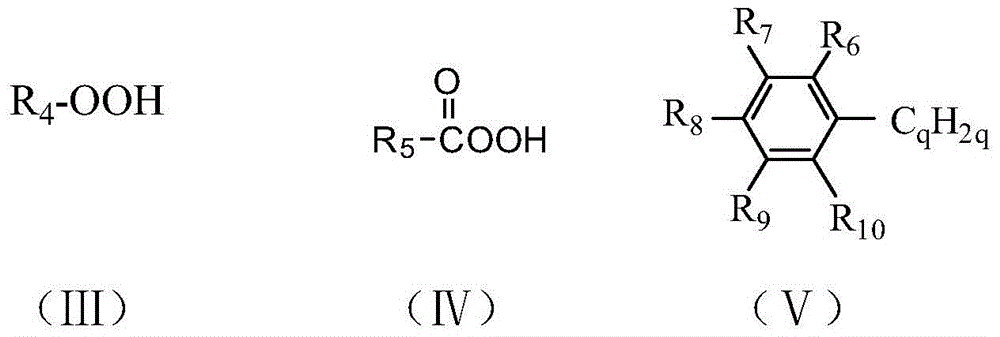Patents
Literature
47 results about "Photodissociation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Photodissociation, photolysis, or photodecomposition is a chemical reaction in which a chemical compound is broken down by photons. It is defined as the interaction of one or more photons with one target molecule. Photodissociation is not limited to visible light. Any photon with sufficient energy can affect the chemical bonds of a chemical compound. Since a photon's energy is inversely proportional to its wavelength, electromagnetic waves with the energy of visible light or higher, such as ultraviolet light, x-rays and gamma rays are usually involved in such reactions.
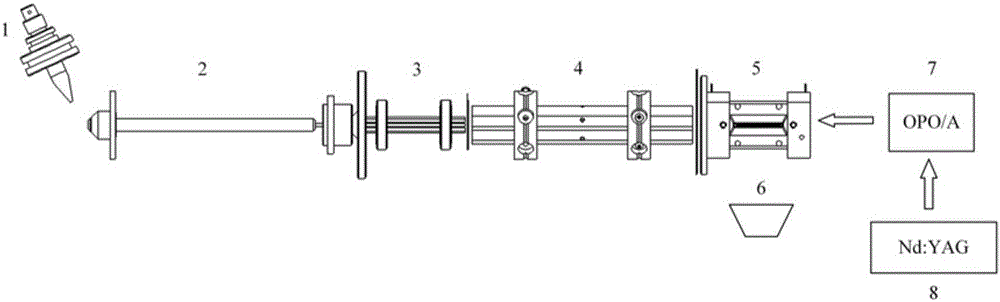
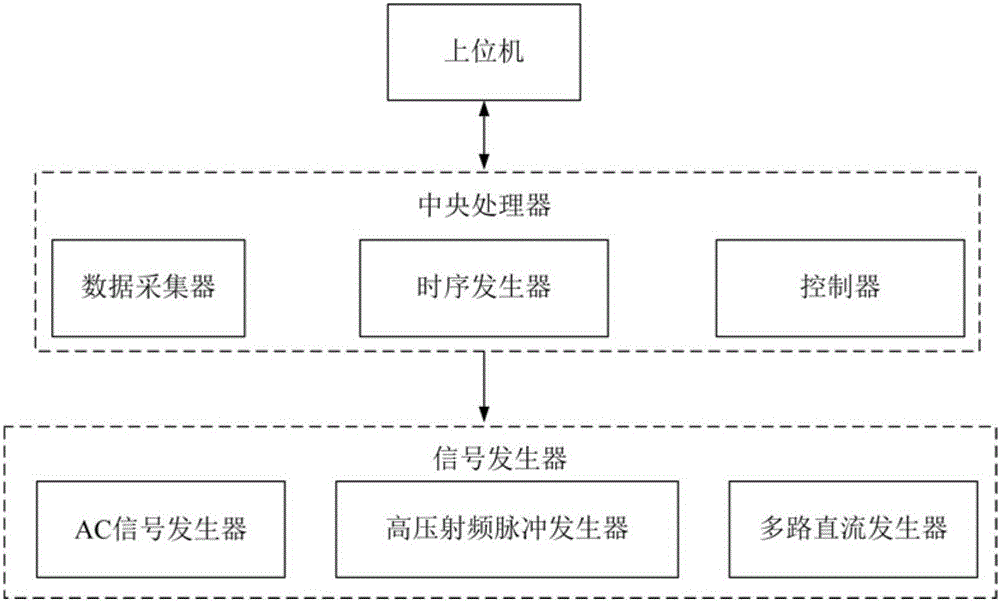
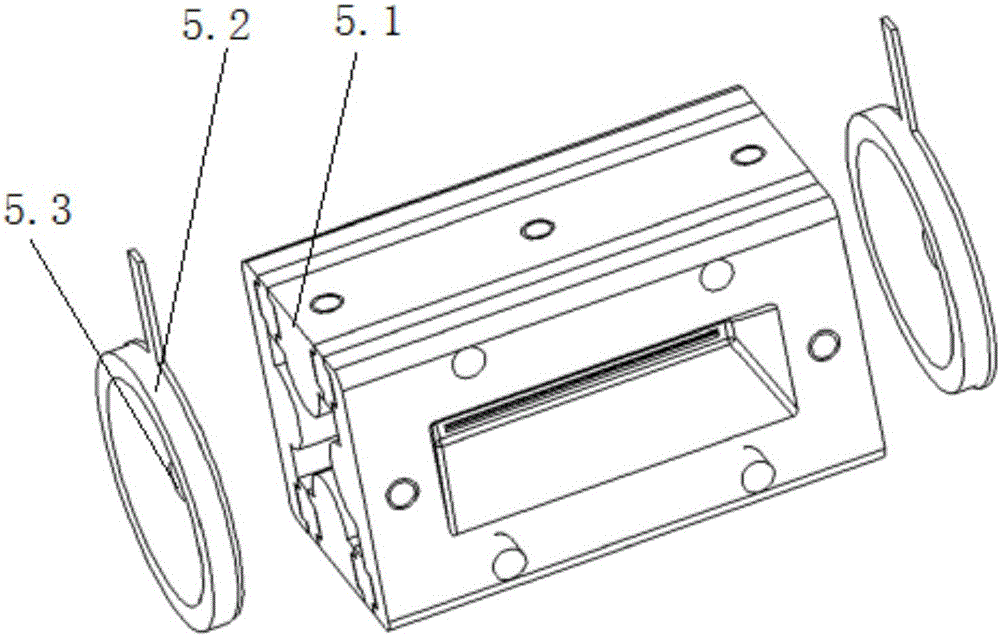
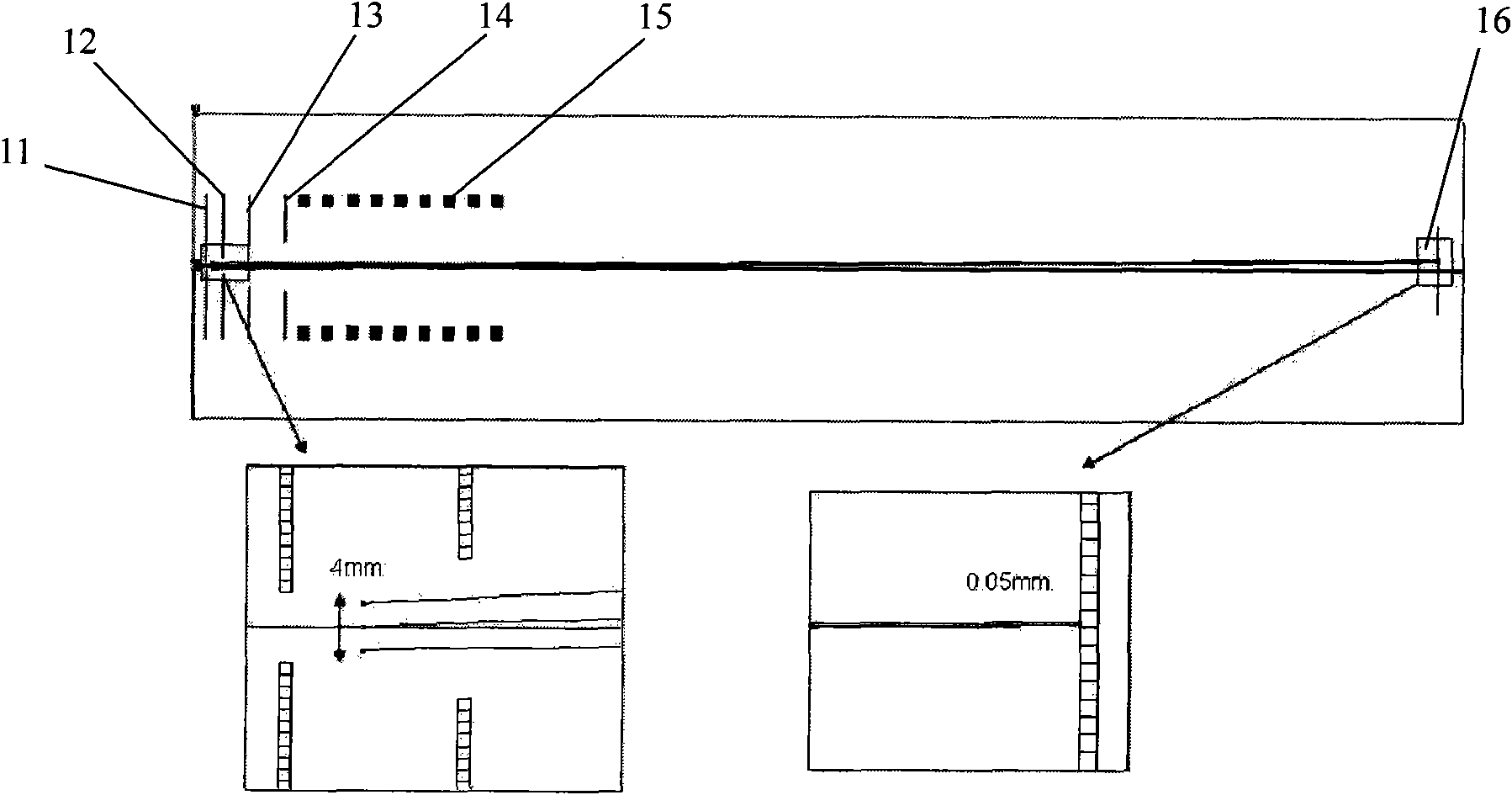
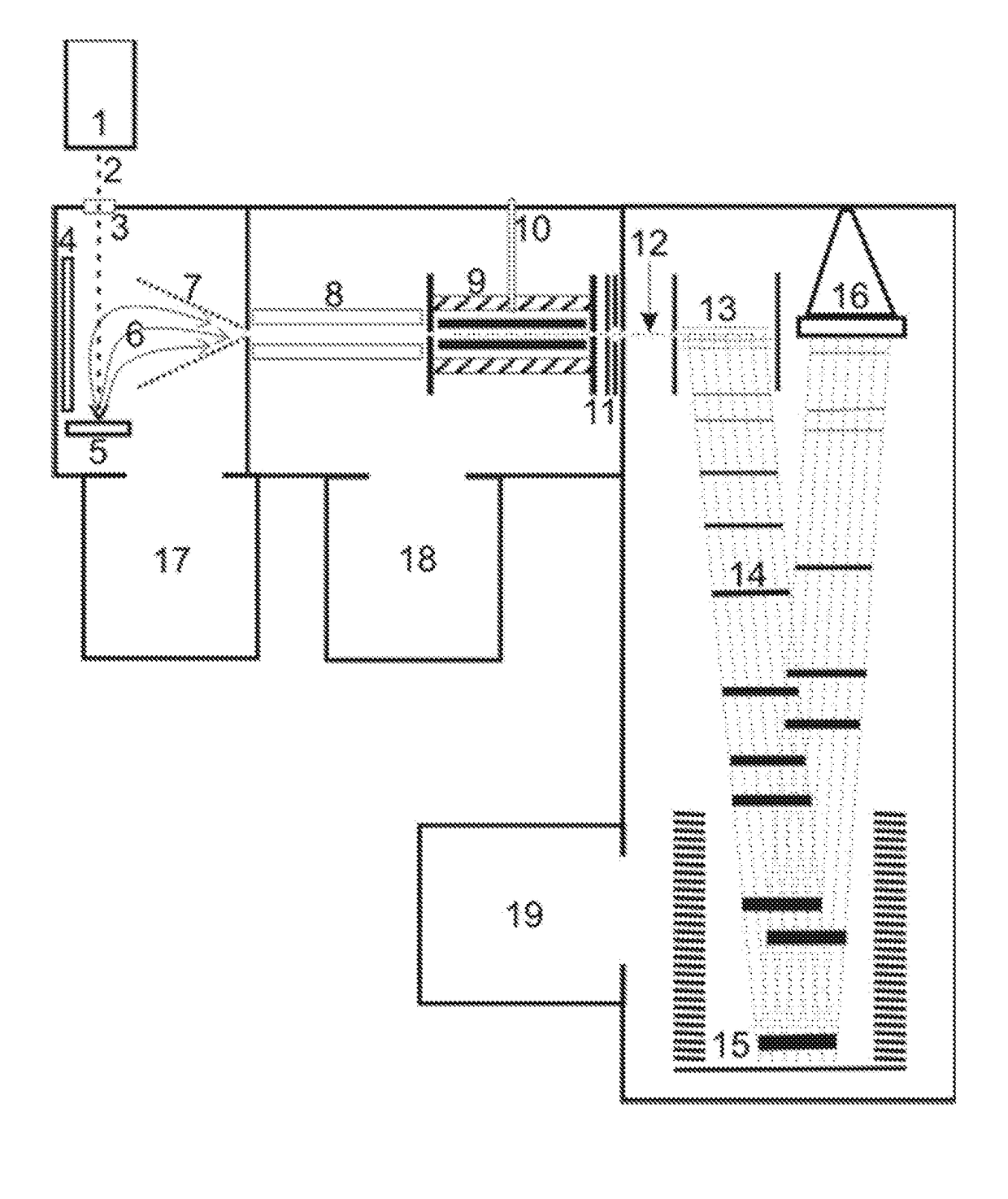
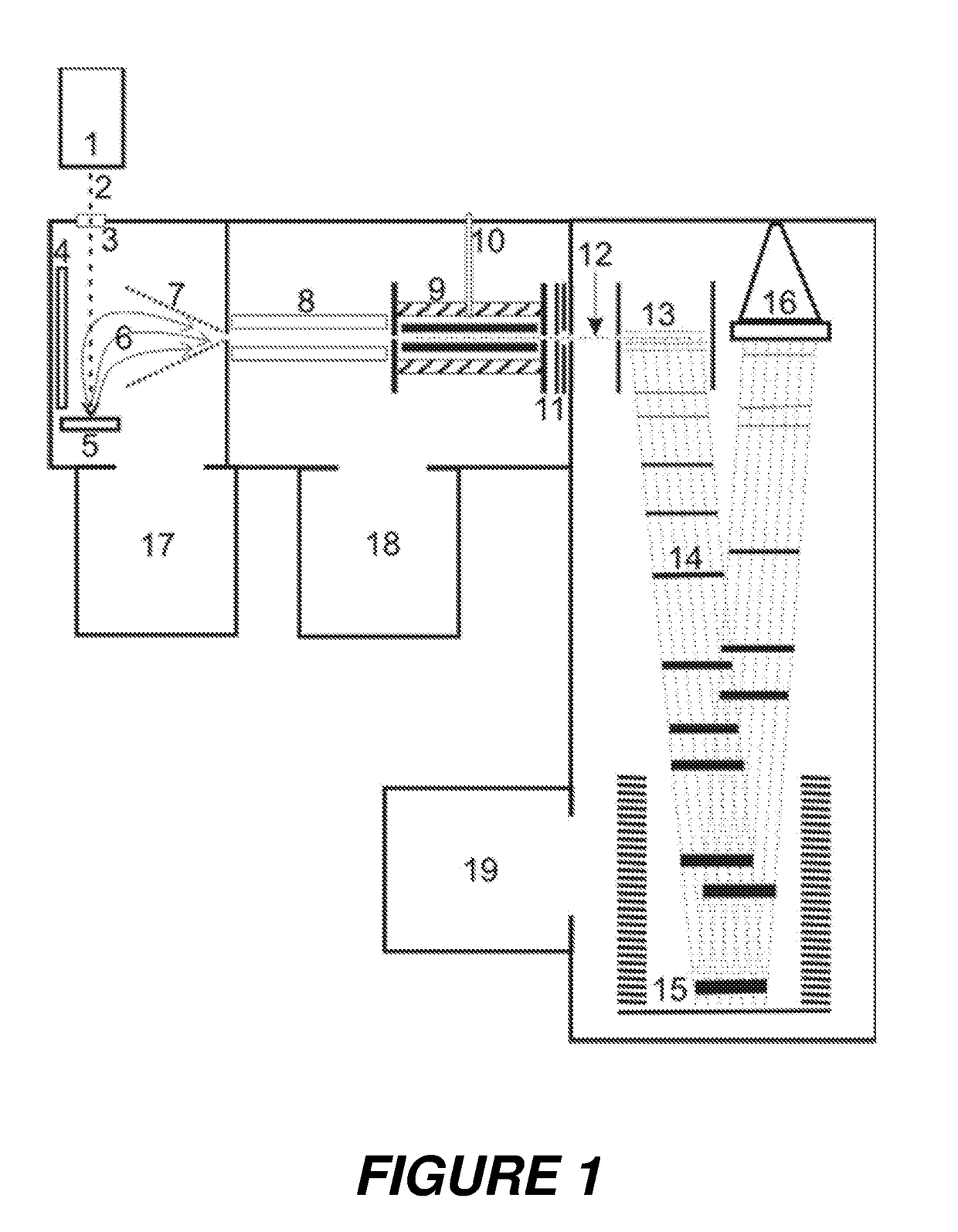
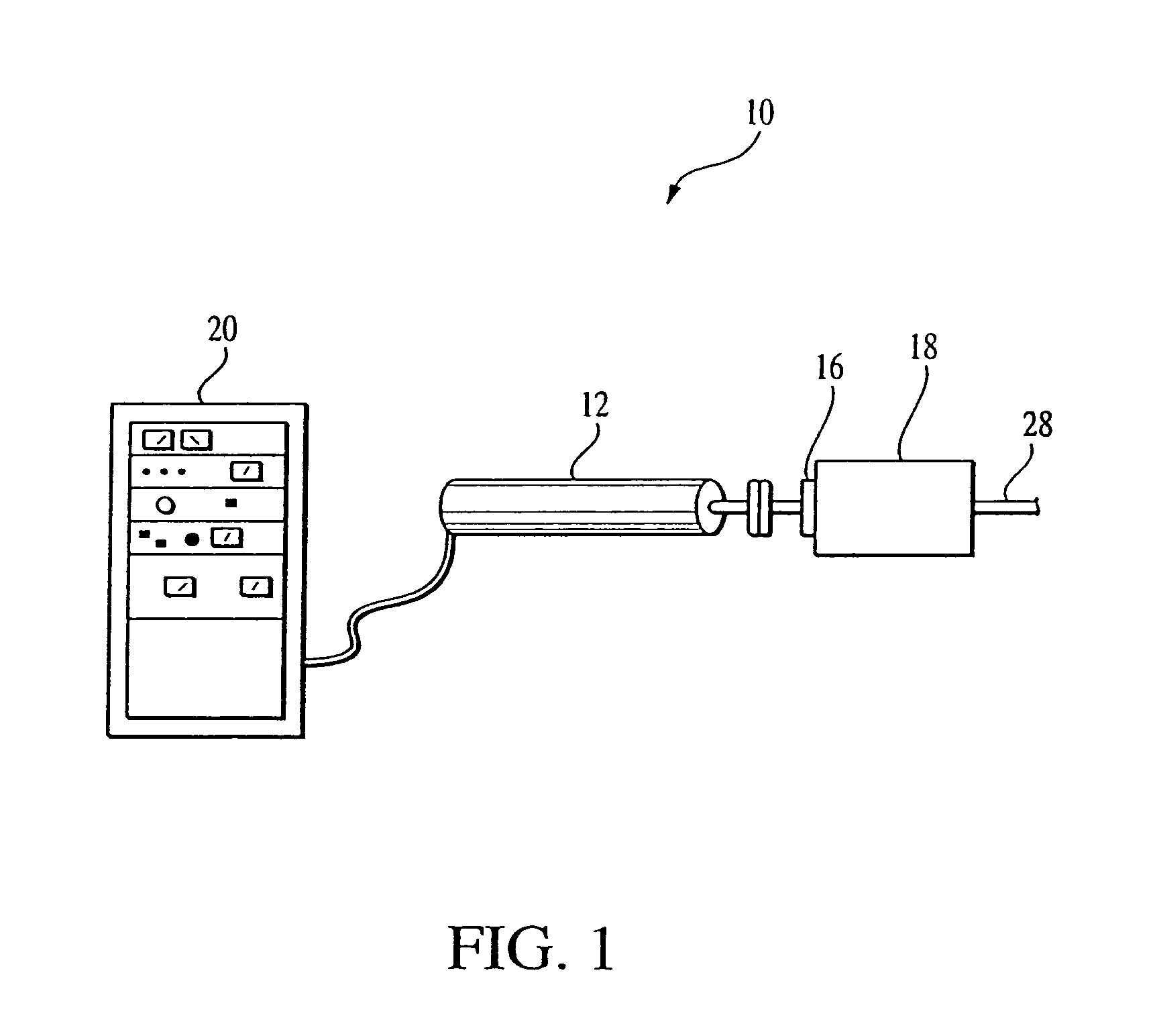
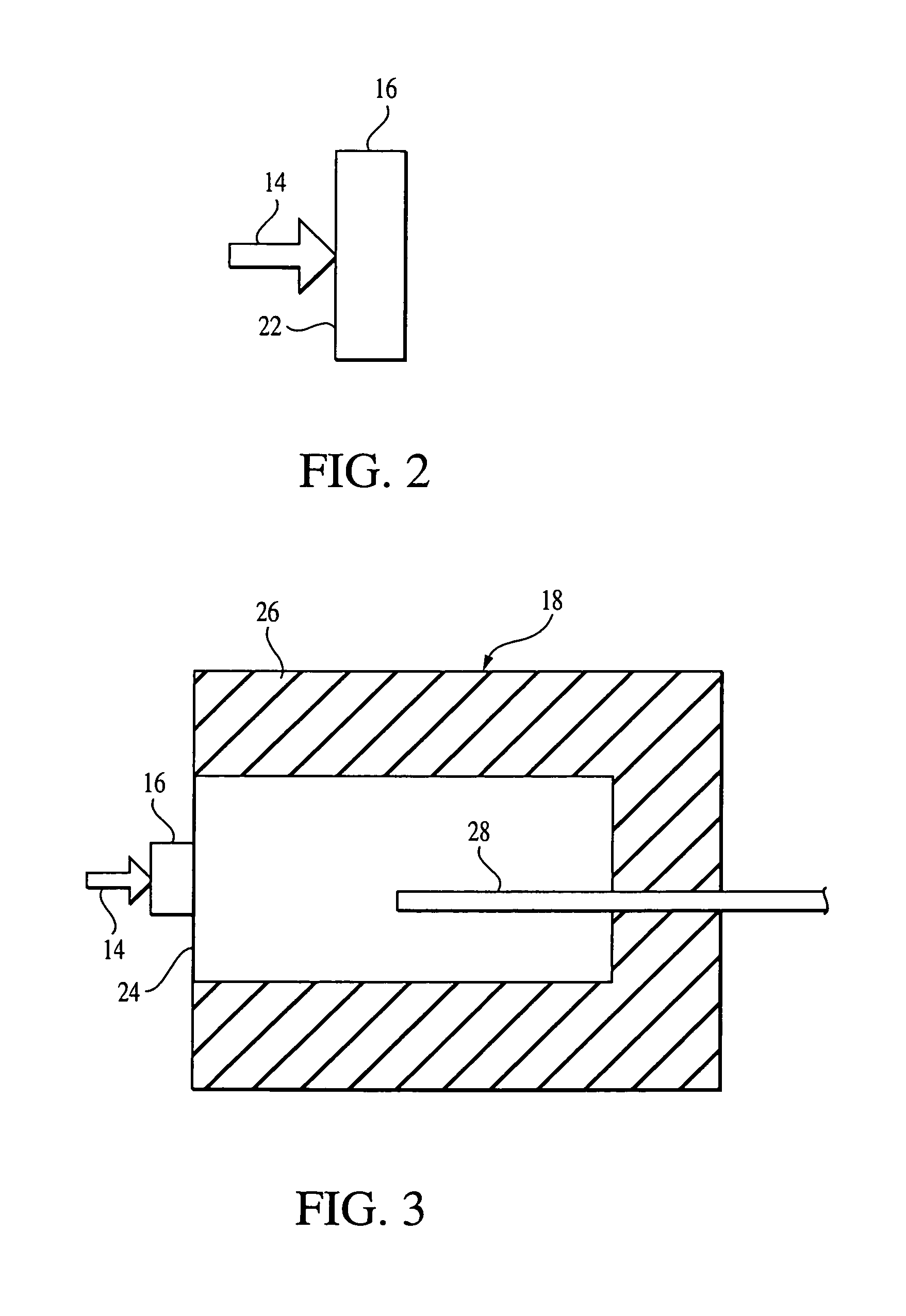
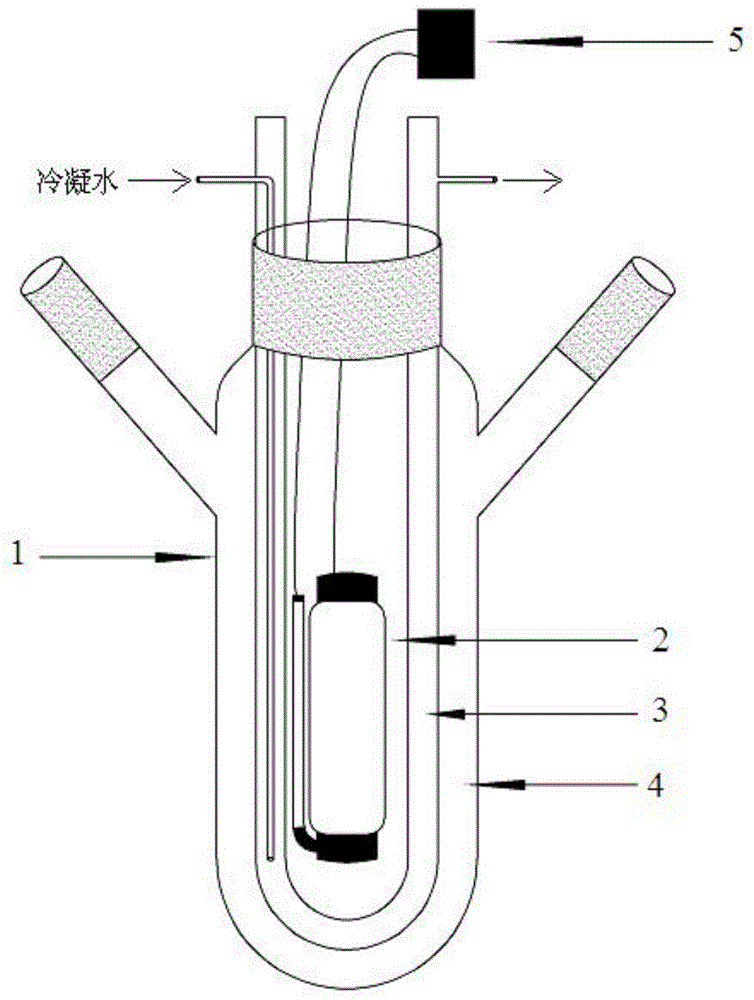
Ion trap mass analyzer based infrared light dissociation spectrograph
InactiveCN105957798AAvoid lostHigh sensitivityStability-of-path spectrometersSpectrographMass analyzer
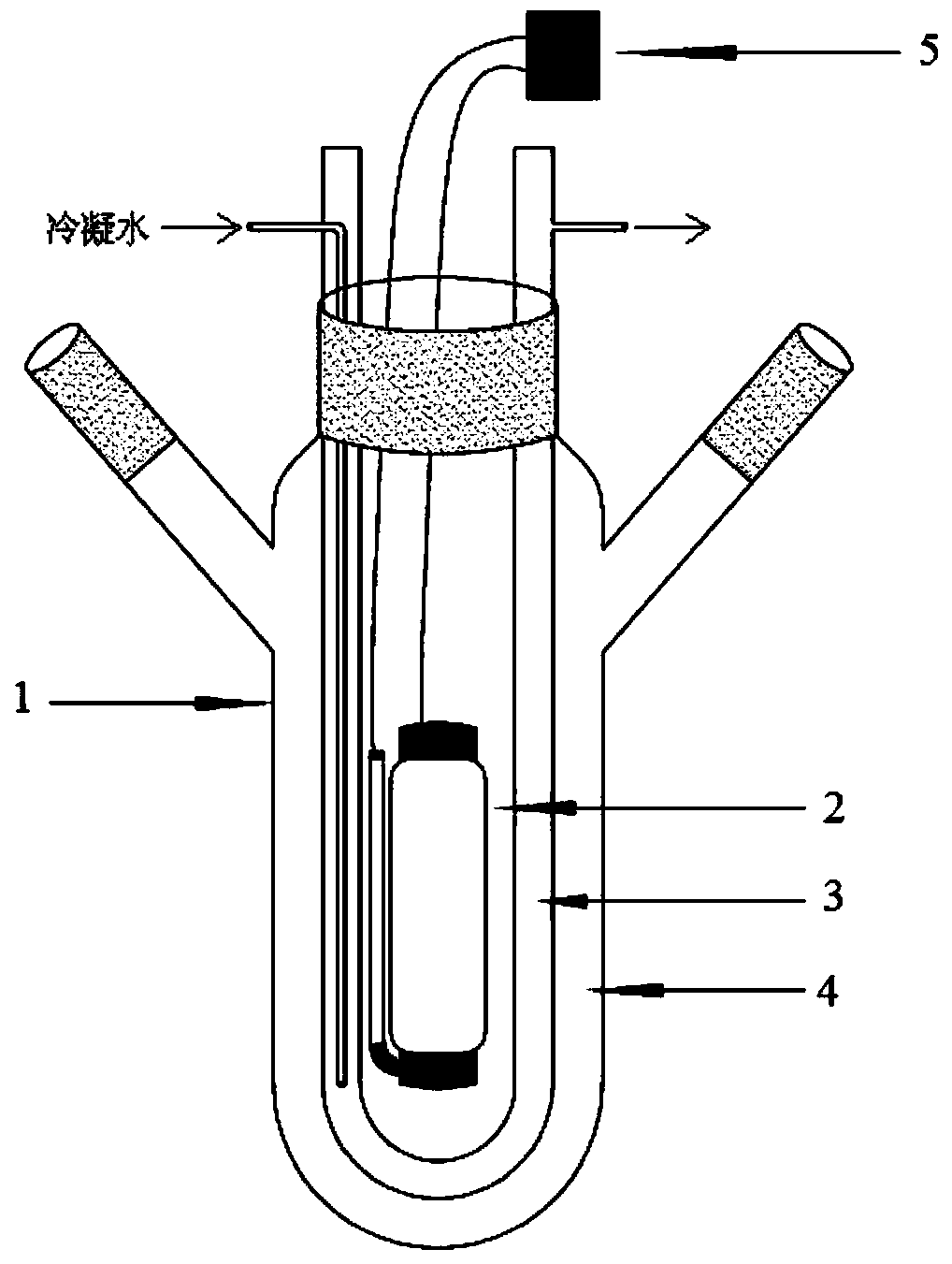
The invention discloses an infrared photodissociation spectrometer based on an ion trap mass analyzer. An ion detector and an infrared laser system are provided, and the transmission line, octopole, hexapole, and low-temperature linear ion trap are set in a four-stage differential pumping vacuum system; the electrospray device is used as an ionization source, and the neutral The substance is ionized into ions, and then transmitted to the low temperature linear ion trap through the transmission line, octopole and hexapole. The low temperature linear ion trap is used as a mass analysis device. The infrared light output by the infrared laser system is incident on the low temperature linear ion trap. Complete ionization, ion cooling, ion selection, infrared photodissociation, mass analysis and emptying in a low temperature linear ion trap. The invention has the characteristics of miniaturization, low price, easy maintenance, good stability, high sensitivity and resolution.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
