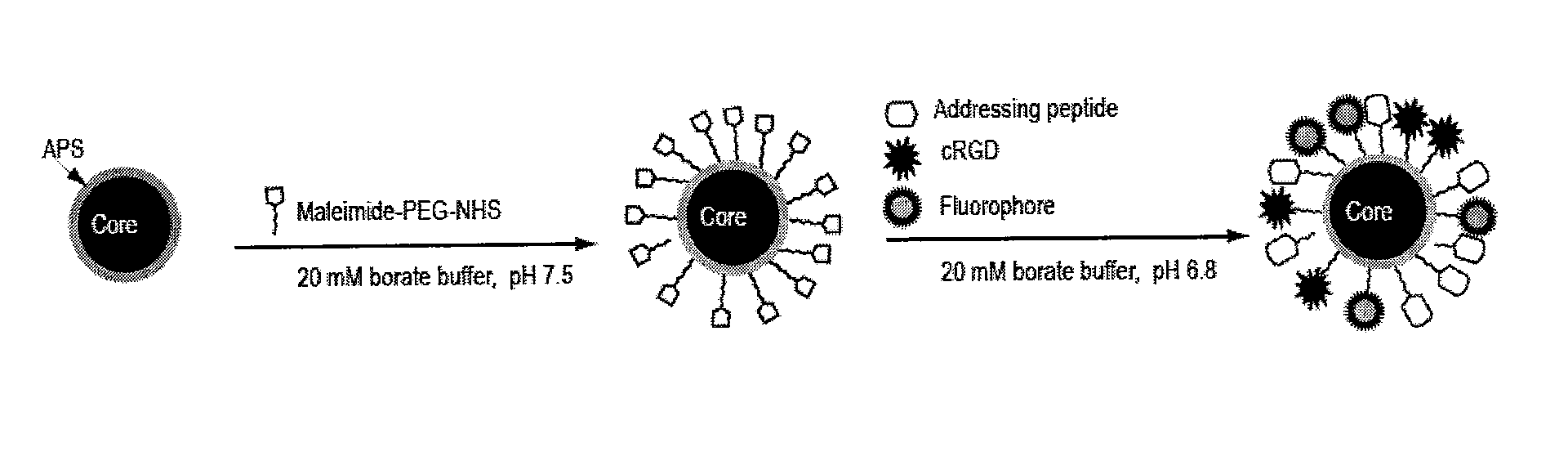
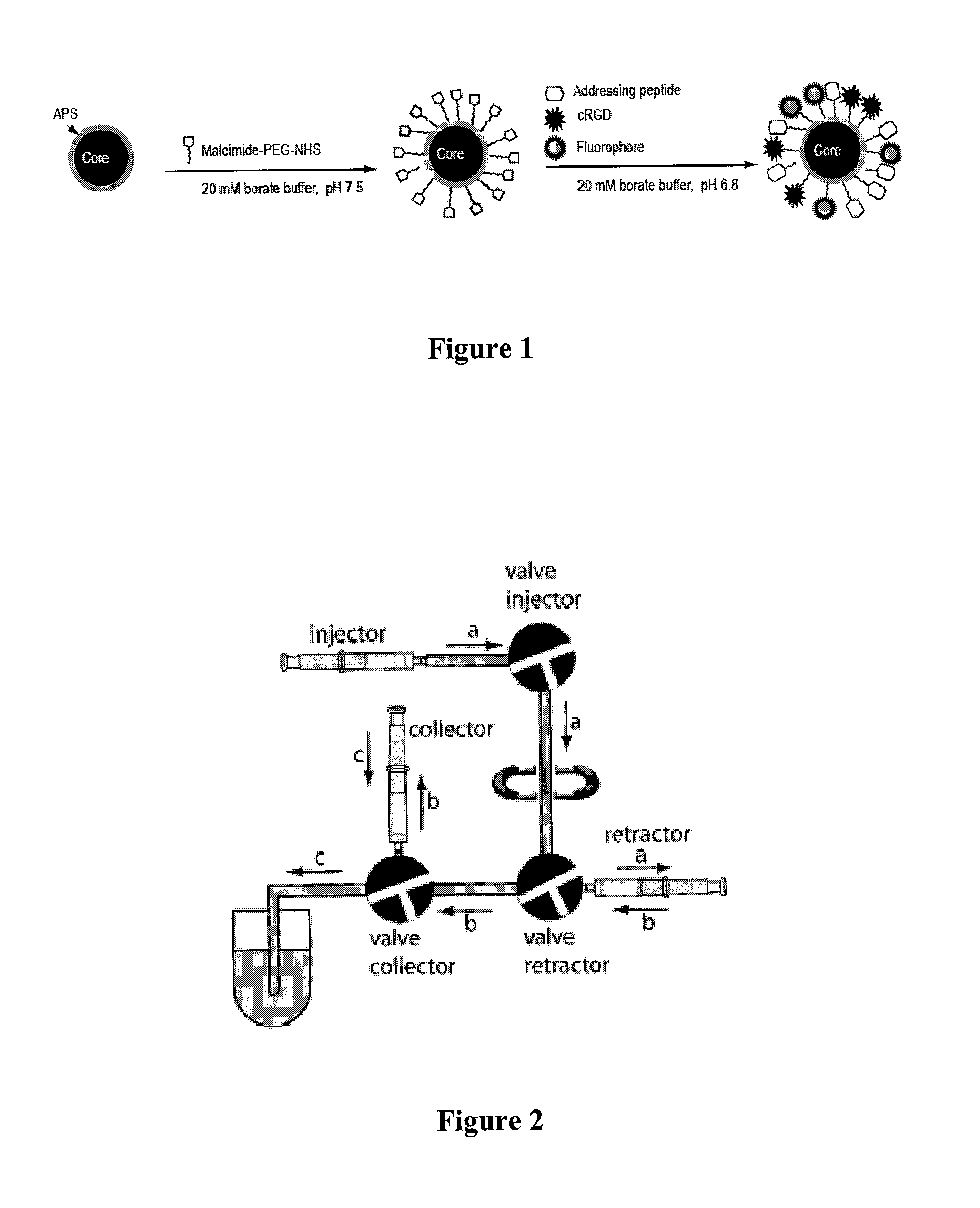
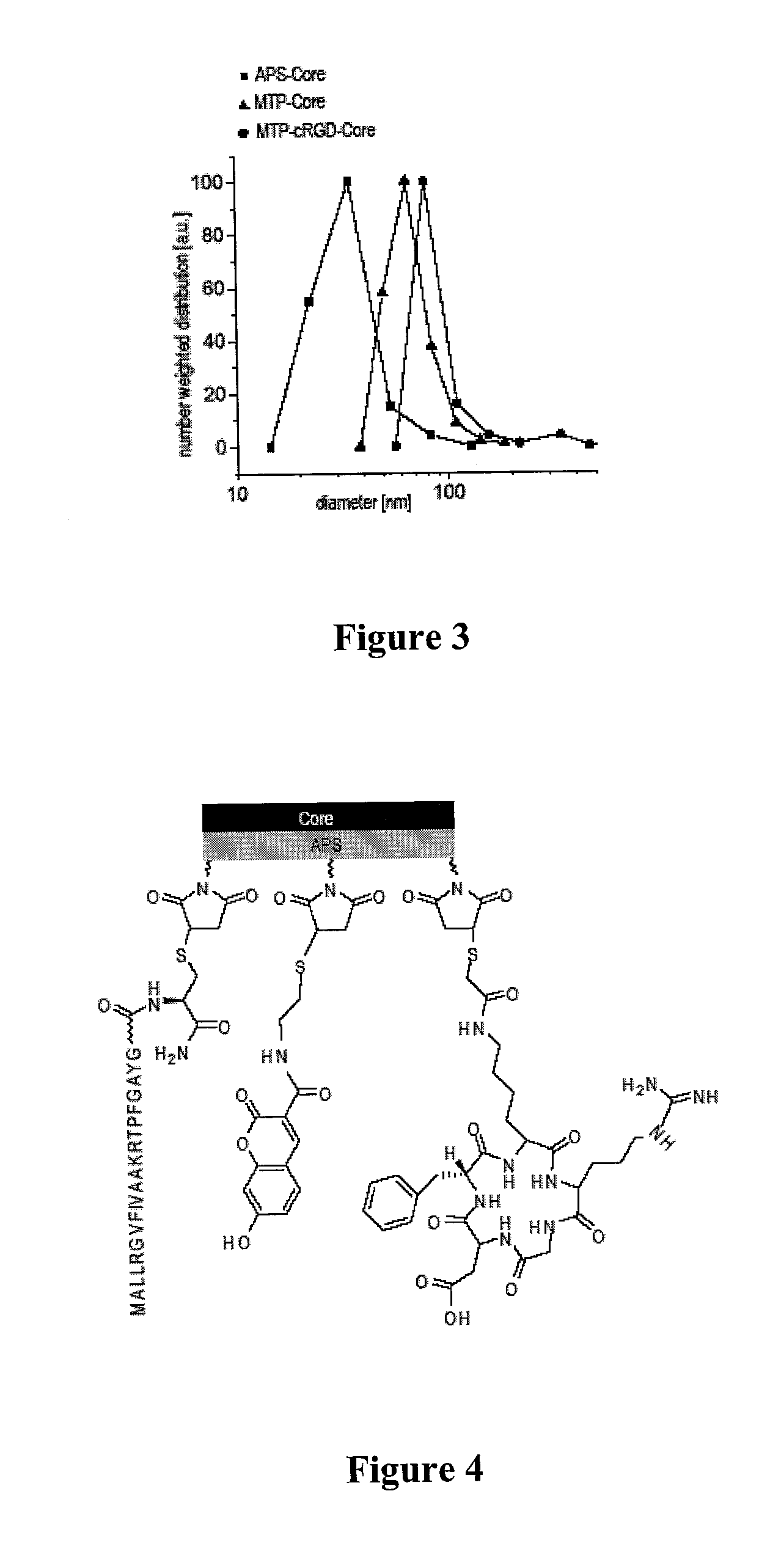
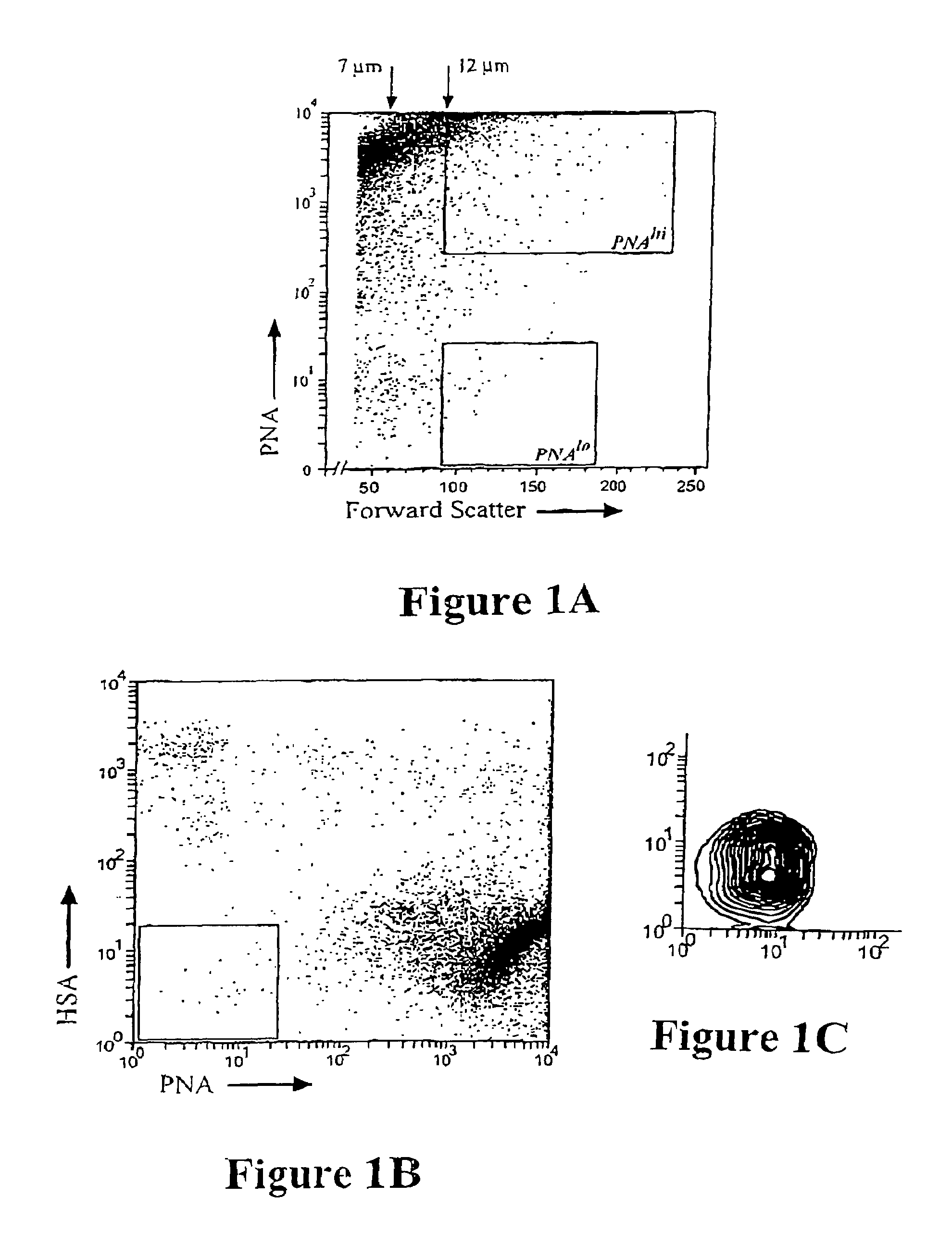
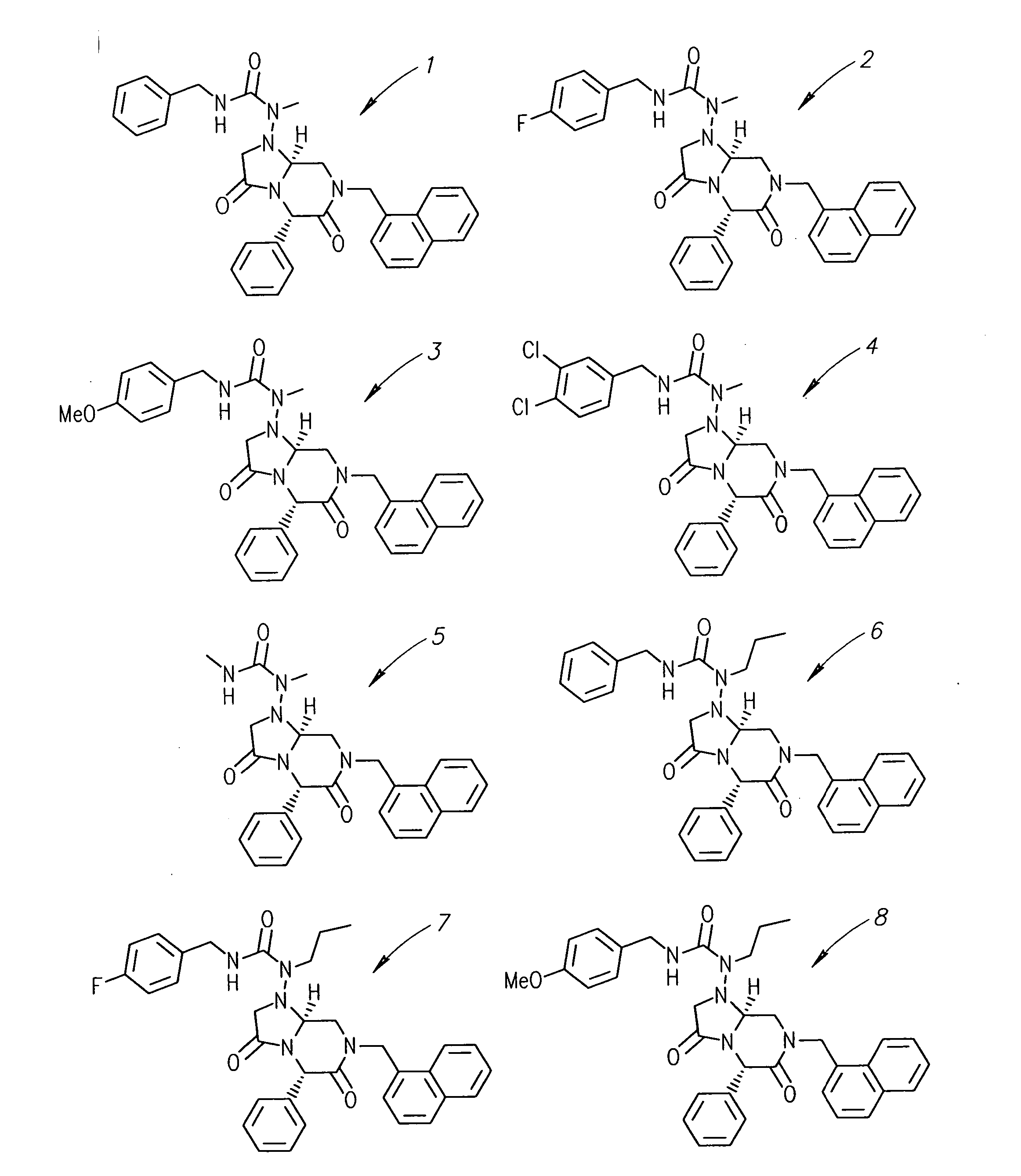
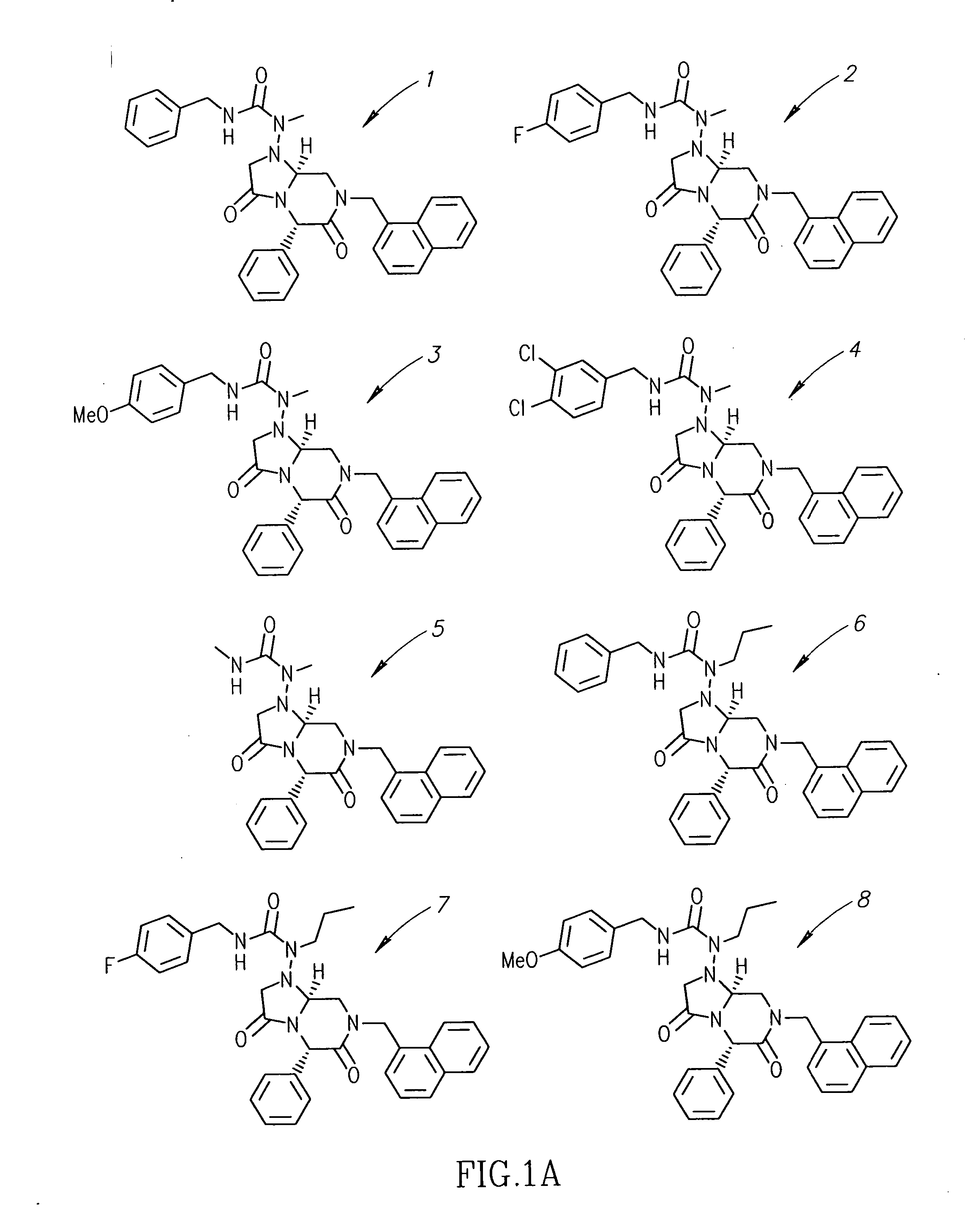
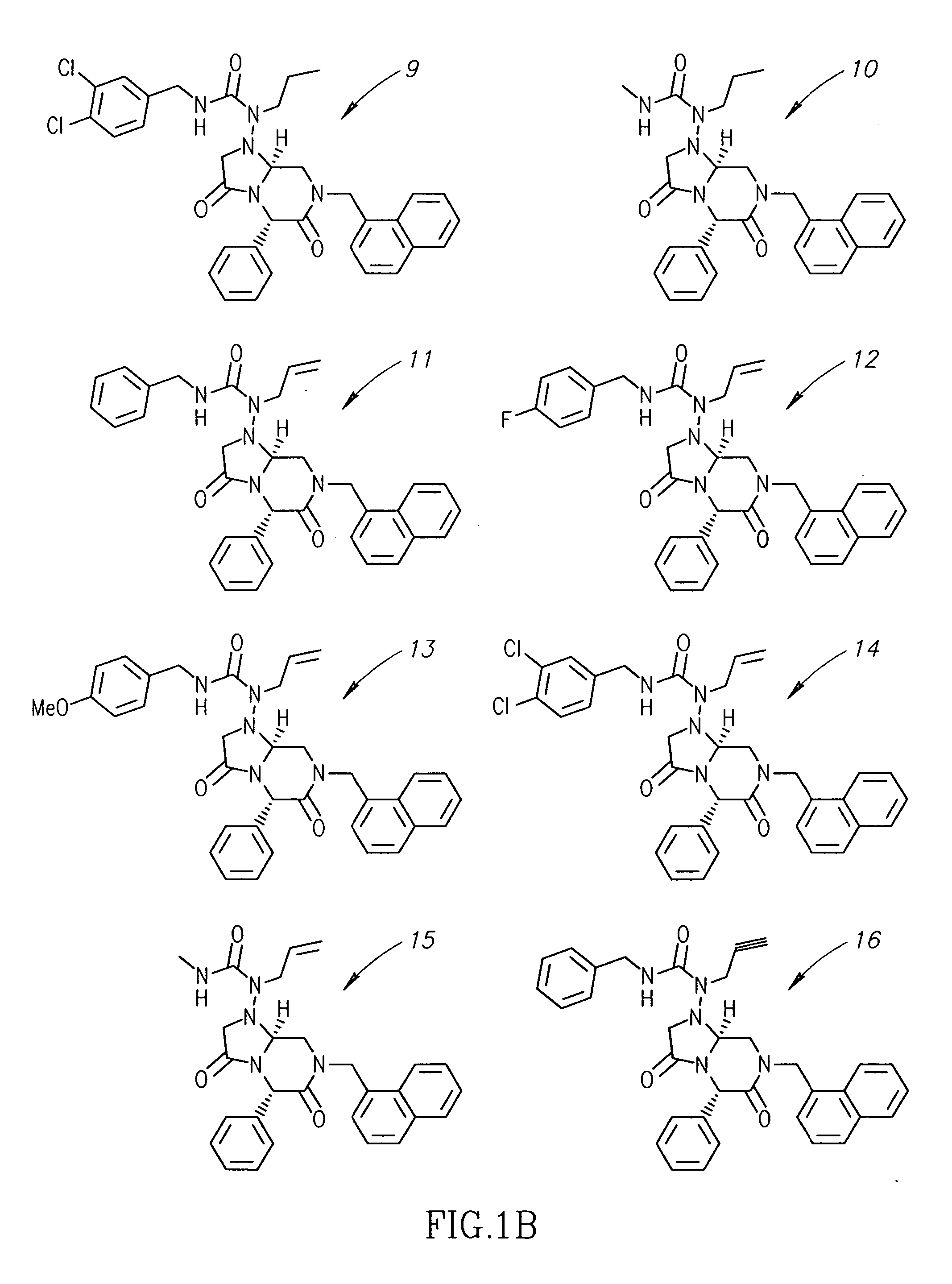
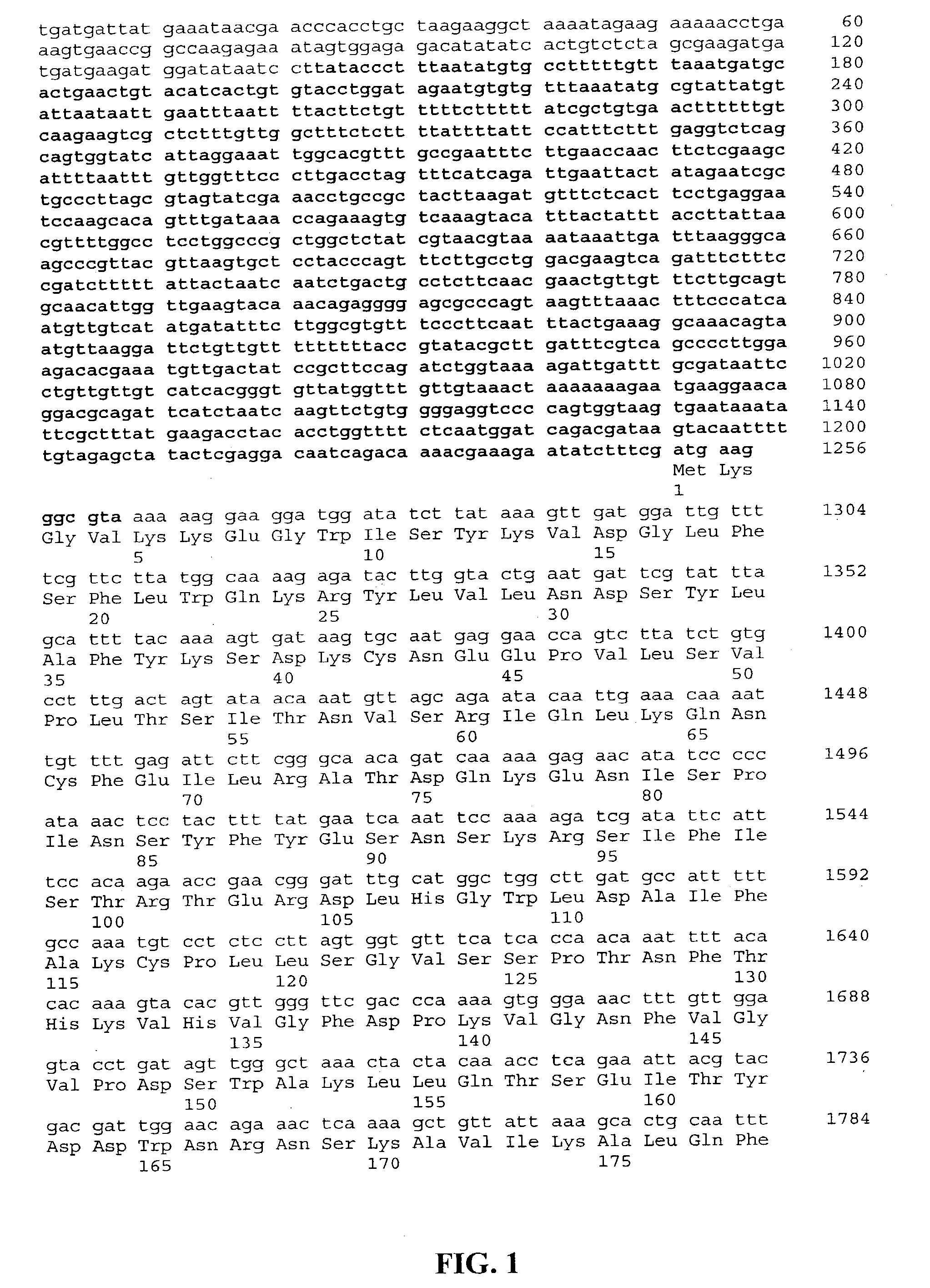
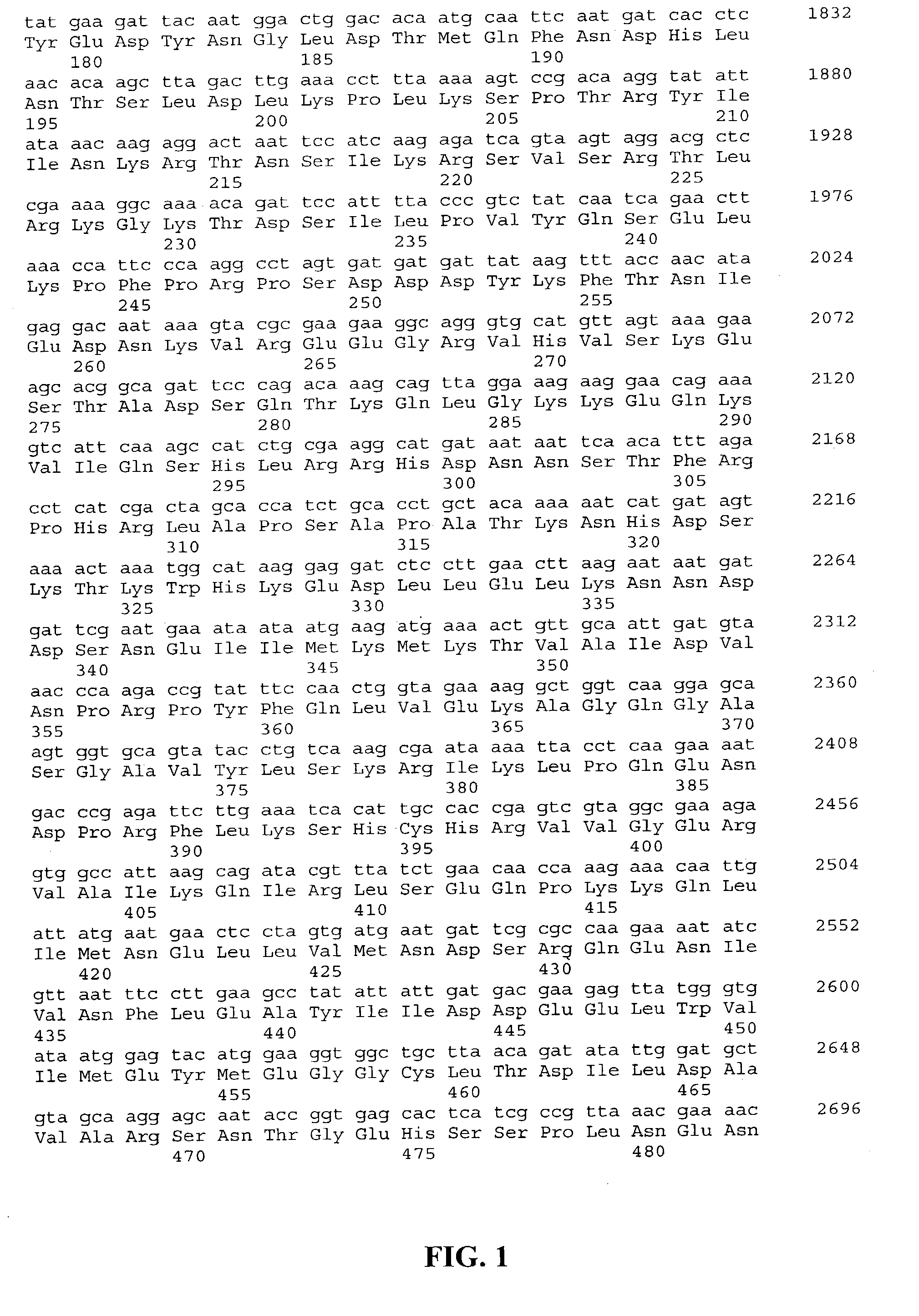
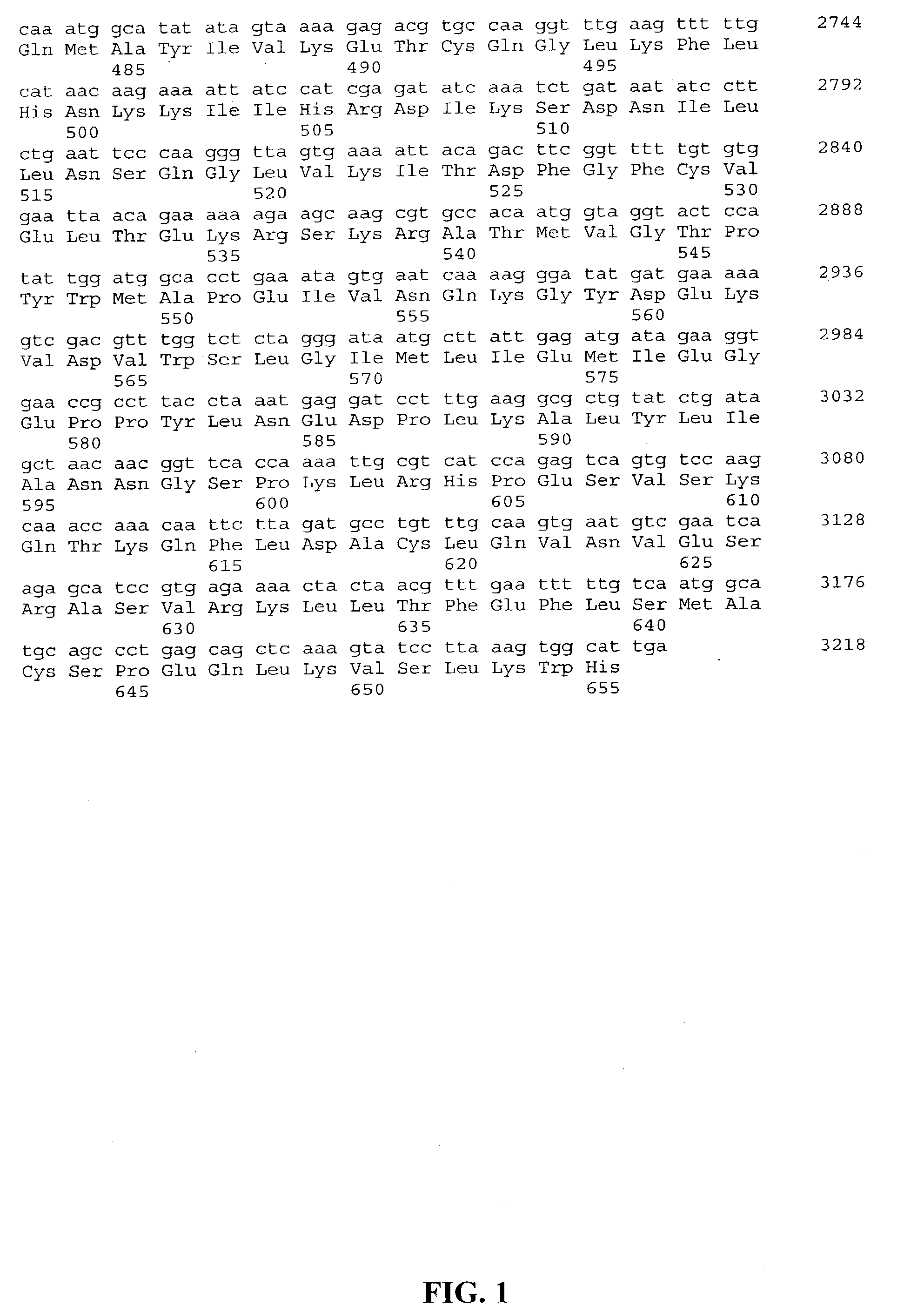
Patents
Literature
78 results about "Chemical library" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A chemical library or compound library is a collection of stored chemicals usually used ultimately in high-throughput screening or industrial manufacture. The chemical library can consist in simple terms of a series of stored chemicals. Each chemical has associated information stored in some kind of database with information such as the chemical structure, purity, quantity, and physiochemical characteristics of the compound.
Synthesis and screening method and kit for lead compound
ActiveCN103882532AEasy to operateSimple and fast operationSequential/parallel process reactionsLibrary tagsCompound (substance)Screening method
Owner:HITGEN INC
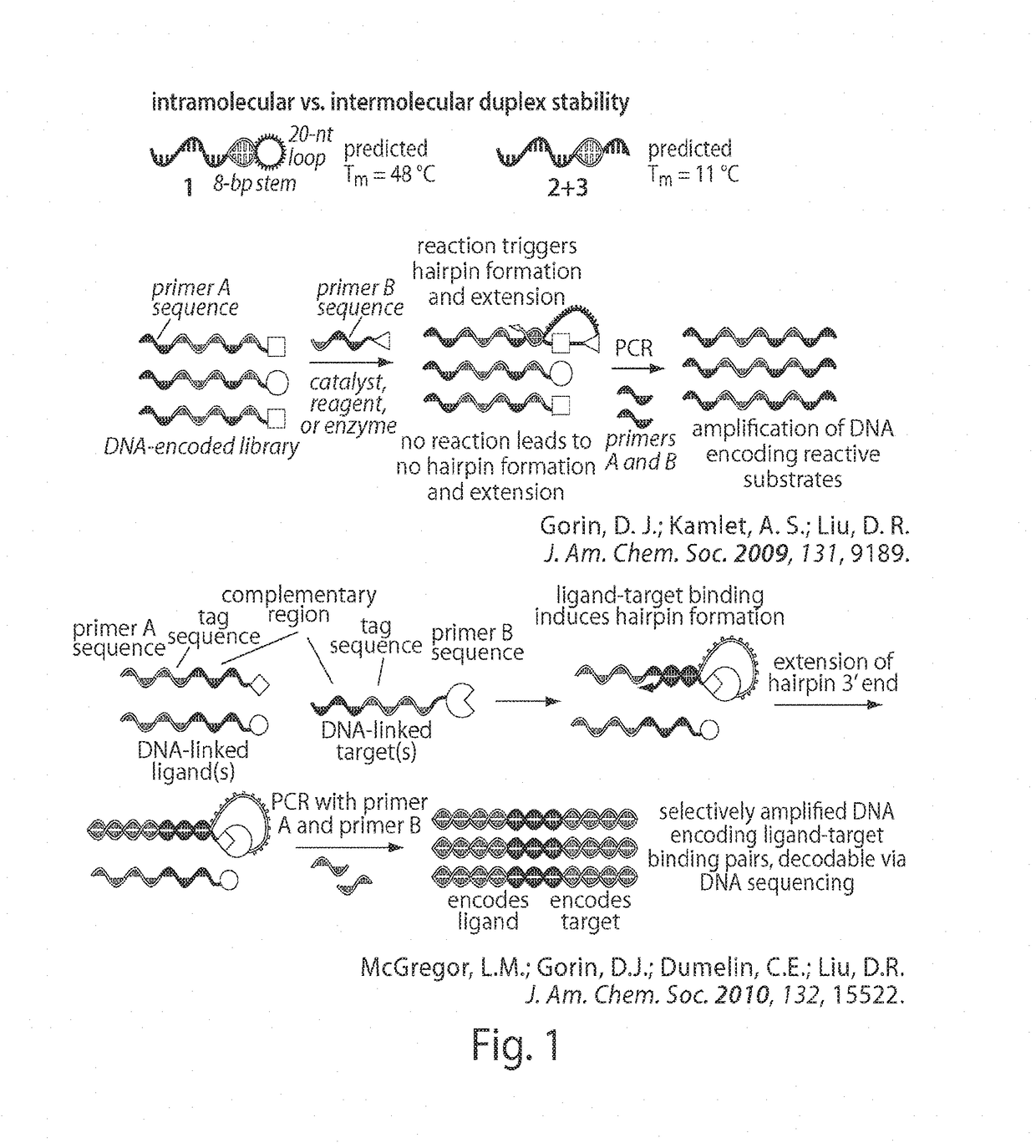
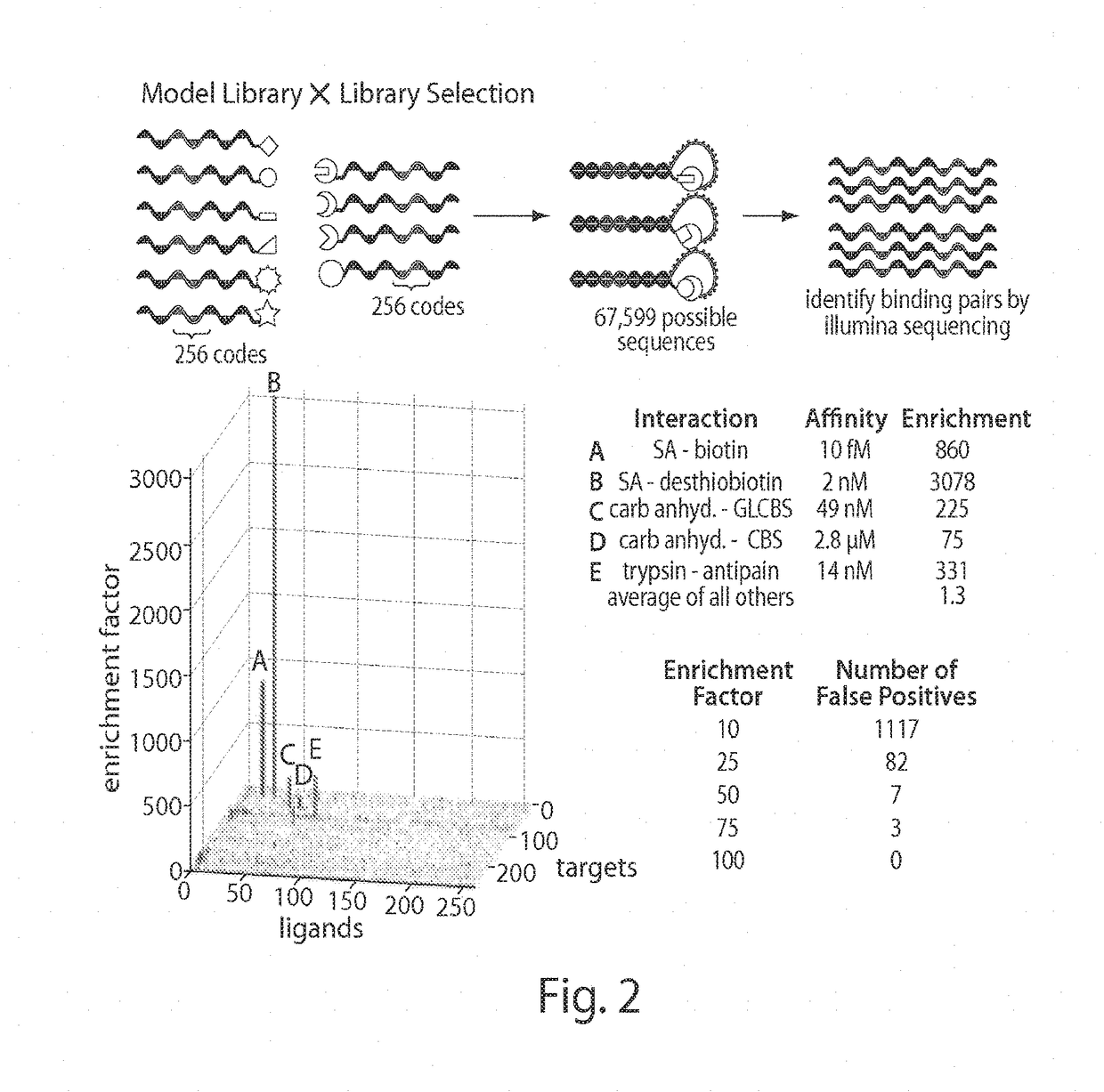
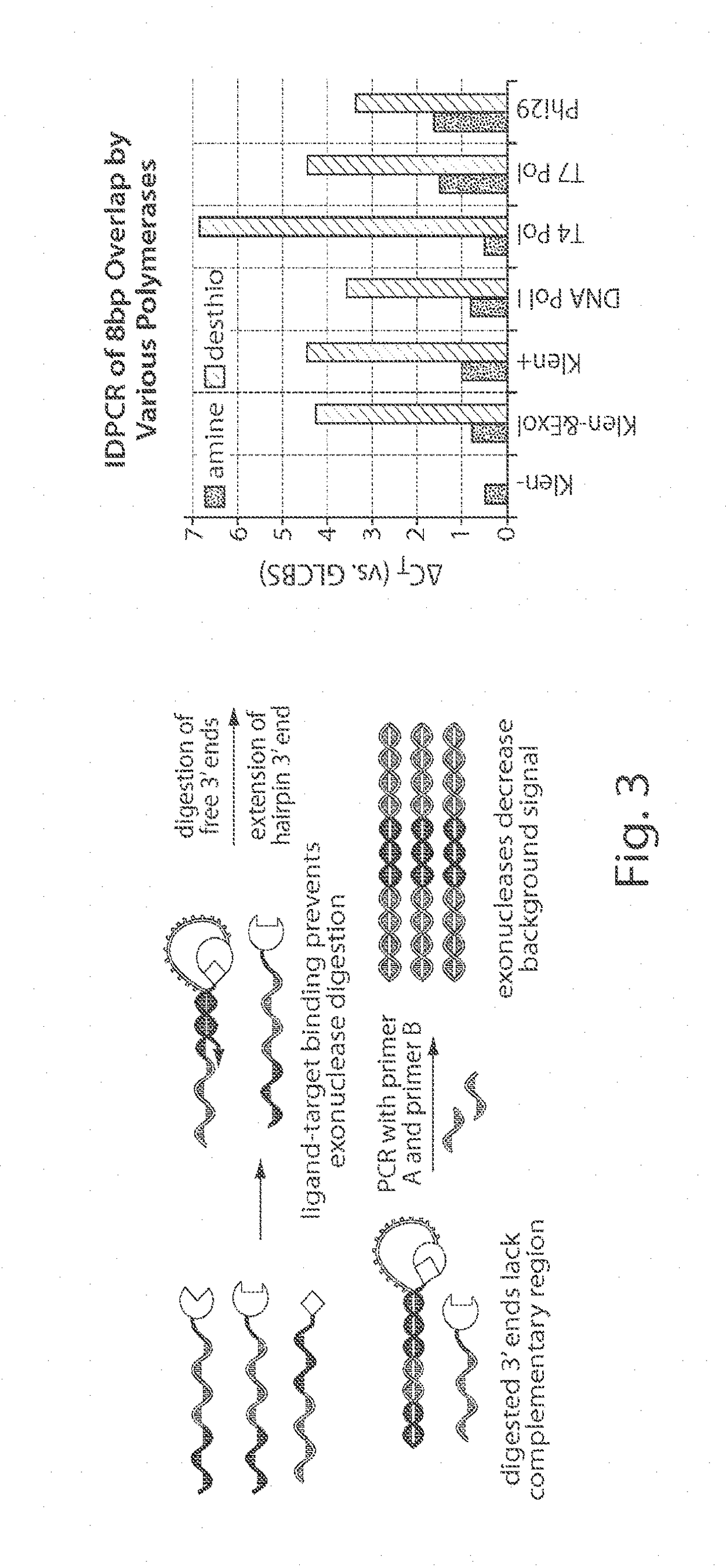
DNA-templated combinatorial library chemistry
InactiveUS7479472B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical compoundChemical library
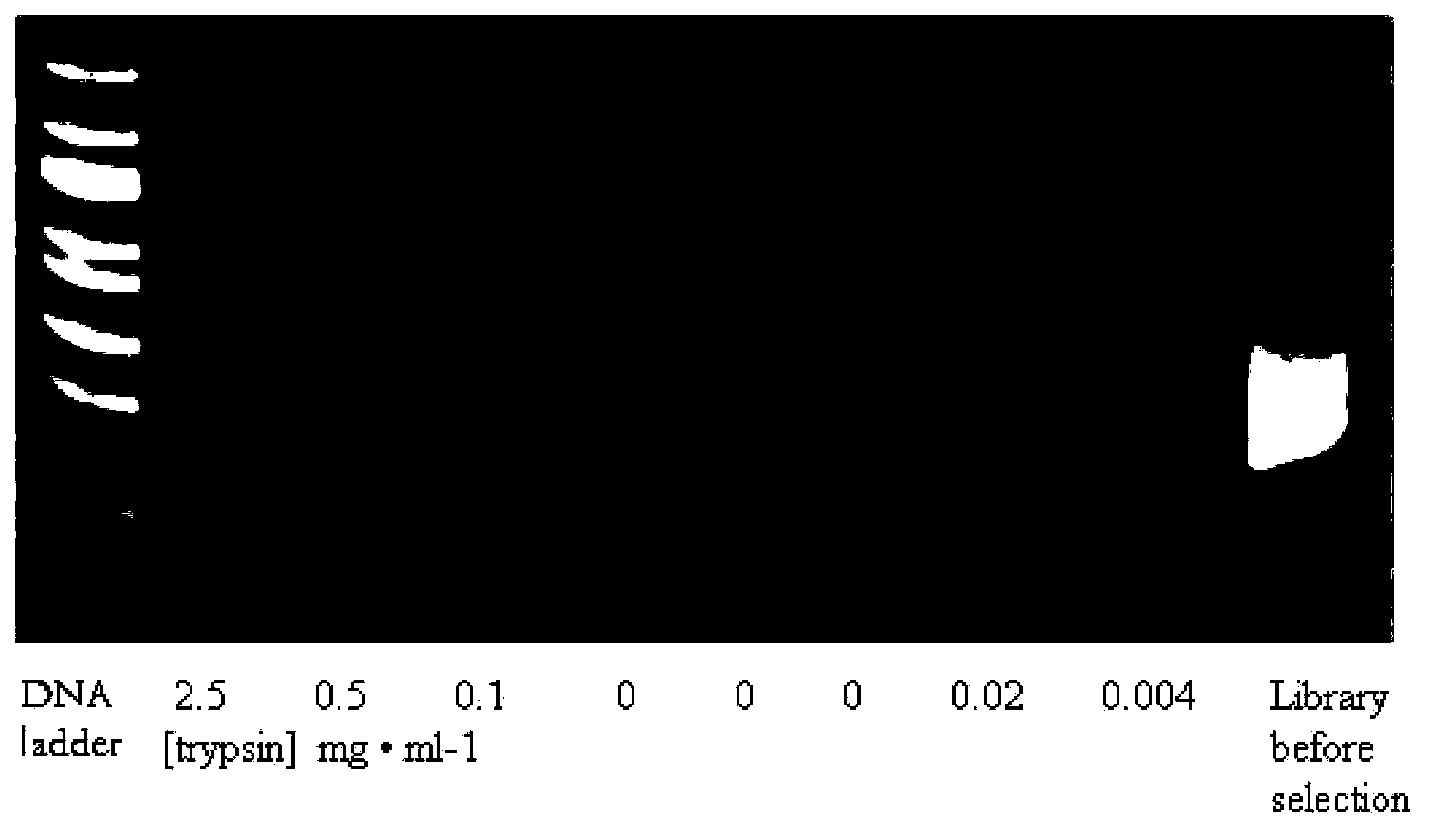
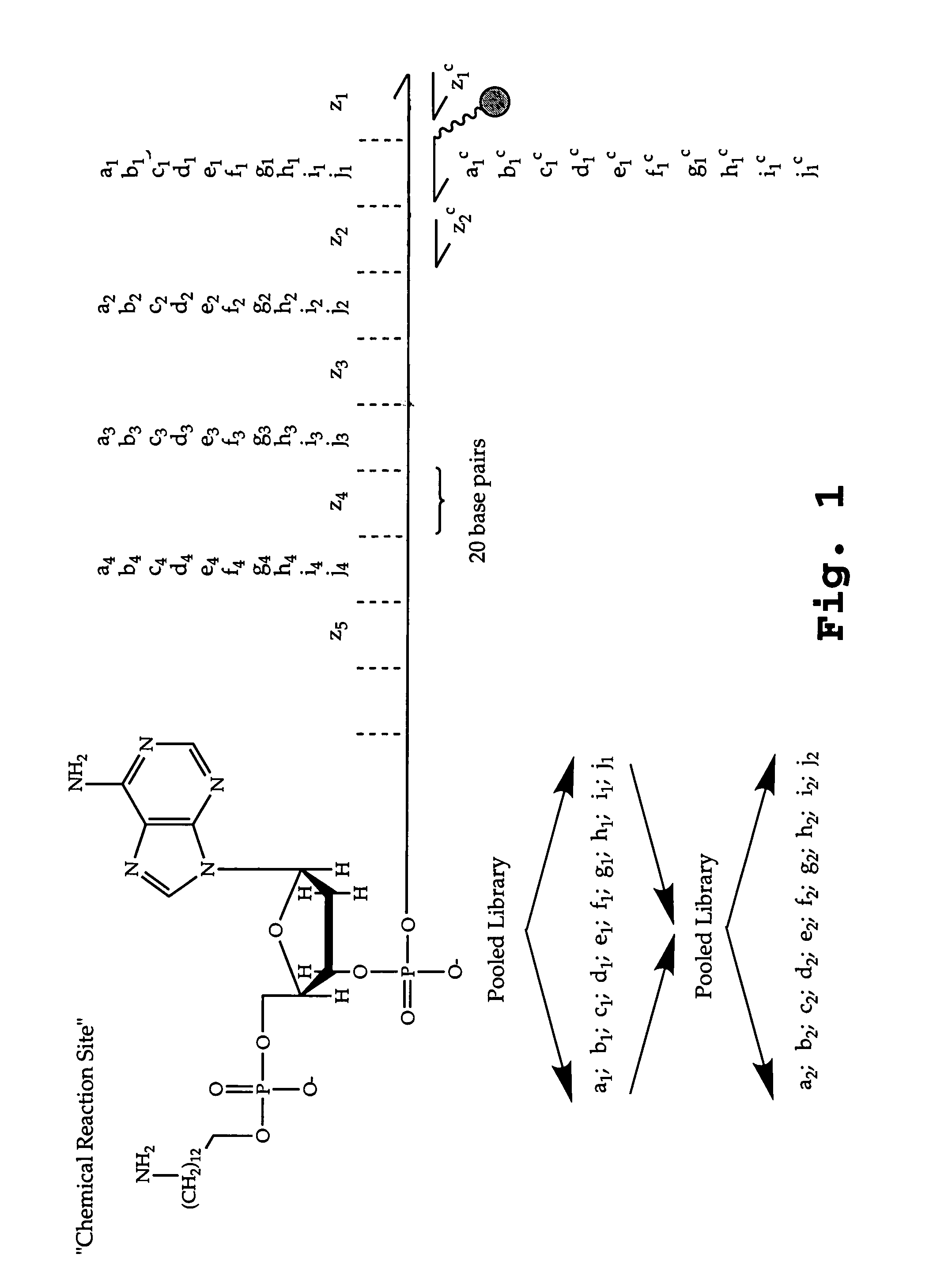
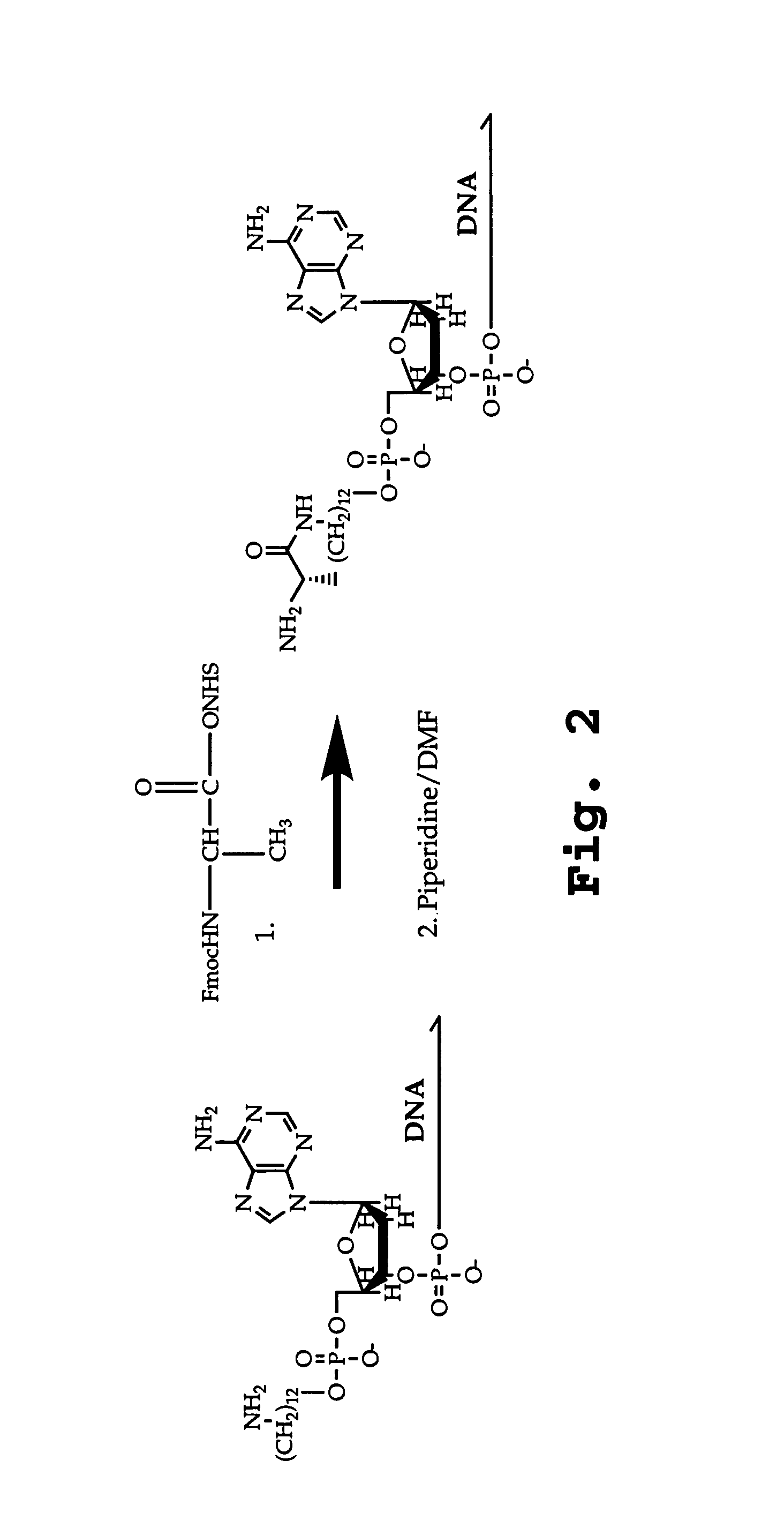
The present invention describes templated combinatorial chemical libraries comprised of a plurality of bifunctional molecules having both a chemical compound and a nucleic acid tag that defines the structure of the chemical compound and directs its synthesis. Also described are methods for producing, enriching and in vitro evolution of the bifunctional molecules of such libraries based on the nucleic acid tags and methods for selecting for library compounds having a desired activity.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Spherical encoded beads
InactiveUS20090032592A1Increase chanceHighly suitableSequential/parallel process reactionsPretreated surfacesEmulsion polymerizationCompound (substance)
