Patents
Literature
685results about "Recovering materials" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
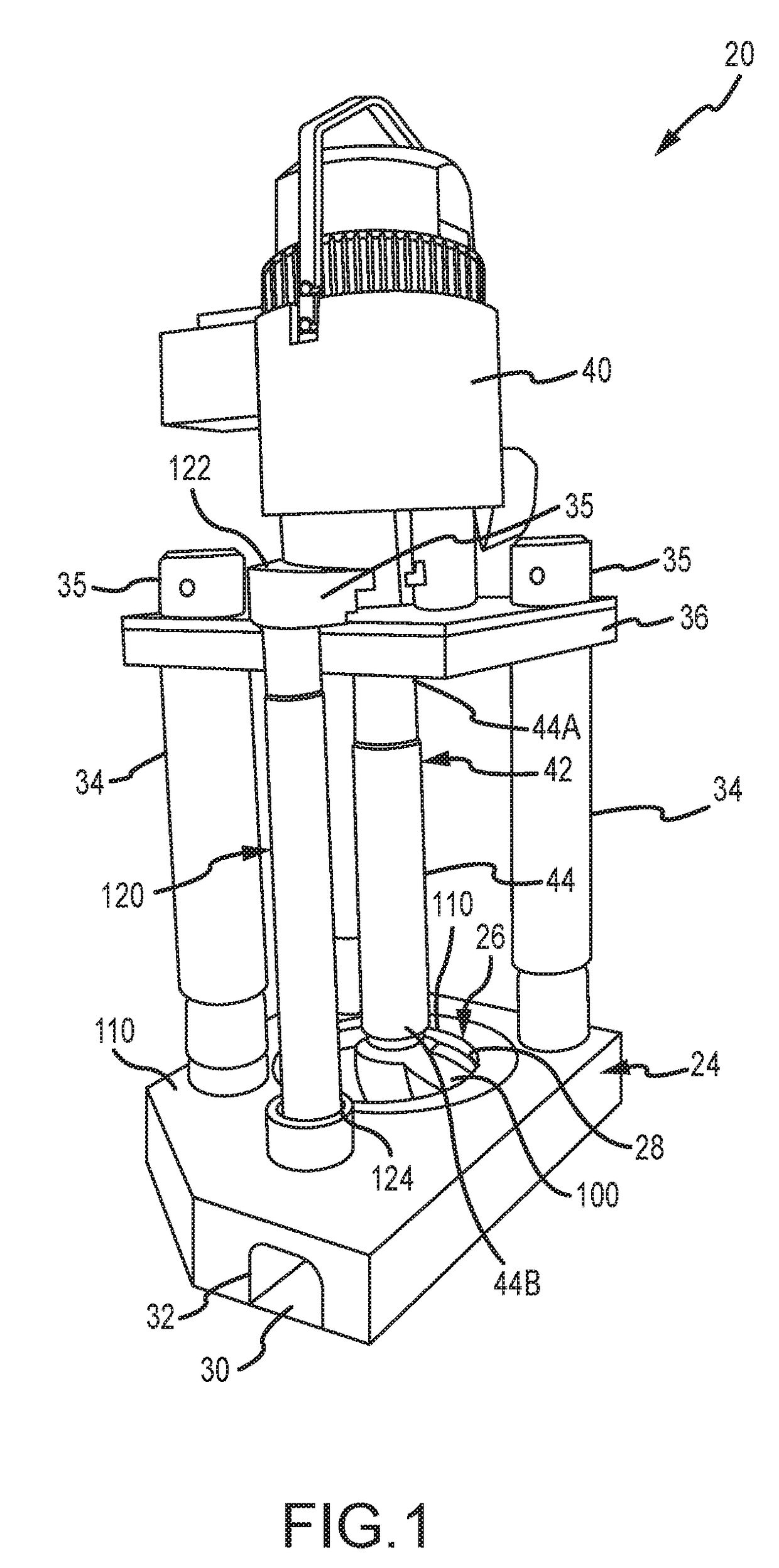
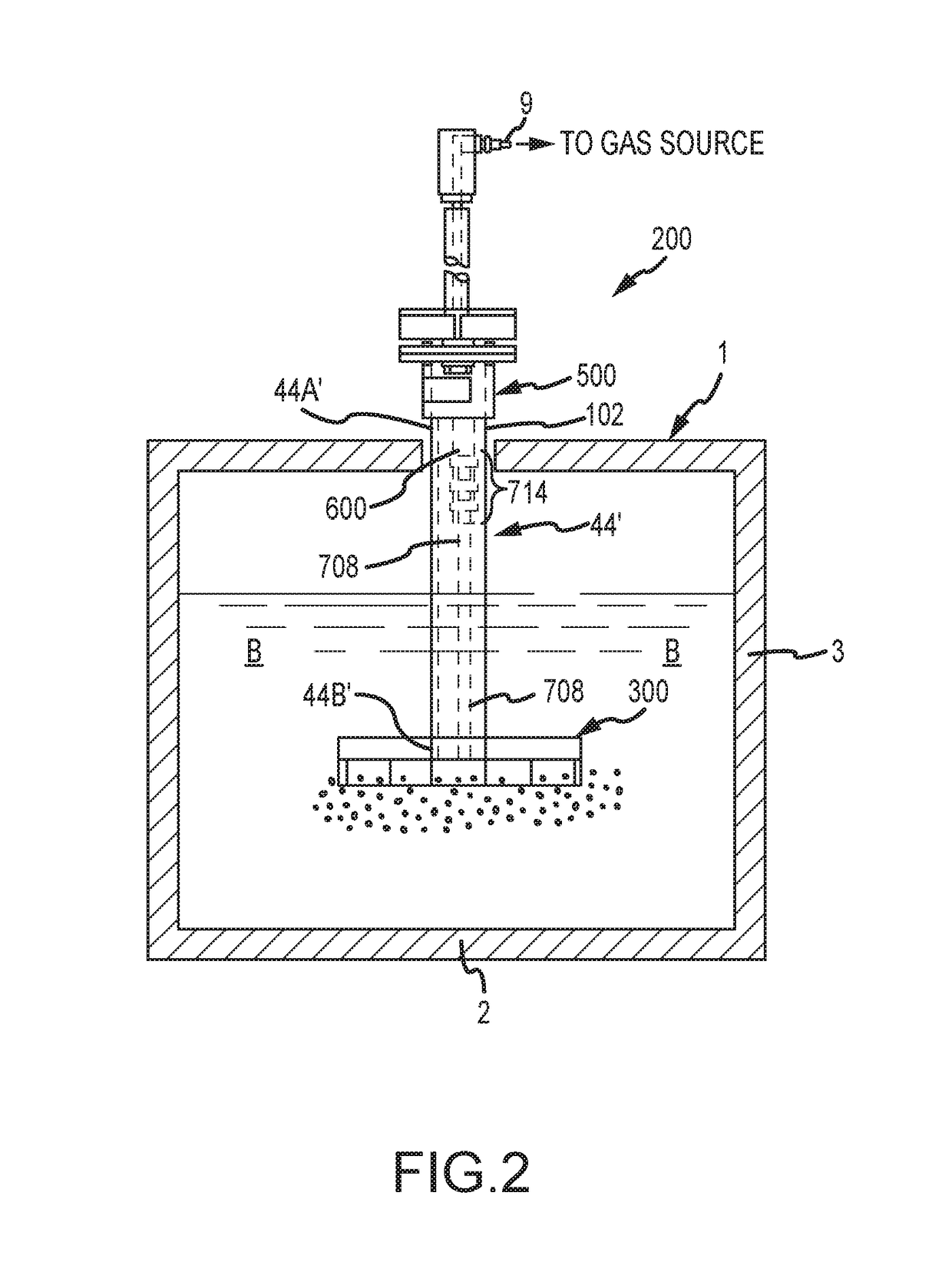
Powder distribution in additive manufacturing of three-dimensional articles
ActiveUS9505057B2Additive manufacturing apparatusTransportation and packagingPowder bedMechanical engineering
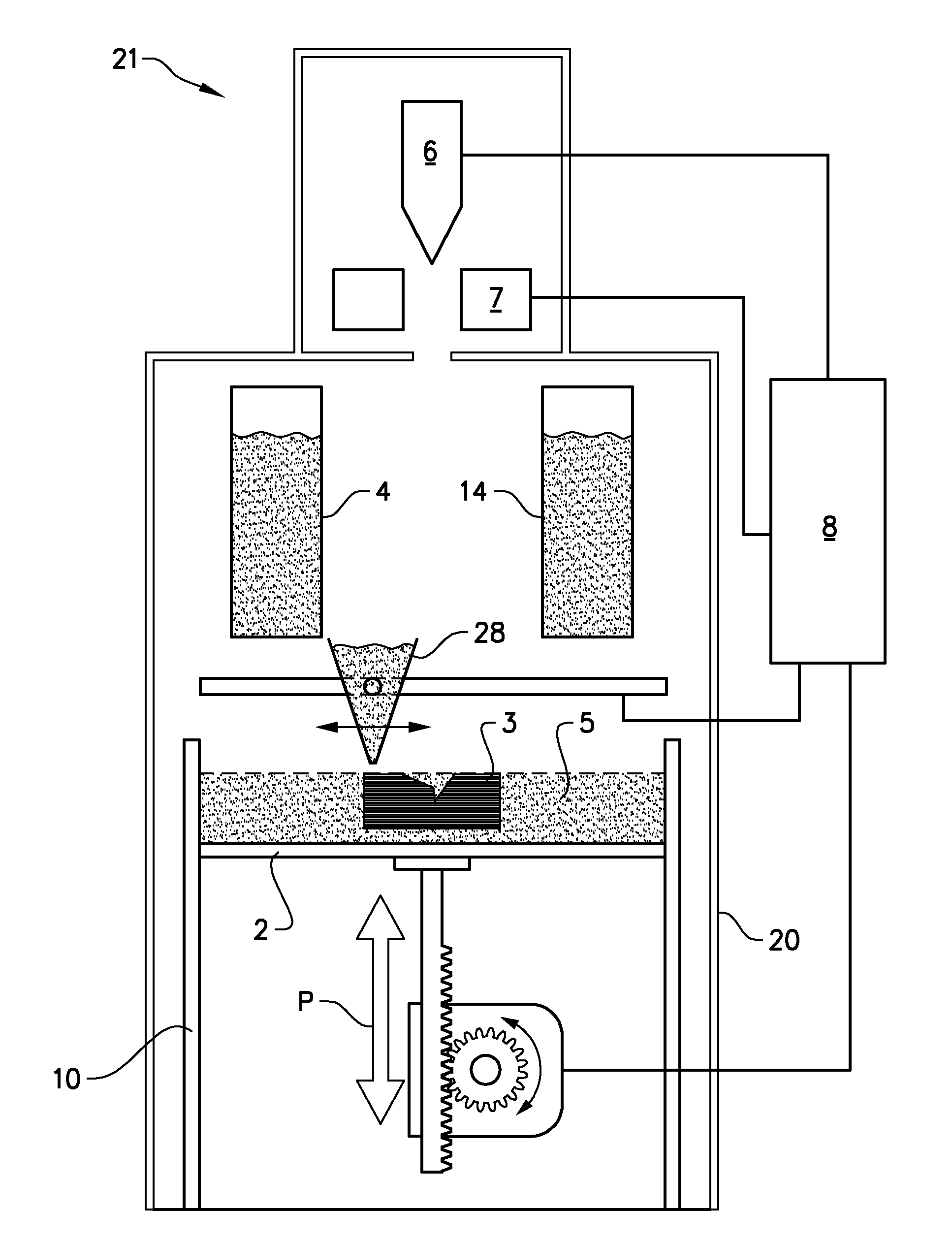
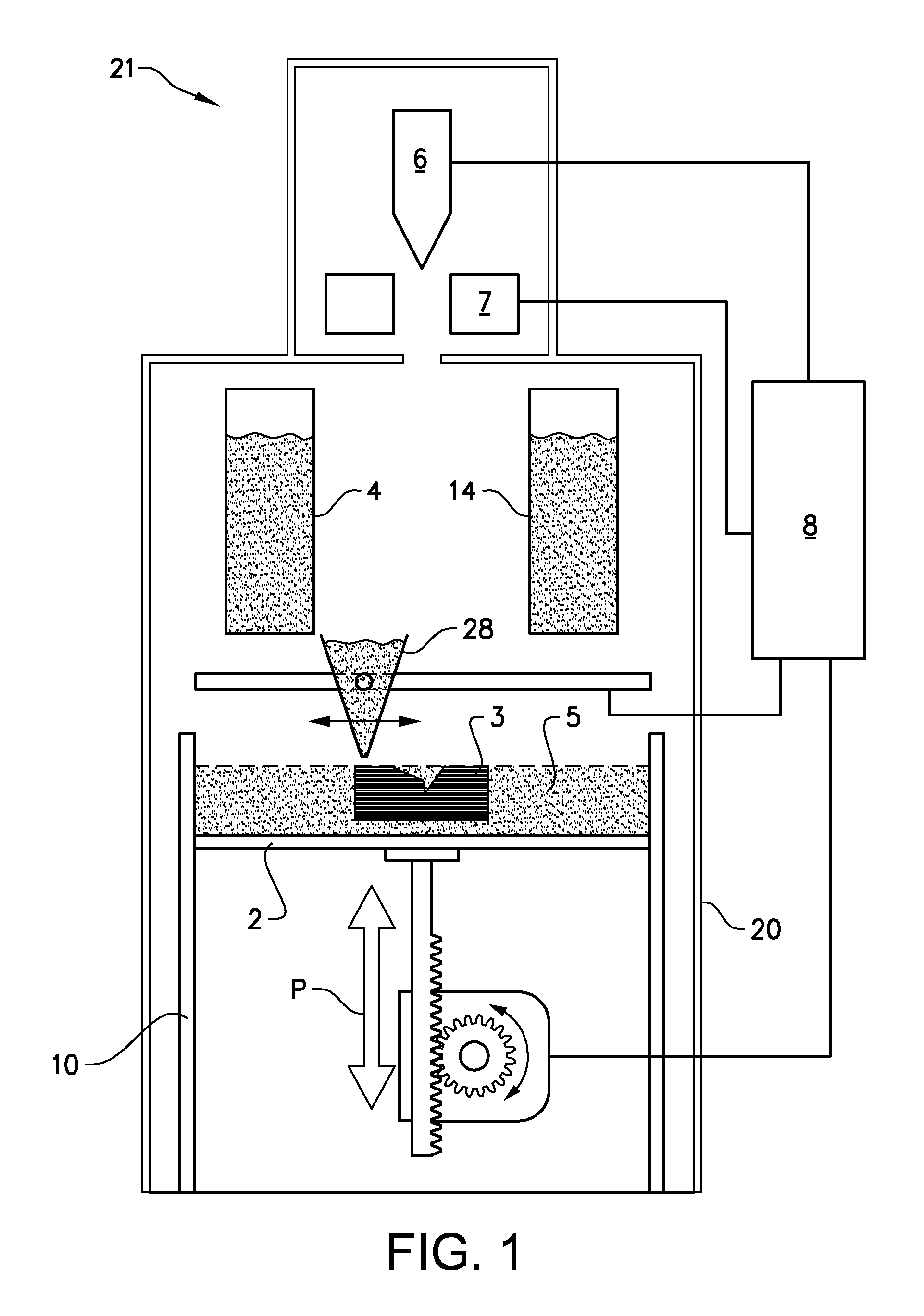
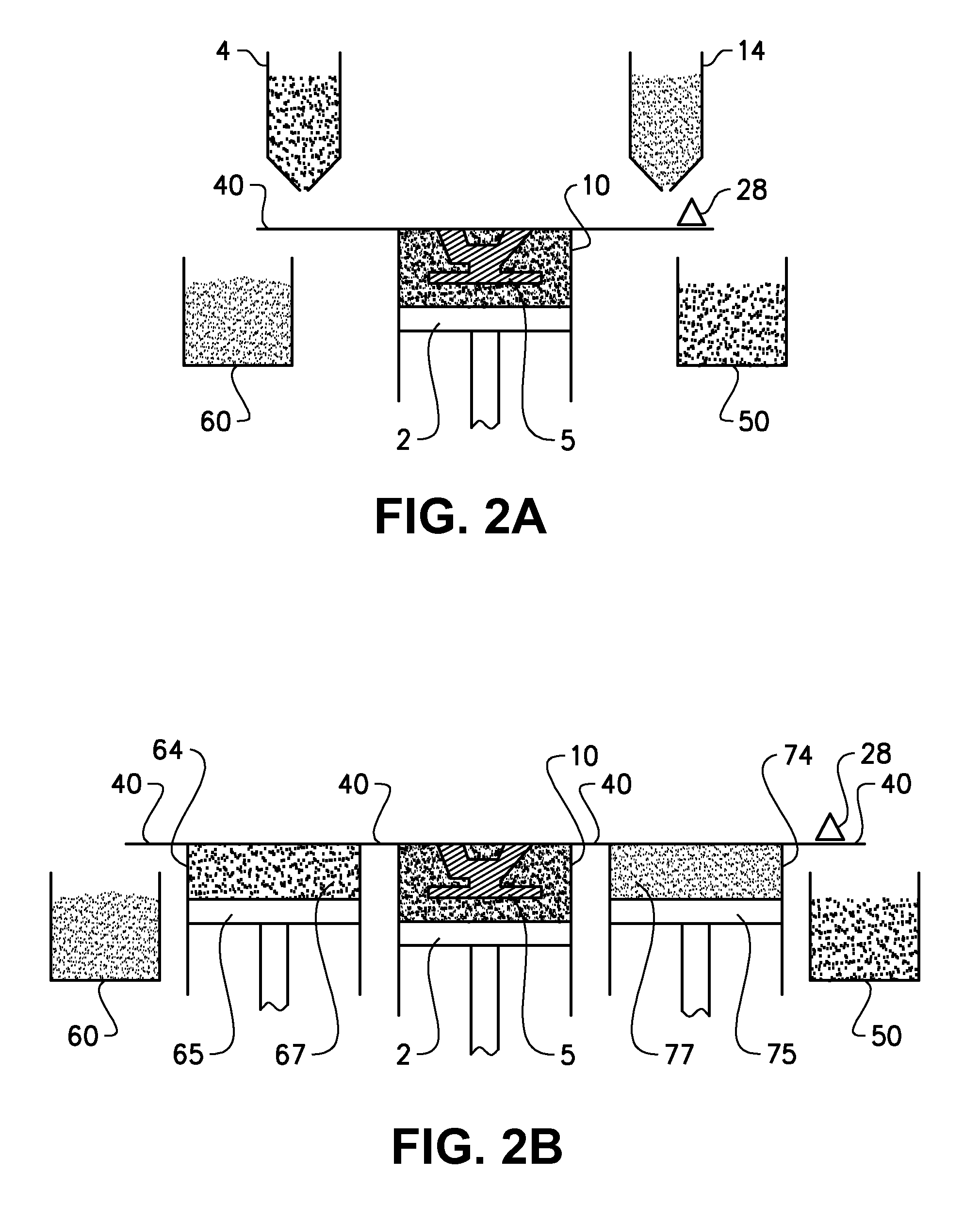
The present invention relates to a method for forming a three-dimensional article through successive fusion of parts of at least one layer of a powder bed provided on a work table. Said method comprising the steps of: providing at least a first and second powder tank, providing a first type of powder in said first powder tank having a first particle size distribution, providing a second type of powder in said second powder tank having a second particle size distribution, providing a first sub-layer of said first type of powder on said work table, providing a second sub-layer of said second type of powder on top of said first layer of said first type of powder, fusing said first and second sub-layers simultaneously with a high energy beam from a high energy beam source for forming a first cross section of said three-dimensional article.
Owner:ARCAM AB
Scrap submergence system
Owner:PYROTECK INC
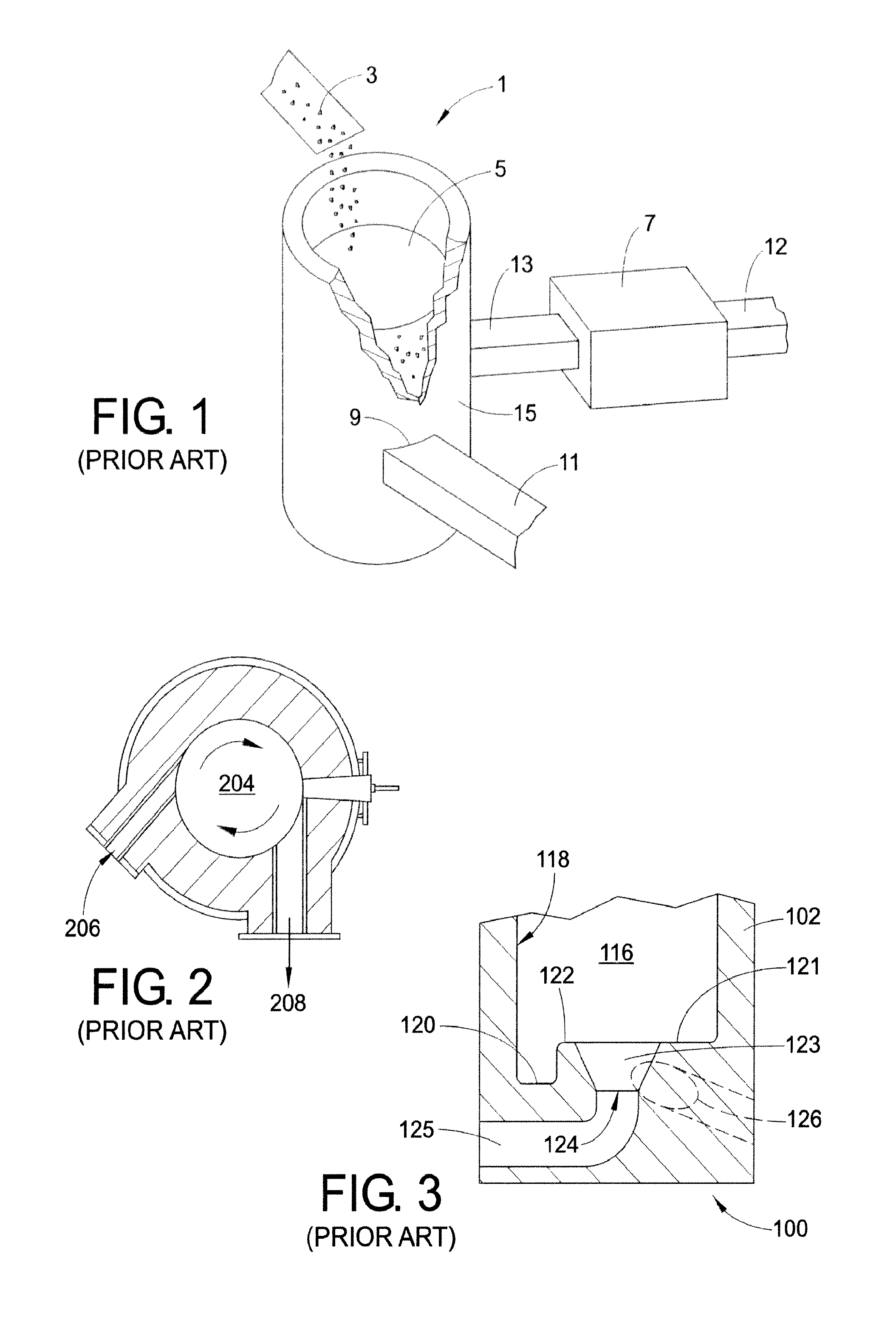
Impact resistant scrap submergence device
A metal scrap submergence device having an open top chamber including side and base walls of a heat resistant material. An inlet is included in a side or base wall of the chamber for receiving molten metal. An outlet is included in the base of the chamber. A ramp extends from the side wall of the chamber to an inner column defining the outlet. The ramp includes a first edge adjacent the side wall and second interior edge adjacent the inner column. The working surface of the ramp between the first and second edges is concave. The inner column includes an end wall disposed opposite the chamber base, the end wall includes rounded inner and outer edges.