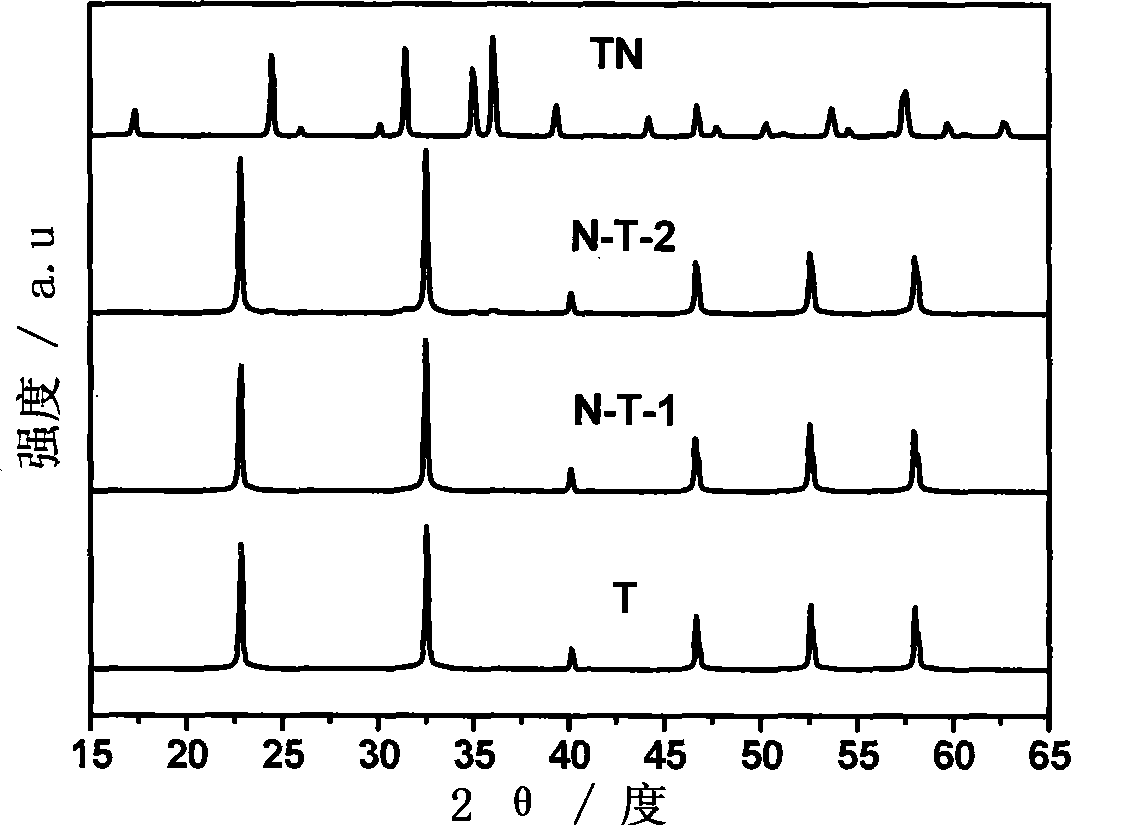
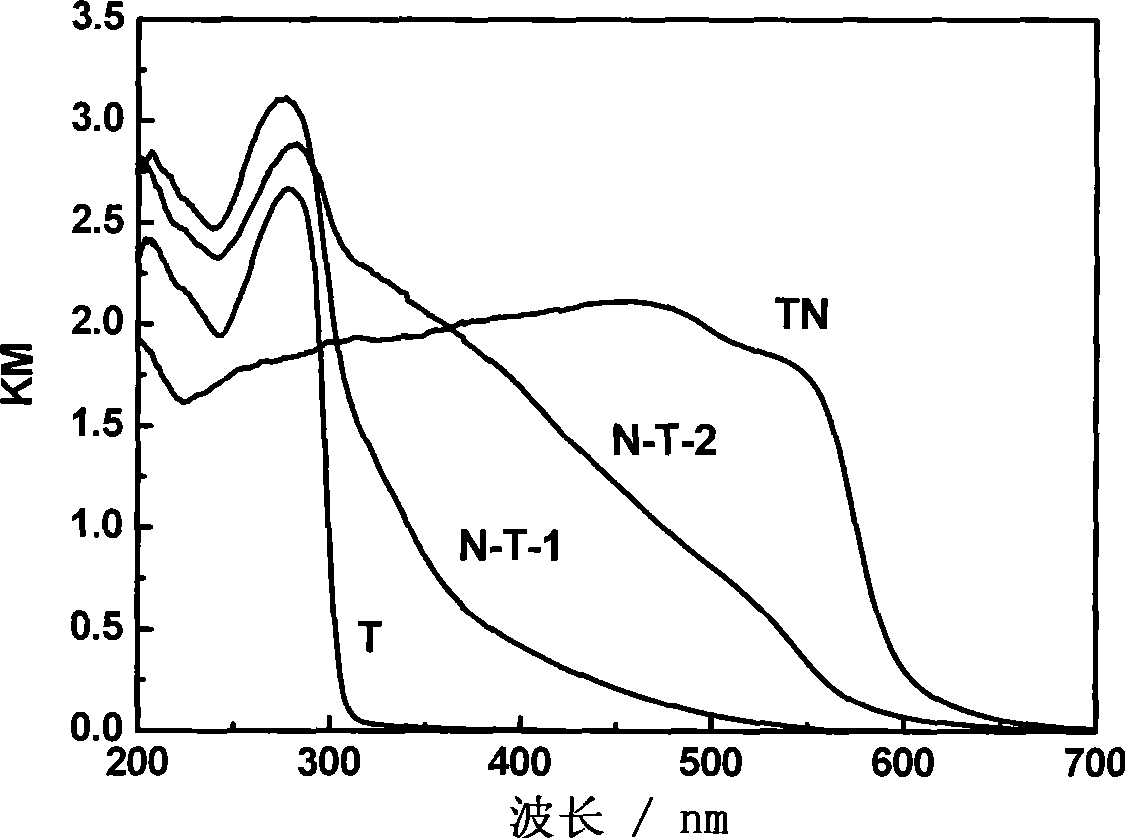
Preparation method of alkali metal tantalate composite visible-light photocatalyst for hydrogen production from photodissociation of water
InactiveCN101474558AAchieve dopingIt can be seen that the absorption is goodHydrogen productionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsNitrogen dopedHeat treated
The invention relates to a preparation method for an alkali tantalate based composite visible-light photocatalyst in hydrogen production by water splitting, in particular to a method that ammonia is used as the nitrogen source to perform nitrogen doping on the alkali tantalate at high temperature. The method has the following steps: (1) dissolving the tantalum-containing precursor in the surfactant acidic solution to produce a uniform tantalum salt solution; (2) adjusting the PH value to 6-9 and adding the hydroxide of an alkali metal to produce a suspension; (3) water-heating the produced suspension in a reaction kettle to produce the alkali tantalate crystal and (4) treating the crystal with the ammonia to produce the alkali tantalate, and then obtaining the nitrogen doped alkali tantalate. The photocatalyst treats the alkali tantalate by high-temperature ammonolysis, which realizes nitrogen doping to the alkali tantalate. The experiment shows that the alkali tantalate is nitrogen doped in the preparation process which has good visible light catalysis and solves the problem of nitrogen doping to the alkali tantalate.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
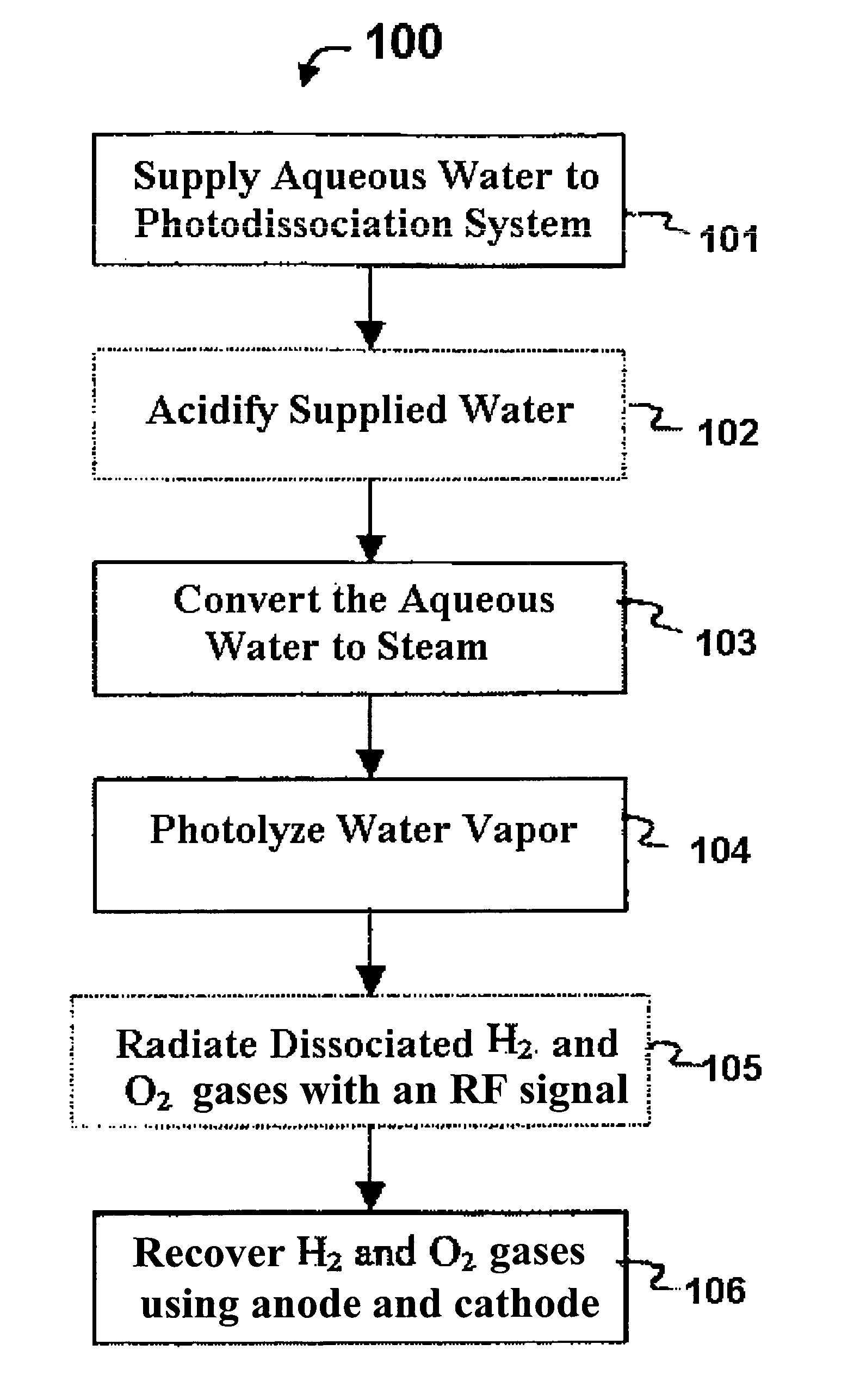
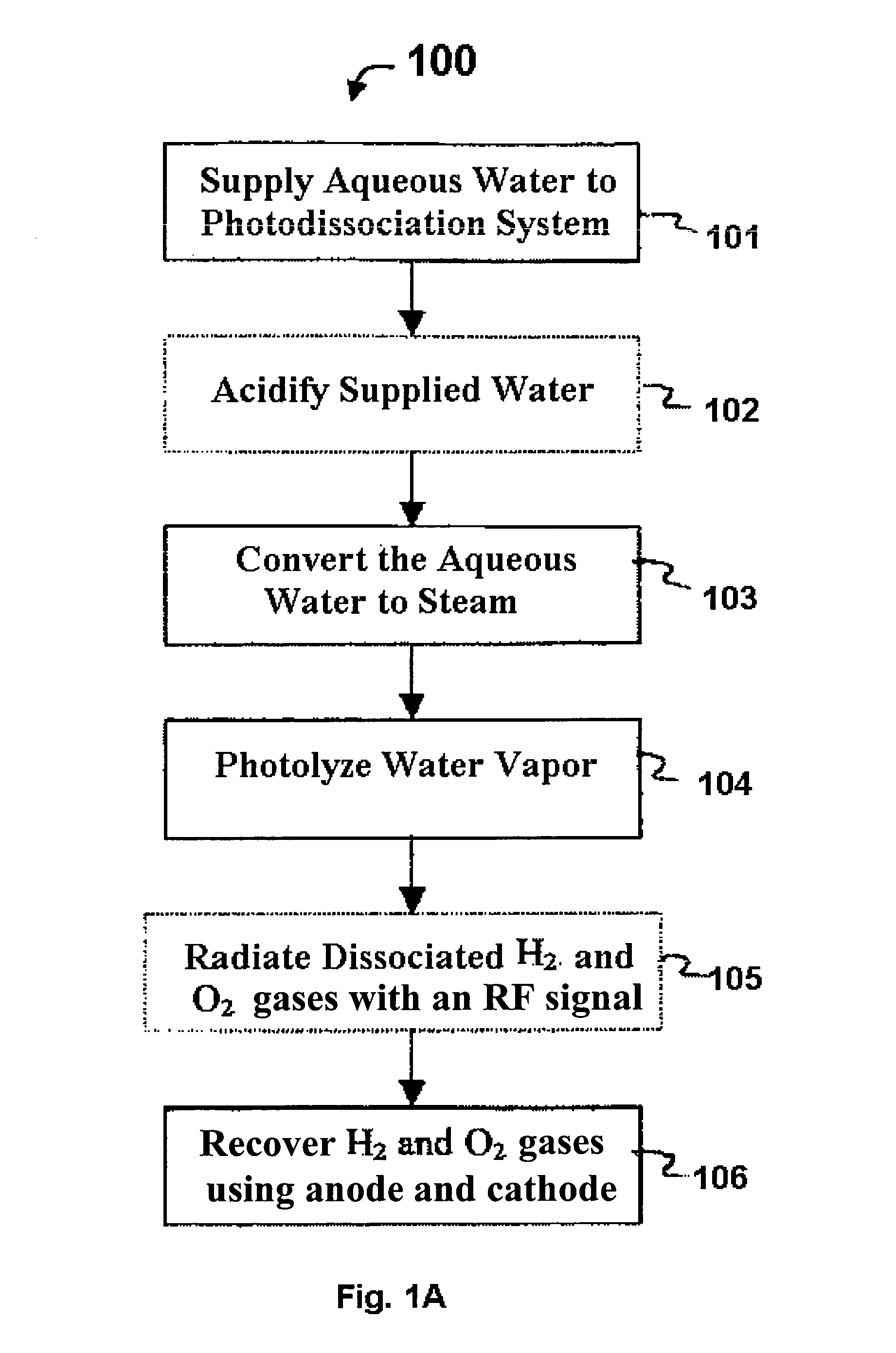
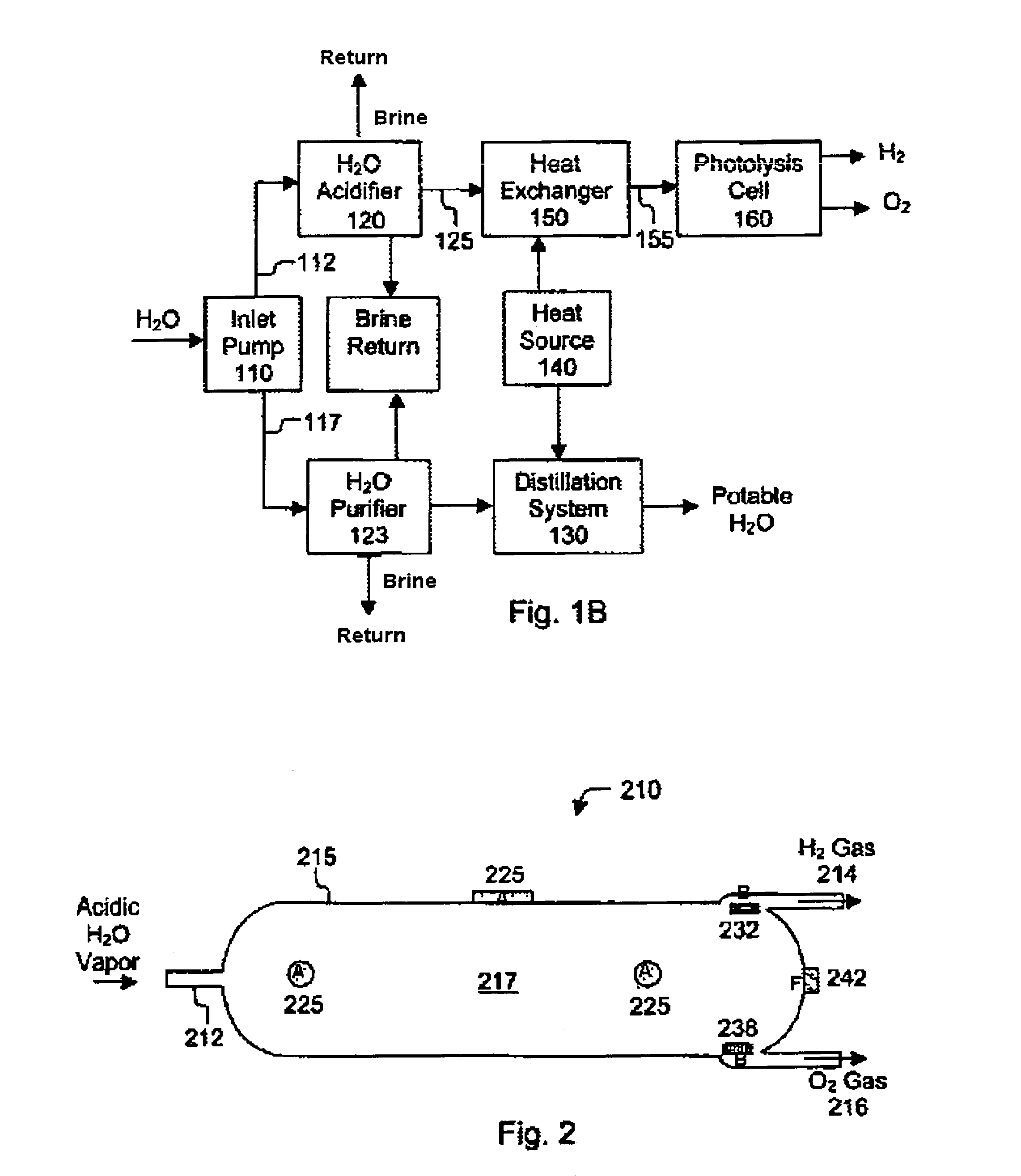
Methods for affecting the ultra-fast photodissociation of water molecules
A method for the ultra-fast photodissociation of water molecules into H2 and O2 gases is presented. Water vapor is initially produced and supplied to a photolysis bottle. Within the photolysis bottle, the water vapor is illuminated by a light signal to dissociate H2 and O2 gases from the water vapor. The dissociated H2 and O2 gases are radiated with an RF signal to inhibit recombination of the dissociated H2 and O2 gases, and the dissociated H2 and O2 gases are subsequently recovered.
