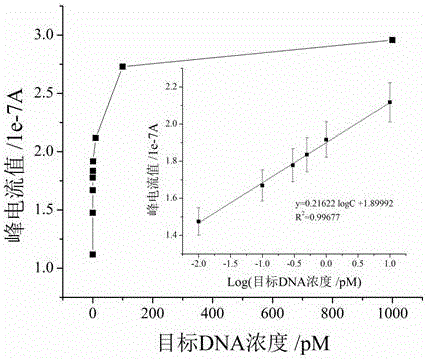
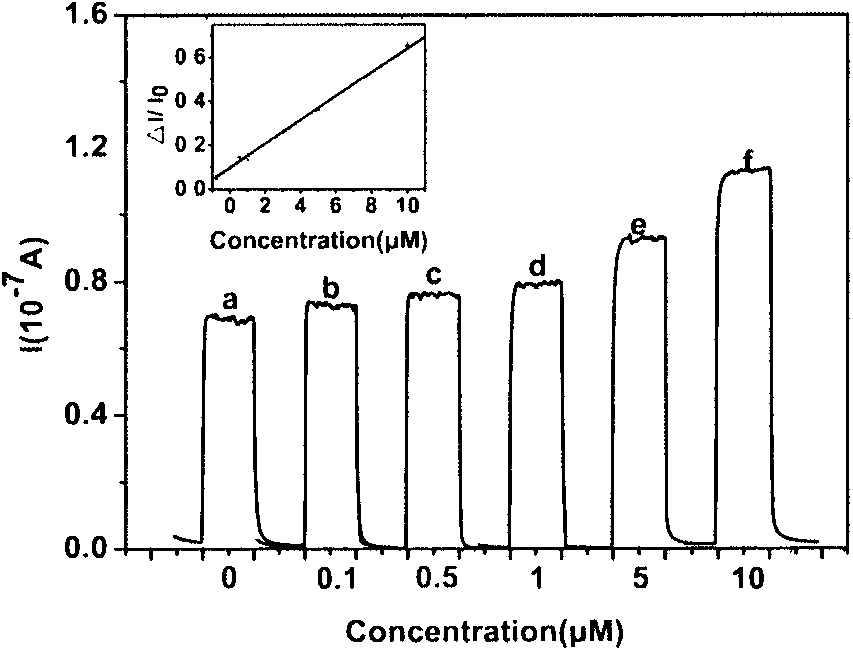
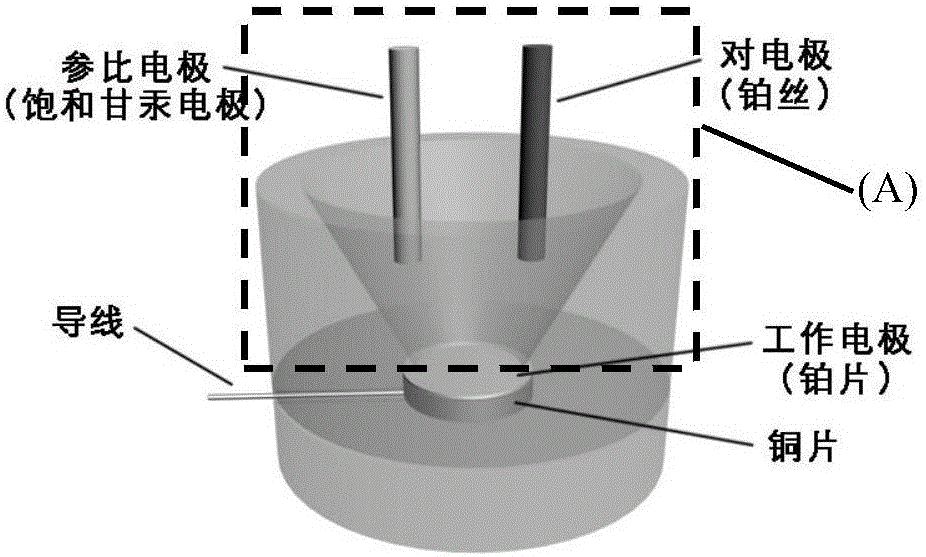
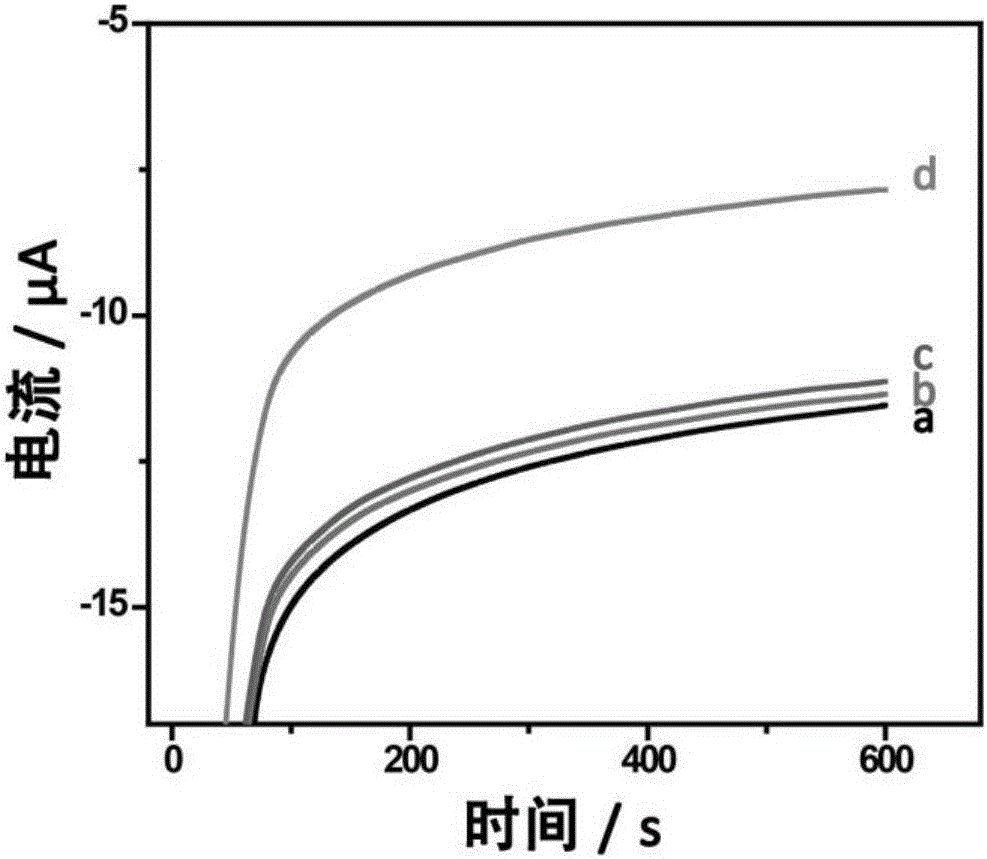
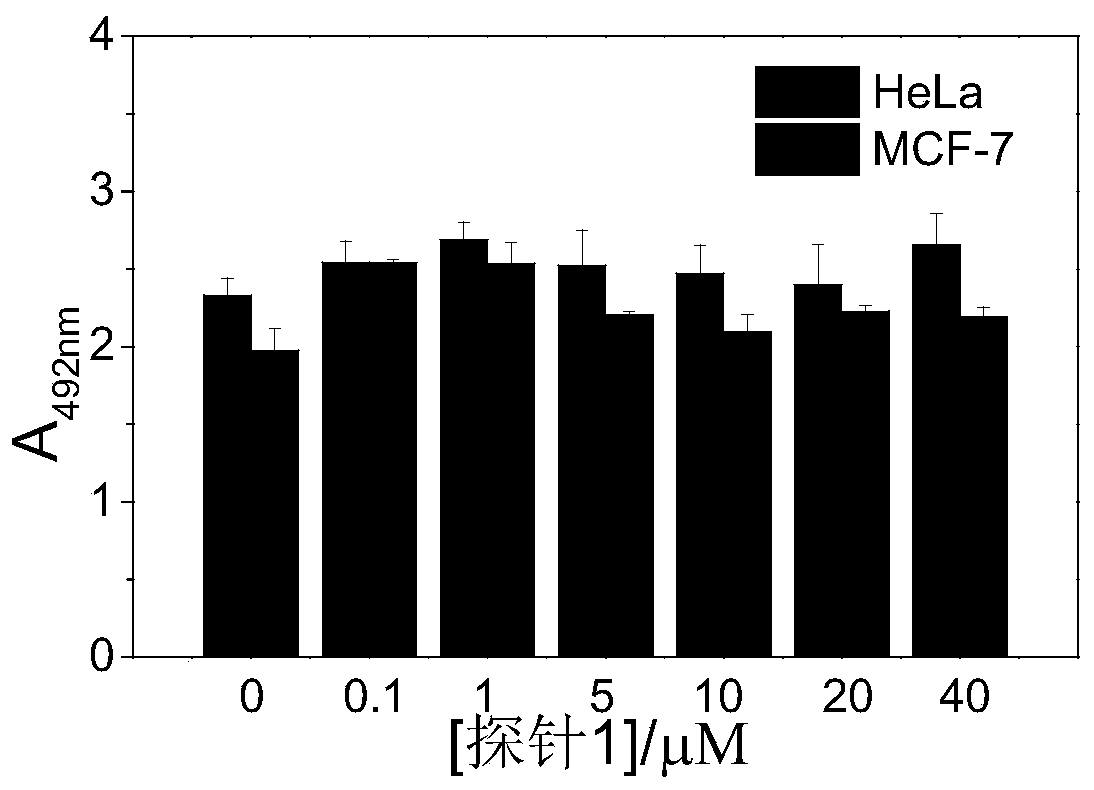
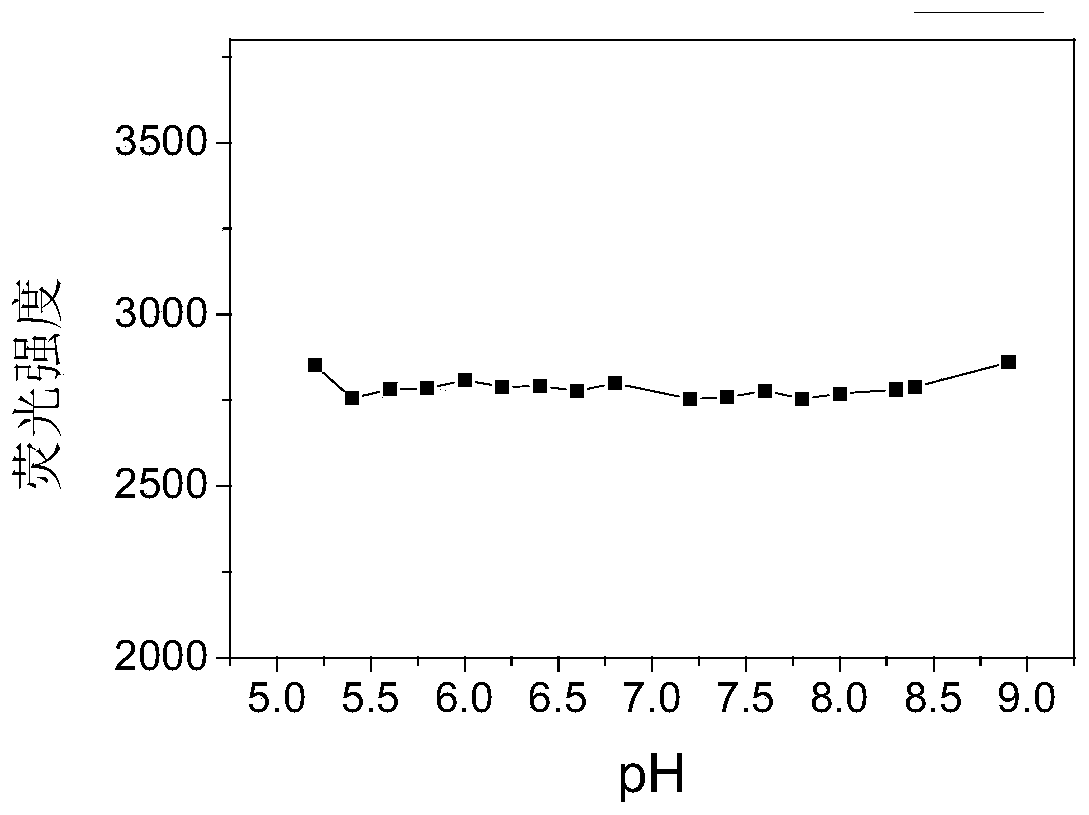
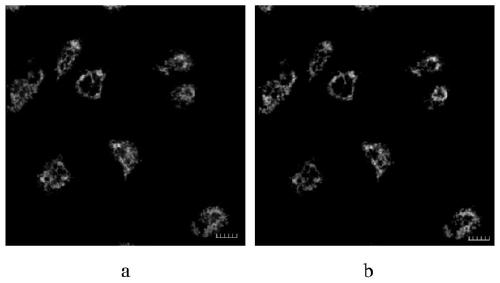
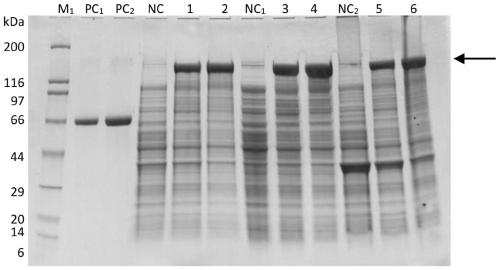
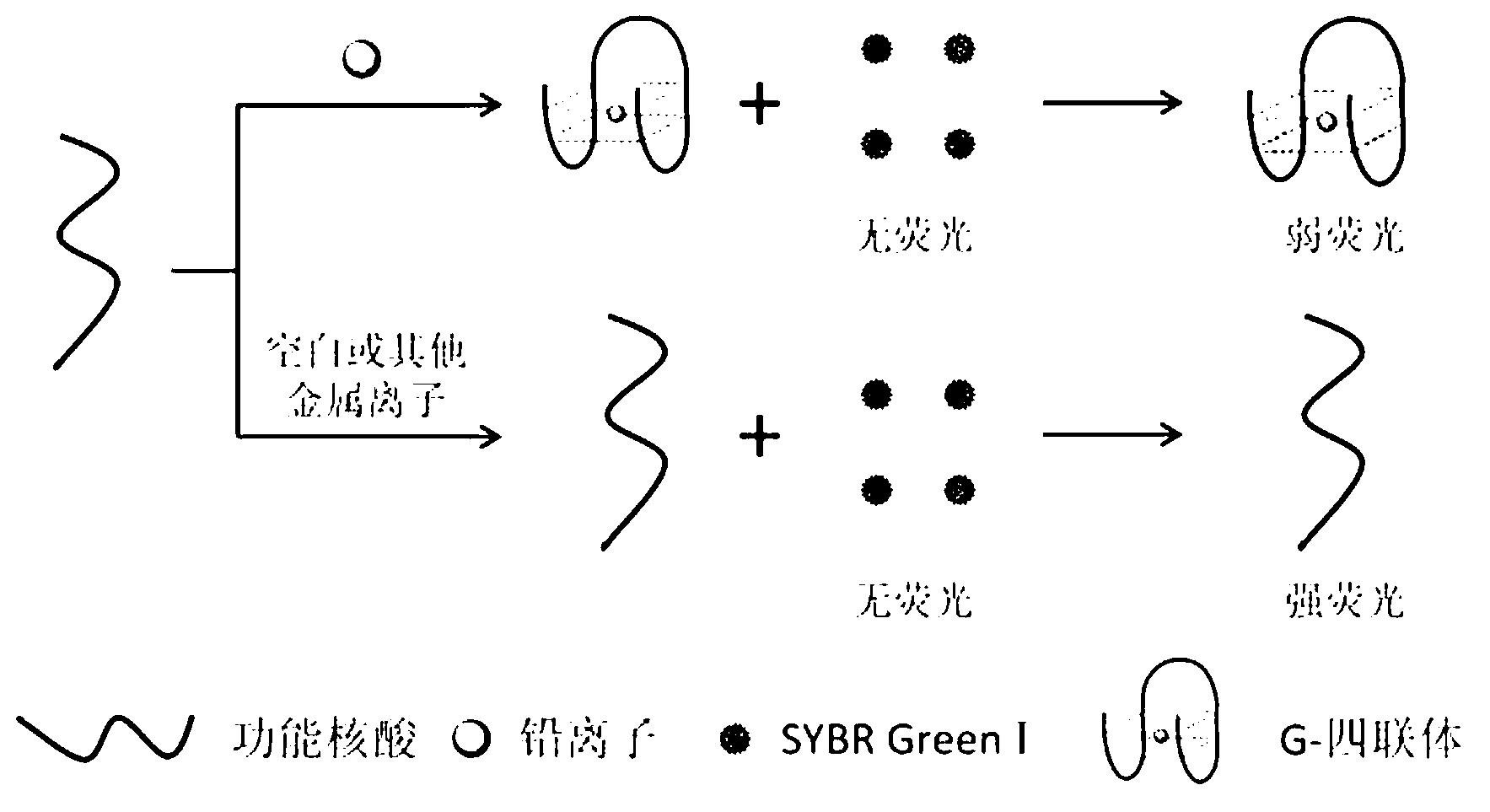Patents
Literature
224 results about "G-quadruplex" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In molecular biology, G-quadruplex secondary structures (G4) are formed in nucleic acids by sequences that are rich in guanine. They are helical structures containing guanine tetrads that can form from one, two or four strands. The unimolecular forms often occur naturally near the ends of the chromosomes, better known as the telomeric regions, and in transcriptional regulatory regions of multiple genes and oncogenes. Four guanine bases can associate through Hoogsteen hydrogen bonding to form a square planar structure called a guanine tetrad (G-tetrad or G-quartet), and two or more guanine tetrads (from G-tracts, continuous runs of guanine) can stack on top of each other to form a G-quadruplex.
