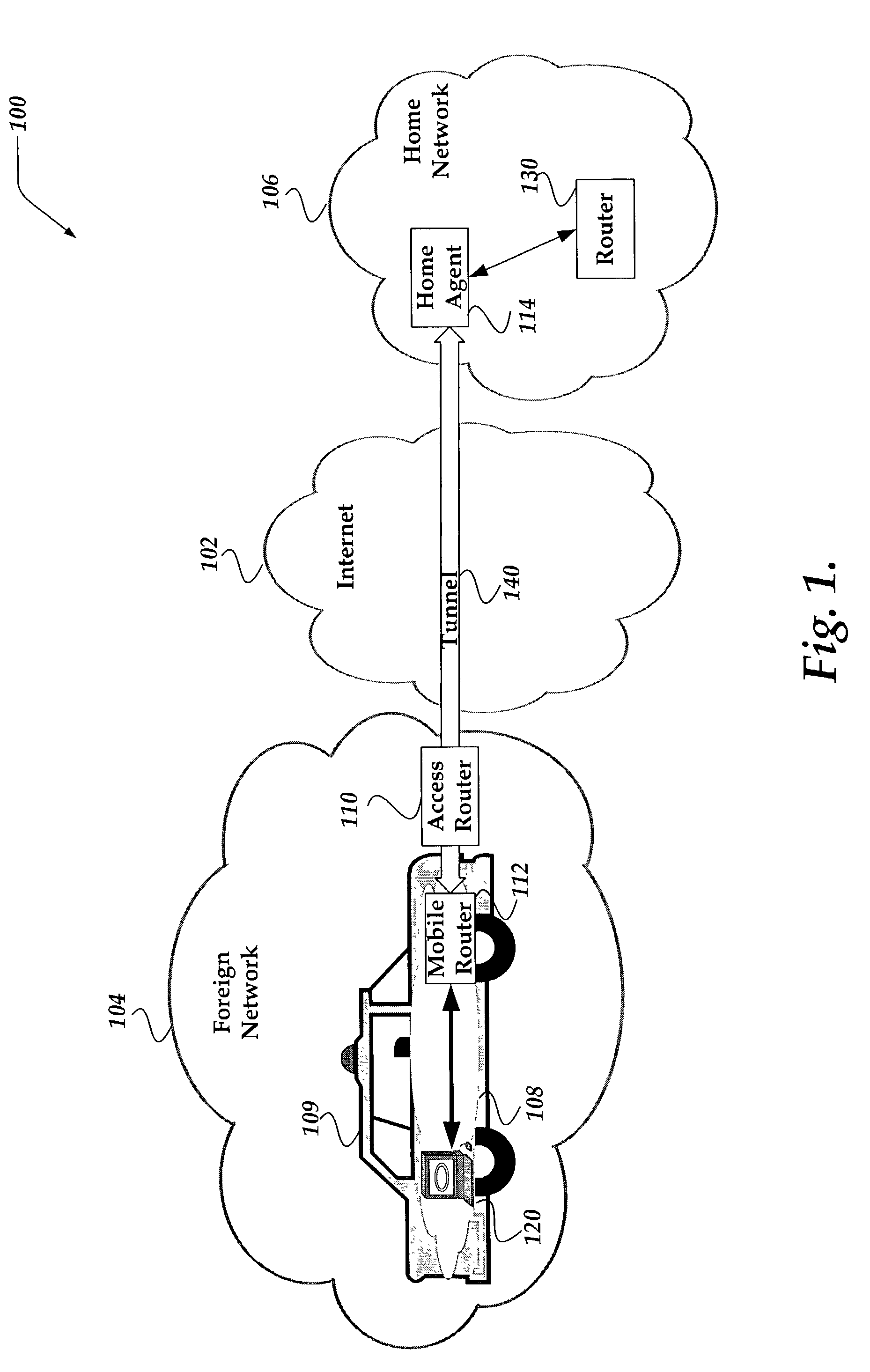
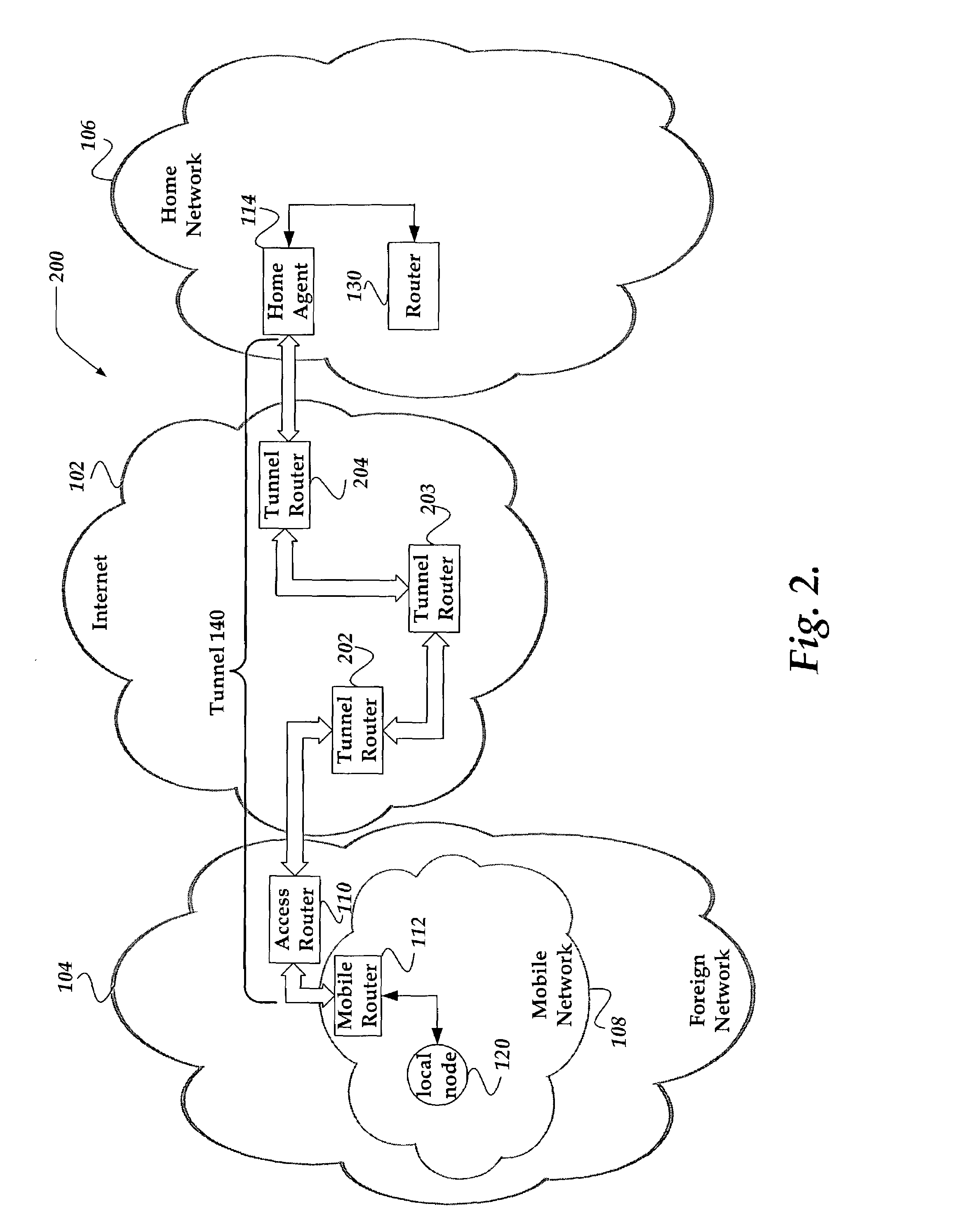
System and method for mobile router cost metric updates for routing protocols
A system and method is directed to updating information in a mobile network. A dynamic signaling routing protocol is extended over bi-directional tunneling between a mobile router and its home agent such that information associated with the home agent of the mobile router reflects roaming of the mobile router as it travels from its home network. The information is determined as a function of a characteristic associated with each link of the tunnel between the mobile router and its home agent. In one embodiment, the information includes a cost metric associated with the cost of the tunnel. The information is advertised to another router. The other router employs the information associated with the tunnel to determine a path for communication.
