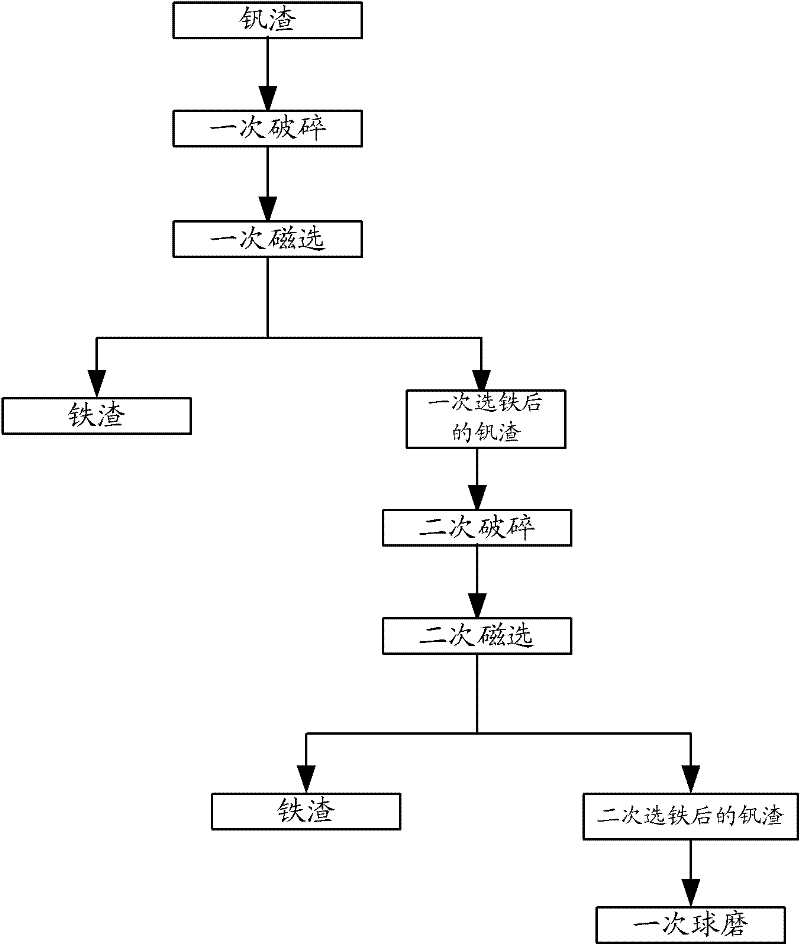
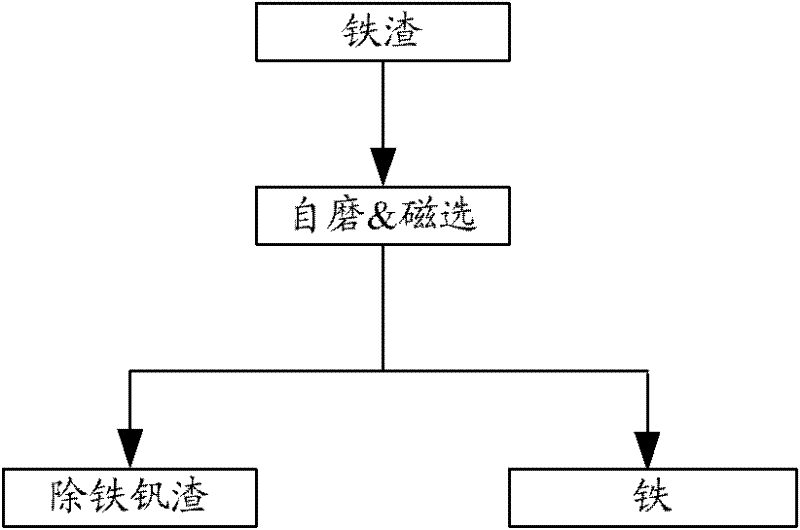
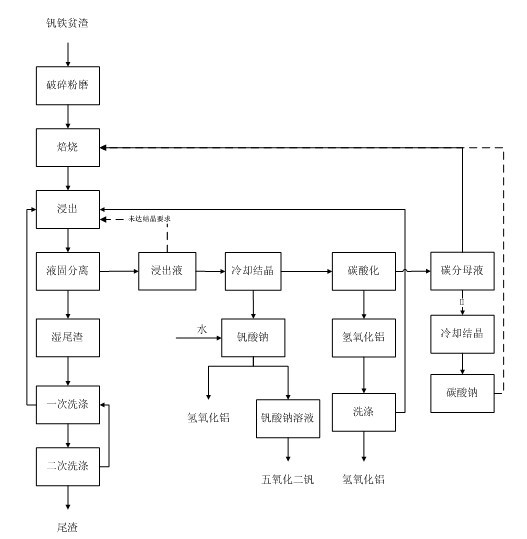
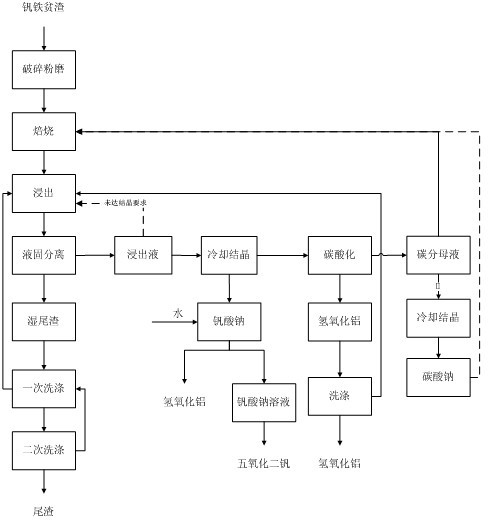
Patents
Literature
294 results about "Sodium Vanadate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sodium Orthovanadate (Vanadate) is a general competitive inhibitor for protein phosphotyrosyl phosphatases. The inhibition by Sodium Orthovanadate is reversible upon the addition of EDTA or by dilution.
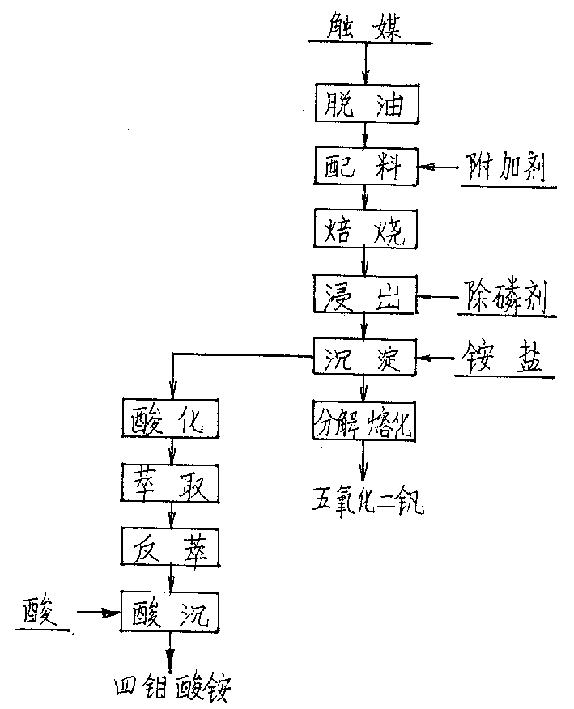
Method for extracting tungsten, titanium and vanadium from waste SCR (selective catalytic reduction) catalyst
InactiveCN102936049ASolve the pollution of the environmentLow equipment requirementsTungsten oxides/hydroxidesTitanium dioxideSlagStrong acids
The invention discloses a method for extracting tungsten, titanium and vanadium from a waste SCR (selective catalytic reduction) catalyst, which comprises the following steps: crushing the waste SCR catalyst, adding a strongly alkaline solution, and reacting; filtering, separating, then adding strong acid into the sodium tungstate and sodium vanadate mixed solution, and reacting to obtain tungstic acid and a sodium salt and vanadic acid mixed solution; regulating the pH value of the sodium salt and vanadic acid mixed solution until precipitate is separated out, thus obtaining ammonium vanadate; then adding sulfuric acid into the tungsten-and-vanadium-removed SCR catalyst, and reacting to obtain a titanyl sulfate solution and solids such as aluminum slag and the like; then adding water into the titanyl sulfate solution, and hydrolyzing to obtain titanic acid and a waste acid solution; and finally, respectively calcining the obtained ammonium vanadate, tungstic acid and titanic acid to obtain vanadium pentoxide, tungsten trioxide and titanium dioxide. According to the invention, tungsten, titanium and vanadium can be extracted from the SCR catalyst through the reaction with strong alkali and strong acid at a low temperature, the equipment requirement is low, the energy consumption is low, some products having added values can be coproduced, and no secondary pollution is generated, thereby facilitating popularization and application.
Owner:成都新智金森环保科技有限公司
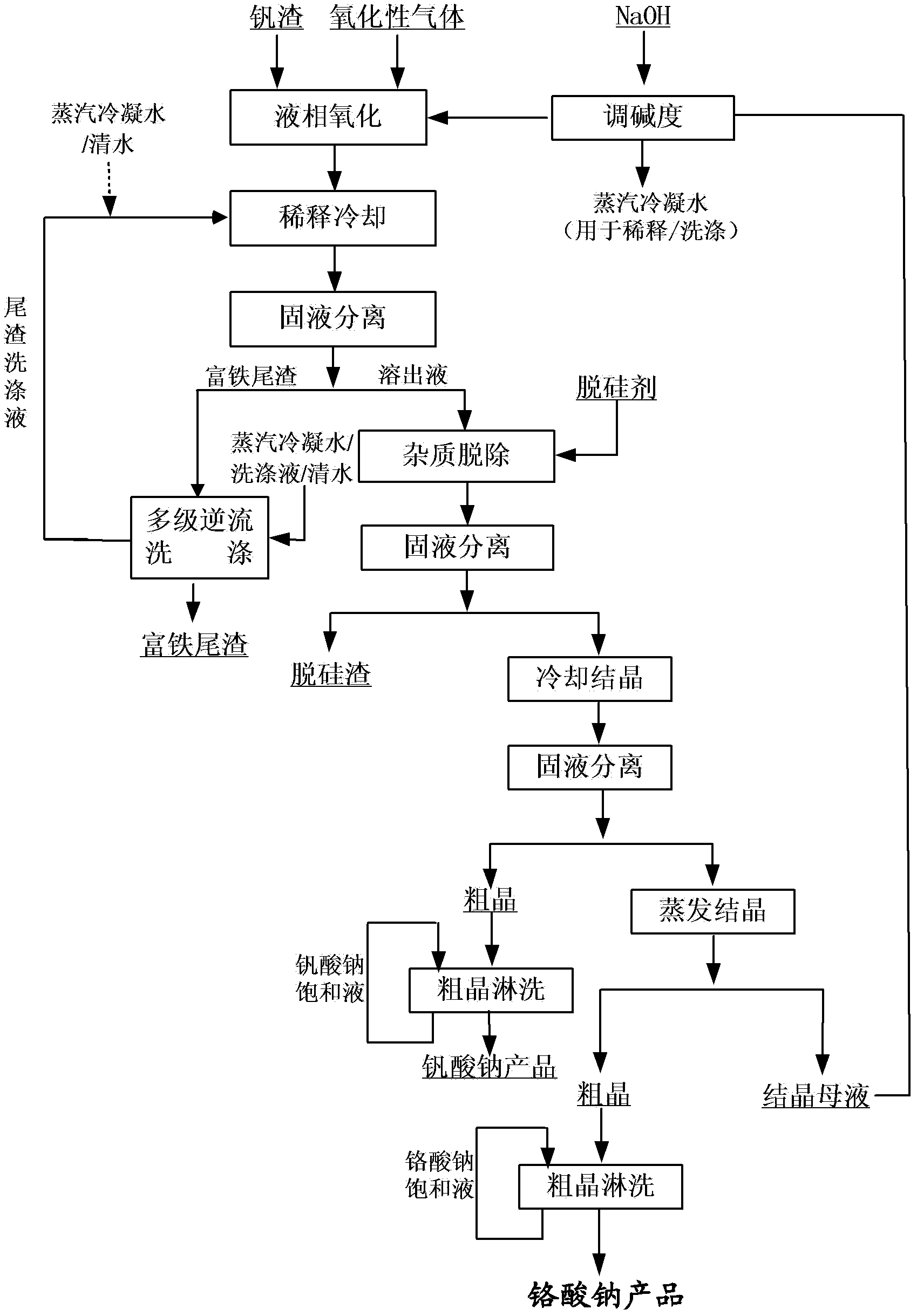
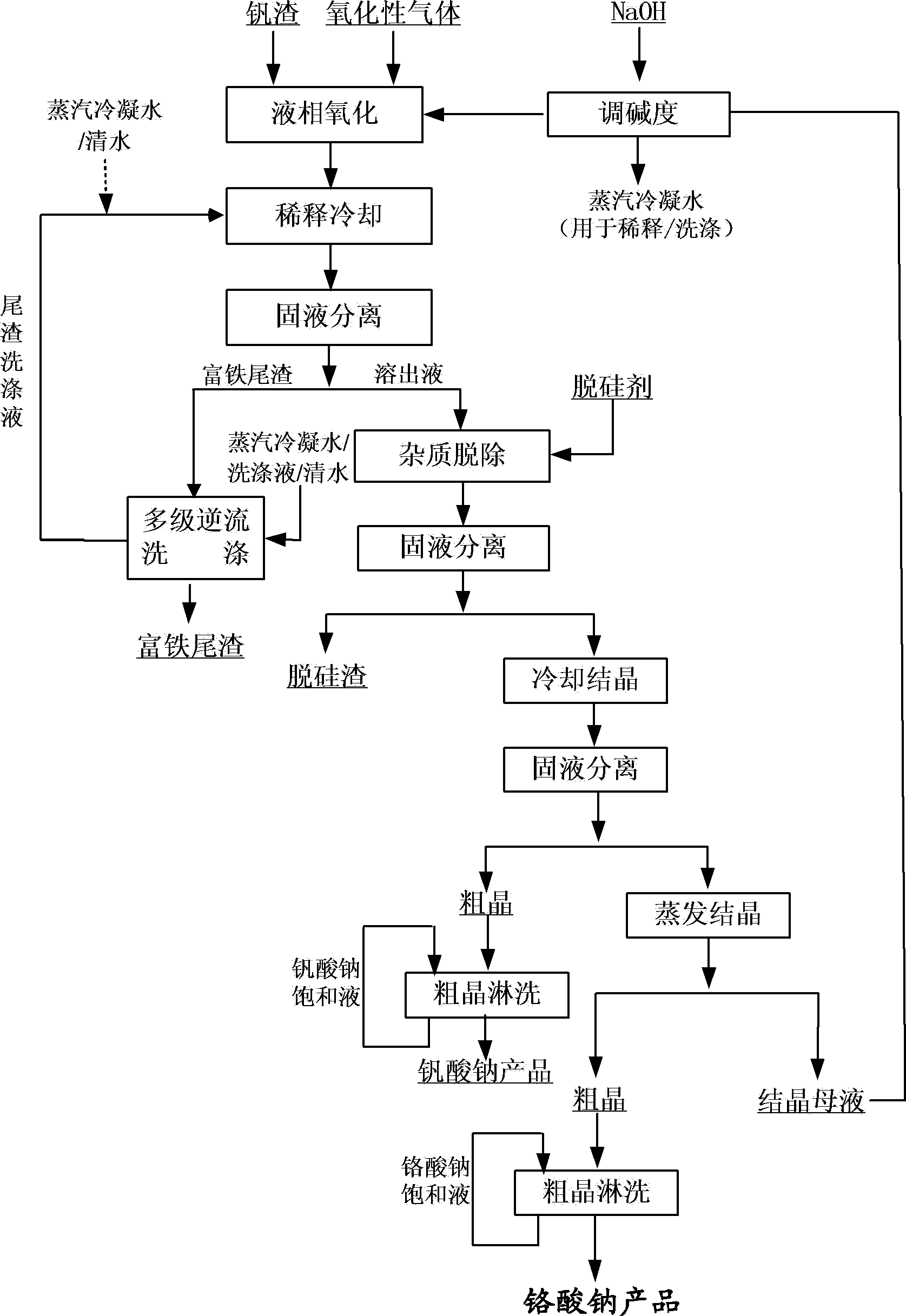
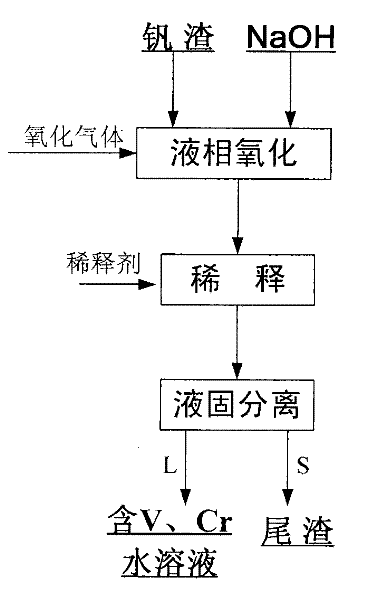
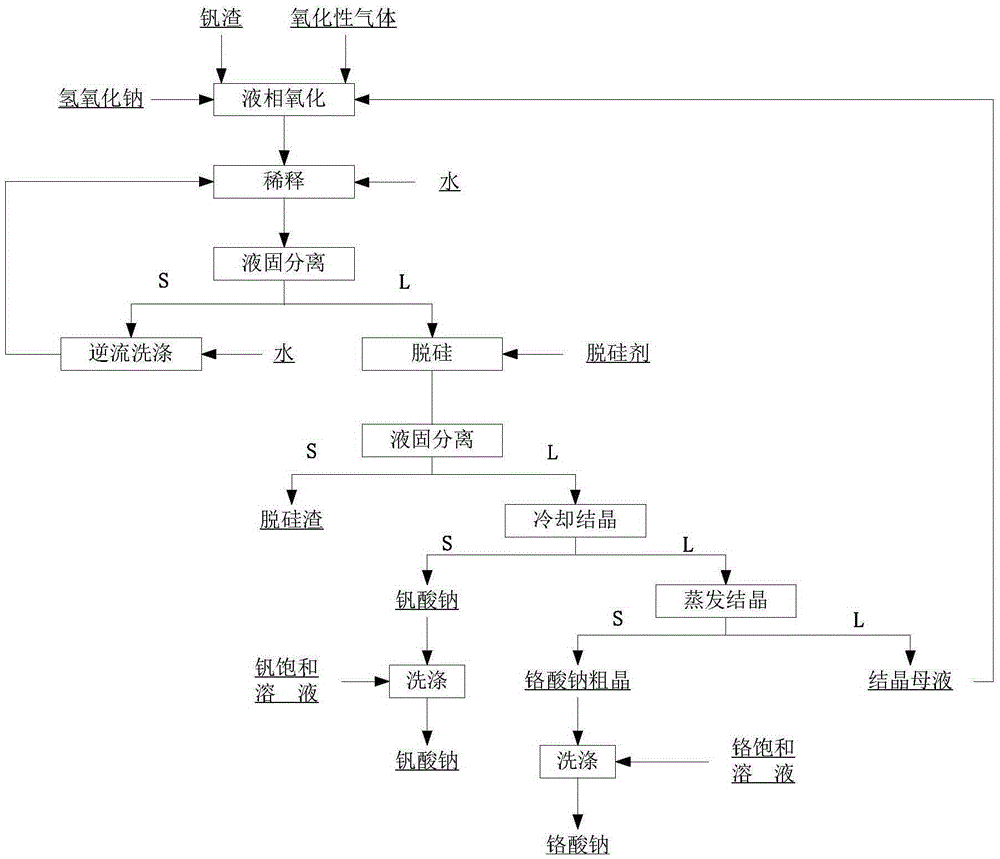
Method for cleaner production of sodium vanadate and sodium chromate by pressure leaching of vanadium slag
ActiveCN102531056ASimple ingredientsAchieve separationChromates/bichromatesVanadium compoundsSlagSlurry
