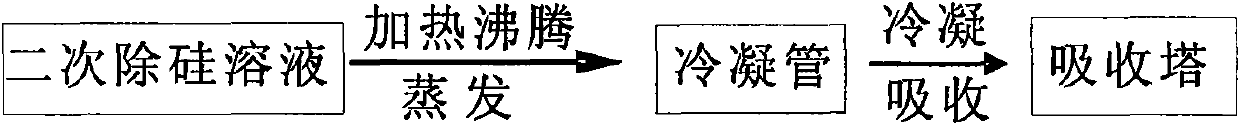
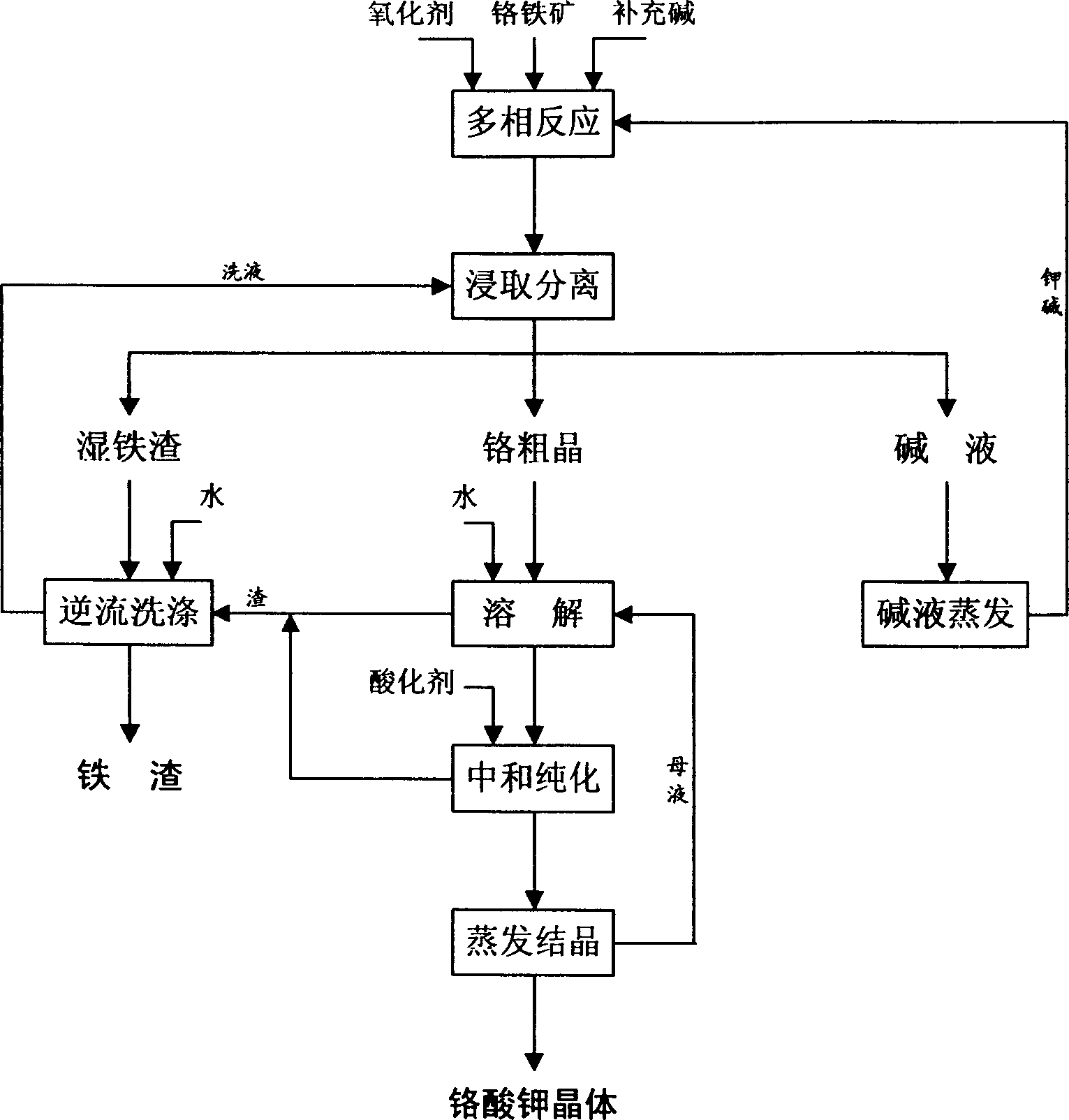
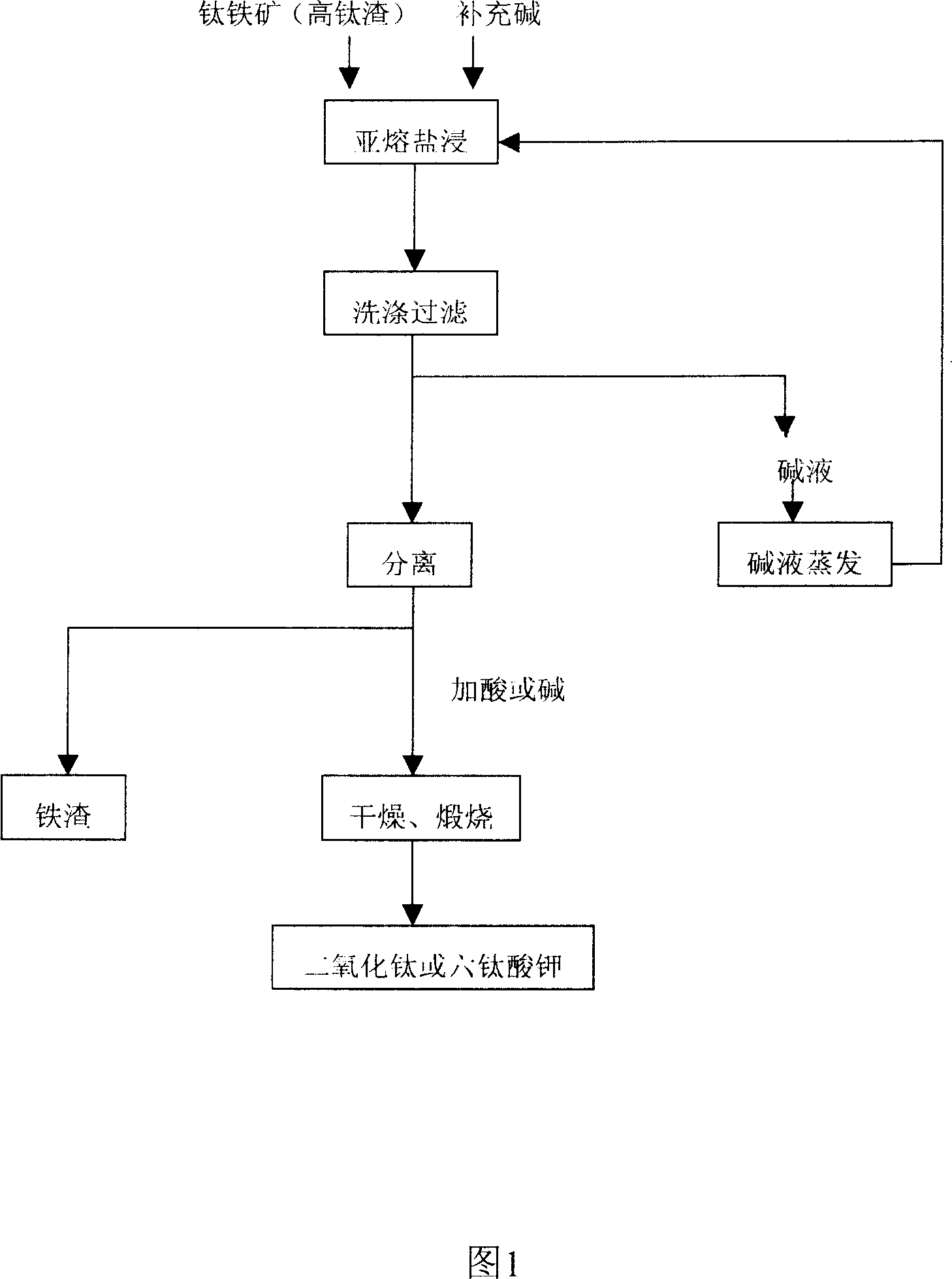
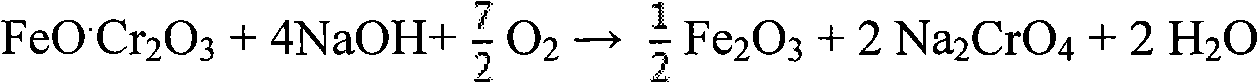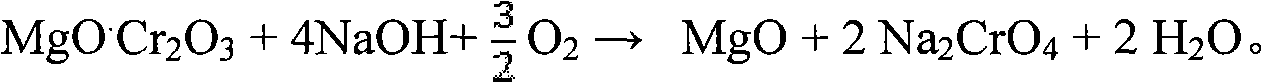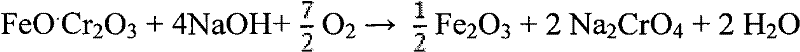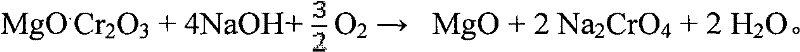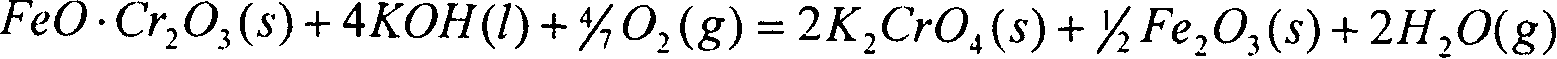Patents
Literature
81results about How to "Reduced slag discharge" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for cleaner production of sodium vanadate and sodium chromate by pressure leaching of vanadium slag
ActiveCN102531056ASimple ingredientsAchieve separationChromates/bichromatesVanadium compoundsSlagSlurry
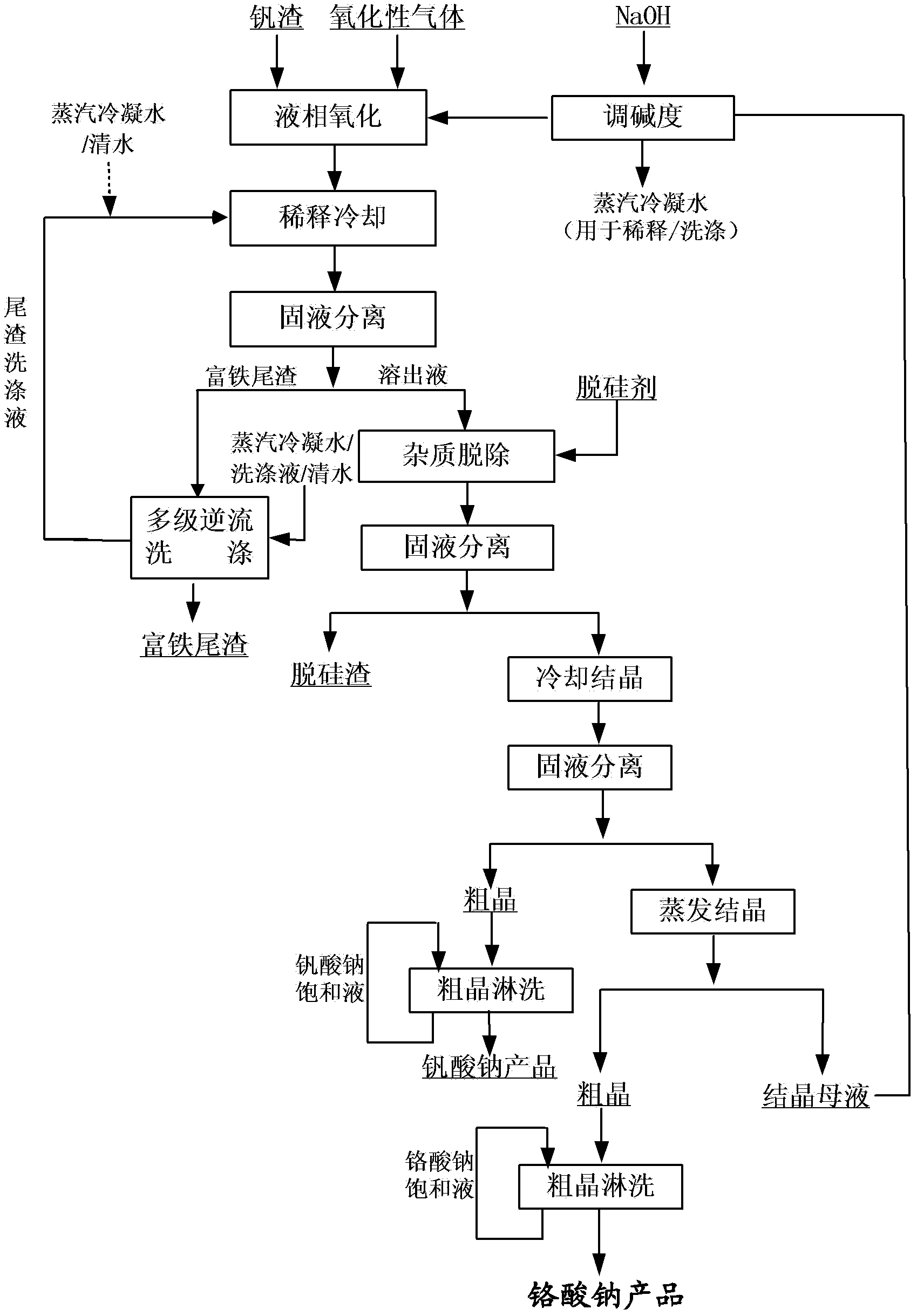
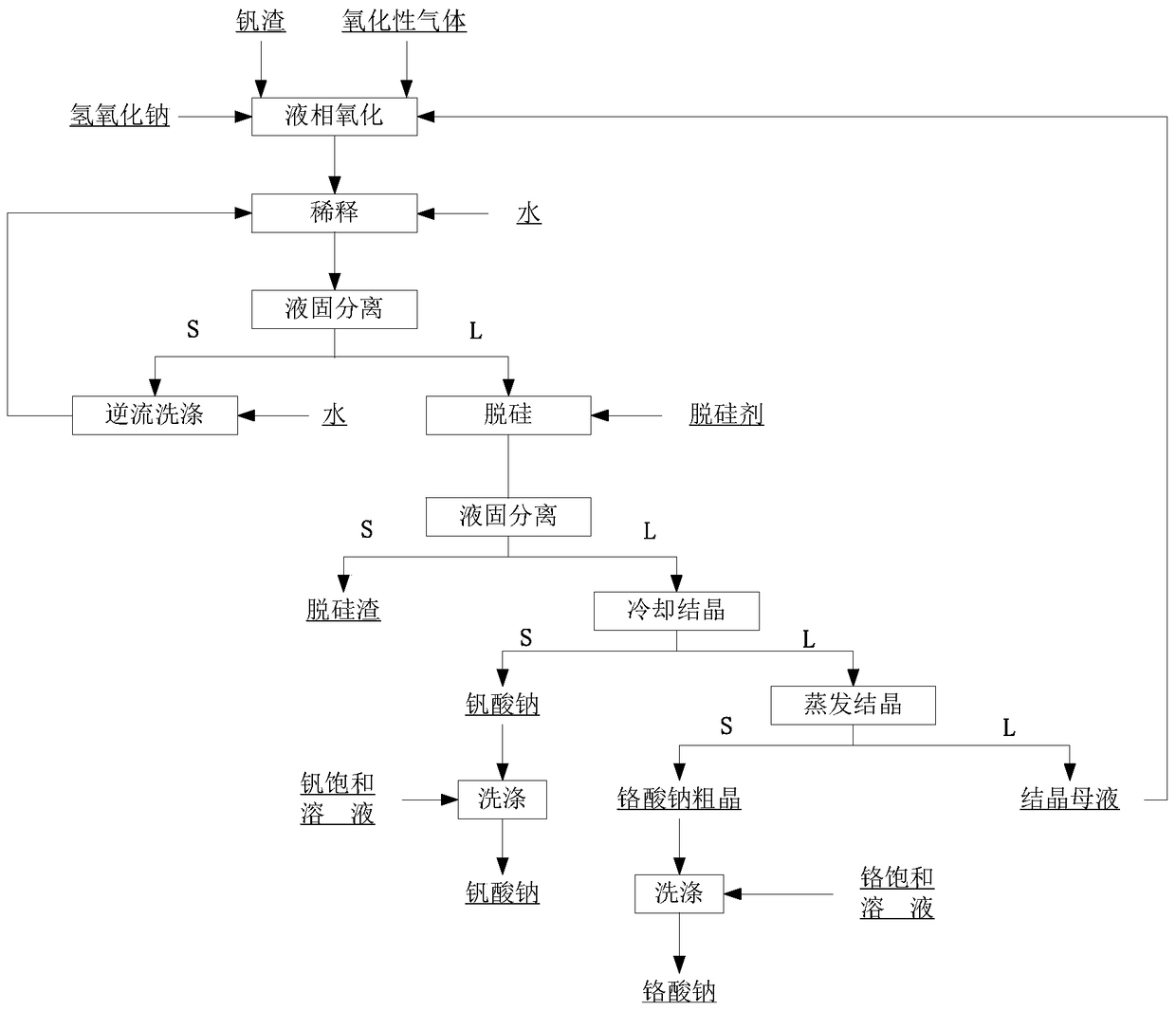
The invention relates to a method for cleaner production of sodium vanadate and sodium chromate by pressure leaching of vanadium slag. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) mixing materials, namely mixing the vanadium slag and a solution of NaOH to obtain a reaction material; (2) reacting, namely performing oxidization reaction on the vanadium slag and oxidizing gas in the solution of NaOH under high pressure to obtain solid-liquid mixed slurry of a solution containing NaOH, Na3VO4, Na2CrO4 and water-soluble impurity components, and iron-rich tailings; (3) performing solid-liquid separation; (4) removing impurities; (5) crystallizing sodium vanadate; and (6) crystallizing sodium chromate. The method is easy to operate and is high in safety; and the operating temperature is greatly lower than the temperature of the traditional vanadium extraction process, energy consumption is low, the high-efficiency co-extraction of vanadium and chromium is realized, and the extraction rate of vanadium and chromium is over 95 percent.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for extracting chromium and vanadium from vanadium slag at low temperature and normal pressure
