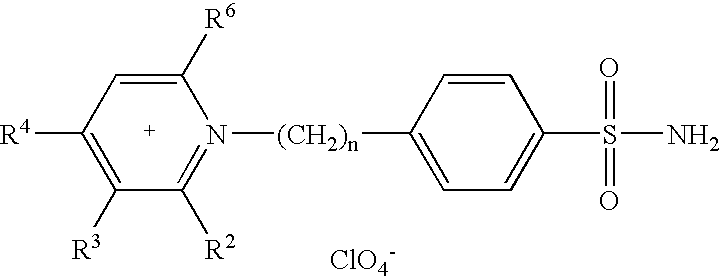
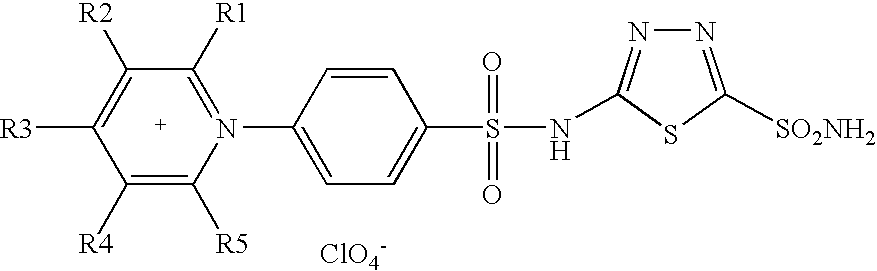
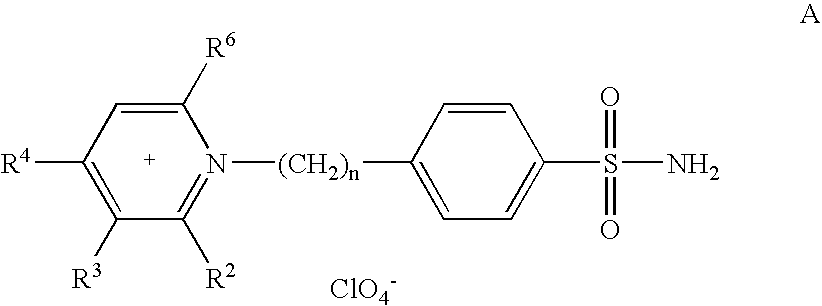
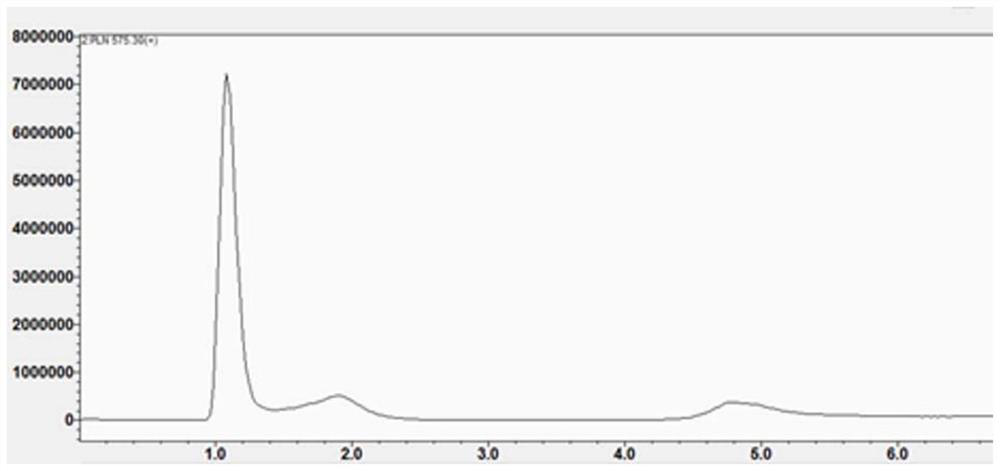
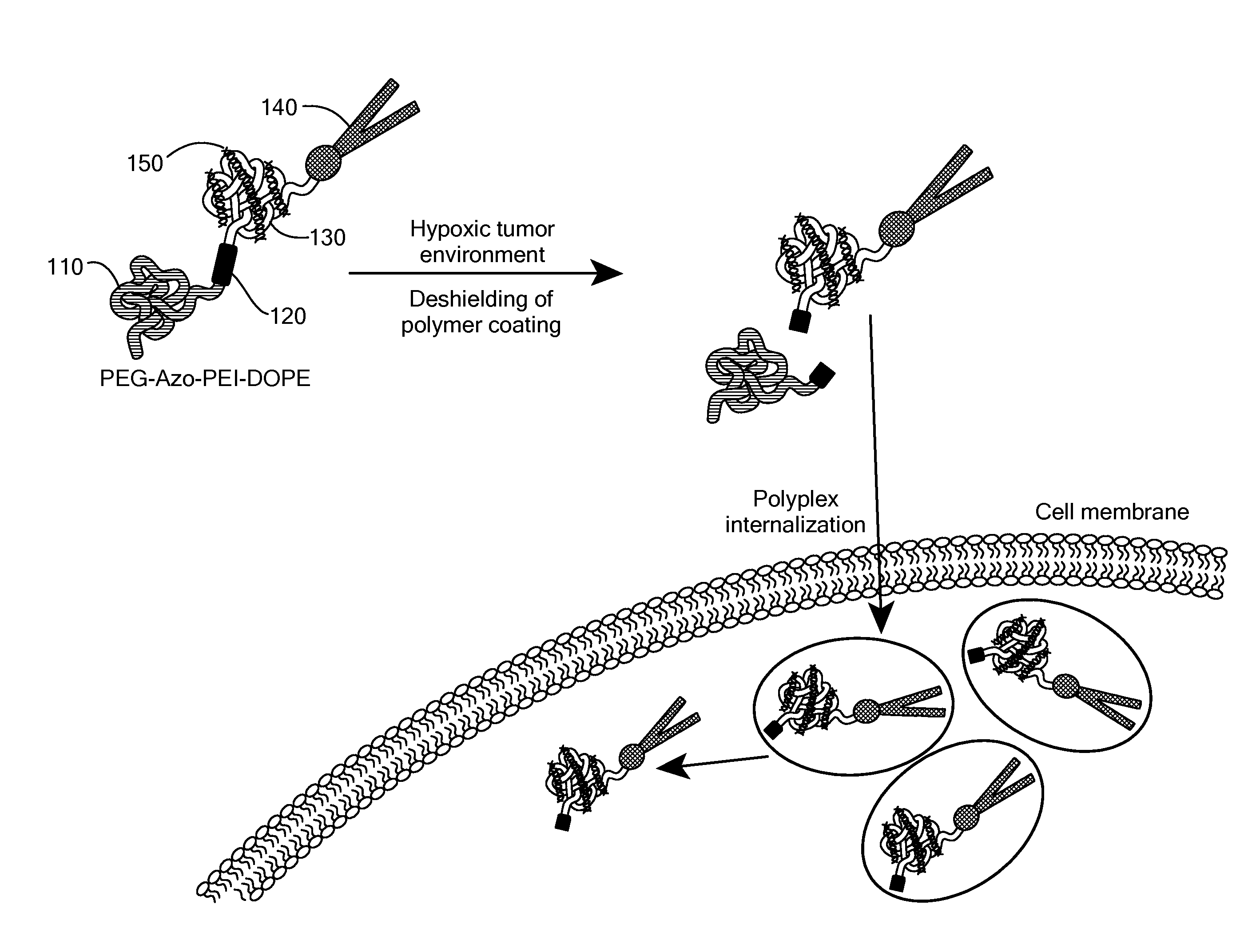
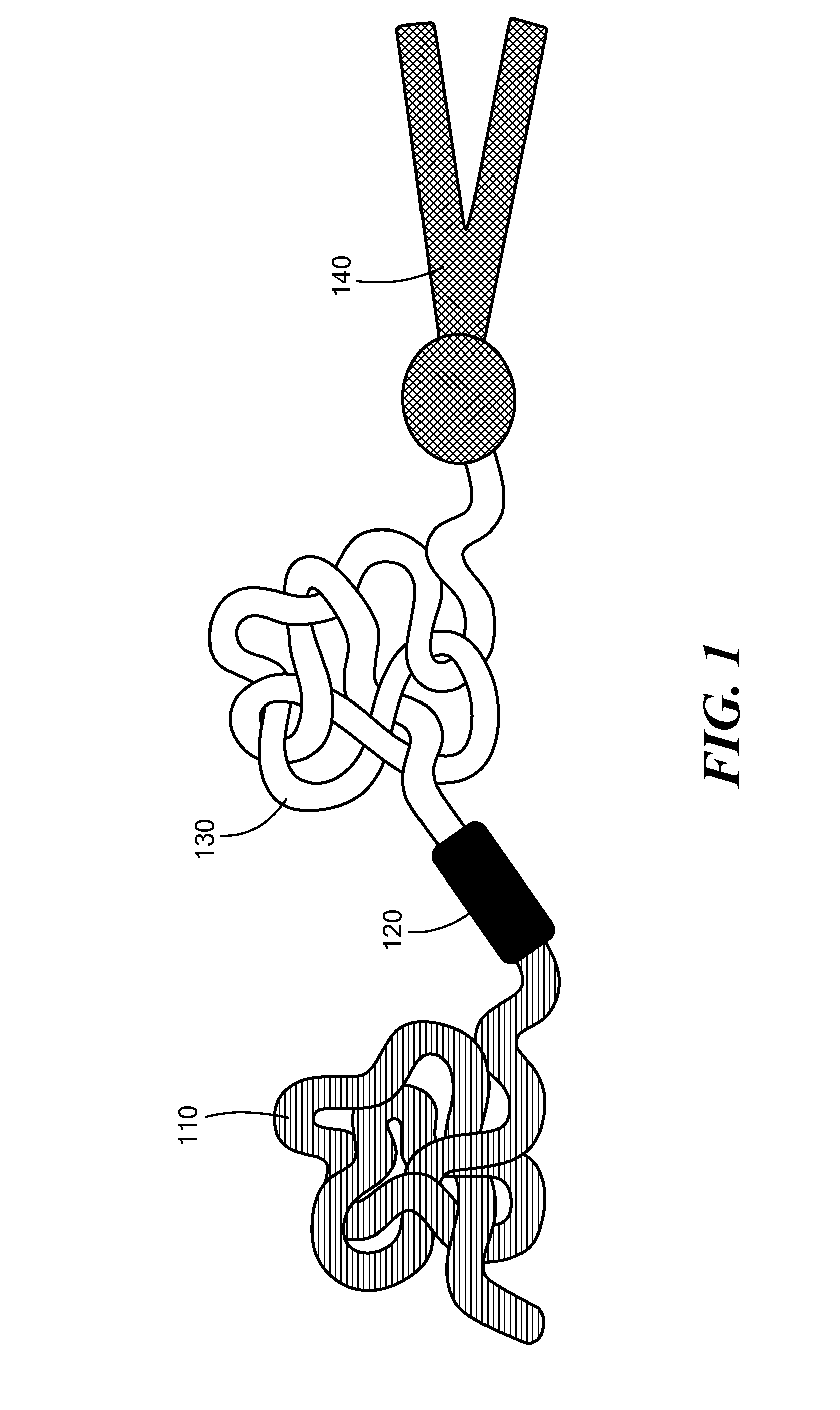
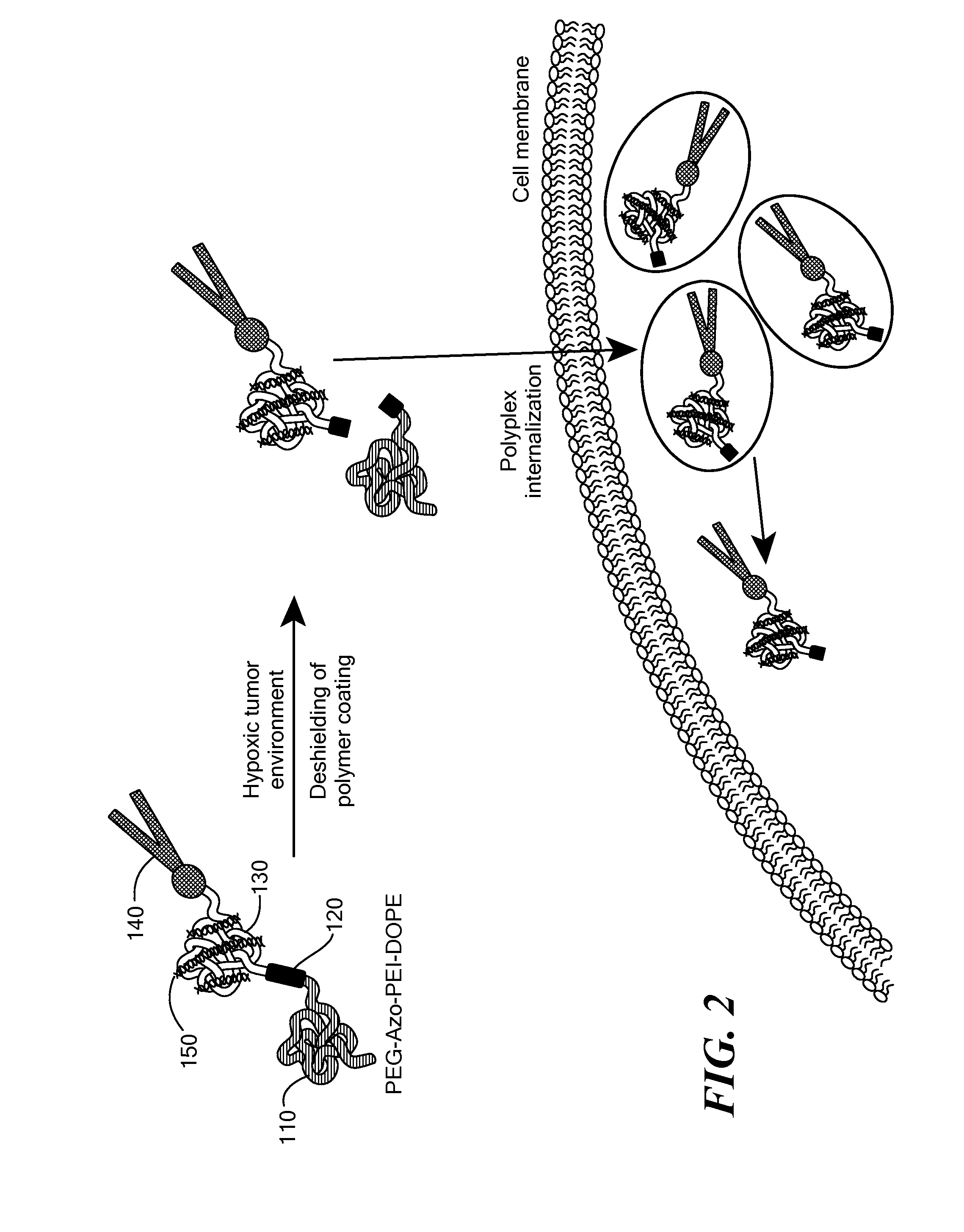
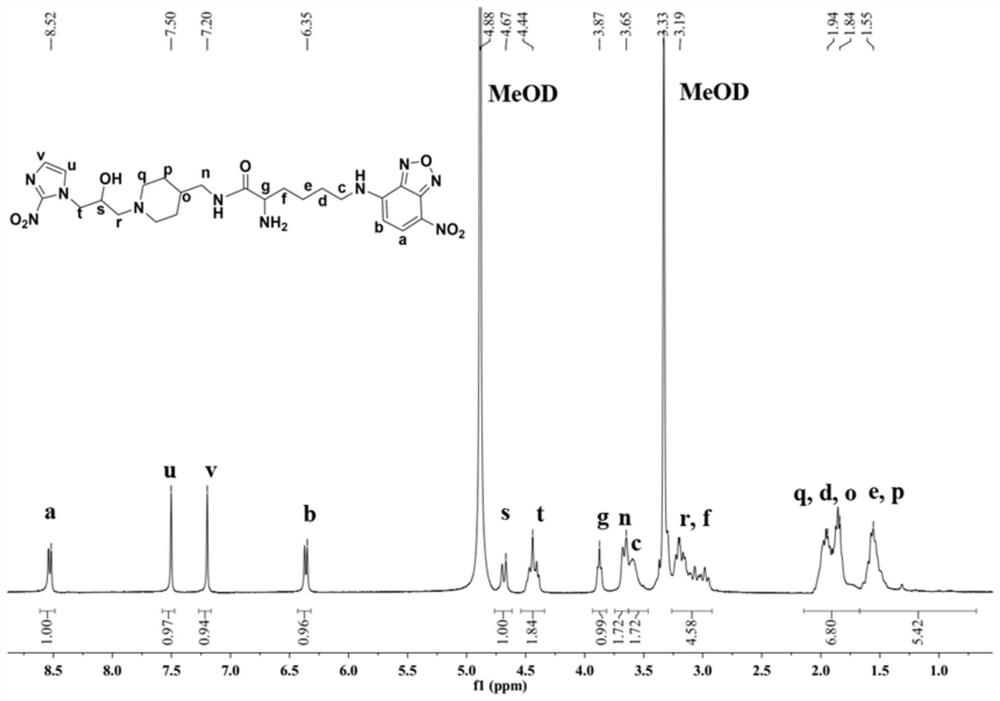
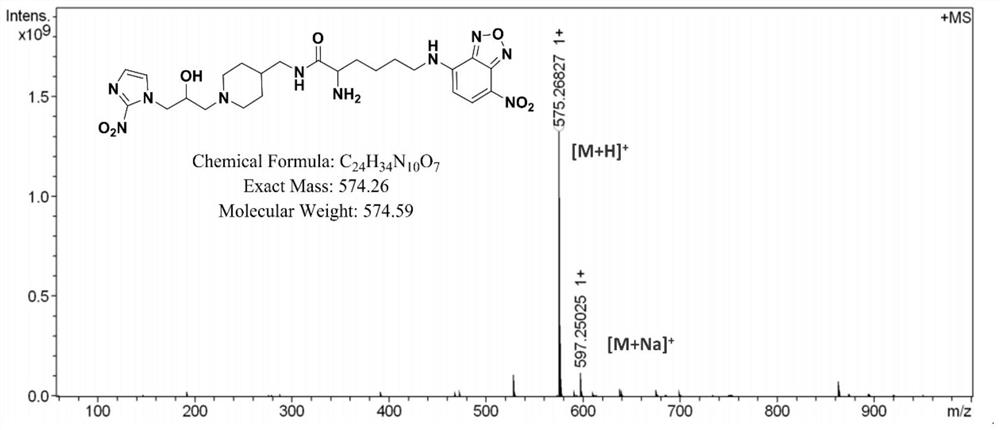
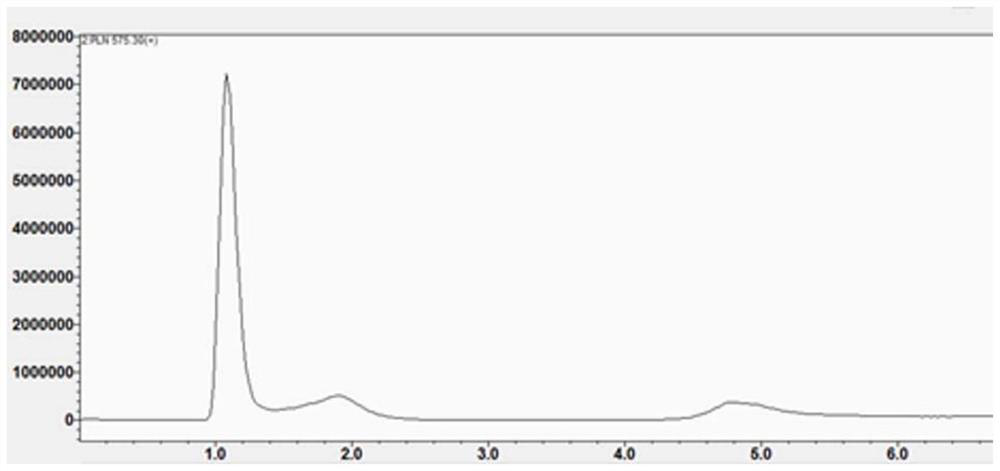
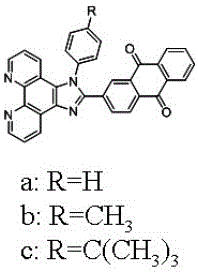
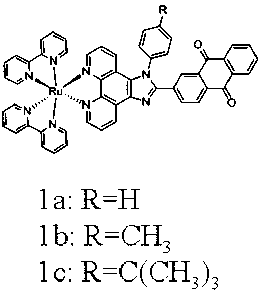Patents
Literature
49 results about "Hypoxic cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cell hypoxia. Definition. noun. Inadequate oxygen supply at the cellular level. Supplement. In cell hypoxia, the cells are unable to use the oxygen effectively. This may be due to a disruption in the activity of oxidative phosphorylation enzymes.