Probe based on G-quadruplex-chlorine heme DNA enzyme and application of probe
InactiveCN105018474AAchieving magnified detectionExcellent long-term storage stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationProtein detectionHeme
The invention provides a probe based on a G-quadruplex-chlorine heme DNA enzyme and a method for detecting protein. The method for detecting the protein facilitates detecting operation and is low in cost and free of marking. The probe has the advantages of being high in sensitivity and low in background noise. When the protein is detected, the detecting operation is easy, consumed time is short, cost is low, and the problems that a method for detecting the protein in the prior art is long in consumed time, high in cost and complex in detecting probe manufacturing are solved.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE
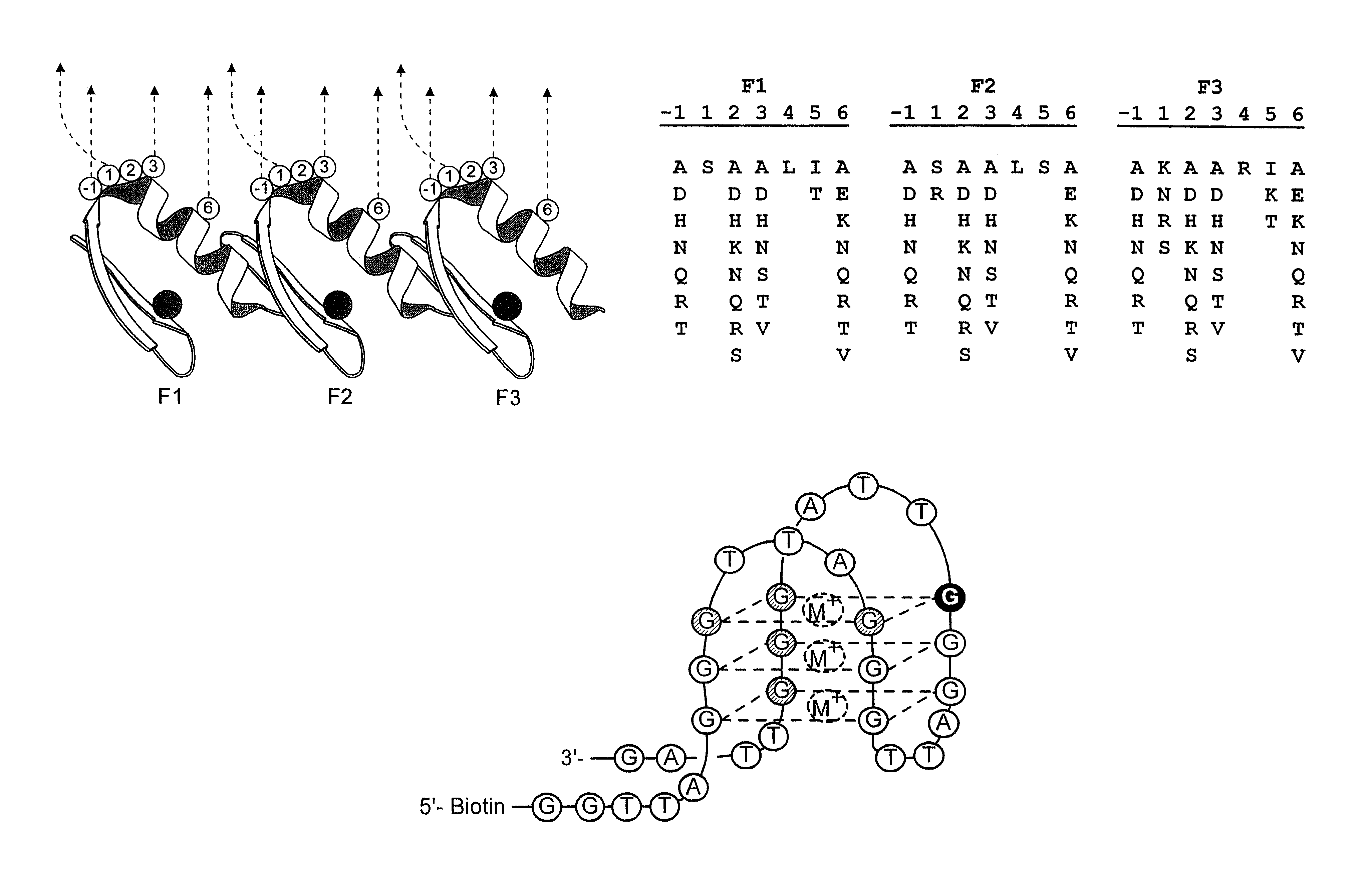
Zinc finger polypeptides capable of binding DNA quadruplexes
InactiveUS6492117B1Facilitates ELISA-based detectionRapid and easily automatedPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsZincZinc finger
The present invention relates to isolated or purified molecule(s) capable of binding to one or more of telomeric, G-quadruplex, or G-quartet nucleic acid(s).
Owner:GENDAQ +2
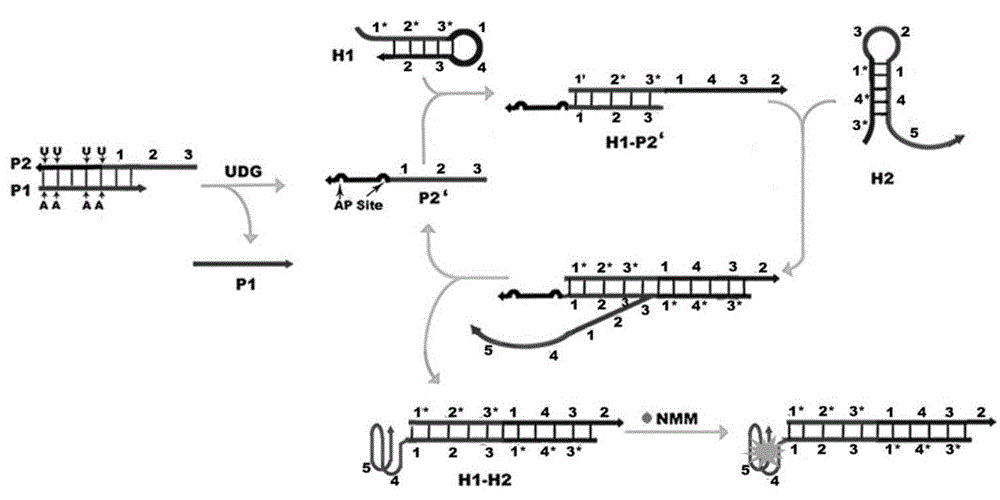
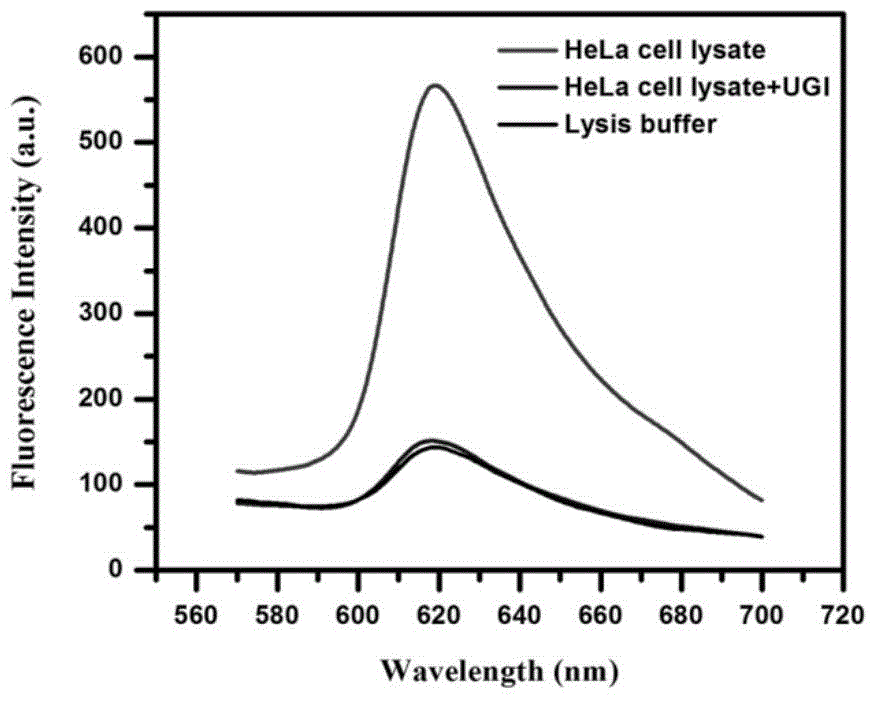
Method for detecting activity of uracil-DNA glycosylase (UDG) based on fluorescence amplification strategy of label-free non-enzyme DNA machines
InactiveCN104630363AImprove hybridization efficiencyEnhanced inhibitory effectMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceNucleotide
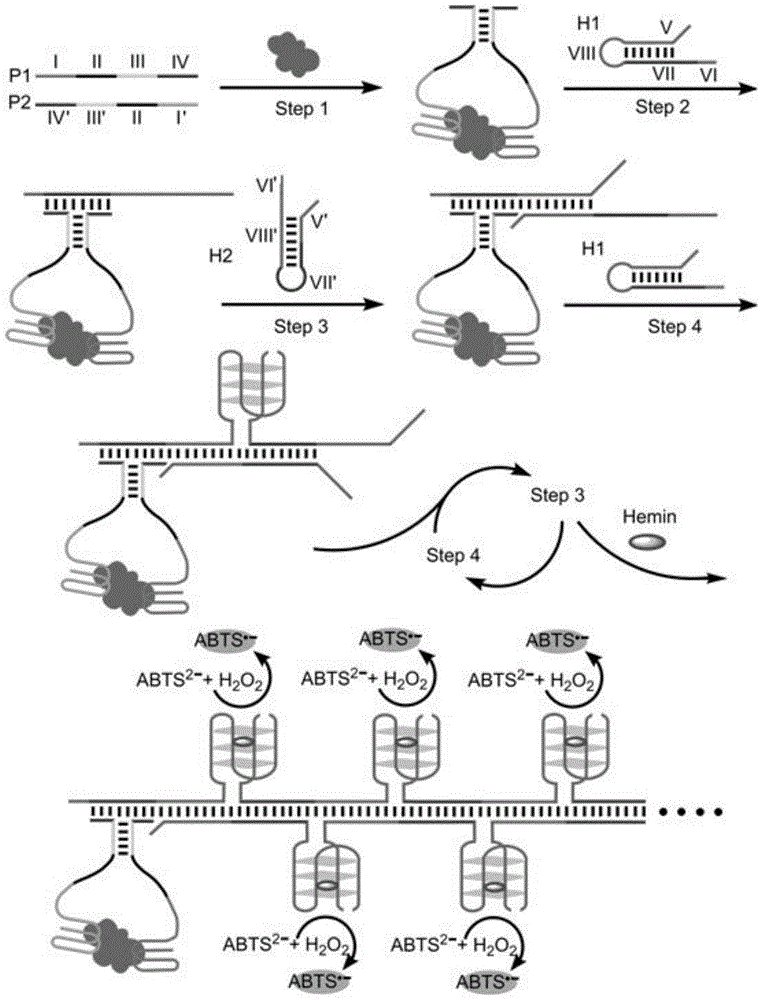
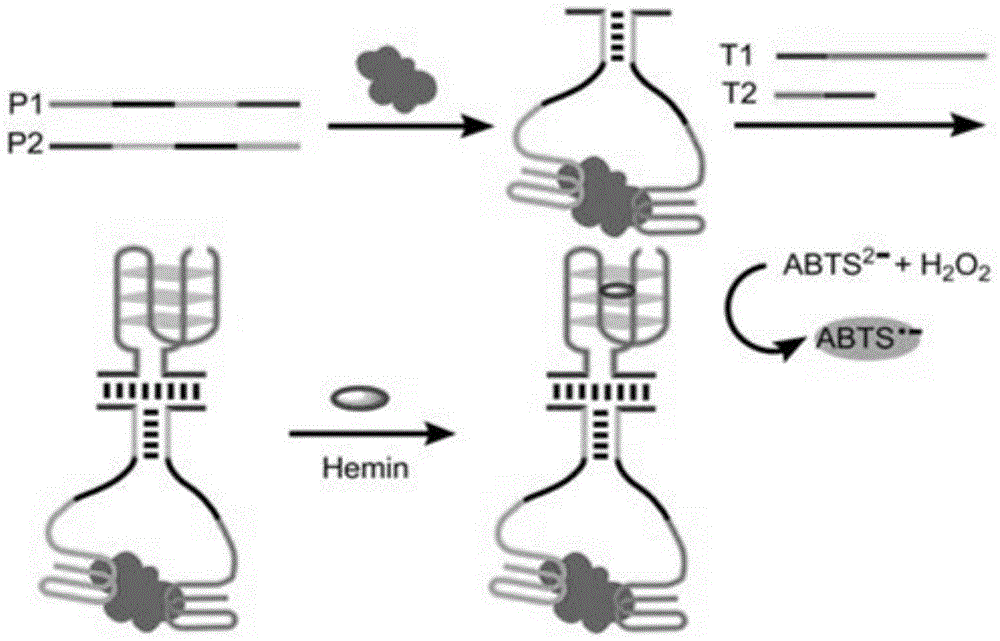
The invention discloses a method for detecting the activity of uracil-DNA glycosylase (UDG) based on a fluorescence amplification strategy of label-free non-enzyme DNA machines, and the method comprises the following steps: (1) the preparation of a probe for the recognition and signal transduction of the UDG: firstly, designing an uracil base and initiation sequence containing double-stranded DNA probe P1-P2, wherein the P1 chain is an inhibition chain and the nucleotide sequence thereof is show in SEQ ID NO.1 in a sequence table; the P2 chain is a uracil-DNA sequence and initiation sequence containing chimeric conjugated chain and the nucleotide sequence thereof is show in SEQ ID NO.2 in the sequence table; and the P1 chain and the P2 chain are partially complemented so as to form the double-stranded DNA probe P1-P2; (2) the construction of a label-free non-enzyme DNA machine: according to an initiation sequence of the P2 chain, designing hairpin probes H1 and H2 which are partially complemented and used for constructing the label-free non-enzyme DNA machine, and grafting a G-quadruplet sequence to the tail end of the hairpin probe H2; and (3) the activity detection of UDG. The method disclosed by the invention successfully realizes background diminishing and signal amplification, and the LOD (limit of detection) is 0.00044 U / mL.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Oligonucleotide probe, and method for detecting target molecule through using it
ActiveCN102827836ARealize quantitative detectionReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSequence designNucleic Acid Probes
The invention provides a signal amplification and signal reporting integrated oligonucleotide probe. The probe is a pair of DNA hairpin sequences designed on the basis of a target molecule and having cohesive ends, substantially is a product combining a hybridization chain reaction fuel molecule with a G-quadruplex sequence, has the characteristic of target molecule signal cascade amplification of the hybridization chain reaction in an enzyme-free isothermal manner, and enables the amplified target molecule signal to be conveniently and simply detected through the introduction of a signal reporting element G-quadruplex sequence. The invention also provides a method of an enzyme-free isothermal nucleic acid probe mediated by the above probe. The method enables the signal of an object to be detected to be amplified and detected under a normal temperature condition without any enzymes, and has the advantages of sensitivity, accuracy, simplicity, and easy implementation.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Novel use of cyanine dye in detection of G-quadruplex DNA
InactiveCN101587066AOvercoming demandsEfficient identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsCyanineUv vis absorbance
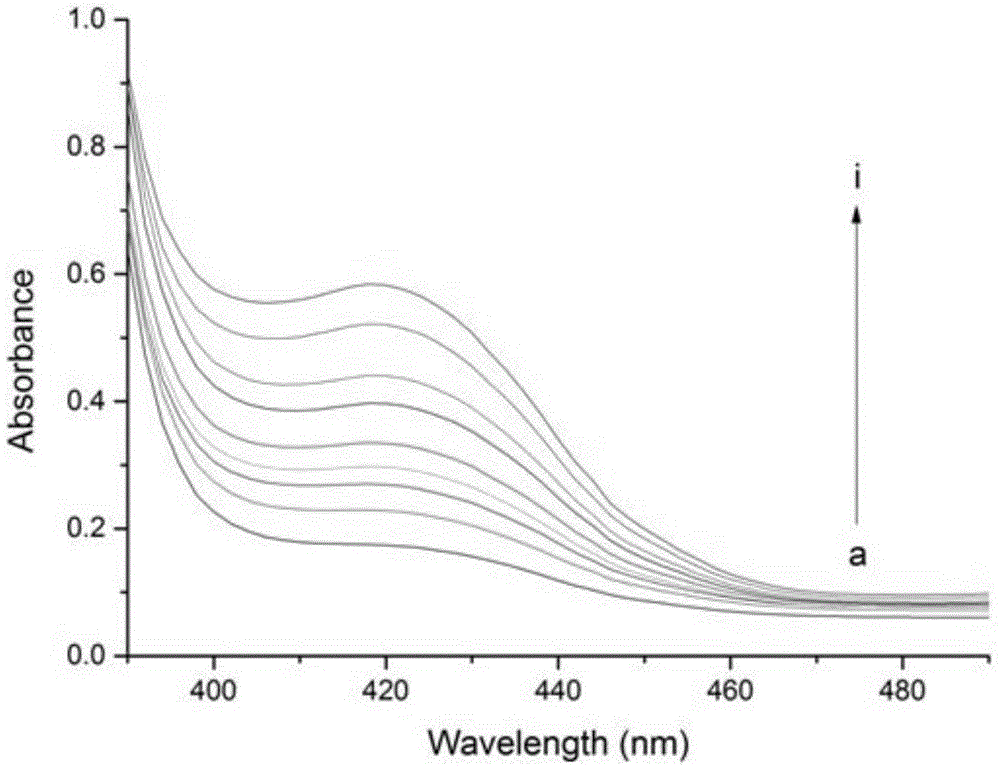
The invention provides novel use of a cyanine dye in the detection of a G-quadruplex DNA. The detection of the G-quadruplex DNA by using the cyanine dye has the advantages of simplicity, quickness and relatively low prices and overcomes the drawbacks of the prior detection technology such as long period, high price and high technical and equipment requirements. The use of the cyanine dye in the detection of the G-quadruplex DNA makes whether a DNA sample in solution has a G-quadruplex structure or a linear double helical structure determined quickly by a UV-visible absorption spectrum, fluorescence spectrum or confocal laser scanning microscopy. By using confocal laser scanning microscopy, the DNA sample assembled on the surface of Au can be marked visually, so the structure of the DNA sample can be recognized and the specific assembly position of the DNA sample on the surface of the Au can be marked at the same time.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fluorescent probe and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106833623AStrong forceEasy to pile upOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceSolubilityDouble bond
The invention provides a fluorescent probe represented by the formula (I), wherein R1 and R2 are independently selected from H or an aromatic vinyl group, and at least one of R1 and R2 is the aromatic vinyl group; R3 is selected from H, F, Cl, Br, OH, OCH3, N(CH3)2 or C1-C6 alkyl; and R4 is selected from C1-C6 alkyl. Compared with the prior art, because the fluorescent probe provided by the invention has a relatively large electronic conjugated system and plane, the intensity of the intramolecular charge transfer effect can affect the molecular fluorescence emission intensity; when the fluorescent probe and the G-quadruplex generate a specific action, the flexibility of intramolecular rotatable double bonds is restricted, the intramolecular charge transfer effect is enhanced, and the fluorescence is also enhanced significantly; moreover, the fluorescent probe provided by the invention has the advantages of low biotoxicity, phototoxicity and photobleaching property, good light stability, good water solubility and good cell membrane permeability.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Electrochemical method of detecting single-chain target DNA concentration based on G-quadruplex-heme compound and polymeric chain type amplification reaction
ActiveCN106525940AHigh sensitivityRealize highly sensitive detectionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrochemistryDifferential pulse voltammetry
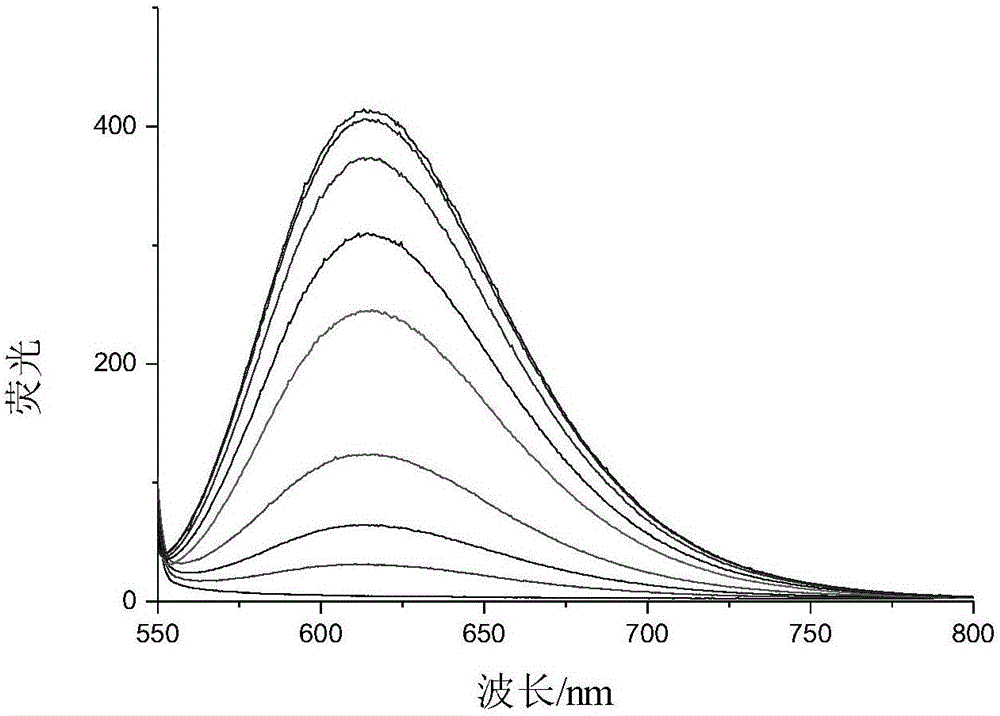
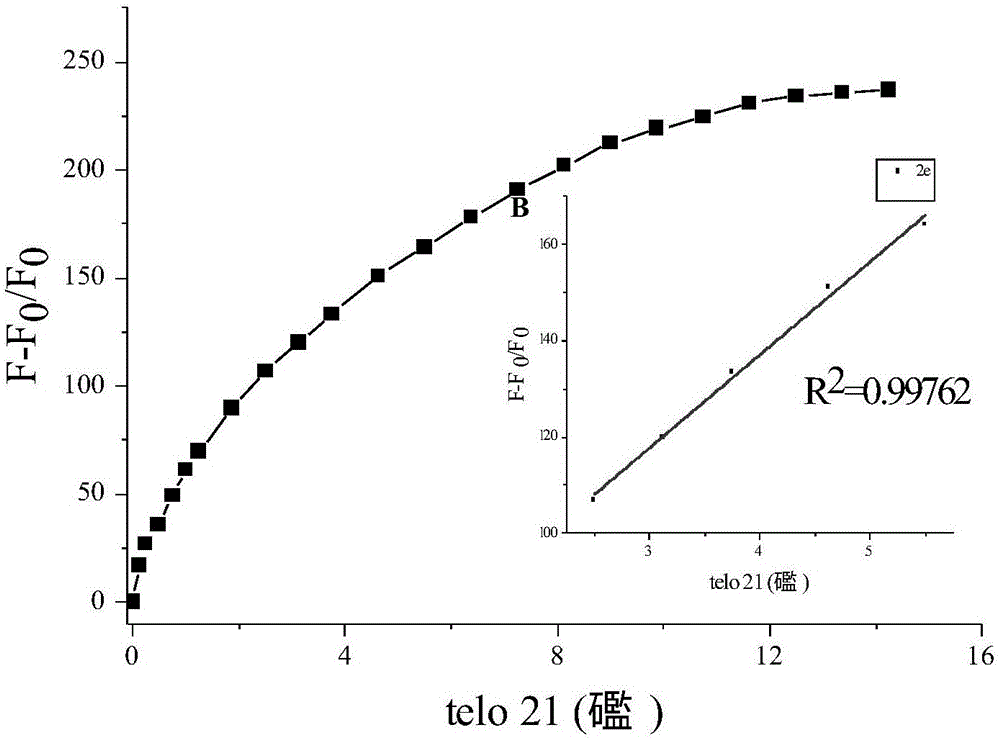
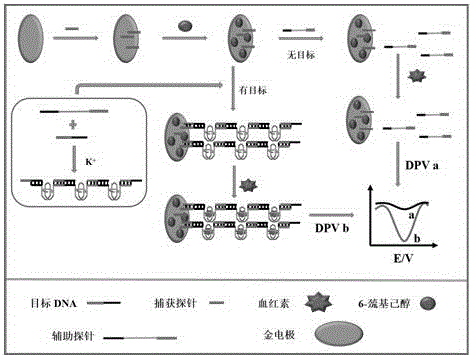
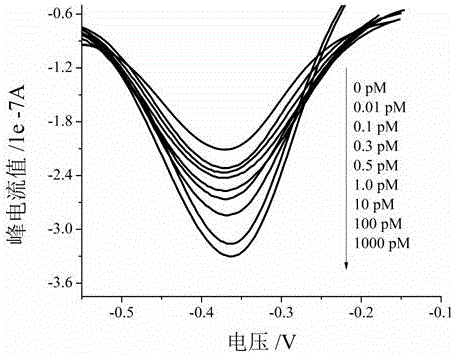
The invention relates to an electrochemical method of detecting single-chain target DNA concentration based on G-quadruplex-heme compound and polymeric chain type amplification reaction, and belongs to the technical field of analytical chemistry. A capture probe and an auxiliary probe are designed, the two ends of the auxiliary probe each contain a nucleotide sequence complemented with the target DNA, and the middle of the auxiliary probe contains a base sequence capable of forming G-quadruplex. The capture probe and the target DNA recognize each other and are subjected to continuous polymeric chain type reaction to form chain-shaped polymer, the chain-shaped polymer is fixed to an electrode through the capture probe on the surface of the gold electrode, and a great number of G-quadruplex structures are introduced onto the surface of the electrode. Then, G-quadruplex and heme are combined to form the compound with powerful electrochemical signals, and the target DNA is detected through the corresponding relation among the electrochemical signals obtained through differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) scanning, the G-quadruplex-heme compound on the surface of the electrode and the concentration of the target DNA added into the system. HIV DNA in the sample is detected through the method, and an ideal effect is obtained. The electrochemical method has the advantages of being high in sensitivity and specificity.