ActiveCN105400967ALow reaction temperatureReduce reaction energy consumptionSlagReaction temperature
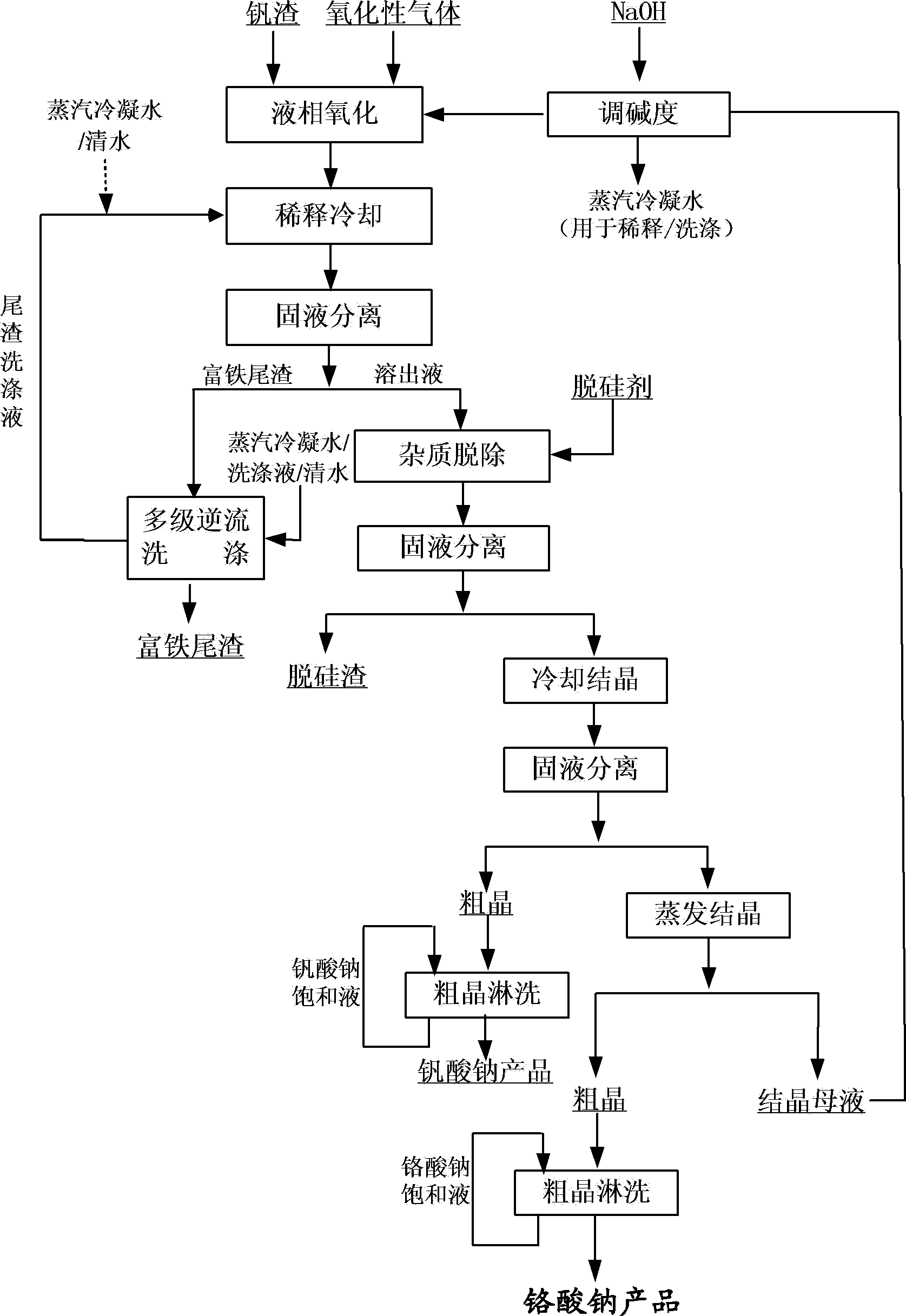
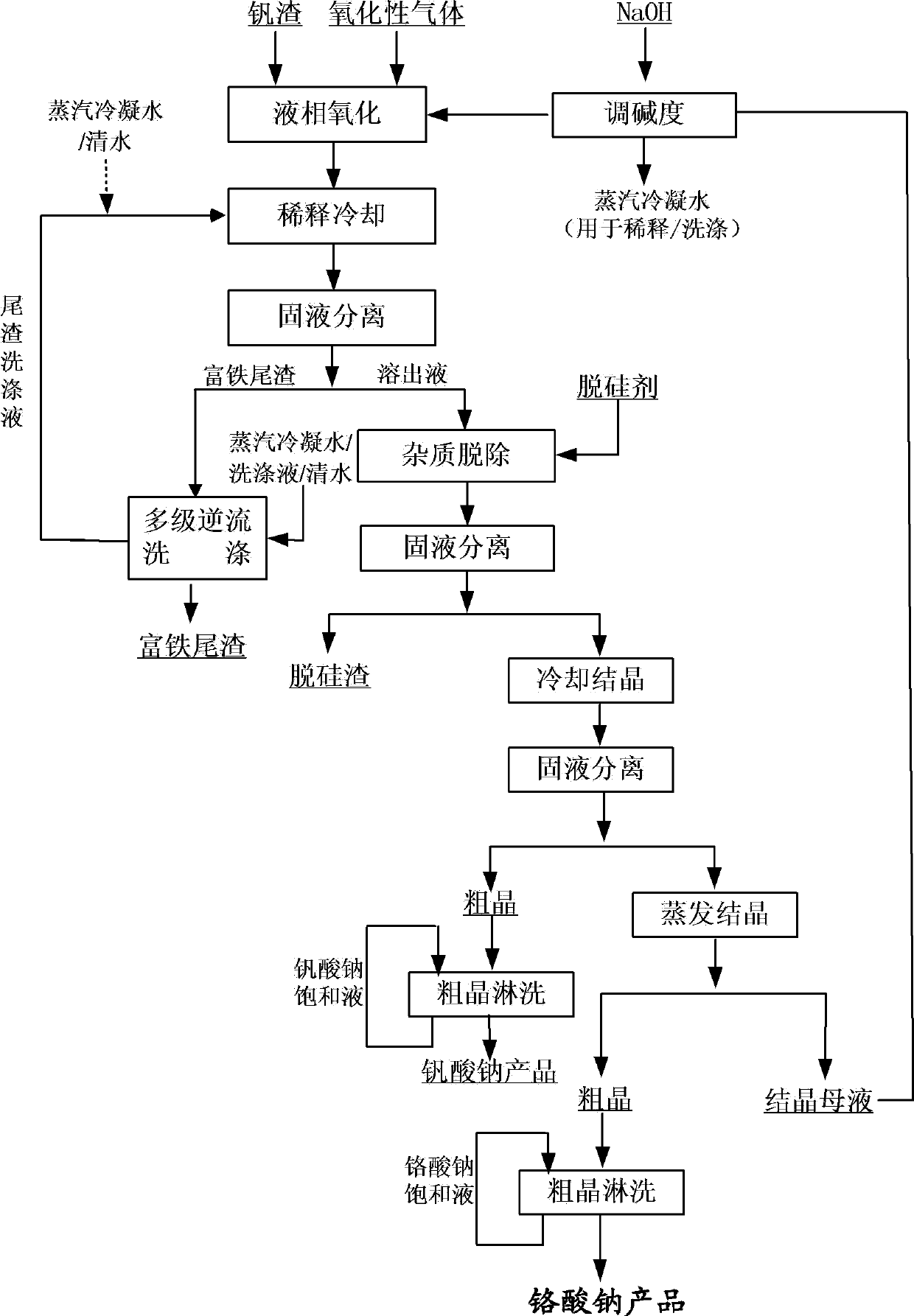
The invention relates to the field of vanadium slag hydrometallurgy and vanadium chemical engineering, in particular to a method for extracting chromium and vanadium from vanadium slag at a low temperature and the normal pressure. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, burdening, wherein the vanadium slag and a NaOH solution are mixed to form reaction slurry; secondly, reaction, oxide gas is led into the reaction slurry through a micro-hole arrangement device to carry out normal-pressure oxidative leaching, and after the reaction, solid-liquid mixed slurry of a solution containing NaOH, Na3VO4, Na2CrO4, water soluble impurity components and iron-rich tailings is obtained; thirdly, solid-liquid separation; fourthly, impurity removing; fifthly, sodium vanadate crystallization; and sixthly, sodium chromate crystallization. According to the method, chromium and vanadium efficient common extraction can be achieved, the extraction efficiency of both chromium and vanadium can be higher than 85%, more importantly, after the micro-hole gas distribution manner is adopted, the oxygen solubility can be obviously improved, the reaction temperature and alkali concentration are obviously reduced compared with those of an existing vanadium extraction method, the operation safety is greatly improved, and reaction energy consumption is reduced.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