Owner:VRINGO INFRASTRUCTURE +1
Methods of network routing having improved resistance to faults affecting groups of links subject to common risks
A number of techniques are described for routing methods that improve resistance to faults affecting groups of links subject to common risks. One of these techniques accounts for failure potentials in physical networks by considering shared risk link groups separately from performance and costs metrics in determining a primary routing path and a backup path. A shared risk link group (SRLG) is an attribute attached to a link to identify edges that have physical links in common and can therefore be simultaneously disrupted due to a single fault. Another technique considers node disjointness and provides a solution of two paths that are as node disjoint as possible and minimizes administrative costs. The techniques may further be combined in a priority order thereby providing a solution of at least two paths that are strictly SRLG disjoint, as node-disjoint as possible, and have minimum administrative costs. Due to the priority order of evaluation and typical network physical configurations of links, with the links associated common fault SRLGs, the priority ordering technique is very efficient in determining at least two paths for routing between a source and destination node.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Optimization-based data content determination
InactiveUS20060085387A1Simple technologyData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalCost metricData content
Improved data content determination techniques are disclosed for use in accordance with information-seeking systems. For example, in one illustrative aspect of the invention, a technique for determining data content for a response to a query comprises obtaining a user query, and dynamically determining data content suitable for generating a response to the query, wherein data content determination is modeled as an optimization operation which attempts to balance context-based selection constraints. Further, the