The present application discloses a composition comprising a plurality of spherical beads, wherein a radiofrequency chip operating at a frequency of in the range of 2.2-2.7 GHz is embedded within each of said beads and wherein essentially each of said beads is individually identifiable on the basis of radiofrequency identification. Alternatives utilizing a ultrasonic identification chip are also disclosed. The beads are preferably made of polymeric material and can for example be used for the synthesis of e.g. solid-phase chemical libraries. Preferred materials include some that minimise interference in biochemical assays (fouling). The invention also relates to batch and continuous methods of producing such compositions, including emulsion-polymerisation methods. In a further aspect, the present invention relates to an apparatus for analysing radiofrequency-encoded beads. Also provided are methods for detecting and / or analysing and / or sorting beads, as well as methods for processing beads once they have been analysed and / or sorted.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
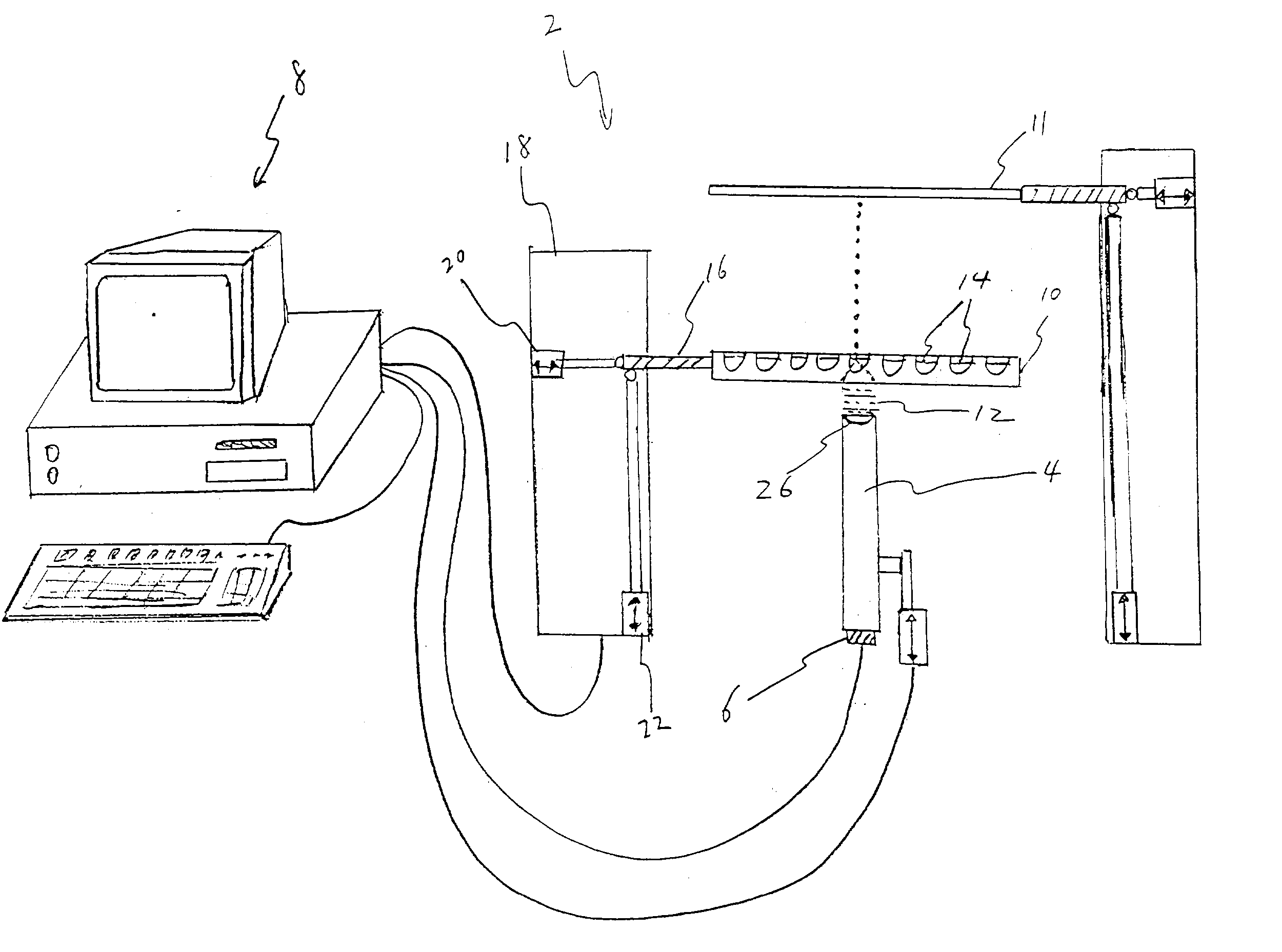
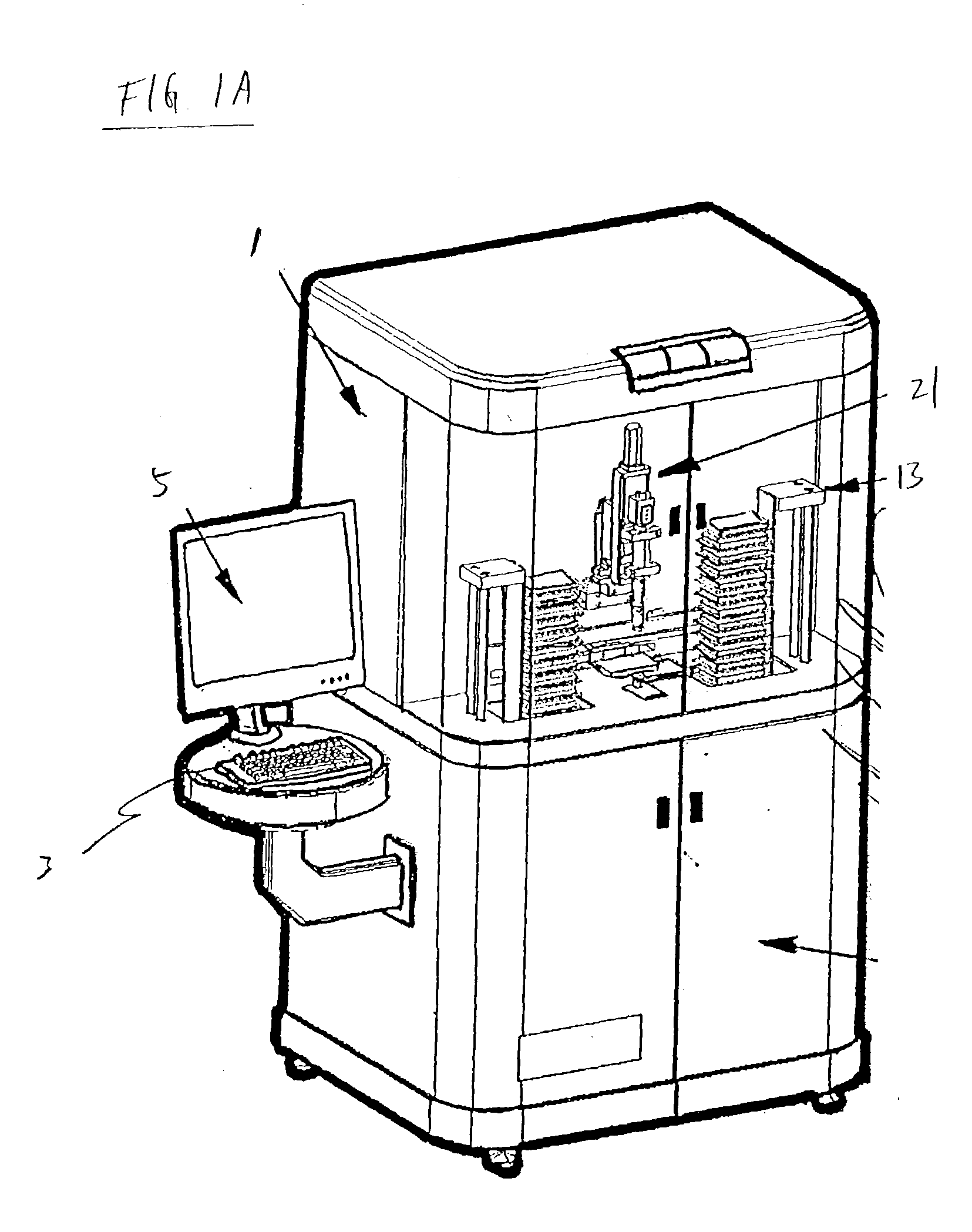
Source and target management system for high throughput transfer of liquids
InactiveUS20040120855A1Spray nozzlesMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsPrecession
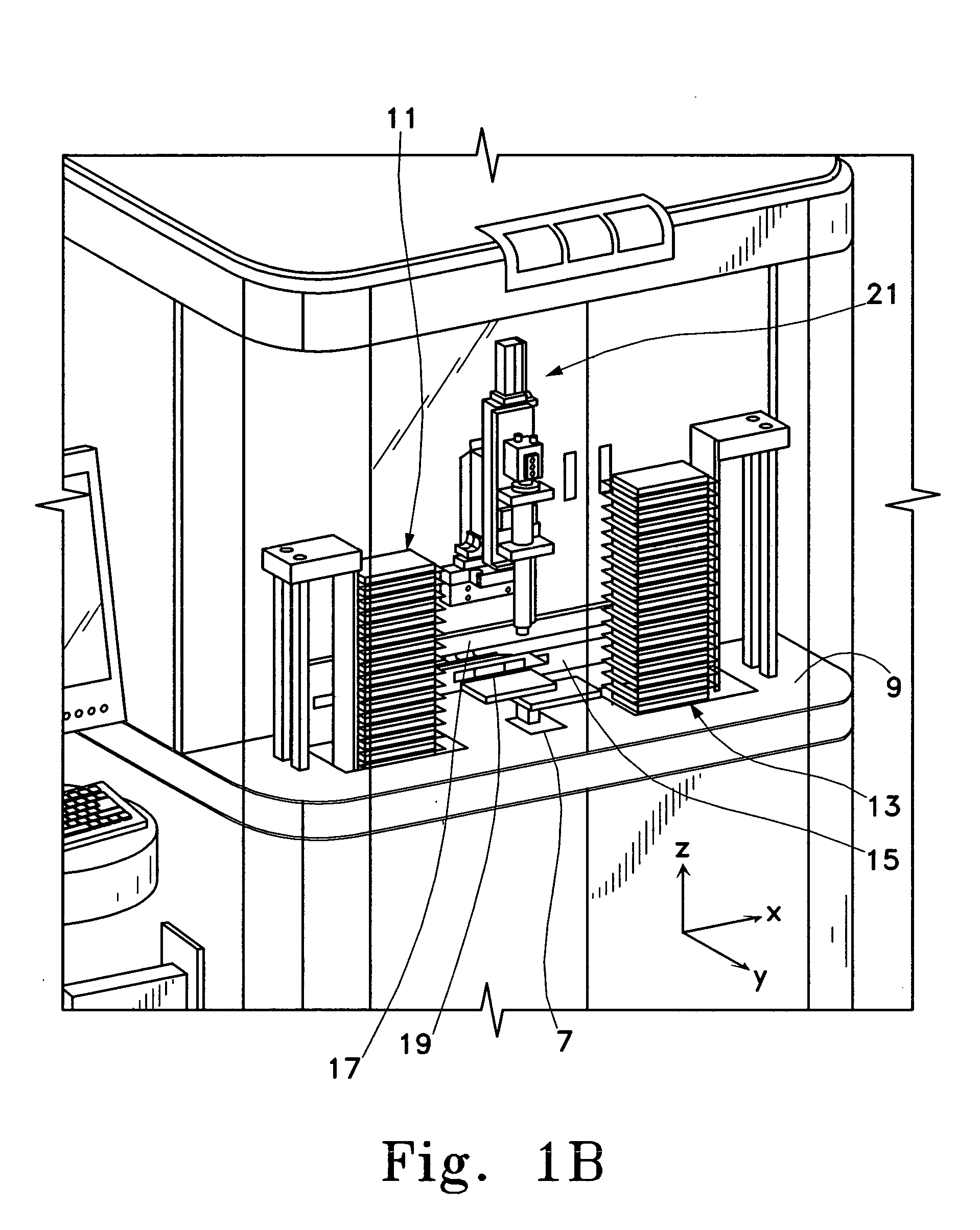
An apparatus for high-throughput screening and generation of chemical libraries. The apparatus comprises computer controlled mechanical displacement devices and storage queues capable of managing a large number of source well plates and target well plates. In one aspect of the invention, precession alignment mechanisms are provided for efficient transfer of liquid from source well plates to target well plates. The apparatus may be configured such that any source fluid in any of the source well plates may be transferred to any target location within any of the target well plates in any sequence defined by the user. The computer controller may track the location of all the source well plates and target well plates and allow user defined association of any source well with any target well in any order defined by the user, thus providing an effective platform for chemical and biochemical synthesis and screening.