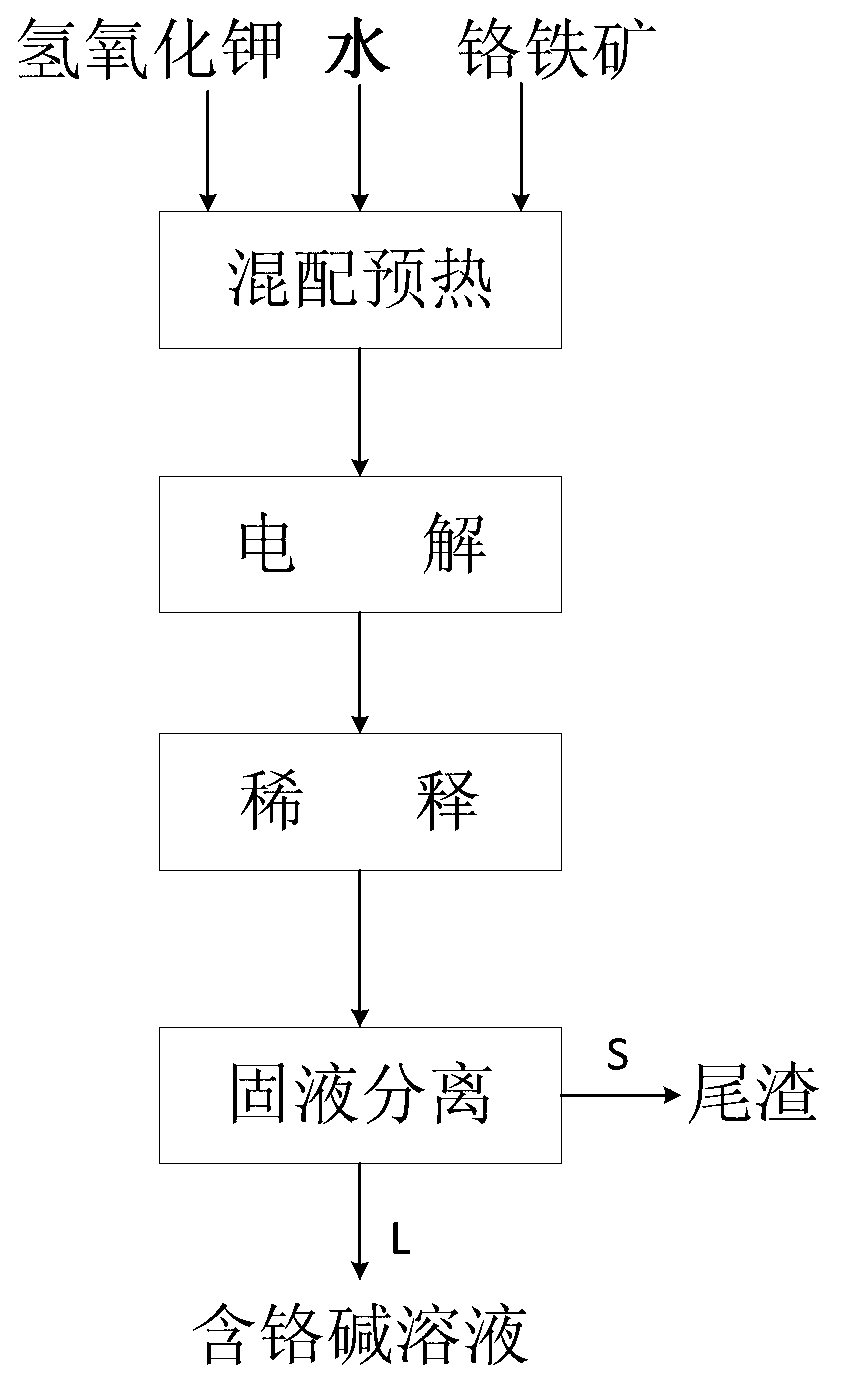
Method for decomposing vanadium slag with solution of potassium hydroxide under normal pressure
InactiveCN101812588ALow reaction temperatureImprove resource utilizationProcess efficiency improvementMass ratioSlag
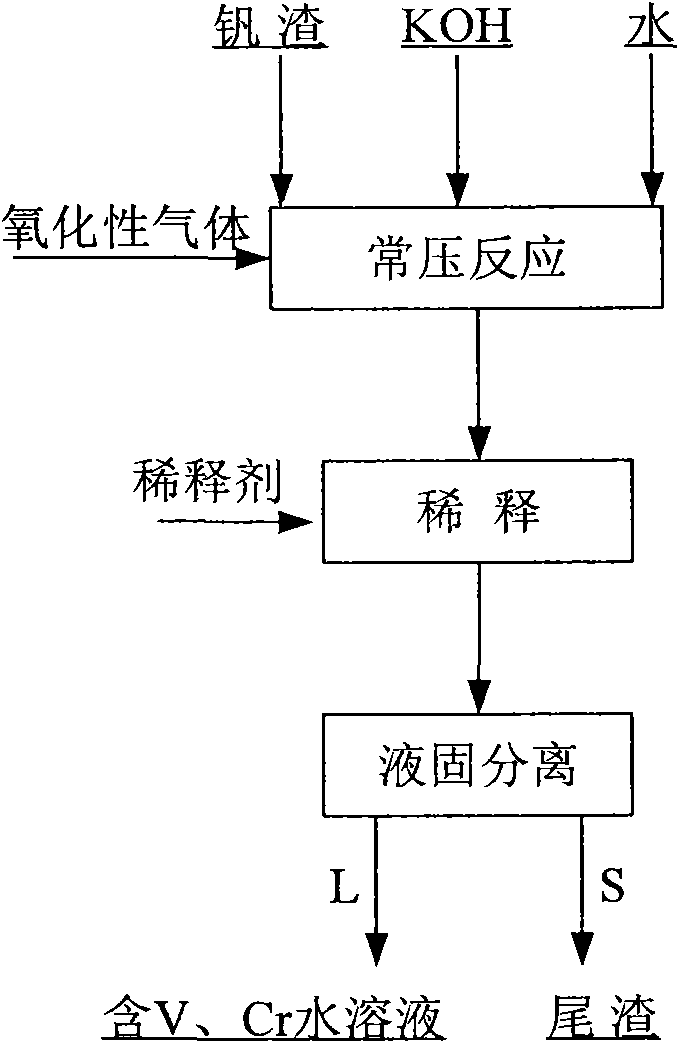
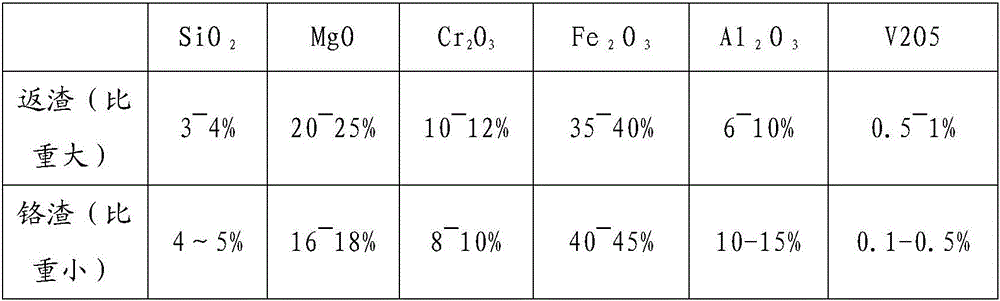
The invention relates to a method for decomposing vanadium slag with solution of potassium hydroxide under normal pressure, which comprises the following steps: adding the vanadium slag or pre-treated vanadium slag, water and KOH into a reactor, controlling the mass ratio of the KOH to the vanadium slag and the concentration of solution of KOH, performing oxidation reaction in the presence of oxidizing gas, and controlling the reaction temperature and reaction time in the reaction process; diluting the obtained reaction slurry with a diluting agent to obtain mixed slurry which contains potassium hydroxide, potassium vanadium, potassium chromate and tailings; and performing filtering separation on the mixed slurry to obtain the tailings and vanadium and chromium-containing aqueous solution. The method is only operated under normal pressure, is easy to perform and has high safety; the operation temperature is far lower than the traditional vanadium extraction temperature; the extraction rate of vanadium is high; and synchronous extraction of chromium in the vanadium slag can be realized. The total amount of the vanadium in the tailings is 0.2-1 weight percent (based on the amount of V2O5) and the total amount of the chromium is 0.2-1 percent (based on the amount of Cr2O3).
