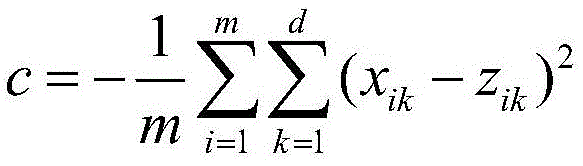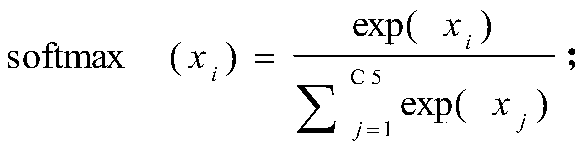Patents
Literature
88 results about "Spectral space" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, a spectral space (sometimes called a coherent space) is a topological space that is homeomorphic to the spectrum of a commutative ring.
Multi-object tracking method and device driven by characteristic trace
InactiveCN101944234AImprove performanceImprove reliabilityImage enhancementImage analysisTime domainMulti target tracking
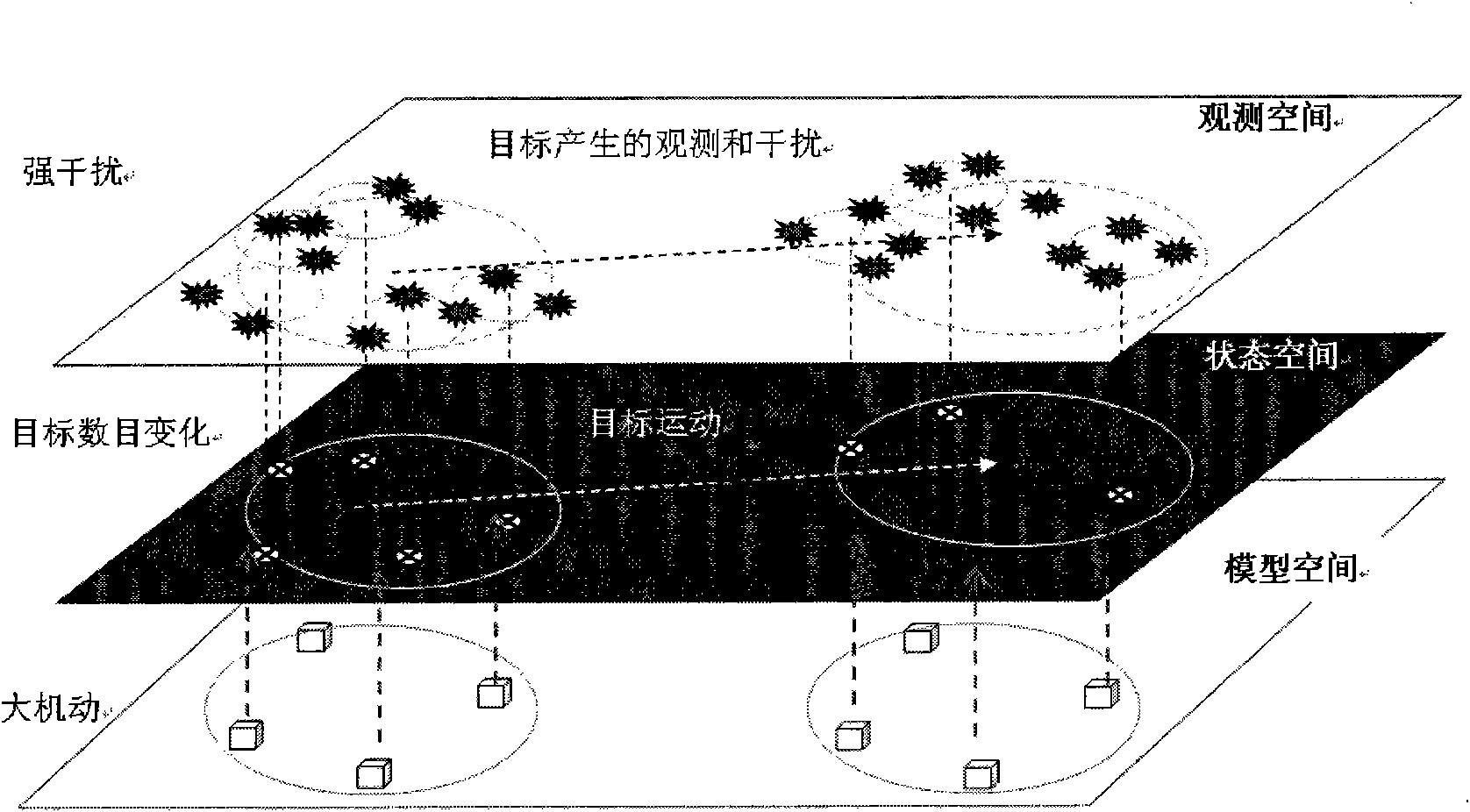
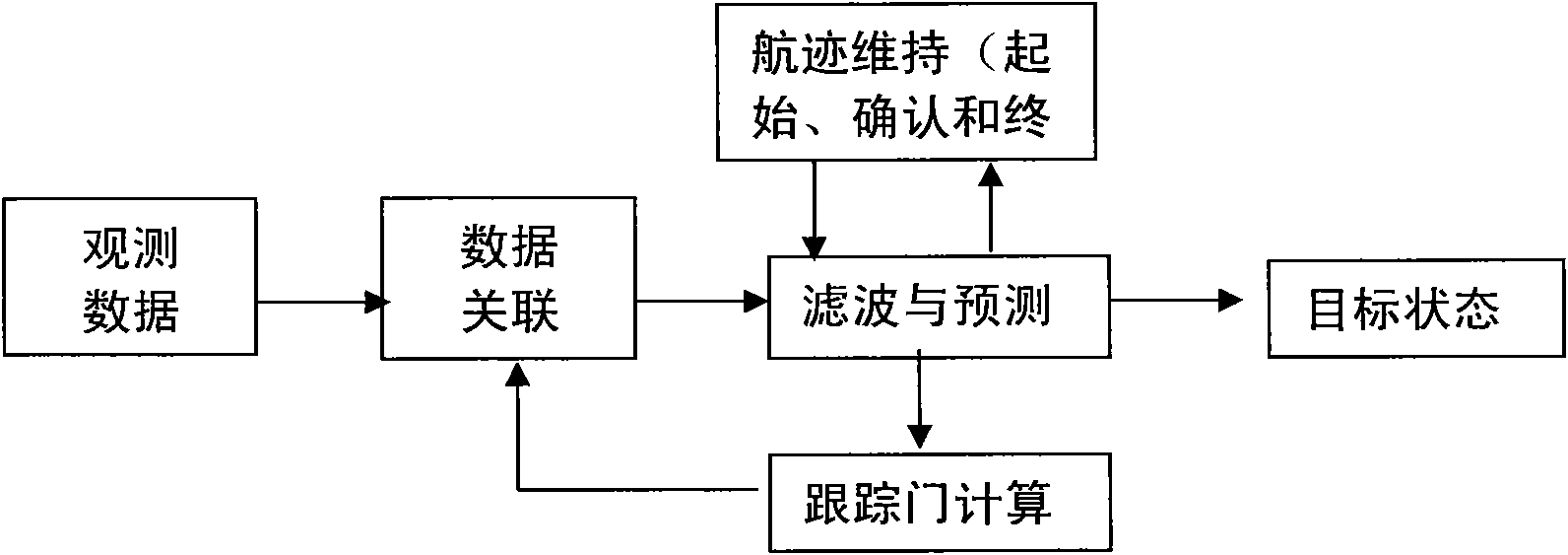
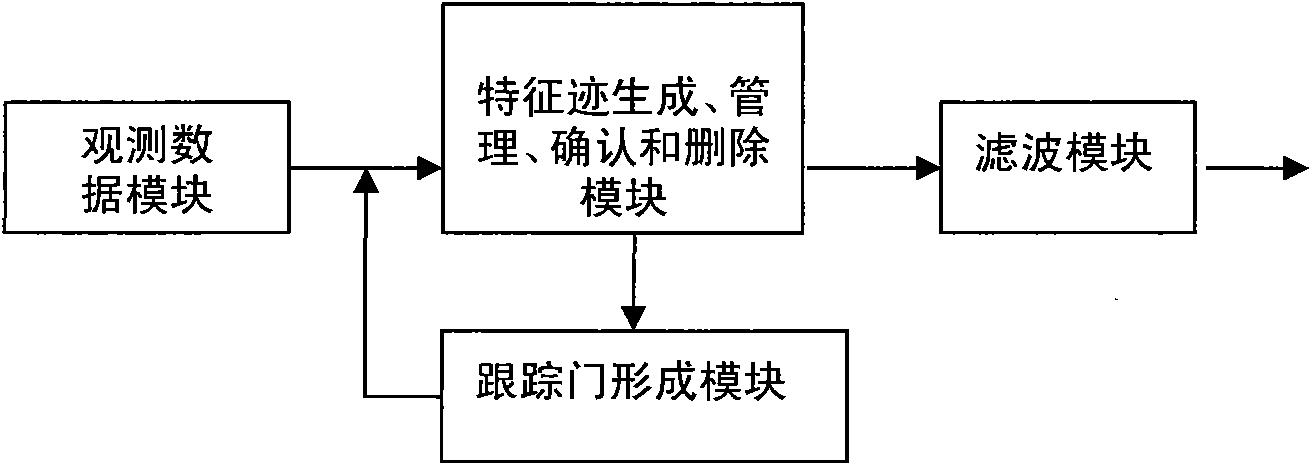
The invention provides a multi-object tracking method and a device driven by a characteristic trace. A device observing data module converts a physical property and a motion property of the object into data of a spectrum, a space and a time domain; a characteristic trace generating, managing, confirming and deleting module is used for forming the characteristic trace, managing, confirming and deleting the characteristic trace, and finally outputting characteristic trace information; a tracking door forming module is used for receiving the characteristic trace data and generating and outputting the data of the adjacent domains by defining adjacent domains by the characteristic trace; a filtering module is used for receiving the characteristic trace data of the characteristic trace generating, managing, confirming and deleting module, and predicting the state and position of an output object. The method provides the characteristic trace based on the physical basis of the multi-object detection and tracking, gives the physical property and the motion property of using the object in the spectrum, the space and the time domain, fuses the measuring data to generate the characteristic trace, and uses the Markov confidence of the characteristic trace to realize the multi-object tracking method with high-precision.
Owner:GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI GSCAS
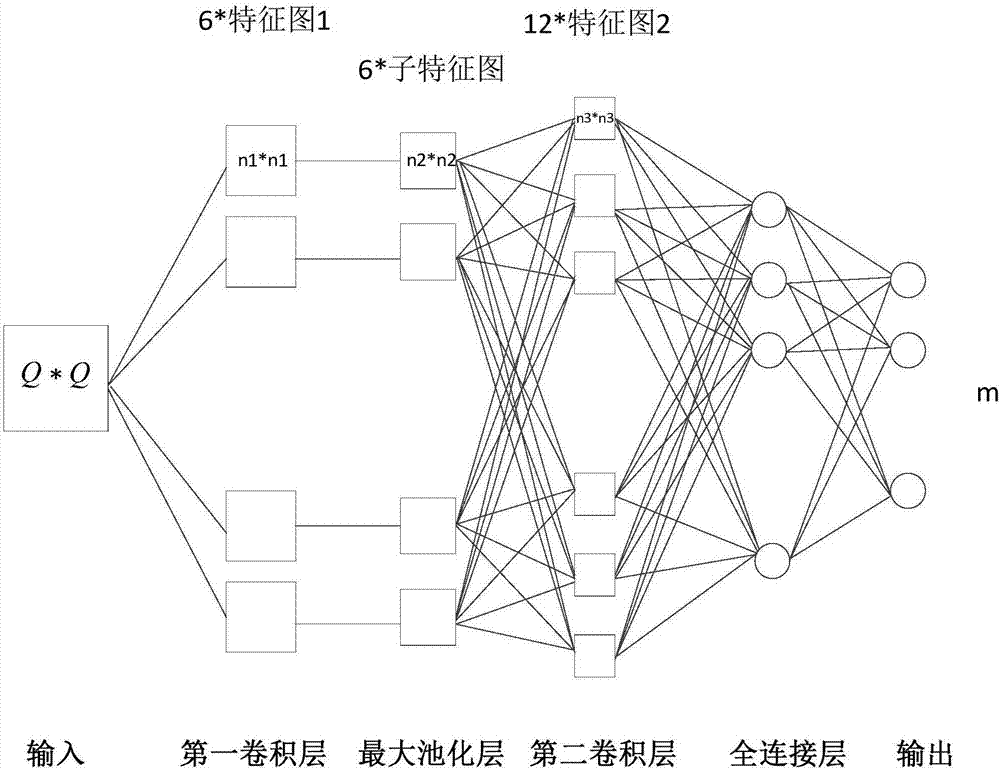
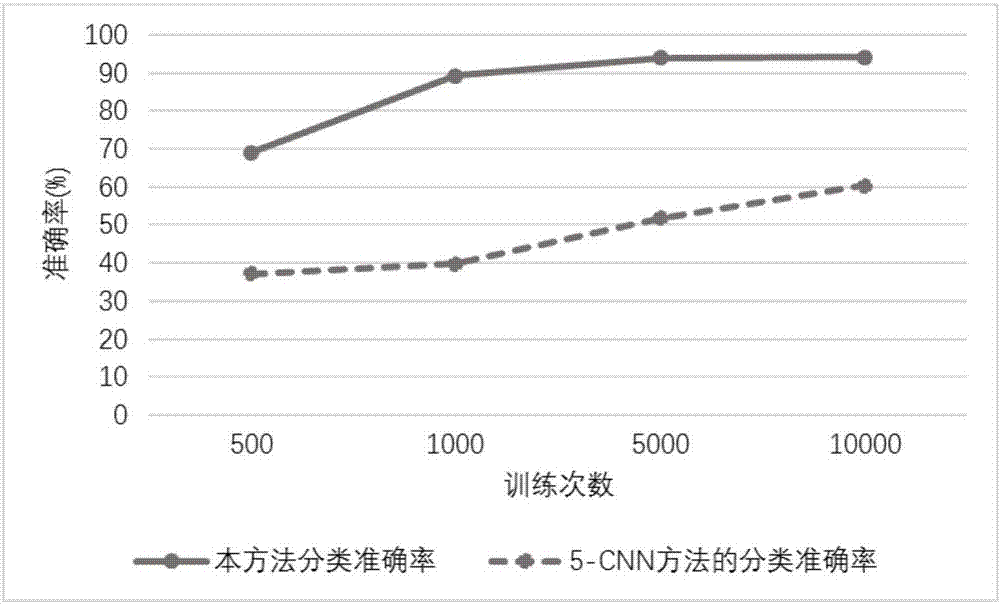
Hyperspectral remote sensing image classification method based on the combination of six-layer convolutional neural network and spectral-space information
ActiveCN107292343ASolve the noise problemTo achieve the combinationCharacter and pattern recognitionMulti bandClassification methods
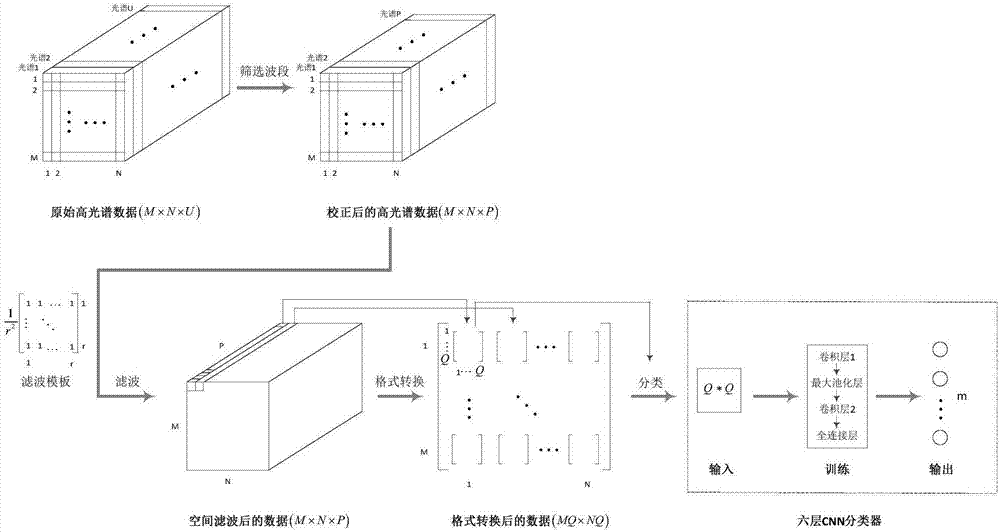
The present invention discloses a hyperspectral remote sensing image classification method based on the combination of six-layer convolutional neural network and spectral-space information. The method comprises: selecting the hyperspectral remote sensing image data of a certain number of bands; performing space mean-filtering on the two-dimensional image data of each selected band and then converting the format of the multi-band data corresponding to each pixel element; converting the one-dimensional vector into a square matrix, meaning that each pixel elements corresponds to a square matrix data; then, designing a six-layer classifier based on the deep learning template with an input layer, a first convolution layer, a largest pooling layer, a second convolution layer, a full connection layer and an output layer; extracting the square matrix data corresponding to several pixel elements as a training set to be inputted into the classifier and training the classifier; extracting the square matrix data corresponding to several pixel elements as a training set to be inputted into the trained classifier; observing the output classification result of the trained classifier; comparing with the real classification information; and verifying the performances of the trainer. With the method of the invention, higher classification accuracy can be obtained than from the currently available 5-CNN method.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
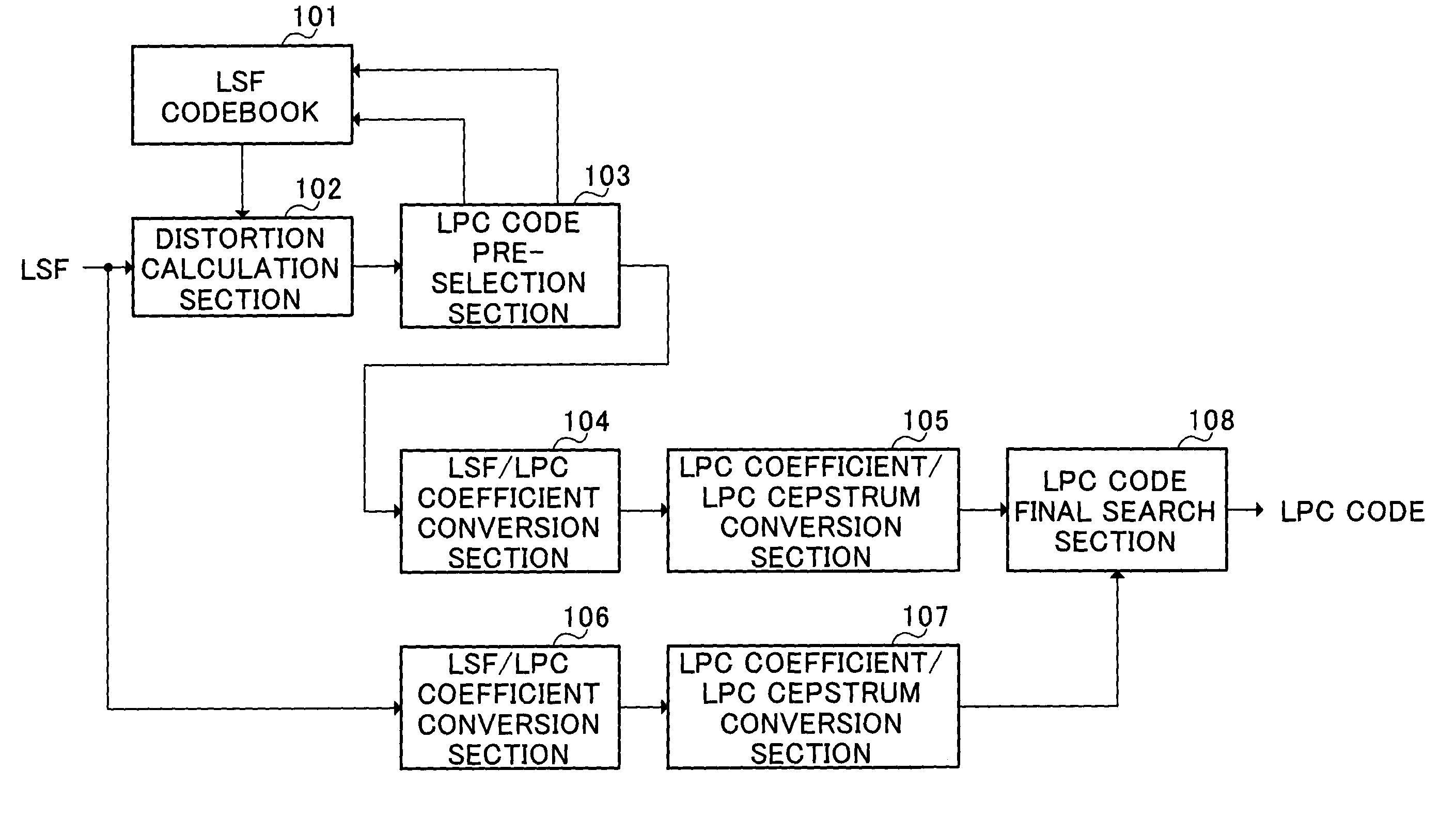
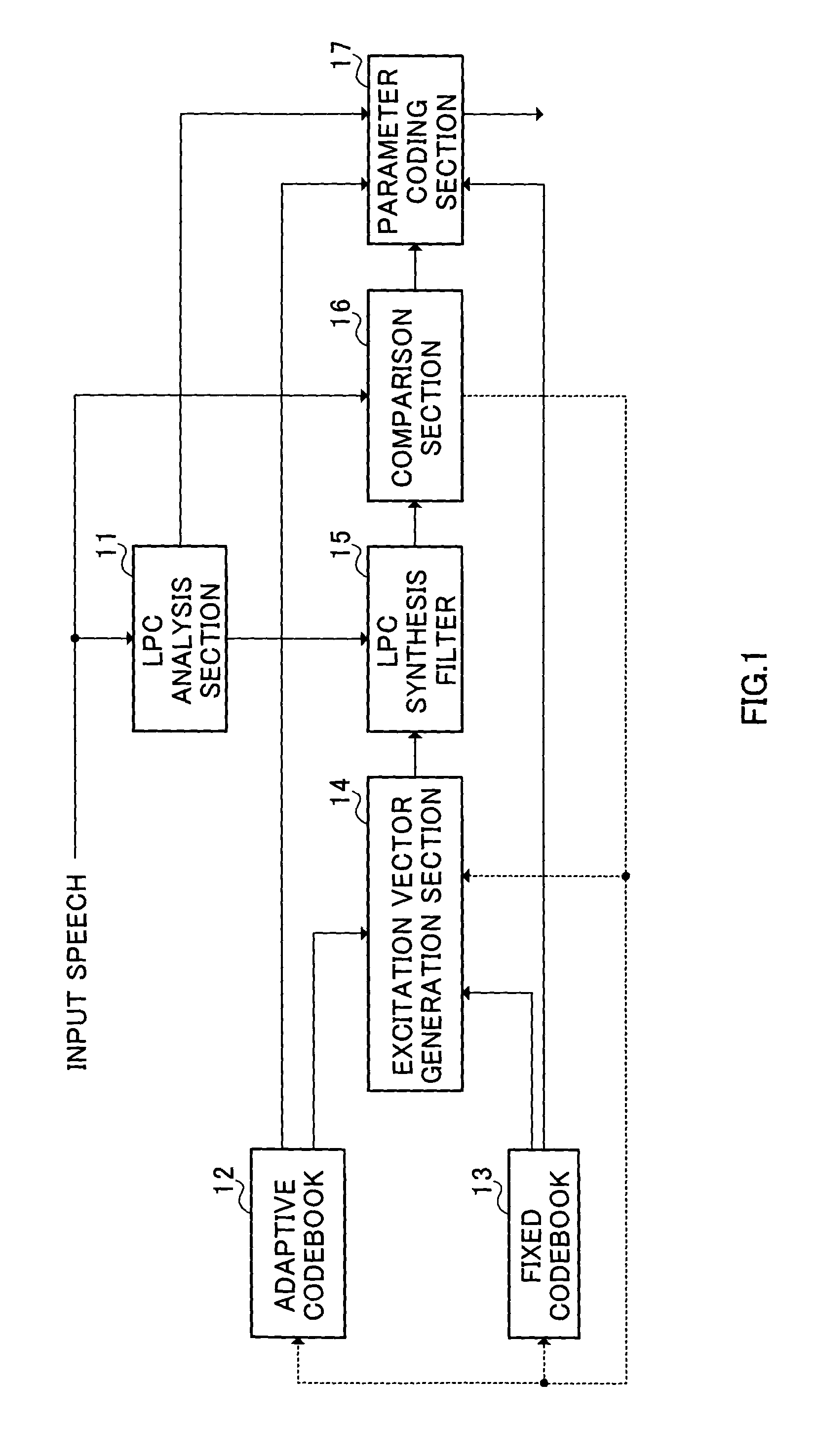
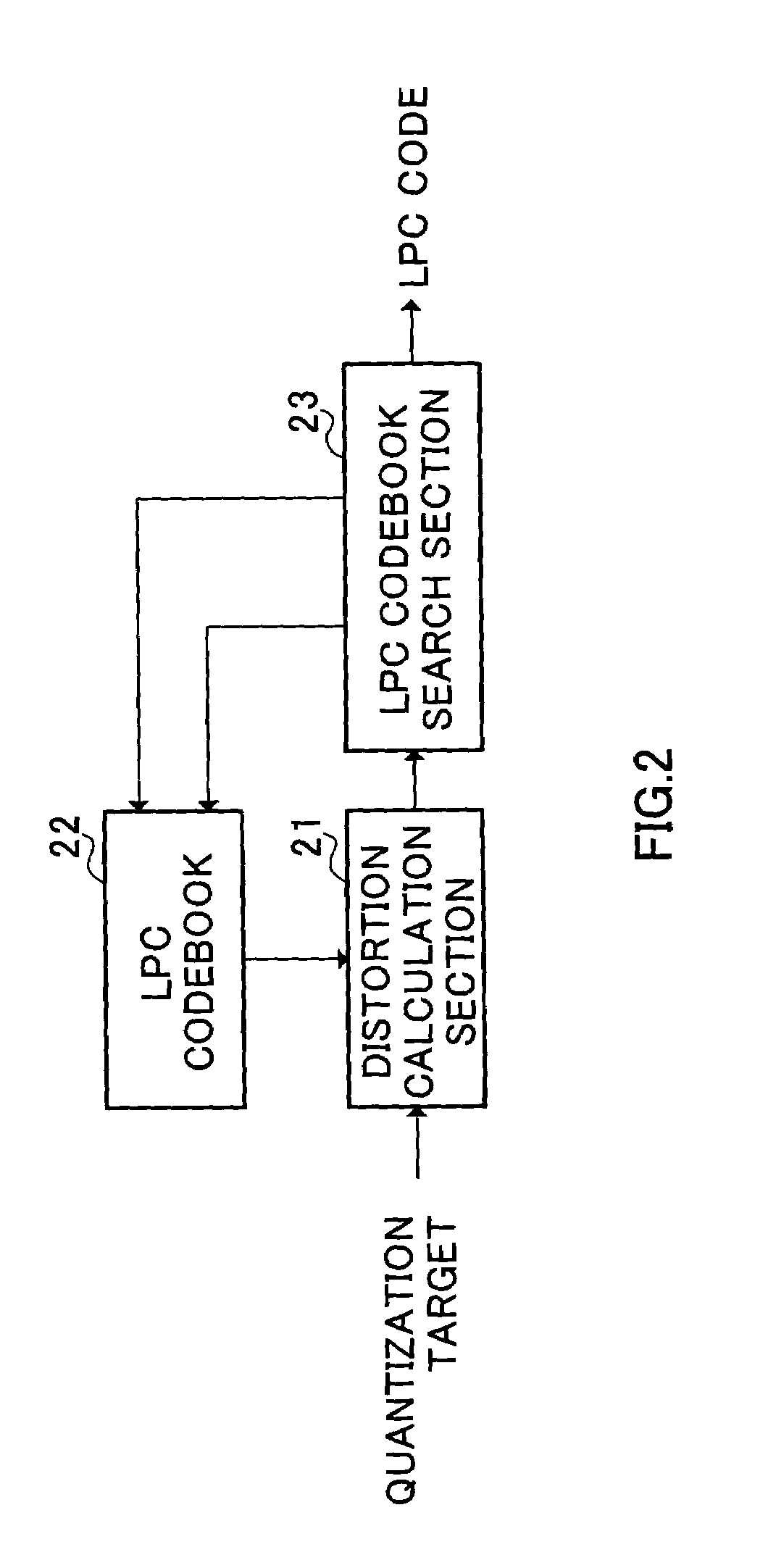
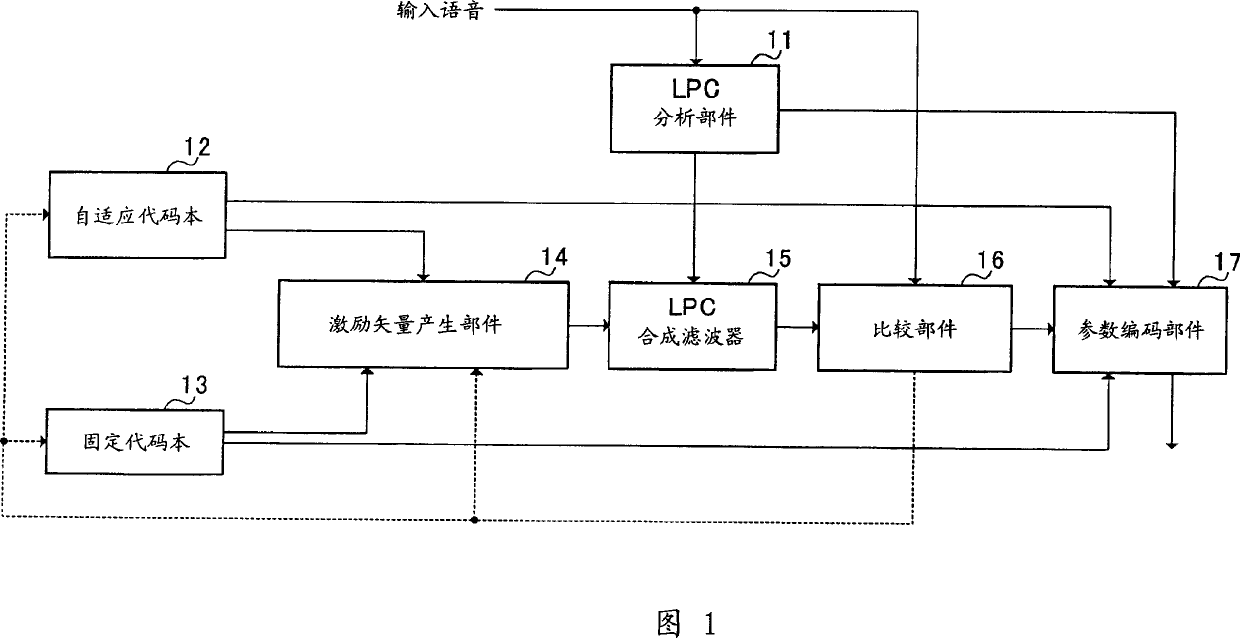