The invention relates to a method for cleaner production of sodium vanadate and sodium chromate by pressure leaching of vanadium slag. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) mixing materials, namely mixing the vanadium slag and a solution of NaOH to obtain a reaction material; (2) reacting, namely performing oxidization reaction on the vanadium slag and oxidizing gas in the solution of NaOH under high pressure to obtain solid-liquid mixed slurry of a solution containing NaOH, Na3VO4, Na2CrO4 and water-soluble impurity components, and iron-rich tailings; (3) performing solid-liquid separation; (4) removing impurities; (5) crystallizing sodium vanadate; and (6) crystallizing sodium chromate. The method is easy to operate and is high in safety; and the operating temperature is greatly lower than the temperature of the traditional vanadium extraction process, energy consumption is low, the high-efficiency co-extraction of vanadium and chromium is realized, and the extraction rate of vanadium and chromium is over 95 percent.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
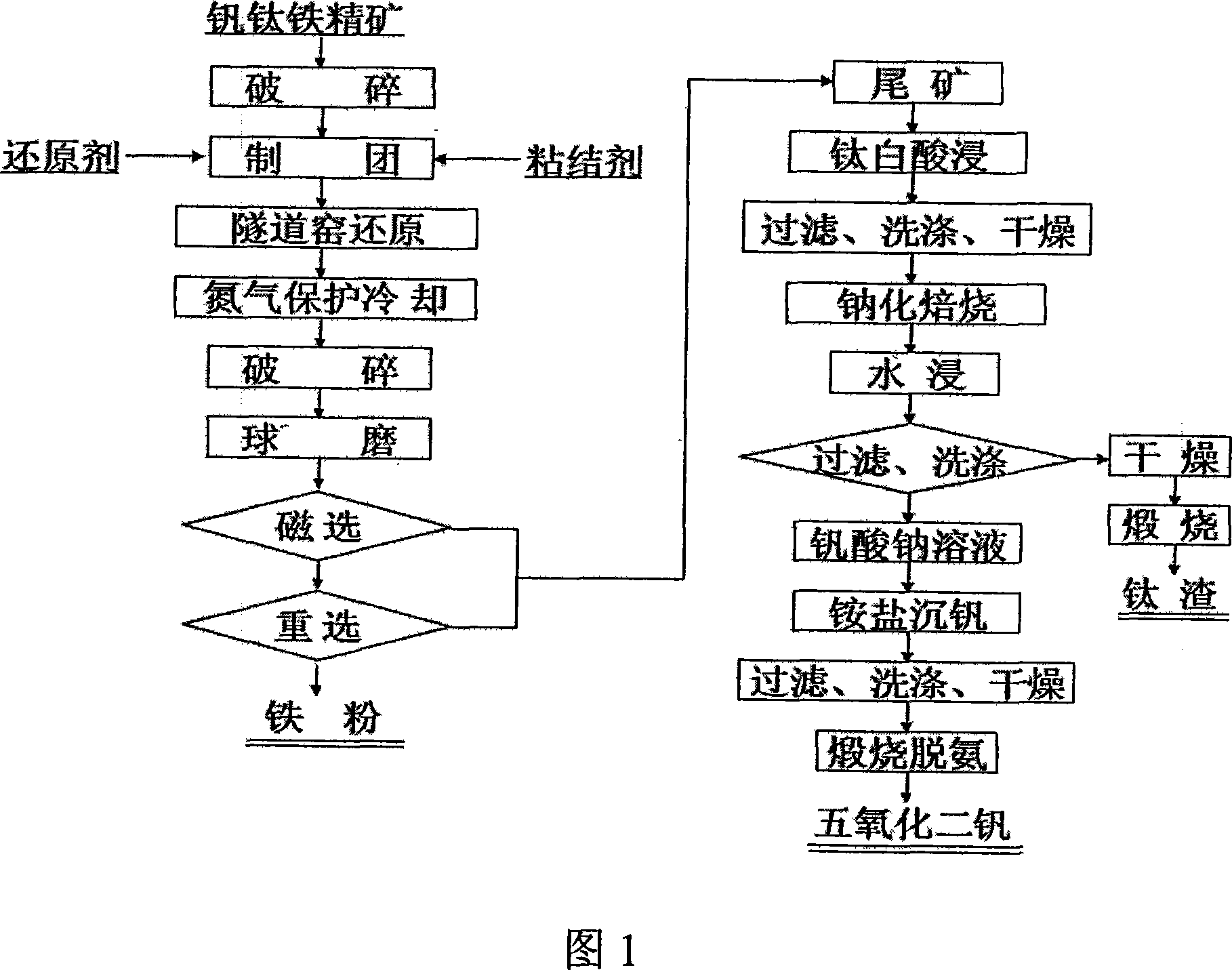
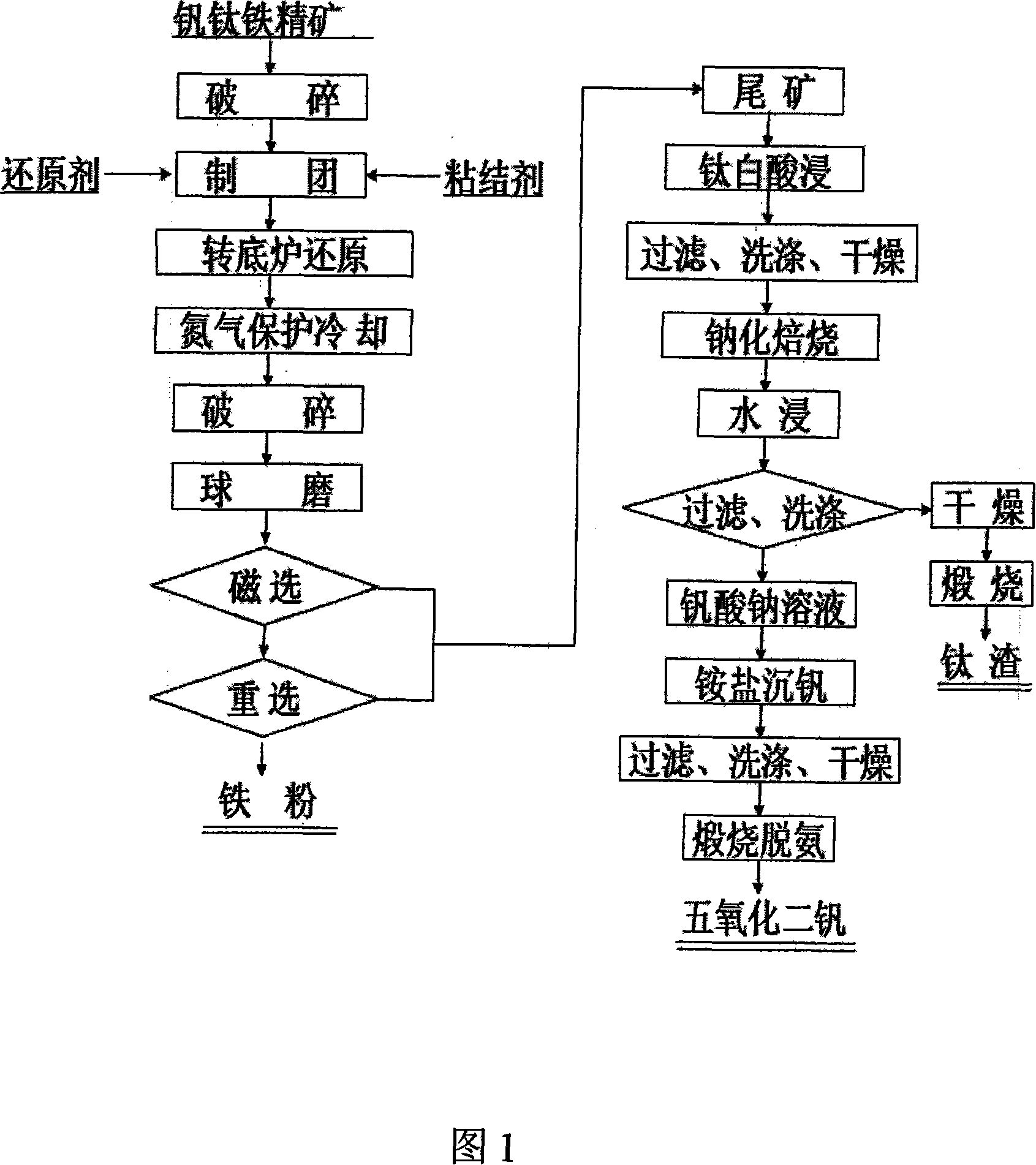
Method for comprehensive utilization of V-Ti-bearing iron ore concentrate by using tunnel kiln reduction-grinding - separation
InactiveCN101113488AAvoid defects such as loopsHigh yieldProcess efficiency improvementTunnel kilnResource utilization
The invention relates to an iron powder production method by using a tunnel kiln to reduce concentrate pellets containing carbon vanadium ferrotitanium with titanium slag and vanadium pentoxide as combined products. Concentrate pellets are made from vanadium-titanium iron concentrate through crashing and damp milling. The iron powder and tailings are obtained by putting the concentrate pellets into the tunnel kiln to be reduced, crashing, wet-grinding, magnetic separation and gravity separation. The tailings are soaked with titania waste acid to eliminate remnants magnesium and iron. Then the tailings are filtrated and dried to obtain a new material. And then the new material is added with sodium salt to do salt roast and then to be soaked by water, then titanium slag and sodium vanadate are obtained respectively after the water soaking. At last, the vanadium pentoxide is obtained by ammonium vanadate precipitating and calcination deaminase to the sodium vanadate liquid. The invention eliminates the disadvantage of high energy consumption by electric furnace smelting and bad separating effect of vanadium and titanium, difficult control of vanadium and titanium trend and low yield rate of extracting vanadium and titanium through converter blowing iron molten, etc. The invention has the advantages of high yield rate of vanadium, titanium and iron and high resources utilization rate and explores a novel practical way for comprehensive utilization of vanadium, titanium and iron concentrate ore.