Owner:LABCYTE
Complex combinatorial chemical libraries encoded with tags
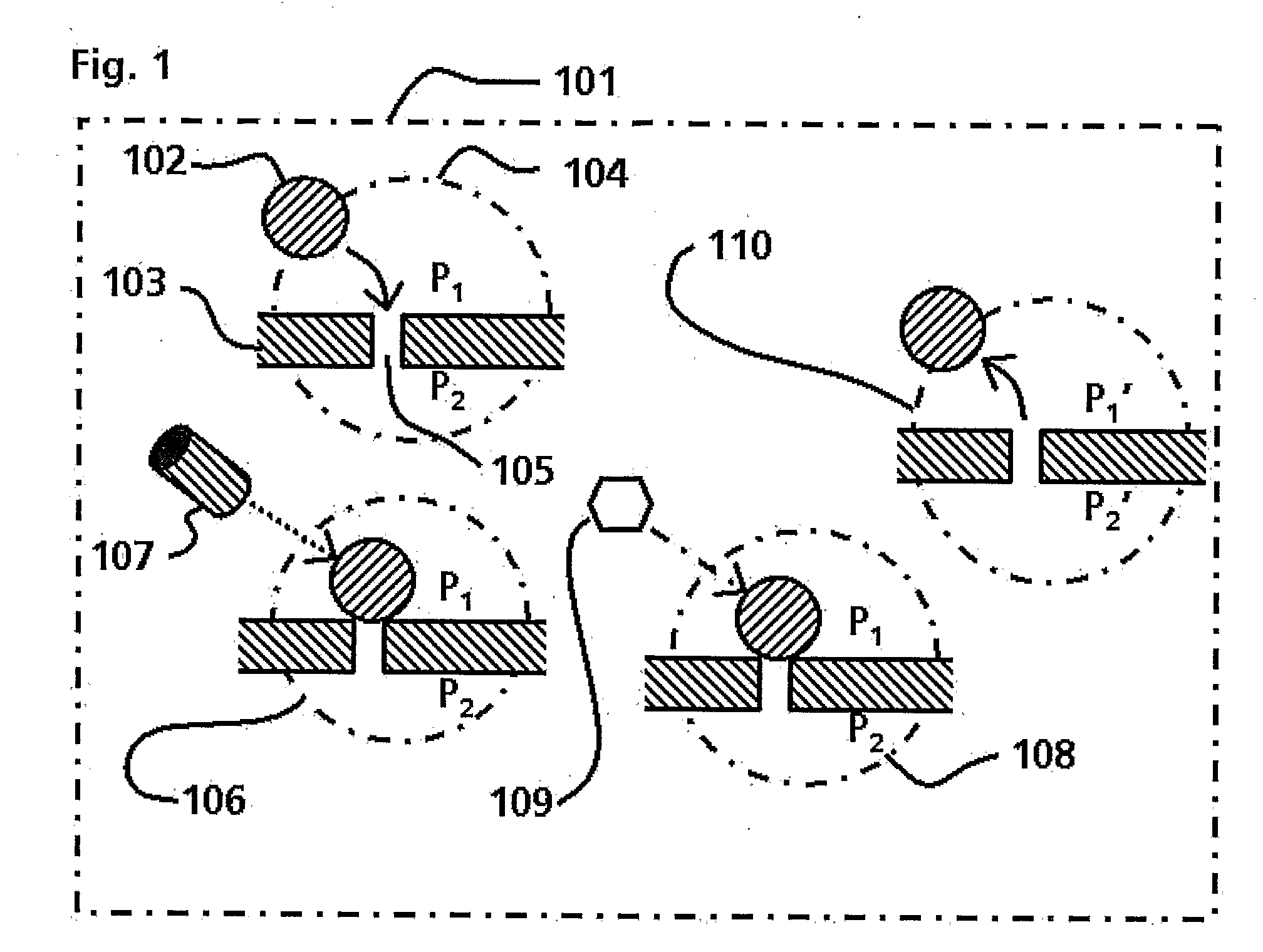
Encoded combinatorial chemistry is provided, where sequential synthetic schemes are recorded using organic molecules, which define choice of reactant, and stage, as the same or different bit of information. Various products can be produced in the multi-stage synthesis, such as oligomers and synthetic non-repetitive organic molecules. Conveniently, nested families of compounds can be employed as identifiers, where number and / or position of a substituent define the choice. Alternatively, detectable functionalities may be employed, such as radioisotopes, fluorescers, halogens, and the like, where presence and ratios of two different groups can be used to define stage or choice. Particularly, pluralities of identifiers may be used to provide a binary or higher code, so as to define a plurality of choices with only a few detachable tags. The particles may be screened for a characteristic of interest, particularly binding affinity, where the products may be detachable from the particle or retained on the particle. The reaction history of the particles which are positive for the characteristic can be determined by the release of the tags and analysis to define the reaction history of the particle.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
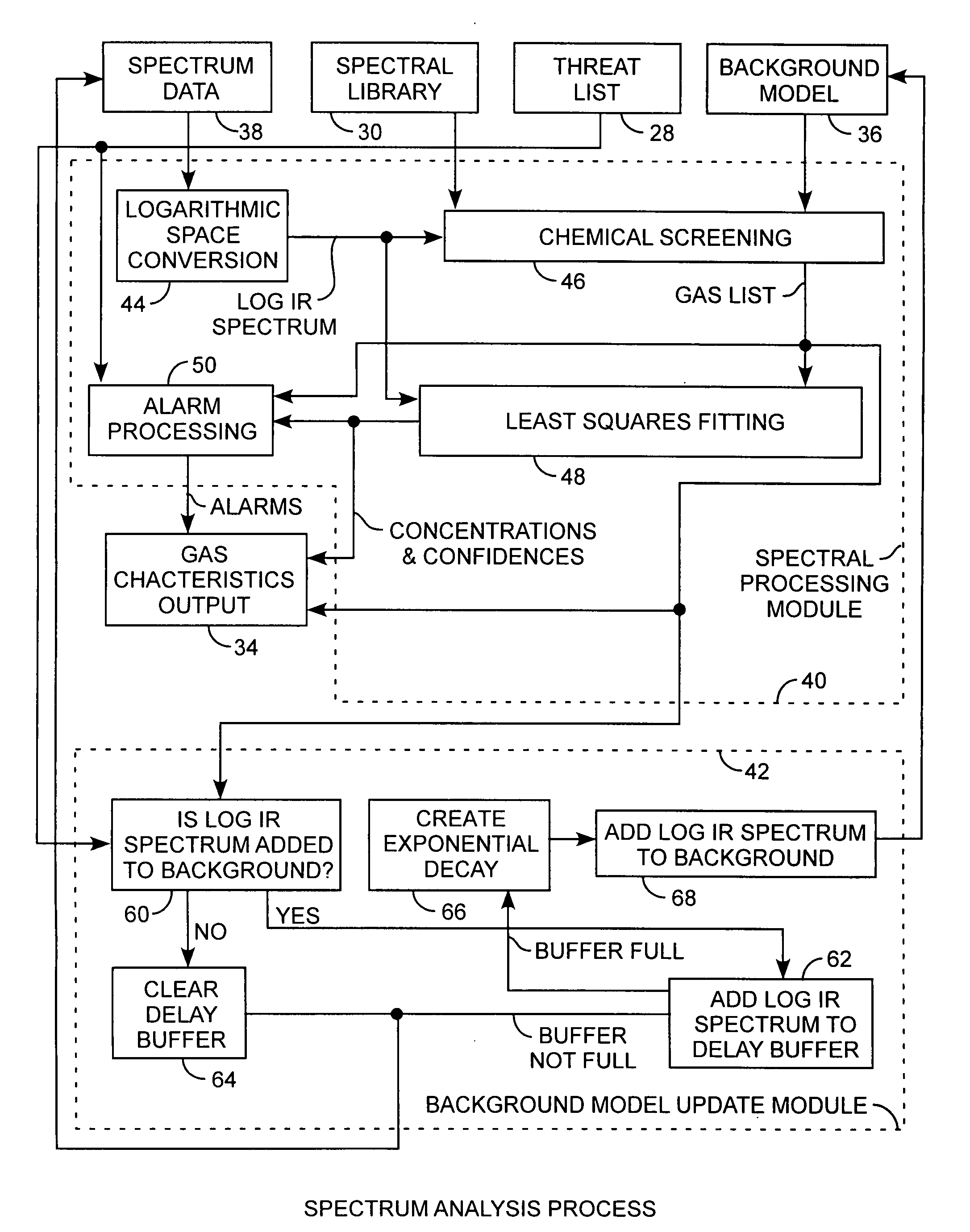
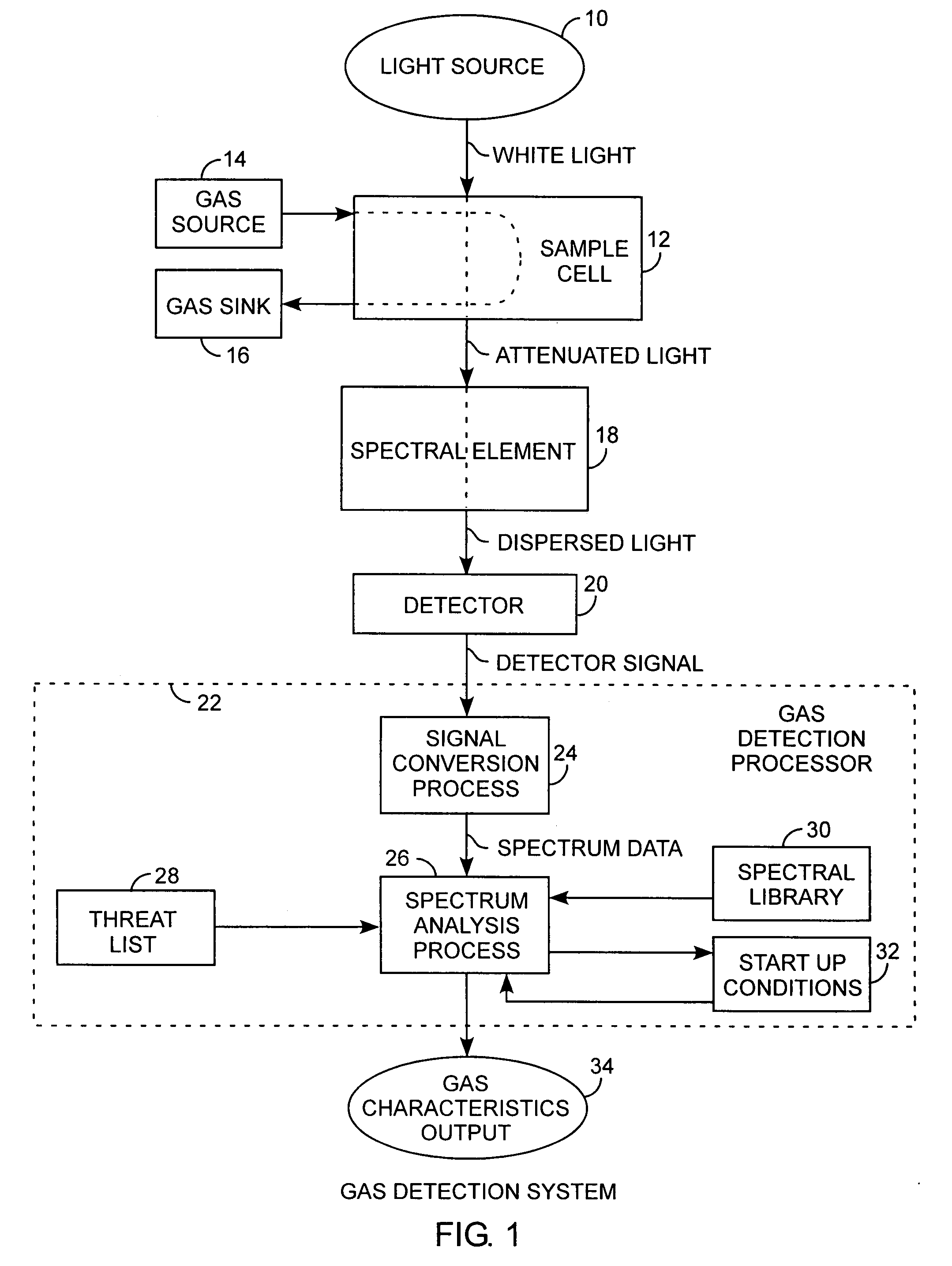
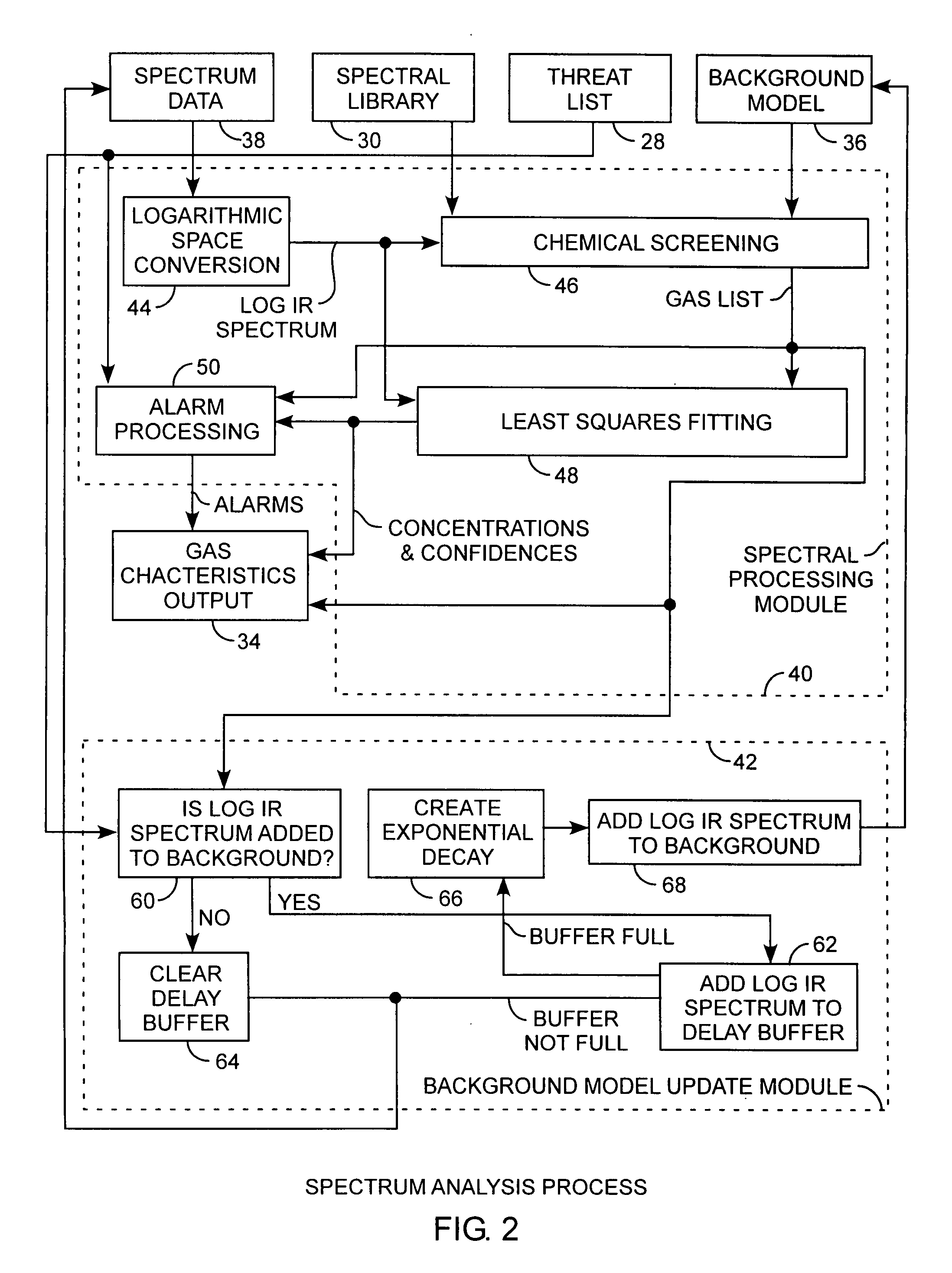
Infrared gas detection and spectral analysis method
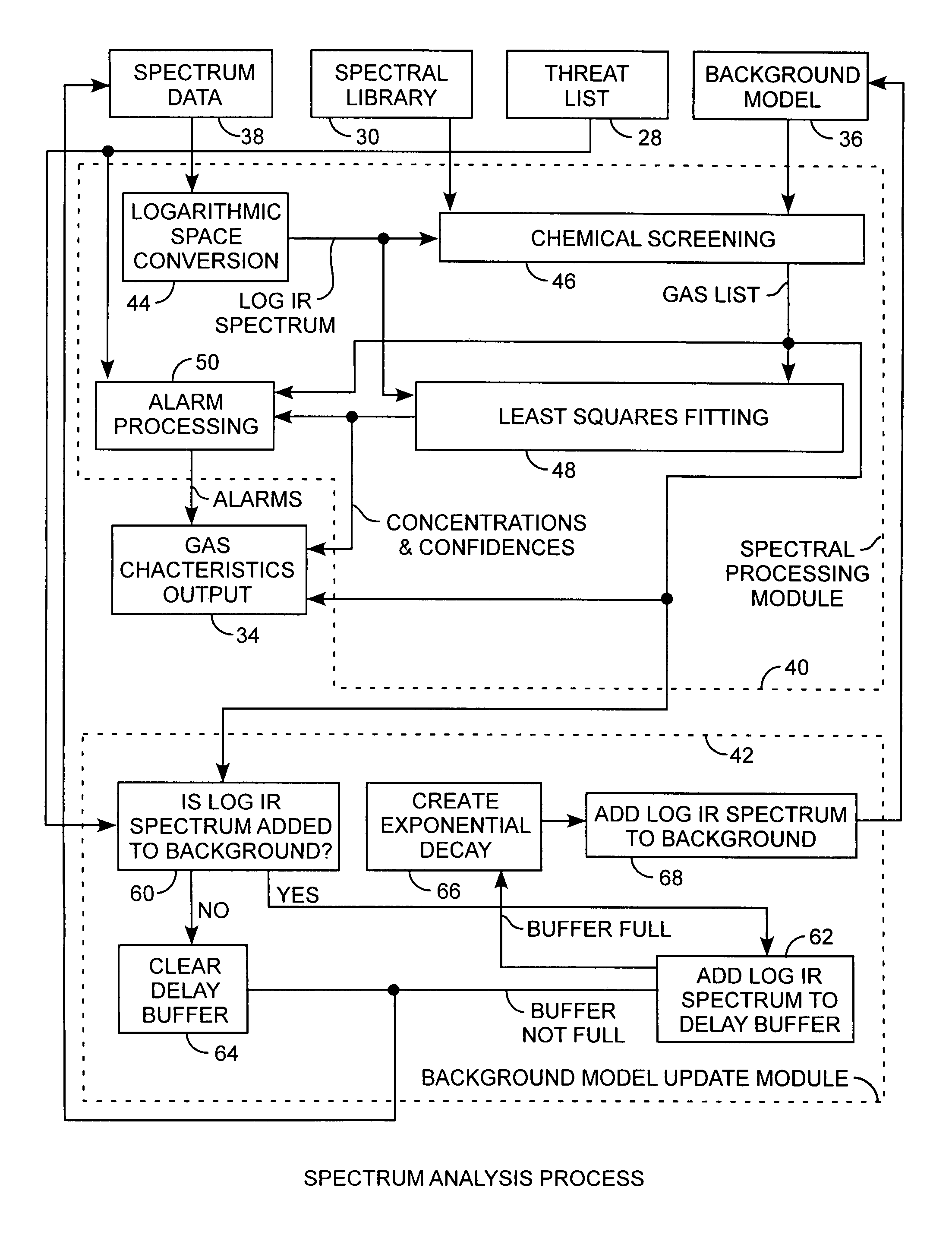
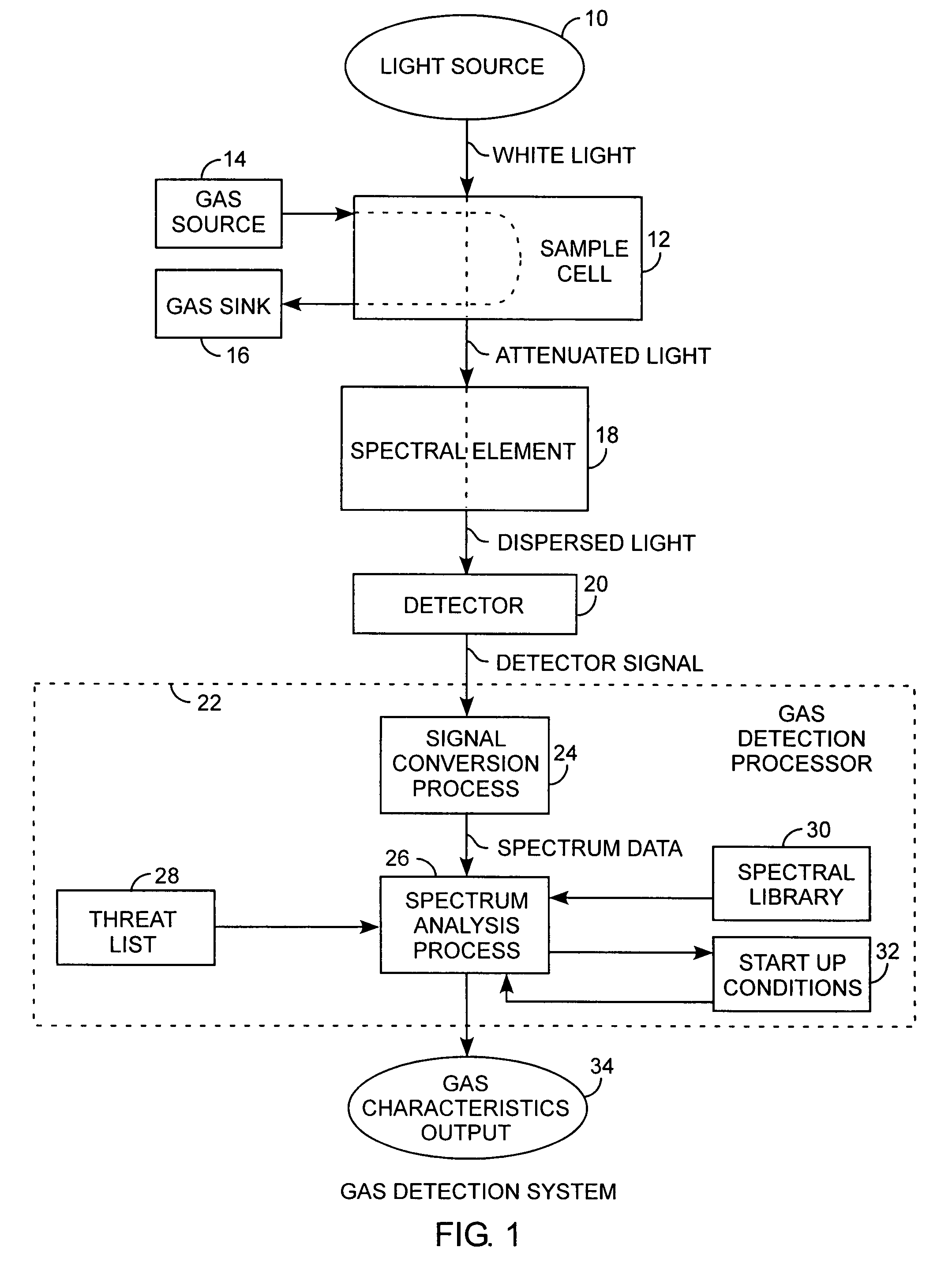
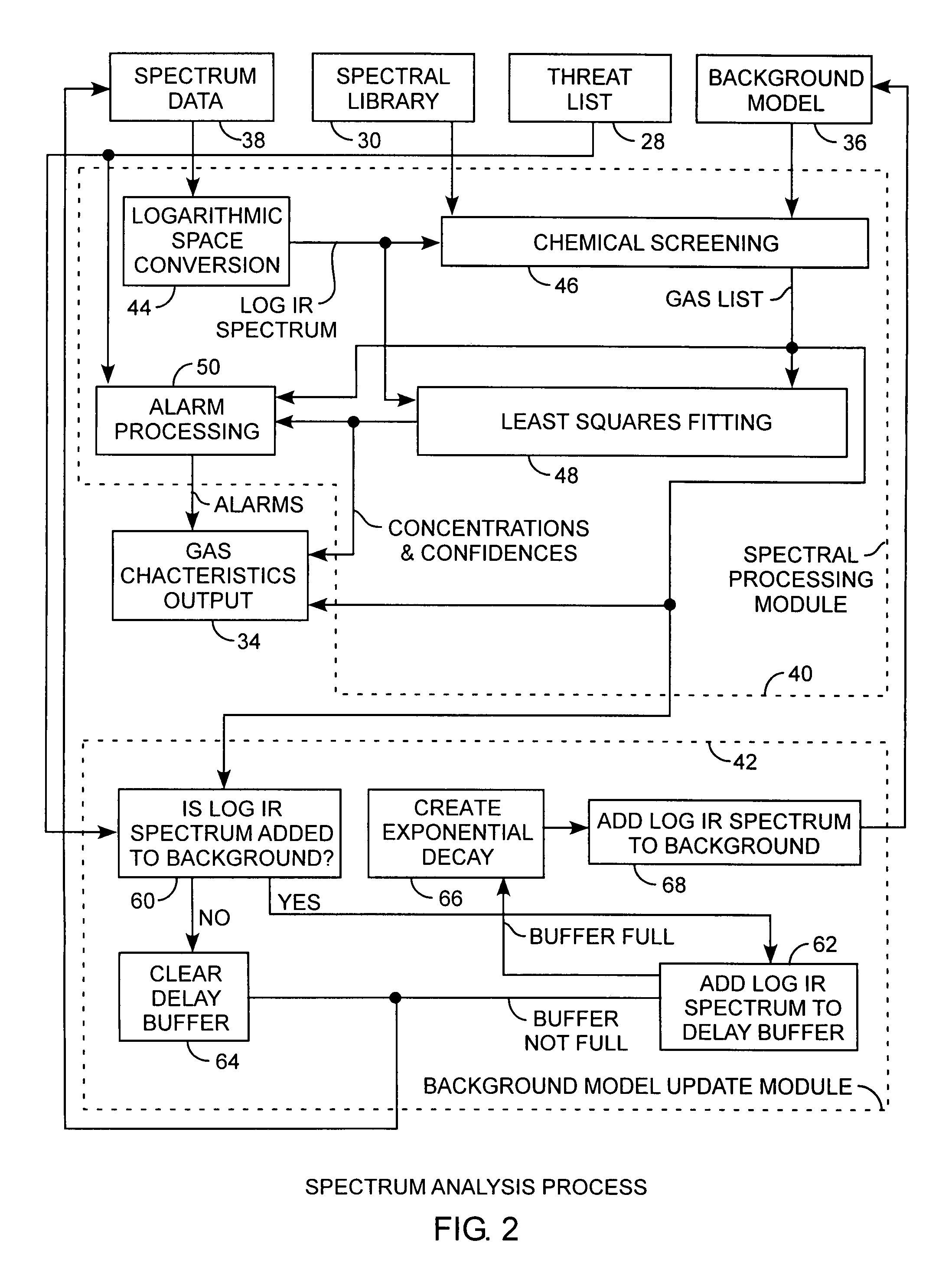
ActiveUS20100090845A1Easy to detectEasy to handleRadiation pyrometryComponent separationLogarithmic spaceChemical library