Owner:PYROTECK INC
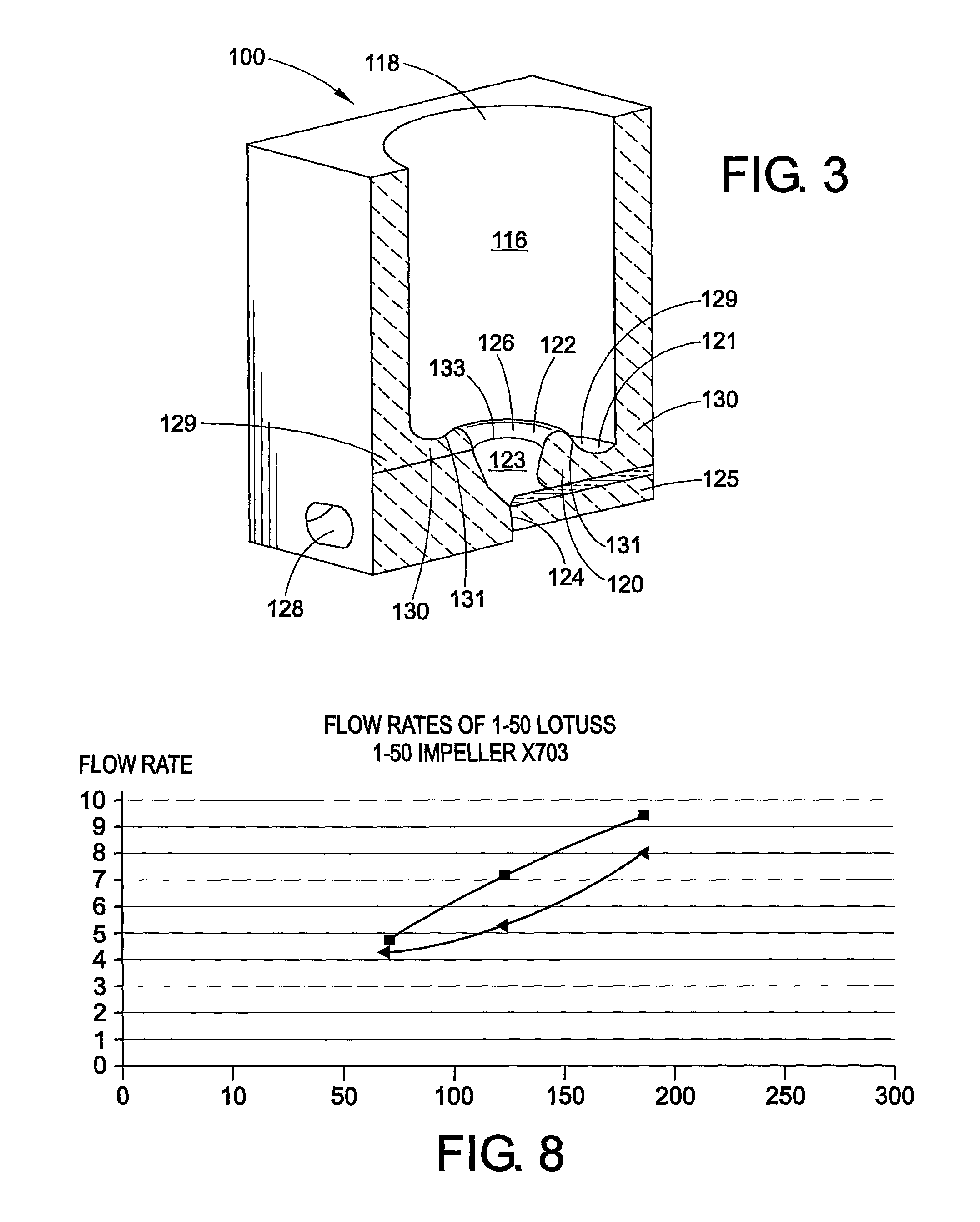
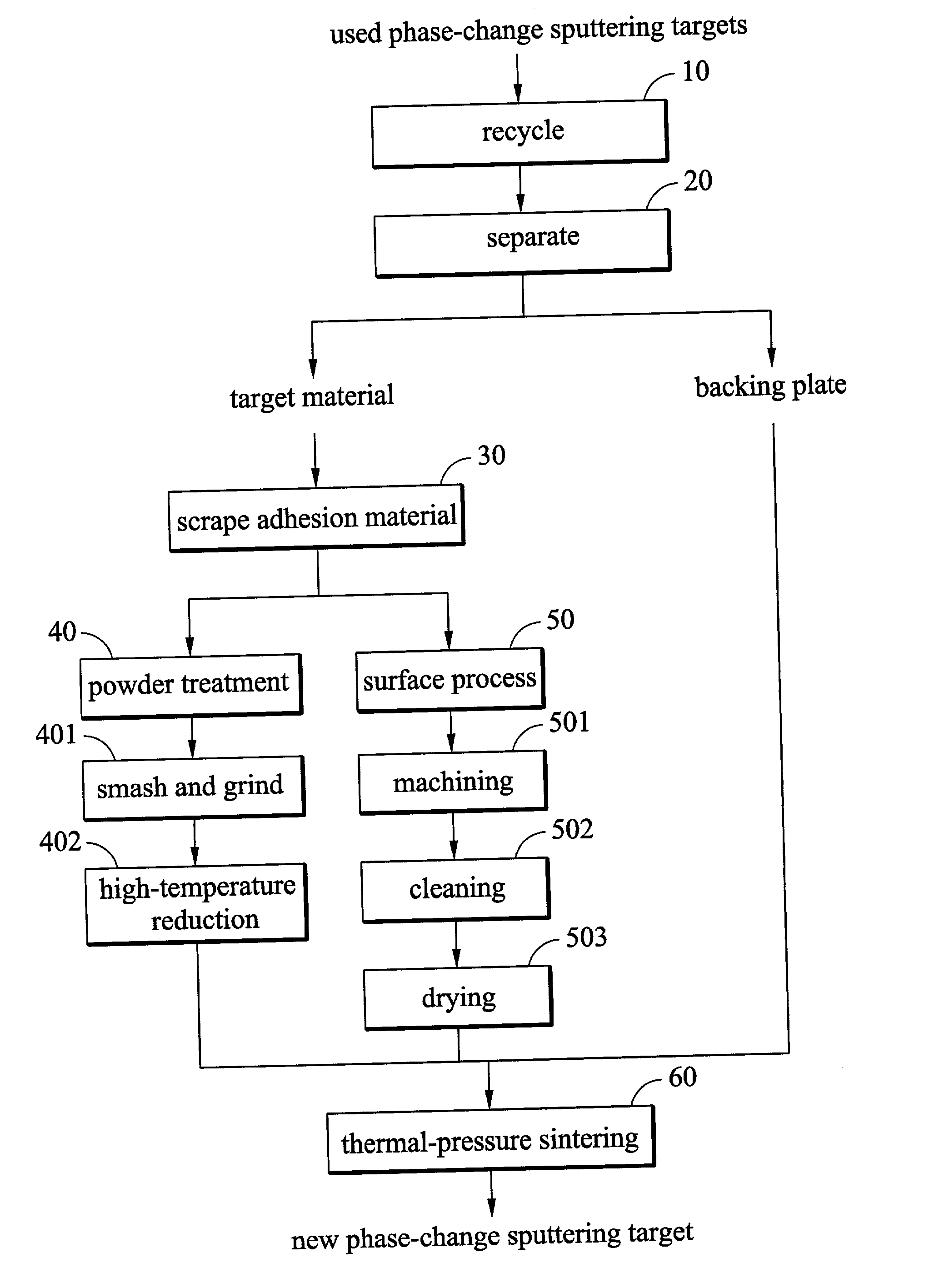
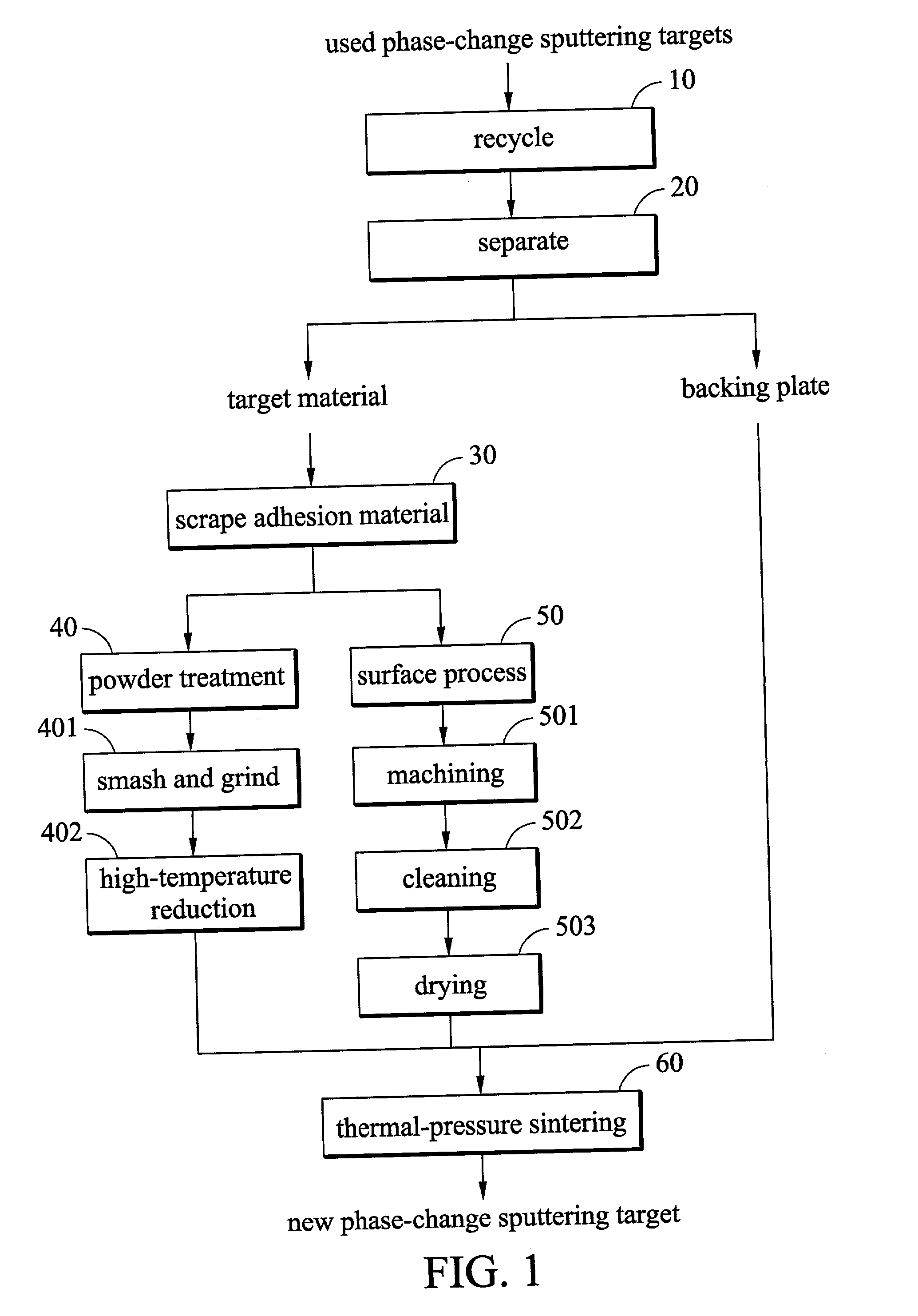
Method of regenerating a phase-change sputtering target for optical storage media
InactiveUS20020130041A1Increase profitReduce material costsMetal recyclingCellsSputteringOptical storage
A method of regenerating a phase-change sputtering target for optical storage media. First, a used powder-metallurgy sputtering target composed of a target material, an adhesion material, and a backing plate is recycled. Then, the target material is separated from the backing plate. Then, the target adhesion material is scraped from the recycled target material Thereafter, the surface of the recycled target material is processed. Finally, the backing plate, a new adhesion material, the recycled target material, and new powders are placed in a vacuum thermal-pressure furnace in sequence to perform a thermal-pressure sintering process. This completes a new phase-change sputtering target
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Rotor and rotor shaft for molten metal
A molten metal rotor receives and retains an end of a molten metal rotor shaft. The rotor shaft has one or more projections at the end received in the rotor. The rotor has an inner cavity, a top surface with an opening leading to the inner cavity, and at least one abutment. The opening includes one or more portions for allowing each projection to pass through the opening and into the inner cavity. The rotor and / or shaft are then rotated so at least one of the outwardly-extending projections is under the top surface of the rotor and is against an abutment. A molten metal pump, rotary degasser scrap melter or other device used in molten metal may utilize a rotor / shaft combination as disclosed herein.
Owner:MOLTEN METAL EQUIP INNOVIATIONS LLC
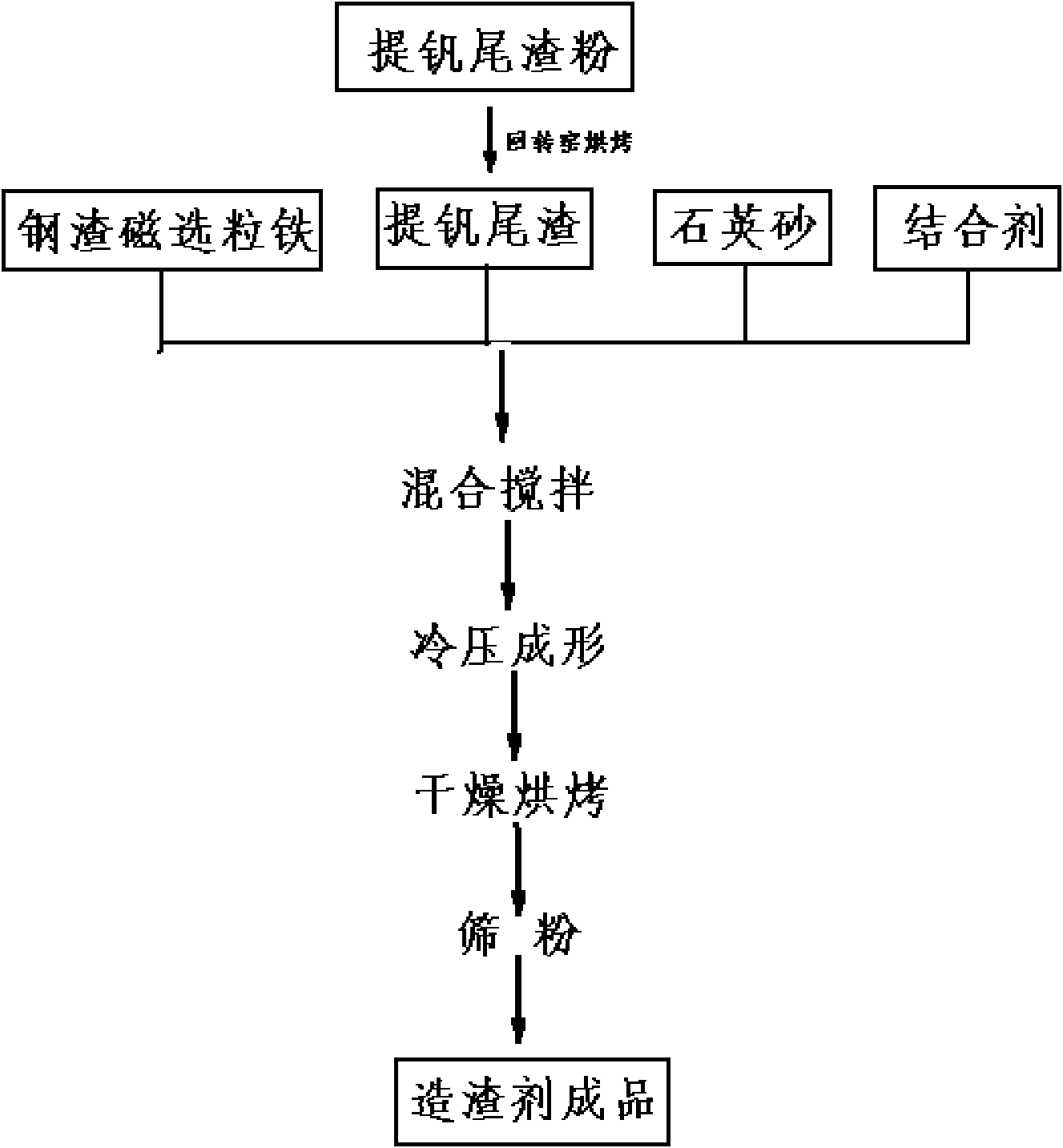
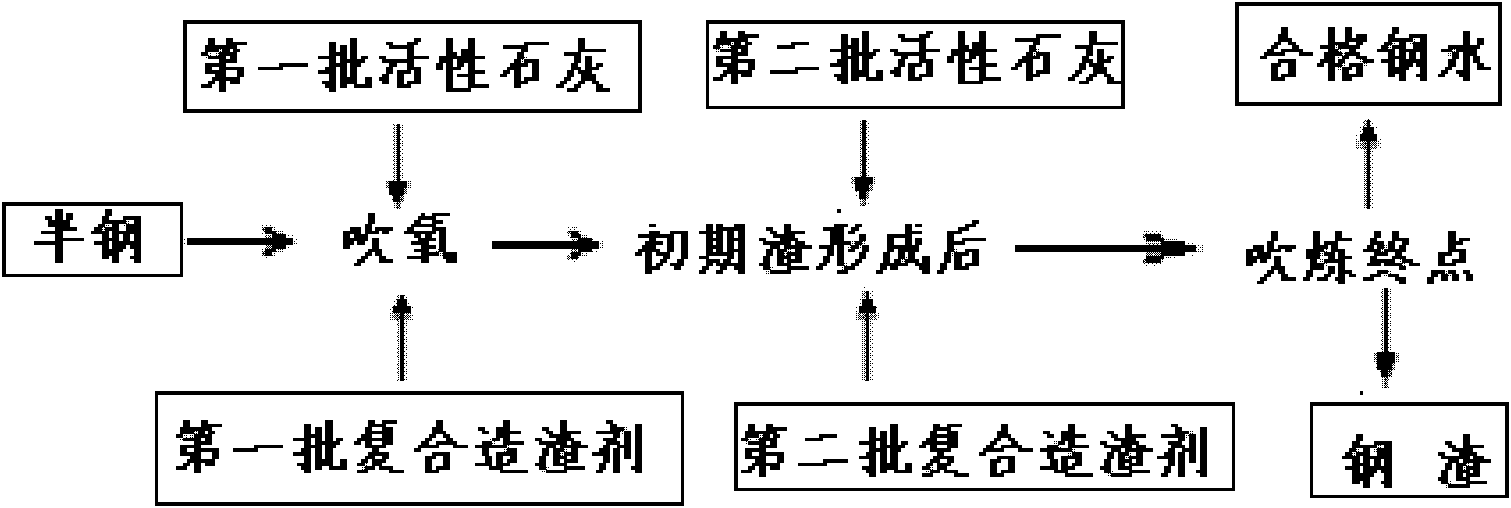
Composite slagging agent for making semisteel, and preparation method and using method thereof
InactiveCN102181610AGood effect of removing PSteelmaking process runs smoothlyRecovering materialsManufacturing convertersHigh magnesiumSlag
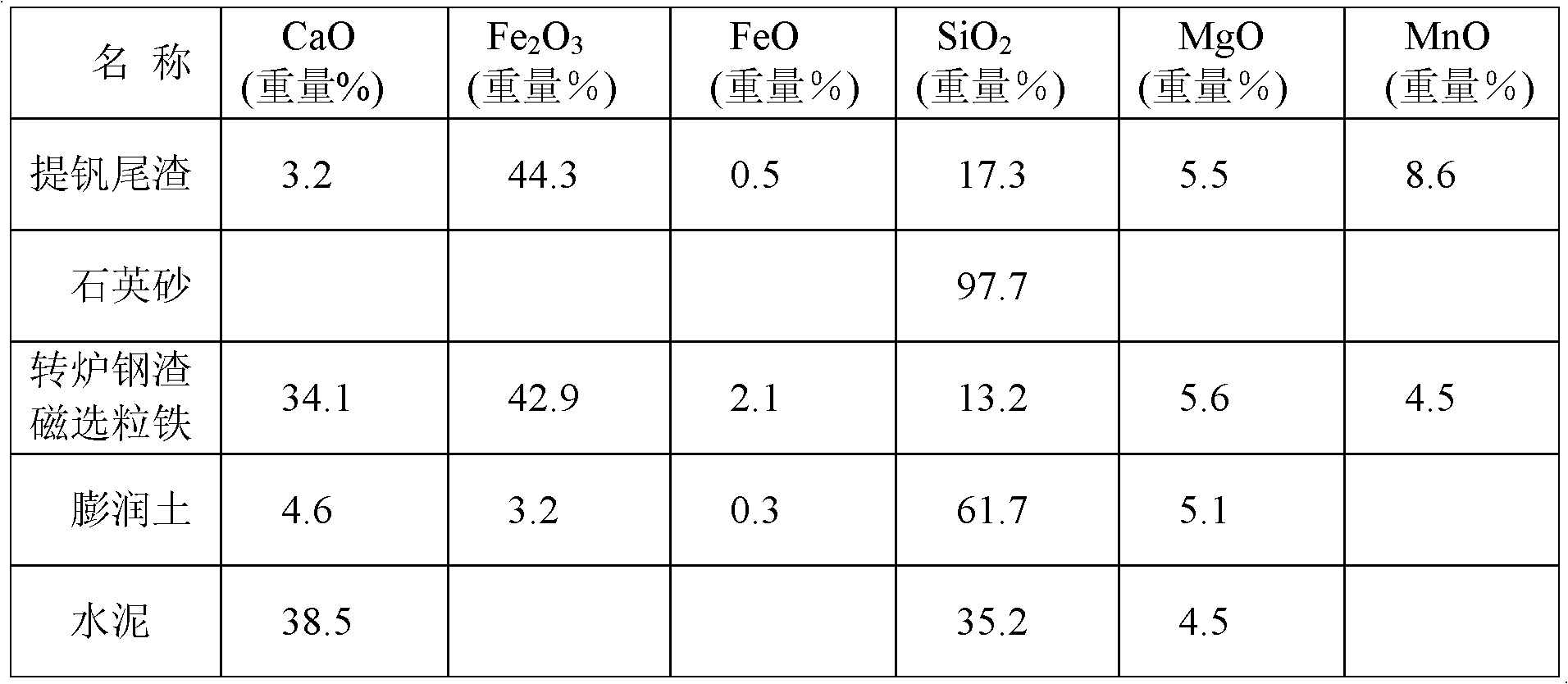
The invention discloses a composite slagging agent for making semisteel, and a preparation method and a using method thereof. The slagging agent comprises the following components in part by weight: 26 to 36 parts of iron-containing oxide, 27 to 35 parts of SiO2, 7 to 13 parts of CaO, 4 to 7 parts of MnO and 4 to 8 parts of MgO, wherein the iron-containing oxide comprises Fe2O3 and FeO in the weight ratio of (50-60):1. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: mixing vanadium-extracted tailings, quartz sand, converter steel slag magnetic ball iron and a binding agent according to a certain mass ratio and uniformly stirring; pressing into pellets; and drying to obtain the slagging agent. The slagging agent prepared by the preparation method can be used for making the semisteel together with active lime and high-magnesium lime. By the composite slagging agent prepared by the method, the defects that the slag is easy to splash and dry, has a poor dephosphorization effect, is extremely difficult to operate and the like are overcome in the semisteel making and using process.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP VANADIUM TITANIUM & RESOURCES +3
Process for recovering base metals from spent hydroprocessing catalyst
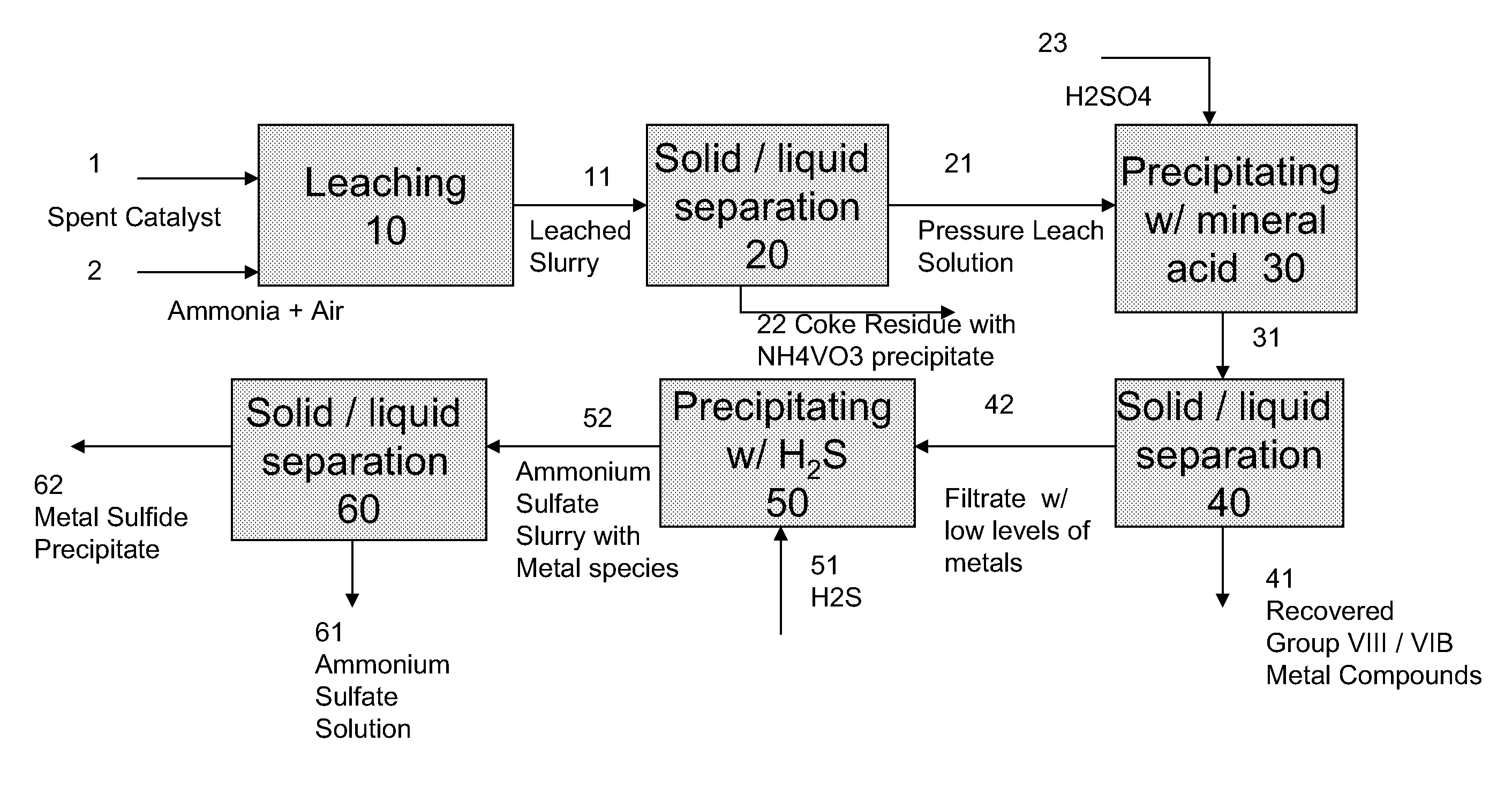
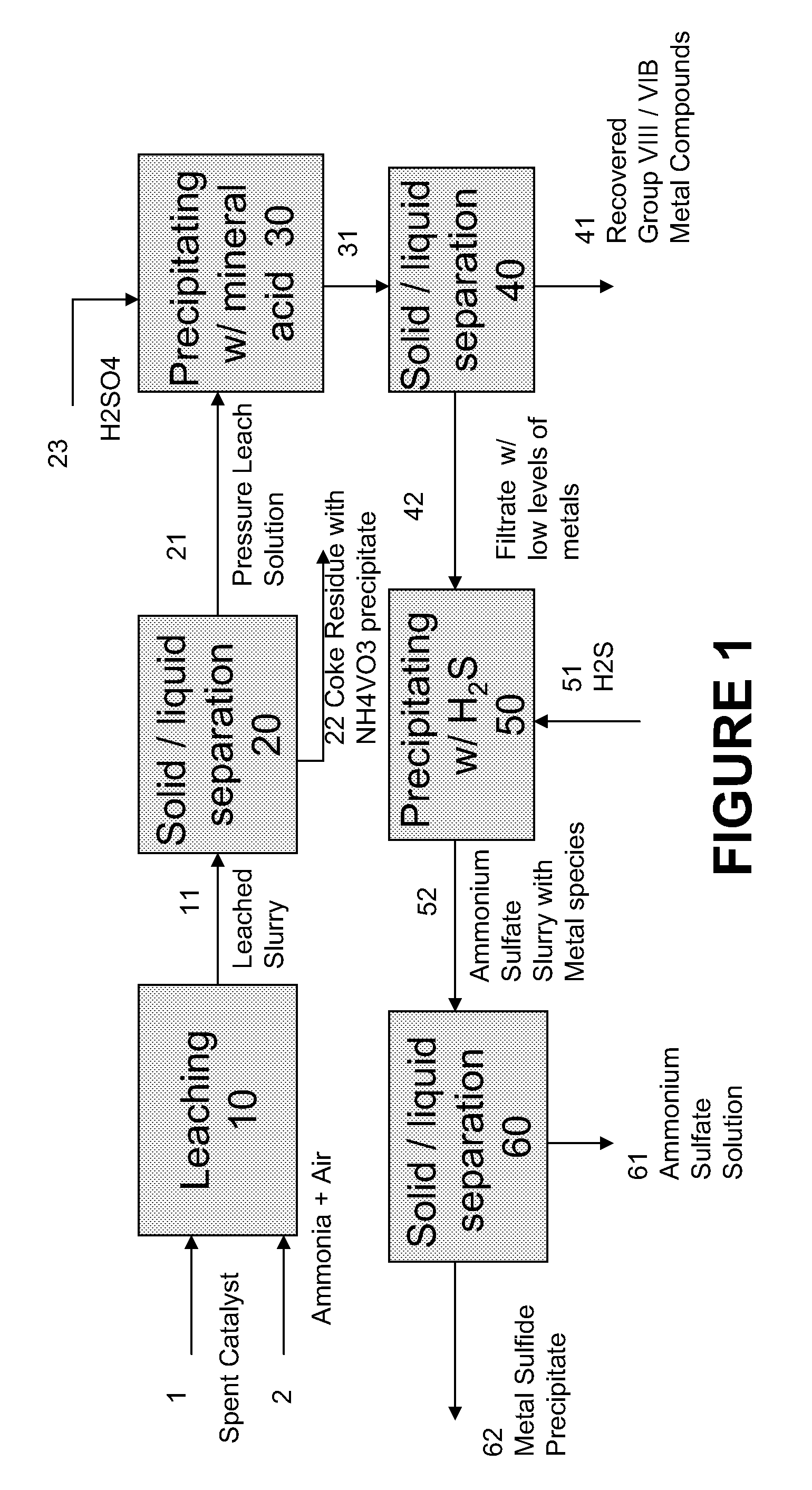
A method for recovering metals from a spent dispersed catalyst originating from a Group VIB metal sulfide catalyst containing at least a Group VB and Group VIII metal for hydrocarbon oil hydroprocessing is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprises the steps of: contacting the spent dispersed catalyst with a leaching solution containing ammonia and air to dissolve the group VIB metal and the Group VIII metal into the leaching solution at sufficient temperature and pressure; forming a slurry containing at least a group VIB metal complex and at least a group VIII metal complex, ammonium sulfate and solid residue containing at least a Group VB metal complex and coke; separating and removing the solid residue containing ammonium metavanadate and coke from the pressure leach solution (PLS); precipitating from the PLS at least a portion of the Group VIB metal and at least a portion of the Group VIII metal by controlling the pH at a pre-selected pH to selectively precipitate as metal complexes the Group VIB and Group VIII metals.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Method for treating a solution containing zinc sulphate
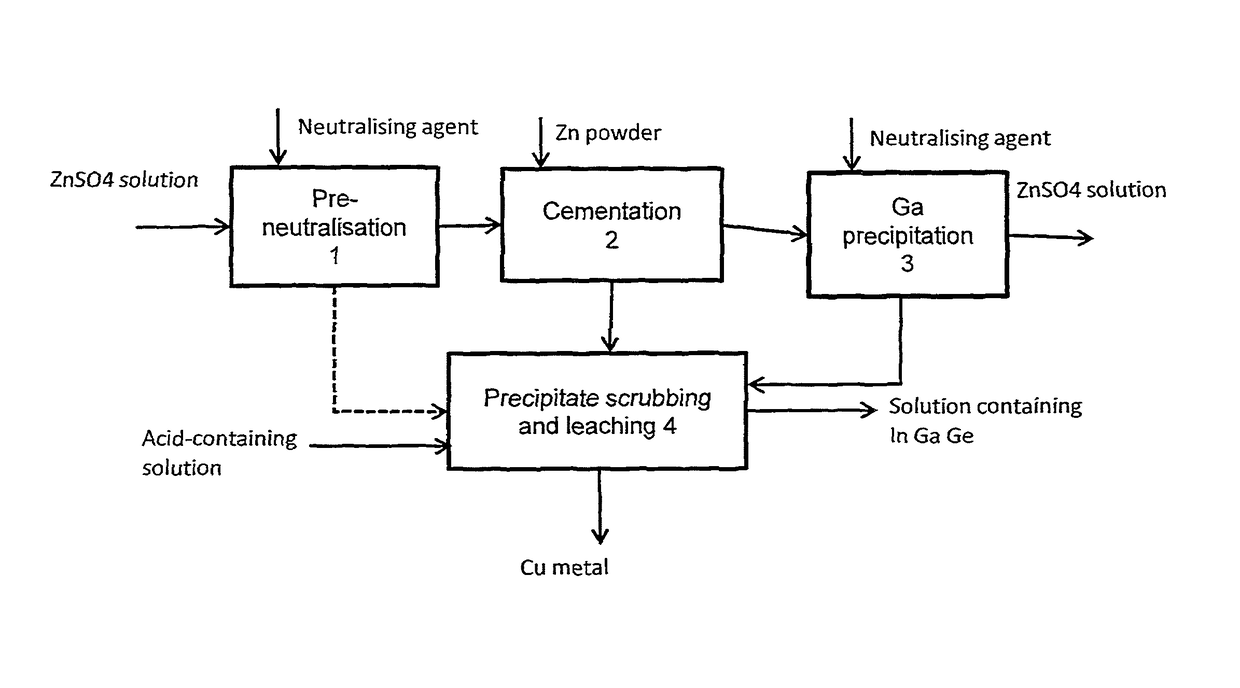
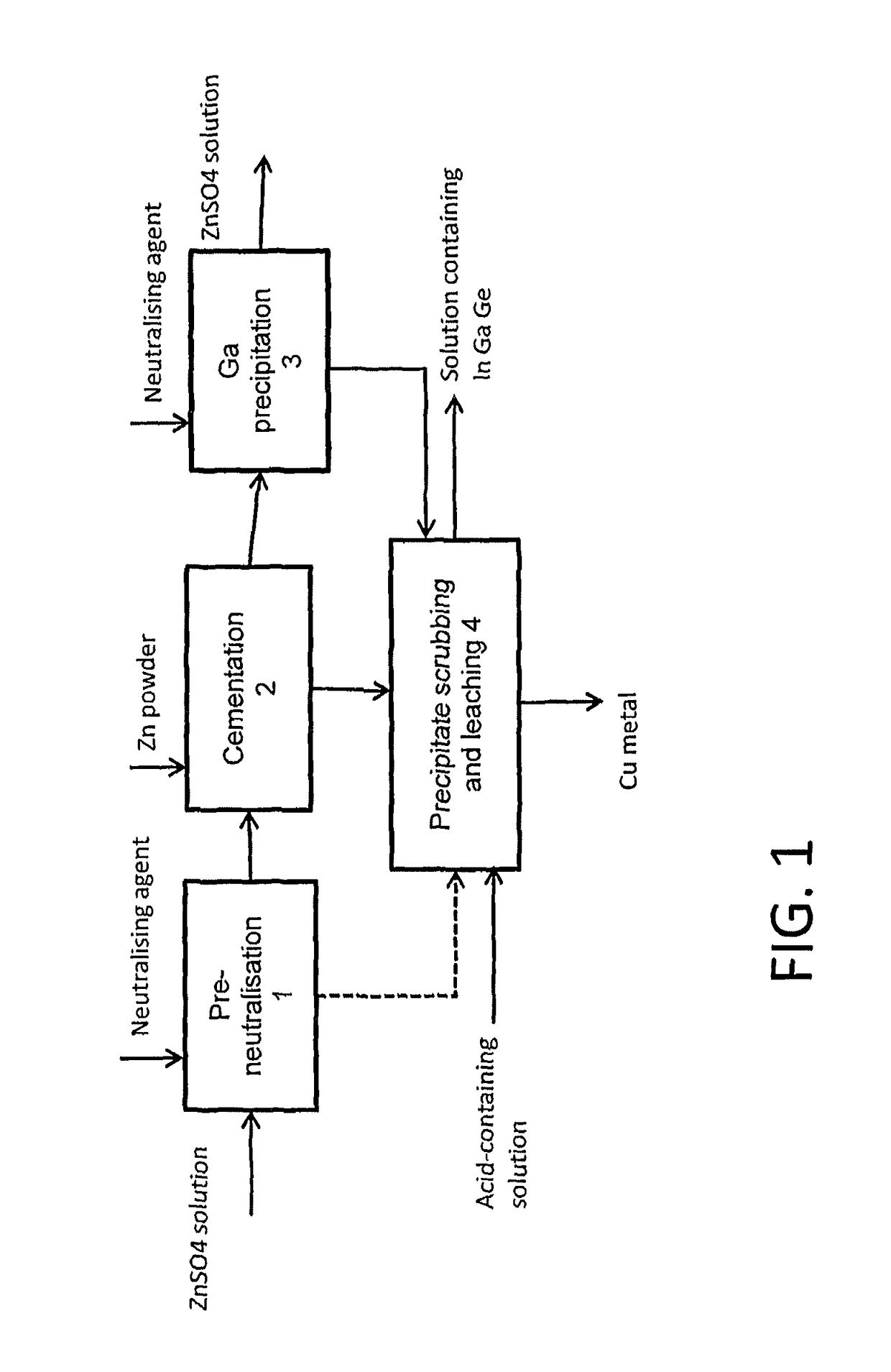
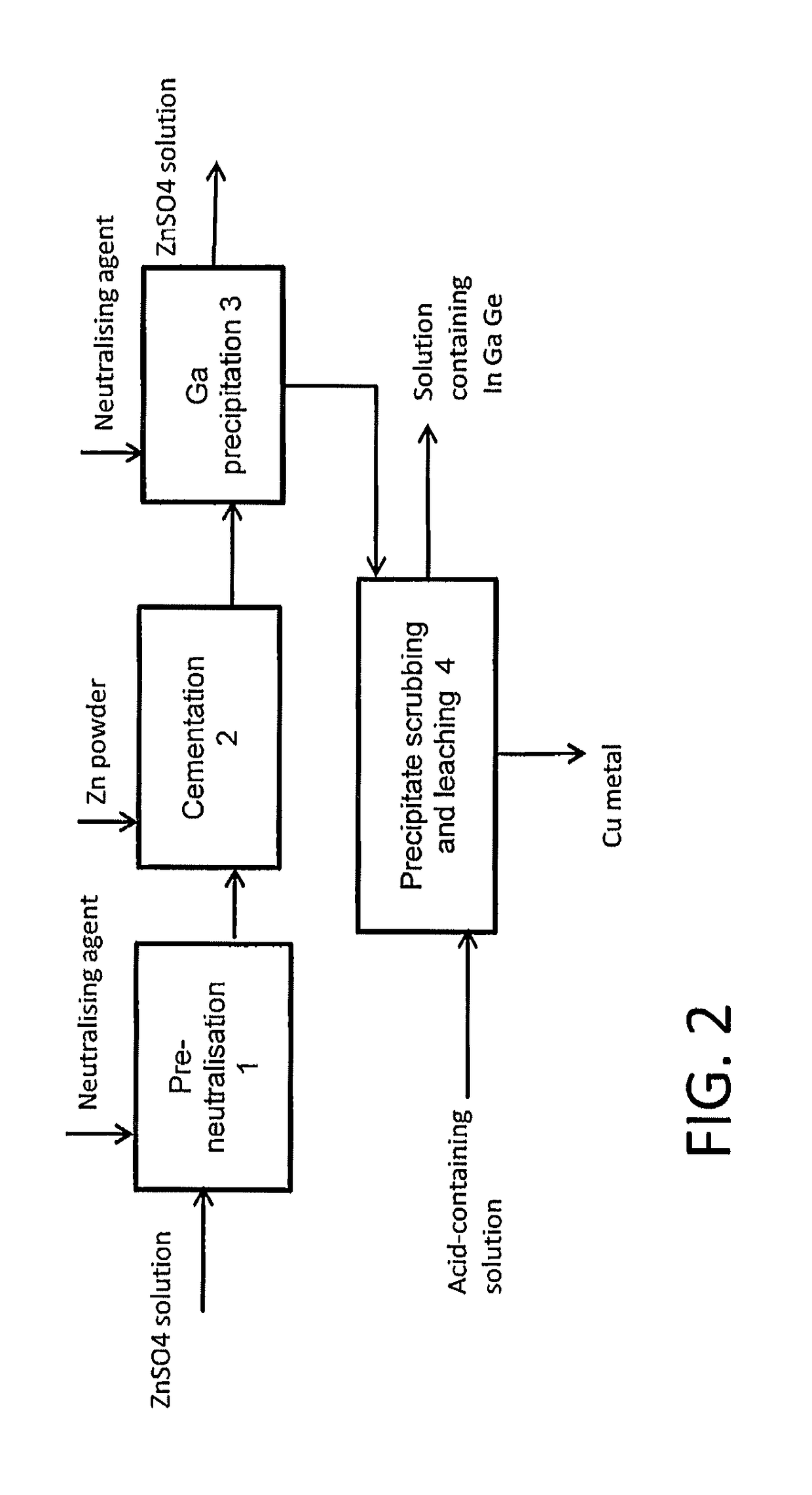
The invention relates to a method for treating a solution containing zinc sulphate, so that at least one of the rare metals such as indium, gallium and germanium can be separated from it. A portion of the metals to be separated can be precipitated from zinc sulphate solution by neutralizing the acidic solution and at least a portion is cemented by means of metal powder. The solid precipitates that are formed can be combined and treated subsequently in some suitable way to leach out the desired metals.
