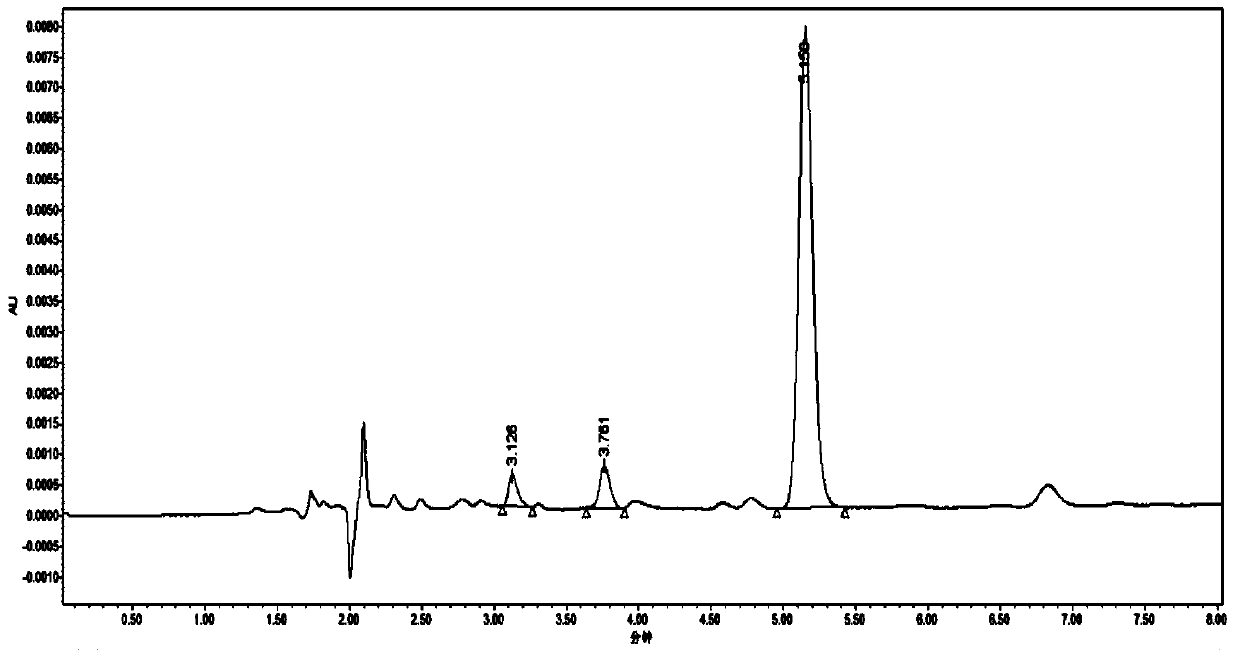
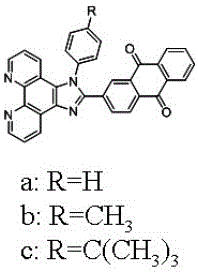
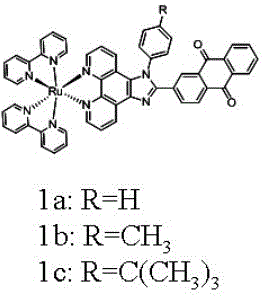
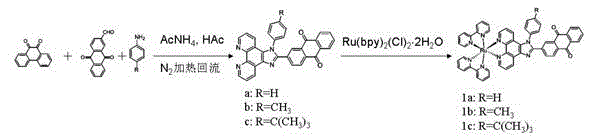
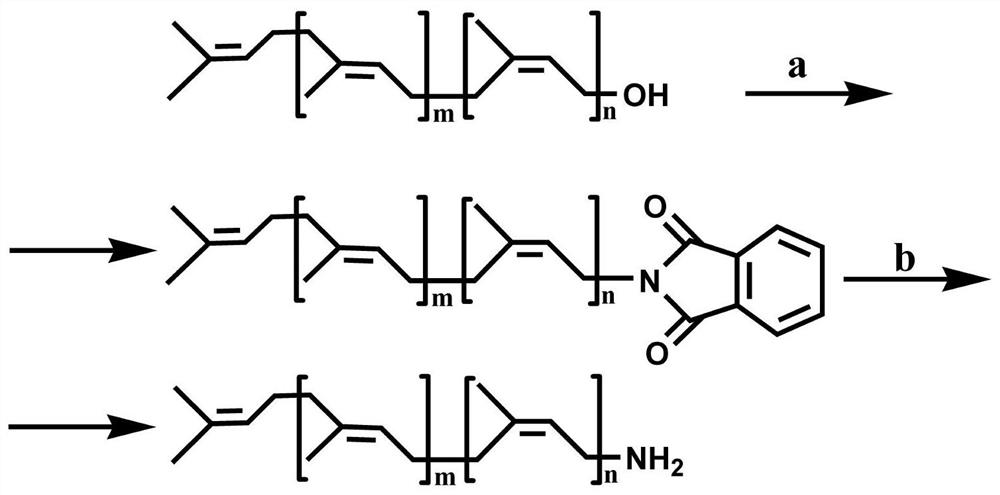
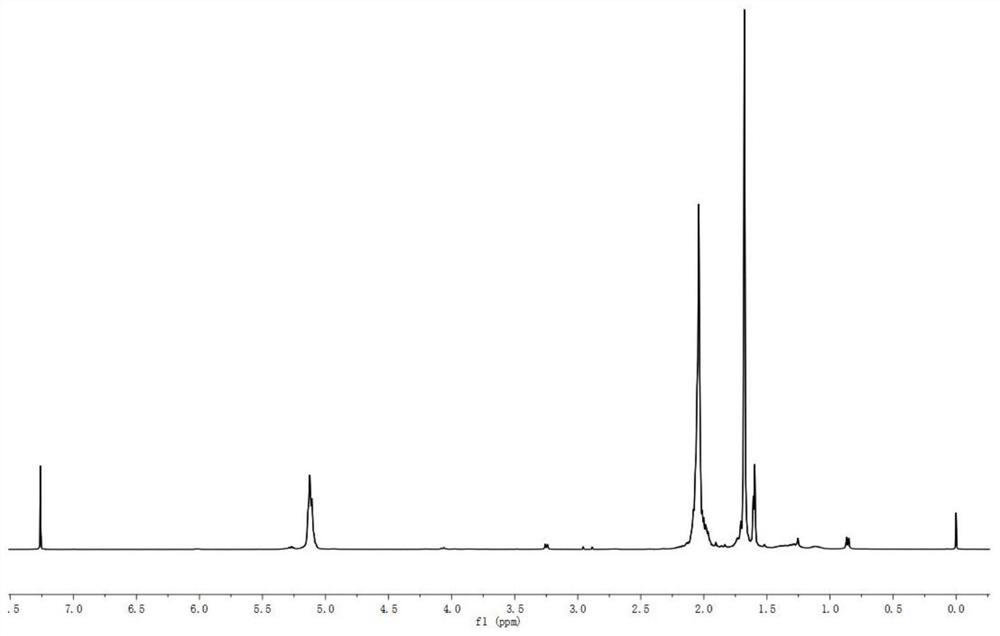
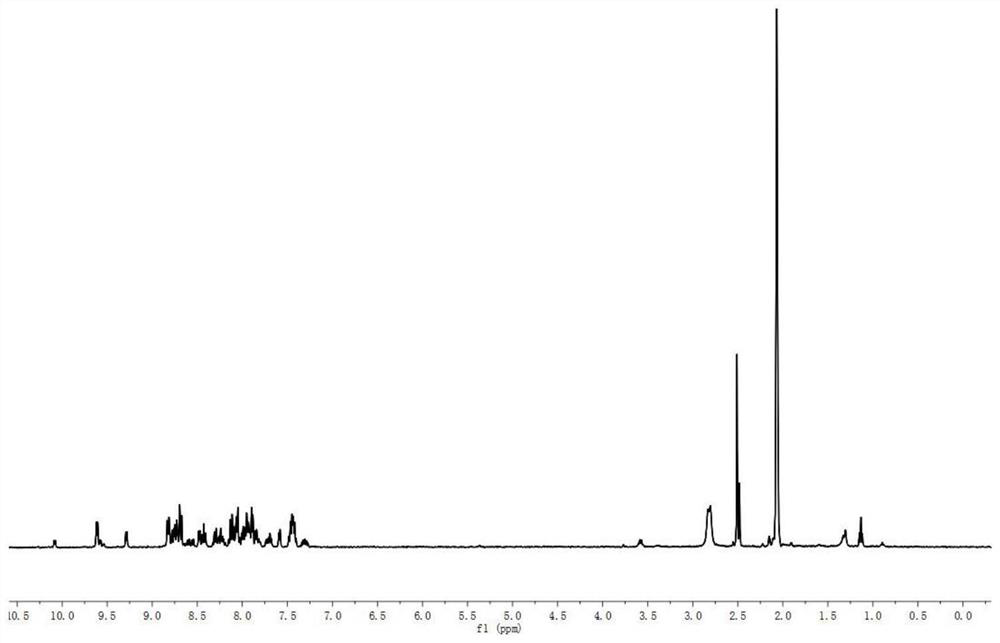
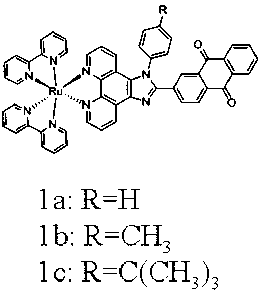Patents
Literature
30 results about "Polypyridine complex" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polypyridine complexes are coordination complexes containing polypyridine ligands, such as 2,2'-bipyridine, 1,10-phenanthroline, or 2,2';6'2"-terpyridine. Polypyridines are multidentate ligands that confer characteristic properties to the metal complexes that they form. Some complexes strongly absorb light via a process called metal-to-ligand charge transfer (MLCT). The properties of these complexes can be tuned by changes in substituents. For example, electron donation, electron withdrawal, and π-conjugating groups, to the polypyridine moiety. The MLCT absorption band can be shifted, the emission wavelength can be changed, and the emission lifetime can be extended.
Ruthenium (II)-polypyridine complex, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102464676AG-quadruplex DNA molecular optical switch with good performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsLithium chlorideFiltration
The invention provides a ruthenium (II)-polypyridine complex. For the ruthenium (II)-polypyridine complex, bipyridyl (bpy) or phenanthroline hydrate (phen) is used as an ancillary ligand, and dipyridine[3,2-a:2',3'-c]phenazine-11,12-imidazole (dppzi) is used as a main ligand. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing 5,6-dinitrobenzimidazole from 5,6-nitrobenzimidazole; reducing 5,6-dinitrobenzimidazole into 5,6-diaminobenzimidazole by using hydrazine hydrate and palladium / carbon; preparing dppzi from phenanthroline hydrate-5,6-dione and 5,6-diaminobenzimidazole and preparing cis-[Ru(bpy)2Cl2].2H2O from ruthenium trichloride, bpy and lithium chloride; preparing cis-[Ru(phen)2Cl2].3H2O from ruthenium trichloride, phen and lithium chloride; carrying out a heating reflux reaction on dppzi and cis-[Ru(bpy)2Cl2].2H2O or cis-[Ru(phen)2Cl2].3H2O under the protection of argon, carrying out cooling, adding ammonium hexafluorophosphate, allowing precipitate to deposit and carrying out filtration and column chromatography so as to obtain a target product. The ruthenium (II)-polypyridine complex provided in the invention can be used as an optical switch for G-quadruplex DNA molecules.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
High efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells
InactiveUS20130160855A1Avoid recombinationLess steric bulkLight-sensitive devicesSolid-state devicesExtinctionIodide
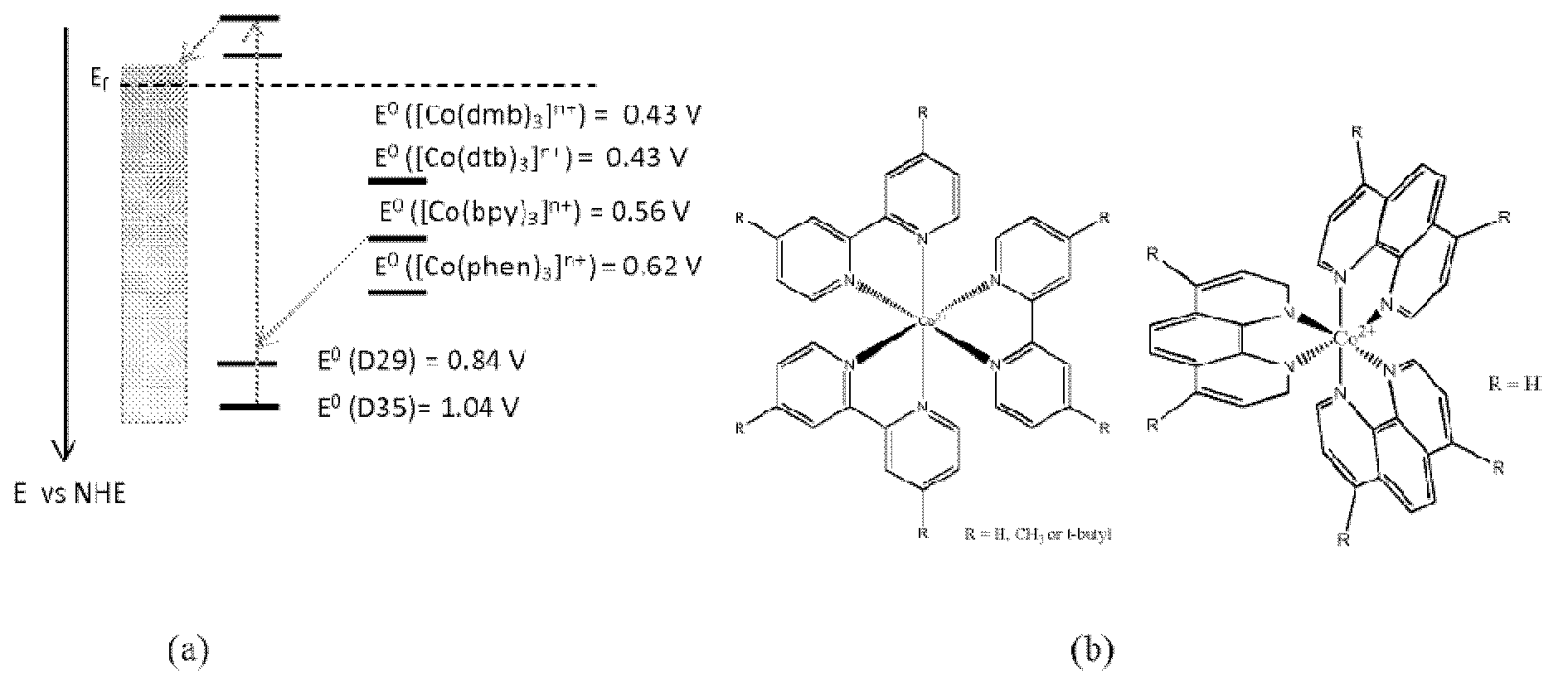
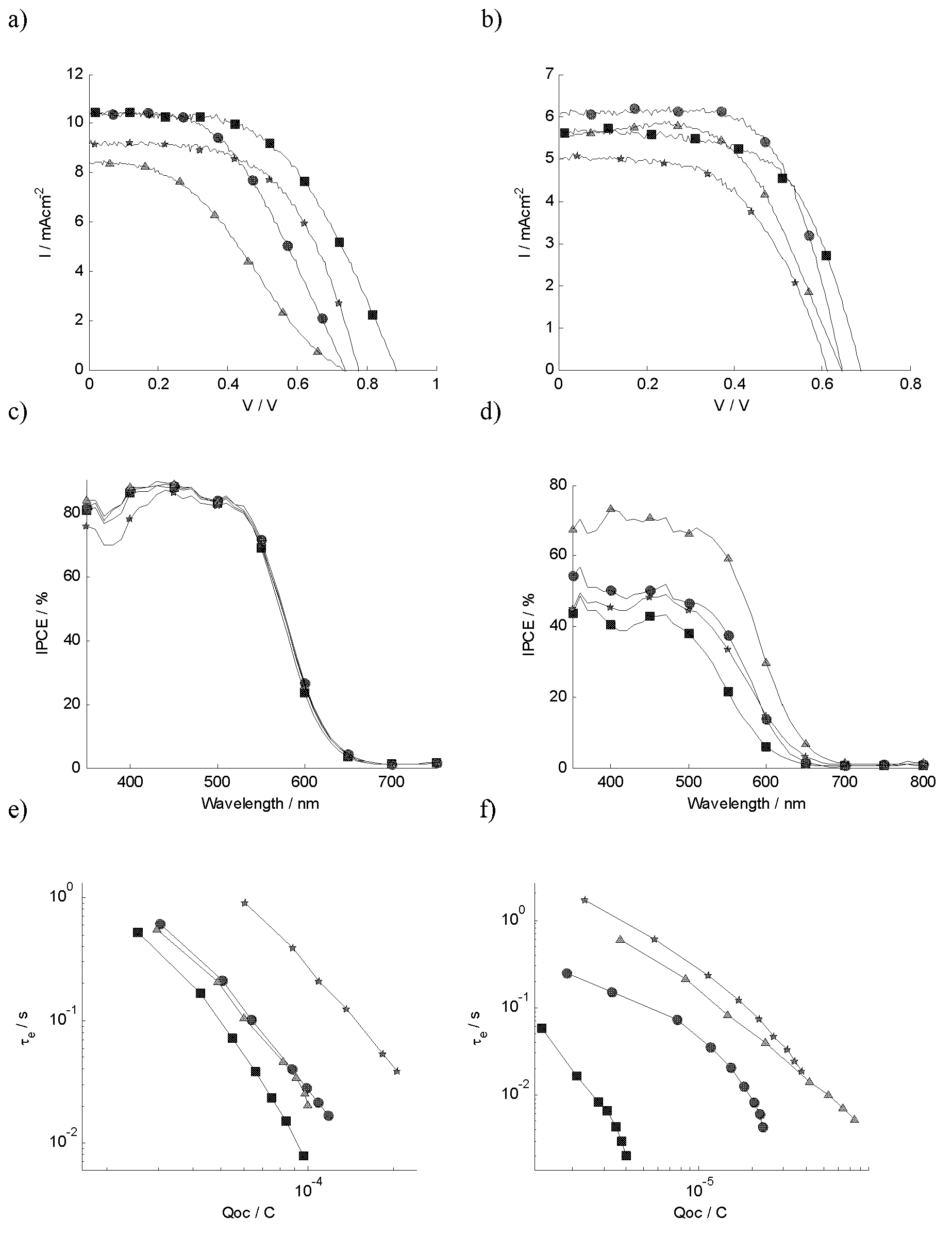
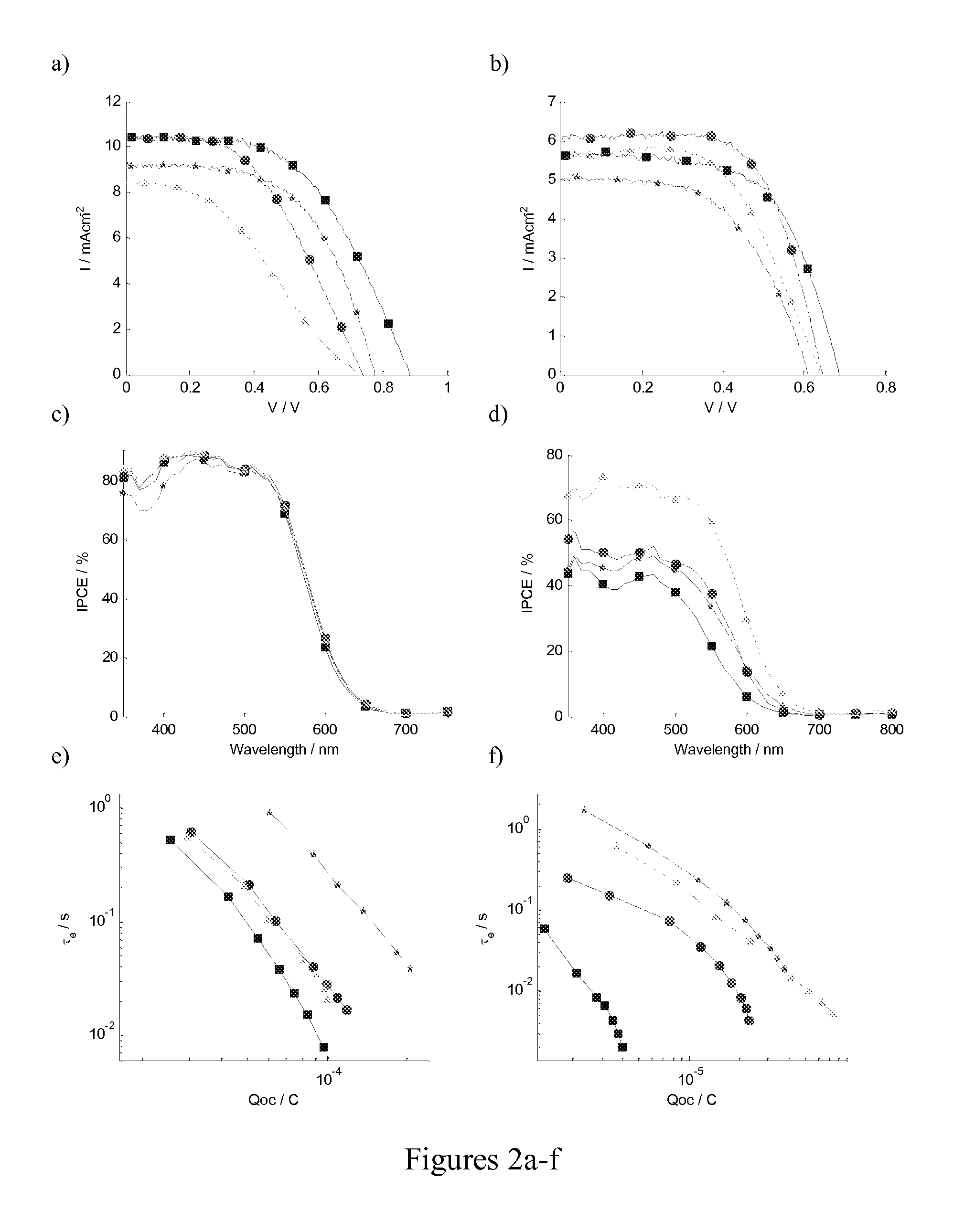
Cobalt polypyridine complexes are interesting alternative redox mediators for large scale manufacturing of dye-sensitized solar cells (DSCs) since they are less aggressive towards metal contacts and absorb less light than iodide / triiodide. Here we have examined the effect of steric properties of triphenylamine-based organic sensitizers and cobalt polypyridine redox mediators on the electron lifetime and overall device performance in DSCs. Matching the steric bulk of the dye and redox mediator was found to minimize recombination and mass transport problems in DSCs employing cobalt redox mediators. Recombination was efficiently slowed down by introducing insulating butoxyl chains on the dye, allowing the use of a cobalt redox mediator with a less steric bulk. The best efficiency of DSCs sensitized with a triphenylamine-based organic dye in combination with cobalt(II / III) tris(2,2′-bipyridyl) match the highest efficiencies obtained so far with iodide-free electrolytes, reaching a 6.3% overall conversion efficiency under AMI.5 condition (1000 Wm-2) and an efficiency of 7.8% at 1 / 10 of a sun. Organic dyes with high extinction coefficient can thus be used instead of standard ruthenium sensitizers to build thin films DSCs in order to overcome mass transport and recombination limitations associated with the cobalt redox couples. DSCs sensitized with organic dyes employing cobalt redox mediators are promising for low light intensity applications since the efficiency and voltage is high at indoor illumination.