step of dynamically determining data content may further comprise modeling the context-based selection constraints as feature-based metrics. The feature-based metrics may be formulated using contextual information. Still further, the step of dynamically determining data content may further comprise performing the optimization operation such that one or more desirability metrics are maximized and one or more cost metrics are minimized, thus balancing the various constraints.
Owner:IBM CORP
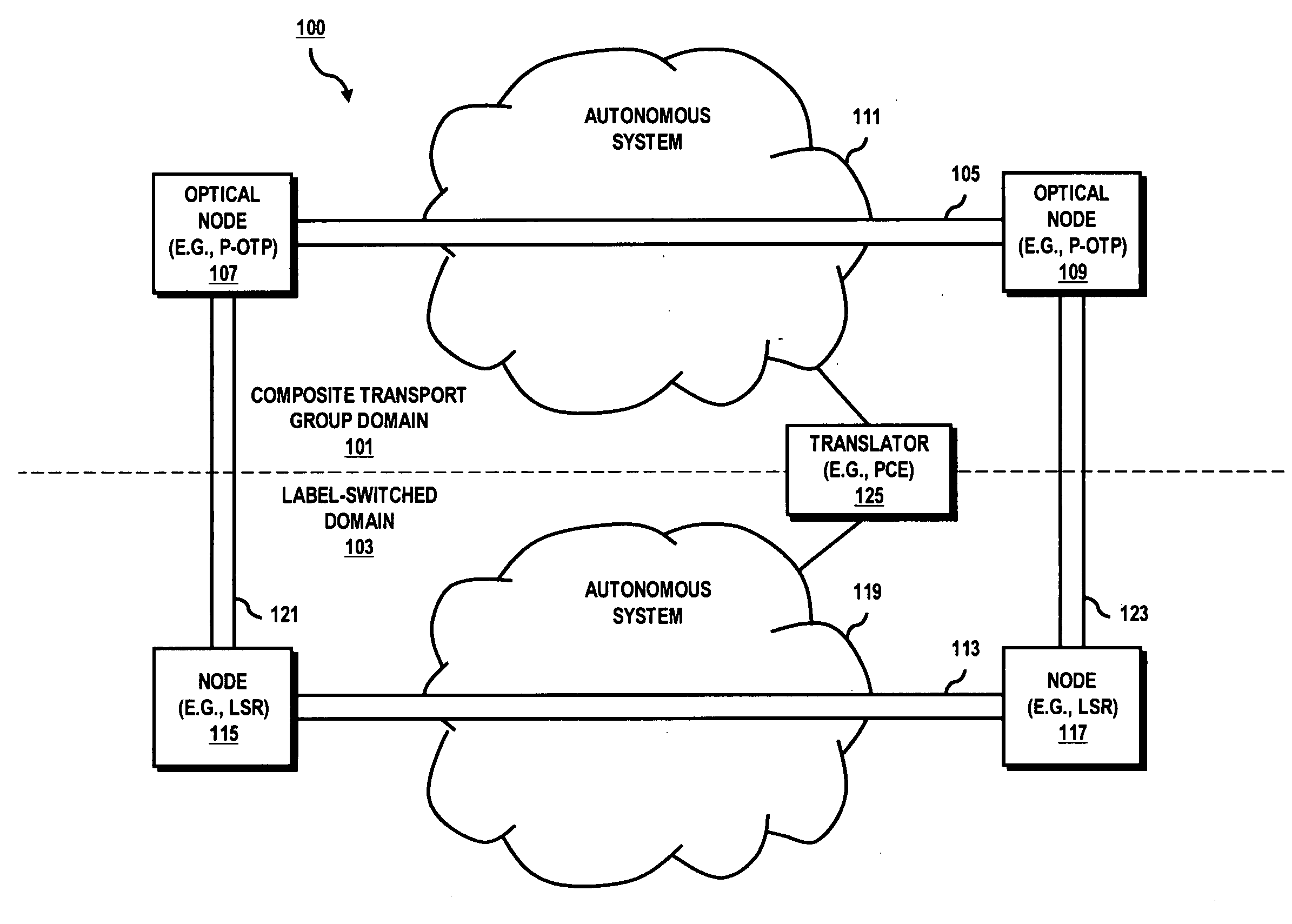
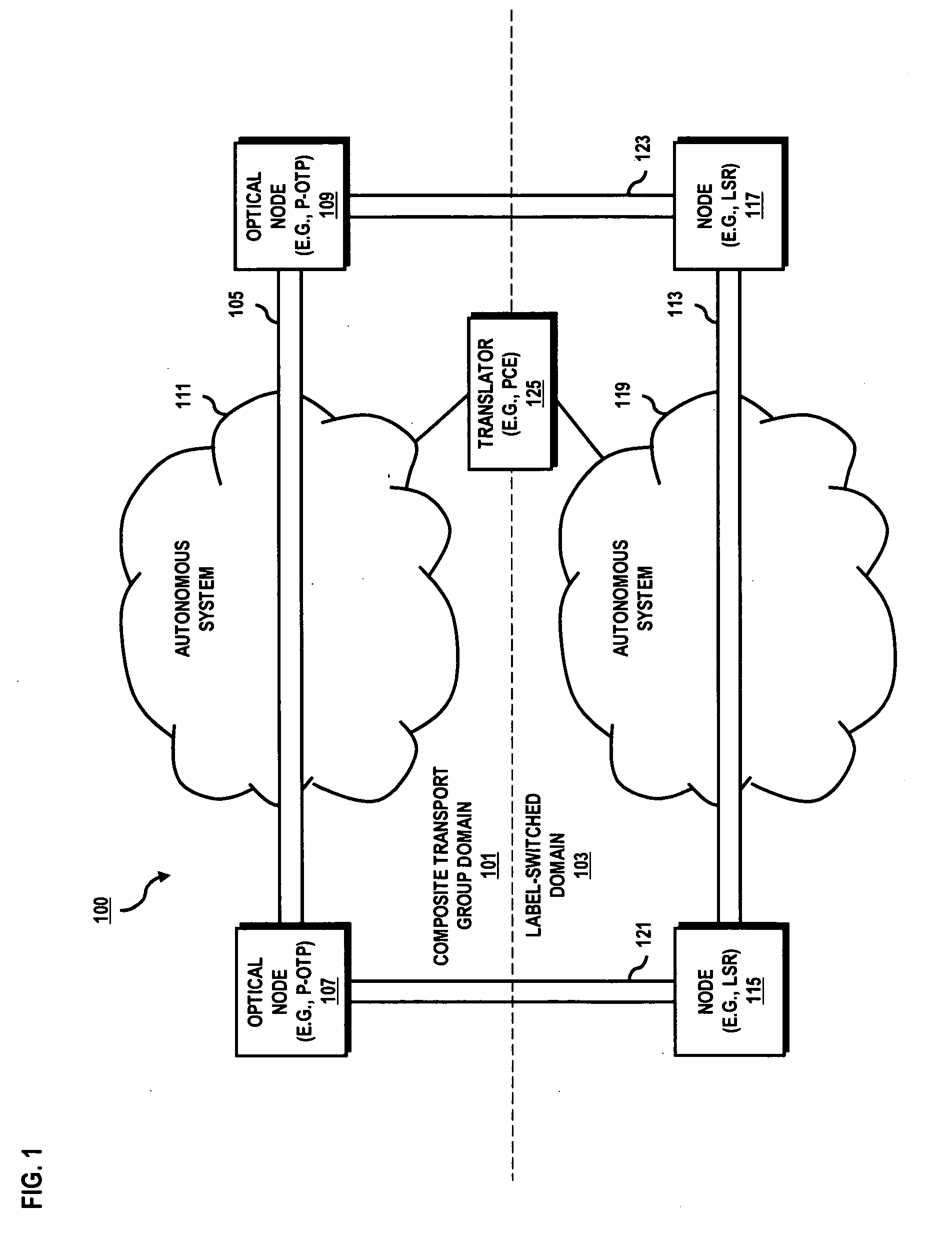
System and method for providing lower-layer path validation for higher-layer autonomous systems
An approach is provided for validating lower layer paths for higher layer networks. A request for path cost information is generated relating to a path traversing a first autonomous system and a second autonomous system, wherein each of the autonomous systems utilizes different cost metrics. The path cost information is received associated with reservation of capacity for the path. The path cost information is evaluated. The reservation is selectively accepted based on the evaluation.