Interaction between the VHL tumor suppressor and hypoxia inducible factor, and assay methods relating thereto
InactiveUS6787326B1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSuppressorTumour suppressor protein
The invention relates to the finding that the VHL tumour suppressor protein regulates hypoxia inducible factor alpha subunits, by targeting HIF alpha for destruction in normoxic, but not hypoxic cells. The invention provides assays for modulators of this interaction, and peptides based upon HIF alpha subunit sequence which may modulate this interaction.
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
CA IX-specific inhibitors
InactiveUS20060057068A1Reduce acidificationIncrease aggressivenessOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementAbnormal tissue growthHypoxic cell
Therapeutic methods for inhibiting the growth of preneoplastic / neoplastic vertebrate cells that abnormally express MN protein are disclosed. Screening assays are provided for identifying compounds, preferably organic compounds, preferably aromatic and heterocylic sulfonamides, which inhibit the enzymatic activity of MN / CA IX and that are useful for treating patients with preneoplastic / neoplastic disease. Further, the CA IX-specific inhibitors when labeled or linked to an appropriate visualizing means can also be used diagnostically / prognostically for preneoplastic / neoplastic disease, and for imaging use, for example, to detect hypoxic precancerous cells, tumors and / or metastases, by selectively binding to activated CA IX, preferably CA IX activated under hypoxic conditions, and not to inactive CA IX. Such detection of hypoxic conditions can be helpful in determining effective treatment options, and in predicting treatment outcome and the prognosis of disease development. Still further, the CA IX-specific inhibitors can be used therapeutically to selectively target hypoxic cells expressing activated CA IX. The CA IX-specific inhibitors can be labelled or conjugated to radioisotopes for radiotherapy of hypoxic cells. Alternatively, the CA IX-specific inhibitors can be used for gene therapy coupled to vectors for targeted delivery to hypoxic preneoplastic / neoplastic cells expressing activated CA IX on their surfaces. In an alternative mode of the invention, CA IX-specific inhibitors may be used therapeutically to target acidic conditions of a tumor, e.g., to increase pHe in order to enhance the efficacy of weak base chemotherapeutic drugs.
Owner:INST OF VIROLOGY SLOVAK ACAD OF SCI +1
Radiotherapy combined with hypoxic cell sensitizers
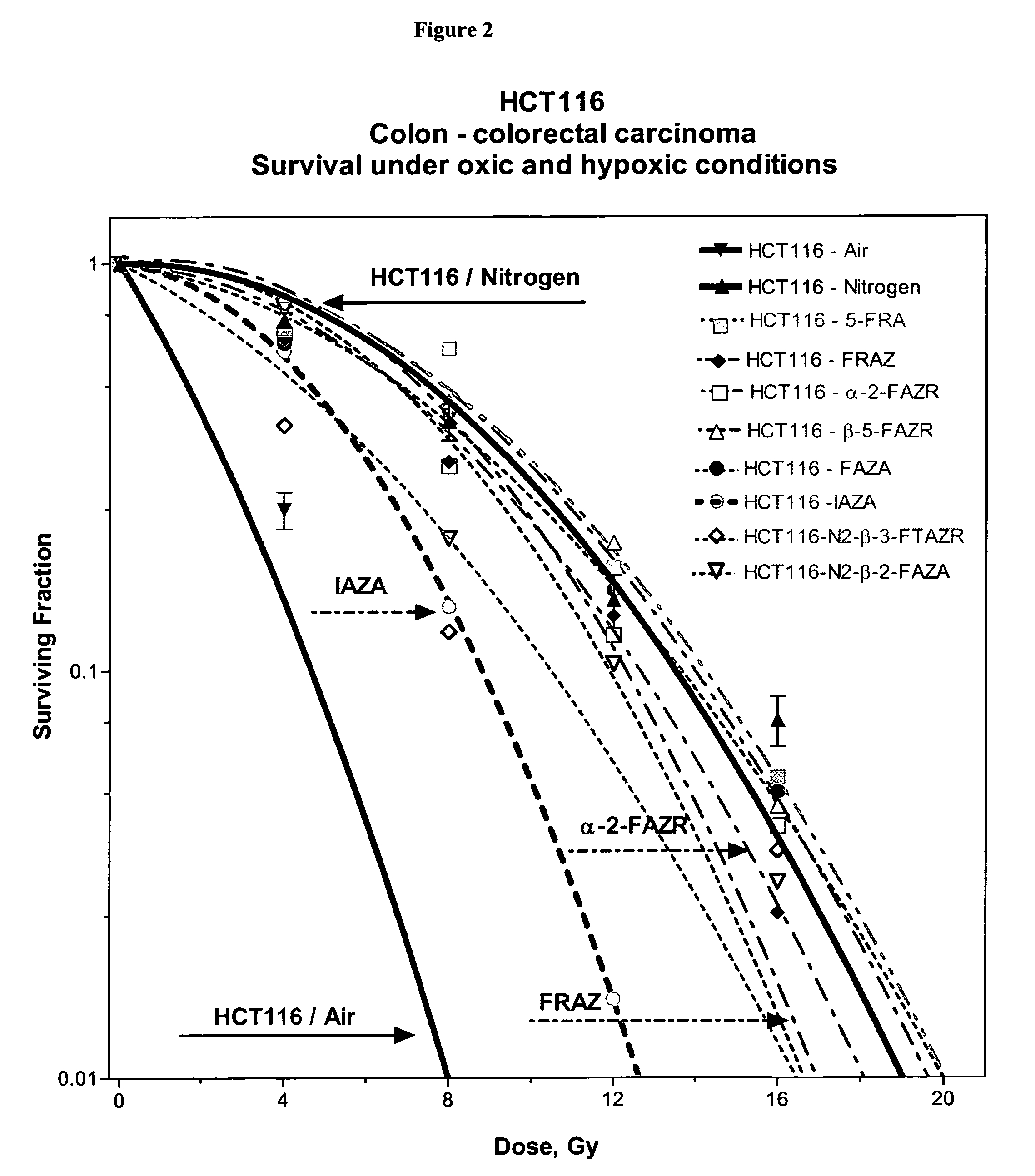
The invention discloses a method of treating cancer in a patient, comprising administering to the patient a radiation sensitizer selected from nitroimidazoles in an amount effective to sensitize a patient to radiation and subjecting the patient to radiation therapy. In certain embodiments the radiation sensitizer is etanidazole or doranidazole.
Owner:INTRAOP MEDICAL
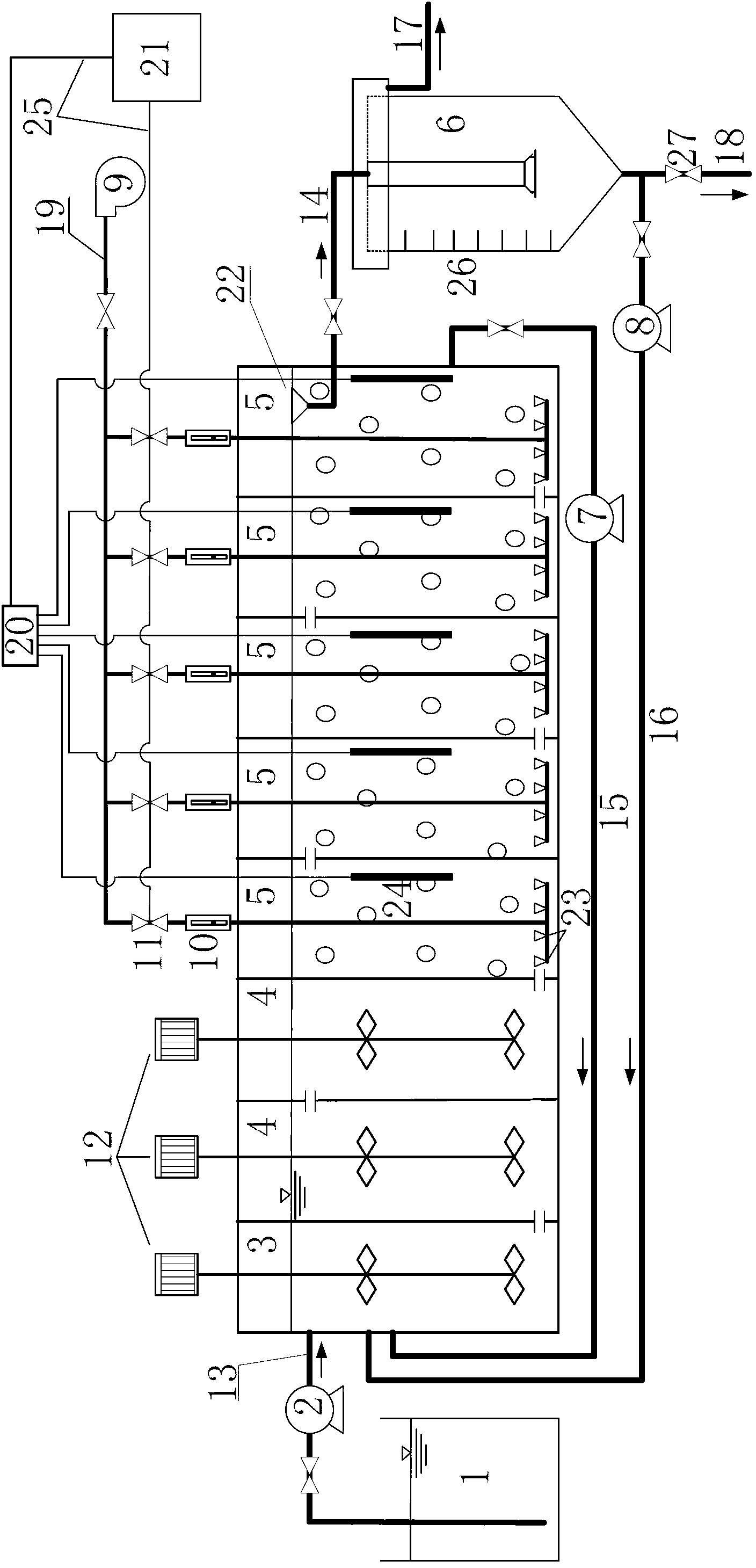
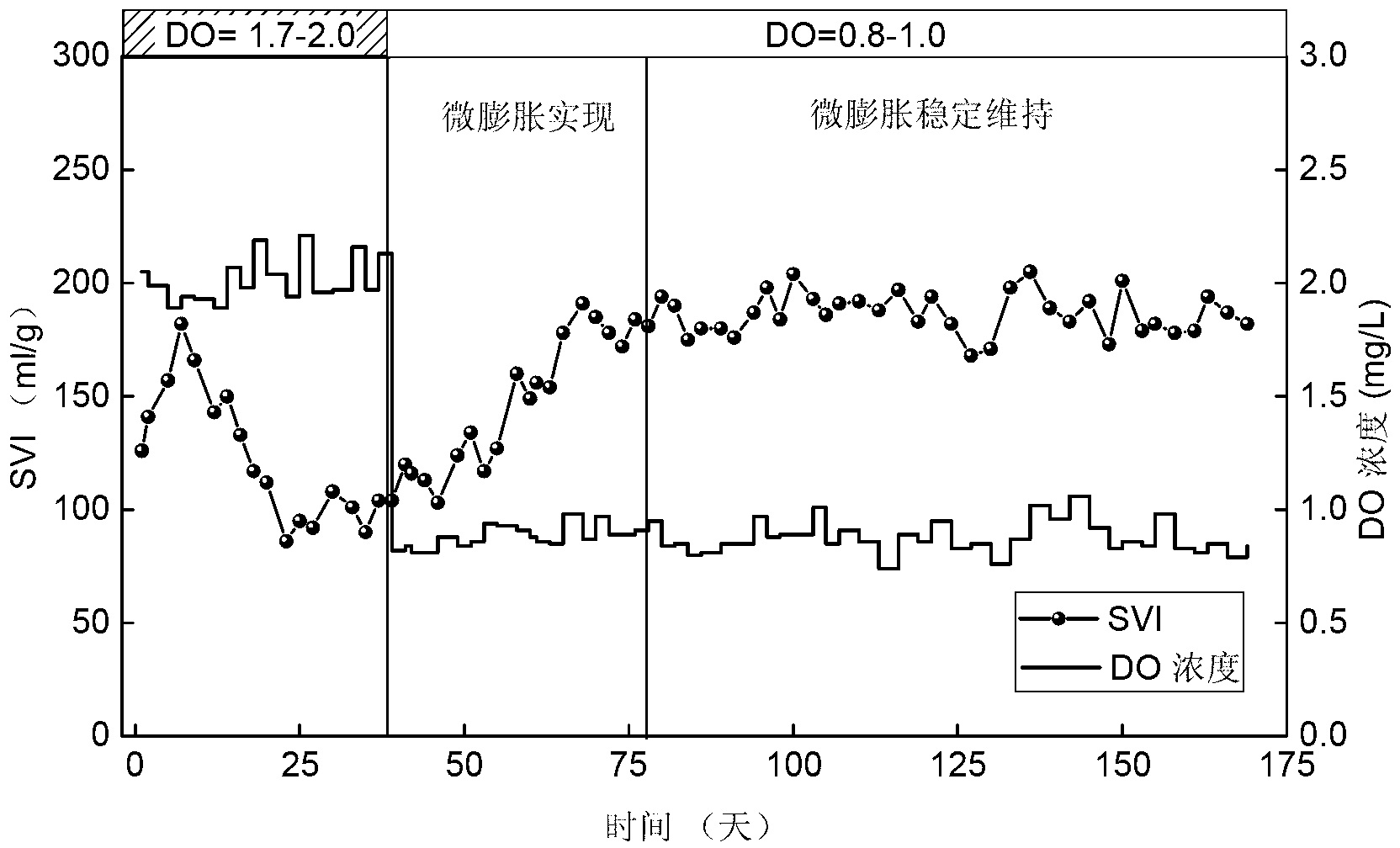
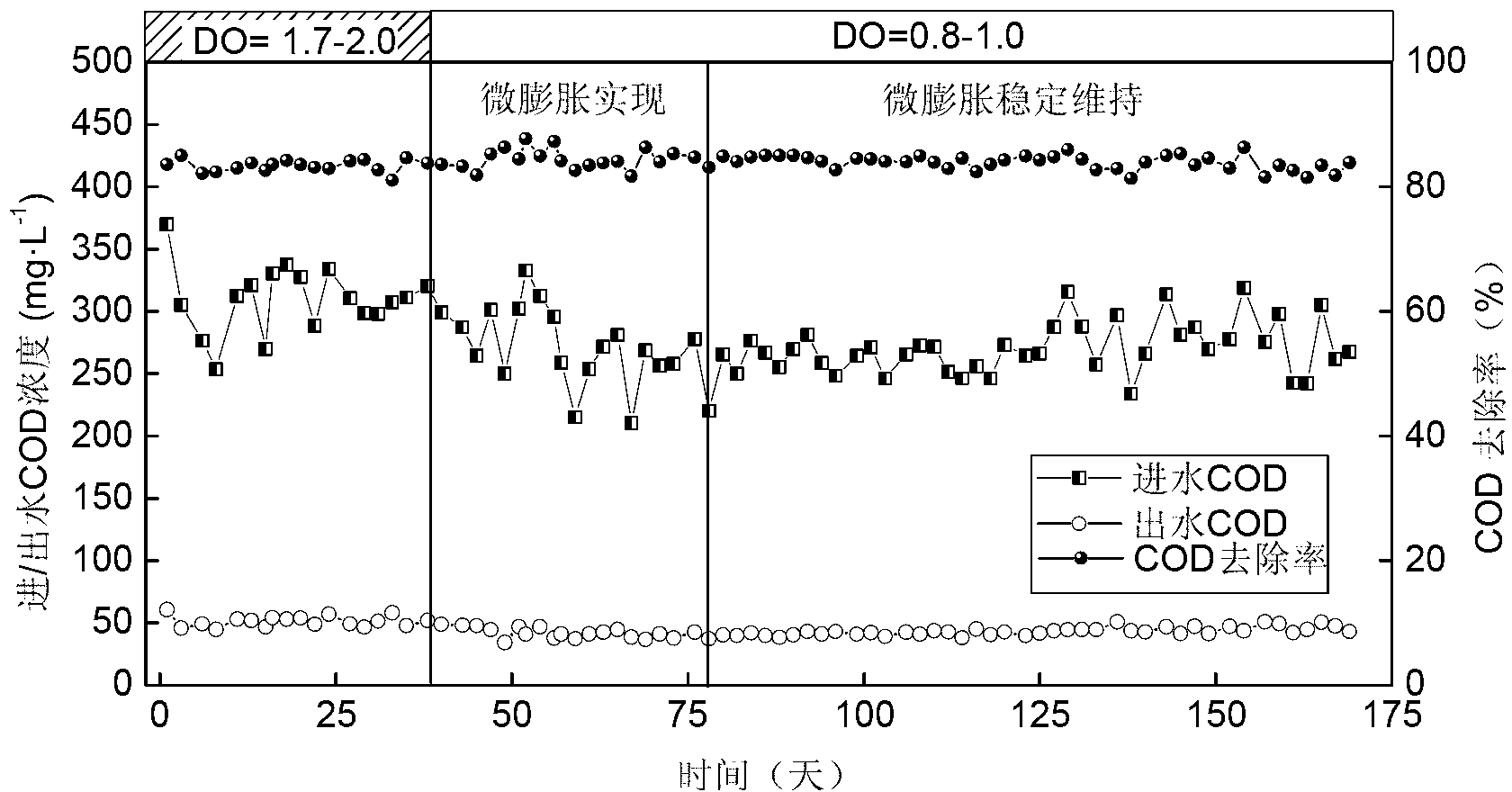
Method for starting and stably keeping micro-expansion of sludge in synchronous biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal system
ActiveCN103011408ASave operating economic costLow running costTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSludgeWater quality
The invention relates to a method for starting and stably keeping the micro-expansion of sludge in a synchronous biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal system, belonging to the field of treating sewage biochemically. A device for implementing the method is formed by connecting a water inlet pool, anaerobic cells, hypoxic cells, aerobic cells and a secondary settling pool in sequence. The wall of the secondary settling pool is provided with a sludge height mark so that the degree of expansion of the sludge can be known in real time. Each aerobic cell is provided with an independent dissolved-oxygen probe, and the dissolved-oxygen probe is connected with a dissolved-oxygen instrument. The control platform of a PLC (programmable logic controller) is used for controlling the concentration of the dissolved oxygen in each aerobic cell accurately according to the parameter set value and the feedback signal of the dissolved-oxygen instrument. The micro-expansion of the sludge in the synchronous biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal system is started by reducing the concentration of the dissolved oxygen in each aerobic cell to 0.8-1.0 mg / L, and the dissolved oxygen is regulated according to monitoring result of the SVI (sludge volume index), the height of the sludge in the secondary settling pool, the quality of the effluent of the device and other parameters so as to keep the micro-expansion of the sludge stable. Due to the adoption of the method, the pollutant removal rate is improved, the quality of the effluent is guaranteed, the aeration energy consumption of the water plant is reduced, and the energy-efficient treatment of the effluent is realized.