Owner:COASTAL HYDROGEN ENERGY
Mass spectrometer
InactiveUS20110168883A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioIncrease dissociationIsotope separationMass spectrometersIon trap mass spectrometryTrapping
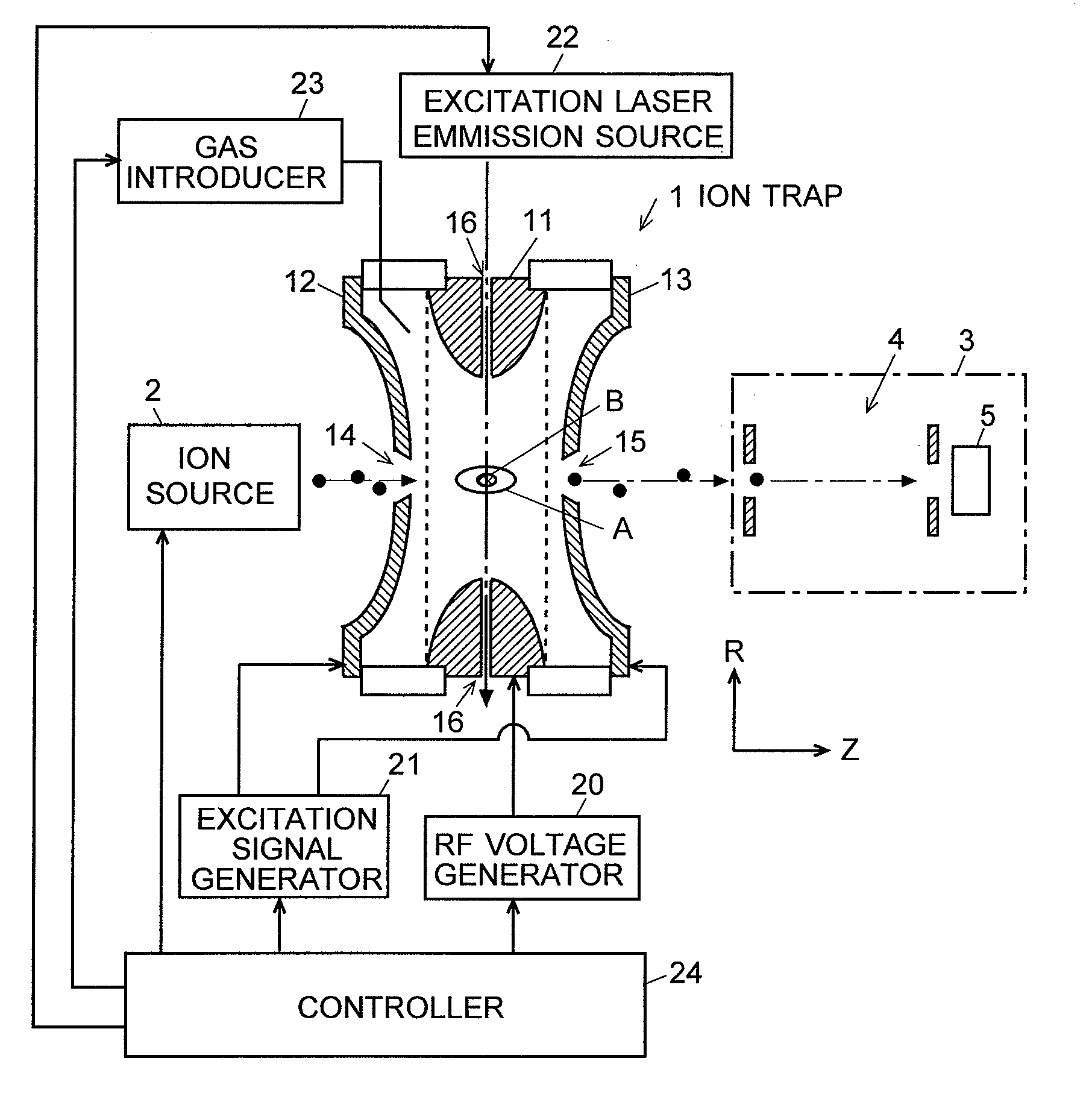
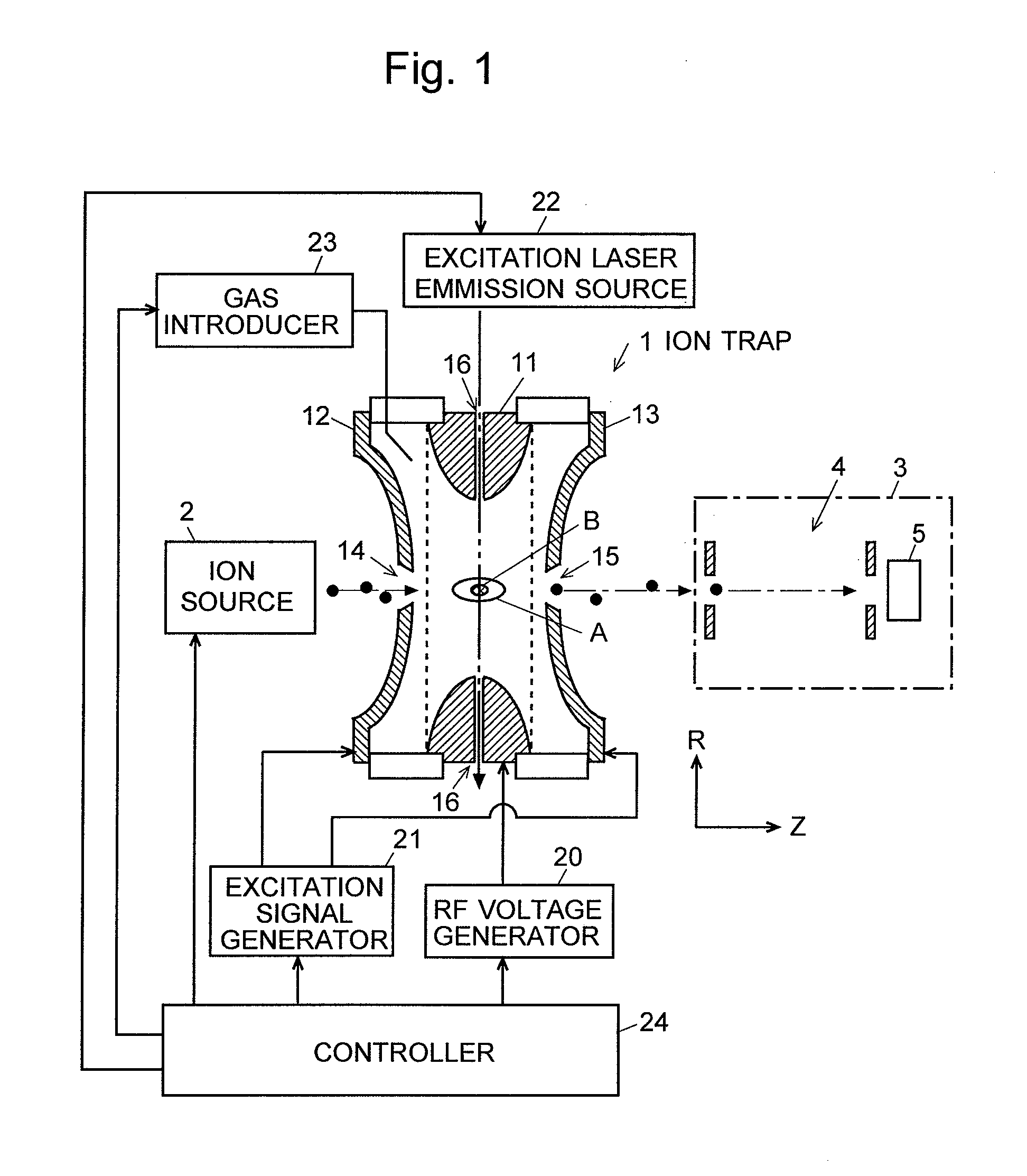
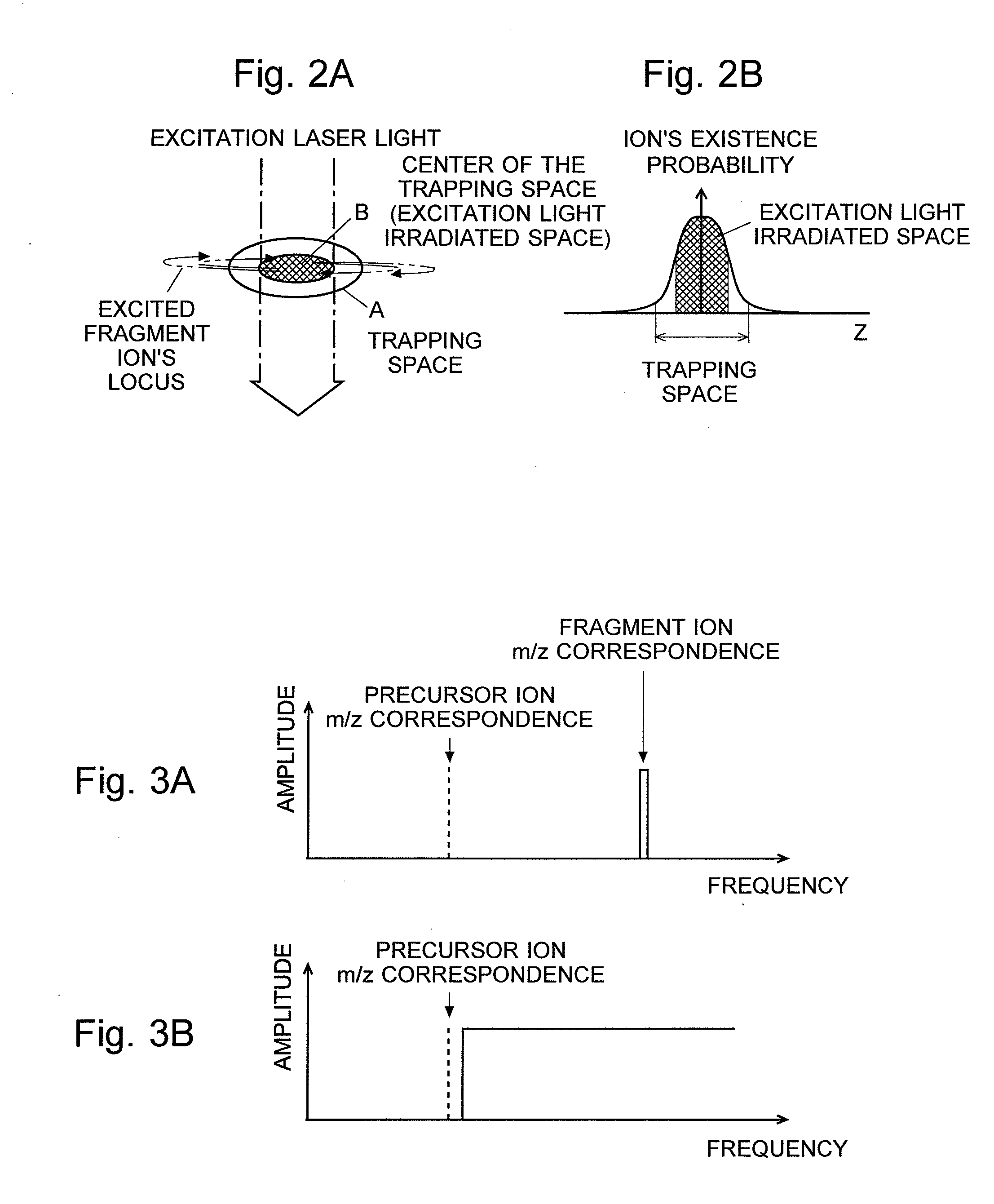
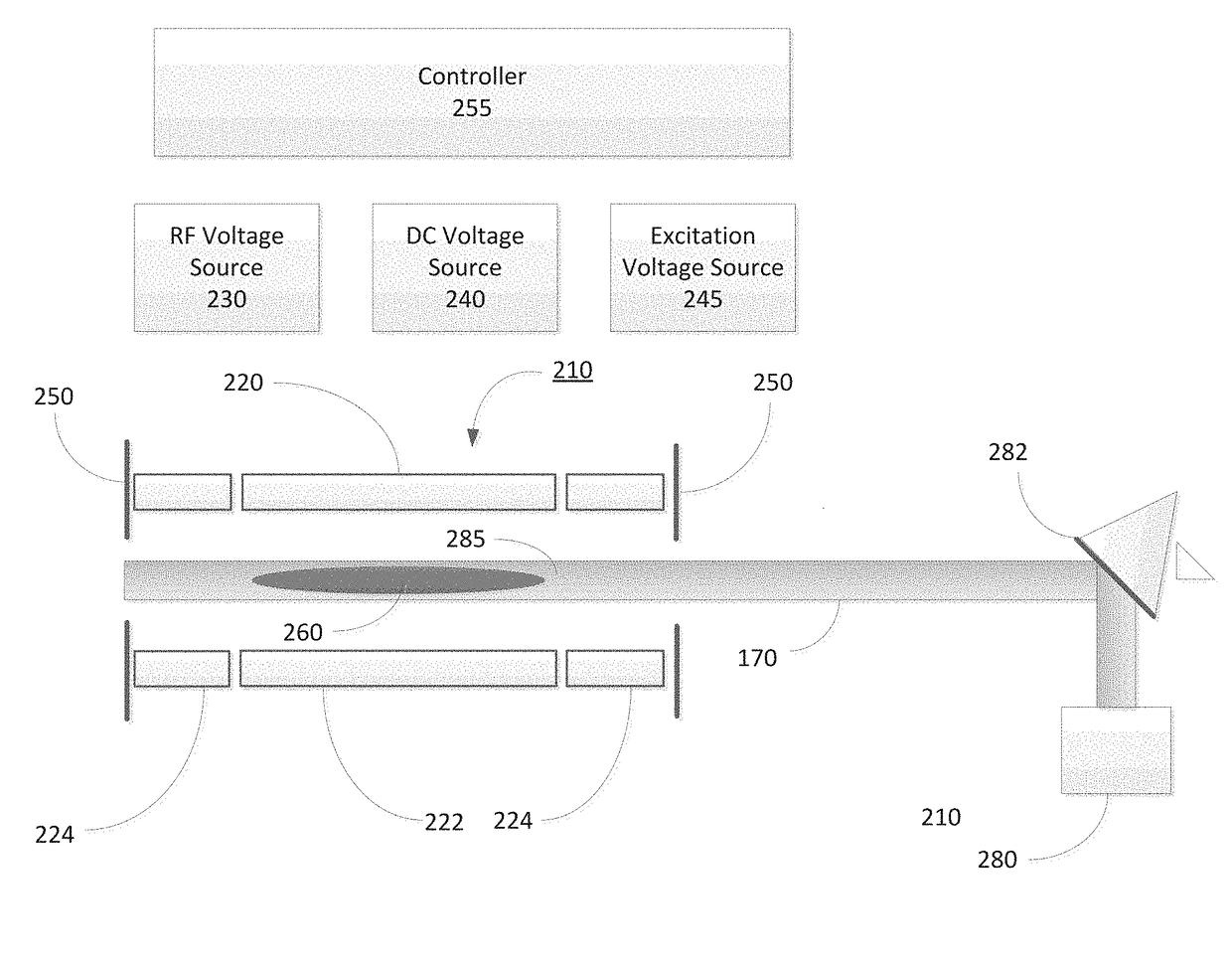
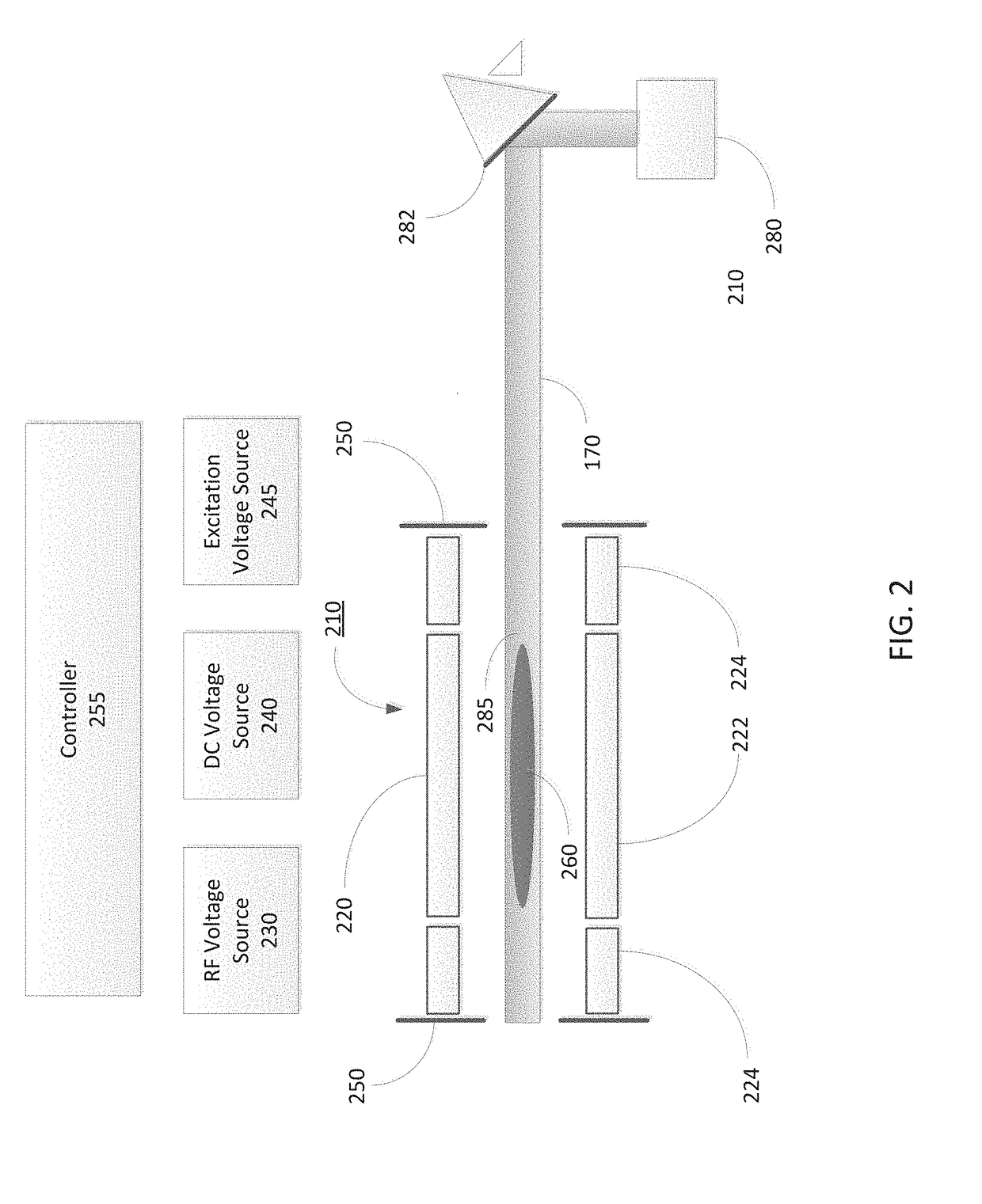
A mass spectrometer is provided that restrains the signal intensity of an MS / MS spectrum from decreasing according to the secondary dissociation of a primary fragment ion generated by a photodissociation. An excitation laser light for causing a photodissociation is irradiated to the trapping space A in the ion trap 1. At the same time, an excitation signal that does not excite a precursor ion but excites fragment ions is applied to the end cap electrodes 12 and 13. Since the selected precursor ions gather around the center of the trapping space A, they are irradiated by the excitation laser light and efficiently dissociated. The fragment ions generated by this are immediately excited by the excitation electric field's effect, and are vibrated wildly to be out of the excitation light irradiated space B. Therefore, the fragment ions are not easily irradiated by the excitation laser light and the secondary dissociation does not easily occur.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Photodissociation reaction method of benzothiophene compound for oxidative desulfurization
ActiveCN104277870AIncrease polaritySettle the lossHydrocarbon oils refiningHydrocarbon oils treatmentPetroleum productPorphyrin
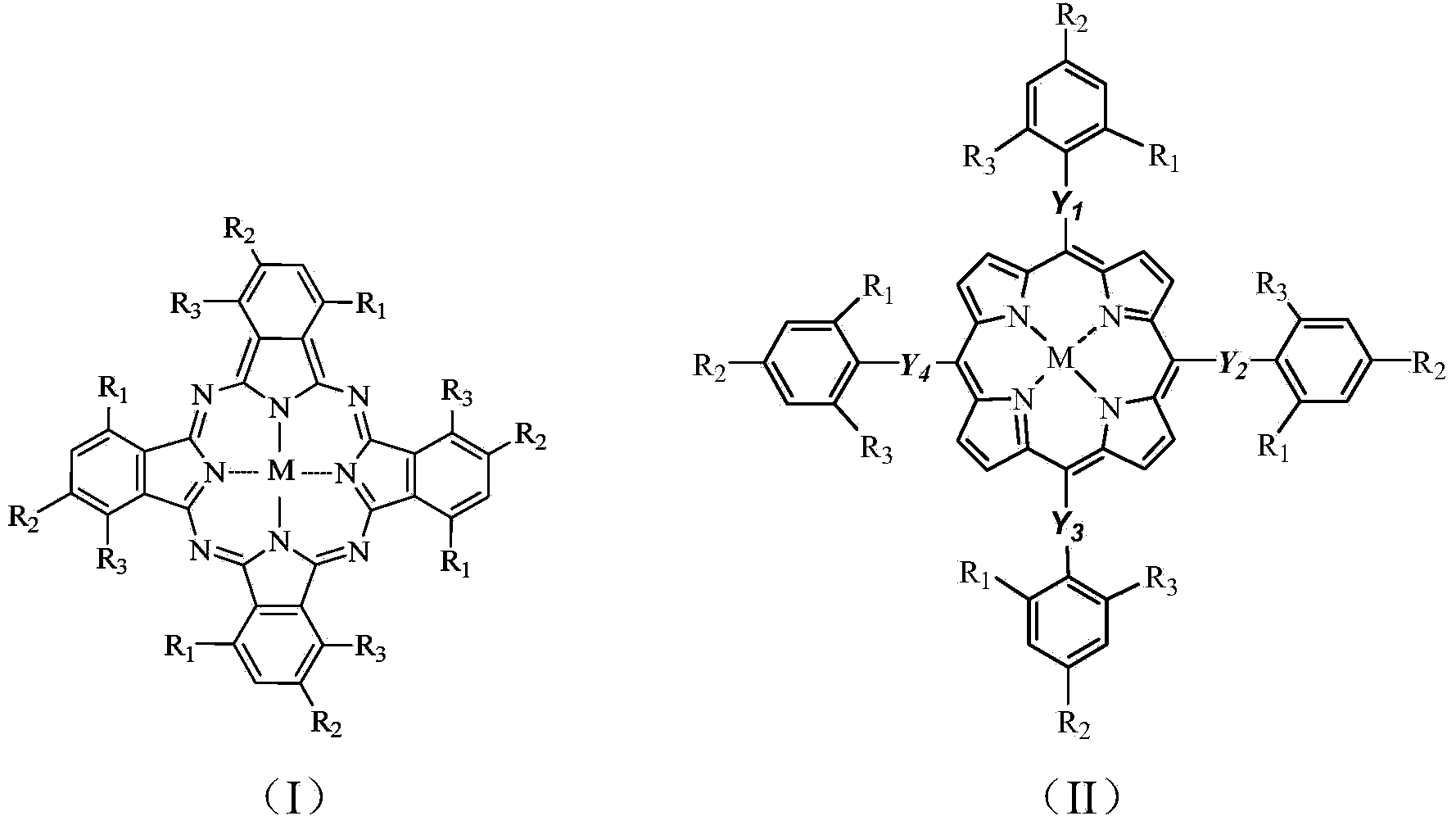
The invention discloses a photodissociation method of a benzothiophene compound for oxidative desulfurization. According to the method, the benzothiophene compound reaches C-S bond fracture reaction under the existence of an oxidizing agent and metal phthalocyanine or metalloporphyrin through illuminating reaction. According to the method disclosed by the invention, under the mild conditions of normal temperature and pressure, the most stable sulfide, namely the benzothiophene compound in an oxidized petroleum product reaches the C-S bond oxidation fracture in the benzothiophene compound, so as to obtain a sulfocompound with relatively strong polarity and sulfur-free hydrocarbon oxide. The conversion ratio of the C-S bond fracture reaches over 90% when metalloporphyrin is a catalyst, and the problems that the C-S bond oxidation fracture reaction in the benzothiophene compound at present needs high temperature, high pressure and a special catalyst, and is high in demands on equipment, and low in productive rate are overcome.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Molecular photodissociation ionization velocity imaging device
InactiveCN101625326AImprove time resolutionHigh precisionFluorescence/phosphorescenceCcd cameraVacuum chamber
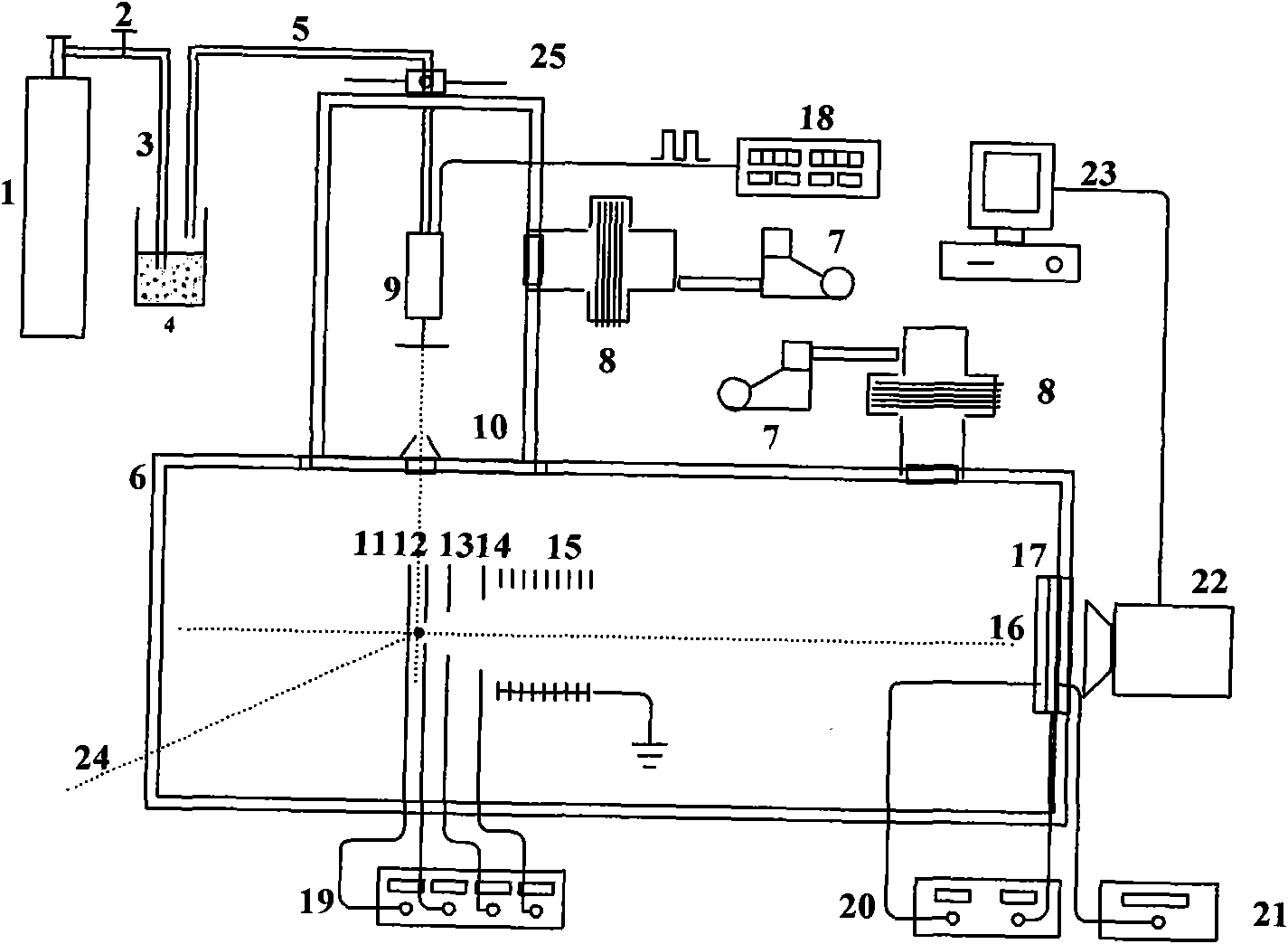
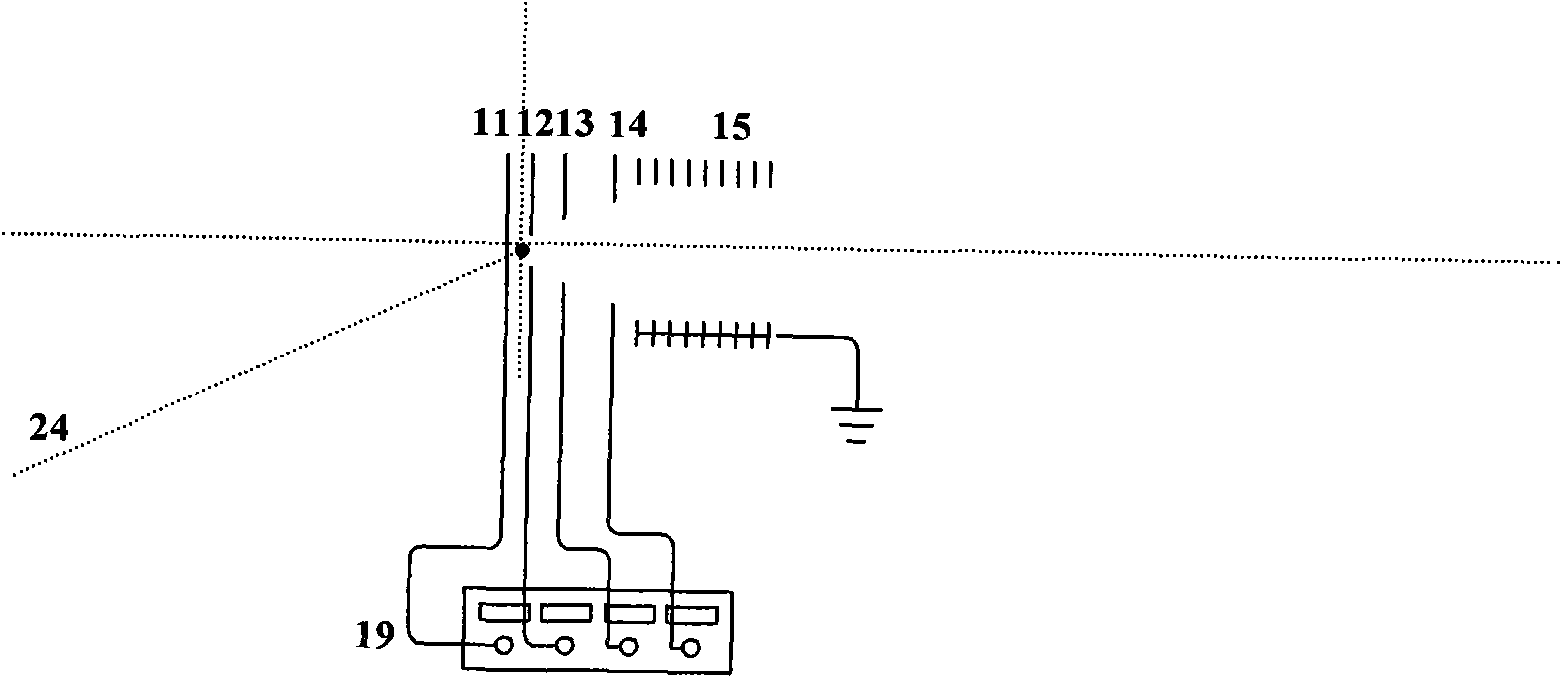
The invention discloses a molecular photodissociation ionization velocity imaging device and relates to a device which uses the ion velocity imaging technology for carrying out slicing and imaging on positive and negative ions and electronic three-dimensional information. The device comprises an inert gas carrier gas source, a pressure reducing valve, a sample cell, a vacuum cavity, a pre-stage dry pump, a molecular pump, a pulse valve, a skimmer, an ion lens group, a micro-channel plate, a fluorescent plate, a CCD camera, a computer and a synchronized laser source. The device designs an ion lens in the traditional ion velocity imaging system to the multi-stage ion lenses and combines the micro-channel plate with rapid response, the fluorescent plate and the enhanced CCD camera with ultra-high time resolution, thereby greatly extending an ion cloud on time scale, leading the ion slicing and imaging precision to achieve 5ns, improving the time resolution, solving the problem of image blur and reducing the cost.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Reduction of chemical noise in a MALDI mass spectrometer by in-trap photodissociation of matrix cluster ions
InactiveUS20070057173A1Reduce noiseLess efficiently absorbedParticle separator tubesIsotope separationIon trap mass spectrometryAnalyte
A MALDI mass spectrometer includes a radiation source, such as a gas or solid state laser, that emits a beam of radiation (typically in the UV or IR wavelengths) directed along the central axis of a linear ion trap in which analyte ions and matrix cluster ions are confined. The radiation beam has a wavelength that is strongly absorbed by the matrix cluster ions. The absorption of radiation by the matrix cluster ions produces dissociation of the matrix cluster ion into fragments having mass-to-charge ratios that lie below a mass-to-charge ratio range of interest. Thus, chemical noise associated with matrix cluster ions is reduced or eliminated.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