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
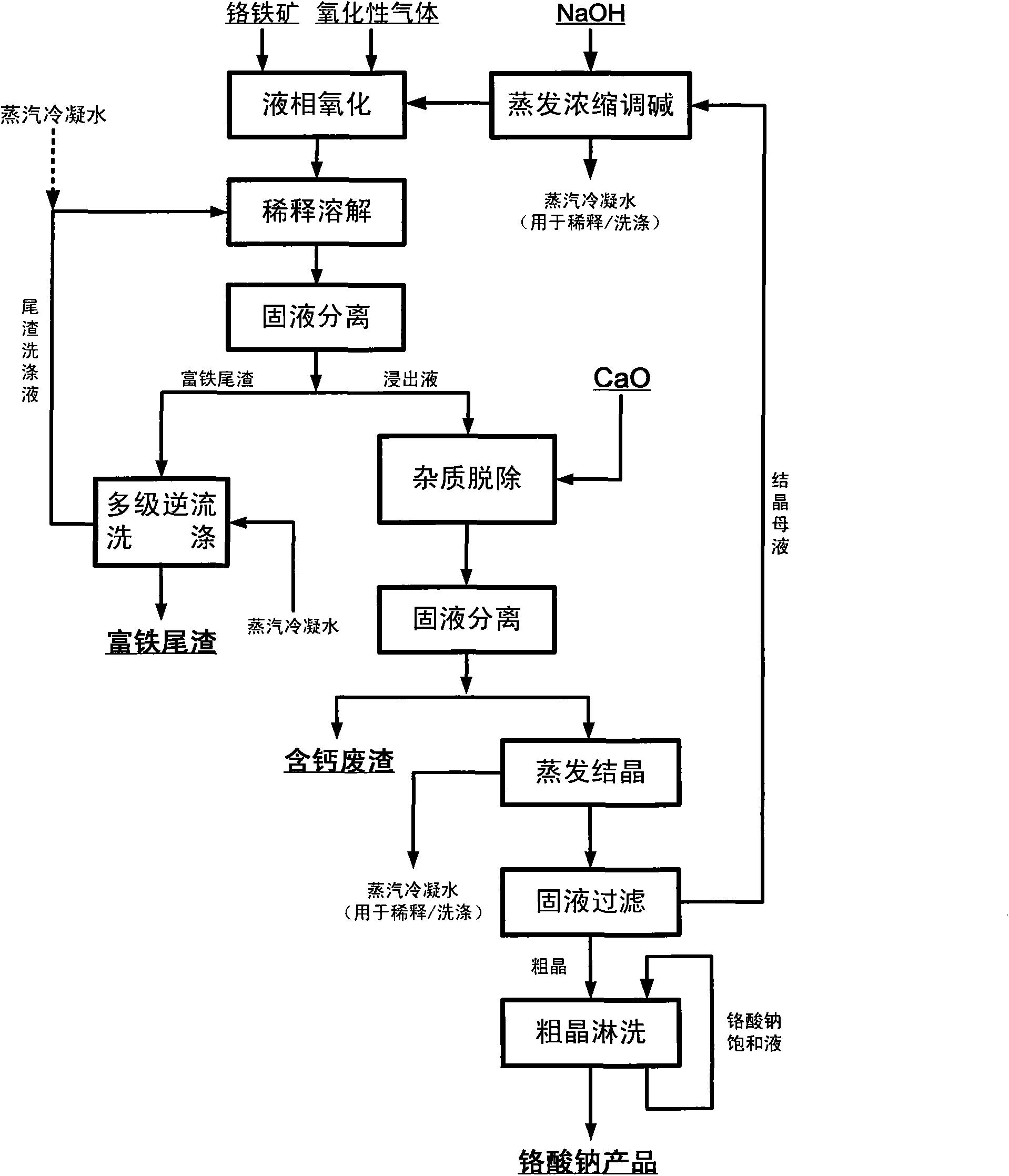
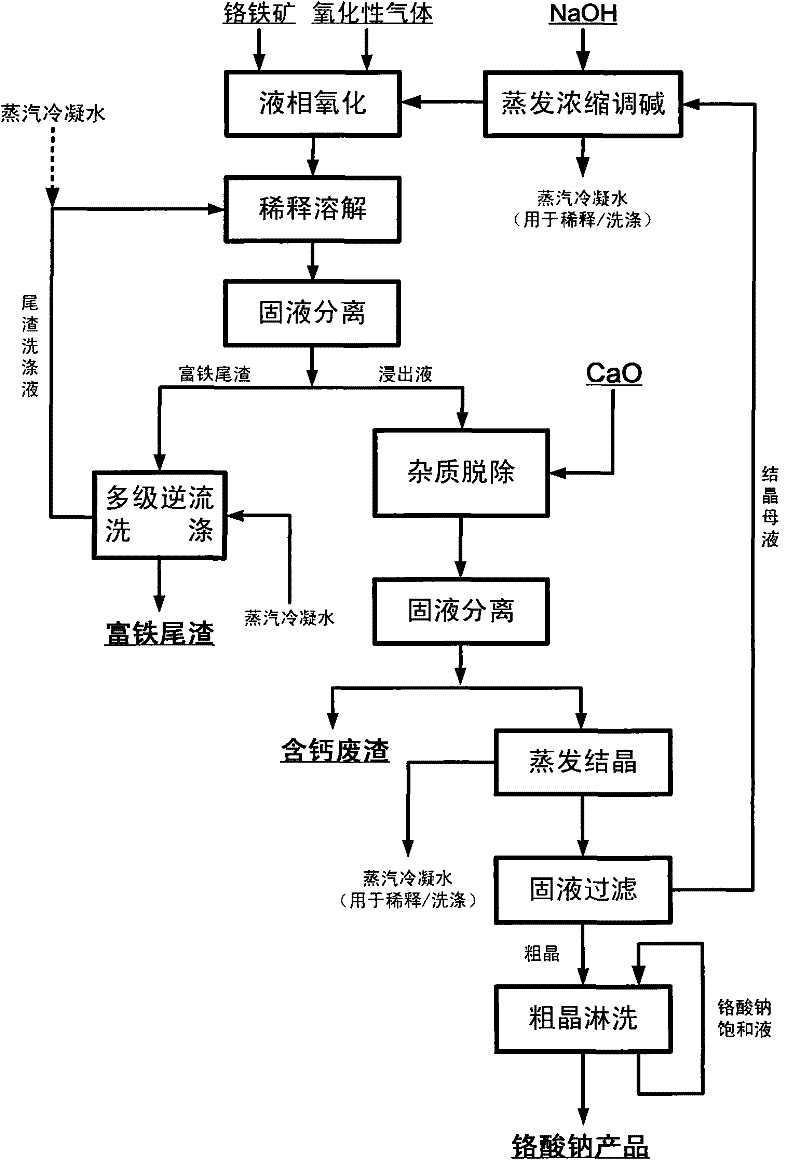
Method for pollution-free production of sodium chromate by pressure leaching of chromite
ActiveCN101817561AObvious superioritySimple ingredientsChromates/bichromatesReaction temperatureHydrometallurgy
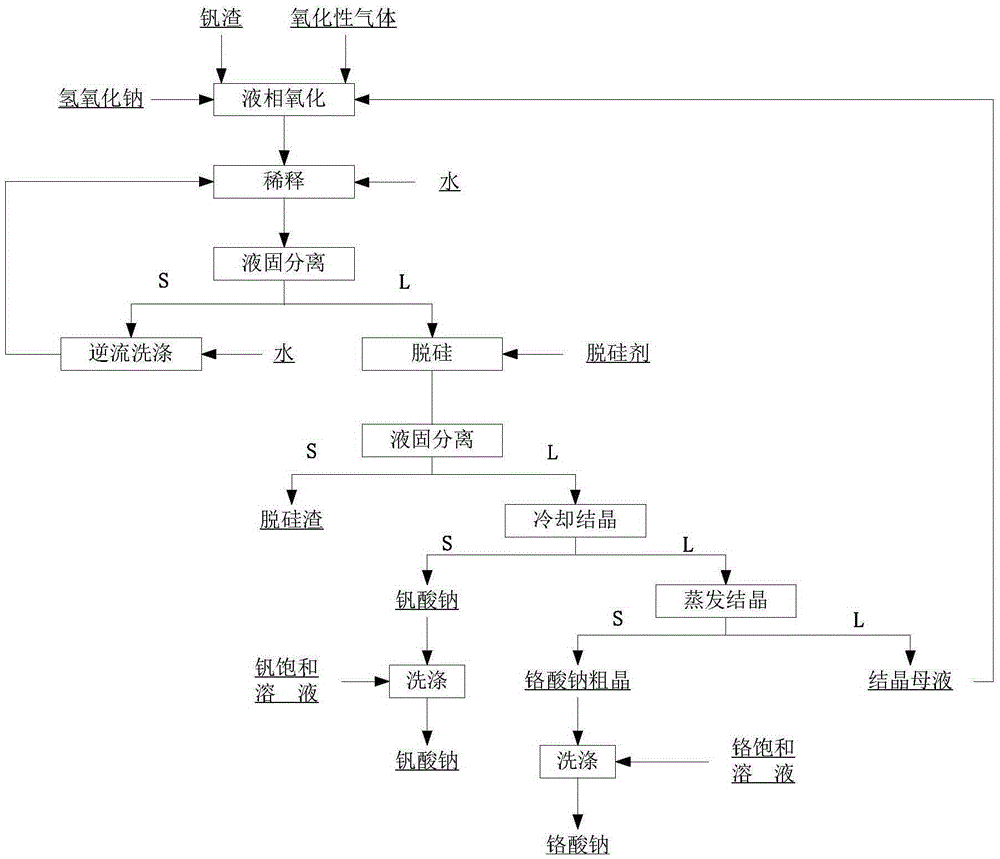
The invention belongs to the field of chromite hydrometallurgy and chromium chemical industry, and in particular relates to a method for the pollution-free production of sodium chromate by pressure leaching of chromite. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) reacting the chromite with oxidizing gas in solution of NaOH; 2) diluting the product obtained by the step 1) and making subcrystalline sodium chromate to fully enter a liquid phase; 3) performing solid-liquid separation on the solid-liquid mixed slurry obtained by the step 2); 4) adding calcium oxide into the obtained diluent for removing impurities; and 5) evaporating and crystallizing the obtained solution without the impurities to obtain a sodium chromate crystal and crystallization mother solution; after the solid-liquid separation, rinsing the sodium chromate crystal by using saturated solution of sodium chromate; and drying to obtain a qualified sodium chromate product. The method has the advantages of simple reaction system component, no difficultly separated phase introduced in the system, contribution to high-efficiency separation of the sodium chromate, great reduction in reaction temperature, low energy consumption, effective reduction in production cost of the sodium chromate, and high chromium leaching yield.
Owner:HUBEI ZHENHUA CHEMICAL CO LTD
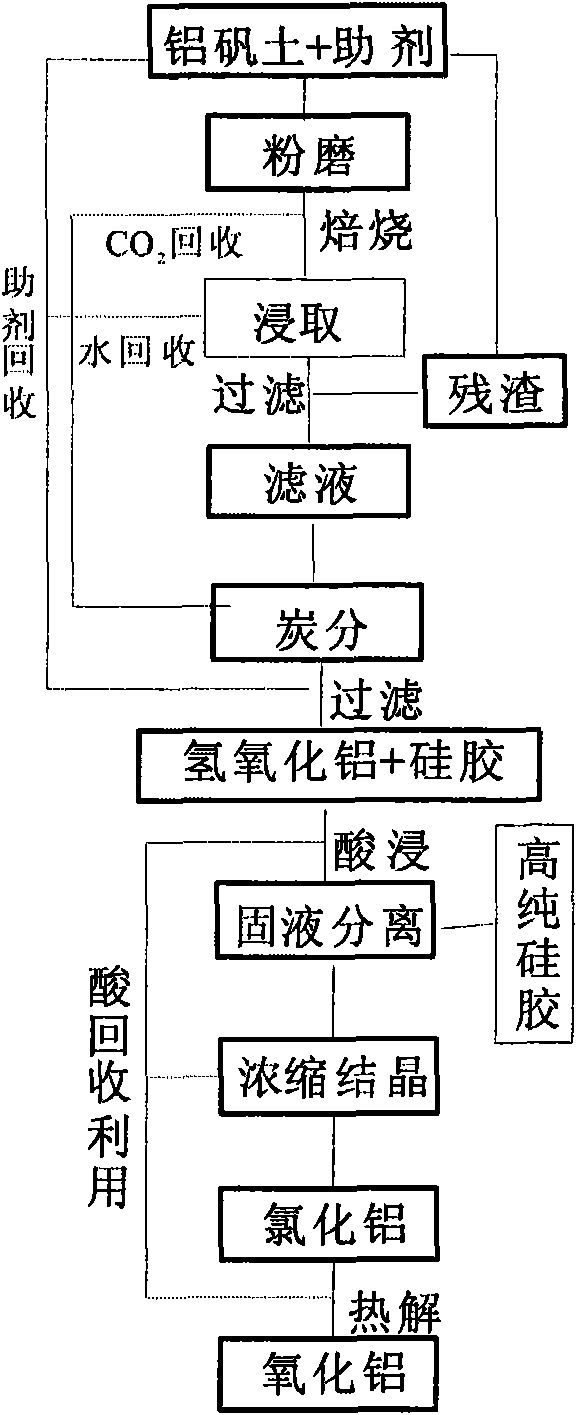
Method for extracting high-purity aluminum oxide and silica gel from beauxite
ActiveCN101767807ALower taste requirementsBreakthrough costAluminium compoundsSilicaProcess engineeringSilica gel
The invention discloses a method for extracting aluminum oxide and silica gel from beauxite (aluminum bauxite). In the method, steps such as cyclic activation, leaching, recovery of carbon, sodium carbonate and water, separation of silicon from aluminum, thermal decomposition and recovery of hydrochloric acid are employed to obtain high-purity aluminum oxide; in addition, CO2 produced in the whole technological process and alkaline, acid and water used in the process of extraction can all be recovered and recycled. The method of the invention features high extraction efficiency of aluminum oxide, simple technological process, high-purity obtained silica gel and major breakthroughs in solving the technical problem that a great deal of waste residue is produced in the process of traditionally extracting aluminum bauxite and deironing is costly.
Owner:北京蔚然欣科技有限公司
Clean production method of potassium chromate
InactiveCN1410358AObvious superiorityReduce energy consumptionChromates/bichromatesReaction temperatureAqueous solution
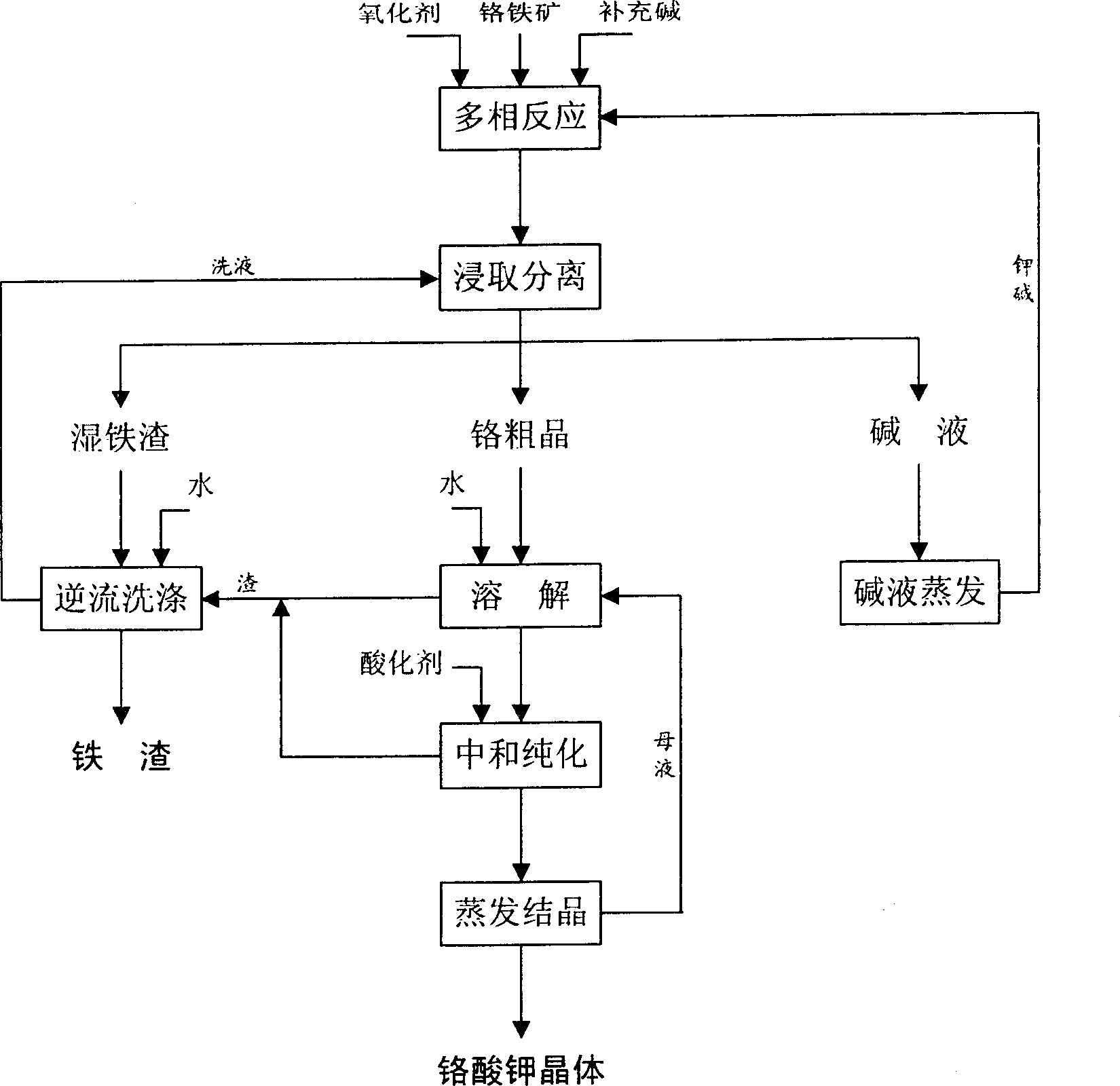
A clean process for preparing potassium chromate includes such steps as reaction of chromite on oxidant in the aqueous solution of KOH to obtain a mixture of alkali solution, chromium salt and iron dregs, immersion extracting, separating coarse crystal of potassium chromate from ion dregs, and alkali solution, dissolving the said coarse crystal, removing impurities and crystallizing. Its advantages are low reaction temp. (250-400 deg.C), high Cr recovering rate (20%) and reduced quantity of Cr dregs.