Owner:DYENAMO
Preparing process of Ru(II) polypyridine complex
InactiveCN1986555AGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsMicrobiological testing/measurementSodium tetrafluoroboratePhenanthroline
The preparation process of Ru(II)-polypyridine complex includes the following steps: preparing 1,10-phenanthroline-5,6-diquinone, pyridine [3, 2-a:2', 3'-c] phenazine as ligand I, and 7,8-dimethyl pyridine [3, 2-a: 2', 3'-c] phenazine as ligand II, Ru(bipy)2Cl2.2H2O (bipy=2, 2'-dipyridyl) as precursor I and Ru(phen)2Cl2.2H2O as precursor II; adding certain amount of Ru(bipy)2Cl2.2H2O / Ru(phen)2Cl2.2H2O, ligand I / ligand II, and mixture liquid of methanol and water, heating reflux for certain time, heating to concentrate, adding water and boiling, freezing, adding sodium tetrafluoborate, filtering and separating out precipitate, re-crystallization in alcohol, and stoving under infrared lamp to obtain the Ru(II)-polypyridine complex. The Ru(II)-polypyridine complex is used as nucleic acid recognizing probe for the analysis and detection of nucleic acid, and has high stability, high sensitivity, high selectivity and other advantages.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Ruthenium (II) polypyridine complex and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105732723AThe synthesis steps are simpleHigh yieldOrganic active ingredientsRuthenium organic compoundsTelomerasePhenanthroline
The invention relates to ruthenium (II) polypyridine complex.The complex uses 2-(1, 10-phenanthroline monohydrate-5-base)-benzimidazole) as the main ligand and 2, 2'-bipyridine or 1, 10'-phenanthroline as the auxiliary ligand, and the chemical formula of the complex is [Ru(bpy)2pbi]2+ or [Ru(phen)2pbi]2+.A preparation method of the complex includes the steps of firstly, preparing pbi; secondly, synthesizing a ruthenium metal compound with the auxiliary ligand group; thirdly, synthesizing the target ruthenium (II) polypyridine complex; fourthly, using silica gel chromatography column separation to obtain the product.The ruthenium (II) polypyridine complex is used for preparing medicine combining with telomere G-quadruplex to increase the stability of the telomere G-quadruplex.Compared with the prior art, the ruthenium (II) polypyridine complex prepared by the method has the advantages that the ruthenium (II) polypyridine complex can recognize, combine and stabilize the telomere G-quadruplex, inhibit telomerase activity and regulate proto-oncogene expression, and a theoretical foundation is provided for anticancer medicine screening.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
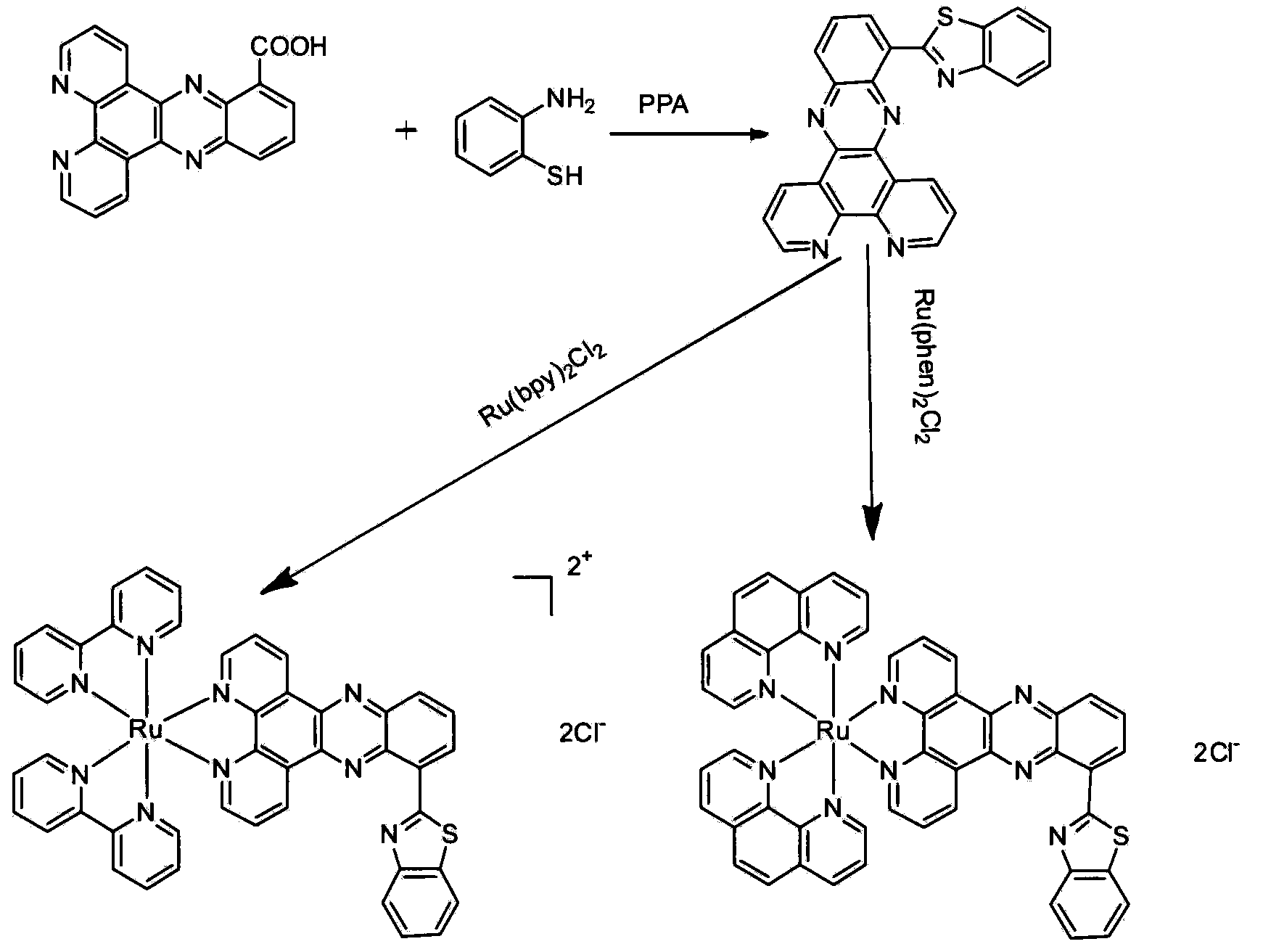
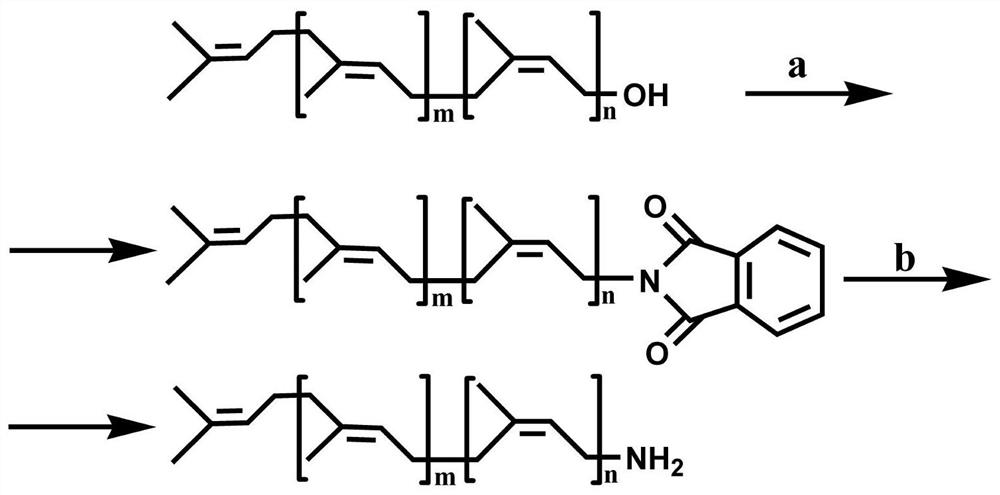
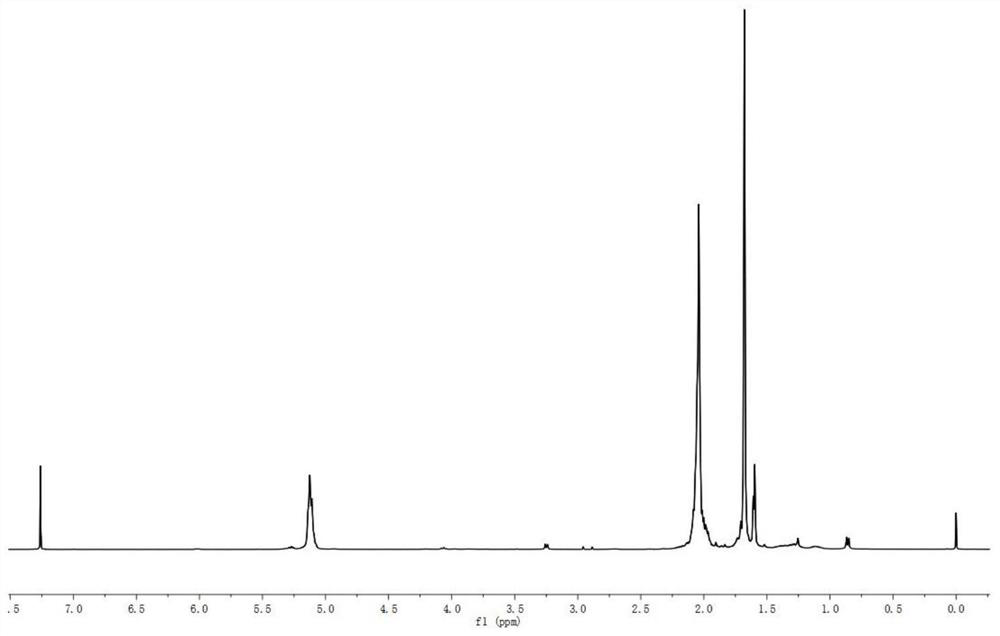
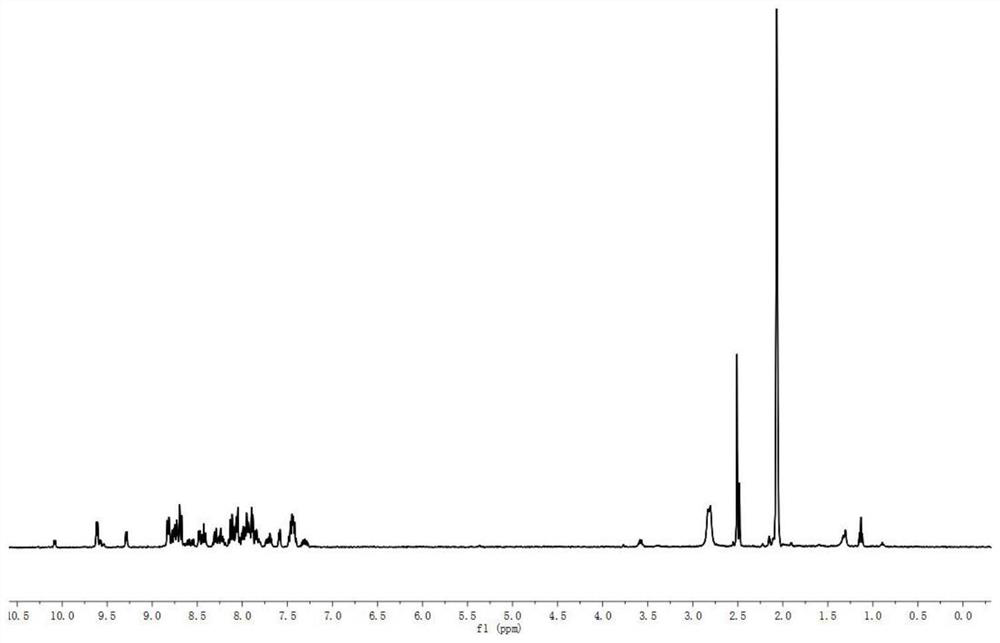
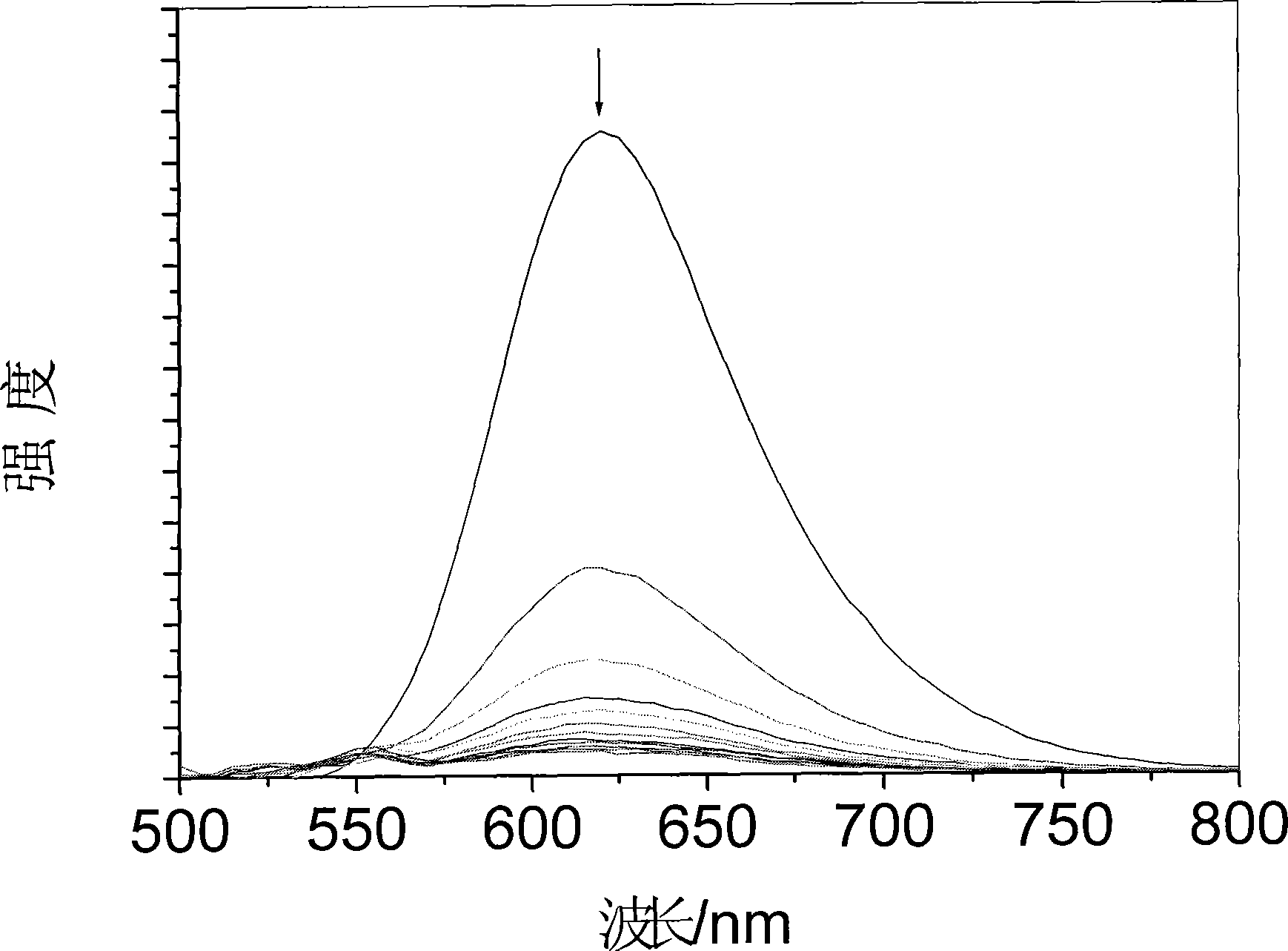
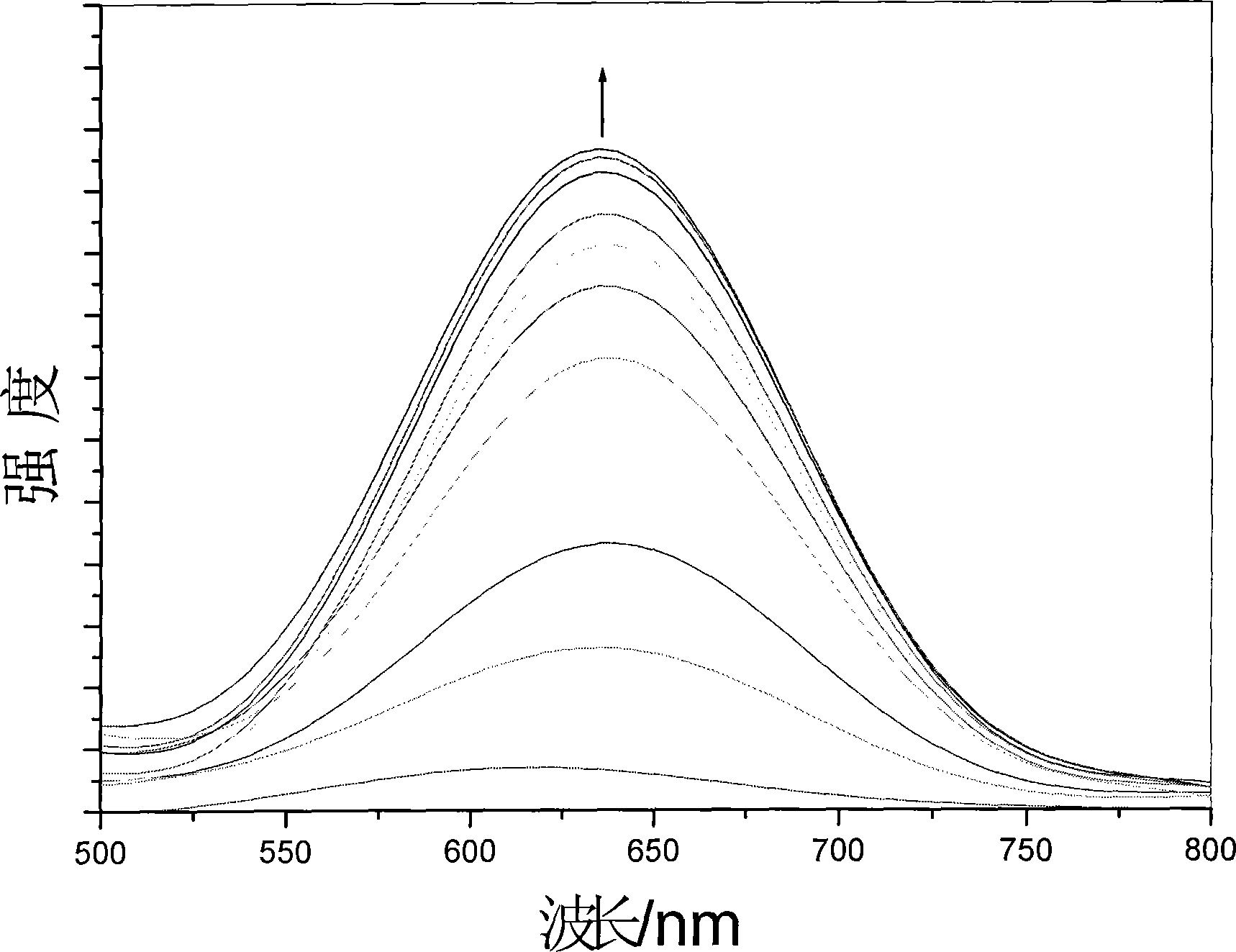
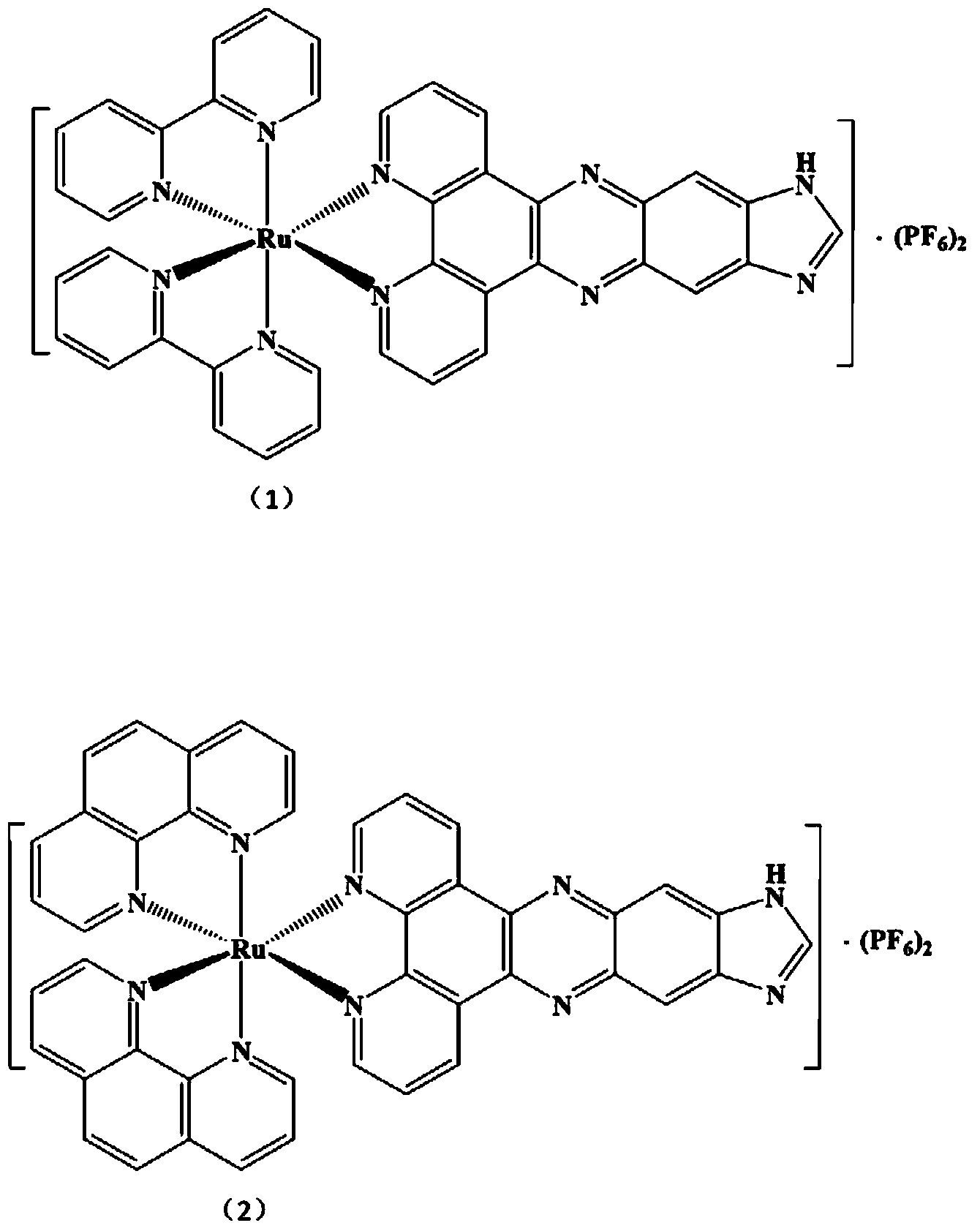
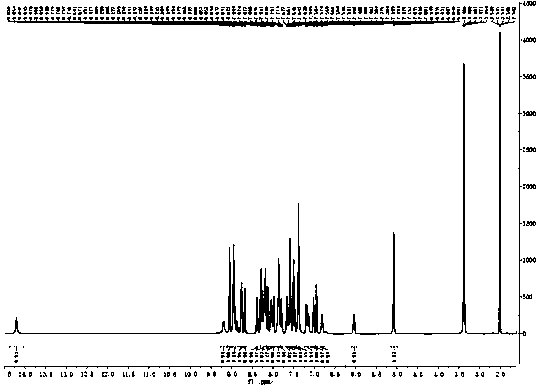
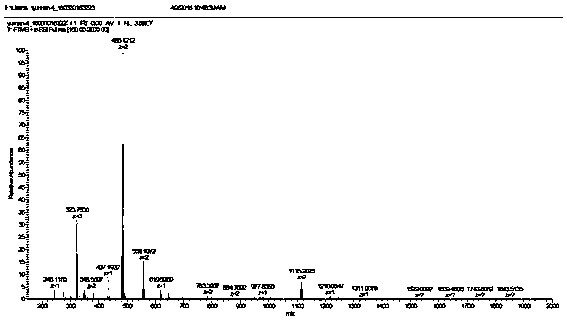
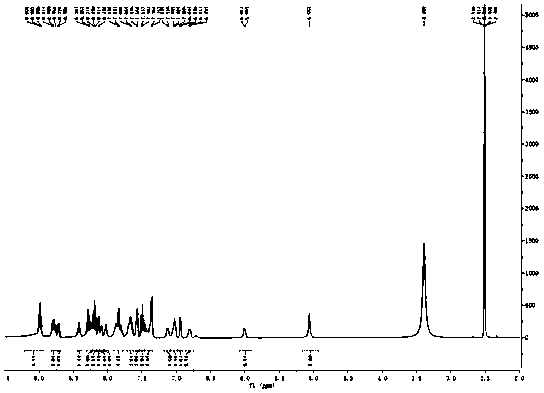
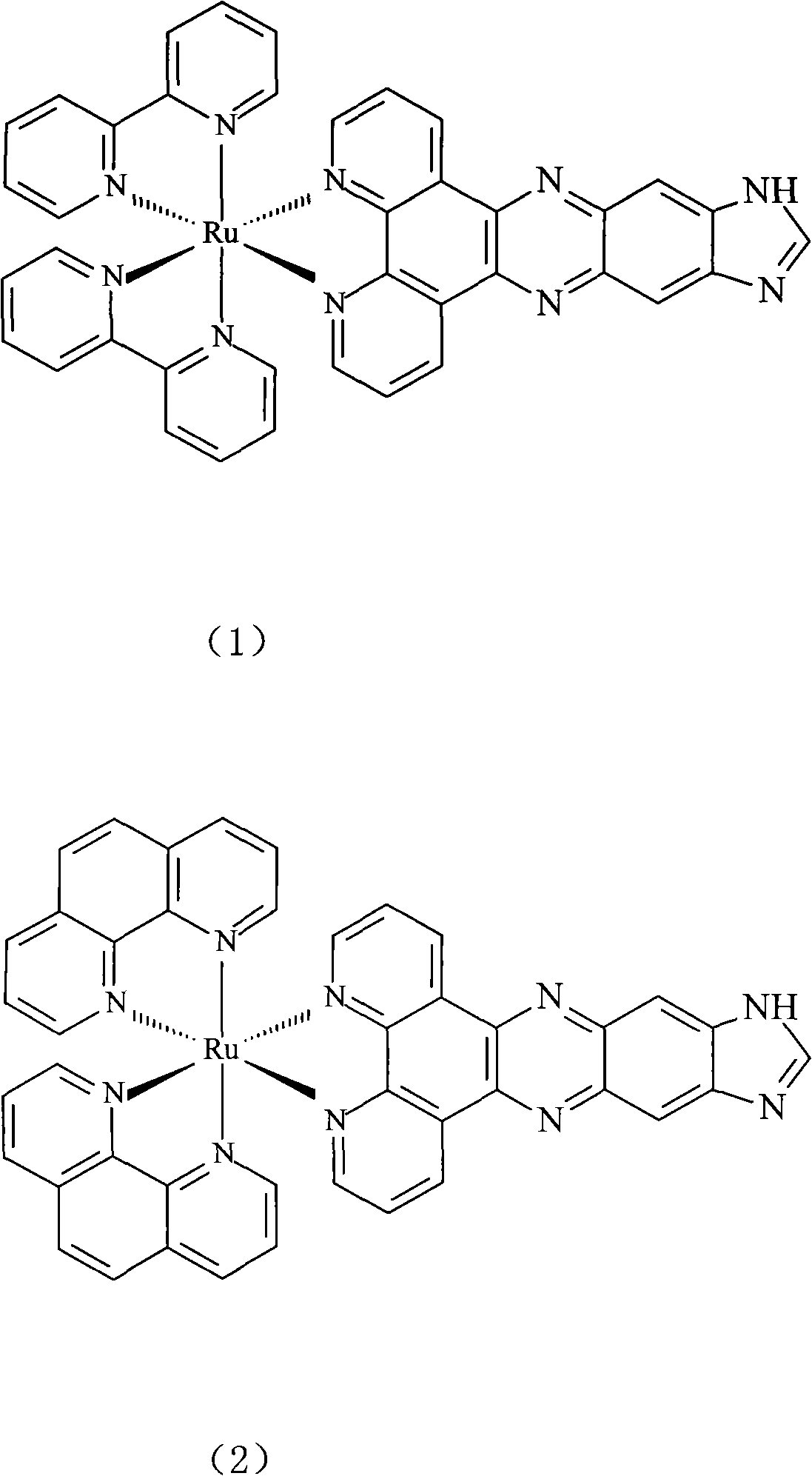
Ruthenium polypyridine complex and preparation method and application of [Ru(L)2(tppp)]<2+> thereof
InactiveCN103788135AGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsMicrobiological testing/measurementPhenanthrolineA-DNA
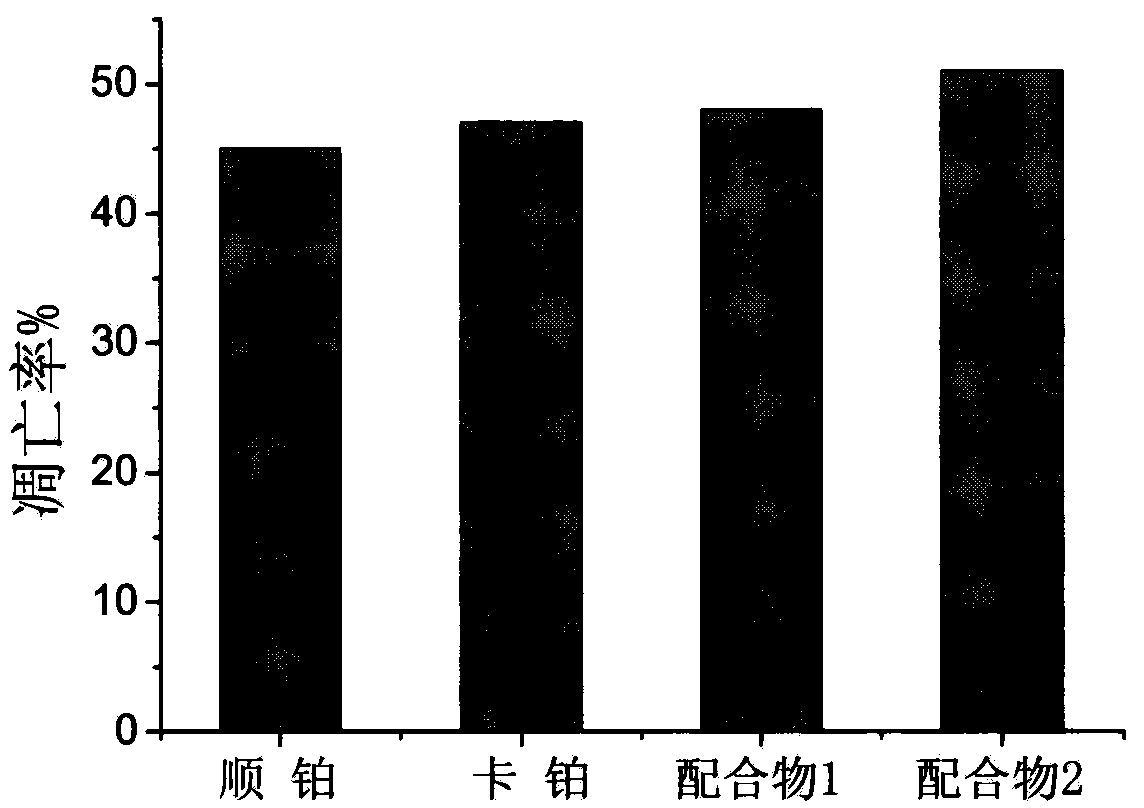
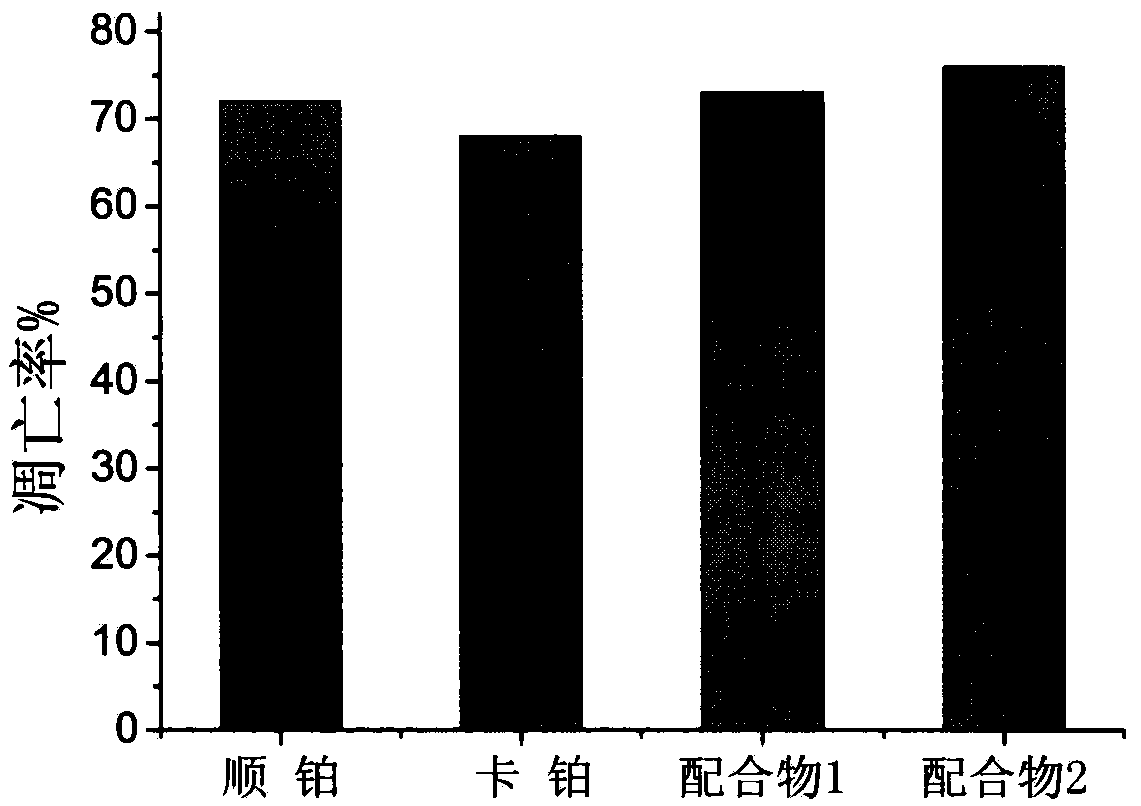
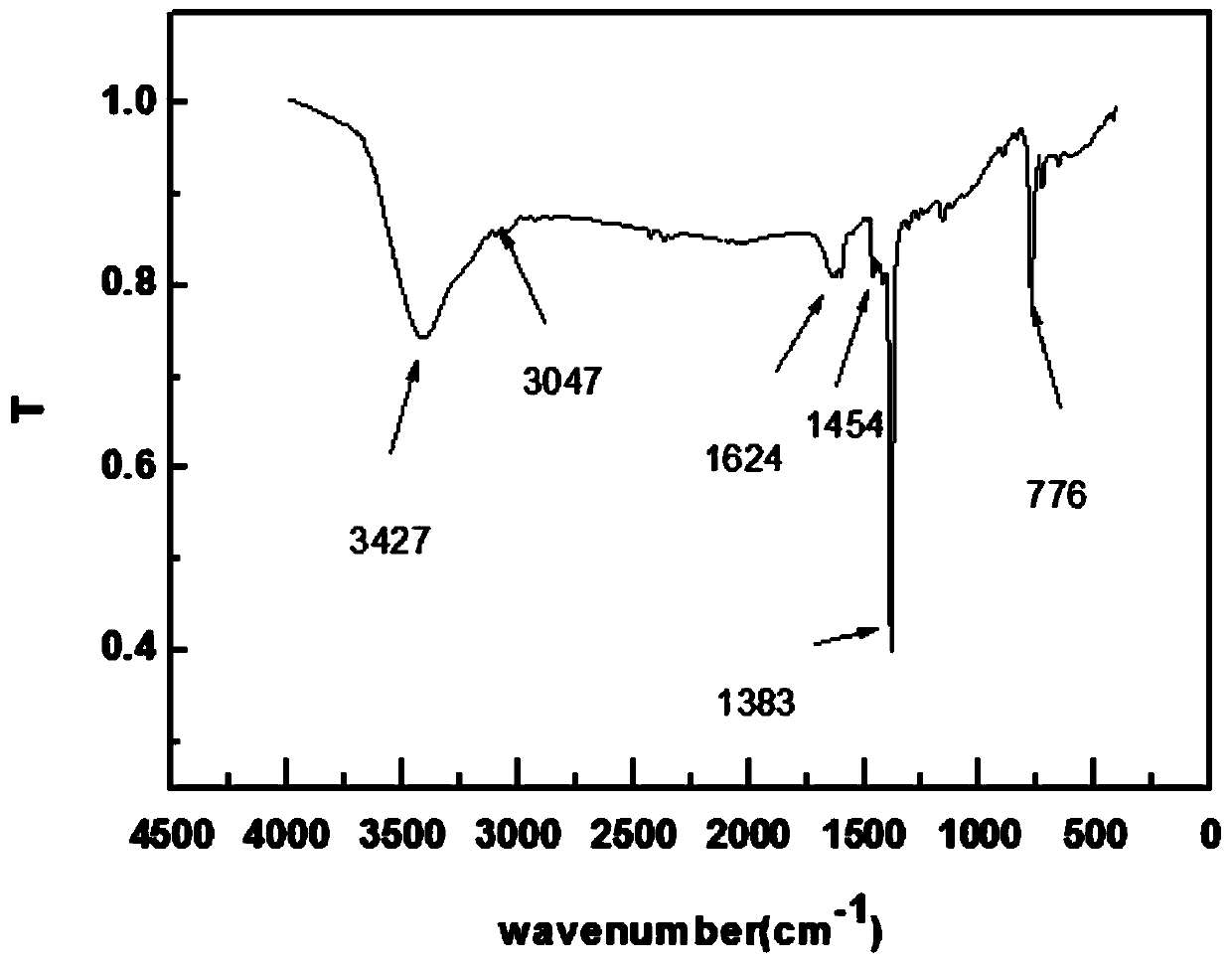
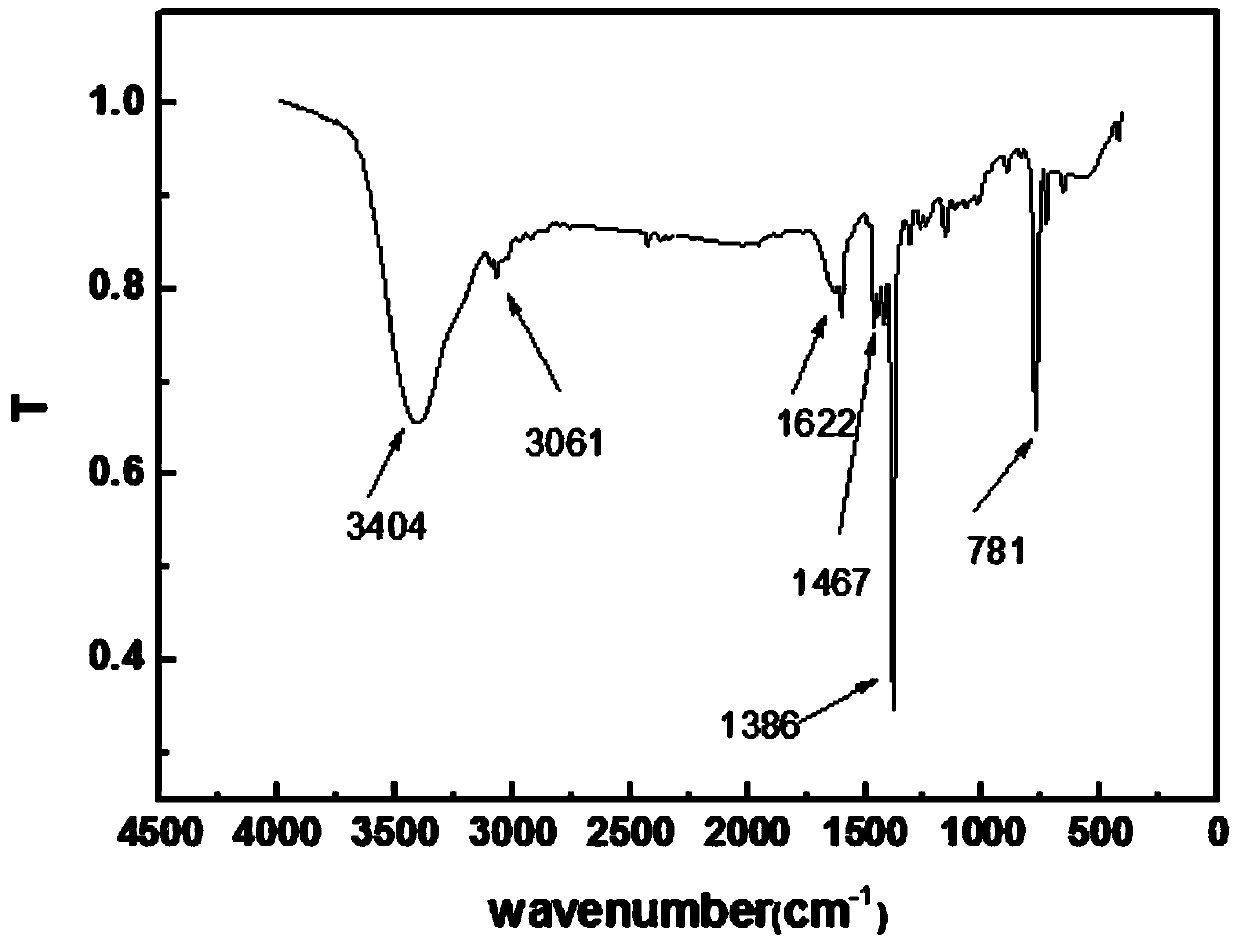
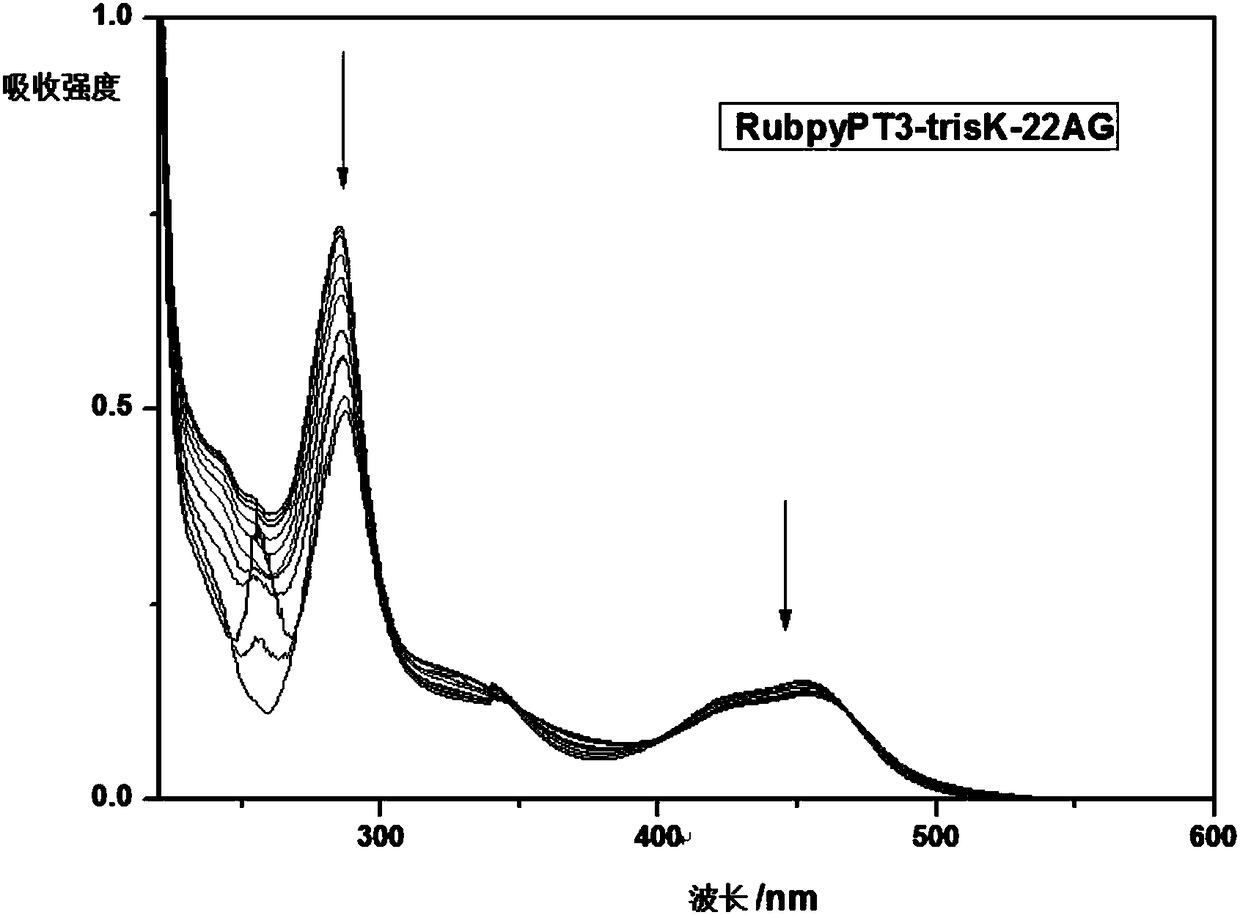