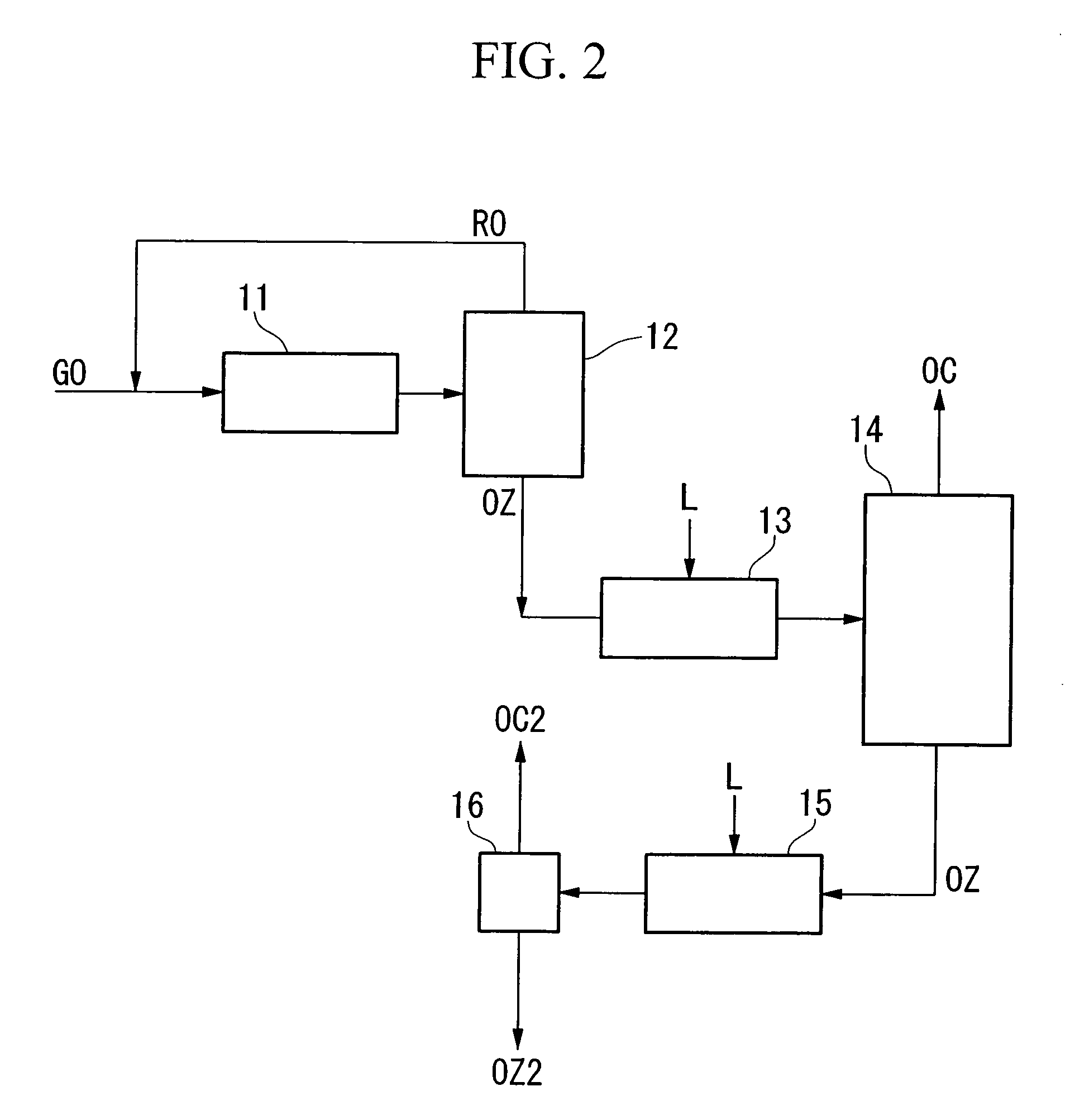
Method for concentrating oxygen isotope
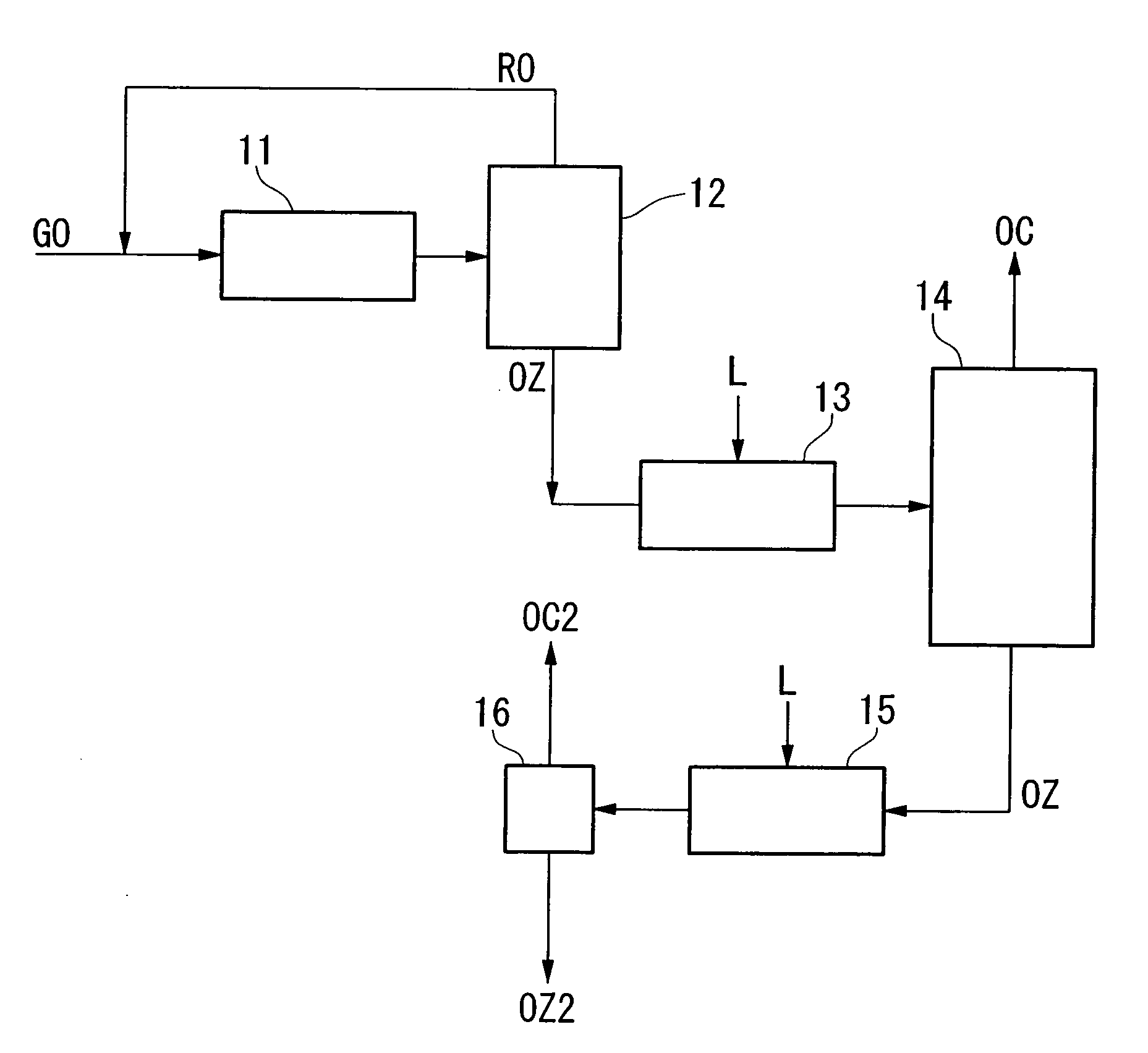
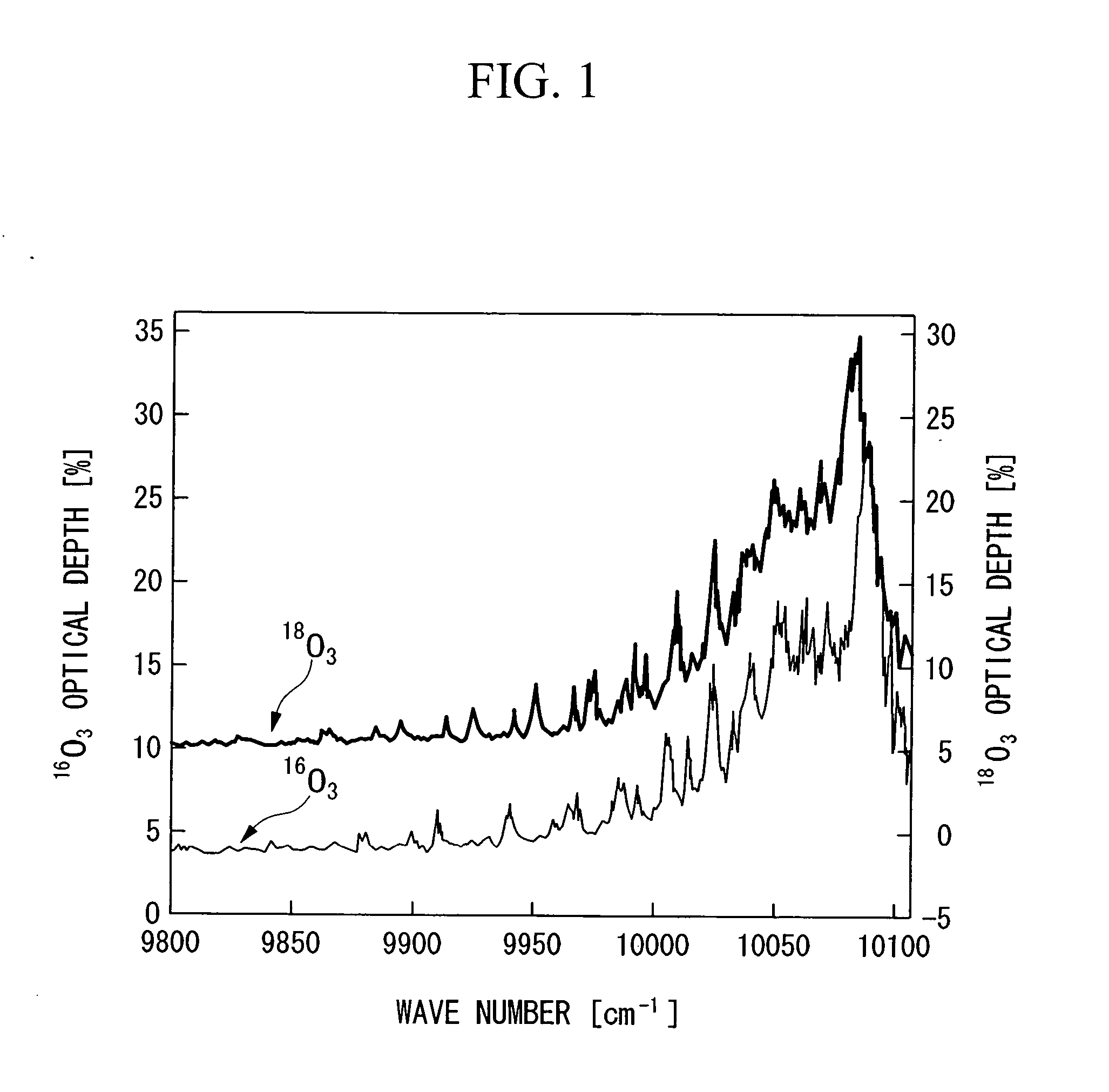
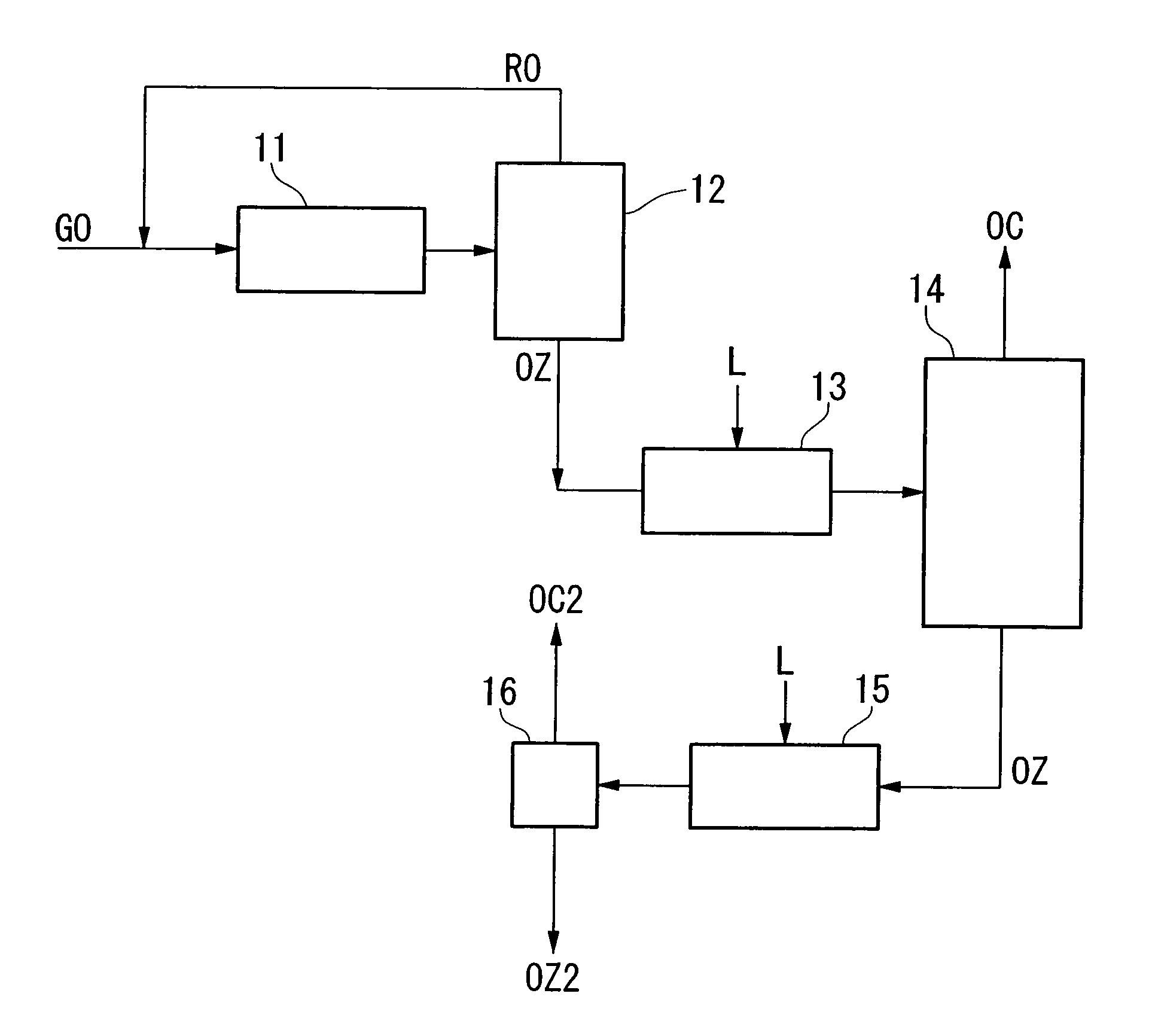
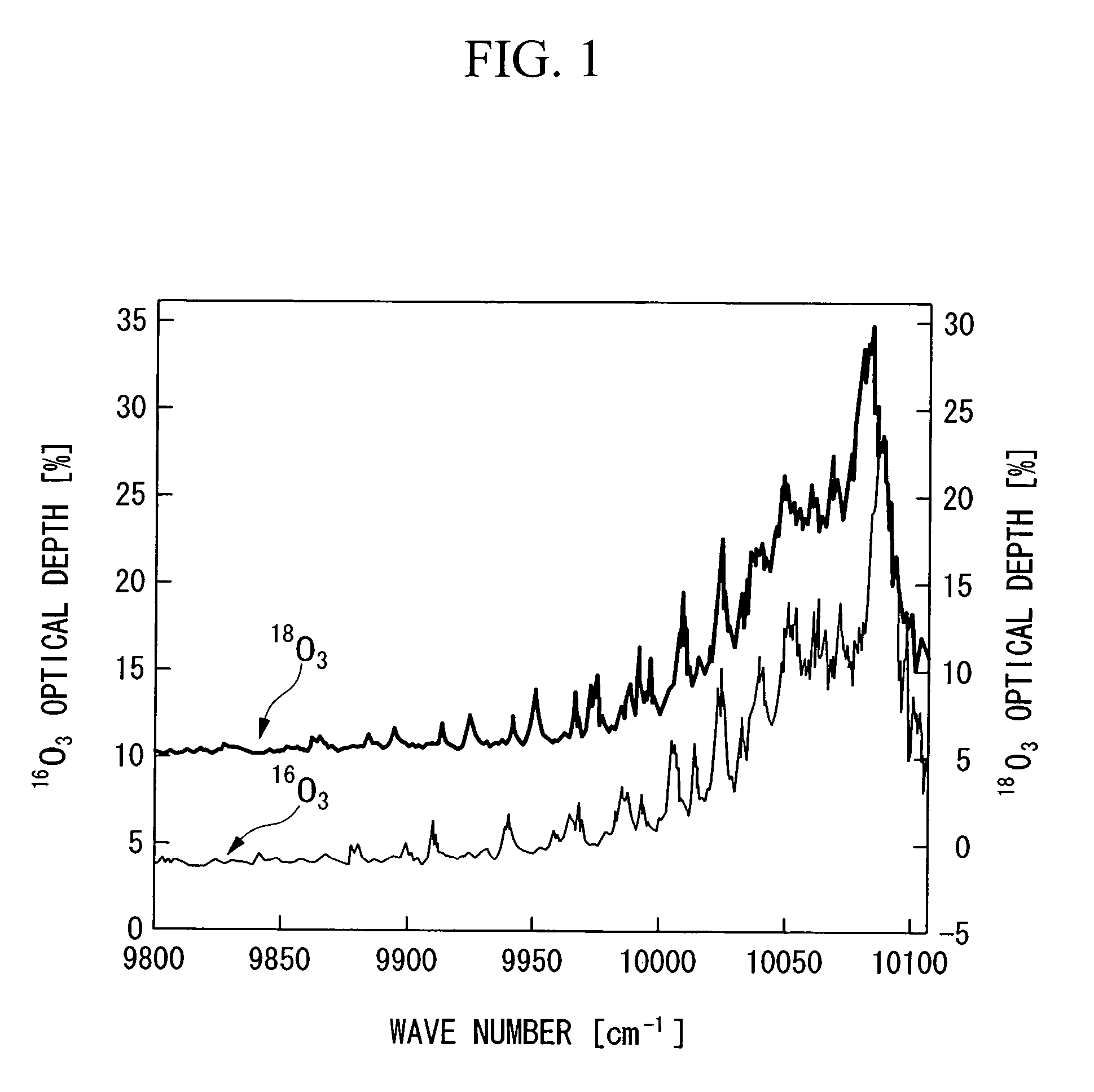
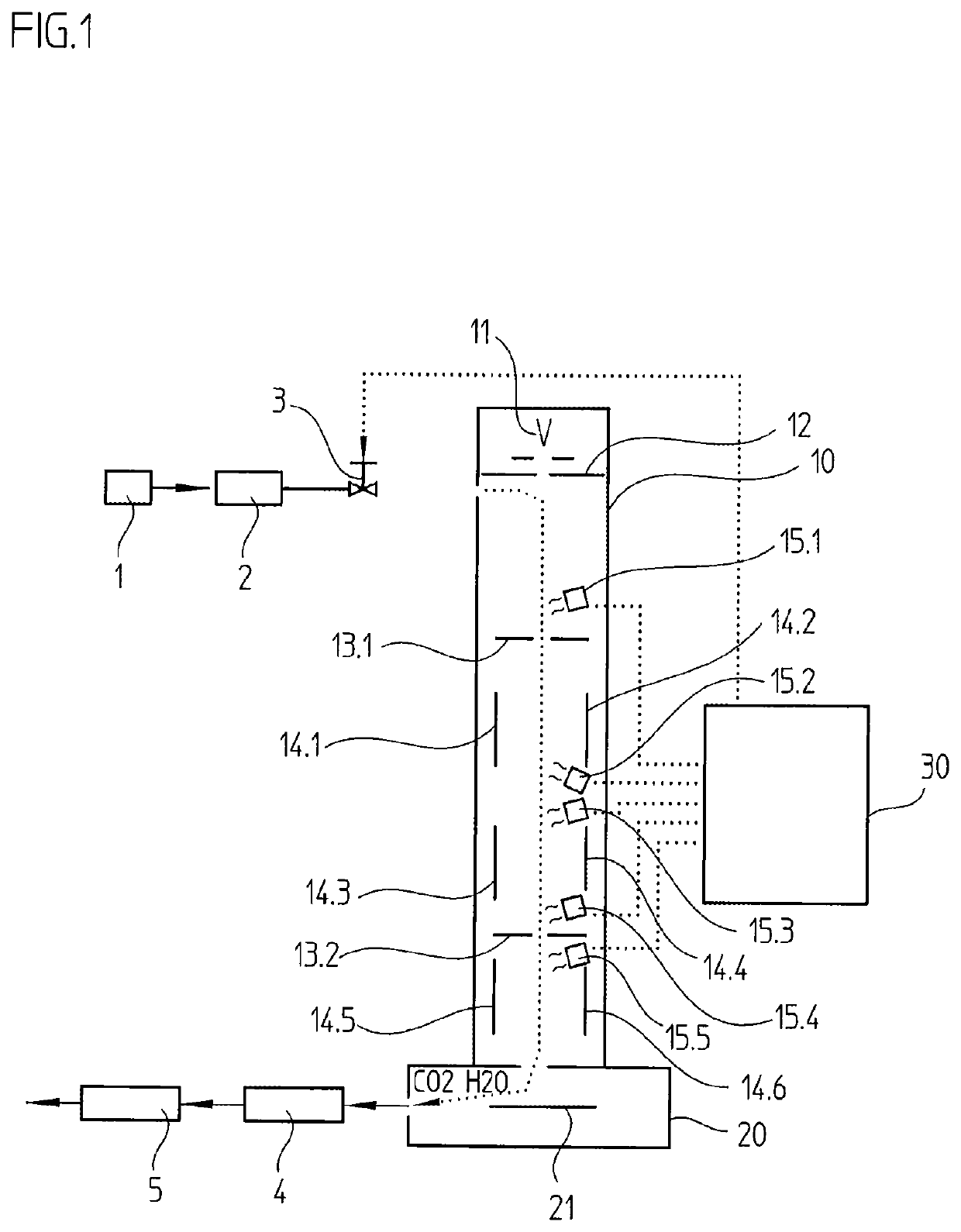
InactiveUS20060249366A1Increased concentration rateReduce ozone concentrationVapor condensationIsotope separationKryptonNoble gas
The object of the present invention is to provide an oxygen isotope concentration method capable of concentrating the stable oxygen isotopes of 17O and 18O which can be carried out using a simple device configuration. The present invention relates to a method for concentrating an oxygen isotope in separated oxygen by irradiating ozone with light, selectively dissociating an isotopomer of ozone containing an oxygen isotope in its molecule into oxygen, followed by dissociating the ozone and separating the formed oxygen from the non-dissociated ozone. The basic configuration of the device is provided with an ozone formation unit 11 that forms ozone from raw material oxygen, an ozone separation unit 12 that separates ozone formed with said ozone generation unit and raw material oxygen, an ozone photodissociation unit 13 that radiates light of a specific wavelength onto the ozone separated by said ozone separation unit 12 and selectively dissociates ozone containing an oxygen isotope in its molecule into oxygen, and an oxygen separation unit that separates the oxygen formed by dissociating ozone in said ozone photodissociation unit 13 and non-dissociated ozone to concentrate the oxygen isotope in the oxygen. The present invention also relates to a method for concentrating an oxygen isotope comprising an ozone photodissociation step, in which light is radiated onto a rare gas-ozone mixed gas containing ozone and at least one type of rare gas selected from krypton, xenon and radon to selectively dissociate ozone containing a specific oxygen isotope in its molecule into oxygen, and an oxygen isotope concentration step, in which the oxygen separated from ozone in said ozone photodissociation step is separated from non-dissociated ozone and rare gas to concentrate the oxygen isotope present in the separated oxygen. An oxygen isotope may also be concentrated in a dissociation reaction product by irradiating a gas containing a peroxide selected from hydroperoxides, (di)alkyl peroxides, peroxyacids including peracids, (di)acyl peroxides, peroxy esters, peroxycarbonates, peroxydicarbonates, diperoxycarbonates, peroxalates, cyclic peroxides, ozonides and endoperoxides, nitrite esters and nitrate esters, and selectively dissociating a peroxide containing a specific oxygen isotope in its molecule.
Owner:NIPPON SANSO CORP
Photodissociation Frame Window, Systems Including a Photodissociation Frame Window, and Methods of Using a Photodissociation Frame Window
An apparatus, method, and frame window configured to clean mesa sidewalls of a template with photodissociation radiation. Material on the mesa sidewalls are removed from the mesa sidewalls by exposing the portion of a first gap adjacent to the mesa sidewalls to the photodissociation radiation.
Owner:CANON KK
Reduction of chemical noise in a MALDI mass spectrometer by in-trap photodissociation of matrix cluster ions
InactiveUS7351955B2Less efficiently absorbedReduce noiseParticle separator tubesIsotope separationIon trap mass spectrometryAnalyte
A MALDI mass spectrometer includes a radiation source, such as a gas or solid state laser, that emits a beam of radiation (typically in the UV or IR wavelengths) directed along the central axis of a linear ion trap in which analyte ions and matrix cluster ions are confined. The radiation beam has a wavelength that is strongly absorbed by the matrix cluster ions. The absorption of radiation by the matrix cluster ions produces dissociation of the matrix cluster ion into fragments having mass-to-charge ratios that lie below a mass-to-charge ratio range of interest. Thus, chemical noise associated with matrix cluster ions is reduced or eliminated.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
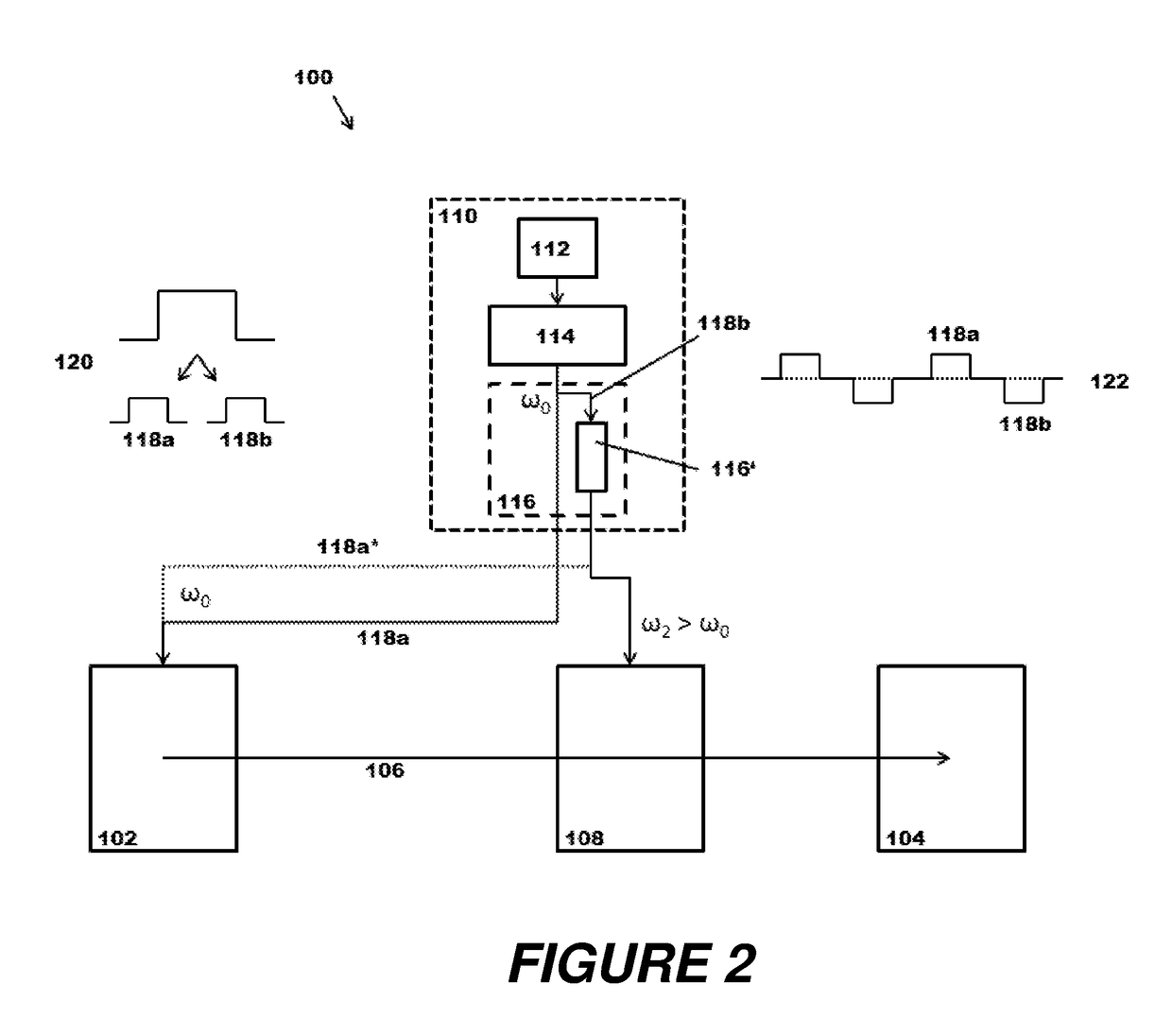
Mass spectrometer with laser system for producing photons of different energies
ActiveCN108206126ATime-of-flight spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsDesorptionPhotodissociation
The invention relates to mass spectrometers with optically pumped lasers, whose laser light can be used for ionization by laser desorption, for the fragmentation of ions by photodissociation (PD), forthe initiation of ion reactions, and for other purposes. The invention provides a laser system for a mass spectrometer, with which at least two laser beams of different wavelengths can be generated for use at different points along an ion path from an ion source to an ion detector in the mass spectrometer.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Mass spectrometer with laser system for producing photons of different energies