Owner:中蓝义马铬化学有限公司
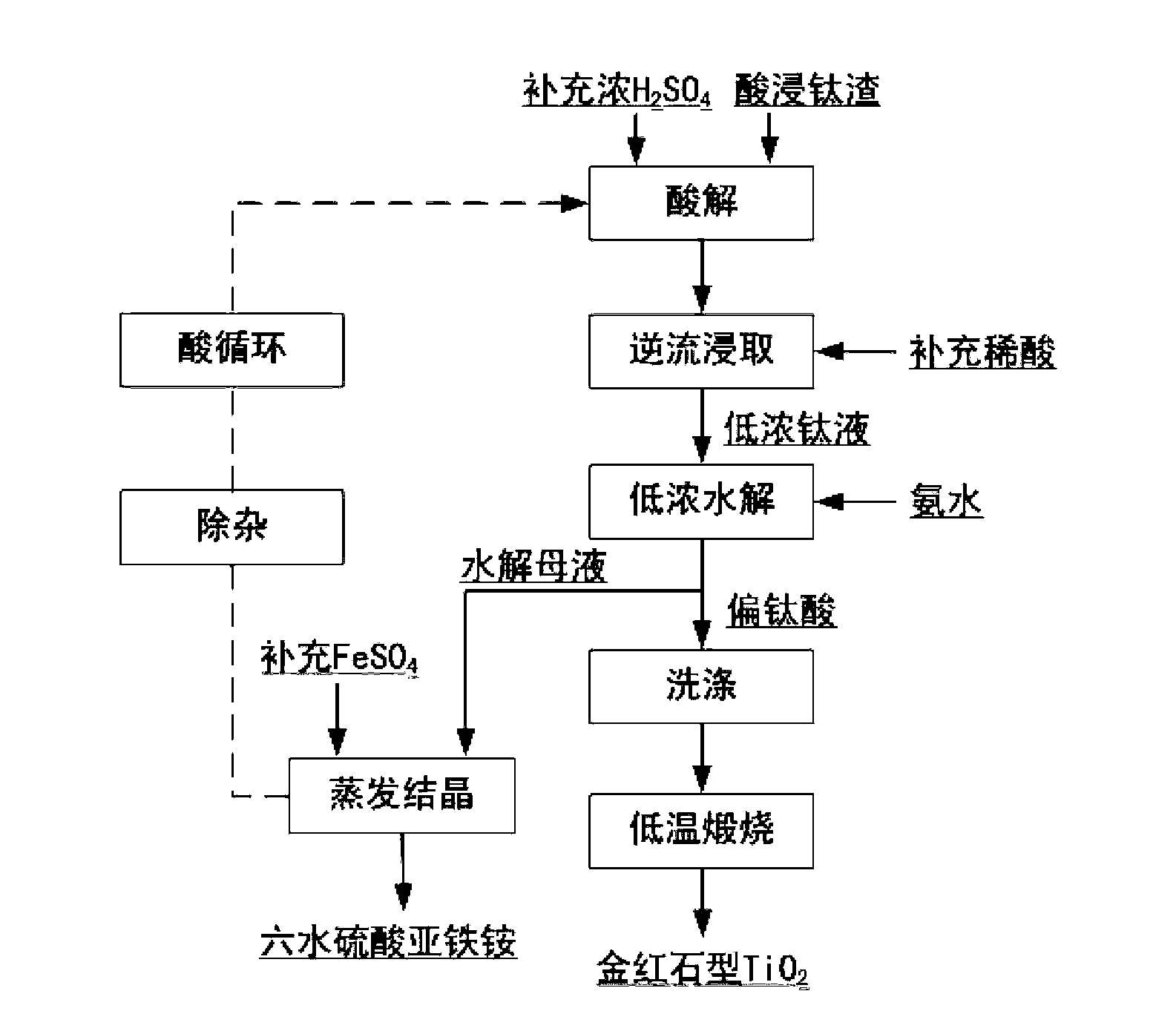
Process for clean producing titanium dioxide and potassium hexatitanate wiskers by titanium iron ore or high-titanium dreg sub-molten salt
The invention relates to a method to produce titanium dioxide and K2Ti6O13 whisker from using ilmenite or high titanium slag as raw material. It includes the following steps: ilmenite or high titanium slag reacting in KOH liquid phase medium, and the weight ratio is 4:1-8:1; gaining the mixture reaction product of alkali liquid, barium titanate and iron enriched slag; taking hydrolysis or acidolysis, burning and purifying to the product to gain purified titanium dioxide and K2Ti6O13 whisker. The reacting temperature is 240-350 degree centigrade and the yield is over 99%. The recycled titanium dioxide could be used as dye, coating, etc; and the K2Ti6O13 whisker could be used as insulating material, refractory material, and friction material.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing rutile-type titanium dioxide
InactiveCN103265069ASimple processReaction medium recyclingTitanium dioxideHydration reactionHydrolysate
The invention belongs to the field of preparation of inorganic metal compounds, and particularly relates to a method for preparing rutile-type titanium dioxide. The method for preparing rutile-type titanium dioxide comprises the following steps: 1) adding sulfuric acid into titanium slag to obtain an acid hydrolysate; 2) leaching the acid hydrolysate obtained in the step 1) with dilute sulfuric acid; 3) filtering the titanium solution obtained in the step 2), adding ammonia water into the obtained filtrate, and adding a reducer to obtain a titanium solution in which the TiO2 concentration is 100-130 g / L; 4) hydrolyzing the titanium solution obtained in the step 3), and filtering to obtain a titanium dioxide hydrate solid and a hydrolysis mother solution; and 5) calcining the titanium dioxide hydrate obtained in the step 4) to obtain the rutile-type titanium dioxide. The invention provides a clean production method for producing rutile-type titanium dioxide from low-grade titanium slag, and provides an effective way for comprehensively utilizing titanium resources and preparing titanium dioxide (titanium white).
Owner:河北中科同创科技发展有限公司
Normal pressure low temperature leaching production method for alumina
InactiveCN1565974AHigh energy consumptionAvoid increased water evaporationAlkali-metal aluminates/aluminium-oxide/aluminium-hydroxide preparationAluminium hydroxideSodium aluminate
The invention relates to a normal pressure low temperature leaching production method for alumina comprising the steps of, (1) subjecting the bauxite to extraction reaction in alkaline solution, filtering to obtain queous alkali and slags containing sodium aluminate, (2) subjecting the queous alkali to compression and cooling down for crystallization, filtering to obtain hydrated sodium aluminate coarse-grain and the filtrated stock solution, dissolving the hydrated sodium aluminate coarse-grain with water or diluted alkaline liquor, obtaining aluminum hydroxide through desiliconization operation, and calcining the obtained aluminum hydroxide.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
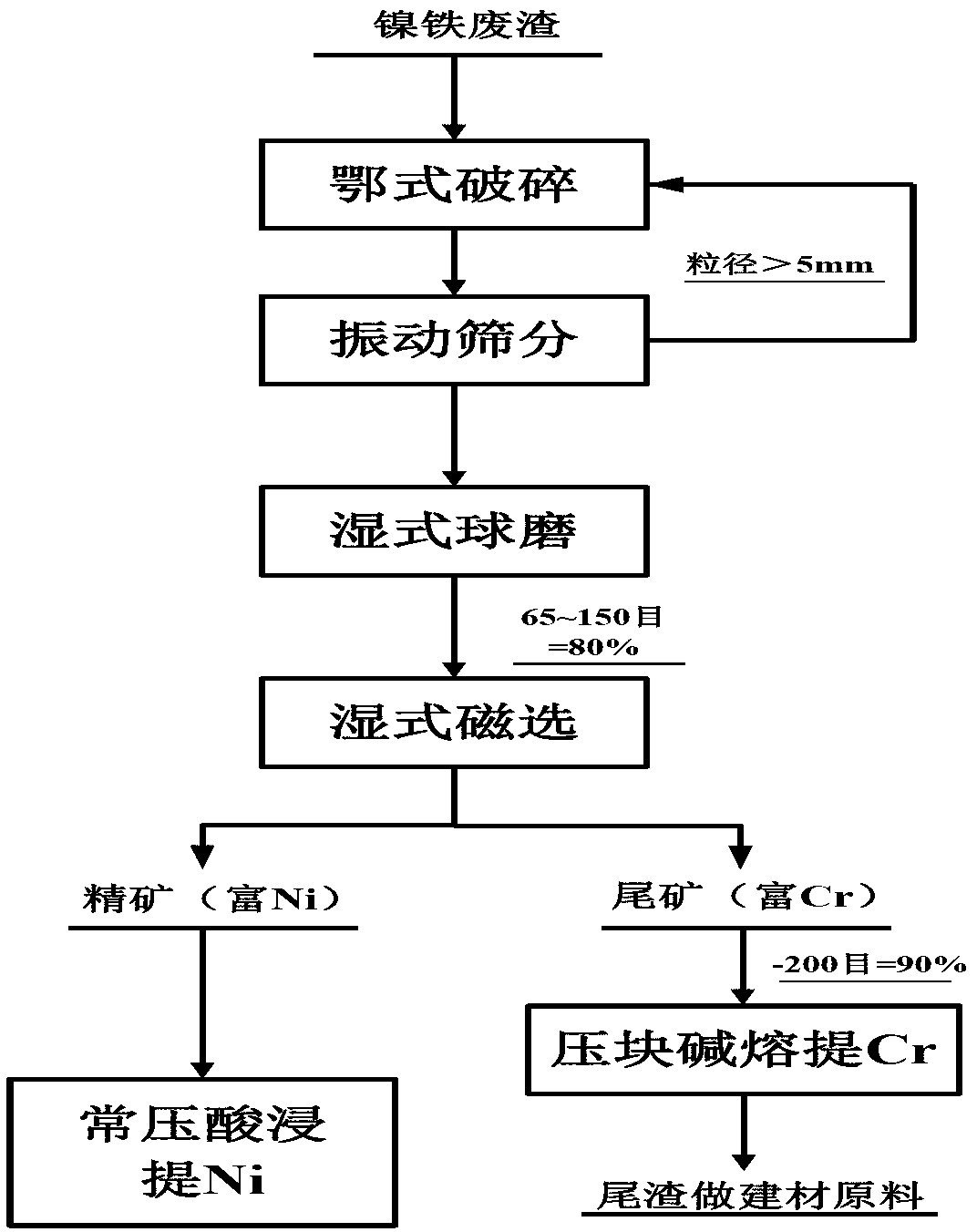
Clean production method for treating waste residues of reduction roasting nickel laterite ore to prepare ferronickel
ActiveCN103276219AEfficient separationEfficient enrichmentProcess efficiency improvementDry mixingLaterite
The invention relate to the technical field of nonferrous metallurgy, and specifically relates to a clean production method for treating waste residues of reduction roasting a nickel laterite ore to prepare ferronickel. The method comprises the following steps of 1) crushing and grinding waste residues of reduction roasting the nickel laterite ore to prepare ferronickel, and then carrying out magnetic separation to obtain a Ni-rich magnetic concentrate and a Cr-rich magnetic tailing; 2) wet-grinding the Cr-rich magnetic tailing, dry mixing a solid alkali and the Cr-rich magnetic tailing and briquetting the mixture; 3) performing an alkali fusion roasting reaction on the briquetted mixture and grinding to prepare samples; 4) washing grinded clinker with clear water and filtering to obtain an alkaline filtrate solution, wherein a water washing temperature is controlled within 30-95 DEG C; 5) preparing chromic oxide by using the alkaline filtrate solution; and 6) extracting Ni from the Ni-rich magnetic concentrate. The clean production method for treating the waste residues of reduction roasting the nickel laterite ore to prepare ferronickel with industrial operationality and environmental friendliness is provided by the invention; and the clean production method provides an effective approach for comprehensive utilization of the nickel laterite ore.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for treating industrial waste water containing chromium, vanadium
InactiveCN1724406AReduced chromium contentAvoid pollutionMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationIndustrial waste waterSewage
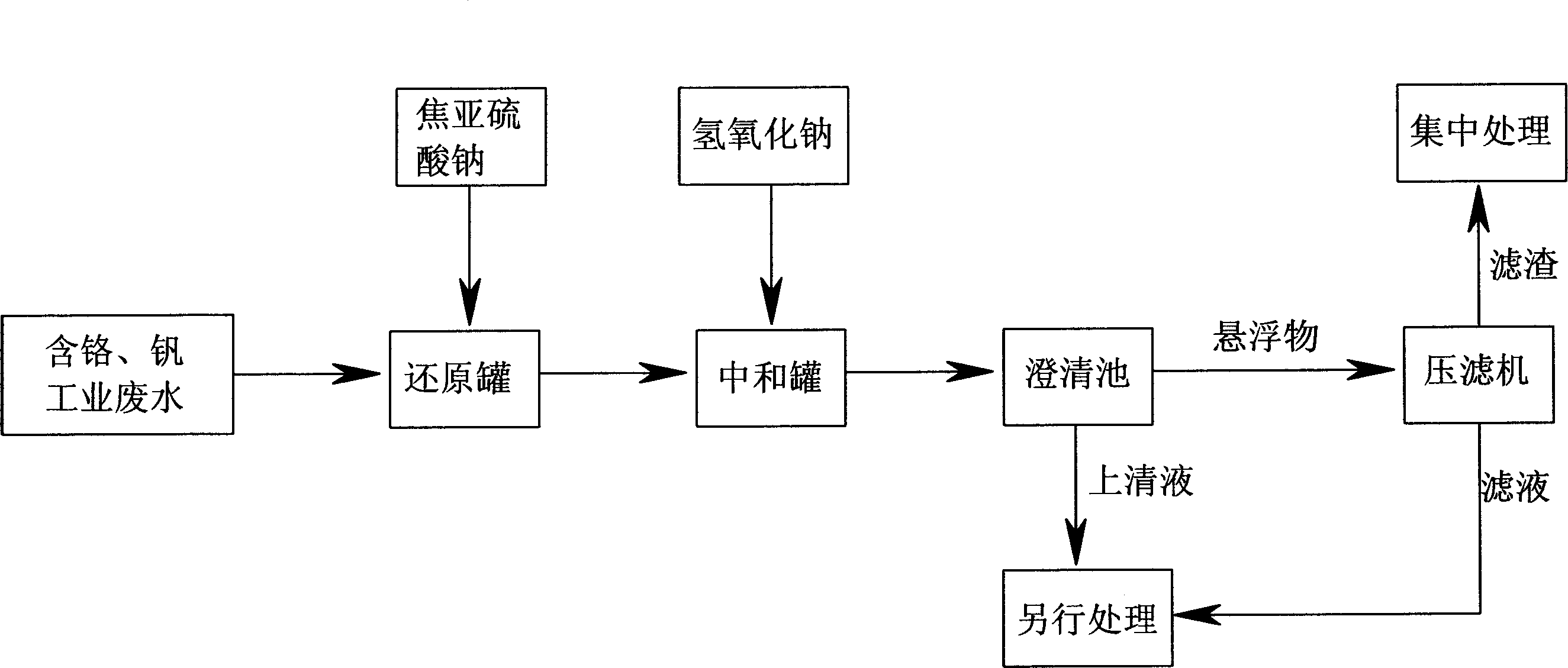
A process for treating the industrial sewage containing Cr and V includes such steps as preparing the solution of sodium pyro-sulfite, proportionally adding it to the sewage in reduction tank, reducing the 6-valence Cr to 3-valence Cr, proportionally adding the solution of sodium hydroxide to the sewage in neutralizing tank for reaction between V2O2 and sodium hydroxide to generate Na2V4O9 * 4H2O, reaction between V4O9 and said 3-valence Cr to generate Cr2(V4O9)3 deposit and changing residual 3-valence Cr to chromium hydroxide deposit, regulating pH=7.5-8.5, clarifying, and press filtering of suspended substance.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP VANADIUM TITANIUM & RESOURCES +1
Zero-power consumption steel-making method using electric-arc furnace
ActiveCN103205529AIncrease profitPromote rapid formationProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnaceElectric arc furnaceSmelting process
The invention discloses a zero-power consumption steel-making method using an electric-arc furnace. The zero-power consumption steel-making method specially comprises the following steps of: controlling the proportion of steel scrap in a furnace burden structure at 20%-30% and the proportion of molten iron at 70%-80%; pushing the steel scrap in a vertical shaft into the furnace by a hydraulic device, wherein the pushing speed is 1-3t / min; adding the molten iron to the furnace at twice through a molten iron adding chute for the furnace wall, wherein the primary molten iron accounts for 40%-80% of the total amount of the molten iron, the iron addition speed is 15-30t / min, the secondary molten iron accounts for 20%-60% of the total amount of the molten iron, and the iron addition speed is 4.5-6.5t / min; simultaneously adding lime to the furnace for slagging, and blowing oxygen for smelting; and when the temperature and components of the molten iron meet the technological requirements, finishing smelting in the electric-arc furnace. The zero-power consumption steel-making method can prevent the molten iron and furnace slag from overflowing from a furnace gate, thus reducing the consumption of slag charges and steel in the smelting process.
Owner:INST OF RES OF IRON & STEEL JIANGSU PROVINCE
Method for extracting chromium by electrochemically decomposing chromite in potassium hydroxide solution
InactiveCN103060838ASubsequent separation is simpleLow reaction temperatureElectrolysis componentsElectrolytic organic productionPotassium hydroxideSlurry
The invention relates to a method for extracting chromium by electrochemically decomposing chromite in a potassium hydroxide solution. The method comprises the steps as follows: filling oxidizing gas into mixed slurry containing chromite, potassium hydroxide and water; carrying out electrochemical oxidization reaction; and after the reaction, carrying out solid-liquid separation on the mixed slurry to obtain tailings and a chromium alkali solution. The method is low in cost, high in extraction efficiency, pollution-free and moderate in process conditions, and the chromium extraction rate can reach more than 95%.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for clean production of titanium dioxide by using potassium hydroxide