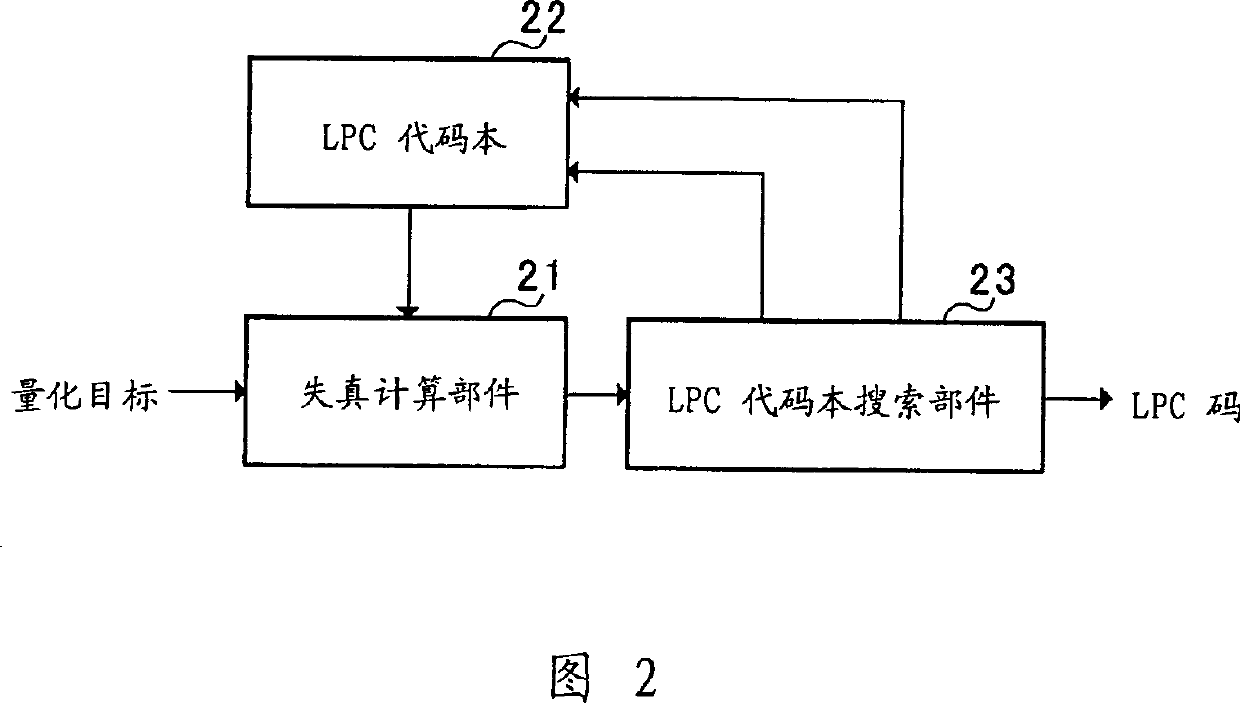
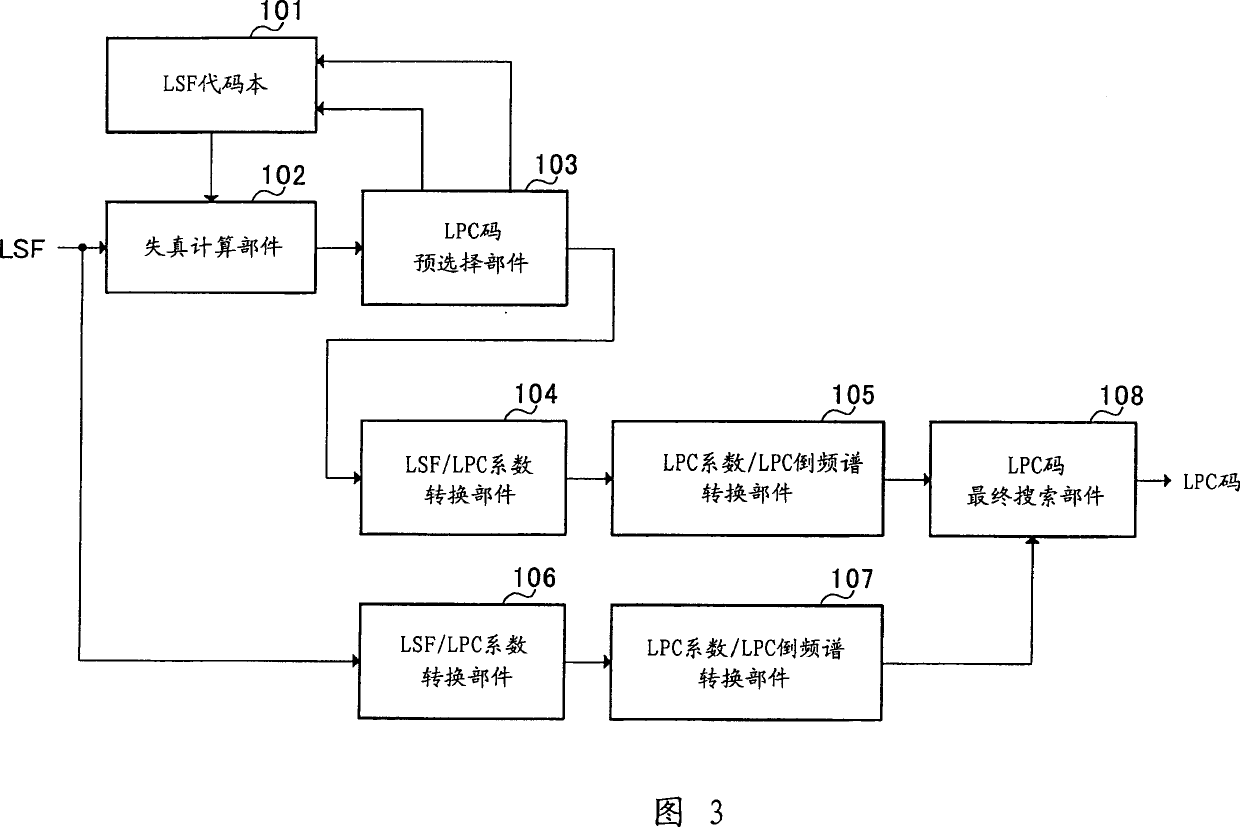
LPC vector quantization apparatus
InactiveUS7392179B2Improve performanceQuality improvementSpeech analysisCode conversionSpeech soundDistortion
The present invention carries out pre-selection on many LPC codevectors stored in an LSF codebook 101 using a weighted Euclidean distortion as a measure and carries out a full-code selection on the LPC codevectors left after the pre-selection using an amount of distortion in a spectral space as a measure. This makes it possible to improve the quantization performance of the LPC parameter vector quantizer and improve the quality of synthesized speech of the speech coder / decoder.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
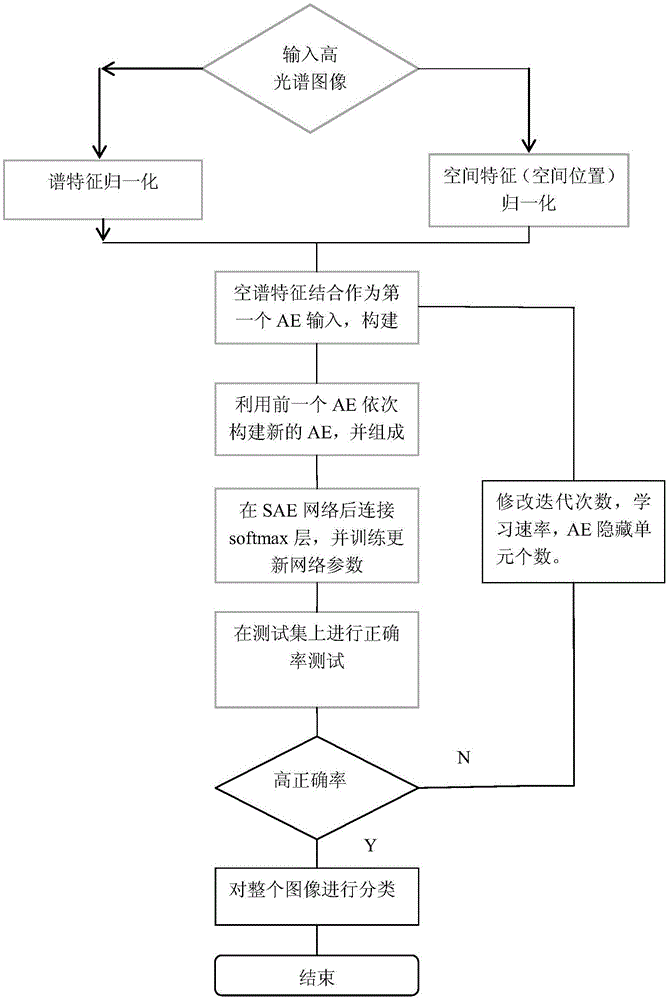
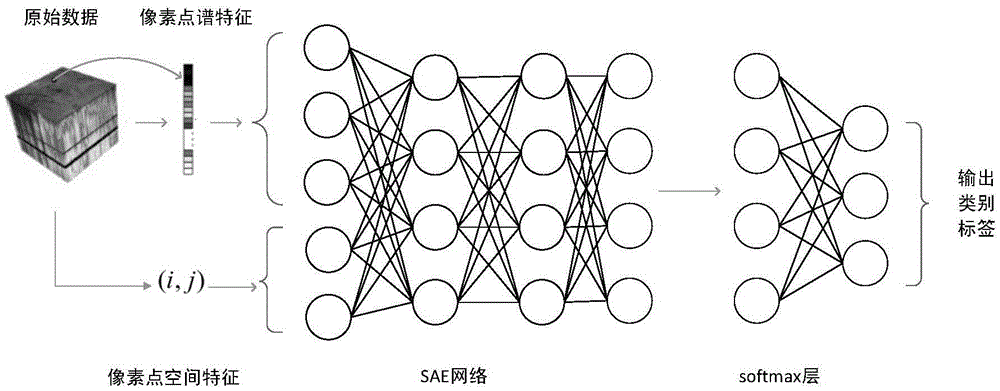
Hyperspectral image spectral-spatial cooperative classification method based on SAE depth network
ActiveCN105654117AImprove accuracySimple extraction methodCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature extractionPrincipal component analysis
The invention relates to a hyperspectral image spectral-spatial cooperative classification method based on an SAE depth network. According to the hyperspectral image spectral-spatial cooperative classification method based on the SAE depth network, the conventional method that neighborhood information is applied to act as spatial features after PCA dimension reduction, spatial position information, i.e. row and column coordinates, of current pixel points are applied to act as the spatial features and then the spatial features are combined with spectral features to act as the spectral-spatial cooperative features of training samples can be substituted. The beneficial effects of the hyperspectral image spectral-spatial cooperative classification method based on the SAE depth network are that the conventional method of spatial feature extraction in spectral-spatial cooperative classification based on the SAE depth network is improved, the spatial position information is applied to act as the spatial features rather than the conventional method of spatial feature extraction that principal component analysis (PCA) dimension reduction is performed in spectral space and then neighborhood space information is extracted to act as the spatial features, the extraction method of the spatial features is simplified, computational burden is reduced and classification accuracy is enhanced in comparison with that of the conventional method.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
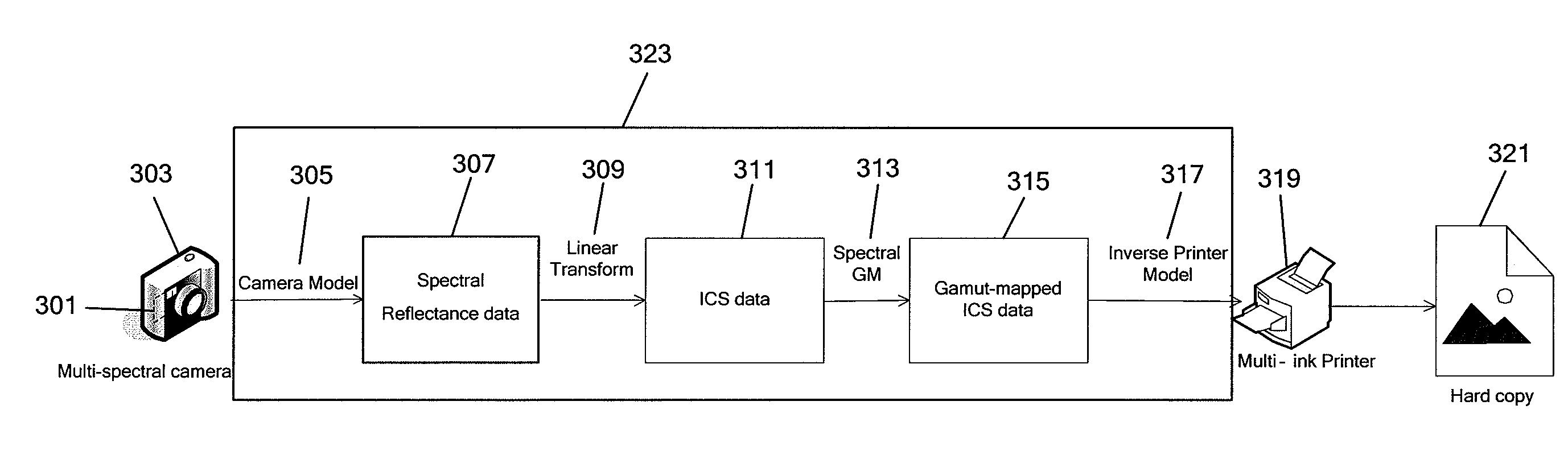
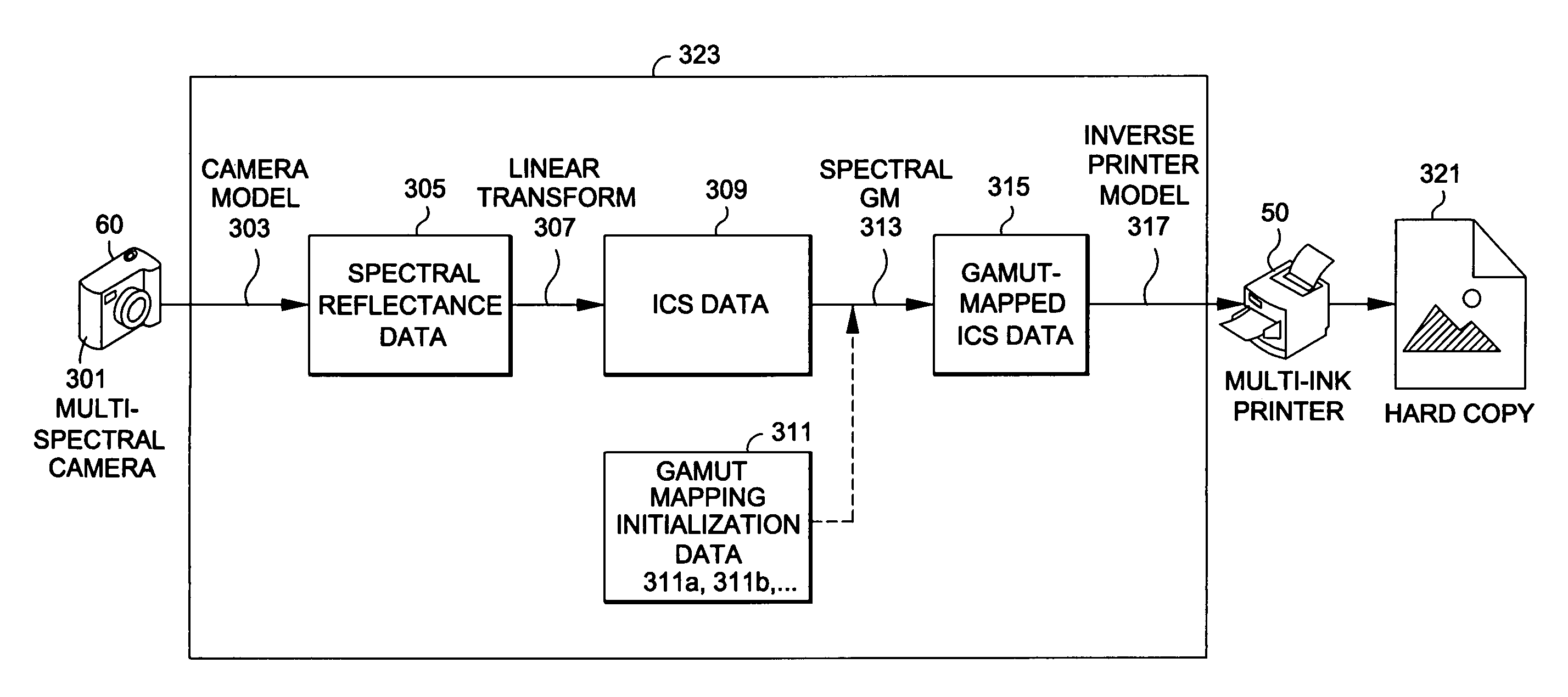
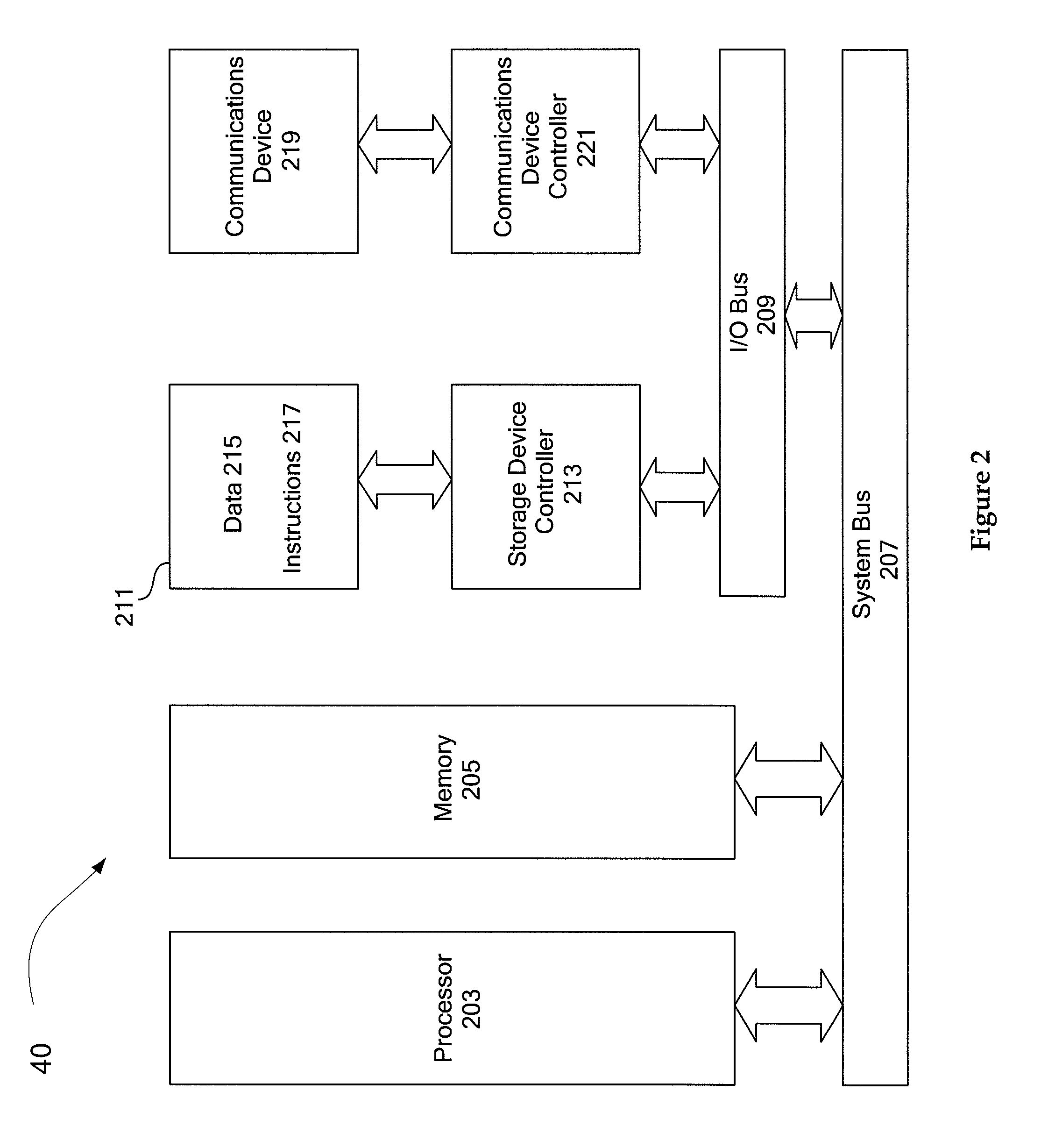
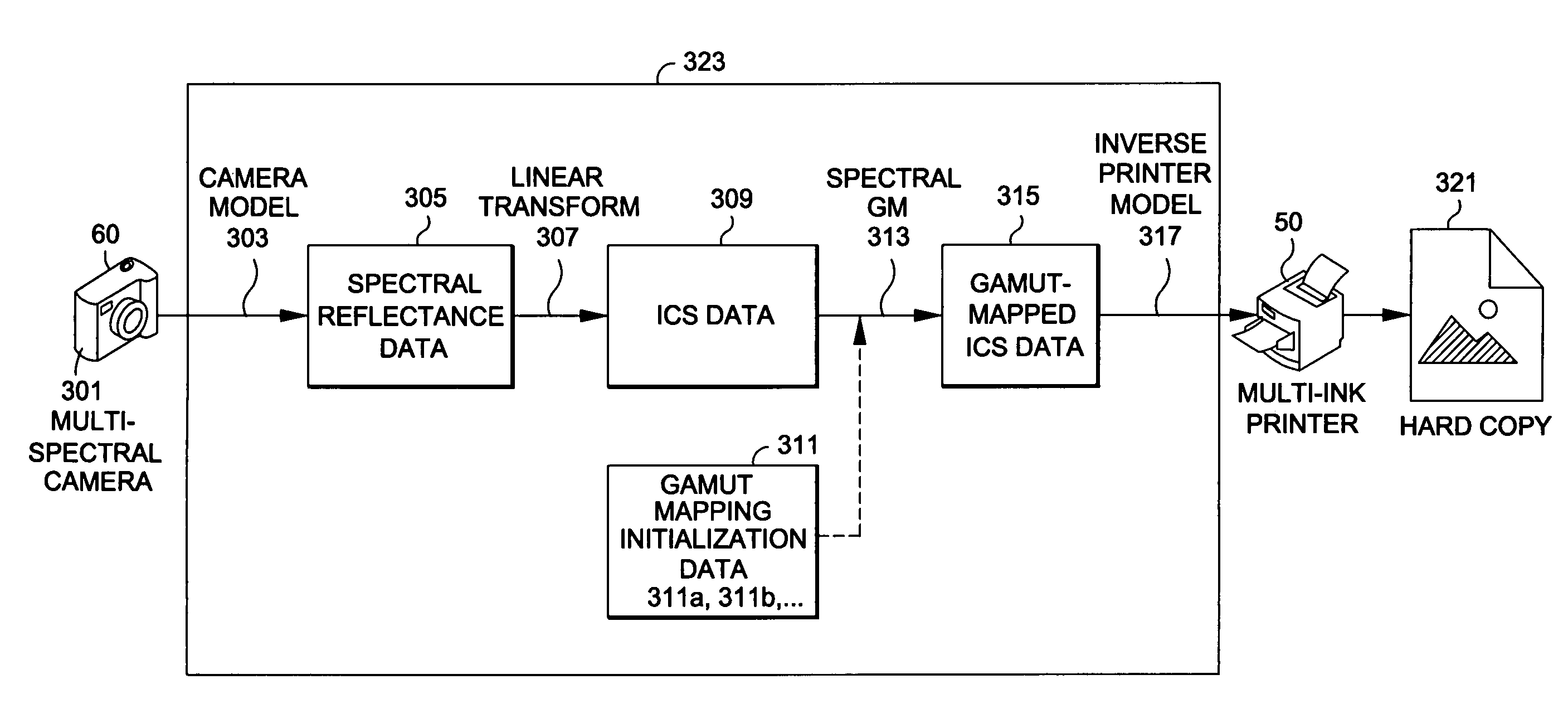
Generating a transformed interim connection space for spectral data
InactiveUS20090141970A1Simpler and efficientPotential benefitCharacter and pattern recognitionPictoral communicationOrthogonal complementLinearity
Generation of a transformed Interim Connection Space for spectral data is provided. A first Interim Connection Space for spectral data in a full spectral space is accessed. A first map, which characterizes a linear transformation from the full spectral space to a first color space, is accessed. A second map, which characterizes a linear transformation from the first Interim Connection Space to the first color space, is determined. The first Interim Connection Space is decomposed into orthogonal subspaces, the orthogonal subspaces including a first subspace that is a null space of the second map and a second subspace that is an orthogonal complement of the null space in the first Interim Connection Space. The transformed Interim Connection Space is generated based on the first subspace and the second subspace.
Owner:CANON KK
Vector quantizing device for LPC parameters