Owner:SDIC XINKAI WATER ENVIRONMENT INVESTMENT CO LTD
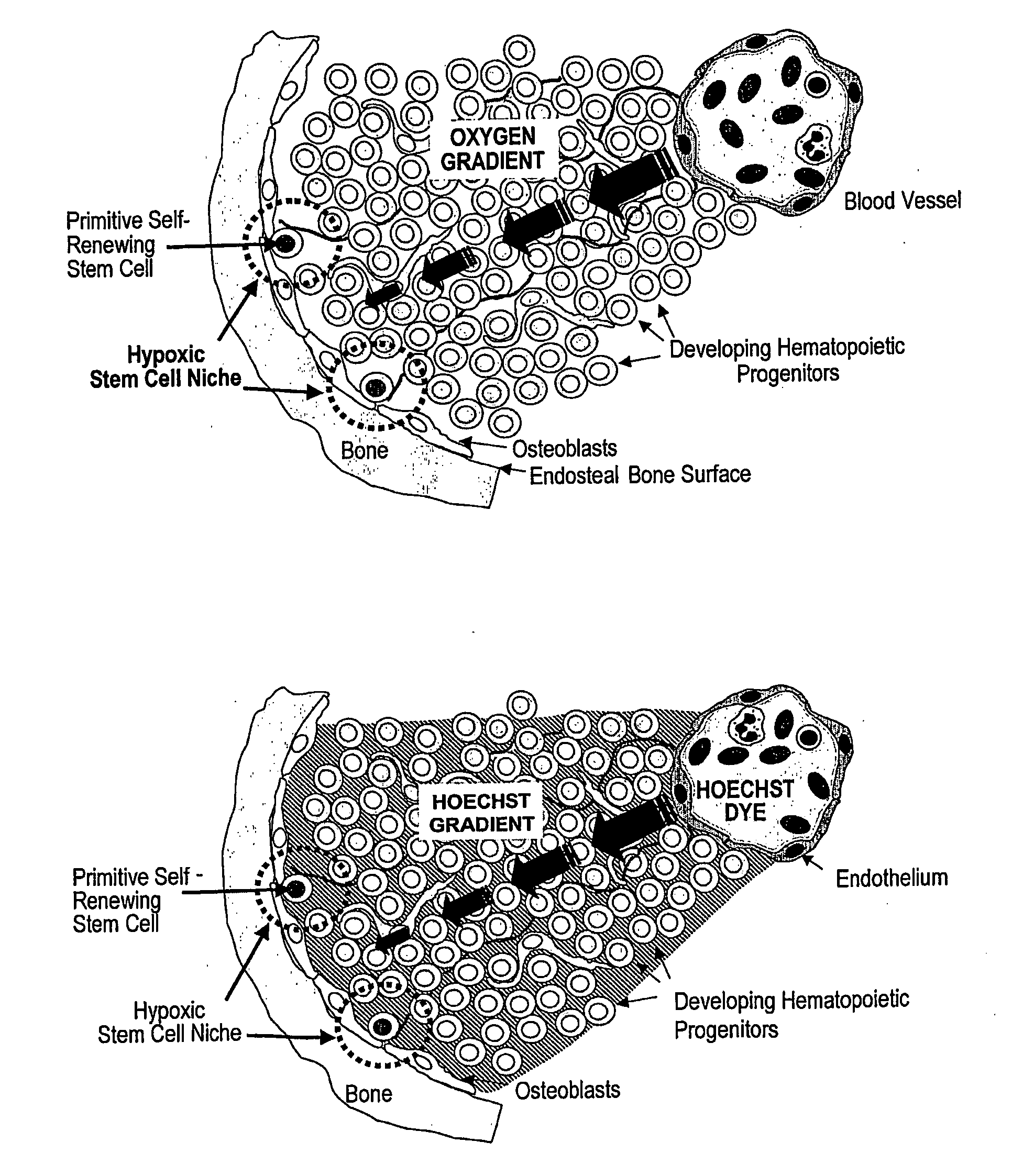
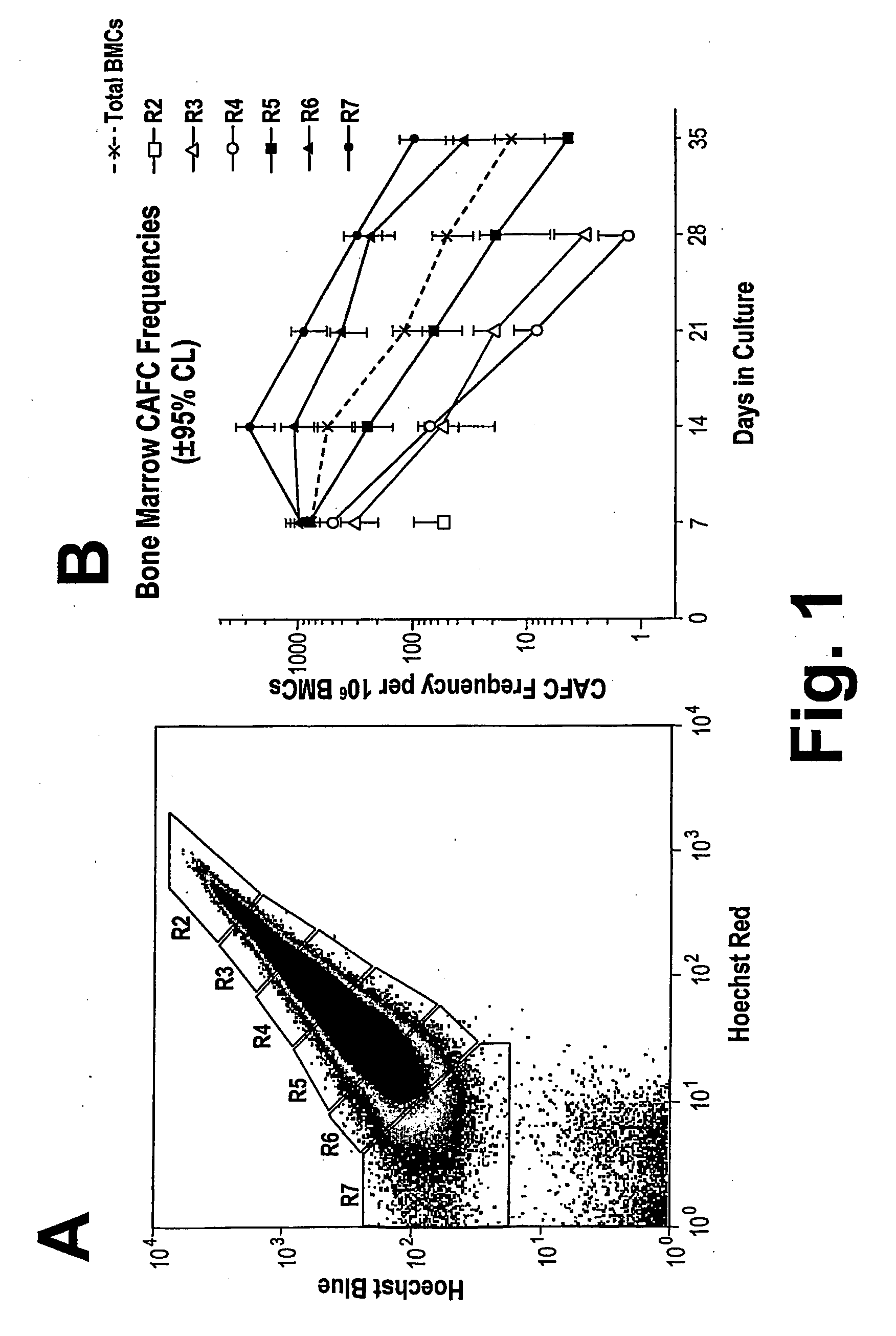
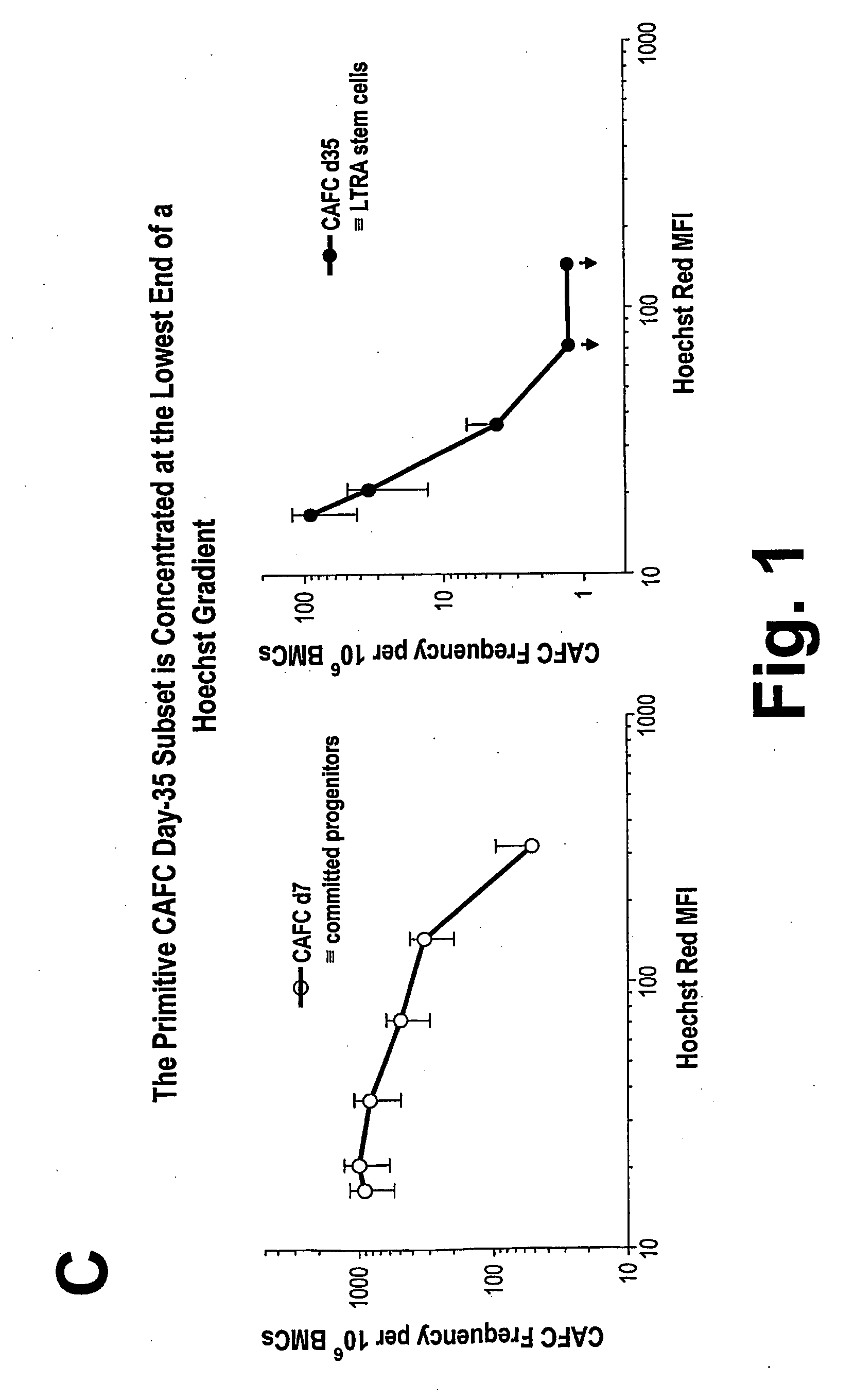
Method for Selectively Depleting Hypoxic Cells
InactiveUS20090136521A1Easy to implantLess toxicityBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsHypoxic cellImproved method
An improved method for selectively depleting hypoxic cells within the bone marrow is disclosed. The method can be used to enhance engraftment of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) in the bone marrow of a host subject. Also disclosed is a method for treating a cancer within the bone marrow of a host subject.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC +1
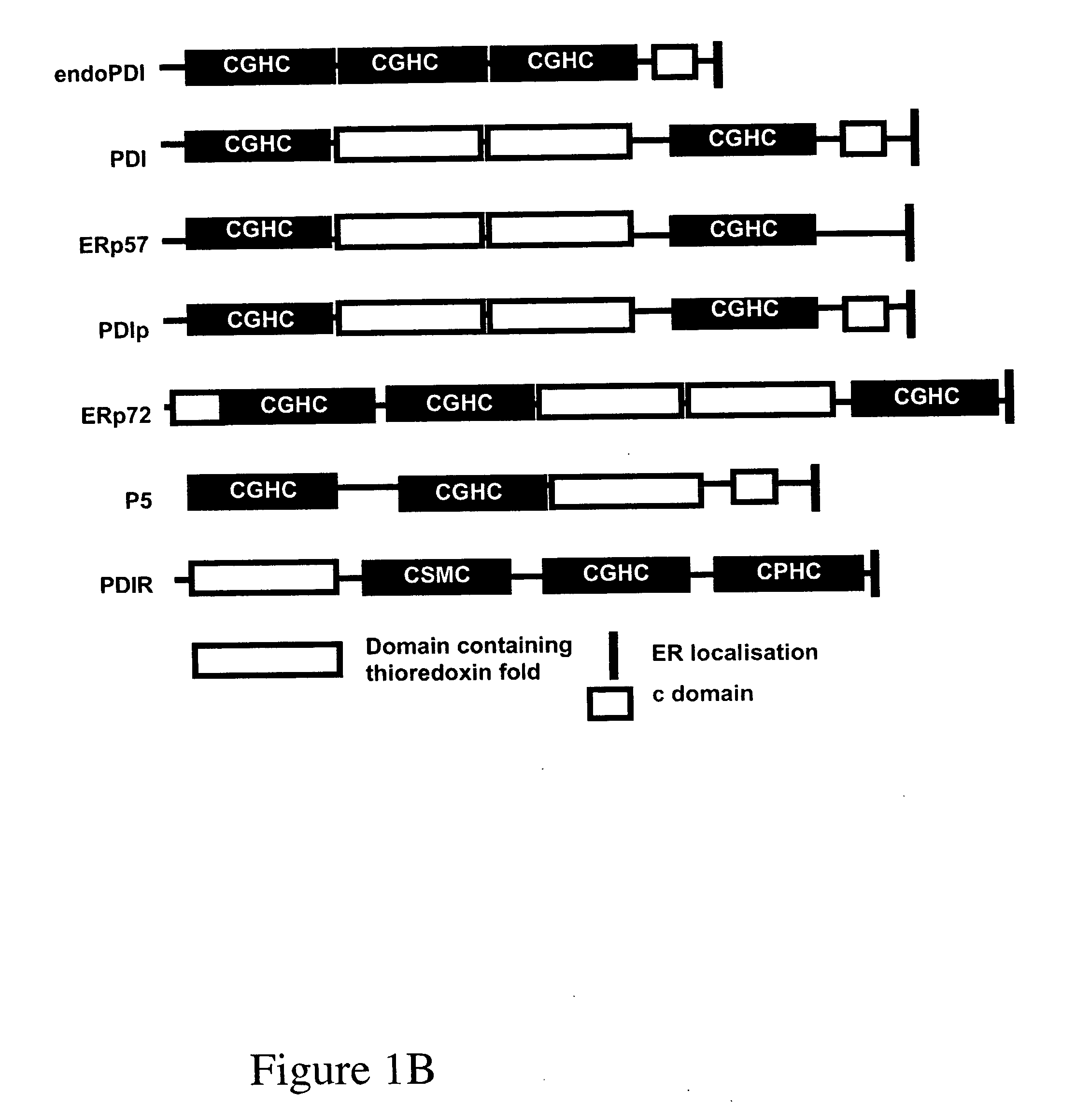
Therapeutic and diagnostic applications of protein disulphide isomerases
InactiveUS20050153361A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningApoptosisAngiogenesis growth factor
An endothelial form of protein disulphide isomerase (endoPDI) is specifically upregulated in endothelial cells in response to hypoxia. Inhibition of endoPDI expression in hypoxic cells induces apoptosis. Thus the invention provides the use of endoPDI as a marker for angiogenesis and as a therapeutic target for the inhibition of angiogenesis. Agents capable of binding to or inhibiting endoPDI may be used for the detection and treatment of solid tumours.
Owner:CANCER RES TECH LTD
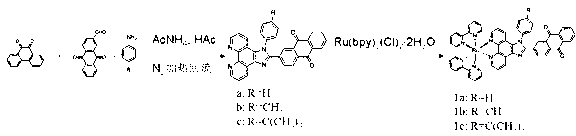
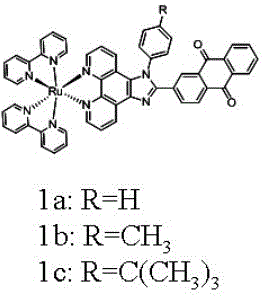
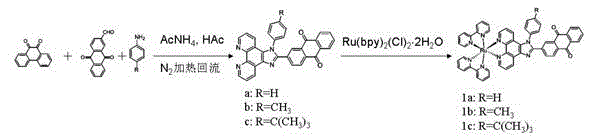
Preparation method and application of anthraquinone polypyridine ligand and ruthenium-anthraquinone complex
InactiveCN103012401ASmall structureStable structureOrganic active ingredientsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsHypoxic cellPyridine ligand
The invention discloses a synthesis method and application of an anthraquinone polypyridine ligand and anthraquinone-ruthenium polypyridine complex. The anthraquinone-ruthenium polypyridine complex has good inhibition activity on the growth of hypoxic cells, and generates obvious fluorescence through reduction in the hypoxic cells; and thus, the compound is a novel biological reduction type hypoxic cell anti-cancer drug and a specific fluorescence probe as well as a drug with application value and taking tumor hypoxia as a target point and a fluorescence probe.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method and kit for inducing hypoxia in tumors through the use of a magnetic fluid
InactiveUS7448389B1Overcomes drawbackNon-toxicHeavy metal active ingredientsEnergy modified materialsAbnormal tissue growthMedicine
A method and kit for inducing hypoxia in tumors includes impeding oxygen supply to non-hypoxic cells in a subject in need thereof by using a magnetic fluid.
