Hyperspectral image dimension reduction method
A hyperspectral image, dimensionality reduction technology, applied in image data processing, graphic image conversion, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of less training samples, information redundancy, Hughes, etc., and achieve the effect of improving classification accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
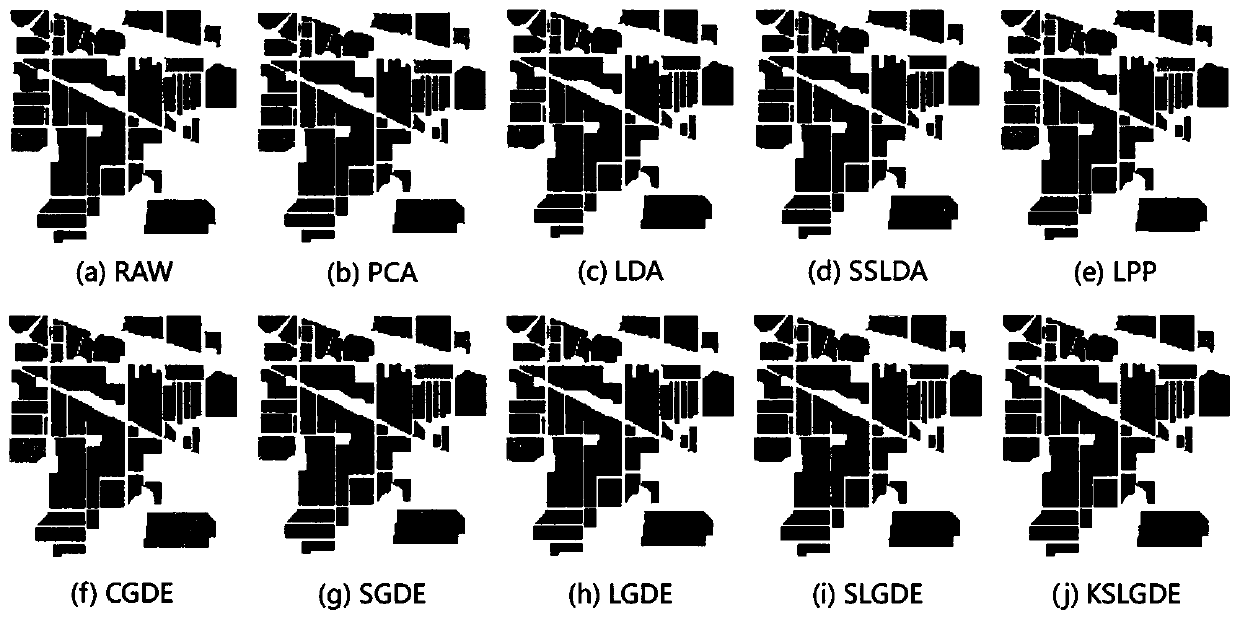
[0087] The technical solution provided by the present invention is applied to the classification of Indian Pines Scene hyperspectral image data. This image was acquired by the AVIRIS sensor at the Indian Pine Test Site in Northwest Indiana. It was filmed on June 12, 1992. It contains a total of 224 bands. The present invention firstly removes four spectral bands whose values are all 0 and 20 noise bands, and then uses 200 of them. The size of this image is 145×145. Its spatial resolution is 20m. There are a total of 10249 pixels with label values in the image, and there are 16 types of objects in total.
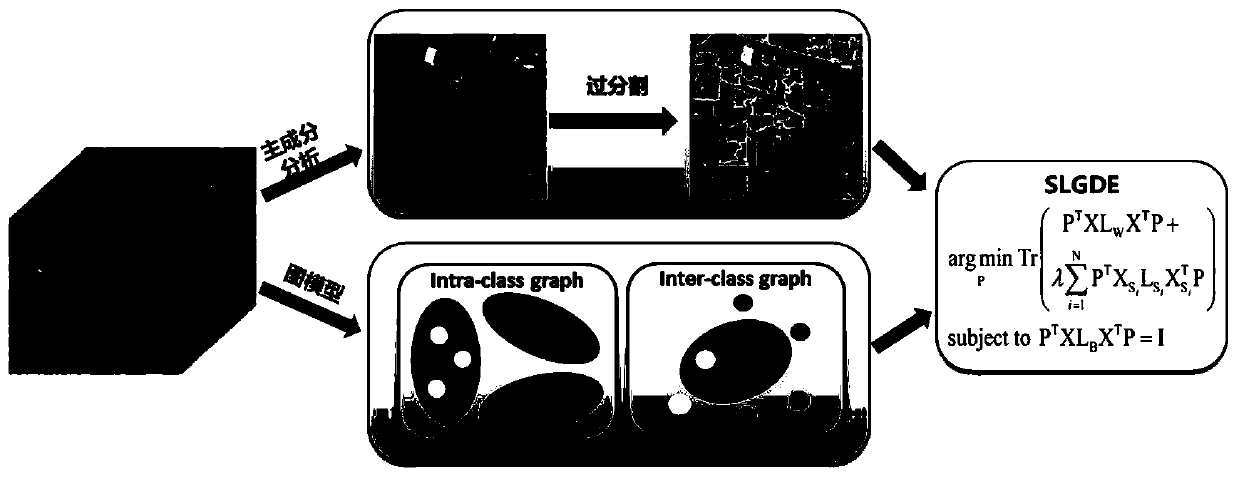
[0088] Using the proposed method of the present invention to fuse the spatial information into the LGDE model in the form of a regular term, and use the kernel form of the LGDE model to capture the nonlinear characteristics of the hyperspectral image, so as to obtain a classification of the hyperspectral image.