ActiveUS20180174815A1Price may become excessiveEasy to useTime-of-flight spectrometersIon sources/gunsDesorptionLaser light
The invention relates to mass spectrometers with optically pumped lasers, whose laser light can be used for ionization by laser desorption, for the fragmentation of ions by photodissociation (PD), for the initiation of ion reactions, and for other purposes. The invention provides a laser system for a mass spectrometer, with which at least two laser beams of different wavelengths can be generated for use at different points along an ion path from an ion source to an ion detector in the mass spectrometer.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Method and apparatus for generating thermal neutrons using an electron accelerator
InactiveUS8666015B2Conversion outside reactor/acceleratorsDirect voltage acceleratorsHigh energyPhotodissociation
Apparatus for generating thermal neutrons includes an electron accelerator for generating an electron beam and a converter for converting the electron beam into photons. A receiving device is provided for receiving the photons and includes a material which provides a photoneutron target for the photons, for producing high energy neutrons in a photonuclear reaction between the photons and the photoneutron target, and for moderating the high energy neutrons to generate the thermal neutrons. The electron beam has an energy level high enough to produce photons of sufficient energy to exceed the photodissociation threshold of the selected target material, but that is sufficiently low as to enable the material to moderate the high energy neutrons resulting from the photonuclear reaction.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Process and apparatus for the conversion of methane gas to higher hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20050189211A1Liquid hydrocarbon mixtures productionHydrocarbonsLiquid hydrocarbonsUltraviolet lights
A process and apparatus are provided for converting methane to higher hydrocarbons, especially for converting economically stranded natural gas to a transportable liquid hydrocarbon product mainly comprised of C3+ hydrocarbons, comprising applying ultraviolet light to methane (or to the natural gas containing the methane) under conditions effective to cause its photodissociation and polymerization to C2+ and higher hydrocarbons.
Owner:KERR MCGEE OIL & GAS CORP
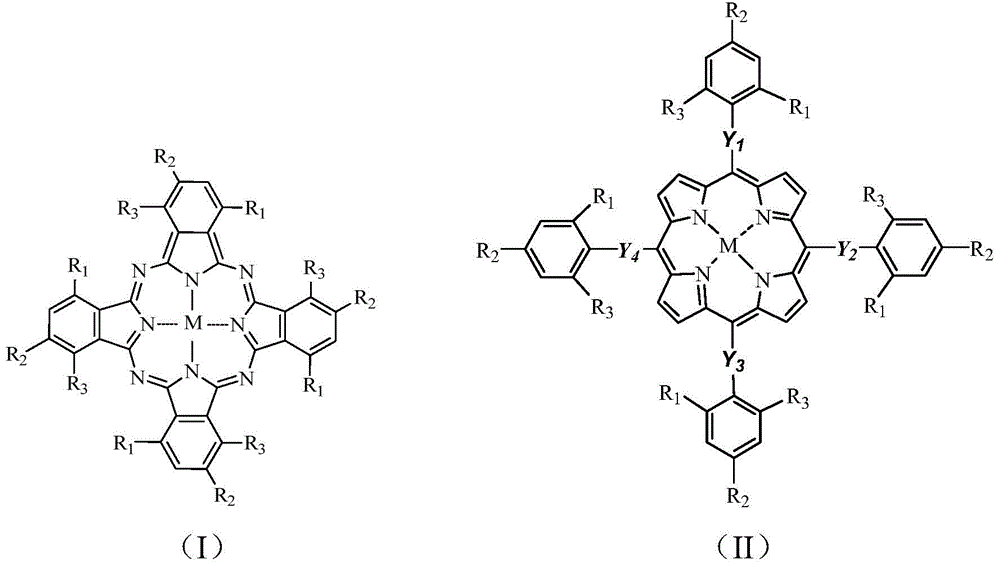
Catalyst and preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN110368999AImprove performanceEasy to makeMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrogenPhotodissociation
The invention relates to a catalyst and a preparation method and use thereof. The catalyst contains transition metal elements, a complex formed by a compound containing a group shown in a formula (I)and a carrier, the complex is dispersed on the carrier, the efficiency of hydrogen produced by water through catalytic photodissociation is up to 6.92 mmol / g / h, compared with a catalyst prepared by atraditional hydrothermal method, the activity of the catalyst is obviously improved, the preparation process of the catalyst is simple, the preparation process conditions are mild, and the hydrothermal and high-temperature calcination reaction conditions are not required.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Method for injecting low-energy electron treatment polluted water body into water
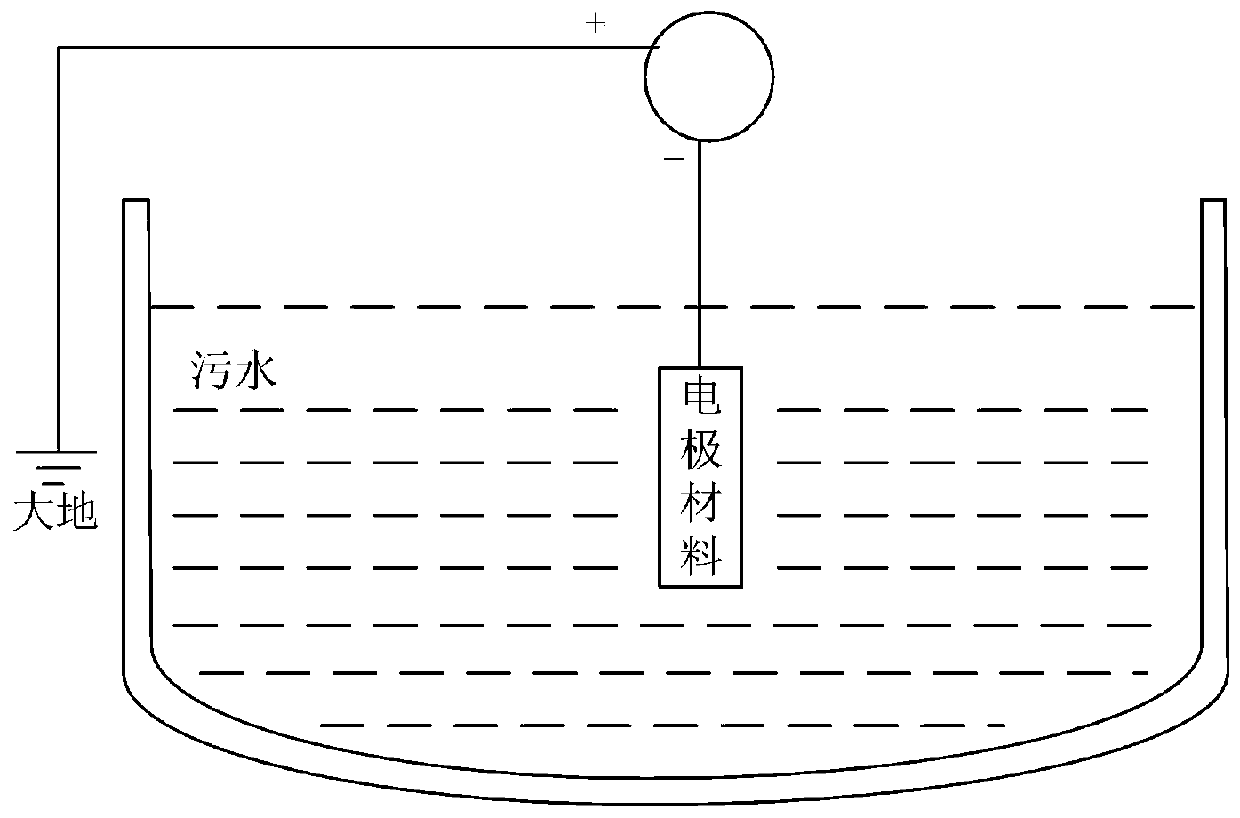
PendingCN110156109AEffective Pollution ControlImprove reliabilityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment by oxidationLow voltageEnvironmental engineering
The invention discloses a method for injecting a low-energy electron treatment polluted water body into water. A low voltage is applied to an electrode material in a water body, low-energy electrons are released from the electrode material, pollution complexes in the water body are gradually dispersed or dissociated under the induction action of negative electrons, and then the sizes of pollutantscan be gradually reduced through dispersion; the water body suffering from the induction action of the negative electrons is placed under sunshine, photolysis and photocatalysis are implemented through sunshine ration, the complexes can be further digested under the action of photolysis, and meanwhile, active dissolved oxygen is generated under the action of photocatalysis, so that pollutant components in a polluted water body can be reduced, and dissolved oxygen indexes can be increased to standard saturation concentrations or above. By adopting the method, the problem that toxic and harmfulpollutants in a conventional water body are not effectively treated can be solved.