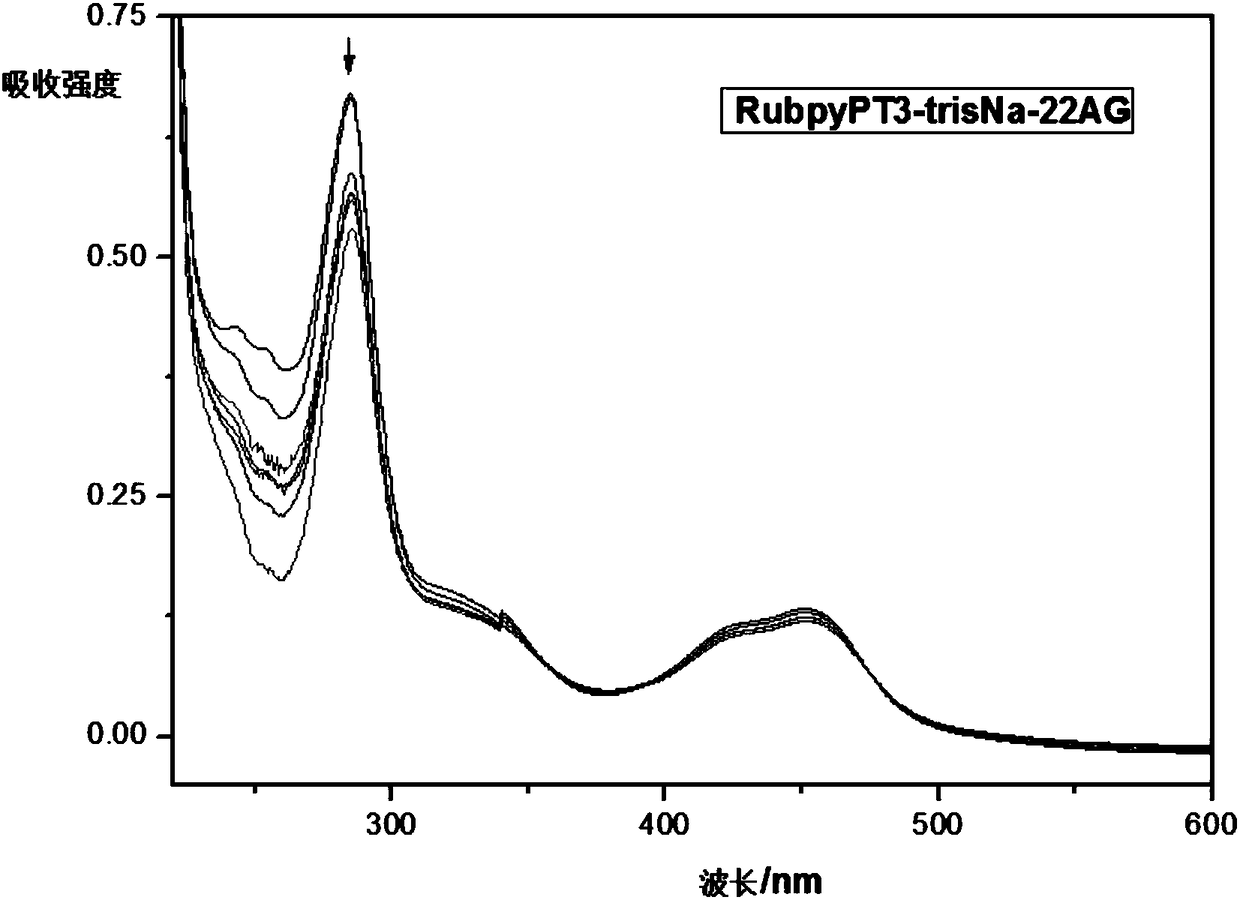
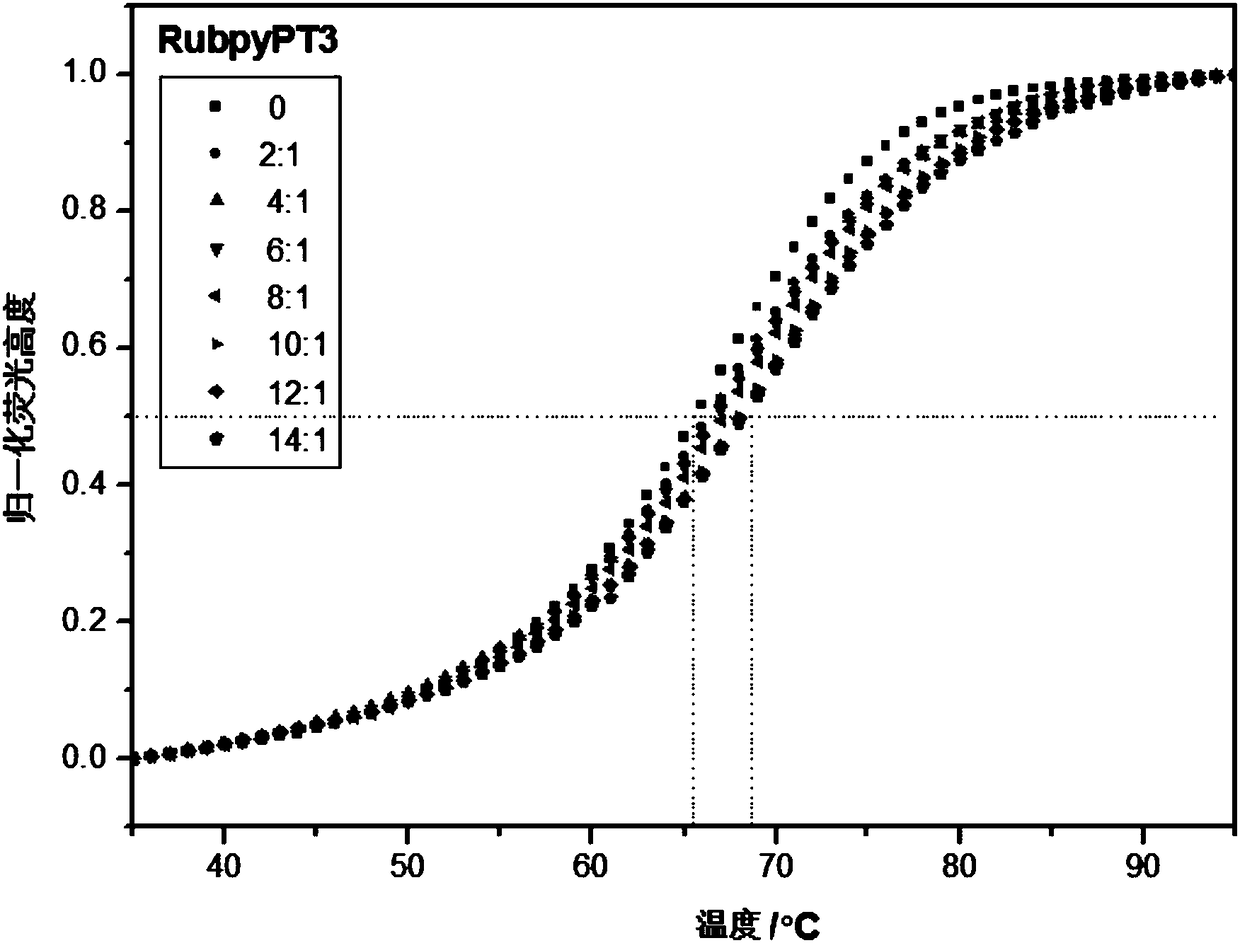
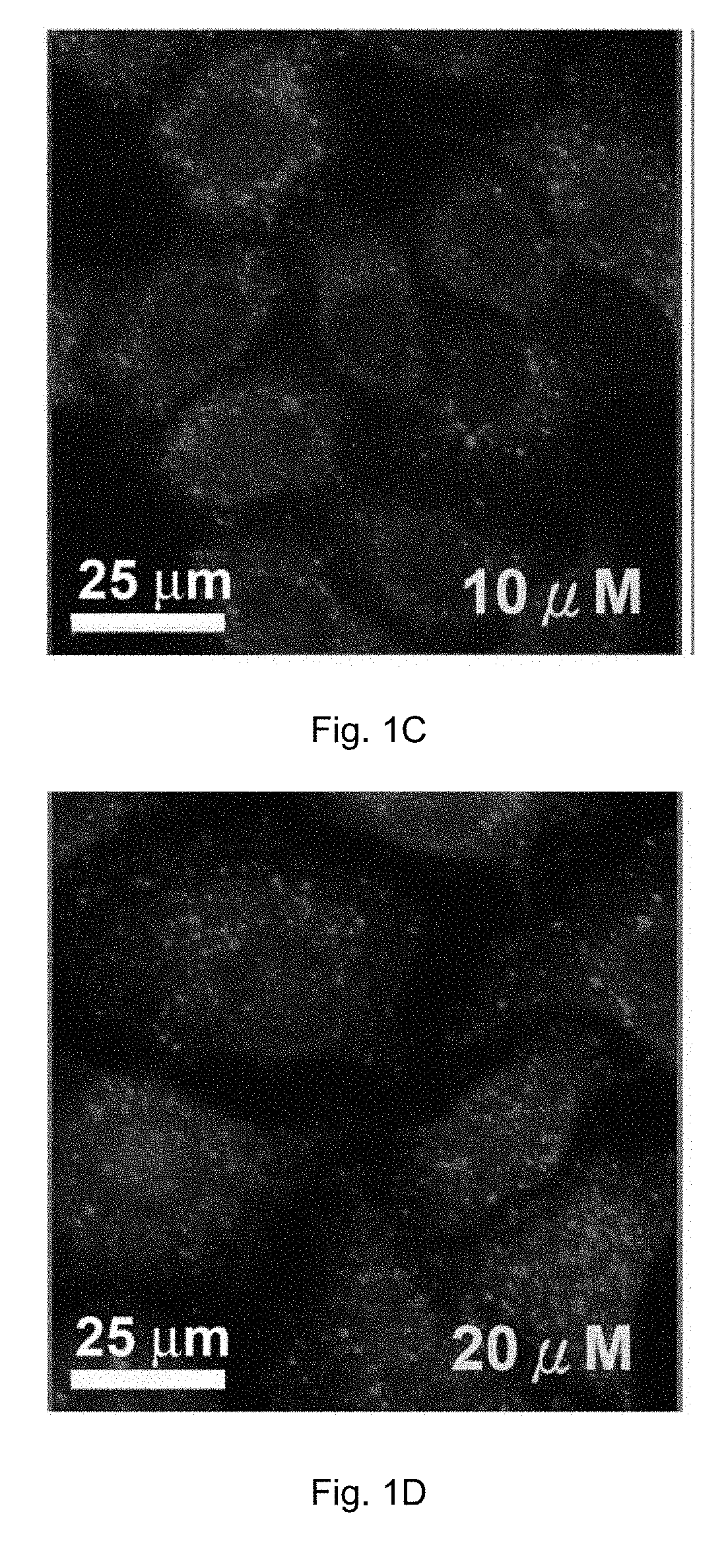
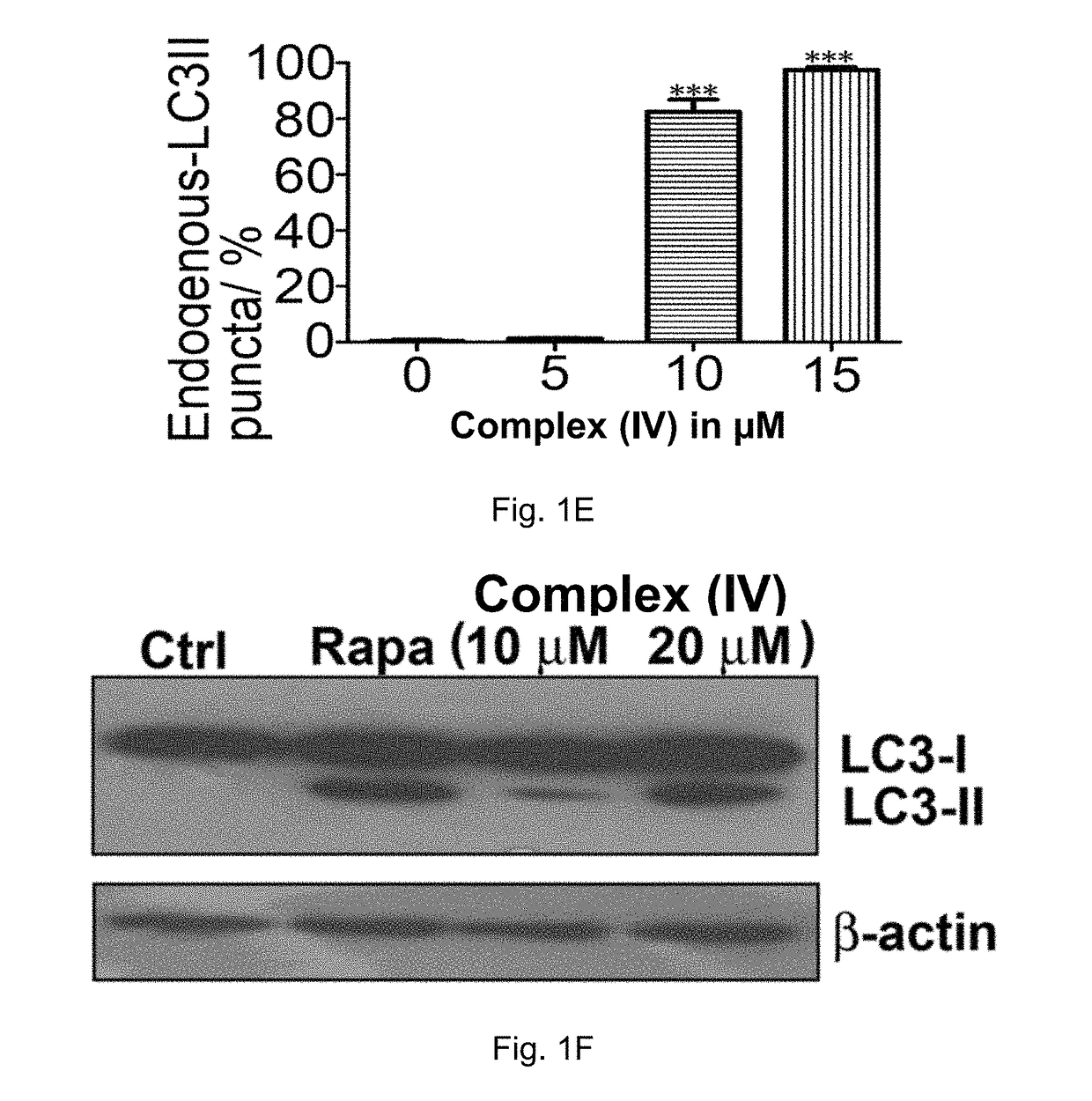
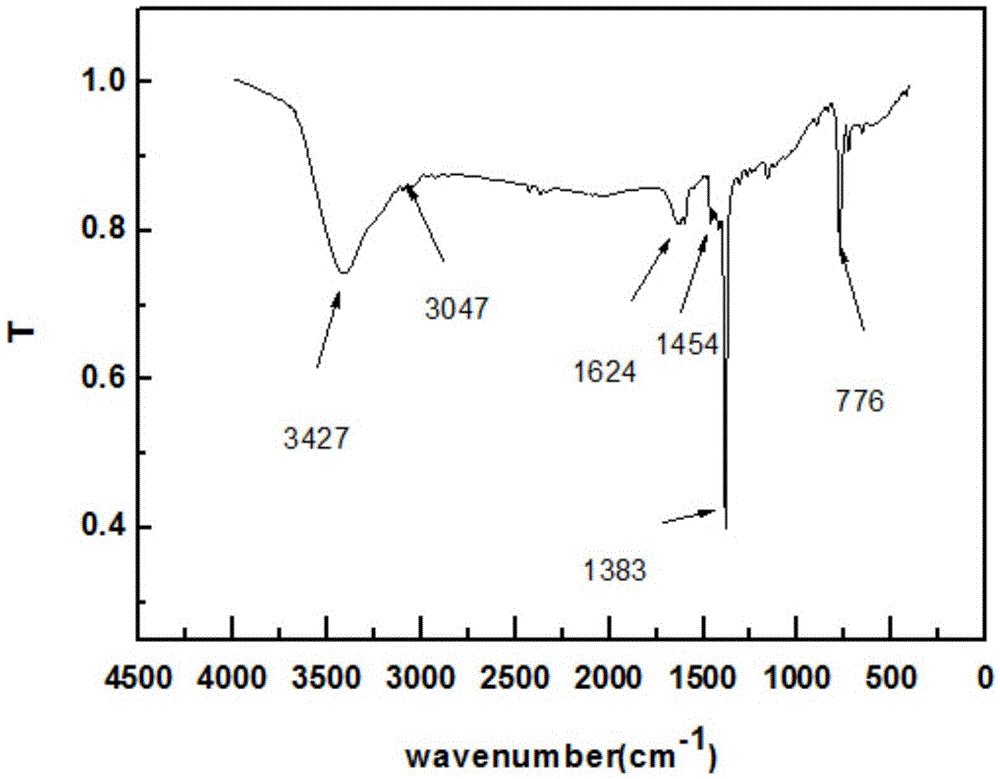
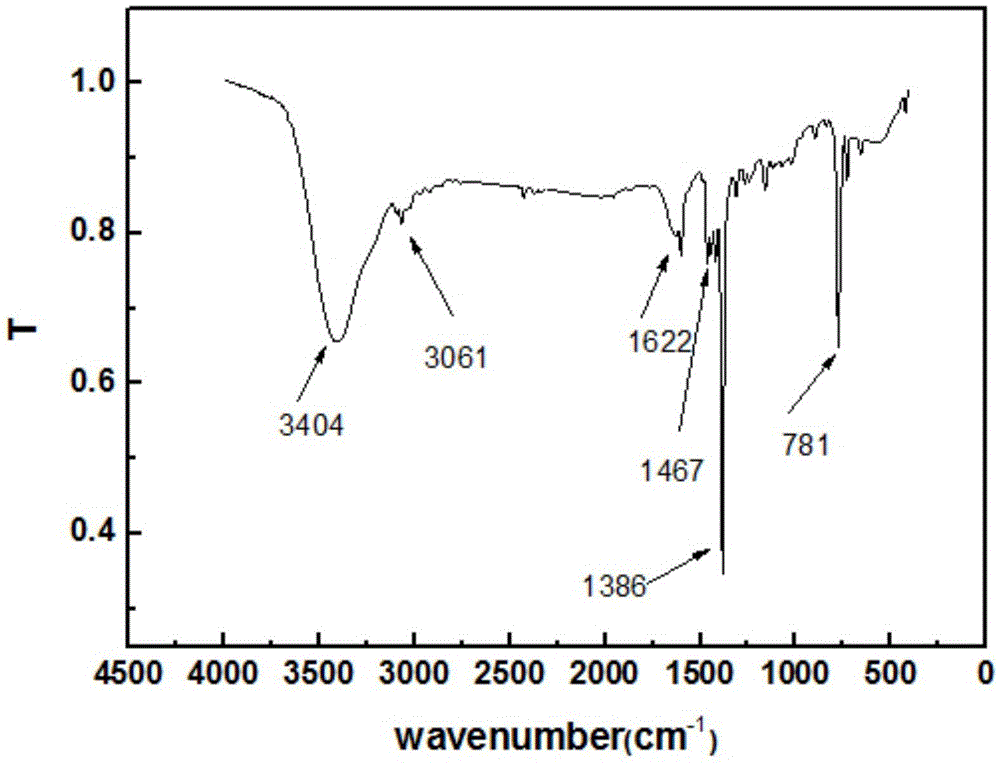
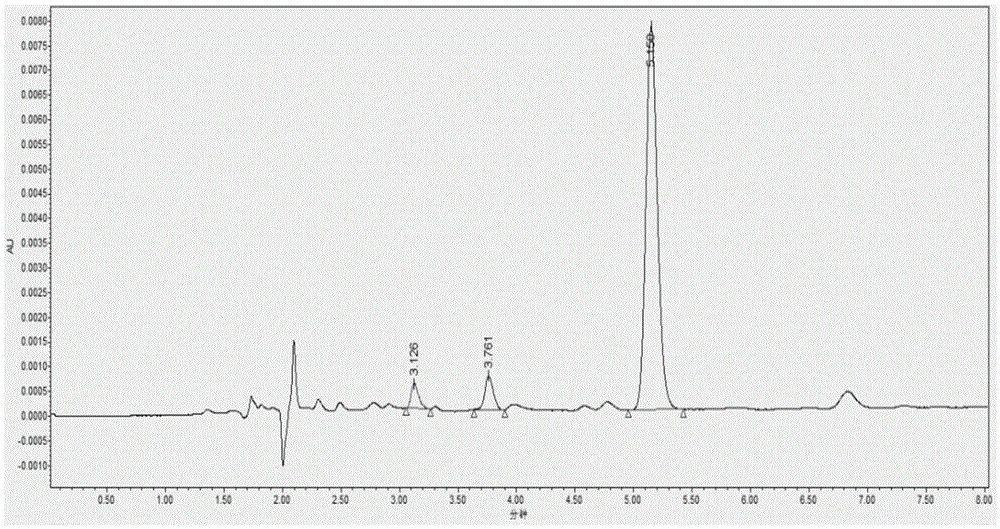
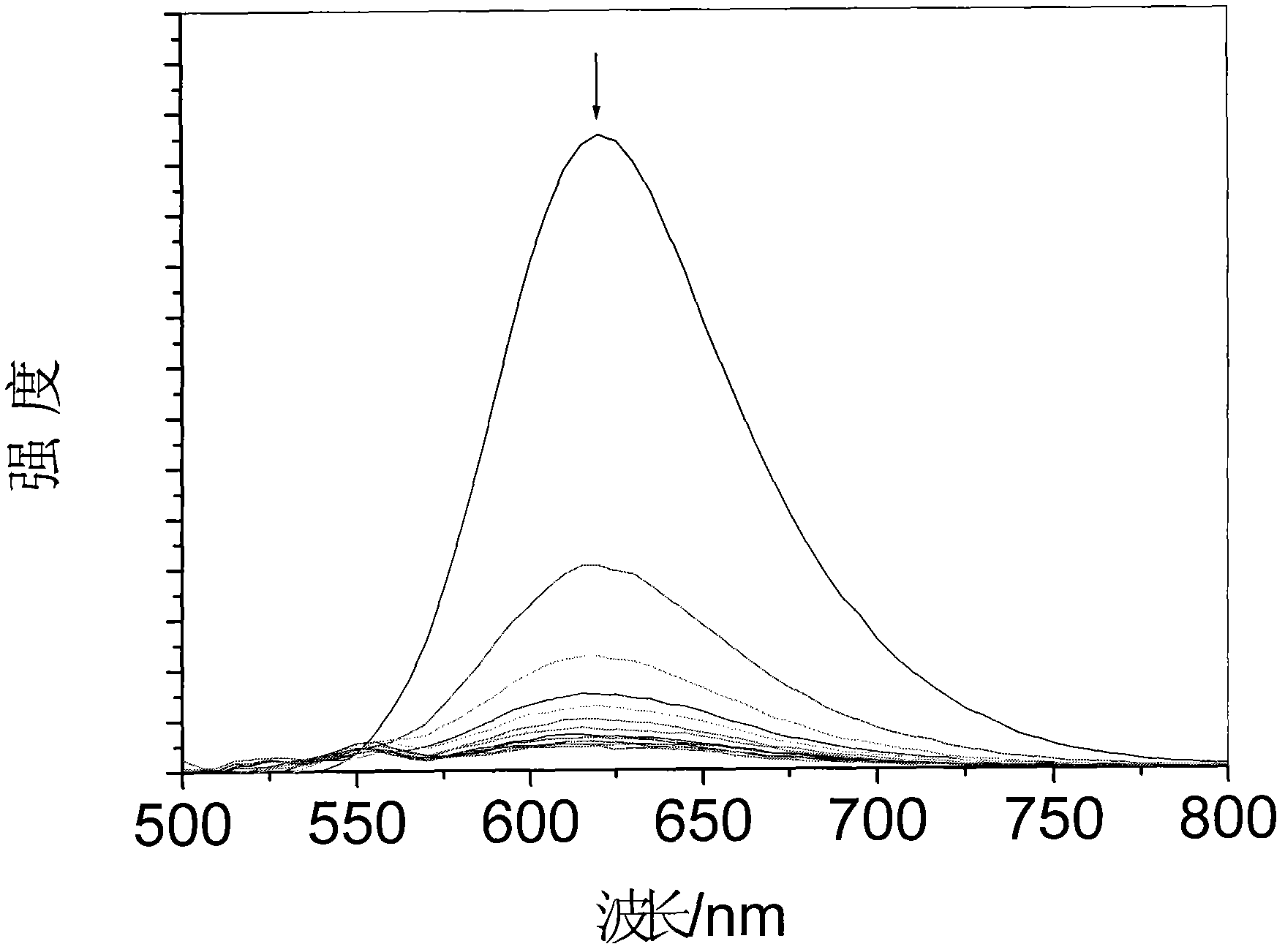
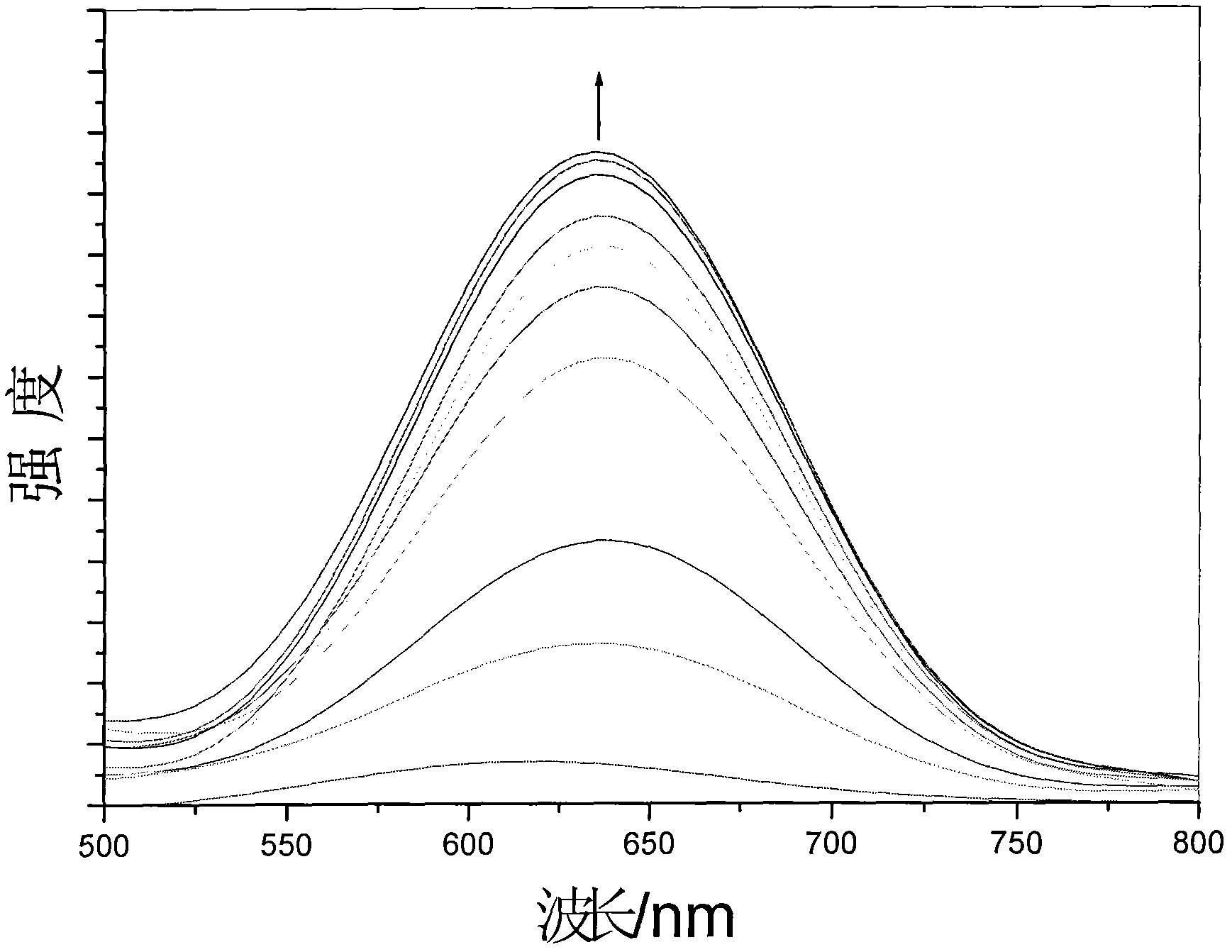
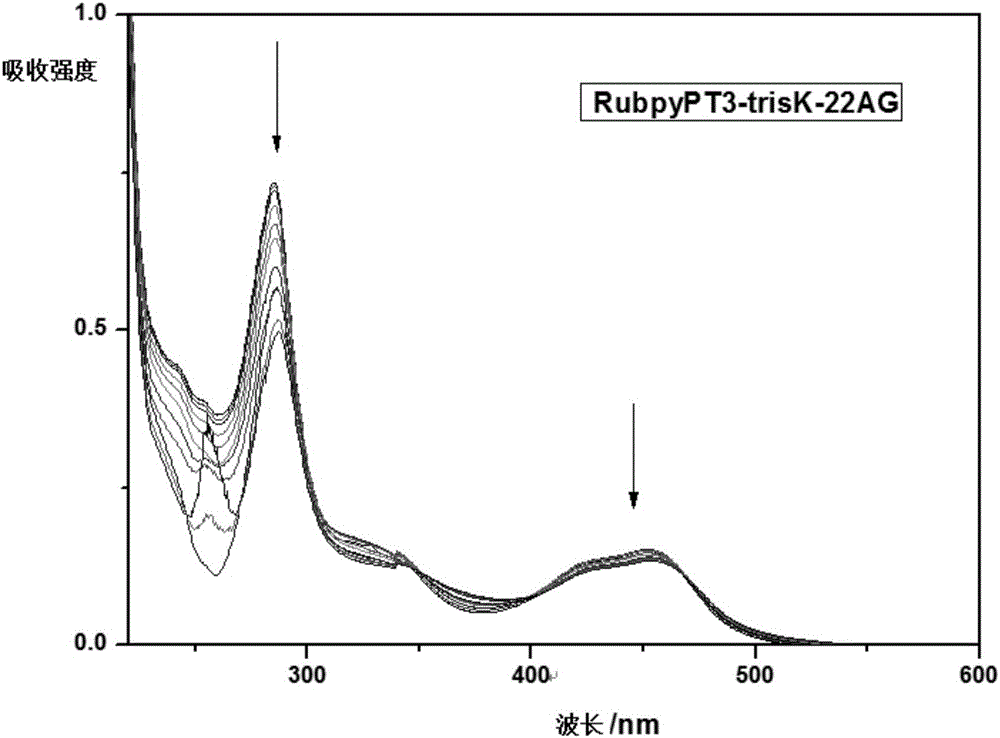
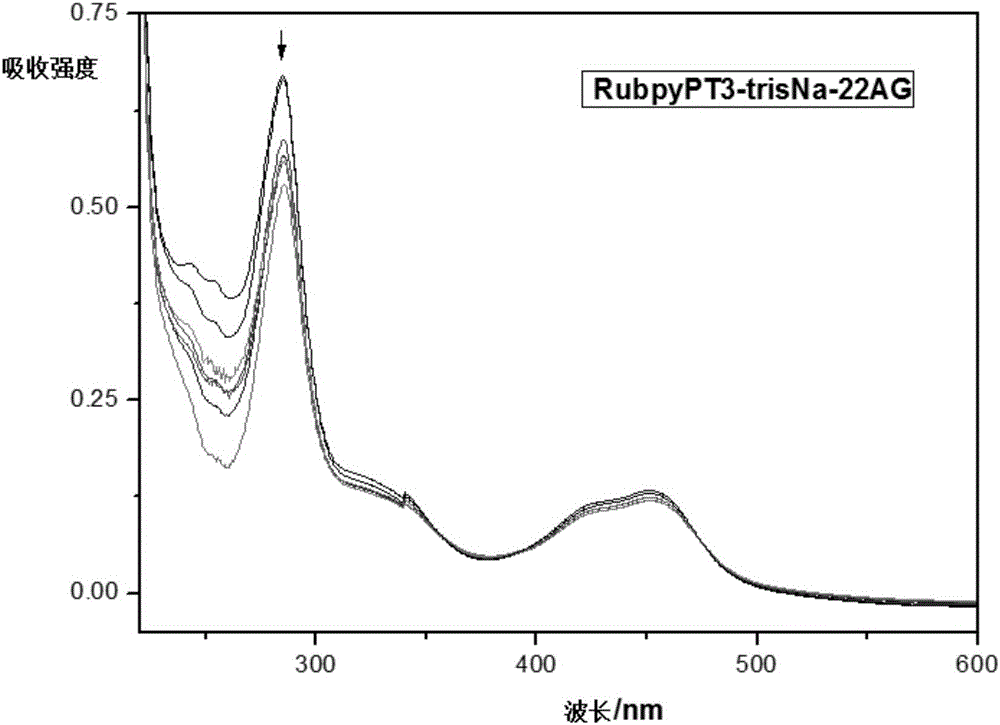
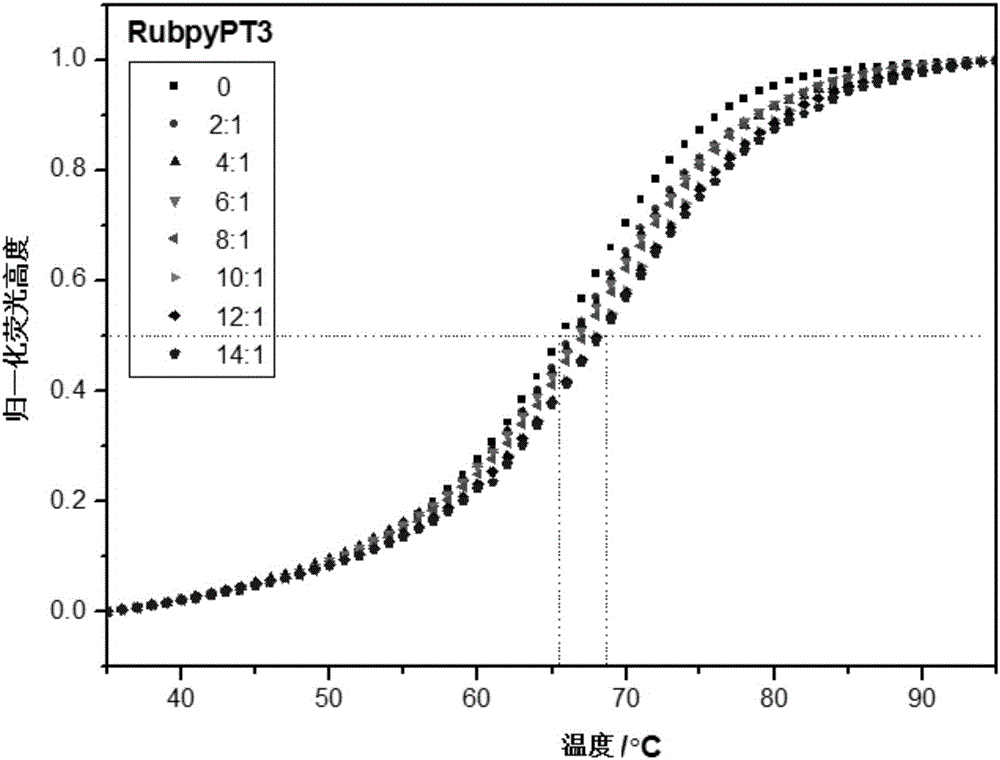
The invention discloses a ruthenium polypyridine complex and a preparation method and application of [Ru(L)2(tppp)]<2+> thereof. 2, 2'-bipyridine and 1,10'-phenanthroline are used as auxiliary ligands, and tppp is used as a main ligand (tppp=12-(2-thienyl)-pyrido[2', 3':5, 6]pyrazino[2,3-f][1,10]phenanthroline. The ruthenium complex disclosed by the invention has a recognition function, a combination function and a stabilization function on a telomere G-quadruplex. According to TO competition, the combining capacity between the complex and the G-quadruplex is stronger than that of double-stranded DNA, indicating that the complex has a recognition function; according to a TO competition experiment and a DNA melting temperature measurement experiment, the combining capacity and stabilizing capacity of the ruthenium complex a2 on the G-quadruplex are obviously stronger than those of a1.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
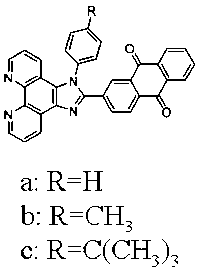
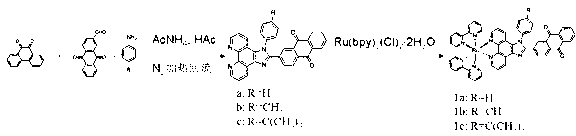
Preparation method and application of anthraquinone polypyridine ligand and ruthenium-anthraquinone complex
InactiveCN103012401ASmall structureStable structureOrganic active ingredientsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsHypoxic cellPyridine ligand
The invention discloses a synthesis method and application of an anthraquinone polypyridine ligand and anthraquinone-ruthenium polypyridine complex. The anthraquinone-ruthenium polypyridine complex has good inhibition activity on the growth of hypoxic cells, and generates obvious fluorescence through reduction in the hypoxic cells; and thus, the compound is a novel biological reduction type hypoxic cell anti-cancer drug and a specific fluorescence probe as well as a drug with application value and taking tumor hypoxia as a target point and a fluorescence probe.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
High efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells
InactiveCN103003903AImprove stabilityLess corrosiveLight-sensitive devicesSolid-state devicesIodideExtinction
Cobalt polypyridine complexes are interesting alternative redox mediators for large scale manufacturing of dye-sensitized solar cells (DSCs) since they are less aggressive towards metal contacts and absorb less light than iodide / triiodide. Here we have examined the effect of steric properties of triphenylamine-based organic sensitizers and cobalt polypyridine redox mediators on the electron lifetime and overall device performance in DSCs. Matching the steric bulk of the dye and redox mediator was found to minimize recombination and mass transport problems in DSCs employing cobalt redox mediators. Recombination was efficiently slowed down by introducing insulating butoxyl chains on the dye, allowing the use of a cobalt redox mediator with a less steric bulk. The best efficiency of DSCs sensitized with a triphenylamine-based organic dye in combination with cobalt(II / III) tris(2,2'-bipyridyl) match the highest efficiencies obtained so