Owner:MATERIALS MODIFICATION INC
Device for cell intermittent hypoxia experiment
ActiveCN103421690ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHypoxic cellEngineering
The invention relates to a device for a cell intermittent hypoxia experiment. The device comprises a cell cultivation case formed by a closed case body, a cell cultivation dish, a humidity and temperature control device, an oxygen gas source, a carbon oxygen gas source, a nitrogen gas source and a main controller. The gas sources are respectively connected with the cell cultivation case through corresponding gas conveying pipelines, control valves are arranged in the gas conveying pipelines, and the main controller controls the control valves to periodically adjust the oxygen content in the cell cultivation case to be changed between a high state and a low state. Due to the fact that the device is provided with the humidity and temperature control device, environment in the case body is made to be suitable for the growth of cells, the main controller controls the control valves to periodically adjust the oxygen content in the cell cultivation case to be changed between the high state and the low state to form a periodic hypoxia environment, the periodic hypoxia environment can be created, and then the study of intermittently-hypoxic cells is carried out.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Detection of hypoxia
InactiveUS20050026974A1Predictable oxygen indicatorAmenable to immunohistochemicalOrganic active ingredientsBiocideTissue proteinTissue hypoxia
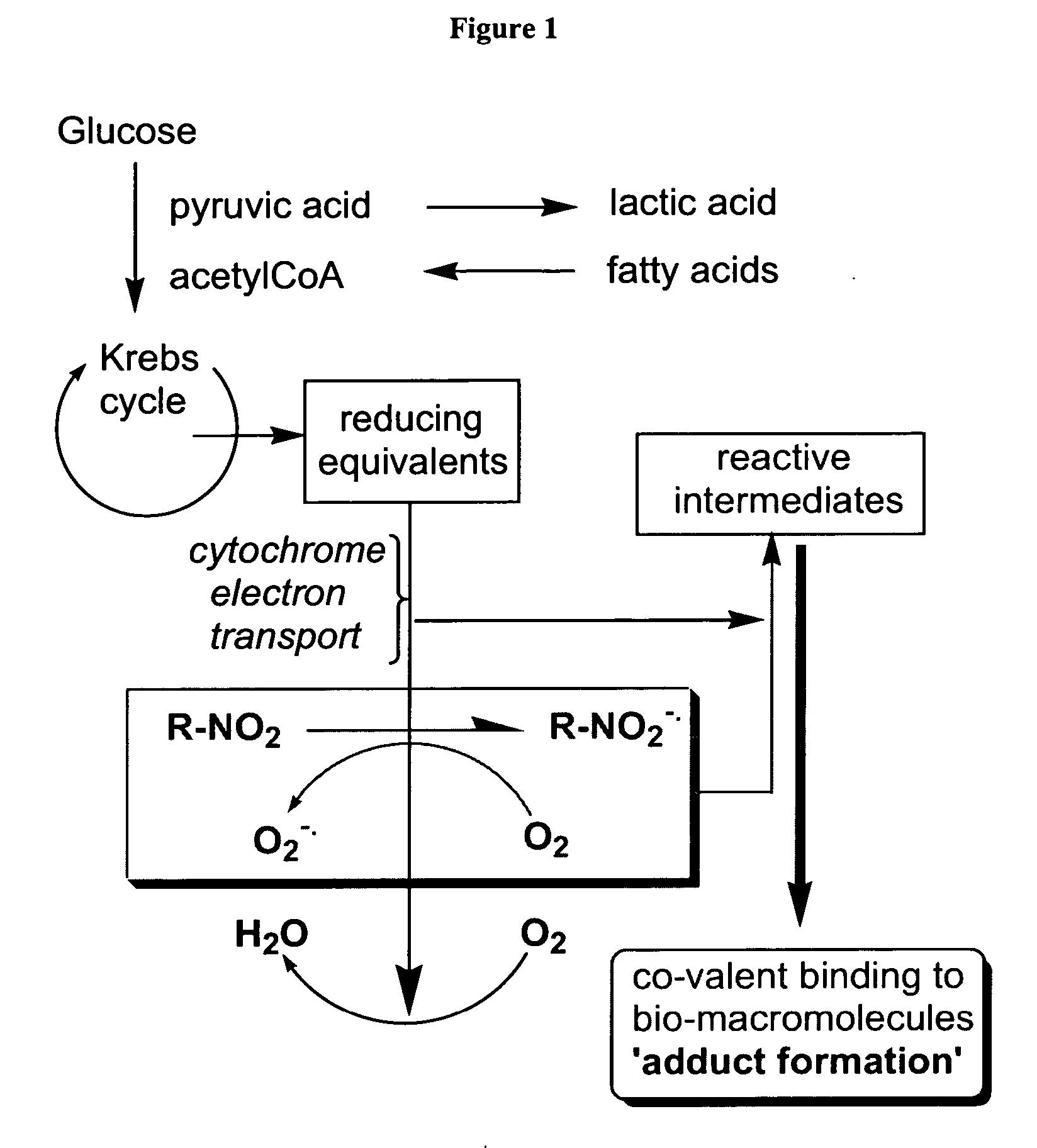
Novel nitroaromatic compounds and immunogenic conjugates comprising a novel nitroaromatic compound and a carrier protein are disclosed. The invention further presents monoclonal antibodies highly specific for the claimed nitroaromatic compounds, the compounds' protein conjugates, the compounds' reductive byproducts, and adducts formed between the compounds and mammalian hypoxic cell tissue proteins. The invention is further directed to methods for detecting tissue hypoxia using immunohistological techniques, non-invasive nuclear medicinal methods, or nuclear magnetic resonance. Diagnostic kits useful in practicing the methods of claimed invention are also provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Radiotherapy combined with hypoxic cell sensitizers
The invention discloses a method of treating cancer in a patient, comprising administering to the patient a radiation sensitizer selected from nitroimidazoles in an amount effective to sensitize a patient to radiation and subjecting the patient to radiation therapy. In certain embodiments the radiation sensitizer is etanidazole or doranidazole.
Owner:INTRAOP MEDICAL
Viruses targeted to hypoxic cells and tissues
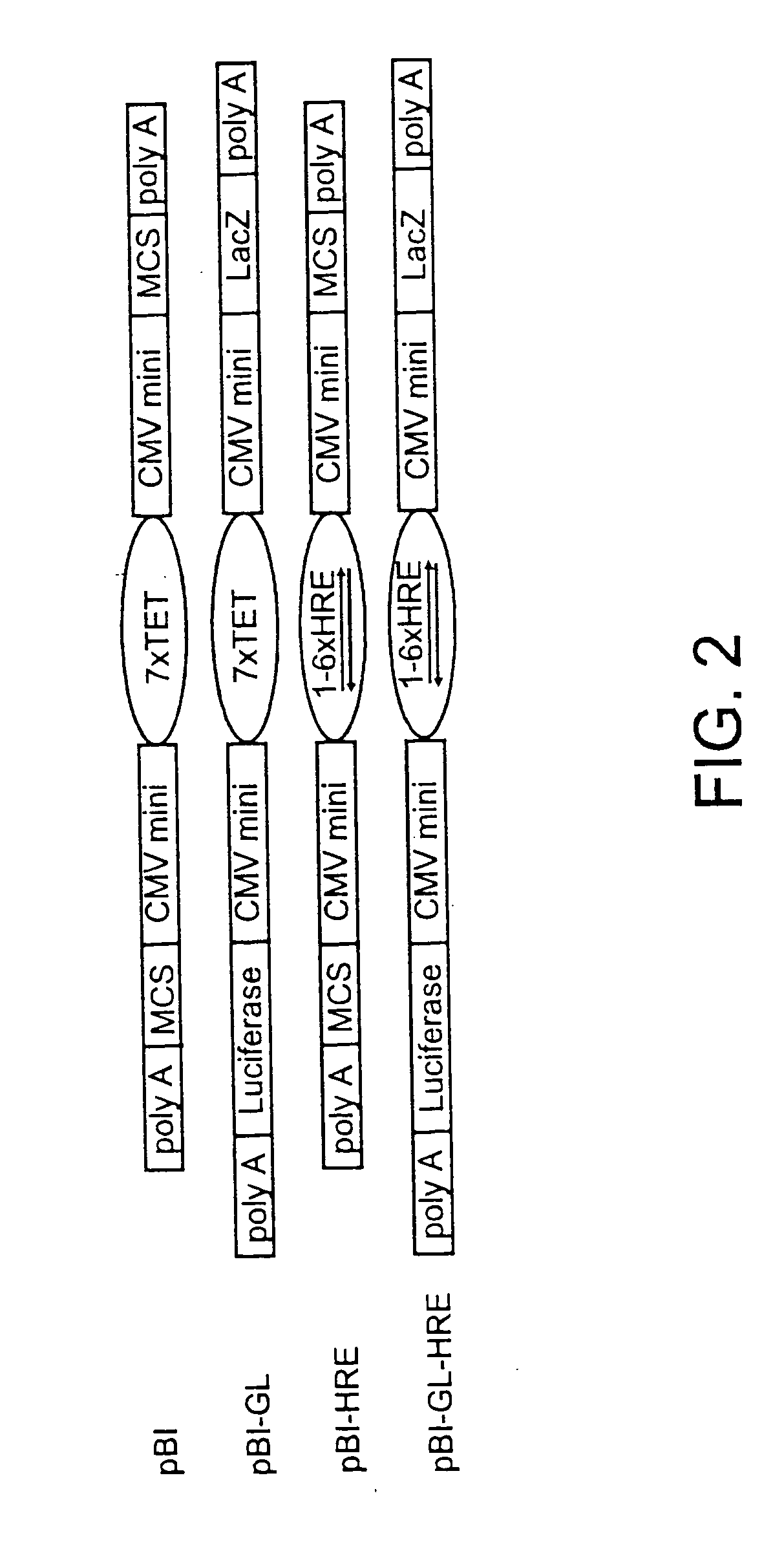
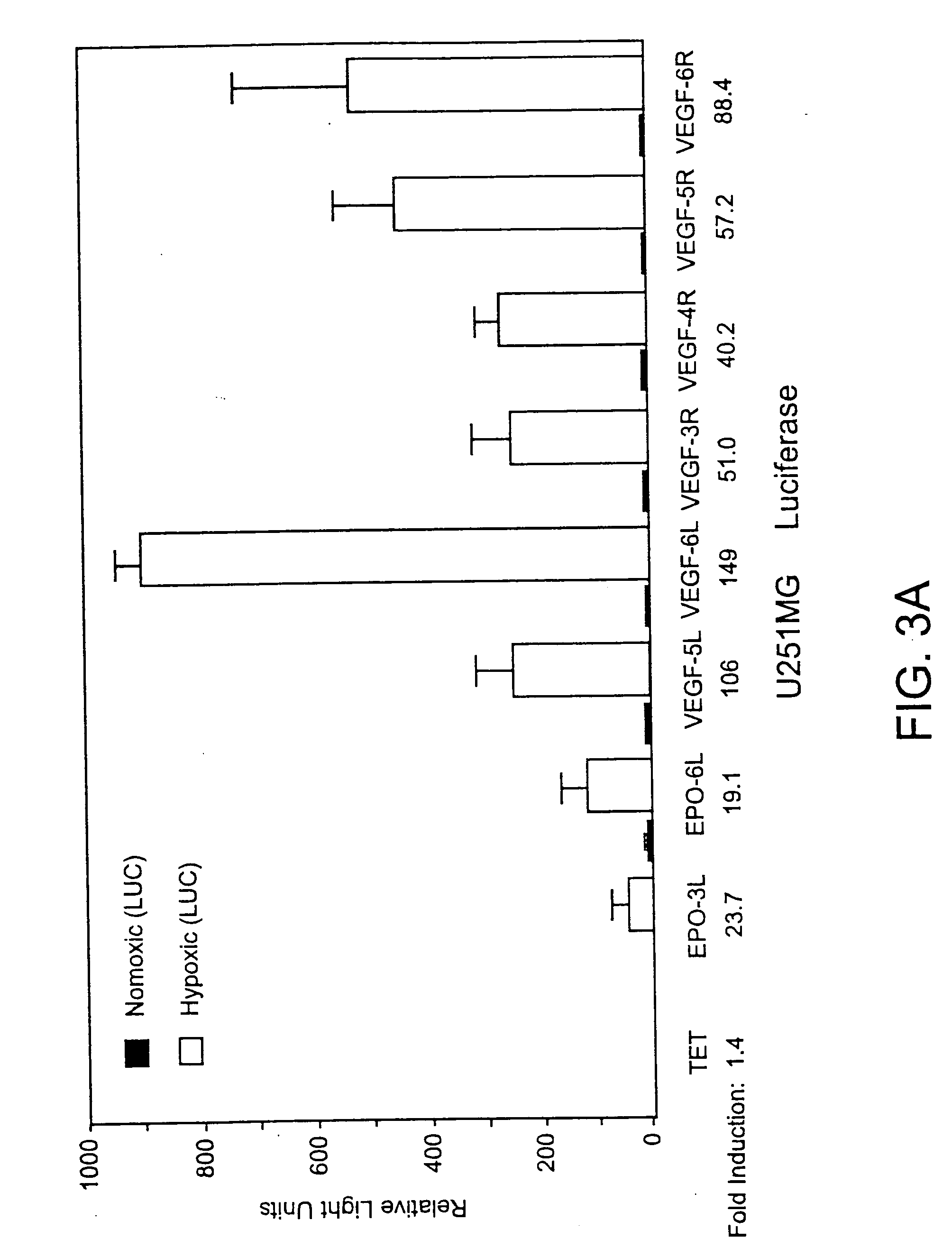
The present invention relates to compositions comprising a novel recombinant virus which replicates selectively in cells or tissues that are hypoxic or have an activated HIF pathway. The novel compositions of the invention comprise a recombinant virus genetically engineered to have a hypoxia / HIF-responsive element, or a multiplicity of such elements, operably linked to a promoter which is in turn operably linked to a nucleic acid(s) encoding a peptide(s) which regulates or modulates replication of the virus and / or encode a therapeutic molecule. The invention also includes constructs useful for screening of agents which interact with proteins or genes in the hypoxia-inducible pathway or are jointly translated under hypoxia and animal models useful for monitoring a variety of hypoxic conditions in a non-invasive manner.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Hypoxia sensitive response type chitosan-nitroimidazole graft, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN110452314AQuick releaseAchieve targeted releasePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthNitroimidazole
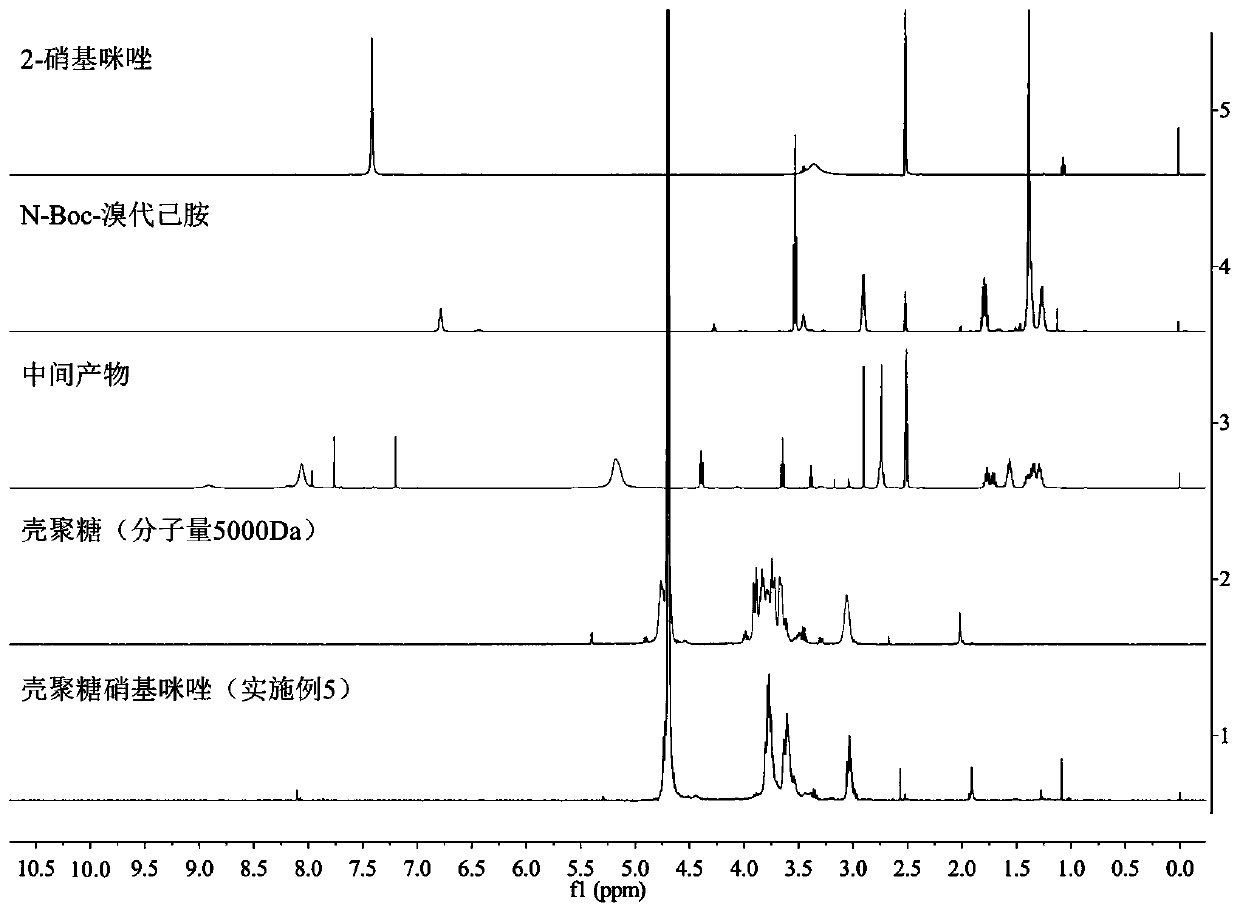
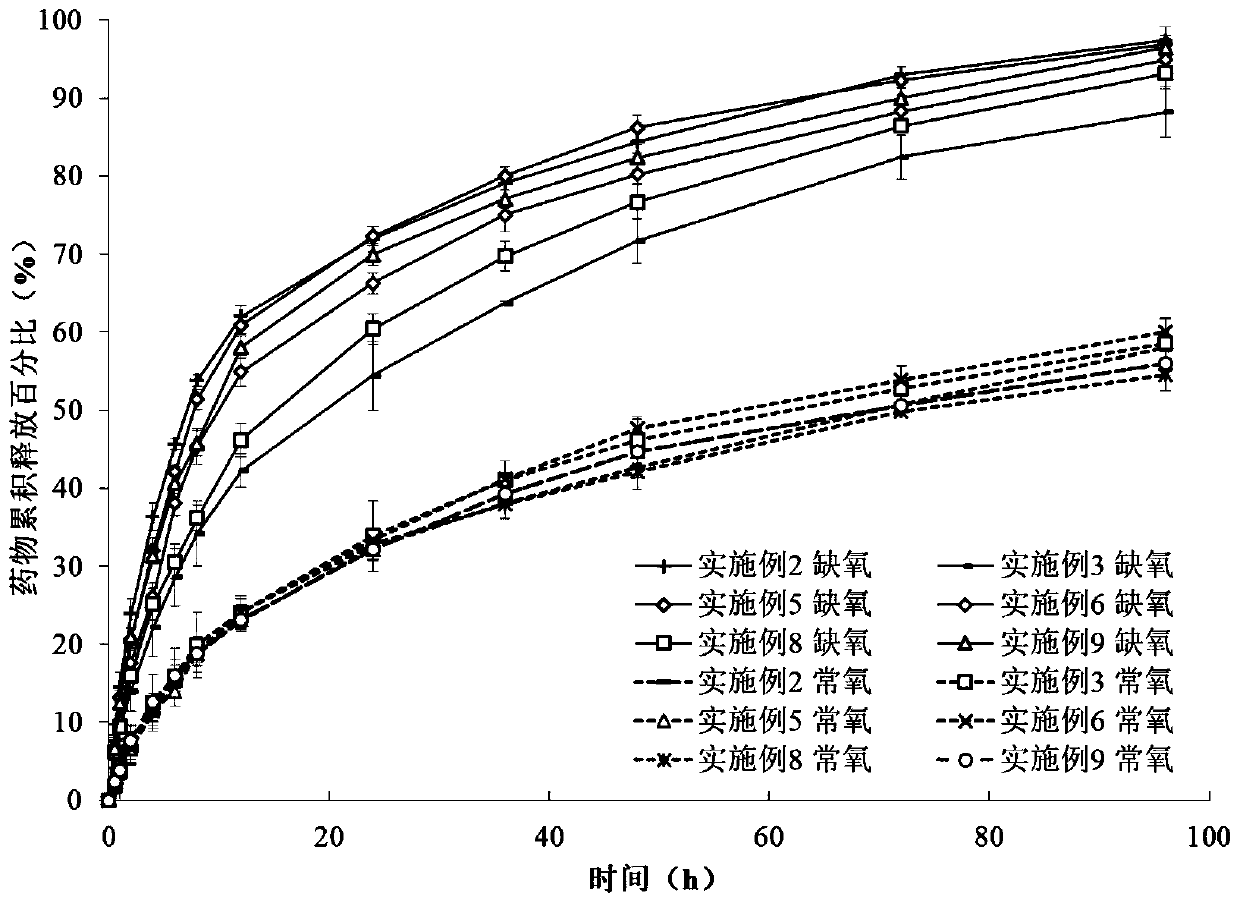
The invention provides a hypoxia sensitive response type chitosan-nitroimidazole graft, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The weight average molecular weight of chitosan is 2000-20000 Da, and the grafting ratio of nitroimidazole is 1-20%. The hypoxia sensitive response type chitosan-nitroimidazole graft is synthesized by adopting chitosan with a good biocompatibility as a hydrophilic material, N-Boc-bromoalkylamine as a bridging group and nitroimidazole as an anoxic sensitive group. The graft material self-aggregates in water to form polymer micelles, and has a low criticalmicelle concentration; and the chitosan-nitroimidazole graft can be used as a drug carrier, and drug-loaded nanoparticles formed by combining the graft with a drug can rapidly release the drug under the action of nitroreductase highly expressed in hypoxia cells, realizes the targeted release of the drug in the environment of hypoxic lesions such as tumors and stroke, and improves the drug effects.The structural formula of the chitosan-nitroimidazole graft of the present invention is shown in the description.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Detection of hypoxia
