Methods for Treating Conditions Associated with MASP-2 Dependent Complement Activation
a technology of dependent complement and activation, which is applied in the direction of drug compositions, extracellular fluid disorders, antibody medical ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of loss of lectin components that would not necessarily inhibit the activation of the system, loss of this beneficial host defense mechanism against infection, etc., to inhibit masp-2-dependent complement activation, and reduce the likelihood
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0506]This example describes the generation of a mouse strain deficient in MASP-2 (MASP-2− / −) but sufficient of MAp19 (MAp 19+ / +).
[0507]Materials and Methods:
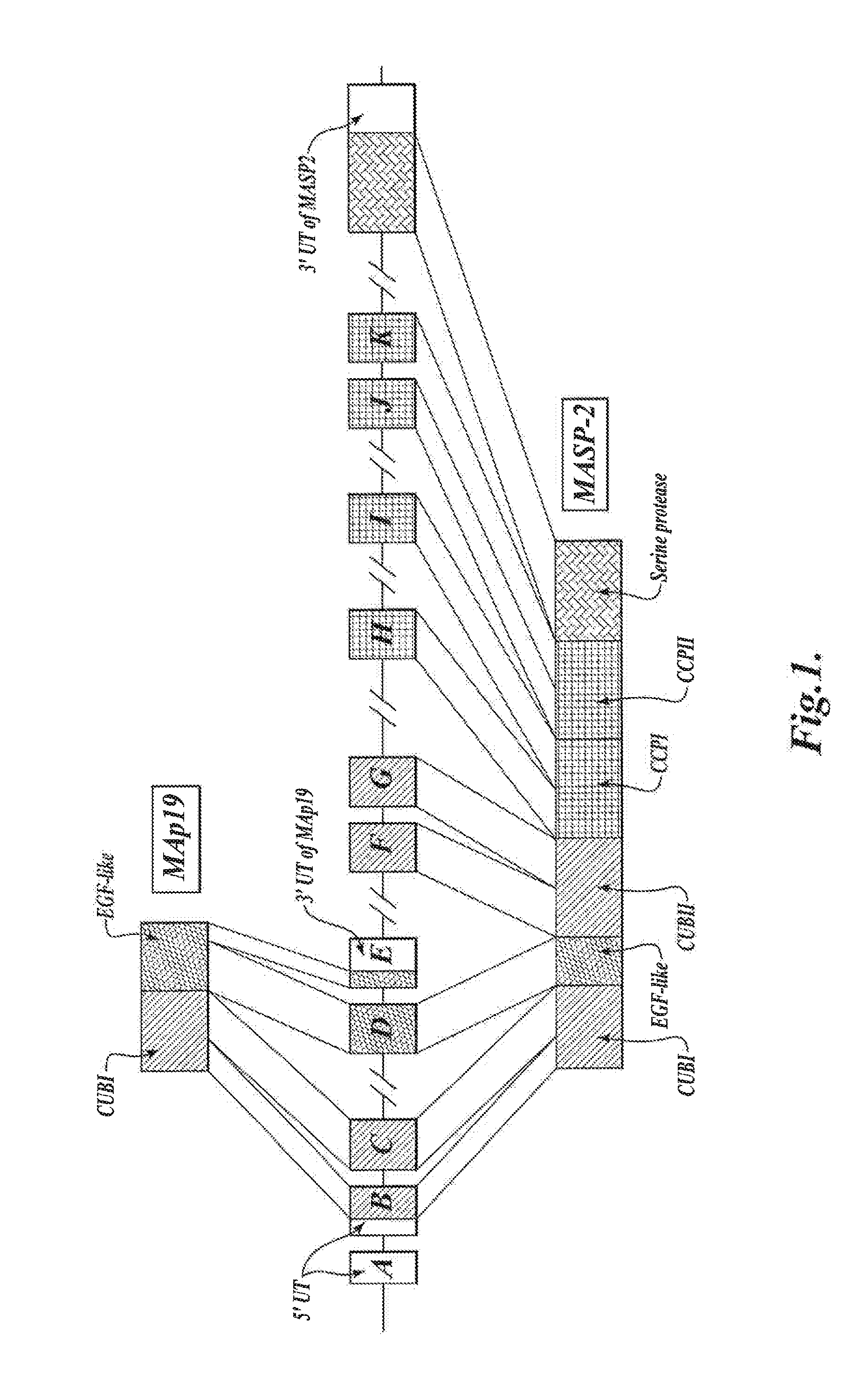
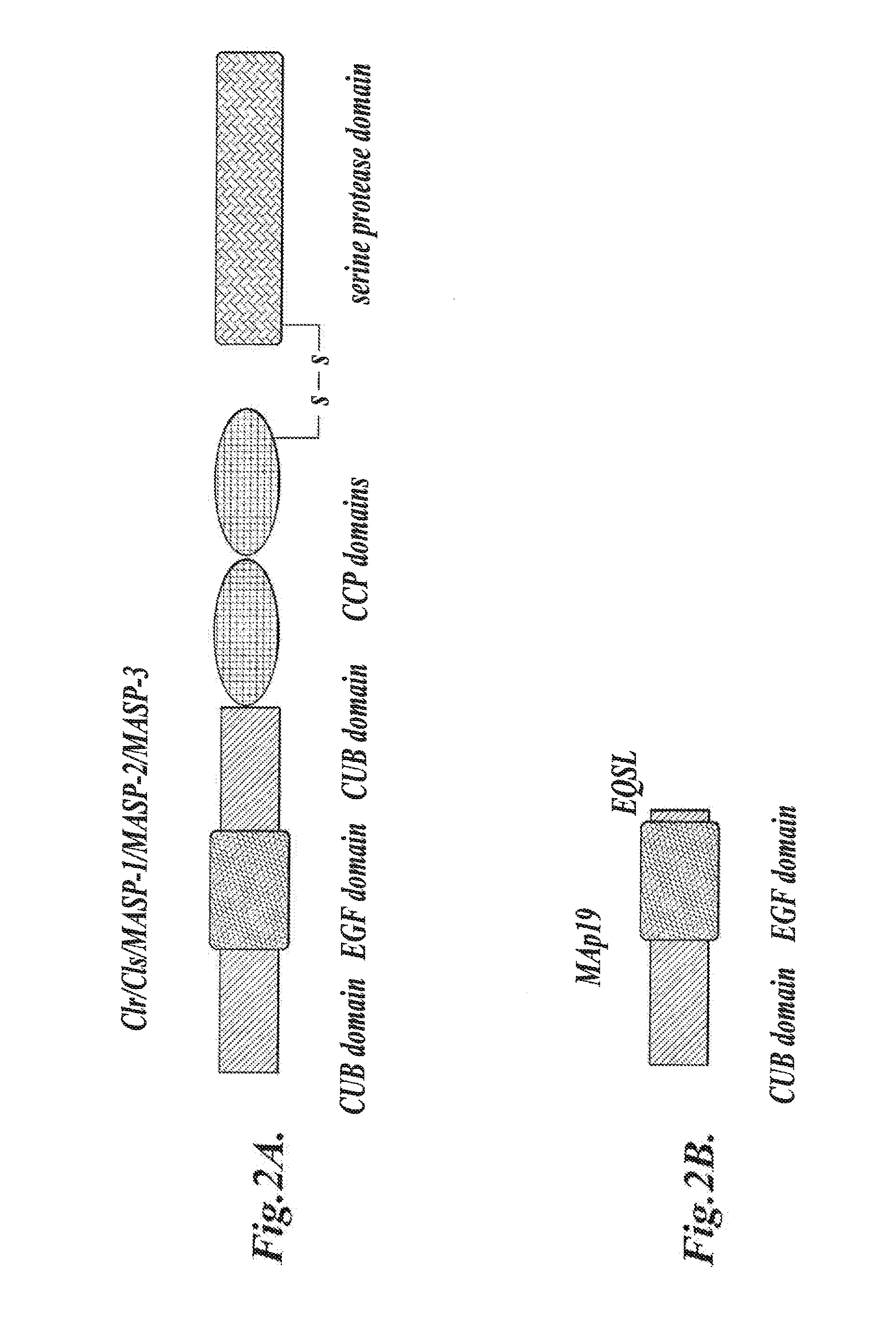
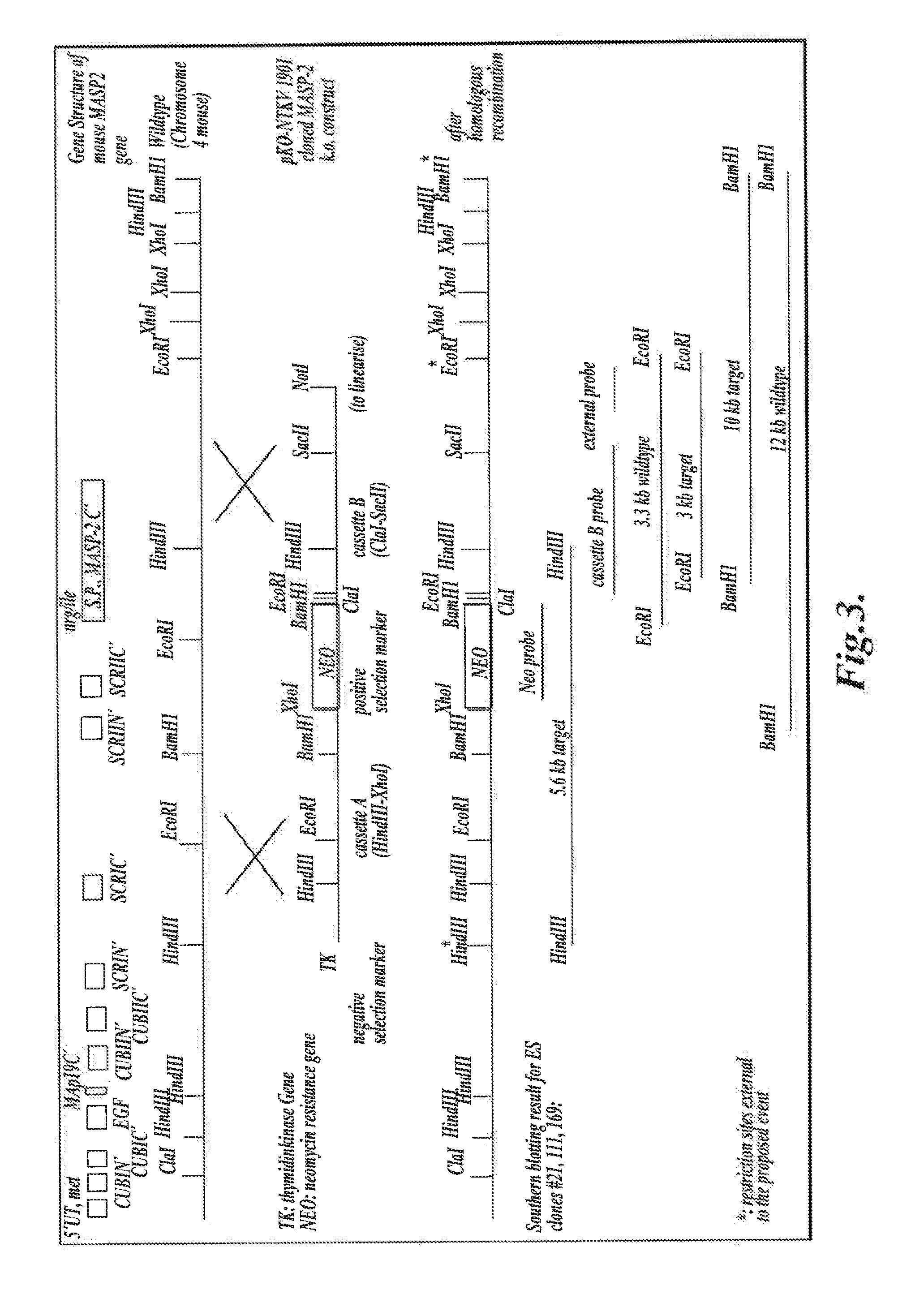
[0508]The targeting vector pKO-NTKV 1901 was designed to disrupt the three exons coding for the C-terminal end of murine MASP-2, including the exon that encodes the serine protease domain, as shown in FIG. 3. PKO-NTKV 1901 was used to transfect the murine ES cell line E14.1a (SV129 Ola). Neomycin-resistant and Thymidine Kinase-sensitive clones were selected. 