far with iodide-free electrolytes, reaching a 6.3 % overall conversion efficiency under AMI.5 condition (1000 Wm-2) and an efficiency of 7.8 % at 1 / 10 of a sun. Organic dyes with high extinction coefficients can thus be used instead of standard ruthenium sensitizers to build thin films DSCs in order to overcome mass transport and recombination limitations associated with the cobalt redox couples. DSCs sensitized with organic dyes employing cobalt redox mediators are promising for low light intensity applications since the efficiency and voltage is high at indoor illumination.
Owner:DYENAMO
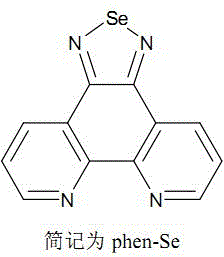
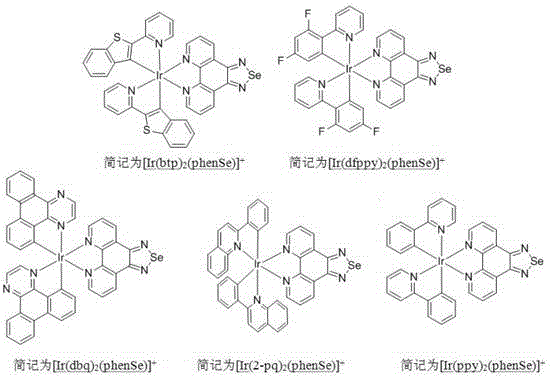
Iridium-selenium polypyridine complex as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102924531AStable structureGood fluorescence propertiesMicrobiological testing/measurementGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsCell membraneCellular Cytotoxicity
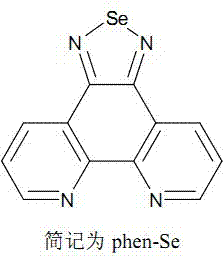
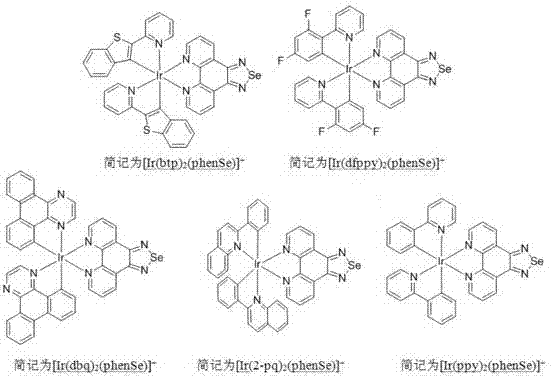
The invention discloses an iridium-selenium polypyridine complex as well as a preparation method and an application of the iridium-selenium polypyridine complex. The iridium-selenium polypyridine complex disclosed by the invention has the chemical formula of [Ir (N-C)2(phenSe)]+(N-C=ppy, dfppy, btp, 2-pq or dbq), is derived from selenium-5, 6-diamine-1, 10-ortho phenanthroline, has a good living cell mitochondria coloring characteristic, a strong cell membrane penetration capacity and low cytotoxicity and has a great application potential in the aspects of biolabeling and cell imaging.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
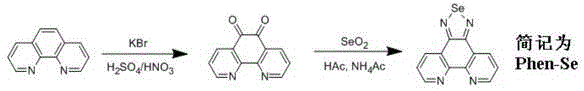
Selenium polypyridine ligand, ruthenium-selenium polypyridine complex, and preparation methods and applications of selenium polypyridine ligand and ruthenium-selenium polypyridine complex
InactiveCN102675348ASmall structureSimple structureGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsLuminescent compositionsPhenanthrolineCell membrane
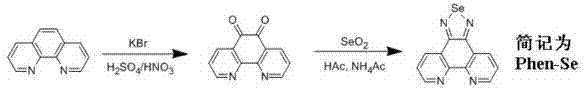
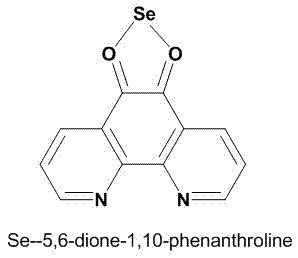
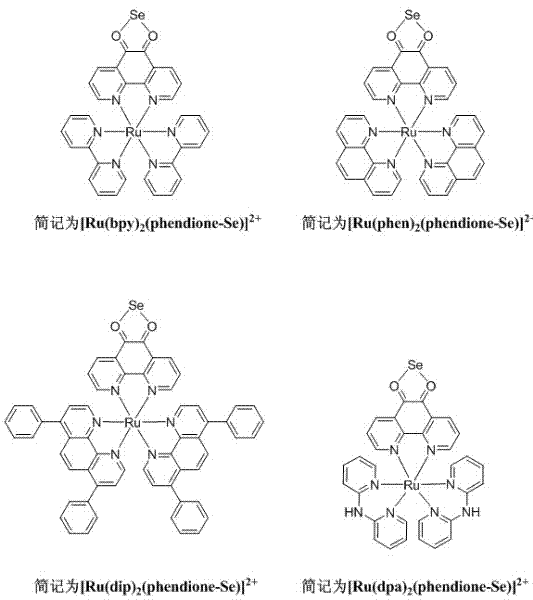
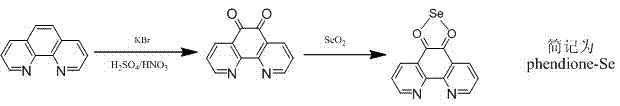
The invention discloses a selenium polypyridine ligand, a ruthenium-selenium polypyridine complex, and preparation methods and applications of the selenium polypyridine ligand and ruthenium-selenium polypyridine complex. The chemical name of the selenium polypyridine ligand provided by the invention is selenium-5,6-diketone-1,10-phenanthroline, which is prepared through the following steps of: taking 1,10-phenanthroline-5,6-diketone and selenium dioxide as the raw materials, and carrying out cooling filtering, washing, drying and the like after a heated reflux reaction. The invention also discloses a ruthenium-selenium polypyridine complex having a chemical formula as follows: [Ru(N-N)2(phendione)Se]2+(N-N=bpy, phen, dip or dpa); the ruthenium-selenium polypyridine complex is a compound derived from selenium-5,6-diketone-1,10-phenanthroline; the complex has excellent live cell nucleus coloring properties, high cell membrane penetrability and low cytotoxicity, and has great application potential in the aspects of biomarker and cell imaging.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
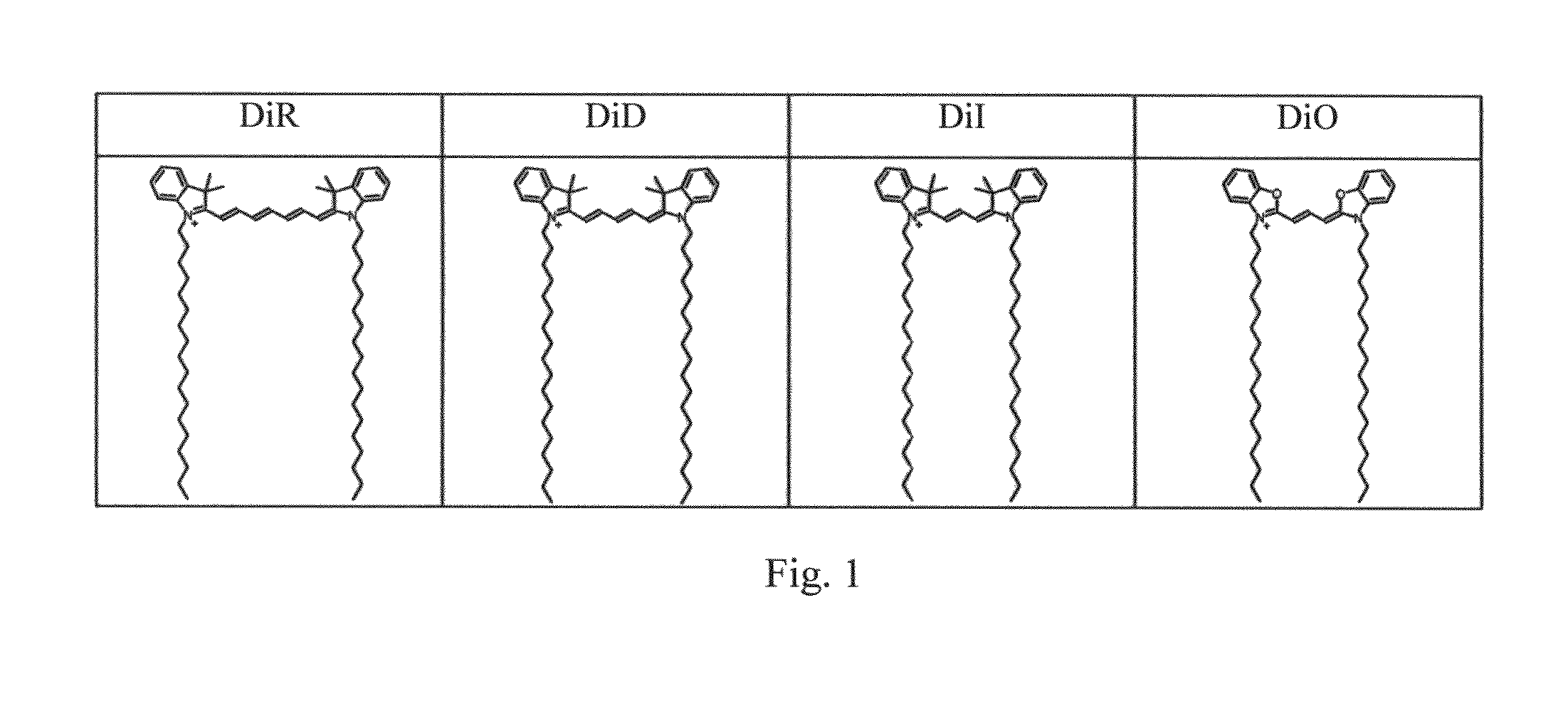
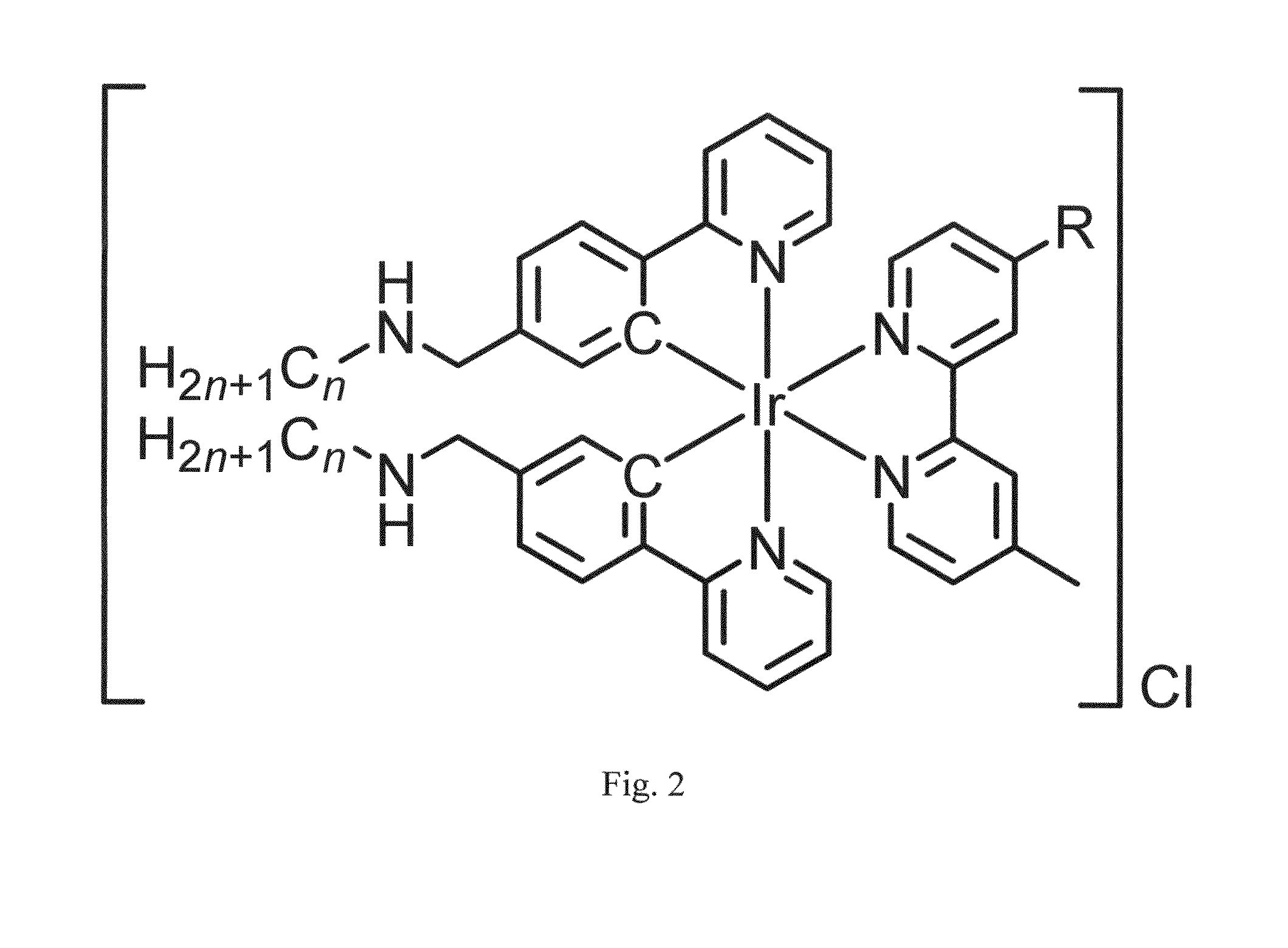
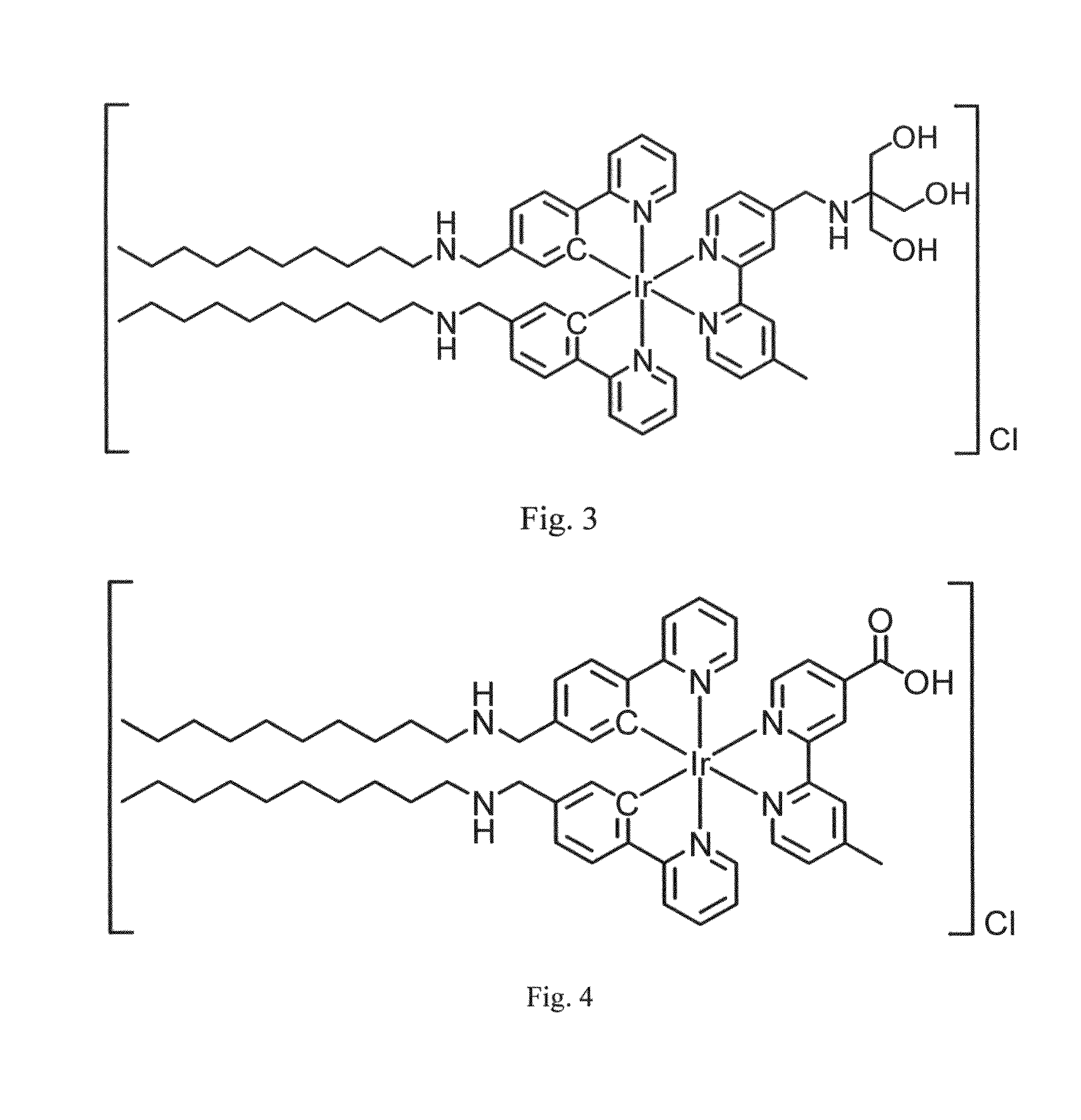
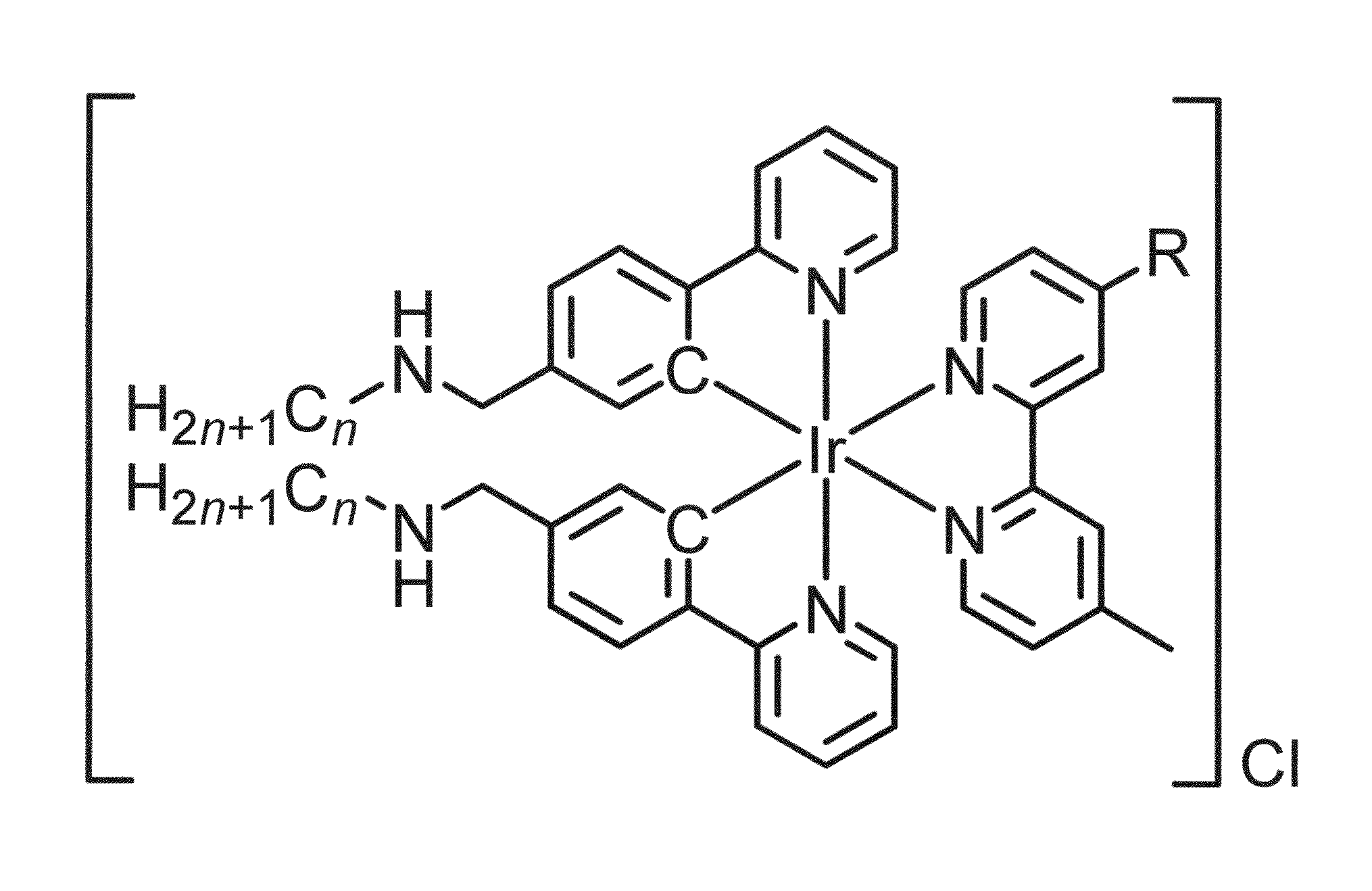