A gas detection system and method for analysis of infrared gas spectra is used for chemical threat detection, quantification and alarm, using a chemical library, a chemical threat list, and a background model that incorporates the data history, allows spectra containing interferent signals into the background model, the model being updated using delay buffering to prevent threat spectra incorporation and using exponential decays to preferentially represent recent background history, all computed in the logarithmic space for rapid detection and alarm.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
Chemical address tags
The present invention provides methods and compositions related to the fields of chemoinformatics, chemogenomics, drug discovery and development, and drug targeting. In particular, the present invention provides subcellular localization signals (e.g., chemical address tags) that influence (e.g., direct) subcellular and organelle level localization of associated compounds (e.g., drugs and small molecule therapeutics, radioactive species, dyes and imagining agents, proapoptotic agents, antibiotics, etc) in target cells and tissues. The compositions of the present invention modulate the pharmacological profiles of associated compounds by influencing the compound's accumulation, or exclusion, from subcellular loci such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, cytoplasm, vesicles, granules, nuclei and nucleoli and other subcellular organelles and compartments. The present invention also provides methods for identifying chemical address tags, predicting their targeting characteristics, and for rational designing chemical libraries comprising chemical address tags.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
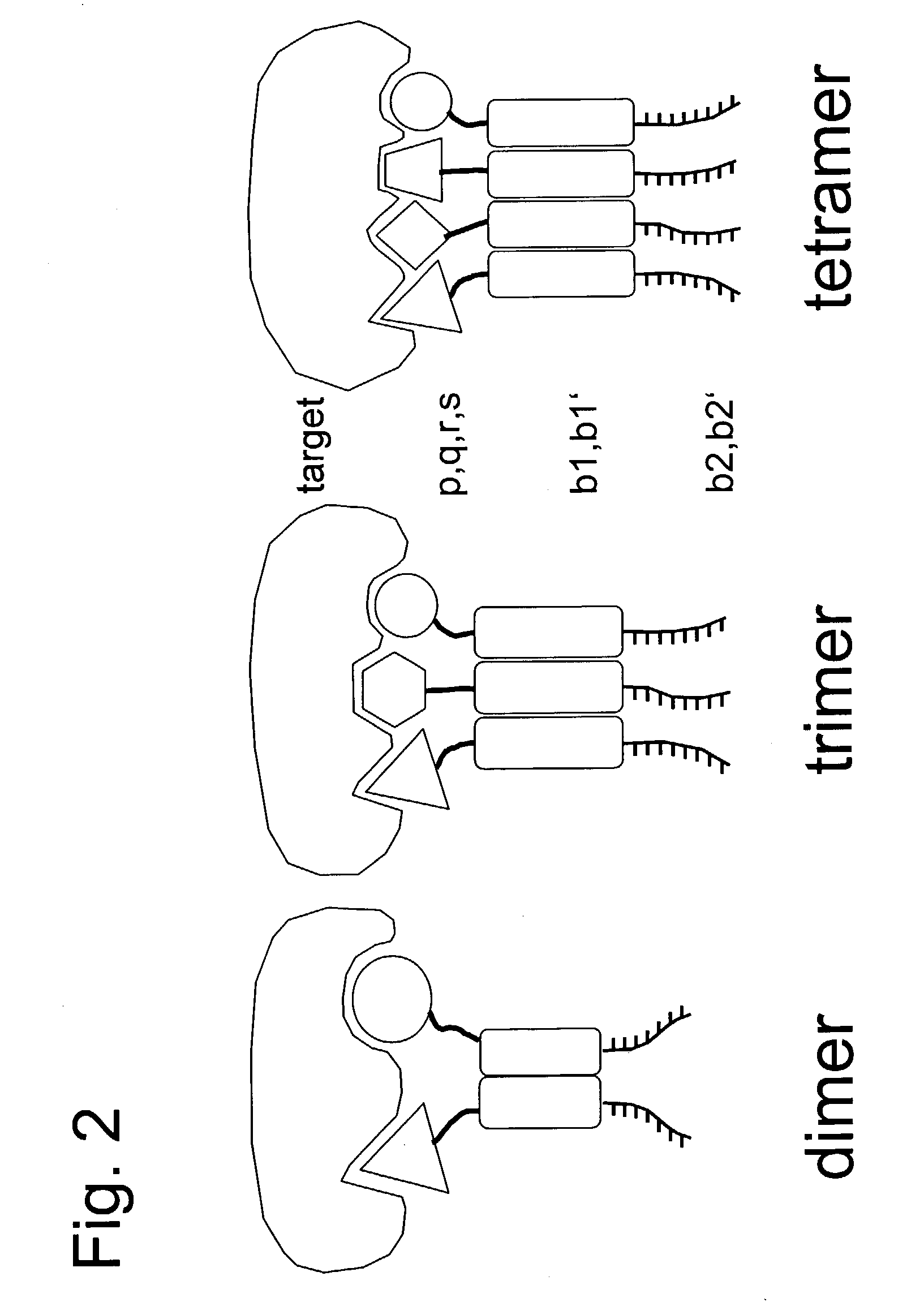
Encoded self-assembling chemical libraries (ESACHEL)
InactiveUS20040014090A1Promote formationSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesChemical MoietyNucleotide
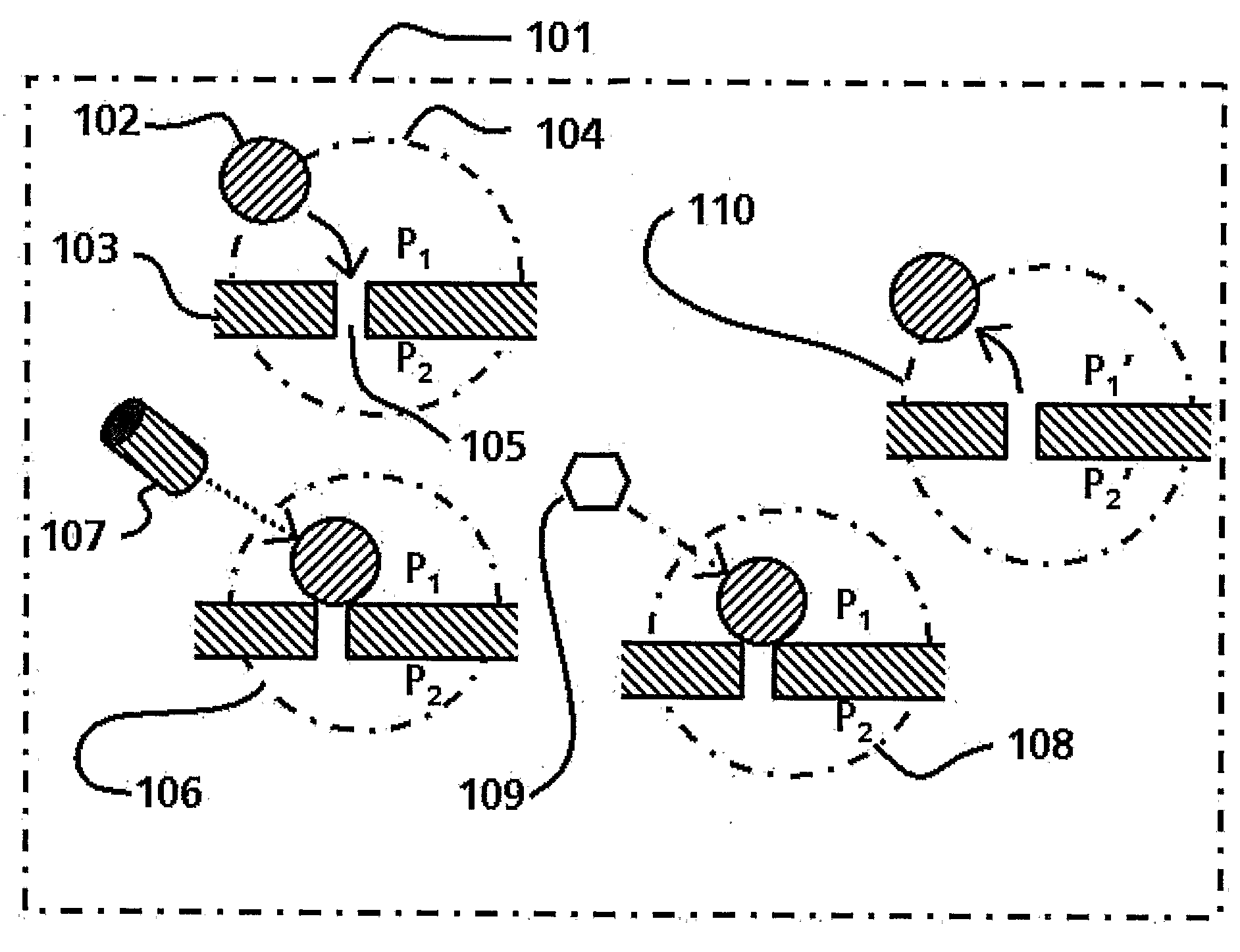
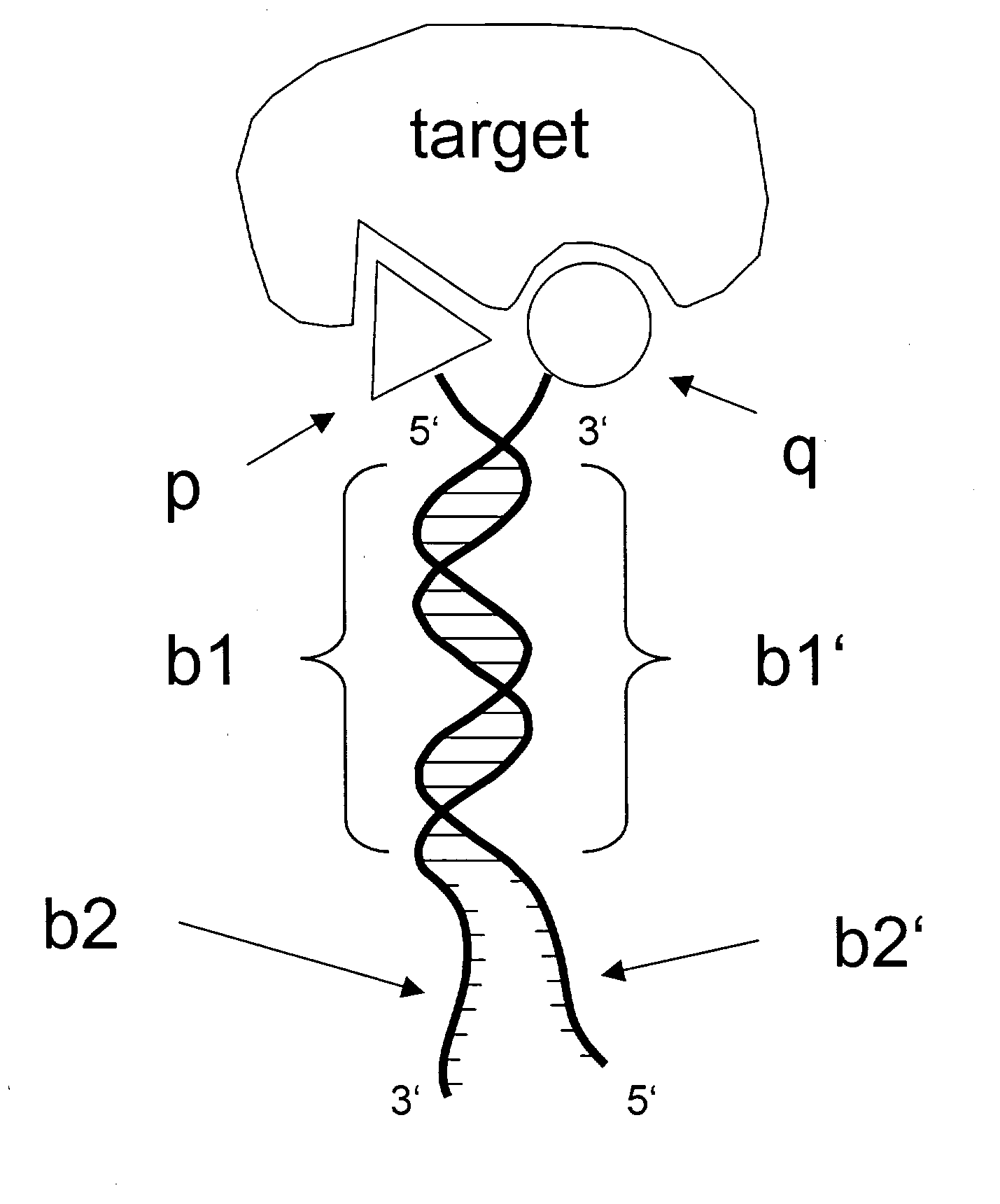
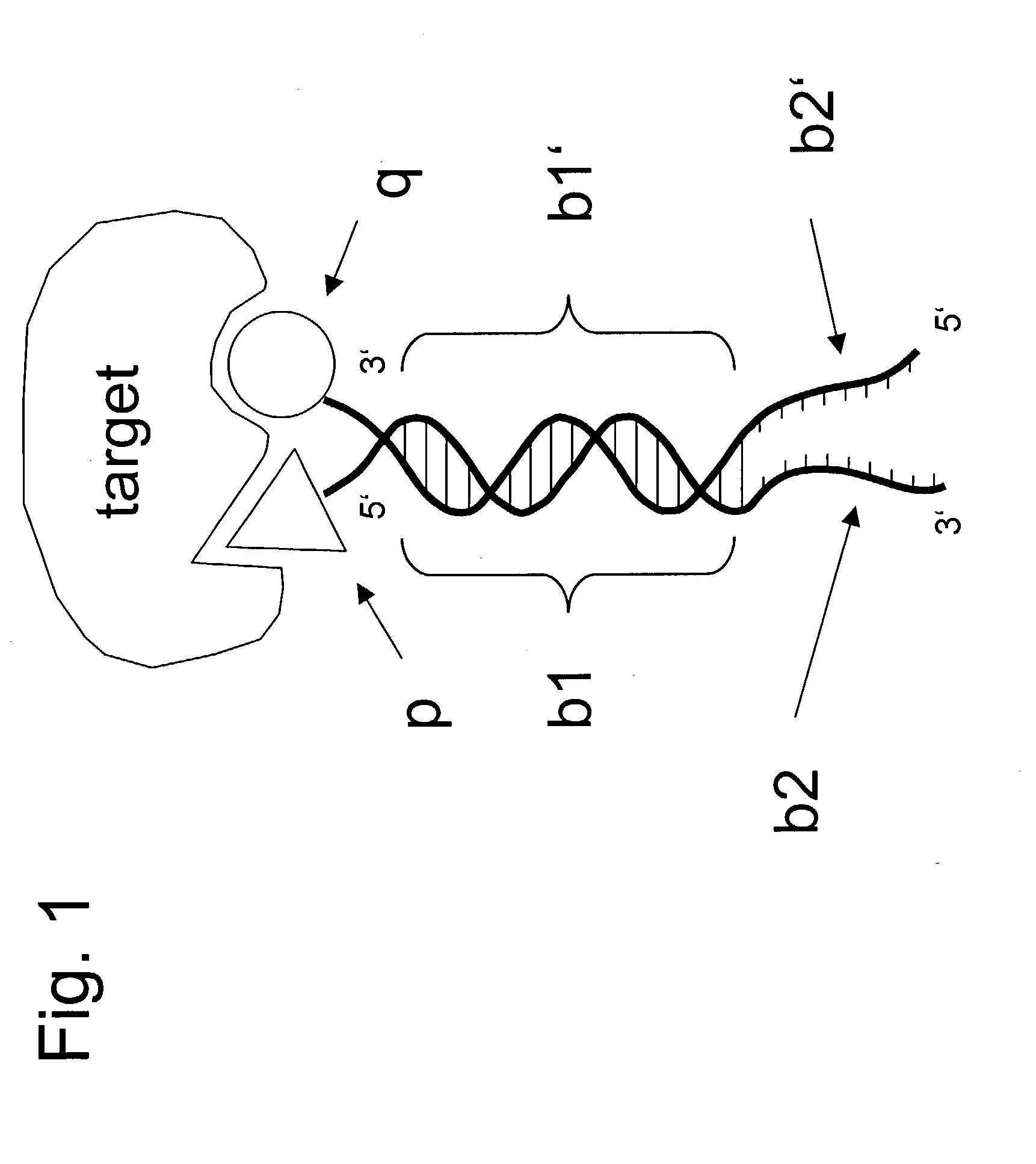
The invention concerns a chemical compound comprising a chemical moiety (p) capable of performing a binding interaction with a target molecule (e.g. a biological target) and further comprising an oligonucleotide (b) or functional analogue thereof. In a first embodiment according to the invention, the chemical compound is characterized in that the oligonucleotide (b) or functional