Owner:ANHUI HUATENG AGRI TECH CO LTD
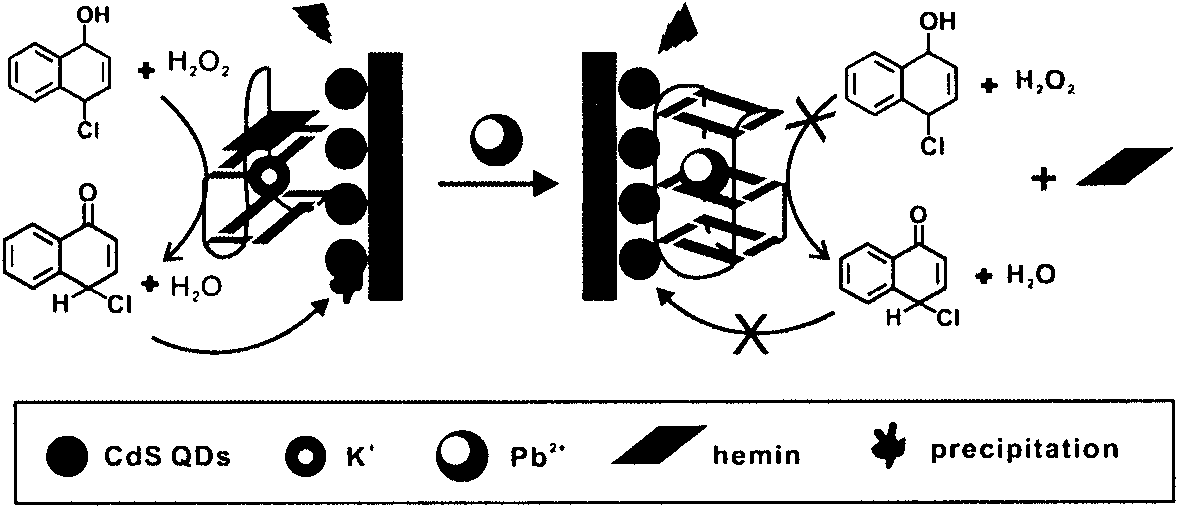
Novel Pb2+ supersensitive detecting method based on photoelectrochemical sensing
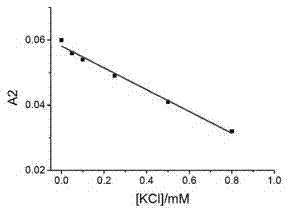
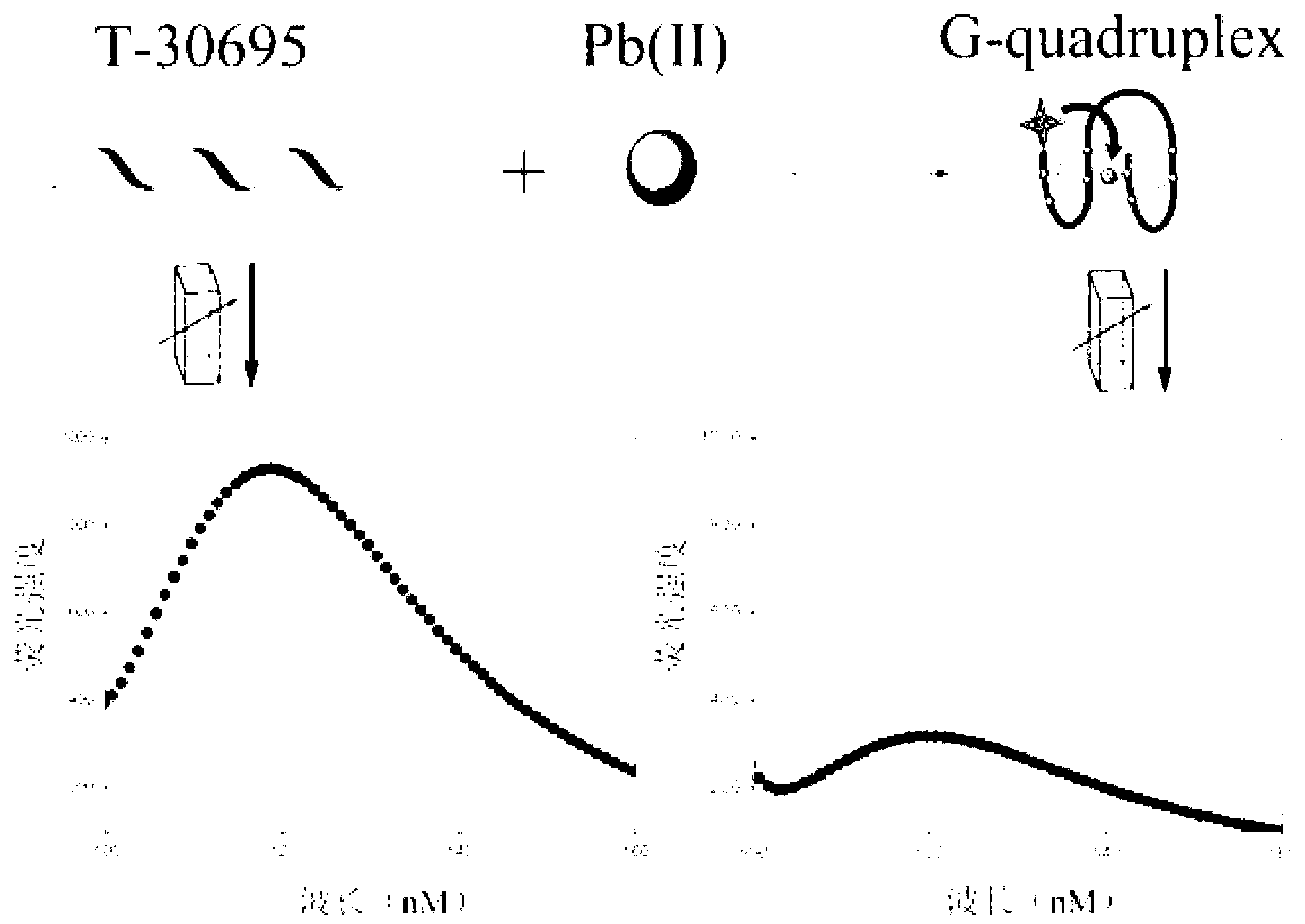
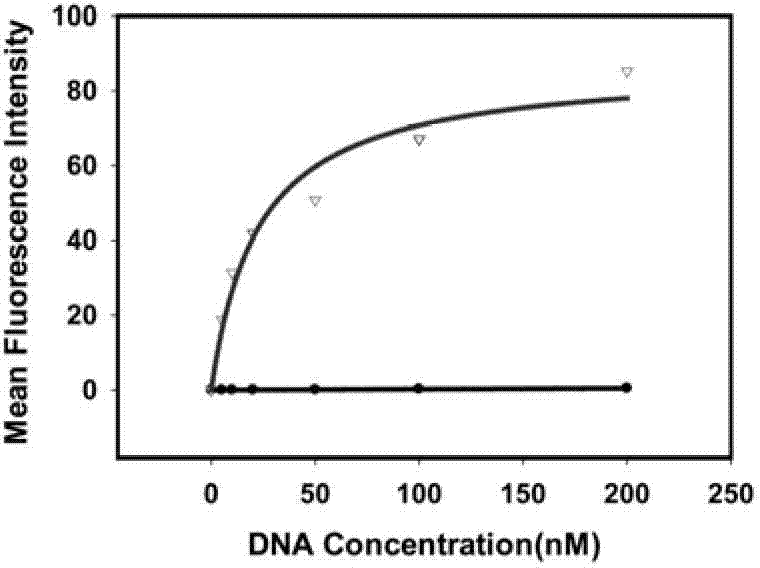
The invention relates to construction of a photoelectrochemical sensor which is based on conformation transition of G-quadruplex DNAzyme, and belongs to the field of photoelectrochemical sensor technology of analytical chemistry, wherein the conformation transition is induced by Pb2+, and the photoelectrochemical sensor is capable of realizing supersensitive sensing of Pb2+ effectively. K+ is replace by Pb2+ to induce the conformation transition of G-quadruplex DNAzyme so as to decrease enzymatic activity, so that enzyme biological catalytic precipitation reaction on an ITO electrode which is modified by CdS quantum dots is influenced, and photoelectrochemical sensing detection of Pb2+ is realized. G-quadruplex DNAzyme is applied in a photoelectrochemical sensing system for detection of Pb2+ for the first time; the photoelectrochemical sensor possesses advantages of high selectivity and high ensitivity; and detection limit of Pb2+ reaches to 1.0*10<-8>M.
Owner:TAIZHOU UNIV
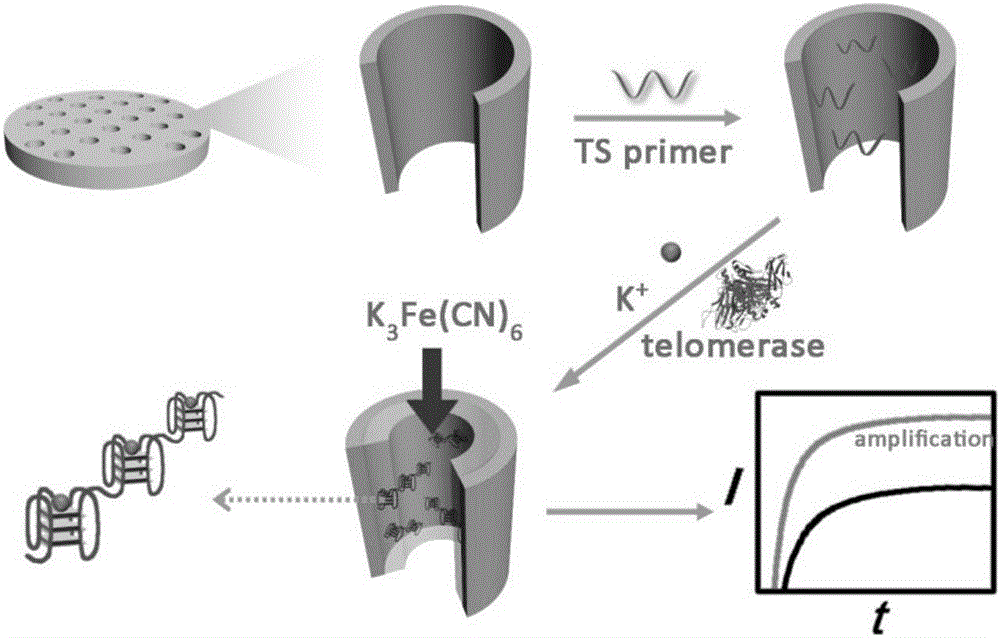
Method for quantitatively detecting telomerase activity based on nano pore channel and electrochemical sensing
ActiveCN105806912AAperture adjustableStable structureMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansTelomerasePower flow
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively detecting telomerase activity based on a nano pore channel and electrochemical sensing.The method comprises the following steps that firstly, a telomerase recognition sequence is connected to the inner wall of a porous anodic alumina template or a polyethylene terephthalate film to serve as a primer; secondly, telomerase amplifies the primer to form a G-rich sequence; a G-quadruplex is formed in the presence of potassium ions; electrochemical detection is conducted on the current produced through indicating molecules of the nano pore channel by utilizing an electrochemical workstation.The method does not need complex material preparation and DNA probe marking, and can avoid the defects of high detection cost, complicated operation and poor reproducibility caused by the complex material preparation and DNA probe marking and has the advantages of being low in cost, quick, simple, convenient, high in sensitivity and good in accuracy.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
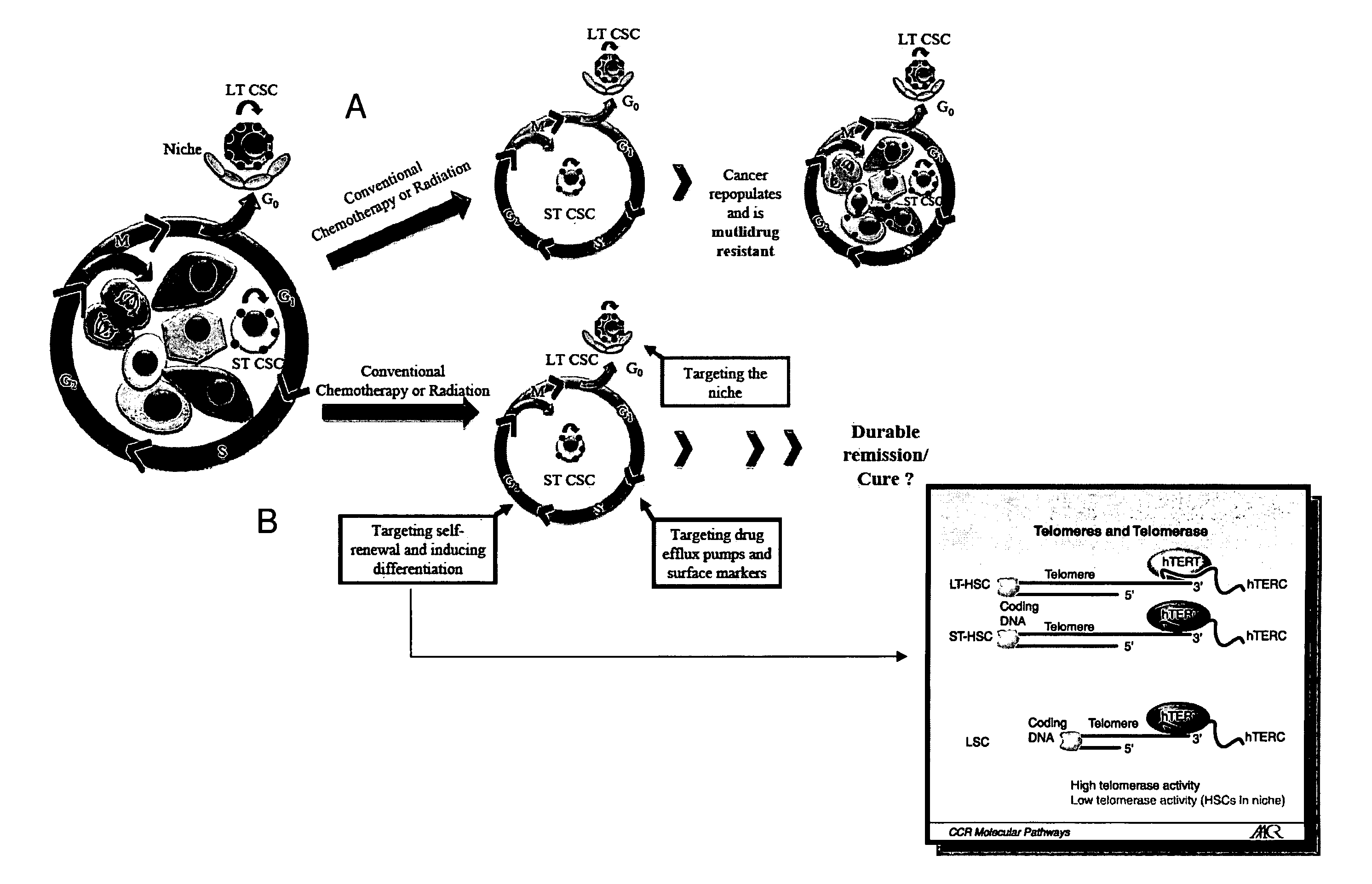
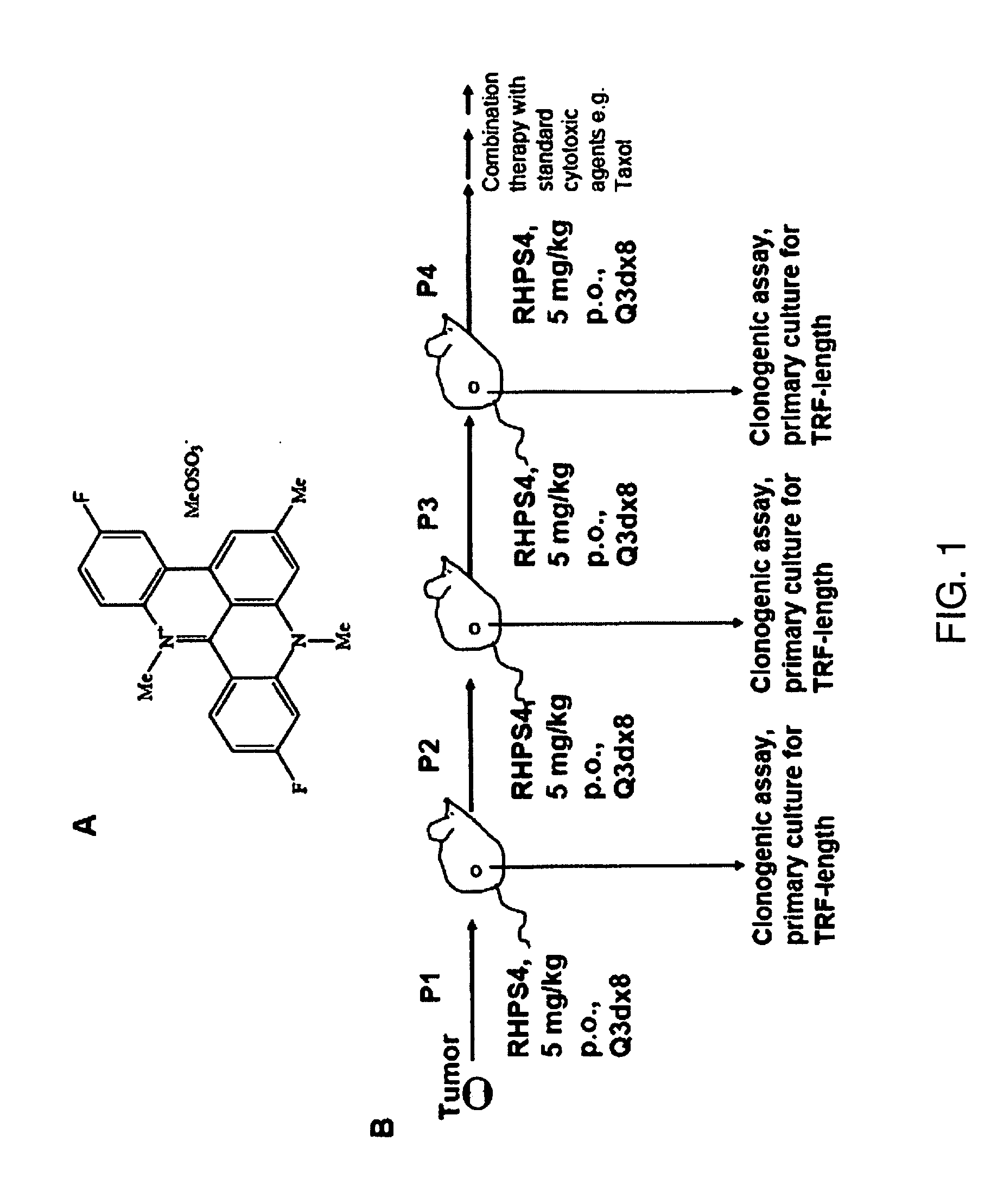
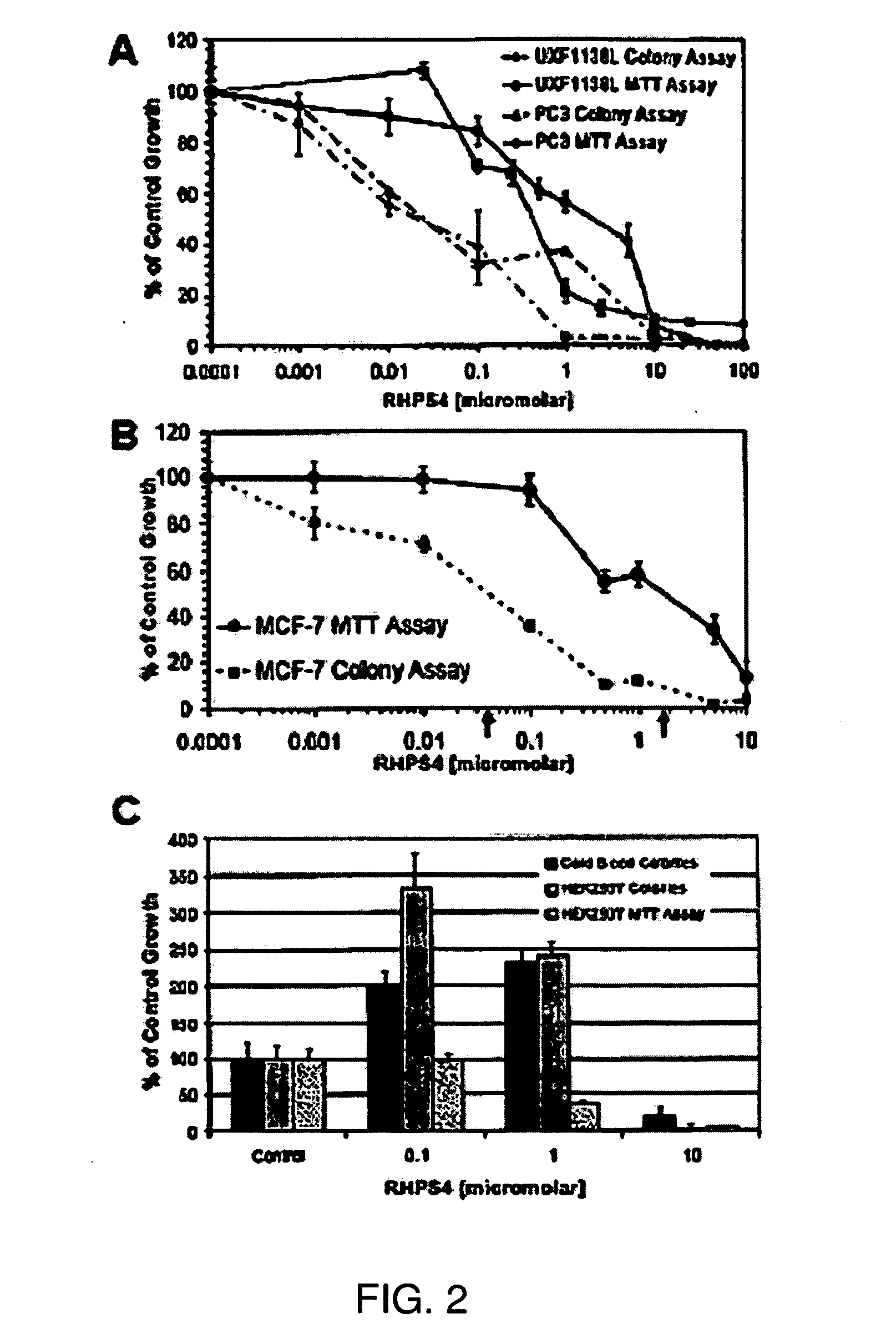
Telomere targeting agents as stem cells directed treatments
InactiveUS20080279961A1Inhibit cell growthInduce cell proliferationHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseTelomerase
It is demonstrated in the present invention that G-quadruplex ligands can be used to both shorten telomeres and inhibit telomerase by causing telomere uncapping. The invention relates to compositions and methods of treating cancer stem cells comprising the administration of G-quadruplex ligands, such as 3,11-difluoro-6,8,13-trimethyl-8H-quino[4,3,2-kl]acridinium methosulfate (RHPS4), which can effectively inhibit or reduce the growth of cancer stem cells. The invention also relates to a synergistic effect in inhibiting or reducing the growth cancer stem cells when a G-quadruplex ligand is combined with a mitotic spindle poison, such as paclitaxel, or other agents used in the treatment of cancer and disease. The invention also relates to RHPS4 inducing non-cancerous cell and non-cancerous stem cell proliferation.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
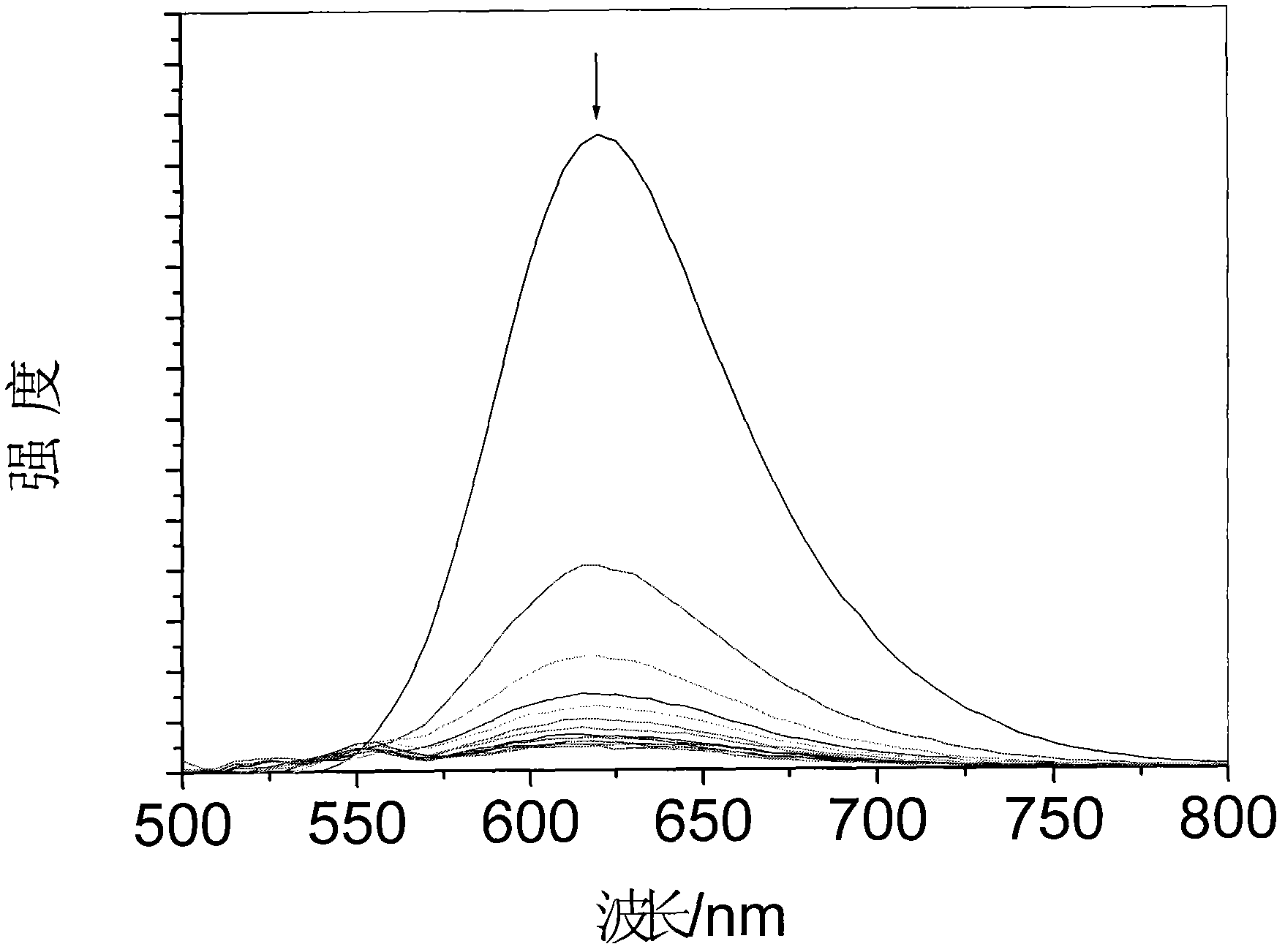
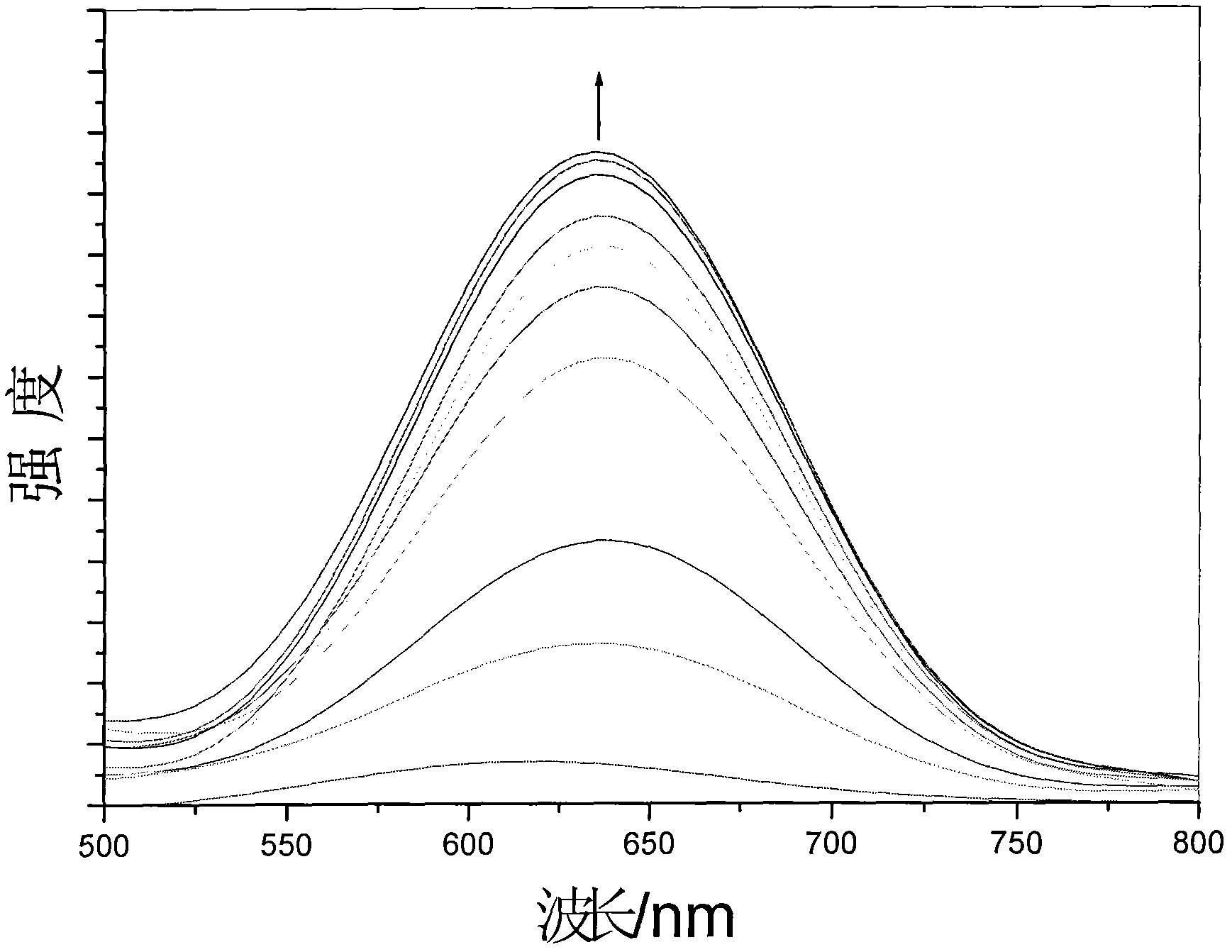
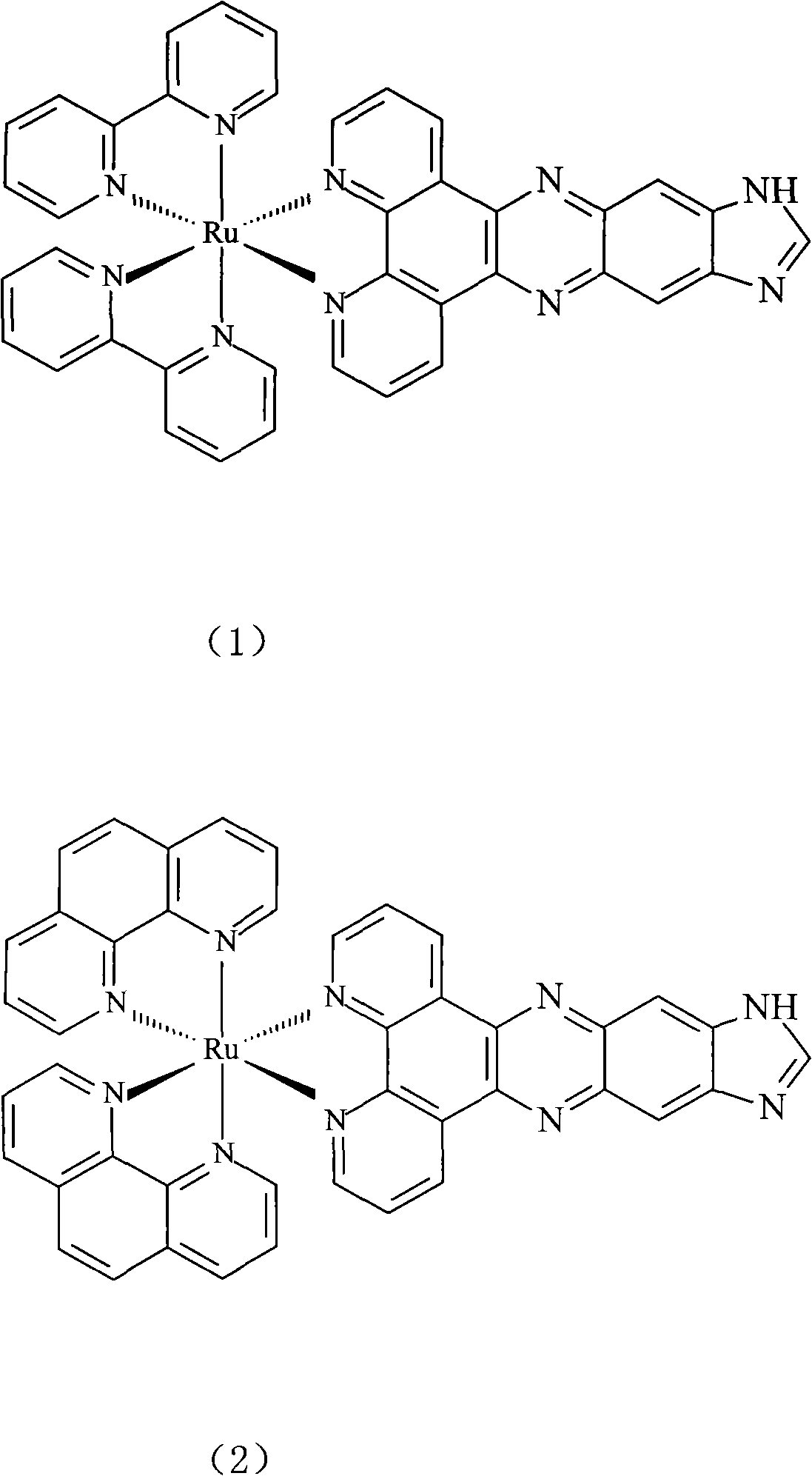
Ruthenium (II)-polypyridine complex, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102464676AG-quadruplex DNA molecular optical switch with good performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsLithium chlorideFiltration