Owner:攀枝花锐龙冶化材料开发有限公司
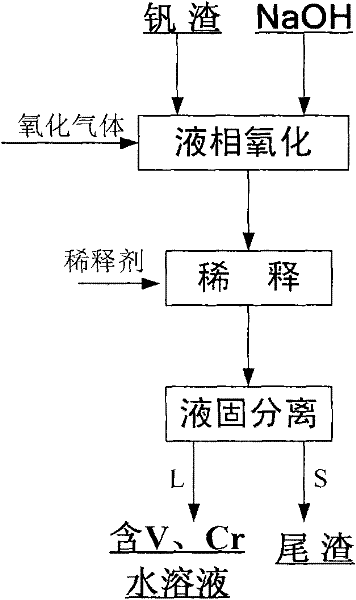
Method for decomposing chromium-containing vanadium slag by using sodium hydroxide molten salt
InactiveCN102127654ALower decomposition temperatureReduce the temperatureProcess efficiency improvementDecompositionSlag
The invention relates to a method for decomposing chromium-containing vanadium slag by using sodium hydroxide molten salt, which comprises the following steps of: weighing NaOH and the vanadium slag in a mass ratio of 2.5:1-6:1; putting the weighed NaOH into a normal pressure reaction kettle, heating to the temperature of between 500 and 600 DEG C, adding the weighed vanadium slag into the NaOH molten salt, introducing oxidizing gas and performing liquid-phase oxidation reaction at the temperature of between 500 and 600 DEG C for 0.5 to 6 hours to obtain reaction slurry after the reaction is finished; diluting by using a diluent until the concentration of the sodium hydroxide in the slurry is 100 to 500g / L to obtain mixed slurry containing the sodium hydroxide, sodium vanadate, sodium chromate and tailings; and performing filtering separation on the mixed slurry at the temperature of between 80 and 130 DEG C to obtain the tailings and aqueous solution containing vanadium and chromium.The decomposition temperature is lower than the conventional sodium treatment roasting temperature, vanadium and chromium resources can be co-extracted, the extraction ratio is high, and the method is easy to operate.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
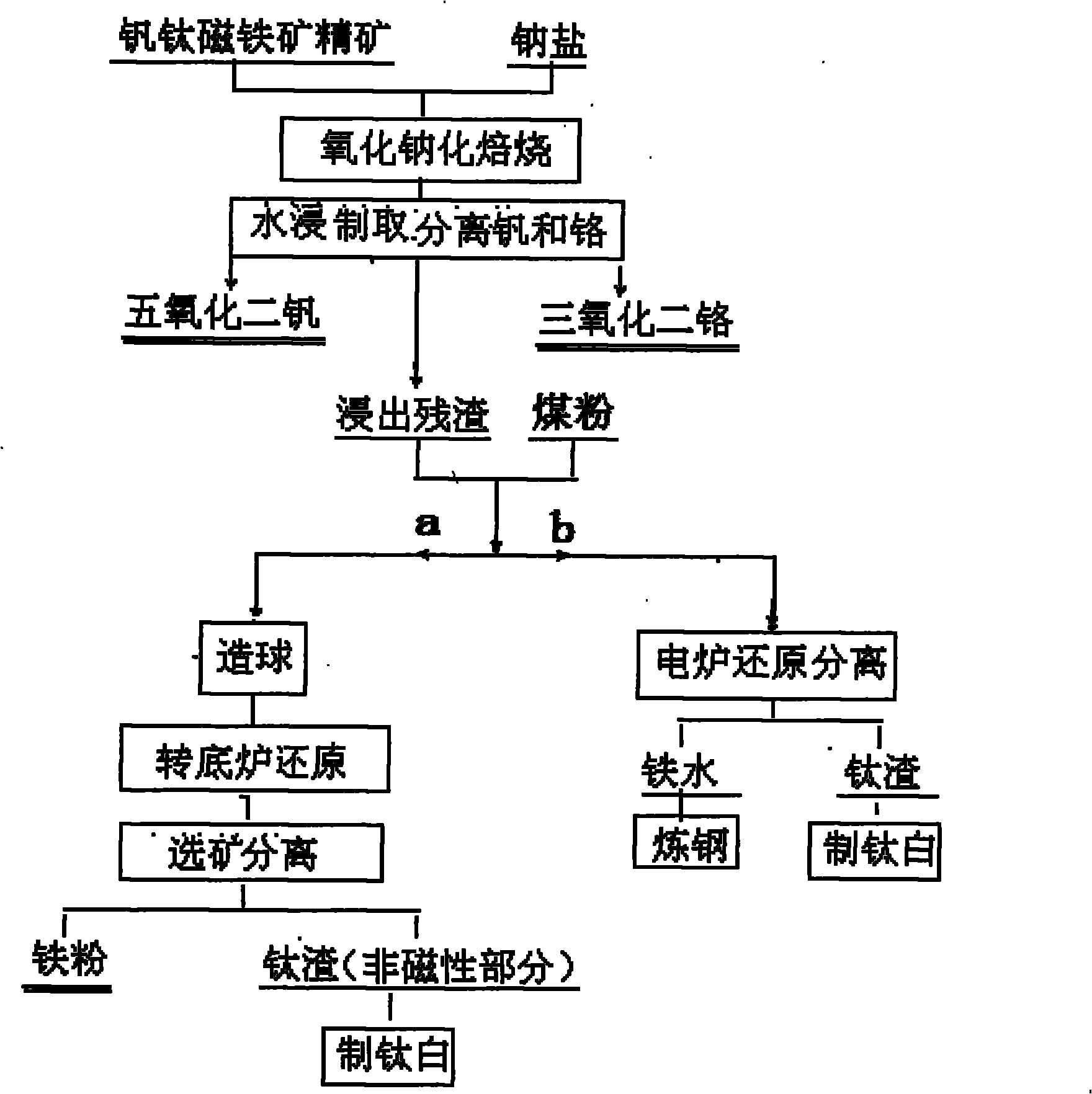
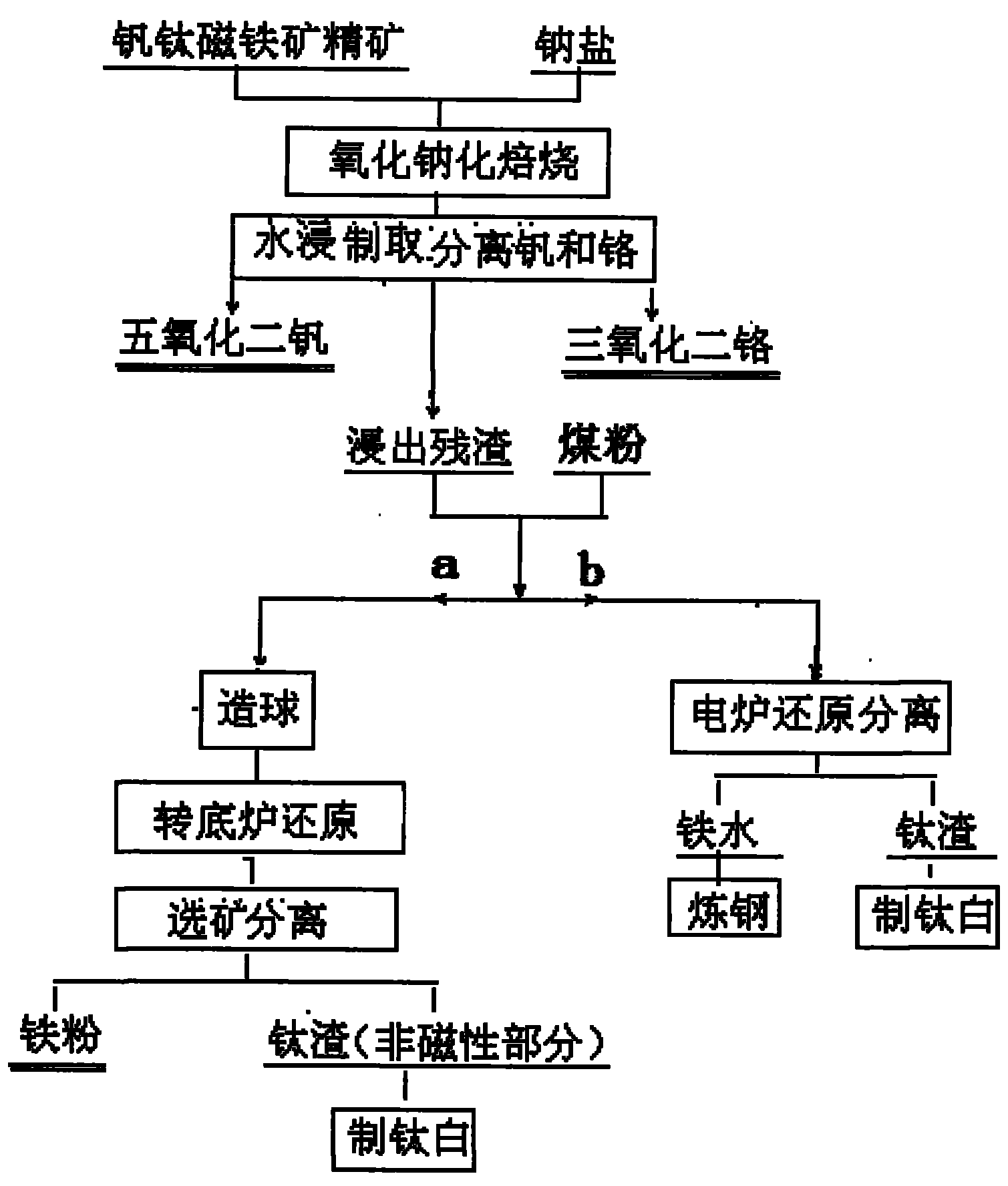
Method for recycling vanadium, chromium, titanium and iron from vanadium-titanium magnetite ore
ActiveCN102061397AHigh recovery rateSimple processProcess efficiency improvementSteelmakingMagnetite
The invention discloses a method for recycling valuable elements from vanadium-titanium magnetite ore, which comprises the following steps of: crushing the ore or concentrate, adding sodium salt, performing oxidizing roasting, converting vanadium and chromium into water-soluble sodium vanadate and sodium chromate, performing water leaching in solution, and separating the vanadium and chromium from the solution to obtain vanadium pentoxide and chromium sesquioxide products; and adding coal dust into the leached residue for pelletizing, reducing in a rotary hearth furnace, magnetically separating iron and titanium, using the obtained magnetic iron powder as a raw material for powder metallurgy or steelmaking, and using a nonmagnetic product containing more than 50 percent of TiO2 as a raw material for extracting the titanium; or reducing iron from the leached residue in an electric furnace, using the obtained molten iron as a raw material for steelmaking and using electric furnace slag containing more than 50 percent of TiO2 as a raw material for extracting the titanium. The method is short in process flow and economical; and the recovery rate of the vanadium, chromium, titanium and iron is high.