Membrane staining dyes containing phosphorescent transition metal polypyridine complexes
ActiveUS20150293108A1Indium organic compoundsMicrobiological testing/measurementCoordination complexPolypyridine complex
The present invention is concerned with a staining dye for staining a biological cell, comprising dye molecules with a positively charged polar head group for attraction to cell membrane of the cell and for refraining the dye molecules from entering the cytoplasm, and one or more hydrophobic groups for interaction with phospholipids of the cell membrane. The dye molecules are phosphorescent transition metal polypyridine complexes having a metal center and ligands which are non-organic fluorophores.
Owner:CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Preparation method and antitumor activity of ruthenium complexes containing benzothiazole
InactiveCN103896986AGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsAntineoplastic agentsSolubility2-Aminothiophenol
The invention discloses ruthenium polypyridine complexes, a preparation method thereof and application of the ruthenium polypyridine complexes as anti-cancer drugs. The ruthenium polypyridine complexes are ruthenium (II) complexes with 2-(10-dipyridine[3,2-a:2',3'-c]phenazine)benzothiazole as a main ligand (BFDPP) and bipyridine (pby) and phenanthroline (phen) as auxiliary ligands. The molecular formulas of the ruthenium (II) complexes are [Ru(pby)2(BFDPP)]C12 and [Ru(phen)2(BFDPP)]C12, respectively, wherein BFDPP is 2-(10-dipyridine[3,2-a:2',3'-c]phenazine)benzothiazole. The preparation method comprises the following steps: reacting o-phenanthroline-5,6-dione with 2,3-diaminobenzoic acid in ethanol so as to prepare a yellow solid; reacting the yellow solid with 2-aminothiophenol in polyphosphoric acid so as to prepare the ligand BFDPP; and reacting the ligand BFDPP with Ru(pby)2C12.H2O or Ru(phen)2C12.H2O and subjecting an obtained solid to column chromatographic purification so as to obtain the ruthenium polypyridine complexes. The preparation method is simple and has mild reaction conditions; the ruthenium polypyridine complexes have good dissolvability in water; the structures of intermediate reaction products and the target products are stable. The complexes provided by the invention have good inhibitory effects on the skin cancer cell line A375 and the breast cancer cell MCF-7.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Simple preparation method of ruthenium polypyridine complex
The invention discloses a simple preparation method of an electrochemiluminescent reagent ruthenium polypyridine complex. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving a ruthenium chloride hydrate and 2, 2'-dipyridyl in a mixed solvent of ethanol and ethylene glycol, wherein the ratio of ruthenium trichloride in the ruthenium chloride hydrate to 2, 2'-dipyridylis 1:4-1:5, and the concentration of ruthenium trichloride in the mixed solvent is 0.02-0.025mol / L; heating to react, wherein the reaction temperature is 70-100 DEG C and the reaction time is 6-10 hours; cooling to room temperature and carrying out rotary evaporation to remove ethanol; adding a saturated sodium chloride solution to separate out solids, filtering, adding water to recrystallize and drying to obtain tri(2, 2'-dipyridyl) ruthenium chloride (II) hexahydrate. The synthetic method is simple and convenient, short in reaction step, easy to operate, less in consumption of organic solvents, simple in post-treatment and high in product purity. The conversation ratio of noble metal ruthenium reaches up to 95%, so that the preparation method is less in environmental protection pressure and convenient for industrialized production.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method and application of anthraquinone polypyridine ligand and ruthenium-anthraquinone complex