analogue comprises at least one self-assembly sequence (b1) capable of performing a combination reaction with at least one self-assembly sequence (b1') of a complentary oligonucleotide or functional analogue bound to another chemical compound comprising a chemical moiety (q). In a second embodiment according to the invention, the chemical compound which comprises a coding sequence (b1) coding for the identification of the chemical moiety (p) is characterized in that the chemical compound further comprises at least one self-assembly moiety (m) capable of performing a combination reaction with at least one self-assembly moiety (m') of a similar chemical compound comprising a chemical moiety (q). The invention comprises corresponding libraries of chemical compounds as well as methods of biopanning of target molecules and of identifying such targets.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
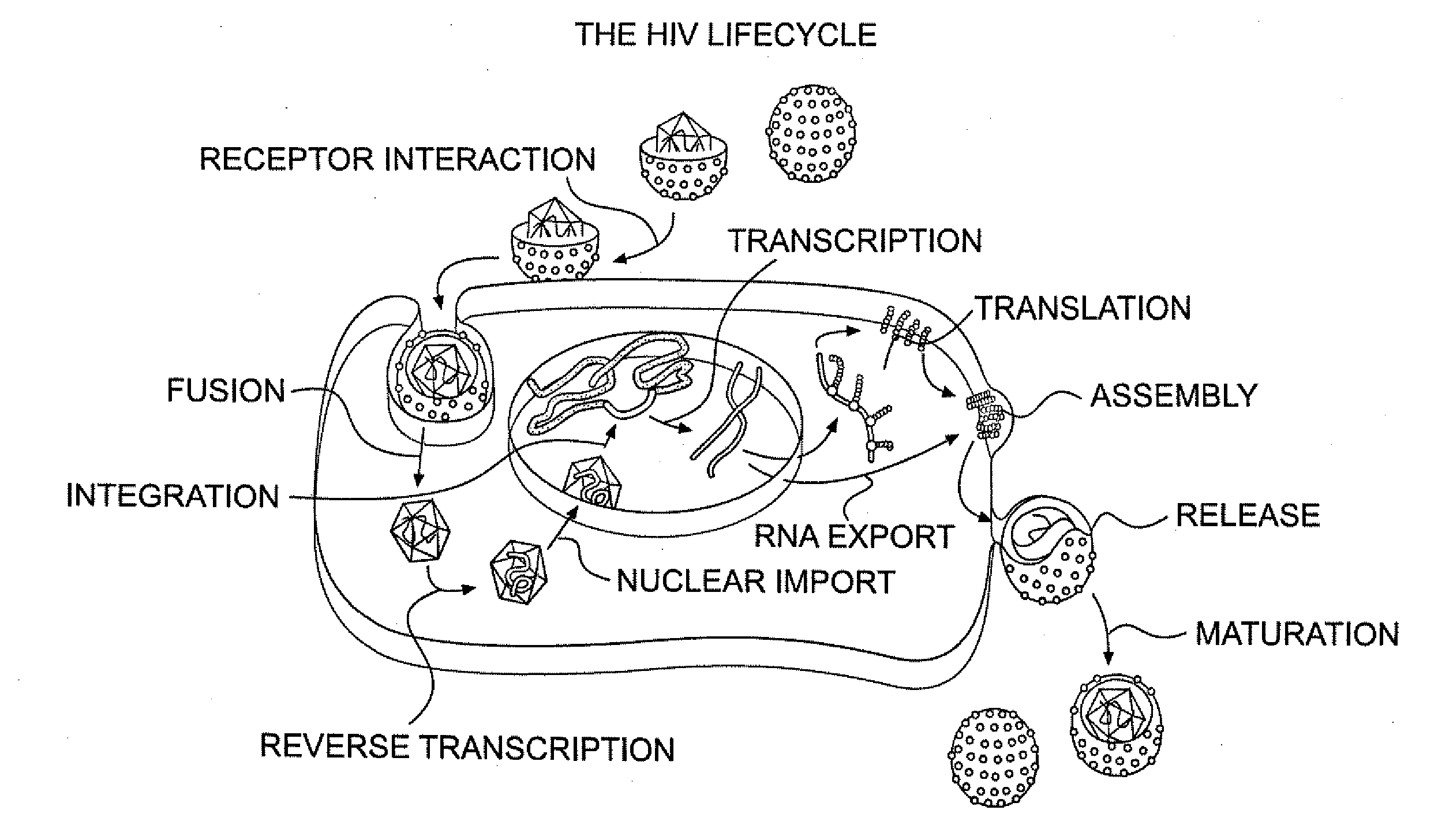
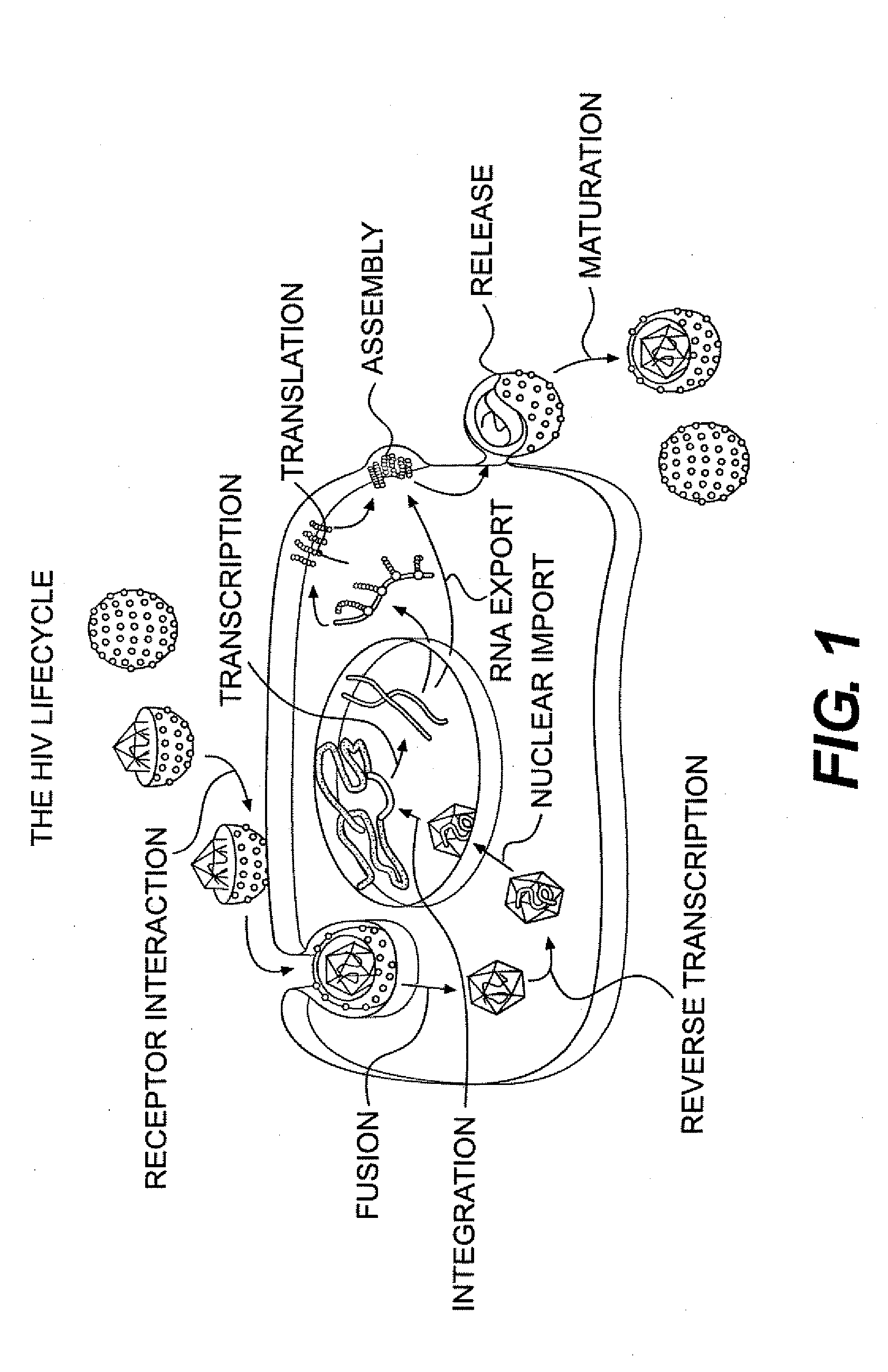
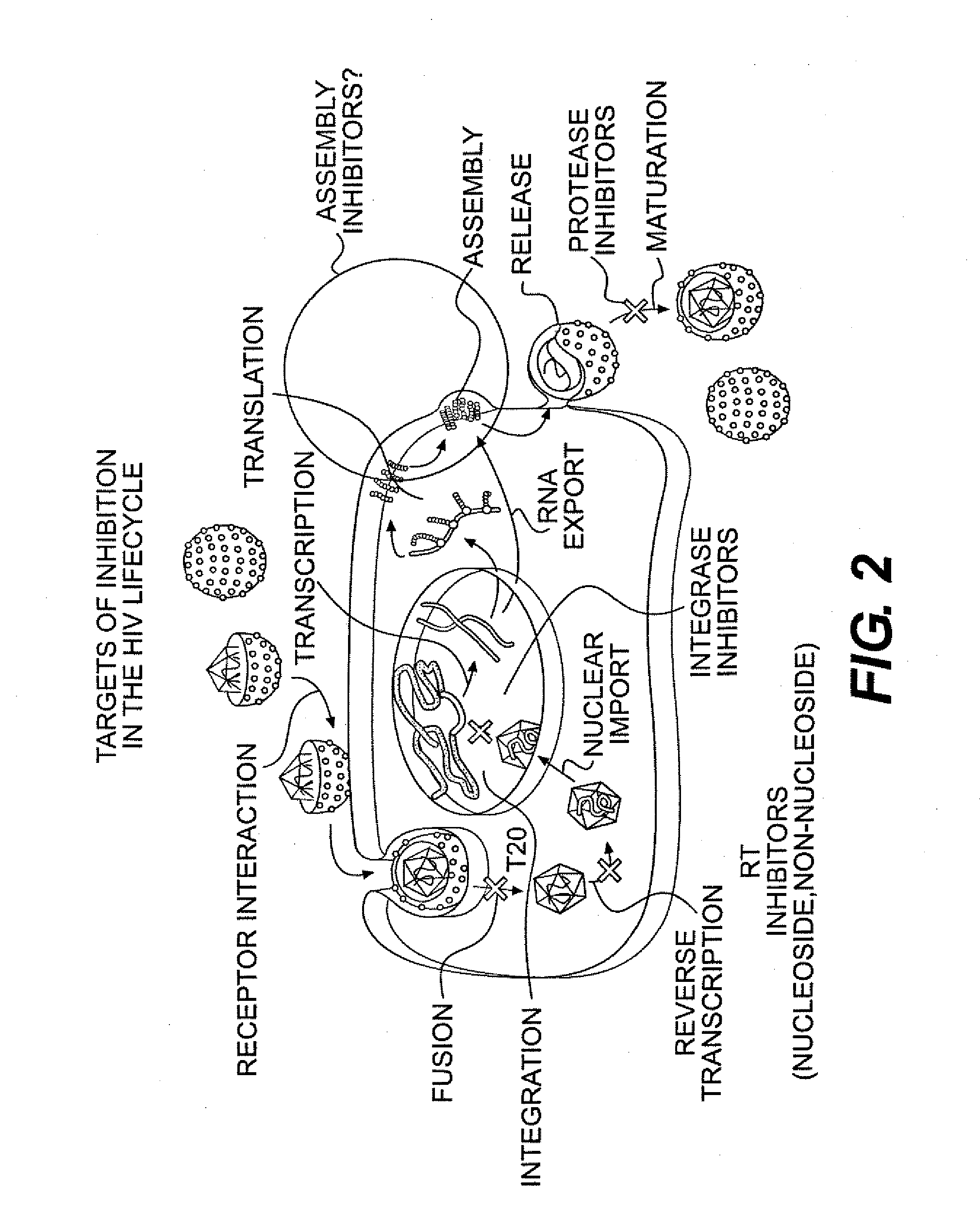
Small molecule inhibitors of hiv-1 capsid assembly
InactiveUS20090176776A1Inhibit HIV replicationInhibition formationBiocideOrganic chemistryDrug targetChemical library
The present invention provides novel methods of treating HIV infections employing small molecule inhibitors identified by chemical library (DIVERSet™ library). These small molecule inhibitors may specifically bind to HIV-1 capsid protein thereby interfering with capsid assembly. The small molecule inhibitors of the present invention can be potential drug targets in the treatment of HIV infection.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA
Microarray channel devices produced by a block mold process
InactiveUS20030203366A1Improve bindingIncrease surface areaBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPeptide librariesBiologic AssaysAssay
Microarrays are made from sections of a molded block having many channels. These channels, which are formed by casting and / or embedding a rod in a moldable solid, are used to immobilize biological and chemical binding components after rod removal. The microarrays can be used in general biological assays, clinical evaluations and chemical library analyses.