Owner:SICHUAN LOMON MINING & METALLURGY +1
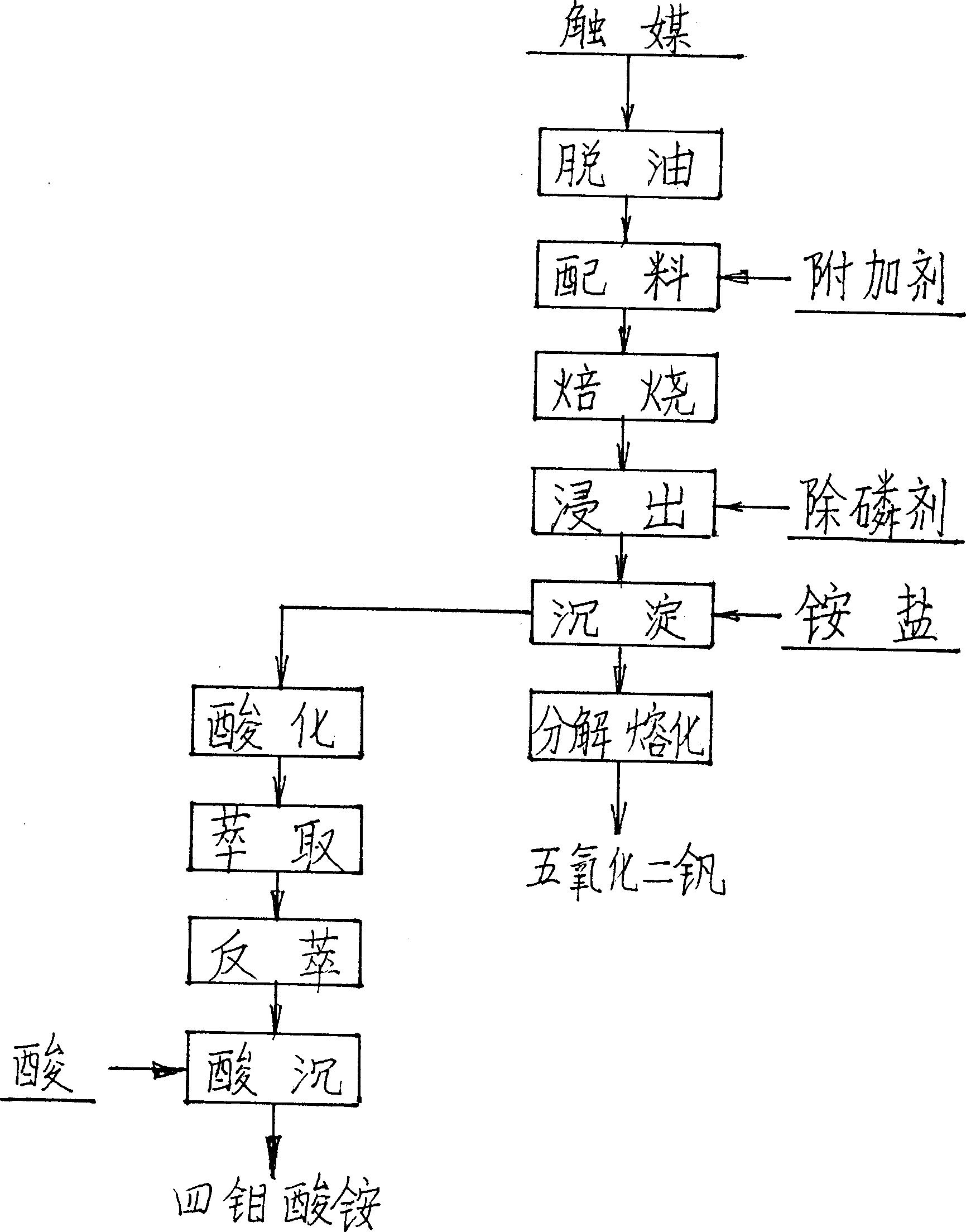
Wet process of extracting vanadium and/or molybdenum from waste catalyst
InactiveCN1453379ALess investmentReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementMagnesium saltAmmonium metavanadate
The present invention is wet process of extracting vanadium and / or molybdenum form waste petrochemical catalyst alumina carrier containing V, Mo and other elements. The wet process includes high-temperature deoiling the catalyst in natural granularity, mixing with sodium carbonate, high-temperature oxidation and roasting in a kiln or furnace to obtain water soluble sodium vanadate and sodium molybdate; countercurrent water soaking of the chamotte to obtain solution containing V and Mo in certain concentration, adding calcium salt and magnesium salt to eliminate P and other impurities, addingammonium salt solution into the clear solution to obtain ammonium metavanadate, decomposing and melting ammonium metavanadate to obtain V2O5 product; adding acid to the supernatant and organic phase extraction of Mo, ammonia water reverse extraction to obtain ammonium molybdate, and adding acid to precipitate ammonium tetramolybdate or molybdate product.
Owner:CITIC JINZHOU METAL
Method for extracting chromium and vanadium from vanadium slag at low temperature and normal pressure
ActiveCN105400967ALow reaction temperatureReduce reaction energy consumptionSlagReaction temperature
The invention relates to the field of vanadium slag hydrometallurgy and vanadium chemical engineering, in particular to a method for extracting chromium and vanadium from vanadium slag at a low temperature and the normal pressure. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, burdening, wherein the vanadium slag and a NaOH solution are mixed to form reaction slurry; secondly, reaction, oxide gas is led into the reaction slurry through a micro-hole arrangement device to carry out normal-pressure oxidative leaching, and after the reaction, solid-liquid mixed slurry of a solution containing NaOH, Na3VO4, Na2CrO4, water soluble impurity components and iron-rich tailings is obtained; thirdly, solid-liquid separation; fourthly, impurity removing; fifthly, sodium vanadate crystallization; and sixthly, sodium chromate crystallization. According to the method, chromium and vanadium efficient common extraction can be achieved, the extraction efficiency of both chromium and vanadium can be higher than 85%, more importantly, after the micro-hole gas distribution manner is adopted, the oxygen solubility can be obviously improved, the reaction temperature and alkali concentration are obviously reduced compared with those of an existing vanadium extraction method, the operation safety is greatly improved, and reaction energy consumption is reduced.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Composite decarbonizing solution for gathering carbon dioxide in mixed gas
InactiveCN101612509AReduce consumptionDispersed particle separationChemical reactionAbsorption capacity
The invention discloses a composite decarbonizing solution for gathering carbon dioxide in mixed gas, belonging to the technical field of gas separation. The composite decarbonizing solution is characterized by consisting of main absorption components including MEA and AEE, auxiliary absorption components including AHPD, AMP, TEA and MDEA, active components including PZ, HEPZ, AEP and DEA, sodium vanadate as an inhibiter, sodium sulfite and copper acetate as antioxidant, and a mixed solvent including NMP, polyethylene glycol and propylene carbonate and water. Because the mixed solvent is used for the composite decarbonizing liquid, on the one hand, the absorption capacity, the purification degree and the desorption rate are improved, and the reaction temperature range is enlarged, and on the other hand, regeneration energy consumption is greatly improved. The invention has the advantages that the composite decarbonizing solution is used for gathering carbon dioxide in various kinds of chemical reaction tail gas, burning stack gas and natural mixed gas and eliminating carbon oxide in city gas, natural gas, and the like, and has social benefit and economic benefit.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
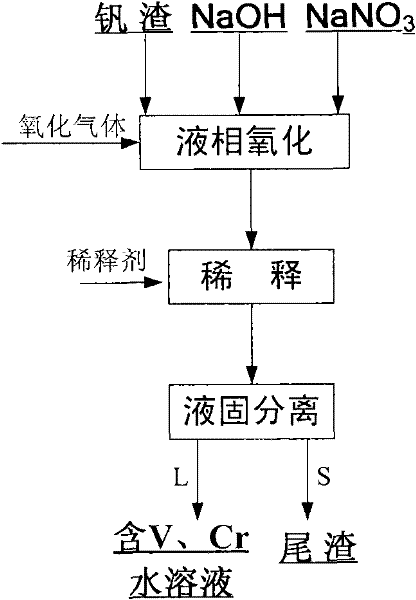
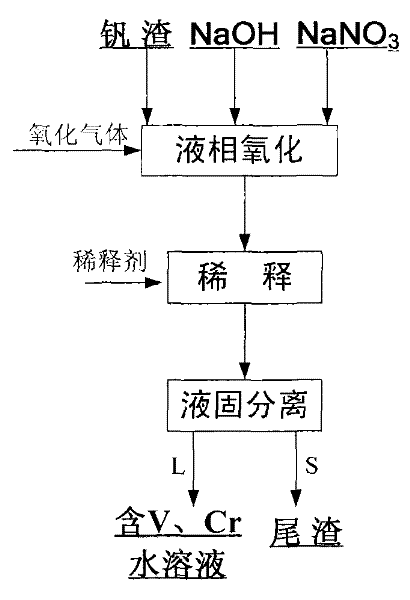
Method for decomposing vanadium slag by liquid phase oxidation
ActiveCN102127656ALow reaction temperatureReduce energy consumptionProcess efficiency improvementSlagResource utilization
The invention relates to a method for decomposing vanadium slag by liquid phase oxidation. The method comprises the following steps of: weighing materials according to a mass ratio of NaOH to NaNO3 of 0.2:1-4:1 and the mass ratio of the total amount of the NaOH and the NaNO3 to the vanadium slag of 2.5:1-6:1; placing the weighed NaOH and NaNO3 into a normal-pressure reaction kettle; heating to the temperature of between 330 and 480 DEG C; adding the weighed vanadium slag into NaOH-NaNO3 molten salt; introducing oxidizing gas; performing liquid phase oxidation reaction at the temperature of between 330 and 480 DEG C for 0.5 to 6 hours to obtain reaction slurry; diluting the reaction slurry with a diluting agent until the sodium hydroxide concentration of feed liquid is between 100 and 500g / L to obtain mixed slurry of sodium hydroxide, sodium nitrate, sodium vanadate, sodium chromate and tailings; and performing filtering separation to obtain the tailings and aqueous solution containingvanadium and chromium. The method has a low reaction temperature, high safety and high utilization rate of vanadium and chromium resources, is operated under normal pressure and is easy to industrially implement, and the vanadium and the chromium in the vanadium slag are extracted together; and the decomposed tailings comprise 0.5 to 1 weight percent of vanadium (based on V2O5) and 0.5 to 1 weight percent of chromium (based on Cr2O3).
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
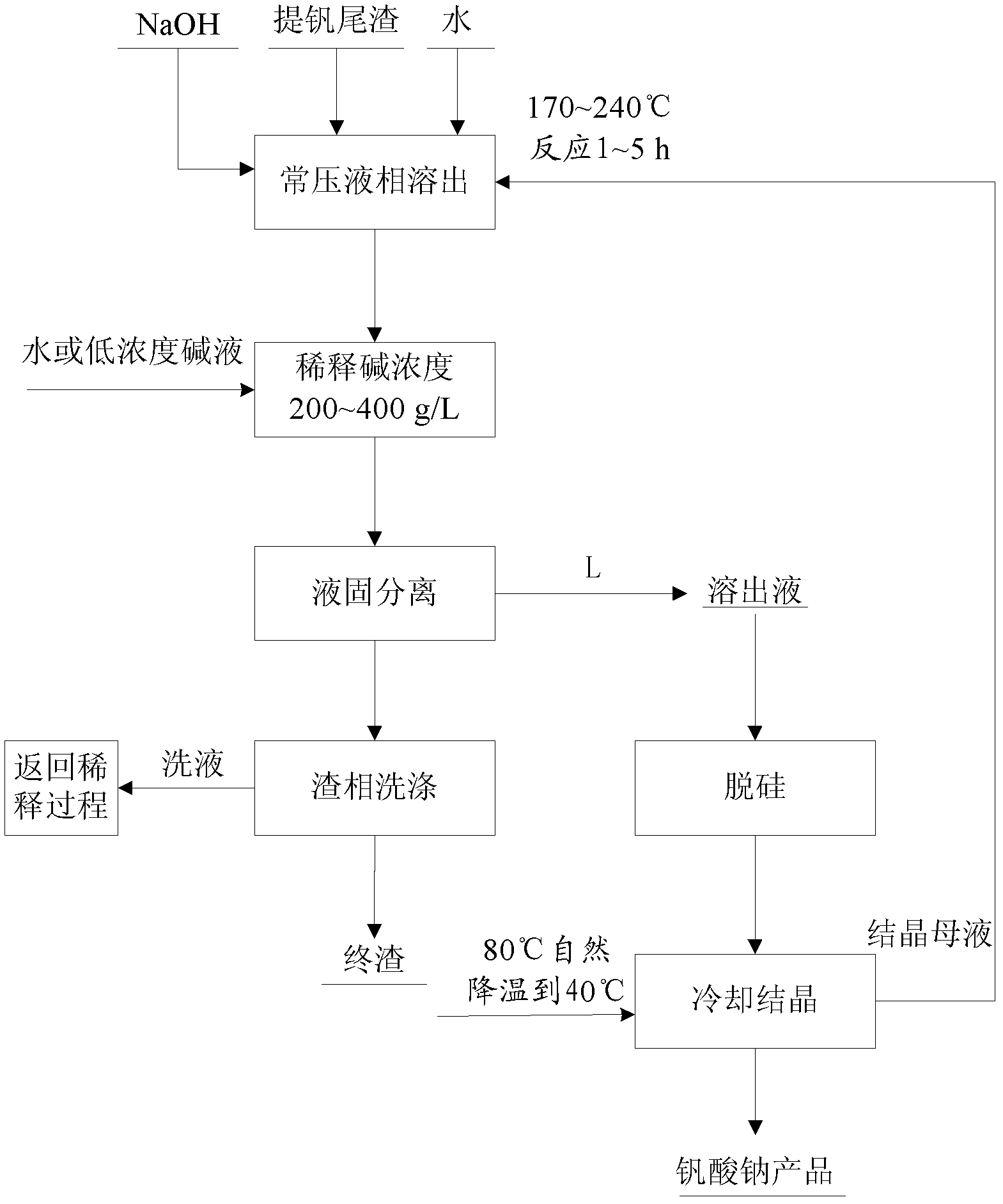
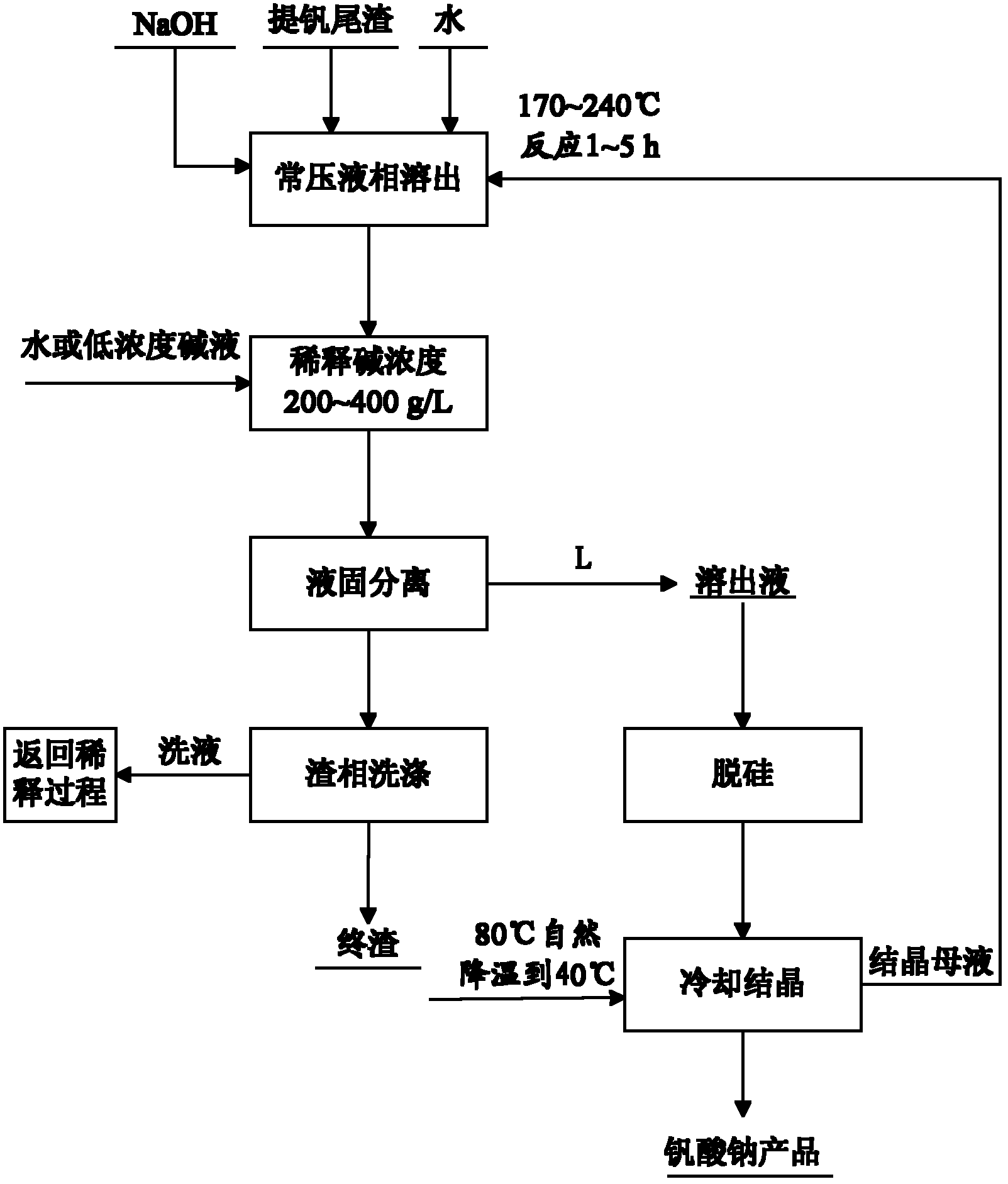
Method for recycling vanadium extraction tailings