InactiveUS6855828B1Useful in oxygen levelMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationLuminescence/biological staining preparationTissue proteinTissue hypoxia
Nitroaromatic compounds and immunogenic conjugates comprising a novel nitroaromatic compound and a carrier protein are disclosed. The invention further presents monoclonal antibodies highly specific for the claimed nitroaromatic compounds, the compounds' protein conjugates, the compounds' reductive byproducts, and adducts formed between the compounds and mammalian hypoxic cell tissue proteins. The invention is further directed to methods for detecting tissue hypoxia using immunohistological techniques, non-invasive nuclear medicinal methods, or nuclear magnetic resonance. Diagnostic kits useful in practicing the methods of claimed invention are also provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Novel compounds for hypoxic cell therapy and imaging
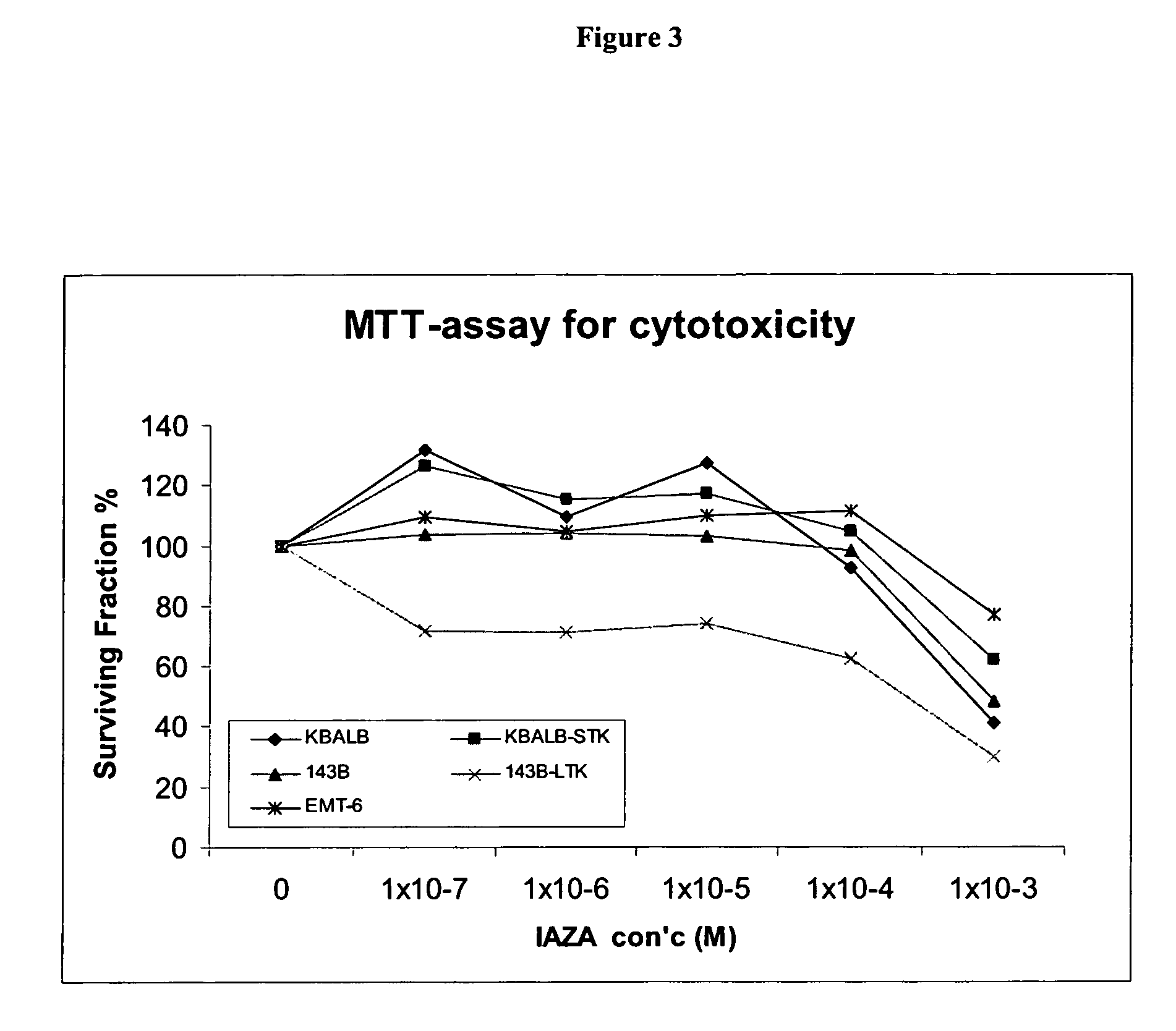
InactiveUS20060270610A1Easy to detectGood effectBiocideSugar derivativesRadical radiotherapyHypoxic cell
The present invention provides for compounds suitable for therapeutic treatment of hypoxic tissues, particularly for application in radiotherapy, chemosensitization, radiosensitization. The present invention further provides for compounds suitable for radioimaging of hypoxic cells.
Owner:WIEBE LEONARD +2
Nanoprobe for detecting hypoxic cells and preparation method and uses of nanoprobe
ActiveCN112121182AAccurately reflect the degree of hypoxiaReflects the degree of hypoxiaPowder deliveryAmino preparation from aminesIntracellularNanoprobe
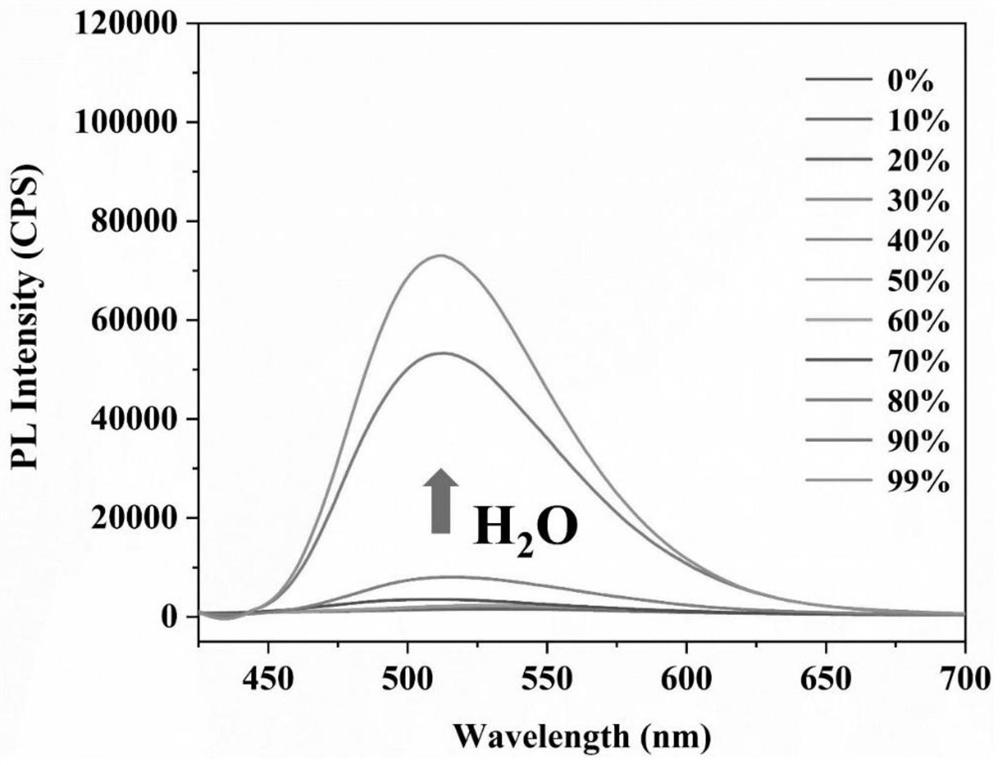
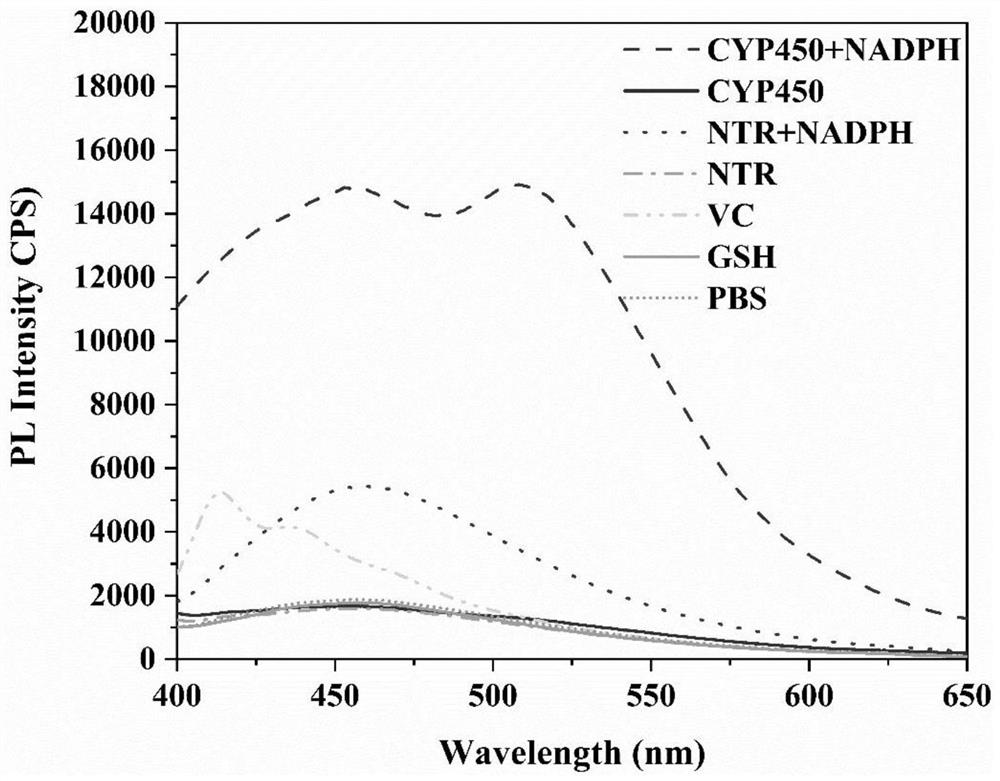
The present invention provides a nanoprobe for detecting hypoxic cells and a preparation method and uses of the nanoprobe. The nanoprobe is formed by self-assembly of fluorescent molecules; the fluorescent molecules are formed by condensing and oxidizing bis (4 (diethylamino) phenyl) ketone; the nanoprobe can realize fluorescence imaging of a hypoxia degree of cells by detecting the content of CYP450 enzyme in the cells; in a hypoxia environment, the nanoprobe is converted into the fluorescent molecules with strong proton adsorption capacity, so that deep penetration of tumors is realized; andthe nanoprobe has advantages of a simple synthesis method, strong water solubility, low toxicity, strong anti-interference capability, high sensitivity and strong deep penetration capability of tumors.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
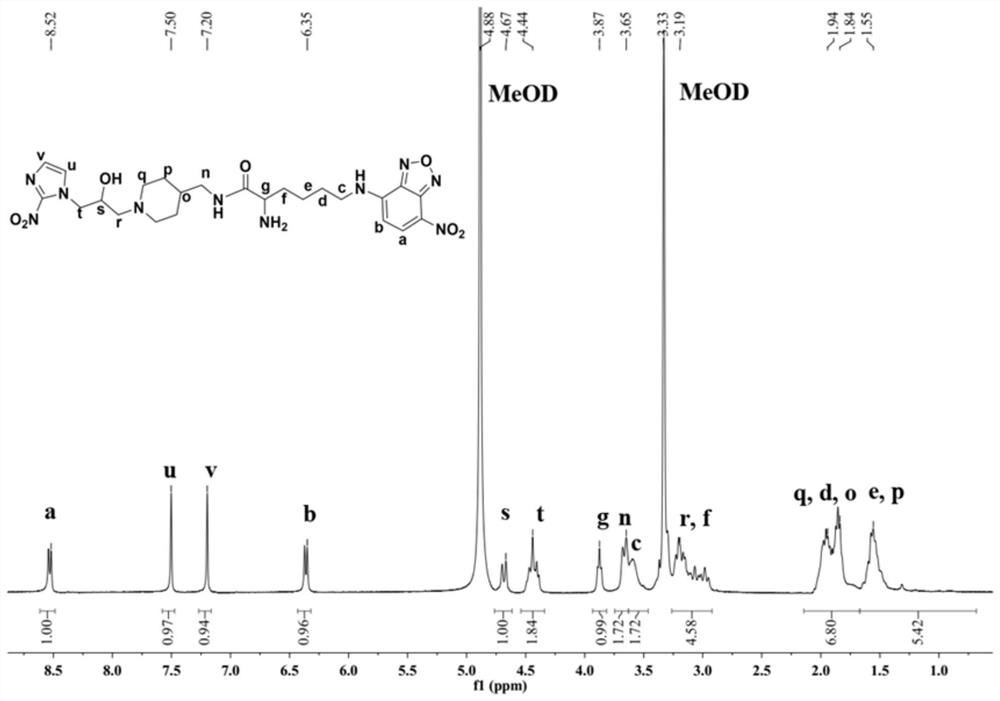
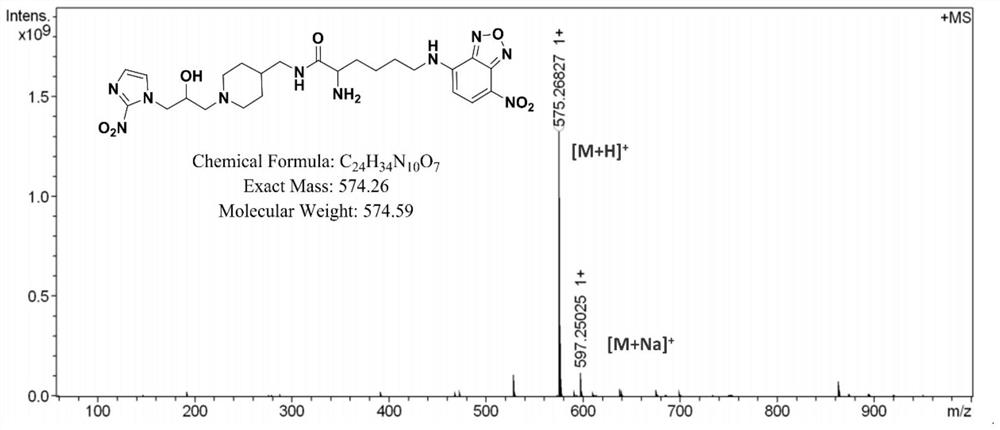
Hypoxia fluorescence imaging probe and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111875597ASimple structureMeet the purpose of performing multiple functionsOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceNitroimidazoleNitrobenzene
The invention provides a hypoxic fluorescence imaging probe as well as a preparation method and application thereof, wherein the hypoxic fluorescence imaging probe has a structure as shown in a formula I, and is named as 1-(1-(2-nitroimidazole)-3-[(4-aminomethyl)-azacyclohexane]-2-propanol)-6-(4-nitrobenzo-2-oxa-1,3-diazole)-lysine, PLN for short; the probe disclosed by the invention can realize specific fluorescence imaging of hypoxic cells by virtue of different macromolecular combinations in different hypoxic environments by virtue of nitroimidazole groups; furthermore, the primary amino groups in the molecules are beneficial to further modification of the molecules.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Interaction between the VHL tumor suppressor and hypoxia inducible factor, and assay methods relating thereto
InactiveUS20050003452A1Maximizing numberMinimize the numberCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsAssayTumour suppressor protein
The invention relates to the finding that the VHL tumour suppressor protein regulates hypoxia inducible factor alpha subunits, by targeting HIF alpha for destruction in normoxic, but not hypoxic cells. The invention provides assays for modulators of this interaction, and peptides based upon HIF alpha subunit sequences which may modulate this interaction.