InactiveCN103012401BSmall structureStable structureOrganic active ingredientsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsHypoxic cellPyridine ligand
The invention discloses a synthesis method and application of an anthraquinone polypyridine ligand and anthraquinone-ruthenium polypyridine complex. The anthraquinone-ruthenium polypyridine complex has good inhibition activity on the growth of hypoxic cells, and generates obvious fluorescence through reduction in the hypoxic cells; and thus, the compound is a novel biological reduction type hypoxic cell anti-cancer drug and a specific fluorescence probe as well as a drug with application value and taking tumor hypoxia as a target point and a fluorescence probe.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
A kind of ruthenium (ii) polypyridine complex and its preparation and application
InactiveCN105732723BStrong interactionStable structureOrganic active ingredientsRuthenium organic compoundsTelomerasePhenanthroline
The invention relates to ruthenium (II) polypyridine complex.The complex uses 2-(1, 10-phenanthroline monohydrate-5-base)-benzimidazole) as the main ligand and 2, 2'-bipyridine or 1, 10'-phenanthroline as the auxiliary ligand, and the chemical formula of the complex is [Ru(bpy)2pbi]2+ or [Ru(phen)2pbi]2+.A preparation method of the complex includes the steps of firstly, preparing pbi; secondly, synthesizing a ruthenium metal compound with the auxiliary ligand group; thirdly, synthesizing the target ruthenium (II) polypyridine complex; fourthly, using silica gel chromatography column separation to obtain the product.The ruthenium (II) polypyridine complex is used for preparing medicine combining with telomere G-quadruplex to increase the stability of the telomere G-quadruplex.Compared with the prior art, the ruthenium (II) polypyridine complex prepared by the method has the advantages that the ruthenium (II) polypyridine complex can recognize, combine and stabilize the telomere G-quadruplex, inhibit telomerase activity and regulate proto-oncogene expression, and a theoretical foundation is provided for anticancer medicine screening.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
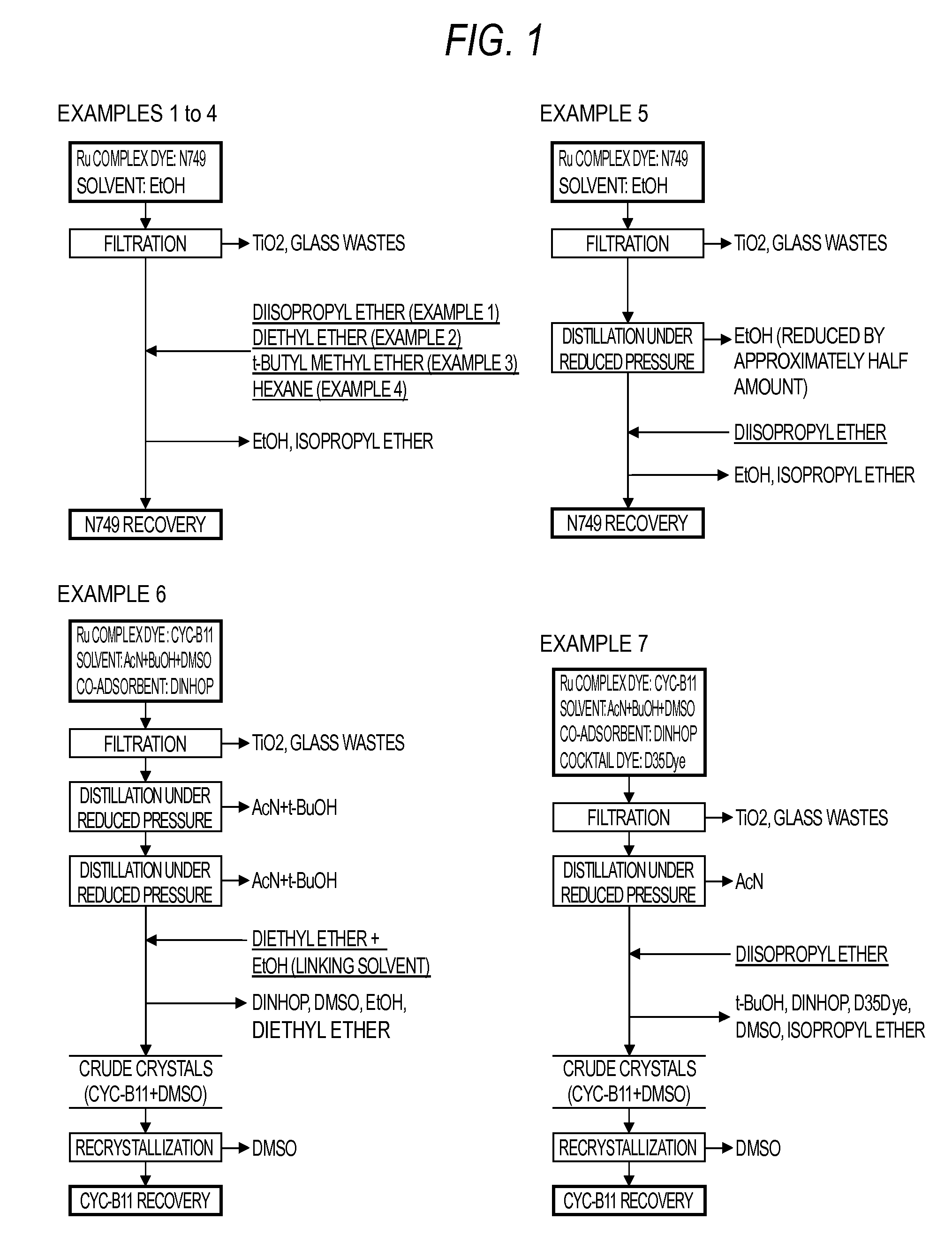
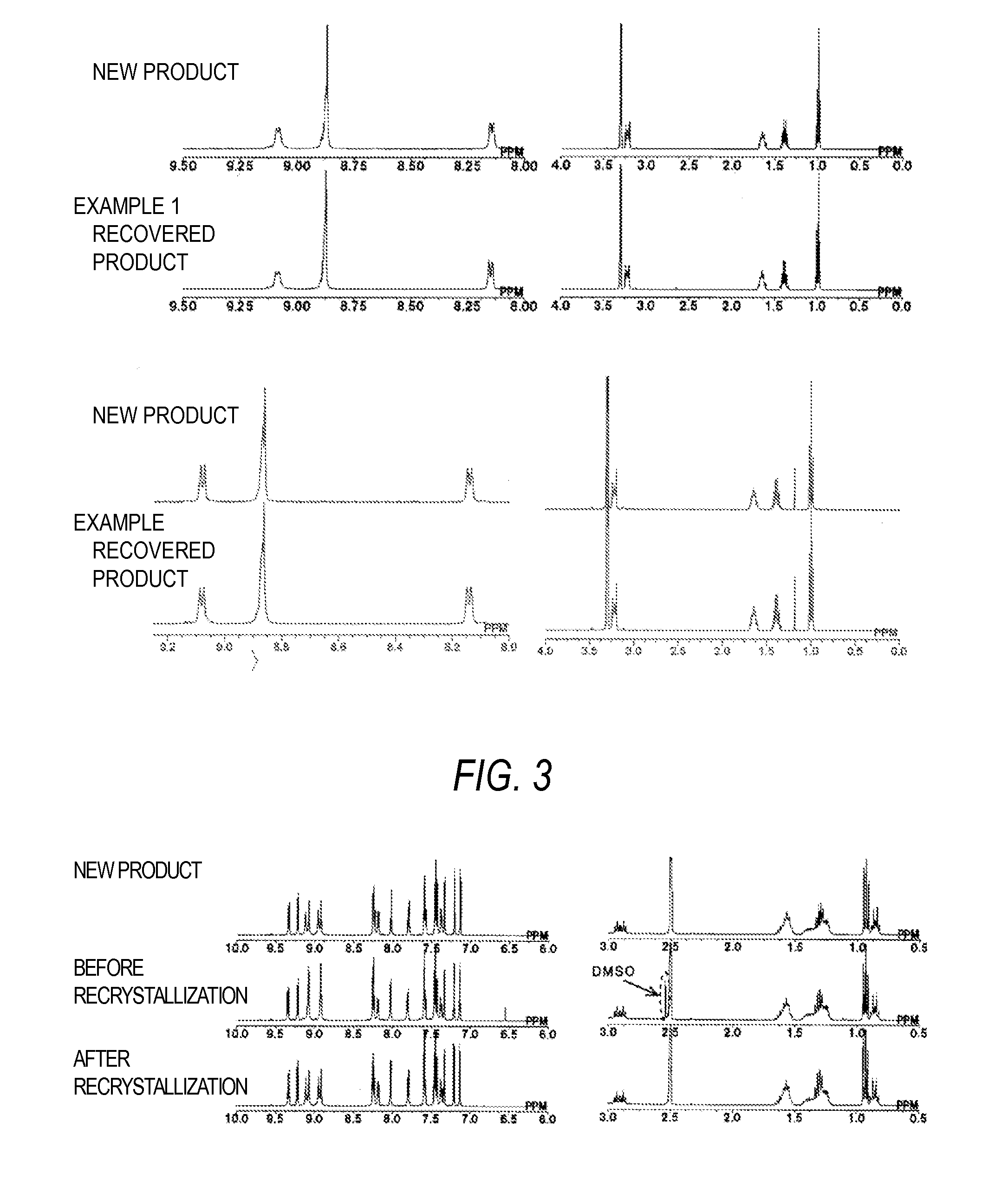
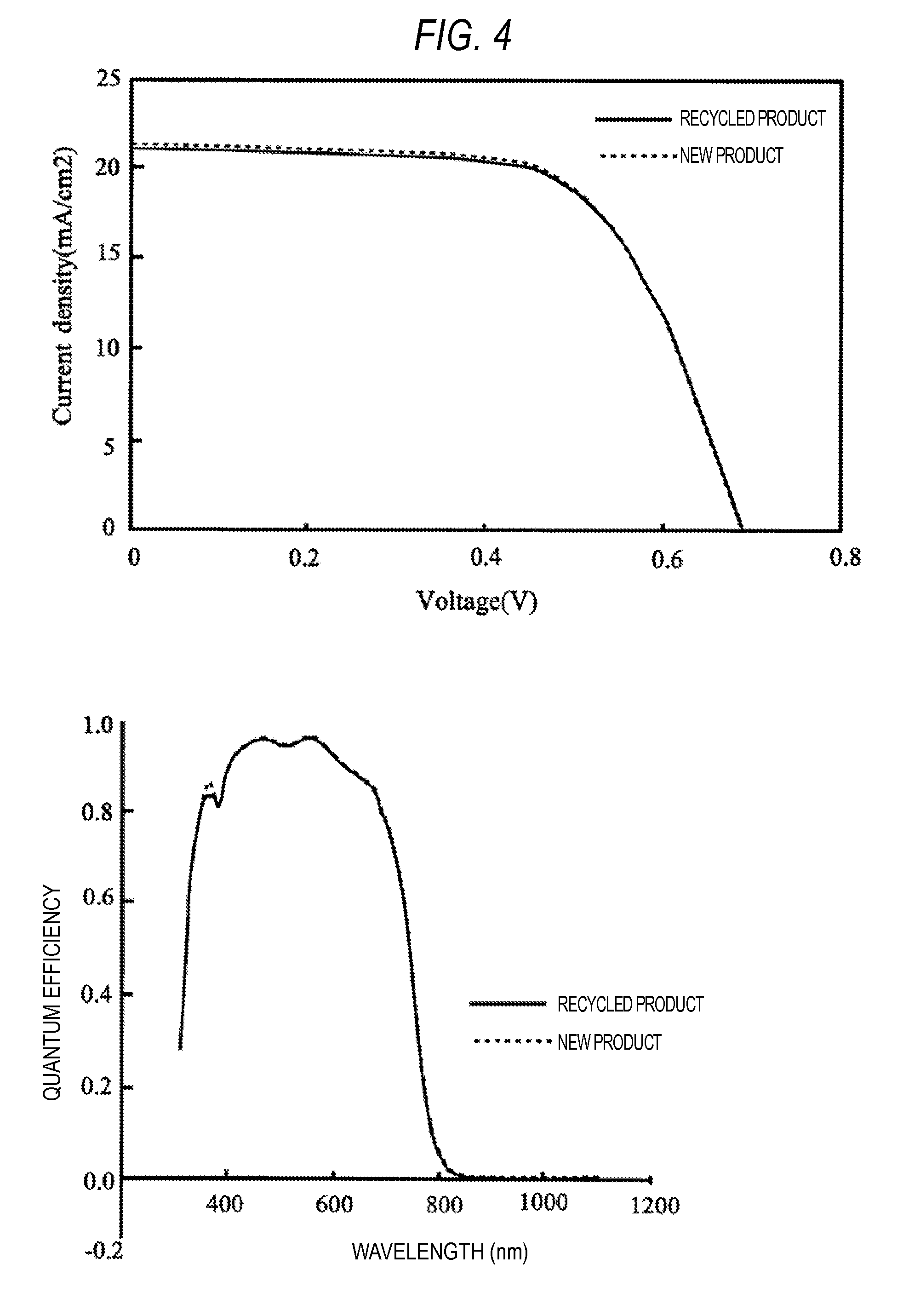
METHOD FOR RECOVERING Ru COMPLEX DYE FROM USED DYE SOLUTION
InactiveUS20150299467A1Efficiently recoverBroad rangeElectrical apparatusFinal product manufactureSolventDye-sensitized solar cell
The present invention relates to a method for recovering Ru complex dye from a used dye solution containing a polypyridine Ru complex as a Ru complex, the used dye solution having been discharged from a step of manufacturing a dye-sensitized solar cell, the method including the steps of:(a): filtering the used dye solution to separate and remove solid content.(b): bringing a separating solvent including an ether-based solvent indicated by a chemical formula CxH(2x+1)—O—CyH(2y+1) (x=1 to 4 and y=1 to 4, with the proviso that x+y≧4) or an alkane-based solvent indicated by a chemical formula CxH(2x+2) (x=5 to 7) into contact with the used dye solution to separate the Ru complex dye.