The invention provides a ruthenium (II)-polypyridine complex. For the ruthenium (II)-polypyridine complex, bipyridyl (bpy) or phenanthroline hydrate (phen) is used as an ancillary ligand, and dipyridine[3,2-a:2',3'-c]phenazine-11,12-imidazole (dppzi) is used as a main ligand. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing 5,6-dinitrobenzimidazole from 5,6-nitrobenzimidazole; reducing 5,6-dinitrobenzimidazole into 5,6-diaminobenzimidazole by using hydrazine hydrate and palladium / carbon; preparing dppzi from phenanthroline hydrate-5,6-dione and 5,6-diaminobenzimidazole and preparing cis-[Ru(bpy)2Cl2].2H2O from ruthenium trichloride, bpy and lithium chloride; preparing cis-[Ru(phen)2Cl2].3H2O from ruthenium trichloride, phen and lithium chloride; carrying out a heating reflux reaction on dppzi and cis-[Ru(bpy)2Cl2].2H2O or cis-[Ru(phen)2Cl2].3H2O under the protection of argon, carrying out cooling, adding ammonium hexafluorophosphate, allowing precipitate to deposit and carrying out filtration and column chromatography so as to obtain a target product. The ruthenium (II)-polypyridine complex provided in the invention can be used as an optical switch for G-quadruplex DNA molecules.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
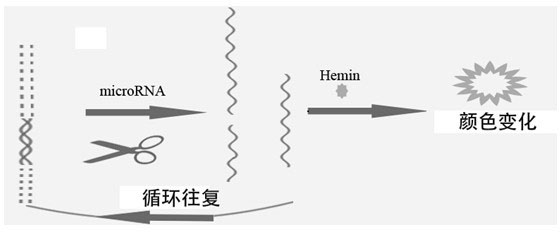
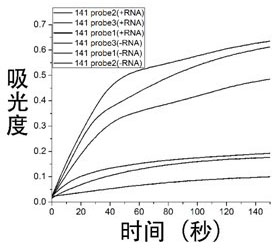
MiRNA (Micro Ribonucleic Acid) detection probe and method for visually detecting miRNA
InactiveCN102618664AEasy to distinguishMeet different testing needsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPeroxidaseHemin
The invention relates to a miRNA (Micro Ribonucleic Acid) detection probe and a method for visually detecting miRNA. The miRNA detection probe comprises three parts: a G-quadruplex forming sequence close to a 3' end, a miRNA complementary sequence of a target to be measured in the middle, and an interference sequence at a 5' end. The probe has a hairpin structure under general conditions. After the target is added, the quantity of base pairs and stability of a DNA-RNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid-Ribonucleic Acid) heterozygote are higher than that of a DNA double chain formed by the interference interface, and a hairpin structure is opened. The opened hairpin structure can release the G-quadruplex forming sequence under the action of a double-chain specific incision enzyme, G-quadruplex is formed under the action of sodium and potassium ions, and a catalyst with peroxidase activity is produced by assembling with Hemin. The method for detecting miRNA disclosed by the invention only requires one probe, a generated signal is visual, and expensive instruments are not required.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
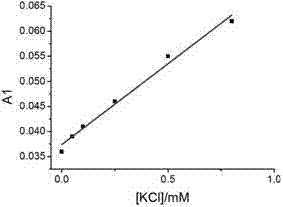
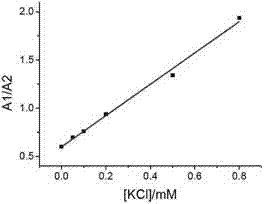
Potassium ion concentration detection method
ActiveCN102735664AStrong specificityRealize visual detectionMethine/polymethine dyesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorCyaninePotassium ions
The invention relates to a potassium ion concentration detection method. According to the method, characteristics comprising that potassium ion regulation allows G-quadruplex DNA structure transformation to be formed and cyanine dye supermolecular aggregates identify the G-quadruplex DNA structure transformation are utilized, a sample to be detected is added to a mixed solution of G-quadruplex DNA and the cyanine dye, the absorbance value at 560-590nm, 500-540nm or 610-670nm or the fluorescence intensity value at 580-640nm is determined, and the corresponding potassium ion concentration value can be obtained through finding the value corresponding to the absorbance value or the fluorescence intensity value on a standard curve. The method has a high specificity, so the method is not affected by sodium ions in the sample; and reagent components is simple, and the reaction process is simple, so errors generated by operations can be effectively reduced, and the test accuracy is high. The method can be rapidly realized through a common ultraviolet-visible absorption detector, a spectrophotometer or a fluorescent spectrometer without special or extra instruments, so the detection cost is low, thereby the popularization and the application of the method in industries are convenient.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Thiaporphyrin, selenaporphyrin, and carotenoid porphyrin compounds as c-myc and telomerase inhibitors