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
Hypoxia-Targeted Delivery System for Pharmaceutical Agents
InactiveUS20160228567A1Increased cellular uptake of polynucleotidesPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsMolecular compositionNanoparticle
Molecular compositions, nanoparticle compositions, and pharmaceutical compositions of the invention provide for the delivery of a polynucleotide to a hypoxic cell or tissue. The compositions can also be used for the delivery a hydrophobic pharmaceutical agent, either alone or in combination with a polynucleotide, to a hypoxic cell or tissue. Methods of making such compositions and methods of using such composition to treat a condition associated with a hypoxic cell or tissue are provided as well. Also provided are kits for use in treating a condition associated with a hypoxic cell or tissue.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Indoloquinone Tumor Radiation Sensitization
This invention generally relates to Indoloquinone caused tumor radiation therapy sensitization. More specifically, this invention relates to the discovery of indoloquinones as a radiation sensitizer (radiation therapy adjuvant) due to its ability to selectively target hypoxic cells and to damage the DNA of these hypoxic cells. Indoloquinones do so with minimal normal cell and tissue toxicity.
Owner:SPECTRUM PHARMA INC
Compositions of pharmaceuticals for use in low energy neutron therapy
InactiveUS20080050309A1High electronegativityImprove stabilityIn-vivo radioactive preparationsSugar derivativesAbnormal tissue growthEtiology
A pharmaceutical, wherein the formulation is a conjugate of a saccharide with one or a plurality of isotopic boron-10 atoms or gadolinium, and having a utility in the binary form of low energy neutron therapy (i.e. boron neutron capture therapy). Further, that the therapy has an indicated use for the selective targeting and killing of oxygenated and hypoxic cells in tumors, and that the pharmaceutical is preferentially taken up by cancer cells. The inclusion of any of a family of saccharides, its derivatives or analogues, including sulfur linkage saccharides as a delivery carrier for boron-10 atoms or the rare element gadolinium is a strategy to take advantage of the hallmark of cancer cells, that being an increased requisite for glucose to sustain a rate of uncontrollable cell division and proliferation. A cancer cell facilitates an increase in availability of molecular glucose by overexpression of glucose transporter proteins on membrane surfaces. The use of a saccharide attached with one or more of isotopic boron-10 atoms or gadolinium is to utilize this known amplification of glucose transport to achieve significantly greater quantities of isotopic boron-10 atoms or gadolinium taken up cancer cells than deposited into healthy cells.Tissues of malignant tumors are not homogeneous, but consist of oxygenated and hypoxic cells. Oxygen deprivation causes cancer cells to be resistant to radiation and to chemotherapeutic agents. It is further noted that the etiology of metastasis is hypoxia induced tumor cells, where oxygen deprivation stimulates activation of genes, and that one gene is responsible for programming oxygen-starved cancer cells to migrate to distant and specific host organs.A saccharide with a ring sulfur atom can participate more readily in biological processes than a sugar with a ring oxygen atom, and such thiosaccharides possess unique physiochemical properties that include penetration of a viscous lipid bilayer membrane of a cancer cell, and resistance to reduction by enzymes, enabling retention of the conjugate within cytoplasm, mitochondria and nuclei of cancer cells. Therefore, an objective is the use of a conjugated boron-10 or gadolinium thiosaccharide as a pharmaceutical for low energy neutron therapy to participate in a boron-10 interception of a passing slow (thermal) neutron to produce an α-particle, high energy Li-7 ion and low energy gamma (γ) rays that are damaging to a cell. The pharmaceutical, when in combination with exposure of a subject to low energy neutrons, is a method of treatment for a subject diagnosed with a cancer, so as to cause a regression of tumors, to inhibit metastasis, and to extend life.
Owner:HADRON SYST
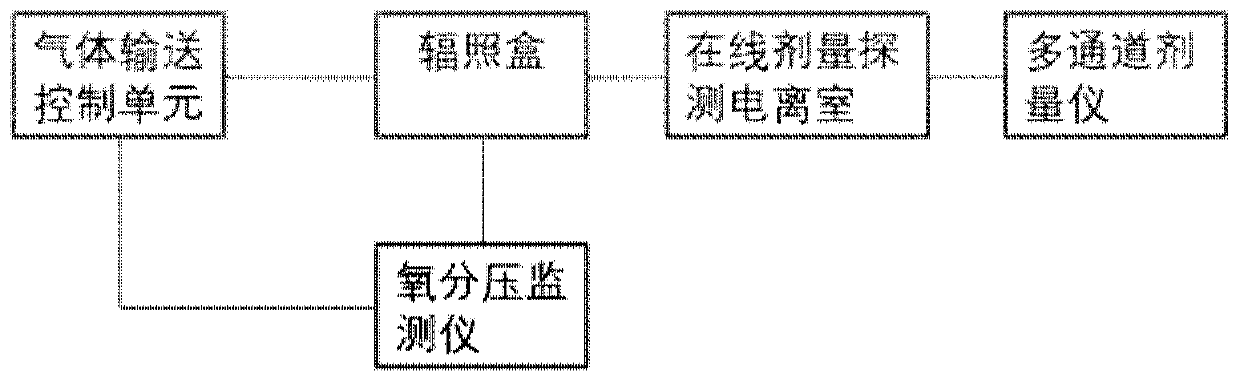
Hypoxic cell irradiation device
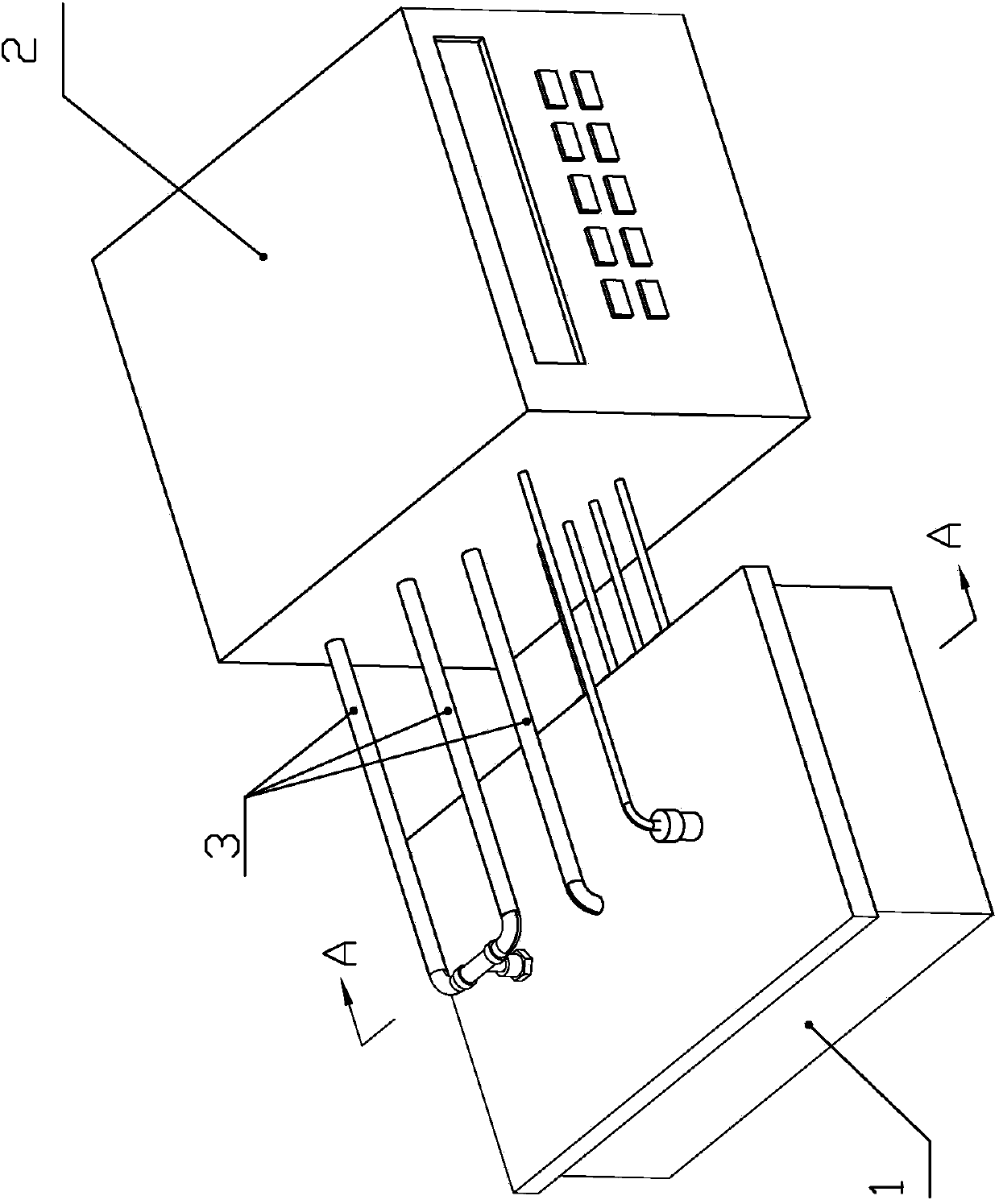
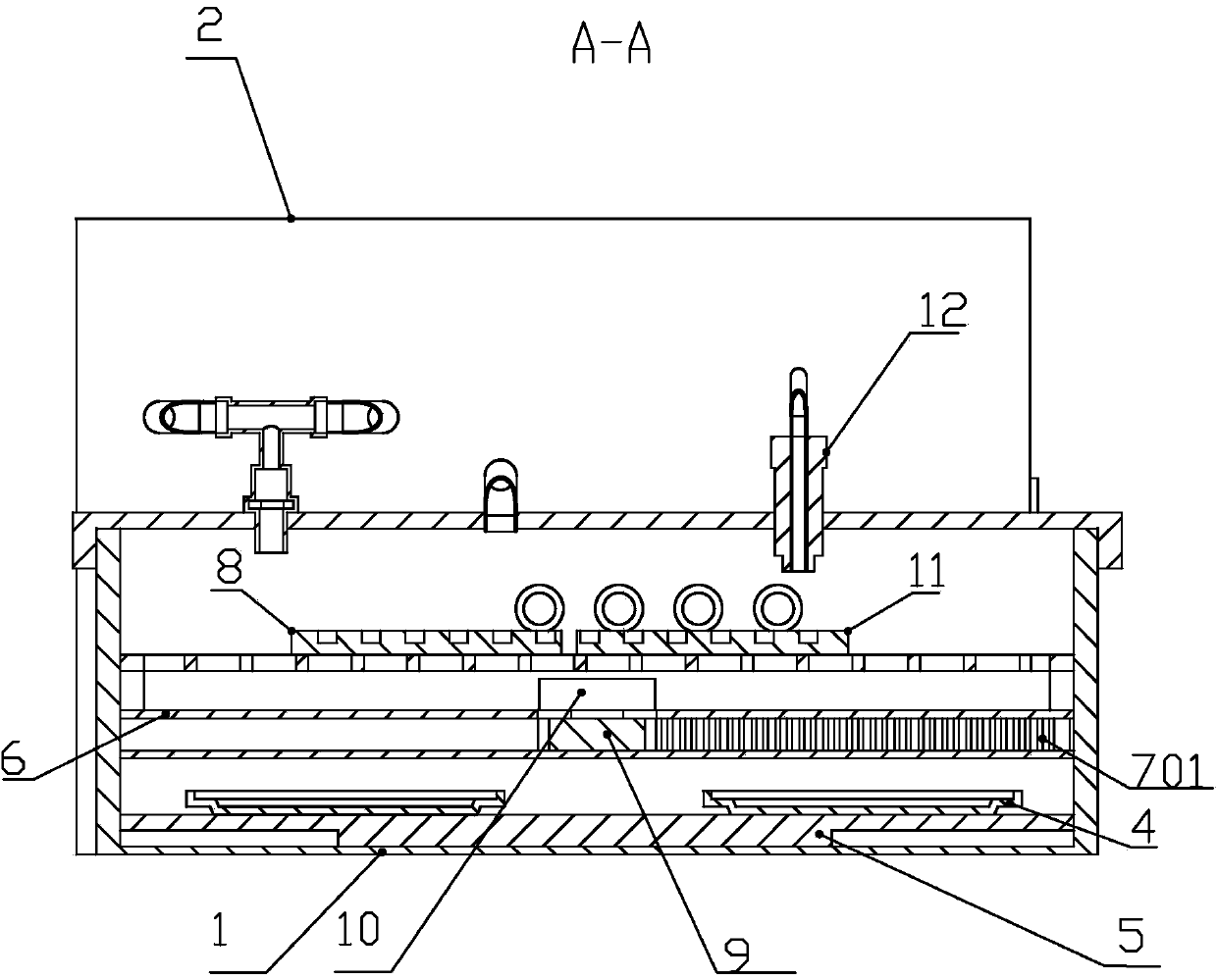
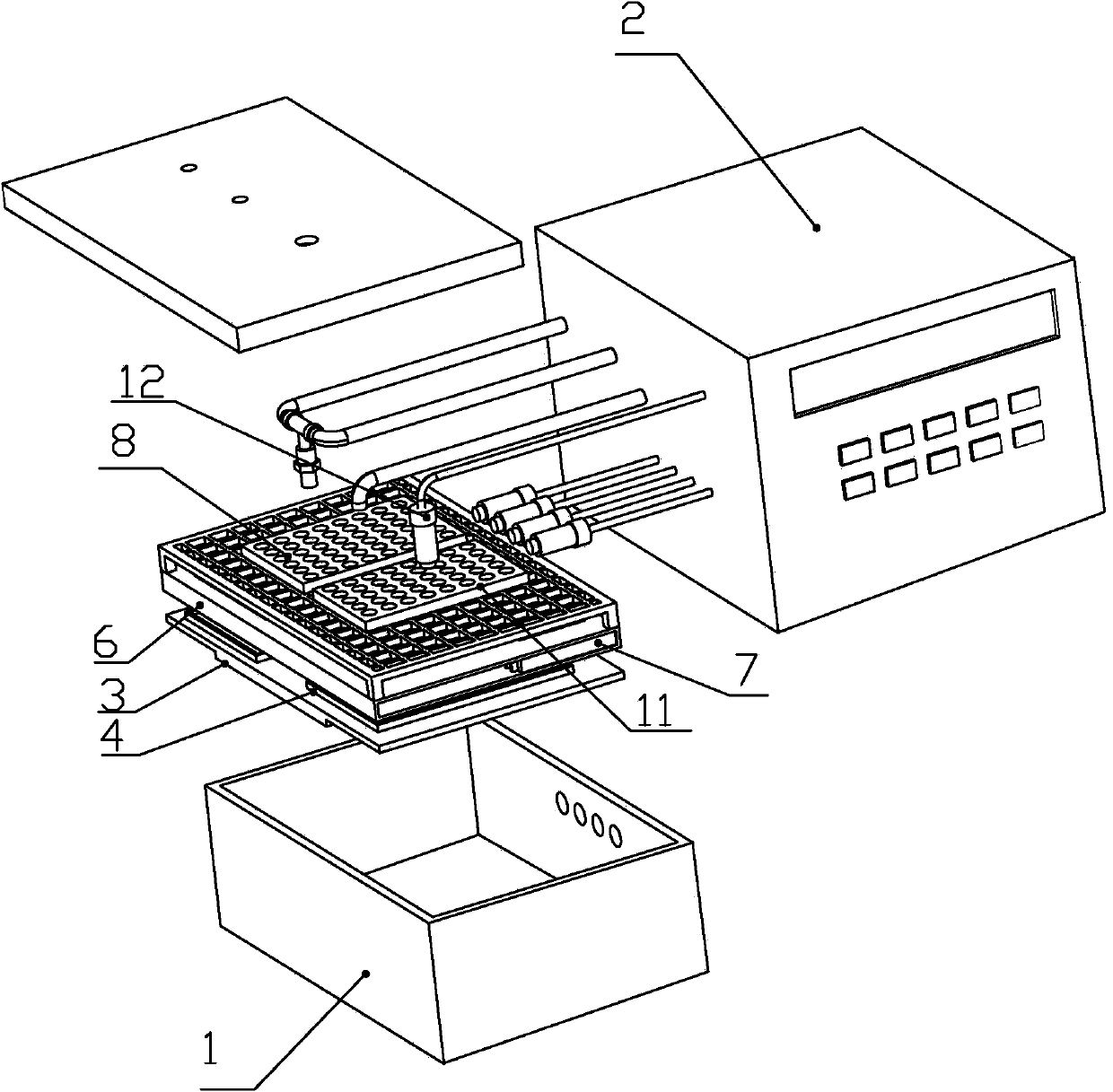