Owner:METSO OUTOTEC (FINLAND) OY
Preparation method of high-purity indium
ActiveCN103103566AHigh purityAdditional purification stepsPhotography auxillary processesRecovering materialsPurification methodsElectrolysis
The invention discloses a preparation method of high-purity indium, which is implemented through preparing an indium sulfate electrolyte from purified water, an analytically pure concentrated sulfuric acid, 4N metal indium, high-purity sodium chloride and analytically pure gelatin, and carrying out two-time electrolysis and then vacuum distillation on electrolytic indium under ultraclean conditions so as to obtain 5N (99.999%)-7N (99.99999%) high-purity indium. According to the invention, because a 5N (99.999%)-7N (99.99999%) high-purity indium product is finally produced by using a method for carrying out two-time electrolysis and then vacuum distillation on electrolytic indium, the advantages such as large flexibility, strong selectivity and high conversion rate of an electrolytic purification method are utilized, and after the secondary electrolysis is completed, the physical purification step of vacuum distillation is increased; and meanwhile, the pollution problem caused by reagents is avoided, and the high purity of indium products is ensured, therefore, the method is easy for industrialization.
Owner:HUNAN CHEM RES INST
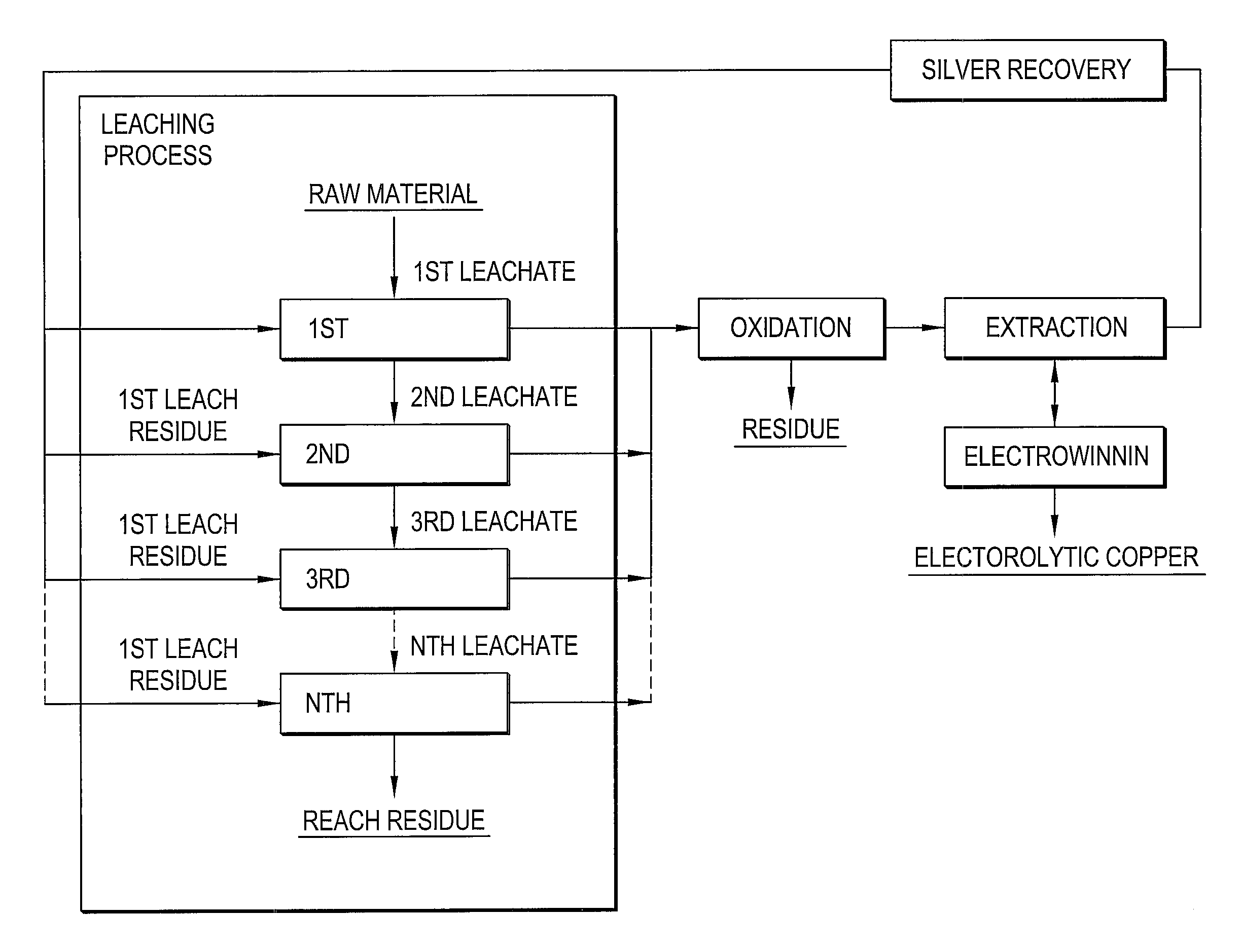
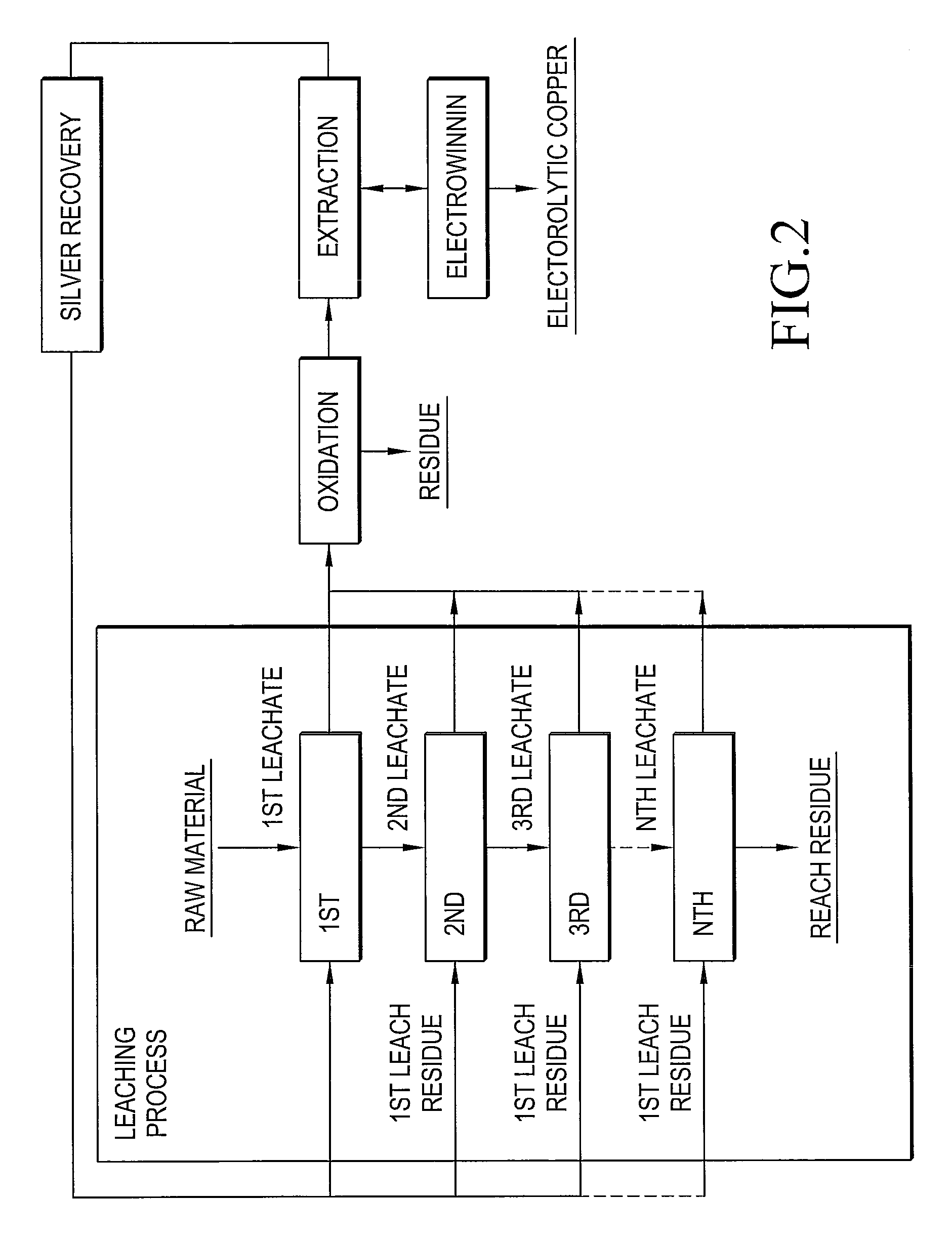
Method for Recovering Gold, Silver, Copper and Iron from Plasma-Caused Slag Containing Valuable Metals
InactiveUS20100314242A1Process environmental protectionRecovering materialsHydrocarbonsCopperMolten slag
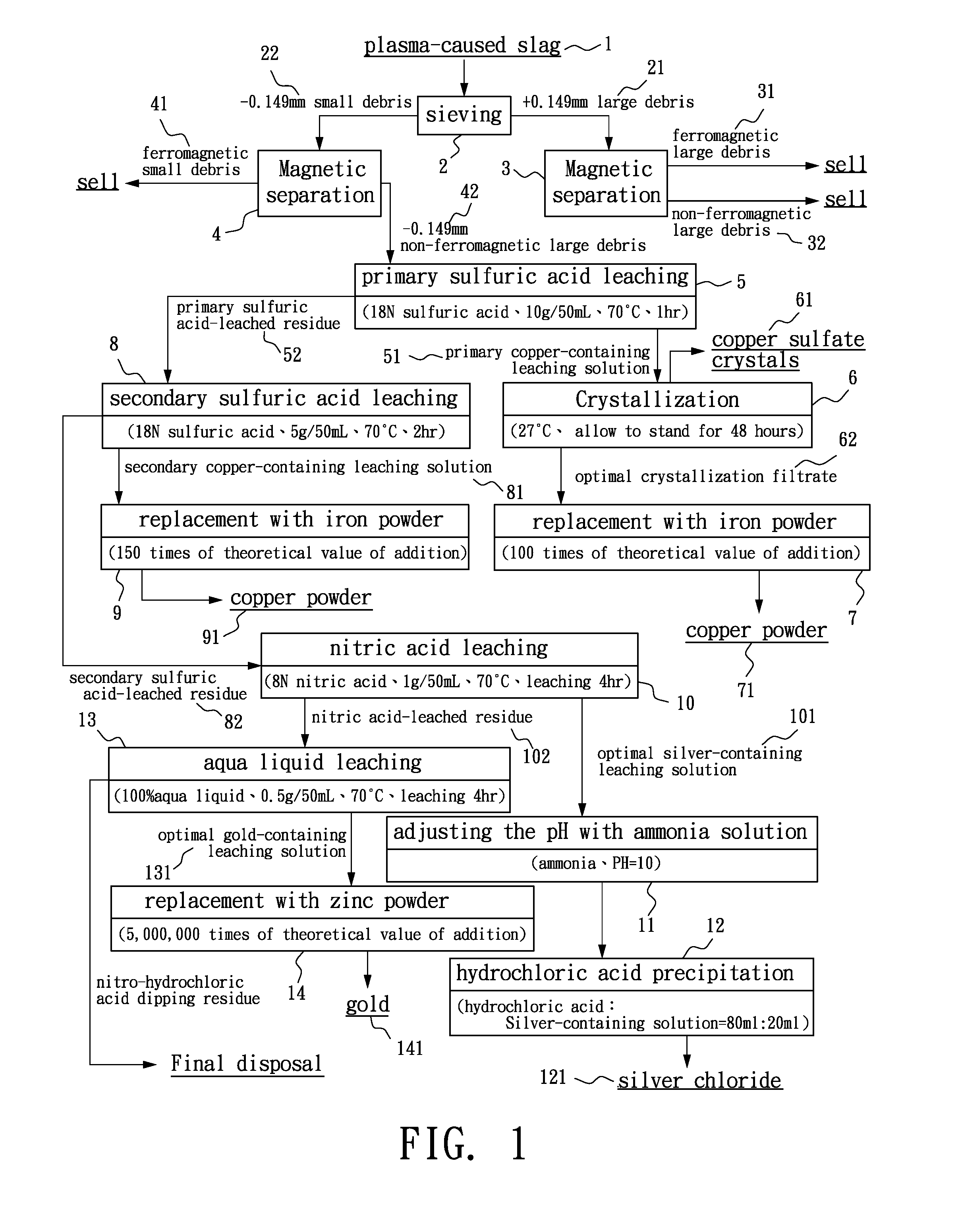
There is disclosed an environmentally friendly method for recovering gold, silver, copper and iron from valuable metal-contained plasma-molten slag. At first, plasma is used to burn the used printed circuit boards, thus producing the slag. Then, the slag is grinded. Then, leaching, crystallization, precipitation, replacement and electric winning are conducted to recover gold, silver, copper and iron.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
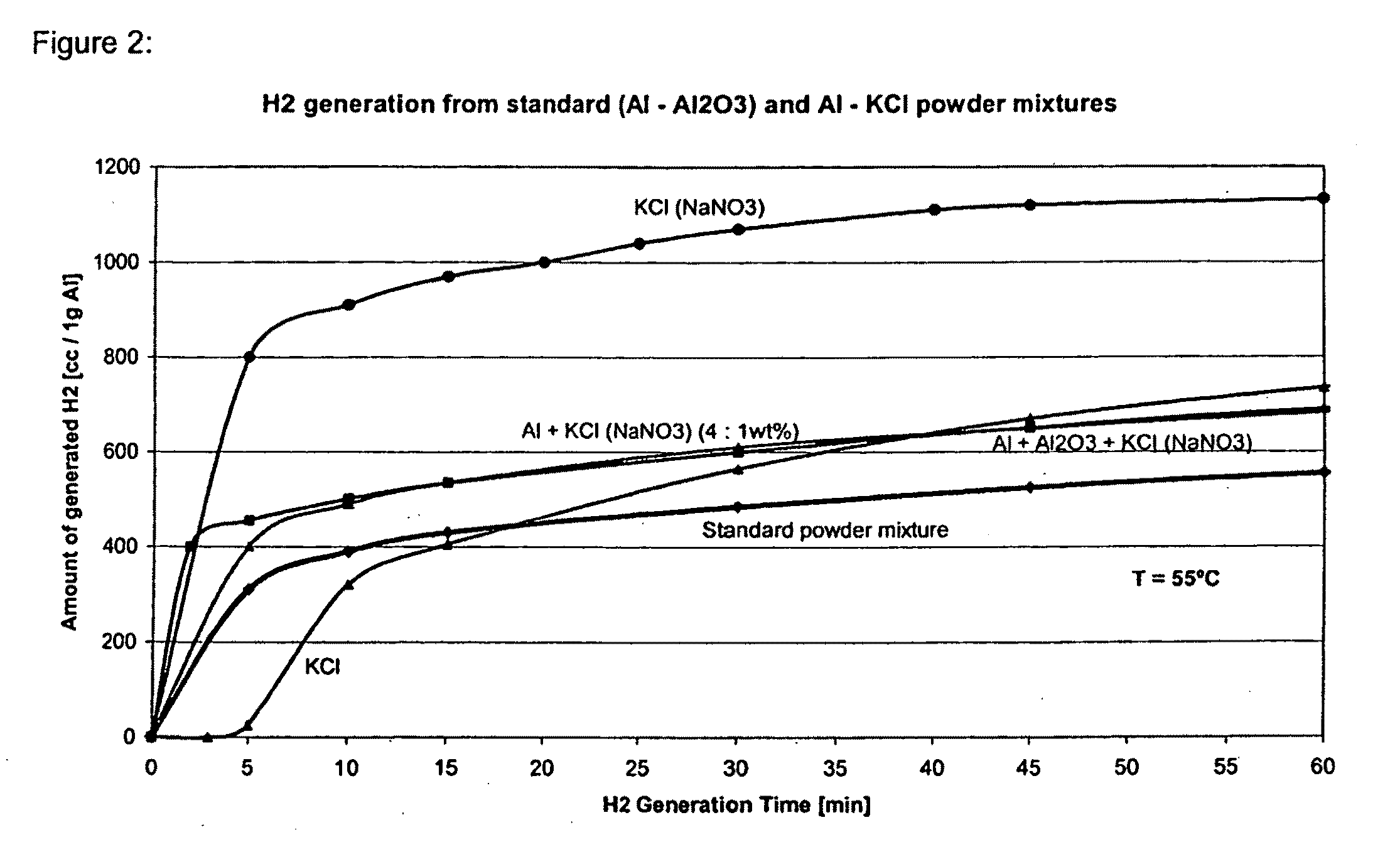
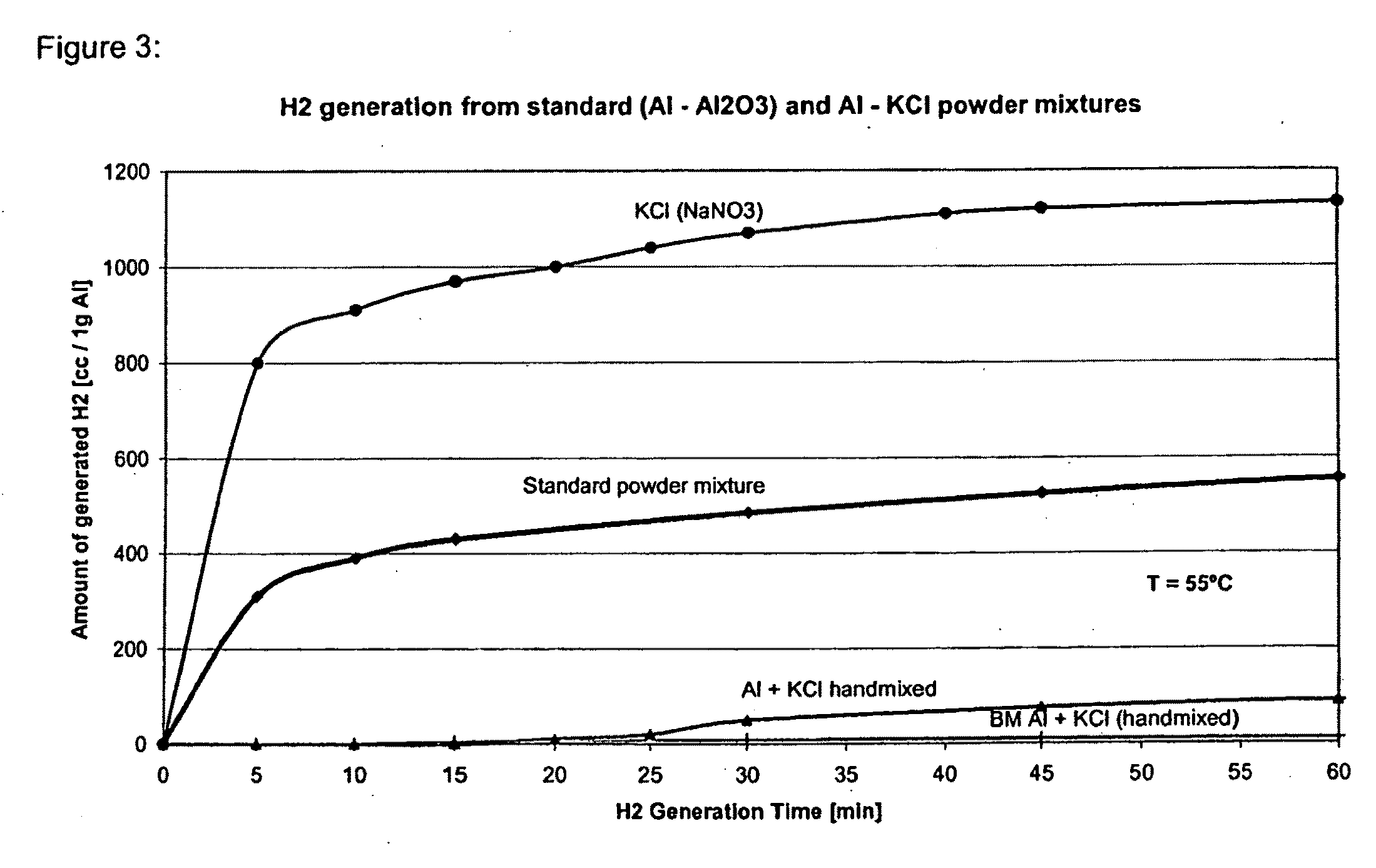
Compositions and methods for generating hydrogen from water
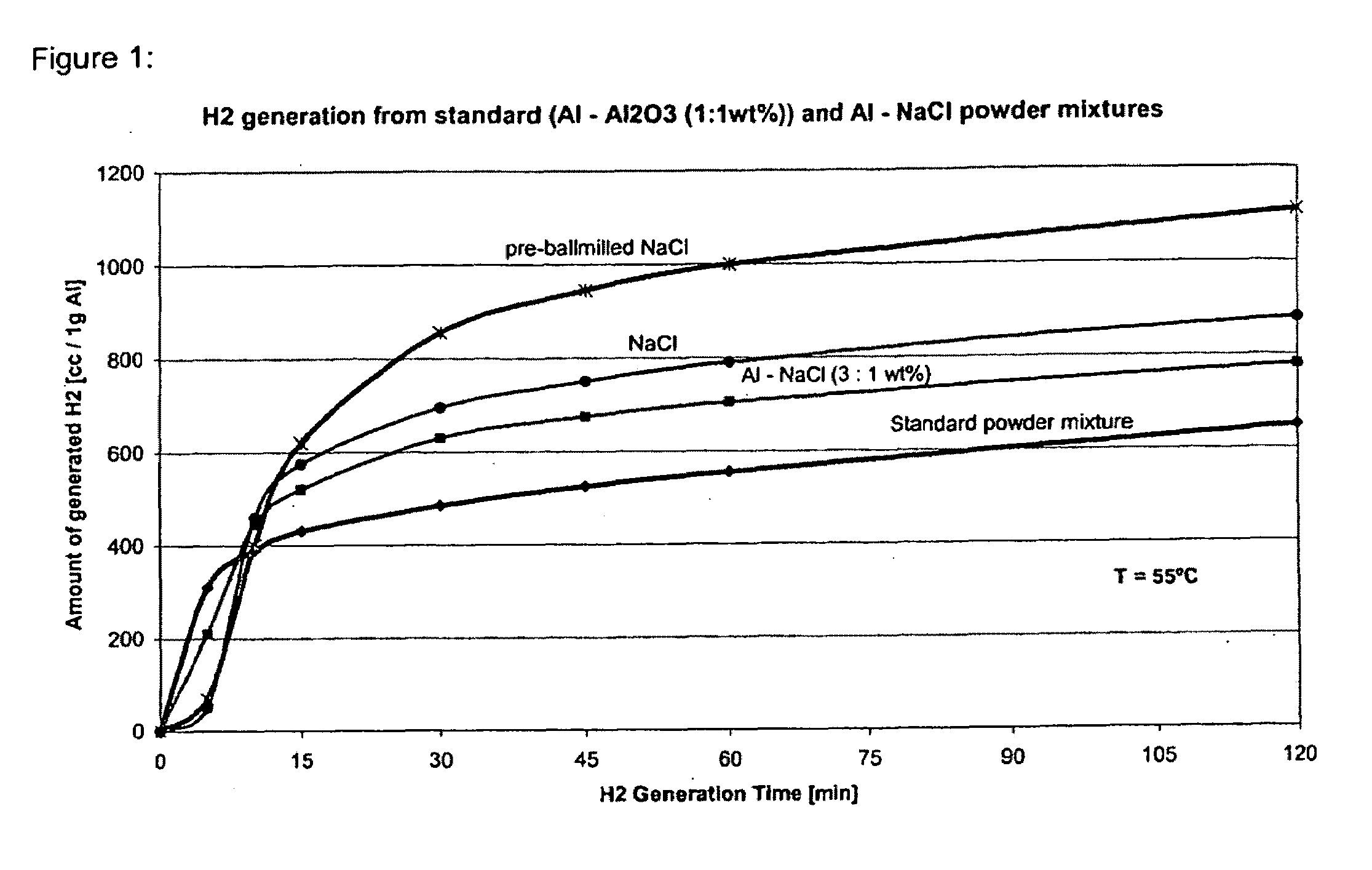
InactiveUS20080317665A1Promote recoveryOther chemical processesRegenerative fuel cellsInorganic saltsHydrogen
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Q345-serie super-thick steel plate having low cost and guaranteeing performances and flaw detection, and production technology thereof
The invention discloses a Q345-serie super-thick steel plate having a low cost and guaranteeing performances and flaw detection, and a production technology thereof. The Q345-serie super-thick steel plate has the thickness of 100 to 200mm. The Q345-serie super-thick steel plate comprises 0.08 to 0.17wt% of C, 0.15 to 0.40wt% of Si, 1.00 to 1.30wt% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.020wt% of P, less than or equal to 0.020wt% of S, less than or equal to 2.0wt% of microalloying elements comprising V, Nb, Ti, Cr and Ni, 0.020 to 0.050wt% of Als and the balance Fe and residual elements. The production technology comprises the following steps of KR molten iron pretreatment, converter smelting, LF refining, vacuum refining, continuous casting, casting blank heating, rolling, slow cooling and heat treatment. Through a reasonable chemical composition design and the LF and VD refining processes, steel cleanliness is guaranteed. Through superheating, rolling and normalizing treatment, the Q345-serie super-thick steel plate having the thickness of 100 to 200mm and guaranteeing performances and flaw detection is prepared by the continuous casting technology. The Q345-serie super-thick steel plate has yield strength of 310 to 400MPa, tensile strength of 490 to 580MPa, percentage elongation of 22 to 27% and V-notch impact energy of 80 to 200J.