600 ES clones were screened and, of these, four different clones were identified and verified by southern blot to contain the expected selective targeting and recombination event as shown in FIG. 3. Chimeras were generated from these four positive clones by embryo transfer. The chimeras were then backcrossed in the genetic background C57 / BL6 to create transgenic males. The transgenic males were crossed with females to generate F1 s with 50% of the offspring showing heterozy...
example 2
[0515]This example demonstrates that MASP-2 is required for complement activation via the lectin pathway.
[0516]Methods and Materials:
[0517]Lectin Pathway Specific C4 Cleavage Assay:
[0518]A C4 cleavage assay has been described by Petersen, et al., J. Immunol. Methods 257:107 (2001) that measures lectin pathway activation resulting from lipoteichoic acid (LTA) from S. aureus, which binds L-ficolin. The assay described by Petersen et al., (2001) was adapted to measure lectin pathway activation via MBL by coating the plate with LPS and mannan or zymosan prior to adding serum from MASP-2− / − mice as described below. The assay was also modified to remove the possibility of C4 cleavage due to the classical pathway. This was achieved by using a sample dilution buffer containing 1 M NaCl, which permits high affinity binding of lectin pathway recognition components to their ligands but prevents activation of endogenous C4, thereby excluding the participation of the classical pathway by dissoci...
example 3
[0540]This example describes the recombinant expression and protein production of recombinant full-length human, rat and murine MASP-2, MASP-2 derived polypeptides, and catalytically inactivated mutant forms of MASP-2
[0541]Expression of Full-Length Human, Murine and Rat MASP-2:
[0542]The full length cDNA sequence of human MASP-2 (SEQ ID NO: 4) was also subcloned into the mammalian expression vector pCI-Neo (Promega), which drives eukaryotic expression under the control of the CMV enhancer / promoter region (described in Kaufman R. J. et al., Nucleic Acids Research 19:4485-90, 1991; Kaufman, Methods in Enzymology, 185:537-66 (1991)). The full length mouse cDNA (SEQ ID NO:50) and rat MASP-2 cDNA (SEQ ID NO:53) were each subcloned into the pED expression vector. The MASP-2 expression vectors were then transfected into the adherent Chinese hamster ovary cell line DXB1 using the standard calcium phosphate transfection procedure described in Maniatis et al., 1989. Cells transfected with thes...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Inhibition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Inhibition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com