[0089] In order to verify the effectiveness of the pre...
Embodiment 2
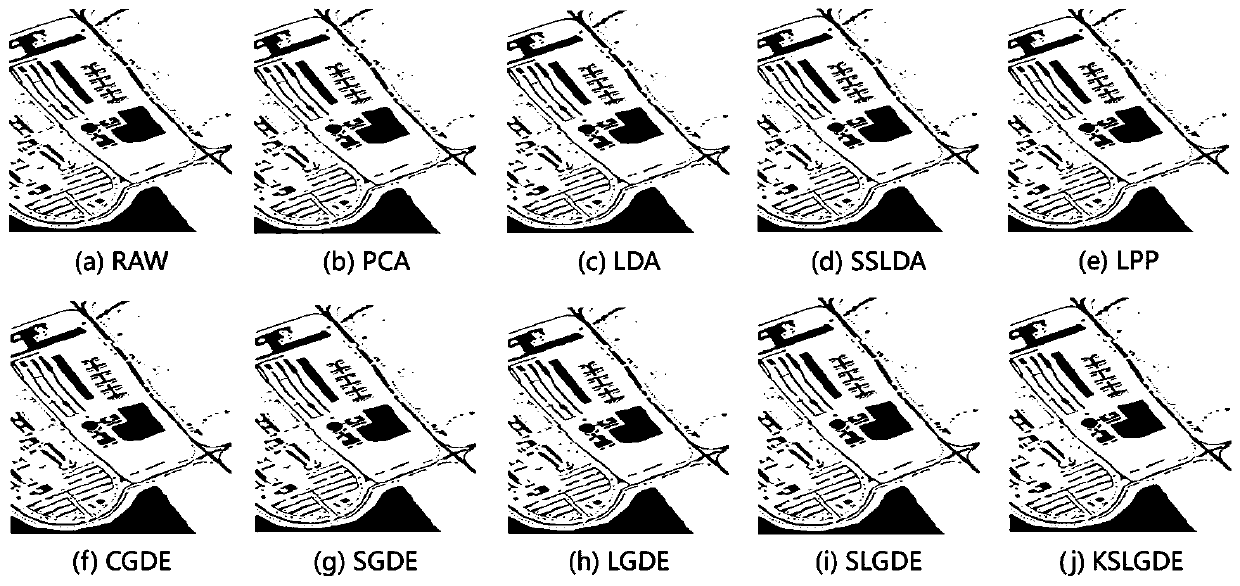
[0105] The technical solution provided by the invention is applied to the classification of Pavia University Scene hyperspectral image data. This image was acquired by a ROSIS sensor flight over Pavia in northern Italy. It was acquired on July 8, 2002. The raw image contains 115 spectral channels from 0.43 μm to 0.86 μm. The present invention uses 103 of the bands after removing the noise bands. The size of the images is 610×340 pixels and the spatial resolution is 1.3m. The images contain a total of 9 categories of objects and each category has more than 1000 samples.
[0106] Using the proposed method of the present invention to fuse the spatial information into the LGDE model in the form of a regular term, and use the kernel form of the LGDE model to capture the nonlinear characteristics of the hyperspectral image, so as to obtain a classification of the hyperspectral image.
[0107]In order to verify the effectiveness of the present invention, the classification result...
Embodiment 3
[0124] The technical solution provided by the present invention is applied to the hyperspectral image data classification of Kennedy Space Center. This image was acquired by the AVIRIS sensor over the Kennedy Space Center. It was acquired on May 23, 1996. The original image contains 224 spectral channels. The present invention uses 115 of these bands after removing the noise bands. The size of the image is 512×614 pixels and the spatial resolution is 18m. The number of images used for surface object classification is 13.
[0125] Using the proposed method of the present invention to fuse the spatial information into the LGDE model in the form of a regular term, and use the kernel form of the LGDE model to capture the nonlinear characteristics of the hyperspectral image, so as to obtain a classification of the hyperspectral image.
[0126] In order to verify the effectiveness of the present invention, the classification results are respectively compared with the original pi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com