The present invention carries out pre-selection on many LPC codevectors stored in an LSF codebook 101 using a weighted Euclidean distortion as a measure and carries out a full-code selection on the LPC codevectors left after the pre-selection using an amount of distortion in a spectral space as a measure. This makes it possible to improve the quantization performance of the LPC parameter vector quantizer and improve the quality of synthesized speech of the speech coder / decoder.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
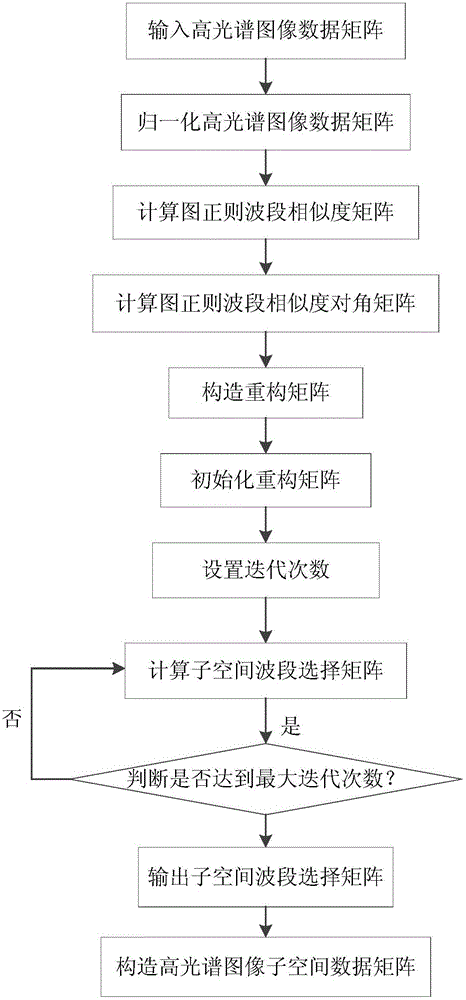
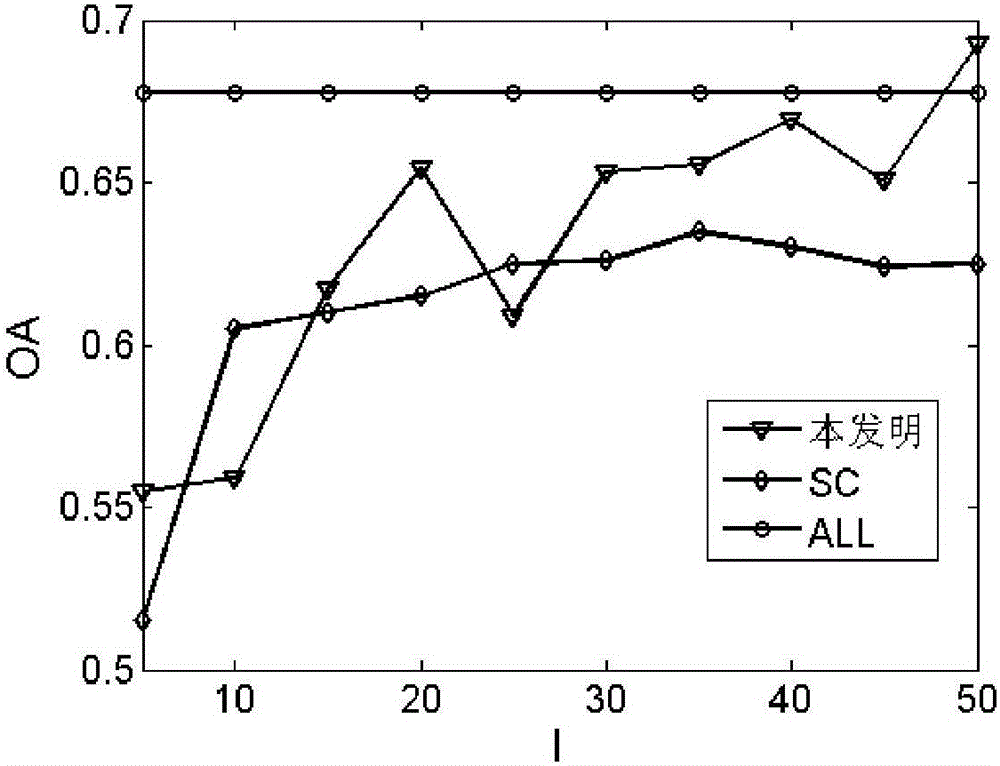
Figure regular hyperspectral image band selection method based on subspace learning
ActiveCN105913092AImprove accuracyOvercome the problem of not utilizing the local structure information of the dataCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmDiagonal matrix
The invention provides a figure regular hyperspectral image band selection method based on subspace learning. The method comprises the concrete realization steps that (1) a hyperspectral image data matrix is inputted; (2) the data matrix is normalized; (3) a figure regular band similarity matrix is calculated; (4) a figure regular band similarity diagonal matrix is calculated; (5) a reconstruction matrix is constructed; (6) the reconstruction matrix is initialized; (7) the number of times of iteration is set; (8) a subspace band selection matrix is calculated; (9) whether the current number of times of iteration is greater than the maximum number of times of iteration is judged, and the step (10) is performed if the judgment result is yes, or one time of current iteration is added and the step (8) is performed; (10) the subspace band selection matrix is outputted; and (11) a subspace data matrix is constructed. A learning mechanism is provided and spectral space geometric structure information is utilized so that the accuracy of band selection can be enhanced.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Gamut mapping in spectral space based on an objective function
InactiveUS20090185200A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsPattern recognitionGamut
Mapping spectral colors in an Interim Connection Space (ICS) of a full spectral space based on an objective function is provided. A spectral color value in the ICS is accessed, and a spectral gamut boundary of the destination gamut is accessed. The spectral color value is mapped into mapped spectral color value based on minimization of an objective function of coordinates of a first subspace of the ICS, by fixing coordinates of a second subspace of the ICS, subject to a constraint that a result is within the spectral gamut boundary. The first subspace is a null space of a transformation from the ICS to a color space, while the second subspace is an orthogonal complement of the first subspace in the ICS. The constraint is determined by a gamut section that is an intersection of the spectral gamut in the ICS and an affine subspace characterized by the fixed coordinates of the second subspace.
Owner:CANON KK
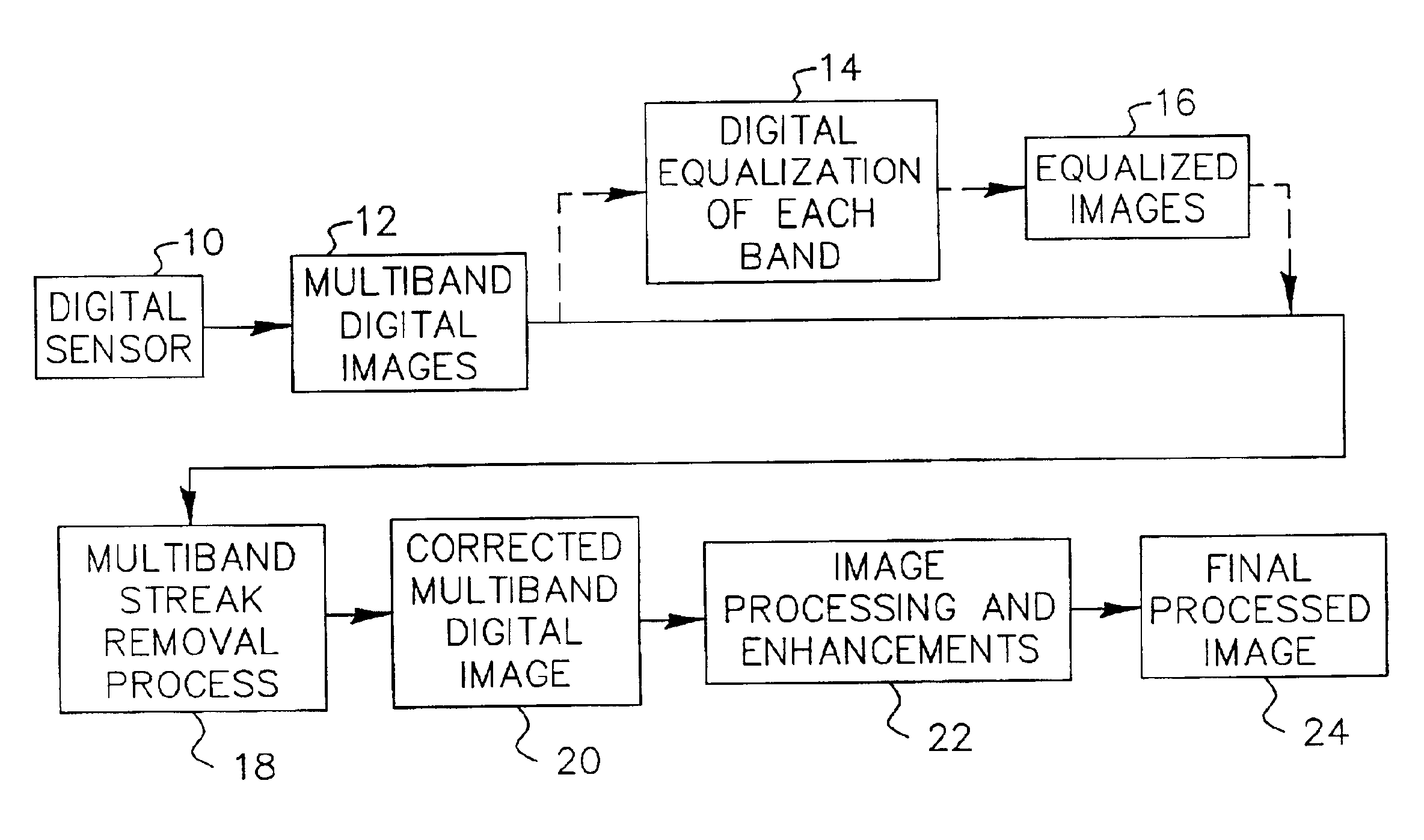
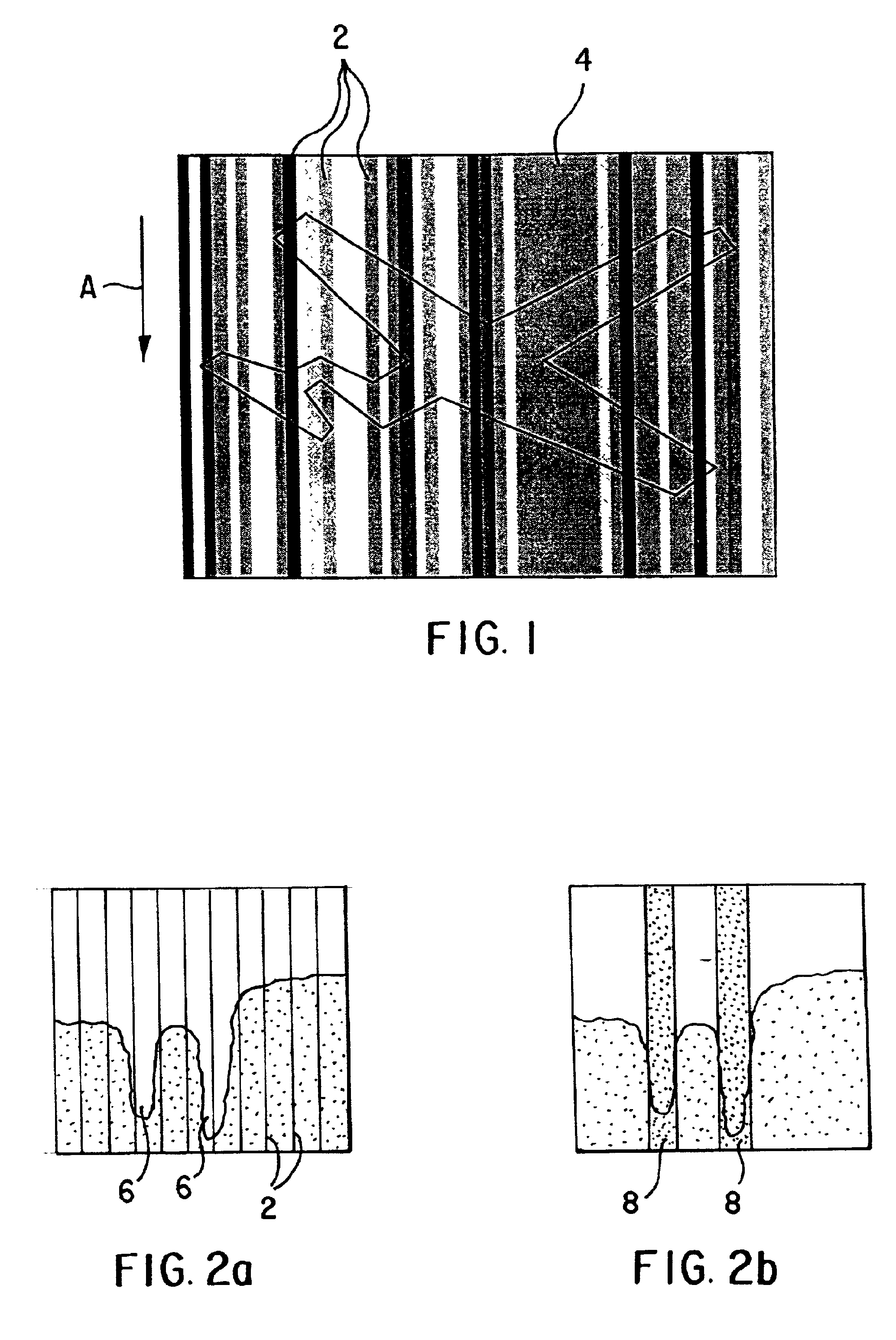
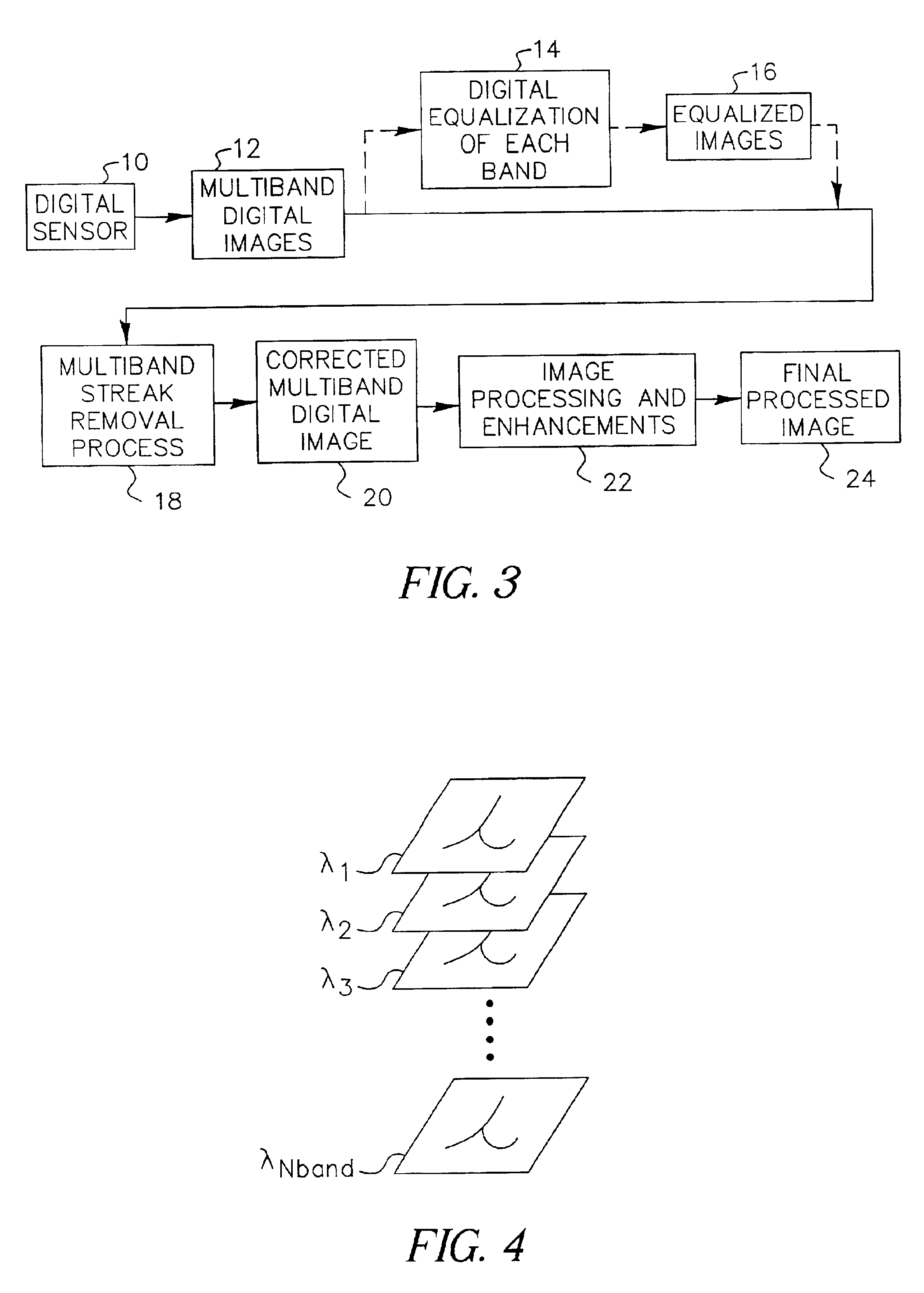
Adaptive process for removing streaks in multi-band digital images
InactiveUS6912322B2Favorable for determinationEliminate StreaksImage enhancementTelevision system detailsMulti bandDigital image
A method of removing streaks from multi-band digital images is presented in which a multi-band image is transformed to an advantageous spectral space, in which a streak removal operation is applied to the image in the advantageous spectral space. The streak removal operation is a method of removing columnar streaks from a multi-band digital image of the type in which it is assumed that pixels in a predetermined spatial and spectral region near a given pixel are strongly related to each other and employing gain and offset values to compute streak removal information, a test is performed for a strong relation between the pixels in a predetermined region spatially and spectrally near a given pixel and streak removal information is computed only if such a strong relationship exists, whereby image content that does not extend the full length of the image in the column direction will not be interpreted as a streak.