Owner:NANYANG HANYE SPECIAL STEEL CO LTD
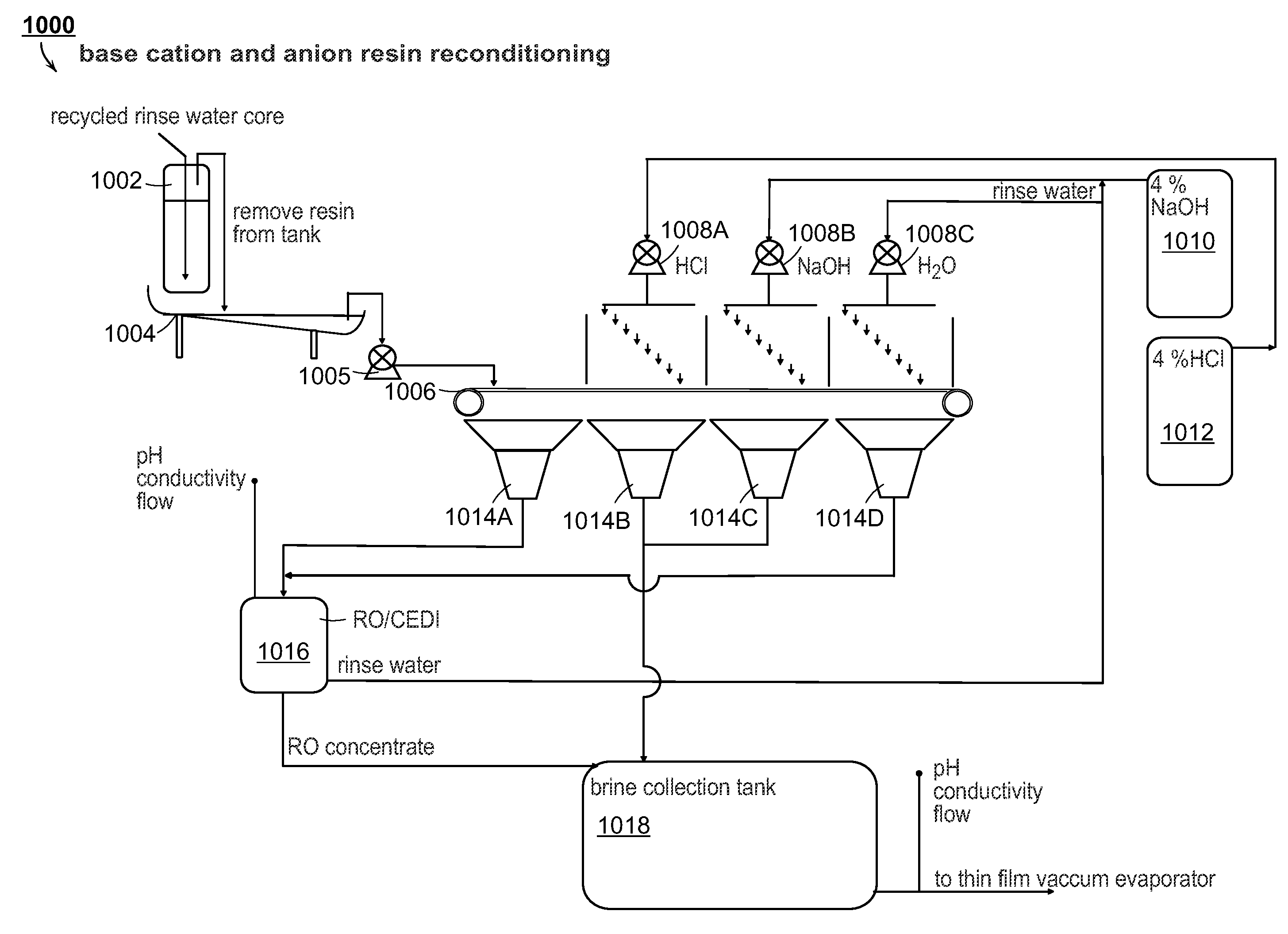
System and method for wastewater treatment
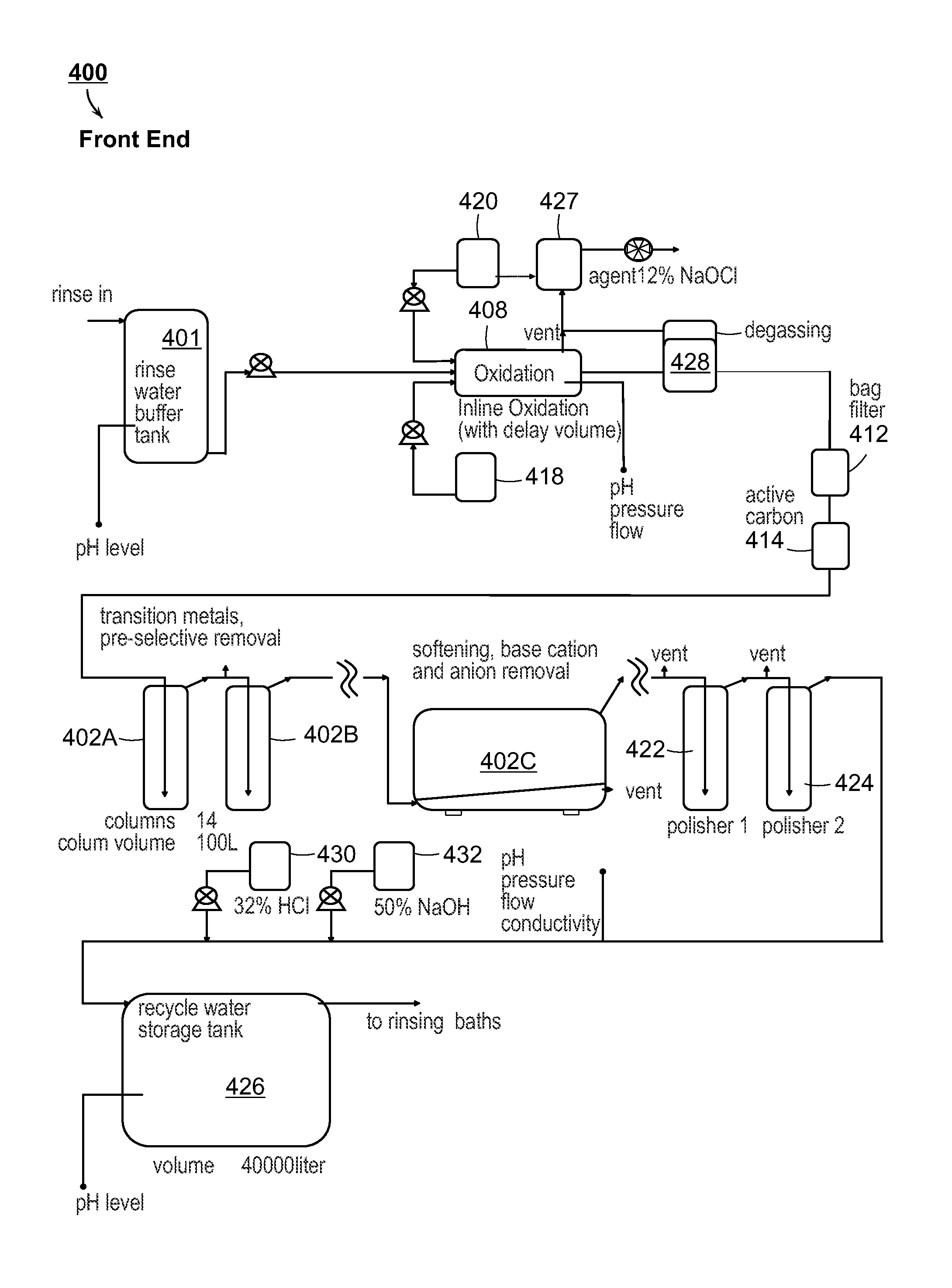
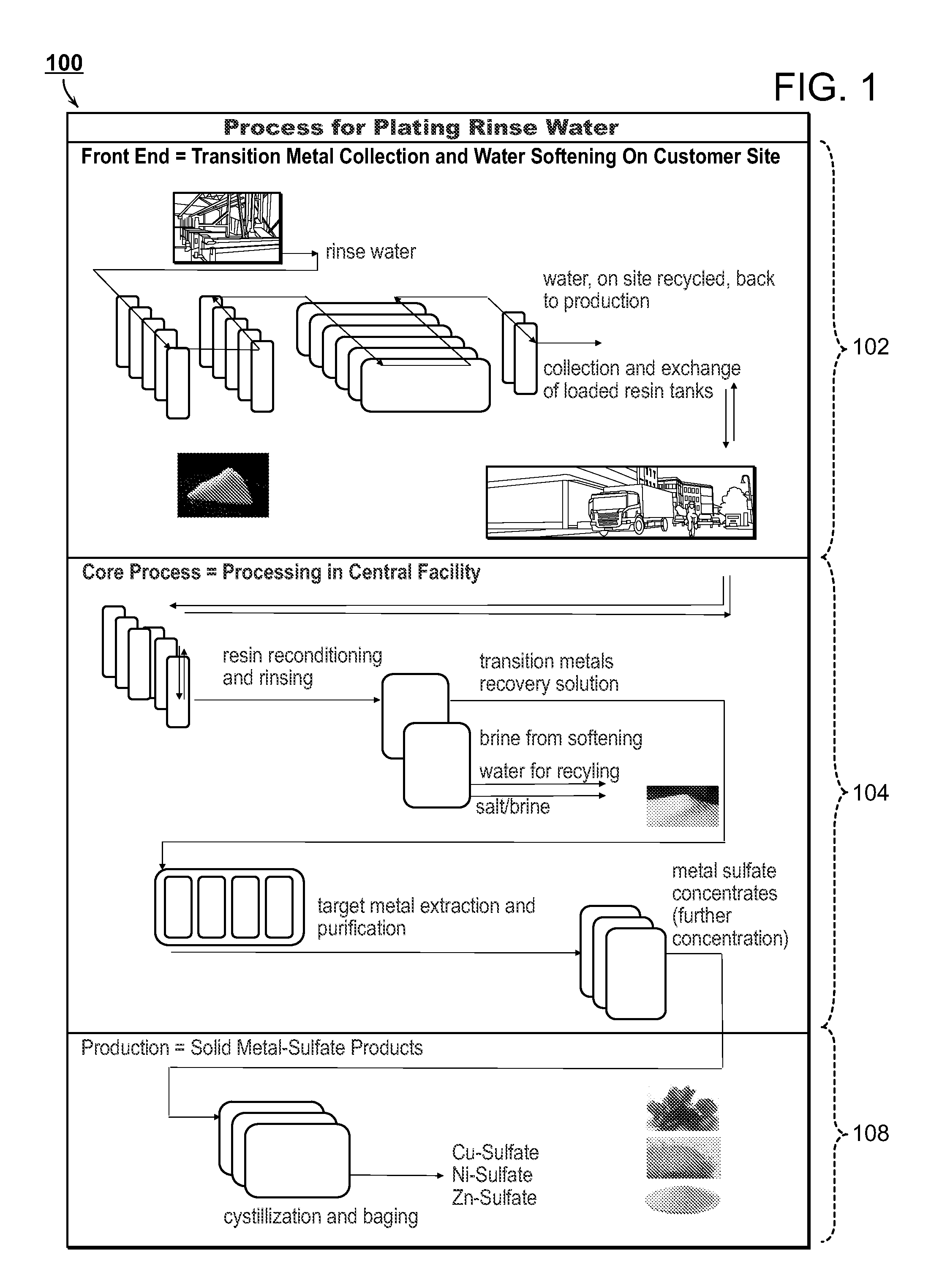
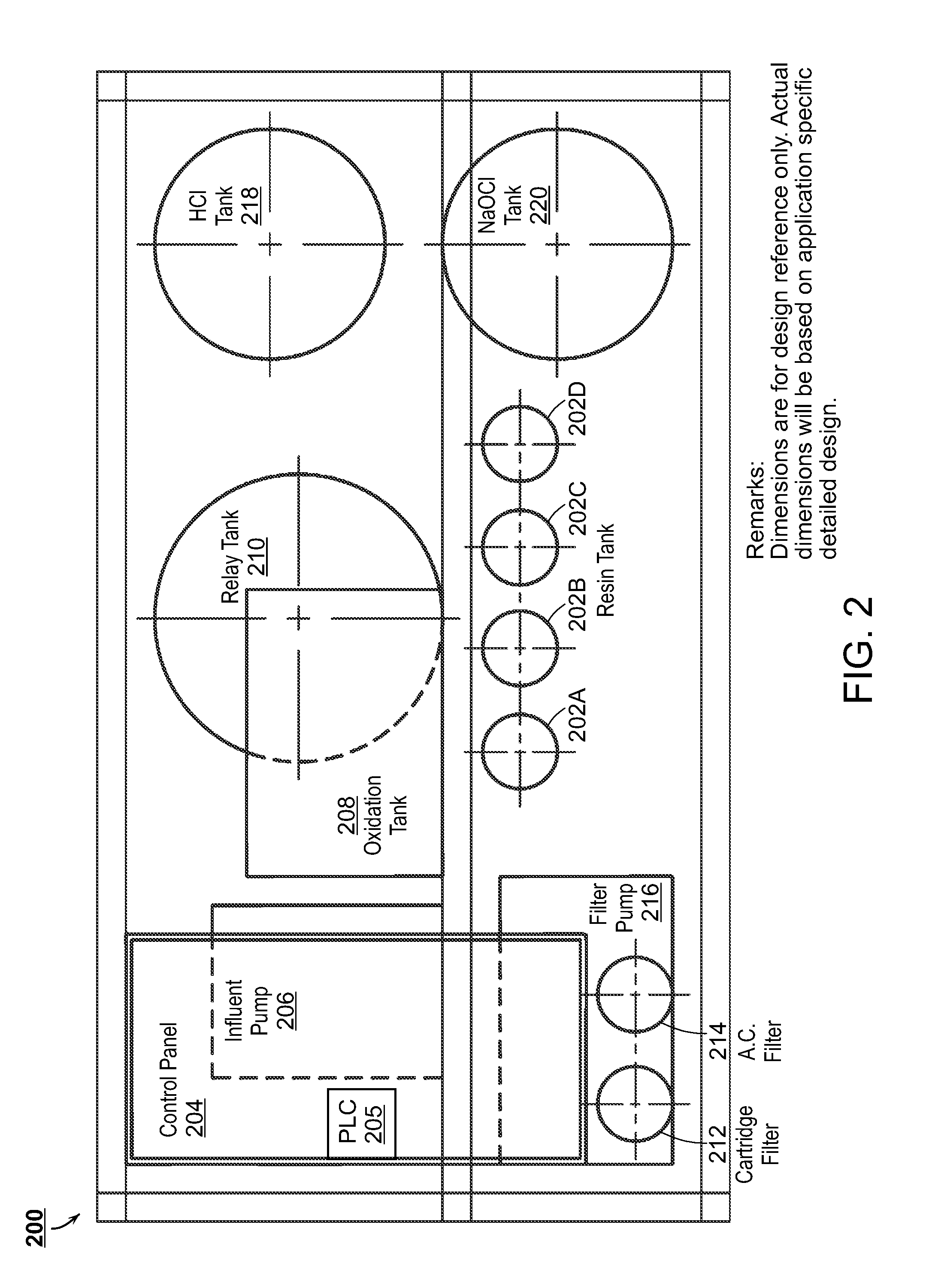
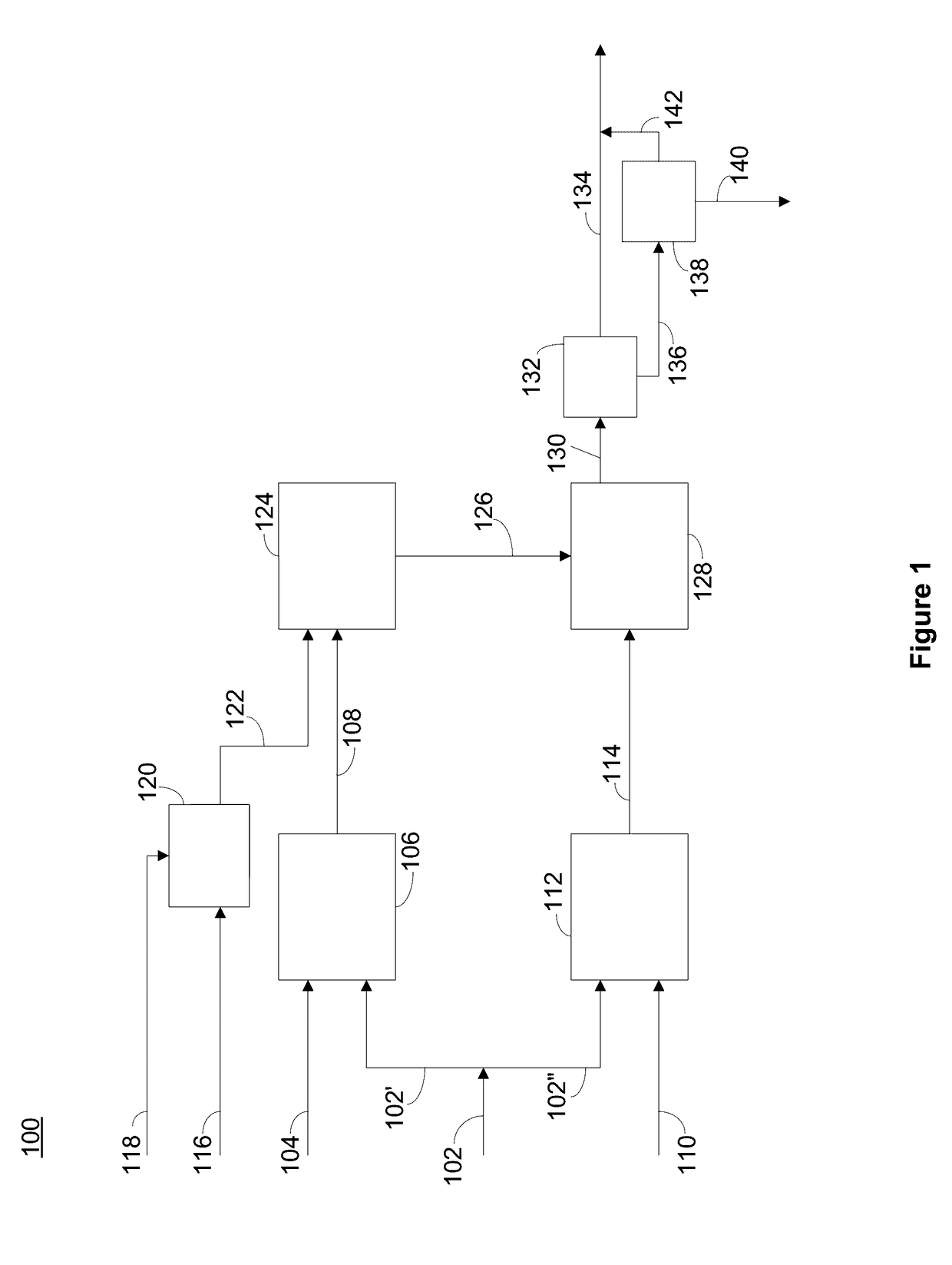
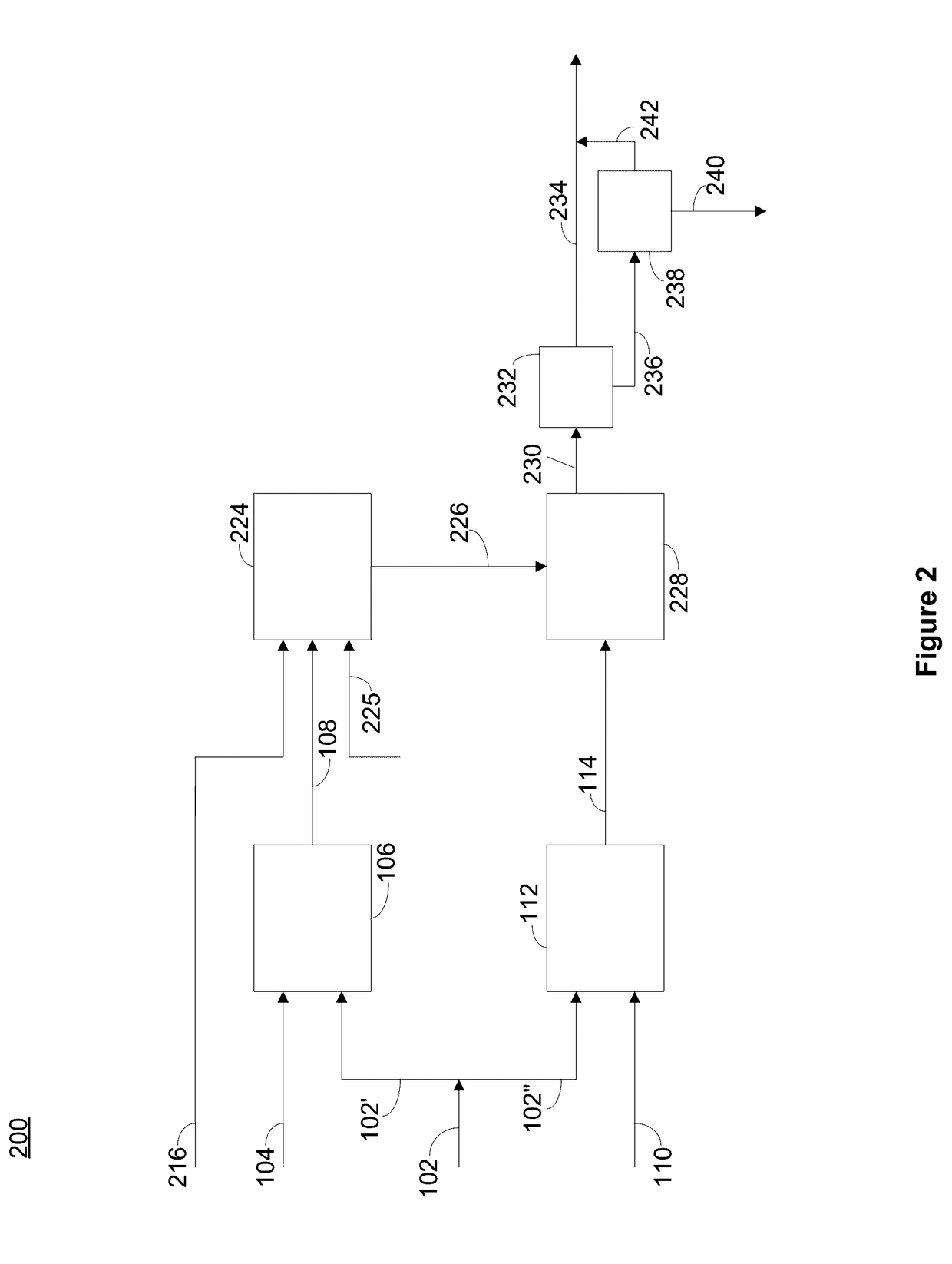
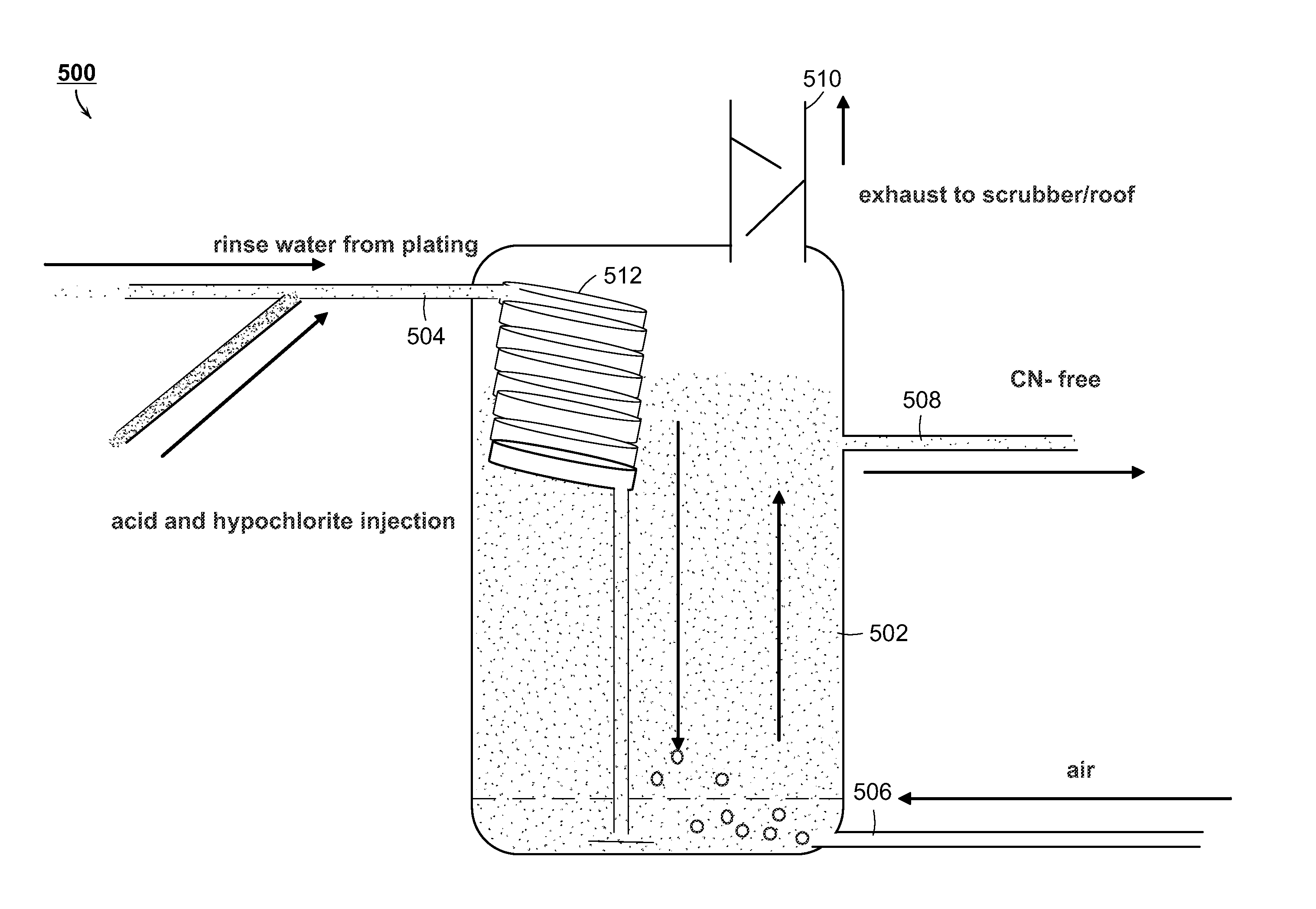
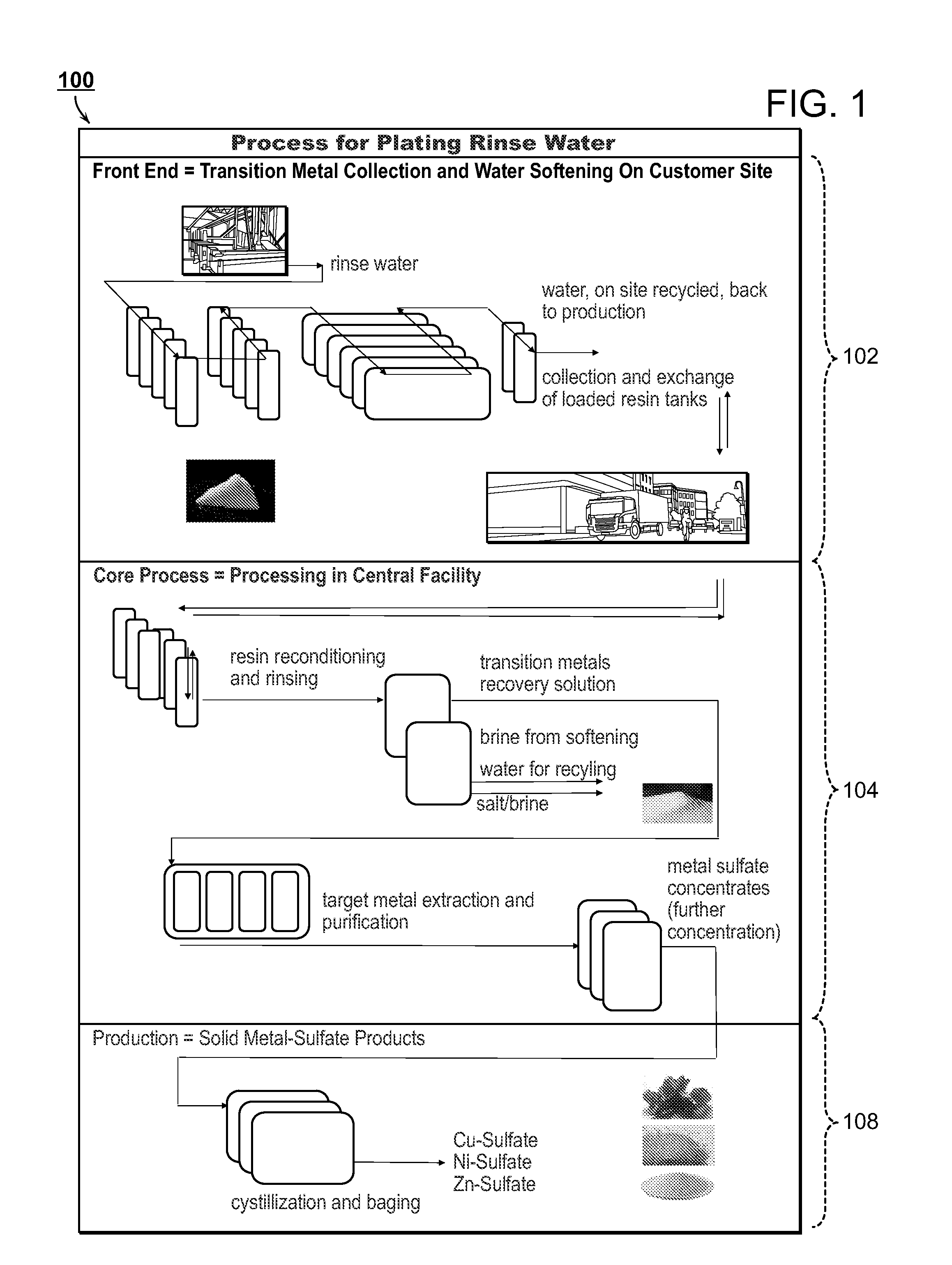
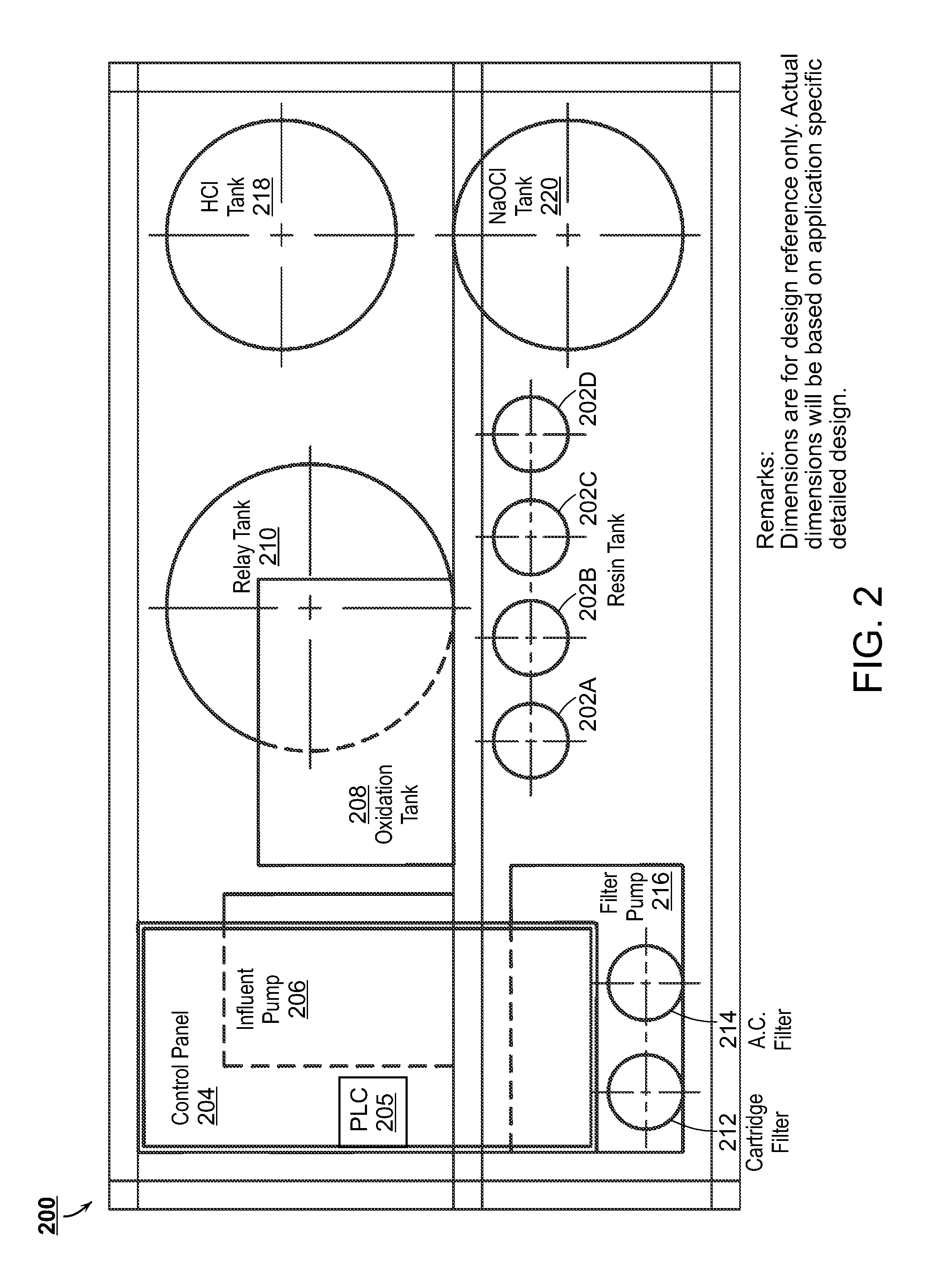
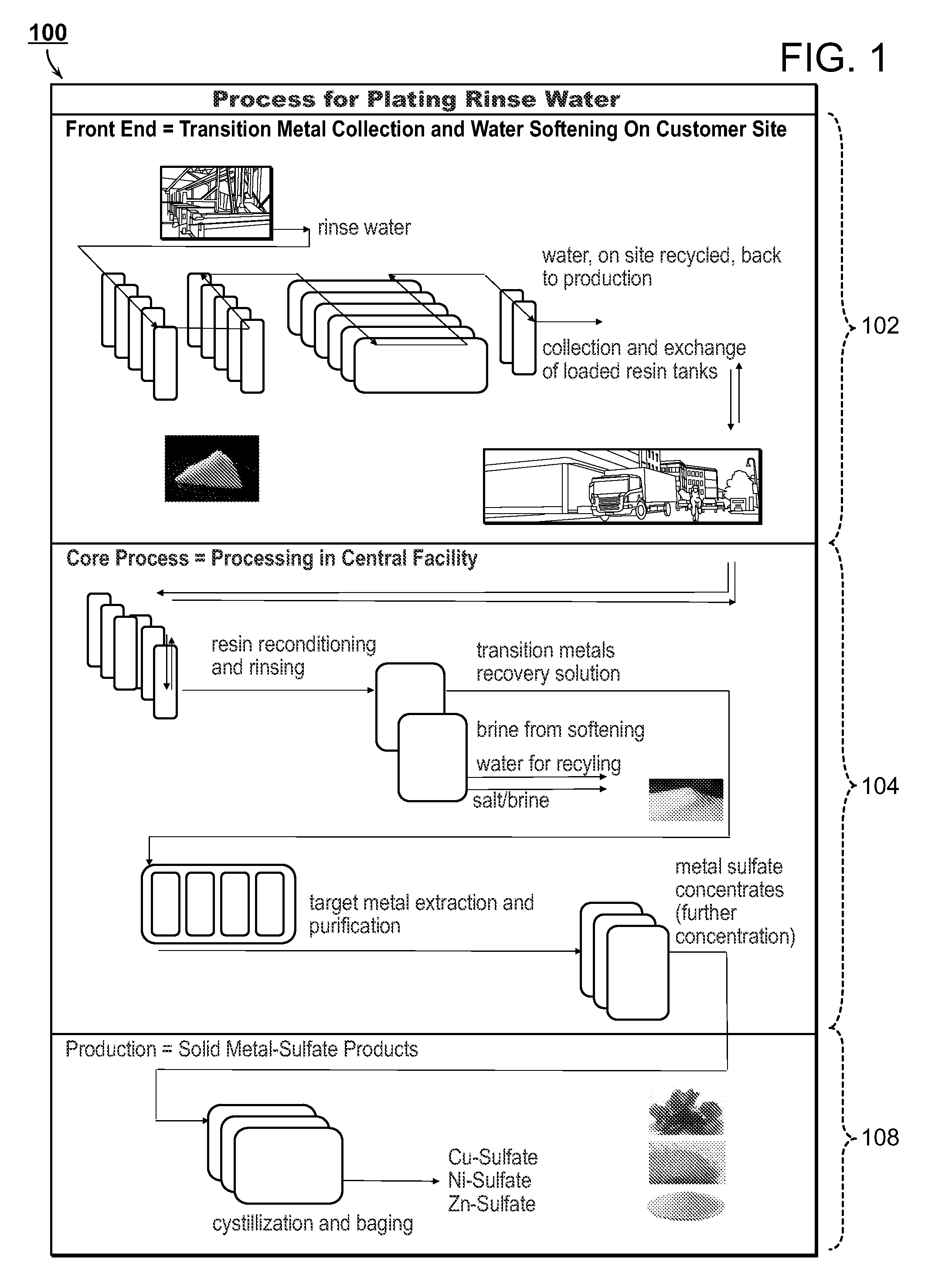
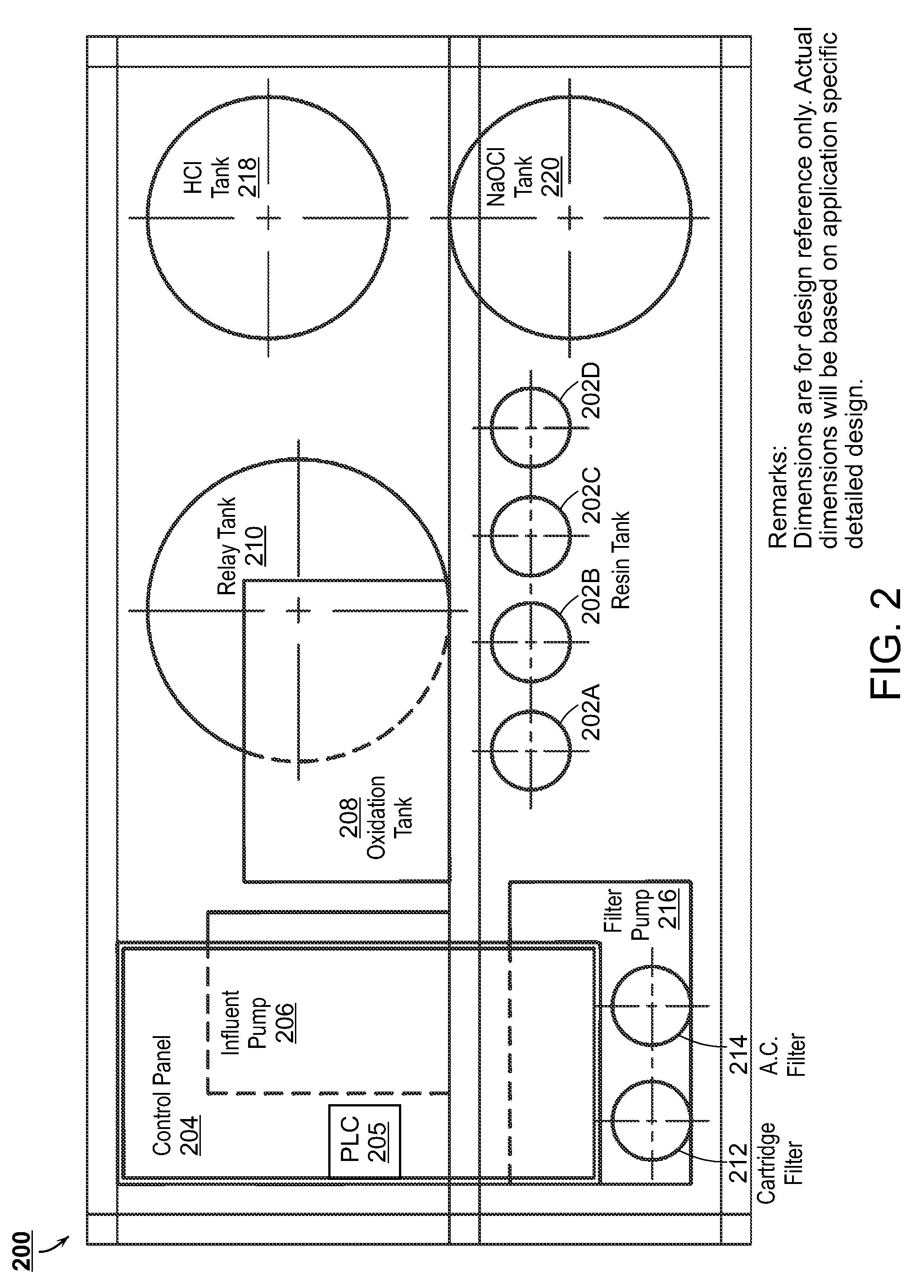
The present disclosure is directed towards systems and methods for the treatment of wastewater. A system in accordance with one particular embodiment may include at least one resin tank including an ion exchange resin configured to target a particular metal. The at least one resin tank may be configured to receive an output from an oxidation reactor configured to receive a flow of wastewater from a wastewater producing process. The system may further include a vacuum filter band system configured to receive a saturated resin tank and to apply a water rinse to the resin to generate a resin slurry, the vacuum filter band system including a vacuum filter band configured to receive the resin slurry. Numerous other embodiments are also within the scope of the present disclosure.
Owner:HYDROIONIC TECH
Simultaneous recovery of potassium chloride and KCL enriched edible salt
The present invention relates to recovery of industrial grade potassium chloride and low sodium edible salt from bittern as part of an integrated process. The process comprises, mixing low sulphate concentrated feed bittern (a by-product of salt industry) of density 31.5 to 32.5° Be (sp.gr. 1.277-1.289) with high density end bittern of density 36.5 to 37.5° Be′ (sp.gr. 1.336-1.35), thereby producing low sodium carnallite, from which industrial grade potassium chloride is produced. The resultant bittern is evaporated in forced evaporation system, thereby producing crude carnallite, from which low sodium salt that would be beneficial to persons suffering from hypertension is produced. When sulphate-rich bittern is used, such bittern is desulphated with CaCl2 that is generated from carnallite decomposed liquor through reaction with lime, and wherein low B2O3-containing Mg(OH)2 is a by-product. The entire content of potassium in feed bittern is recovered in the process of the invention.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
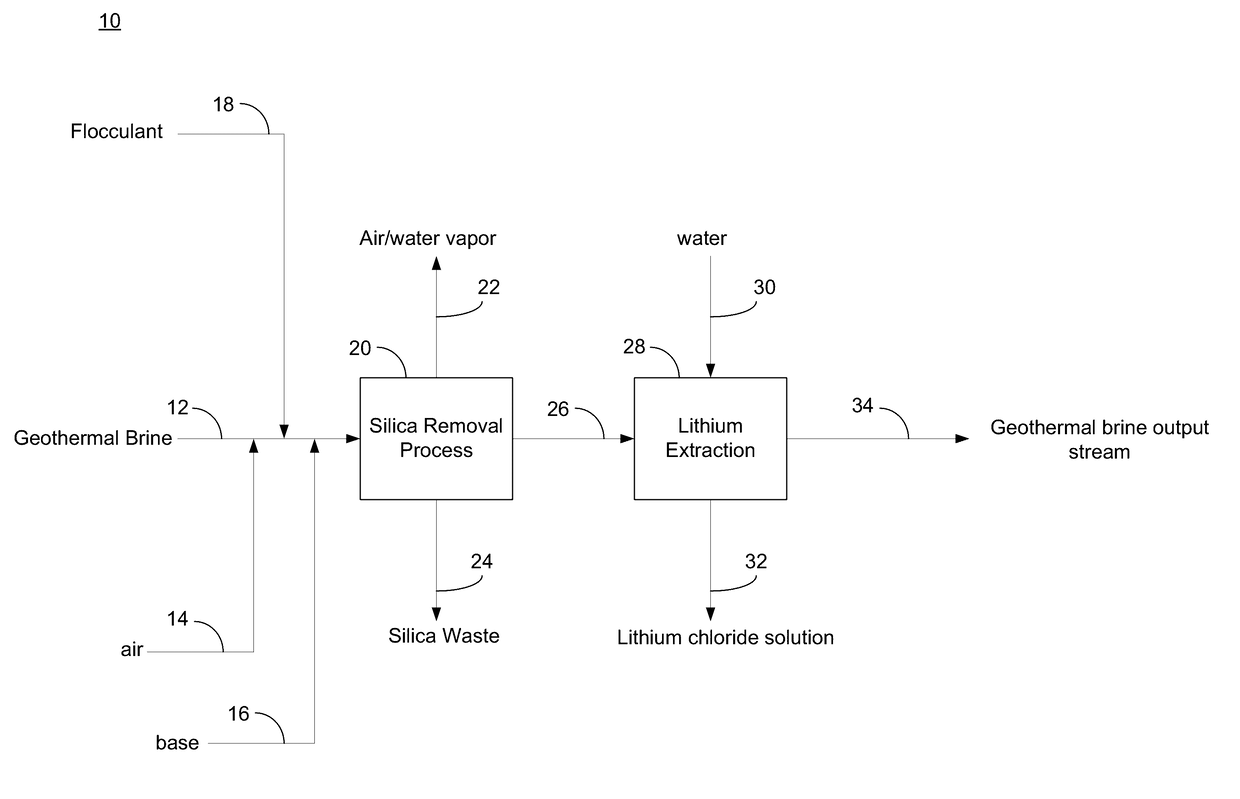
Treated geothermal brine compositions with reduced concentrations of silica, iron, and zinc