The present invention has identified thiaprophyrin, selenaporphyrin, and carotenoid porphyrin compounds that bind the G-quadruplex formed by the folding of single-stranded human telomeric DNA. These compounds have been shown to be effective telomerase and c-myc inhibitors and are contemplated to be useful in developing cancer treatments.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
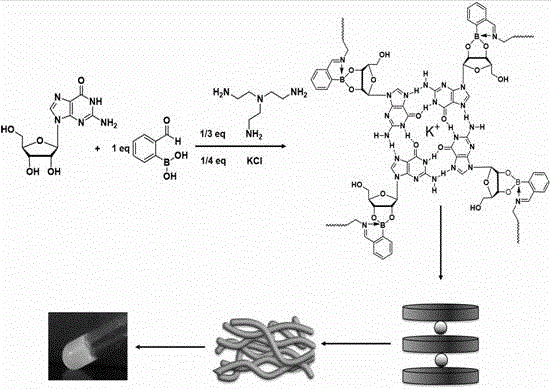
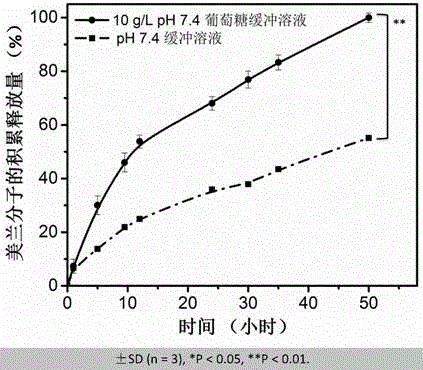
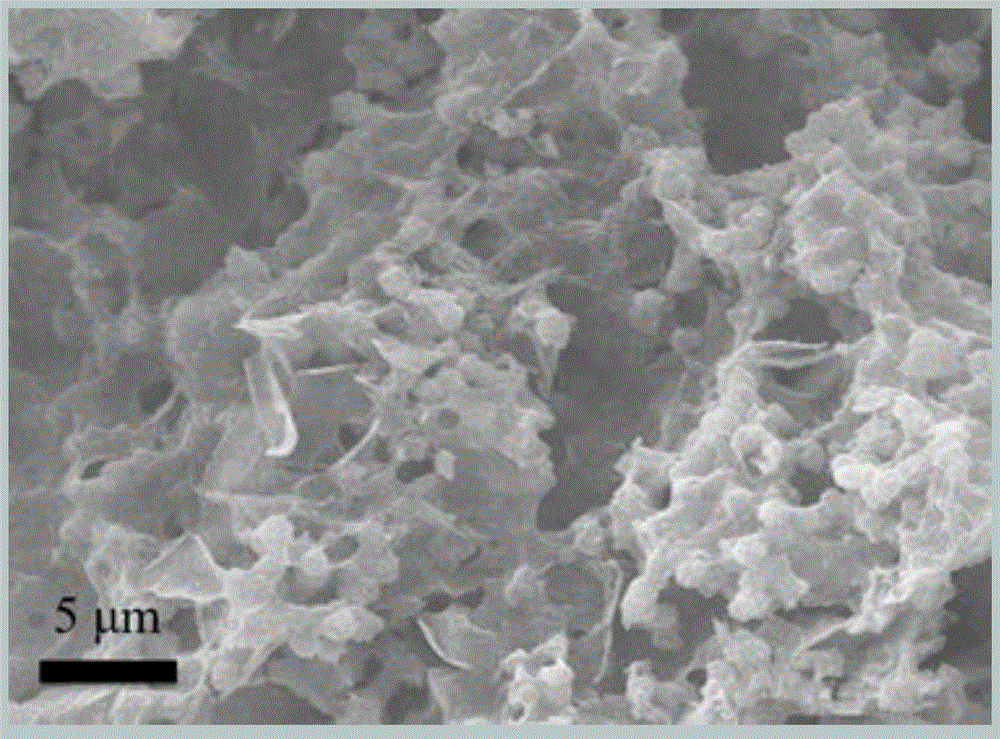
Sugar response supramolecular gel with G-quadruplex structure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105622692AHigh strengthSugar responsiveOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivatives2-formylphenylboronic acidRaw material
Disclosed is sugar response supramolecular gel with a G-quadruplex structure. A preparation method includes: taking sugar response of 2-formylphenylboronic acid as a center; utilizing a vicinal diol structure that vernine has to react with the 2-formylphenylboronic acid to form dynamic covalent bond boron ester bond; enabling primary amine in tri(2-amino ethyl)amine and aldehyde group of the 2-formylphenylboronic acid to form dynamic imine bond; forming the G-quartet structure when potassium ions among basic groups of vernine are stable. The sugar response supramolecular gel can be used for detecting release effect of methylthionine chloride in a glucose solution and an acidic solution. The sugar response supramolecular gel and the preparation method have the advantages that the gel prepared by the method is stable, high in strength, high in sugar response performance and capable of loading a lot of macromolecular / micromolecular gel; raw materials related to the preparation method are simple, and the supramolecular gel can be prepared by utilizing micromolecules while complex synthesis steps are not needed, so that cost is low, production process is simple, products can be stored for a long time without going bad, the raw materials are low in toxicity, and the preparation method is easy to popularize and apply.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
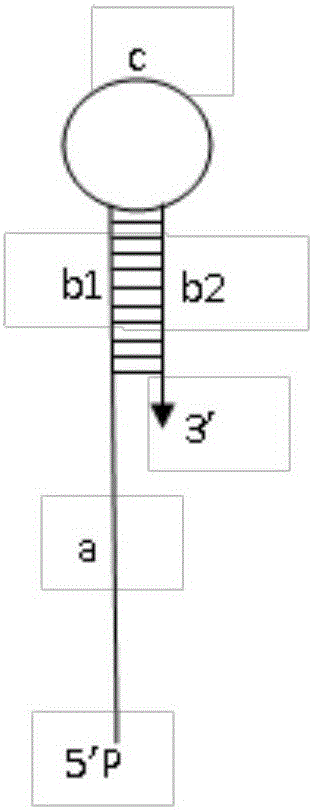
Oligonucleotide probe
ActiveCN105802963AAvoid interferenceEasy to manufactureMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleic Acid ProbesSingle strand
The invention belongs to the technical field of nucleic acid probes and provides an oligonucleotide probe. The probe sequentially comprises a sequence complementary with a target sequence, a G-quadruplex closing sequence and a G-quadruplex sequence from the 5' terminal to the 3' terminal, wherein the G-quadruplex closing sequence is complementary with part of G-quadruplex sequence to form a stable hairpin structure, and the G-quadruplex sequence is closed in the probe. During target molecule detection, the probe firstly recognizes the target sequence and forms a double-stranded structure, then, the hairpin structure is opened under the digestion action of Lambda exonuclease, the G-quadruplex sequence is released, the procedures are repeated, finally, a trace amount of target molecule information is converted into a large quantity of G-quadruplex sequences, and the G-quadruplex sequences are converted into readable light signals, electric signals and the like. The probe has the advantages of good stability, low cost, easiness in preparation, high throughput and high sensitivity and specificity, can directly detect single-stranded nucleic acid and can also indirectly detect double-stranded nucleic acid and other molecules capable of inducing generation of single-stranded nucleic acid.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Visual sensor based on functional nucleic acid of cadmium and application thereof
ActiveCN107966436AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsHeminCadmium Cation
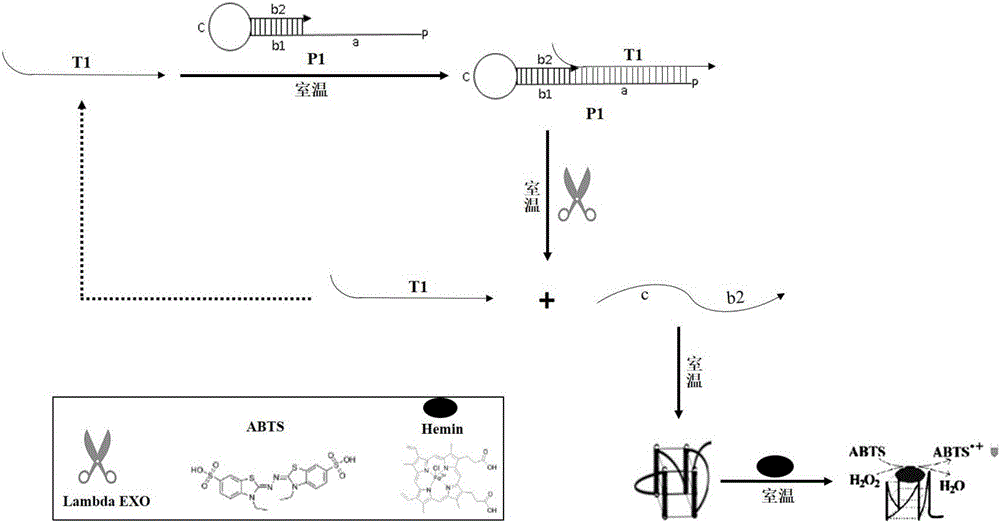
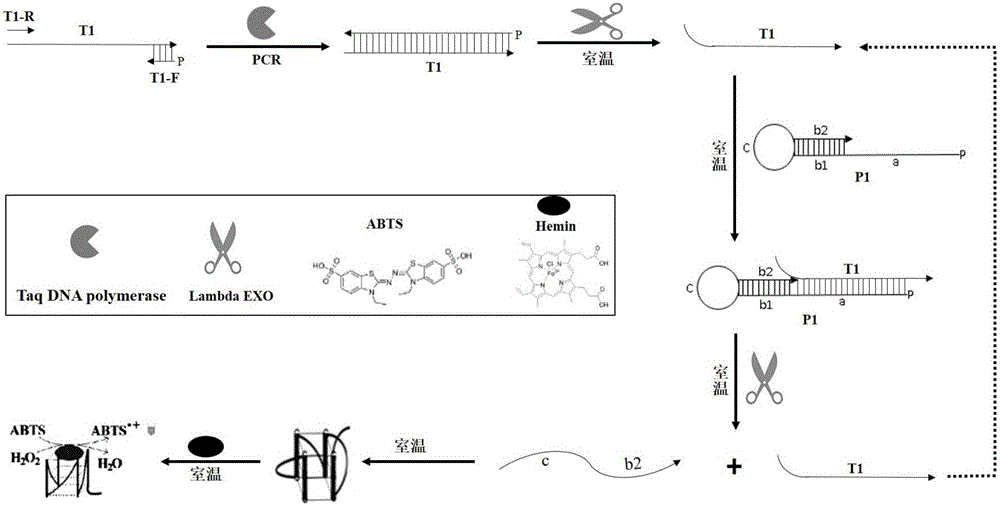
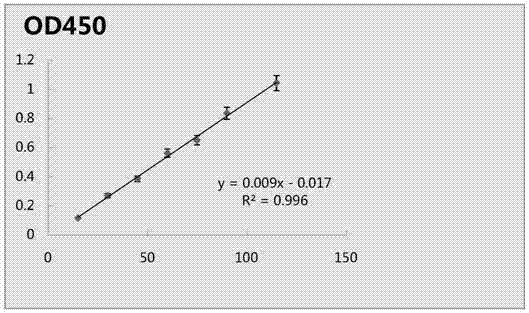
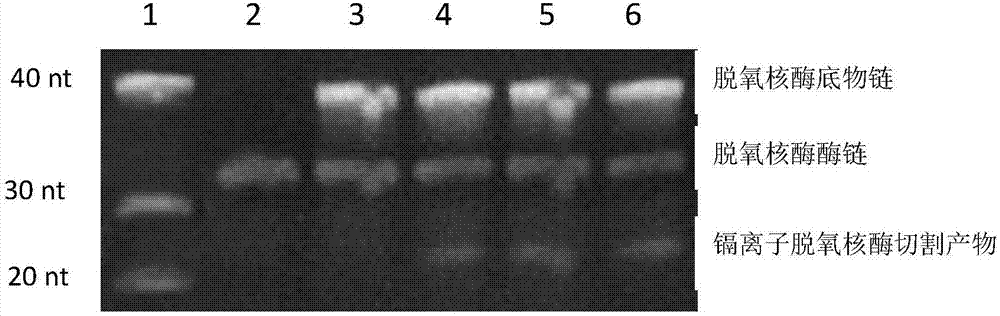
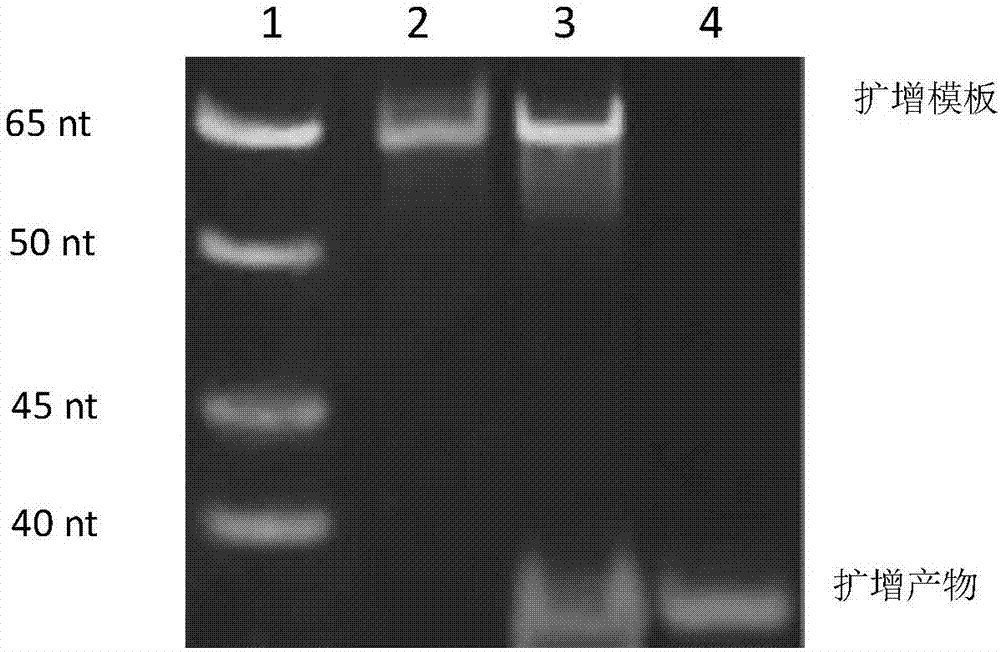