Owner:EXCELIS INC
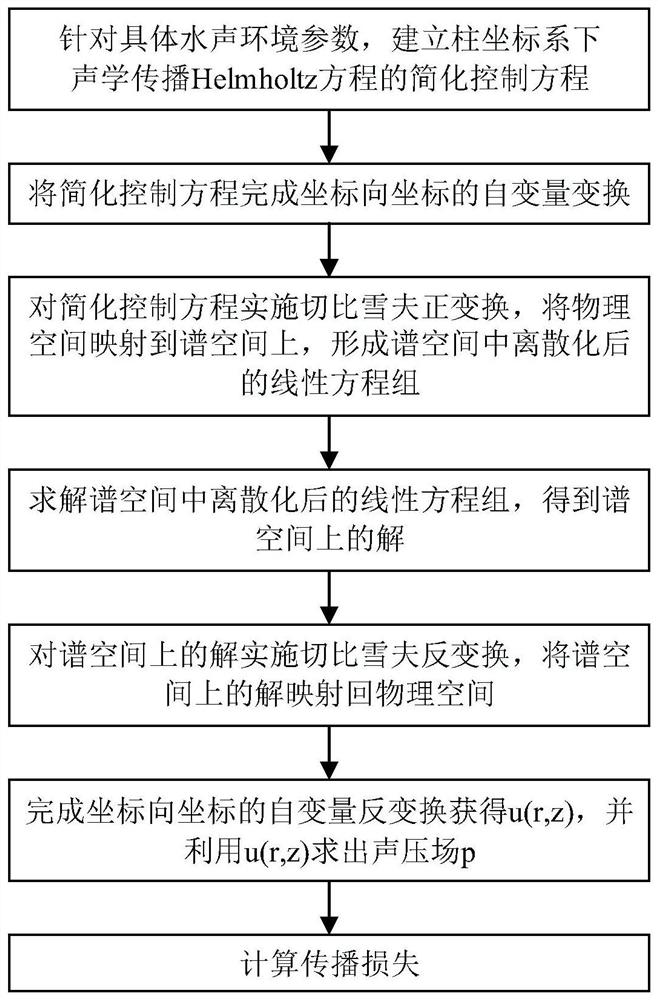
Underwater sound field numerical simulation method and system based on Chebyshev polynomial spectrum and medium
ActiveCN111639429ASpeed up the simulationGet the most out of your computing performanceDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsPhysical spaceDiscretization
The invention discloses an underwater sound field numerical simulation method and system based on a Chebyshev polynomial spectrum and a medium. The method comprises the following steps: establishing asimplified control equation of an acoustic propagation Helmholtz equation under a cylindrical coordinate system; completing independent variable transformation from a z coordinate to an x coordinateby using the simplified control equation; implementing Chebyshev forward transformation on the simplified control equation, and mapping a physical space to a spectral space to form a discretized linear equation set in the spectral space; solving the discretized linear equation set in the spectral space to obtain a solution in the spectral space; implementing Chebyshev inverse transformation on thesolution in the spectral space, and mapping the solution in the spectral space back to the physical space; completing independent variable inverse transformation from an x coordinate to a z coordinate to obtain u (r, z), and solving a sound pressure field p; calculating propagation losses. The method is suitable for obtaining higher calculation precision under the condition that few discrete gridpoints are used, the calculation performance of a hardware platform can be brought into full play, and the speed of numerical simulation is remarkably increased.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
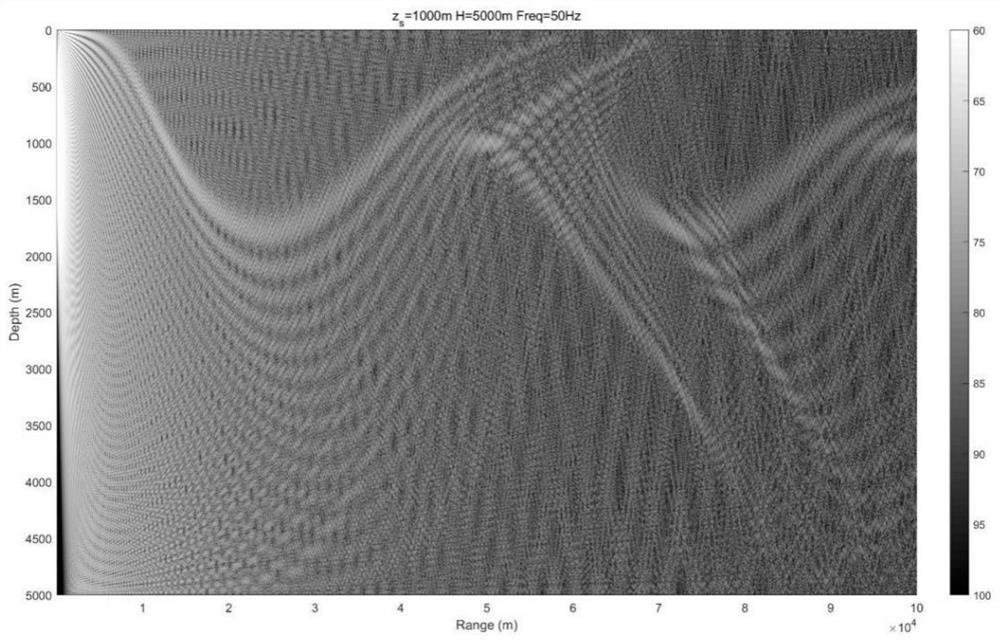
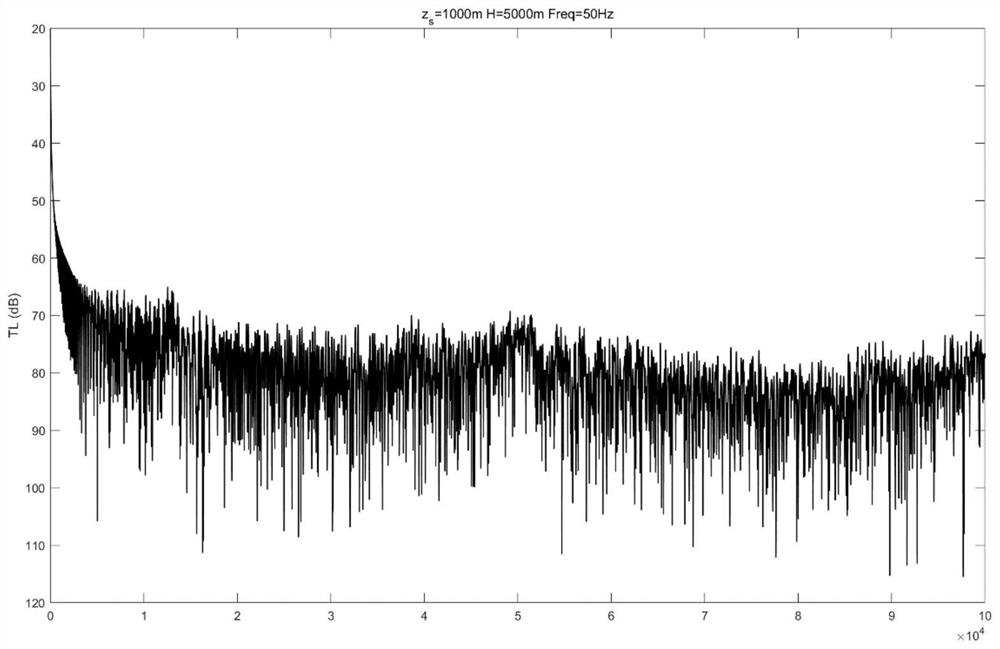
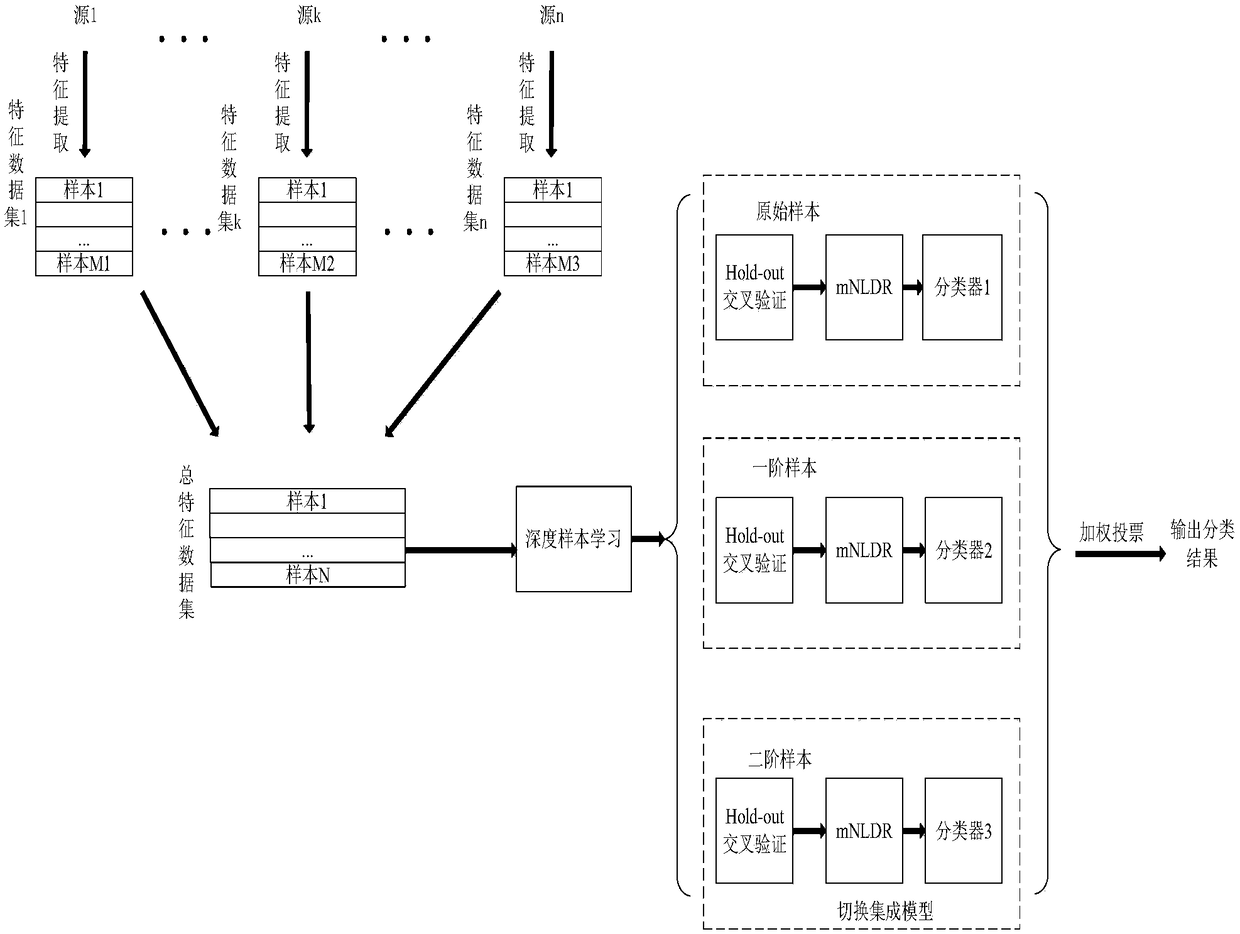
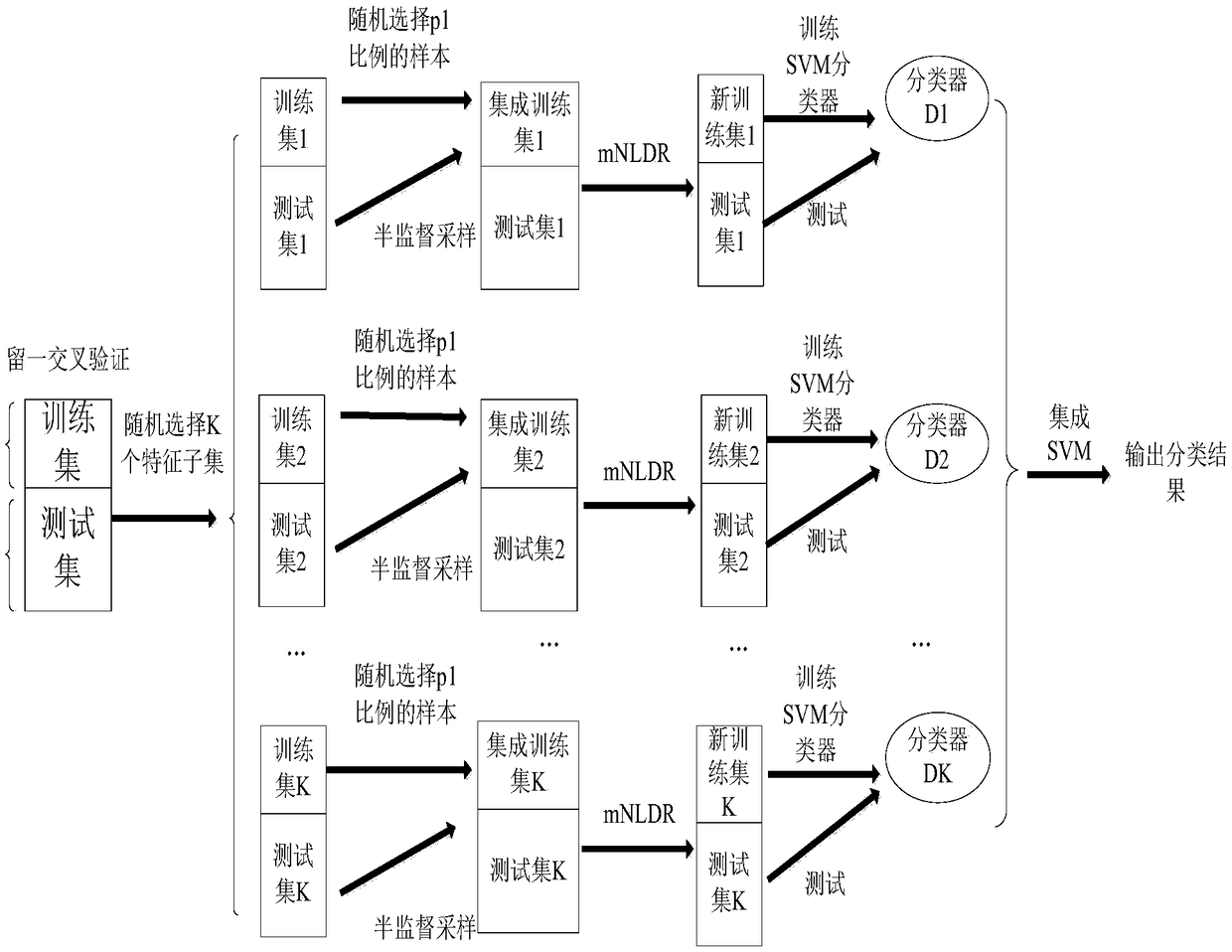
Multi-source heterogeneous data fusion method based on deep subspace switching ensemble learning
ActiveCN108985365AIncrease diversityImprove separabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionData setFeature extraction
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Generating a device independent interim connection space for spectral data
InactiveUS20090141322A1Wide applicabilityThe result is accurateTelevision system detailsDigitally marking record carriersComputer graphics (images)Orthogonal complement
Generation of an Interim Connection Space (ICS) of a full spectral space is provided. A space of illuminants is accessed, and the full spectral space is decomposed into a first subspace that is an orthogonal complement of a metameric black subspace for the space of illuminants. The Interim Connection Space is generated based on the first subspace. The generated ICS can be used, for example, for rendering an image on an additive color destination device. One image rendering workflow includes accessing color data of the image in an ICS, transforming the color data from the ICS into a device dependent color space of an additive color destination device, and rendering the transformed color data on the destination device.