Owner:LARGE SCALE PROFEOMICS
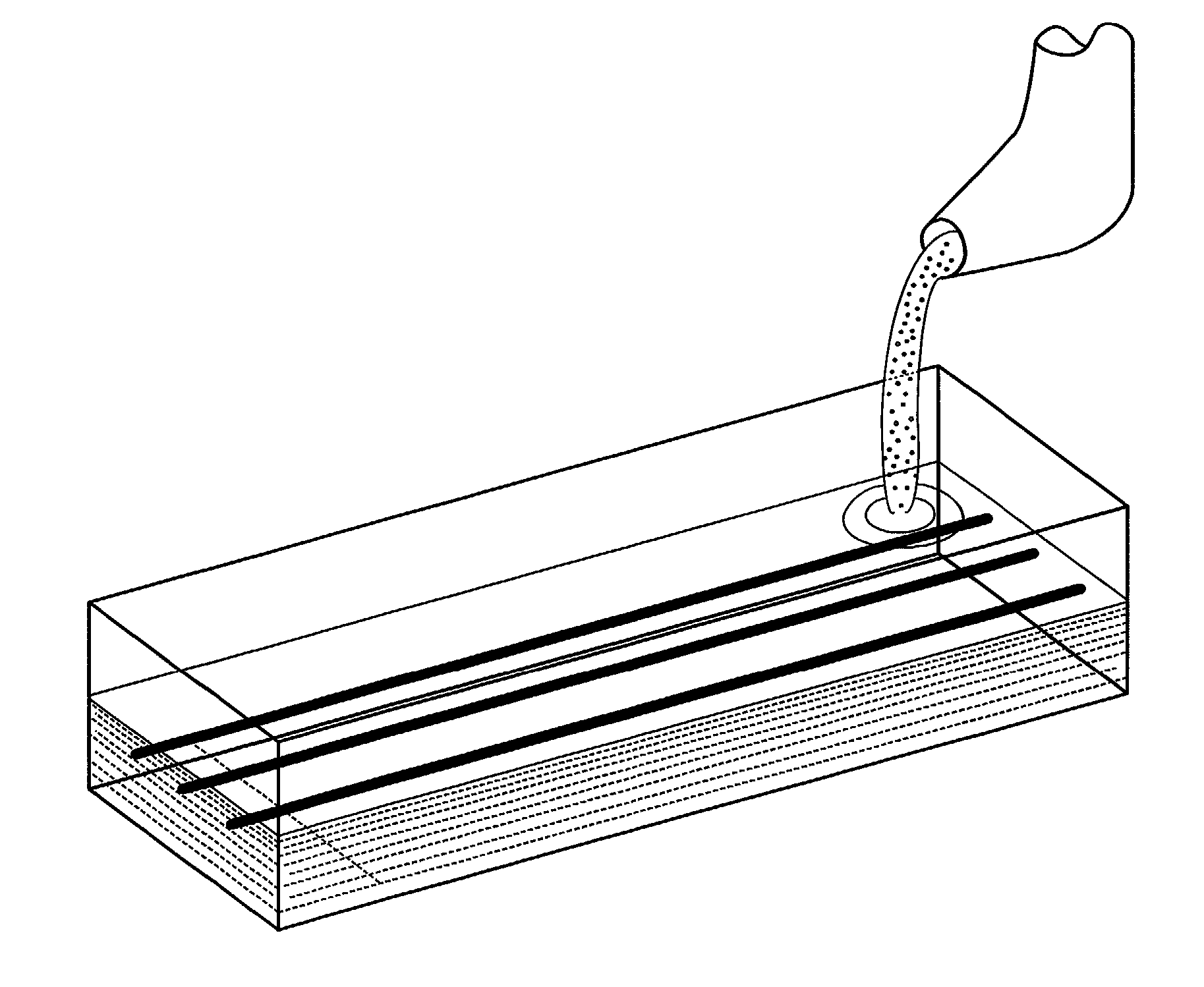
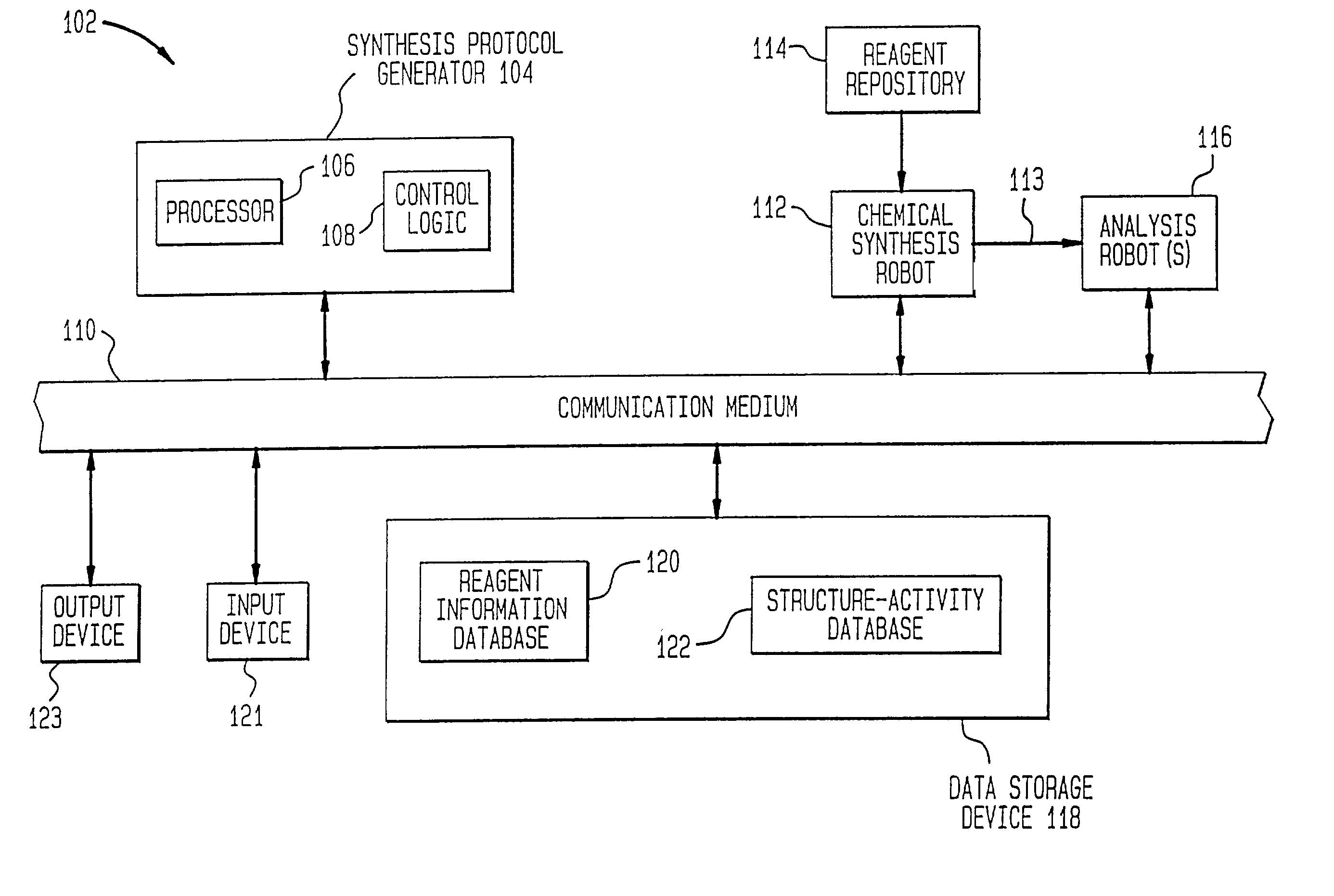
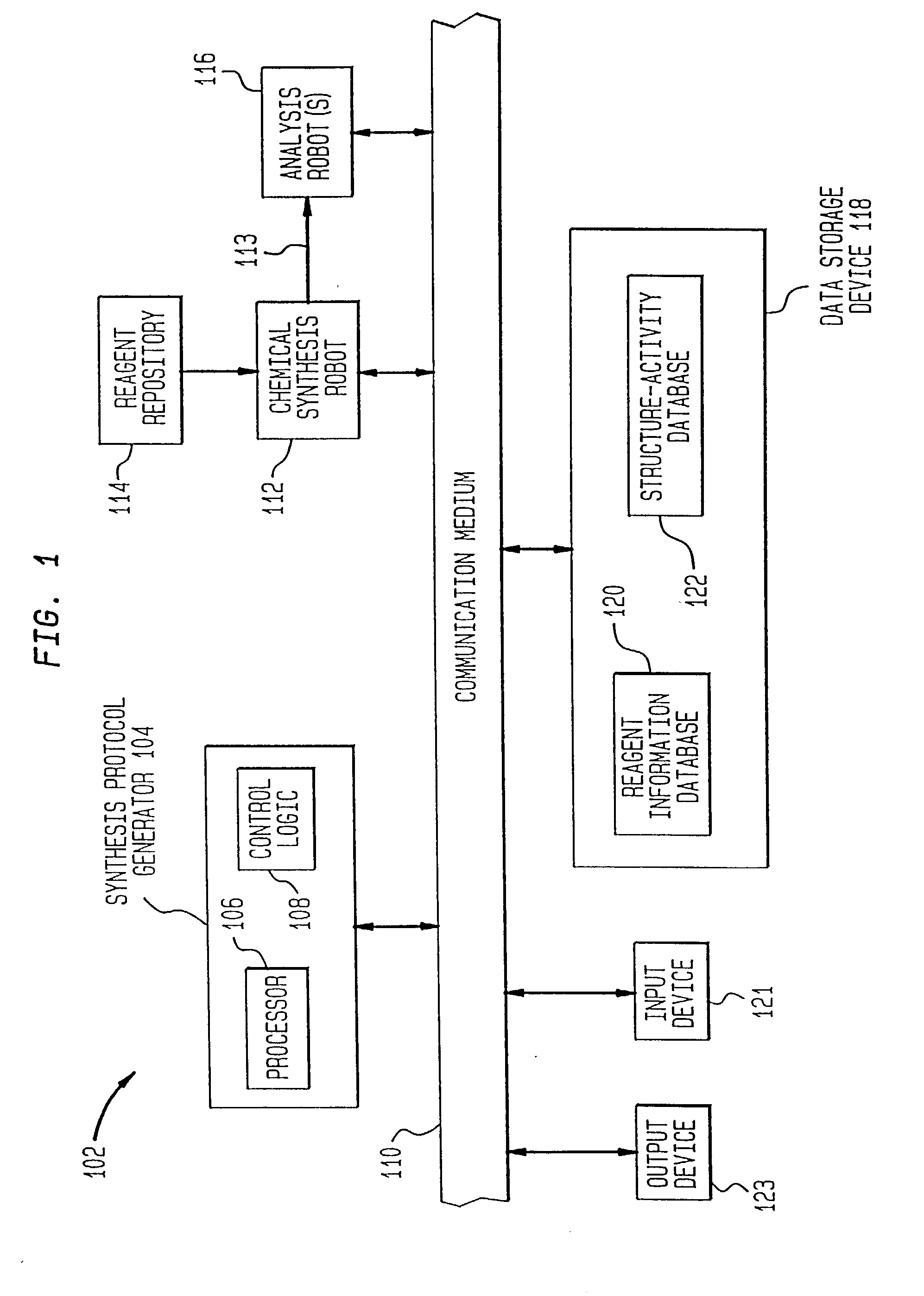
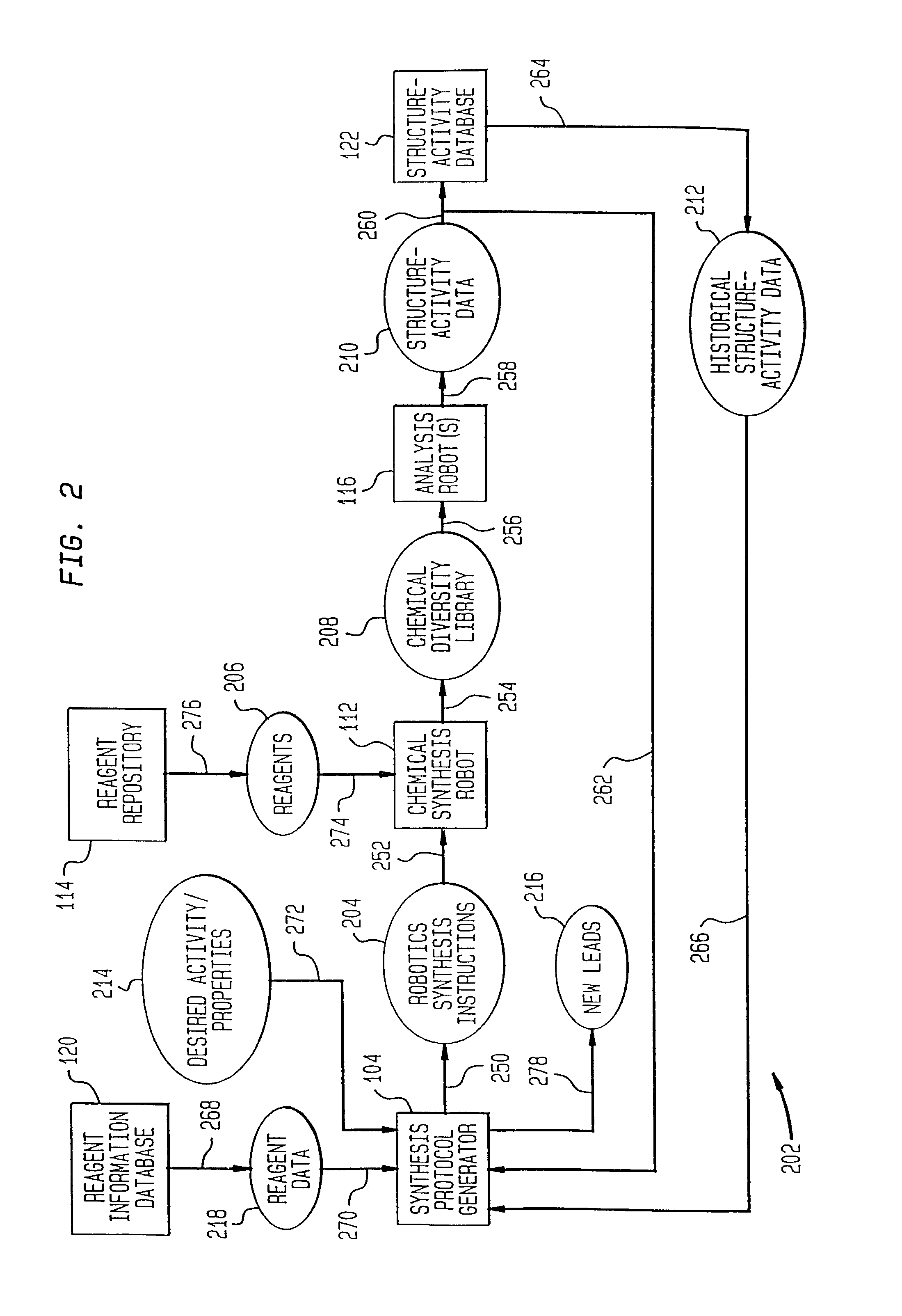
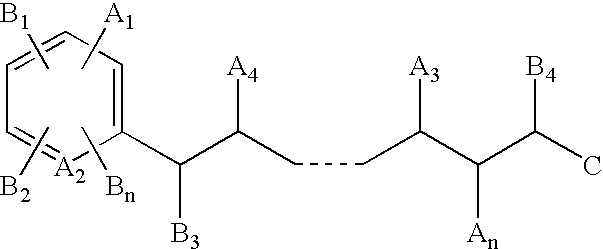
Method of generating chemical compounds having desired properties
InactiveUS20030033088A1Chemical property predictionSequential/parallel process reactionsStructure propertyChemical compound
A computer based, iterative process for generating chemical entities with defined physical, chemical and / or bioactive properties. During each iteration of the process, (1) a directed diversity chemical library is robotically generated in accordance with robotic synthesis instructions; (2) the compounds in the directed diversity chemical library are analyzed to identify compounds with the desired properties; (3) structure-property data are used to select compounds to be synthesized in the next iteration; and (4) new robotic synthesis instructions are automatically generated to control the synthesis of the directed diversity chemical library for the next iteration.
Owner:AGRAFIOTIS DIMITRIS K +3
Mass defect labeling for the determination of oligomer sequences
InactiveUS6962818B2Automatically filter out chemical noiseImproved absolute mass accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOligomerChemical noise
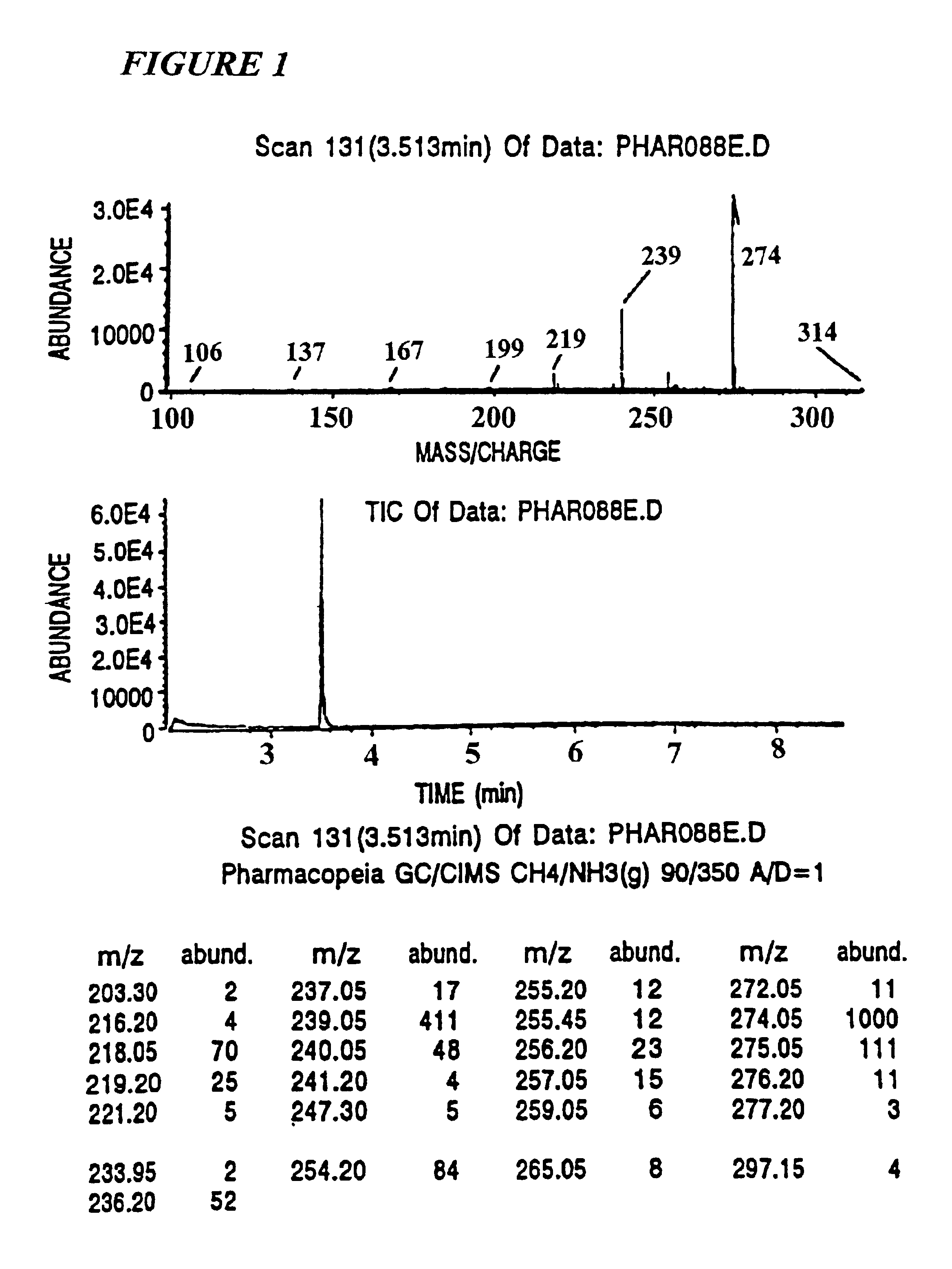
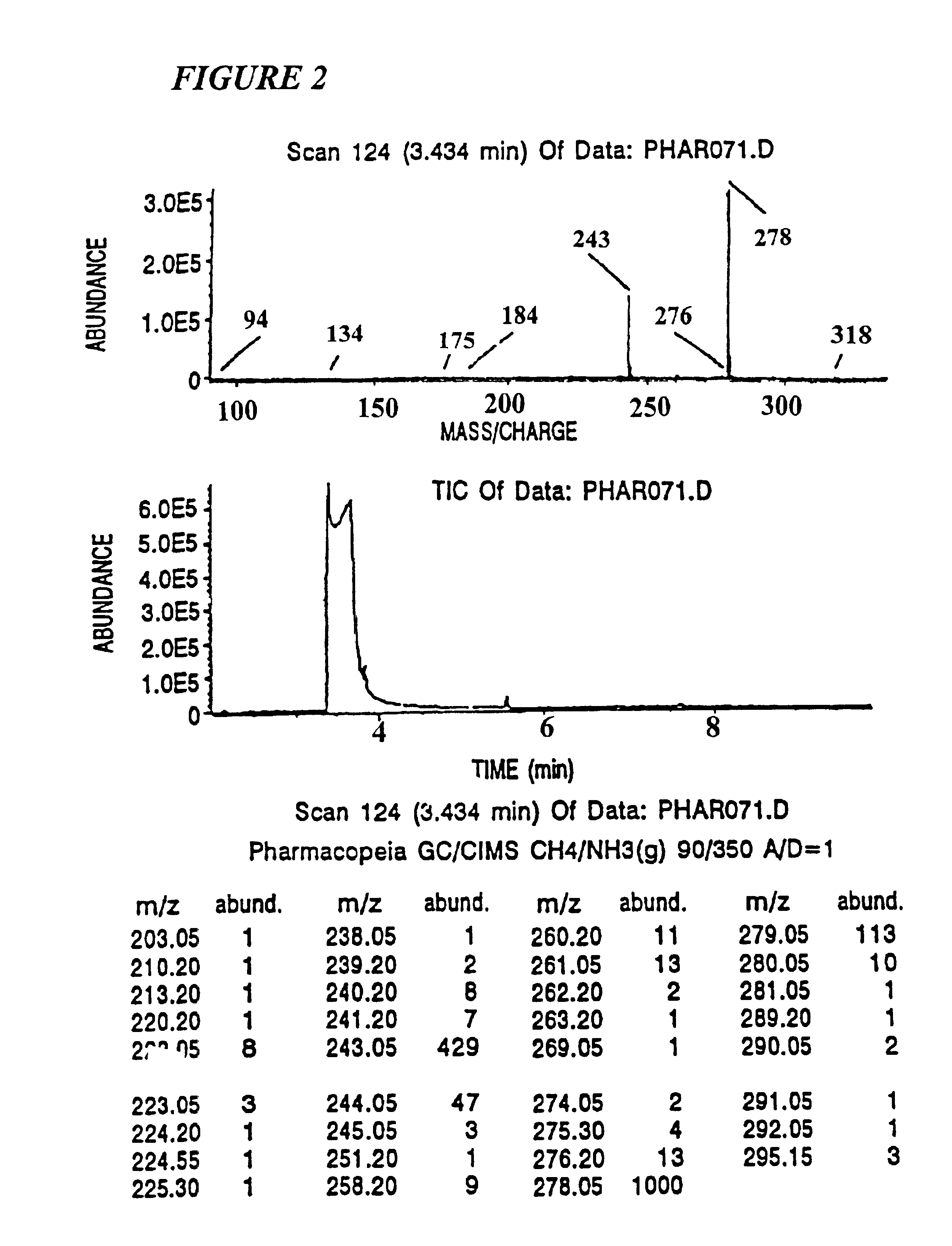
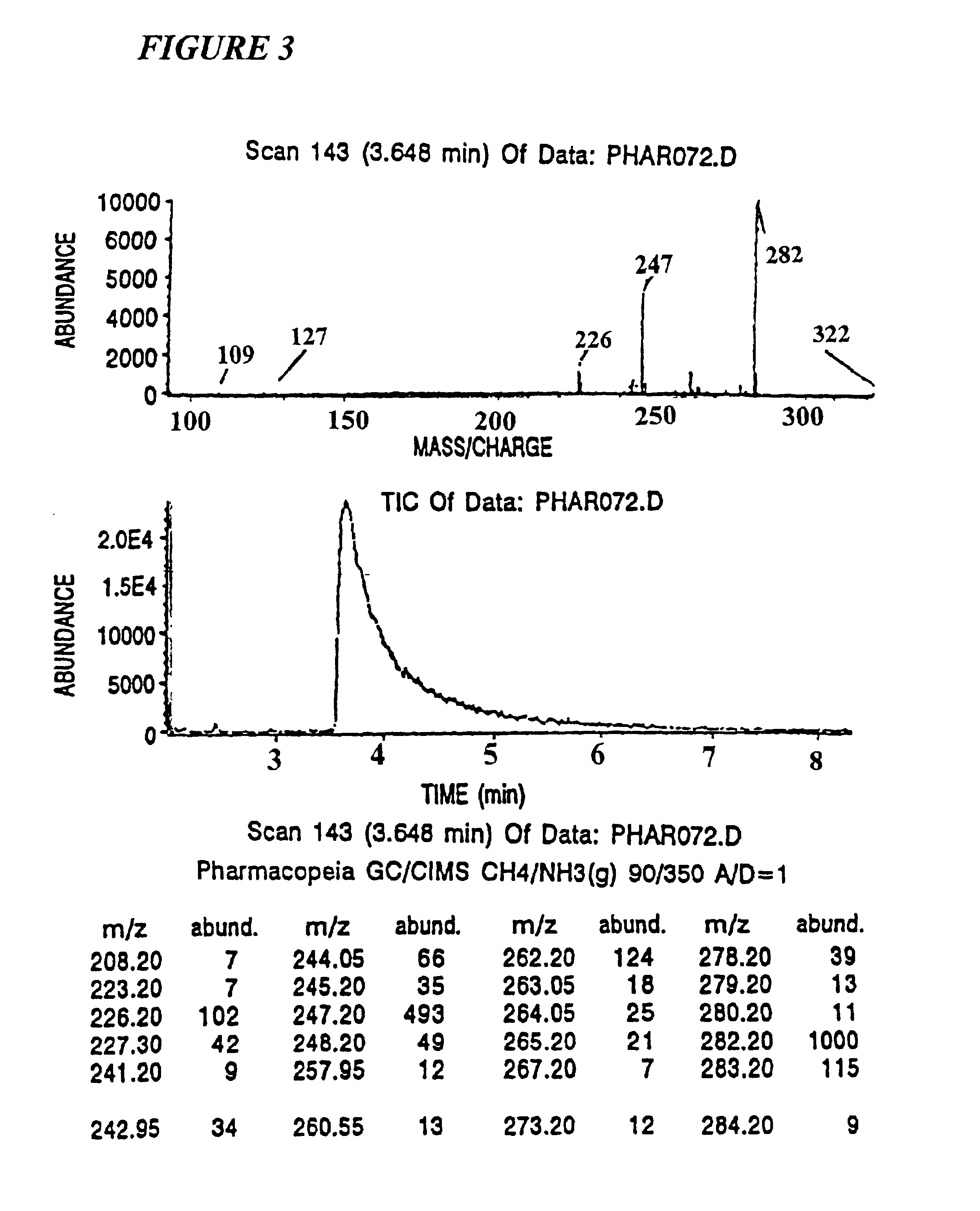
Mass tagging methods are provided that lead to mass spectrometer detection sensitivities and molecular discriminations that are improved over other methods. In particular the methods are useful for discriminating tagged molecules and fragments of molecules from chemical noise in the mass spectrum. These mass tagging methods are useful for oligomer sequencing, determining the relative abundances of molecules from different samples, and identifying individual molecules or chemical processing steps in combinatorial chemical libraries. The methods provided are useful for the simultaneous analysis of multiple molecules and reaction mixtures by mass spectrometric methods.