ActiveCN101172649AObvious superiorityLow reaction temperaturePigmenting treatmentTitanium dioxideSeparation technologyPotassium hydroxide
The invention belongs to the preparation of inorganic metallic compound and the processing filed of mineral resource, in particular to a preparation method for preparing titanium dioxide (titanium pigment) through high titanium slag and sodium hydroxide without pollution. The invention is characterized in that the high titanium slag is taken as the raw material; the high titanium slag and the potassium hydroxide having temperature range from 350 DEG C to 550 DEG C are reacted to prepare a medium product; the medium product is then washed through water (or carbonatation), acid solubled, reduced, hydrolyzed and burned to prepare anatase or rutile titanium dioxide. The alkali circulation, the acid circulation and the separation technology of the invention greatly reduce the production energy consumption, simplify the production process, reduce the device investment and increase the technology maneuverability, thereby providing an effective method for the comprehensive use of the titanium resource and the preparation of titanium dioxide (titanium pigment).
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
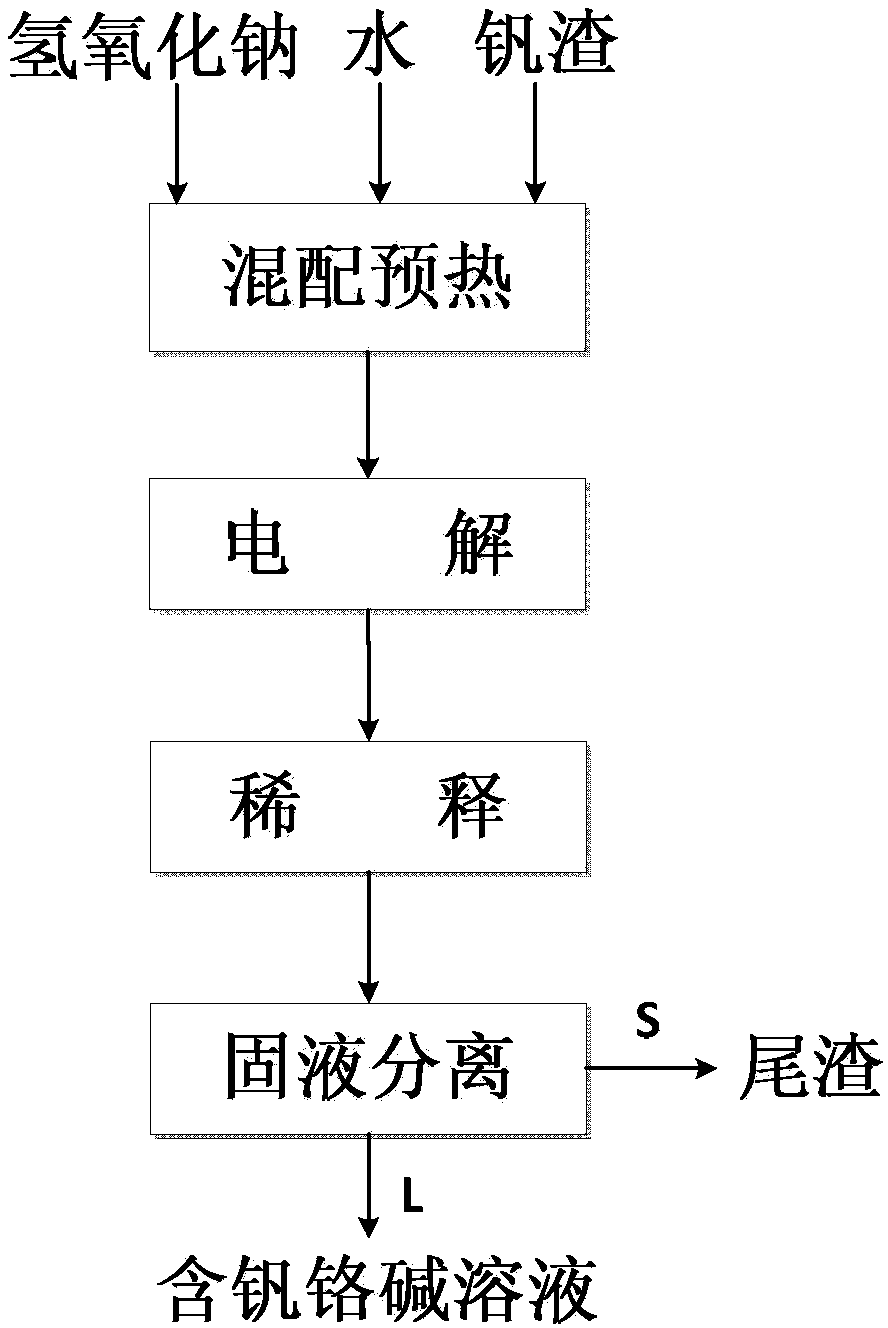
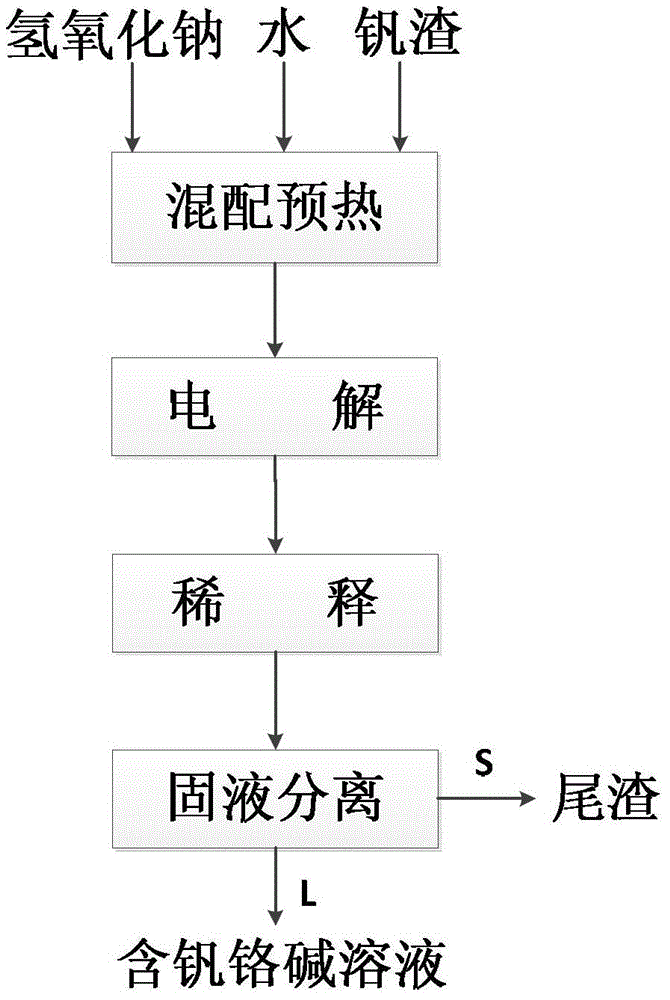
Method for synchronously extracting vanadium and chrome in electrochemical reinforced vanadium slag decomposition of sodium hydroxide solution
ActiveCN104294040ASimple ingredientsLow reaction temperatureProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisDecomposition
The invention relates to a method for synchronously extracting vanadium and chrome in electrochemical reinforced vanadium slag decomposition of sodium hydroxide solution. The method comprises the following steps: (1) ingredient preheating: vanadium slag and sodium hydroxide water solution are mixed and heated to prepare mixed slurry; (2) electrolysis: the preheated slurry is added in an electrolytic bath; and oxide gas is fed in the solution for electrolyzing to obtain reactive slurry; and (3) solid-liquid separation: the reactive slurry in the step (2) is filtered and separated to obtain tailings and vanadium and chrome-contained aqueous alkali. The method is low in operation temperature, low in energy consumption and simple in operation, and can realize efficient coextraction of the vanadium and the chrome; the extraction rate of the vanadium can reach 85-99%; and the extraction rate of the chrome can reach 80-95%.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Clean production process for processing low-grade laterite-nickel ore by sodium hydroxide alkali fusion method
InactiveCN101864523AObvious superiorityImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementEvaporationLaterite
The invention relates to a clean production process for processing low-grade laterite-nickel ore by a sodium hydroxide alkali fusion method. The process comprises the following steps: taking laterite-nickel ore as a raw material, carrying out roasting reaction on the laterite-nickel ore and sodium hydroxide at high temperature, washing and filtering the roasted material, and leaching valuable metal salts in the laterite-nickel ore, such as water-soluble chromium, aluminium and the like generated after the reaction. High-temperature roasting damages the crystal lattice structure of the laterite-nickel ore, thereby greatly improving the leaching rate of nickel and cobalt in the subsequent high-pressure acid leaching process and the grade of Fe in acid leaching dregs; filtrate is prepared into chromium salt, aluminium salt and recyclable sodium hydroxide by operations, such as evaporation, crystallization, separation and the like, so that the laterite-nickel ore product is diversified. The leaching rate of hexavalent chromium in the laterite-nickel ore is more than 90%, the leaching rate of trivalent aluminium is more than 75%, the leaching rate of the nickel is more than 98%, the leaching rate of the chromium is more than 94%, and the Fe content of fine iron powder in the acid leaching dregs is more than 61%.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for pollution-free production of sodium chromate by pressure leaching of chromite
ActiveCN101817561BObvious superioritySimple ingredientsChromates/bichromatesChemical industryFluid phase
The invention belongs to the field of chromite hydrometallurgy and chromium chemical industry, and in particular relates to a method for the pollution-free production of sodium chromate by pressure leaching of chromite. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) reacting the chromite with oxidizing gas in solution of NaOH; 2) diluting the product obtained by the step 1) and making subcrystalline sodium chromate to fully enter a liquid phase; 3) performing solid-liquid separation on the solid-liquid mixed slurry obtained by the step 2); 4) adding calcium oxide into the obtained diluent for removing impurities; and 5) evaporating and crystallizing the obtained solution without the impurities to obtain a sodium chromate crystal and crystallization mother solution; after the solid-liquidseparation, rinsing the sodium chromate crystal by using saturated solution of sodium chromate; and drying to obtain a qualified sodium chromate product. The method has the advantages of simple reaction system component, no difficultly separated phase introduced in the system, contribution to high-efficiency separation of the sodium chromate, great reduction in reaction temperature, low energy consumption, effective reduction in production cost of the sodium chromate, and high chromium leaching yield.
Owner:HUBEI ZHENHUA CHEMICAL CO LTD
A kind of method for extracting vanadium and chromium in vanadium slag at low temperature and normal pressure
ActiveCN105400967BLow reaction temperatureReduce reaction energy consumptionSlagReaction temperature
The invention relates to the field of vanadium slag hydrometallurgy and vanadium chemical engineering, in particular to a method for extracting chromium and vanadium from vanadium slag at a low temperature and the normal pressure. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, burdening, wherein the vanadium slag and a NaOH solution are mixed to form reaction slurry; secondly, reaction, oxide gas is led into the reaction slurry through a micro-hole arrangement device to carry out normal-pressure oxidative leaching, and after the reaction, solid-liquid mixed slurry of a solution containing NaOH, Na3VO4, Na2CrO4, water soluble impurity components and iron-rich tailings is obtained; thirdly, solid-liquid separation; fourthly, impurity removing; fifthly, sodium vanadate crystallization; and sixthly, sodium chromate crystallization. According to the method, chromium and vanadium efficient common extraction can be achieved, the extraction efficiency of both chromium and vanadium can be higher than 85%, more importantly, after the micro-hole gas distribution manner is adopted, the oxygen solubility can be obviously improved, the reaction temperature and alkali concentration are obviously reduced compared with those of an existing vanadium extraction method, the operation safety is greatly improved, and reaction energy consumption is reduced.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method for producing sodium chromate through calcium-free enriched oxygen or pure oxygen roasting
InactiveCN106495220AHigh Chromium ConversionRapid roasting reactionChromates/bichromatesEnergy consumptionBarium chromate