Owner:CANON KK
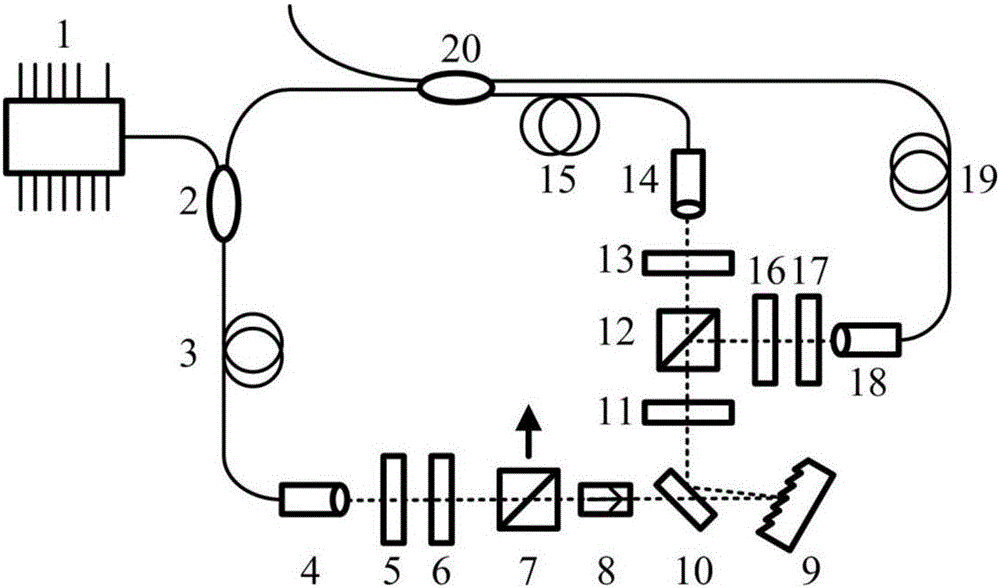
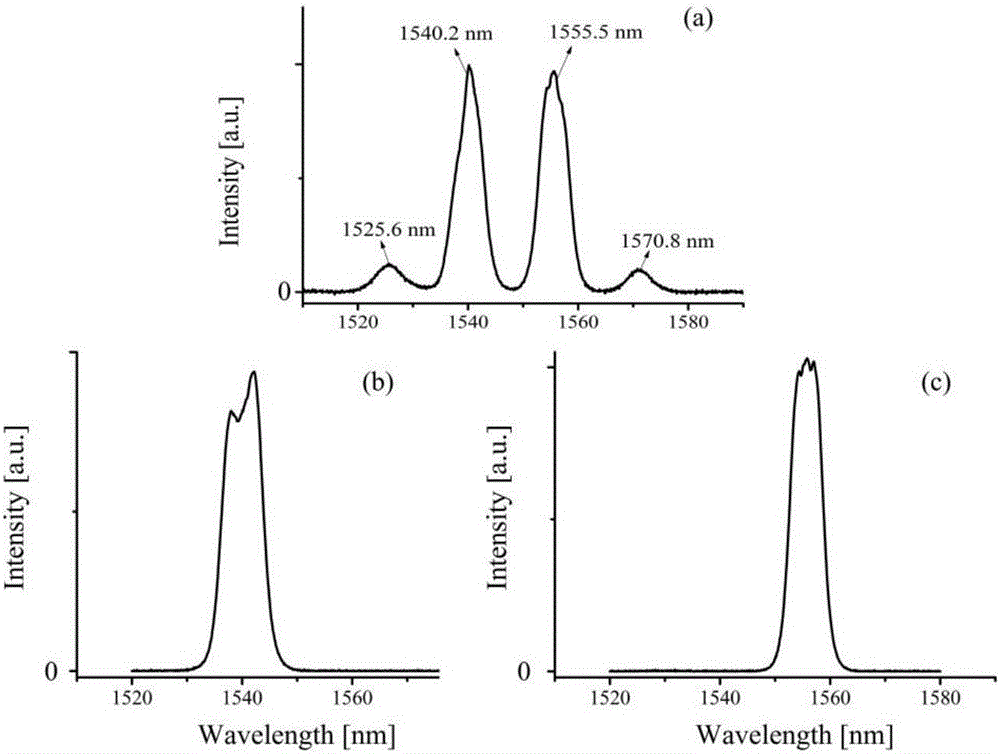
Multi-wavelength synchronous output fiber laser based on nonlinear polarization rotation mode locking
ActiveCN106058620AImprove stabilityIncrease long offset rangeActive medium shape and constructionGratingBeam splitting
The invention relates to a multi-wavelength synchronous output fiber laser based on nonlinear polarization rotation mode locking, which comprises a semiconductor laser, a wavelength division multiplexer, a gain fiber, a first collimating mirror, a first half wave plate, a first quarter wave plate, a first polarization beam splitter, a Faraday isolator, a glaring grating, and a silver mirror. According to the first half wave plate, a nonlinear polarization rotation technology is adopted for mode locking, a saturable absorber which is likely to be damaged can be prevented from being used, and the stability of the laser is enhanced. According to the same laser gain fiber and the nonlinear polarization mode locking device, the distance between two wavelengths under mutual cross phase modulation effects in the laser cavity is increased, and thus, a cavity length misadjustment range for two laser cavities in the case of synchronous mode locking can be increased. Through changing the angle of a beam-splitting grating, the output wavelength of the laser can be tuned, the gap between the two wavelengths can be changed through changing the position of the collimator in the spectral space, and through changing the position of the collimator away from the beam-splitting grating, the pulse spectral width and the pulse width of laser output pulses can be changed.
Owner:SICHUAN GUANGZHENG TECH
Spectral gamut mapping based on a colorimetric gamut mapping
InactiveUS20090148040A1Simple methodDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsGamutOrthogonal complement
Mapping spectral colors in an Interim Connection Space (ICS) of a full spectral space based on a colorimetric gamut map in a color space is provided. A spectral color value in the ICS is accessed, and the spectral color value is transformed into a calorimetric color value in the color space. The calorimetric color value is mapped into mapped calorimetric color value in a first subspace of the ICS. Mapping the colorimetric color value includes gamut-mapping the calorimetric color value using the calorimetric gamut map, followed by identifying the color space with the first subspace. An intersection of a spectral gamut in the ICS and an affine subspace characterized by the mapped colorimetric color value is determined, and the spectral color value is projected onto the intersection. The first subspace is an orthogonal complement of a null space of a transformation from the ICS to the color space.
Owner:CANON KK
Generating an interim connection space for spectral data
InactiveUS20090141321A1Reduce lossesImprove accuracyDigitally marking record carriersVisual presentation using printersSpectral spaceLinear transform
Generation of an Interim Connection Space for spectral data in a full spectral space is provided. A set of linear maps is accessed, each linear map characterizing a linear transformation from the full spectral space to a colorimetric space, and spectral measurement data is accessed. The linear maps can for example be determined by a set of illuminants. The full spectral space is decomposed into a first subspace that minimizes a loss of a spectral component in the spectral measurement data under a projection along a second subspace onto the first subspace. The second subspace is a null subspace of the set of linear maps. The Interim Connection Space is generated based on the first subspace. The Interim Connection Space can include, for example, a linear map characterizing a linear transformation from the Interim Connection Space to the full spectral space, and a linear map characterizing a linear transformation from the full spectral space to the Interim Connection Space.
Owner:CANON KK
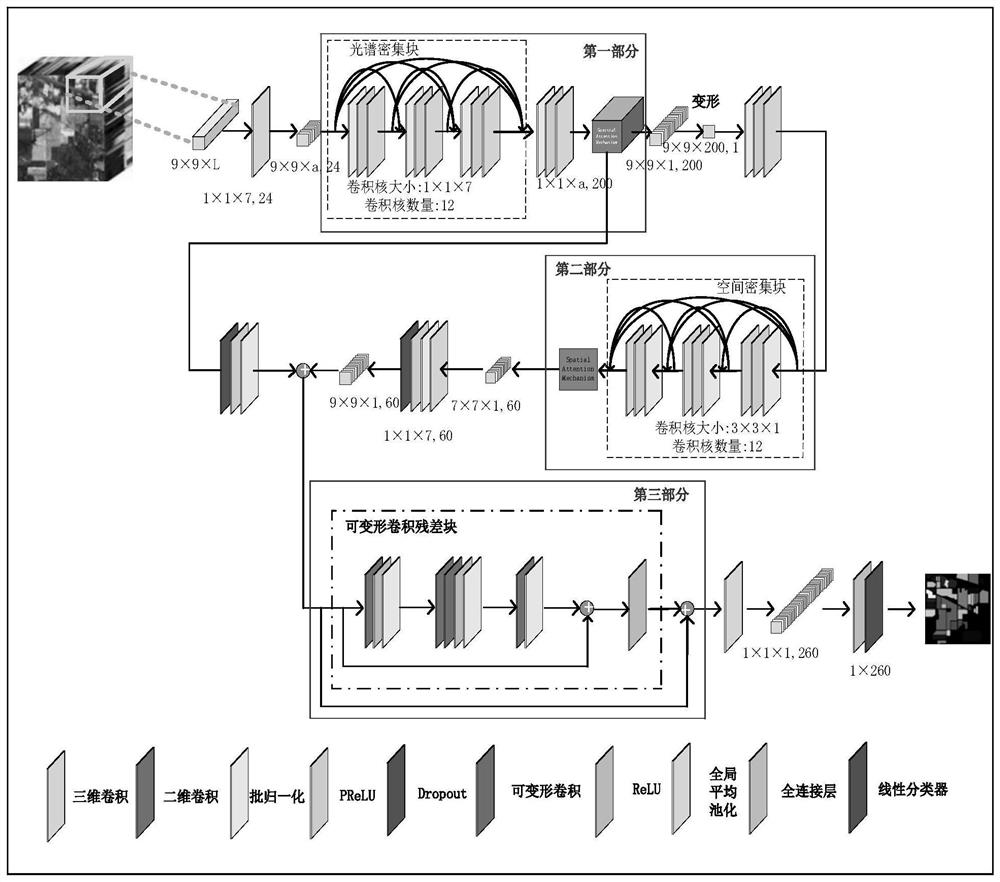
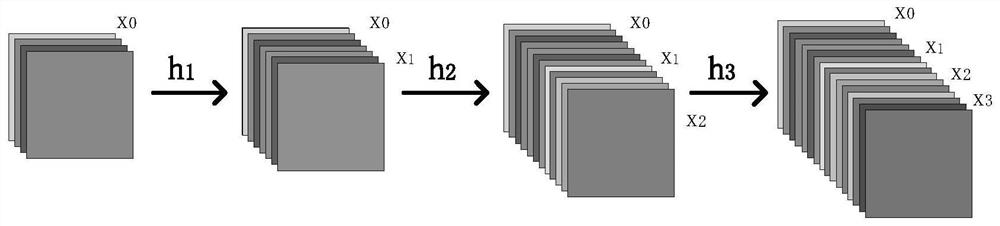
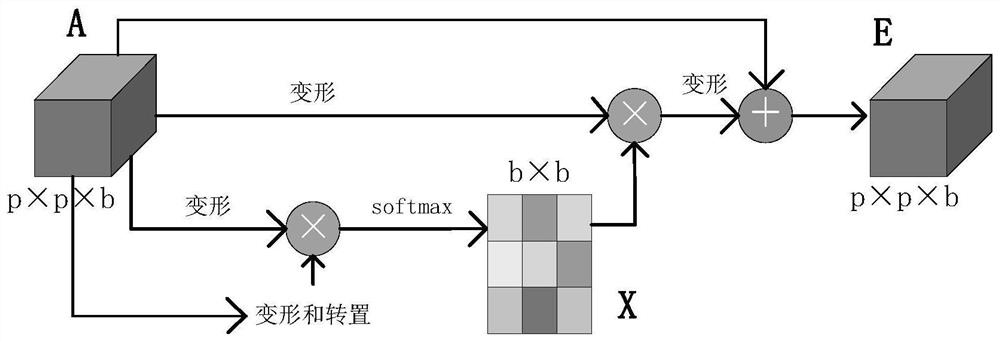
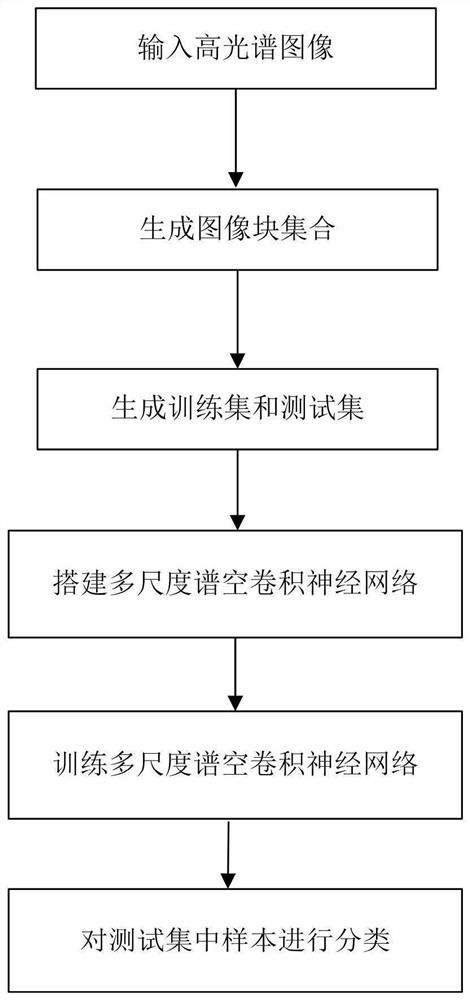
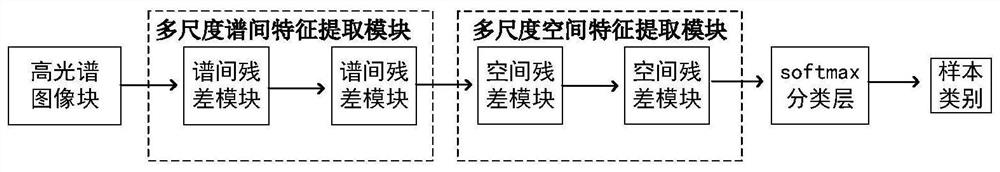
Hyperspectral image classification method based on spectral space attention fusion and deformable convolutional residual network
ActiveCN113361485AEnhancing the ability to represent spatial spectral featuresAccurate classificationInternal combustion piston enginesCharacter and pattern recognitionData setHyperspectral image classification
The invention relates to a hyperspectral image classification method, and concretely relates to a hyperspectral image classification method based on spectral space attention fusion and a deformable convolutional residual network. The objective of the invention is to solve the problem of low classification accuracy of hyperspectral images caused by insufficient spectrum and spatial feature extraction and overfitting under small samples due to the fact that the hyperspectral images contain abundant information in the existing hyperspectral image classification. The method comprises the following steps: 1, acquiring a hyperspectral image data set and a corresponding label vector data set; 2, establishing an SSAF-DCR network based on spectrum space attention fusion and a deformable convolution residual error; 3, inputting the x1, the x2, the Y1 and the Y2 into a network SSAF-DCR, and performing iterative optimization by adopting an Adam algorithm to obtain an optimal network; and 4, inputting x3 into the optimal network to carry out classification result prediction. The method is applied to the field of hyperspectral image classification.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY
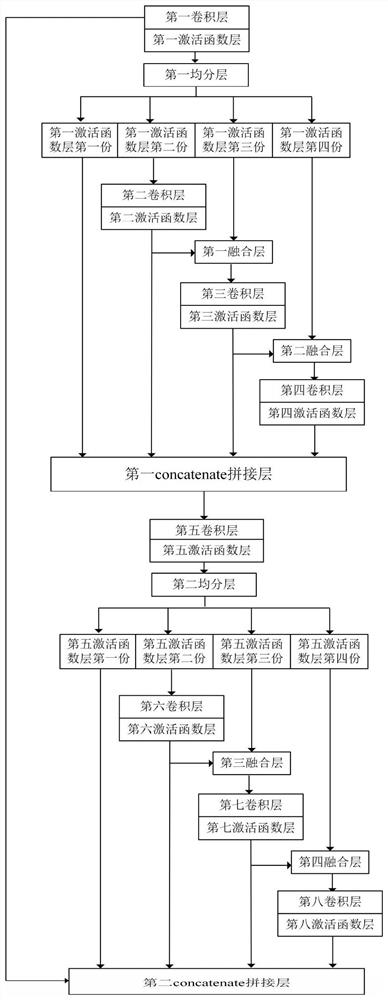
Hyperspectral image classification method based on multi-scale spectral space convolutional neural network
ActiveCN111639587AImprove classification accuracyOvercome the disadvantage of only extracting features of a single scaleClimate change adaptationScene recognitionStochastic gradient descentTest sample
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image classification method of a multi-scale spectral space convolutional neural network, and mainly solves the problems that in the prior art, only single-scale features are extracted during inter-spectral feature extraction and spatial feature extraction, and the classification effect on ground object categories with inconcentrated sample distribution or small sample size is poor. According to the implementation scheme, the method comprises the following steps: 1) inputting a hyperspectral image to generate a training sample set and a test sample set with different sample numbers; 2) constructing a multi-scale spectral space convolutional neural network; 3) inputting the training set into a multi-scale spectral space convolutional neural network toobtain a prediction category, calculating hinge cross entropy loss by using the prediction category and a real label, and training the network by using a stochastic gradient descent method until thehinge cross entropy loss converges; and 4) inputting the test sample into the trained multi-scale spectral space convolutional neural network to obtain a classification result. The method can obtain high-accuracy classification under the condition of few training samples, and can be used for ground object type detection of a hyperspectral image.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method of monitoring appearance of surface of tyre
Method of detecting an anomaly on the surface of a tyre comprising the following steps in the course of which: A - the image of a given anomaly present on the surface of at least one tyre is produced, B - a multivariate image of the said surface, in which each pixel is represented in the form of a pixel vector, is constructed, with the aid of a collection of filters, in a filter space, the components of each pixel vector having a value corresponding to the value of this pixel in the image transformed with the aid of each of the filters of said collection C - with the aid of a linear function, this multivariate image is transformed from the filter space into a spectral space of given dimension whose variables are the filters or combinations of filters of said collection, so as to form a spectral image, D - a classifier is constructed by determining, for this anomaly, those zones, representative of the spectral space, in which the points of the spectral image, of said anomaly transformed into said spectral space, lie in a statistically representative manner.
Owner:MICHELIN & CO CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN +1
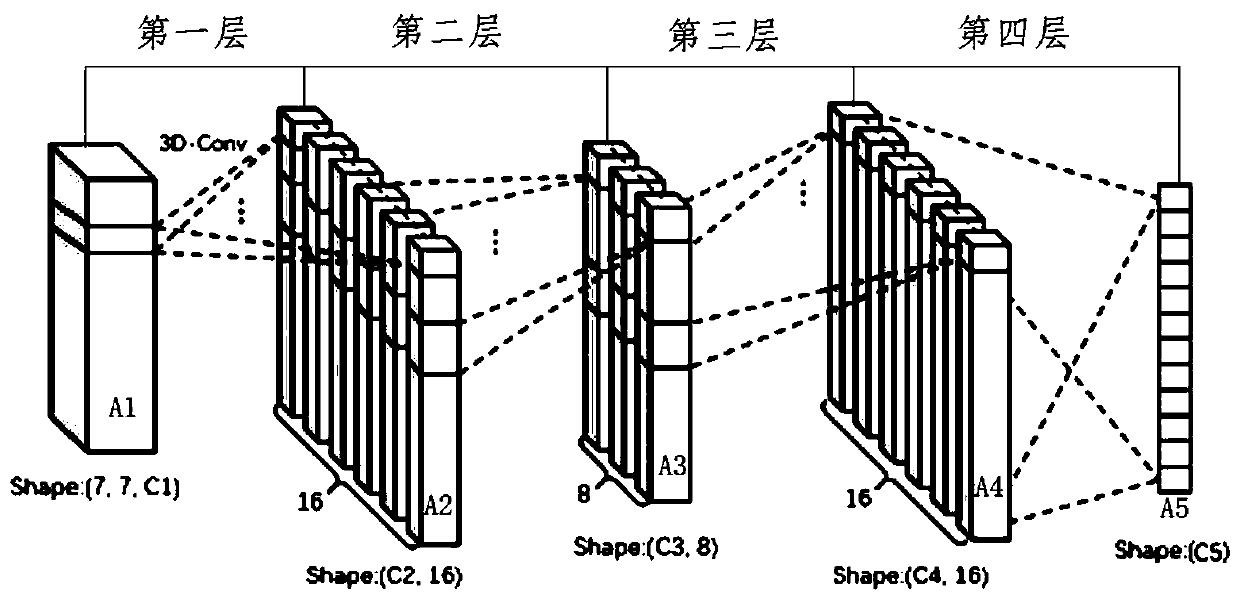
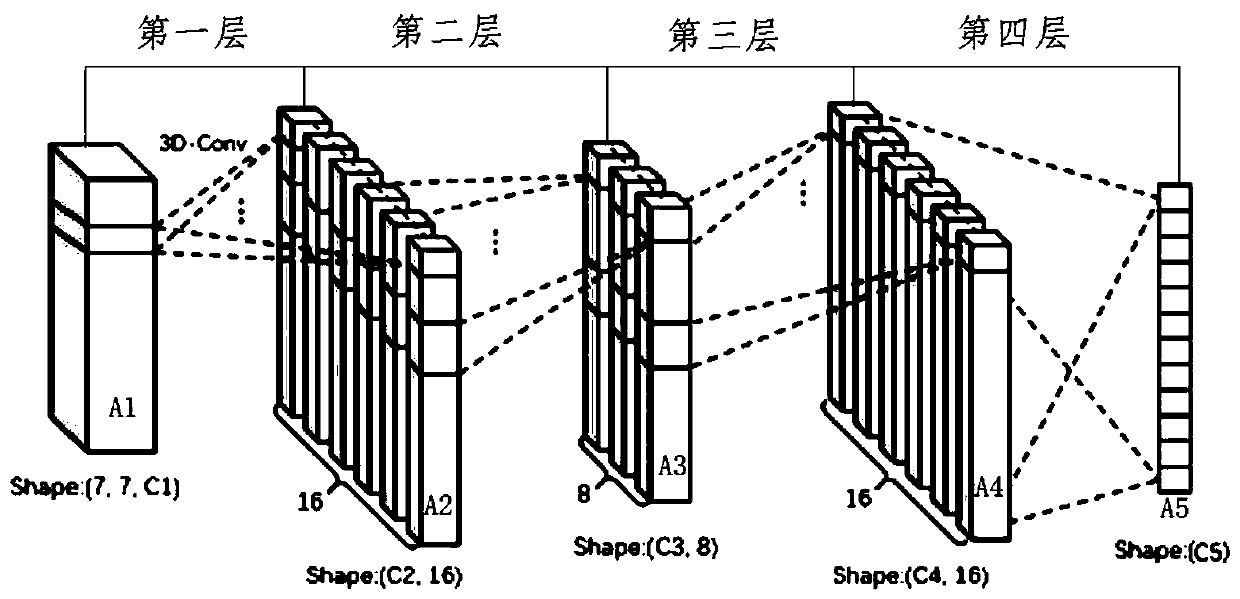
A hyperspectral image classification algorithm based on 3D convolution spectral space feature fusion
ActiveCN109711269AIncrease training speedNo lossClimate change adaptationCharacter and pattern recognitionSmall sampleHyperspectral image classification
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image classification algorithm based on 3D convolution spectral space feature fusion, and the algorithm reduces the correlation between spectral features through employing PCA whitening, and greatly improves the training speed of a neural network. According to the method, the data is subjected to feature extraction in a manner of combining 3D convolution operation and 1D convolution operation; compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that the classification precision can be higher, the representation effect on small samples is better, the calculation efficiency is higher, no information loss exists in the feature fusion process, the efficient and accurate classification can be completed, and in addition, the classification precisionis obviously promoted by using the 3D convolution hyperspectral image spectral space feature fusion method.