Belonging to the technical field of metal ion detection, the invention discloses a visual sensor based on functional nucleic acid of cadmium and application thereof. The sensor consists of a molecularrecognition component, a signal amplification component and a signal conversion component. The molecular recognition component is composed of cadmium ion deoxyribozyme, which comprises a substrate chain and an enzyme chain. The signal amplification component includes an isothermal amplification system and hemin, and the isothermal amplification system includes an amplification template. The signal conversion component includes a color developing agent. The visual sensor is constructed based on cadmium ion deoxyribozyme, isothermal index amplification reaction and G-quadruplex liquid phase sensing technology, has the advantages of simplicity and rapidity, high sensitivity, high specificity, high salt resistance, low cost and the like, and can be used for field detection of cadmium ions inthe environment.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for detecting potassium ion by preparing biosensor based on G-quadruplex and gold nanoparticle
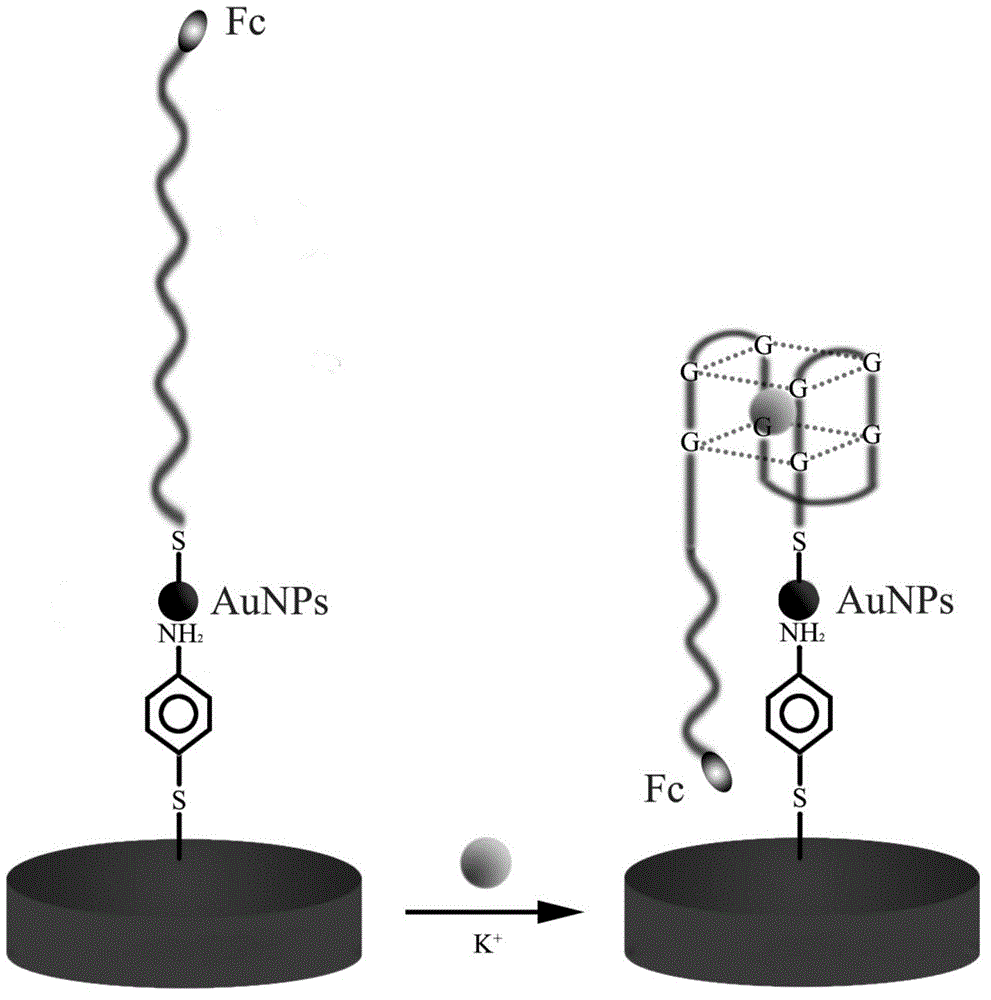
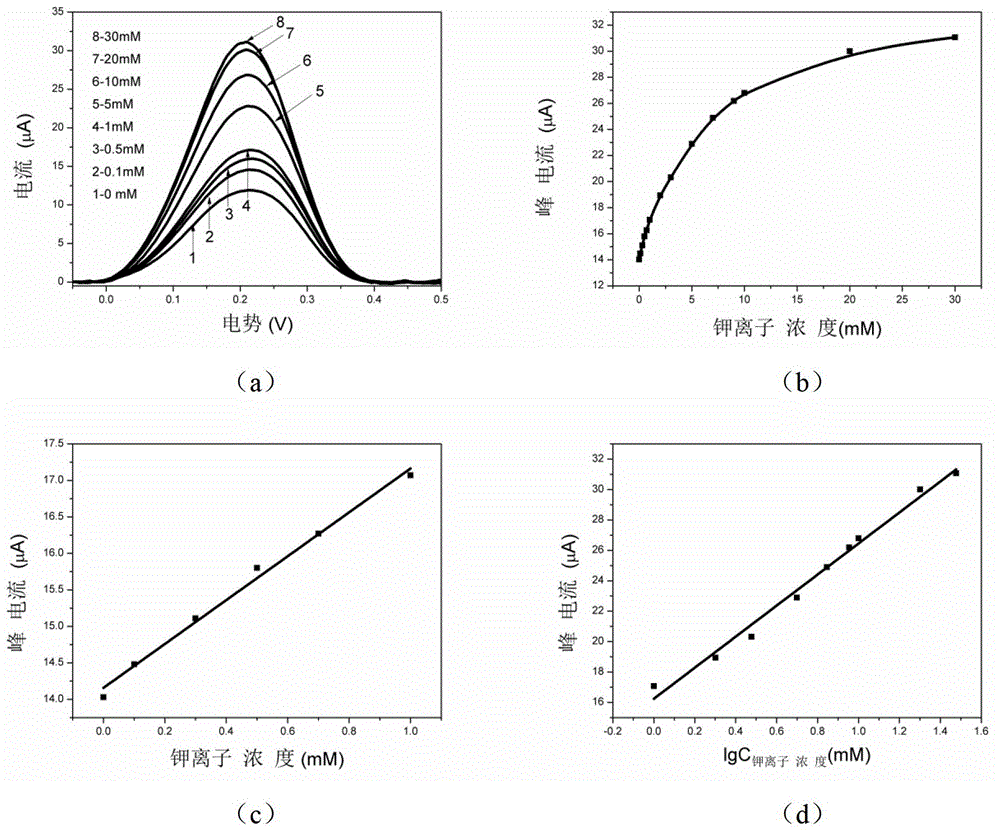
InactiveCN102866185AHigh sensitivityGood linear relationshipMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical biosensorA-DNA
The invention discloses a method for detecting a potassium ion by preparing a biosensor based on a G-quadruplex and a gold nanoparticle, and belongs to the field of the biosensor. A detection method comprises the following steps of: modifying the gold nanoparticle on the surface of a gold electrode by taking para-aminothiophenol (p-ATP) as a medium, fixing a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) marked by ferrocene (Fc) and capable of forming a G-quadruplex structure onto the surface of the gold nanoparticle by a sulfydryl self-assembly action, and taking the DNA as an aptamer to prepare an electrochemistry biosensor to detect the potassium ion. The method for detecting the potassium ion by preparing the biosensor based on the G-quadruplex and the gold nanoparticle has the advantages that the detection is simple and quick, the sensitivity is high, the real-time detection can be carried out on the potassium ion, the minimum detection concentration to the potassium ion reaches 0.1 mM, and the linear range of the detection is large. In a concentration range of 0.1-1 mM, a square wave volt-ampere peak current is in a well linear relation with the concentration of the potassium ion; and in a concentration range of 1-30 mM, the square wave volt-ampere peak current is in a well linear relation with the logarithm of the concentration of the potassium ion.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
High sensitive and jettisonable multicomponent chemiluminescent imaging immunosensor
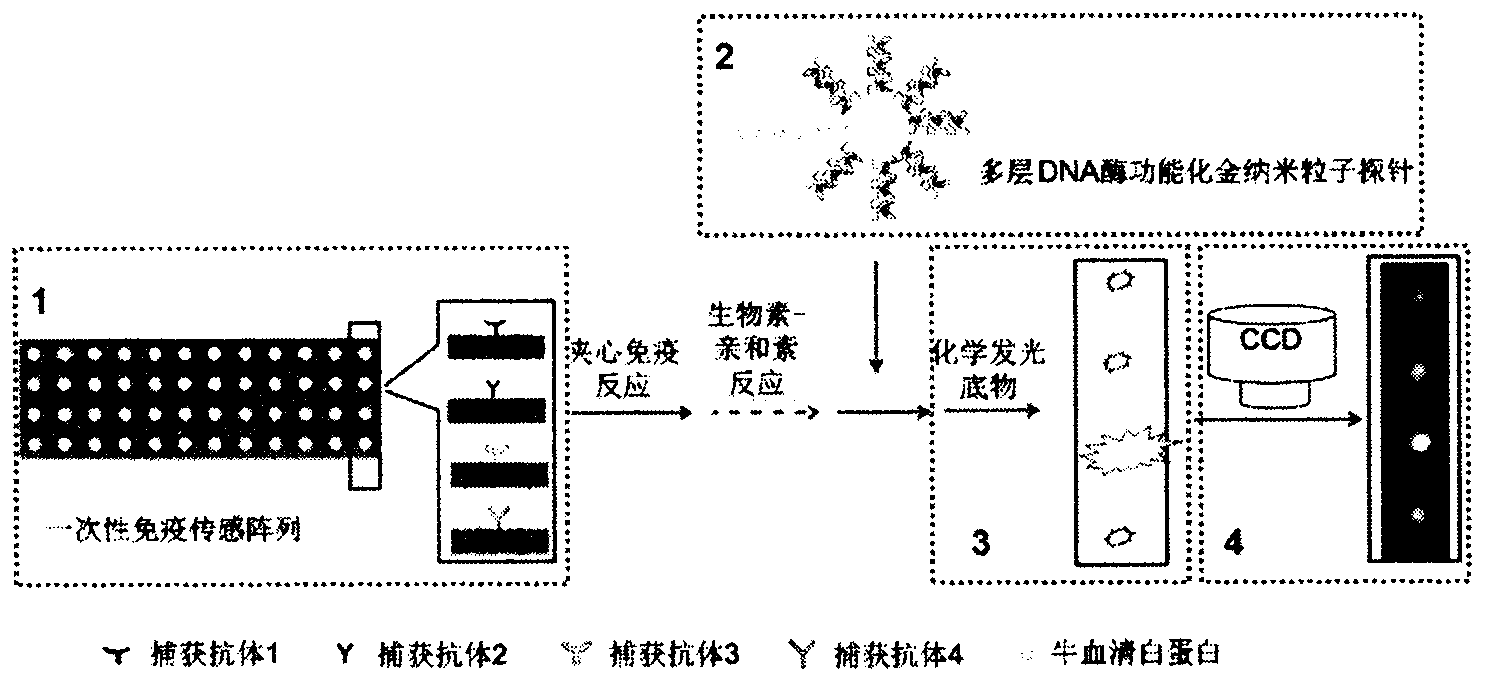
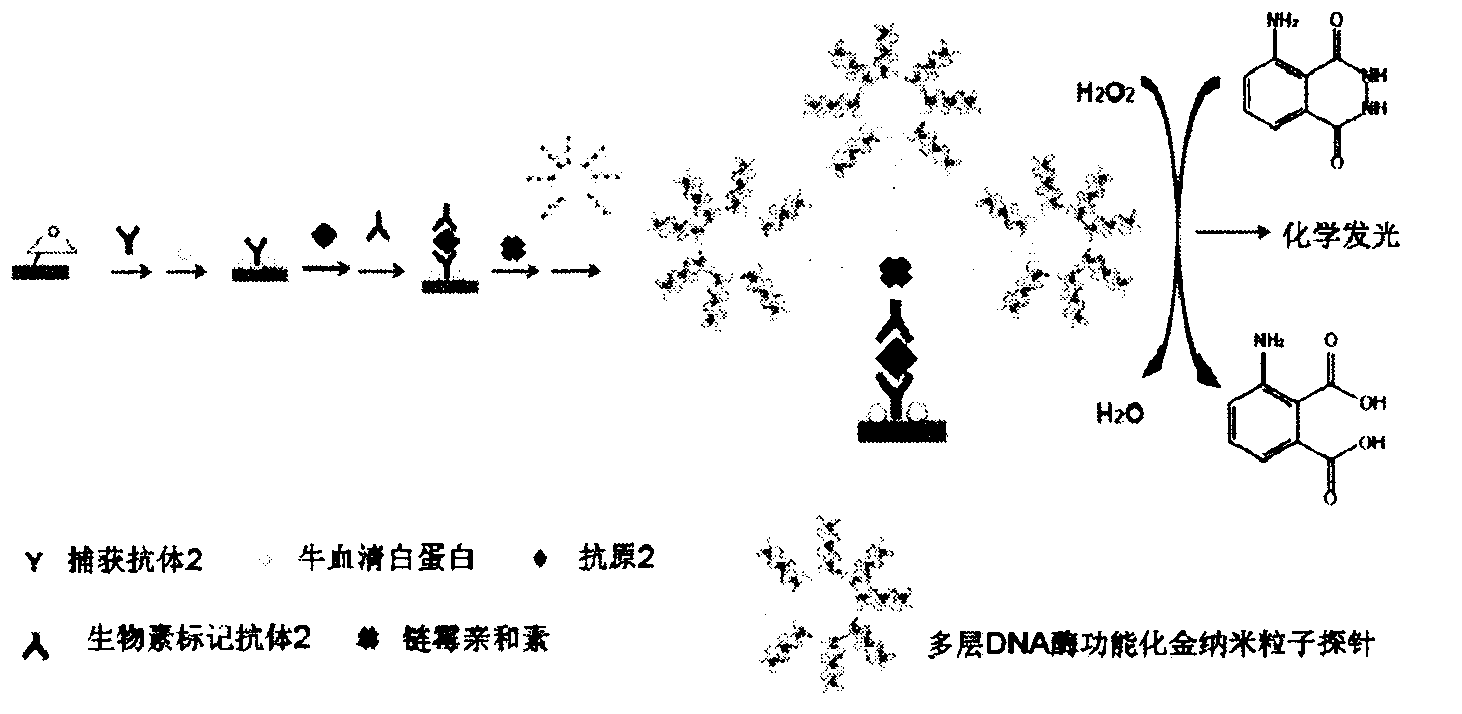
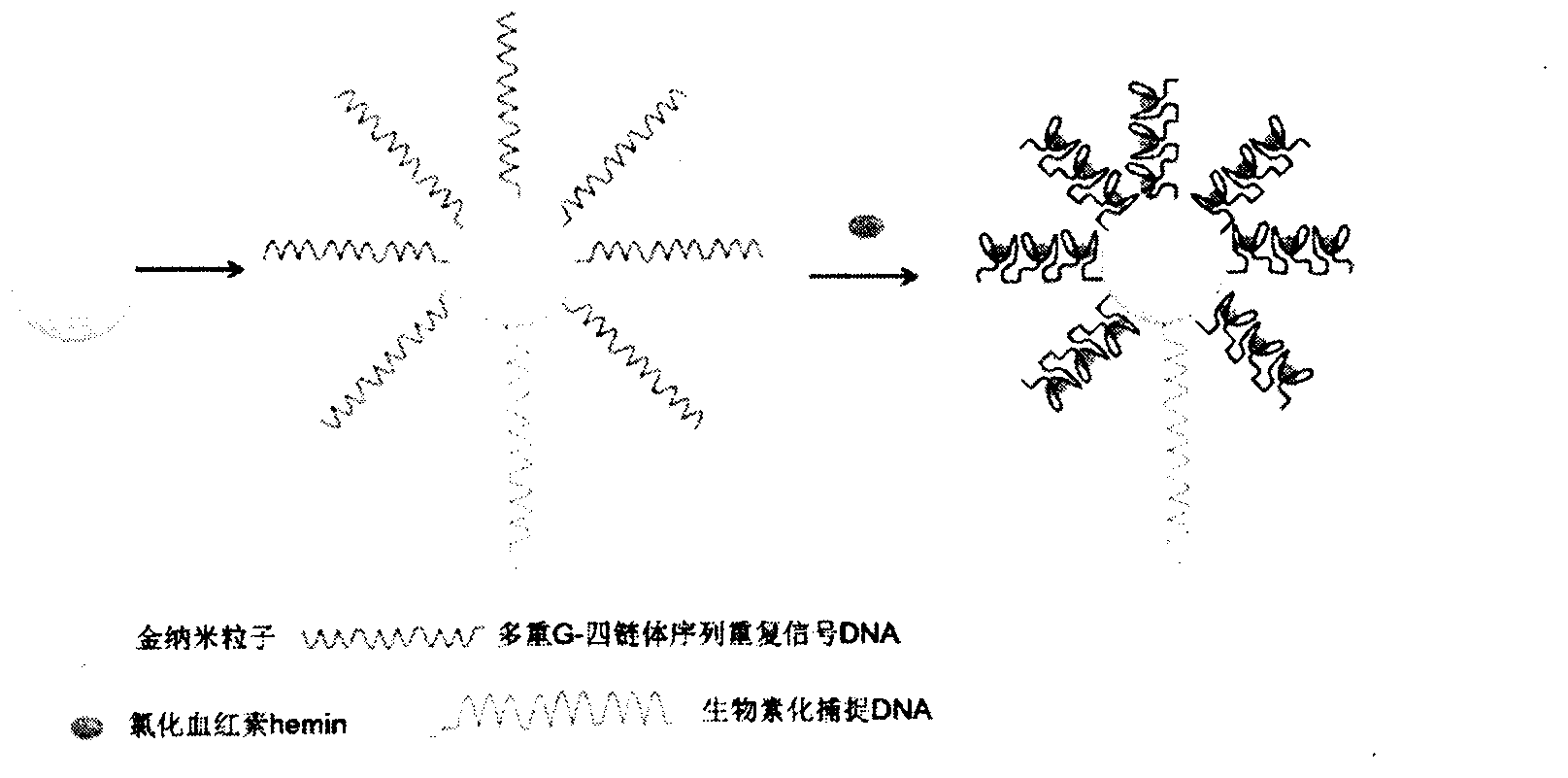
InactiveCN103575896AAchieving Simultaneous High Sensitivity Image ImmunoassaysEasy to makeMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological testingSensor arrayPeroxidase
The invention relates to a high sensitive and jettisonable multicomponent chemiluminescent imaging immunosensor. The immunosensor is prepared by: constructing a 4*12 array on a silanized glass slide by a screen printing technique, and coating the array points with different capture antibodies to construct a jettisonable multicomponent immune sensor array; immobilizing biotinylated capture DNA and multiple G-quadruplex sequence repeat signal DNA on gold nanoparticle surfaces simultaneously, combining G-quadruplex signal DNA with heme to form DNA enzyme so as to prepare a multilayer DNA enzyme functionalized gold nanoparticle probe; and based on sandwich immunoassay, forming a sandwich immune complex on the sensor array, carrying out biotin-avidin reaction, labeling different immune complexes with the multilayer DNA enzyme functionalized gold nanoparticle probe; and making use of the peroxidase characteristics of DNA enzyme to catalyze reaction between chemiluminescent substrate H2O2-luminol to obtain a sensitive chemiluminescent signal, thus realizing high sensitive image immunoassay of a variety of protein. The immunosensor has the advantages of simple design, low cost, high sensitivity, high throughput and good repeatability, etc., and has certain clinical application value.