InactiveCN102251119ALow reaction temperatureImprove resource utilizationProcess efficiency improvementProcess equipmentPresent method
The invention relates to a method for recycling vanadium extraction tailings. The method comprises steps that: vanadium extraction tailings and NaOH are decomposed in a reactor; obtained reaction slurry is diluted by water or low concentration lye, such that mixed slurry is obtained; the mixed slurry is filtered under a temperature of 80 to 130 DEG C, such that an aqueous solution containing sodium hydroxide, sodium vanadate and sodium silicate is obtained; the solution is desilicated by using a desilication agent; the desilicated solution is naturally cooled and crystallized, such that vanadate is obtained. According to the method, the operation temperature is lower than the boiling point of the solution, the process can be carried out under normal pressure, and ventilation is not required, such that the method is easy to operate, and is safe. A recycling rate of vanadium is 93 to 99%, and a total vanadium content in a finished tailing is lower than 0.1 wt%, which is calculated according to the amount of vanadic anhydride. Compared to a fire roasting technology, the temperature adopted in the present method is greatly reduced, and the recycling rate of vanadium is increased by times. Compared to a present wet-processing technology, equipment requirement is simple, no pressure is required to be applied during the reaction process, and the recycling rate of vanadium is increased by approximately 25%.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method for comprehensive utilization of vanadium titanium and iron ore concentrate by using rotary hearth furnace reduction-grinding - separation
The present invention relates to a method of using a rotary hearth furnace to deoxidize the ore concentrate pellets containing carbon and vanadium and titanium and iron for producing iron powder and joint titanium slag and vanadic oxide. The vanadium and titanium and iron ore concentrate is made into pellets positioned in the rotary hearth furnace for deoxidizing and then crashing, after the wetmilling, the crashed pellets are dressed by the magnetic separation and reelected to get the iron powder and the mine tailing, which is lixiviated by titanium dioxide waste acid to remove the titanium slag and the sodium vanadate solution, at last, the sodium vanadate solution is added with sodium salt to sink vanadium, and calcinations to remove ammonia, thereby getting the vanadic oxide product. The present invention eliminates the shortcomings that the fusion energy consumption of the electric furnace is high, the separation effect of vanadium and titanium is bad, the run of vanadium and titanium is difficult to control, and the yield of extracting vanadium and titanium from the molten iron blown in the rotary hearth furnace is low. The present invention has the advantages of high yield of vanadium and titanium and iron and high utilization rate of resources, and develops a doable new route for the comprehensive utilization of the vanadium and titanium and iron ore concentrate.
Owner:攀枝花锐龙冶化材料开发有限公司
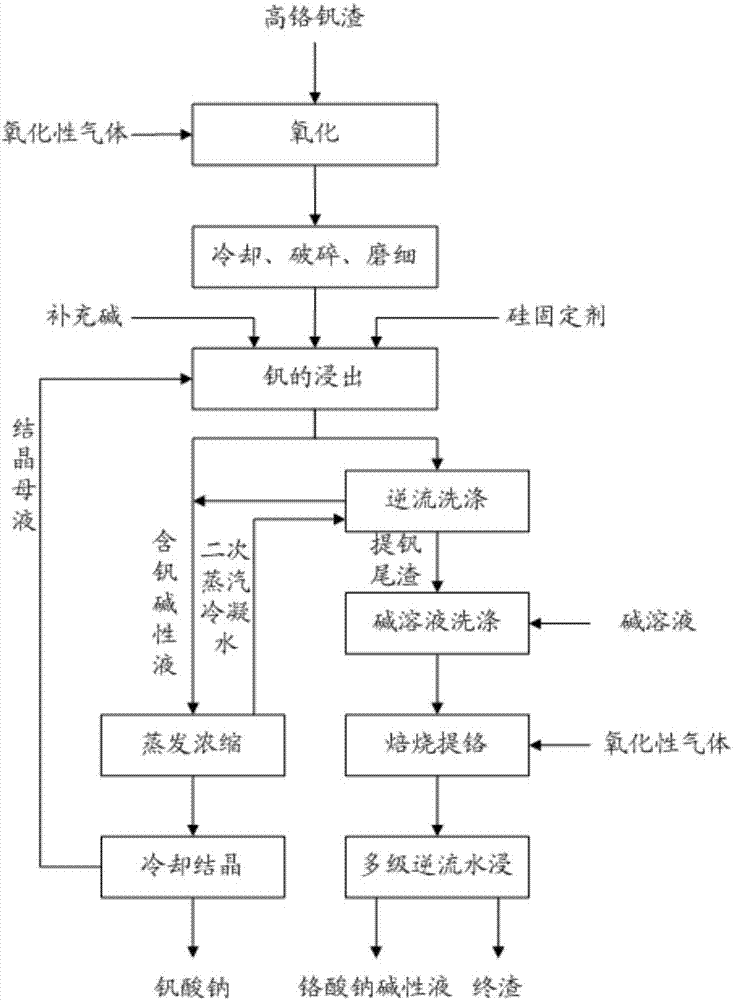
Cleaning process for producing sodium vanadate and sodium chromate alkali solution by high chromium vanadium slag
ActiveCN103757425AImprove resource utilizationImprove separation rateChromates/bichromatesVanadium compoundsSlagSilicon
The invention relates to a cleaning process for producing sodium vanadate and sodium chromate alkali solution by high chromium vanadium slag. The method provided by the invention comprises the main steps of: introducing oxidizing gas into the high-temperature high chromium vanadium slag separated from molten iron to oxidize vanadium into pentavalent vanadium; leaching vanadium out of the high chromium vanadium slag with an alkali solution, adding a silicon fixing agent for synchronized fixing of silicon, evaporating and concentrating the alkali leaching solution, cooling and crystallizing to prepare sodium vanadate, and reusing the cooling crystallization mother liquor; and conducting immersion cleaning and mixing on the vanadium-extracted tailings subjected to multistage countercurrent washing with alkali solution with a certain concentration, carrying out a roasting reaction in roasting equipment, and immersing reaction clinker with water and filtering to obtain an alkali solution of sodium chromate and the final slag. The method has the advantages of simple process, strong operability, recovery rate of vanadium greater than 98%, recovery rate of chromium more than 95% and separation rate of vanadium and chromium greater than 99%, thereby achieving efficient extraction and separation of vanadium and chromium.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
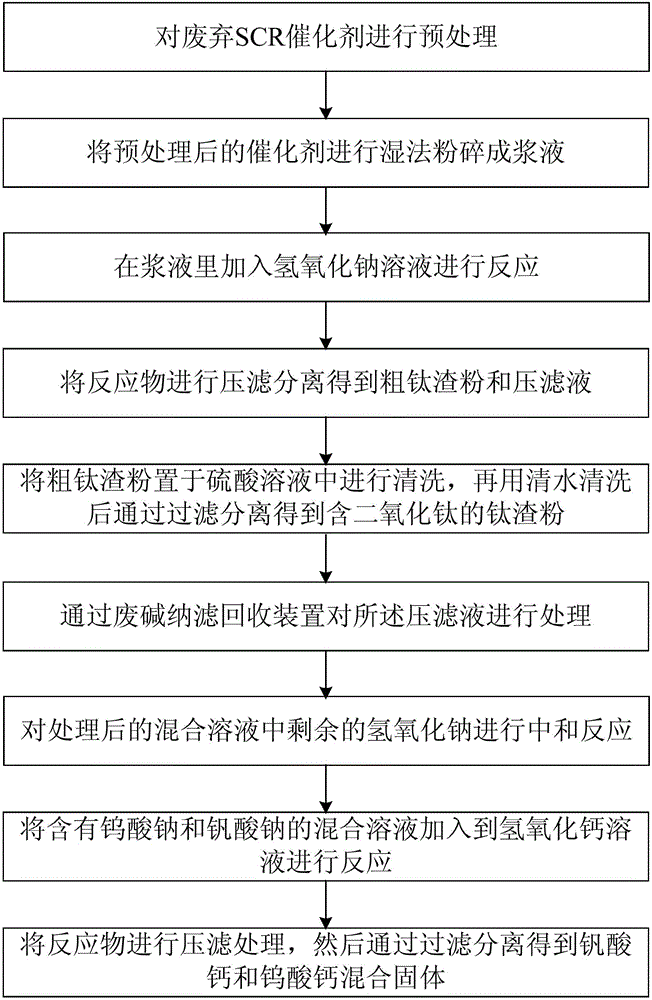
Method for extracting titanium slag, tungsten and vandic salt from waste SCR catalyst
ActiveCN106119544ASolve harmless disposalLow investment requirementProcess efficiency improvementSlurryCalcium tungstate
The invention provides a method for extracting titanium slag, tungsten and a vandic salt from a waste SCR catalyst. The method comprises the steps that the waste SCR catalyst is preprocessed and crushed into slurry by use of a wet method; a sodium hydroxide solution is added into the slurry for reaction; coarse titanium slag power and compression filtrate are obtained by filter-pressing and separating the slurry by use of a plate-and-frame filter press; the coarse titanium slag power is placed into a sulfuric acid solution for cleaning, cleaned with clear water, and then filtered and separated for obtaining titanium slag powder containing titanium dioxide; and the compression filtrate is treated through a waste alkali nanofiltration recovery device, the compression filtrate containing sodium tungstate and sodium vanadate is added into a saturated calcium hydroxide solution for reaction, products from the reaction are subjected to filter pressing, and then calcium vanadate and calcium tungstate mixed solid bodies are obtained through filtering and separating.