Owner:上海金铎禹辰水环境工程有限公司
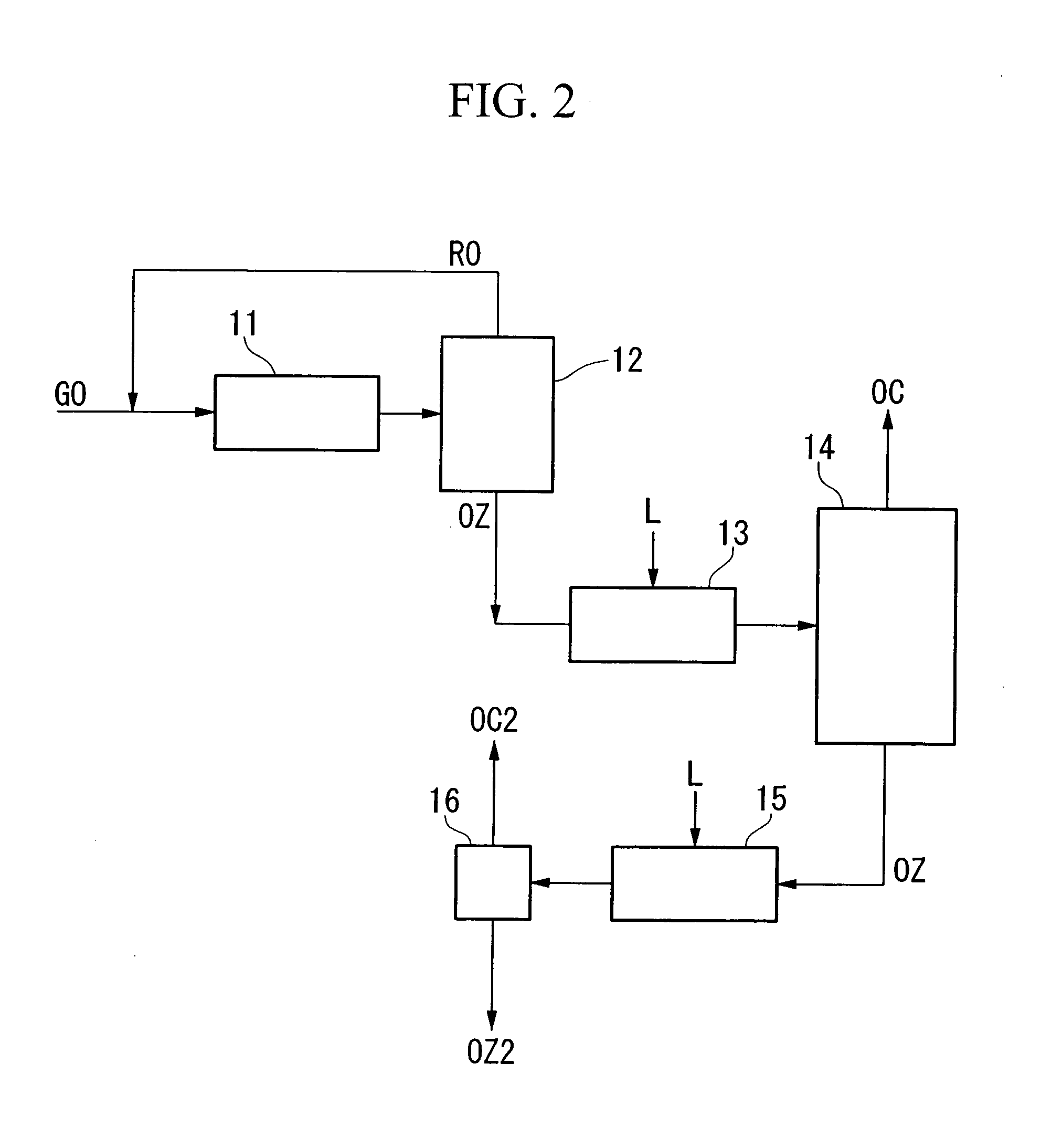
Method for concentrating oxygen isotope
A method of concentrating the stable oxygen isotopes of 17O and 18O by irradiating ozone with light, selectively dissociating an isotopologue of ozone containing an oxygen isotope in its molecule into oxygen, followed by dissociating the ozone and separating the formed oxygen from the non-dissociated ozone.In the ozone photodissociation step, light is radiated onto a rare gas-ozone mixed gas containing ozone and at least one rare gas selected from krypton, xenon and radon is used to selectively dissociate ozone containing a specific oxygen isotope in its molecule into oxygen then the oxygen isotope is separated from non-dissociated ozone and rare gas to concentrate the oxygen isotope present in the separated oxygen.
Owner:NIPPON SANSO CORP
Camptothecin preparation capable of inhibiting organism endothelial cell differentiation, and application
InactiveCN103688957AInhibition of differentiationDelayed photolysisBiocideNematocidesActive componentPhotodissociation
The invention discloses a camptothecin preparation capable of inhibiting organism endothelial cell differentiation, and an application, and belongs to the technical field of plant source pesticides. The camptothecin preparation is characterized by comprising 0.5-2.3% of camptothecin extract dry powder, 1.2-5.3% of inorganic base, 82-97% of solvent, 0.7-2.1% of synergist and 1-5% of stabilizer. According to the camptothecin preparation capable of inhibiting the organism endothelial cell differentiation, and the application, a substance after a camptothecin extract reacts with the inorganic base serves as an active component, a certain synergistic component and a certain stabilizing component are added, and the obtained preparation participates in a process of inhibiting the organism endothelial cell differentiation, so that growth and development of injurious insects are inhibited; when the camptothecin preparation serves as a pesticide in a field, photodissociation and loss of the active component in an environment can be reduced, the biological activity can be exerted enduringly, and effects of organism endothelial cell differentiation inhibition and field disease and insect damage control are exerted; and the camptothecin preparation is convenient to prepare, low in cost, stable in effect, and less in dosage.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
A photolysis reaction method of benzothiophene compounds for oxidative desulfurization
ActiveCN104277870BIncrease polaritySettle the lossHydrocarbon oils refiningHydrocarbon oils treatmentPetroleum productPorphyrin
The invention discloses a photodissociation method of a benzothiophene compound for oxidative desulfurization. According to the method, the benzothiophene compound reaches C-S bond fracture reaction under the existence of an oxidizing agent and metal phthalocyanine or metalloporphyrin through illuminating reaction. According to the method disclosed by the invention, under the mild conditions of normal temperature and pressure, the most stable sulfide, namely the benzothiophene compound in an oxidized petroleum product reaches the C-S bond oxidation fracture in the benzothiophene compound, so as to obtain a sulfocompound with relatively strong polarity and sulfur-free hydrocarbon oxide. The conversion ratio of the C-S bond fracture reaches over 90% when metalloporphyrin is a catalyst, and the problems that the C-S bond oxidation fracture reaction in the benzothiophene compound at present needs high temperature, high pressure and a special catalyst, and is high in demands on equipment, and low in productive rate are overcome.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
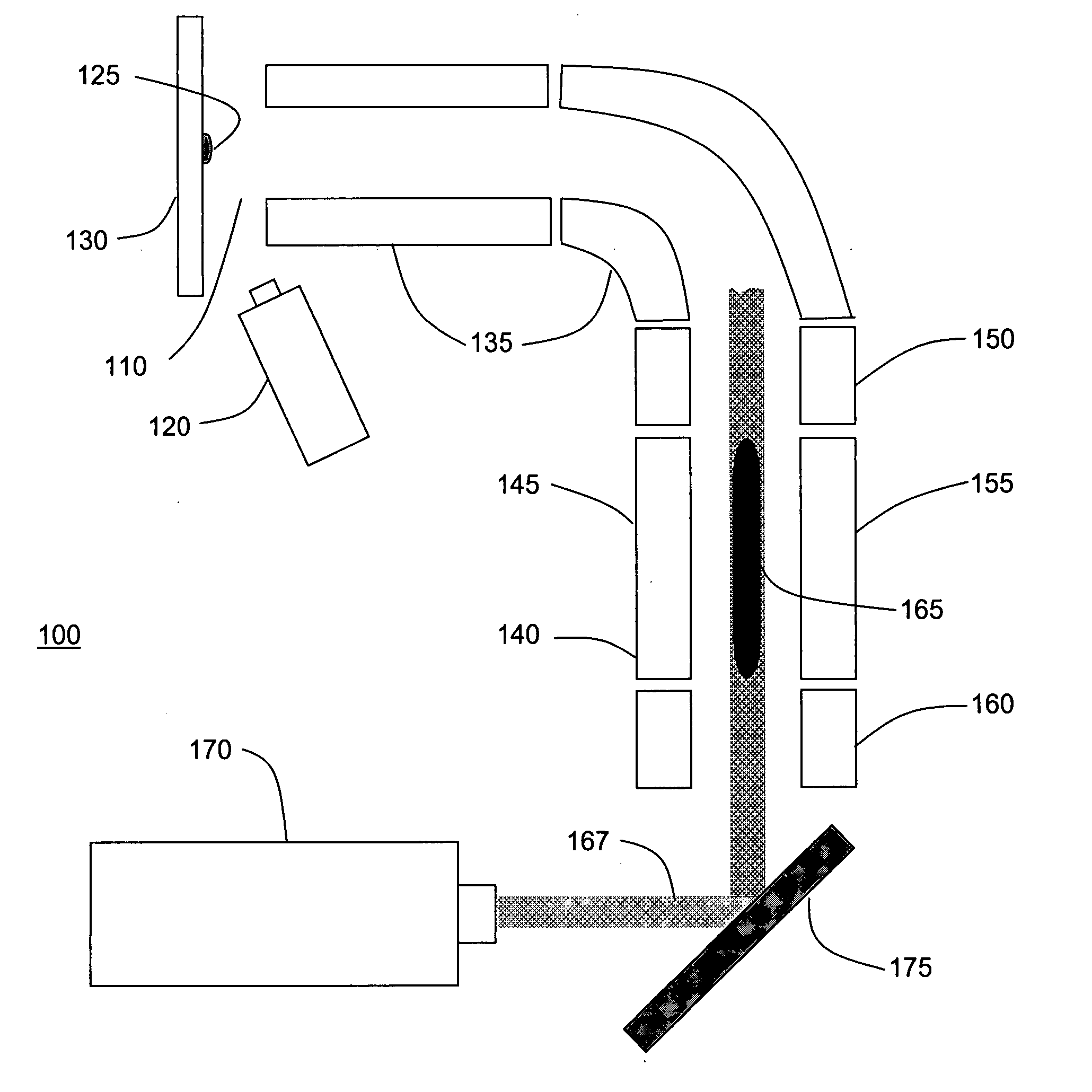
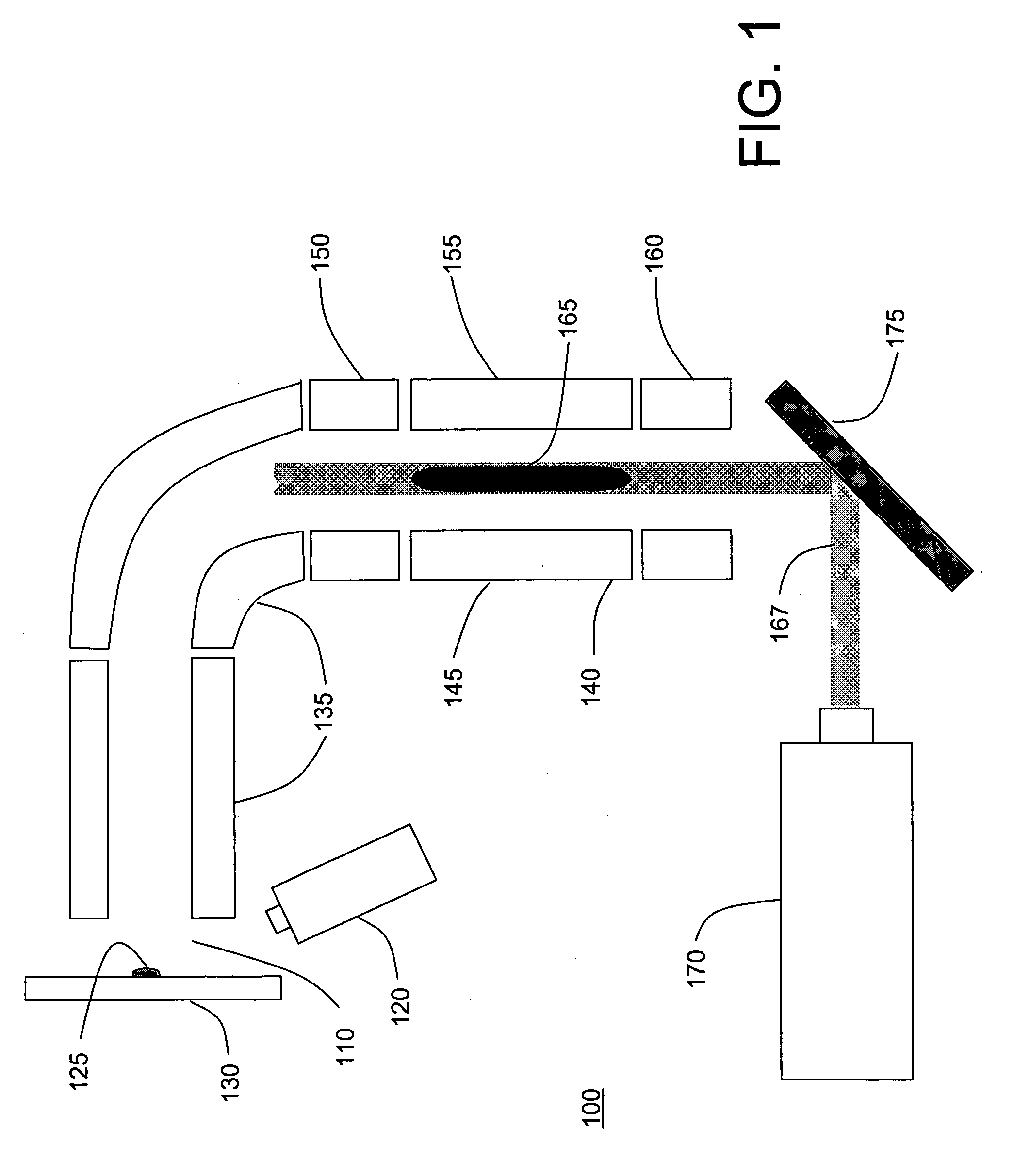
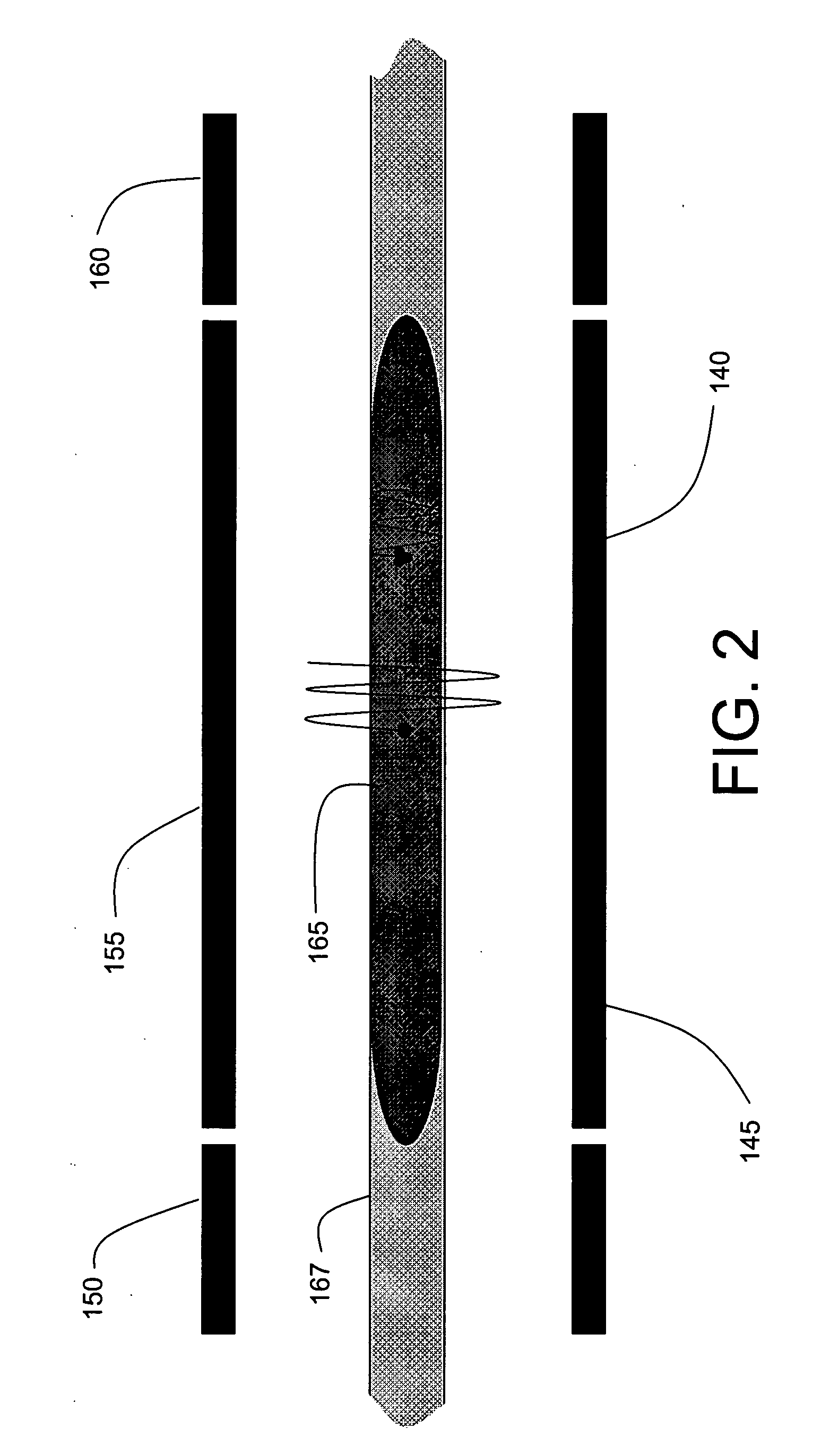
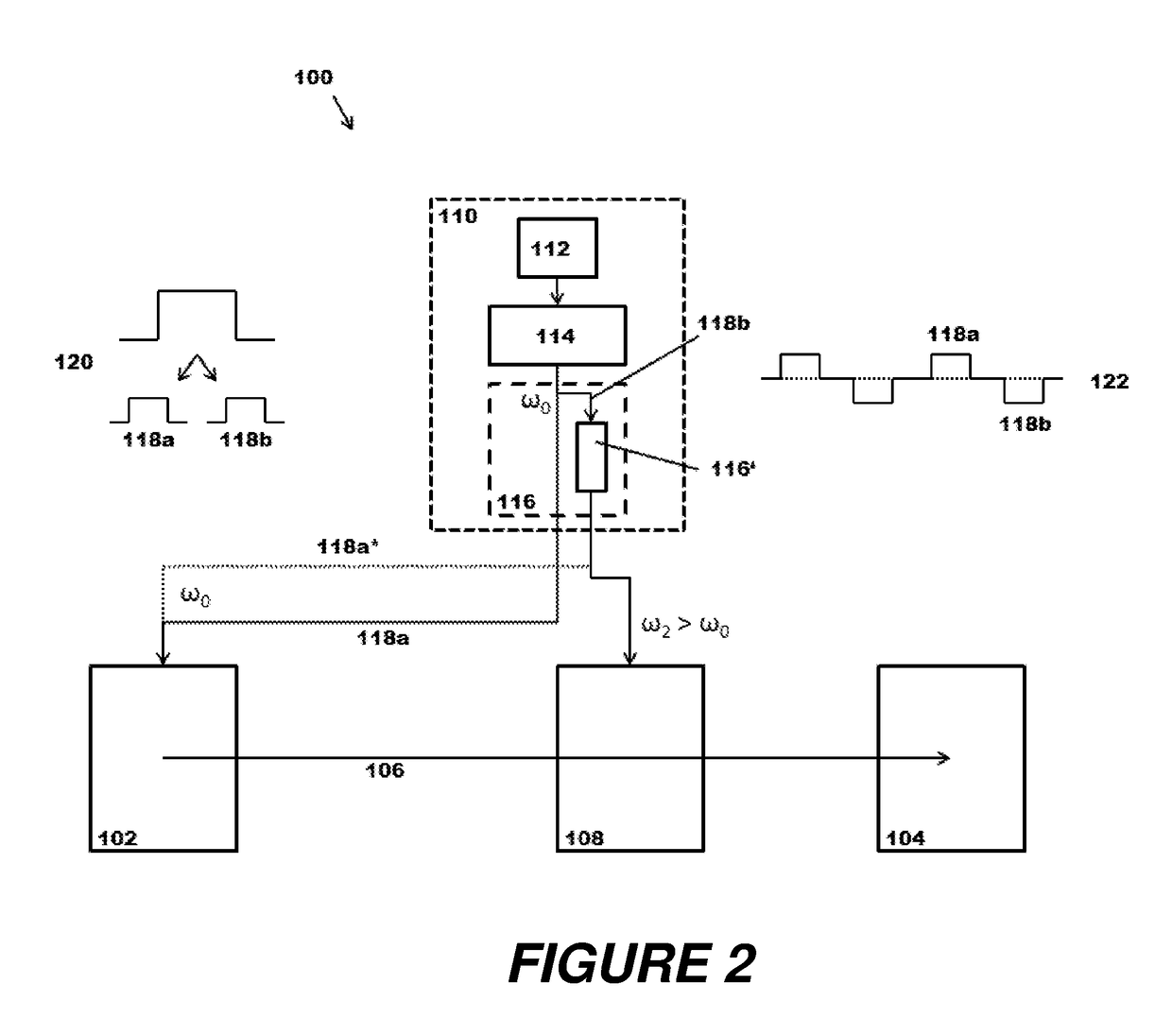
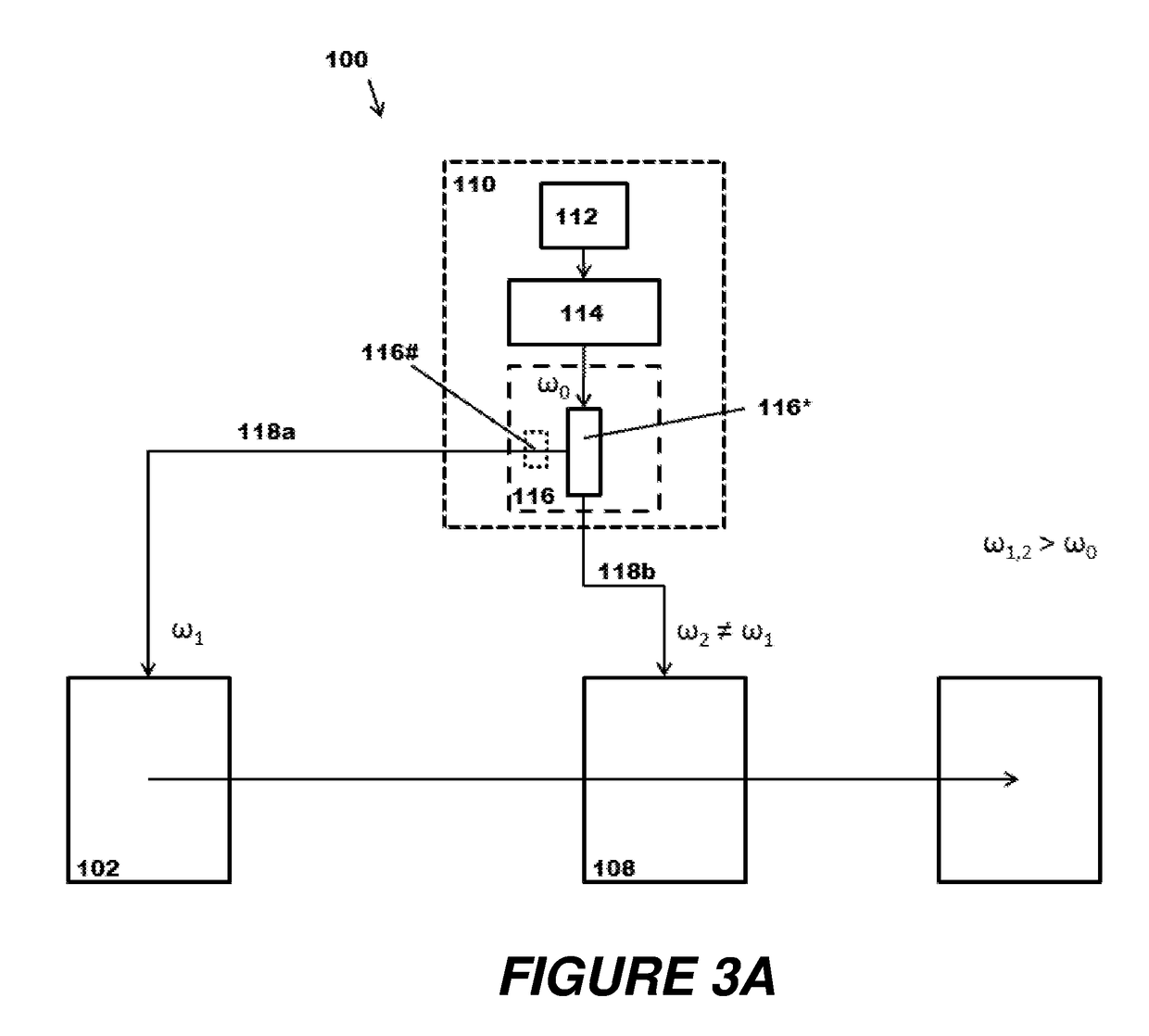
Methods of Ultraviolet Photodissociation for Mass Spectrometry
ActiveUS20180190481A1High molecular weightWide coverageMass spectrometersMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryPhotodissociation
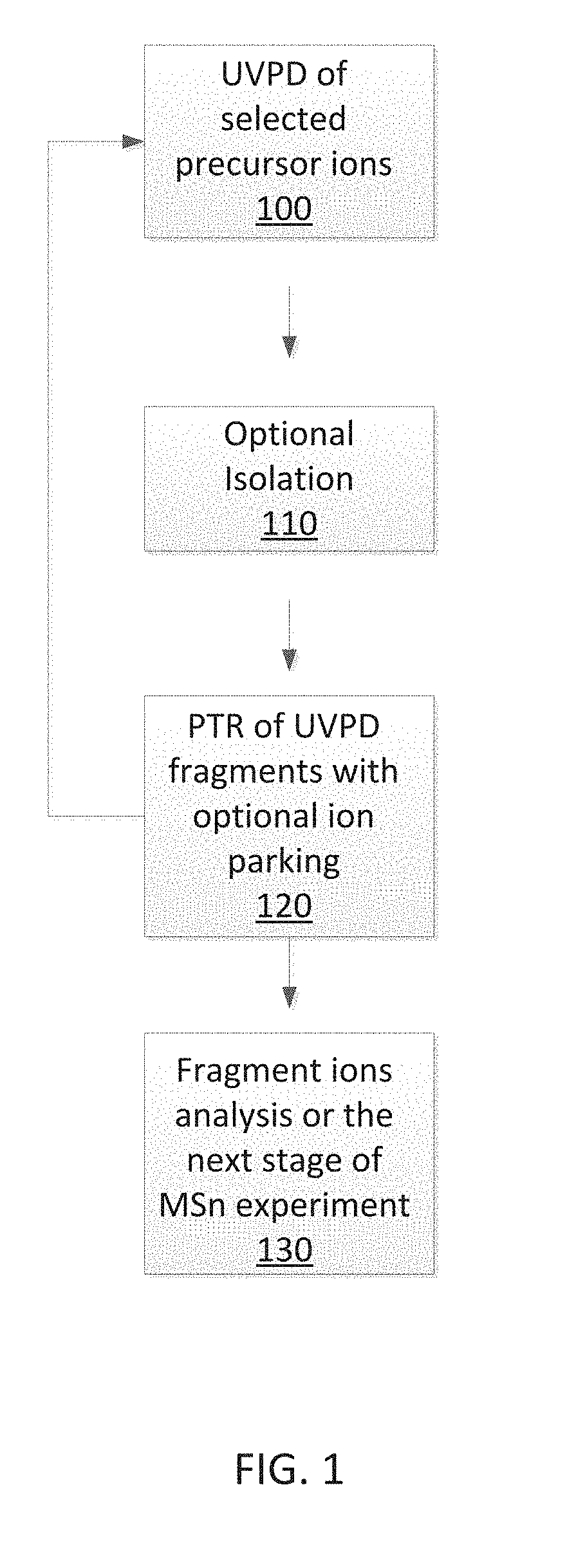
A method is described that involves simplification of UVPD mass spectra and comprises selecting precursor ions for UVPD fragmentation, performing UVPD fragmentation on selected precursor ions to give UVPD fragment ions. PTR may then be performed on the UVPD fragment ions with optional ion parking to yield charge-state reduced UVPD fragment ions. The UVPD-PTR steps may be repeated above n times where n=1 to 50. Ion parking may enhance the intensity of selected lower fragment ion charge states or to increase the intensity of peaks in selected m / z ranges. After a number of PTR-UVPD iterations, fragment ions are mass analyzed. The method provides a way of simplifying UVPD mass spectral product ions by lowering fragment ion charge states and spreading out resulting product ions in m / z mass spectral space when compared to using UVPD fragmentation alone.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