Owner:JIANGSU CANCER HOSPITAL +1
Potassium ion concentration detection kit and system thereof
ActiveCN102735623AStrong specificityRealize visual detectionMethine/polymethine dyesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPotassium ionsReagent
The invention relates to a potassium ion concentration detection kit and a system thereof. The kit and the system, which utilize characteristics comprising that potassium ion regulation allows G-quadruplex DNA structure transformation to be formed and cyanine dye supermolecular aggregates identify the G-quadruplex DNA structure transformation, have high specificities, and are not affected by sodium ions in a sample. Reagent components are simple and the reaction process is simple, so errors generated by operations can be effectively reduced, and the test accuracy is high. The kit and the system of the invention allow rapid detection to be realized without special or extra apparatuses, and the detection cost is low, so the popularization and the application of the kit and the system are convenient.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
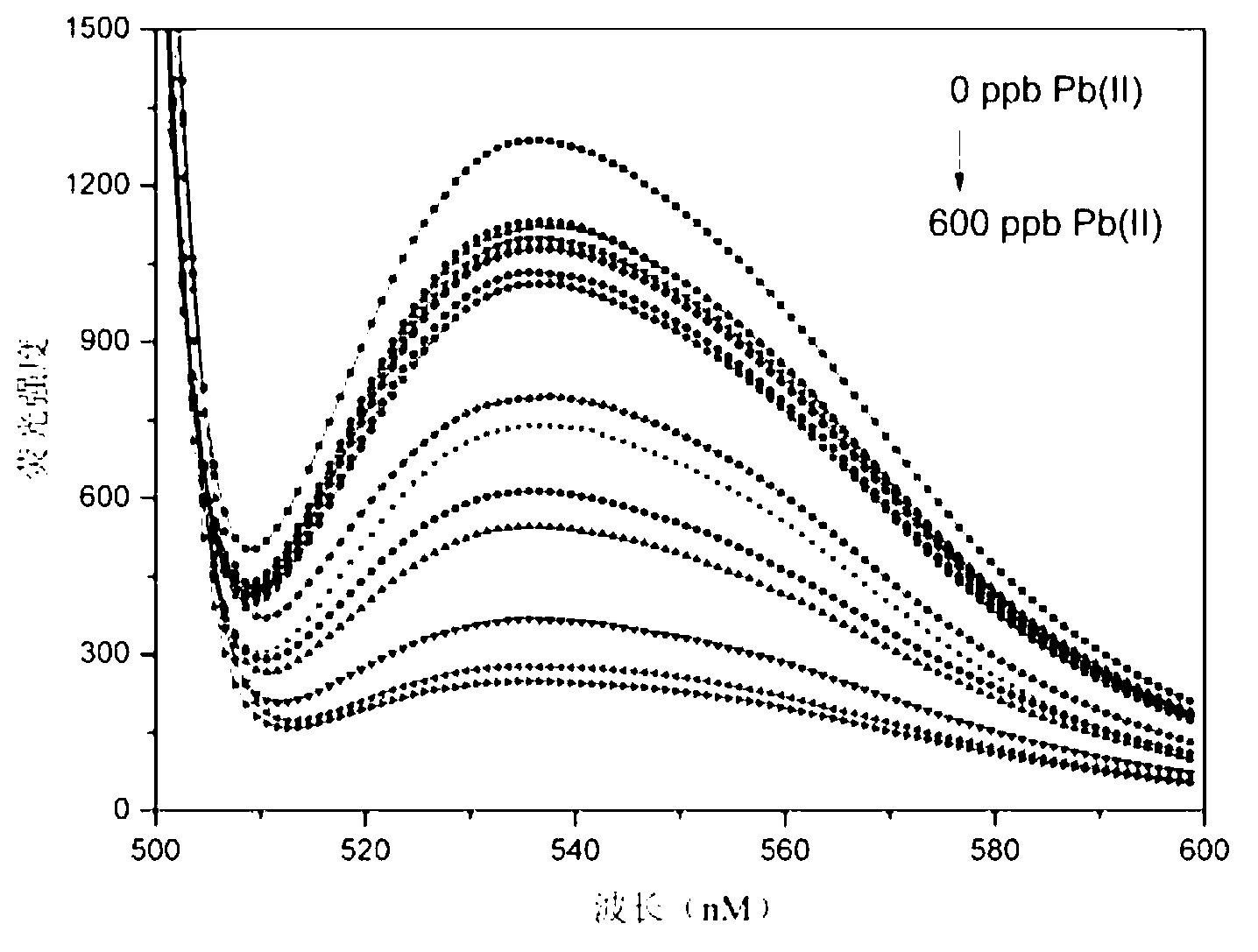
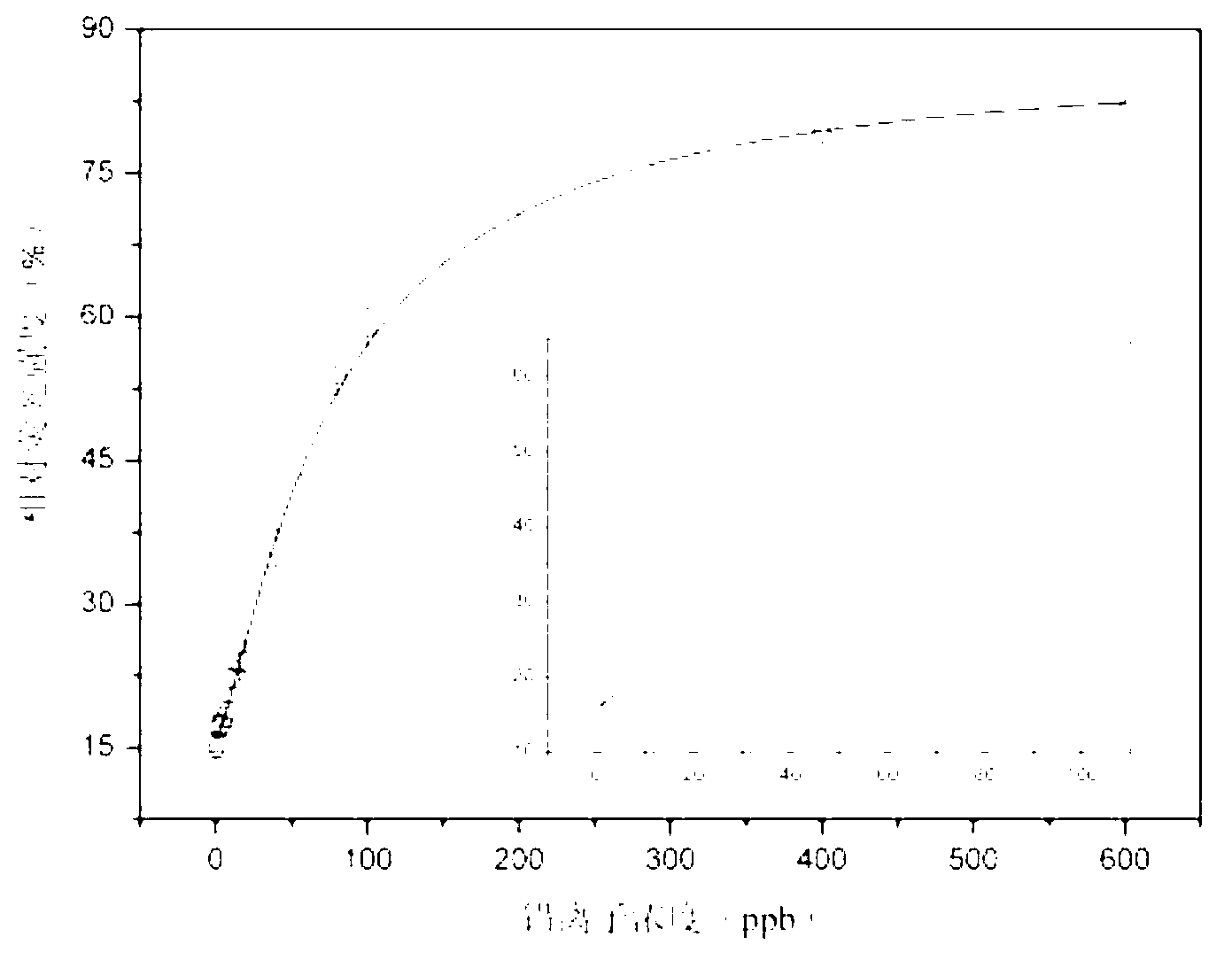
Method for detecting lead ions by forming G-quadruplex quenching fluorescent light by using functional nucleic acid
InactiveCN103245652ALower synthesis costShorten the lengthMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationWater qualityFluorescent quenching
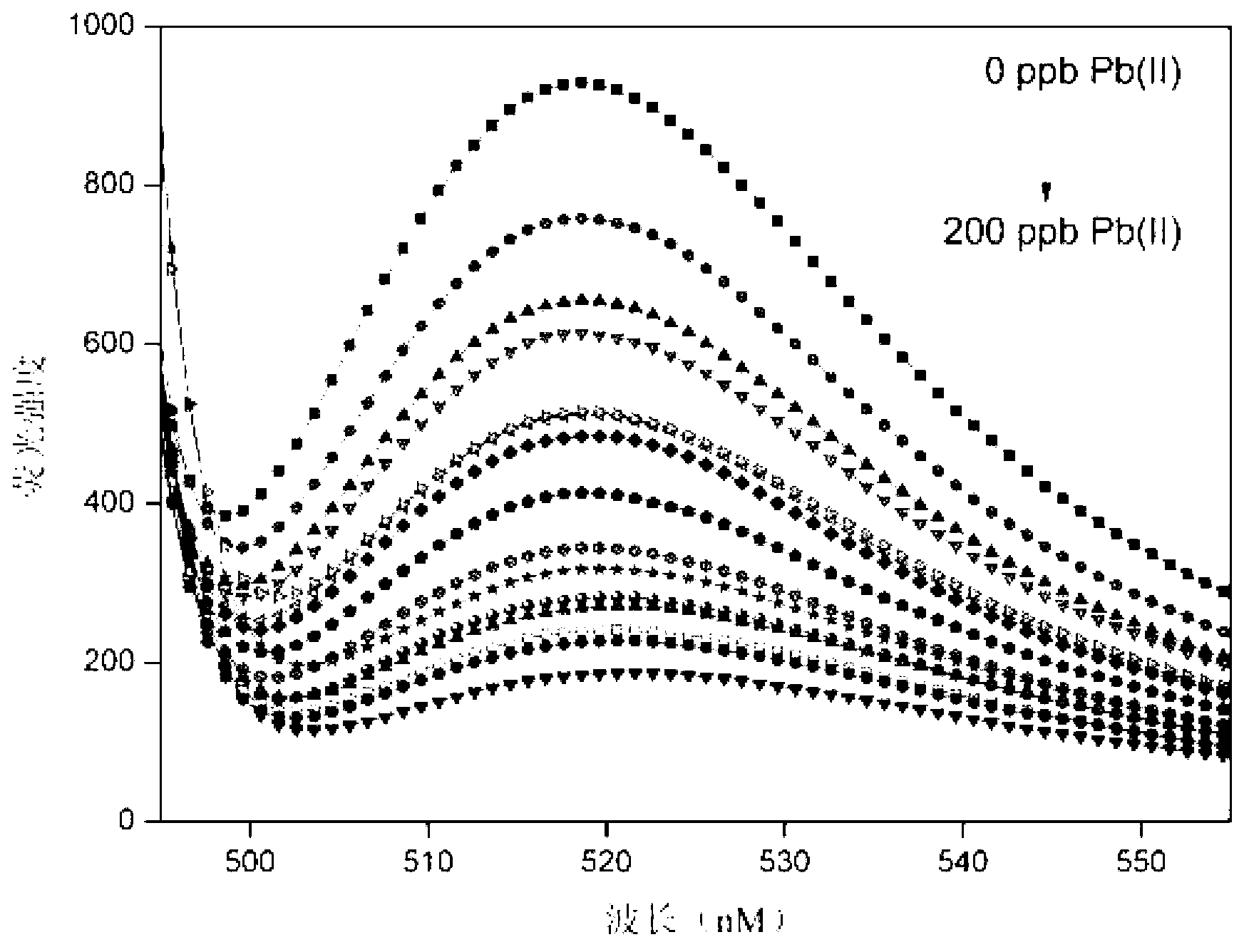
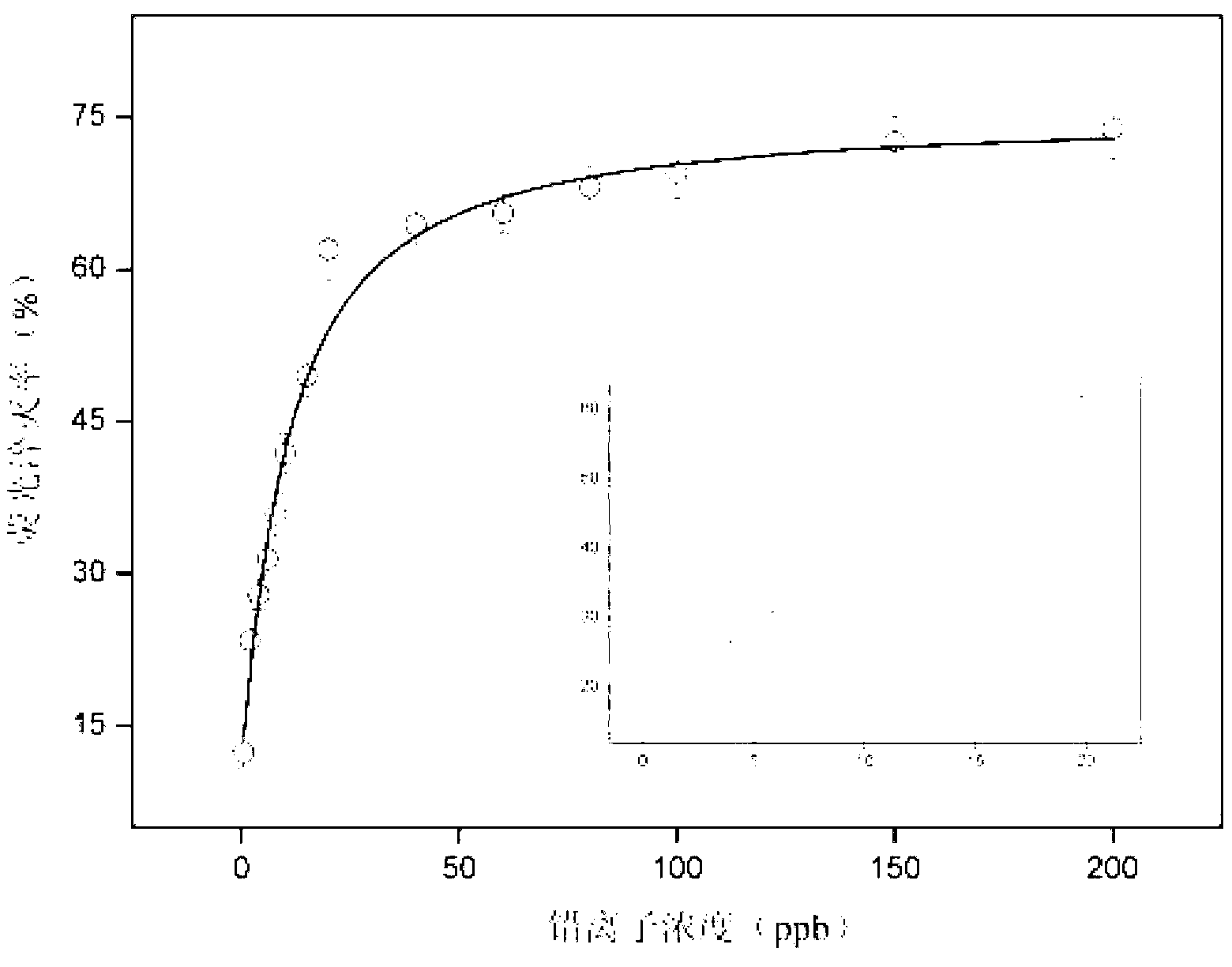
The invention relates to a method for detecting lead ions by forming G-quadruplex quenching fluorescent light by using functional nucleic acid, belonging to the technical field of water quality detection. The method comprises the following steps of: marking the functional nucleic acid by using carboxy fluorescein to construct a lead ion detection system, wherein when lead ions are added into the detection system, the lead ions promote the functional nucleic acid to form a G-quadruplex structure to cause fluorescence signals of the whole system to significantly change around 520nm, and the change of the fluorescence signals is in a positive relationship with the concentration of the lead ions; then carrying out fluorescence spectrum scanning by adopting a fluorescent photometer to obtain a fluorescence quenching rate standard curve; and mixing a water sample to be tested and ultrapure water, namely contrast samples, with a mother solution of the functional nucleic acid respectively, and comparing the fluorescence quenching rates of two mixed products at a part of which the wavelength is 480nm with the fluorescent quenching rate standard curve to obtain the concentration of the lead ions in the water sample to be tested. By adopting the method, the defects that a lot of assistants are needed to be introduced during the detection of the lead ions by using the existing functional nucleic acid, a complex catalytic reaction is related and the like are overcome, and efficient water body lead ion detection of which the lowest detection limit is 0.77ppb and the cost is low is realized by adopting simple operation.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Viable cell mitochondria G-quadruplex targeted fluorescent probe and application thereof
ActiveCN110055054AGood biocompatibilitySimple ingredientsOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceCyanineBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses novel application of a cyanine dye to viable cell mitochondria G-quadruplex detection. The cyanine dye is a structural compound shown as a formula (I) or a stereoisomer of thecompound shown as the formula (I). A cyanine dye fluorescent probe has advantages of high biocompatibility, low cytotoxicity, low molecular weight and low biological sample damages, and real-time observation of cell samples can be realized without being affected by pH values of cells.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
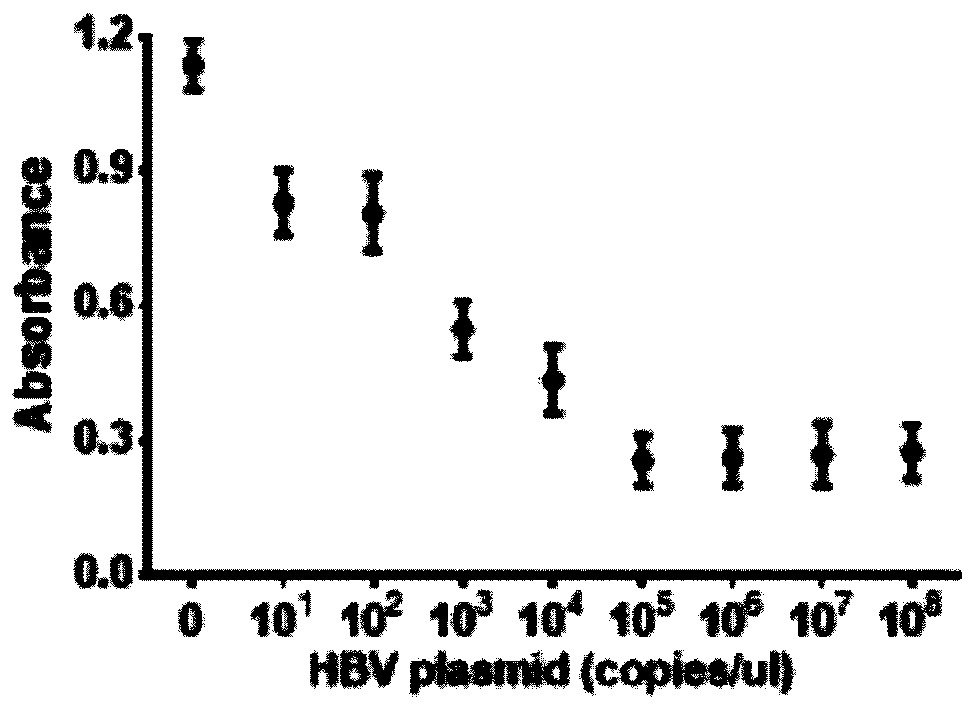
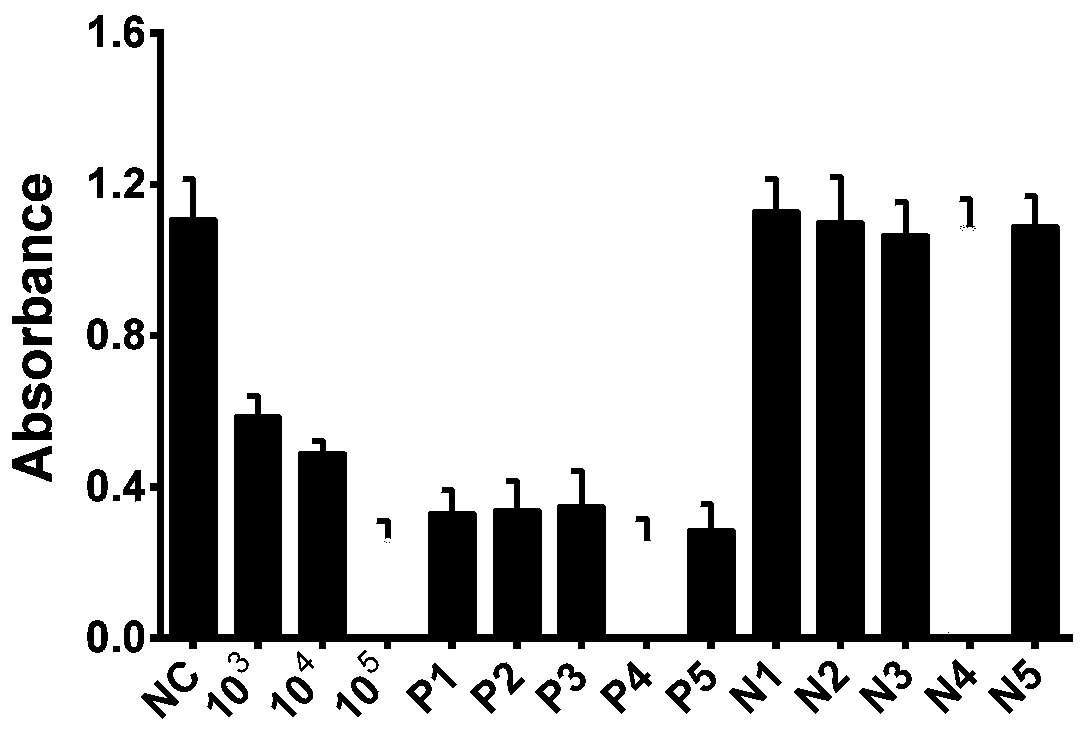
Detection method and application of HBV based on CRISPR-Cas12a and G-quadruplex hemin
ActiveCN109837356AThe detection method is simpleImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHeminABTS
The present invention provides a detection method and an application of HBV based on CRISPR-Cas12a and G-quadruplex hemin. Processes are as follows: DNA extracted from serum of HBV patients is used asa template, a RPA reaction system comprising an amplification primer pair, rehydration buffer and ddH2O is added to lyophozyme powder, then MgAc is added, the materials are mixed evenly and the mixture is incubated to obtain a RPA product; PS2.M DNA is dissolved in a Tris-HCL solution and a Hemin solution is added to the solution to obtain a PS2.M / Hemin solution; FnCas12a and HBV crRNA are addedto a Tris-HCl buffer and incubated to prepare a Cas12a / crRNA complex solution; and the RPA product, PS2.M / Hemin solution and Cas12a / crRNA complex solution are incubated, and ABTS and H2O2 are added for treatment, and absorbance is measured. The detection method is fast, low in cost, high in accuracy, high in sensitivity and simple in equipment.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV CANCER CENT
Self assembling nucleic acid nanostructures
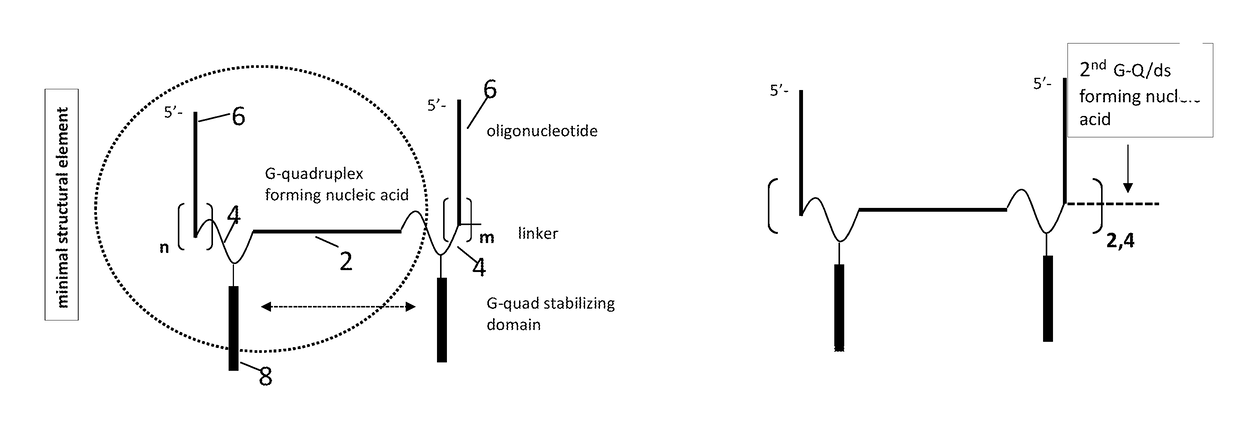
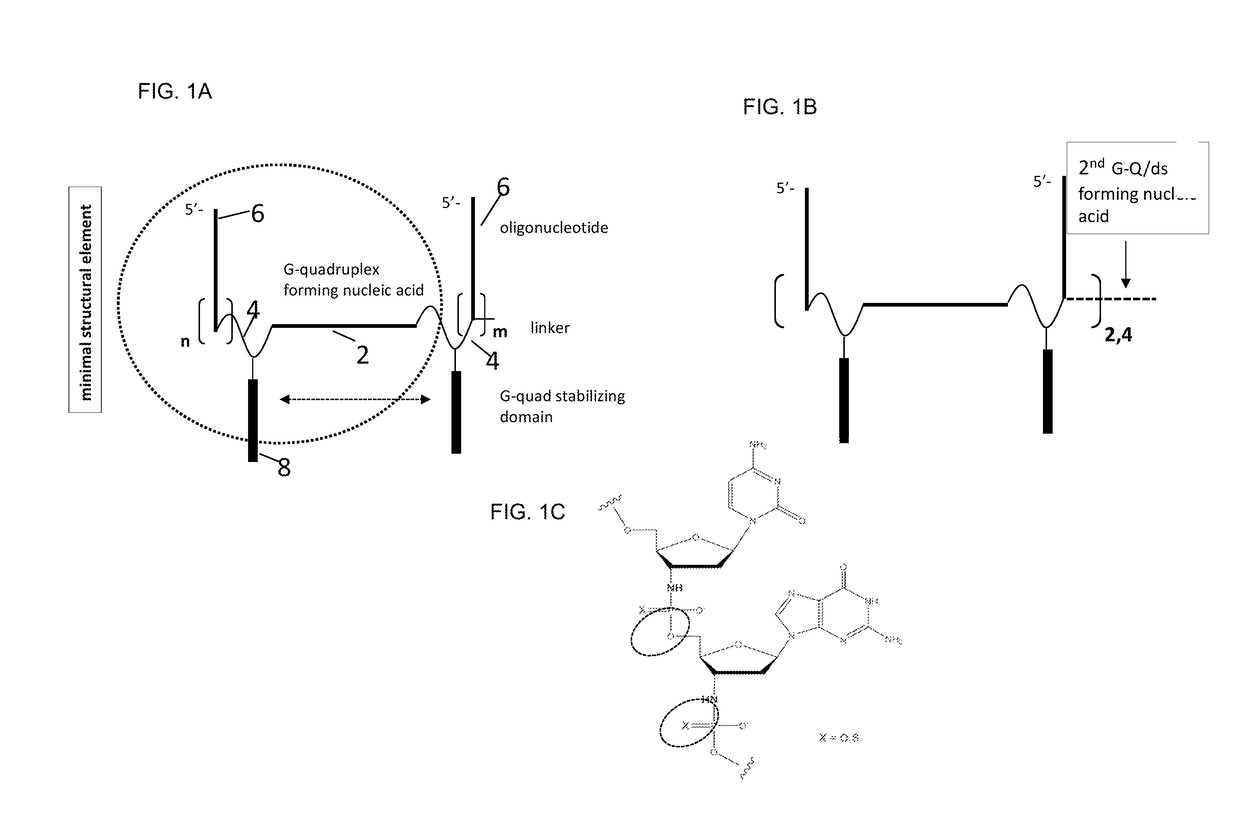
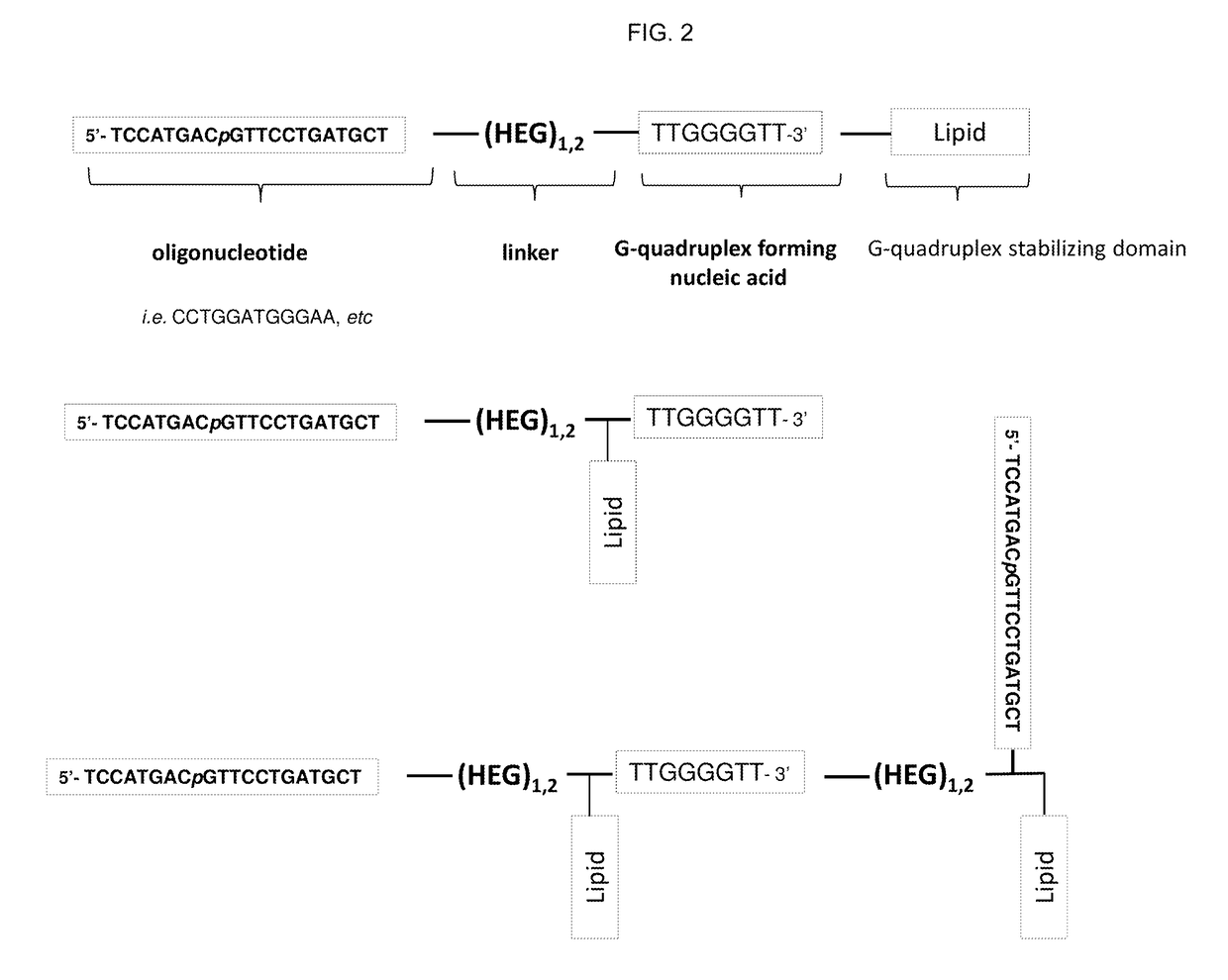
Stable self-assembling nucleic acid nanostructures comprising: —a plurality of oligonucleotides, —a plurality of G-quadruplex forming nucleic acids linked to the plurality of oligonucleotides, and —a plurality of G-quadruplex stabilizing domains linked to the G-quadruplex forming nucleic acids. The nucleic acid nanostructures are suitable for use as agonists or antagonists of nucleic acid interacting complexes, such as Toll-like receptors; for inhibiting DNA or RNA expression; for stimulating or inhibiting an immune response; and for treating diseases such as cancer, infectious diseases, allergies and allergic diseases, and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:EXICURE INC
Substituted coumarin-thiazole orange derivative, preparation method therefor and use of substituted coumarin-thiazole orange derivative
ActiveCN105367566AGood selective binding abilityGood choiceOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementStructural formulaPerylene derivatives