This invention relates to treated geothermal brine compositions containing reduced concentrations of iron, silica, and zinc compared to the untreated brines. Exemplary compositions contain concentration of zinc ranges from 0 to 300 mg / kg, concentration of silica ranges from 0 to 30 mg / kg, concentration of iron ranges from 0 to 300 mg / kg. Exemplary compositions also contain reduced concentrations of elements like lithium, manganese, arsenic, barium, and lead. Exemplary compositions include Salton Sea brines containing a concentration of zinc less than 10 mg / kg, a concentration of silica ranging from less than 10 mg / kg, and a concentration of iron less than 10 mg / kg.
Owner:TERRALITHIUM LLC
Method for Collection of Valuable Metal from ITO Scrap
ActiveUS20100316544A1Simple processEasy to collectAluminium compoundsPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysisIndium
Proposed is a method for collecting valuable metal from an ITO scrap including the steps of subjecting the ITO scrap to electrolysis in pH-adjusted electrolyte, and collecting indium or tin as oxides. Additionally proposed is a method for collecting valuable metal from an ITO scrap including the steps of subjecting the ITO scrap to electrolysis in an electrolytic bath partitioned with a diaphragm or an ion-exchange membrane to precipitate hydroxide of tin, thereafter extracting anolyte temporarily, and precipitating and collecting indium contained in the anolyte as hydroxide. With the methods for collecting valuable metal from an ITO scrap described above, indium or tin may be collected as oxides by roasting the precipitate containing indium or tin. Consequently, provided is a method for efficiently collecting indium from an ITO scrap of an indium-tin oxide (ITO) sputtering target or an ITO scrap such as ITO mill ends arisen during the manufacture of such ITO sputtering target.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
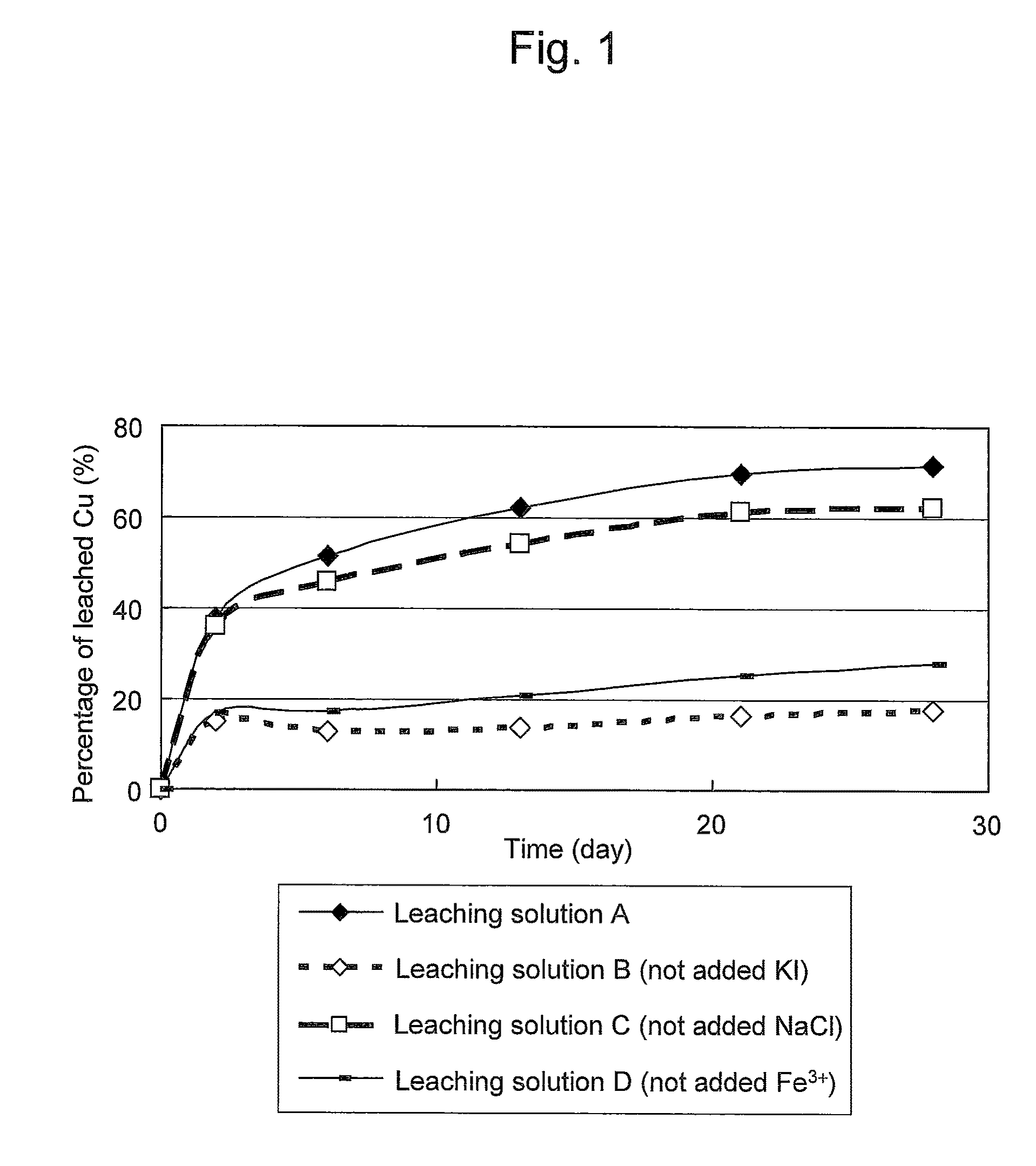
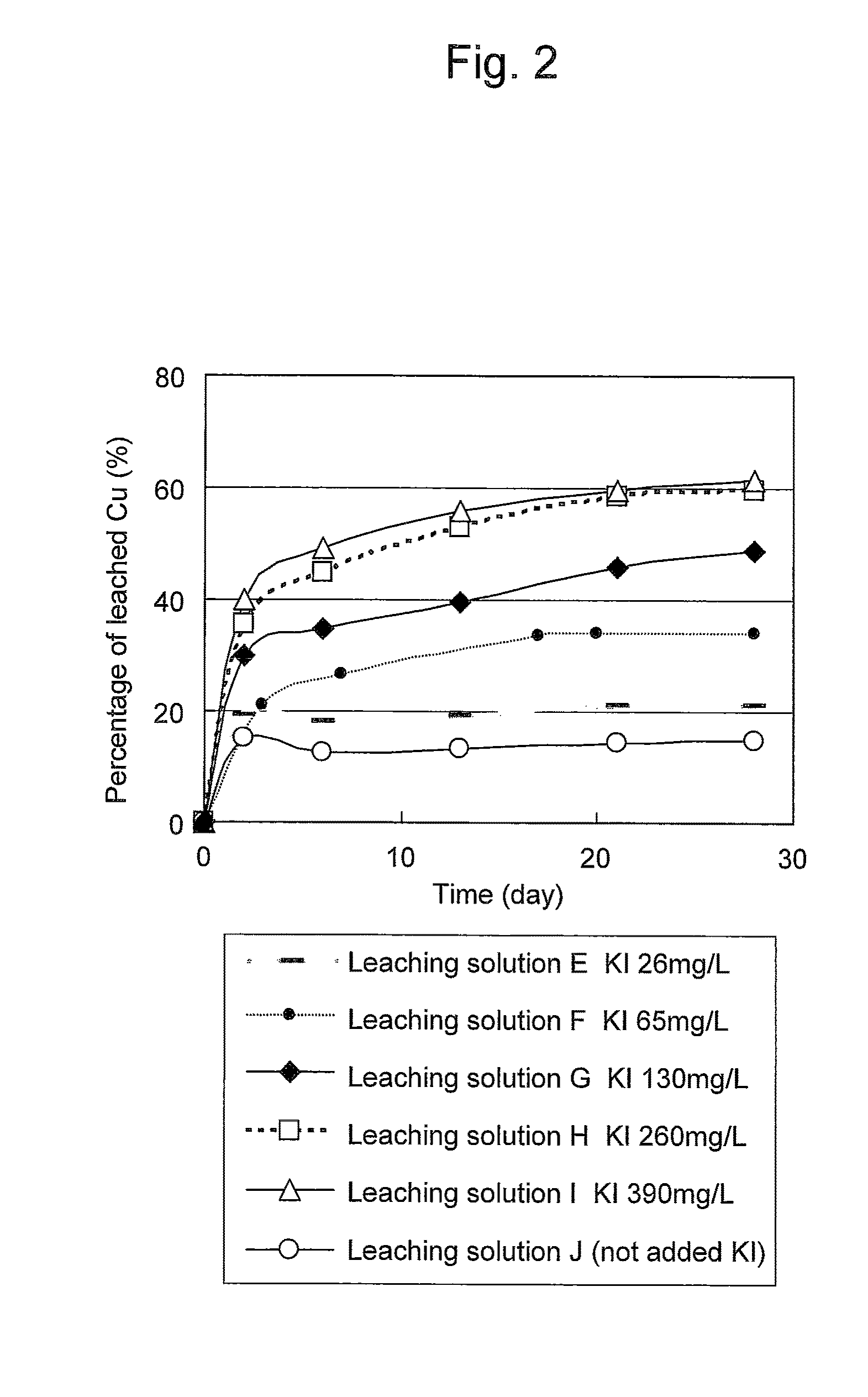
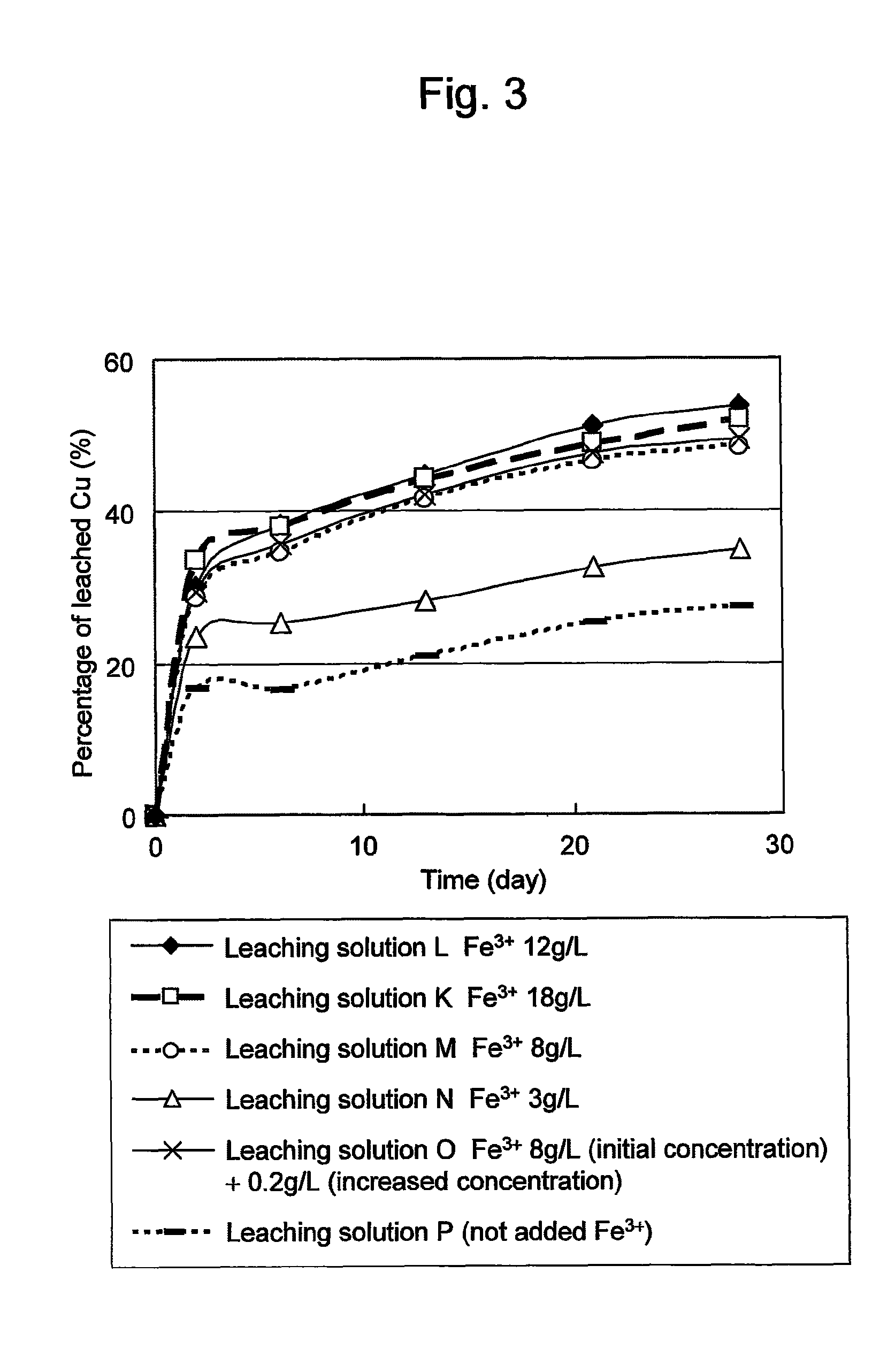
Method of leaching copper sulfide ore with the use of iodine
ActiveUS8163063B2Efficient leachingEfficient executionSolvent extractionGold compoundsPregnant leach solutionChalcopyrite
An object of the present invention is to provide a method of efficiently leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore containing chalcopyrite or enargite as a main constituent under versatile conditions for actual operation.A method of leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore, characterized by comprising using, as a leaching solution, a sulfuric acid solution containing iodide ions and ferric (III) ions in an excessive amount relative to the iodide ions and leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore; or a method of leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore, characterized by comprising leaching copper from a copper sulfide ore with the use of a leaching solution further containing water-soluble ligands such as chloride ions that can stabilize ferric (III) ions in addition to the above components, is provided.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CORP