Owner:安徽思凯瑞环保科技有限公司
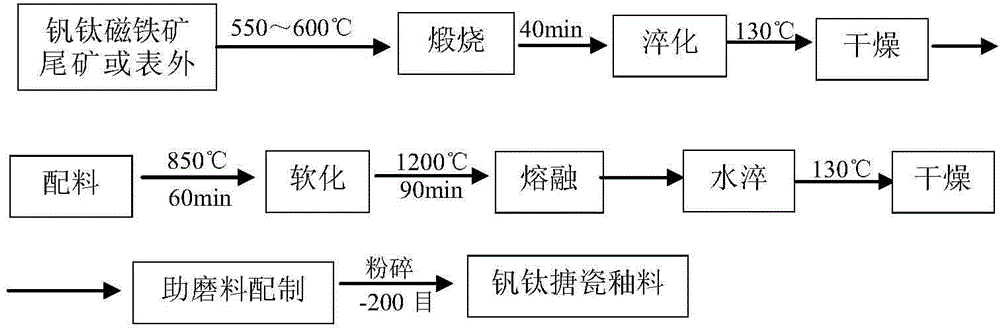
Vanadium-titanium enamel glaze material, and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of enamel material, and specifically relates to a vanadium-titanium enamel glaze material, and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method is used for solving technical problems that cost of a conventional vanadium-titanium enamel glaze material is high, glossiness of enamel glaze obtained via sintering is not high enough, fishscaling is observed, and acid and alkali resistance is not high enough. The vanadium-titanium enamel glaze material is prepared from, by mass, 22 to 28 parts of pretreated vanadium-titanium magnetite titanium separation tailing or vanadium-titanium boundary ore, 20 to 22 parts of feldspar powder, 5 to 8 parts of quartz sand, 24 to 26 parts of borax, 1.5 to 2 parts of sodium nitrate, 3.5 to 5.5 parts of lithium carbonate, 5 to 7 parts of fluorite powder, 0.1 to 0.3 part of sodium fluosilicate, 3 to 5 parts of cryolite, 2 to 4 parts of limestone, 3 to 4 parts of cobalt nitrate, 1 to 2 parts of nickel nitrate, 2 to 3 parts of sodium vanadate, and 1 to 2 parts of antimony oxide. Firm combination of the vanadium-titanium enamel glaze material with carbon steel billet can be realized; acid and alkali resistance is higher than that stipulated by national standard; and the vanadium-titanium enamel glaze material can be used for a plurality of matrixes such as hot-rolled carbon steel and cast iron.
Owner:PANZHIHUA UNIV
Smokeless polishing treatment solution for high-gloss aluminum profile and method of use
The invention provides a smoke-free polishing treatment solution for a high-gloss aluminum sectional material and a use method thereof. The smoke-free polishing treatment solution is characterized by comprising 85% H3PO4, 98% H2SO4, 30% hydrogen peroxide or potassium permanganate or perchloric acid or sodium molybdate or ammonium persulfate or sodium vanadate, cerium nitrate or sodium silicate, imidazoline or benzotriazole or phytic acid or thiourea, sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate or sodium benzene sulfonate or sodium toluene sulfonate or sodium xylene sulfonate, and nickel chloride or nickel sulfate or lead acetate. Compared with the prior art, the smoke-free polishing treatment solution provided by the invention has advantage of no generation of high-pollution NOx yellow smoke, and enables the surface of the aluminum sectional material to have excellent gloss and no pitting microscopic defects.
Owner:GUANGDONG XINGFA ALUMINUM
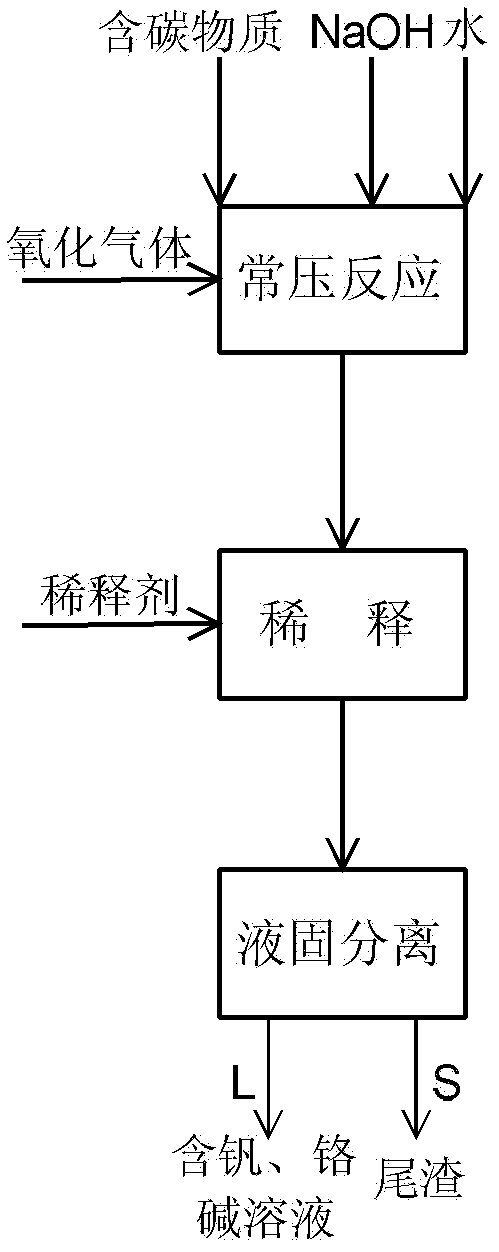
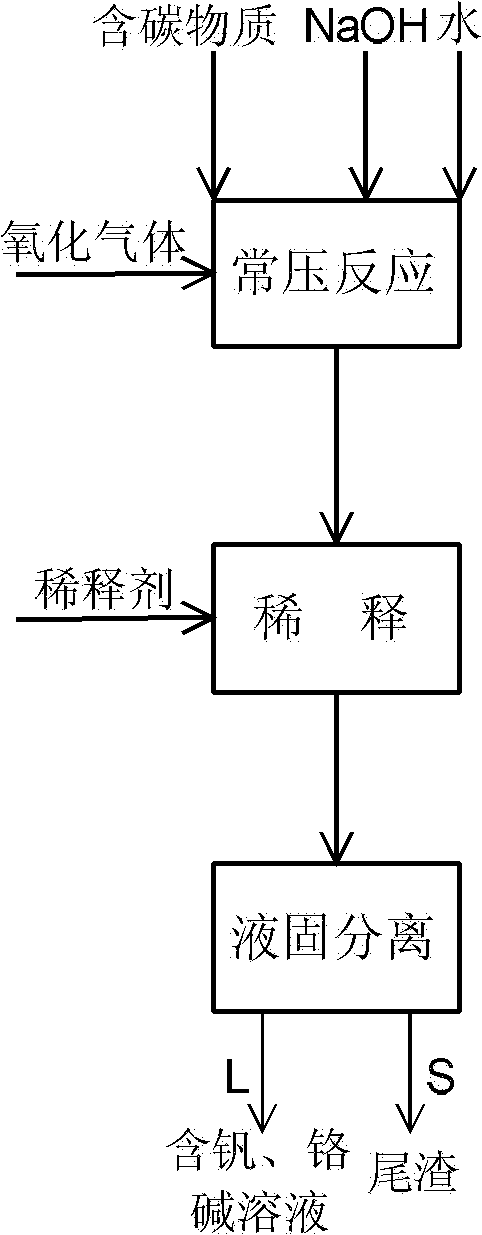
Method for decomposing vanadium slag under normal pressure by adding carbon-containing substance into sodium hydroxide solution
The invention relates to a method for decomposing vanadium slag under normal pressure and extracting vanadium and chromium by adding a carbon-containing substance into a sodium hydroxide solution. The method comprises the following steps of: uniformly mixing the vanadium slag and the carbon-containing substance, and adding the mixture, water and NaOH into a normal pressure reactor; introducing oxidizing gas for oxidization reaction, and diluting reaction slurry obtained by the reaction by using a diluent to obtain mixed slurry containing NaOH, sodium vanadate, sodium chromate, sodium silicate and tailings; and filtering and separating the mixed slurry to obtain the tailings, and an alkaline solution containing the vanadium and the chromium. The operating temperature of the method is below the boiling point of the solution, and the method can be implemented under normal pressure, and is easy to implement and high in safety; and the operating temperature is far lower than the temperature of the traditional vanadium extracting process, the extraction ratio of the vanadium is high, the chromium can be partially extracted synchronously, the total vanadium contained in the tailings is 0.2 to 0.6 weight percent (based on V2O5), and the leaching rate of the chromium is 8-20 percent.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for extracting vanadium from vanadium-containing iron ore concentrate pellets
The invention provides a process for extracting vanadium from vanadium-containing iron ore concentrate pellets which comprises, charging right amount of sodium salt into iron concentrate powder, carrying out water dipping treatment to dissolve the soluble sodium vanadate into water, charging sulphuric acid into sodium vanadate solution, concentrating and mixing, agitating, precipitating vanadium pentoxide, filtering and drying into powdery or tablet form vanadium pentoxide end product.
Owner:王洪东
Polishing composition and polishing method using the same
ActiveUS20080173843A1Other chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPotassiumSingle crystal
A polishing composition contains a vanadate such as ammonium vanadate, sodium vanadate, and potassium vanadate and an oxygen donor such as hydrogen peroxide and ozone. It is preferable that the polishing composition further contains at least either one of abrasive grains and a pH adjusting agent. The polishing composition can be suitably used for polishing a silicon carbide wafer such as a hexagonal silicon carbide single crystal wafer.
Owner:FUJIMI INCORPORATED
Resourceful utilization method of waste catalyst
InactiveCN104628035AAchieving zero emissionsNo secondary pollutionMolybdeum compoundsCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesPtru catalystIon exchange
The invention relates to a resourceful utilization method of a waste catalyst. The resourceful utilization method comprises the following steps of putting the waste catalyst into a de-oiling furnace and carrying out de-oiling, decarburization and desulfurization treatment by virtue of the heat value to obtain a de-oiled material; mixing and stirring the de-oiled material and sodium salt to obtain a mixture, putting the mixture into a rotary kiln and carrying out sodium modification and roasting on the mixture at 900-1100 DEG C to obtain a sodium-modified material; carrying out multistage leaching on the sodium-modified material, recovering metallic nickel and aluminum to obtain a nickel-aluminum powder product and a leaching solution; adding a sulfate precipitating agent, precipitating to remove silicon, aluminum and phosphorus impurities to obtain a mixed solution of sodium molybdate and sodium vanadate; separating molybdenum from vanadium by virtue of an ion exchange method to obtain a sodium molybdate solution and a pure sodium vanadate solution; adding an ammonium salt precipitating agent into the pure sodium vanadate solution, precipitating to recover vanadium to obtain a high-purity ammonium metavanadate product and a sodium sulfate solution; extracting, purifying and enriching molybdenum with a solvent to obtain a pure sodium molybdate solution and a sodium sulfate solution; adding a sulfuric acid precipitating agent into the sodium molybdate solution and precipitating to recover molybdenum to obtain a high-purity molybdic acid product and a sodium sulfate solution; carrying out ion exchange on the sodium sulfate solution, recovering molybdenum and vanadium in the solution, carrying out multi-effect concentration crystallization to obtain a product anhydrous sodium sulfate, recovering sodium sulfate in the produced solution and returning condensed water.
Owner:DALIAN DONGTAI RESOURCE RENEWABLE
Method for recycling vanadium pentoxide and sodium dichromate
ActiveCN102021345AEfficient separationRealize comprehensive utilizationSolid waste disposalProcess efficiency improvementProcess engineeringSodium dichromate
Owner:GANSU JINSHI CHEM
Method for producing vanadium pentoxide by roasting vanadium slag
ActiveCN102242274AReduce the amount addedReduce unit consumptionProcess efficiency improvementSlagSodium silicate
The invention discloses a method for producing vanadium pentoxide by roasting vanadium slag. An addition amount of an additive is determined according to the difference between the content of vanadium in the vanadium slag and the amount of impurities, and a proportioning parameter of the additive is further optimized, thus the treatment of a subsequent process is convenient. According to the method for producing the vanadium pentoxide by the roasting the vanadium slag, disclosed by the invention, the influence of SiO2 and Fe on the conversion ratio of clinkers is reduced by regulating the proportion of salt to alkali; the addition amount of the alkali is reduced when the content of the SiO2 is increased, and the addition amount of the salt is increased; and the method is beneficial to reducing of the generation amount of sodium silicate and increasing of the generation amount of sodium vanadate, and additive proportioning parameters are optimized by aiming to high contents of silicon and iron in the vanadium slag. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a suitable high-silicon high-iron vandadium slag roasting method and a corresponding additive proportion are promotedpertinently, thus the conversion ratio of the clinkers is largely increased, the product yield is remarkably increased and the unit consumption of the vanadium slag is remarkably reduced.
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
Method for recycling tungsten, vanadium and titanium from SCR waste catalysts
InactiveCN106011503ASequential extractionAchieve mutual separationProcess efficiency improvementTungstateRaffinate
The invention discloses a method for recycling tungsten, vanadium and titanium from SCR waste catalysts. The method comprises the following steps: after the SCR waste catalysts are cleaned, the SCR waste catalysts are smashed and screened, sodium carbonate is doped into the SCR waste catalysts to be evenly stirred, mixed powder is sintered at a high temperature to obtain a sintered material, water is added for leaching out, and a sodium salt mixed solution containing tungsten and vanadium is obtained; under the condition that the pH value of the solution is large than 12, tungsten is selectively extracted, and an ammonium salt solution is used for reverse extraction to obtain an ammonium tungstate solution; under the condition that the pH value of raffinate obtained after tungsten extraction ranges from 10 to 11.5, vanadium is extracted, and a sodium hydroxide solution is used for reverse extraction to obtain a sodium vanadate solution containing a small amount of tungsten; and titanium is left in leaching residues to obtain a rich-titanium material. According to the method, separation of tungsten and vanadium from impurities such as phosphorus, arsenic and silicon is achieved, and primary separation and efficient enrichment of tungsten, vanadium and titanium are achieved.