The invention discloses a method for producing sodium chromate through calcium-free enriched oxygen or pure oxygen roasting, mainly aims to solve problems that conventional calcium-free roasting rotary kiln production in China and outer countries is relatively low in chromium conversion rate, long in kiln material reaction time, relatively high in roasting temperature and the like, and aims to achieve the purposes that through enriched oxygen roasting (or pure oxygen roasting), the reaction velocity is increased, the chromium conversion rate is increased, the energy consumption is reduced, the waste residue discharge is reduced, the production efficiency is improved and the cost is lowered.
Owner:GANSU JINSHI CHEM
Method for cleaner production of sodium vanadate and sodium chromate by pressure leaching of vanadium slag
ActiveCN102531056BSimple ingredientsAchieve separationChromates/bichromatesVanadium compoundsSlagSlurry
The invention relates to a method for cleaner production of sodium vanadate and sodium chromate by pressure leaching of vanadium slag. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) mixing materials, namely mixing the vanadium slag and a solution of NaOH to obtain a reaction material; (2) reacting, namely performing oxidization reaction on the vanadium slag and oxidizing gas in the solution of NaOH under high pressure to obtain solid-liquid mixed slurry of a solution containing NaOH, Na3VO4, Na2CrO4 and water-soluble impurity components, and iron-rich tailings; (3) performing solid-liquid separation; (4) removing impurities; (5) crystallizing sodium vanadate; and (6) crystallizing sodium chromate. The method is easy to operate and is high in safety; and the operating temperature is greatly lower than the temperature of the traditional vanadium extraction process, energy consumption is low, the high-efficiency co-extraction of vanadium and chromium is realized, and the extraction rate of vanadium and chromium is over 95 percent.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Clean production method of potassium chromate
InactiveCN1162330CObvious superiorityReduce energy consumptionChromates/bichromatesReaction temperatureAqueous solution
A clean process for preparing potassium chromate includes such steps as reaction of chromite on oxidant in the aqueous solution of KOH to obtain a mixture of alkali solution, chromium salt and iron dregs, immersion extracting, separating coarse crystal of potassium chromate from ion dregs, and alkali solution, dissolving the said coarse crystal, removing impurities and crystallizing. Its advantages are low reaction temp. (250-400 deg.C), high Cr recovering rate (20%) and reduced quantity of Cr dregs.
Owner:中蓝义马铬化学有限公司
Method for extracting vanadium from vanadium containing material
ActiveCN106967890AReduce dosageSolve the problem of ammonium formation wallProcess efficiency improvementSlagMass ratio
The invention relates to a method for extracting vanadium from a vanadium containing material. The vanadium containing material is sintered, and clinker is obtained; then the clinker is mixed with ammonium salt and stearic acid, the mass ratio of the ammonium salt to the clinker is 1: (1-10), and reaction materials are obtained; and the reaction materials are sequentially subjected to the amination reaction and the deamination reaction, and then vanadium-containing lixivium is obtained. By means of the method, efficient vanadium extraction is achieved, the vanadium extraction rate reaches 95% or above, the usage amount of the ammonium salt is greatly reduced, and the production cost is reduced; and meanwhile the problem of amination material attachment in a roller reactor under the condition of the low liquid-solid ratio is solved. By means of the method, simple and clean separation of vanadium can be achieved, the water consumption amount and the slag discharging amount are reduced, meanwhile, dust and waste gas harmful to people and the environment cannot be generated, the reaction energy consumption is obviously reduced, and industrial popularization is facilitated.
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
Waste paper pulping fine screening tailing treatment technology
InactiveCN110331611AGuaranteed purification effectLarge amount of slag dischargePaper material treatmentPulp and paper industrySlurry
The invention relates to the fields of pulping and papermaking, and concretely relates to a waste paper pulping fine screening tailing treatment technology. The technology comprises the following steps: (1) waste paper pulping fine screening tailings are fed into a transition tank 1, and then goes through a primary fine screen to obtain a primary good pulp and a primary tail pulp, and the primarygood pulp enters a residue remover; (2) the primary good pulp goes through a medium-consistency stand tube 1, and the primary tail pulp is fed into a secondary fine screen to obtain a secondary good pulp and a secondary tail pulp; (3) the secondary good pulp returns to the primary fine screen, and the secondary tail pulp is fed into an end fine screen to obtain a third good pulp and a third tail pulp; (4) the third good pulp returns to the secondary fine screen, the third tail slurry is fed into a transition tank 2, and then is sequentially processed by a fluffer, a medium-consistency stand tube 2 and a flotation tank to obtain a fourth good pulp and residues; and (5) the fourth good pulp returns to the transition tank 1 and is processed, and the residues are fed into a waste tank. The technology can reduce the residue discharge amount of the waste paper pulping fine screening section by 10-20% on the basis of ensuring the quality of the pulp.
Owner:SHANYING INT HLDG CO LTD
Clean production technology for processing low-grade laterite-nickel ore by sodium carbonate alkali fusion
InactiveCN101864524AImprove leaching rateRaise the gradeProcess efficiency improvementEvaporationLaterite
The invention relates to a clean production technology for processing low-grade laterite-nickel ore by sodium carbonate alkali fusion. The invention takes laterite-nickel ore as a raw material, causes laterite-nickel ore and sodium carbonate to roast at high temperature, washes and filters the roasted material to leach valuable metal salts, such as water-soluble chromium, aluminum and the like generated in the laterite-nickel ore after reaction. High-temperature roasting damages the crystal lattice structure of the laterite-nickel ore so as to greatly improve the leaching rate of subsequent high-pressure acid leaching technical nickel and cobalt and improve the grade of Fe in acid leaching dregs; filtrate is prepared into chromium salt and aluminum salt by operations, such as evaporation, crystallization, separation and the like, so that the laterite-nickel ore product is diversified. The leaching rate of hexavalent chromium in the laterite-nickel ore is more than 90%, the leaching rate of trivalent aluminum is more than 65%, the leaching rate of nickel is more than 98%, the dipping rate of the chromium is more than 94%, and Fe content of fine iron powder in the acid leaching dregs is more than 61%.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Comprehensive utilization method of middle-low grade phosphorite
ActiveCN106277012AReduced slag dischargeLow costCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesPhosphorus compoundsAmmonium sulfateSlag
The invention relates to the technical field of comprehensive utilization of phosphorite, in particular to a comprehensive utilization method of middle-low grade phosphorite. The method comprises the following steps: treating by adopting nitric acid, filtering, washing filter residues, removing calcium, adjusting the pH, concentrating and drying; the leaching efficiency of phosphorus element in the phosphorite is increased, acid in the residues is washed, and by virtue of calcium removal treatment, the removed calcium is converted by adopting an ammonium sulfate solution to obtain calcium carbonate, so that the slag discharging amount is reduced, the waste of sulfur element is avoided, and the phosphorite treatment cost is decreased; and by virtue of the subsequent neutralization of the calcium removing solution, the phosphorus is precipitated in a form of magnesium ammonium phosphate, nitrate radicals and phosphate radicals are separated, and the added value of products is increased.