Owner:TARGET DISCOVERY
Method for fast substructure searching in non-enumerated chemical libraries
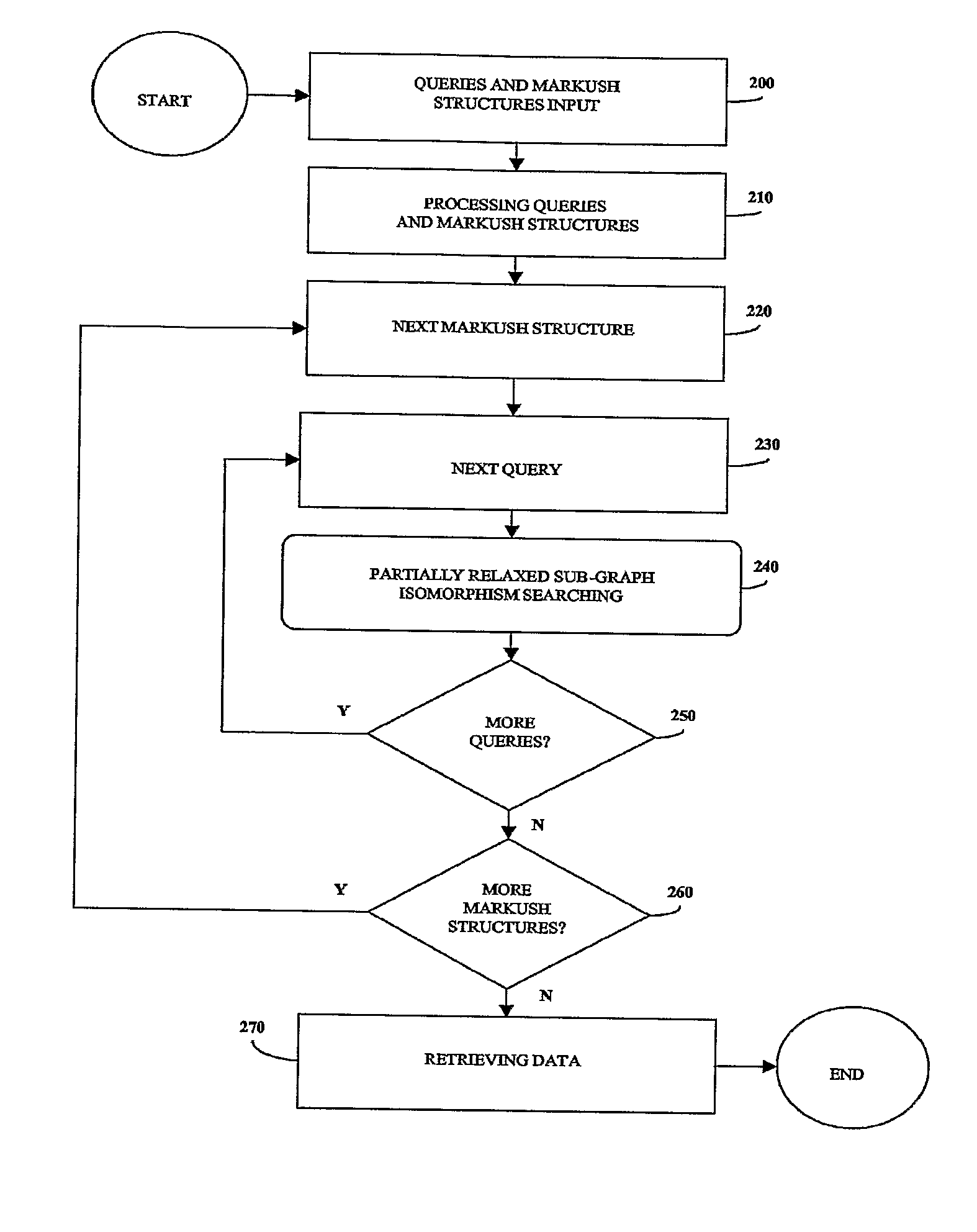
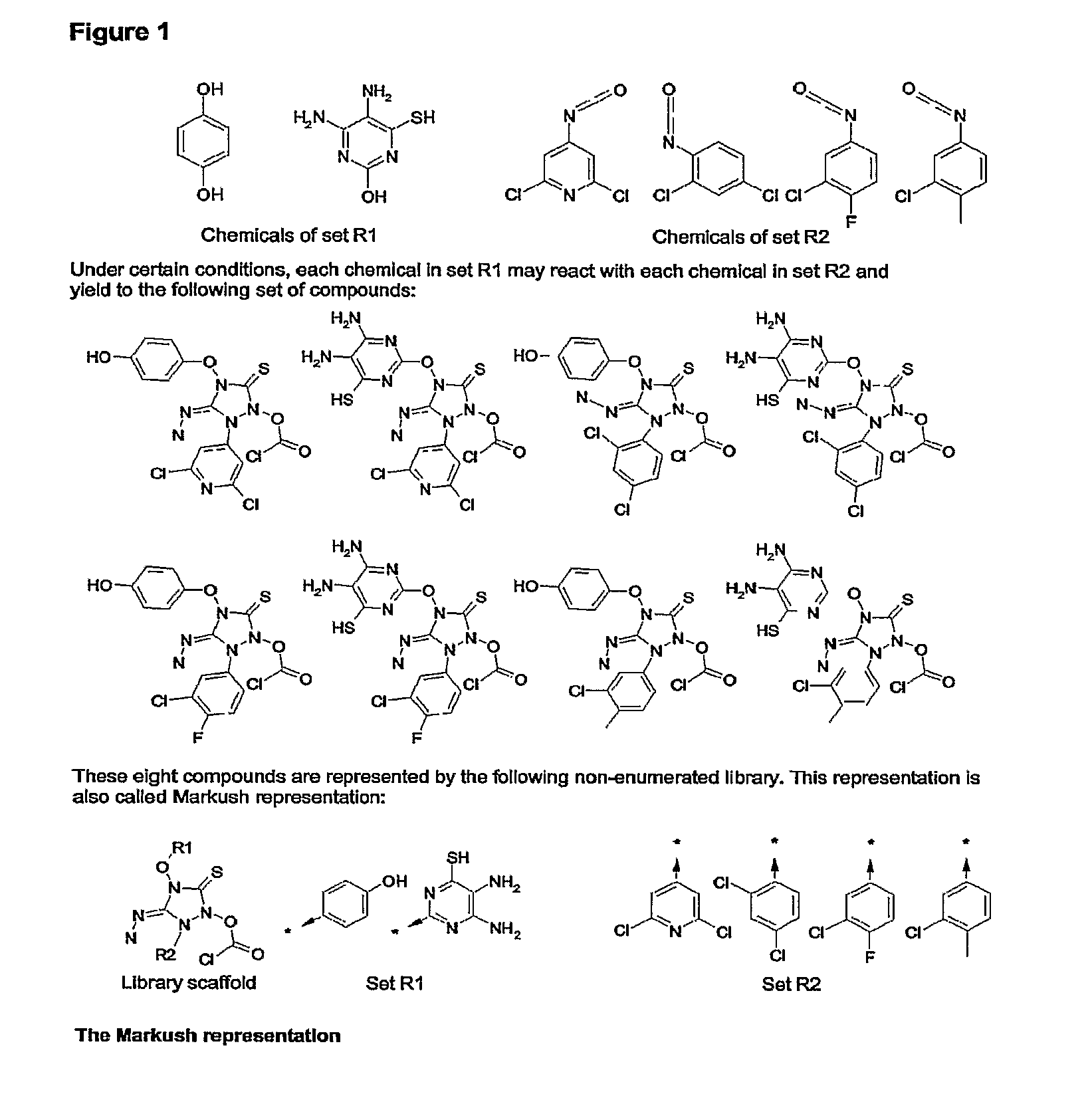
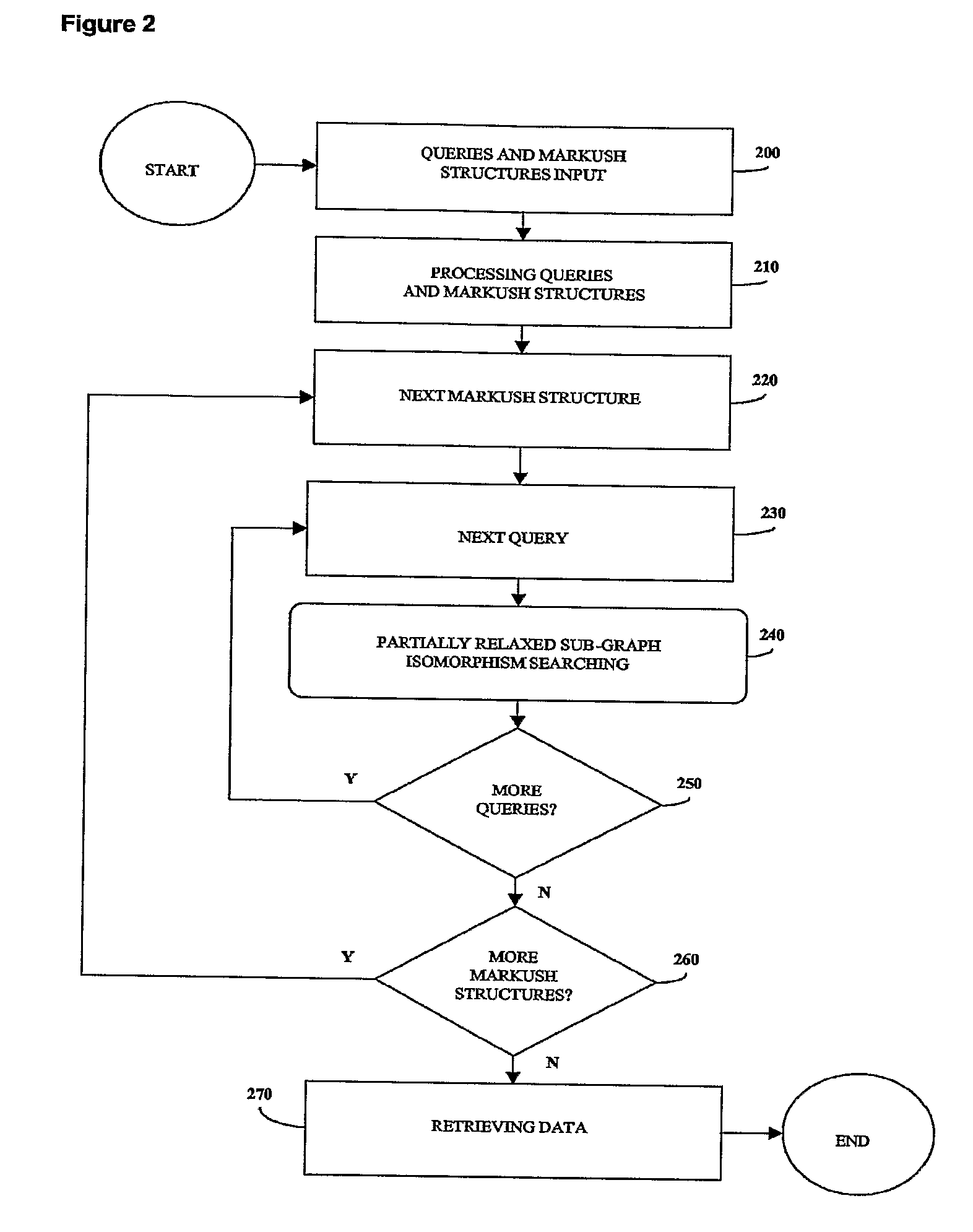
InactiveUS20070260583A1Reduce the required powerRetrieves hits very fastlyChemical structure searchLibrary screeningChemical libraryComputer science
Owner:LAB SERONO SA
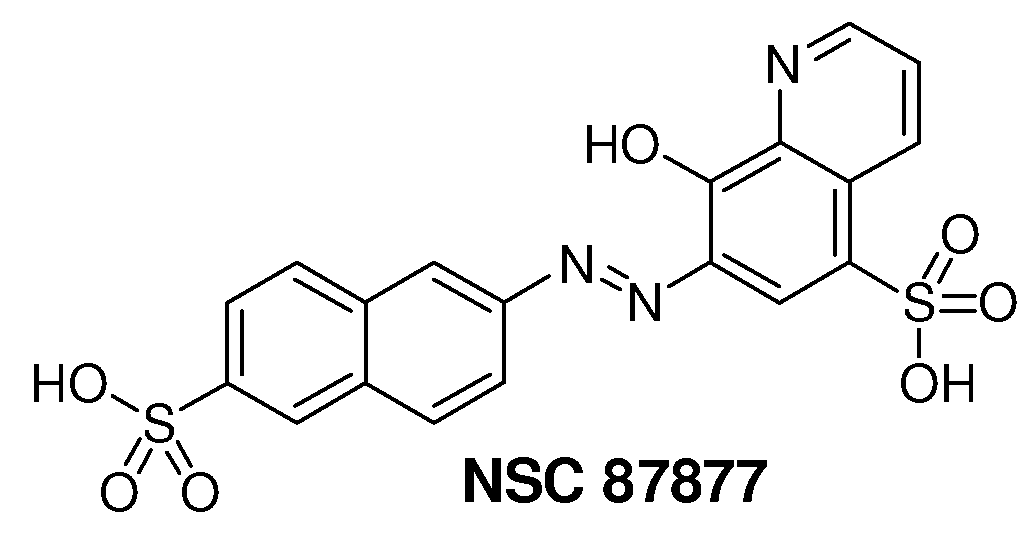
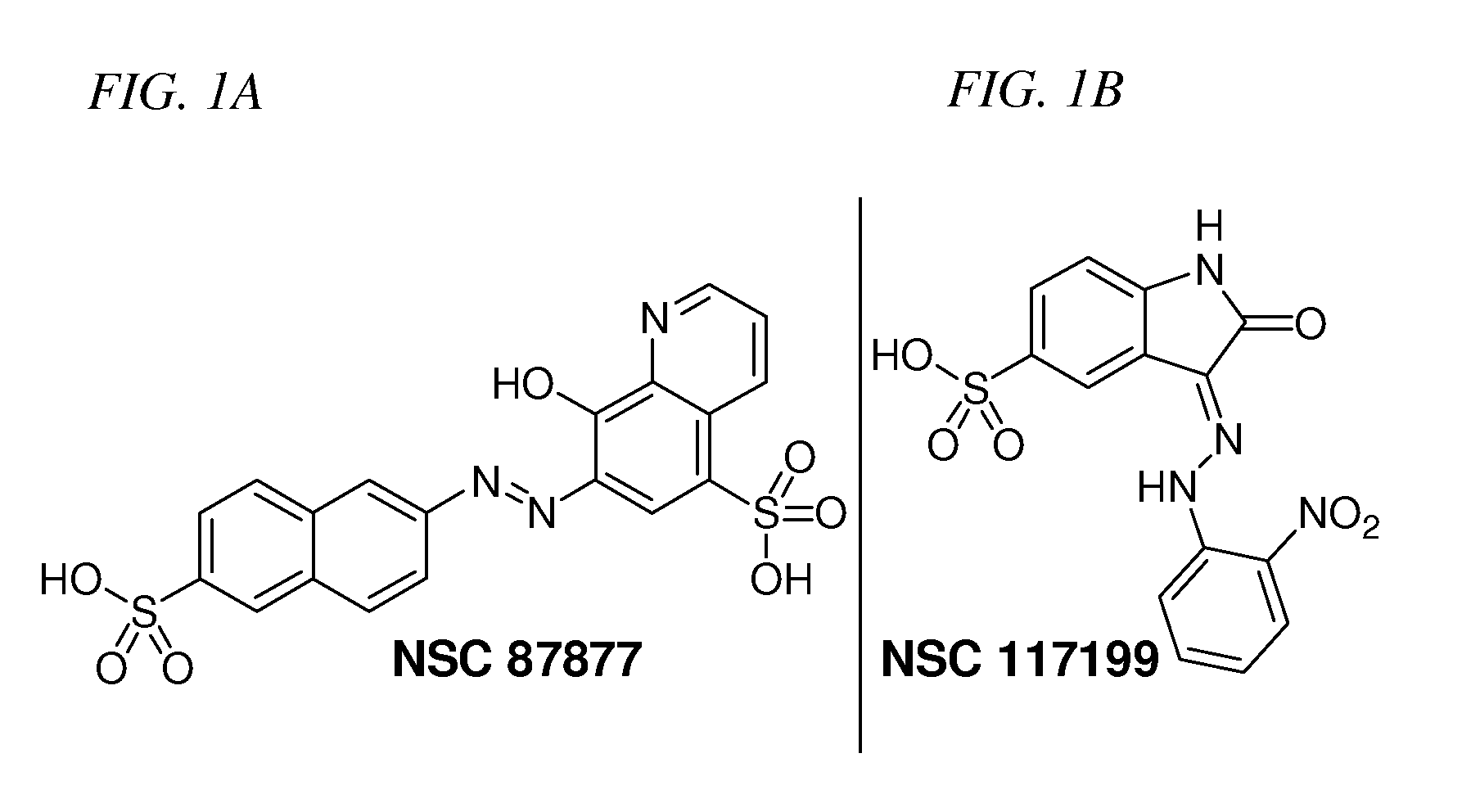
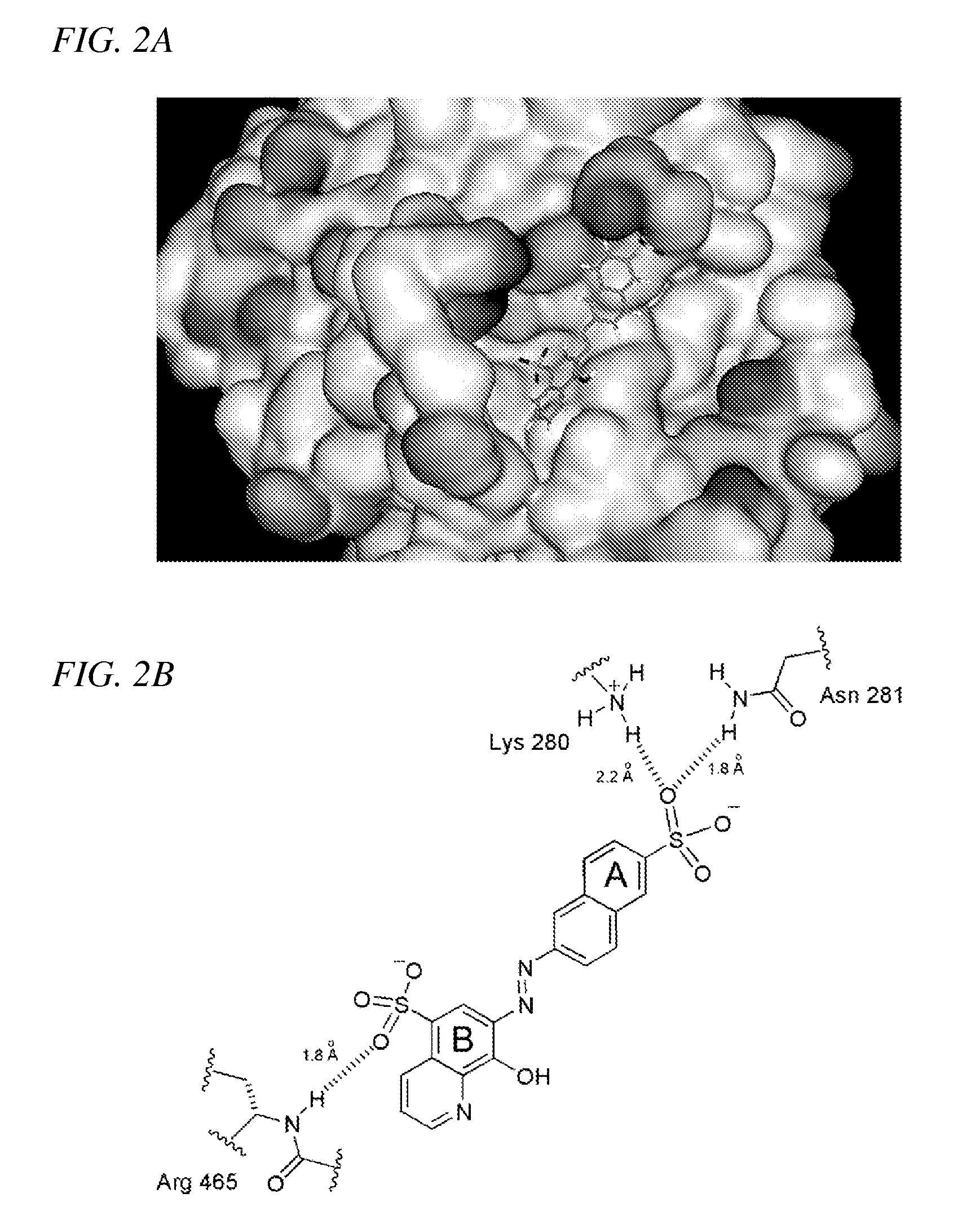
Inhibition of Shp2/PTPN11 Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase by NSC-87877, NSC-117199 and Their Analogs
Compounds and associated methods for inhibiting a protein tyrosine phosphatase. By a combination of experimental and virtual screenings of the NCI Diversity Set chemical library, NSC-87877 and NSC-117199 have been identified as Shp2 PTP inhibitors. Significantly, NSC-87877 is active in cell-based assays and has no detectable off-target effects in the EGF-stimulated Erk1 / 2 activation pathway. Additionally, a number of analogs of NSC-117199 have been produced. These analogs exhibit enhanced protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibition and are found to be potent and / or selective inhibitors of Shp1 and / or Shp2 protein tyrosine phosphatases.
Owner:H LEE MOFFITT CANCER CENT +1
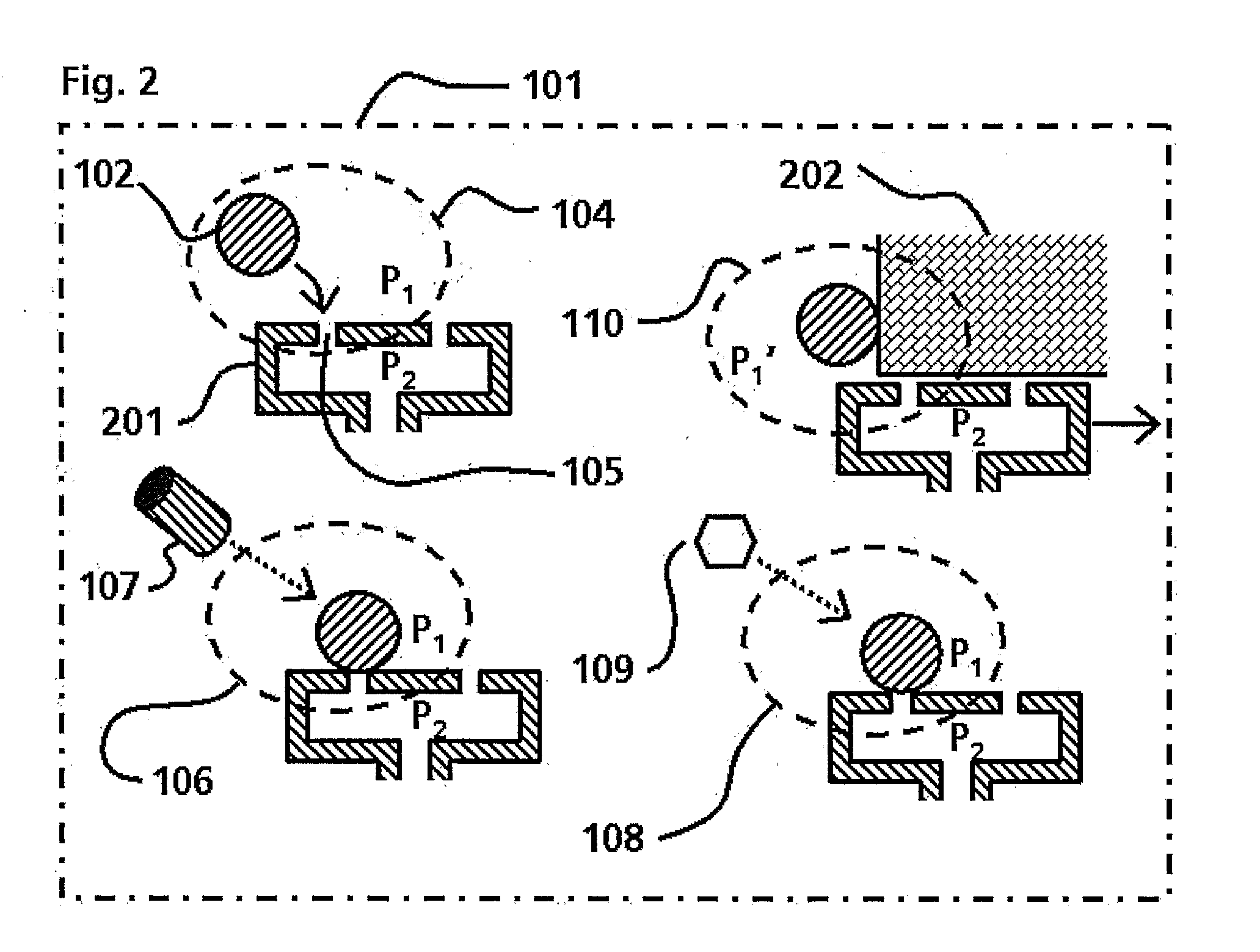
DNA-templated combinatorial library device and method for use
InactiveUS20060099626A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCompound (substance)Chemical library
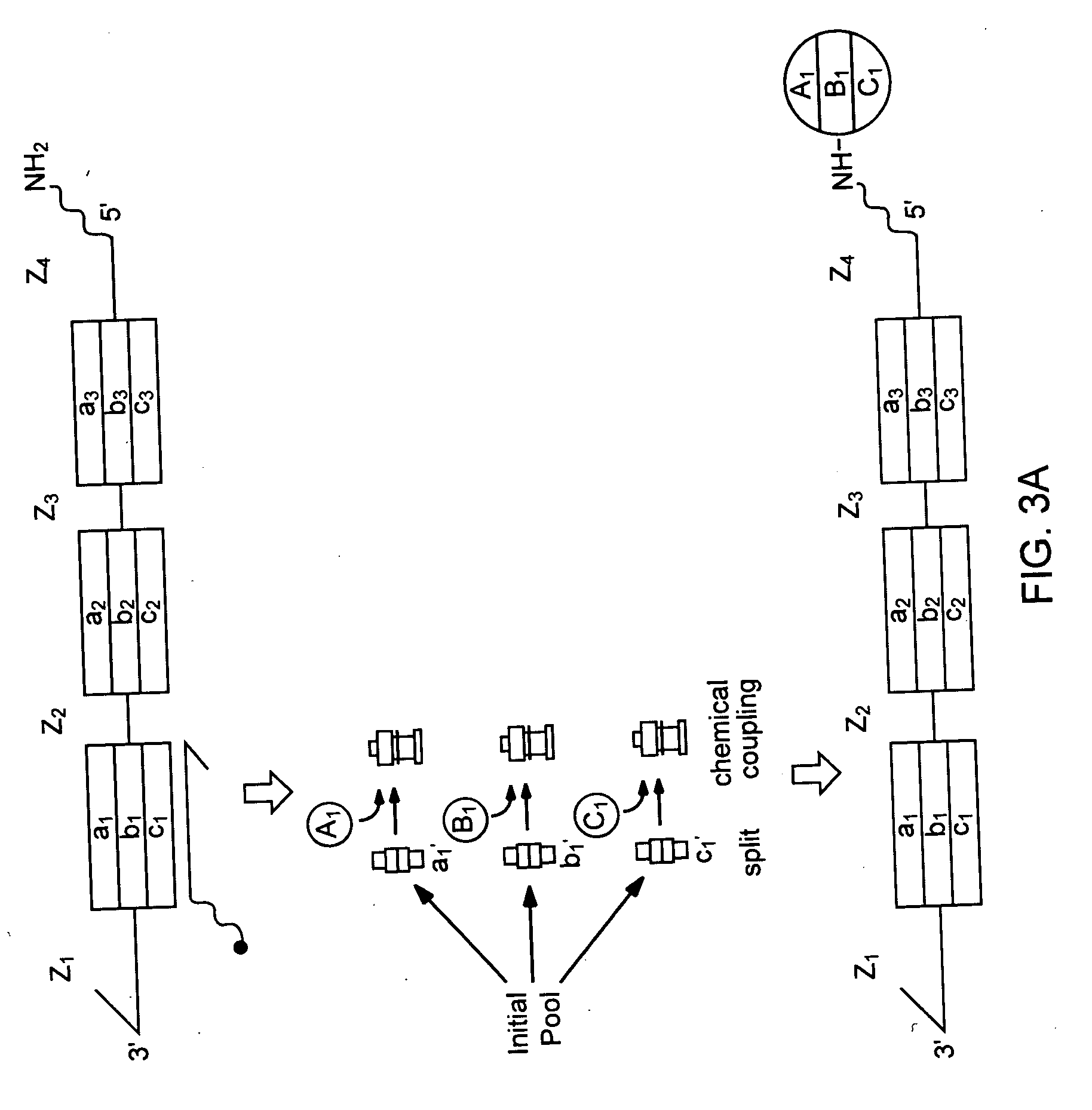
The present invention provides a device and method for synthesizing nucleic acid-templated combinatorial chemical libraries. The device includes a splitting filter having an array of immobilized capture nucleic acids and a chemical coupling filter having an array of non-specific binding features, wherein the plates are positioned to provide for alignment between the capture sites of the first filter and the non-specific binding features of the second filter plate. The molecules bound to the splitting filter can be transferred to the chemical coupling filter and then reacted with site-specific reagents to chemically modify the bound molecules.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Oligonucleotide encoded chemical libraries
ActiveUS20190358629A1Increase concentrationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningMonomer compositionChemical compound
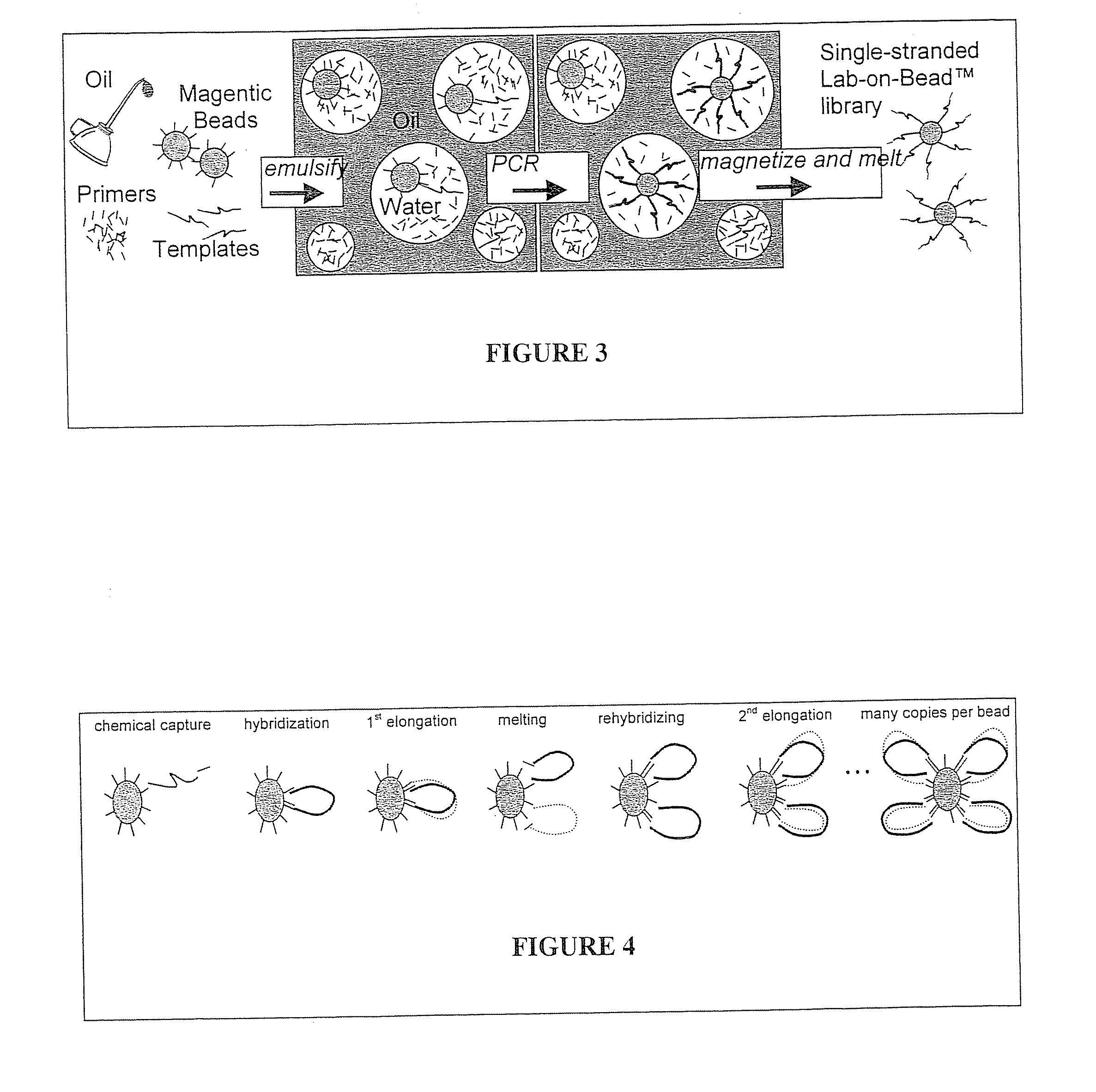
This application provides a bead with a covalently attached chemical compound and a covalently attached DNA barcode and methods for using such beads. The bead has many substantially identical copies of the chemical compound and many substantially identical copies of the DNA barcode. The compound consists of one or more chemical monomers, where the DNA barcode takes the form of barcode modules, where each module corresponds to and allows identification of a corresponding chemical monomer. The nucleic acid barcode can have a concatenated structure or an orthogonal structure. Provided are method for sequencing the bead-bound nucleic acid barcode, for cleaving the compound from the bead, and for assessing biological activity of the released compound.