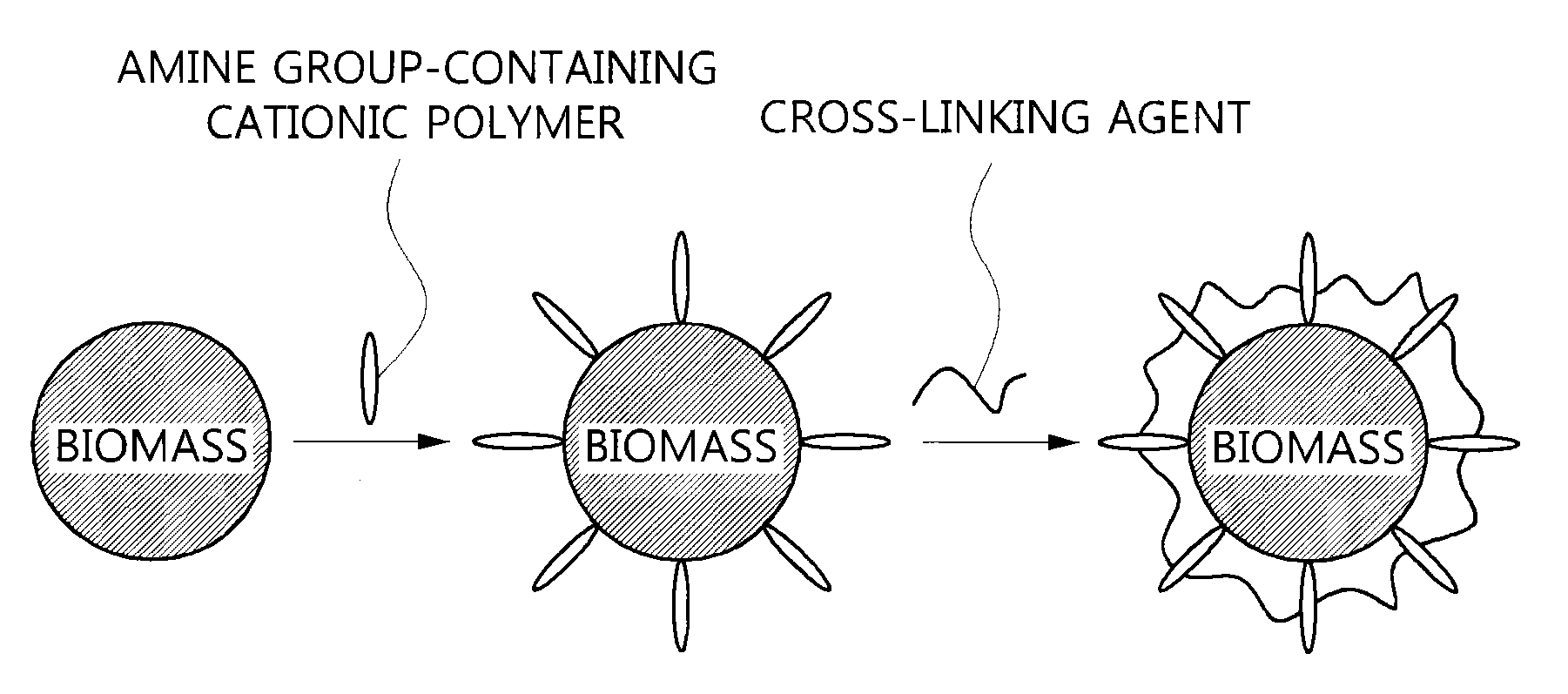
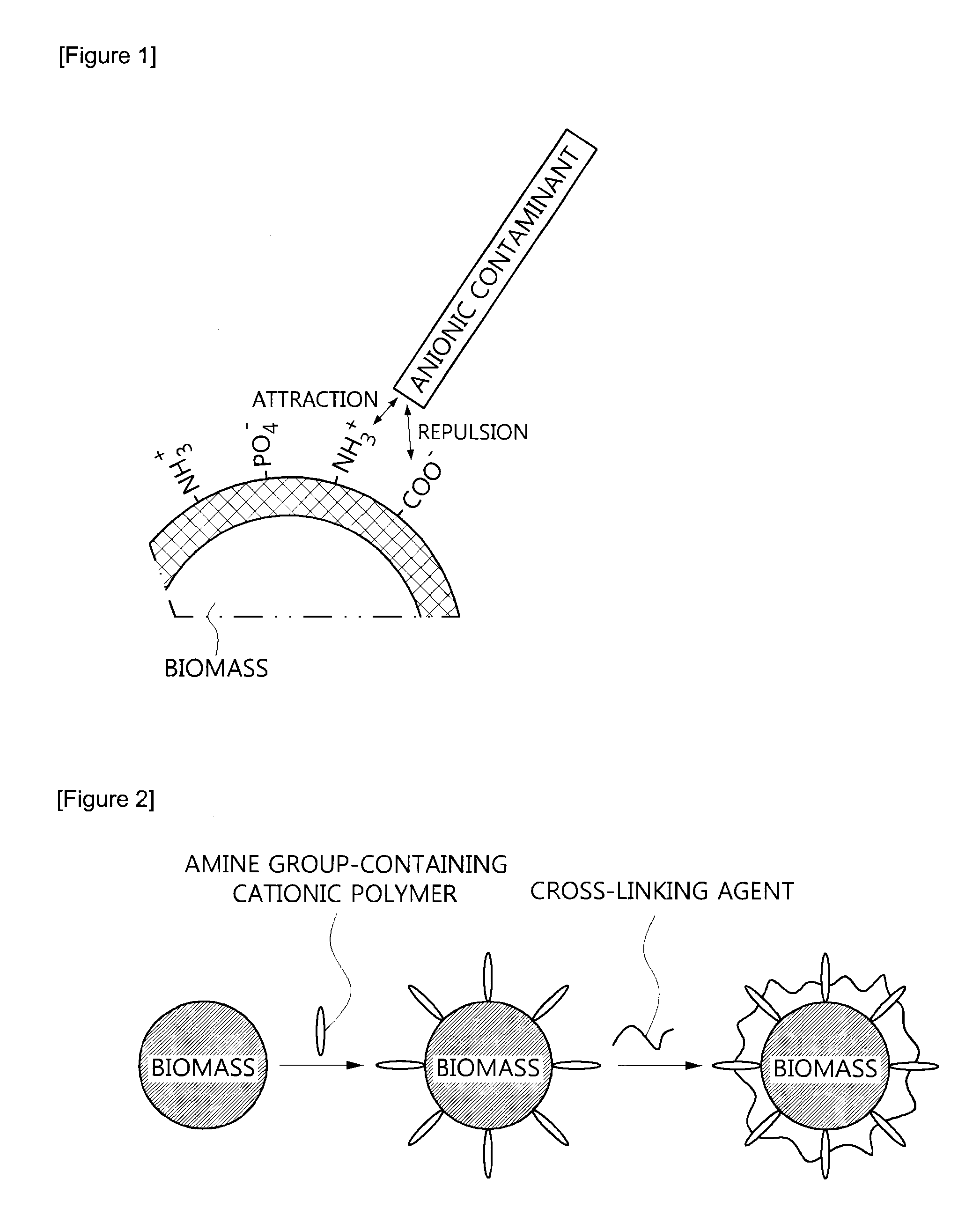
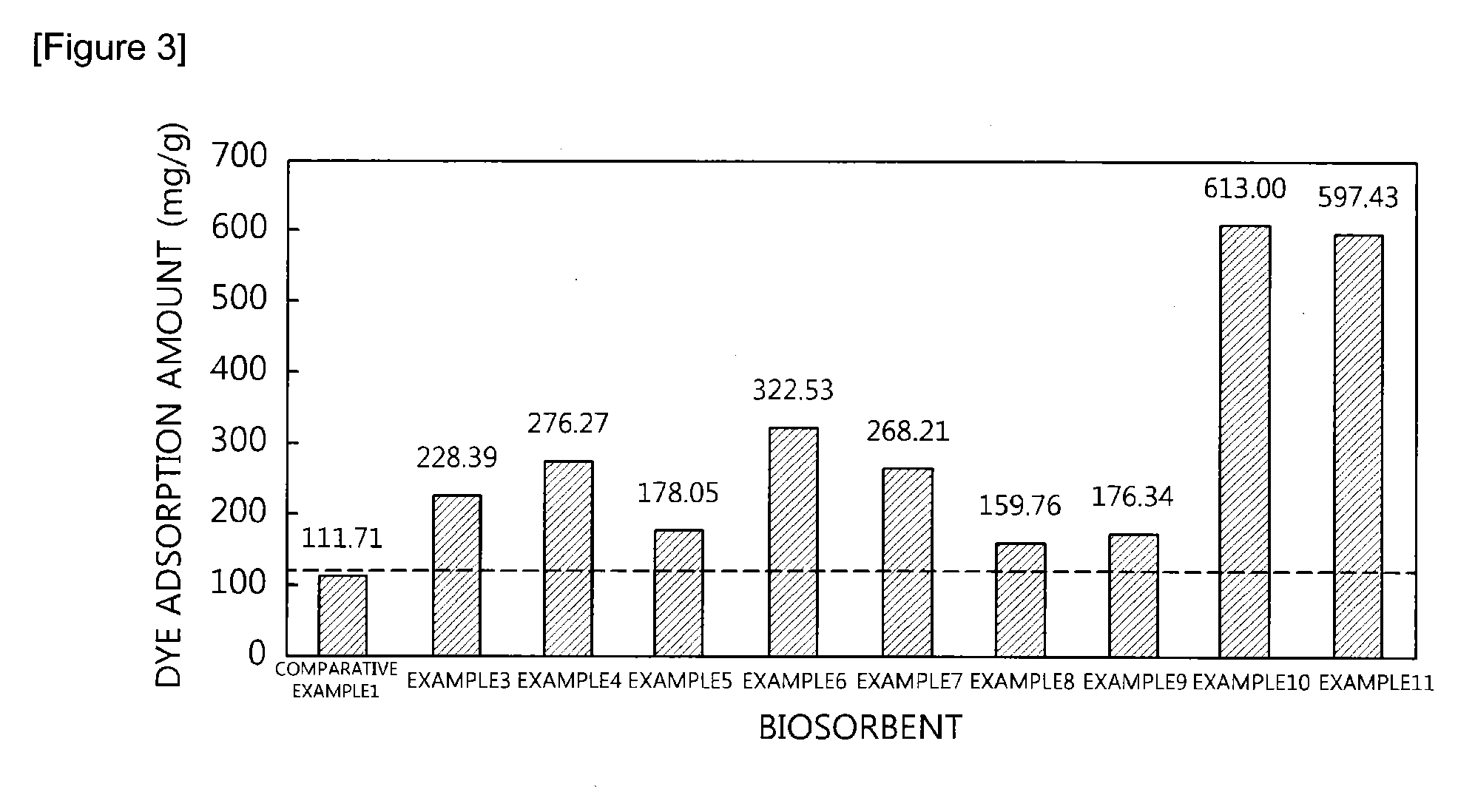
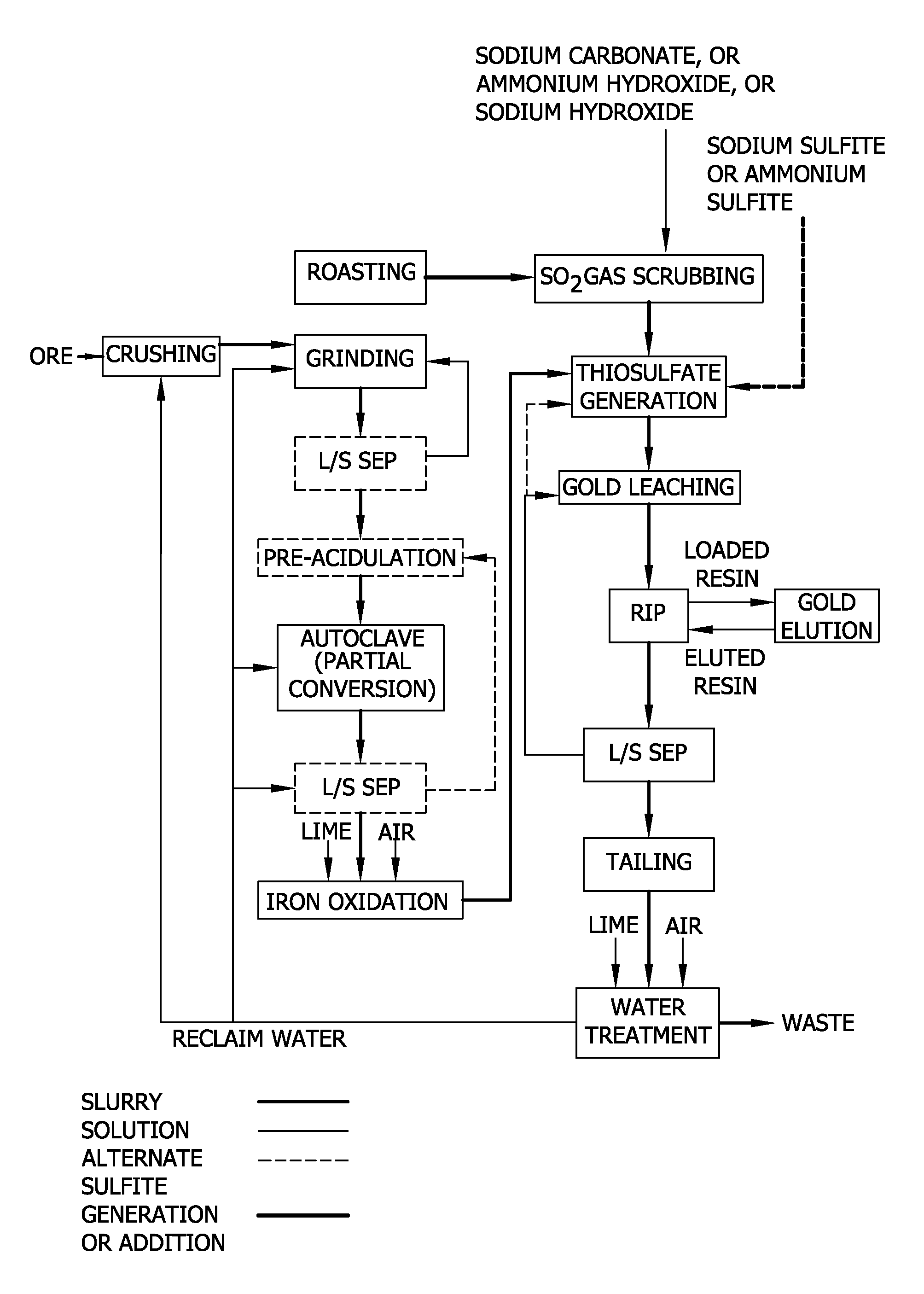
Surface-modified biomass, preparation method thereof, and method for recovering valuable metals using the same
InactiveUS20120036962A1Easy to useImprove adsorption capacityMaterial nanotechnologyWater contaminantsRecovery methodPolymer
The present invention relates to a surface-modified biomass which is crosslinked with an amine group-containing cationic polymer on the surface of a cell biomass, its preparation method, and a method for recovering valuable metals using the same. The surface-modified biomass of the present invention has an advantage of improving adsorption of and affinity with anionic pollutants as a result of further introducing a cationic functional group by crosslinking of the amine group-containing cationic polymer on the surface of the biomass. In addition, the method for recovering valuable metals with the present invention is environment-friendly, economical, and harmless to the human body.
Owner:IND COOP FOUND CHONBUK NAT UNIV
Method of recovering Pd from low-concentration waste Pd ion liquid with becteria thallus
The present invention relates to the recovery of micro amount of noble metal and the used bacteria is lichenoid bacillus No.R08. R08 bacillus thallus solution of 0.4-2.0 g / L concentration and water solution of Pd ion of 30-300 mg / L are first mixed and vibrated at 5-60 deg.c pH 2.0-3.5 and 130 Hz vibration frequency for 3-90 min; the mixed liquid is then filtered; and filtered Pd adsorbing bacillus thallus is set at room temperature for 6-48 hr and burned at 550-800 deg.c for 1.5-3 hr to obtain metal Pd. The simple process is especially suitable for recovering Pd from low concentration solution and the Pd ion adsorbing rate may reach 99%.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
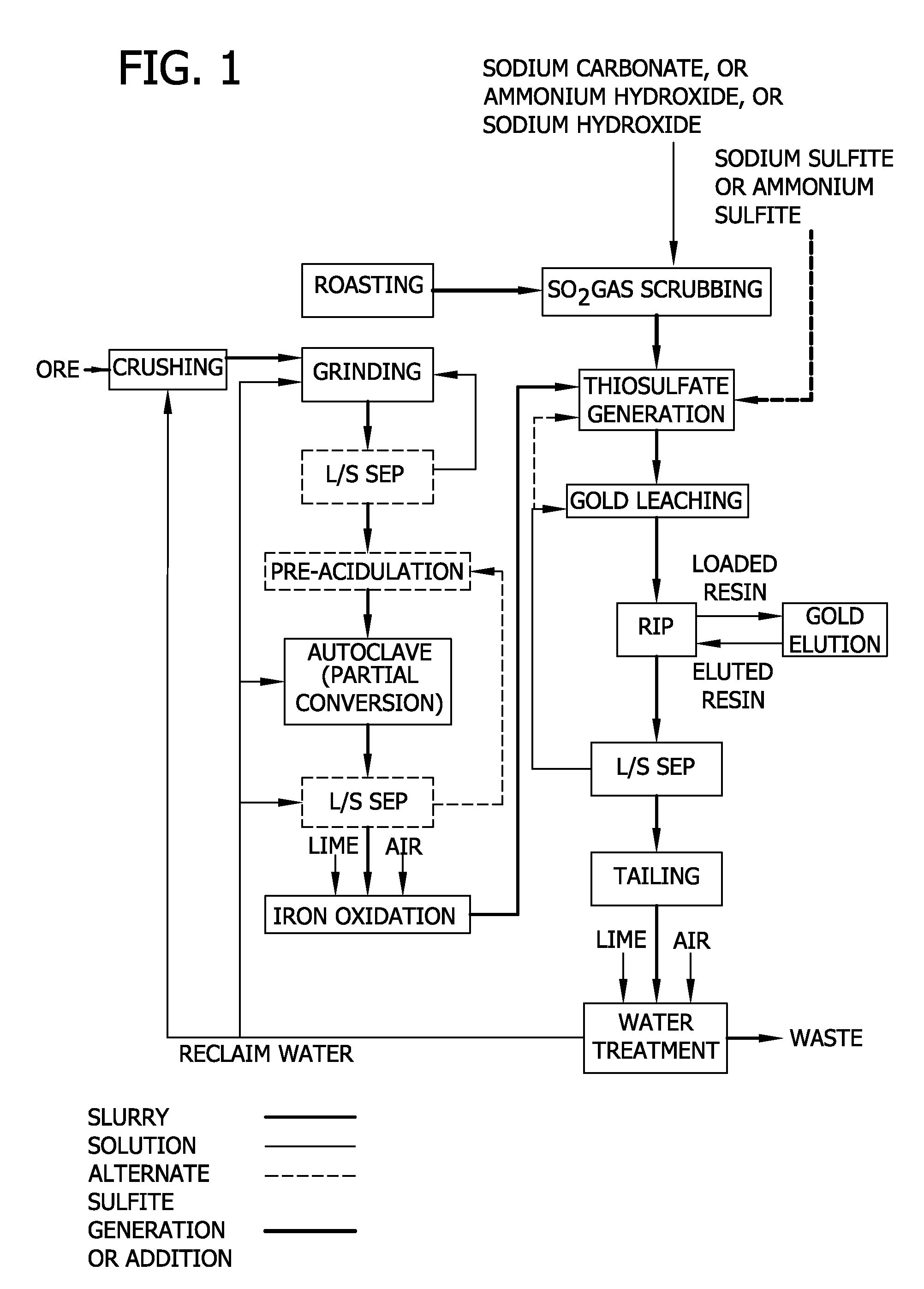
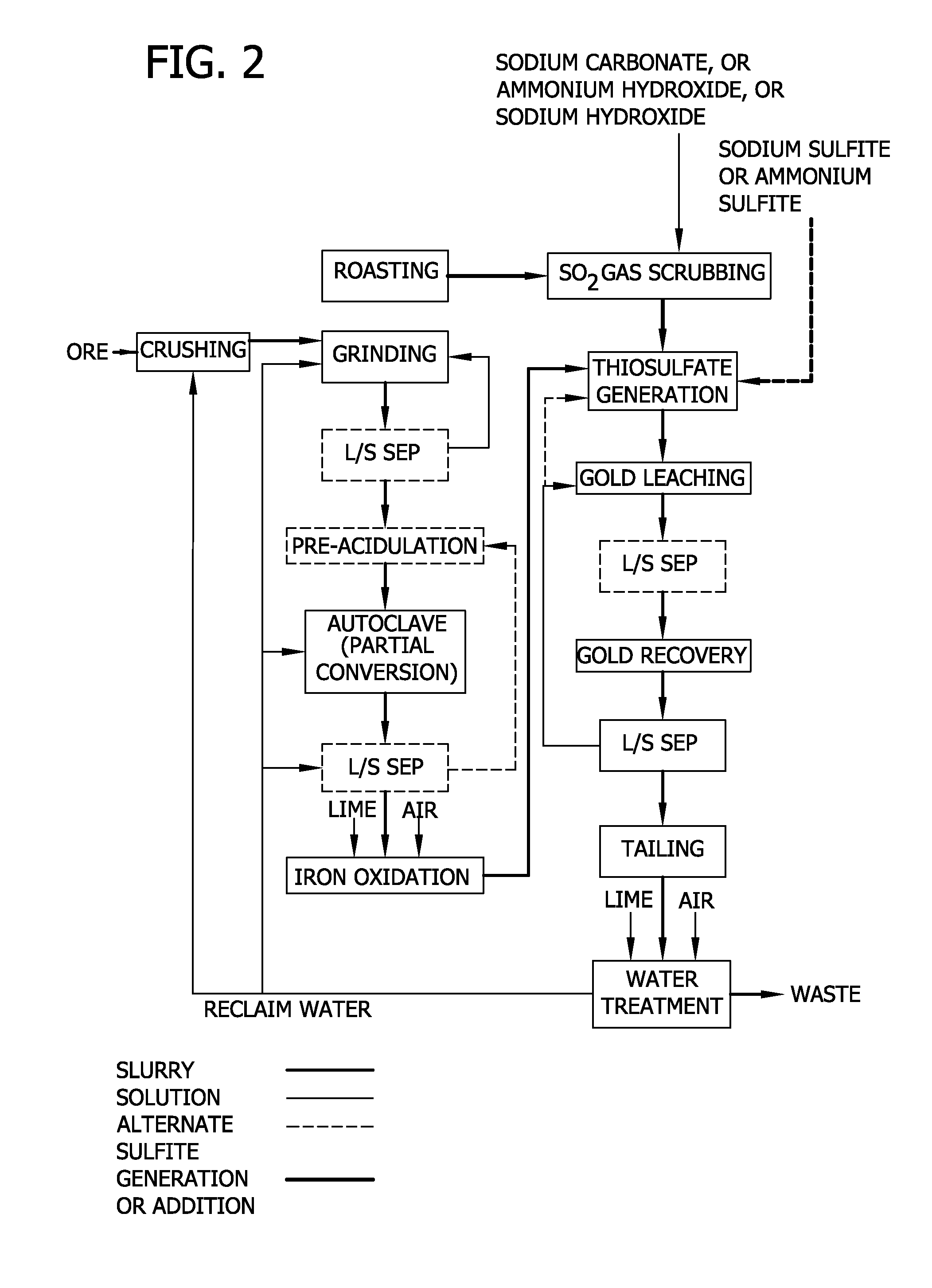
Thiosulfate generation in situ in precious metal recovery
Precious metal recovery by thiosulfate leaching where thiosulfate lixiviant is generated in situ employing elemental sulfur generated from partial oxidation of sulfidic precious metal-bearing feed and / or employing reactants from processing effluent.