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
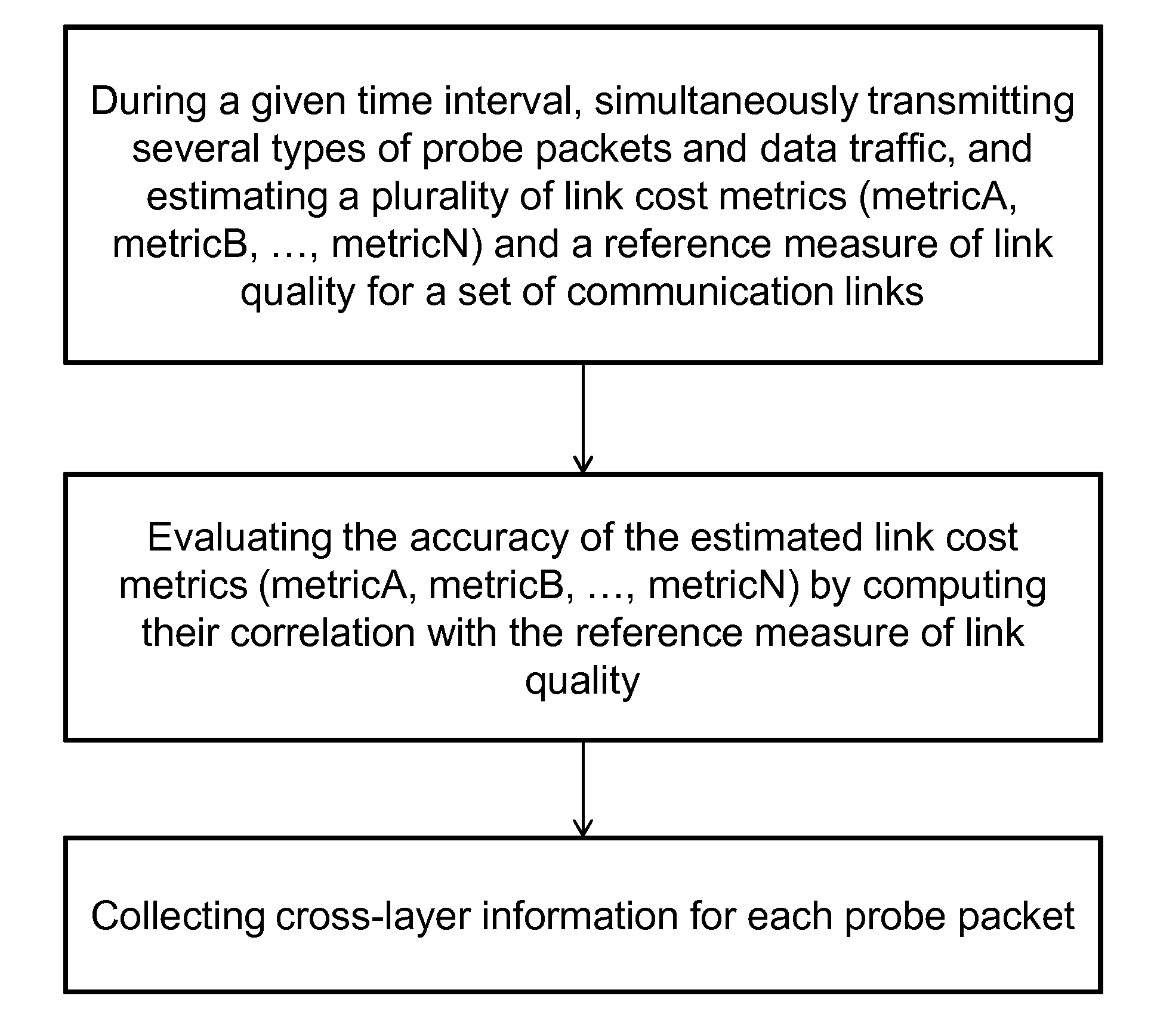
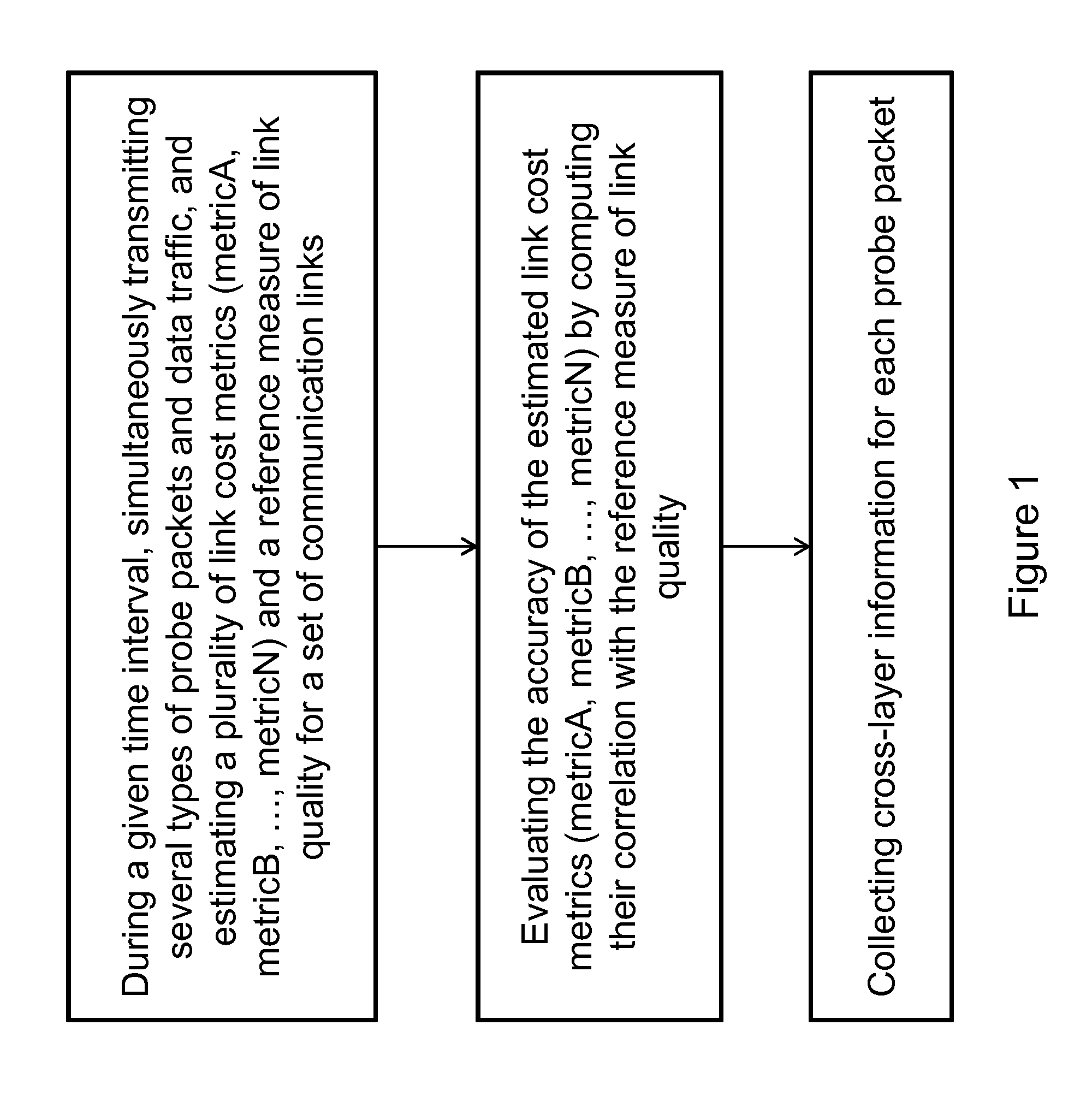
Method for evaluating link cost metrics in communication networks
The present invention relates to a method for measuring link cost metrics and evaluating their accuracy with respect to reference measure of link quality in a communication network, said method comprising the steps of: during a given time interval, simultaneously transmitting several types of probe packets and data traffic, and estimating a plurality of link cost metrics (metricA, metricB, . . . , metricN) and a reference measure of link quality for a set of communication links; evaluating the accuracy of the estimated link cost metrics (metricA, metricB, . . . , metricN) by computing their correlation with the reference measure of link quality; and collecting cross-layer information for each probe packet.