Owner:无锡市华东电力设备有限公司
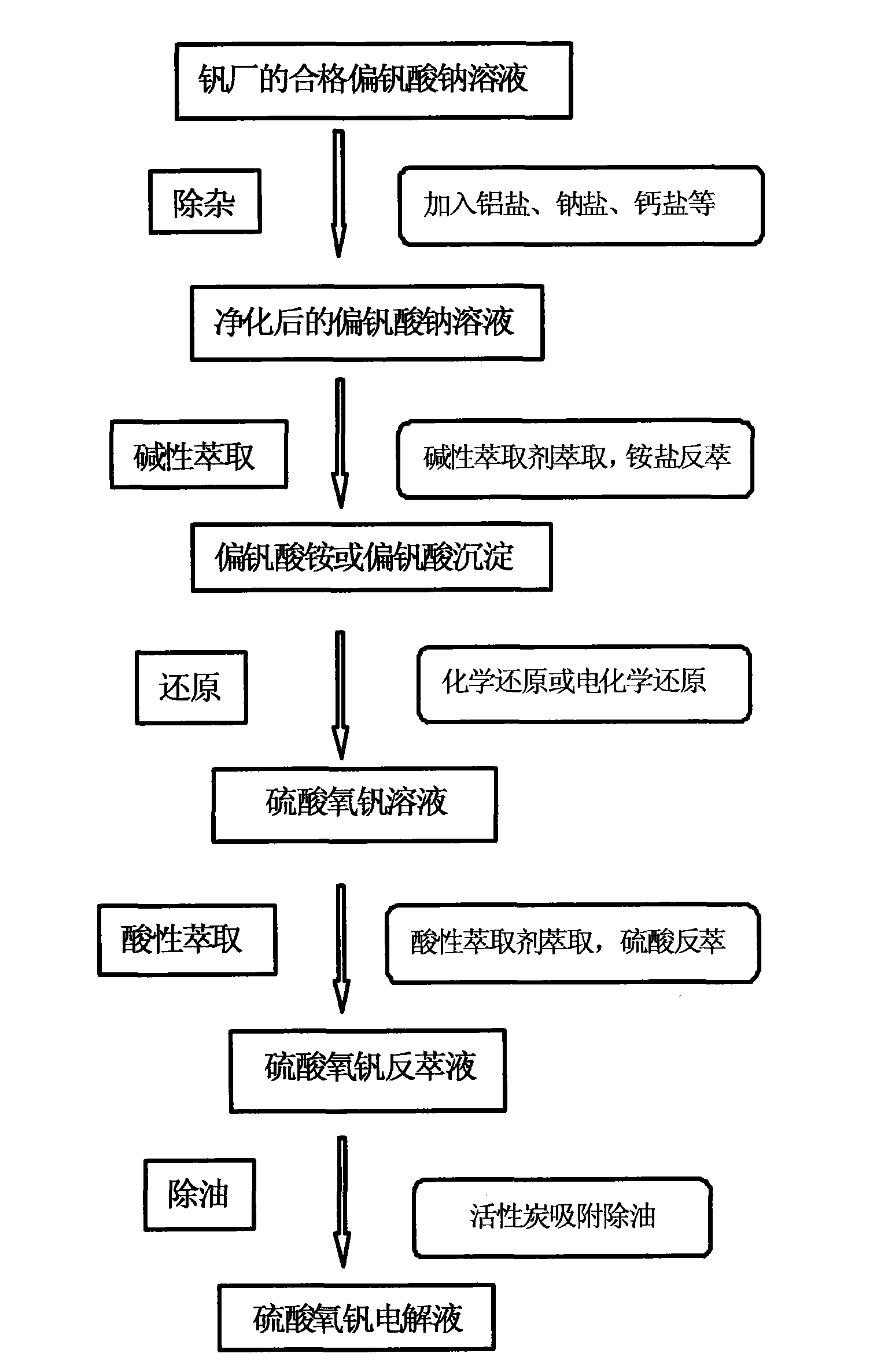
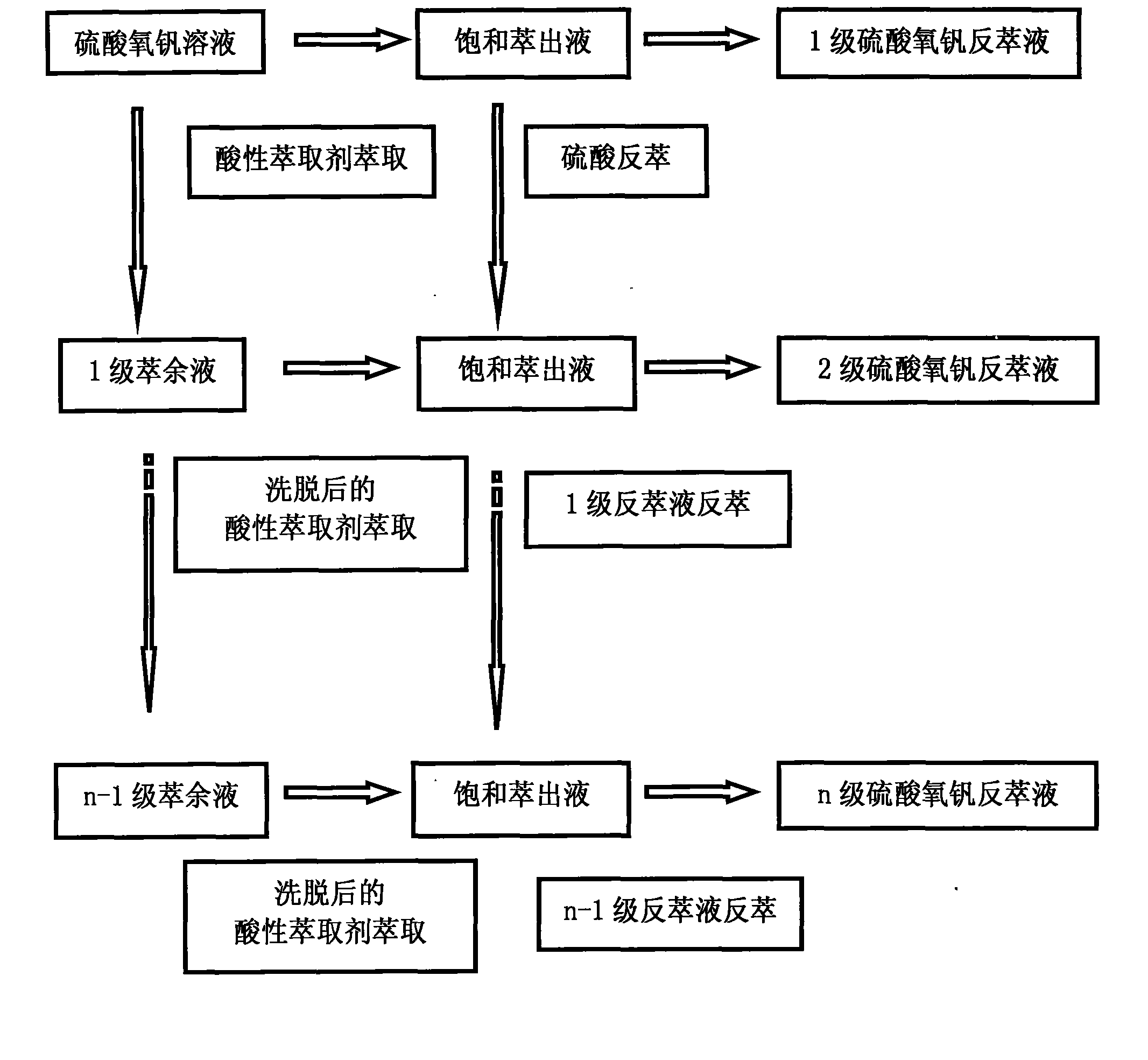
Two-stage extraction preparation method for high-purity vanadyl sulfate solution
InactiveCN103505903AHigh purityIncrease concentrationFinal product manufactureRegenerative fuel cellsHigh concentrationVanadyl sulfate
The invention relates to a two-stage extraction preparation method for a high-purity vanadyl sulfate solution, and is characterized in that the method comprises a series of steps: employing a qualified pentavalent vanadium solution produced by a vanadium factory, after purification by an initial impurity removal process, extracting pentavalent vanadium by an amine extractant, reducing pentavalent vanadium into tetravalent vanadium by adding a reductant, and extracting tetravalent vanadium by an acid extractant; the high-purity tetravalent vanadyl sulfate solution is prepared directly from the pentavalent sodium vanadate solution without a solid state process. The high-purity and high-concentration vanadyl sulfate electrolyte solution with the concentration of 1-4 M is obtained. The method adopts the qualified pentavalent vanadium solution as the raw material, the consumed reagents in the preparation process are commonly used, and the price is low; the extractants applied in the preparation process can be repeatedly used, and thus the cost is low; and the method has the advantages of simple preparation steps and mild reaction conditions, requires no high temperature, and enables the obtained electrolyte solution to have high purity.
Owner:NO 63971 TROOPS PLA
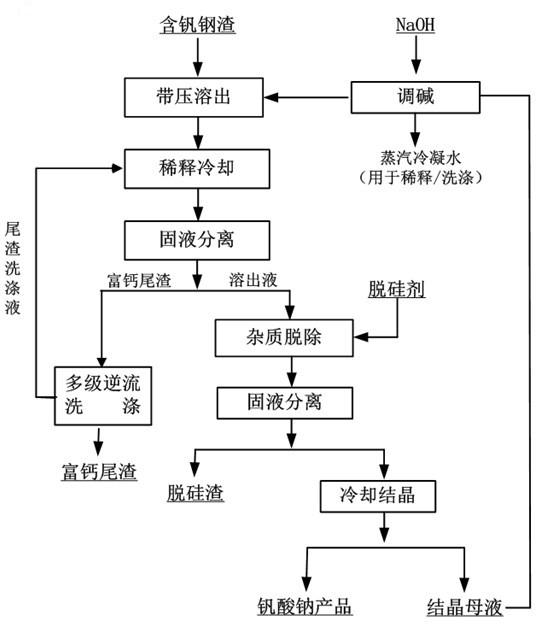
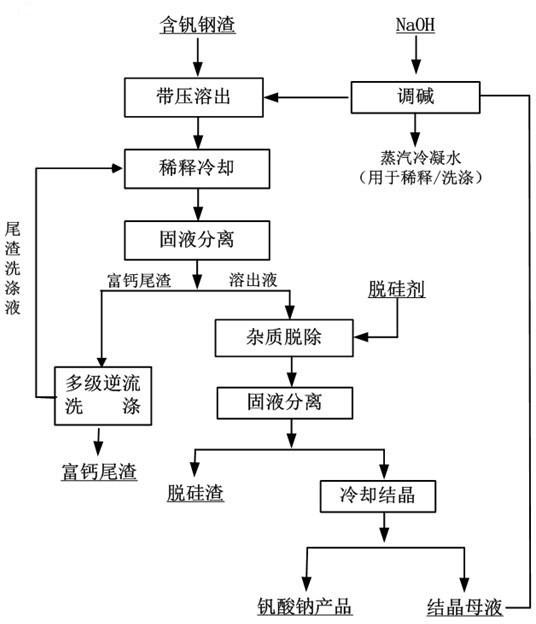
Method for recycling vanadium from vanadium-containing steel slag
InactiveCN102586613ASimple ingredientsAchieve purificationProcess efficiency improvementSlagReaction temperature
The invention discloses a method for recycling vanadium from vanadium-containing steel slag, which comprises the following steps, (1) reaction: the vanadium-containing steel slag is reacted in NaOH solution with the mass concentration being 10%-50%, and reaction slurry is obtained; the mass ratio of the NaOH solution to the steel slag is (3:1)-(10:1), the reaction temperature is 180 DEG C to 350 DEG C, the reaction time is 0.5-10h, and the reaction pressure is 0.3-12MPa; (2) dilution: the reaction slurry is diluted through a diluent so as to enable the concentration of sodium hydroxide in the slurry to be 100-400g / L, and mixed slurry is obtained; (3) solid-liquid separation: solid-liquid separation is carried out to the mixed slurry, and calcium-rich tailings and dissolved-out liquid are obtained; (4) impurity removal: a desiliconization agent is added into the dissolved-out liquid to perform impurity removal, then solid-liquid separation is performed, and impurity-removed liquid and silicon-containing slag are obtained; and (5) crystallizing: the impurity-removed liquid is cooled and crystallized, and a sodium vanadate product is obtained. The method effectively reduces production cost of vanadium, and the vanadium leaching rate can be 99%.
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
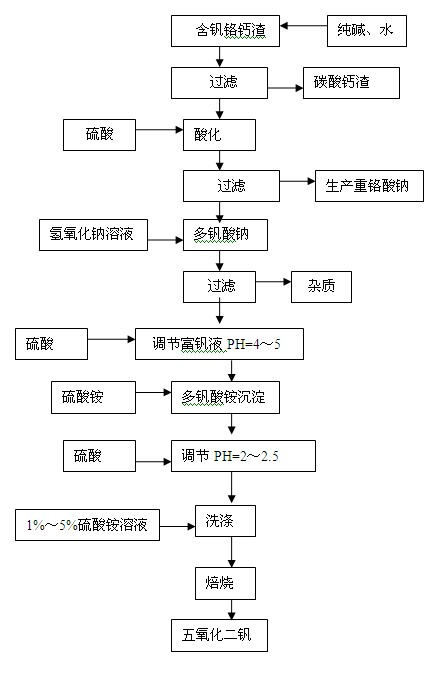
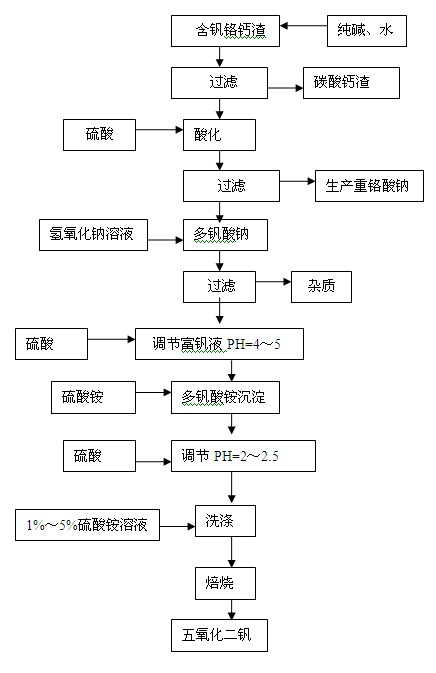
Method for preparing vanadium pentoxide
The invention provides a method for preparing vanadium pentoxide from leachate containing sodium vanadate. The method comprises the following steps of: providing the leachate containing sodium vanadate; adding ammonium sulfate to the leachate containing sodium vanadate, and adjusting the pH value to 1.5-2, and heating at the temperature of 90-100 DEG C to generate a mixed liquid containing an ammonium poly-vanadate precipitate; filtering and washing the mixed liquid containing the ammonium poly-vanadate precipitate to obtain the ammonium poly-vanadate precipitate and vanadium precipitation mother liquor; and heating for decomposing and oxidizing the ammonium poly-vanadate precipitate at the temperature of 400-500 DEG C to generate vanadium pentoxide. The method for preparing vanadium pentoxide has at least one of the following advantages: high efficiency, low cost, low energy consumption, safety and environmental protection.