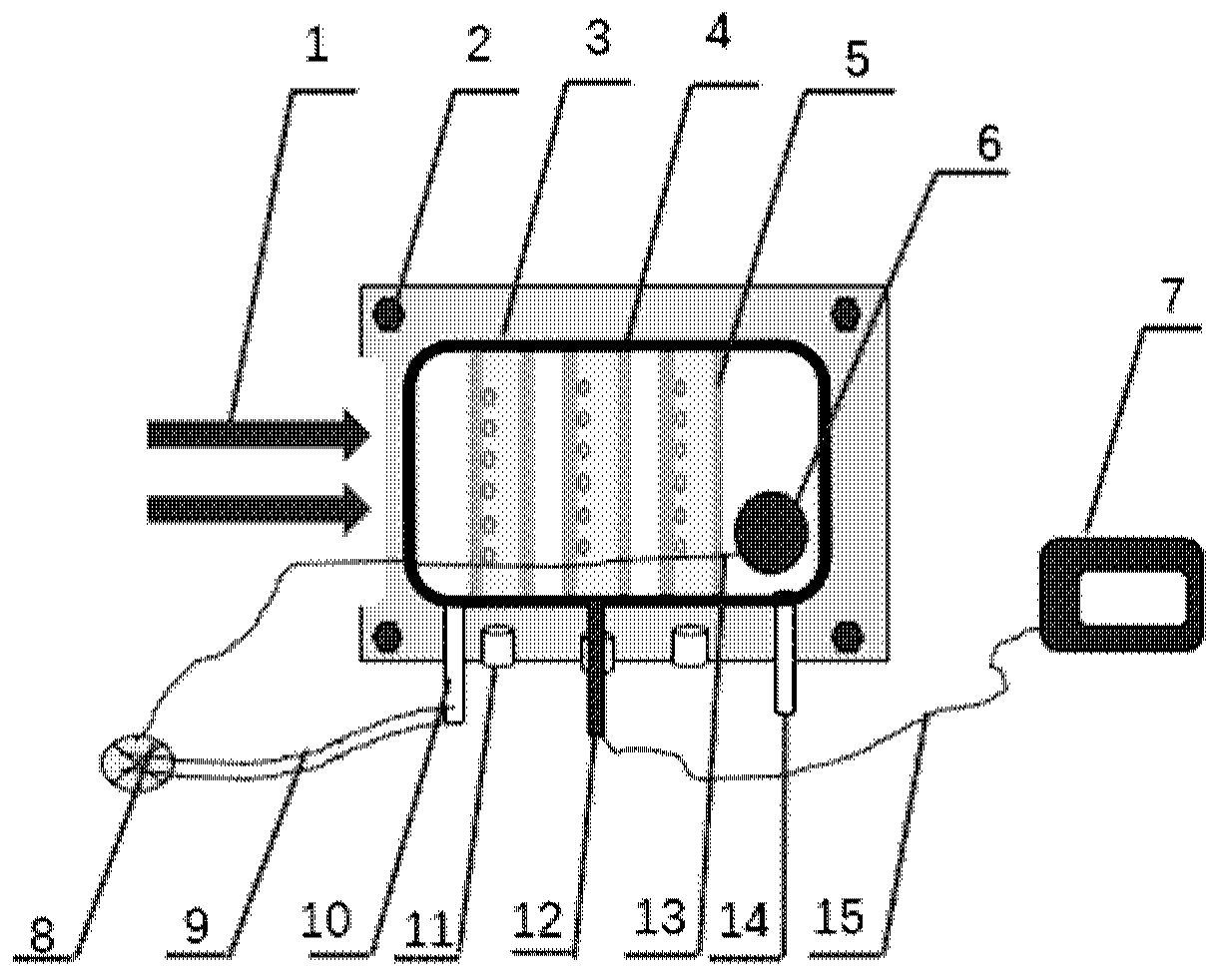
ActiveCN109847199AAccurate monitoringAccurate measurementDosimetersX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyHypoxic cellEngineering
The invention discloses a hypoxic cell irradiation device. The hypoxic cell irradiation device comprises an irradiation box, an air control unit and a dosage monitoring unit, wherein the irradiation box adopts a box-shaped structure consisting of 6 irradiation box wall plates in a spiced combination manner, and an air inlet, an air outlet and a plurality of sockets are formed in the irradiation box side walls; the air control unit is connected with the irradiation box through the socket, and is used for controlling air in the irradiation box; and the dosage monitoring unit is connected with the irradiation box through the socket and is used for detecting the irradiation dosage in the irradiation box. According to the hypoxic cell irradiation device disclosed by the invention, the dosage ofdifferent positions in the irradiation box can be accurately monitored and measured, and accurate physical dosage data is provided for measurement of relative biological effects on the hypoxic cellsin different positions.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
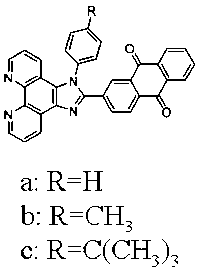
Novel prenylarene compound and use thereof
InactiveUS20130065937A1Avoid choiceToxic reductionBiocideOrganic chemistryCancer preventionPrenylation
A compound represented by the general formula (C):(wherein R101 represents a substituted or unsubstituted aromatic heterocyclic group,R102, R103, R104 and R105 may be the same or different, and each represents a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, an alkyl group having 1 to 3 carbon atoms, or a haloalkyl group having 1 to 3 carbon atoms, andR106 represents a hydrogen atom, or a saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbon group which is a straight or branched chain having 1 to 12 carbon atoms, butexcluded is the case where R101 is a 3-furyl group, R102, R103, R104 and R105 are all methyl groups, and R106 is a methyl group, a 4-methyl-3-pentenyl group or a 4,8-dimethyl-3,7-nonadienyl group); ora pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof has selective inhibitory activity on hypoxic cell growth in a broad range of the concentration and therefore is useful as an active ingredient of a medicament for cancer prevention or treatment.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
Virus growing in hypoxic cell or virus vector expressing gene therein
InactiveUS20110286972A1Effectively treat and preventOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderHypoxic cellViral vector
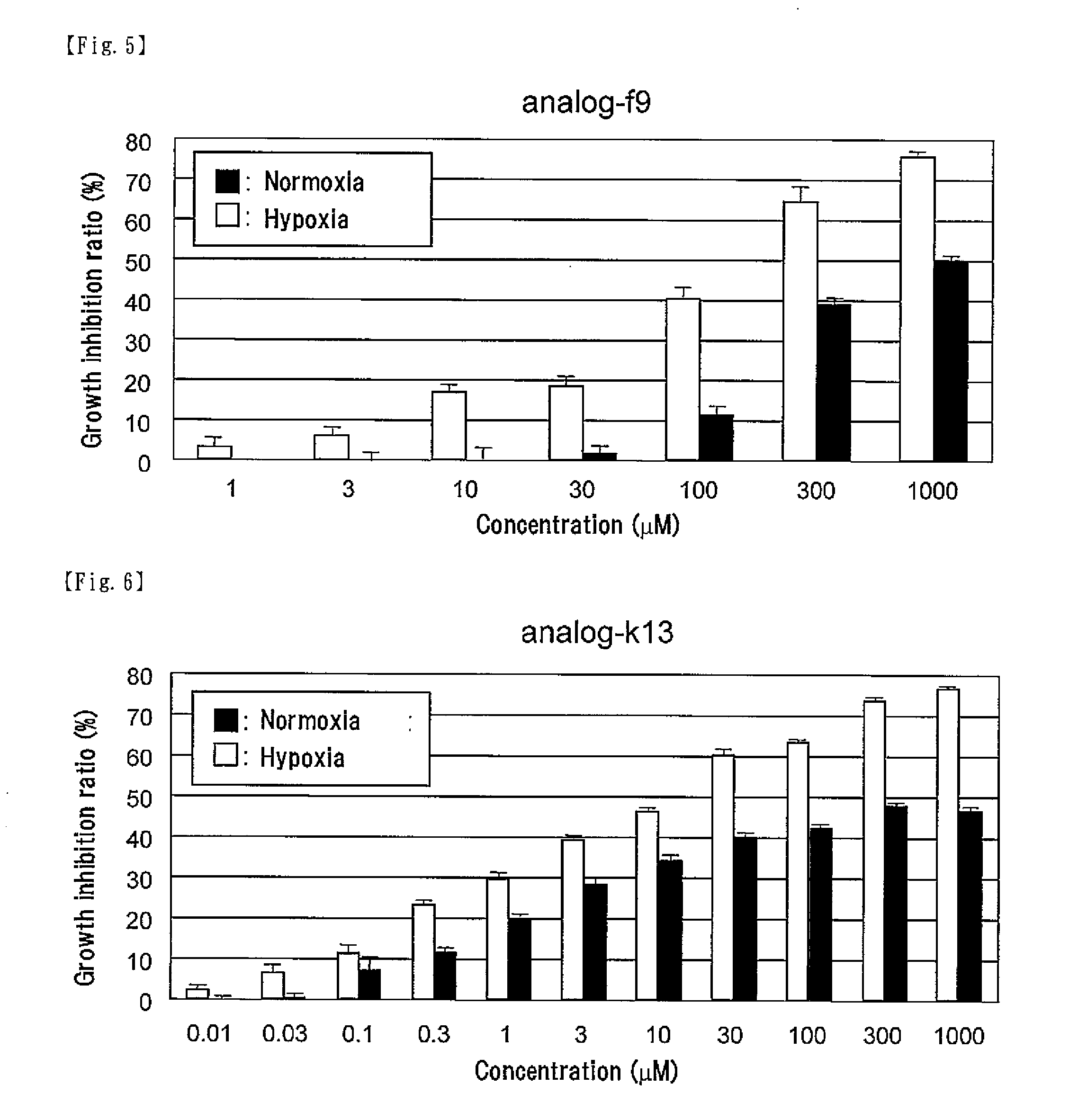
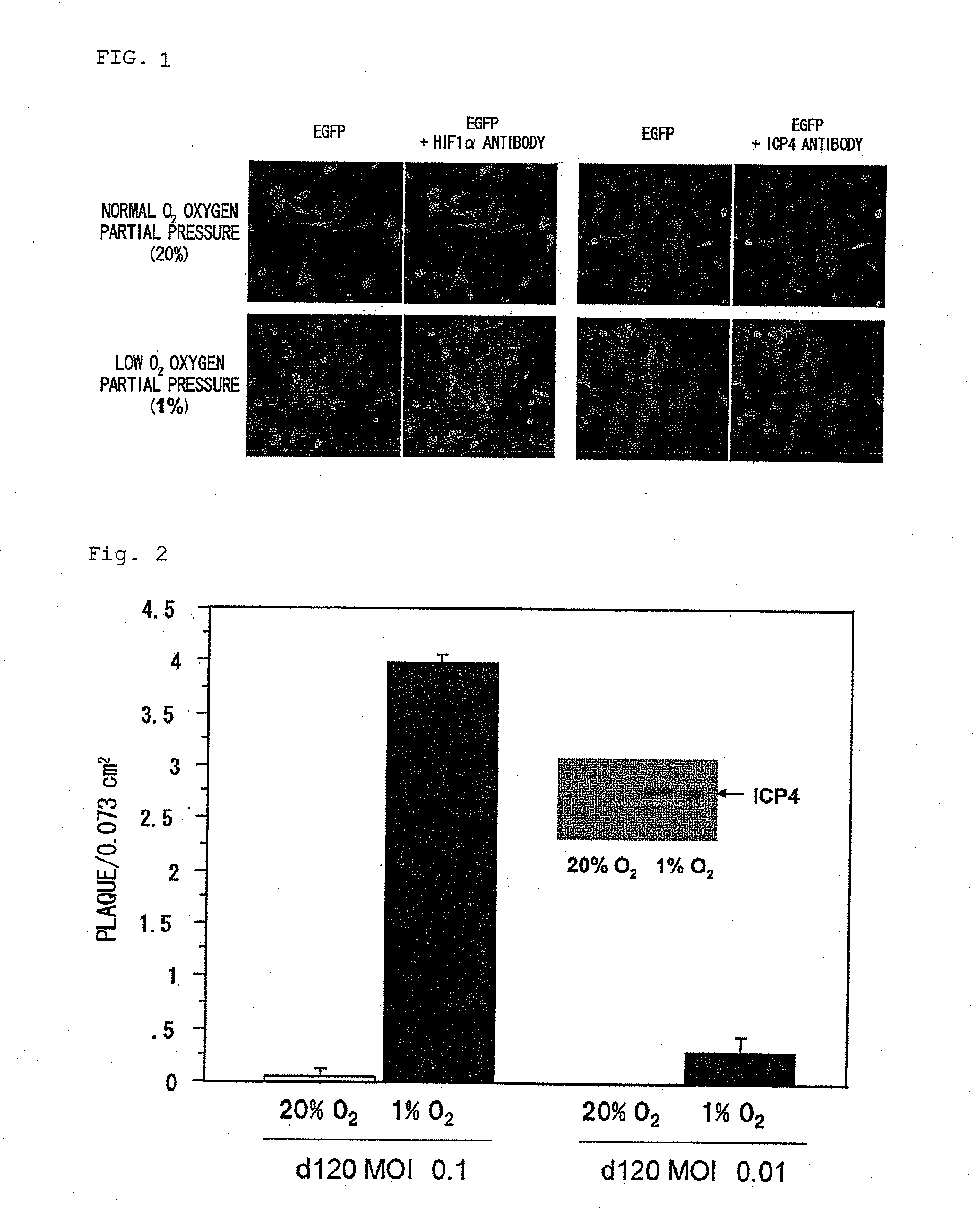
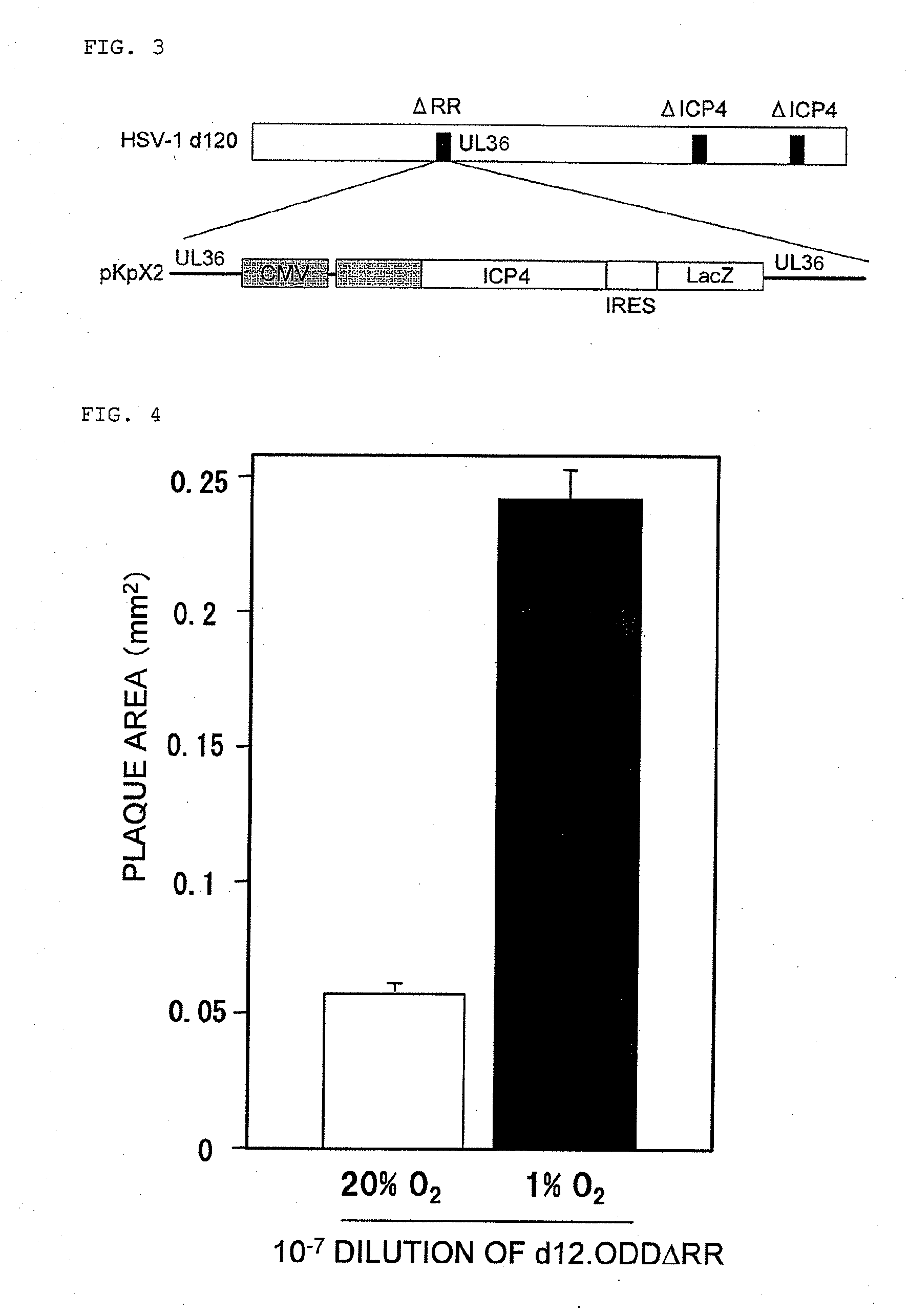
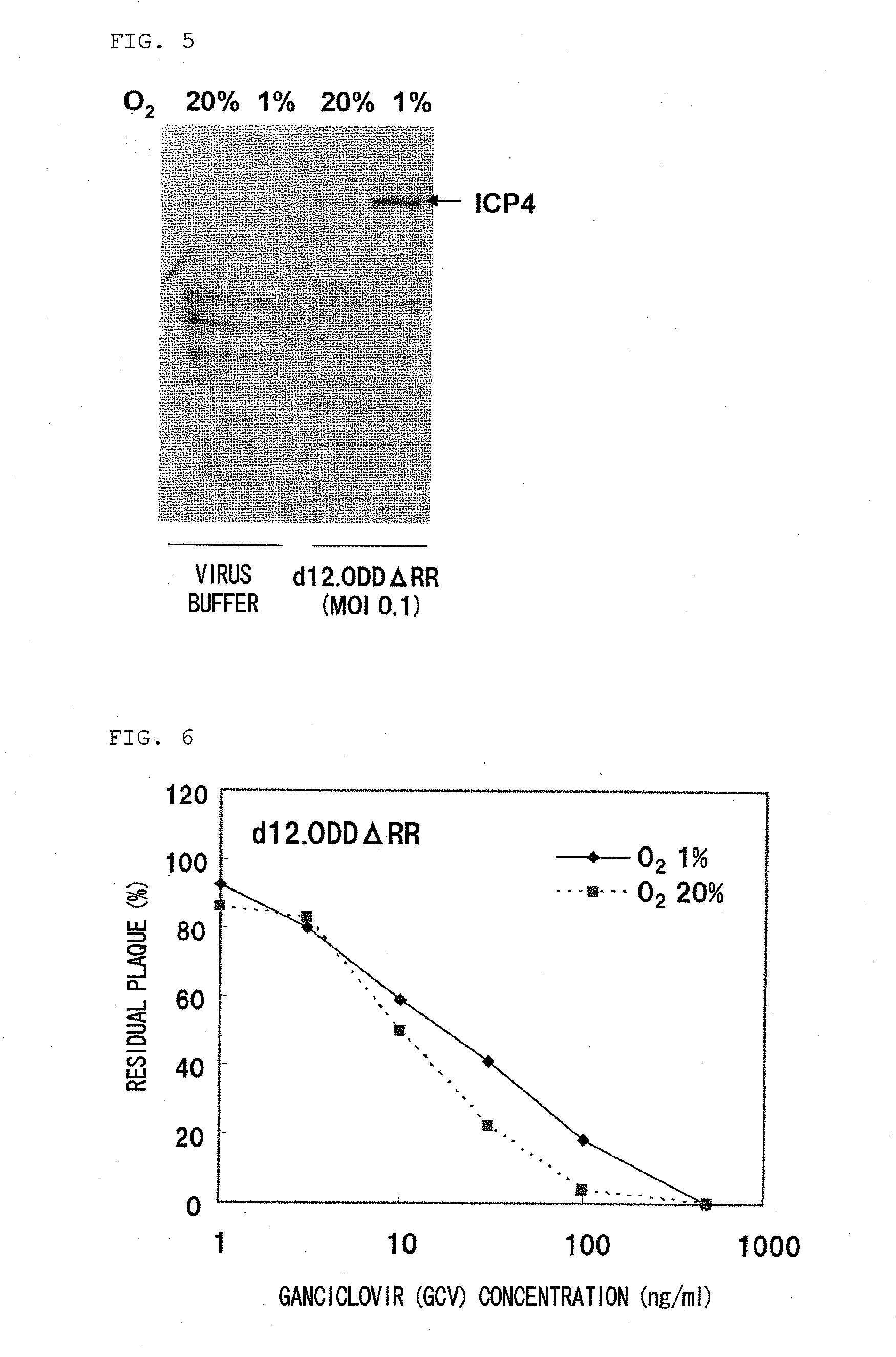
The present invention provides a virus or a viral vector capable of expressing a gene specifically in a cell having replication ability in a hypoxic state such as a cancer stem cell and injuring the cell, and pharmaceutical composition comprising the same. Specifically, the present invention provides a virus or a viral vector which comprises a gene encoding a fusion protein of an ODD and a protein essentially required for viral proliferation, and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +2
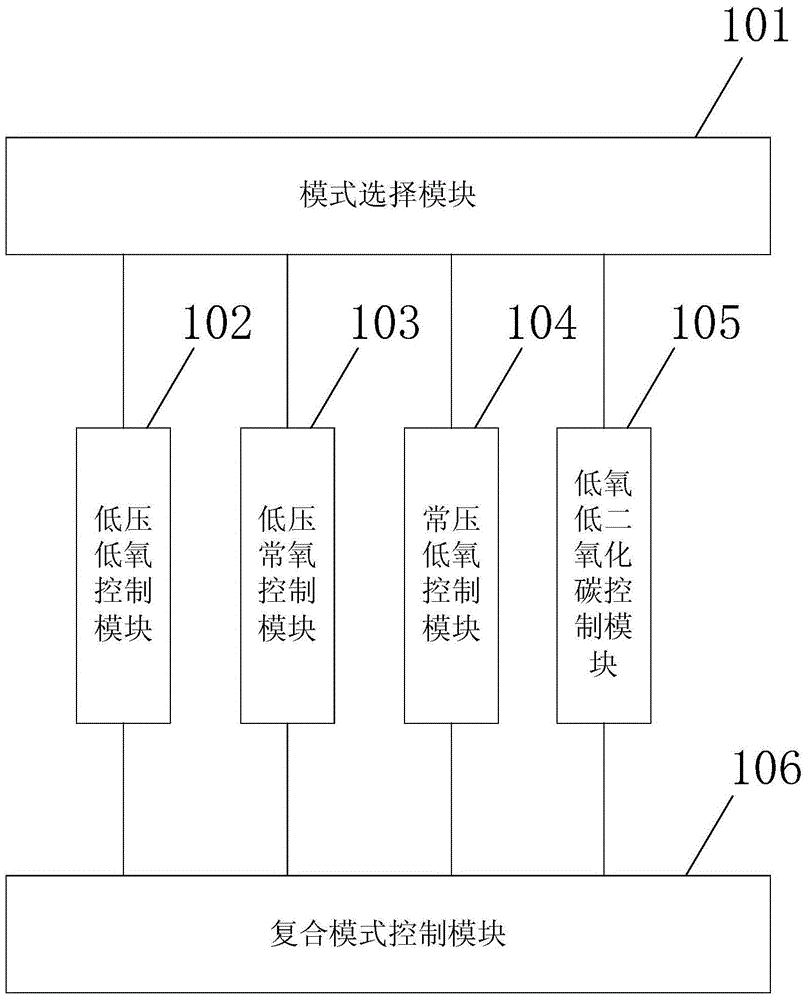
A low-pressure hypoxic cell experimental device
InactiveCN104862218BIncrease authenticityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMode controlComputer module
The invention provides a low-pressure and low-oxygen cell experiment device which comprises a mode selection module, a low-pressure and low-oxygen control module, a low-pressure and normal-oxygen control module, a normal-pressure and low-oxygen control module, a low-oxygen and low-carbon dioxide control module and a composite mode control module. With the adoption of the mode selection module, the low-pressure and low-oxygen control module, the low-pressure and normal-oxygen control module, the normal-pressure and low-oxygen control module and the low-oxygen and low-carbon dioxide control module, tests can be carried out in different modes as required; the test simulation authenticity is improved; with the adoption of the composite mode control module, the tests can be carried out sequentially in combination with the different test modes, so that the influence of different environments on a cell experiment is effectively simulated.