Owner:TANAKA PRECIOUS METAL IND
A photoactive polypyridine ruthenium complex and its application
ActiveCN110857310BRuthenium organic compoundsOrganic active ingredientsAnticarcinogenic EffectPhotodynamic therapy
The present invention is based on [Ru(bpy) 3 ] 2+ Ru(II) complexes with different conjugation systems were synthesized by modifying the ligands of the polypyridine ruthenium complexes as the core, and the ligand conjugation structure was studied for the generation of singlet oxygen in such complexes. rate impact. In the photodynamic therapy of tumors, the complexes of the present invention have the maximum singlet oxygen production rate, and not only have higher phototoxicity under light, but also increase the uptake of the complexes by cells. The increase in the amount leads to the possible chemical anti-cancer effect after it enters the cells, further improving its anti-tumor activity.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
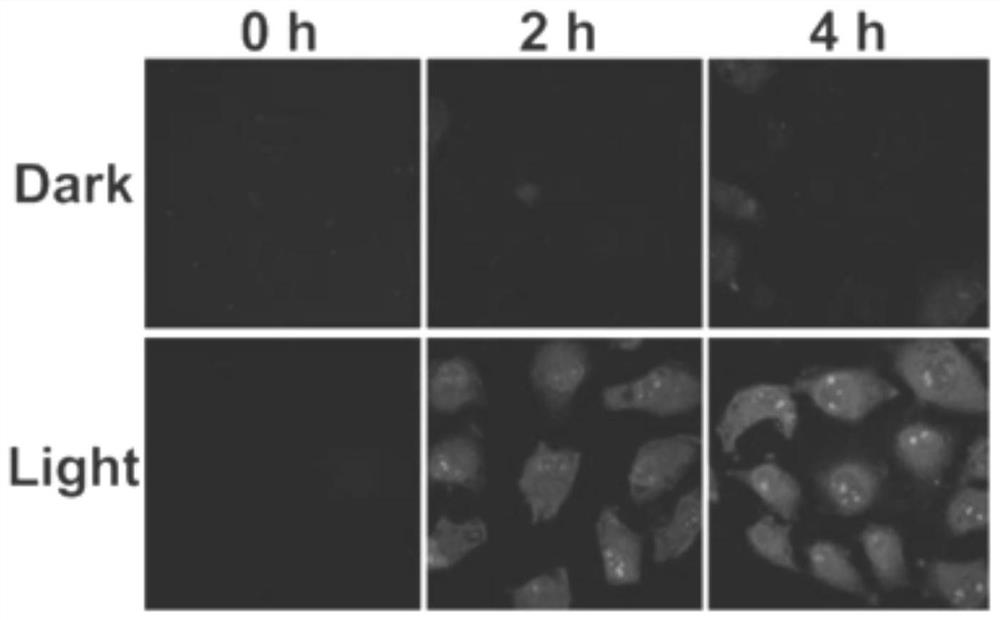
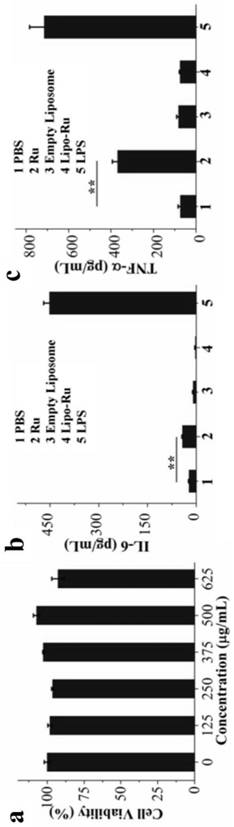
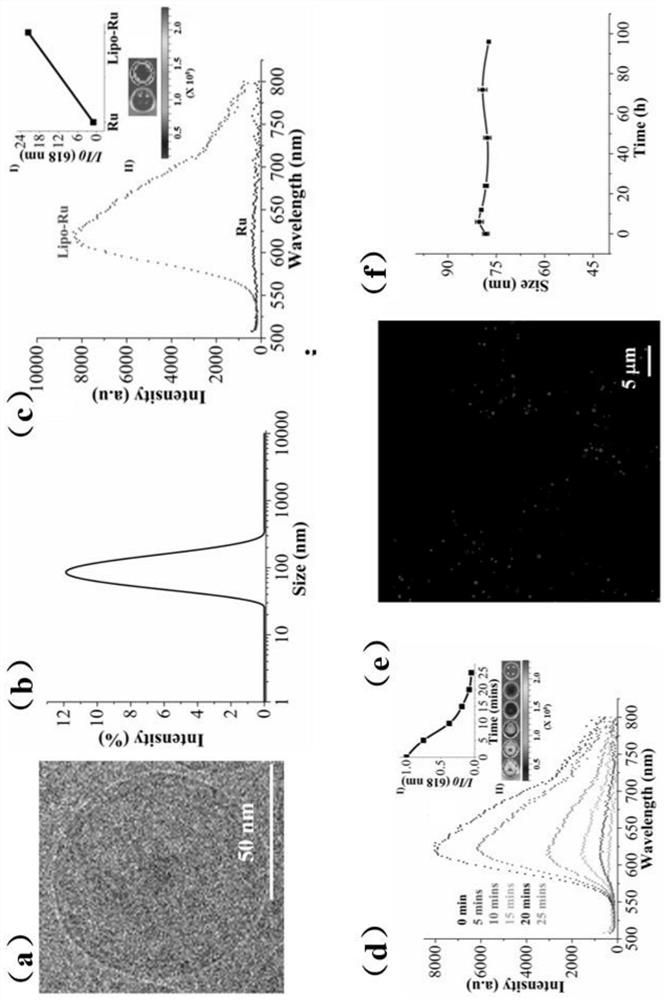
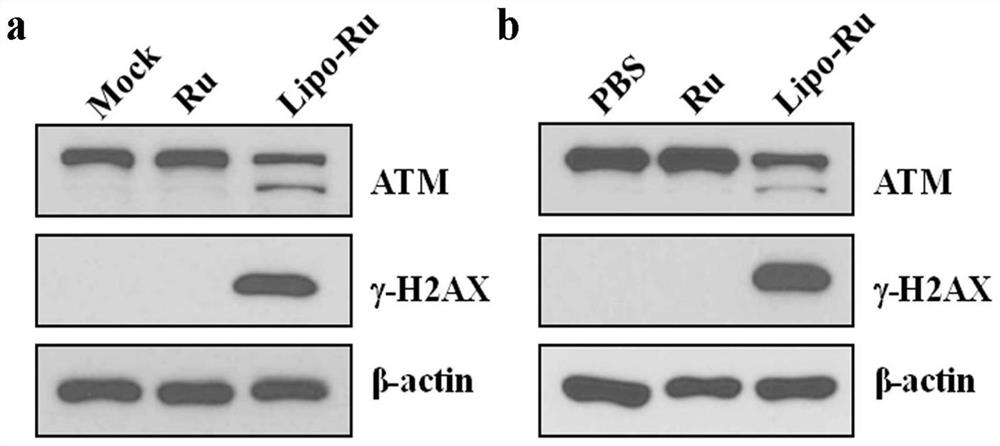
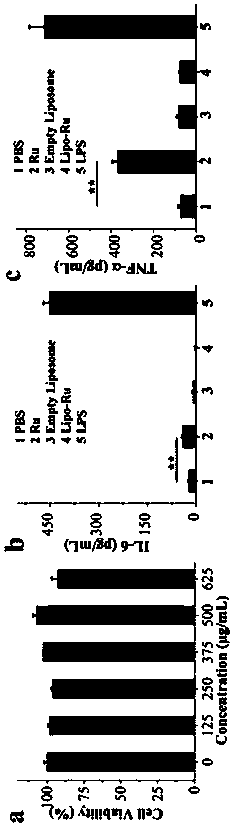
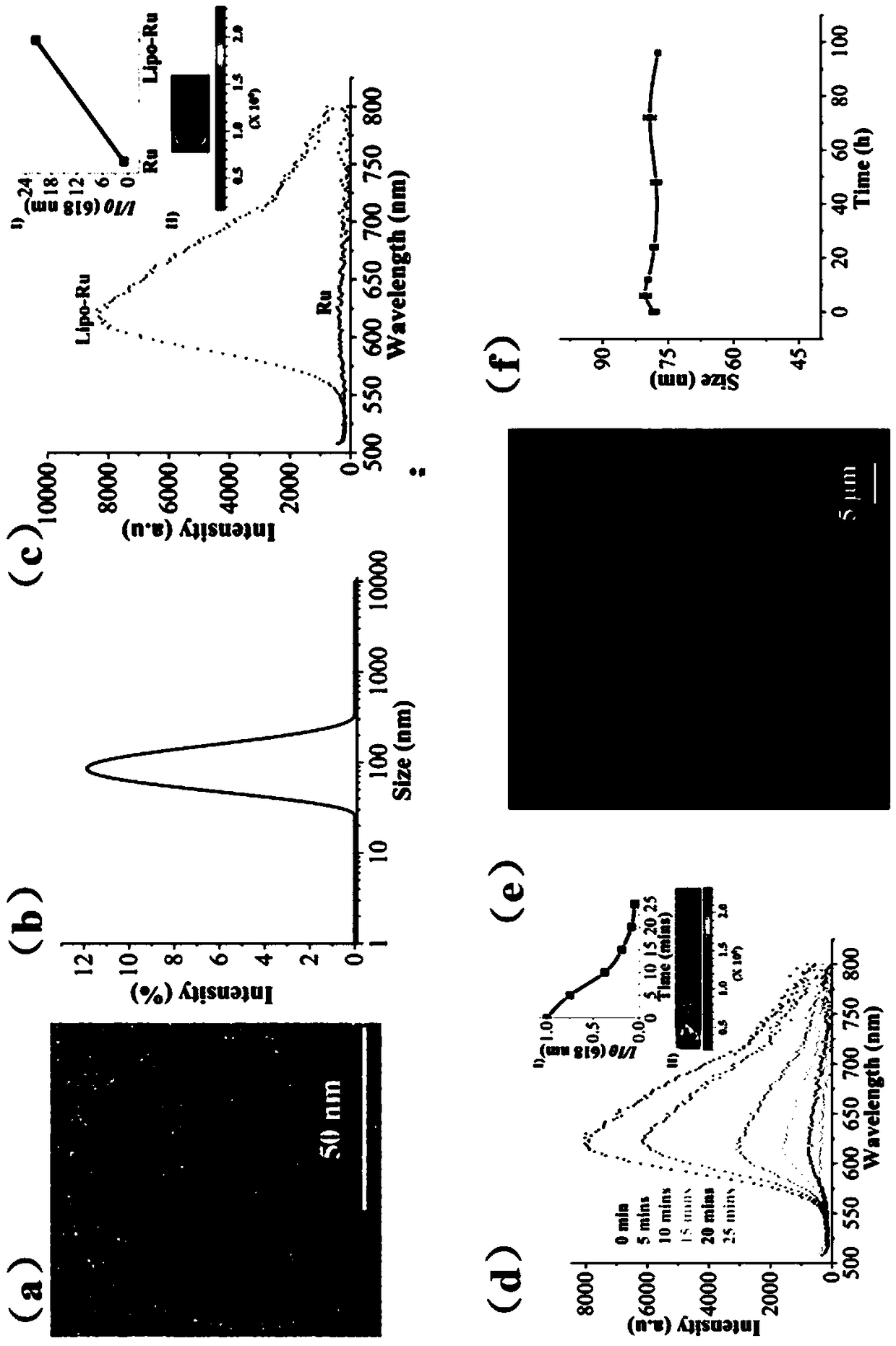
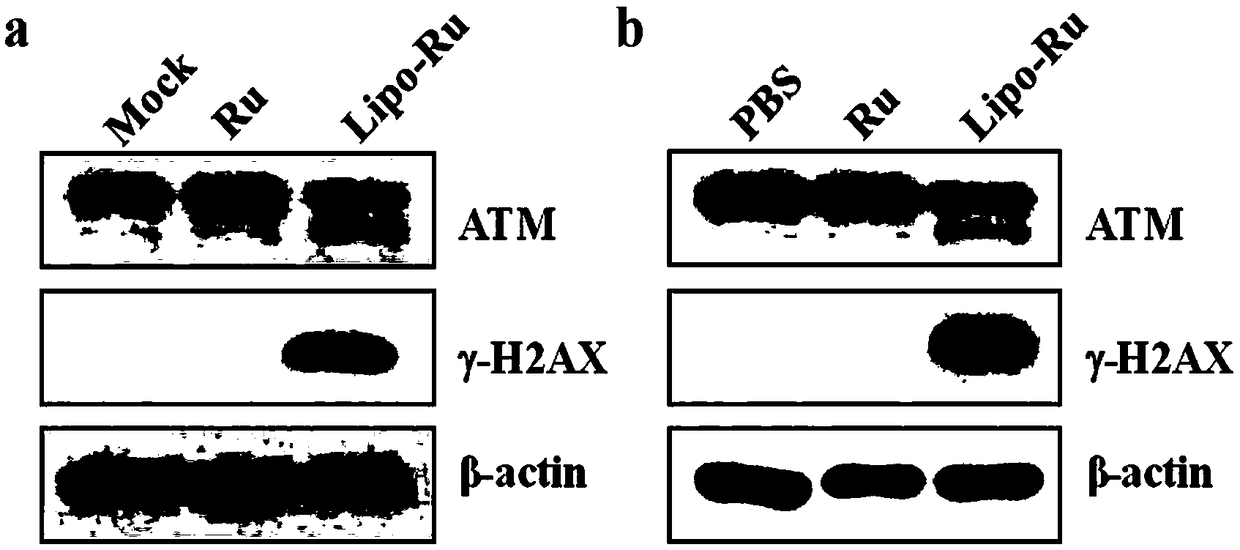
A kind of liposome-encapsulated ruthenium polypyridine complex and its application
ActiveCN108743533BSmall toxicityPromote absorptionHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic non-active ingredientsImaging agentEthyl group
The invention discloses a liposome-encapsulated ruthenium polypyridine complex and its application. By using dichlorobis(2,2'-bipyridine) ruthenium and ruthenium acetate as anticancer metal complexes, compared with cis Platinum and ruthenium complexes have low toxicity and side effects, are easy to absorb and excrete quickly, and can inhibit tumor growth and metastasis; at the same time, they are encapsulated with liposomes, and by adding blending agents, antioxidants, buffers, antibacterial agents and stabilizers , wherein the blending agent has selected bis(triethanolamine) diisopropyl titanate, trimethoxy[2-(7-oxabicyclo[4.1.0]heptyl-3-yl)ethyl]silane, (3S, 6E,10S)‑6,10‑dimethyl‑3‑isopropylcyclodec‑6‑ene‑1,4‑dione and diethylene glycol ether, under the combined action of these substances, can greatly improve The mutual coordination between liposomes and ruthenium complexes makes the final liposome-encapsulated ruthenium polypyridine complexes have good biocompatibility and low toxicity; It can be used as a chemotherapeutic or imaging agent in treatment.