Owner:CHINA ENFI ENGINEERING CORPORATION
Cleaner production process for synchronously extracting vanadium and aluminum from aluminothermic vanadium iron slag
ActiveCN102586610ARealize co-existenceAchieve separationProcess efficiency improvementSlagAluminium hydroxide
The invention relates to a cleaner production process for synchronously extracting vanadium and aluminum from aluminothermic vanadium iron slag, and belongs to the technical field of metallurgy. The technical scheme is that: the vanadium iron slag is subjected to sodium oxide roasting by using high-proportion Na2CO3 as a roasting transforming agent, vanadium and aluminum of a clinker obtained after sodium oxide roasting are synchronously dissolved out by using an aqueous solution, sodium vanadate crystals containing aluminum hydroxide are crystallized, the purity of the obtained Al(OH)3 is over 95 percent, the purity of vanadium pentoxide is over 98 percent, the co-extraction of the vanadium and the aluminum, the separation of the vanadium and the aluminum and the cyclic utilization of sodium salt are realized, the recovery rate of the vanadium is over 85 percent, the recovery rate of the aluminum is over 60 percent, the weight of tailings is reduced by 40 to 50 percent after leaching, and the tailings can be used for preparing an aluminum-magnesium flocculant by an acid method. The high-efficiency extraction of the vanadium is realized, the resource reutilization of an aluminum element in the slag is also realized, wastewater discharge is avoided in the whole production process, CO2 gas for carbonation can be replaced by roasting flue gas, the proportion of carbon emission isreduced, and the process has remarkable economic and environmental benefits, and can be effectively applied to the treatment of the aluminothermic vanadium iron slag and related materials.
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
Ammonium metavanadate preparation method
ActiveCN103420416AReduce dosageReduce the burden onVanadium compoundsAmmonium metavanadateSodium salt
The present invention discloses an ammonium metavanadate preparation method, which comprises that: a sodium vanadate solution contacts an ammonium salt under an acid condition, and the contacting product is subjected to precipitation and separation to obtain an ammonium polyvanadate solid; and the ammonium polyvanadate solid contacts water and an ammonium vanadate structure reforming agent to convert the ammonium polyvanadate into ammonium metavanadate, and the contacting product is subjected to solid-liquid separation to obtain an ammonium metavanadate solution, wherein the ammonium vanadate structure reforming agent is one or a plurality materials selected from ammonium carbonate, ammonium bicarbonate and ammonia water. According to the ammonium metavanadate preparation method, ammonium ions of the original ammonium polyvanadate can be completely utilized so as to reduce ammonium salt consumption; alkality of the ammonium vanadate structure reforming agent is completely adopted to achieve ammonium polyvanadate dissolving, such that the sodium salt (sodium hydroxide, sodium carbonate, and the like) is not required to be adopted to dissolve the ammonium polyvanadate so as to simplify steps and reduce cost; and no converted ammonia gas escapes so as to reduce burden on the environment .
Owner:PANGANG GRP PANZHIHUA STEEL & VANADIUM
Method of separating and recovering sodium vanadate, sodium chromate and sodium carbonate from vanadium slag vanadium extraction liquor
ActiveCN107760868AHigh efficiency of separation and recoveryEasy to separateCarbonate purificationChromates/bichromatesSlagWastewater
The invention relates to a method of separating and recovering sodium vanadate, sodium chromate and sodium carbonate from vanadium slag vanadium extraction liquor. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: firstly, separating and recovering vanadium in the vanadium slag vanadium extraction liquor by means of a calcium salt precipitation method; then concentrating and enrichingsodium vanadate and sodium carbonate in molybdenum precipitation post liquor by means of an electrodialysis process; returning fresh water obtained by electrodialysis to vanadium slag for a sodium modification and cinder roasting leaching step for recycled use; and separating and recovering sodium vanadate and sodium carbonate in strong water by means of a circular concentration-crystallization method. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of being good in separating effect of sodium vanadate, sodium chromate and sodium carbonate, simple in process, simple to operate, free of waste water and residual slag, environment-friendly and the like, and is suitable for industrialized application of vanadium slag vanadium extraction.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
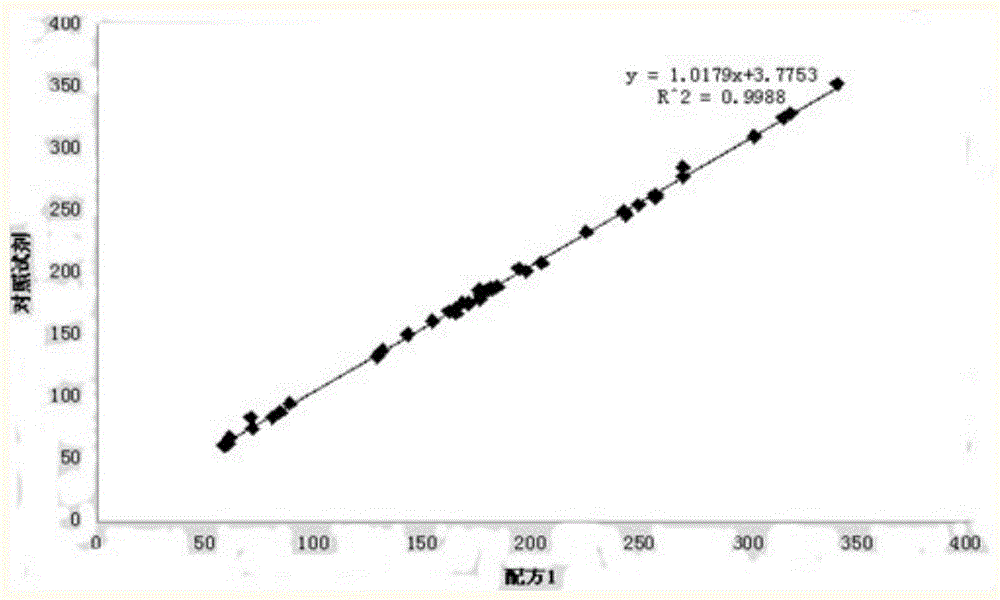
Kit for detecting 1, 5-anhydro-D-ghlcitol in human blood
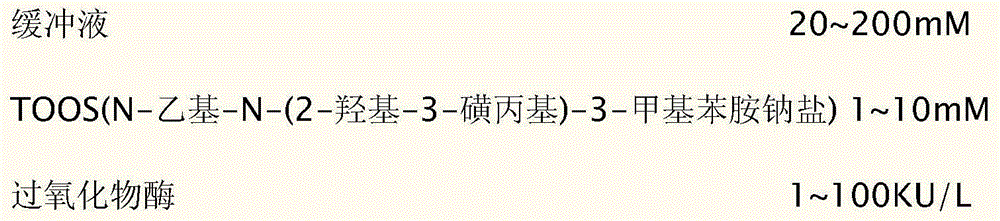
ActiveCN104483487AImprove featuresImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological testingPeroxidaseSurface-active agents
The invention discloses a kit for detecting 1, 5-anhydro-D-ghlcitol in human blood. R1 comprises components as follows: 20-200 mM of a buffer solution, 1-10 mM of 4-aminoantipyrine, 0.2-2 mM of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), 1-10 mM of PEP (phosphoenolpyruvate), 1-50 KU / L of ATP-HK, 1-50 KU / L of pyruvate kinase, 1-50 KU / L of ascorbic acid oxidase, 0.05-10 mM of sodium vanadate, 0.01%-5% of a surface active agent, 0.1%-10% of a stabilizer and 0.01%-1% of a preservative; and R2 comprises components as follows: 20-200 mM of a buffer solution, 1-10 mM of TOOS (N-ethyl-N-(2-hydroxy-3-sulfopropyl)-3-methylaniline,sodium salt), 1-100 KU / L of POD (peroxidase), 10-200 KU / L of PROD (pyranose oxidase), 0.01%-5% of a surface active agent, 0.1%-10% of a stabilizer and 0.01%-1% of a preservative. The kit has the advantages that endogenous interference of glucose, bilirubin, ascorbic acid, blood lipid and the like is effectively prevented and the stability is good.
Owner:NINGBO MEDICAL SYSTEM BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
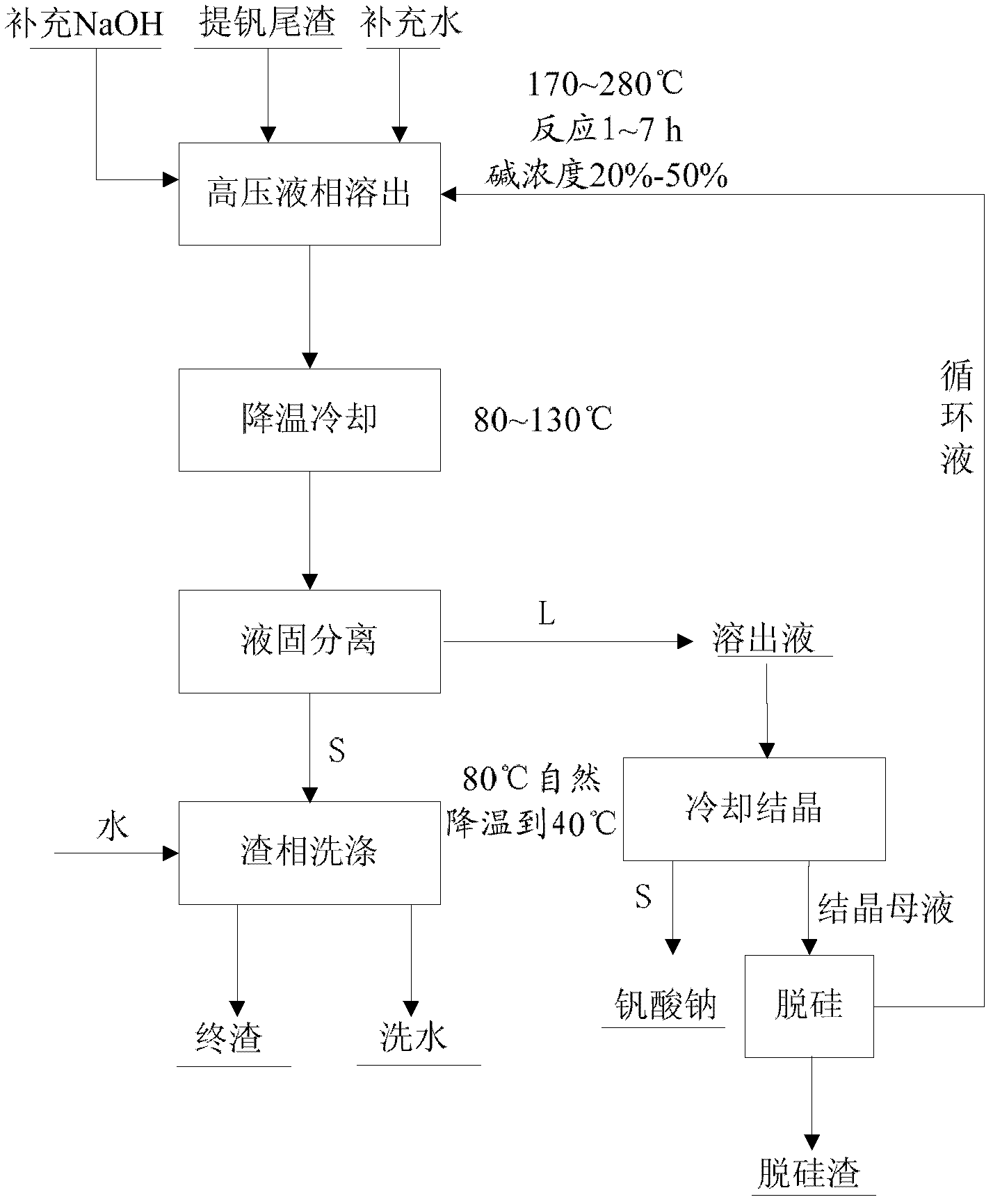
Method for recovering vanadium by decomposing vanadium extraction tailings by using sodium hydroxide solution
ActiveCN102876896ALow reaction temperatureImprove resource utilizationProcess efficiency improvementSlagSlurry
The invention relates to a method for recovering vanadium by decomposing vanadium extraction tailings by using a NaOH solution under pressure. The process flow is shown in an attached drawing. The method comprises the following steps of: adding vanadium extraction tailings, a circulation fluid, and supplemented NaOH or a supplemented NaOH aqueous solution into a reactor and reacting, cooling obtained reaction slurry to a temperature of 80 to 130 DEG C, filtering to obtain an aqueous solution containing sodium hydroxide, sodium vanadate and sodium silicate, naturally cold-crystallizing the solution to obtain sodium vanadate and crystallization mother liquor, adding a desiliconization agent into the crystallization mother liquor for treatment, and returning an obtained solution which is taken as the circulation fluid. By the method, the circulation fluid is not required to be evaporated and concentrated and can directly enter the next reaction, gas is not required to be introduced, the recovery rate of vanadium is 80 to 95 percent, and the total content of vanadium in final slag is less than 0.2 weight percent (based on vanadium pentoxide). Compared with a fire roasting process, the method has the advantages that the temperature is greatly reduced, and the recovery rate of vanadium is greatly increased.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com