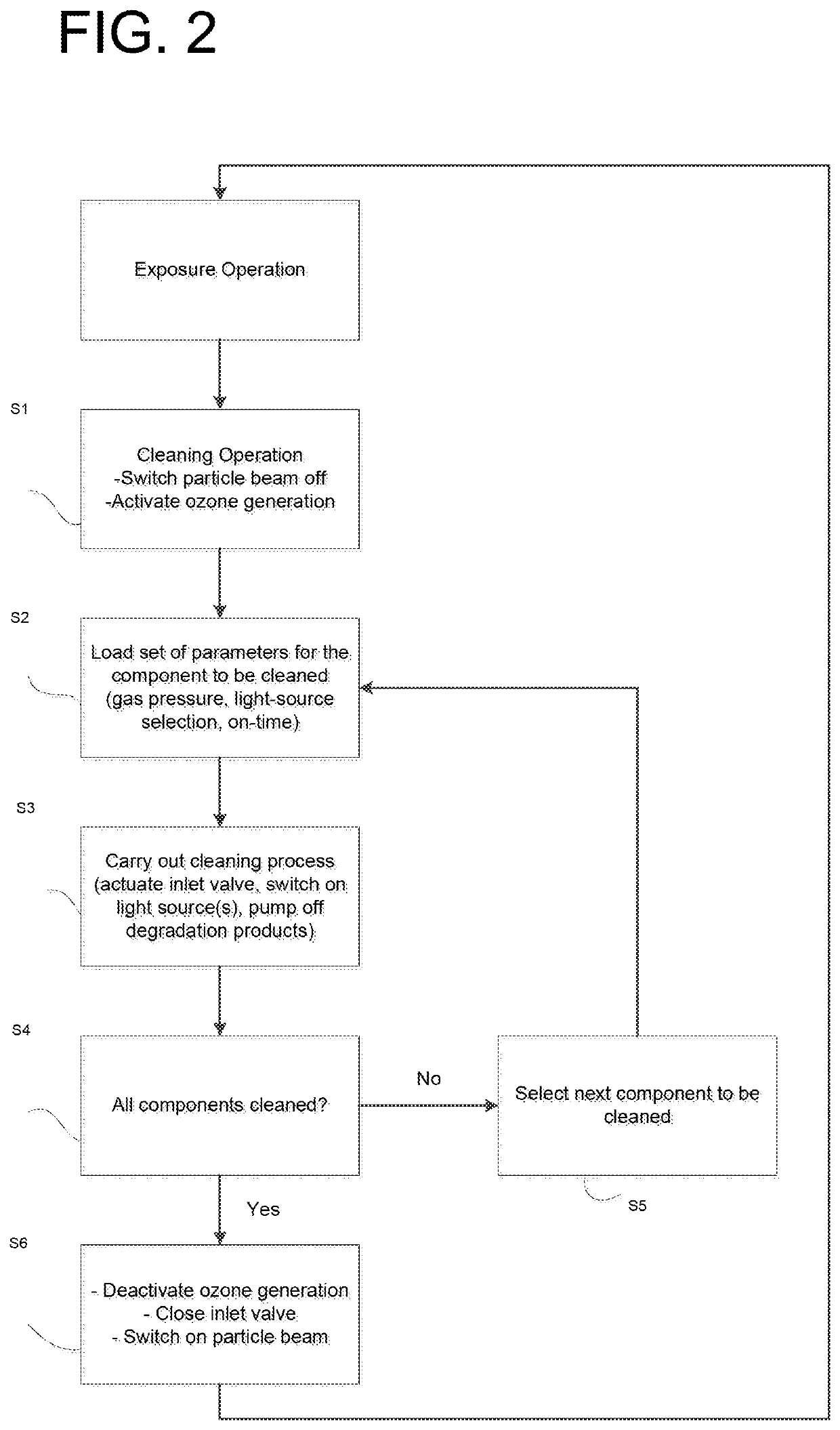
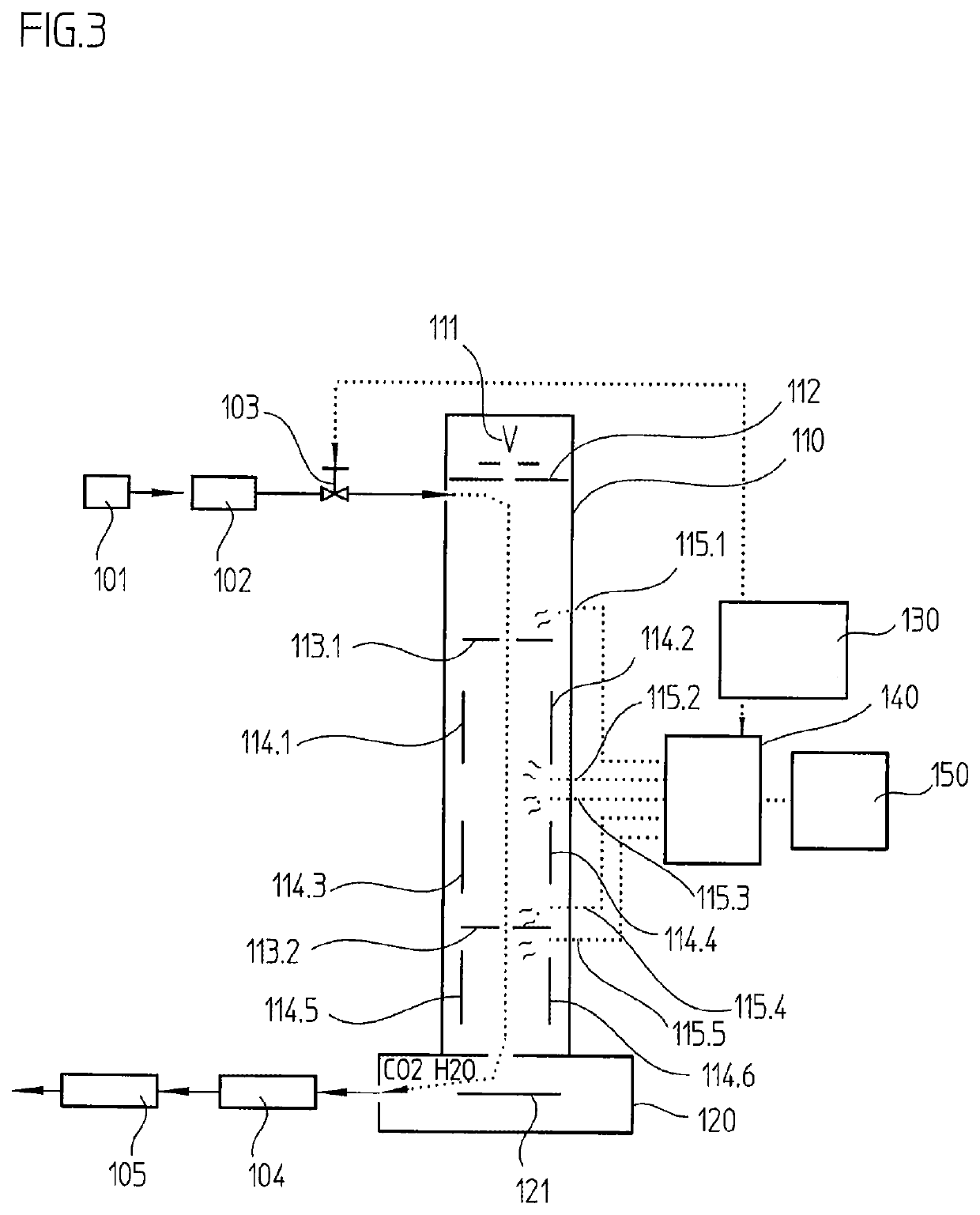
Particle beam apparatus and method for operating a particle beam apparatus
ActiveUS10814361B2Shorten the timeStress minimizationElectric discharge tubesCleaning using gasesParticle beamControl cell
In a particle beam apparatus and a method for operating a particle beam apparatus, the particle beam apparatus has a column having a particle-beam optical system for generating a particle beam, to thereby expose a desired pattern in a vacuum sample chamber in an exposure operation. In a cleaning operation, a regulable gas stream having photodissociatable gas is fed to the column and / or the vacuum sample chamber via a gas-feed system. The photodissociation of the supplied gas is brought about in the cleaning operation with the aid of a plurality of light sources distributed spatially in the column and / or in the vacuum sample chamber. In the cleaning operation, individual light sources are able to be switched on and off selectively with respect to time via a control unit connected to the light sources, in order to clean individual elements in the column and / or in the vacuum sample chamber in targeted fashion.
Owner:VISTEC ELECTRON BEAM
Drying method of hot peppers
InactiveCN105285065AMaintain colorRed colorClimate change adaptationFruits/vegetable preservation by dehydrationHot peppersEngineering
The invention discloses a drying method of hot peppers. The drying method comprises the following steps of S1, selecting clean complete fresh hot peppers; S2, performing one-stage baking: putting the selected hot peppers in a hothouse, and setting the temperature to 70-73 DEG C and the baking time to 4 hours; S3, putting the hot peppers after one-stage baking at an adumbral outdoor ventilated place to be spread for airing so that the inside and the outside of the hot peppers maintain balanced water, wherein the time for spreading the hot peppers for airing is 5-6 hours; S4, performing two-stage baking: putting the aired hot peppers in an airtight room, and opening hot blast for baking the hot peppers; and S5, putting the hot peppers after the two-stage baking in a bamboo basket, and placing the hot peppers in the bamboo basket under natural conditions for 1 day. The hot peppers which are baked and processed by the method disclosed by the invention are not easy to generate charring caused by high temperature, red brilliant color of the hot peppers can be maintained, and the photodissociation reaction of capsanthin is not easy to produce, so that the appearance and the nutrient components of the hot pepper can be guaranteed at the same time.
Owner:富川富兴果蔬有限责任公司
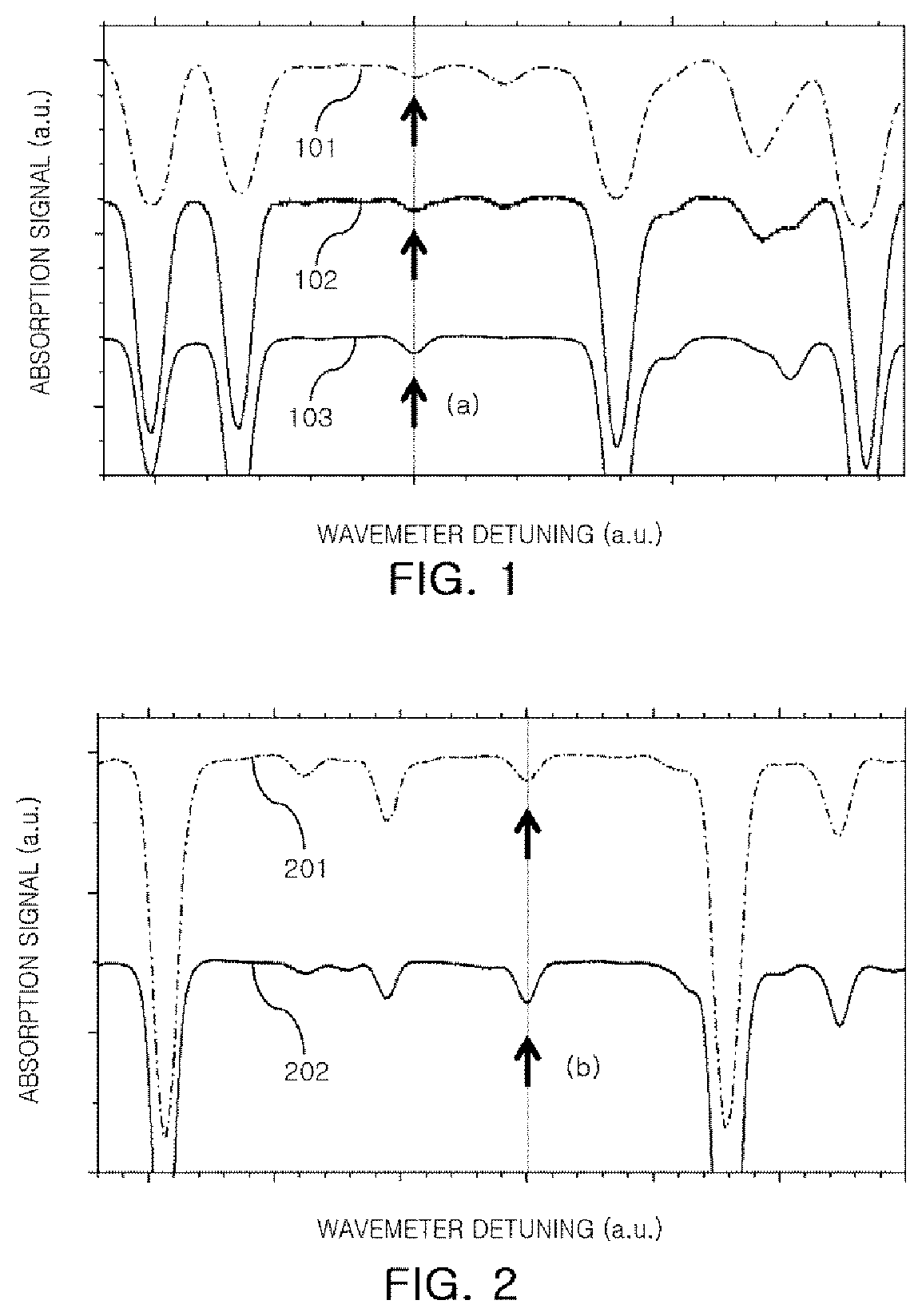
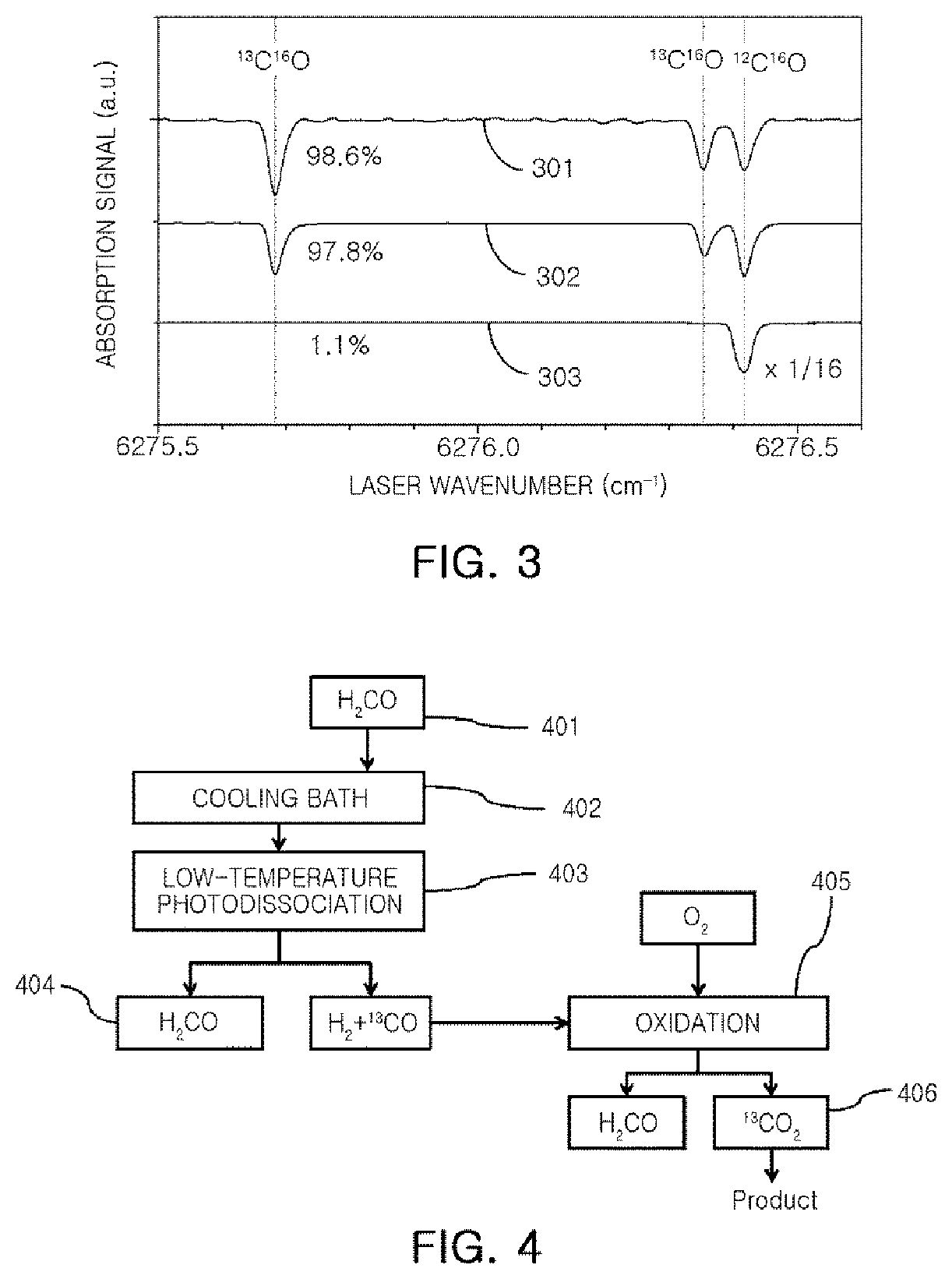
Method for separating carbon isotope and method for concentrating carbon isotope using the same
The present disclosure relates to a method for separating a carbon isotope and a method for concentrating a carbon isotope using the same, the method for separating a carbon isotope including: cooling a formaldehyde gas to a temperature of from 190K to 250K; and obtaining a mixed gas and residual formaldehyde by photodissociating the cooled formaldehyde gas, the mixed gas including carbon dioxide containing a carbon isotope and hydrogen.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
Method for producing transparent conducting film glass
The invention discloses a method for producing transparent conducting film glass. The method comprises the following steps: (1) introducing a gaseous-state shielding layer precursor containing silane and an oxygen source to the glass surface at a temperature ranging from 460 to 480 DEG C by taking an inert gas as a carrier in an annealing kiln, carrying out photodissociation of the gaseous-state shielding layer precursor by use of a parallel incident laser beam and thus carrying out a chemical vapor reaction to form a shielding layer which is 50-90nm thick on the glass surface; (2) in the annealing kiln and in the glass temperature range of 435-455 DEG C, introducing a gaseous-state conducting layer precursor containing pre-gasified zinc and aluminum sources and the oxygen source to the glass surface on which the shielding layer is already deposited by taking the inert gas as the carrier, and causing the photodissociation of the gaseous-state conducting layer by use of the parallel incident laser beam and thus carrying out the chemical vapor reaction to form a conducting layer which is 250-400nm thick on the glass surface. The method has the advantages that the temperatures of the coating reactions are effectively reduced so that the quality of the film can be improved, and the utilization rate of the precursor gases is increased so that the working conditions of a float line can be kept stable.