Owner:BARRICK GOLD
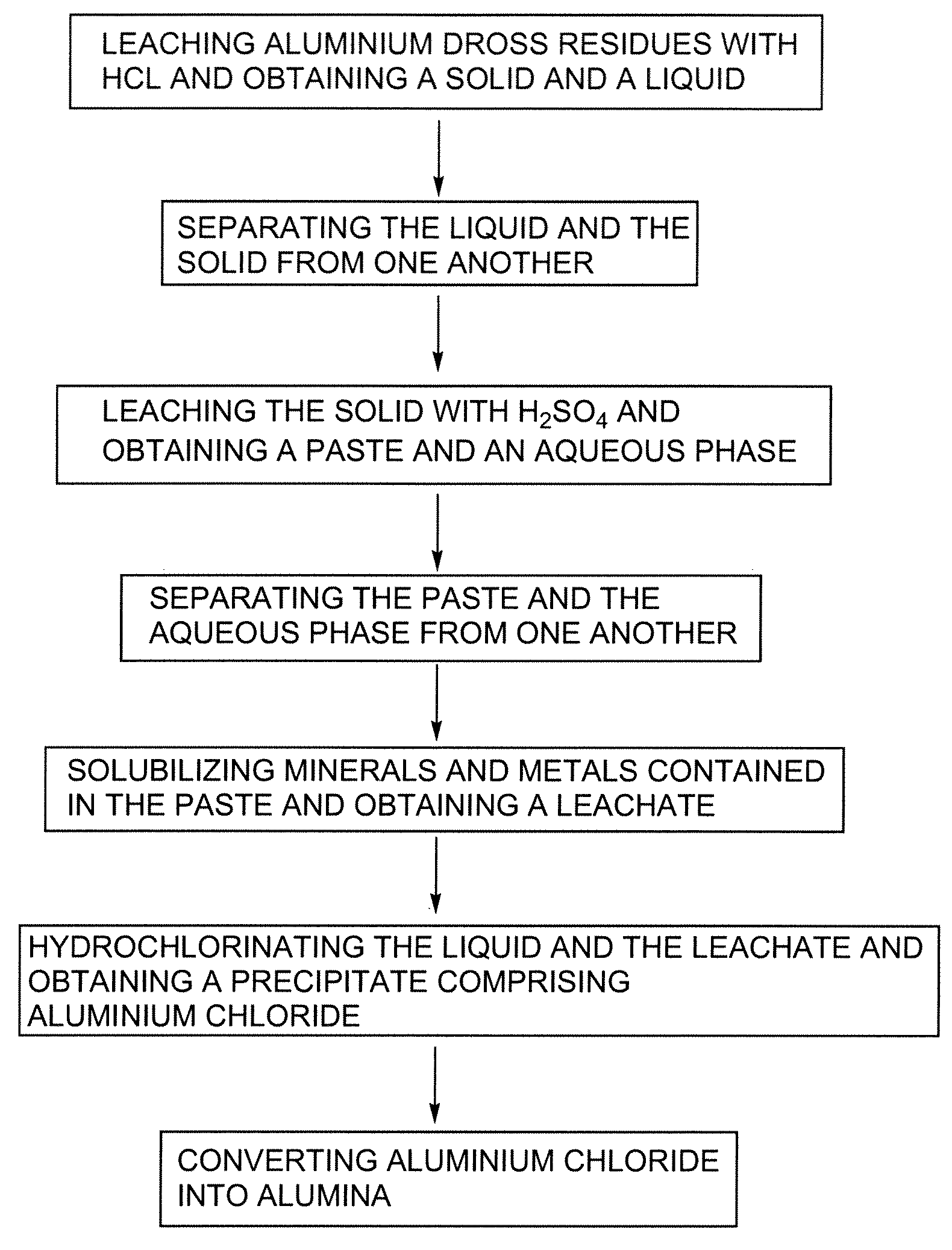
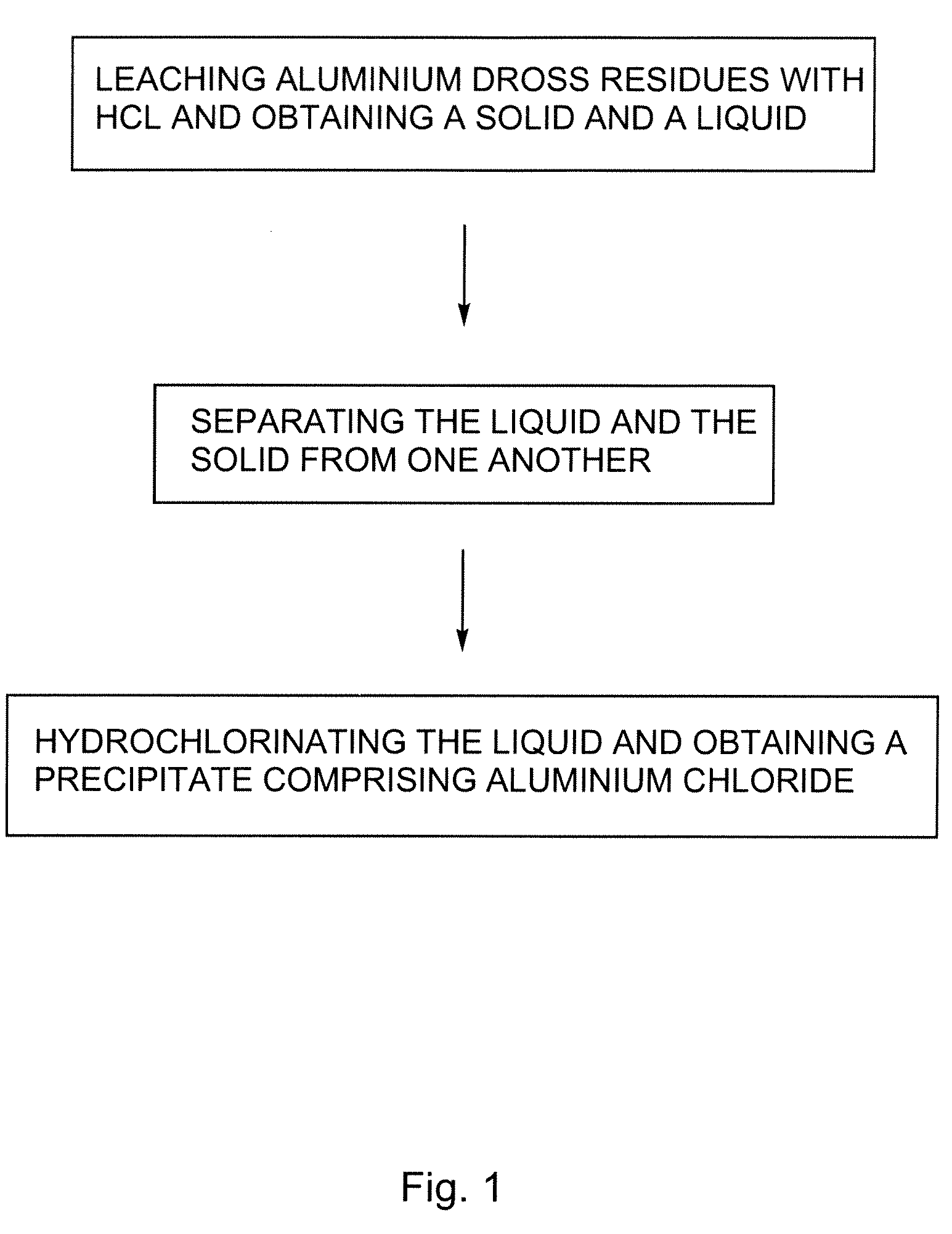
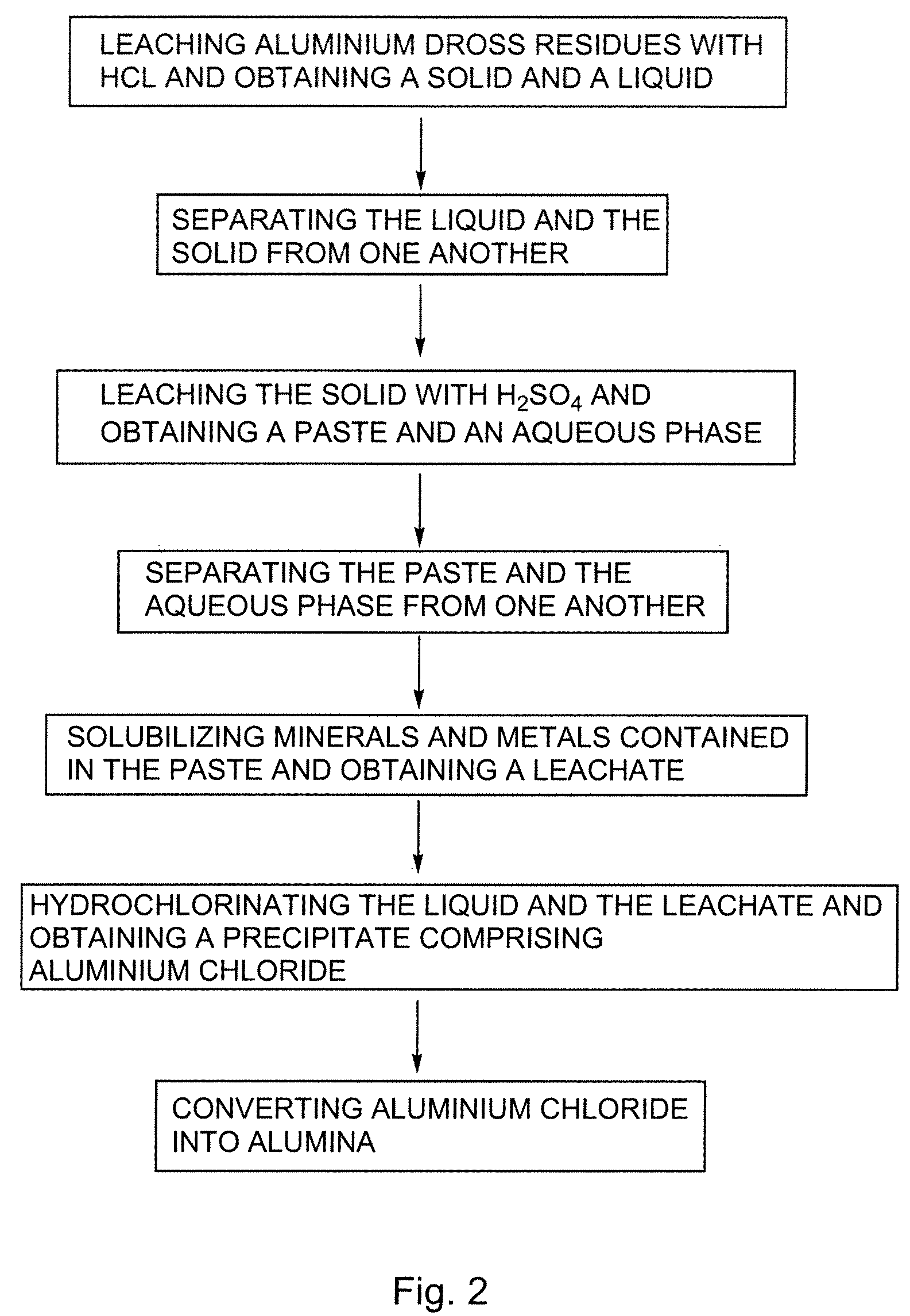
Processes for treating aluminium dross residues
InactiveUS7651676B2Low costHigh yieldSolvent extractionGallium/indium/thallium compoundsAluminium chlorideLeachate
There is provided a process for preparing aluminium chloride comprising: leaching aluminium dross residues with HCl so as to obtain a mixture comprising a solid and a liquid; and hydrochlorinating the liquid obtained from the mixture, so as to form a precipitate comprising aluminium chloride. Such a sequence can also be used for preparing alumina. In such a case, the process can further comprise the step of converting the so-obtained aluminium chloride into alumina. In the processes previously defined, the solid so-obtained can also be leached with H2SO4, thereby generating a leachate. The leachate can also eventually be hydrochlorinated so as to increase the yield of the desired product obtained i.e. alumina or aluminium chloride.
Owner:EXP SERVICES INC
Waste heat recovery structure for steel making electric arc furnaces, steel making electric arc furnace facility, and waste heat recovery method for steel making electric arc furnaces
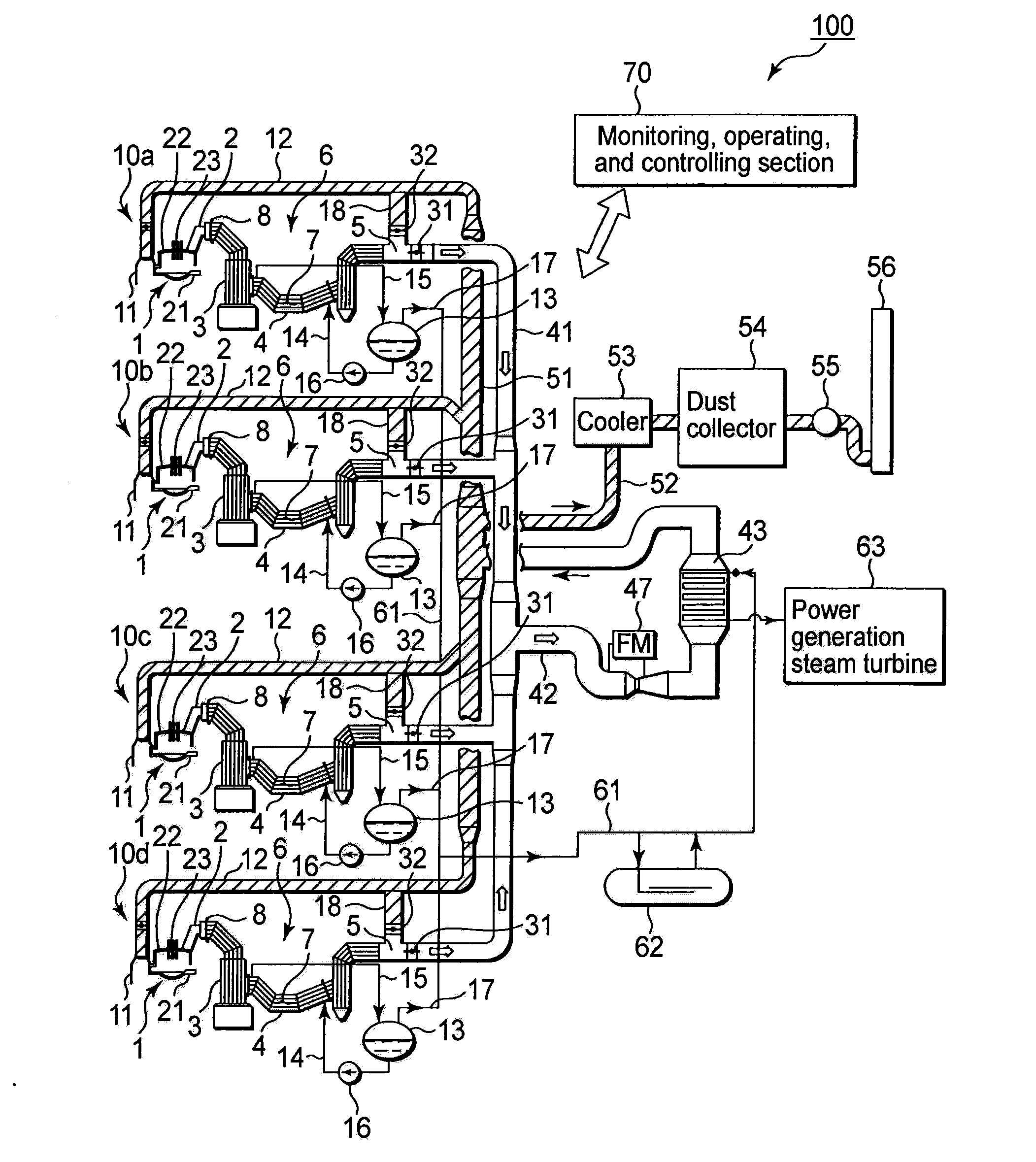
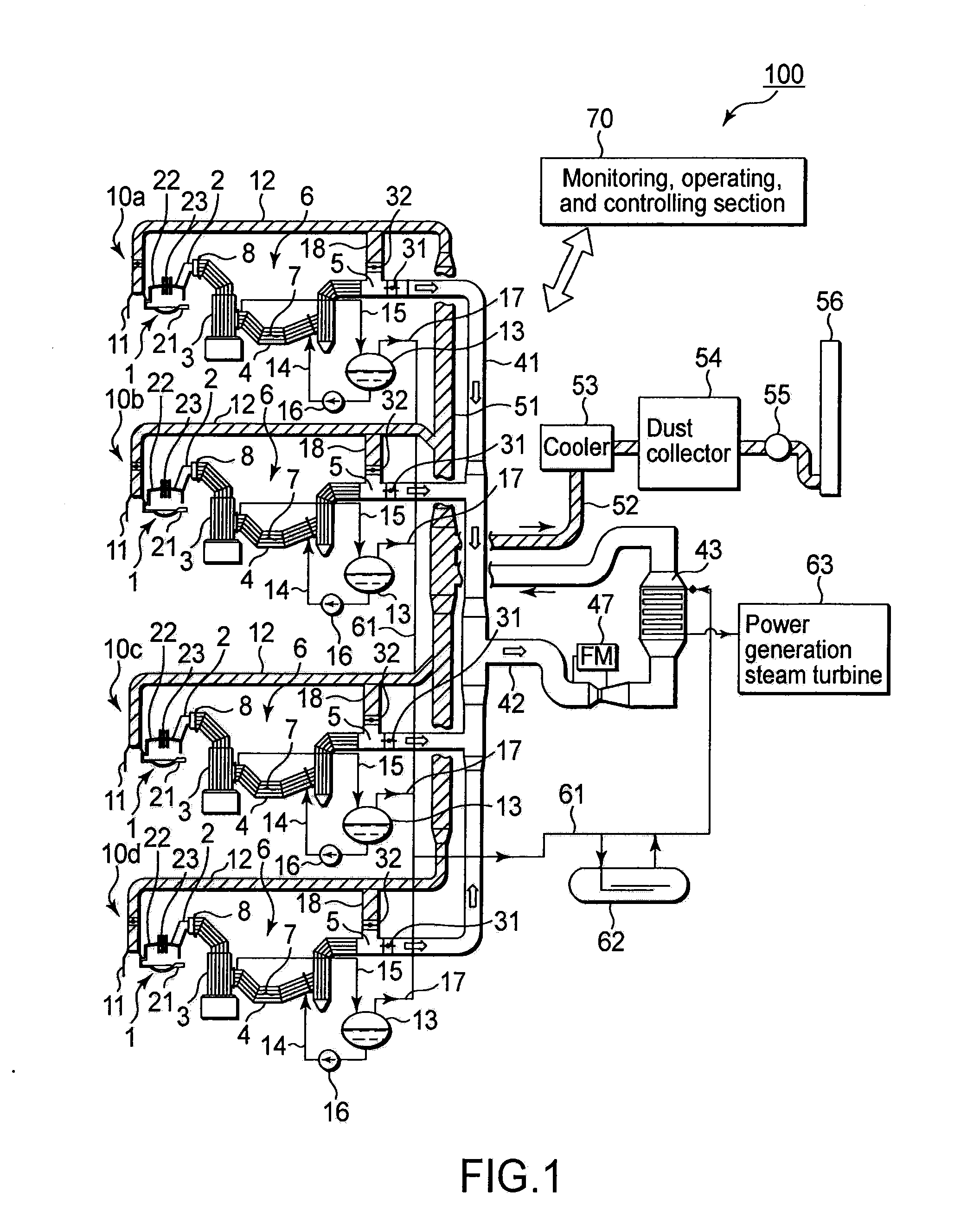
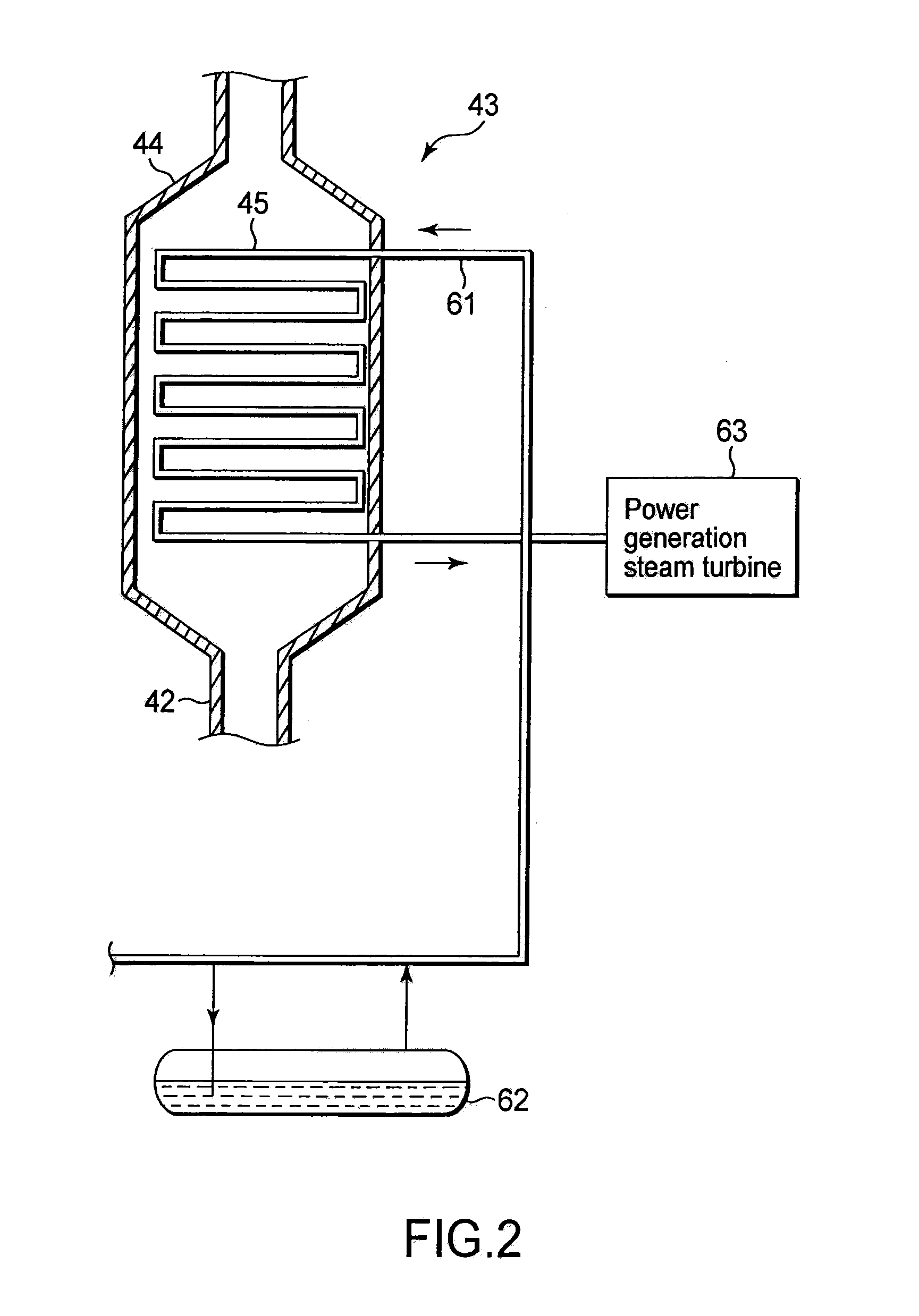
ActiveUS20120320941A1Minimize changesEffective recoverySteam generation heating methodsRecovering materialsWaste heat recovery unitRecovery method
A waste heat recovery structure includes a first exhaust gas flow path provided to each of steel making electric arc furnaces to discharge exhaust gas thereinto; a waste heat boiler disposed on the first exhaust gas flow path to recover waste heat as saturated steam from exhaust gas; a steam accumulator configured to store steam formed by confluence of saturated steam parts, each generated by the waste heat boiler; a steam super heater configured to turn steam into superheated steam by heating; a second exhaust gas flow path configured to lead exhaust gas from the waste heat boiler to the steam super heater to use it for superheating; a third exhaust gas flow path configured to discharge exhaust gas from the waste heat boiler not through the steam super heater; and a switching device configured to switch flow paths between the second and third exhaust gas flow paths.
Owner:JP STEEL PLANTECH CO
Exhaust gas processing system and method for rotary hearth type reducing furnace
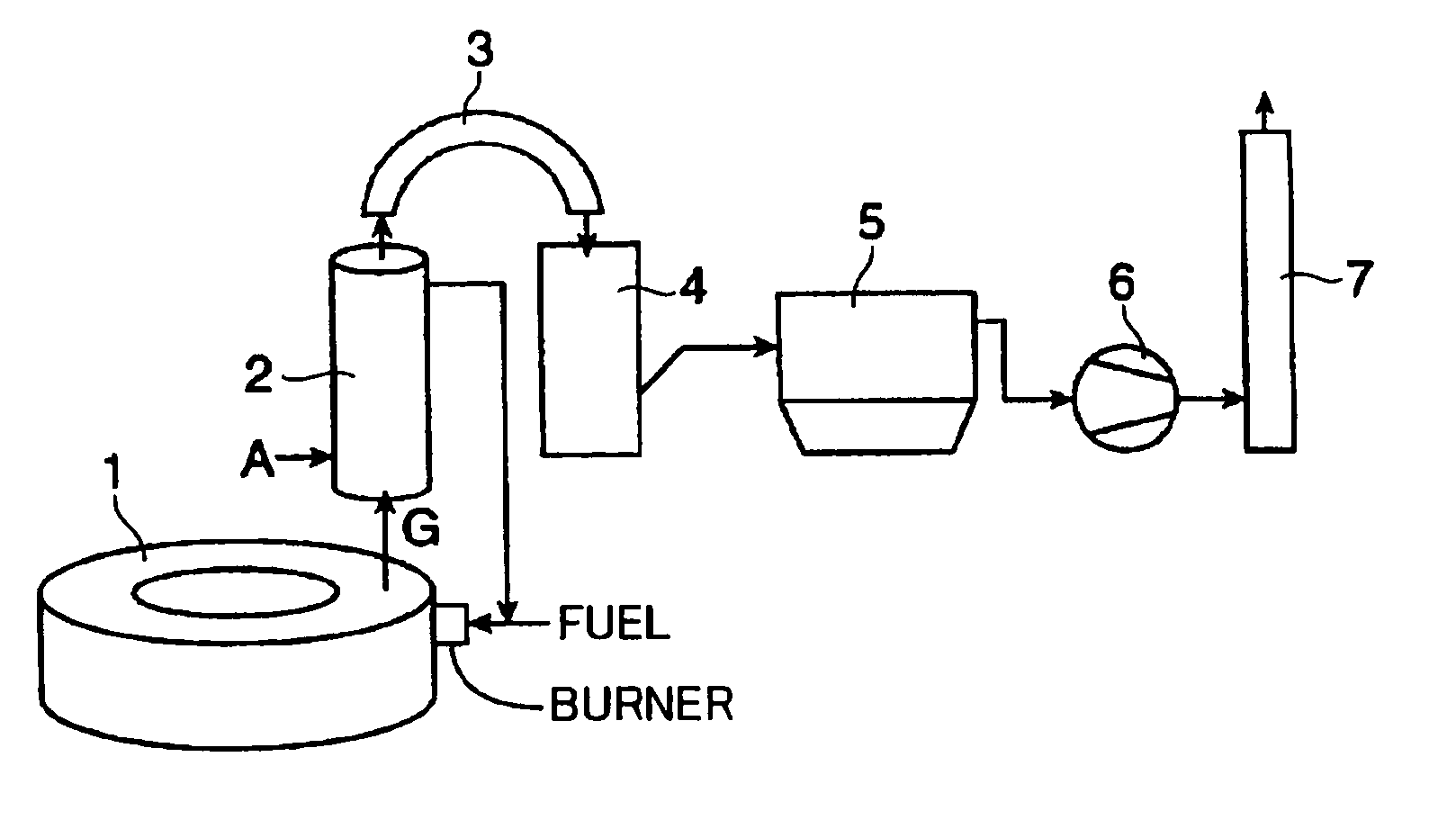
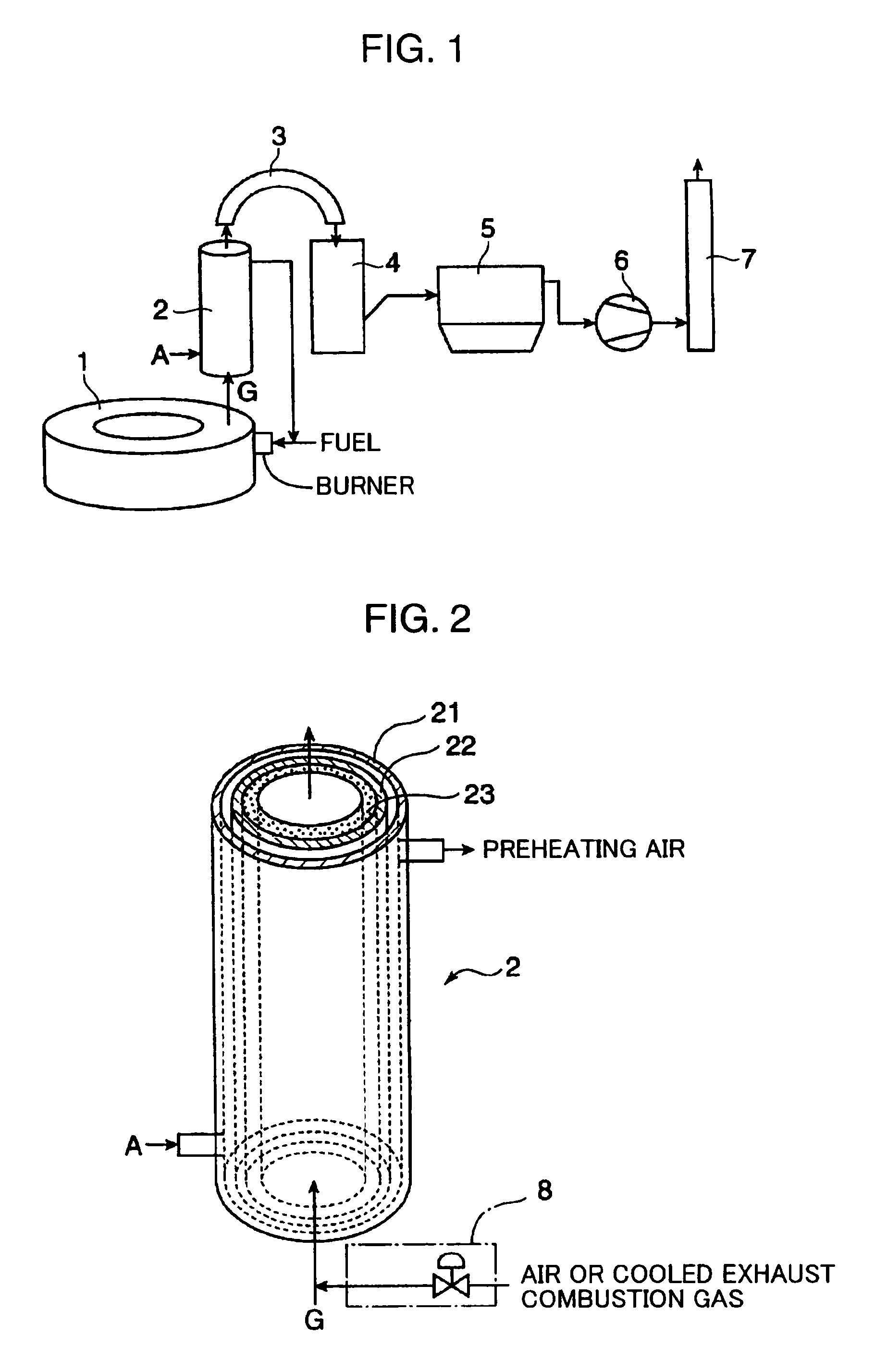
InactiveUS20100186644A1Rapid coolingEasy to disassembleRotary drum furnacesCorrosion preventionCombustorRefractory
Provided are an exhaust gas processing system and method capable of effectively utilizing the sensible heat of an exhaust gas for preheating air for burner combustion in a rotary hearth type reducing furnace while preventing troubles caused by adhesion of dust such as blockage in an exhaust gas processing facility for a rotary hearth type reducing furnace and corrosive deterioration in the facility without increasing the facility costs excessively. The system comprises a radiant heat exchanger 2 for heat exchange between an exhaust gas exhausted from the rotary hearth type reducing furnace and air. The radiant heat exchanger 2 includes an inner cylinder 22 made of metal surrounding a space through which the exhaust gas flows; an outer cylinder 21 disposed on an outer side in a radial direction of the inner cylinder to define a flow channel between the inner cylinder and the outer cylinder 21 for allowing the air to flow so as to exchange heat with the exhaust gas; and a highly thermal conductive refractory 23 applied to an inner side of the inner cylinder 22 so as to cover an inner surface thereof.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
System and method for wastewater treatment
InactiveUS20100163497A1Water treatment parameter controlSpecific water treatment objectivesEnd systemRadio frequency
The present disclosure is directed towards systems and methods for the treatment of wastewater. A system in accordance with one particular embodiment may include a front end system including at least one resin tank having an ion exchange resin configured to target a particular metal. The at least one resin tank may be configured to receive an output from an oxidation reactor configured to receive a flow of wastewater from a wastewater producing process. The system may further include a radio frequency identification (RFID) system associated with the front end system, the at least one resin tank including one or more radio frequency identification (RFID) tags configured to record at least one characteristic associated with the at least one resin tank. Numerous other embodiments are also within the scope of the present disclosure.