The invention belongs to the field of biochemistry and particularly relates to a substituted coumarin-thiazole orange derivative, a preparation method therefor and use of the substituted coumarin-thiazole orange derivative. The substituted coumarin-thiazole orange derivative provided by the invention has a structural formula represented by a formula I shown in the description. The invention also provides the preparation method for the substituted coumarin-thiazole orange derivative and use of the substituted coumarin-thiazole orange derivative in fluorescent recognition of G-quadruplex. The substituted coumarin-thiazole orange derivative provided by the invention has the advantages that the toxicity is low, the selectivity is good, the sensitivity is high, raw materials are simply and easily obtained, the whole synthesis route is high in operability, reaction conditions are relatively mild, the overall cost is relatively low, and the like, thereby undoubtedly having better market competitiveness compared with the existing inefficient G-quadruplex fluorescent probes.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Application of supramolecular ordered structure in detection of G-quadruplex DNA
InactiveCN101587070AEasy to understandMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsOrder structureBiology
The invention discloses the use of a supramolecular ordered structure in the detection of a G-quadruplex DNA. The method realizes the detection of the G-quadruplex DNA by detecting the change of the aggregation state of the supramolecular ordered structure. The detection of the G-quadruplex DNA by using the supramolecular ordered structure has the advantages of simplicity, quickness and relatively low price and overcomes the drawbacks of the prior detection technology such as long period, high price and high technical and equipment requirements.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of fluorescent biosensor of double-cycle and double quenching system based on functionalized graphene quantum dots
InactiveCN109593831AGood water solubilityEnhanced fluorescence emission intensityMicrobiological testing/measurementDissolutionQuenching
The invention relates to a preparation method of a fluorescent biosensor of a double-cycle and double quenching system based on functionalized graphene quantum dots. The method comprises the followingsteps: weighing raw materials including citric acid, histidine and pentaethylene hexamine at the molar ratio of 0.01:0.1:1 to 1:1:1, uniformly mixing, adding deionized water, then performing ultrasonic dissolution to obtain a reaction solution, placing the reaction solution in an oven, reacting for 0.5-10h at an oven temperature of 150-250 DEG C to directly obtain a crude product of pentaethylenehexamine-histidine graphene quantum dot PEHA-GQD-His after reaction, then obtaining an LDNA-capped pentaethylene hexamine-histidine graphene quantum dot PEHA-GQD-His solution, finally forming a G-quadruplex / DNase, and finally adding 0.5-100[mu]l of H2O2 with the molar concentration of 0.1-10[mu]M to obtain the fluorescent biosensor of the double-cycle and double quenching system.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Nucleic acid aptamer of epithelial cell adhesion molecule and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102827845AMaintain native conformationNo toxicityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingProtein targetSingle strand dna
The invention relates to a nucleic acid, in particular to a nucleic acid aptamer of the epithelial cell adhesion molecule and a preparation method thereof. The invention provides a high-specificity and high-affinity nucleic acid aptamer of the epithelial cell adhesion molecule EpCAM and a preparation method and applications thereof. The nucleic acid aptamer of the epithelial cell adhesion molecule EpCAM is of the G-quadruplex structure or the stem-loop structure. The preparation method comprises the following steps: designing and synthetizing a single-stranded DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) random oligonucleotide library, screening the target oligonucleotide sequence, and identifying the binding specificity and affinity of the sequence to the target protein through the flow cytometry. The screened nucleic acid aptamer is non-toxic, has small molecular weight and good permeability, is easy in synthesis and marking and can only perform specific identification to the EpCAM protein and perform specific identification and specific expression to the cell line of the EpCAM protein; and the nucleic acid aptamer can not identify the cell line which does not express the protein.
Owner:苏州德运康瑞生物科技有限公司
Method for detecting lead by G-quadruplex fluorescence method formed by using unlabeled functional nucleic acid
InactiveCN103305622AEasy to operateHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceWater quality
The invention discloses a method for detecting lead by a G-quadruplex fluorescence method formed by using unlabeled functional nucleic acid, and belongs to the technical field of water quality testing. The method comprises the following steps that: a lead ion detection system is established through the functional nucleic acid and a DNA intercalating agent; if no lead ion exists in the detection system, the DN intercalating agent is intercalated into the functional nucleic acid, and fluorescence is released at 535 nm; after the lead ions are added into the detection system, the functional nucleic acid is promoted by the lead ions to form a G-quadruplex structure, and the DNA intercalating agent reacts with the G-quadruplex to suppress the release of the fluorescence at the 535 nm; on the base that a released fluorescence signal is in inverse ratio to the concentration of the lead ions, the lead ions can be quantitatively detected by determining the fluorescence signal. According to the method, the shortcomings a complex catalytic reaction is needed and the like because the functional nucleic acid is required to be labeled in the prior art are overcome; the method has the characteristics of simplicity in operation, high sensitivity, high selectivity, low cost and high efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Fluorescent probe for selectively detecting RNA G-quadruplex in cells as well as preparation method and application of fluorescent probe
ActiveCN108191752AExcellent optical propertiesEnhanced push-pull electronic effectOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceTriflic acid
The invention provides a fluorescent probe for selectively detecting an RNA G-quadruplex in cells as well as a preparation method and application of the fluorescent probe. The fluorescent probe has astructure represented by a formula (I) shown in the description, wherein Ar is an aromatic ring or an aromatic heterocyclic ring; R1 is fluorine, amino or an amine substituent; and A<-> is a N methylated anion, an iodide ion, a p-toluenesulfonic acid ion or a trifluoromethanesulfonic acid ion. The fluorescent probe provided by the invention can specifically detect and recognize the RNA G-quadruplex in the cells, the detection process is not interfered by other components, and the real-time tracking of the movement process and folding and unfolding process of the RNA G-quadruplex in living cells is realized; and the fluorescent probe has a simple preparation process, low costs and a stable structure, is convenient for storage, and has broad application space in the biological function research of the RNA G-quadruplex.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com