Owner:(CNBM) BENGBU DESIGN & RES INST FOR GLASS IND CO LTD +1
Mass spectrometer with laser system for producing photons of different energies
ActiveUS10236173B2Price may become excessiveEasy to useTime-of-flight spectrometersIon sources/gunsDesorptionLaser light
The invention relates to mass spectrometers with optically pumped lasers, whose laser light can be used for ionization by laser desorption, for the fragmentation of ions by photodissociation (PD), for the initiation of ion reactions, and for other purposes. The invention provides a laser system for a mass spectrometer, with which at least two laser beams of different wavelengths can be generated for use at different points along an ion path from an ion source to an ion detector in the mass spectrometer.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
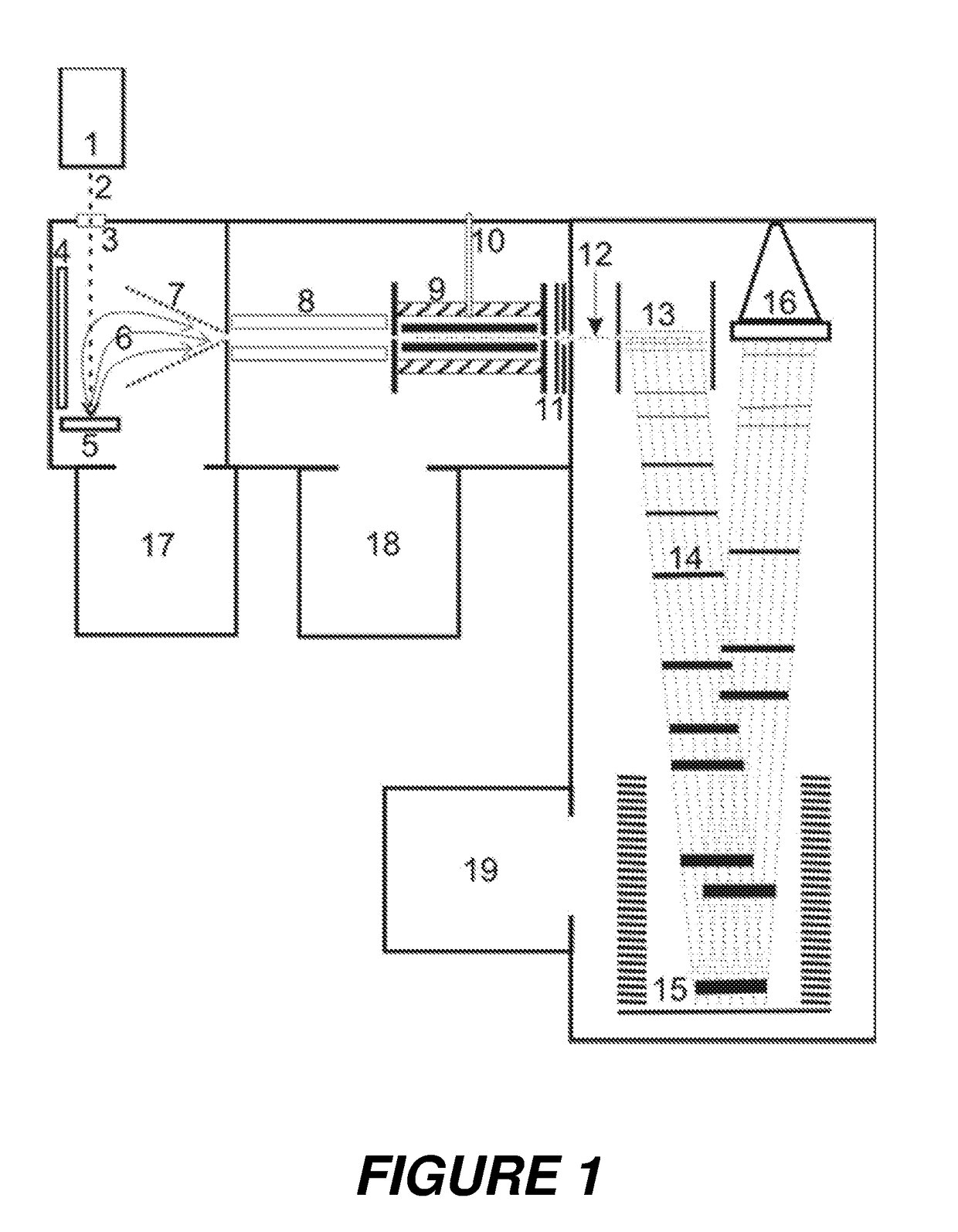
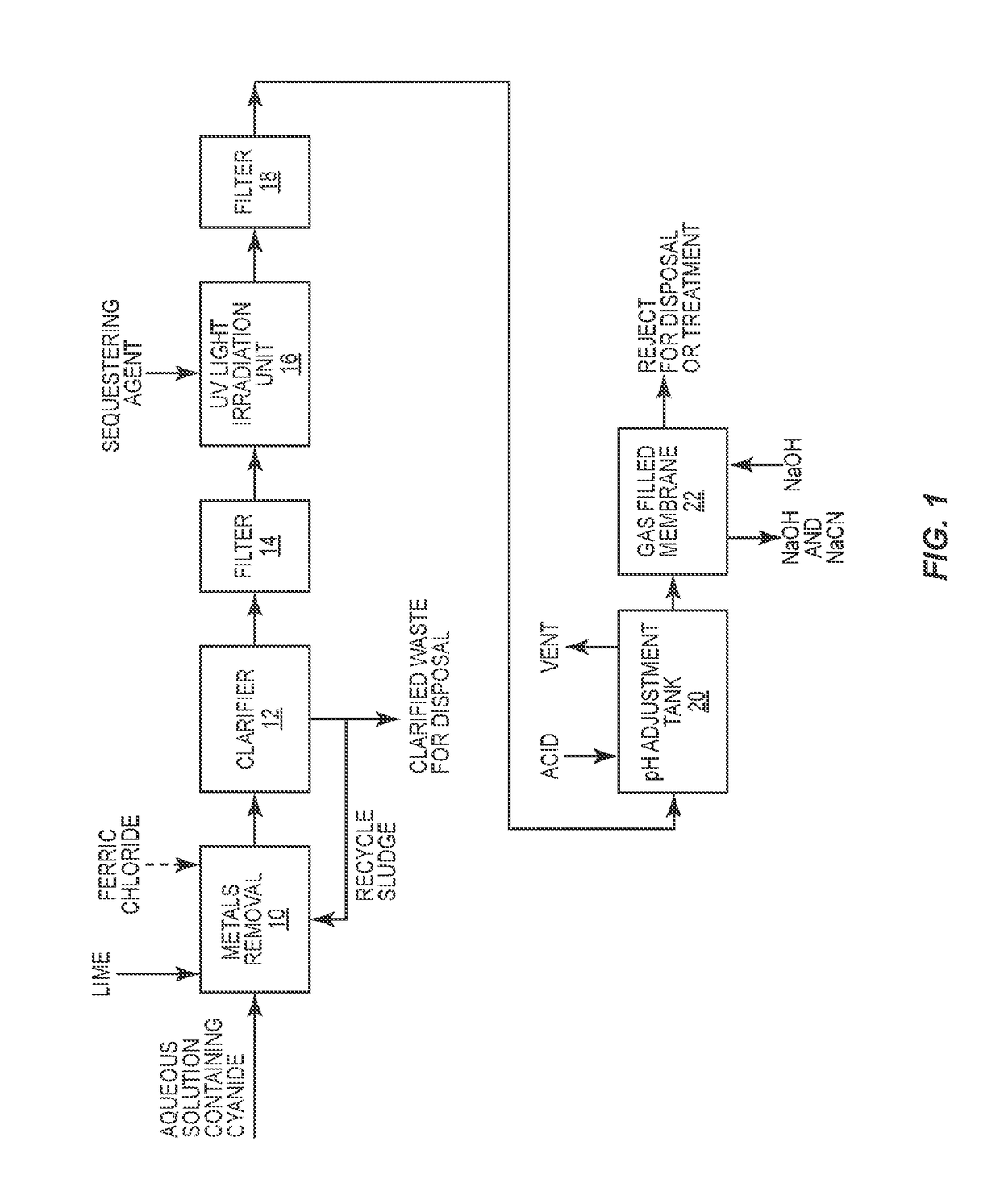
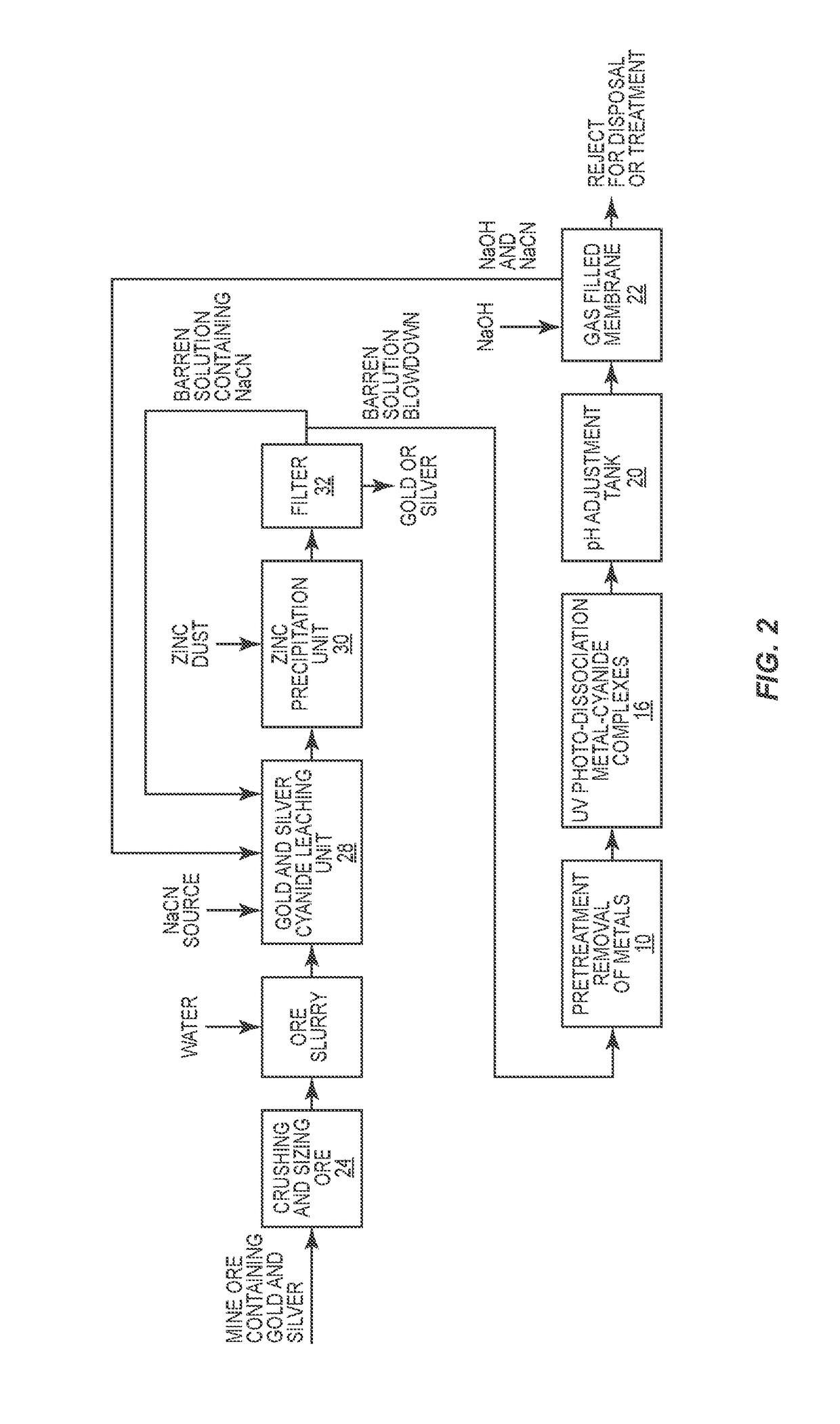
Method for recovering cyanide from a barren solution
A process is disclosed for recovering cyanide used to leach gold or silver from ore. In the course of leaching gold or silver from ore, a barren solution is generated. A portion of the barren solution containing sodium cyanide is recycled to the cyanidation process while blowdown from the barren solution is subjected to pre-treatment, UV photodissociation and pH adjustment. Ultimately, a volatile hydrocyanic acid is formed and is absorbed into a sodium hydroxide solution through the employment of a gas-filled membrane. This forms sodium cyanide that can be recycled and used in the cyanidation process to leach gold or silver from ore.
Owner:VEOLIA WATER SOLUTIONS & TECH SUPPORT
Sunscreen lotion and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108852964AEvenly distributedAvoid enteringCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSunscreen agentsActive agent
The invention discloses sunscreen lotion and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of cosmetic production. According to the preparation method, arabinoxylan is used as a raw material to obtain an anti-ultraviolet (UV) light active agent, so that molecules are enabled to have a higher ultraviolet absorption capacity in a UVB band, the sunscreen lotion is strong in ultraviolet absorption in a range of 250-320nm, good in light stability and higher in safety factor to the skin, and the irritation is greatly reduced; a stable emulsifying active agent, formed by carrying outhydrogenation on lecithin in presence of a Pd / C catalyst, can play roles of moisturizing, emulsifying and dispersing, resisting oxidation, and the like; the emulsifying active agent can also be usedas a surfactant and can also be used for conditioning the skin; cortex magnoliae officinalis, phyllostachys pubescens leaves and herba speranskiae tuberculatae are added into the sunscreen lotion, sothat the shelf life of the sunscreen lotion is prolonged, the safety performance of the sunscreen lotion is improved, and the problem that the protective effect of a sun-screening agent is reduced byphotodecomposition, so that sunscreen products need to be repeatedly applied within a short time can be solved. The sunscreen lotion provided by the invention solves the problems that the existing sunscreen lotion is high in irritation, easily causes allergy, and is poor in moisturizing effect on the dry skin after being applied.
Owner:袁杰
A method of producing transparent conductive film glass
The invention discloses a method for producing transparent conductive film glass, which comprises the following steps: (1). In an annealing kiln, a gaseous shielding layer precursor containing silane and an oxygen source is used as a carrier with an inert gas, and the temperature is On the glass surface at 460-480 ℃, use the parallel incident laser beam to make the gaseous shielding layer precursor photodissociate and undergo a chemical gas phase reaction, and deposit a shielding layer with a thickness of 50-90nm on the glass surface; (2). After annealing In the kiln, the glass temperature is within the range of 435-455 °C, and the gaseous conductive layer precursor containing the prefabricated vaporized zinc source, aluminum source, and oxygen source is passed into the glass layer on which the shielding layer has been deposited. On the glass surface, the laser beam is incident in parallel to cause the photodissociation of the precursor of the gaseous conductive layer to undergo a chemical gas phase reaction, forming a conductive layer with a thickness of 250-400nm on the glass surface. The invention effectively reduces the temperature of the coating reaction, is beneficial to improving the quality of the film, improving the utilization rate of the precursor gas, and is beneficial to the stability of the working condition of the float line.
Owner:(CNBM) BENGBU DESIGN & RES INST FOR GLASS IND CO LTD +1
Preparation method of alkali metal tantalate composite visible-light photocatalyst for hydrogen production from photodissociation of water
InactiveCN101474558BAchieve dopingIt can be seen that the absorption is goodHydrogen productionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsNitrogen dopedHeat treated
The invention relates to a preparation method for an alkali tantalate based composite visible-light photocatalyst in hydrogen production by water splitting, in particular to a method that ammonia is used as the nitrogen source to perform nitrogen doping on the alkali tantalate at high temperature. The method has the following steps: (1) dissolving the tantalum-containing precursor in the surfactant acidic solution to produce a uniform tantalum salt solution; (2) adjusting the PH value to 6-9 and adding the hydroxide of an alkali metal to produce a suspension; (3) water-heating the produced suspension in a reaction kettle to produce the alkali tantalate crystal and (4) treating the crystal with the ammonia to produce the alkali tantalate, and then obtaining the nitrogen doped alkali tantalate. The photocatalyst treats the alkali tantalate by high-temperature ammonolysis, which realizes nitrogen doping to the alkali tantalate. The experiment shows that the alkali tantalate is nitrogen doped in the preparation process which has good visible light catalysis and solves the problem of nitrogen doping to the alkali tantalate.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing nano-micro level sun-screening agent with emulsification function
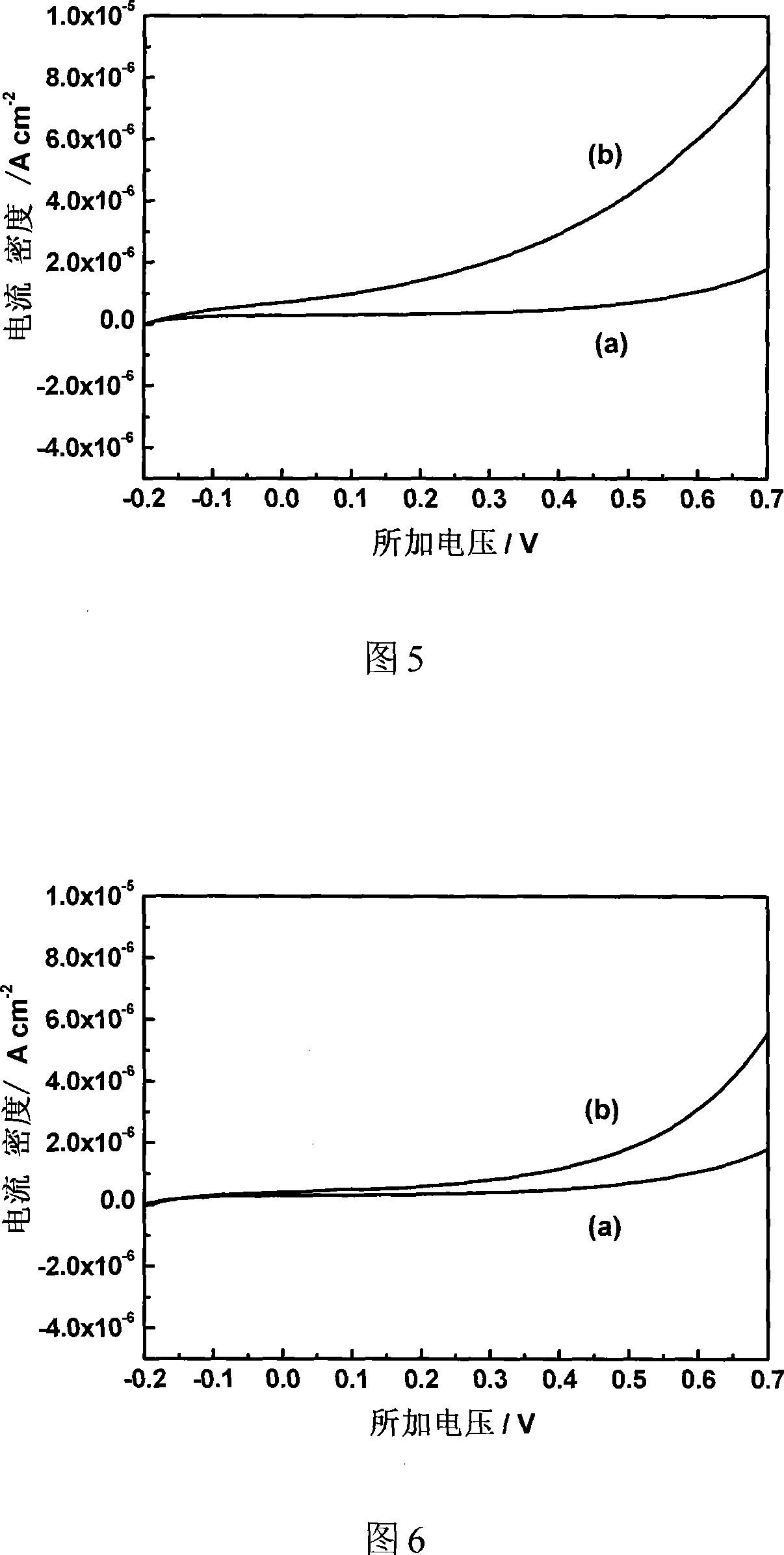
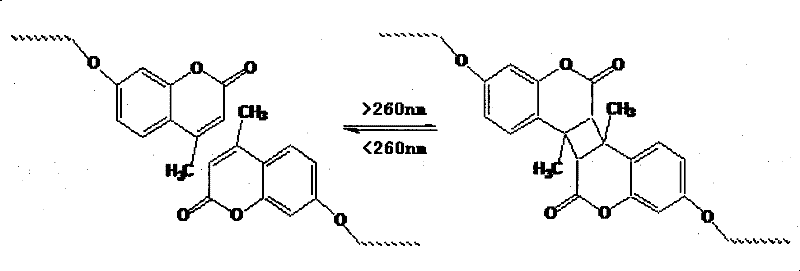
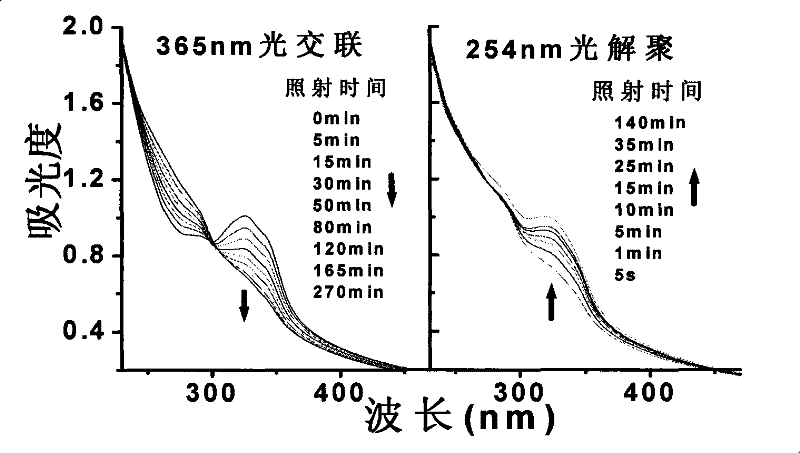
InactiveCN101313882BGreat absorptionImprove absorption rateCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsScreening effectUltraviolet
The invention relates to a preparation method for a nano and micro sun-screening agent with emulsifying function, belonging to the photosensitive amphiphilic copolymer micelle particle preparation technical field. The method prepares the photosensitive amphiphilic copolymer micelle particle which integrates the emulsifying and sun-screening effects through self-assembly of photosensitive amphiphilic copolymer. The micelle diameters are in the nanometer range, the micelle particle can effectively absorb ultraviolet between 270 and 350 nm for photocrosslinking reaction, and can absorb the ultraviolet again when the ultraviolet is less than 260 nm after photodissociation. The micelle particle can be used as the macromolecular sun-screening agent and has the advantages of low toxicity, low permeability, good skin affinity and feeling. The copolymer micelle is not only provided with photosensitive units but also provided with hydrophilic / lyophobic microdmain, can also reduce the tension ofoil-water boundary, and has the emulsifying function. The preparation method has easily obtained monomers, simple reaction conditions and high yield, can control the macromolecular micelle particle through the self-assembly technology, and has potential application value in the cosmetics and washing product field when added with the monomers provided with functional groups.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com