Owner:BAUDER RAINER +1
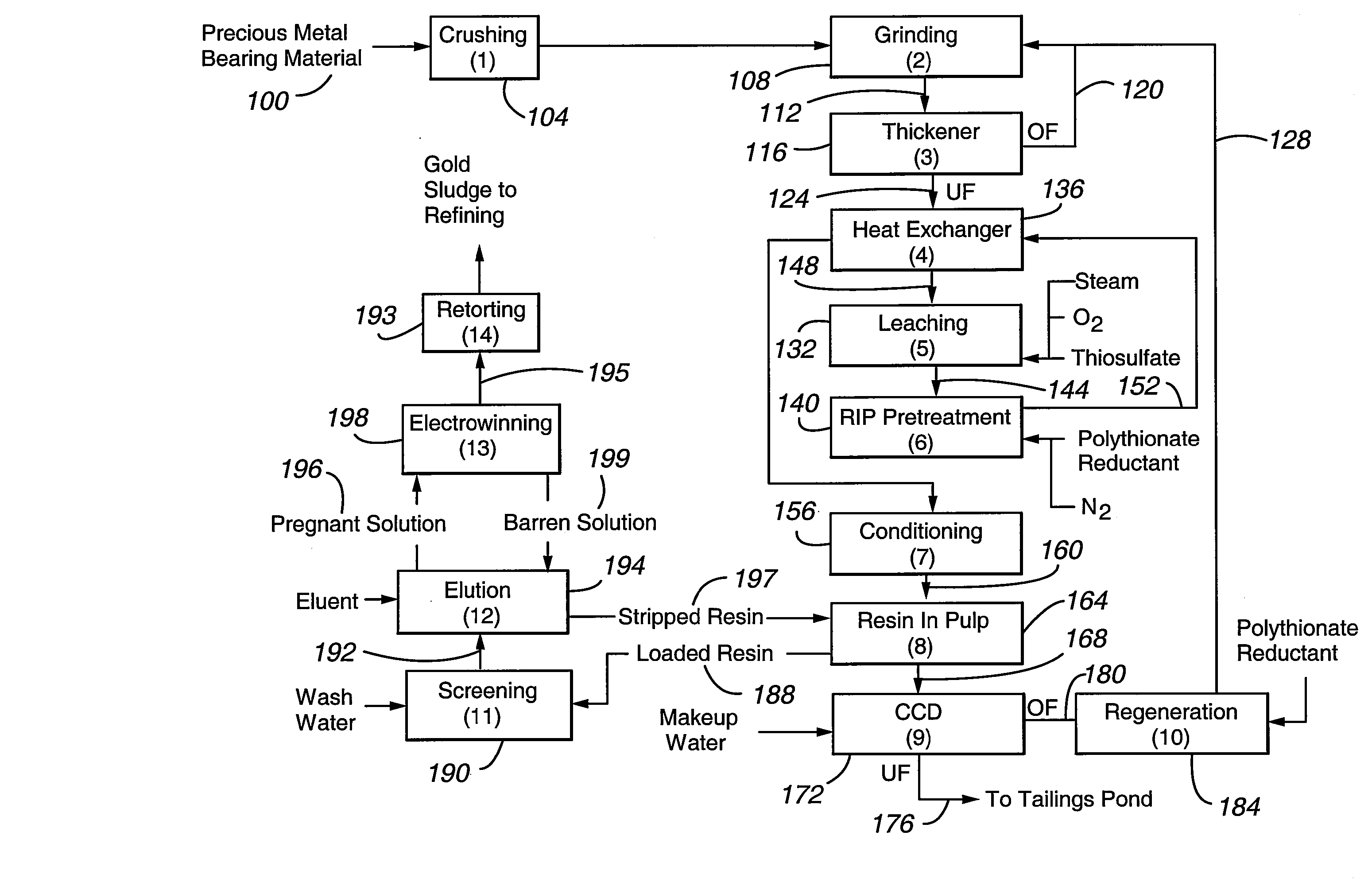
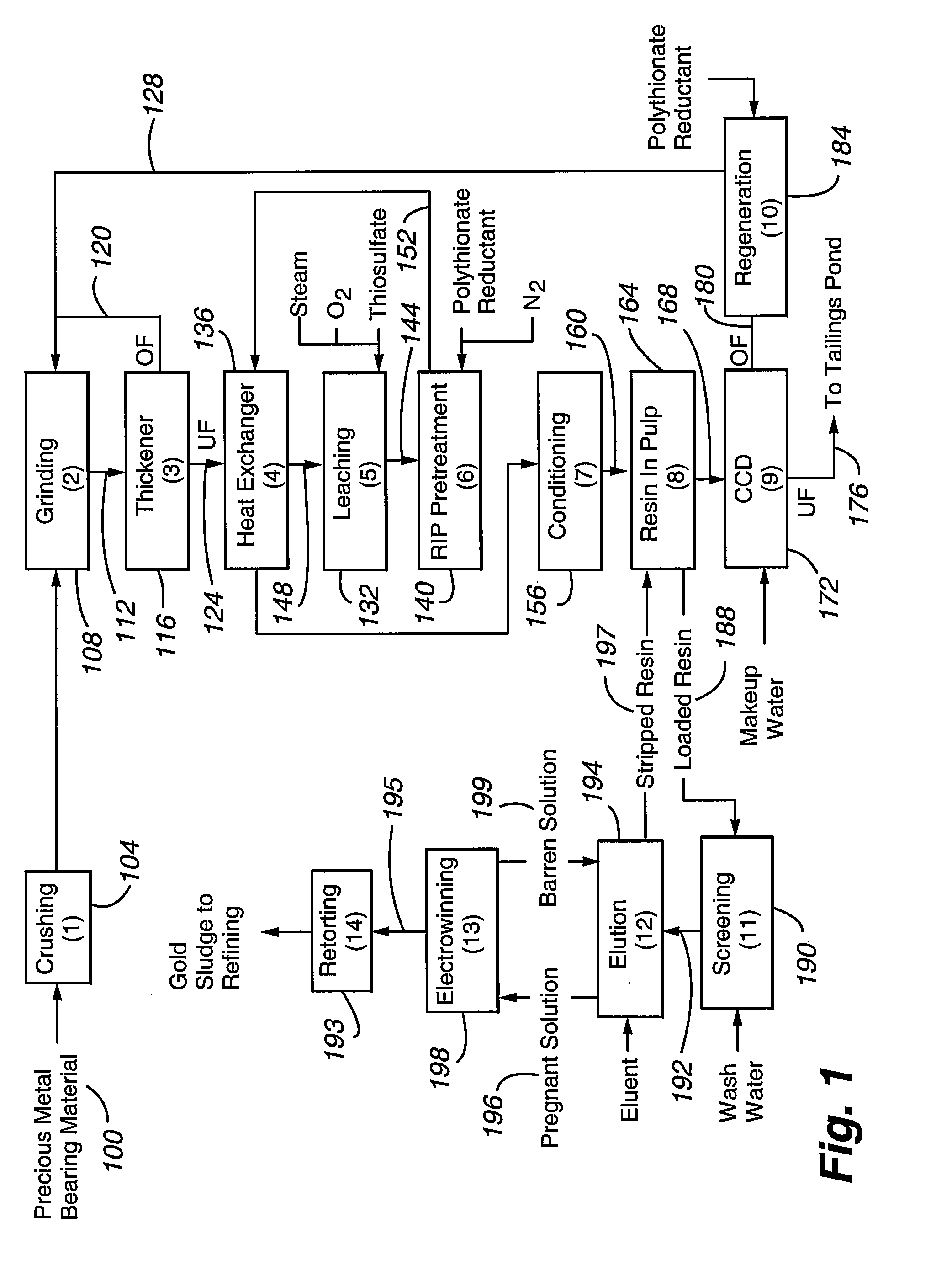
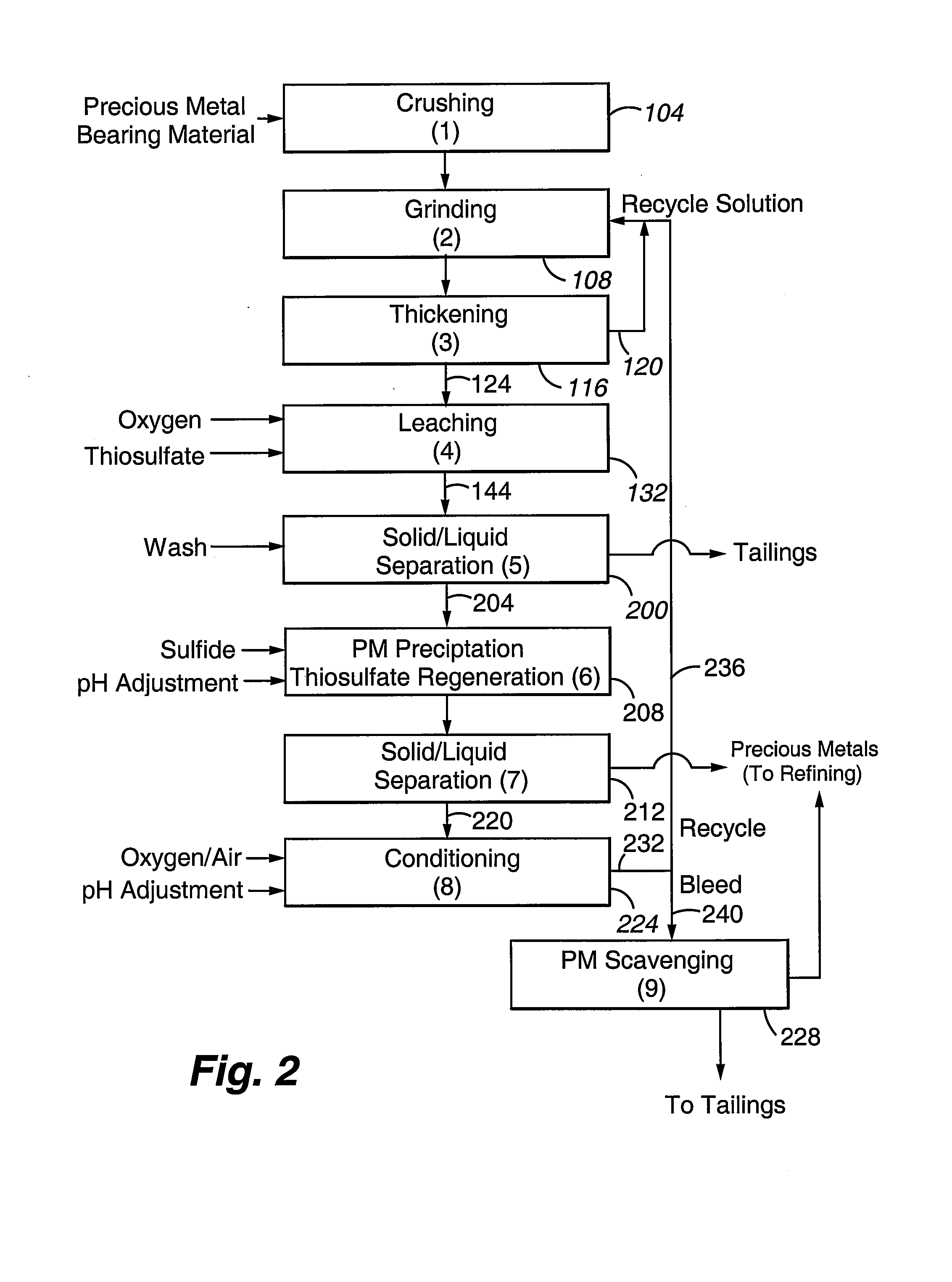
Method for thiosulfate leaching of precious metal-containing materials
Processes are provided for recovering precious metals from refractory materials using thiosulfate lixiviants. The processes can employ lixiviants that include at most only small amounts of copper and / or ammonia and operate at a relatively low pH, reduction of polythionates, inert atmospheres to control polythionate production, and electrolytic solutions which provide relatively high rates of precious metal recovery.
Owner:PLACER DOME TECHN SERVICES
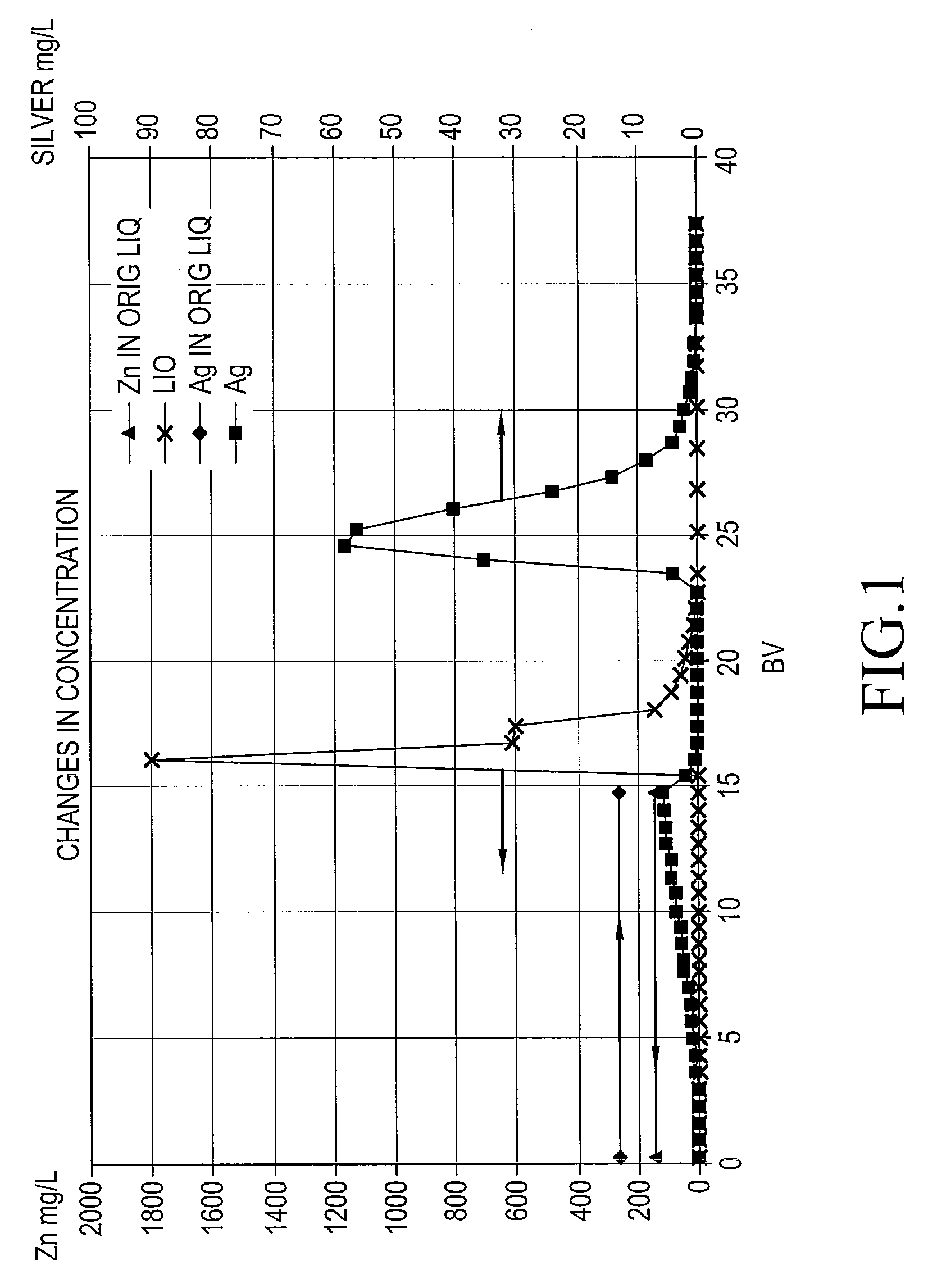
Method of recovering silver using anion-exchange resin
The present invention provides a method of recovering silver safely and efficiently from a chloride or bromide bath containing various metals. Specifically, a method of recovering silver from a hydrochloric acid solution containing alkali and / or alkali earth metal chloride, silver; copper and iron ions, comprising the steps of: (1) bringing the solution into contact with a strong-base anion-exchange resin to adsorb silver; copper, and iron on the anion-exchange resin; (2) then washing the anion-exchange resin with water to remove the adsorbed copper and iron; and (3) then bringing the ion-exchange resin into contact with a hydrochloric acid solution to elute the adsorbed silver, is provided.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
System and method for wastewater treatment
The present disclosure is directed towards systems and methods for the treatment of wastewater. A system in accordance with one particular embodiment may include a vacuum filter band system configured to receive a saturated resin tank from a front end system, the vacuum filter band system configured to generate a slurry from the saturated resin tank and to provide a cascading resin rinse to the slurry. The system may further include a repetitive stripping system configured to receive a metal-filled purification unit from a metal specific purification system. The repetitive stripping system may be further configured to sequentially apply the contents of a plurality of acid tanks to the metal-filled purification unit to generate a metal salt. Numerous other embodiments are also within the scope of the present disclosure.
Owner:HYDROIONIC TECH
Method of ore processing
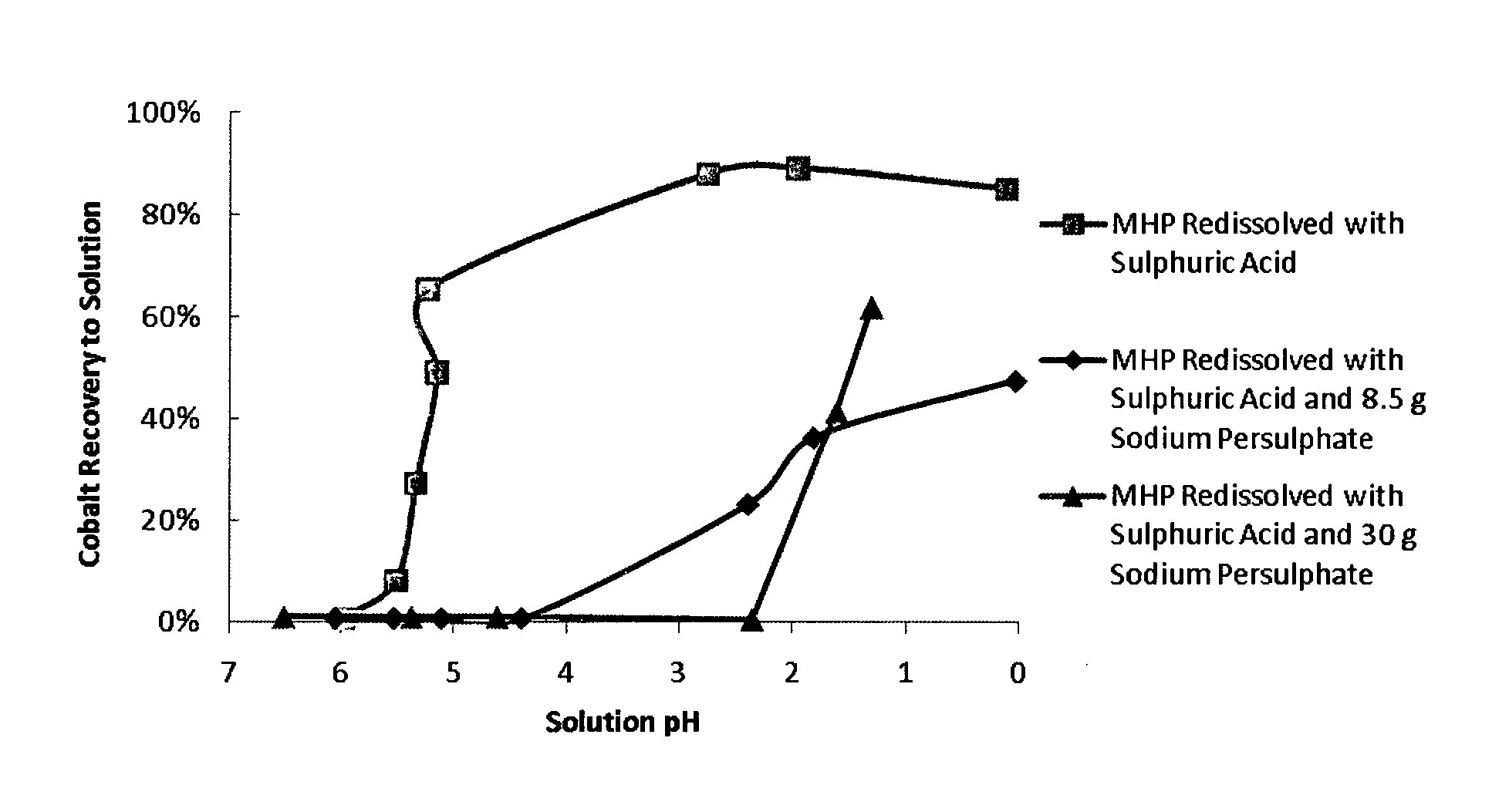
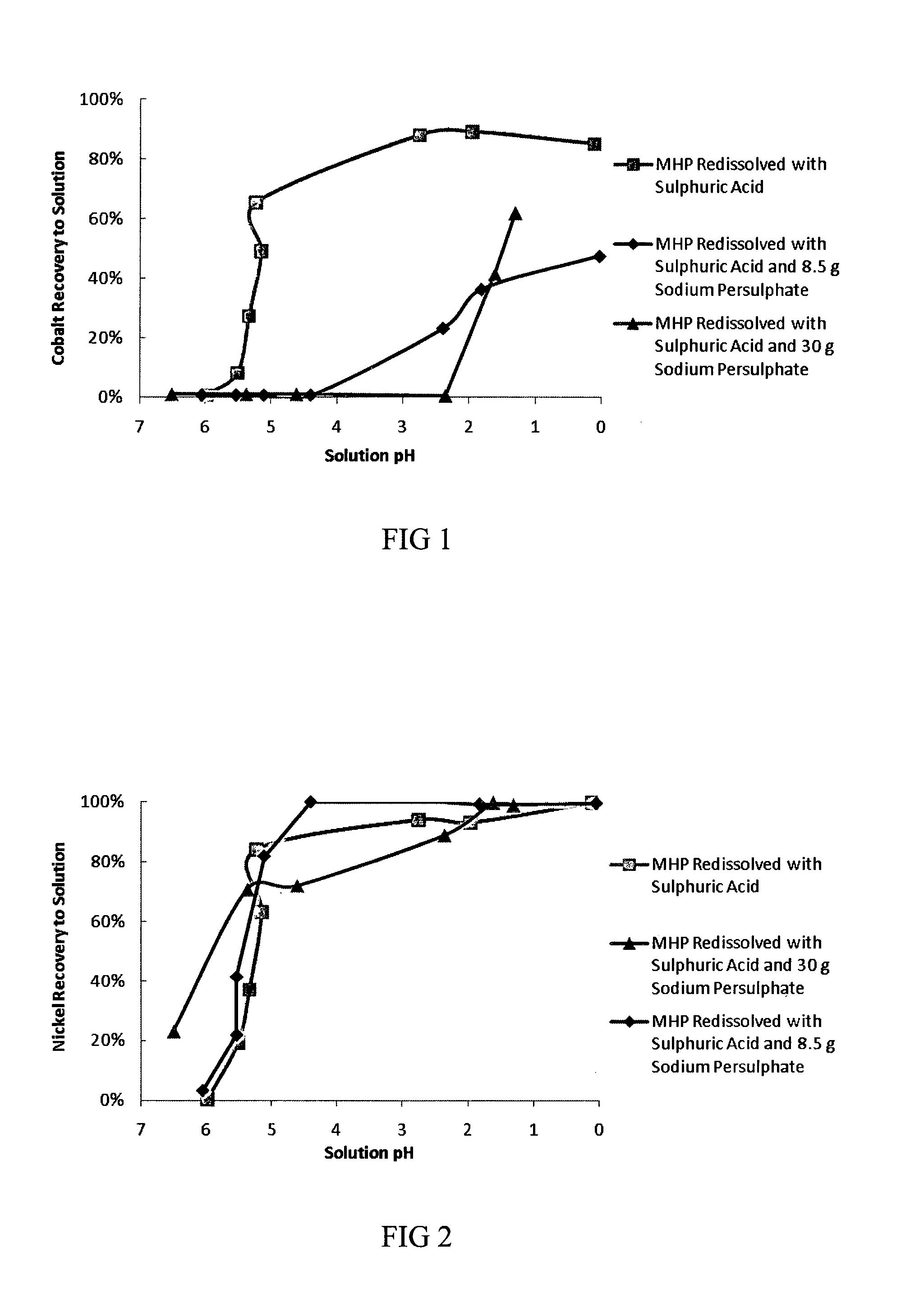
A method of selectively leaching a metal such as nickel from an ore or ore processing intermediate comprising the metal and cobalt. The ore or ore processing intermediate is contacted with an acidic leach solution comprising an amount of an oxidising agent sufficient to oxidise a major portion of the cobalt to thereby cause it to be stabilised in the solid phase while a major portion of the metal is dissolved for subsequent recovery.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
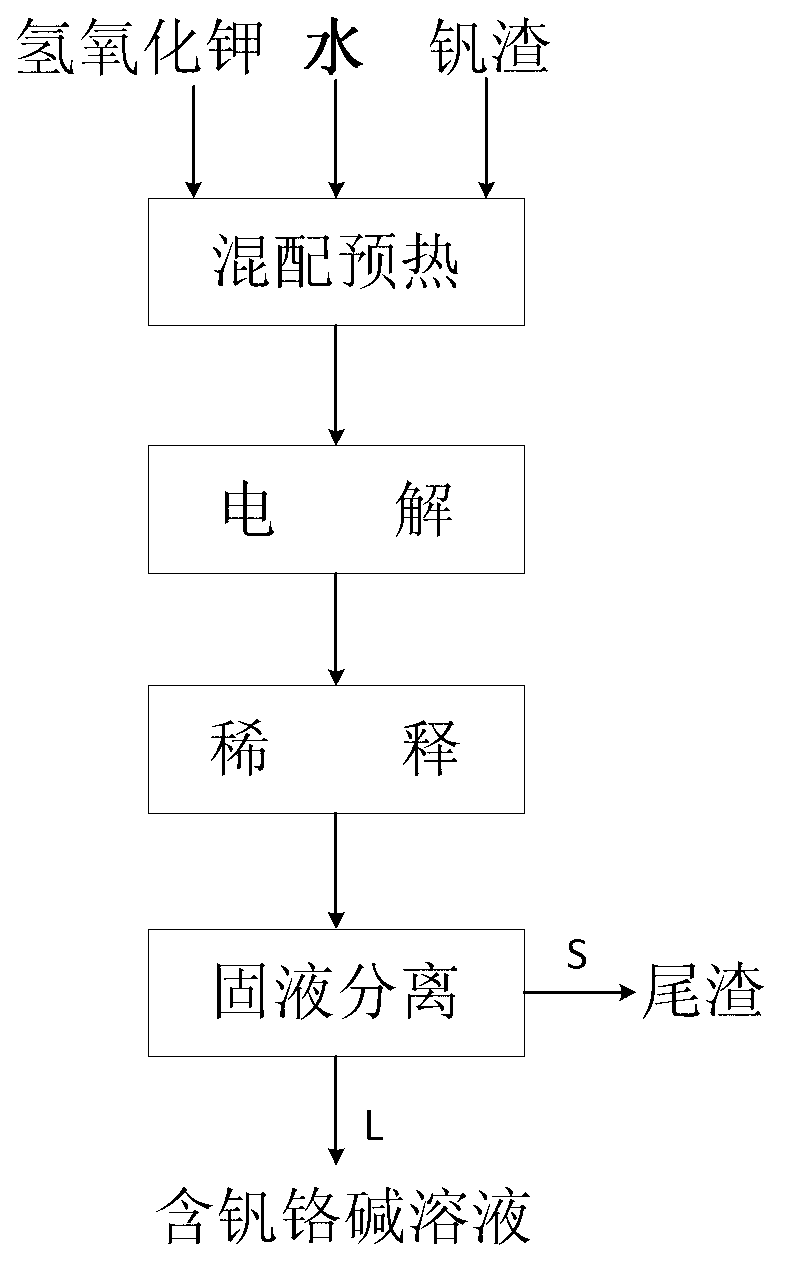
Method for synchronously extracting vanadium and chromium by electrochemically decomposing vanadium slag in potassium hydroxide solution
ActiveCN103060843AReduce concentrationEfficient extractionPhotography auxillary processesRecovering materialsSlagPotassium hydroxide
The invention relates to a method for synchronously extracting vanadium and chromium by electrochemically decomposing vanadium slag in a potassium hydroxide solution. The method comprises the steps as follows: introducing oxidizing gas into mixed slurry containing the vanadium slag, potassium hydroxide and water; carrying out electrochemical oxidization reaction; and after the reaction, carrying out solid-liquid separation on the mixed slurry to obtain tailings and a vanadium and chromium alkali solution. The method is low in cost, high in extraction efficiency, pollution-free and moderate in process conditions, and can be used for efficiently and synchronously extracting vanadium and chromium; the vanadium extraction rate can reach 85-99%; and the chromium extraction rate can reach 80-95%.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-carbon high-chromium stainless bearing steel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103014536AImprove cleanlinessReduce oxygen contentRecovering materialsElectric furnaceHigh carbonNiobium
The invention relates to a high-carbon high-chromium stainless bearing steel and a preparation method thereof. The high-carbon high-chromium stainless bearing steel comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 0.9-0.95% of carbon, 0.80-0.85% of silicon, 0.3-0.35% of manganese, less than 0.025% of sulfur, less than 0.02% of phosphorus, 0.15-0.3% of molybdenum, 3.5-4.0% of chromium, 0.01-0.02% of nitrogen, 0.1-0.2% of nickel, 0.02-0.03% of niobium, 0.02-0.03% of vanadium and the balance of iron. The technical scheme provided by the invention is beneficial to deoxidation effect, enhances the cleanliness of the bearing steel, and lowers the oxygen content in the bearing steel.
Owner:LIXING JINYAN STEEL BALL (NINGBO) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com