Owner:BEIJING SHIJITAN HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIVERSTY
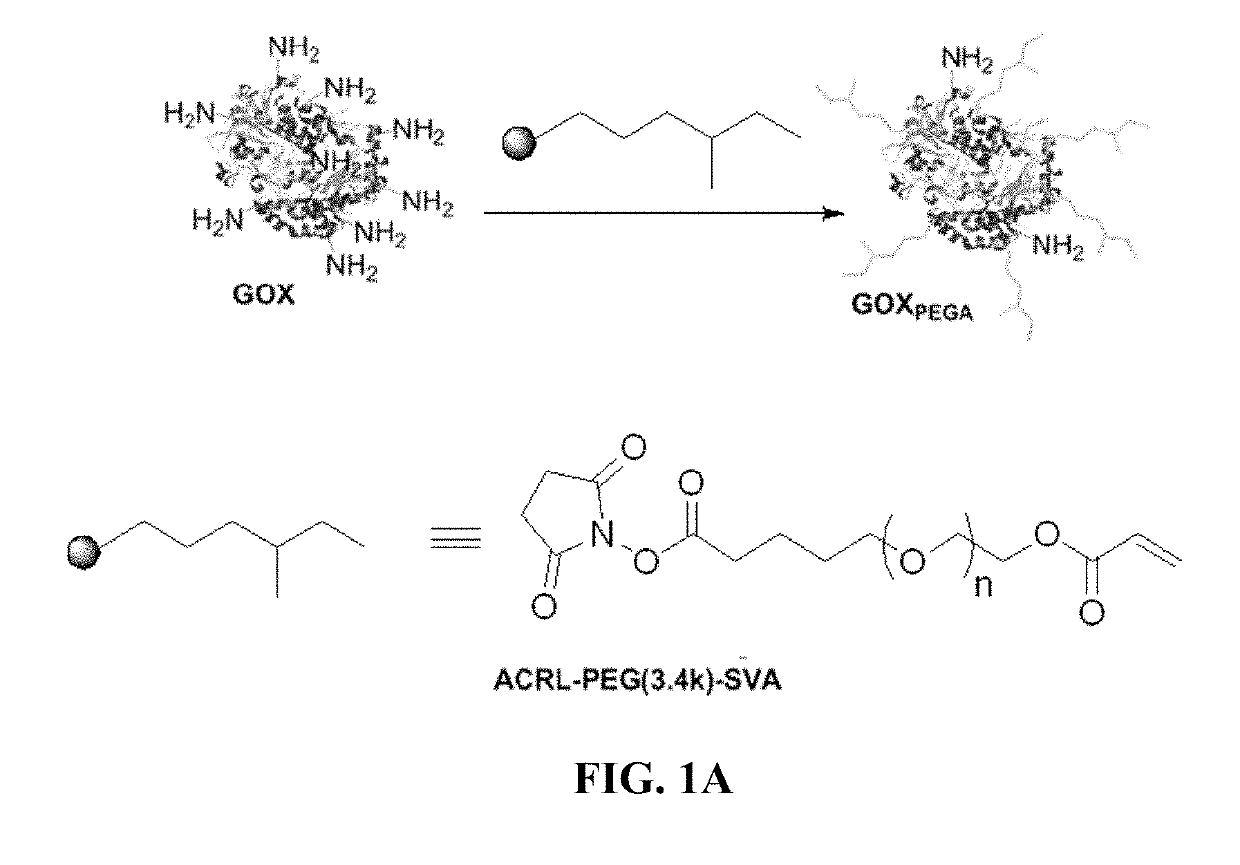
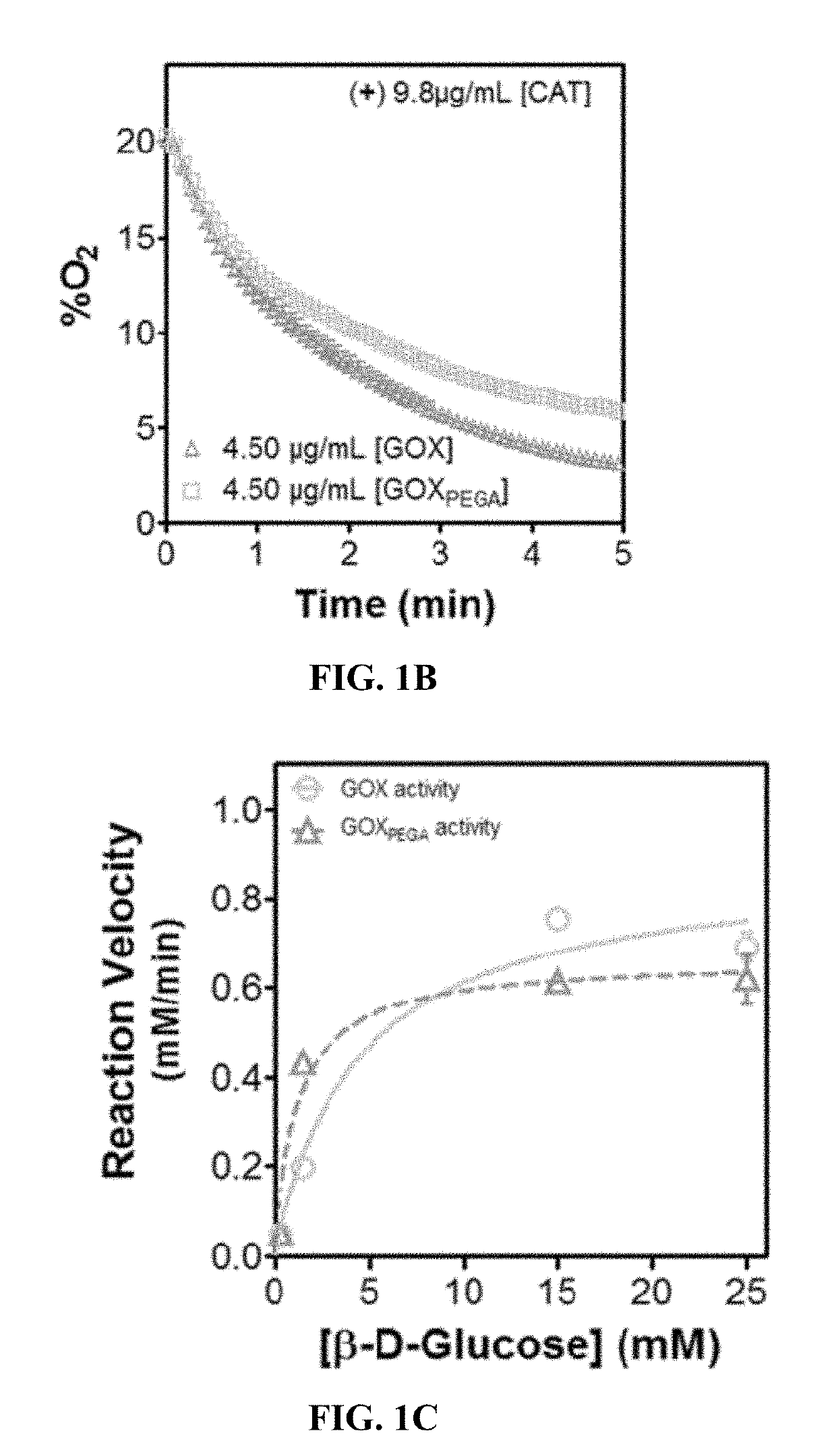
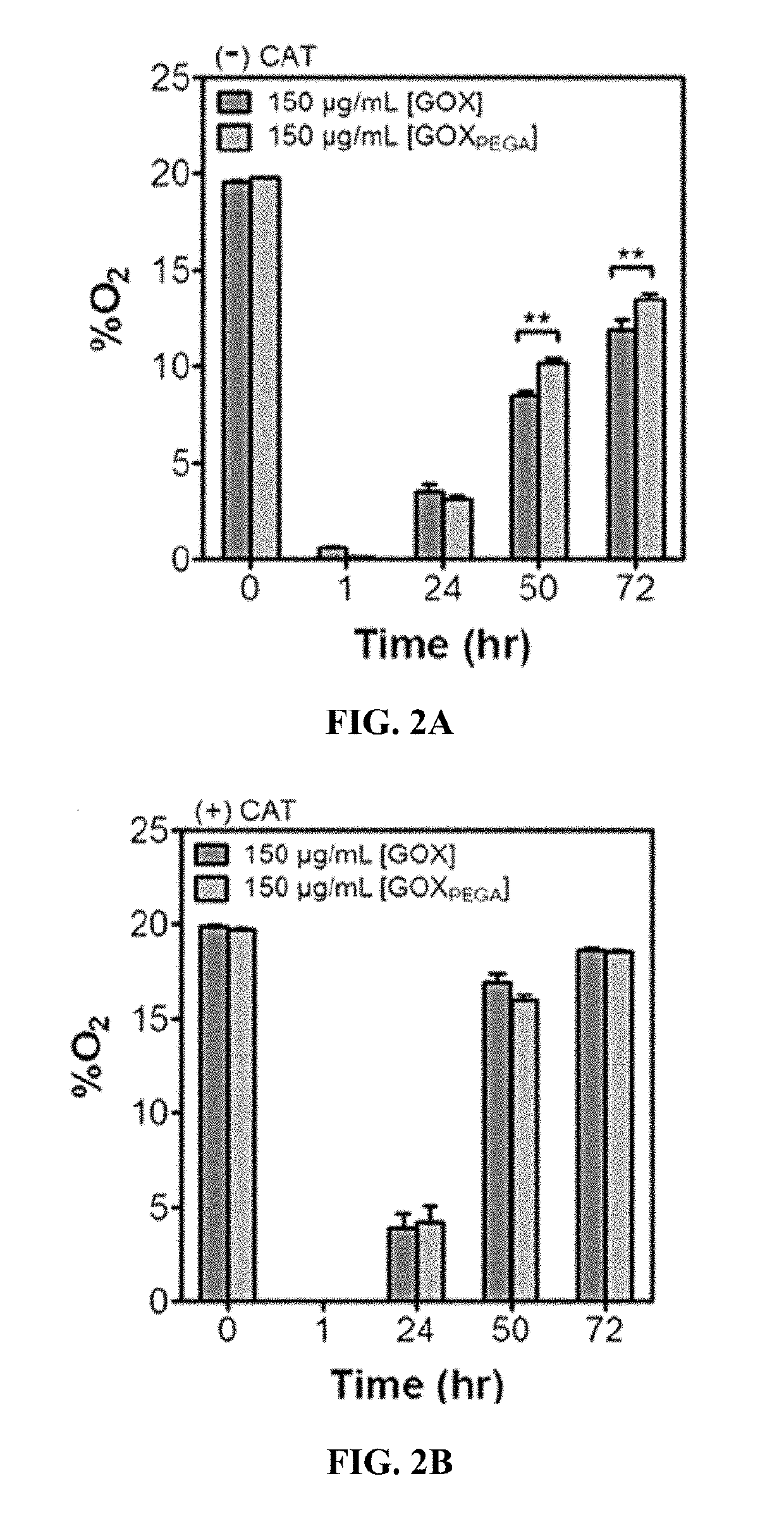
Stabilization of enzyme-immobilized hydrogels for extended hypoxic cell culture
ActiveUS20190177683A1Reduce adverse effectsReduces H2OApparatus sterilizationCulture processPolyethylene glycolHypoxic cell
Embodiments of the current invention include a hydrogel formed from crosslinked polyethylene glycol into which acrylated glucose oxidase has been immobilized through crosslinking to the gel. These hydrogels can be used to create hypoxia under ambient conditions for at least 72 hours and can be used to create hypoxic gradients. These embodiments permit the study of cells under a variety of hypoxic conditions.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Self-immobilized micromolecular fluorescent probe as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN114478352ATo achieve the mark effectAchieve in situ anchoringOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceNitroreductaseIntracellular
The invention discloses a self-immobilized micromolecular fluorescent probe as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The probe can be used for carrying out in-situ efficient and selective detection and imaging on overexpressed nitroreductase in hypoxic or hypoxic cells. And a chemical tool is provided for exploring the distribution of nitroreductase in cells in an anoxic state and solid tumor hypoxia imaging.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
A hypoxic fluorescent imaging probe and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN111875597BSimple structureTo achieve the purpose of specific fluorescence imagingOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceNitroimidazoleHypoxic cell
The present invention provides a hypoxic fluorescent imaging probe and its preparation method and application. The hypoxic fluorescent imaging probe has a structure shown in formula I, named as: 1-(1-(2-nitroimidazole)-3 ‑[(4‑aminomethyl)azepine]‑2‑propanol)‑6‑(4‑nitrobenzo‑2‑oxa‑1,3‑oxadiazole)‑lysine, abbreviated PLN; the probe of the present invention can achieve specific fluorescence imaging of hypoxic cells through the nitroimidazole group of the probe to macromolecules in cells in different hypoxic environments, and the primary amino group in the molecule is beneficial Further modification of the molecule.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Preparation method and application of anthraquinone polypyridine ligand and ruthenium-anthraquinone complex
InactiveCN103012401BSmall structureStable structureOrganic active ingredientsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsHypoxic cellPyridine ligand
The invention discloses a synthesis method and application of an anthraquinone polypyridine ligand and anthraquinone-ruthenium polypyridine complex. The anthraquinone-ruthenium polypyridine complex has good inhibition activity on the growth of hypoxic cells, and generates obvious fluorescence through reduction in the hypoxic cells; and thus, the compound is a novel biological reduction type hypoxic cell anti-cancer drug and a specific fluorescence probe as well as a drug with application value and taking tumor hypoxia as a target point and a fluorescence probe.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
An integrated device for baffle denitrification phosphorus removal and cod degradation
The invention discloses an integrated device for baffle denitrification phosphorus removal and COD degradation, which includes a reaction chamber, a transmission module and an oxygen supply module, wherein the reaction chamber includes a first anaerobic compartment, a second anaerobic compartment, Medium sinking cell, nitrification cell, anoxic cell, aerobic cell and final sinking cell, each cell is separated by an overflow partition, and the transmission module includes a sludge overtaking component and a sludge return component, The oxygen supply module consists of aeration equipment and 2 air distribution pipes. Beneficial effects of the present invention Adopt the double anaerobic chamber with buffer function design, reduce the impact of abnormal water inflow and high nitrate nitrogen of return sludge on denitrifying phosphorus accumulating bacteria, and avoid the impact of denitrifying phosphorus accumulating bacteria Oxygen ensures the absolute anaerobic of the second anaerobic compartment, and improves the stability and high efficiency of the treatment process of the device of the present invention.
Owner:SINOPEC YANGZI PETROCHEM +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com