Owner:LIAONING TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
Gamut mapping in spectral space based on an objective function
Mapping spectral colors in an Interim Connection Space (ICS) of a full spectral space based on an objective function is provided. A spectral color value in the ICS is accessed, and a spectral gamut boundary of the destination gamut is accessed. The spectral color value is mapped into mapped spectral color value based on minimization of an objective function of coordinates of a first subspace of the ICS, by fixing coordinates of a second subspace of the ICS, subject to a constraint that a result is within the spectral gamut boundary. The first subspace is a null space of a transformation from the ICS to a color space, while the second subspace is an orthogonal complement of the first subspace in the ICS. The constraint is determined by a gamut section that is an intersection of the spectral gamut in the ICS and an affine subspace characterized by the fixed coordinates of the second subspace.
Owner:CANON KK
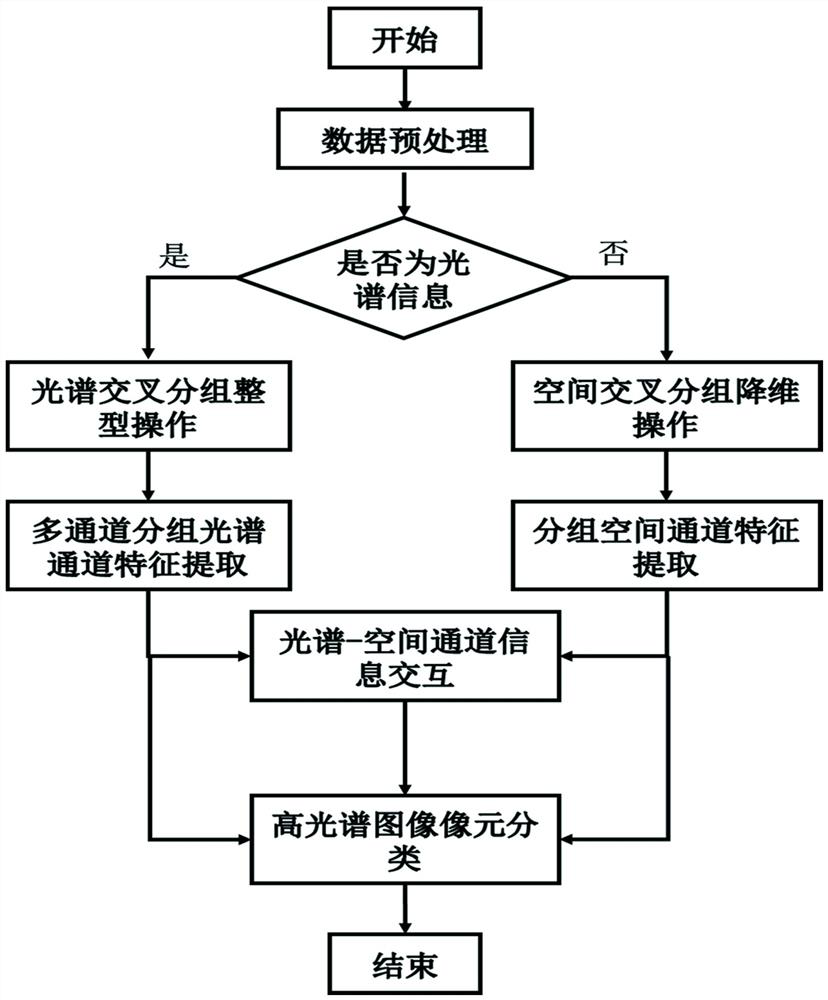
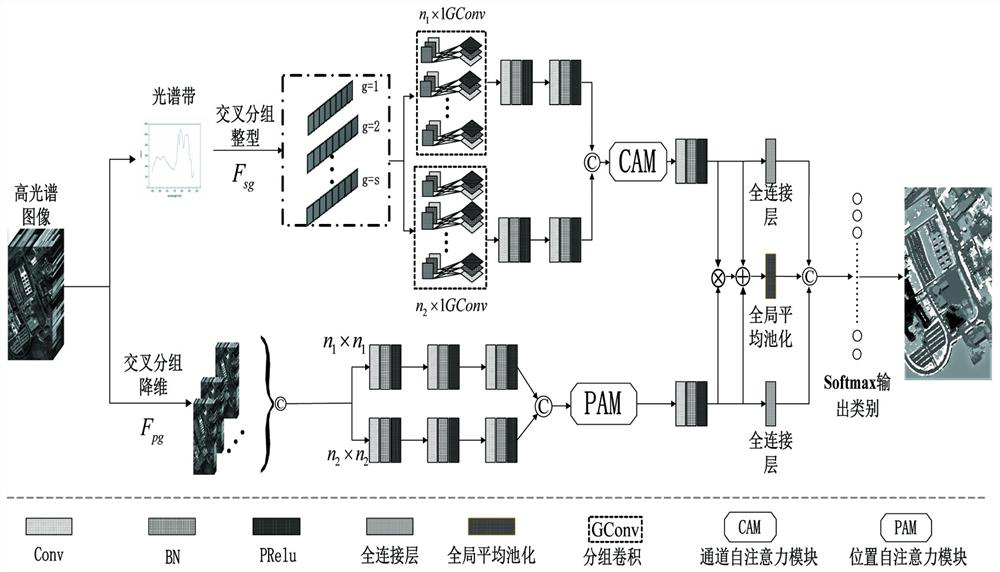
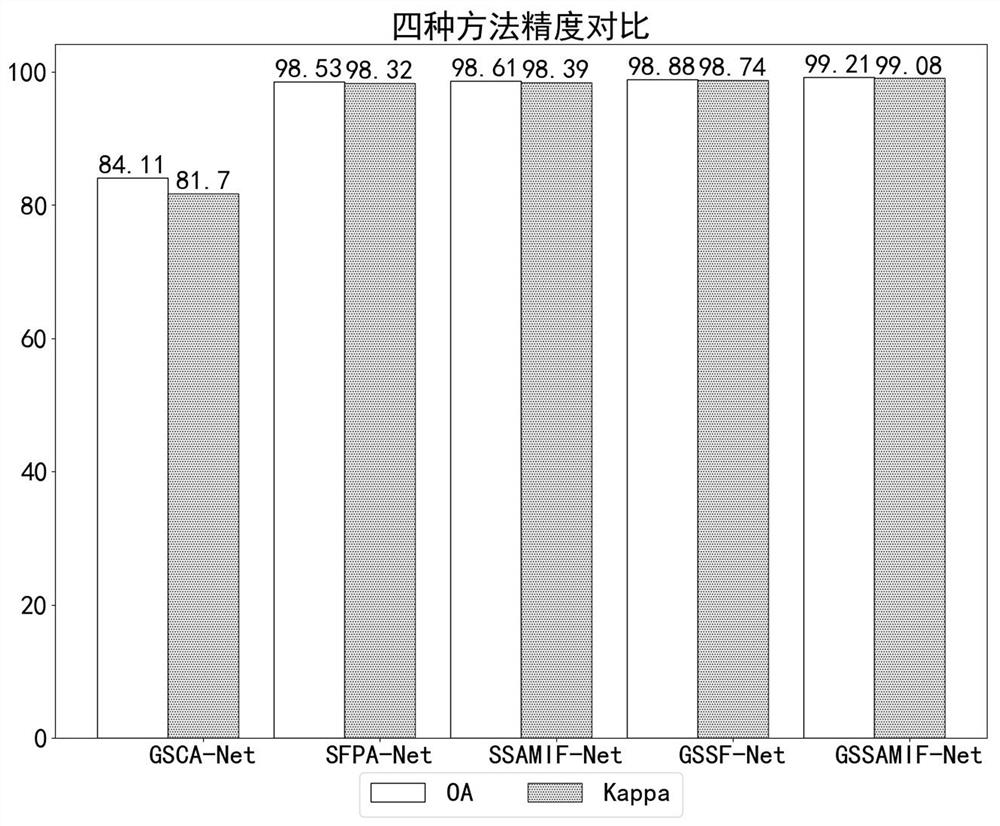
Hyperspectral image classification method based on cross-grouping spatial-spectral feature enhancement network
ActiveCN112200090ASolving the Curse of DimensionalitySolve overfittingScene recognitionColor/spectral properties measurementsRadiologyHyperspectral image classification
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image classification method based on a cross-grouping spatial-spectral feature enhancement network. The hyperspectral image classification method comprises thefollowing steps: 1) cross-grouping spectral features; 2) extracting multichannel grouping spectral characteristics; 3) performing spatial feature cross grouping; 4) extracting grouping space features;5) performing spectral space channel information interaction; and 6) performing hyperspectral image pixel classification. According to the method, spectral spatial feature information is utilized toperform cross grouping and feature extraction operation on spectral features and spatial features respectively, so that the correlation between adjacent spectra can be effectively weakened; channel self-attention and pixel position self-attention operations are adopted to enhance features obtained by cross grouping, information interaction and fusion are carried out on spatial features and spectral features, the fused features are used for classification, and the network classification performance can be improved.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
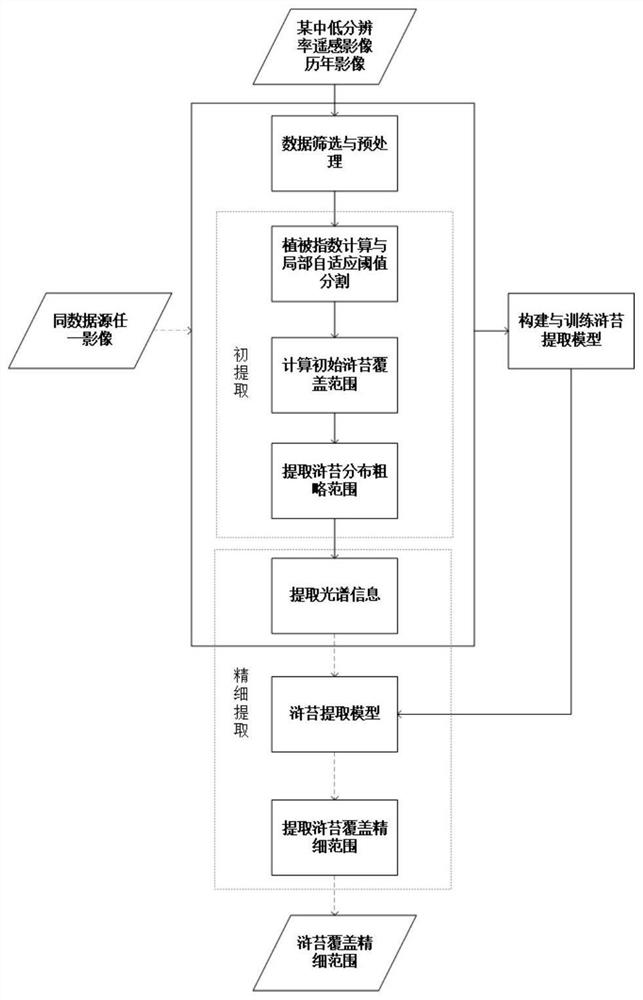
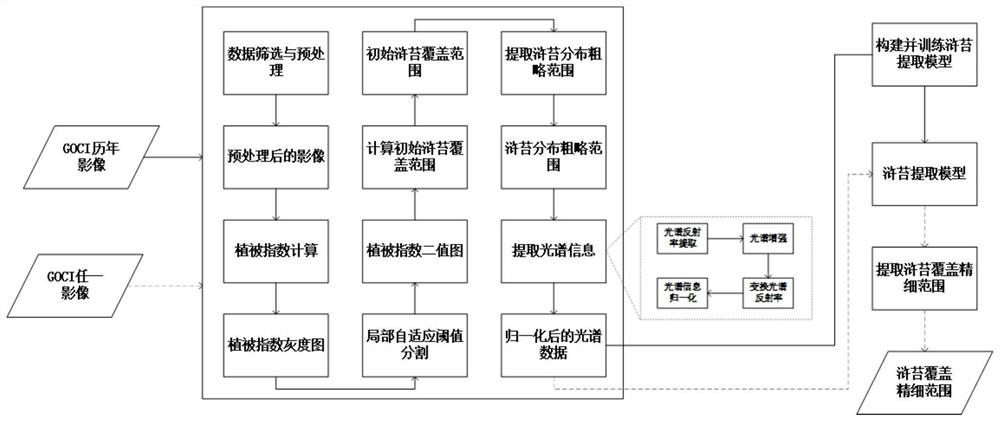
Medium-low resolution remote sensing image enteromorpha coverage information fine extraction method
ActiveCN112258523AImprove universalityImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisVegetation IndexData source
The invention discloses a medium-low resolution remote sensing image-based enteromorpha coverage information fine extraction method. The method comprises the basic steps of screening and preprocessinga data source; calculating four vegetation indexes of the preprocessed image to obtain a grey-scale map of each vegetation index, and performing local adaptive threshold segmentation on each grey-scale map; calculating an initial enteromorpha coverage range; extracting an enteromorpha distribution rough range and spectral information thereof; constructing and training an enteromorpha prolifera extraction model; and extracting an enteromorpha prolifera coverage fine range. The method provided by the invention is scientific and reasonable, comprehensively considers the accuracy of extracting enteromorpha coverage information by a plurality of vegetation indexes, neural network sample balance and spectral space-time characteristics of enteromorpha pixels in medium-low resolution remote sensing images, and can improve the universality and accuracy of the enteromorpha coverage information extraction method to a certain extent.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
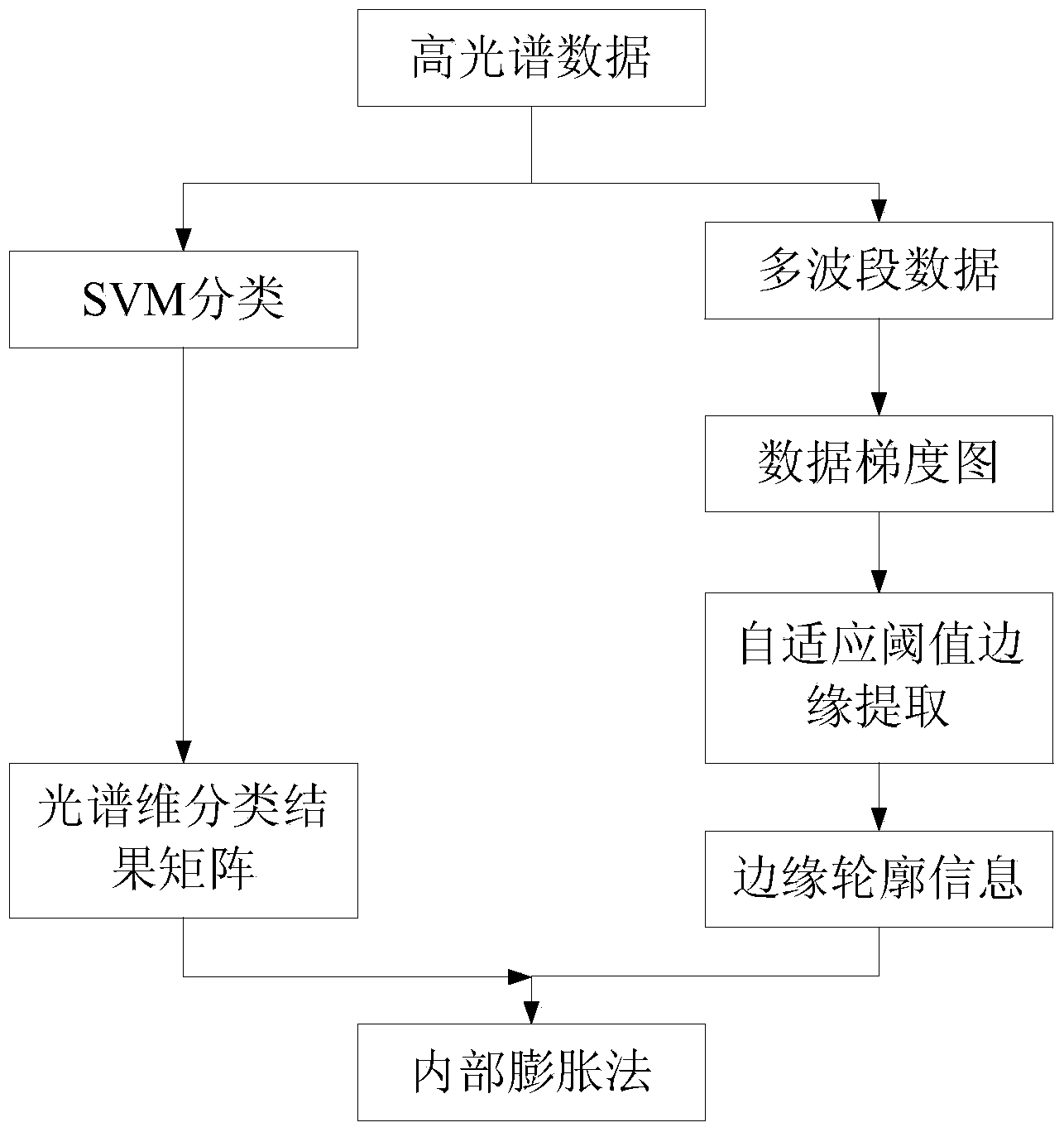
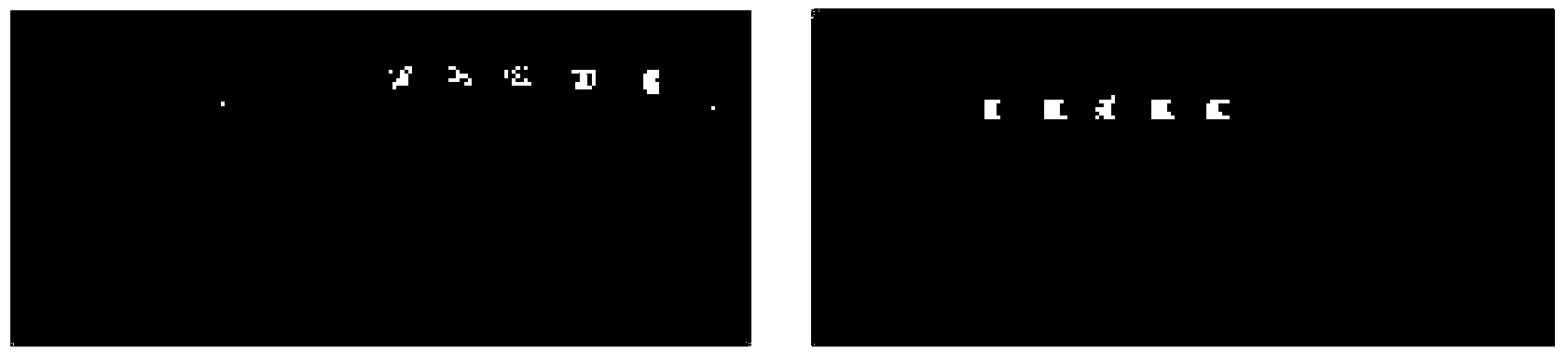
High spectral classification result optimization method combining with space information
ActiveCN103886326ATake advantage ofImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionClassification methodsEdge extraction
The invention discloses a high spectral classification result optimization method combining with space information. A conventional high spectral image classification technology mainly focuses on how to use the classification information of spectral spaces better, but ignores the information of image spatial domains. According to the invention, in the process of carrying out self spectral feature classification by using self data, spectral classification results are supplemented by adopting spatial domain effective information combining self-adaptive threshold edge extraction with an internal expansion method. According to the invention, an SVM (support vector machine) based classification method is adopted for carrying out spectral domain classification on data firstly; then, effective spatial domain information is introduced by using the self-adaptive threshold edge and the internal expansion method so as to correct spectral classification results. According to the invention, information contained in hyperspectral data is used more fully, and the precision of hyperspectral image classification is improved.
Owner:奥谱天成(湖南)信息科技有限公司
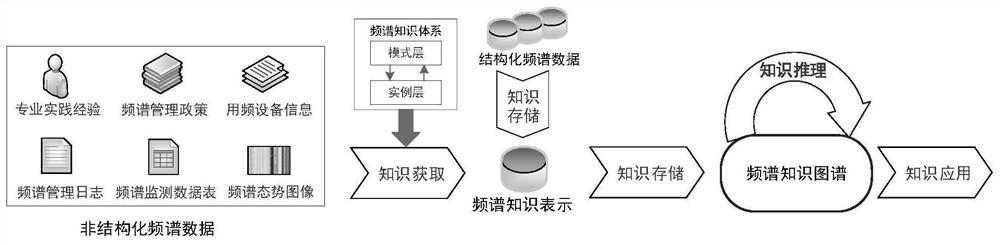
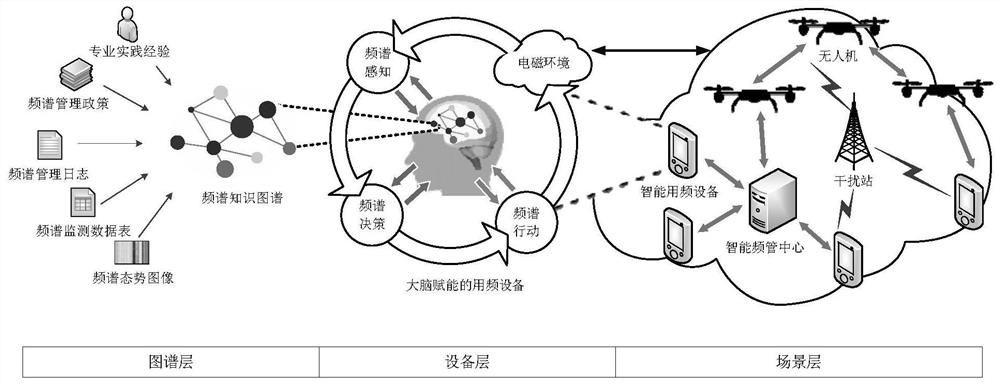
Intelligent spectrum management and control framework based on spectrum knowledge graph
ActiveCN113038614AImprove management and control efficiencyImprove the level of intelligenceTransmission monitoringHigh level techniquesFrequency spectrumExecution unit
The invention provides an intelligent spectrum management and control framework based on a spectrum knowledge graph. The framework comprises a map layer, a device layer and a scene layer. And the graph layer is a driving kernel of the intelligent spectrum management and control framework, namely a multi-domain associated spectrum knowledge graph. And the equipment layer is an execution unit of the intelligent frequency spectrum management and control framework and mainly refers to intelligent frequency equipment for configuring a frequency spectrum knowledge graph. And the scene layer is the application presentation of the intelligent spectrum management and control framework. And the intelligent frequency management center issues a frequency management task to the intelligent frequency equipment in the scene, and the intelligent frequency equipment realizes a given frequency spectrum management and control target and reports information to the intelligent frequency management center at the same time. And the intelligent frequency management center expands and perfects the spectrum knowledge graph according to diversified scenes and tasks. Modeling characterization of the multivariate relation in the spectrum space can be achieved, the intelligent level of spectrum management and control under the complex environment is improved, and the method becomes a new tool in the field of spectrum management and control in the future.