Owner:PLEXIUM INC
Magnetic, paramagnetic and/or superparamagnetic nanoparticles
The present invention relates to nanoparticles having a mean diameter of <500 nm and comprising, at their surface, a selected material. The nanoparticles are taken up by cells under physiological conditions and can be used to isolate interaction partners of the selected material within the cells. The present invention provides important advantages in that it opens up new ways of identifying cellular components and of delivering a substance of interest specifically to a selected cell compartment. The nanoparticles are also useful as a tool of diagnosis and for the constitution of chemical libraries.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Method of purification of cells
The present invention relates generally to a method for the generation of a substantially homogeneous population of undifferentiated cells. More particularly, the present invention relates to the purification of a substantially homogeneous population of stem cells and their progenitor or precursor cells. Even more particularly, the present invention provides a population of neural stem cells (NSCs). The subject invention is particularly directed to NSCs and precursor cells with the capacity to differentiate into cells and cell lineages required for the development, maintenance or repair of the central nervous system in an animal such as a mammal. The present invention is further directed to NSCs and progenitor and / or precursor cells which are capable of proliferation and differentiation into multiple cell lineages, such as but not limited to neurons, oligodendrocytes, glia and astrocytes. The subject invention further contemplates the use of NSCs and / or precursor cells for the repair or regeneration of tissue, such as tissue associated with the central nervous system, in an animal including a mammal. The NSCs of the present invention may be used to identify naturally occurring molecules such as cytokines as well as molecules obtained from natural product screening or screening of chemical libraries which induce proliferation of the NSCs. Such molecules are useful in the development of therapeutics.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Method for screening antithrombotic drug based on magnetic bead separation
ActiveCN105784879AReasonable process designDiscover synergiesComponent separationPeptide preparation methodsAntithrombotic AgentProtein target
The invention discloses a method for screening an antithrombotic drug based on magnetic bead separation. According to the method, magnetic separation and chemical information collection (liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry) techniques are adopted; a target protein bonder is analyzed; the method is used for screening and evaluating the antithrombotic action of a drug. According to the method for screening the antithrombotic drug based on the magnetic bead separation, an optimal incubation temperature, an incubation time, a pH (potential of Hydrogen) value of a solution during incubation, ionic strength and a denaturizing cleaning solution are screened out through lots of experiments. A screening and evaluating method provided by the invention can be used for screening a large-scale natural product library or a combinatorial chemical library; in comparison with a conventional ultraviolet screening method, the screening efficiency can be obviously improved; a screening time is shortened; moreover, a synergistic effect between compounds can be discovered; the method for screening the antithrombotic drug based on the magnetic bead separation has the advantages of strong operability, quickness, high efficiency, accuracy, good repeatability and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Compositions, Methods, and Kits for Identifying Candidate Molecules from Encoded Chemical Libraries
InactiveUS20120021940A1Rapidly select and characterizeRapid, automated screening of small molecule librariesNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementSubject matterChemical library
The subject matter relates to relates to a one-bead-one-sequence composition, a library of tagged chemicals comprising a plurality of one-bead-one-sequence compositions, a method for identifying a candidate molecule from a library of tagged chemicals, and a composition produced by a process, all as described herein.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV
System, method and computer program product for fast and efficient searching of large chemical libraries
InactiveUS7416524B1Reduces of resourceExcessive amount of resourceOrganic chemistry methodsLibrary screeningAlgorithmChemical compound
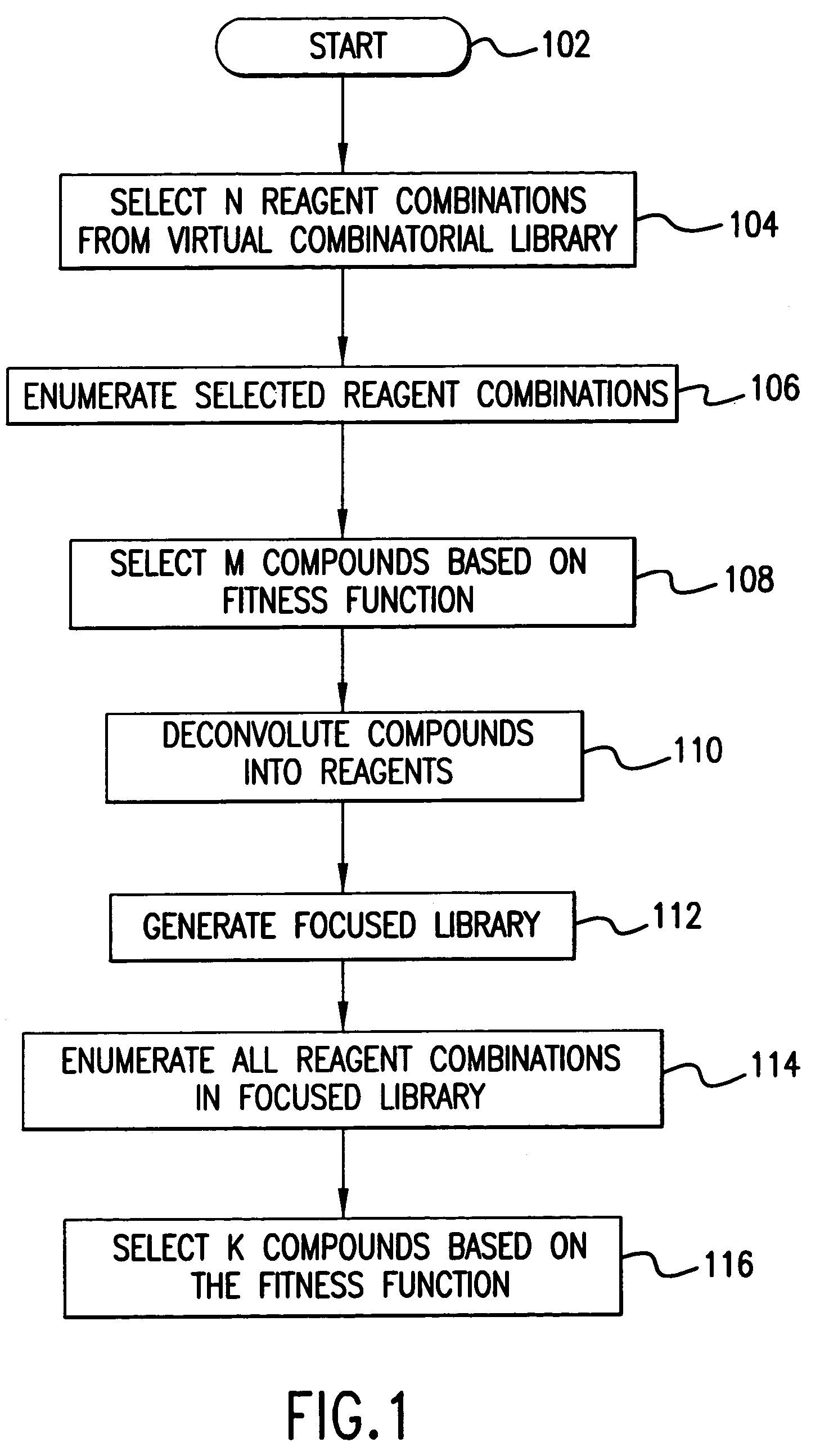
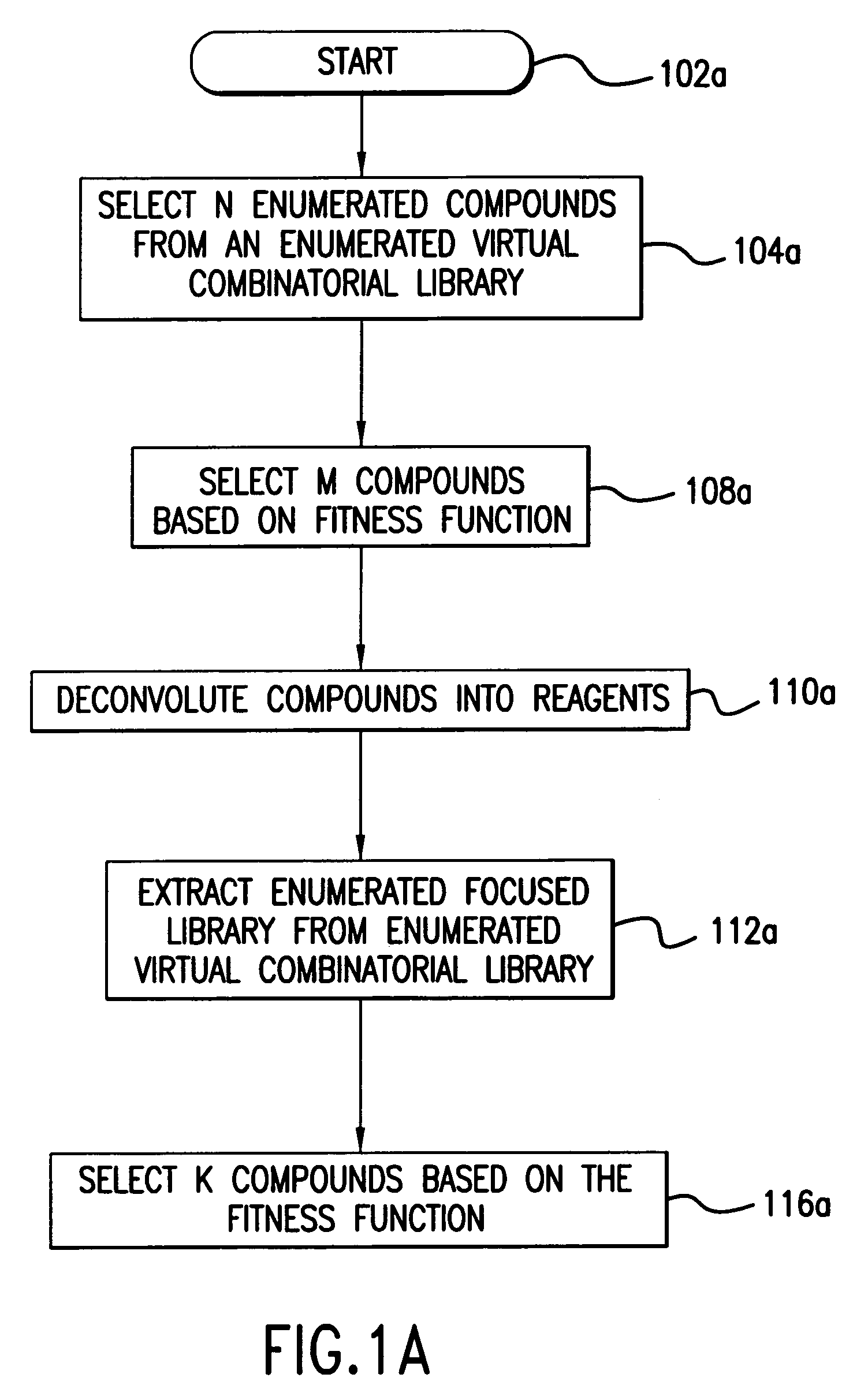
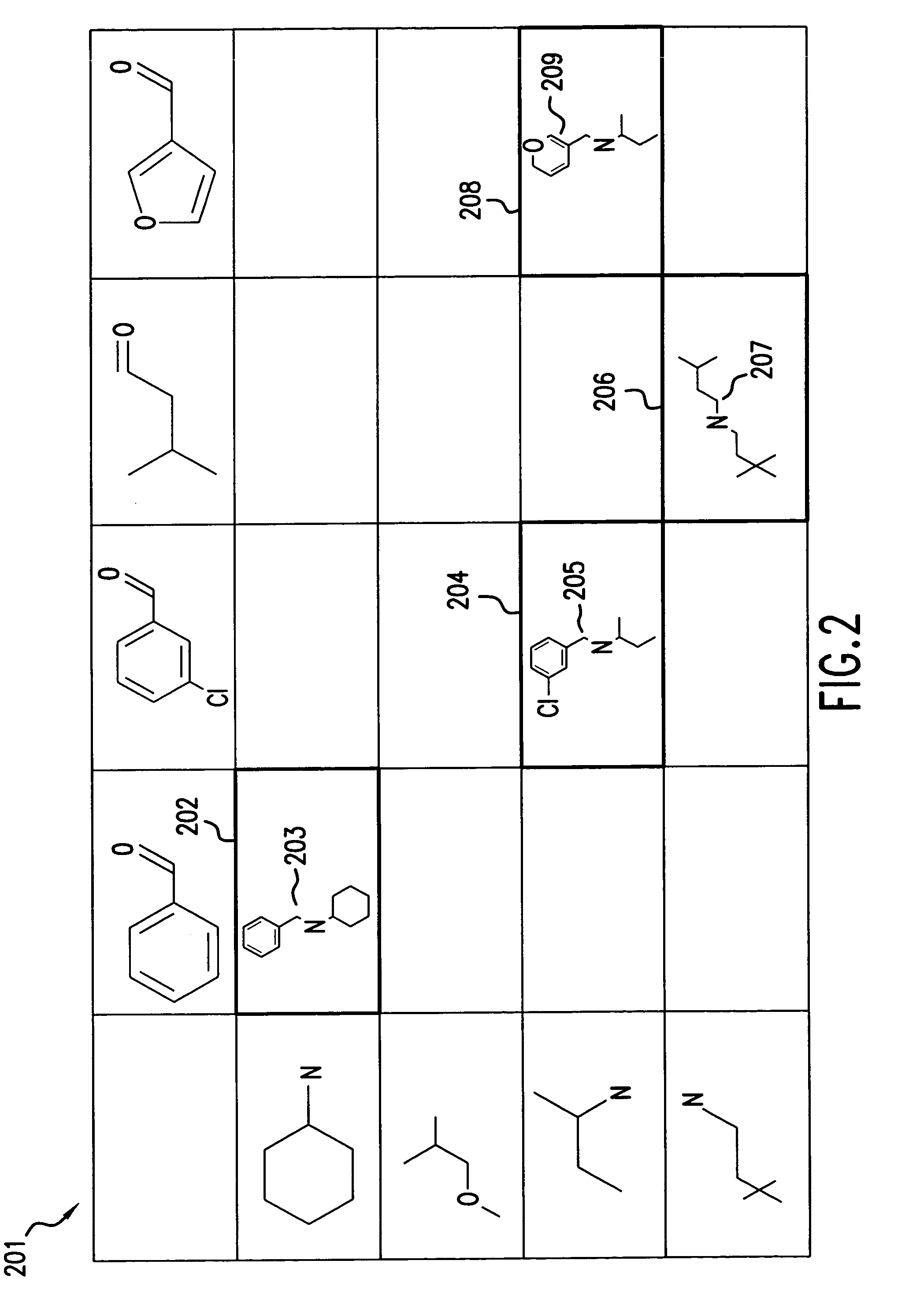
A system, method, and computer program product for fast and efficient searching of large virtual combinatorial libraries based on a fitness function. According to the method of the present invention, a first set of N reagent combinations are selected, for example, at random, from a virtual combinatorial library. Each reagent combination in the first set is then enumerated to produce a first set of enumerated compounds. M number of compounds of the first set of enumerated compounds are selected based on the fitness function. The M compounds are then deconvoluted into reagents to generate a focused library. Substantially every reagent combination associated with the focused library is enumerated to produce a second set of enumerated compounds. K number of compounds of the second set of enumerated compounds are then selected based on the fitness function. These K compounds represent a near optimal selection of compounds based on the fitness function.
Owner:3 DIMENSIONAL PHARMA
Oligonucleotide encoded chemical libraries
InactiveUS20190210018A1Preventing and minimizingMinimizing and preventing leakage of fluidMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDNA barcodingChemical compound
This application provides a bead with a covalently attached chemical compound and a covalently attached DNA barcode and methods for using such beads. The bead has many substantially identical copies of the chemical compound and many substantially identical copies of the DNA barcode. The compound consists of one or more chemical monomers, where the DNA barcode takes the form of barcode modules, where each module corresponds to and allows identification of a corresponding chemical monomer. The nucleic acid barcode can have a concatenated structure or an orthogonal structure. Provided are method for sequencing the bead-bound nucleic acid barcode, for cleaving the compound from the bead, and for assessing biological activity of the released compound.
Owner:PLEXIUM INC
Chemical testing
ActiveUS20180024121A1Easy and inexpensive to manufactureEasy to handleMicrobiological testing/measurementCell culture supports/coatingCelluloseCulture cell
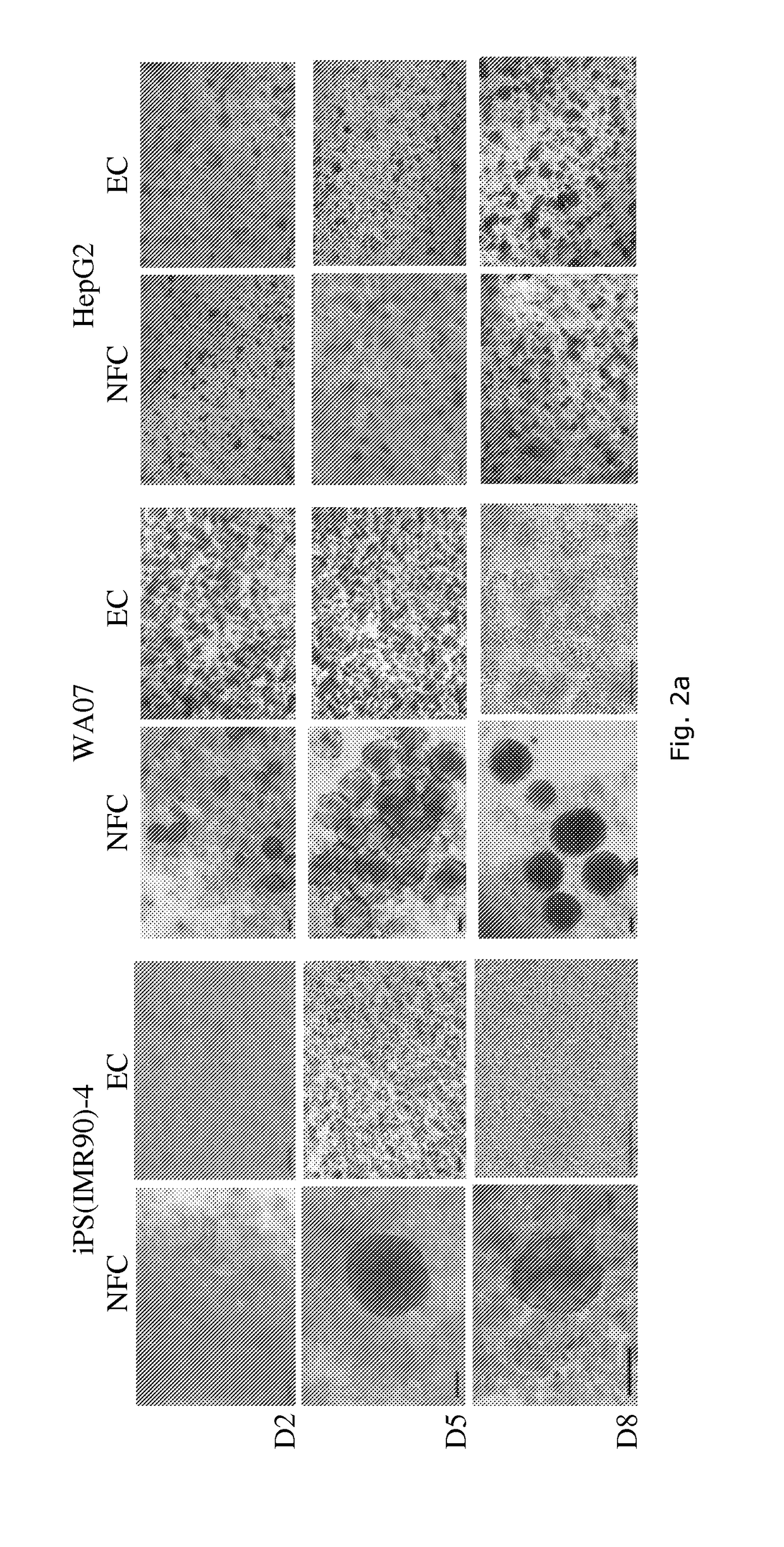
The present invention relates a method for chemical testing, comprising culturing cells in a first plant-derived nanofibrillar cellulose (NFC) hydrogel to obtain in vivo like cells; exposing the in vivo like cells to a test chemical;optionally within another plant-derived NFC hydrogel; incubating the exposed in vivo like cells; detecting during or after incubating, the impact of the test chemical on the in vivo like cells by at least one detection; and removing the plant-derived NFC hydrogel at least once at any stage after obtaining the in vivo like cells and before at least one detection used for detecting the impact of the test chemical on the in vivo like cells. The invention further relates to the use of plant-derived NFC hydrogel in a method for chemical testing, the use of in vivo like cells obtained by culturing cells in plant-derived NFC hydrogel for chemical testing and to a kit for chemical testing comprising plant-derived NFC hydrogel, instructions and a cell or test chemical library.
Owner:UPM-KYMMENE OYJ
Infrared gas detection and spectral analysis method
ActiveUS7956761B2Easy to detectEasy to handleRadiation pyrometryComponent separationFrequency spectrumLogarithmic space
A gas detection system and method for analysis of infrared gas spectra is used for chemical threat detection, quantification and alarm, using a chemical library, a chemical threat list, and a background model that incorporates the data history, allows spectra containing interferent signals into the background model, the model being updated using delay buffering to prevent threat spectra incorporation and using exponential decays to preferentially represent recent background history, all computed in the logarithmic space for rapid detection and alarm.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
In situ interaction determination
ActiveUS10053725B2Quick identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMetabolitePost translational
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
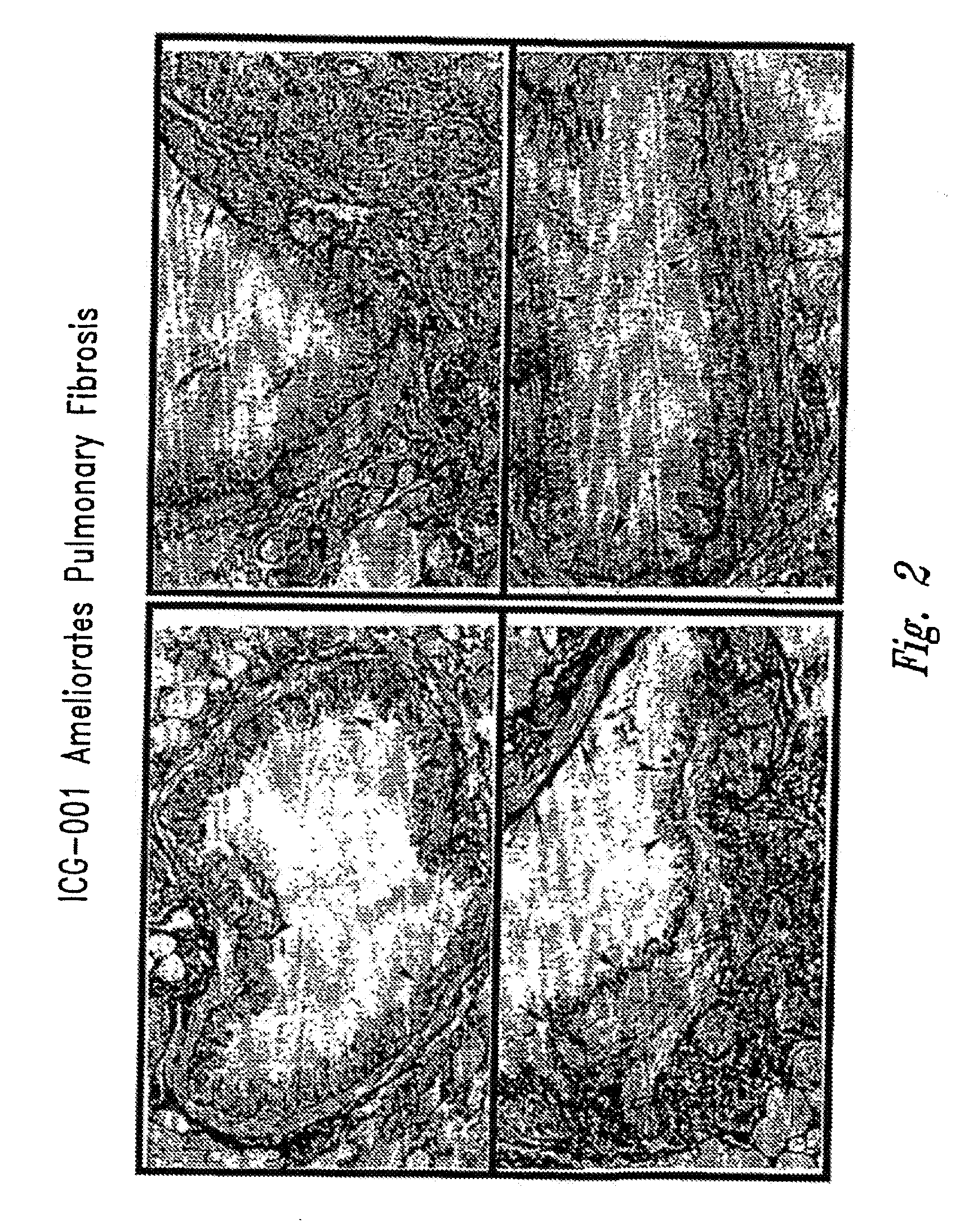
Alpha-helix mimetics and methods relating to the treatment of fibrotic disorders
The invention provides α-mimetic structures and a chemical library relating thereto. Additionally, the invention provides methods wherein α-mimetic compounds are used to treat fibrotic disorders.
Owner:INST FOR CHEM GENOMICS
Cellular arrays comprising encoded cells
InactiveUS20050158702A1Determine effectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSensor arrayFiber
A biosensor, sensor array, sensing method and sensing apparatus are provided in which individual cells or randomly mixed populations of cells, having unique response characteristics to chemical and biological materials, are deployed in a plurality of discrete sites on a substrate. In a preferred embodiment, the discrete sites comprise microwells formed at the distal end of individual fibers within a fiber optic array. The biosensor array utilizes an optically interrogatable encoding scheme for determining the identity and location of each cell type in the array and provides for simultaneous measurements of large number of individual cell respnses to target analyses. The sensing method utilizes the unique ability of cell populations to respond to biologically significant compounds in a characteristic and detectable manner. The biosensor array and measurement method may be employed in the study of biologically active materials in situ environmental monitoring, monitoring of a variety of bioprocesses, and for high throughput screening of large combinatorial chemical libraries.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Methods of using glucan synthase pathway reporter genes to screen for antifungal compounds
The present invention relates to methods of using nucleotide sequences from the promoter region of at least one of seven S. cerevisiae genes whose expression is an indicator of the inhibition or modulation of the glucan synthase pathway in S. cerevisiae. This invention envisions using at least one target polynucleotide sequence, each target polynucleotide sequence being operably linked to the promoter region of one of the seven glucan synthase pathway reporter genes, to screen chemical libraries and natural products for compounds which can be used as antifungal agents for use against a variety of fungal pathogens. This invention also envisions using the methods of the invention to assay the efficacy of and / or specificity of antifungal agents, and / or to monitor the activity of the glucan synthase pathway.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Methods relating to the treatment of fibrosis
The invention provides α-helix mimetic structures of formula (I) with the definitions of A, B, D, E, G, W, R1 and R2 as set out in the description and a chemical library relating thereto. The compounds, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds, and methods of the invention using the compounds, relate to the reversal of fibrotic conditions, such as pulmonary fibrosis.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com