Owner:MAGNOLIA LICENSING LLC
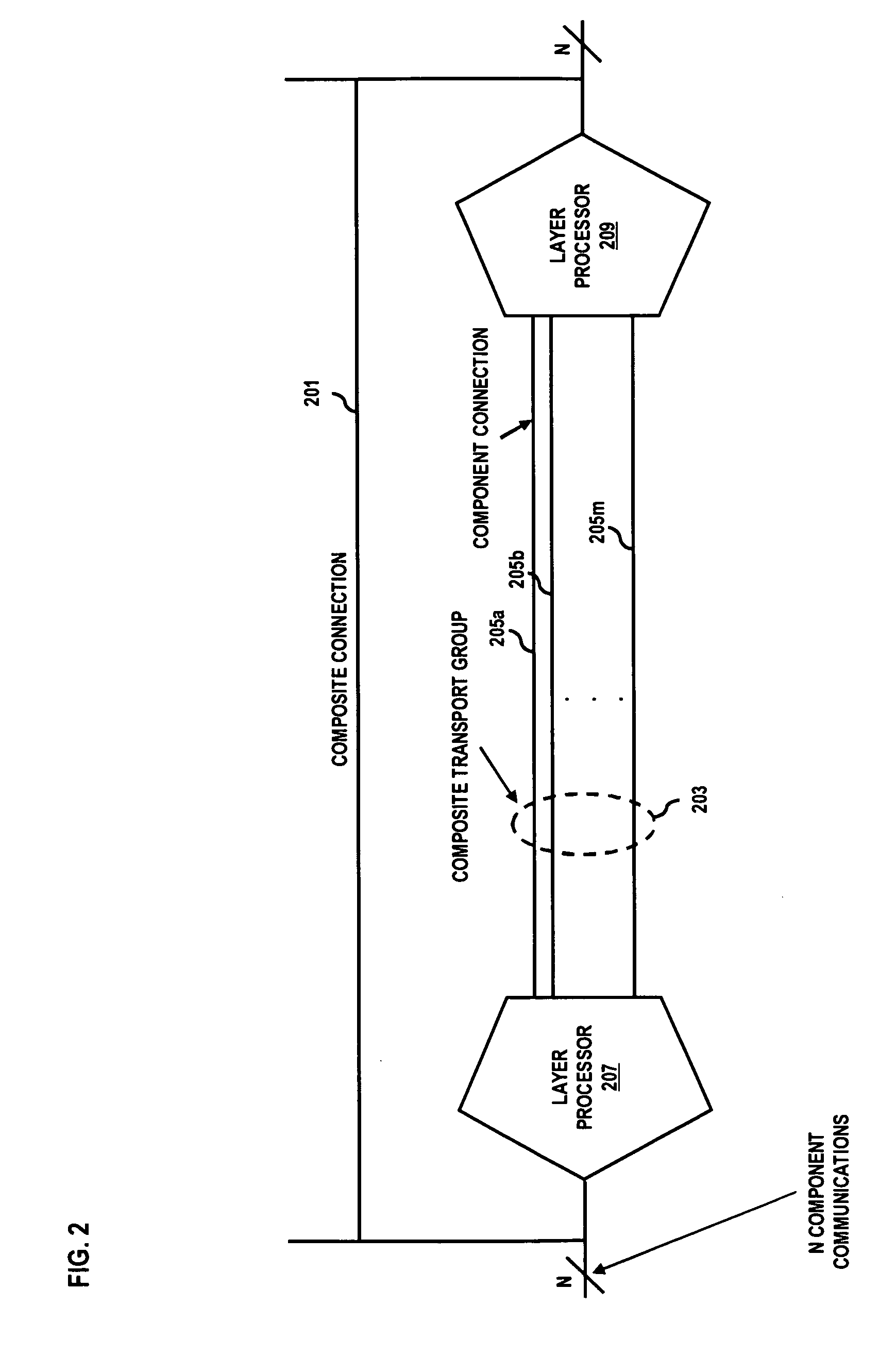
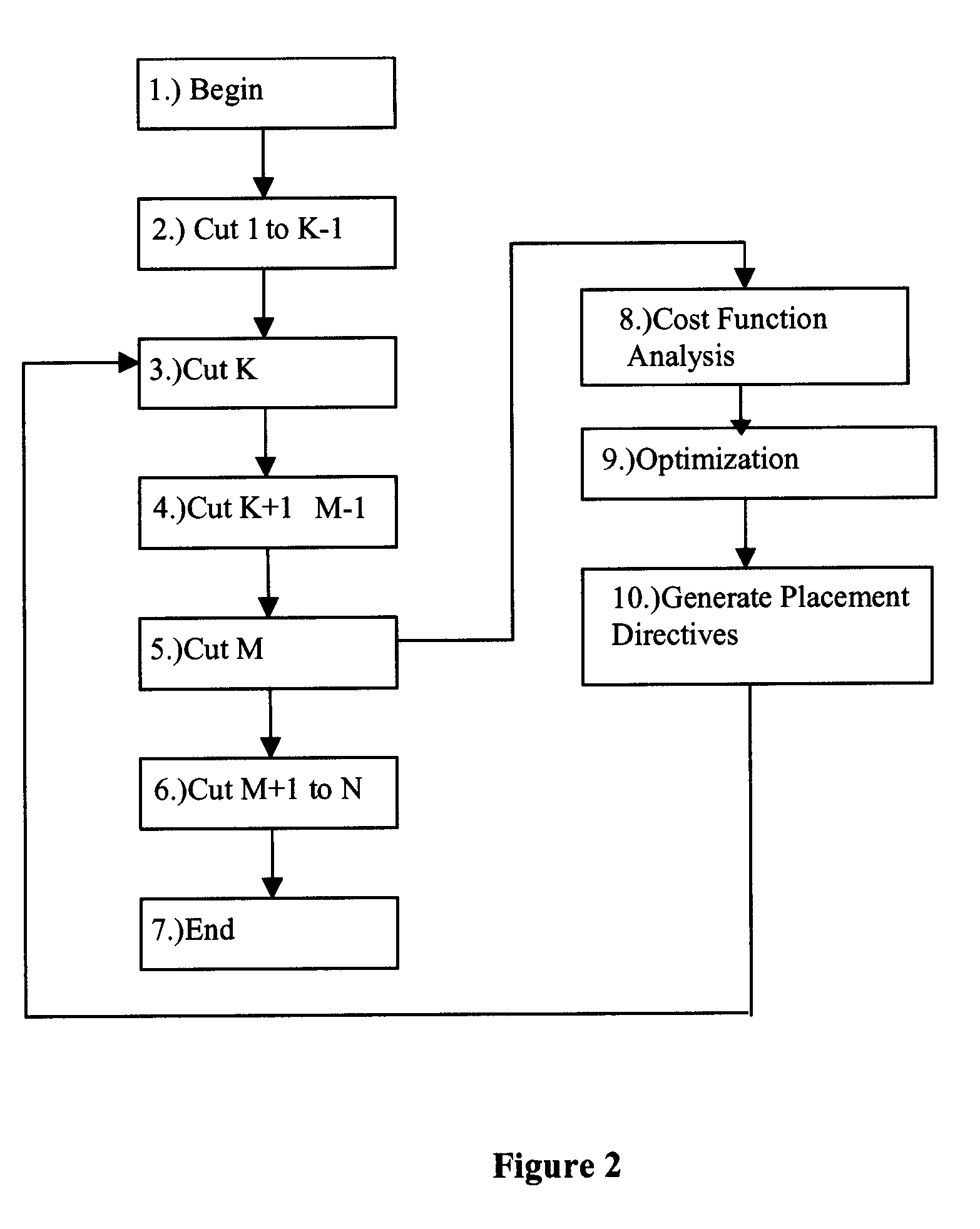
Method for successive placement based refinement of a generalized cost function
InactiveUS20050166164A1Quality improvementMulti-objective optimisationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationCost metricComputer science
A generalized method for optimizing the global placement of a VLSI chip across multiple cost metrics, such as total wire length, timing, congestion, and signal integrity is described. The method relies upon a “look ahead” technique, combined with any generic cost function that can be used to set placement directives. These placement directives include net weights and cell spreading. The method of performing the placement involves the iterative reuse of the process of successive partitioning. This iterative reuse establishes the capability of looking ahead to determine what is to happen. Based on the look ahead, it is possible to evaluate the qualities of the placement about to be generated. The method proceeds through the placement from while maintaining the current state of the placement along with the look-ahead state of the placement. Directives are generated and modified in order that the next steps applied to the current state of the placement will cause it to change to achieve an ultimate higher quality final output.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com