Method for synchronously extracting vanadium and chromium by electrochemically decomposing vanadium slag in potassium hydroxide solution
A kind of potassium hydroxide and electrochemical technology, which is applied in the direction of optics, process efficiency improvement, photography process, etc., can solve the problems of high reaction temperature, temperature reduction, high temperature, etc., and achieve lower reaction temperature, less slag discharge, and vanadium-containing The effect of low chromium content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
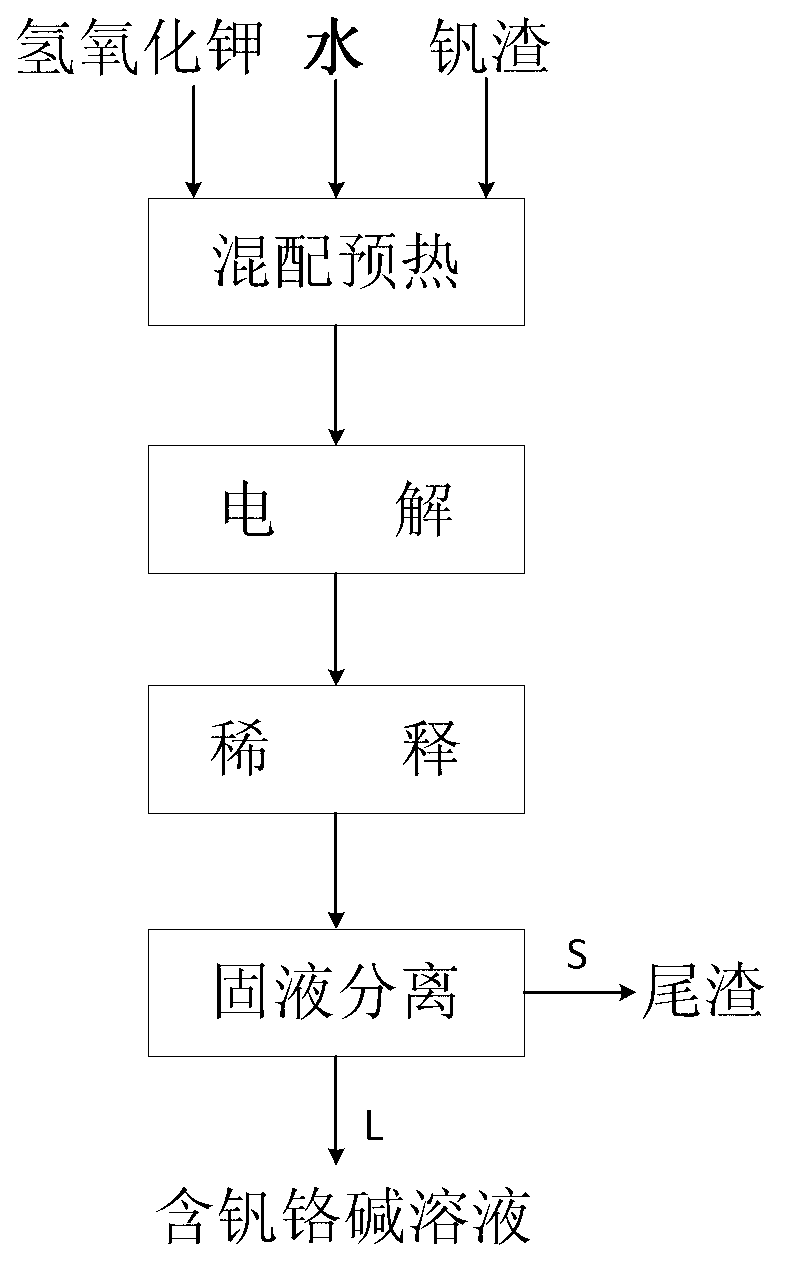
[0054] As an embodiment of the present invention, the method for synchronously extracting vanadium chromium by electrochemically decomposing vanadium slag in a potassium hydroxide solution of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0055] (1) Ingredients preheating: mix and heat the sieved -200 mesh vanadium slag and potassium hydroxide aqueous solution to obtain a raw material slurry, and preheat to 120-200°C, wherein the mass ratio of potassium hydroxide to vanadium slag is ≥3 : 1, the potassium hydroxide aqueous solution mass concentration is 50-70%;
[0056] (2) Electrolysis: Add the raw material slurry obtained in step (1) into an atmospheric pressure electrolytic cell, pass oxidizing gas into the solution and apply mechanical stirring, control the gas flow rate to 0.6-1.5L / min, and the stirring rate to 600 -1200rpm, use stainless steel plate as anode, stainless steel rod as cathode, control anode current density ≥300A / m 2 , electrolysis for more than 1h, ...
Embodiment 1
[0061] A method for synchronously extracting vanadium chromium by electrochemically decomposing vanadium slag in a potassium hydroxide solution, comprising the steps of:
[0062] (1) Ingredients preheating: mix and heat the sieved -200 mesh vanadium slag and potassium hydroxide aqueous solution to prepare a mixed slurry, and preheat to 120-200°C, wherein the mass ratio of potassium hydroxide to vanadium slag is 4: 1. The mass concentration of potassium hydroxide aqueous solution is 50%, that is, weigh 35g of vanadium slag, 165g of KOH (containing 15% water), and 115g of pure water;
[0063] (2) Electrolysis: Add the raw material slurry obtained in step (1) into the normal pressure electrolyzer, pass oxygen into the solution and apply mechanical stirring, control the gas flow rate to 1.0L / min, and the stirring rate to 700rpm. As the anode, the stainless steel rod is used as the cathode, and the anode current density is controlled to 725A / m 2 , electrolysis 8h;
[0064] (3) Di...
Embodiment 2
[0067] A method for synchronously extracting vanadium chromium by electrochemically decomposing vanadium slag in a potassium hydroxide solution, comprising the steps of:
[0068] (1) Ingredients preheating: mix and heat the sieved -200 mesh vanadium slag and potassium hydroxide aqueous solution to prepare a mixed slurry, and preheat to 150°C, wherein the mass ratio of potassium hydroxide to vanadium slag is 6:1, The mass concentration of potassium hydroxide aqueous solution is 55%, that is, weigh 20g of vanadium slag, 141.20g of KOH (containing 15% water), and 77.00g of pure water;
[0069] (2) Electrolysis: Add the raw material slurry obtained in step (1) into an atmospheric pressure electrolytic cell, pass oxidizing gas into the solution and apply mechanical stirring, control the gas flow rate to 1.0L / min, and the stirring rate to 850rpm, to The iron plate is used as the anode, the stainless steel rod is used as the cathode, and the anode current density is controlled to 100...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com