Owner:ARMY ENG UNIV OF PLA
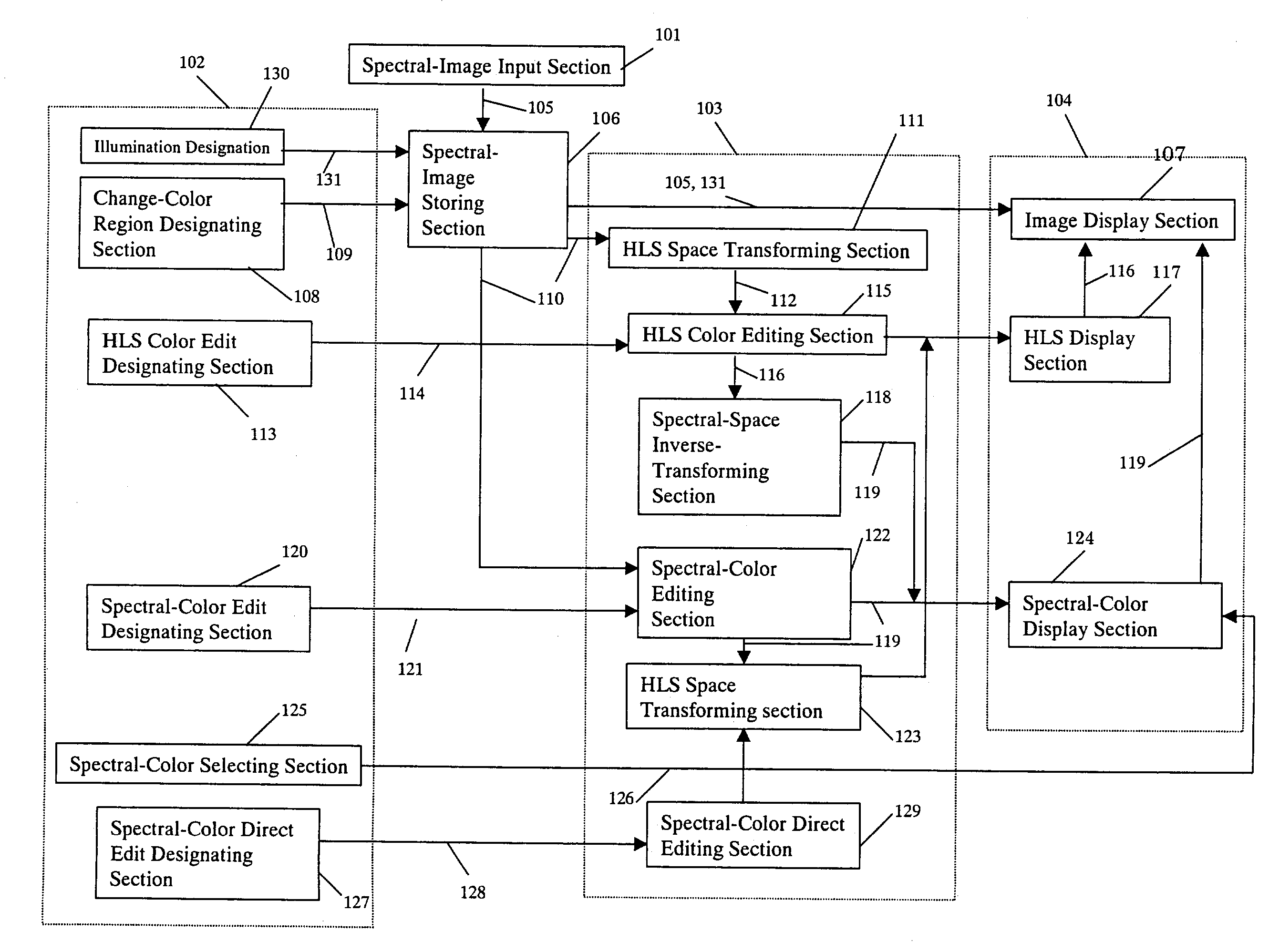
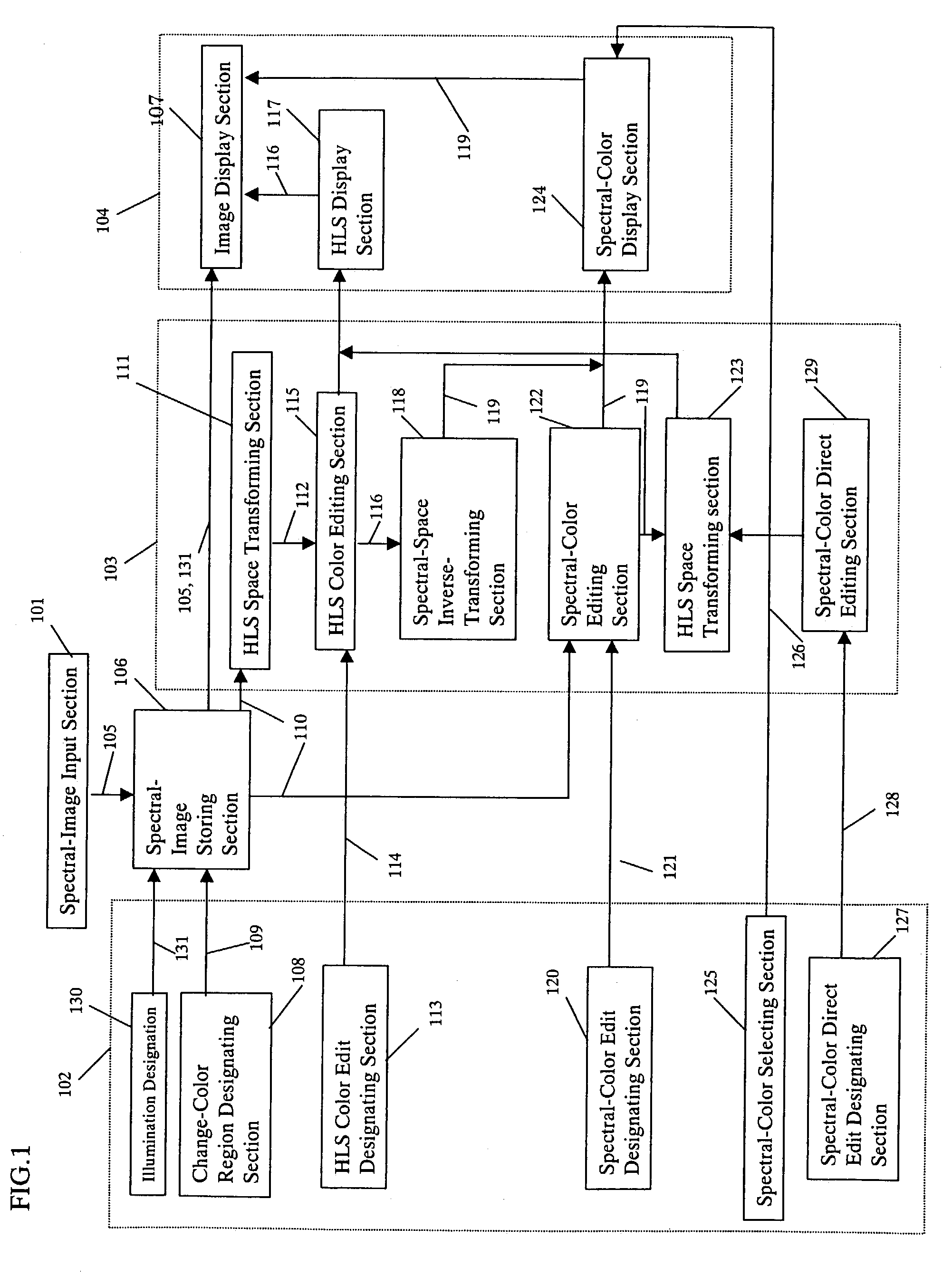
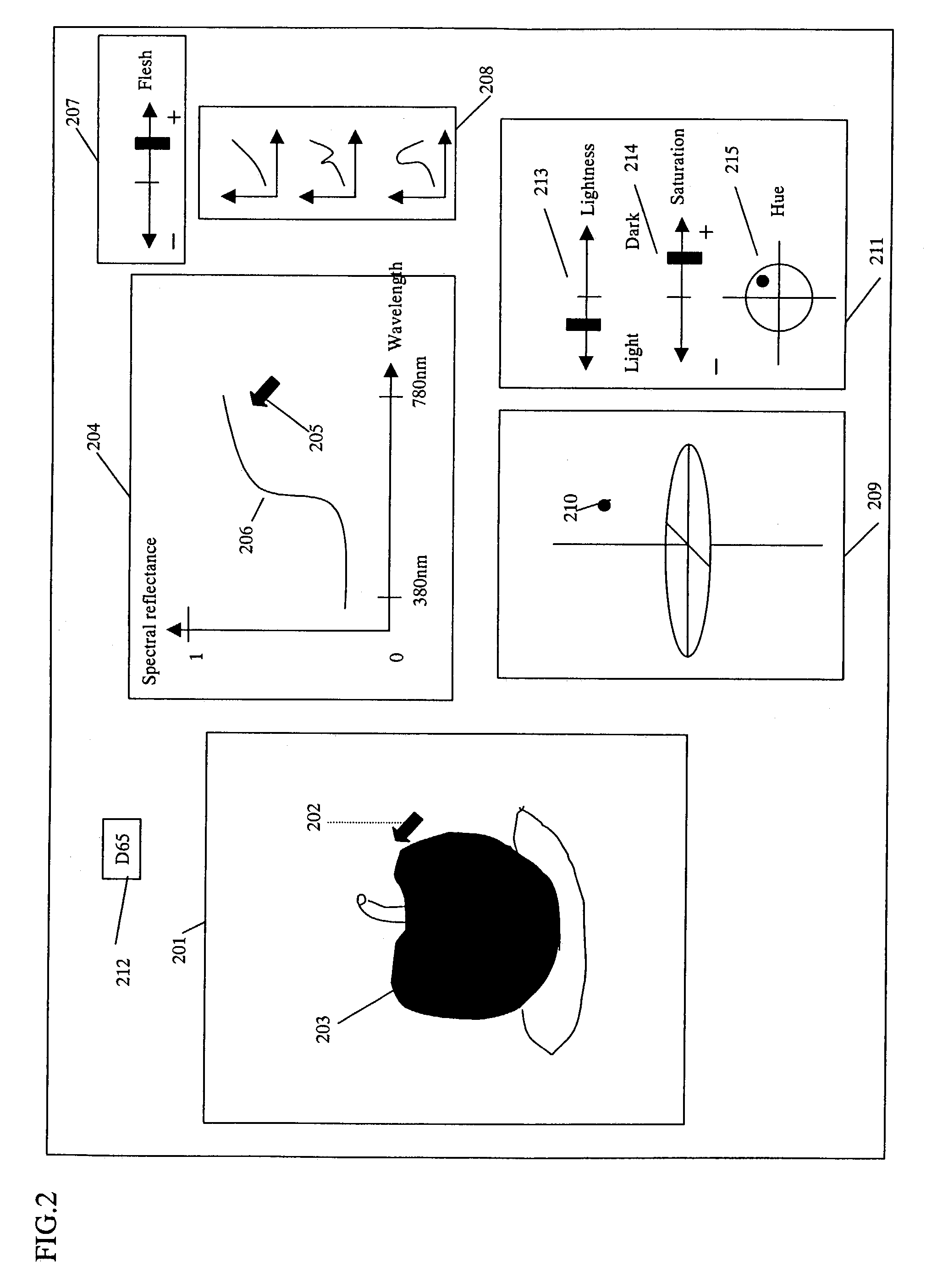
Apparatus and method for editing colors
ActiveUS7312899B2High saturationEasy to handleDigitally marking record carriersColor measuring devicesRadianceColor correction
Disclosed is an apparatus and method for color-editing capable of simply carrying out color-editing spectral values, such as spectral reflectance, spectral transmittance, spectral radiance and spectral radiant intensity. When color-editing a spectral value of spectral image, the spectral color is transformed into a low-dimensional color space easy for the human to handle in an HLS space transforming section and color-editing and color-correction are carried out in the low-dimensional color space in on HLS color-editing section thereby generating a proper spectral value from a transformed low-dimensional color in a spectral-space inverse-transforming section. Also, a spectral color editing section receives a spectral editing instruction signal and transforms a wavelength width of a spectral color peak to a narrow one, thereby improving saturation.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
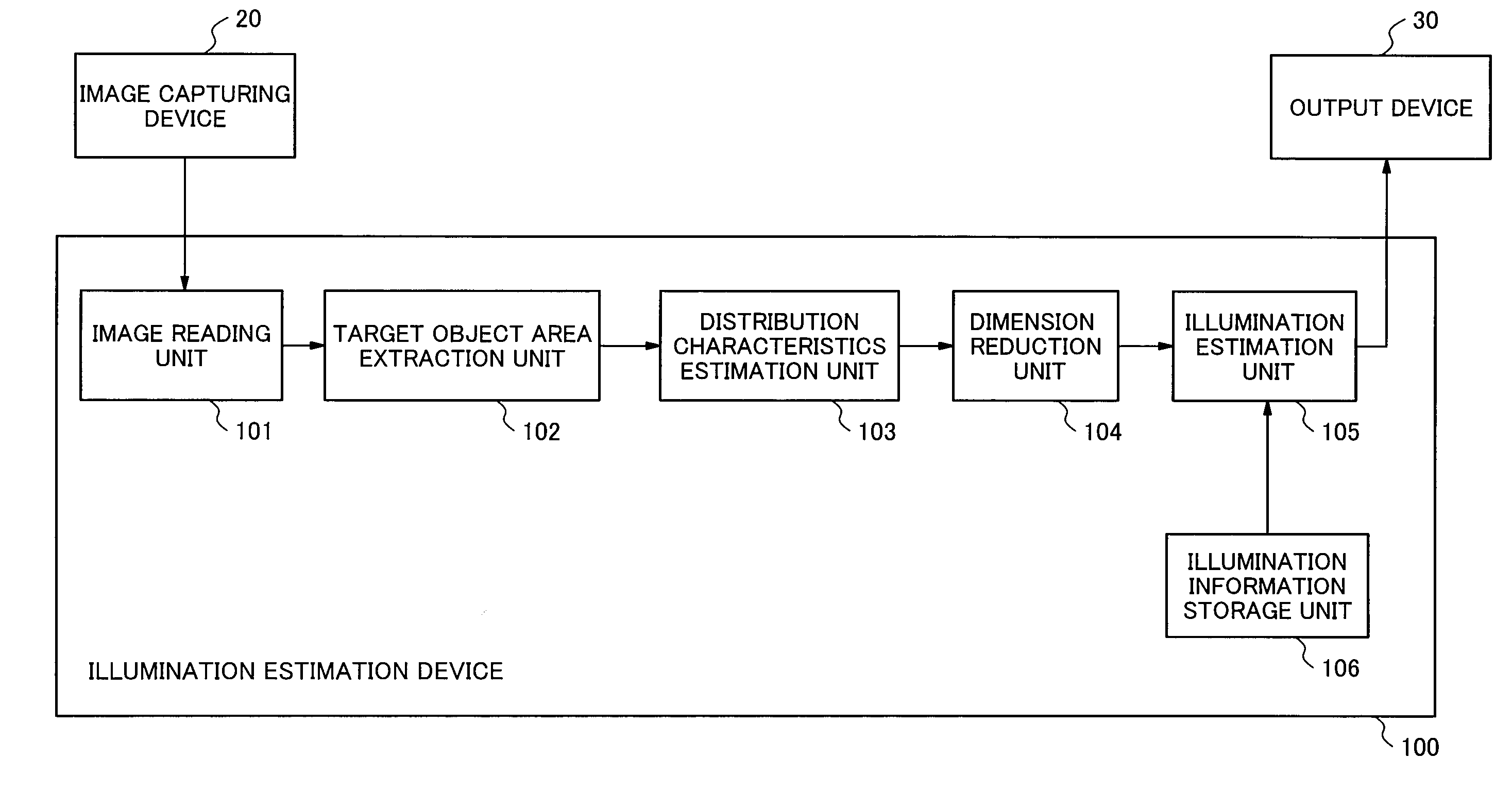
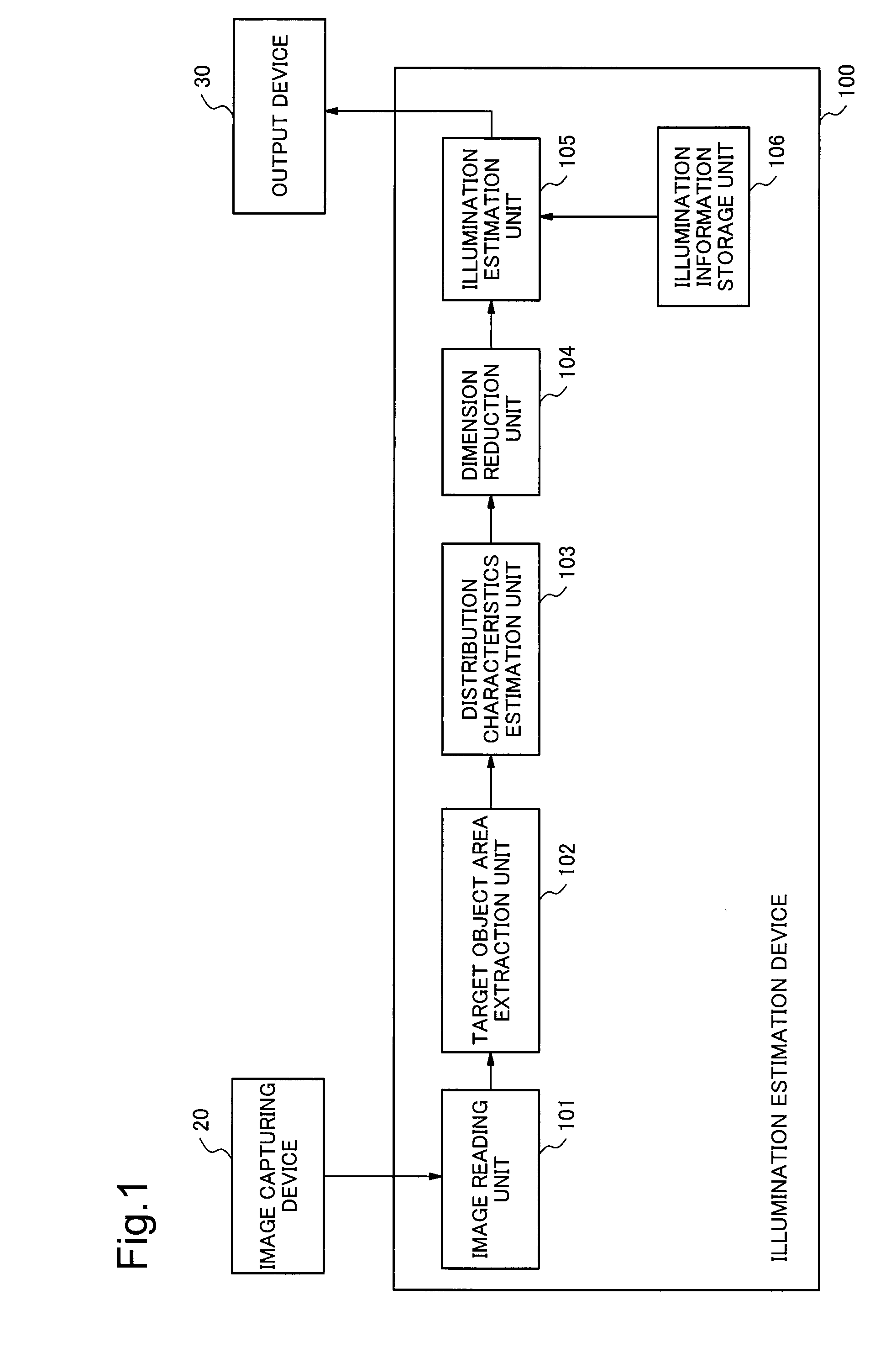
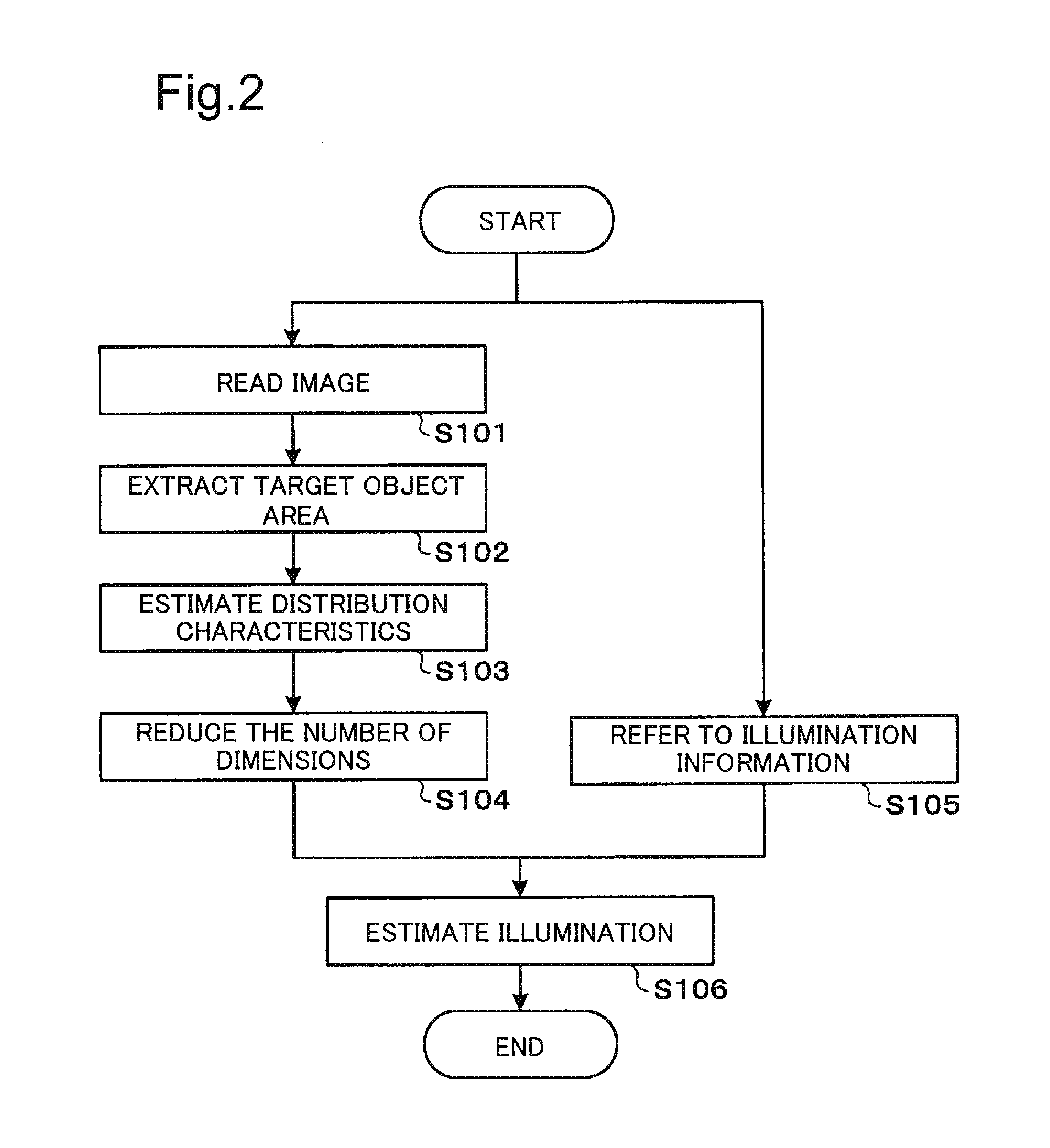
Illumination estimation device, illumination estimation method, and storage medium
ActiveUS20160119558A1Accurate representationImage enhancementTelevision system detailsIlluminanceEstimation methods
Illumination estimation device includes: target object area extraction unit which extracts an object area from a multispectral image, the object area being an area, including specular reflection, of an object; distribution characteristics estimation unit which estimates information representing a subspace that approximates a distribution of observation values in a spectral space, as distribution characteristics, the distribution characteristics being characteristics of a spreading manner of the observation values in the object area within the spectral space; dimension reduction unit which selects a distribution characteristic to be used from among the distribution characteristics estimated by the distribution characteristics estimation unit depending on the number of dimensions to be reduced, the number of dimensions to be reduced being determined in advance by a light environment; and illumination estimation unit which estimates spectral characteristics of illumination based on the subspace information to be represented by the distribution characteristic selected by the dimension reduction unit.