Owner:铜仁市万山区盛和矿业有限责任公司
Method for clean production of titanium dioxide by using sodium hydroxide
ActiveCN100542968CObvious superiorityLow reaction temperaturePigmenting treatmentTitanium dioxideResource utilizationSeparation technology
The invention belongs to the field of preparation of inorganic metal compounds and processing of mineral resources, and in particular relates to a method for cleanly producing titanium dioxide (titanium self-powder) from high-titanium slag and using sodium hydroxide. Using high-titanium slag as raw material, make it react with sodium hydroxide at 350-550°C to prepare an intermediate product, then wash (or carbonate), acid dissolve, reduce, hydrolyze, and calcinate the intermediate product to prepare anatase or Rutile titanium dioxide. The alkali cycle, acid cycle and separation technology of the present invention greatly reduces production energy consumption, simplifies the production process, reduces equipment investment, improves process operability, and provides comprehensive utilization of titanium resources and preparation of titanium dioxide (titanium dioxide) an effective way.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Electrochemical treatment method for arsenic-containing soot
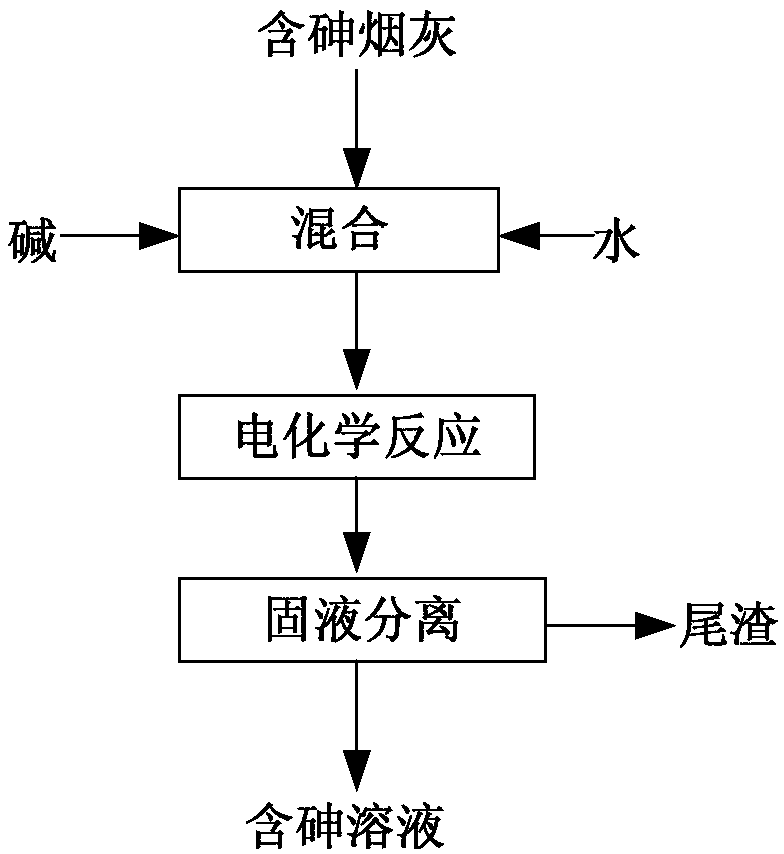
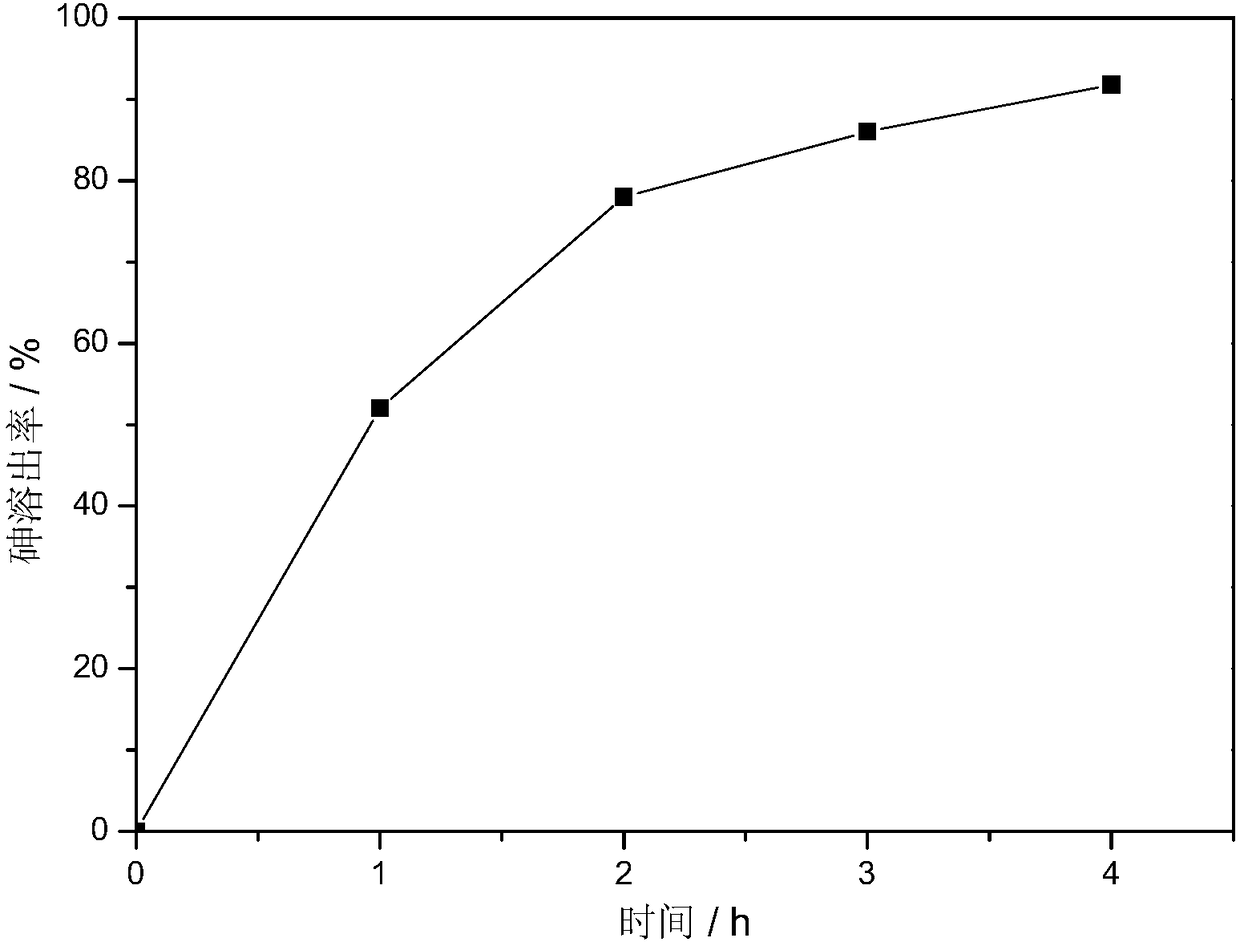
ActiveCN108570684AEfficient extractionReduce concentrationElectrode shape/formsProcess efficiency improvementElectrochemical responseSolvent
The invention provides an electrochemical treatment method for arsenic-containing soot. The electrochemical treatment method comprises: (1) mixing an alkali and a solvent or mixing an alkali solutionand arsenic-containing soot to obtain a mixture; (2) placing the mixture as an electrolyte in an electrochemical reaction device, carrying out an electrochemical reaction, and introducing an oxidizinggas into the electrolyte during the electrochemical reaction; and (3) carrying out solid-liquid separation on the reaction product obtained in the step (2) to obtain the arsenic-containing solution.According to the present invention, the method has advantages of high extraction rate of arsenic, cleaning property, no pollution, mild process condition, low cost and low requirements on equipment; the impurity is not introduced so as to conveniently perform the subsequent separation; the concentration of the used alkali is low so as to reduce the alkali consumption; and the automation degree ishigh so as to reduce the manpower input, the good economic and social benefits can be provided, and the good application prospect can be provided.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Vertical grinding machine for glass fiber
The invention belongs to the technical field of grinding equipment and relates to a vertical grinding machine for glass fiber. The vertical grinding machine comprises a separator blanking pipe, a grinding roller, a separator rotor, a dust collecting pipe, an upper air ring, a lower air ring, a scraping plate, a dreg discharging hole, an air intake direction, a main speed reducer, an air intake valve, a feeding tank, a before-grinding belt scale, a material retaining ring and a manhole door; the vertical grinding machine is characterized in that the separator blanking pipe is vertically and downwards lengthened until the distance from the separator blanking pipe to the horizontal plane of a grinding disc is 250mm; the lengthened part of the separator blanking pipe is a cylindrical steel pipe of which the diameter is 426mm; the feeding tank extends inside the separator blanking pipe; the extension part of the feeding tank is hermetically connected with the part, in contact with the extension part of the feeding tank, of the separator blanking pipe; the height of the material retaining ring is increased by 140mm, and the clearance between each air ring and the material retaining ring is reduced to 30mm; a handle of the manhole door is additionally provided with a protective lock switch. The vertical grinding machine disclosed by the invention is reasonable, simple and convenient in structural design, low in cost, capable of improving the grinding efficiency and reducing the amount of discharged dregs, also capable of reducing abrasion, and capable of improving the safety as well during overhauling of equipment.
Owner:SHANDONG FIBERGLASS GRP
A method for synchronously extracting vanadium chromium by electrochemically strengthening the decomposition of vanadium slag in sodium hydroxide solution
ActiveCN104294040BSimple ingredientsLow reaction temperatureProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisSlag
The invention relates to a method for synchronously extracting vanadium and chrome in electrochemical reinforced vanadium slag decomposition of sodium hydroxide solution. The method comprises the following steps: (1) ingredient preheating: vanadium slag and sodium hydroxide water solution are mixed and heated to prepare mixed slurry; (2) electrolysis: the preheated slurry is added in an electrolytic bath; and oxide gas is fed in the solution for electrolyzing to obtain reactive slurry; and (3) solid-liquid separation: the reactive slurry in the step (2) is filtered and separated to obtain tailings and vanadium and chrome-contained aqueous alkali. The method is low in operation temperature, low in energy consumption and simple in operation, and can realize efficient coextraction of the vanadium and the chrome; the extraction rate of the vanadium can reach 85-99%; and the extraction rate of the chrome can reach 80-95%.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
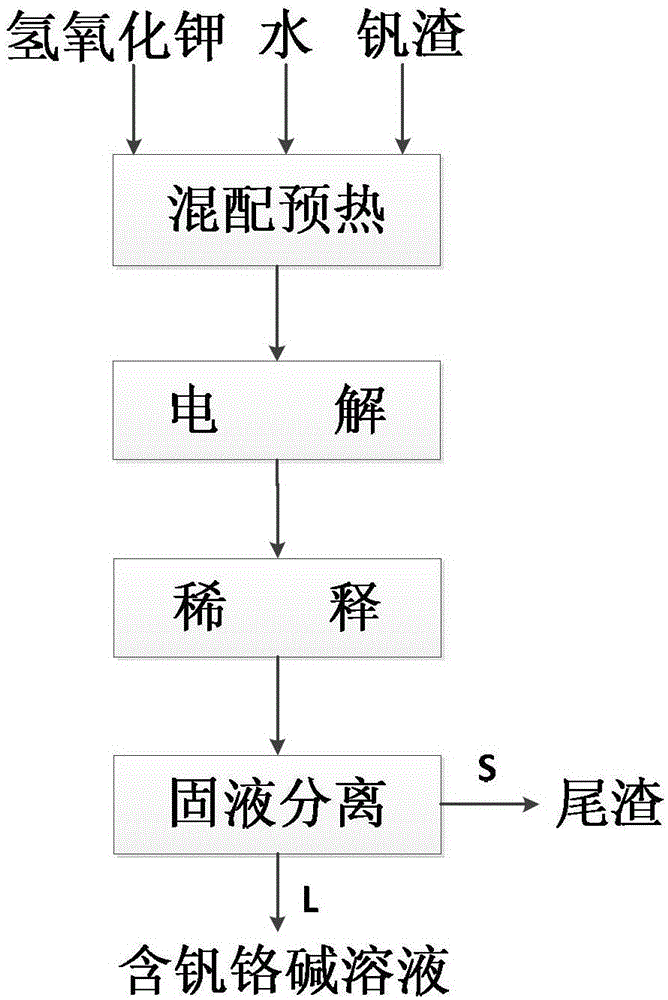
A method for simultaneously extracting vanadium chromium by electrochemically decomposing vanadium slag in a low-temperature low-concentration potassium hydroxide solution
ActiveCN103421950BSimple ingredientsLow reaction temperaturePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisSlag
The invention relates to a method for synchronously extracting vanadium and chromium during electrochemical resolving of vanadium slag in low-temperature low-concentration potassium hydroxide solution. The method comprises the following steps: (1) batching and heating: mixing and heating vanadium slag and potassium hydroxide solution to prepare mixed slurry; (2) electrolysis: adding the preheated slurry into an electrolysis bath, leading oxidizing gas into the solution, and carrying out electrolysis to obtain reaction slurry; (3) solid-liquid separation: filtering the reaction slurry of the step (2) for separation, so as to obtain tail slag and aqueous alkali containing vanadium and chromium. The method has the advantages that the operation temperature is low; the energy consumption is low; the operation is easy; efficient co-extraction of vanadium and chromium can be realized; the extraction rate of vanadium can be 85 to 99 percent; the extraction rate of chromium can be 80 to 95 percent.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com