Owner:WENZHOU INST OF BIOMATERIALS & ENG
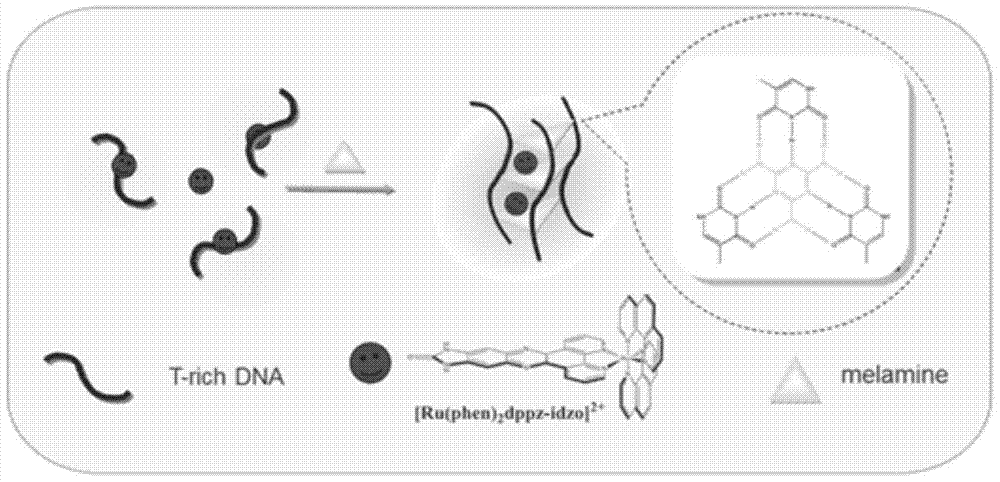
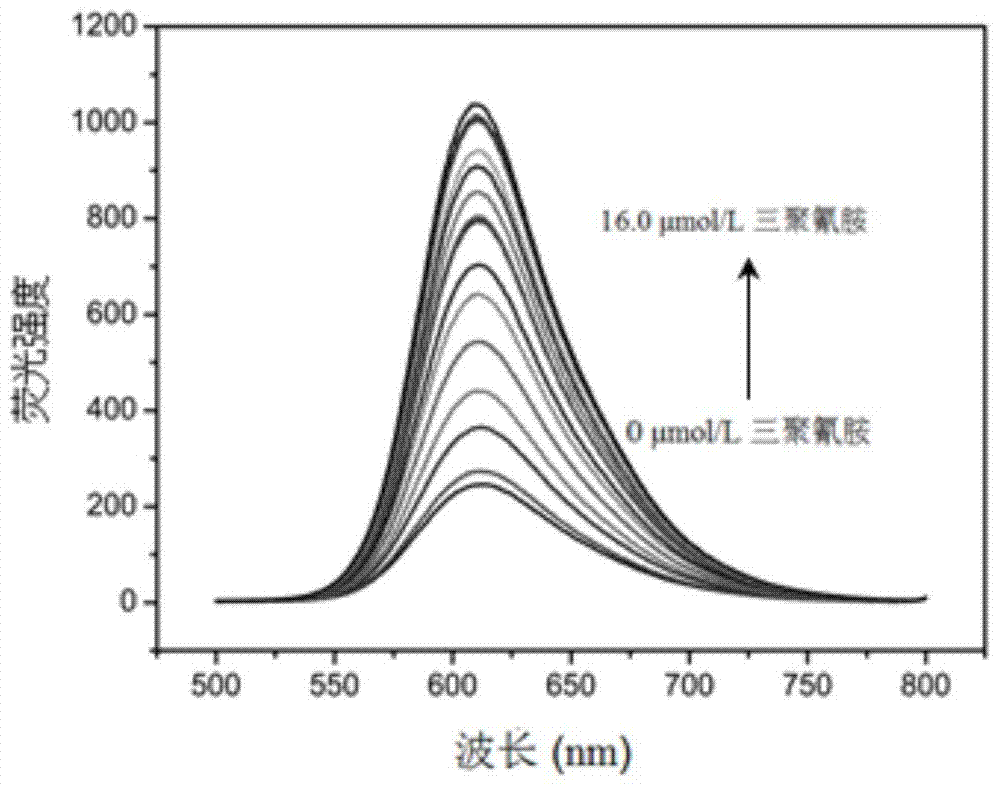
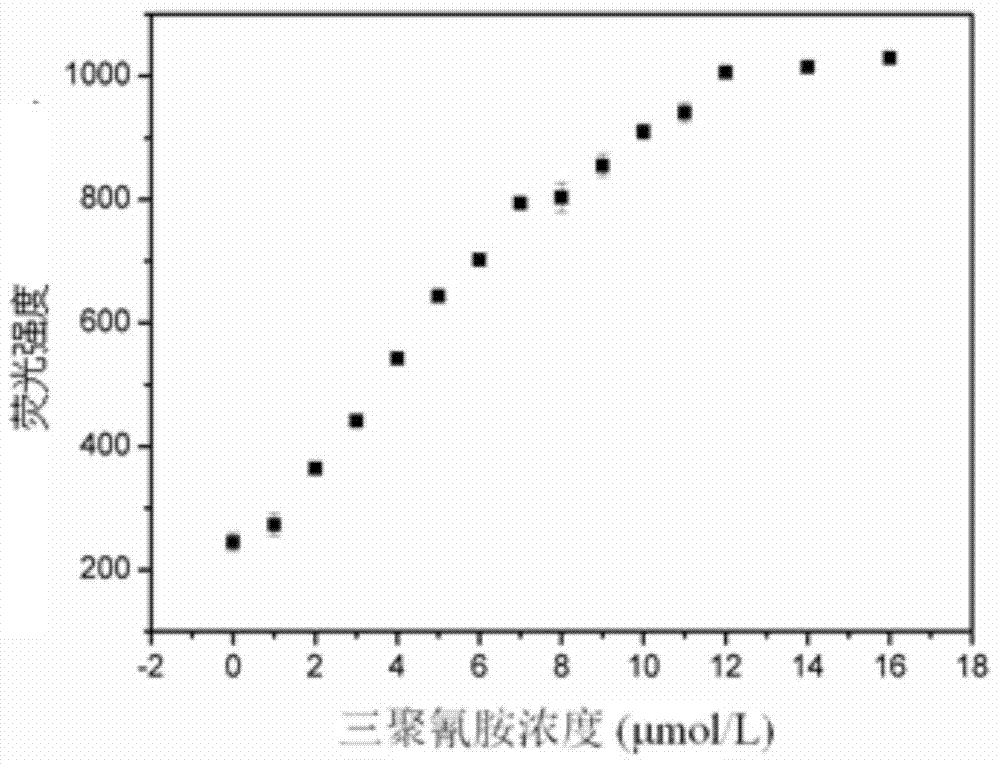
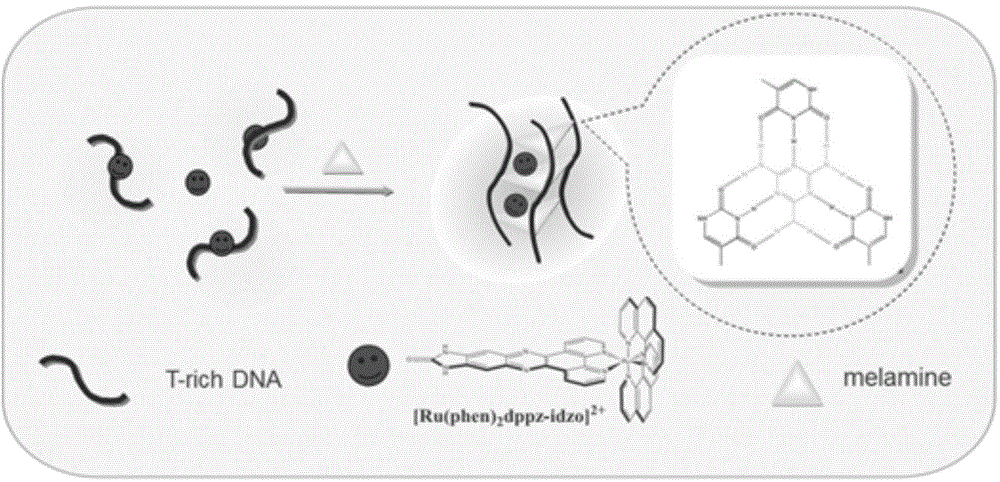
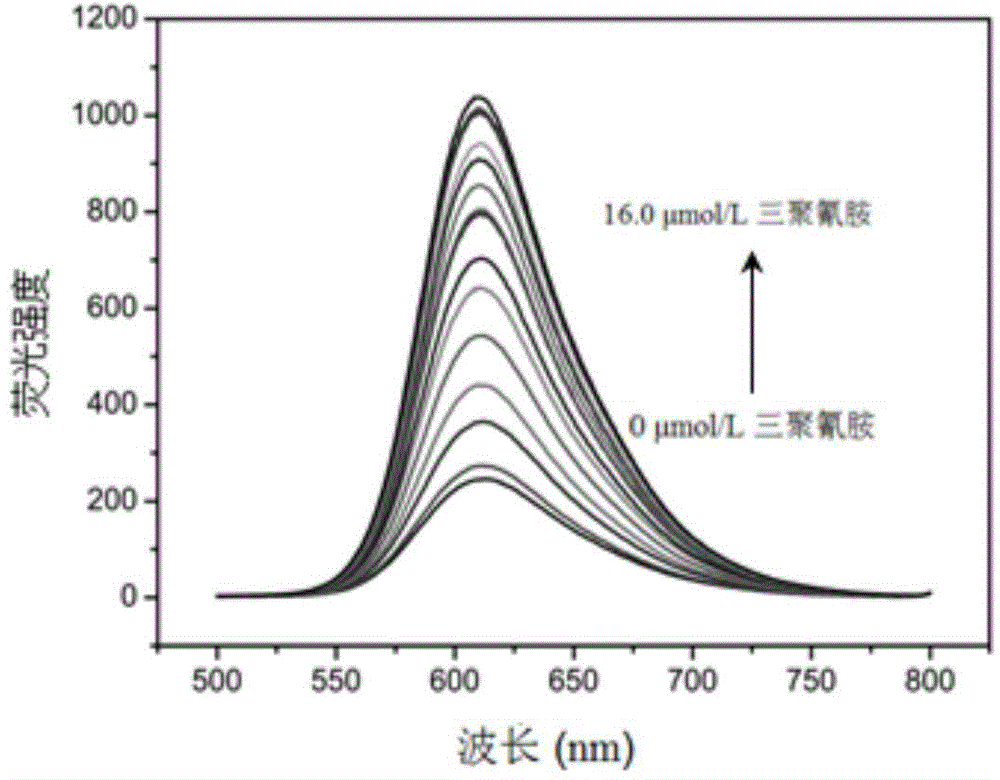
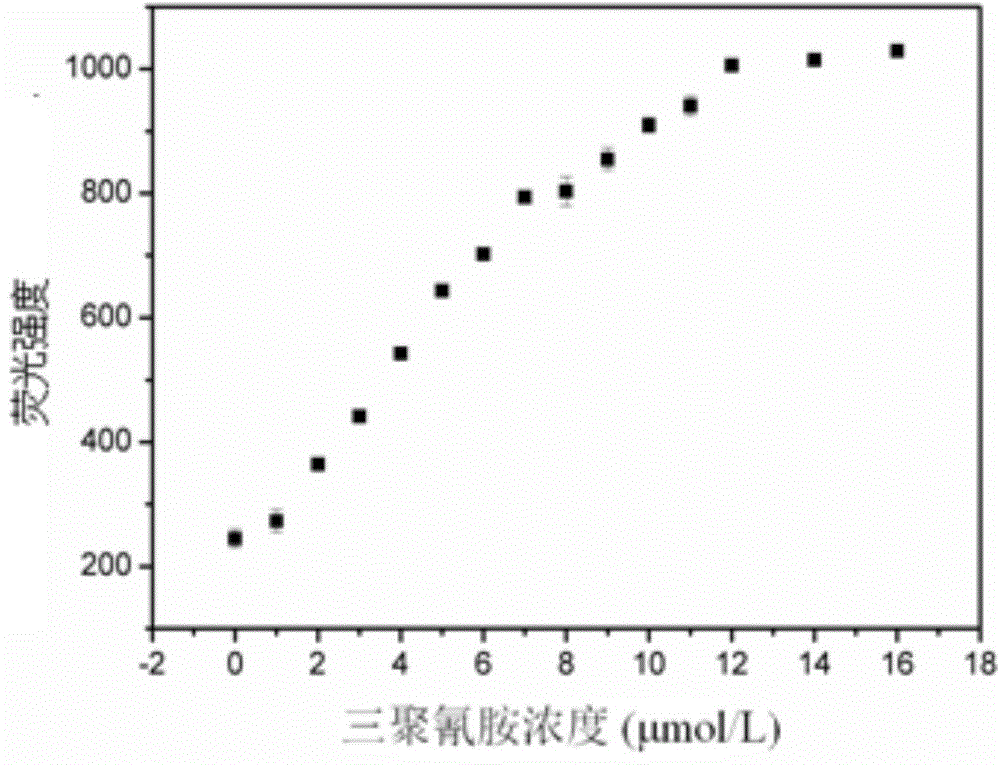
Melamine fluorescence spectroscopic detection method based on metal ruthenium polypyridine complex
InactiveCN104792757BSimplify detection stepsFast processPreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescencePhenanthrolineSingle strand
The invention relates to a melamine fluorescence spectrum detection method based on metallic ruthenium polypyridine complex. Melamine and DNA rich in thymine can form the effect of three special hydrogen bonds, so that the DNA can be transformed into three strands from a single strand, and as (Ru(phen)2dppz-idzo)<2+> (phen is 1,10-phenanthroline, dppz is bispyridine phenazine, and idzo is imidazolone) has strong insertion effect on three-strand DNA, fluorescence enhanced range of the three-strand DNA is obviously higher than that of single-strand DNA. When the concentration of the melamine is 0 to 7.0 micro mol / L, the concentration of the obviously and a fluorescence response value have a good linear relation, linear regression equations are respectively F=199.96+85.41c (C: micro mol / L), and a linear coefficient R2 is 0.9923. Meanwhile, by adding melamine with different concentrations to pure milk samples through a constructed method, a satisfactory recovery rate is obtained.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Cobalt-polypyridyl complex for treatment of cancer, a pharmaceutical composition and a kit comprising it
ActiveUS20180050044A1Effective targetingHigh cytotoxic activityAntineoplastic agentsHeavy metal compound active ingredientsCell invasionAutophagic death
A method for treating a subject suffering from a cancer, in particular a multidrug-resistant cancer includes administrating a cobalt-polypyridyl complex to the subject. A method for suppressing the growth of cancer cells, in particular inducing autophagy of the cancer cells, inducing cell cycle arrest of the cancer cells and / or inhibiting cell invasion of the cancer cells and for specifically targeting cancer cells with multidrug-resistance includes contacting said cancer cells with the cobalt-polypyridyl complex. A pharmaceutical composition and a kit are provided and include the cobalt-polypyridyl complex. Unexpectedly, the cobalt-polypyridyl complex is especially suitable to treat cancer, in particular multidrug-resistant cancer with an exceptionally increased cytotoxic activity towards multidrug-resistant cancer cells.
Owner:MACAU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Melamine fluorescence spectrum detection method based on metallic ruthenium polypyridine complex
InactiveCN104792757ASimplify detection stepsFast processPreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescencePhenanthrolineSingle strand
The invention relates to a melamine fluorescence spectrum detection method based on metallic ruthenium polypyridine complex. Melamine and DNA rich in thymine can form the effect of three special hydrogen bonds, so that the DNA can be transformed into three strands from a single strand, and as (Ru(phen)2dppz-idzo)<2+> (phen is 1,10-phenanthroline, dppz is bispyridine phenazine, and idzo is imidazolone) has strong insertion effect on three-strand DNA, fluorescence enhanced range of the three-strand DNA is obviously higher than that of single-strand DNA. When the concentration of the melamine is 0 to 7.0 micro mol / L, the concentration of the obviously and a fluorescence response value have a good linear relation, linear regression equations are respectively F=199.96+85.41c (C: micro mol / L), and a linear coefficient R2 is 0.9923. Meanwhile, by adding melamine with different concentrations to pure milk samples through a constructed method, a satisfactory recovery rate is obtained.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Ruthenium polypyridine complex as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111825603AMeasuring smallAcidogenic reaction time is shortRuthenium organic compoundsPhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusUltraviolet lightsPhotoacid
The invention discloses a ruthenium polypyridine complex, the structure of the ruthenium polypyridine complex is shown as a formula 1, the ruthenium polypyridine complex is used as a photoacid generator, and the problems that the existing photoacid generator needs to be irradiated by ultraviolet light to generate acid, the acid generation reaction time is long, the dosage of required raw materialsis large and the efficiency is low can be solved. The invention also discloses a preparation method and application of the ruthenium polypyridine complex.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Lipidosome encapsulated ruthenium polypyridine complex and application thereof
ActiveCN108743533ASmall toxicityPromote absorptionHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic non-active ingredientsSide effectAntioxidant
The invention discloses lipidosome encapsulated ruthenium polypyridine complex and an application thereof. Dichlorobis(2,2'-bipyridine) ruthenium and ruthenium acetate are taken as anticancer metal complex, and compared with cis-platinum, the ruthenium complex has low toxic and side effects, is easily absorbed and excreted rapidly and can suppress tumor growth and metastasis; meanwhile, the ruthenium complex is encapsulated with lipidosome, a blender, an antioxidant, a buffer agent, an antibacterial agent and a stabilizer are added, the blender adopts a mixture of titanium bis(triethanolamine)diisopropoxide, triethoxy[2-(7-oxabicyclo[4.1.0]hept-3-yl)ethyl]silane, (3S,6E,10S)-6,10-dimethyl-3-propan-2-ylcyclodec-6-ene-1,4-dione and diethylene glycol monoethyl ether, and under the joint action of the substances, intercoordination of lipidosome and the ruthenium complex can be greatly improved, and the finally prepared lipidosome encapsulated ruthenium polypyridine complex has good biocompatibility and low toxicity; furthermore, the lipidosome encapsulated ruthenium polypyridine complex can cause more serious DNA damage and can serve as a chemotherapeutic drug or a photographic developer in cancer therapy.
Owner:WENZHOU INST OF BIOMATERIALS & ENG
Iridium-selenium polypyridine complex and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN102924531BStable structureGood fluorescence propertiesGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsMicrobiological testing/measurementIridiumCell membrane
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Membrane staining dyes containing phosphorescent transition metal polypyridine complexes
ActiveUS9441003B2Indium organic compoundsPreparing sample for investigationBiological cellCell membrane
The present invention is concerned with a staining dye for staining a biological cell, comprising dye molecules with a positively charged polar head group for attraction to cell membrane of the cell and for refraining the dye molecules from entering the cytoplasm, and one or more hydrophobic groups for interaction with phospholipids of the cell membrane. The dye molecules are phosphorescent transition metal polypyridine complexes having a metal center and ligands which are non-organic fluorophores.
Owner:CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Ruthenium polypyridine complex with triethylamine structure as well as preparation method and application of ruthenium polypyridine complex
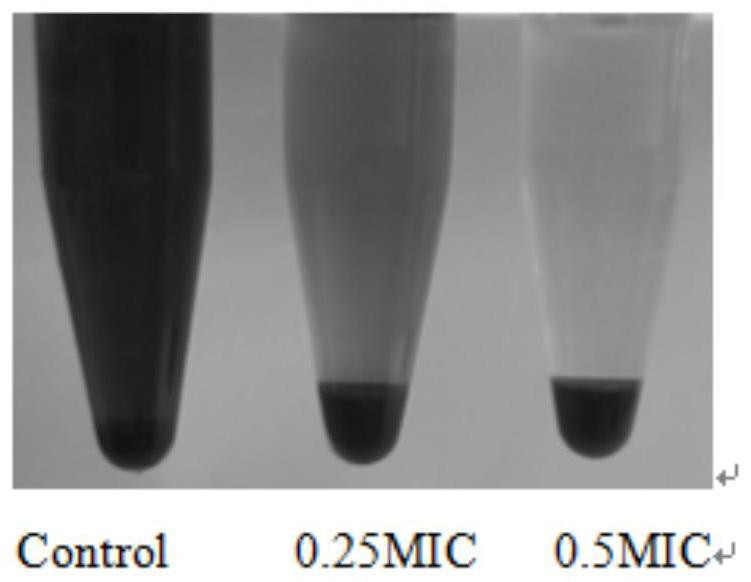
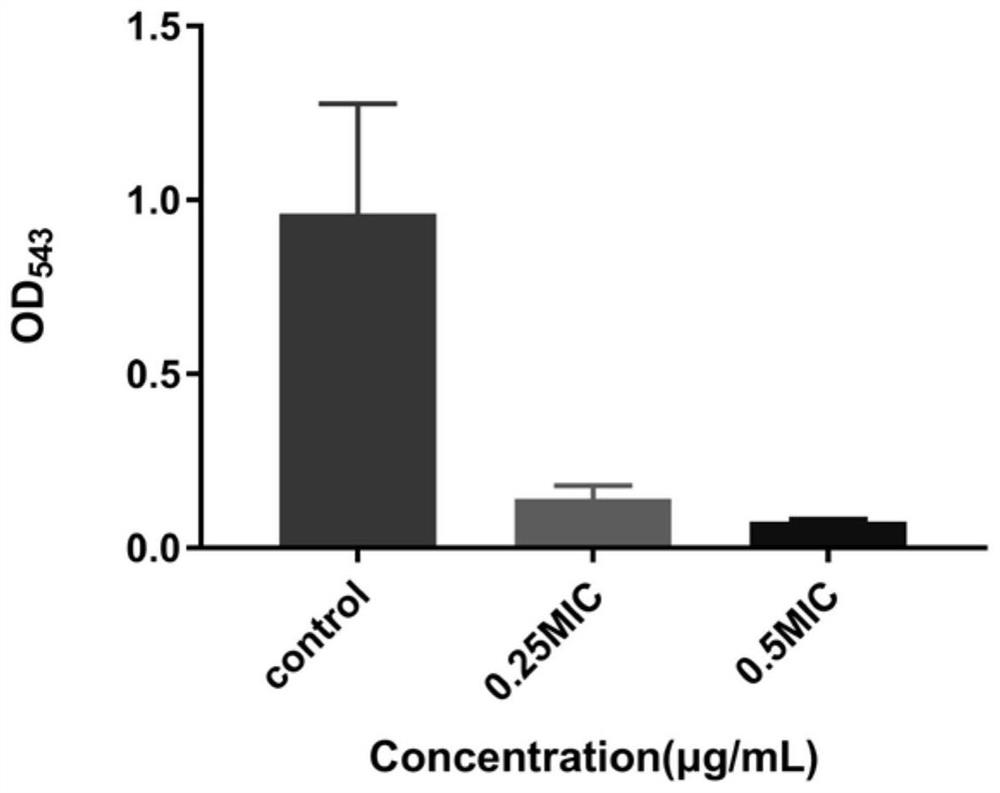
ActiveCN114751942ALittle hemolysisIncreased sensitivityAntibacterial agentsRuthenium organic compoundsHemolysisRed blood cell
The invention discloses a ruthenium polypyridine complex with a triethylamine structure as well as a preparation method and application of the ruthenium polypyridine complex. The complex contains metal ions and is charged, so that compared with traditional small organic molecules, the complex has the advantages that the bacterial cell membrane penetrating capacity and retention effect of the complex are enhanced, and the metal complex can be modified by different ligands due to the multi-coordination configuration of the metal complex, so that the biological activity of the metal complex is higher. Tests prove that the ruthenium polypyridine complex with the triethylamine structure can effectively reduce the hemolysis effect of toxins released by staphylococcus aureus on red blood cells, and the ruthenium complex has no tendency to trigger drug resistance of bacteria and can significantly improve the sensitivity of staphylococcus aureus to aminoglycoside antibiotics.
Owner:JIANGXI SCI & TECH NORMAL UNIV
A kind of preparation method of ruthenium polypyridine complex
The invention discloses a simple preparation method of an electrochemiluminescent reagent ruthenium polypyridine complex. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving a ruthenium chloride hydrate and 2, 2'-dipyridyl in a mixed solvent of ethanol and ethylene glycol, wherein the ratio of ruthenium trichloride in the ruthenium chloride hydrate to 2, 2'-dipyridylis 1:4-1:5, and the concentration of ruthenium trichloride in the mixed solvent is 0.02-0.025mol / L; heating to react, wherein the reaction temperature is 70-100 DEG C and the reaction time is 6-10 hours; cooling to room temperature and carrying out rotary evaporation to remove ethanol; adding a saturated sodium chloride solution to separate out solids, filtering, adding water to recrystallize and drying to obtain tri(2, 2'-dipyridyl) ruthenium chloride (II) hexahydrate. The synthetic method is simple and convenient, short in reaction step, easy to operate, less in consumption of organic solvents, simple in post-treatment and high in product purity. The conversation ratio of noble metal ruthenium reaches up to 95%, so that the preparation method is less in environmental protection pressure and convenient for industrialized production.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
A kind of synthetic method of Ginkgo biloba polyprenol metal complex with light control activity
ActiveCN112250879BGood dark stabilityLight-controlled anti-tumor performance is goodOrganic active ingredientsDrug photocleavagePhotodissociationBiology
The invention discloses a synthesis method of ginkgo biloba polyprenol metal complex with light control activity. The method comprises the following steps: using high-purity ginkgo biloba polyprenol as a raw material, replacing the terminal hydroxyl group of the polyprenol with an active group with stronger coordination ability by means of chemical modification, and then combining it with a ruthenium polypyridine complex Carry out complexation reaction to synthesize Ginkgo biloba polyprenol-ruthenium polypyridine metal complex; the prepared complex has good photodissociation efficiency and light-controlled anti-tumor properties, and can be used as a high-value Ginkgo biloba polyprene Provide theoretical reference and technical support for the development of alcohol functional products.
Owner:INST OF CHEM IND OF FOREST PROD CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Ruthenium (II)-polypyridine complex, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102464676BGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsMicrobiological testing/measurementLithium chlorideFiltration
The invention provides a ruthenium (II)-polypyridine complex. For the ruthenium (II)-polypyridine complex, bipyridyl (bpy) or phenanthroline hydrate (phen) is used as an ancillary ligand, and dipyridine[3,2-a:2',3'-c]phenazine-11,12-imidazole (dppzi) is used as a main ligand. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing 5,6-dinitrobenzimidazole from 5,6-nitrobenzimidazole; reducing 5,6-dinitrobenzimidazole into 5,6-diaminobenzimidazole by using hydrazine hydrate and palladium / carbon; preparing dppzi from phenanthroline hydrate-5,6-dione and 5,6-diaminobenzimidazole and preparing cis-[Ru(bpy)2Cl2].2H2O from ruthenium trichloride, bpy and lithium chloride; preparing cis-[Ru(phen)2Cl2].3H2O from ruthenium trichloride, phen and lithium chloride; carrying out a heating reflux reaction on dppzi and cis-[Ru(bpy)2Cl2].2H2O or cis-[Ru(phen)2Cl2].3H2O under the protection of argon, carrying out cooling, adding ammonium hexafluorophosphate, allowing precipitate to deposit and carrying out filtration and column chromatography so as to obtain a target product. The ruthenium (II)-polypyridine complex provided in the invention can be used as an optical switch for G-quadruplex DNA molecules.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Preparation method of tetranuclear Ru(II) polypyridine complex containing flexible isopodand bipyridyl bridging ligand
The invention provides a preparation method of a tetranuclear Ru(II) polypyridine complex containing a flexible isopodand bipyridyl bridging ligand. The method comprises the steps of firstly reactinga compound 1 with Ru(bpy)2Cl2.2H2O, reacting the product with o-phenanthroline-5,6-dione to obtain a precursor complex 2, and reacting the complex 2 with RuCl3.3H2O to obtain a complex 3. According tothe method provided by the invention, through the above synthetic process, the flexible isopodand bipyridyl bridging ligand is introduced into the tetranuclear Ru(II) polypyridine complex 3.
Owner:QUJING NORMAL UNIV
Synthetic method of ginkgo leaf polyprenol metal complex with light-operated activity
ActiveCN112250879AGood dark stabilityLight-controlled anti-tumor performance is goodOrganic active ingredientsDrug photocleavageGinkgo bilobaChemical modification
The invention discloses a synthetic method of a ginkgo leaf polyprenol metal complex with light-operated activity. The method comprises the following steps: taking high-purity ginkgo leaf polyprenol as a raw material, replacing terminal hydroxyl of polyprenol with an active group with stronger coordination ability by a chemical modification means, and then carrying out complexation reaction with aruthenium polypyridine complex to synthesize the ginkgo leaf polyprenol-ruthenium polypyridine metal complex. The prepared complex has good photoinduced dissociation efficiency and light-operated anti-tumor performance, and can provide theoretical reference and technical support for development of high-valued ginkgo leaf polyprenol functional products.
Owner:INST OF CHEM IND OF FOREST PROD CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![Ruthenium polypyridine complex and preparation method and application of [Ru(L)2(tppp)]<2+> thereof Ruthenium polypyridine complex and preparation method and application of [Ru(L)2(tppp)]<2+> thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/0fbf1a76-be7d-442f-b09c-11677a79929f/140123143309.PNG)
![Ruthenium polypyridine complex and preparation method and application of [Ru(L)2(tppp)]<2+> thereof Ruthenium polypyridine complex and preparation method and application of [Ru(L)2(tppp)]<2+> thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/0fbf1a76-be7d-442f-b09c-11677a79929f/140123143312.PNG)
![Ruthenium polypyridine complex and preparation method and application of [Ru(L)2(tppp)]<2+> thereof Ruthenium polypyridine complex and preparation method and application of [Ru(L)2(tppp)]<2+> thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/0fbf1a76-be7d-442f-b09c-11677a79929f/140123143315.PNG)