Owner:NEC CORP
Image multispectral analysis method used for video monitoring or machine vision field
InactiveCN104217434ASolve perceptionResolve identifiabilityImage analysisClosed circuit television systemsVideo monitoringVisibility
The invention discloses an image multispectral analysis method used for a video monitoring or machine vision field, belongs to the fields of image processing, video monitoring and intelligent transportation, and particularly relates to a video image histogram spectrum segmentation method applied to the video monitoring or machine vision field, and a method for local spectrums to extend and stretch to whole spectral space. A gray scale histogram spectrum of an integral video image is segmented according to requirements, and then, an interested spectrum is stretched to expand to the whole spectral space. Only the interested gray scale spectrum is stretched to the whole spectral space, or each spectrum is stretched to the whole spectral space one by one, so that the dynamic range of the corresponding image of a corresponding spectrum is expanded, the visibility of image details is improved, and the perception and identification problems of vision information under a condition of a wide dynamic range can be favorably solved, and uninterested spectrums can be removed so as to save data bandwidth.
Owner:NANJING GMINNOVATION TECH CO LTD
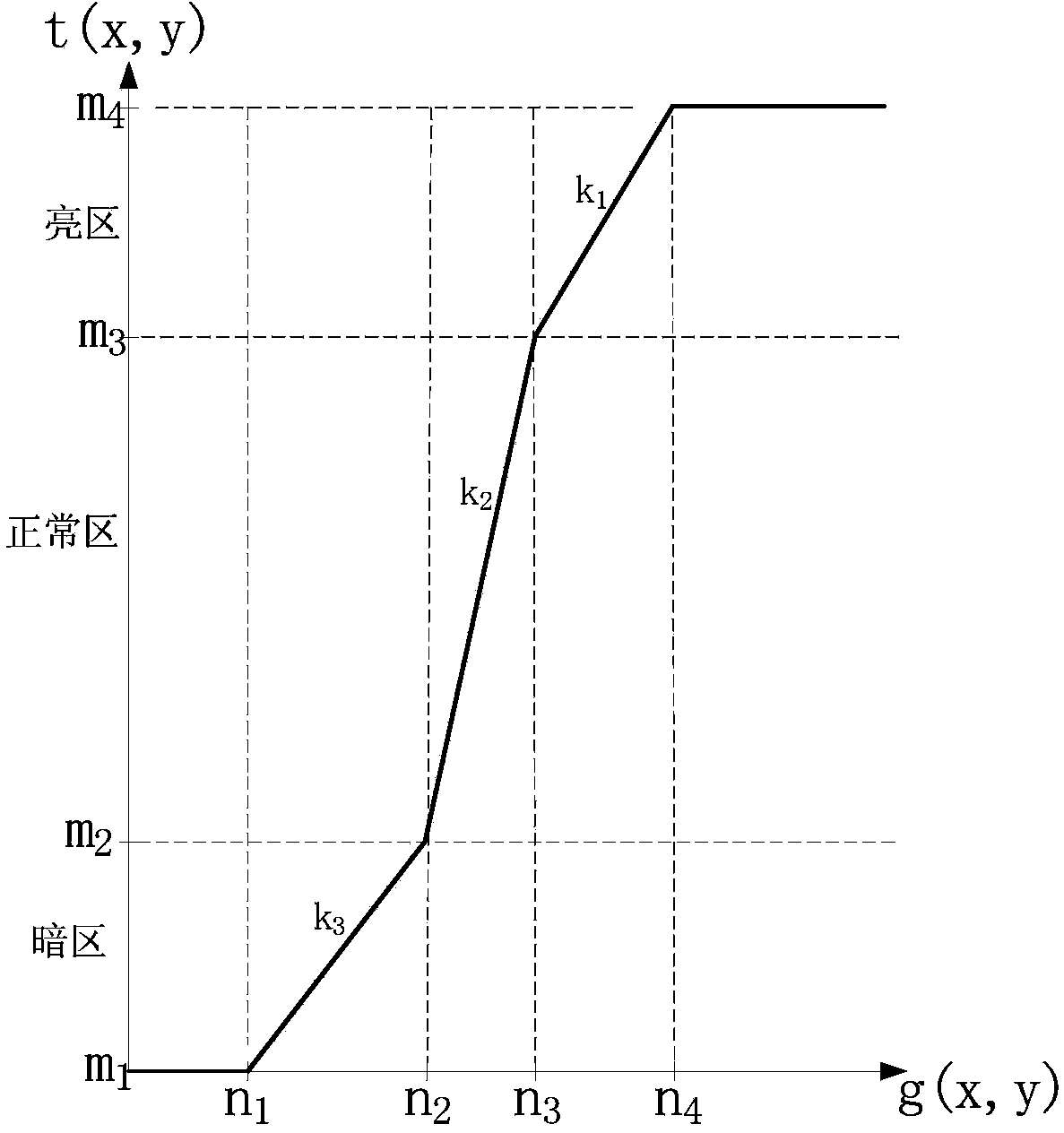
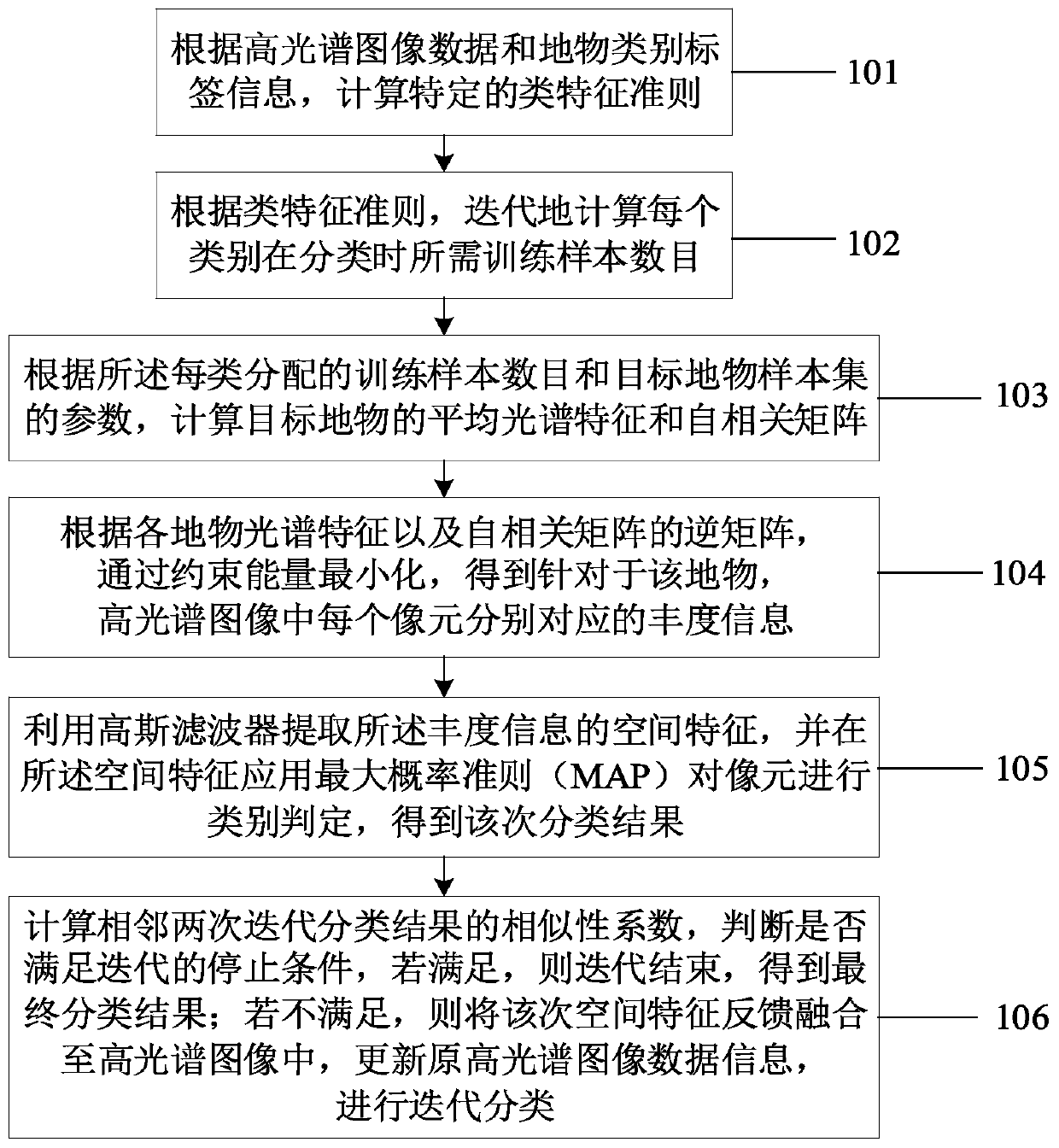
Hyperspectral image spectral space classification method based on class characteristic iterative random sampling
ActiveCN110738171ATo solve the classification accuracy is not highClimate change adaptationScene recognitionObject ClassImaging data
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image spectral space classification method based on class characteristic iterative random sampling. The method comprises the following steps: calculating classcharacteristic criteria of each class according to hyperspectral image data and ground object class label information; iteratively calculating the number of training samples which should be allocatedto each category during classification according to a category feature criterion; calculating an average spectral characteristic and an autocorrelation matrix of a target ground object according to the number of the distributed training samples of each type and the parameter information of the target ground object sample set; calculating abundance information corresponding to each pixel in the hyperspectral image for the ground object through a constraint energy minimization method according to the average spectral characteristic of each ground object and the inverse matrix of the autocorrelation matrix; and calculating a similarity coefficient of two adjacent iterative classification results according to the classification image information, judging whether the similarity coefficient meets an iterative classification cut-off condition, and carrying out iterative classification on the fused and updated data.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Hyperspectral image dimension reduction method
PendingCN110070485ATake advantage ofImprove classification accuracyGeometric image transformationKernel principal component analysisAlgorithm
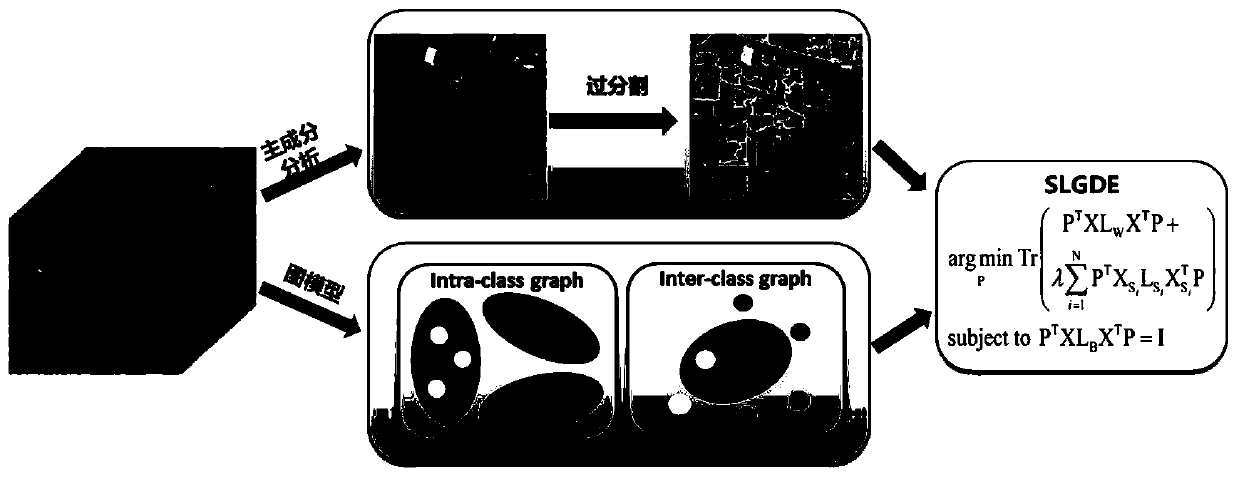
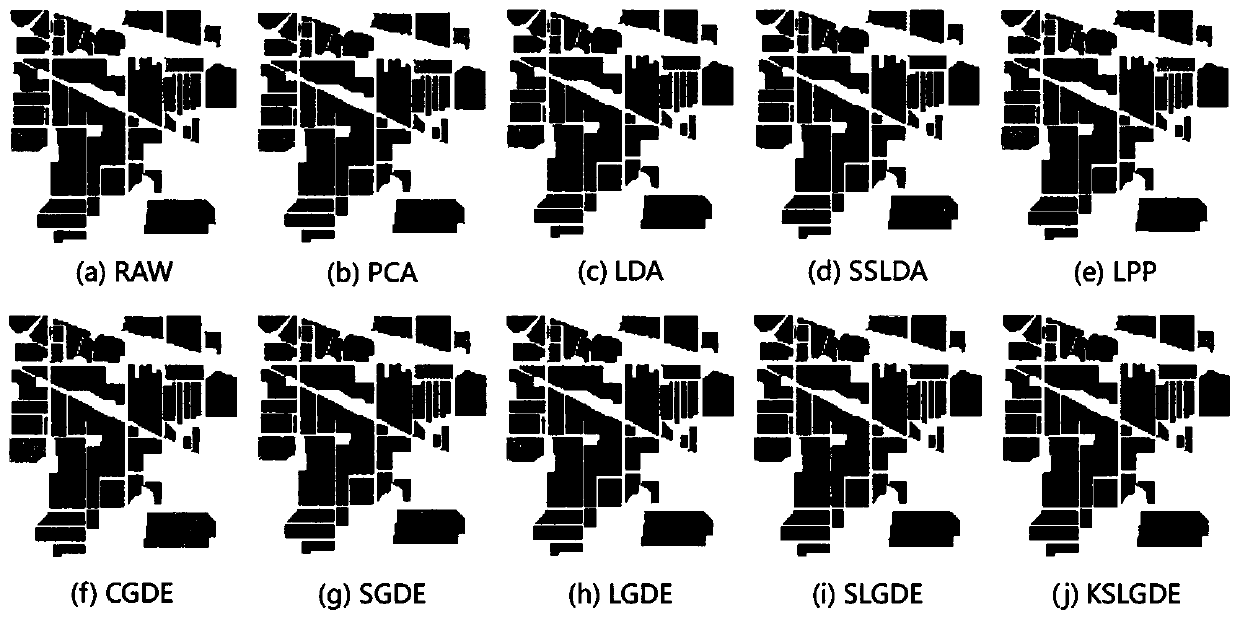
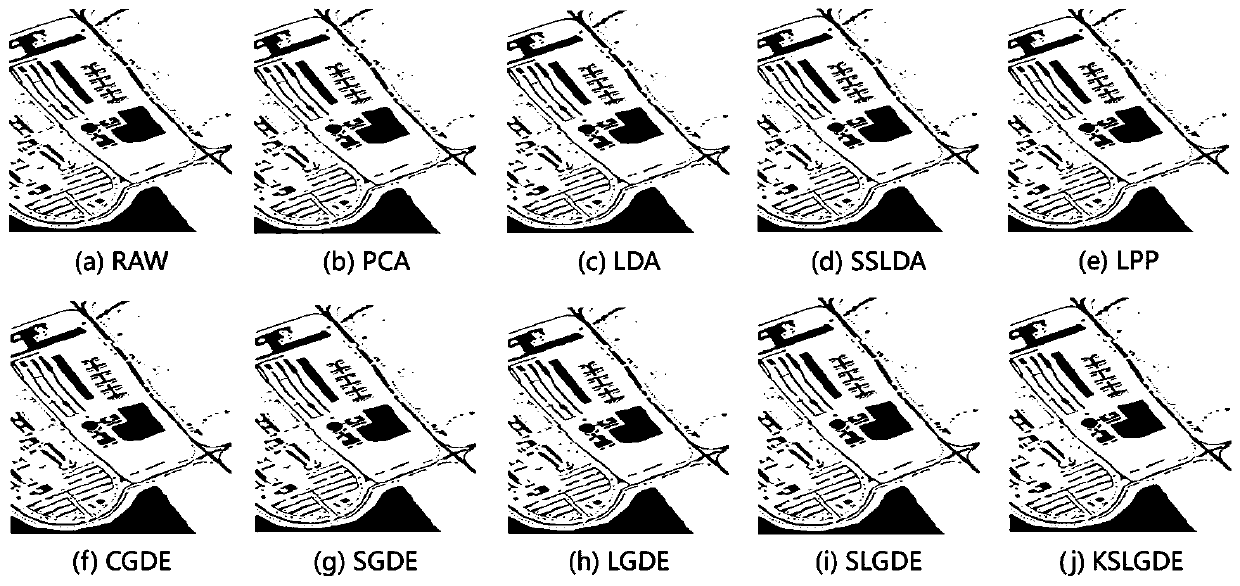
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image dimension reduction method, which comprises the following steps: firstly, dividing an original hyperspectral image into non-overlapped superpixels by using an over-segmentation method; next, as the pixel point in one super-pixel usually belongs to the same kind of objects, describing the spatial information by using an intra-class graph in the invention; and finally, introducing the intra-class graph based on the super-pixel level into an LGDE model as a regular item. In addition, in order to effectively capture the nonlinear characteristics of thehyperspectral image, the invention expands the linear LGDE into a kernel version. An original pixel point classification method (RAW), a principal component analysis (PCA), a linear discriminant analysis (LDA) method, a spectral space linear discriminant analysis (SSLDA) method, a local reservation projection (LPP) method, a collaborative graph-based discriminant analysis (CGDE) method, a sparsegraph-based discriminant analysis (SGDE) method, and a local graph-based discriminant analysis (LGDE) method are compared. Under the same experiment conditions, the classification result of the methodis more accurate.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Hyperspectral image classification method and device combined with spectral space multi-layer perceptron
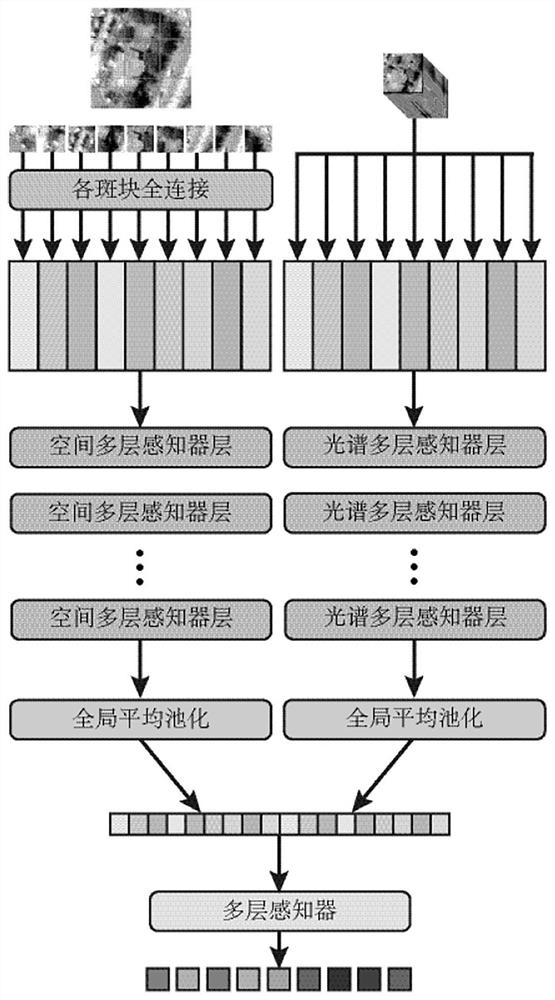
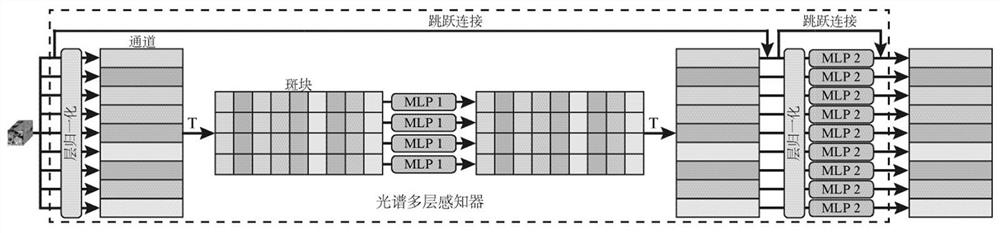
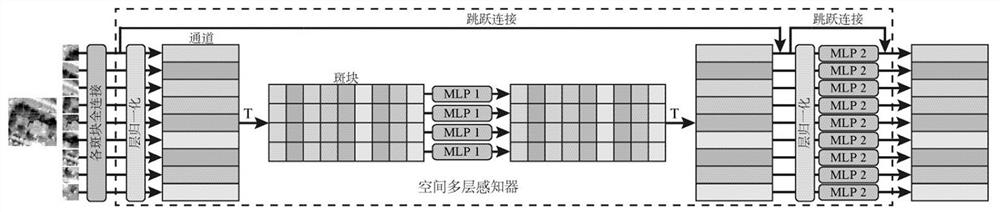
PendingCN113850316AEffective classificationImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionComputer vision
The invention belongs to the technical field of hyperspectral image classification, and particularly relates to a hyperspectral image classification method and device combined with a spectral space multi-layer perceptron, and the method comprises the steps: firstly extracting global spectral features from a hyperspectral image through a spectral multi-layer perceptron; then extracting local spatial features from the hyperspectral image by using a spatial multilayer sensor; and finally, fusing the global spectral features and the local spatial features by using a multi-layer perceptron to perform joint classification on the hyperspectral image. The spectral features and the spatial features can be extracted from the hyperspectral image, the features can be effectively fused and then combined classification is carried out, and the invention has high classification precision.
Owner:PLA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE INFORMATION ENG UNIV PLA SSF IEU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com